Page 1

4-Slot NAS RAID Server
NAS-3410
User’s Manual
Page 2

Electronic Emission Notice
Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used
in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful
interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
CE Notice
This device complies with the EMC directive of the European Community and meets or exceeds
the following technical standard:
EN 55022 ~ “Limits and Methods of Measurement of Radio interference Characteristics of
information Technology Equipment.” This device complies with CISPR Class A standard.
Warning: This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio interference in which
case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Safety Information
To reduce the risk of fire or electric shock, install the unit in a temperature-controlled indoor area
free of conductive contaminants. Do not place the unit near liquids or in an excessively humid
environment.
Do not allow liquids or foreign objects to enter the unit.
All servicing of this equipment must be performed by qualified service personnel. Remove rings,
watches and other jewelry before servicing the unit.
Before maintenance, repair or shipment, the unit must be completely switched off and unplugged
and all connections must be removed.
Page 3
Safety Notices:
To avoid the potential effects on the environment and human health as a result of the
presence of hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, end users of
electrical and electronic equipment should understand the meaning of the crossed-out
wheeled bin symbol. Do not dispose of WEEE as unsorted municipal waste and have to
collect such WEEE separately.
Caution:
This unit is provided real-time clock circuit. There is a
danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced.
Caution:
Before connect or disconnect power cord of the power
supply, ensure to turn the power supply switch OFF to
avoid the risk of equipment damage.
Copyright
Copyright © 2005 by PLANET Technology Corp. All rights reserved. No part of this publication
may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any
language or computer language, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic,
optical, chemical, manual or otherwise, without the prior written permission of PLANET.
PLANET makes no representations or warranties, either expressed or implied, with respect to
the contents hereof and specifically disclaims any warranties, merchantability or fitness for any
particular purpose. Any software described in this manual is sold or licensed "as is". Should the
programs prove defective following their purchase, the buyer (and not PLANET, its distributor, or
its dealer) assumes the entire cost of all necessary servicing, repair, and any incidental or
consequential damages resulting from any defect in the software. Further, PLANET reserves the
right to revise this publication and to make changes from time to time in the contents hereof
without obligation to notify any person of such revision or changes.
All brand and product names mentioned in this manual are trademarks and/or registered
trademarks of their respective holders.
Revision
User’s Manual for PLANET 4-Slot NAS RAID Server
Model: NAS-3410
Rev: 1.0 (October, 2005)
Part No. EM-NAS3410
Page 4

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction -----------------------------------------------------------------1
1.1 Features --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1
1.2 Package Contents--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1
1.3 Physical Details -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2
Chapter 2 Initial Installation-----------------------------------------------------------4
2.1 Hardware Installation Procedures ------------------------------------------------------------------------4
2.2 Setting the IP Addresses------------------------------------------------------------------------------------6
2.3 Accessing the Administration Home Page--------------------------------------------------------------8
Chapter 3 Server Configuration---------------------------------------------------- 10
3.1 Server Information and Settings ------------------------------------------------------------------------10
3.2 Modifying the Administrator’s Password -------------------------------------------------------------- 11
3.3 Enabling UPS Support ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 11
3.4 Server Maintenance----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------12
3.5 Shutting Down the Server -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 13
3.6 Upgrading the Firmware ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------13
3.7 License for Optional Features---------------------------------------------------------------------------13
Chapter 4 Network Configuration ------------------------------------------------- 15
4.1 Network Information----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------15
4.2 TCP/IP Settings ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------16
4.3 Windows Settings-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------17
4.4 UNIX/Linux Settings----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------18
4.5 Macintosh Settings----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 20
4.6 NetWare Network Settings-------------------------------------------------------------------------------20
4.7 Web Data Access Settings -------------------------------------------------------------------------------21
4.8 FTP Data Access Settings-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 21
4.9 SNMP Settings---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 22
4.10 Email Settings----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------23
4.11 SSL Settings------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------23
Chapter 5 Storage Management -------------------------------------------------- 25
5.1 Volume Usage and Status--------------------------------------------------------------------------------25
5.2 Creating a Volume------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------27
5.3 Deleting a Volume------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------28
Page 5

5.4 Expanding a RAID-5 Volume ----------------------------------------------------------------------------28
5.5 Migrating Data Volumes----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 29
5.6 SmartExtend – Add More NAS Capacity--------------------------------------------------------------29
5.7 Volume/Disk Scan------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------31
5.8 Hot-swapping------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 32
Chapter 6 Security Control----------------------------------------------------------33
6.1 Security Information----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------33
6.2 Creating the Local User and Local Group Accounts-----------------------------------------------34
6.3 Caching Windows Domain User Accounts -----------------------------------------------------------35
6.4 Creating UNIX/Linux Host --------------------------------------------------------------------------------37
6.5 Creating Share and Assigning Share Permissions-------------------------------------------------37
6.6 Aggregate Volumes under a Share---------------------------------------------------------------------39
6.7 Configuring File and Folder Security and ACL ------------------------------------------------------ 40
6.8 Managing Quotas-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------42
Chapter 7 Disc Sharing and Data Archiving------------------------------------ 51
7.1 Start to Use the Disc Server Function ----------------------------------------------------------------- 51
7.2 Creating Disc Images--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------51
7.3 Managing Discs--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 52
7.4 Sharing Discs------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 53
7.5 Burning Disc Images---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------53
7.6 Archiving Data to CD/DVD Discs -----------------------------------------------------------------------54
Chapter 8 User Access -------------------------------------------------------------- 56
8.1 Workgroup or Domain Mode-----------------------------------------------------------------------------56
8.2 Accessing from Windows OS----------------------------------------------------------------------------56
8.3 Accessing from Web Browsers--------------------------------------------------------------------------57
8.4 Accessing from MacOS -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------59
8.5 Accessing from FTP Clients------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 60
8.6 Accessing from NFS Clients -----------------------------------------------------------------------------61
Chapter 9 Backup and Recovery-------------------------------------------------- 58
9.1 Snapshot – Fast Point-In-Time Copies---------------------------------------------------------------- 58
9.2 Tape Backup and Restore--------------------------------------------------------------------------------60
9.3 Using a Tape Library--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 63
9.4 SmartSync – NAS-to-NAS Data Replication---------------------------------------------------------68
Page 6

9.5 Loading and Writing CD/DVD Discs -------------------------------------------------------------------74
9.6 Backup and Restore System Profiles------------------------------------------------------------------77
Chapter 10 Virus Protection -------------------------------------------------------- 79
10.1 Information--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------79
10.2 Real-time, Manual and Schedule Scanning-------------------------------------------------------- 79
10.3 Configuring Scan Settings------------------------------------------------------------------------------80
10.4 Updating Virus Pattern File-----------------------------------------------------------------------------81
Chapter 11 Event Logs and System Status------------------------------------- 84
11.1 Thermal Settings ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------84
11.2 Checking the Event Logs-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 85
11.3 Viewing System Status-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------86
11.4 Share Access Counts ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------87
Appendix A NAStart Utility----------------------------------------------------------- 90
Installation---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------91
System Requirement -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------91
Installing TCP/IP Protocol for Microsoft Networks-------------------------------------------------91
Installing NAStart ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 91
Discovering NAS-3410-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------92
To set the automatic refresh interval ------------------------------------------------------------------92
Server Quick Setup Using NAStart-------------------------------------------------------------------- 92
Importing and Exporting System Settings -----------------------------------------------------------------93
To export system settings of a NAS Server ---------------------------------------------------------93
To import system settings into NAS Servers-------------------------------------------------------- 93
Browsing & Administering Servers --------------------------------------------------------------------------94
Browsing Servers------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------94
Tool Bar Functions-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------95
Mirroring CD/DVD Remotely----------------------------------------------------------------------------------97
Archiving Files As a CD/DVD Image---------------------------------------------------------------------- 100
Burning Disc Images------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 103
Supported CD Formats--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 103
Appendix B Specification-----------------------------------------------------------104
Page 7
Chapter 1
Introduction
To accommodate the increasing storage demands for enterprise, small business, SOHO, and
home use, PLANET provides a reliable and affordable solution, the NAS-3410. Regardless of the
operating systems installed in your network, the NAS-3410 has straightforward setup procedures
and can be installed in any existing network environment using its simple and intuitive
management interface.
1.1 Features
• 4 ATA 133 hot swappable IDE trays
• Supports RAID 0, 1, 5, JBOD with global hot-spare and RAID expansion
• Support smart-signaling & network-type UPS
• Two integrated 10/100/1000M Gigabit Ethernet ports
• Multi-protocol system support for Microsoft, Apple, UNIX/LINUX, and Novell networks
• Multi-language support and user friendly web management interface
• Fully integrated ability for Windows 2000 domains, NT 4.0 domains, and UNIX NIS domains
• Supports ACL (Access Control List) settings
• User quota control and folder quota control
• Built-in Trend Micro antivirus software
• NAS-to-NAS data synchronization with SmartSync
• Advanced RAID bad sector recovery mechanism
• E-mail notification, SNMP management (MIB II) and system buzzer alerts
• NAStart software utility for quick setup and system configuration backup
• Environmental monitoring of system/CPU temperature, CPU fan speed and CPU voltages
• Snapshot provides the ultimate solution to satisfying short-term backup needs (optional)
• The SmartExtend technology (IP Storage Aggregation) allows you to add NAS capacity on
demand (optional)
• Backup and archive important data to the local tape drive, or CD/DVD writer (optional)
1.2 Package Contents
The following items should be included:
• NAS Server unit (including 4 HDD trays)
• Power cord
• Screws
1
Page 8
• Quick Installation Guide
• CD-ROM
Note: there are four utilities included in the CD-ROM: NAStart, eMulateCD, eContent, and
Second Copy 2000. You can find the detailed usage of respective utility in its on-line help.
Moreover, this manual also includes the instruction for NAStart in Appendix A.
If any of the above items are damaged or missing, please contact your dealer immediately.
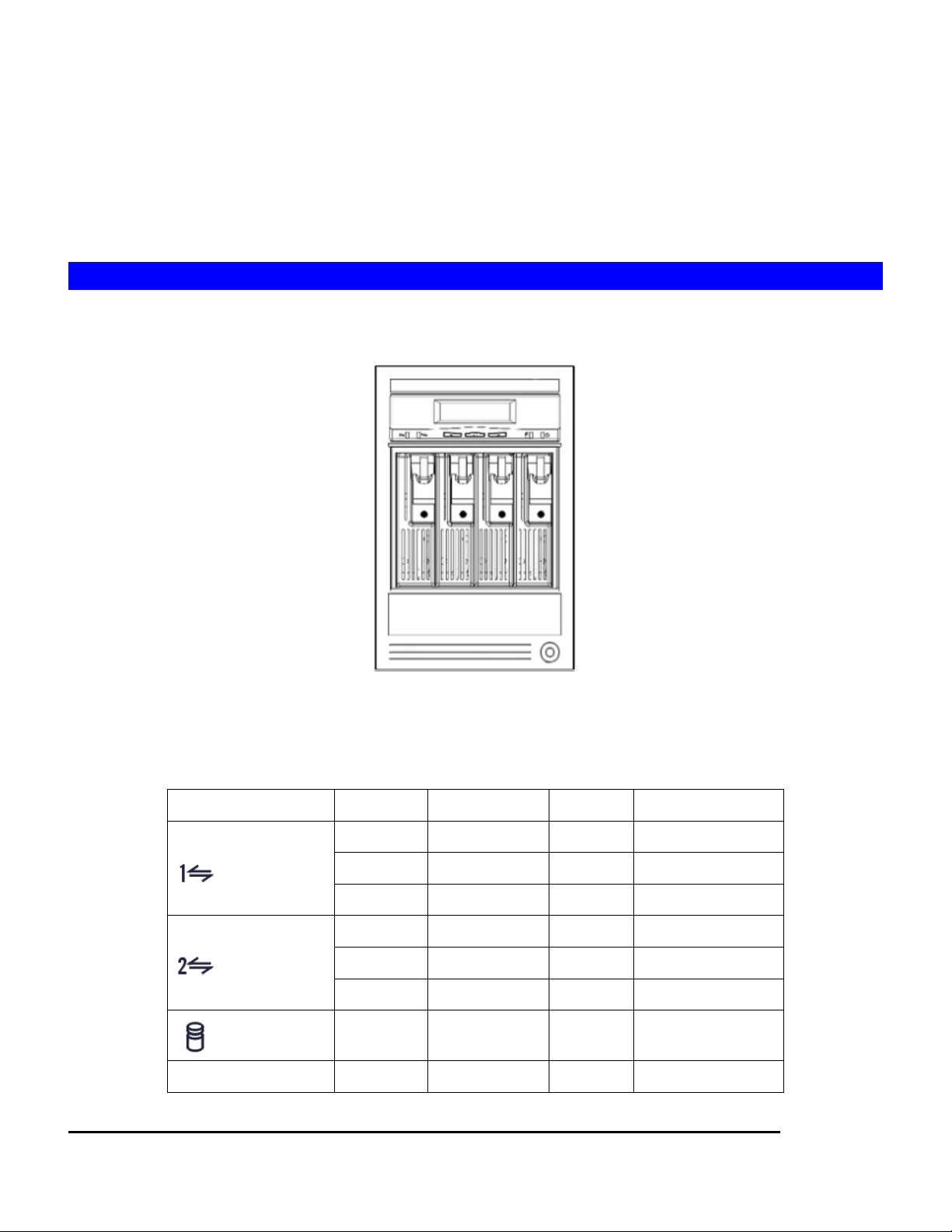
1.3 Physical Details
Front View
Power button: When the A/C power cable is in socket, the NAS-3410 will start to initiate. Press
this button twice to shutdown the NAS-3410. Press once again to switch on the server.
LED definition:
On Off Blink
Amber 1000M link No link 1000M activity
LAN 1
LAN 2
HD Access
Green 100M link No link 100M activity
Yellow 10M link No link 10M activity
Amber 1000M link No link 1000M activity
Green 100M link No link 100M activity
Yellow 10M link No link 10M activity
Red – – IDE activity
Green Power on – –
2
Page 9
Green Power on – –
Power/Fault
Yellow Fault – –
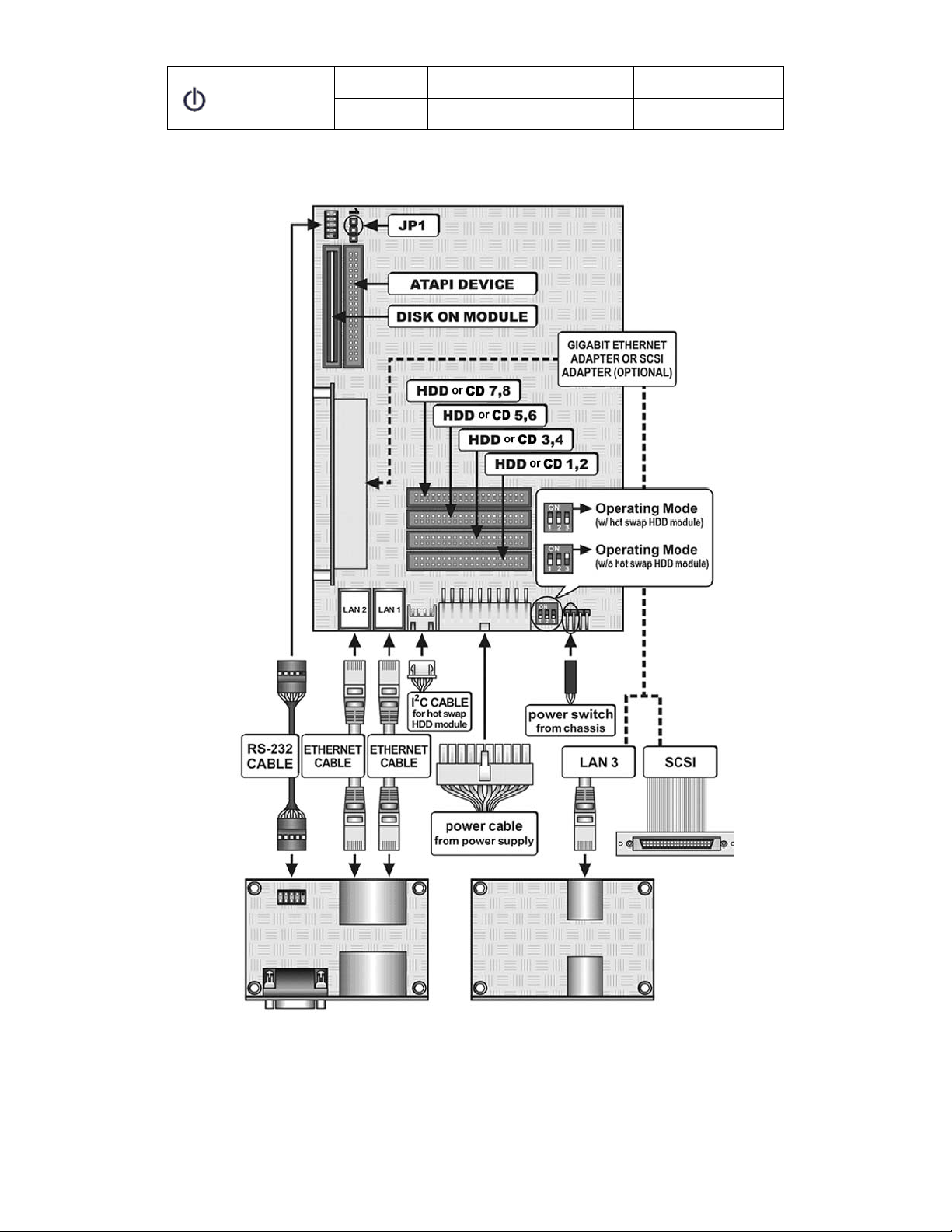
NAS System Board Diagram
3
Page 10

