Page 1

Multi-Homing Security
Gateway
MH-5000
User’s Manual
Page 2

Multi-Homing Security Gateway User’s Manual
Copyright
Copyright (C) 2004 PLANET Technology Corp. All rights reserved.
The products and programs described in this User’s Manual are licensed products of PLANET Technology, This User ’s Manual
contains proprietary information protected by copyright, and this User’s Manual and all accompanying hardware, software, and
documentation are copyrighted.
No part of this User’s Manual may be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated, or reduced to any electronic medium or
machine-readable form by any means by electronic or mechanical. Including photocopying, recording, or information storage and
retrieval systems, for any purpose other than the purchaser's personal use, and without the prior express written permission of
PLANET Technology.
Disclaimer
PLANET Technology does not warrant that the hardware will work properly in all environments and applications, and makes no
warranty and representation, either implied or expressed, with respect to the quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for a
particular purpose.
PLANET has made every effort to ensure that this User’s Manual is accurate; PLANET disclaims liability for any inaccuracies or
omissions that may have occurred.
Information in this User’s Manual is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of PLANET.
PLANET assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be contained in this User’s Manual. PLANET makes no commitment
to update or keep current the information in this User’s Manual, and reserves the right to make improvements to this User ’s Manual
and/or to the products described in this User’s Manual, at any time without notice.
If you find information in this manual that is incorrect, misleading, or incomplete, we would appreciate your comments and
suggestions.
CE mark Warning
This is a class A device, in a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference, in which case the user may be required
to take adequate measures.
Trademarks
The PLANET logo is a trademark of PLANET Technology.
This documentation may refer to numerous hardware and software products by their trade names. In most, if not all cases, these
designations are claimed as trademarks or registered trademarks by their respective companies.
Customer Service
For information on customer service and support for the Multi-Homing Security Gateway, please refer to the following Website URL:
http://www.planet.com.tw
Before contacting customer service, please take a moment to gather the following information:
Multi-Homing Security Gateway serial number and MAC address
¨
¨ Any error messages that displayed when the problem occurred
¨ Any software running when the problem occurred
Steps you took to resolve the problem on your own
¨
Page 3

Revision
User’s Manual for PLANET Multi-Homing Security Gateway
Model: MH-5000
Rev: 1.0 (September, 2004)
Part No. EM-MH5Kv1
Multi-Homing Security Gateway User’s Manual
Page 4

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Quick Start................................................................................................1
1.1 Check Your Package Contents.....................................................................................1
1.2 Five steps to configure MH-5000 quickly......................................................................1
1.3 Wiring the MH-5000......................................................................................................4
1.4 Default Settings and architecture of MH-5000..............................................................6
1.5 Using the Setup Wizard................................................................................................7
1.6 Internet Connectivity...................................................................................................10
1.6.1 LAN1-to-WAN1 Connectivity.......................................................................................................11
1.6.2
WAN1-to-DMZ1 Connectivity......................................................................................................12
Chapter 2 System Overview...................................................................................16
2.1 Typical Example Topology..........................................................................................16
2.2 Changing the LAN1 IP Address..................................................................................17
2.2.1
2.2.2
2.2.3 The design principle...................................................................................................................19
2.2.4 Web GUI design principle...........................................................................................................19
2.2.5 Rule principle..............................................................................................................................19
From LAN1 to configure MH-5000 LAN1 network settings...........................................................17
From CLI (command line interface) to configure MH-5000 LAN1 network settings.......................18
Chapter 3 Basic Setup............................................................................................21
3.1 Demand......................................................................................................................21
3.2 Objectives...................................................................................................................21
3.3 Methods......................................................................................................................21
3.4 Steps...........................................................................................................................21
3.4.1
3.4.2 Setup DMZ1, LAN1 Status..........................................................................................................23
3.4.3 Setup WAN1 IP alias..................................................................................................................25
Setup WAN1 IP..........................................................................................................................21
Chapter 4 System Tools..........................................................................................28
4.1 Demand......................................................................................................................28
4.2 Objectives...................................................................................................................28
4.3 Methods......................................................................................................................28
4.4 Steps...........................................................................................................................32
4.4.1
4.4.2 DDNS setting..............................................................................................................................34
4.4.3 DNS Proxy setting......................................................................................................................35
4.4.4 DHCP Relay setting....................................................................................................................35
4.4.5
4.4.6
General settings.........................................................................................................................32
SNMP Control............................................................................................................................36
Change MH-5000 interface.........................................................................................................37
Chapter 5 Remote Management.............................................................................38
5.1 Demands.....................................................................................................................38
I
Page 5

5.2 Methods......................................................................................................................38
5.3 Steps...........................................................................................................................39
5.3.1 Telnet.........................................................................................................................................39
5.3.2
5.3.3
5.3.4 ICMP..........................................................................................................................................39
WWW.........................................................................................................................................39
SNMP.........................................................................................................................................39
Chapter 6 NAT.........................................................................................................40
6.1 Demands.....................................................................................................................40
6.2 Objectives...................................................................................................................41
6.3 Methods......................................................................................................................41
6.4 Steps...........................................................................................................................42
6.4.1 Setup Many-to-one NAT rules.....................................................................................................42
6.4.2
6.5 NAT modes introduction..............................................................................................50
6.5.1
6.5.2
6.5.3 One-to-One type.........................................................................................................................51
6.5.4 NAT modes & types....................................................................................................................52
Setup Virtual Server for the FtpServer1.......................................................................................46
Many-to-One type.......................................................................................................................50
Many-to-Many type.....................................................................................................................51
Chapter 7 Routing...................................................................................................53
7.1 Demands.....................................................................................................................53
7.2 Objectives...................................................................................................................54
7.3 Methods......................................................................................................................54
7.4 Steps...........................................................................................................................54
7.4.1
7.4.2 Add a policy routing entry...........................................................................................................56
Add a static routing entry............................................................................................................54
Chapter 8 Firewall...................................................................................................59
8.1 Demands.....................................................................................................................59
8.2 Objectives...................................................................................................................59
8.3 Methods......................................................................................................................59
8.4 Steps...........................................................................................................................60
8.4.1 Block internal PC session (LAN à WAN)....................................................................................60
8.4.2
Setup Alert detected attack.........................................................................................................63
Chapter 9 VPN Technical Introduction..................................................................65
9.1 VPN benefit.................................................................................................................65
9.2 Related Terminology Explanation...............................................................................65
9.2.1 VPN...........................................................................................................................................65
9.2.2
9.2.3 Security Association...................................................................................................................65
9.2.4 IPSec Algorithms........................................................................................................................65
9.2.5 Key Management.......................................................................................................................66
9.2.6
IPSec.........................................................................................................................................65
Encapsulation.............................................................................................................................67
II
Page 6

9.2.7 IPSec Protocols..........................................................................................................................67
9.3 Make VPN packets pass through MH-5000................................................................68
Chapter 10 Virtual Private Network – IPSec..........................................................69
10.1 Demands.....................................................................................................................69
10.2 Objectives...................................................................................................................69
10.3 Methods......................................................................................................................69
10.4 Steps...........................................................................................................................70
10.4.1 DES/MD5 IPSec tunnel: the IKE way..........................................................................................70
10.4.2 DES/MD5 IPSec tunnel: the Manual-Key way.............................................................................80
Chapter 11 Virtual Private Network –Dynamic IPSec............................................88
11.1 Demands