Chapter 2
Initial Installation
2.1 Hardware Installation Procedures
Step 1: Pull out a HDD tray from the NAS-3410 mobile rack.
Step 2: Configuring the jumper on your hard disk using Cable Select (CS) before installing to the
hard disk tray. (Refer to your hard disk’s user manual for the instruction)
Step 3: Secure and mount a hard disk onto the HDD tray using four screws under the tray.
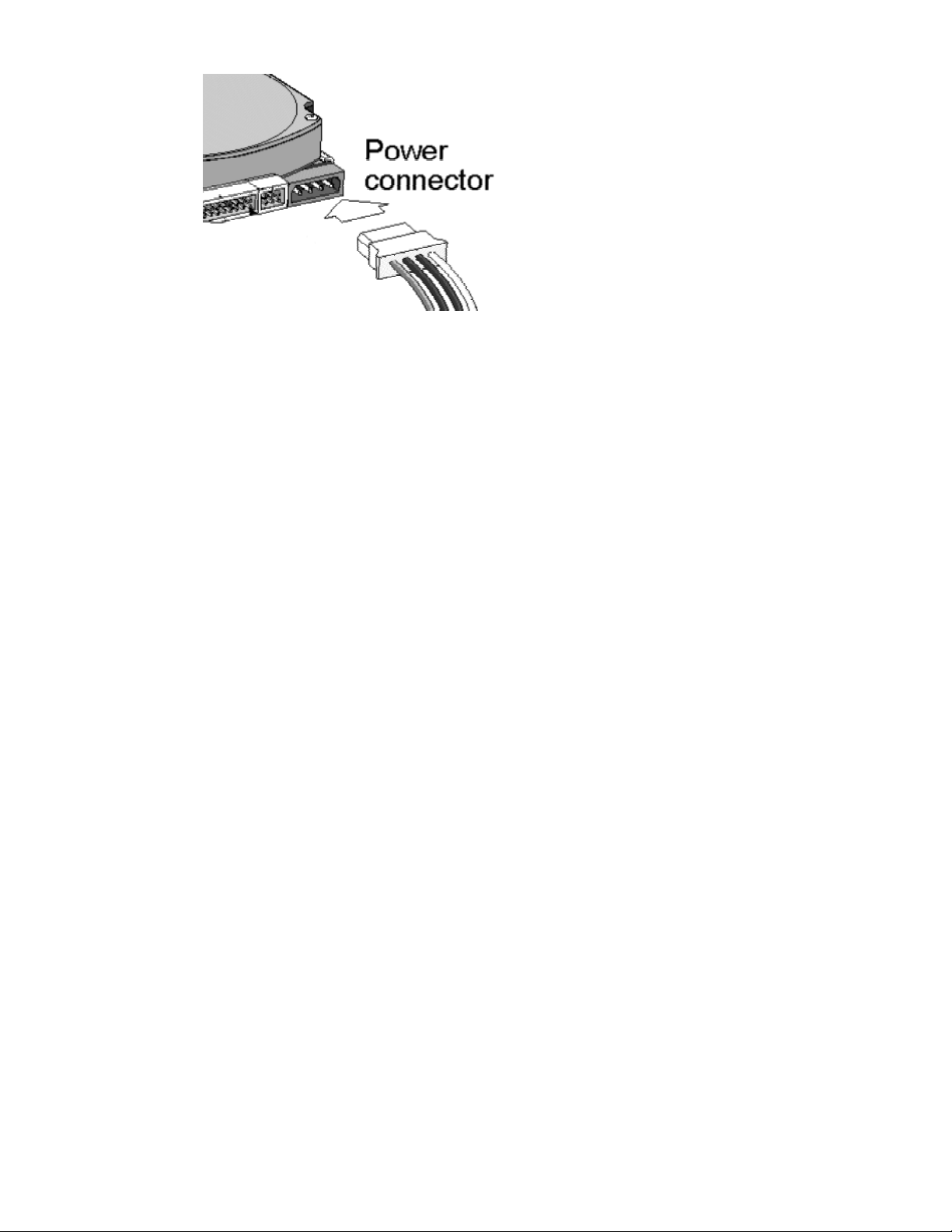
Warning: When connecting the power connector to the HDD, the connector has rounded
edges on the top of the connector that should be placed in the proper position to
avoid equipment damage or electric shock.
4
Page 11
Step 4: Insert the HDD tray back in the mobile rack. Make sure the lever of the mobile rack is
properly in place.
Step 5: Repeat Step 1 to Step 3 if necessary for the other HDD trays.
Step 6: Connect your NAS-3410 to the network by attach a LAN cable from the LAN port located
at the back of your NAS-3410. (At least one network connection is required)
Step 7: Plug the power cord into the power connector on you NAS-3410.
Step 8: Make sure the power switch on the power supply is in ON position.
Step 9: Press the power button on the lower right hand corner of your NAS-3410.
Step 10: Wait for the server to boot up. The boot up process takes approximately 2 minutes and
the real-time status will be displayed on the front LCD panel.
More Info. About HDD Trays
The NAS-3410 has 4 hot-swappable HDD trays, which can be used to install 3.5” IDE hard drive
each. You don’t’ need to turn off the server when replacing a failed hard drive. The hard drive must
be 3.5” ATA66/100/133 IDE compliance. However, DO NOT use any other drive tray which is not
designed for NAS-3410, or a serious damage might be caused.
For best flexibility, the NAS-3410 is designed to fit most types of hard drive form various hard disk
drive vendors. But each of them might have slightly different mechanical dimension. We strongly
recommend applying hard drives with the same type or with the same dimension to NAS-3410.
5
Page 12
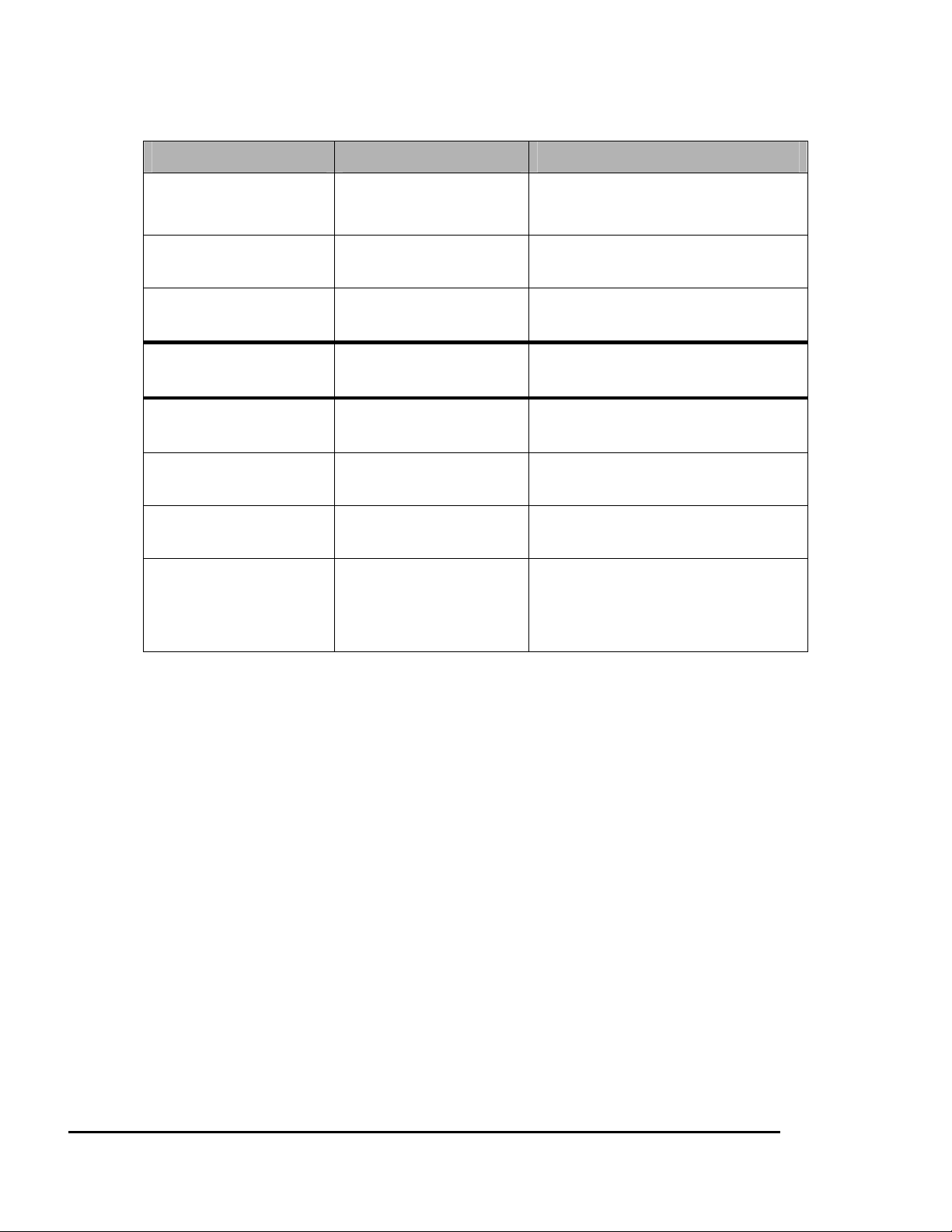
Verify the HDD status
LED 1 (Power/Fault) LED 2 (HD Access)
Green Blinks Off (Master)
Red On (Slave)
Green On Red On during
access
Green Blinks Fast Red On RAID building, rebuilding,
Amber On Off HDD is ready for being
Amber Blinks Fast Off HDD carrier fan error. Blinking
Amber Blinks Slowly Off Disk faulty. Blinking interval is
Green/Amber
Interleaves
Off Off No power
Off IDE cable connect error
Meaning
Powering up
HDD is being accessed
expanding or disk-scanning
hot-unplugged
interval is about 0.5 second.
about 2 seconds.
Hard disk is absent
IDE cable is not connected
6
Page 13

Page 14
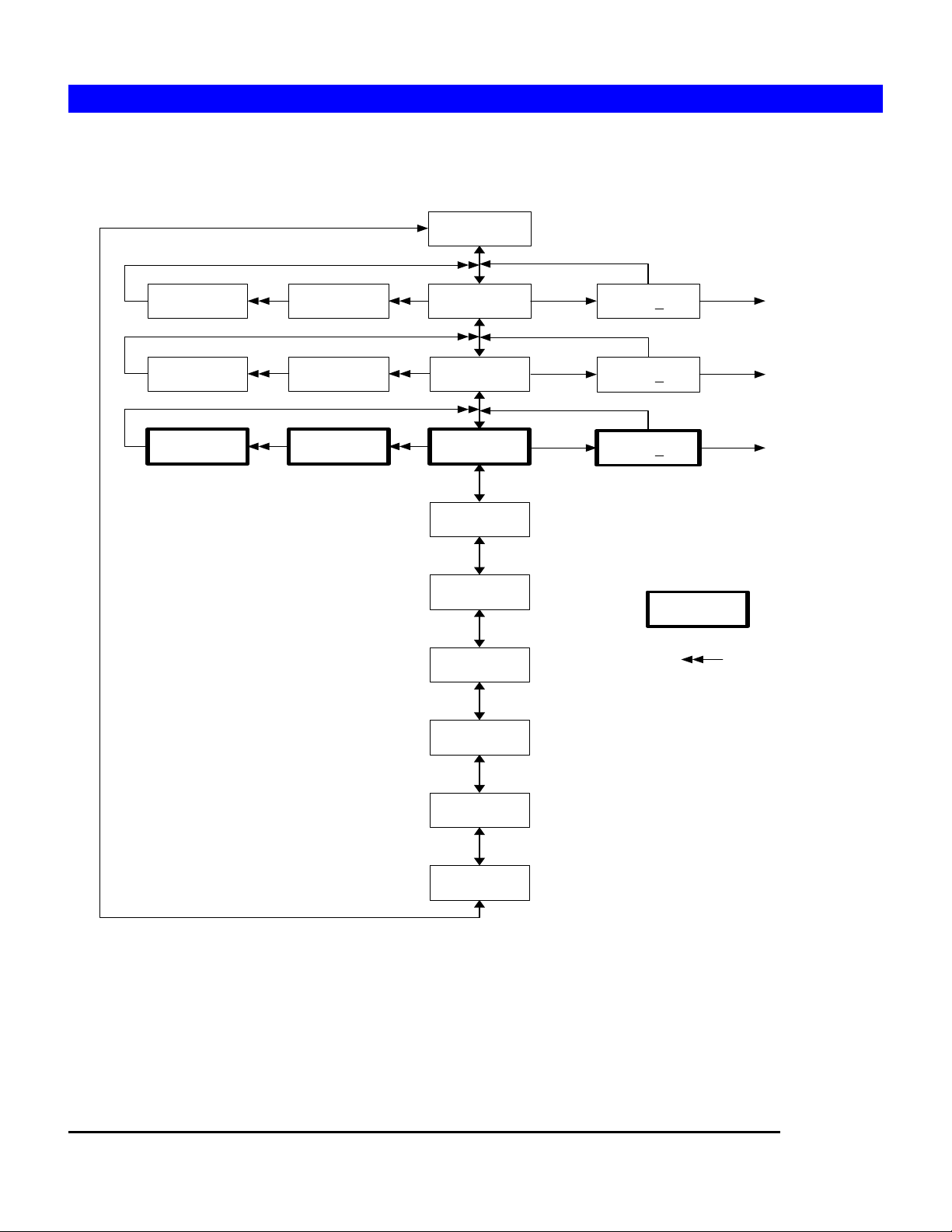
2.2 Setting the IP Addresses
LCD console flow chart
LCD menu console flow chart
System Ready
No
LAN 1 mask :
255.255.0.0
LAN 2 mask :
255.255.0.0
LAN 3 mask :
255.255.0.0
LAN 1 gateway :
192.168.1.254
LAN 2 gateway :
192.168.2.254
LAN 3 gateway :
192.168.3.1
LAN 1 IP:
192.168.1.1
LAN 2 IP:
192.168.2.1
LAN 3 IP:
192.168.3.1
Server Name:
NASD8040000
Data/Time:
8/21/2002 05:30
Firmeware Ver.:
V1.00
CPU Fan Speed:
3994 RPM
Enter Yes
No
Enter Yes
No
Enter Yes
Configure LAN 1?
Yes / No
Configure LAN 2?
Yes / No
Configure LAN 3?
Yes / No
Configure LAN 1
IP/Gateway/Mask
Configure LAN 2
IP/Gateway/Mask
Configure LAN 3
IP/Gateway/Mask
Only display when
Gigabit Ethernet
Adapter is installed
System will
automatically display
the next screen every
two seconds when idle
Thermal (oC)
67 40
Voltage (V)
1.44 3.30 4.68
Configuring the IP addresses using the LCD console
1. After NAS-3410 is boot up, the LCD console shows System Ready. Press the right button.
6
Page 15
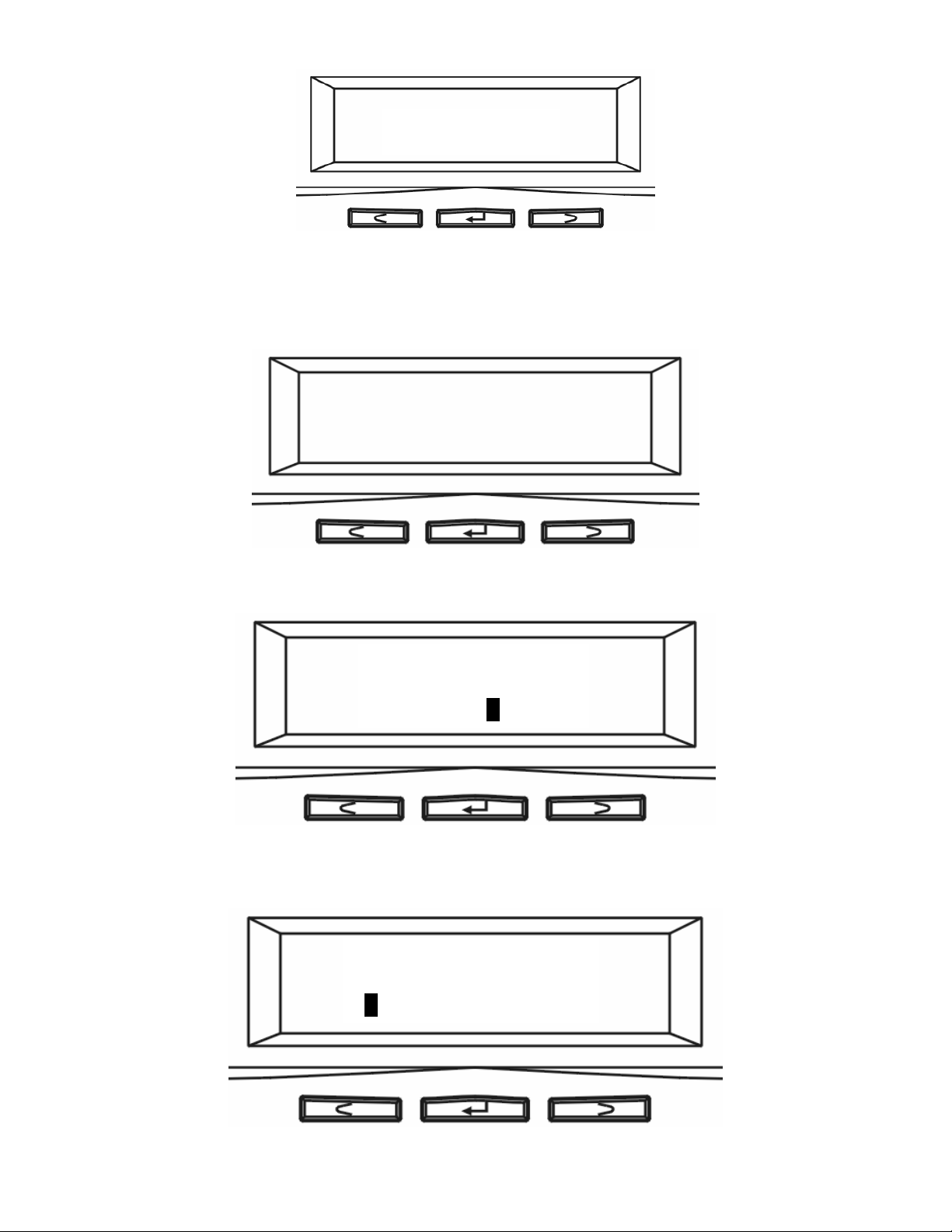
System Ready
2. The IP address of LAN1 is shown. Press the middle button to configure LAN1 IP address. Note
that the symbol at the right hand upper corner indicates that the IP address can be
configured using the LCD console.
LAN1 IP:
192.168.1.1
3. Move the cursor to Yes by pressing the left button and then press the middle button to confirm.
Configure LAN 1?
Yes/No
4. Move the cursor to the correct position using the left or right button. Then press the middle
button to change that number.
LAN1 IP:
192.168.1.1
7
Page 16
5. After you edit the last digit of the IP address, press the right button and configure the Subnet
Mask address.
6. Repeat Steps 4 to Steps 5 to configure the Subnet Mask and Gateway address.
7. After you edit the last digit of the Gateway address, press the right button. Move the cursor to
Save and save the setting or Edit to repeat the above process or Abort to quit the
configuration process without saving.
Exit LAN 1 Menu?
Save/Edit/Abort
8. Repeat the above process to configure the other LAN port.
2.3 Accessing the Administration Home Page
You can configure the detail settings of your NAS-3410 in the administration home page. To
access the administration home page, type the IP address of your NAS-3410 in the address field
of the web browser:
8
Page 17

http://192.168.1.1 /admin/
or Run the utility NAStart utility provided in the CD-ROM, right-click on a NAS server on the
left-hand tree-view pane. Select Admin page item from the right-click menu to open the
administration page. It will prompt for username and password. By factory default, the username
is admin and no password is needed.
9
Page 18

Chapter 3
Server Configuration
This chapter describes how to name the server, specify the server date and time, upgrade the OS
firmware, shut down the system and use UPS with the NAS-3410.
3.1 Server Information and Settings
Click Server from the administration homepage. You will see the Information page describing the
summary information of the NAS-3410.
The Information page is divided into two sections. The General Settings section shows the
parameters which can be modified on the ServerÆGeneral page.
Server Name
Server Comment
Date/Time
Time Zone
Language (Codepage)
Name of the NAS-3410. A NAS-3410 has one unique name,
applicable to all network protocols.
The text which is shown in the comment field when browsing
network computers in Windows Network Neighborhood
Server date and time in 24-hour format
The time zone setting of the server relative to the Greenwich
standard time
The language used by the server to interpret the server name,
user names, share names, file names, etc. Technically, it specifies
the codepage which is used to interpret the characters.
CP437-DOSLatinUS: Latin characters for the United States
CP850-DOSLatin1: Latin characters for West European
CP932-Shift JIS: for Japanese
CP936-Chinese GB: for Simplified Chinese
CP949-Unified Hangul: for Korean
CP950-Chinese Big5: for Traditional Chinese
Mac Roman: Latin characters for Macintosh
Configure from LCD
System LCD Banner
10
Indicates whether users can configure the server from the LCD
console
Indicates the banner text which is displayed on the LCD console
when it receives no user input or event messages for a period of
time
Page 19

UPS Support
Indicates whether the UPS support is enabled or not
Auto Power Restoration
System folder resides in
The System Information section shows the hardware and firmware status of the server.
Firmware Version
Processor Speed
Memory Capacity
No. of HDD/CD/tape
LAN1/2/3 Ethernet
Address
PCI Slot
If enabled, the server will power on automatically when the power
restores after abnormal shutdown
Display the volume name of which the system folder is located
The version number of the OS firmware
The CPU operating frequency
The total size of the main memory
Display the number of HDD/CD/tape installed in the system
The Ethernet MAC addresses of the network controller chips and
their types
Display the type of the add-on adaptor installed in the system
3.2 Modifying the Administrator’s Password
Admin is a built-in user account for the administrator. It is like the root account in UNIX or the
administrator account in Windows 2000 or XP. Using this account, users have access to the
administration homepage and all the storage resources. By default, the password for this user
account is empty. To prevent security vulnerability, it is strongly suggested to specify the password
when performing the first-time setup of the NAS-3410.
To specify or modify the administrator’s password, please select the ServerÆPassword menu on
the administration homepage. Input the current admin password in the Old Admin Password field,
and the new password in the New Admin Password and Confirm Admin Password fields. Then
click Apply.
The administrator can delegate the administrator’s privilege to other users by including them into
the Admins built-in group. Please select the SecurityÆAccount menu. Select Admins* in the
Local User/Group window and click Property. Specify the users to have the privilege and click
Apply.
3.3 Enabling UPS Support
The NAS-3410 supports UPS and basic power management functions. It sends alerts when there
are power events like utility power failure or low battery capacity. When power events occur, the
NAS-3410 can shut down itself automatically to prevent potential data loss.
11
Page 20

To use smart-signaling UPS, connect UPS to the NAS-3410 with an RS-232 cable. Then go to the
ServerÆUPS Settings menu on the administration page to enable UPS support.
To use network-type UPS, connect the UPS to the LAN first. Then go to the ServerÆUPS
Settings page on the administration page. Enable UPS support, select Network UPS from the
UPS Type menu and enter the UP IP address below.
Below are the shutdown options on the page.
Shut down immediately when
battery is low
Shut down in x minutes when
AC fails
Turn off UPS when shut down
by power failure
Specify whether to shut down the server when UPS battery
is low.
Note:
When utility power fails, the NAS-3410 will always shut
down.
Specify how many minutes to wait before shutting down the
server when a power event occurs.
If checked, the NAS-3410 will turn off the UPS while it is
shutting down by power failure. If not, the UPS will still be
working when the server is shut down.
3.4 Server Maintenance
For maintenance or technical support purpose, it is helpful and sometimes necessary to have an
overview of all system settings, current system status and, event better, all event logs. It also
helps a lot if a server itself can send out these files by email.
The NAS-3410 does all the above within several mouse-clicks.
First of all, you have to create a system folder, which is used for storing these files. The system
folder is also required when performing tape backup jobs. To create the system folder, please
open the Administration Page and go to the ServerÎMaintenance menu. On the menu page,
select a volume to contain the system folder. And click Apply to create the system folder.
Once the system folder is created, you are able to save the system settings and event logs as
HTML files. On the same page, choose the files to save and click the Apply button. Before saving
the files, you can preview them by clicking the Preview: hyperlinks. Previewing will not create any
files in the system folder.
After generating these files, you can see them appear in the table. Click any hyperlink to view the
content of a file.
To email the save files, choose the files to save and check the Send the saved files by email
check-box. Enter the email address to send to. And click Apply to send them out by email, while
12
Page 21

saving copies in the system folder.
3.5 Shutting Down the Server
Shutdown, reboot and startup actions
The NAS-3410 can be shut down by pressing the power button twice at the front of the server
case. The whole shutdown process might take seconds to minutes until data are all safely saved
to the hard disks.
To shut down the server from the Administration Homepage, select Shutdown from the Server
menu and click the Reboot or Shutdown button.
You can specify the actions to take during the next startup.
Recalculate user quota information
Reset configuration to factory default
Recalculate the storage consumption per user
during the next startup. It may take much time if
there are a huge amount of files in disk.
Reset the server settings, network settings and
event configuration to factory default during the
next startup.
The settings related to the storage, like shares,
ACLs, user database, will not be cleared.
Scheduled shutdown and power-on
To set the automatic power-on and shutdown schedules, select the ServerÆShutdown menu.
Click the Schedule tab to modify the schedules.
On the schedule settings page, you can set daily or day of month schedules. Check the Enable
check-boxes and specify the time of powering on or shutting down. Remember to click the Apply
button to submit the changes.
3.6 Upgrading the Firmware
Once you get the image file of the new firmware, open the Administration Homepage of the
NAS-3410 and select the ServerÆUpgrade menu. Specify the full path of the image file or click
the Browse… button to find it. Click Apply to begin. The process might take several minutes. The
server will reboot after the firmware is upgraded.
3.7 License for Optional Features
Optional software features of the NAS-3410s are disabled by default. You have to get a license
key from your vendor and activate the optional features before you can use them.
13
Page 22
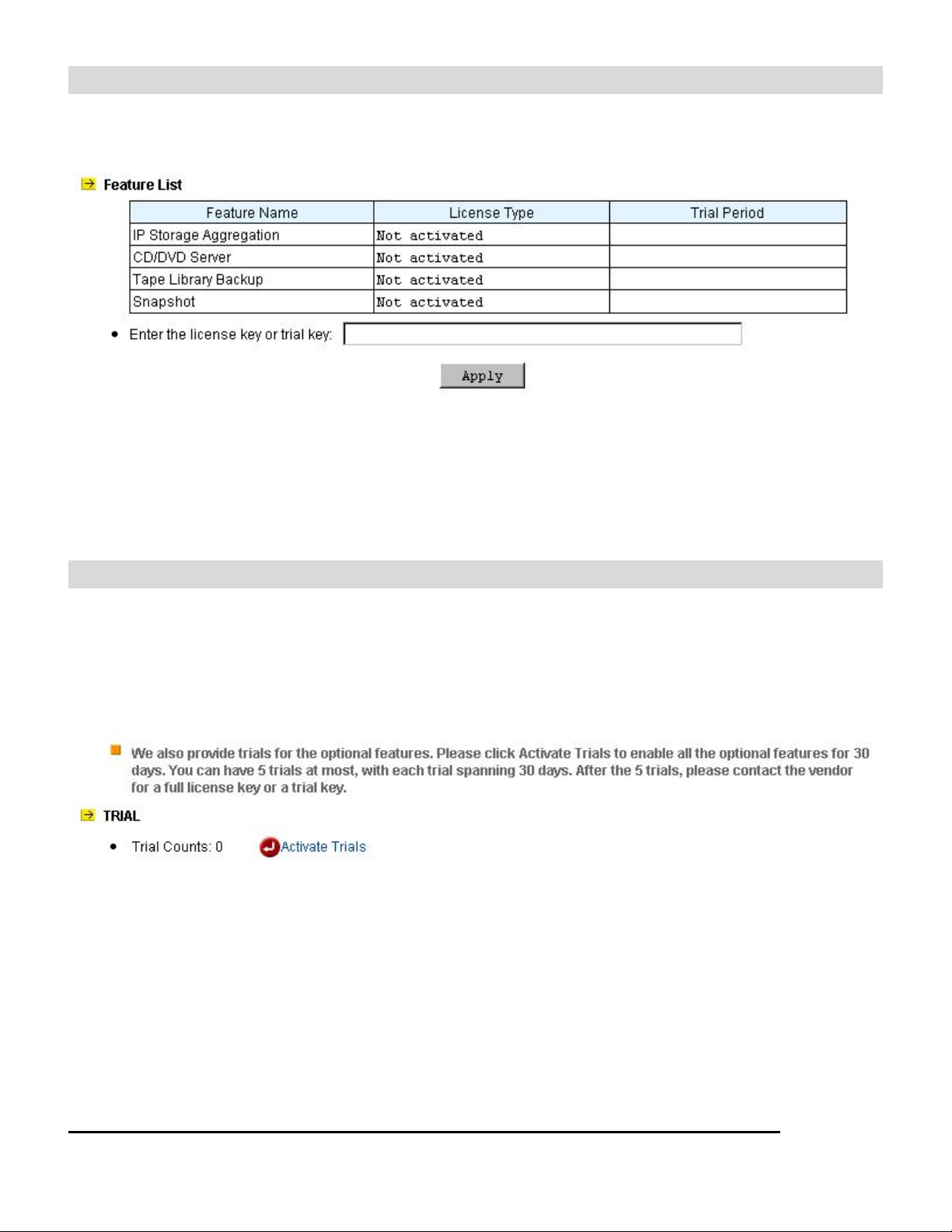
Activating Optional Features
To activate the optional features, please follow the steps.
1. Open the Administration Page, select License from the Server menu. The page is like:
2. Enter the license key in the input field. A license key is a string of 24 characters. The
characters can be any numbers or English letters. Please note that license keys are
case-sensitive.
3. Click Apply to save the settings.
4. The activation is successful if the License Type becomes Full.
Enable Trials
Administrators can have trials of the optional features. Each trial spans 30 days. During the trial
period, the optional features are full functional.
Click the Activate Trials hyperlink to enable the trial. It activates all the optional features. Up to 5
trials can be used. The used trial count is displayed on the same page.
14
Page 23

Chapter 4
Network Configuration
This chapter details concepts and procedures for configuring the NAS-3410 and establishing the
system that can communicate among various OS platforms. Management protocol and email
notification setting are also covered in this chapter.
4.1 Network Information
The Network Information screen is the summary of the current network settings of the NAS-3410.
It provides the administrator a quick look of the basic network setting of the NAS-3410.
The Information page is divided into two sections. The Network Protocols section displays the
current network protocol settings of the server.
Protocol Type
Configuration
Security Policy
The TCP/IP Suite Settings section shows the various TCP/IP settings of the server.
Port
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Gateway
Speed/Mode
Network Teaming Mode
Obtain TCP/IP settings from
Display network protocol supported by the server
Current status of the network protocol. Status: Enabled or Disabled
Display type of the security policy of the network protocol
Display Ethernet port #.
An identifier for a network resource on a TCP/IP network.
A subnet mask used to determine what subnet an IP
address belongs to.
A node on a network that work as a point of entry to another
network
10/100/1000 Mbps and full/half Duplex
Display the current network teaming mode.
Display the IP settings is either assigned automatically from
DHCP or assigned manually
WINS Server IP Address
DNS Server IP Address
DNS Suffix
15
Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS), manages the
association of network resources name and its IP addresses
without the user or an administrator having to be involved in
each configuration change.
IP address of the domain name system (DNS) server which
located the domain names and translate it into IP addresses.
Display the DNS suffix
Page 24

NTP Time Server IP Address
The IP address of the NTP (Network Time Protocol)
server, which is used to synchronize system time
automatically over the net. The system time will be
synchronized with the NTP server every 24 hours.
SMTP Server Address
HTTP Proxy Server IP
Address
IP address or server name of the SMTP (Simple Mail
Transfer Protocol) server used in sending and receiving
e-mail.
IP address of the HTTP proxy server. Next to the IP address
is the port number.
4.2 TCP/IP Settings
Network Teaming Mode
TCP/IP handles network communications between network nodes that are connected to the
network. It is important to setting up correct TCP/IP setting that for NAS-3410 to function properly.
The NAS-3410 provides two on-board Gigabit Ethernet ports (LAN1 & LAN2). You can configure
the Ethernet ports using the following operating modes:
Stand Alone: Each LAN1 & LAN2 are configured with a unique IP address, which are
independent to each other.
Fault Tolerance: Uses LAN2 to take over for the LAN1 if LAN1 is fail to connect to the network
which designed to ensure server availability to the network.
Load Balancing: Offers increased network bandwidth by allowing transmission to multiple
destination addresses using both LAN1 and LAN2. If the traffic of one of the LAN port starts to get
congested, requests are then forwarded to the other LAN port with more capacity until the traffic of
both LAN ports start to get balance. Note that only the LAN1 Ethernet port receives incoming
traffic. Load Balancing also incorporates Fault Tolerance protection.
Link Aggregation: combines both LAN1 & LAN2 into a single channel, appearing to use a single
MAC address to provide greater bandwidth. It must be used with a network switch having the Link
Aggregation or Trunking function.
Wake-On-LAN
NAS-3410 also supports Wake-On-LAN (available for LAN1 only). Wake-On-LAN allows
administrators to remotely power on your NAS-3410 to perform maintenance task on the server
with no need to go to the server physically.
Jumbo Frame Support
16
Page 25
The NAS server can support jumbo frames, using packet sizes to 9K bytes instead of the standard
Ethernet's 1500 bytes. Using the jumbo frames, the NAS server reduces the networking overhead
and would hence increase network throughput. In addition to enabling the jumbo frame support on
the NAS server, you must also enable the support on the Gigabit switches and client PCs so that
they can communicate using jumbo frames.
Configuring TCP/IP Settings
1. Select a Network Teaming Mode from the pull-down menu that suit you need.
2. Enable or Disable Wake On LAN (Available for LAN1 only).
3. Click the Obtain IP settings automatically radio button to obtain IP addresses of your
NAS-3410 from DHCP, BOOP or RARP server on the network.
4. Or, click the Use the following IP settings radio button to assign the IP addresses manually.
5. Input the WINS server IP address.
6. Input the DNS server IP address.
7. Input the DNS Suffix.
8. Input the NTP Time Server IP Address if available.
9. Click Apply to save the setting.
To disable a LAN port, enter 0.0.0.0 in its IP address field. If you happen to disable all LAN ports
and cannot access the administration page, please use the LCD panel to change the IP address
to non-zero values.
4.3 Windows Settings
NAS-3410 is using SMB/CIFS protocol- short for Server Message Block/Common Internet File
System, a protocol used by Microsoft to share files, directories and devices with the Windows
client.
You can configure the Windows Network Settings using the following operating mode:
Workgroup Mode: NAS-3410 becomes a member of a workgroup and communicates with the
clients using its internal user database for authentication and do not require other authentication
server present in the network.
Domain Mode: NAS-3410 becomes member of a domain and communicates with the client using
the user database stored in an authentication server which must be present in the network
Optionally, you can register the NAS-3410 to the domain. Once registered, the NAS-3410 will be
created as a machine account on the domain controller. And it will use Netlogon as the
authentication mechanism, which provides better integration into the Windows network
environment.
17
Page 26
Configuring Windows Network Settings
1. Click the Enable Windows Network (SMB/CIFS Protocol) checkbox to enable access for SMB
client.
2. Enter the Workgroup/Domain name.
3. Click the Workgroup Mode radio button if you want to configure NAS-3410 in Workgroup
Mode.
4. Or, click the Domain Mode radio button if you want to configure NAS-3410 in Domain Mode.
5. Select the option to support Unicode.
6. Select the option to disconnect idle connection automatically. Server will disc onnect the
connections which have been idle for 5 minutes if this option is enabled.
7. Click Apply to save the setting.
4.4 UNIX/Linux Settings
NAS-3410 can export shares to UNIX/Linux client via NFS protocol. UNIX/Linux client then can
mount the shares and gain access to the content of the shares.
UNIX/Linux client uses UNIX user identification, typically consisting of User Identifier (UID) and
Group Identifier (GID), for access control. Non-NFS clients do not use UIDs and GIDs for
identification. Since NAS-3410 is intended for working in a heterogeneous network, files created
by non-NFS client could possess incorrect ownership information and generate inaccurate quota
information for UNIX/Linux clients due to the unmatched UID and GID. A mapping is needed to
maintain the correct identity of the user using multiple protocols to access NAS-3410, for example
Windows and UNIX/Linux clients. Windows based clients need to map the Windows user name to
UID/GID before forwarding a request to retain the correct ownership information for UNIX/Linux
clients.
By default, the NAS-3410 maps all non-NFS users, including local users and domain users, with
the same UID/GID as defined on this page. If the administrator wants to have different UID/GID for
different users, he should click the Modify button to modify the user mapping to UID/GID.
UID: User ID. The numerical number assigned to a user in Unix/Linux permissions. NFS uses UID
to determine permissions on files and directories.
GID: Group ID. A part of POSIX permissions that determine groups of users. NFS files have a GID
assigned to them.
Permission: Three numbers are used for setting the file permission. Each of the three numbers
corresponds to the type of users-
18
Owner, Members of a group and Everyone Else.
Page 27

Number Read
(R)
0 No No No
1 No No Yes
2 No Yes No
3 No Yes Yes
4 Yes No No
5 Yes No Yes
6 Yes Yes No
7 Yes Yes Yes
Example: If the permission of a file is set to 777, this file has read, write and execute permissions
for the owner, the group and for other users.
Write
(W)
Execute
(X)
Configuring UNIX/Linux Network Settings
1. Click the Enable UNIX/Linux Network (NFS Protocol) checkbox to enable access for NFS client.
2. Enter the default permission for files created via non-NFS protocol. (Default setting = 755)
3. Click Apply to save the settings.
4. Click the Modify icon and enter the default UID and GID. (Default setting = 0)
5. Choose to map all users to the default UID/GID or assign UID/GID for each user manually.
6. Click Set Default link to set the UID/GID of all users to the default UID/GID. Note that the value
‘-1’ represent that the UID/GID is equal to the default UID/GID configured above. Or,
7. Click Apply to save the settings
Configuring NIS settings
The NIS (network information services), formerly known as Yellow Pages, is a UNIX standard for
centralizing the management of UNIX resources. The NAS-3410 supports the retrieval of user
accounts and their UID/GID from a NIS server.
If the NIS support is enabled, the NAS-3410 can auto-map NIS users with local/domain users. It
matches user names and assigns the UID/GID of the matched NIS users to local/domain users.
The user auto-mapping function provides better and tighter integration between NFS clients and
other network operating systems.
The steps of enabling NIS support are as follows:
1. Check the Enable NIS Support checkbox.
2. The NIS domain name is required. Please fill in the correct name in NIS Domain Name field.
3. If you do not know the IP address of the NIS server, please specify Find by broadcast.
Otherwise, specify the IP address in the fields.
19
Page 28
4. After enabling the NIS support, you can auto-mapping NIS users with local/domain users. In
UNIX/Linux menu, click the Modify icon.
5. Click the Auto-map with NIS users link to map with the users in the configured NIS server.
6. Click Apply to save the settings.
4.5 Macintosh Settings
NAS-3410 supports two kinds of protocols used for Mac OS clients – AppleTalk and TCP/IP
(Open Transport). Also, NAS-3410 provides two kinds of security polices for Macintosh Network
AFP client.
Local account authentication: Authenticate user using NAS-3410’s internal user database.
Local and domain authentication: If Windows Network is enabled, you can enable both local
and domain authentication for AFP client.
Current Zone: A division between groups of machines when viewed using AppleTalk. AppleTalk
Zones can be seen in the Chooser, the AppleTalk Control Panel, and the Network Browser.
AppleT alk Address: It is a unique number that identify the server on the network. The number to
the left of the dot is the network number. The number to the right of the dot is the node number.
Configuring Macintosh Network Settings
1. Click the Enable Macintosh Network (AFP Protocol) checkbox to enable access for AFP client.
2. Select a protocol and click the radio button beside it.
3. Click the Local account authentication radio button to authenticate user using the server’s local
user database.
4. Or, click the Local and domain account authentication radio button to use both local account
and Microsoft domain security authentication.
5. Select the Current Zone from the pull down menu or Default Zone is assigned by default.
6. Click Apply to save the setting.
4.6 NetWare Network Settings
NAS-3410 operates in a manner similar to a Novell NetWare 3.12 file server. Setting up your
NAS-3410 and shared among Novell NetWare clients. A share can be mapped to the NAS-3410
using NetWare clients. You can enable specific local users or local groups to have access to the
share from within the Administration Homepage.
Server Name: The default NetWare server name is the server name followed by an underscore
and followed by "NW".
Security Policy: The policy that the NAS-3410 used for authentication.
20
Page 29
Frame: Frame types determine how packets of network data are formatted on different LANs. The
default setting is AUTO in the NAS-3410.
Internal Network Number: A logical network number that identifies an individual NetWare server
on the LAN.
Configuring NetWare Settings
1. Click the Enable NetWare Network (NCP Protocol) checkbox to enable access for NetWare
client.
2. The NetWare server name is the original server name following by a “_NW”. For example, if the
server name of the NAS-3410 is “ABC” then the NetWare server name will be “ABC_NW”.
3. Click Apply to save the setting.
4.7 Web Data Access Settings
This section shows the parameters that you can set up for user to access NAS-3410 user’s home
page. You can configure the user access constraint, authentication policy and default setting by
defining the Access Control, Security Policy and Default User Page settings.
Configuring Web Data Access
1. Click the Enable Web Data Access (HTTP Protocol) checkbox to enable Web data accessing.
2. Choose Allow file download only or Allow file upload and download.
3. Click the Local account authentication radio button to authenticate user using the server’s local
user database.
4. Or, click the Local and domain account authentication radio button to use both local account
and Microsoft domain security authentication.
5. Select the default type of the folder display on the user page. You can choose from Detail View,
Large Icons or Small Icons.
6. Click the checkbox beside the Allow users to modify ACL to give users the privilege to modify
the ACL table entries.
7. Click Apply to save the setting.
4.8 FTP Data Access Settings
Configuring FTP Data Access
NAS-3410 supports File Transfer Protocol (FTP) that allows users to transfer files via the Internet.
By properly configuring the FTP settings, you can effectively control how users access the content
in your NAS-3410 via FTP.
1. Click the Enable FTP Data Access checkbox to enable FTP data accessing.
2. Select the Access Control type. Click the Allow file download only or Allow file upload and
21
Page 30
download radio button.
3. Select the appropriate Security Policy. Check the Allow anonymous login and map to:
check-box, and select a local user from the pull down menu. User using the anonymous login
will then possess the same security privilege as the selected local user.
4. Or, click Allow individual user login. Select Local account authentication to authenticate user
using the local user database or click the Local and domain account authentication radio button
to use both local account and Microsoft domain security authentication.
5. Select the User Limit. Click the Unlimited radio button or specify the maximum number of users
allowed to access the content in your NAS-3410 via FTP.
6. Specify the Home Directory when user connects to the NAS-3410 via FTP. Note that you must
select a volume to create a FTP home directory.
7. Specify the permission of the home directory by clicking the Set icon.
8. Click Apply to save the setting.
4.9 SNMP Settings
Simple network management protocol (SNMP) provides the ability to monitor and gives status
information of the SNMP agent to the SNMP management console. NAS-3410 behaves as an
SNMP agent that answers requests from management console and sends trap information to it.
The following options should be configured to using SNMP protocol:
Community: A name serves as a simple authentication. The communication between the SNMP
management console and the NAS-3410 cannot be established if the community names are
mismatch.
IP: IP address of the SNMP management console
Trap: A trap is a voluntary message send out from a SNMP agent (which is in this case your
NAS-3410) when there is an event occurred.
Management: Configure the SNMP management console as Read Only or Full Control.
Location: Provide location information of the SNMP agent.
Contact: Provide name of the contact person who has the management information of the SNMP
agent.
Configuring SNMP Settings
1. Click the Enable SNMP Protocol checkbox to enable SNMP accessing.
2. Enter a Community name.
3. Enter the IP address of the management console.
4. Select Yes from the pull down menu if you want the corresponding management console to
22
Page 31

receive trap message.
5. Select Read Only from the pull down menu if you want the corresponding management console
has read only privilege.
6. Repeat Step 2 to Step 5 if more than one management console is available. NAS-3410
supports up to 4 management consoles.
7. Enter the location information of your NAS-3410.
8. Enter the name of the contact person who has the management information of the NAS-3410.
9. You can check the checkbox beside Send a test trap to send sample trap information to validate
your setting of the SNMP settings.
10. Click Apply to save the setting.
4.10 Email Settings
You can configure email notification to notify you when there is an event occurred to the
NAS-3410. Enter the information of the SMTP server on your network in this menu; you can
configure what kind of event should trigger the email notification process in the
EventÆConfigurationÆAdvance menu.
Configuring Email Settings
1. Click the Enable SMTP Protocol checkbox to enable SMTP protocol.
2. Enter the SMTP Server Address.
3. Enter an existing user account name of the SMTP server.
4. Enter the password of the account.
5. Enter up to two email addresses you want to send email notification to when event occurred.
6. Click the Send a test email checkbox if you want to send out a test email to validate your email
setting.
7. Click Apply to save the setting.
4.11 SSL Settings
The NAS-3410 enables secure web access by supporting SSL 3.0, both for the user homepage
and the administration homepage. To use SSL 3.0, the NAS-3410 will generate a server certificate
for authentication and data encryption. By default, the server certificate is issued to the NAS-3410
designated by its IP address. You can also specify to use the server's full name on the server
certificate. The server's full name is the server name appended with its DNS suffix, such as
nas.company.com. Please refer to the TCP/IP settings for DNS suffix.
For clients to access server web-pages with secure connection, they have to install the CA
certificate first. Suppose that the server's IP address is 192.168.1.10, please open
http://192.168.1.10/admin/CA for the certificate. Choose to install the certificate when a dialog-box
23
Page 32

pops up. Once the CA certificate is installed, the client can access all NAS-3410s' web pages with
SSL connection.
Suppose that the server IP address is 192.168.1.10. To access the NAS-3410's web pages with
SSL connection, please open https://192.168.1.10/ for the user homepage, or
https://192.168.1.10/admin/ for the administration homepage. If the server certificate with the
server name is chosen, please open https://[server_name] instead.
24
Page 33

Chapter 5
Storage Management
This chapter describes how to create a single-disk volume or a RAID volume. It also outlines the
steps of deleting a volume, expanding a RAID-5 volume and assigning hot-spare disks. After a
volume is created, please refer to the next chapter for more information about sharing data and
assigning permissions.
5.1 Volume Usage and Status
A volume is a logical storage unit. Each volume holds a complete file-system. A volume can exist
on a single disk or a RAID group consisting of two or more disks.
Volume View
List of Volumes
It displays all the volumes in the NAS-3410. Volume Name shows the volume name which is
defined when creating a volume. Each volume name is also a hyperlink. It opens a page for
showing the detailed information of that volume. Members indicate the hard disks which compose
the volume. RAID Type indicates whether this volume is JBOD (a single hard disk), RAID 0, RAID
1 or RAID 5. Please refer to the next section for more information about RAID.
Free Space indicates the volume usage by showing the free storage space in the volume and the
percentage. Total Space indicates the volume size.
Status indicates the disk activity on the volume. The disk activity may be one of the following:
Ready
Not Ready
Degraded
Faulty
Faulty (RW)
The volume is mounted and ready for data access.
The volume is not mounted successfully. It is not accessible.
One of the volume members is defective. Data are still intact and
accessible, but the volume is no longer protected by RAID. Data backup
and RAID rebuilding are strongly suggested when a volume is in this state.
Two or more hard disks in the volume are not functional.
It is not possible to perform any data access or recover any data.
Two or more volume members are defective.
Inaccessible
Apply (Ready)
25
There might be data loss, but it is possible to recover some data. Please
copy data to a safe place immediately when a volume is in this state.
Two or more volume members are missing. The volume is not mounted
and data cannot be accessed.
The volume settings on the server and those on the hard disks are
Page 34

Apply (Degraded)
Apply (Faulty RW)
Apply (Rebuild)
Apply (Expand)
inconsistent.
It means that the server has to read and apply the volume settings from
the hard disks.
After the volume settings are restored, it will return to the last known state,
which is specified in parentheses.
Checking
Mounting
Create (xx%)
Rebuild (xx%)
Expand (xx%)
Scan (xx%)
Hot-Spare Disks
A hot-spare disk will be used to rebuild a RAID automatically whenever a RAID volume is
degraded because of a bad or missing hard disk.
Free disks
These hard disks are not used yet. They can be used to create volumes or assigned as hot-spare
disks.
Volume Details and Renaming a Volume
Checking the file-system.
Mounting the volume for data access.
Creating a volume. The progress is shown in percentage.
Rebuilding a RAID. The progress is shown in percentage.
Expanding a RAID. The progress is shown in percentage.
Scanning hard disks for bad sectors. The progress is shown in
percentage.
To change the name of a volume, click its Volume Name hyperlink in the List of Volumes table. It
brings to another page for displaying detailed information of the volume. You can modify the
volume name on that page.
Device View
It is a list of all the storage devices connected with the NAS-3410, including hard disks,
CD/DVD-ROM, CD/DVD writers and tape drives.
List of hard disks
In Volume shows to which volume the hard disk belongs. Location indicates the IDE channel and
master/slave position of the hard disk. Model Name shows the model or the manufacturer of the
hard disk. Capacity shows the unformatted capacity of the hard disk. Status indicates the disk
status or disk activity, being one of the following.
On-line
No init
26
The hard disk is a member of a mounted volume which is ready for data
access.
The hard disk is not initialized yet. A no-init disk must be a free disk, which can
Page 35

be used to create a volume or be assigned as a hot-spare disk.
Defective
Off-line
Backup/Archiving Devices
These are either CD/DVD-ROM drives, CD/DVD writers or tape drives. Type indicates what kind
of device it is. Mode indicates the data transfer mode of the storage device interface.
Device type could be CD-ROM, CD-R, CD-RW, DVD-ROM, DVD+R, DVD+RW,
DVD-ROM+CD-RW or Tape.
The hard disk contains bad sectors.
The hard disk is not mounted and not accessible.
Data Transfer Modes
Data transfer modes could be PIO x, DMA x, MDMA x, or UDMA x. PIO means Programmed
Input/Output, of which data transfers are performed by host CPU. DMA means Direct Memory
Access, of which data transfers are done by device controllers and use little host CPU time.
MDMA is multi-word DMA. UDMA is Ultra DMA, which is a faster DMA mode.
PIO Modes
PIO Mode 2: 8.3 Mbytes/sec
PIO Mode 3: 11.1 Mbytes/sec
PIO Mode 4: 16.6 Mbytes/sec
DMA Modes
Multiword DMA Mode 2: 16.6Mbytes/sec
Ultra DMA Mode 2: 33 Mbytes/sec
Ultra DMA Mode 3: 44 Mbytes/sec
Ultra DMA Mode 4: 66 Mbytes/sec
Ultra DMA Mode 5: 100 Mbytes/sec
Ultra DMA Mode 6: 133 Mbytes/sec
5.2 Creating a Volume
The first thing for the administrator to do with the storage is to create a volume on the hard disks.
Then he or she can share the storage for user access and set security control.
To create a volume, first go to the VolumeÆCreate page. Specify the volume name in the
Volume Name field and choose the volume type (JBOD, RAID 0, 1 or 5). Then choose the hard
disks to be included in the volume. Last, click Apply to submit changes. The progress of volume
creation is shown on the VolumeÆInformation page.
Below are the volume types.
JBOD
27
Just a Bunch Of Disks.
A JBOD-type volume contains only one hard disk as
its member.
Page 36

RAID 0
RAID level 0 is disk striping only, which distribute data
evenly over multiple disks for better performance. It
does not provide safeguards against failure.
RAID level 0 uses two or more hard disks.
RAID 1
RAID 5
Hot Spare
Write-Once Volume:
When setting a Write-Once volume, you are not allowed to erase or change what you have written
RAID level 1 uses disk mirroring, which provides
100% duplication of data. It offers high reliability, but
doubles storage cost.
RAID level 1 uses two hard disks.
RAID level 5 distributes data and parity bits over
multiple disks for both performance and fault
tolerance. A RAID volume can still work whe n a hard
disk fails.
RAID level 5 uses three or more hard disks. Building a
RAID-5 volume may take hours depending on
capacity.
The hot-spare disks are global, which means they are
not bound to any specific RAID volumes. Whenever a
RAID volume goes degraded because of a bad hard
disk, a hot-spare disk will be taken immediately to
recover that RAID volume.
on this volume. This setting CANNOT be reverted in any situation, please think it twice before you
enable it.
5.3 Deleting a Volume
To delete a volume, go to the VolumeÆDelete page. Select the volume to be deleted and click
the Delete button. Please be very careful because all data in the volume will be destroyed and the
RAID configuration will be erased also. All hard disk members in this volume will become free
disks after the deletion.
5.4 Expanding a RAID-5 Volume
RAID-5 volume expansion makes it possible to enlarge volume capacity without rebooting the
NAS-3410. Volume capacity grows on the fly. Moreover, you do not have to change any share
permissions, security controls and quota settings after volume expansion. Storage management
becomes much easier.
To expand a RAID-5 volume, please go to the VolumeÆExpand page. Select a RAID-5 volume to
be expanded. Then choose the free disks as new members. Click Apply to submit changes. The
progress of RAID expansion is shown on the VolumeÆInformation page.
28
Page 37

To expand a SmartExtend volume, please open the administration page of the SmartExtend target
system. When the target volume is connected to the initiator, use the VolumeÆExpand function
to expand the target volume.
5.5 Migrating Data Volumes
Migrating a data volume is to duplicate a volume block by block. It helps administrators migrate or
duplicate data between volumes of different RAID types or capacity. During data migration, both
the source volume and the target volume will be un-mounted, not available for client access.
To migrate data, select a source volume, and the target volume to migrate to. Choose Data
migration and click Apply. The target volume will inherit all the security and quota settings of the
source volume. No differences will be observed by clients before and after the migration.
To duplicate a volume, select a source volume and the target volume. Choose Data duplication
and click Apply. The target volume will stay on-line after the data duplication.
5.6 SmartExtend – Add More NAS Capacity
The SmartExtend feature can add NAS capacity over LAN. A SmartExtend initiator can connect
up to 10 SmartExtend target volumes via the Giga- or Fast-Ethernet ports. A target volume can
provide up to 2TB of capacity, so it can increase NAS capacity by as much as 20TB.
The following table explains some terms used by SmartExtend.
SmartExtend Initiator
SmartExtend Target
SmartExtend Target Volumes
SmartExtend
Network-Attached Devices
Exported SmartExtend Target
Volumes
A NAS head. It can add more capacity by connecting with
SmartExtend target volumes over network. A SmartExtend
initiator can connect to 10 SmartExtend target volumes at
most.
A system which contains target volumes. Target volumes
are used to add capacity to a SmartExtend initiator.
JBOD or RAID groups on a SmartExtend target system.
Once connected, SmartExtend target volumes appear as
free disks on a SmartExtend initiator system. Different from
a locally-attached hard disk, a SmartExtend device is
network-attached.
Target volumes must be exported to network first before
being seen and used by SmartExtend initiators.
Group Allowed/Login User
29
The use of a SmartExtend target volume is restricted to the
SmartExtend initiator and the user group which are
assigned when it is exported. Only the specified
SmartExtend initiator can use the target volume. And the
initiator must provide a user account for authentication
when it tries to connect to the target volume.
Page 38

Connected/
Disconnected
Indicates the status of a SmartExtend target volume. If
connected, a SmartExtend initiator can access data in the
SmartExtend target volume. A SmartExtend initiator will try
to connect to every target volume in the target volume list
when it starts up.
Automatic Recovery of
Broken Connections
If network is not very stable, a SmartExtend target volume
might be disconnected occasionally. A SmartExtend initiator
will try to recover a broken connection every 5 minute. The
feature improves data availability even in a poor network.
Configuring SmartExtend Step By Step
At least two NAS-3410s are required, one as an initiator, another as a target. SmartExtend
initiators provide all NAS file-sharing functions, acting as NAS heads connecting to SmartExtend
targets. SmartExtend targets are network-attached RAID systems for SmartExtend. They have no
NAS functions.
The SmartExtend function is an optional feature which must be activated by a license key. Please
contact the vendor to obtain the license key.
All NAS-3410 can become SmartExtend targets. You do not have to activate the function.
Follow the steps below to build a SmartExtend connection between an initiator and a target.
on the SmartExtend initiator system
1. After getting the license key, go to the Server
activate the feature.
2. Go to the ServerÆGeneral page. Change the SmartExtend mode to NAS with SmartExtend
Initiator.
on the SmartExtend target system
3. Go to the ServerÆGeneral page, change the SmartExtend mode to SmartExtend Target.
4. Go to the VolumeÆCreate page, create a JBOD or RAID volume. It is suggested to create
hot-spare disks after you create a RAID-1 or RAID-5 volume.
5. Check the VolumeÆInformation page and make sure that the volume is created successfully.
6. Go to the VolumeÆSmartExtend page. Export the target volume by clicking the Export
Volume button.
(a) First specify the target volume to be exported.
(b) Specify the group who can use the target volume. A SmartExtend initiator must provide a
Æ License page to enter the license key and
30
Page 39

user account when it tries to use the target volume. The user account must be a member of
this group.
(c) Specify a SmartExtend initiator which will connect to this target volume.
(d) Apply the settings.
7. On the VolumeÆSmartExtend page, you will see the target volume in the list, but the Status
column will show Disconnected. You will need to build the connection from the SmartExtend
initiator side.
on the SmartExtend initiator system
8. Go to the VolumeÆSmartExtend page, click the Add button.
(a) Choose the SmartExtend target system from the SmartExtend Target List or specify the
IP address manually. Click the Next button.
(b) On the page, it will list all the target volumes found on the SmartExtend target system.
Choose the target volume to connect to.
(c) Specify the username and password for authentication. It must be a member of the group
specified in Step 6.(b)
(d) Click the Finish button.
9. On the VolumeÆSmartExtend page, you will see the target volume listed in the table. It will
need about 10-30 seconds to build the connection, depending on network traffic. Click the
Refresh hyperlink to refresh the page. The device name should be SED01, standing for
SmartExtend Device number 01.
10. Go to the VolumeÆInformation page, check if SED01 is in the Free Disks list. If yes, it
means that it is not initialized yet. Go to the VolumeÆCreate page to initialize it.
Now you are done. Repeat the above steps until all SmartExtend volumes are created ok.
Expanding a SmartExtend RAID-5 Volume
To expand a SmartExtend volume, please open the administration page of the SmartExtend target
system. When the target volume is connected to the initiator, use the VolumeÆExpand function
to expand the target volume.
5.7 Volume/Disk Scan
Volume/Disk scan is especially useful for disk diagnostics and repairs lost or cross linked clusters
in Volume/Disk. All readable data will be placed in new clusters and defective cluster will mark as
31
Page 40

bad in the file system. All the newly added devices will be scanned before usage to ensure the
data integrity in the NAS Server.
Select the volumes or disks you want to scan, click Scan Now button to start scanning. Or, click
Schedule to set the time for NAS Server to perform scanning at the scheduled time.
Disk Auto-scanning
To make sure that the hard disks contain no bad sectors before putting into use, it is suggested to
perform disk-scanning before taking such actions as creating a volume, expanding a volume,
migrating data or assigning a hot-spare disks. If disk auto-scanning is enabled, the NAS server
can scan disks automatically when you perform these actions. If the hard disks have ever been
scanned in the last 30 days, the auto-scanning will be skipped so that the auto-scanning will not
be activated too often.
To enable the feature, please click the Configure hyperlink on the VolumeÆScan page. Set the
Disk Auto-scanning item to Enabled.
5.8 Hot-swapping
You may have to change hard disks in some situations, such as hard disk failure, degraded RAID
or general maintenance. The NAS-3410 supports HDD hot swapping. Below are the instructions
of replacing hard disks.
1. Identify which hard disk fails. The amber LED of the HDD tray will blink to indicate hard disk
failure.
2. Turn off the failed HDD by pressing the red button on the HDD tray.
3. When the amber LED is steady on, it is ready for being unplugged. Unplug the HDD tray and
replace the HDD with a good one.
4. Plug in the HDD tray. Wait until the Green LED is steady on. Then you are done.
When a RAID volume is degraded and there is no available hot-spare disk for rebuilding, the
RAID volume will stay in the degraded state. In this state, you can hot-unplug the failed hard disk
and plug in a good one in the same HDD tray. The RAID volume will rebuild automatically with the
new hard disk.
32
Page 41

Chapter 6
Security Control
This chapter covers how to setting up the security control of the files, folders and shares stored in
NAS-3410. Managing Access Control List (ACL) file level security, file ownership and user quota
are also covered in this chapter.
You can configure the following types of security control on the NAS-3410:
1. Create, edit and delete user accounts in the local user database.
2. Create shares.
3. Configure Files, Folders and shares permission.
4. Configure local account, domain account and UNIX/Linux Hosts permission.
5. Maintain the ACL table.
6. Configure the local user and domain user quota limit.
6.1 Security Information
The Security Information screen is the statistic of the current security setting of the NAS-3410. It
provides administrator a summary of the security database and the status of the operation mode.
The Information page is divided into two sections. The Security Database section display the
number of shares, number of ACL nodes and number of user/group.
Number of Shares
Number of ACL Nodes
Number of Accounts
Local User/Group
Domain User/Group
Trust Domain User/Group
Host Entry
Total number of share created in NAS-3410.
Total number of ACL node created. ACL tells NAS-3410 which
access right each user has to a folder or an individual file.
The total account number of the Local User/Group, Domain
User/Group, Trust Domain User/Group and Unix/Linux Host
Entry.
Total number of local user/group. A local user or group is an
account that can be granted permissions and rights from
NAS-3410.
Total number of domain user/group. Domain users or groups are
managed by the network administrator.
Total number of trust domain user/group.
Total number of Unix/Linux host entered.
The Security Configuration section shows the current security configuration settings of the
server.
33
Page 42

Windows Security Mode
Display the status of the Windows Network operating mode.
Status: Domain Mode or Workgroup Mode
Workgroup/Domain
Name
Domain Login Account
ACL Security Control
User Quota Control
Display either the workgroup name or domain name
Display the username for retrieving the domain user list in the
domain.
Display the status of the ACL Security Control. Status: Enabled or
Disabled
Display the status of the User Quota Control. Status: Enabled or
Disabled
6.2 Creating the Local User and Local Group Accounts
A local user or group is an account that can be granted permissions and rights from your
NAS-3410. You can add local user to a local group. Groups are indicated by a * sign at the suffix
of the name. You can also grant administrator privilege to a local group. Groups with administrator
privilege are indicated by a # sign at the suffix of the name.
To create a local user:
1. Go to SecurityÆAccountÆLocal Account menu.
2. Click the Add User button.
3. Type in the user name and enter the password.
4. Re-type the password to confirm.
5. Click Apply to save the setting.
To create a local group:
1. Go to SecurityÆAccountÆLocal Account menu.
2. Click the Add Group button.
3. Type in the group name.
4. If you want to grant the administrator privilege to this group, click the Grand administrator
privilege check box.
5. Select the users from the left hand windows and click the >> button to join the group.
6. Click Apply to save the setting.
To view and change local user property,
1. Go to SecurityÆAccountÆLocal Account menu.
2. Select a user.
3. Click the Property button.
4. If you want to change the password, enter a new password and confirm.
34
Page 43

5. If you want to disable this user account, click the Disable user account checkbox.
6. Select a group from the left hand window and click the >> button to add the user as a
member of this group in the Member of section.
7. Click Apply to save the setting.
To view and change local group property,
1. Go to SecurityÆAccountÆLocal Account menu.
2. Select a group.
3. Click the Property button.
4. If you want to grant the administrator privilege to this group, click the Grand administrator
privilege check box.
5. You can see all the members of this group in the right hand window.
6. Select a user from the left hand window and click the >> button to add this user to the
group.
7. Click Apply to save the setting.
The NAS server provides a mechanism for administrators to create multiple accounts at one time.
It imports accounts from a text file and create local accounts accordingly. The text file defines
some parameters related to the accounts, like passwords, user quotas, groups, etc. Also it can be
used to create user folders in a batch. Below is an example of the text file.
# username, password, group, user quota, user folder, folder quota, create default ACL
user001, aa1aa1, groupA, 1GB, /vol-1/users/user001, 1GB, yes
user002, bb2bb2, groupA, 1GB, /vol-1/users/user002, 1GB, yes
user101, 101101, groupB,10GB, /vol-1/users/user101,10GB, no
It is suggested that administrators use Microsoft Excel to maintain the account file, then save it
as .CSV files, in which fields are delimited by commas. Thus, the advance features of Microsoft
Excel, like filling in a series of numbers or items, easy copy and paste, can be used.
To mass import local accounts,
1. Go to SecurityÆAccountÆLocal Account menu.
2. Click the Mass Import button.
3. Select a file to import.
4. Click the Apply button.
5. If there are any errors, it will be displayed in the pop-up window after clicking the Last
Import hyperlink.
6.3 Caching Windows Domain User Accounts
Domain users and groups are managed by your network administrator. Windows network use a
35
Page 44

domain controller to store the information of all the domain users and groups. When the Windows
Network is set to using Domain Mode in your NAS-3410, you need to cache domain account in
the NAS-3410’s local user database. By caching domain accounts, it speeds up the process of
setting permissions and quotas.
To retrieve Windows domain user/group:
1. Go to SecurityÆAccount menu.
2. Click the Domain Account tab.
3. If you have not entered the valid Domain Login Account for retrieving Windows domain
users and groups, click the Modify button. Otherwise, go to Step 7.
4. Enter a User Name and User Password of an existing account of the domain which
shown in the Domain Name field.
5. Click Apply to save the setting.
7. You can change to another domain from the pull down menu which has the trust
relationship with the current domain to retrieve domain users and groups.
8. Select the domain users or groups from the left hand windows and click the >> button to
join the authorized list which will be stored at the local user database.
9. Click Apply to save the setting.
Synchronize user database
This function synchronizes the domain accounts cached in the NAS user database with the native
domain controller. New domain accounts in the domain controller will be added to the NAS user
database, while the non-existent domain accounts will be removed from the NAS user database.
Due to the limitation of system resource, the user database synchronization will be skipped if there
are more than 10,240 domain accounts in the domain controller.
To synchronize with the domain controller, please click the 'Synchronize user database'
hyperlink. You can also set up the NAS server to synchronize the NAS user database
automatically by checking the option - Synchronize the user database with the native domain
automatically. The synchronization interval is one hour.
Update user database
Changes of user accounts on the domain controller will not affect the NAS-3410 automatically.
You have to do it manually. The 'Update user database' function on the Domain Account tab of
the SecurityÆAccount menu helps you find the user accounts which have already been deleted
from the domain controller, yet still remain in the NAS user database. You can choose to delete
them from the database. ACL and share permission will be also updated by removing the entries
related to those users.
DC Host Table
36
Page 45

When the domain controllers' NetBIOS names cannot be resolved by the network services, go to
the 'DC Host Table' function on the Domain Account tab of the SecurityÆAccount menu, You
can enter the mapping of the NetBIOS names to IP addresses in the DC Host Table.
6.4 Creating UNIX/Linux Host
For NAS-3410, NFS client’s mount privileges are granted specifically to UNIX/Linux host created
by the administrator. If a UNIX/Linux host is granted access right to a share in the NAS-3410, user
of the UNIX/Linux host can have access to the share. Administrator should create a UNIX/Linux
host list prior to grant access right to them.
To create a list of the UNIX/Linux host:
1. Go to SecurityÆAccount menu.
2. Click the UNIX/Linux Host tab.
3. Enters a single host IP address in the first text box.
4. Or, enter the start IP address in the first text box and the last 3 digits of the end IP address
in the second text box to input a range of the host IP addresses of the Host IP field.
5. Click the Add button to add the host IPs to the host list.
6. Click Apply to save the setting.
6.5 Creating Share and Assigning Share Permissions
You can share a specific folder in any volume created in the NAS-3410 with others on the network.
When you create a share, you can assign the permission to the share that other users will be
allowed or denied when they access the share over the network.
To create a new share:
1. Go to SecurityÆFile/Folder menu.
2. Locate the volume you want to share on the volume lists.
3. Click the Create hyperlink to share the corresponding volume. Then go to Step 9.
4. If you want to share an existing folder under a volume, click the volume name hyperlink.
Click the folder hyperlink until you reach the desire directory. Then, go to Step 8.
5. If you want to share a new folder under a volume, click the folder hyperlink until you reach
the desire directory path.
6. Click the Create Folder button to create a new folder.
7. Enter a new folder name.
8. Click the Create hyperlink to share the corresponding folder.
9. Enter a unique share name in the Share Name field. The share name is what user will see
when they connect to this share. The actual name of the folder does not change.
10. To add a comment about the share, type the text in Comment.
37
Page 46

11. To limit the number of users who can connect to the share, on the User limit, click Allow
and enter a number of users.
12. Select the protocols you want to share.
13. Click Apply to save the setting.
To assign share permission of a share for local account and domain account:
1. Go to SecurityÆShare menu.
2. Locate the share and click
3. Highlight the users or groups from the left hand windows.
4. Select the appropriate permission from the pull down menu at the bottom of the left hand
windows.
5. Click the >> button to join the privileged list.
6. You can modify the permission of the users or groups in the privileged list by first highlight
the users or groups and then select the appropriate permission from the pull down menu at
the bottom of the right hand windows.
7. Click Apply to save the setting.
You can assign the following share permission to a user on NAS-3410:
No Access (NA) – Account has been denied access to the share.
Read Only (RO)– Account is allowed to read the share.
Change (CH)– Account is allowed to read and write to the share.
Full Control (FC) – Account is allowed to read both read and write and change permission to the
file or folder.
to assign or modify share permission to this share.
To assign share permission of a share for UNIX/Linux Host:
1. Go to SecurityÆShare menu.
2. Locate the share and click
3. Click the UNIX/Linux Host tab.
4. Assign the UID, GID and Permission of this share. It will overwrite the ownership and
permission of the mount point once the share is mounted by the NFS client. If the NIS
support is enabled, the UID and GID pull-down menus will list all NIS users for you to
choose.
5. You can allow all hosts to access the share with read/write or read only permission. Then
go to Step 9.
6. Or, you can specify privileged hosts by highlight the host IP from the left hand windows.
7. Select the appropriate permission from the pull down menu at the bottom of the left hand
windows.
38
to assign share permission to this share.
Page 47

8. Assign which UID/GID the root account of the UNIX host should be converted into when
accessing the share. This is the ‘root squash’ function.
9. Click the >> button to join the privileged list.
10. You can modify the permission of the hosts in the privileged list by first highlight the
privileged host and then select the appropriate permission from the pull down menu at the
bottom of the right hand windows.
11. Click Apply to save the setting.
12. If you want to remove shares, check the corresponding checkbox located at the end of the
row and click
You can assign the following share permission to UNIX/Linux Hosts on NAS-3410:
Read Only (RO) – the host is allowed to read the share.
Read Write (RW) – the host is allowed to read and write to the share.
.
6.6 Aggregate Volumes under a Share
An aggregation share is a virtual share which groups multiple volumes. It provides access to
multiple volumes from one single share, with each volume appearing as a single folder under the
share. Utilized on SmartExtend volumes, which are usually big in size, an aggregation share can
present several tera-bytes of data to network users. The NCP protocol does not work on
aggregation shares.
The directory hierarchy is like:
\\nas\share01\vol-001
\\nas\share01\vol-002
\\nas\share01\vol-003
vol-001, vol-002, vol-003 are volume names. Users will not be able to create any folders or files in
the root level of the aggregation share.
To create an aggregation share, please click the Create Aggregation Share button on the
SecurityÆShare menu of the administration page. Specify the share name and click Apply. Then
choose the volumes to aggregate on the Share Target tab.
To change the member volumes, click the --Show Members-- hyperlink under the Share Target
column of the share list table. Specify the volumes to aggregate and click Apply.
Up to 8 aggregation shares can be created on a NAS server. Each aggregation share can hold up
to 20 local or SmartExtend volumes.
39
Page 48

6.7 Configuring File and Folder Security and ACL
Access Control Lists (ACL) are associated with each file and folder, as well as the list of users
and groups permitted to use that file or folder. When a user is granted access to the file or folder,
an ACL node is created and added to the ACL for the file or folder.
If you assign permissions to a local user, a Security ID (SID) created by NAS-3410 will be referred
by the ACL for the file and folder security. If the local user is then deleted, and the same name is
created as the previous one, the new user does not have permissions to the file or folder, because
the SID will not be the same. The administrator will have to re-configure all the group
memberships and access rights to the files and folders.
Since the Security ID (SID) for domain user is issued and maintain by the domain controller on the
network. Administrator do not need to re-configure all the group memberships and access rights to
the files and folders if the domain user is deleted from the local user database and the same
name is created as the previous one.
There are two built-in user accounts: Admin and Guest. And two built-in group accounts: Admins
and Everyone.
Every user of NAS-3410 including local and Domain user is the member of the Everyone group.
By default, when a volume is created, Admins and Admin will be granted Full Control permission
and Everyone will be granted Read/Write permission to the volume.
After you set permissions on a volume, all the new files and folders created under the volume
inherit these permissions. If you do not want them to inherit permissions, uncheck the Inherit
from parent folder when you set up the permissions for the files and folder.
Configuring file and folder security:
1. By default, ACL control is enabled.
2. Go to SecurityÆFile/Folder menu.
3. Locate the file or folder you want to configure the permission.
4. Click the
Control.
5. Clear the Inherit from parent folder check box.
6. Select the users or groups from the left hand windows and click the >> button to join the
privileged user/group list.
7. If you want all the subfolders and files inherit the new permission you have just set, check
icon. If the icon is disabled, go to SecurityÆACL menu to enable the ACL
the Propagate to all subfolders and files check box.
8. Click Apply to save the setting.
You can assign the following File/Folder permission to a user on NAS-3410:
40
Page 49

No Access (NA) – Account has been denied access to the file or folder.
Read Only (RO) – Account is allowed to read the file or folder
Write Only (WO) – Account is allowed to write to the file or folder
Read Write (RW) – Account is allowed to read and write to the file or folder, but not to delete it.
Modify (MO) – Account is allowed to read, write and delete the file or folder
Full Control (FC) – Account is allowed to read both read and write and change permission to the
file or folder.
Set file/folder permission in Windows Network
NAS-3410 provides a simple, efficient way to set up and maintain file/folder security in Windows
Network. To change permissions, you must have been granted permission to do so by the
administrator. Below is the permission mapping table of NAS-3410 in Windows Network:
File/Folder
Permission in
NAS-3410
No Access (NA)
Read Only (RO)
Folder Permission in
Windows Network
Full Control
Modify
Read & Execute
List Folder Contents
Read
Write
Full Control
Modify
; Read & Execute
; List Folder Contents
; Read
Write
Full Control
File Permission in
Windows Network
Full Control
Modify
Read & Execute
Read
Write
Full Control
Modify
Read & Execute
; Read
Write
Full Control
41
Modify
Read & Execute
Write Only (WO)
List Folder Contents
Read
; Write
Read/Write (RW) Full Control Full Control
Modify
Read & Execute
Read
; Write
Page 50

Modify
Modify
Modify (MO)
Full Control (FC)
; Read & Execute
; List Folder Contents
; Read
; Write
Full Control
; Modify
; Read & Execute
; List Folder Contents
; Read
; Write
; Full Control
; Modify
; Read & Execute
; List Folder Contents
; Read
; Read & Execute
; Read
; Write
Full Control
; Modify
; Read & Execute
; Read
; Write
; Full Control
; Modify
; Read & Execute
; Read
; Write
; Write
To set, view, change or remove file/folder permission in Windows Network:
1. Locate the file or folder you want to set permission
2. Right-click the file or folder, click Properties Æ Security
3. Change permission from an existing groups or users, click the Allow or Deny checkbox
4. Or, remove the groups or users by clicking the Remove button.
To change owner of a file or folder
1. Go to SecurityÆFile/Folder menu.
2. If you want to change the owner’s name of the corresponding file and folder, click the
owner’s name hyperlink. Select a new owner from the user list.
3. Check the checkbox beside Apply to all sub folders and files if you want to propagate
the ownership to all sub folders and files.
4. Click Apply to save the setting.
6.8 Managing Quotas
Configuring user quota:
NAS-3410 supports two types of quotas: user quota and folder quota. User quota monitors the
disk space usage of each user. It is based on file ownership, and is independent to which volume
42
Page 51

that the file and folder located. Below are the descriptions of the parameters when setting up user
quotas.
User Name User name in the local user database.
UID The user ID set in the user mapping table in Network ÆUNIX/Linux menu.
GID The group ID set in the user mapping table in NetworkÆUNIX/Linux menu.
Type User type. Local or Domain.
In Use Total amount of disk space used by the user.
Quota Limit The amount of disk space in MB a user is allowed to use.
1. Click the Enable user quota control checkbox to enable user quotas.
2. Enter quota limit in MB for the user under the Quota Limit column.
3. You can click the
amount of disk space used by each user.
4. Click Apply to save the setting.
To set all quotas to the same value, please specify the quota value in the Set all quotas to xx MB
input field. Click the Set hyperlink to save settings.
Recalculate to obtain the most updated information of the total
Configuring folder quota:
Folder quota monitors the amount of data that can be stored on the folder on which folder quota is
applied regardless of who saves there. It can limit the total amount of data stored in the NAS-3410
to effectively control the proper consumption of the storage resources. Note that is it prohibited to
set folder quota to the Volume root or “System folder” and its sub-folders.
Folder Name The path and folder name that the folder quota has been applied.
In Use Total amount of disk space used.
Quota Limit The amount of data that can be stored in the respective folders.
Delete quota entries by selecting the check box at the end of each quota entries and
click this icon.
1. Click the Enable folder quota control checkbox to enable folder quotas.
2. Click the
3. Click the Select Path to browse for target folder.
4. Enter the quota limit in MB.
43
Add to add folder quota to a folder.
Page 52

5. Click Apply to save the settings.
6. You can click the
amount of disk space in use on each folder.
To set all quotas to the same value, please specify the quota value in the Set all quotas to xx MB
input field. Click the Set hyperlink to save settings.
Recalculate to obtain the most updated information of the total
44
Page 53

Chapter 7
Disc Sharing and Data Archiving
Disc Server creates and manages CD and DVD disc images for easy and fast disc sharing. It
relieves the efforts of handling huge amount of discs. Thousands of discs can be kept online for
user access. To protect those disc images, all NAS servers are equipped with a robust RAID
sub-system, which features hot-spare disks and strong data protection.
7.1 Start to Use the Disc Server Function
The Disc Server function is an optional feature on NAS-3410. To active the function on these
models, please get a license key from your vendor and enter the key on the ServerÆLicense
menu of the administration page.
It requires some simple configuration before using the Disc Server function. Please open the
administration page, select Quick Setup from the Disc Server menu. On the page, select the CD
or DVD device which will duplicate the disc image automatically when a disc is inserted. Then
specify the folder to store the duplicated disc images. Click Apply to save the settings.
Insert a disc into the CD or DVD device. It should start duplicating the disc image immediately.
When it finishes, network users can access the disc by opening the MIRROR share of the NAS
server.
7.2 Creating Disc Images
Using the local optical device to duplicate disc images
The simplest and fastest way to create a disc image is to use the CD or DVD device of NAS
server to duplicate the inserted discs. Usually a CD can be duplicated in 5 to 10 minutes.
To configure a device so that it can automatically duplicate any inserted discs, please go to the
Disc ServerÆDisc Caching menu page of the administration page. In the Device List table, click
the hyperlink text in the CD Device’s Function column and change the CD function to Disc
Mirroring.
The Disc Mirroring Settings section will appear on the page. Select a folder as the target location.
The folder is called Disc Image Folder, which is a folder especially for storing disc images. In
addition to create a new disc image, it can also replace an existing disc image with the duplicated
one. If the disc image being replaced is shared, the duplicated disc image will inherit all the share
51
Page 54

settings and permissions. The CD replacement will happen once and it will return to the previous
settings.
The disc image’s name can be either inherited from the CD label or user-defined. A user-defined
name will only apply once to the next duplicated disc image.
If you set the CD function to 'Direct Access', it will mount any disc inserted in the CD/DVD device.
The mounted disc will appear as a folder under the default CDROM share.
Copying disc images via network filing protocols or SmartSync
The disc images are stored in the disc image folders. Administrators can also copy or sync the
disc images from one NAS to another, using Windows Explorer, MacOS Finder or SmartSync.
When disc images are copied to a disc image folder, the NAS server will not recognize them
immediately . Administrators must command the NAS server to discover disc images manually or
set up the NAS server to discover disc image regularly.
To discover disc images manually, please open the Disc ServerÆDisc Images administration
page and click the Re-scan images hyperlink to the right of the page.
To set up the NAS to discover disc images regularly, please open the Disc ServerÆInformation
page. Configure the Disc Server Settings to enable the NAS server to scan for disc images
every one hour.
Using the remote mirroring software to create disc images
Please refer to Appendix A for how to use the remote mirroring software.
7.3 Managing Discs
Once the disc image is created in the NAS server, it can be seen on the Disc ServerÆAll Disc
Images menu of the administration page.
If the disc images are not created or duplicated by the NAS server or by the remote mirroring
software, administrators will have to re-scan the disc image folders for disc images manually. For
example, if disc images are copied from another NAS server to a disc image folder over network
using the Windows or other OS platforms, the NAS server will not be able to list them on the Disc
Images page. In such cases, administrators have to click the Re-scan images hyperlink text to
the right of the page.
To change the disc name:
To change the disc name, click on the hyperlink text in the Disc Na me column. On the same page,
it also shows detailed information of the disc image.
52
Page 55

To delete a disc image:
To delete a disc image, check the check-boxes to the right and click the Delete icon.
7.4 Sharing Discs
Administrators can choose to share a single disc, multiple discs or a disc image folder. If a single
disc is shared, its content will be shown when users open the network share. If multiple discs are
shared, the discs will appear as individual folders under the network share. The folder names are
the same as the disc names. If a disc image folder is shared, all the discs in the disc image folder
will appear as individual folders under the network share.
To share a single disc:
To share a single disc, go to the Disc ServerÆDisc Images menu of the administration page.
Click the Create hyperlink in the Share column. Click Apply to share the disc. Enter the Share
Permissions tab to assign user permissions if you want to restrict user access. The Unix/Linux
Setting tab is for configuring NFS security settings. Please refer to section 6.5 Creating Share and
Assigning Share Permissions for the details of share permissions and NFS security settings.
You can also go to the Disc ServerÆDisc Shares page to share a single disc. Click the Create
Disc Share button. Specify the share name and click Apply to create the share. Select the disc to
share in the Share Target tab and click Apply.
To share multiple discs:
To share multiple discs, go to the Disc ServerÆDisc Shares page. Click the Create Group
Share button. Specify the share name and click Apply to save settings. Select the discs to share
in the Share Target tab and click Apply. Use the Share Permissions tab or the Unix/Linux
Setting tab if you want to restrict user access.
To share a disc image folder:
To share a disc image folder, go to the Disc ServerÆDisc ImagesÆDisc Image Folder menu of
the administration page. Click the Create hyperlink in the Share column. Specify the share name
and click Apply. Use the Share Permissions tab or the Unix/Linux Setting tab if you want to
restrict user access.
You can also go to the Disc ServerÆDisc Shares page to share a disc image folder. Click the
Create Disc Folder Share button. Specify the share name and click Apply to create the share.
Select the disc image folder to share in the Share Target tab and click Apply.
7.5 Burning Disc Images
To burn an existing disc image, select Disc Recording from the Disc Server menu on the
53
Page 56

administration page. To do disc recording, the CD function must be configured as Loader/Writer.
To change the CD function, please click the hyperlink in the Function column of the Device List
table.
Next, select a disc image by clicking the Select a Disc hyperlink. After the selection is made, the
disc image information will be shown underneath, including image size, disc format and disc
volume label. Check the Erase disc before writing option if it is a rewriteable disc which contains
data. Click Apply to start the disc recording.
7.6 Archiving Data to CD/DVD Discs
Data archiving is to move or copy regularly NAS data to CD/DVD discs. Administrators can set file
filters, mostly based on file date/time, to specify what to burn. One of the applications is to move
obsolete data out of the NAS server so that disk space can be freed for future uses.
If used with the Disc Server function, the Data Archiving function becomes more versatile. You can
choose to turn some less-frequently-used files to read-only disc images first, which can be
mounted by the Disc Server function to share to network users in read-only forms. When the
archived data are not in use for a long time, you can then choose to burn them to discs, freeing
the hard disk space.
The Archive Folder
During data archiving, the NAS server will first create disc images in the archive folder, which is
a disc image folder specifically for storing archived data in the form of disc images. Firstly specify
the location of the archive folder on the Disc ServerÆData ArchivingÆSummary page before
you use the data archiving function.
Summary Logs
On the Disc ServerÆData ArchivingÆSummary page are also shows the summary logs, which
keep track of the execution summary of the data archiving tasks.
In addition, they keep records like which disc images are created, which are burned and which are
not . Click the View hyperlink under the Discs column of the Summary Logs table to view the list
of disc images. For those disc images not burnt yet, you can choose to burn them.
Setting Up Data Archiving Tasks
On the Disc ServerÆData ArchivingÆTasks page, you can create tasks to archive data
manually or scheduled.
Task Name
54
Specifies the name of the data archiving task, for management
Page 57

purposes
Source Folders
Disc Label
Date Extension
Disc Type
Advanced Settings – File
Filtering
Specify the data to be archived. The folders, not preserving the
full paths, will be archived to CD/DVD discs
Specifies the labels of the CD/DVD discs.
If the date extension is enabled, it will append the date of
archiving to the disc labels. For example, ARCH20041010_01 is
the first disc created by the data archiving task on October 25,
2004 with the date extension. The second disc will be
ARCH20041010_02 if more than one disc is created.
Specifies the media for burning. It can be a CD, a DVD or a
dual-layer DVD. The NAS server will create disc images that
match the size of the disc type, and then burn the disc images.
At first the settings are hidden. Please click the Show hyperlink
to display the advanced settings.
The file filters specify which files in the source folders to include
for data archiving. You can choose to include only the files which
are in the specified date range. Or, you can choose to include the
files which are N days old. Or, you can choose to include only the
files of which the archive bits are set. The NAS server will clear
the archive bits of the source files which are archived, if not
deleted.
Advanced Settings – Skip
Archiving (Do archiving
only if…)
Archiving Schedule
Options
You can set constraints so that the archiving task is activated
only when one of the following conditions is met.
if the free volume space is lower than n% – in other words,
the data archiving will be skipped if the free volume space is high
if the archived data are over n MB/GB – that is to say, the data
archiving will be skipped if the archived data are below the
threshold
Specifies the schedule of the archiving task. If the schedule is
due, the NAS server will check if the conditions specified in the
Advanced Settings are met. If met, then perform the data
archiving task.
Delete source files after the archiving is completed – if
checked, the NAS server will delete the source files to free up
disk space after data are successfully archived as disc images or
burned to discs.
Burn Disc – if checked, it will archive data to CD or DVD discs.
Multiple CD/DVD writers can be specified here. Please note that
the CD/DVD functions must be set to Loader/Writer before
putting into use for burning.
55
Page 58

Chapter 8
User Access
The NAS-3410 fits into the network environment as soon as it is properly configured. This chapter
describes how to get the NAS-3410 ready for user accesses from various network OS.
Before reading on, please make sure that the NAS-3410 is configured with an IP address and a
volume is created successfully. For the rest of the sections, we assume that the server name is
NASSERVER, the IP address is 192.168.170.172 and there is a volume named volume01.
8.1 Workgroup or Domain Mode
The NAS-3410 can work in either the workgroup mode or the domain mode. In the workgroup
mode, the administrator creates accounts for the NAS-3410 and maintains the user database per
server. User authentication is done by checking the local user accounts. In the domain mode, the
NAS-3410 can retrieve user names from the domain controller and rely on the domain controller
to authenticate users. It can also authenticate users by local accounts.
In the domain mode, when a Windows user requests to access a shared folder, the user will be
authenticated with the domain accounts first, then the local accounts. If the user is assigned with
proper access rights in the share permissions and the ACL settings, the user will be allowed to
access the shared folder.
For those using MacOS, web browsers or FTP to access the NAS-3410, the security control
mechanism is similar. If set to the workgroup mode, the NAS-3410 authenticates all users from
various network operating systems with local accounts only. If set to the domain mode, the
NAS-3410 can be configured to use different security policies for different network file protocols –
either authenticated by local accounts only, or by both local and domain accounts.
For example, the NAS-3410 can authenticate Windows users by querying the domain controller,
while at the same time check the MacOS users with local user accounts. The administrator can
set the SMB/CIFS protocol to the domain mode and configure the AFP protocol to apply Local
account authentication.
8.2 Accessing from Windows OS
There are some configuration jobs to do before Windows users can access the NAS-3410. Please
enter the administration homepage first.
56
Page 59

1. Please configure the NAS-3410 to operate either in the workgroup mode or the domain mode.
Go to the NetworkÆWindows menu and select either Workgroup Mode or Domain Mode.
Also specify the workgroup/domain name. It will require a server reboot afterwards.
2. Create local accounts if the NAS-3410 is in the workgroup mode.
Go to the SecurityÆAccountÆLocal Account page and use the Add User or Add Group
button to create local accounts.
3. Get domain accounts from the domain controller if the NAS-3410 is in the domain mode.
Go to the SecurityÆAccountÆDomain Account page. Then click the Modify button and
give a domain user account for logging on to the domain controller to retrieve domain
accounts. Next, use the >> and << buttons to specify the domain accounts to be
cached in the NAS-3410.
4. Share the volume to network users.
Go to the SecurityÆFile/Folder menu. Find the volume01 entry and click Create in the
Sharing column (or click Modify if the volume has been shared). On the Property page,
check the Windows Network (SMB/CIFS) check-box and click Apply.
5. Set the share permissions.
After sharing the volume, specify the access rights of local users/groups and domain
users/groups.
Now Windows users can access the NAS-3410. They can run the Windows Explorer and open the
path of
Windows users can also map a network drive to \\nasserver\volume01 or use the net use
command in the Command Prompt window. The command will be like:
net use n: \\nasserver\volume01
\\nasserver. The shared folder volume01 will appear in the window.
8.3 Accessing from Web Browsers
In addition to the administration homepage, the NAS-3410 provides the user homepage for normal
users to access data in the server. With a web browser, users can download files, create folders,
upload files and modify ACL.
To enable user access from web, please follow the steps.
1. Enable the user homepage.
Open the administration page and enter the NetworkÆWeb menu. Check the Enable Web
Data Access check-box. Specify whether to allow local accounts only or allow both local and
domain accounts to access the user page. Check other parameters and click Apply.
2. Create local user accounts or retrieve domain accounts from the domain controller,
depending on whether the NAS-3410 is in the workgroup mode or the domain mode.
57
Page 60

3. Share the volume to network users.
Go to the SecurityÆFile/Folder menu. Find the volume01 entry and click Create in the
Sharing column (or click Modify if the volume has been shared). On the Property page,
check the Web Access (HTTP) check-box and click Apply.
4. Set the share permissions.
After sharing the volume, click the Share Permissions tab to specify the access rights of
local users/groups and domain users/groups.
Now users can run the web browser and open the IP address of 192.168.170.172 to browse the
NAS-3410. When the user homepage is opened, it prompts for user name and password. Then it
will display all shared folder after user login. The user homepage will be like:
In the top right corner of the user page are the tool-bar icons, which provide access to various
functions like creating folder or uploading files. Below the tool-bar are the server name and the
login user. Lower on the page is a file browsing area.
Tool-bar icons
Admin Page: switches to the administration home page.
Change View Mode: changes the views of the file browsing area between Detail, Large
Icons and Small Icons.
Change Password: modifies the password of the login user. It allows a local user to change
the password.
Create Folder: creates a new folder in the current path if the login user has the access right.
58
Page 61

Upload File: uploads files to the current path if the login user has the access right.
Help: opens a new browser window with help information
File Browsing
When the user page is opened, the file-browsing window shows all the shares in the server. All the
folders and files are presented as hyperlinks. If a folder is clicked, it will show its content in the
same window. When a file is clicked, it will either open the file in another browser window or pop
up a dialog-box for download. To move to the upper level of directory, click the
icon.
To delete files or folders, check the checkboxes in the Delete column. And click the Delete icon
to delete them.
To rename a file or folder, click the Rename icon
If a user has the Full Control access right for a file or folder, he can modify its ACL by clicking the
ACL icon in the Permission column.
, input the name and press the Enter key.
Up Directory
8.4 Accessing from MacOS
After setting the NAS-3410 to operate in the workgroup mode or the domain mode, follow the
steps below to configure for MacOS user access.
1. Enable the Macintosh Network support (the AFP protocol).
Open the administration page and enter the NetworkÆMacintosh menu. Check the Enable
Macintosh Network check-box and specify the security policy and the AppleTalk zone. Then
click Apply. In the workgroup mode you can only select Local account authentication as
the security policy. In the domain mode, you can select either one.
2. Create local user accounts or retrieve domain accounts from the domain controller,
depending on whether the NAS-3410 is in the workgroup mode or the domain mode.
3. Share the volume to network users.
Go to the SecurityÆFile/Folder menu. Find the volume01 entry and click Create in the
Sharing column (or click Modify if the volume has been shared). On the Property page,
check the Macintosh Network (AFP) check-box and click Apply.
4. Set the share permissions.
After sharing the volume, specify the access rights of local users/groups and domain
users/groups.
After the configuration is done, MacOS 8 or OS 9 users can use the MacOS Chooser or Network
Browser to access the NAS-3410. Mac OS X users can use the Connect to Server function to
59
Page 62

open the NAS-3410.
For example, open the Connect to Server window in Finder.
You can either type the IP address of NASServer in the Address field. And click Connect to put it
on Desktop. Or you can click AppleTalk in the middle left window pane to find the zone and the
server. Once you find the server, click Connect to put it on Desktop.
8.5 Accessing from FTP Clients
You can set an FTP home directory in the NAS-3410 for user access. Login authentication is done
by checking the ACL of the FTP home directory. During an FTP session, the server always checks
ACL when it receives any FTP requests, such as ls, put, get, etc. Local accounts and domain
accounts are both supported, depending on the security policy.
After setting the NAS-3410 to operate in the workgroup mode or the domain mode, follow the
steps below to configure for FTP access.
1. Enable the FTP Data Access feature.
Open the administration page and enter the NetworkÆFTP menu. Check the Enable FTP
Data Access check-box and specify the security policy. In the workgroup mode you can only
select Local account authentication as the security policy. In the domain mode, you can
60
Page 63

select either one. Then specify the FTP home directory as volume01 and click Apply to save
the settings.
2. Create local user accounts or retrieve domain accounts from the domain controller,
depending on whether the NAS-3410 is in the workgroup mode or the domain mode.
3. Configure the folder security settings of volume01 to control user access.
Click the Set hyperlink to specify the access rights (ACL) for the FTP home directory –
volume01. These will be the accounts which are allowed to login the NAS using ftp software.
Note that the Inherited List will be cleared if you uncheck the Inherit from parent folder
check-box and click Apply button.
Now, run an FTP client to connect to 192.168.170.172. Login as the user you assign in step 3
above. Then you will be able to access volume01.
8.6 Accessing from NFS Clients
The security control of the NAS-3410 for NFS clients follows the traditional UNIX-style trust-host
mechanism and UID/GID checking. Follow the steps below to enable NFS support and export the
volume for NFS clients to mount.
1. Enable the UNIX/Linux Network support (the NFS protocol).
Open the administration page and enter the NetworkÆUNIX/Linux menu. Check the Enable
UNIX/Linux Network check-box and click Apply.
2. Go to the SecurityÆAccountÆUNIX/Linux Host page and add the hosts that might be
trusted to access the NAS-3410.
3. Export the volume to NFS clients.
Go to the SecurityÆFile/Folder menu. Find the volume01 entry and click Create in the
Sharing column (or Modify if the volume has been shared). On the Property page, check
the UNIX/Linux Network (NFS) check-box and click Apply.
4. Enter the UNIX/Linux Setting tab. Add NFS clients to the privileged host list. And assign UID,
GID and permission octets to the exported volume.
After the volume is exported, use one of the NFS clients in the privileged host list to mount the
volume. Please login as the root and use the following command to mount volume01 under the
/mnt directory.
mount 192.168.170.172:/volume01 /mnt
Once mounted, the /mnt directory will link to volume01 and inherit the same UID, GID and
permission as you specify in the configuration steps. The users on the NFS client with proper
access rights will be able to access the /mnt directory and hence the NAS-3410.
61
Page 64

Chapter 9
Backup and Recovery
9.1 Snapshot – Fast Point-In-Time Copies
Snapshots are read-only copies of file-systems at a specific point in time. Snapshot distinguishes
itself in its speed. Creating a snapshot is not involved with copying user data, thus usually taking
less than a second.
The concept of snapshot is very different from tape backups. Data are not copied to any media
during backup. Instead, it just informs the NAS that all the data blocks in use should be preserved,
not being overwritten. That is why it can be so fast. The “copy” occurs during everyday file access.
When a file is modified after a snapshot is created, its original data blocks are protected from
being overwritten. The new updates are written to a new location. The file-system maintains
records and pointers to keep track of the snapshot data and file changes.
The snapshot feature is an optional feature on NAS-3410.
Snapshot Management
To manage snapshots, please open the administration page. Enter the
BackupÆSnapshotÆManage page and select a volume.
Viewing Snapshot Information
On the page shows the snapshots existing on the volume and their information. Snapshot Used
Space indicates the disk space used by snapshot data. In the table – List of Snapshots, Space
to Free indicates the disk space which will be freed if a snapshot is deleted. Activity indicates
whether the snapshot is being deleted or rolled back.
Configuring Snapshot Settings
Show the .snap folder
Name the .snap folder as
~snap
With the .snap folders enabled, end-users can access
snapshot data without intervention of MIS people, retrieving
previous versions of files from the .snap folders.
Administrators can choose to show the .snap folders under
the root of a volume, or under all folders.
Using the AFP protocol, the folders with names beginning
with dot (.) will be hidden and not able to be accessed by
Macintosh clients. To make the .snap folders visible, the
administrators can choose to show the .snap folders as
~snap instead so that the folders can be accessed by
Macintosh clients.
58
Page 65

Delete snapshots if free
space is low
If enabled, it will automatically delete the oldest snapshots to
free more disk space when the free space is lower than the
specified percentage.
Snapshot Policy
They specify how many hourly, daily, weekly and monthly
snapshots to keep, respectively. If the limit is exceeded, the
oldest snapshot of the same type will be deleted. If not
specified, it will keep the snapshots until being manually
deleted.
Creating Snapshots
There are several ways to create snapshots. One is to create a snapshot manually by selecting a
volume and clicking the Create Snapshot button on the SnapshotÆManage page. It will create a
snapshot with a name like manual-20041010.190000, which indicates a snapshot created
manually at 19:00:00 of October 10, 2004. Another method is to set schedules to create
snapshots regularly. Moreover, the NAS server will create snapshots automatically when doing
tape backup, SmartSync and CD/DVD-burning tasks. Then it reads in source data from the
automatically created snapshots, instead of the current active file-system, to prevent the open-file
issue.
Deleting Snapshots
To delete snapshots, check the check-boxes in the List of Snapshots table and click the Delete
icon to delete the selected snapshots. You can make multiple selections to delete several
snapshots at a time. The NAS server will delete the snapshots one by one.
Snapshot Roll-back
Snapshot roll-back is to restore the volume to the state when the selected snapshot was taken.
Snapshot roll-back is useful if most data are lost or destroyed by virus attacks or human errors.
Snapshot roll-back is much faster than restoring from tapes. Please note that the roll-back
operation is dangerous because the whole volume will be restored to the previous state. If you
want to restore only part of the data, please simply copy them from the .snap folders to the current
file-system.
Snapshot Scheduling
To manage snapshot schedules, please open the administration page. Enter the
BackupÆSnapshotÆSchedule page.
To add a snapshot schedule, either click the Add Schedule icons next to the volume names, or
click on the Add Schedule button on the bottom of the page.
To delete snapshot schedules, check the check-boxes to the right and click the Delete icon.
To modify a snapshot schedule, click the hyperlink of the snapshot schedule in the Schedule
59
Page 66

column.
There are four types of schedules – hourly, daily, weekly and monthly. Each volume can have up
to 8 schedules of any types.
9.2 Tape Backup and Restore
The NAS-3410 builds in backup software for data protection. The backup software features full or
incremental backup, scheduled tasks and multi-volume backup. The administrator is able to define
backup policy by incorporating one or more backup tasks. It can also utilize the hardware
compression capability. It is simple, yet powerful enough to fulfill most backup demands.
The backup software requires the system folder to operate. To specify the system folder, please
open the Administration Page and go to the ServerÎMaintenance page. Then specify a
volume to contain the system folder. If there exists no system folder in the specified volume, it will
create one automatically.
Adding Backup Tasks
To arrange backup schedules, please open the Administration Page and go to BackupÎTape
Backup page. Click the Backup tab. You will see a list of scheduled tasks on that page.
To add a task, click the Add Task button. Then follow the steps below.
1. Select a tape drive for backup.
2. Input the tape label for identifying tapes. It will append backup start date/time to the tape label
when running a backup task.
3. Specify whether it will be a full or incremental backup task. A full backup task copies all
selected folders and files into tapes. An incremental backup task only copies modified or newly
created files since last backup. It checks archive bits and only back up those with archive bits
set.
4. Choose which folders to back up. Click the Select Folders hyperlink and select what to back
up. Your selection will be copied to the lower lis t-box, which indicates the folders to back up.
5. Specify backup schedule. You can start the backup immediately or arrange a schedule. The
schedule can specified at any weekday or a day of a month.
60
Page 67

6. Specify whether to overwrite the tape. If yes, the backup task will rewind the tape to the
beginning and overwrite it with backup files. If not, it will append the backup to the tape, not
overwriting any existing data on tape.
7. Specify whether to enable hardware compression capability when the tape drive has the
feature.
8. Click the Apply button.
Restoring Files from Tape
To restore data from tape, please open the administration page and go to BackupÎTape Backup
page. Click the Restore tab and follow the steps below.
1. Specify the Tape Drive for restoring.
2. Specify a backup set to restore by selecting a backup index. The backup indexes are required
to restore data from tape. When the backup indexes are missing, you have to import them from
tapes for further restoring operation. To import backup indexes, please select a tape drive and
click the Import hyperlink.
3. Choose whether to restore all the files in the backup set, or only certain files or folders. For the
latter, it requires Java virtual machine for the UI. Please go to
Java virtual machine.
4. Click the Next button.
61
http://java.sun.com for the latest
Page 68

5. To restore selected files or folders, please make selections on the Java UI in the What to
Restore item.
6. Choose the target location. It can restore data to either the original location or an alternative
location.
If the original location is selected, it will restore data to the location where they are originally
backed up. Please note that if the original volume is missing, it will not restore anything.
The alternative location means any user-defined path. Please use the Select Path hyperlink to
specify the path. It will restore files and the full directory hierarchy under the specified path.
7. Specify whether to restore the ACL settings together with the files.
8. Specify whether to overwrite the existing files with the backup files.
9. Click the Apply button to start to restore.
Checking Task Progress, Viewing Logs
When a tape task is running, you can view its progress on the Summary page. On the upper
Summary page is a list of tape drives. Any task currently running will be shown as a hyperlink in
the Status column. Click a hyperlink to watch task progress and details. It shows Ready without
hyperlinks if there is no running task.
After a backup or restoring task finishes, it will keep summary logs in the system folder. On the
lower Summary page are the logs. They keep records of the statistics and errors of the
backup/restoring tasks ever executed. Click a hyperlink in the Tape Label column to see its
details. To delete logs, please check the check-boxes to the right and click the Delete icon.
62
Page 69

9.3 Using a Tape Library
First, set up the tape library so that it can be controlled by software. Please refer to the tape
library’s instruction manuals for details. Then, connect the tape library to the NAS server with a
SCSI cable. The NAS server supports up to two tape libraries.
The tape library support is an optional feature on NAS-3410.
Managing Devices, Tapes and Tape Cleaning
When the NAS server starts up, it will initialize the tape library. It might take a while. To view the
status, please open the administration page and enter BackupÆTape LibraryÆDevices. When it
finishes the initialization, you will see a page as below.
Inserting and removing tape cartridges
The NAS server will initialize the tape library at start-up and lock the door. To insert or remove
tapes from the tape library with no cartridge access ports (CAP), please unlock the door first. Then
follow the tape library's instruction manuals to insert or remove tapes. Afterwards, lock the door
again so that the tape library can resume to work. It will start the inventory process automatically
to read in all media information after the door is locked.
For some tape libraries which have cartridge access ports (CAP), use the 'Import/Export' function
to insert or remove tapes from the tape library. To insert a tape, first place the tape in the CAP by
following the tape library's instruction manual. Use the 'Import' function to move the tape to an
empty slot. The NAS server will read the tape and add it to its inventory. To remove a tape, use the
'Export' function to move it to the CAP.
63
Page 70

Inventorying tape slots
It checks all the slots of the tape library to see if they are occupied and reads in media information
from all the tapes. The whole process may take a while, depending on the number of tapes and
the tape drive speed.
Erasing a tape
The quick-erasing function overwrites the tape header only. It takes much less time than erasing a
tape, which wipes out all data in the tape. To quick-erase or erase a tape, please click the radio
button in front of the slot and click the Quick Erase or Erase button.
Retensioning a tape
To retension a tape is to wind the tape evenly so that it is properly tensioned. Use this feature only
when there are errors accessing the tape. To retension a tape, please click the radio button in
front of the slot and click the Retension button.
Scanning a tape for backup indexes
If the backup index files are missing, the NAS server will not be able to restore the data. In this
case, please insert the tapes and scan them for backup indexes. The NAS server will copy the
backup indexes from the tapes. To scan a tape, please click the radio button in front of the slot
and click the Scan button.
Defining a Media Pool
A media pool is a group of tapes managed as a unit. You must define a media pool before
assigning any backup schedules.
To define a media pool, please go to the BackupÆTape LibraryÆMedia Pool menu and click
New Pool.
64
Page 71

Each media pool is divided into two sets, the save set and the scratch set.
The save set is consisted of the tapes containing important data which cannot be overwritten. On
the other hand, the scratch set is consisted of the tapes which are free to be overwritten. At the
very beginning, all tapes are empty and locate in the scratch set. When the NAS server backs up
data to a tape, the tape is moved to the save set. After the retention period is passed, the tape
expires and is moved to the scratch set for recycling.
The retention period is the number of days for which the tape must be kept in the save set after it
is last written. You can define the retention period when creating a backup task.
Backing Up Data
To start a backup task immediately, please go to the BackupÆTape LibraryÆBackup menu on
the administration page. Click the Backup Now button and specify the following.
65
Page 72

1. Specify the task name. The created backup set will be named after the task name, appended
by date/time.
2. Choose a tape library and the tape drive. Usually the tape drive is set to Auto, allowing the
NAS server to choose any available tape drive to do the backups.
3. Select backup media. If you have defined any media pool, just select one. If not, you can
choose the tapes to use for this backup task.
4. Choose to make full backups or incremental backups. A full backup will copy all source data.
An incremental backup will only copy those data with archive bits set. After backup, the archive
bits of the source data will be cleared.
5. Specify what to backup by selecting the folders to be backed up.
6. Specify whether to enable the hardware compression capability of the tape drives.
7. Click Apply to start to back up.
To create a backup task, please go to the BackupÆTape LibraryÆBackup menu on the
administration page. Click the Add Task button and specify the following parameters.
66
Page 73

1. Specify the task name. The created backup set will be named after the task name, appended
by date/time.
2. Choose a tape library.
3. Specify what to backup by selecting source folders.
4. Add backup schedules by clicking the Add a Schedule hyperlink.
A. Select the tape drive. Usually it is set to Auto, allowing the NAS server to choose any
available tape drive to do the backups.
B. Select backup media. Please define a media pool on the BackupÆTape LibraryÆMedia
Pool menu if there is no media pool.
C. Choose to make full backups or incremental backup. A full backup will copy all selected
data. An incremental backup will only copy those data with archive bits set.
D. Set schedules.
E. Specify the tape retention period. A retention period is the number of days in which you
want to keep the backup data from being overwritten. For example, if the retention period
is set to 7 days, the tape will remain in the save set as long as it has been used and be
moved to the scratch set when it has not been used for 7 days.
F. Set overwrite options. If Overwrite the media is selected, it will only use blank tape or
scratch tape for backups and write data from the beginning of the tapes. If Append to the
media is selected, it will append data to the last used tape.
5. Specify whether to enable the hardware compression capability of the tape drives.
6. Click Apply to start to back up.
Restoring Data
To restore data, go to the BackupÆTape LibraryÆRestore menu. First, select the backup task
which created the backup sets. Then select a backup set and specify whether to restore all files or
67
Page 74

only partial of them. To view the information of the backup set, click the hyperlink in the Backup
Type column.
Next, choose to restore all files or only certain files or folders. For the latter, you need to install
Sun Java virtual machine v1.4 or higher. Please go to http://java.sun.com and download the
software. Use the Java UI to select the files or folders to be restored.
Next, choose the destination: the original location or alternative location. If the original location is
selected, it will restore the files to exactly where they are backed up. If the original volume is
missing, it will not restore anything. If the original folders are missing, it will create the folders
automatically.
If the alternative location is selected, it will restore data to a user-specified location. The full tree
hierarchy of backup data will be reconstructed under that location.
Restore security: when checked, it will restore the access control lists (ACL) together with the
data.
Overwrite Options – specify whether to overwrite the existing files with the backed up files.
Checking Task Progress, Viewing Logs
When a task is running, you can view its progress on the Devices page. On the upper page is a
list of tape libraries and tape drives. Any currently running tasks will be shown as hyperlinks in the
Status column. Click a hyperlink to watch task progress and details. It shows Idle with no
hyperlinks if there is no running task.
After a backup or restoring task finishes, it will keep summary logs in the system folder. On the
Summary page you will see the summary logs. They keep records of the execution summary
information of the backup or restoring tasks. Click a hyperlink in the Task Name column to see its
details. To delete logs, please check the check-boxes to the right and click the Delete icon.
9.4 SmartSync – NAS-to-NAS Data Replication
The NAS-3410s are integrated with the SmartSync function for NAS-to-NAS data replication. Two
or more NAS-3410s are required, one as the SmartSync server, others as the SmartSync clients.
The SmartSync server is like an ftp server. The SmartSync clients can either replicate their data to
the SmartSync server, or copying data from the SmartSync server, depending on the task settings.
There are three operating modes of SmartSync - "mirror" for one-to-one data replication,
"backup" for disk-based backup, "distribute" for one-to-many data distribution. The following
sections describe the usage and applications of these operating modes.
Building a Mirror Site
68
Page 75

Two NAS-3410s are required, one as the SmartSync server, another as the SmartSync client. It
will replicate data from the SmartSync client to the SmartSync server.
On the NAS-3410 which acts as the SmartSync server, create a sync point in it. A sync point is a
folder in the SmartSync server which is exposed to SmartSync clients for data replication. A sync
point of mirror mode receives data from a SmartSync client and builds an identical data copy in it.
To create a sync point, please go to the BackupÎSmartSync ÎServer menu on the
Administration Page. Click the Add button to open the page below. On the page you should
provide the sync point name and specify which group is allowed to replicate data to this sync point.
Set the mode to “Mirror”.
On the NAS-3410 which acts as the SmartSync client, set up a SmartSync task, which defines the
schedule settings and the source folder.
To set up a SmartSync task, please go to the BackupÎSmartSync ÎTask menu on the
Administration Page. Click the Add Task button.
69
Page 76

There are four steps to take when adding a SmartSync task.
Step 1 is to specify the IP address of the SmartSync server. Please enter the IP address of the
NAS-3410 where you create the sync point. The second input box is for the port number. By
default, port 873 is used to get remote SmartSync server information such as sync point names. If
the port is remapped by a firewall or a NAT device, you must specify the remapped port number
here.
Step 2 is to choose a sync point of “Mirror” mode in the SmartSync server. Please also provide a
user account with the privilege to replicate data to the sync point.
Step 3 is to complete the task settings. On the page you should provide the task name, select the
source folder to replicate, specify the schedule and configure the SmartSync options.
Step 4 is for confirmation, showing the brief information of the task settings.
Making Disk-to-disk Backups
Two or more NAS-3410s are required, one as the SmartSync server, the rest as the SmartSync
clients. It will backup data from the SmartSync clients to the SmartSync server.
On the NAS-3410 which acts as the SmartSync server, create a sync point of “Backup” mode,
which receives data from SmartSync clients and creates data backups in it.
To create a sync point, please go to the BackupÎSmartSync ÎServer menu on the
Administration Page. Click the Add button to open the page below. On the page you should
provide the sync point name and specify which group is allowed to replicate data to this sync point.
Set the mode to “Backup”.
70
Page 77

The GFS media rotation mechanism is the policy of managing backup versions. The policy is
described as below. Basically it will check for obsolete versions and delete them when a new
backup version is created. X, Y, Z are user-defined numbers.
a. It will keep all the backup versions today.
b. It will keep one backup version per day in the last X days, except today.
c. It will keep one backup version per week in the last Y weeks prior to the X days.
d. It will keep one backup version per month in the last Z months prior to the Y weeks.
On the NAS-3410 which acts as the SmartSync client, set up a SmartSync task, which defines the
schedule settings and the source folder.
To set up a SmartSync task, please go to the BackupÎSmartSync ÎTask menu on the
Administration Page. Click the Add Task button.
There are four steps to take when adding a SmartSync task.
71
Page 78

Step 1 is to specify the IP address of the SmartSync server.
Step 2 is to choose a sync point of “Backup” mode in the SmartSync server. Specify the action
as “Backup to server”. Please also provide a user account with the privilege to replicate data to
the sync point.
Step 3 is to complete the task settings. On the page you should provide the task name, select the
source folder to replicate, specify the schedule and configure the SmartSync options.
Step 4 is for confirmation, showing the brief information of the task settings.
Restoring Files from the SmartSync Backups
To restore data from the SmartSync server, please create a SmartSync task on the client. Open
the Administration Page and enter the BackupÎSmartSync ÎTask menu. Click the Add Task
button.
Follow the steps to take to add the SmartSync task.
Step 1 is to specify the IP address of the SmartSync server.
Step 2 is to choose a sync point of “Backup” mode in the SmartSync server. Specify the action
as “Restore from server”. Please also provide a user account with the privilege to replicate data
to the sync point.
Step 3 is to complete the task settings. On the page you should provide the task name, select
which backup version to restore, specify the target folder and configure the SmartSync options
and the overwrite options. The overwrite options specify whether to overwrite the target with the
files of the same names.
Step 4 is for confirmation, showing the brief information of the task settings.
Distributing File Updates to Multiple Sites
Two or more NAS-3410s are required, one as the SmartSync server, others as the SmartSync
clients. It will replicate data from the SmartSync server to the SmartSync client.
On the NAS-3410 which acts as the SmartSync server, create a sync point of “Distribute” mode,
which distributes data to the SmartSync clients as they request.
To create a sync point, please go to the BackupÎSmartSync ÎServer menu on the
Administration Page. Click the Add button to open the page below. On the page you should
provide the sync point name and specify which group is allowed to request data from this sync
point. Set the mode to “Distribute”.
72
Page 79

On the NAS-3410 which acts as the SmartSync client, set up a SmartSync task, which defines the
schedule settings and the target folder.
To set up a SmartSync task, please go to the BackupÎSmartSync ÎTask menu on the
Administration Page. Click the Add Task button.
Follow the steps to take to add the SmartSync task.
Step 1 is to specify the IP address of the SmartSync server.
Step 2 is to choose a sync point of “Distribute” mode in the SmartSync server. Please also
provide a user account with the privilege to request data from the sync point.
Step 3 is to complete the task settings. On the page you should provide the task name, select the
target folder to receive data, specify the schedule and configure the SmartSync options.
Step 4 is for confirmation, showing the brief information of the task settings.
73
Page 80

The SmartSync Options
When setting up a SmartSync task, you will see the following SmartSync options.
• Compress the data stream during data transmission: when checked, it will compress data
before transmitting to the SmartSync server. Sometimes it will make it faster to complete a task.
However, it takes extra CPU time to compress data and may have performance penalty if
compression ratio is low.
• Contain security information: when checked, it will send ACL information to the SmartSync
server.
• Bandwidth control: limits the maximum bandwidth for the task.
• Include/exclude file pattern: for excluding or including certain file types in the
synchronization. For example, to exclude WORD files, type -*.doc; . To exclude all WORD
files except those beginning with abc, type +abc*;-*.doc; .
• Perform quick synchronization: quick synchronization will only check file date, time and size
when matching files, instead of checking block-by-block. It will speed up the synchronization a
lot, while taking the risk that files might not be made identical.
• Generate transaction logs: when checked, it will record which files are added, updated or
deleted during the data replication. The transaction logs are displayed on the SmartSync
Summary page.
9.5 Loading and Writing CD/DVD Discs
Connecting a CD or DVD writer to the NAS-3410, you will be able to load data from CD/DVD discs
or burn files on writeable CD/DVD discs. The CD and DVD burning feature turns the NAS-3410
into a device that publishes data, beyond the powerful data storage function.
Loading CD/DVD Data
The Loader function copies data from a CD or DVD disc to any location inside the NAS-3410.
This function is useful when you try to restore the archived data on CD/DVD discs or simply copy
files from discs to the server.
Note that the NAS-3410 recognizes only data CD or DVD, such as ISO 9660. Multimedia CD
formats such as audio CD or video CD are not supported.
To load data from CD/DVD discs, please insert the source disc into the CD or DVD device first.
Open the Administration Page and select BackupÆLoader/Writer. Then follow the steps below.
74
Page 81

1. Select a Source Device where you insert the disc to be loaded. Above the Source Device
item you will see a device list for your reference.
2. Specify the destination. Click the Select Path hyperlink and select a target path.
3. Choose whether to overwrite the existing files. “Overwrite with newer files” means it will
overwrite the target if the files on the CD/DVD disc are newer.
4. Click Apply to start copying data.
When it is copying disc, you can see the progress by clicking the hyperlink in the Status column of
the Device List. A separate browser window will pop up. The progress is indicated by the
progress bar, the Processed Folders item, the Processed Files item and the Size Processed
item.
Writing CD/DVD Discs
75
Page 82

The NAS-3410 supports CD or DVD burning. It can use ISO-9660 CD format to write data to CD
or DVD discs. Supported devices are CD-RW, DVD-RW and DVD+RW writers. Dual-layer DVD
writing is also supported.
To write data to CD/DVD discs, please insert a blank disc into the CD/DVD writer first. Next, open
the Administration Page and enter the BackupÆLoader/Writer page. Then follow the steps
below.
1. Click the Writer tab in BackupÆLoader/Writer menu
2. Select the Target Device where you want to burn the blank CD/DVD disc(s). Above the Target
Device item you will see a device list for your reference.
3. Specify the source folders. Please click Select Folders and specify which folders to burn.
4. Specify the volume label of the CD or DVD disc.
5. Check the overwrite option if you want erase a rewriteable disc first before burning.
6. Click Apply to start burning CD or DVD discs.
76
Page 83

When it is writing to disc, you can see the progress by clicking the hyperlink in the Status column
of the Device List. A separate browser window will pop up. The progress is indicated by the
progress bar, the Processed Folders item, the Processed Files item and the Size Processed
item. You can also check the Task Phase to see what the CD/DVD writer is doing.
If it requires more than one disc to burn the source data, it will prompt for a new disc after the first
disc is burned ok. In this case, the Task % progress bar indicates the total task progress, which
means the percentage of the source data which have been burned to discs. The Disc % progress
bar indicates the CD/DVD writing percentage of the current disc.
9.6 Backup and Restore System Profiles
To recover from system failures, it requires restoring data and system configurations. Tape backup
and SmartSync are for restoring data, while system profiles are used for recovering system
configurations. System profiles are the backups of all system configurations, user database and
security information.
Backing Up System Profiles
To back up system configurations, please open the administration page and go to
BackupÎSystem Profile. System profiles are saved manually or on a regular basis as defined
on the page. System profiles will be saved locally on HD. The current backups are displayed on
the lower page. To delete a system profile, check its check-box and click the Delete icon.
Recovering the system configurations when a disaster happens
If there is any system failure which causes corrupt system configurations, the first step is to reset
77
Page 84

the system configurations to factory default. Go to the ServerÎShutdown page. Check the
Reset configuration to factory default option and click the Reboot button.
The second step is to restore system configurations using one of the system profiles. Go to the
BackupÎSystem ProfilesÎRestore page. Select a system profile and choose which part of the
system settings to restore. Then click the Apply button.
A system profile can also be created by the NAStart software. To recover from a system profile
saved by NAStart, click the An external file item and find the system profile. Specify restore
options and click the Restore button.
Restore options are:
• Server, network and backup settings – includes all settings in the Server, Network,
Backup and EventÎConfiguration menus. Please note that the admin password will not be
restored during the recovery.
• User accounts and quota settings – includes local accounts, current domain accounts and
trust domain accounts, together with their quota settings. User accounts will be appended to
the existing user database – local accounts with the same names will be overwritten; domain
accounts with the same SID will be overwritten; others will be added to the existing user
database.
• Security Information, including network shares and ACLs – includes all network shares,
share permissions and access control lists.
78
Page 85

Chapter 10
Virus Protection
Most storage systems are vulnerable to virus attacks. An infected file in you NAS-3410 can be
exchanged among the clients system in the network and resulting in corrupted data or causing
productivity loss. The integrated Trend Micro antivirus software in NAS-3410 is the best-of-breed
security product that delivers the reliable antivirus protection to prevent virus from spreading
before they get to you.
10.1 Information
The Information screen is the summary of the current antivirus settings. It gives you a
comprehensive overview of the current status of antivirus general settings, real-time scans history
and scan task summary of your NAS-3410. General settings display the present condition of the
following items.
Real-time Scan
Virus Scan Schedule
Virus Scan Status
Pattern Update Schedule
Last successful update
Scan engine version
Virus pattern version
Quarantine Folder
The real-time scan history display the date time that the virus is found, virus name, action taken
and the full path name of the infected file. And, the scan task summary display the start time of
each manual or scheduled scan task.
Display real-time scanning is either disabled or enabled
Display schedule virus scanning is either disabled or enabled
Display virus scanning is either idle or scanning.
Display the status, schedule for the next virus pattern file
update
Display the date/time of the last successful virus pattern file
update
Display the current scan engine version
Display the current virus pattern file version
Display the folder name and path where virus infected files are
located and quarantine
10.2 Real-time, Manual and Schedule Scanning
The embedded antivirus utility provides several options for virus protection, including real-time,
manual and scheduled scanning to offer comprehensive antivirus and content security solutions
for enterprise customers.
Note:
79
Page 86

Antivirus requires the system folder to operate. Please go to the Server Æ Maintenance page
and specify the volume where the system folder resides.
Note:
For the first-time operation, please go to the Virus ScanÆ Update page to obtain the most
updated virus pattern file. Otherwise, the antivirus function cannot work.
Enabling Real-time Scanning
The real-time scanning function provides antivirus protection while users are reading or writing
files to the NAS-3410.
1. Click the Enable Real-time scan checkbox to enable real-time scanning.
2. Select scan direction. Incoming files are those that are being stored in NAS-3410 whereas
outgoing files are copied or moved from NAS-3410 to other location.
3. Click Apply to save the settings.
Configuring Manual Scanning
The manual and scheduled scanning function can scan any folders for infected files. The scan
results will be listed as a scan task summary on the Information page.
1. Go to Virus ScanÆ Setting page to configure the scan settings required. See “Configuring
Scan Settings” on Section 10.3.
2. Click the Manual tab to go to the manual scanning page.
3. Click the Select Folders hyperlink to specify the folders you want to perform the manual
scan.
4. Click Apply to save the settings.
Configuring Schedule Scanning
1. Click the Enable Scheduled Scan For Infected Files checkbox to enable scheduled
scanning.
2. Click the Select Folders hyperlink to specify the folders you want to perform the scheduled
scan.
3. Configure the start time and recurrence pattern for the scheduled scanning.
4. Click Apply to save the settings.
10.3 Configuring Scan Settings
All virus scan has two options that need to be configure.
z File Type to Scan – you can limit scanning to specific file types.
z Action When Virus Found – three actions (quarantine, clean, delete) can be chose from
when virus is found.
80
Page 87

File Types to Scan
1. Click the desire scan file type.
2. If All file types is selected, all files regardless to its file extension will be scanned.
3. If Files with specified file extensions Only is selected, specify using the recommended
extensions recommended by Trend Micro or specify the file extension manually.
4. Note that the maximum scanning layer of a compressed file is set to 2 layers for all real-time,
manual and scheduled scan.
Actions When Virus Found
1. Click the desire action when virus was found.
2. Click Apply to save the settings.
10.4 Updating Virus Pattern File
Virus pattern update can be performed either manually or according to the schedule. It is required
to perform a manual update immediately when the antivirus function is activated for the first time.
Configuring a manual update
1. To download virus patterns from Internet, select Trend Micro update server on internet.
Please note that you have to specify the DNS server IP address on the NetworkÎTCP/IP
menu of the Administration Page.
81
Page 88

2. Or, you can download the virus pattern file in ZIP format from Trend Micro’s website –
http://www.trendmicro.com manually. Select A virus pattern file in ZIP format here and
specify the location of the virus pattern file.
3. Click Apply to save the settings.
Configuring a scheduled update
1. Click the Enable Scheduled Update of Virus Pattern Files checkbox to enable scheduled
update.
2. Configure the download schedule. Select the start time and recurrence pattern for the
scheduled update.
3. Click Apply to save the settings.
82
Page 89

Page 90

Chapter 11
Event Logs and System Status
This chapter covers the Event Notification and System Status pages. You can collect information
about the system, hardware and security event of you NAS-3410. NAS-3410 records three kinds
of logs:
• System Log
• Device Log
• Security Log
All the events are categorized into three levels: Info, Warning and Error. In
EventÆConfiguration menu, you can configure the level of the logs. Use the Advance or Basic
button to switch between the display of advance and basic information. The Advance view shows
all the information in the Basic view plus additional event notification setting that may be of
interest to the more advanced user. Various notification methods are provided by NAS-3410 to
ensure non-stop operation and data integrity:
• LCD alert – provides warning and error level notification:
o Warning level notification such as very low disk space is detected on volume;
hot spare disk is consumed and so on.
o Error level notification such as CPU fan failed; volume is degraded or faulty
and so on.
• Web Reminder* – provides instant notification in the administration homepage.
• Email Alert* – provides notification via email.
• SNMP Trap* – sends SNMP trap to the Network Manager System (NMS) such as HP
Open View.
• Buzzer Alert* – an audio sound will goes off from the build-in buzzer in NAS-3410
when event occurred. To turn off the buzzing sound, either press any button on the LCD
front-panel or click the Mute Buzzer icon
* You can configure what kind of events should initiate the notification process in
EventÆConfigurationÆAdvance menu.
on the Administration Page.
11.1 Thermal Settings
User can also define the thermal scheme of the NAS-3410 so that NAS-3410 can give off warning
message or shutting down when the system or CPU temperature is over a pre-defined threshold
84
Page 91

temperature.
Configuring thermal settings:
1. Go to Thermal Settings in EventÆConfiguration menu.
2. Enable CPU Fan Control if you want NAS-3410 to adjust the CPU fan speed automatically
based on the CPU and System temperature. Otherwise, the CPU fan will always run at full
speed.
3. You can set the NAS-3410 to give off warning message or shutdown base on the CPU or
System temperature. Check the Warning and Shutdown checkboxes and select the proper
temperature from the pull down menu.
4. Click Advance button to configure the way of notification for various events.
5. Click Apply to save the setting.
11.2 Checking the Event Logs
You can view a summary of all the events occurred on your NAS-3410: Web Reminder, System
Log, Device Log & Security Log. The severity of each event will be determined by NAS-3410
and displayed in different colors:
• Information = Green
• Warning = Yellow
• Error = Red
Viewing Web Reminder
Web Reminder is the warning message that appear at the first screen of the administrator home
page to alert administrator that one or multiple critical events of your NAS-3410 has been found.
Administrator can, therefore be aware of the status of the NAS-3410 immediately when entering
the administrator home page. Click the hyper-link of the Web Reminder message and it will
directly lead you to the Web Reminder summary menu.
Go to EventÆWeb Reminder menu to see a summary of all the critical events occurred on your
NAS-3410.
Viewing System Log
In the EventÆSystem Log menu, you can:
4. Select the number of most recent events show on a screen.
5. Select the severity level for the events you want to see.
6. Click Refresh or
7. Click Clear or button to clear the log.
85
button to refresh the screen.
Page 92

Viewing Device Log
In the EventÆDevice Log menu, you can:
8. Select the number of most recent events show on a screen.
9. Select the severity level for the events you want to see.
10. Click Refresh or
11. Click Clear or button to clear the log.
button to refresh the screen.
Viewing Security Log
In the EventÆSecurity Log menu, you can:
12. Select the number of most recent events show on a screen.
13. Select the severity level for the events you want to see.
14. Click Refresh or
15. Click Clear or button to clear the log.
16. Select the protocols and click the Refresh button to show the corresponding events. Default
event represent general security event of your NAS-3410 that is not related to any protocols.
button to refresh the screen.
11.3 Viewing System Status
System Status displays a comprehensive view of the system fan status, thermal status and
system voltage. You can use this information to quickly find out the problem of your NAS-3410
and take appropriate action. In StatusÆEnvironment page, you can monitor the CPU fan status,
CPU and System temperature plus the System Voltages. Click Refresh to obtain the latest figure.
Viewing the Open Files
In StatusÆOpen Files menu, it provides the following information about all the open files on
NAS-3410:
• R/W – read/write privileges of the opened file.
• User – the name of the user who has opened the file.
• Protocol - the protocol used for the network connection: SMB, NFS, AFP or FTP.
• File Name – lists the name and path of the opened file.
Viewing the Active Connections
In the StatusÆConnections:
86
Page 93

• Current Connections – configure and show the protocol used by the client that is
currently connecting to the NAS-3410 by click the check box beside the protocol you
want to show on the list.
• User – the name of the user who has connected to NAS-3410.
• Computer – the computer name of the client connecting to the NAS-3410.
• Address – the IP address of the client connecting to the NAS-3410.
• Protocol – the protocol used for the network connection: SMB, NFS, AFP or FTP.
• Connected Time – the date / time that the connection is established.
• Open Files – total number of the open files.
• Disconnect – disconnect a particular connection by check the disconnect check box
and click the
icon.
Viewing the System Load
In the StatusÆLoad:
• CPU & Memory – You can see the CPU usage and memory usage here. Total
memory and the current free memory are also shown here.
• Network –The network throughput in percentage are showed on here.
11.4 Share Access Counts
On the StatusÆAccess Counts menu page it displays how many times the shares have been
accessed. The count is added by one whenever a connection to the share is established by
Windows clients, NFS clients, MacOS clients and NetWare clients.
There are several share types.
Normal Share – indicates a shared folder in any data volume.
Aggregation Share – indicates a share of grouping of several volumes.
System Share – indicates the MIRROR share which holds all CD/DVD volumes.
Disc Share – indicates a share of a single CD/DVD volume.
Group Share – indicates a share of grouping of several CD/DVD volumes.
Disc Folder Share - indicates a share of disc image folder.
87
Page 94

Appendix A
NAStart Utility
NAStart is a powerful software that discover and administer NAS Servers on the network, and
remotely loads disc images into the NAS Server. You can either duplicate a whole CD or build an
image from a group of files. Sharing and publishing data was never been so easy.
Use NAStart to display and modify the setting you have created. You can also perform server
settings replication from a configured server to other NAS Servers on the network. Server
parameters of a NAS Server can be imported into other NAS Server to avoid tedious setup
process to each individual unit on the network.
Features:
Server Management -
z Discovers all NAS Servers on the network
z Configures NAS Servers for the first-time setup or quick setup
z Export / Import NAS Servers system settings
Creating CD Images Remotely -
z Remotely loads CD images from a local CD-ROM drive into a NAS Server
z Collect and duplicates files into NAS Servers as a single CD image
z Allows users to assign 6 different destination servers when building CD images
z Fully integrates the CD-R function of the NAS Server
z Supports up to 16 different tasks
User Interface -
z Explorer-like user interface together with user friendly wizards
z Task Manager monitors all on-going and scheduled tasks
90
Page 95

Installation
System Requirement
• IBM PC or compatible with 80486 processor or higher
• At least 8 MB of free memory (16 MB is recommended)
• Minimum 5MB of free hard disk space
• VGA or higher resolution monitor
• Microsoft Windows 95/98/98SE/ME, Windows NT/2000/XP
Installing TCP/IP Protocol for Microsoft Networks NAStart communicates with NAS Servers through the TCP/IP protocol. You must install Client for
Microsoft Networks and the TCP/IP protocol in Windows to use NAStart. Installing NAStart
You are ready to install this utility if the TCP/IP protocol is installed in your computer. To install
NAStart, insert the Utility CD into the CD-ROM drive. On the auto-run interface, click “NAStart
Utility”. If the auto-run interface does not appear, go to E:\Utility\NAStart and run NAStart.exe,
where E is the drive letter of the CD-ROM drive.
Follow the instructions in the setup wizard to install NAStart. It will create shortcuts on Desktop
and in the Programs folder of the Start menu.
91
Page 96

Discovering NAS-3410
When startups, NAStart automatically discover all the NAS-3410s on the network and display a list
of server under the node Local Server. NAStart will automatically refresh the server list at a
specified interval. The default interval is 10 minutes.
NAStart can also locate NAS servers by IP addresses. It is useful when NAS servers are on the
Internet or located in different network segments from the NAStart. To locate NAS servers by IP
addresses, select Remote NAS List from the File menu. Click the Add button and enter the IP
address of the NAS server.
To set the automatic refresh interval
1. Go to Tool Æ NAStart Options menu.
2. Enter a number between 1 to 60 minutes.
3. Click OK.
Server Quick Setup Using NAStart
You can perform initial setup for your NAS-3410 using NAStart.
1. Click the
2. Or, go to Server -> Server Quick Setup.
3. Select a NAS Server from the server list and click Next button.
4. Choose the Network Teaming Mode from the pull down menu. If you are not clear about this
feature, continue with the default value.
5. If you want the IP settings to be assigned automatically, click Obtain IP settings
automatically.
6. Or, you can specify the IP settings manually.
7. Click Next button to go to the next page.
8. Enter the Server Name, Server Comment, and Workgroup/Domain Name and select either
the Workgroup mode or Domain mode. Note that this is the server name as it appears on
the network which is irrelevant to the network protocol used.
9. Click Next button to go to the next page.
10. Change the admin password if necessary.
Click the OK button to save the settings. Note that server may need to reboot for certain
parameters changes to take effect.
button on the toolbar.
92
Page 97

Importing and Exporting System Settings
This section describes how to export the system settings of a NAS Server into a file. This file can
be read into another NAS Server on the network by using the import feature. Import System
Settings and Export System Settings form a combined process of replicate system settings
from one configured NAS Server to another NAS Server.
To export system settings of a NAS Server
1. Highlight the server from the server list.
2. Right click the server and select Export System Settings.
3. Or, go to Server -> Export System Settings menu.
4. You will prompt for the administrator password to proceed.
5. Select a location where you want to save and specify the name of the export file.
6. Click Save.
To import system settings into NAS Servers
1. Right click any NAS Server and select Import System Settings
2. Or, go to Server -> Import System Settings menu.
3. You will prompt for the administrator password to proceed.
4. You have the option to select a server or an export file as the source.
5. Click Next.
6. Select the type of system settings you want to import into the target server. The detail content
of the system settings are displayed in the preview text box beside each selection.
7. Click OK. NAS Server will reboot automatically.
93
Page 98

Browsing & Administering Servers
Browsing Servers
Below is the main window of NAStart. Upon execution, NAStart brings up Windows Explorer for
you to drag & drop files into My Container for later image building. You can disable this option by
choosing Tool->NAStart Options and un-checking the option - "Open Windows Explorer when
NAStart starts".
The main window consists of a file menu, a tool bar, a tree view pane on the left, a list view pane
on the right and a status bar on the bottom.
On the tree view pane are listed all the NAS Servers found by the NAStart on the network. Also
included is My Computer as the one in Windows Explorer. My Container keeps information of
the files/folders that can be built as a CD image in a NAS Server using the "Build Image" function.
If you click on any item on the tree view pane, its content will be displayed in the list view pane.
The status bar indicates NAStart status & information. The left of the status bar shows function
hint or item properties. To the right it displays the PC date and time.
You can browse the Domain Name, IP Addresses of each NAS Server just by mouse over it.
Note:
If a NAS Server is protected by the admin password, you have to enter the password to set up or
write to the server.
94
Page 99

The following are some icon representations:
NAS Network: display all the NAS Servers found on the LAN.
NAS Server: represents a NAS Server
Disc Image Folder: contains disc images of the NAS Server. You can
double click to view its content.
Disc Image: represents a mirrored CD/DVD image.
The following are some examples of browsing the servers.
Example 1. Content of a disc image folder
It displays all the disc images, path name, size, status and file system.
Tool Bar Functions
The tool-bar provides an easy access to the main functions of NAStart. The following explains
what the tool-bar icons represent.
Refresh: manually updates the directory content of My Computer or NAS Network.
Up Directory: moves the cursor one level up.
95
Page 100

Tree View Mode: expands or shrink the directory tree in the tree view pane (to the left).
List View Mode: changes the view mode of items in the list view pane (to the right).
Save Container: saves data in My Container into a container file.
Load Container: loads a container file into My Container.
Mirror CD: starts the "Mirror CD" wizard for duplicating CD images into the NAS Server.
Build Image: starts the "Build Image" wizard to build a CD image from My Container into a
NAS Server.
Server Quick Setup: configures some fundamental parameters of a selected NAS Server.
You can configure an un-initialized or initialized server.
Wizard: brings up a wizard for access to major functions: "Mirror CD", "Build Image" and
"Server Quick Setup".
Task Manager: opens a task manager window which displays and controls all ongoing and
scheduled tasks.
Help: opens the Help window for display help information.
96
 Loading...
Loading...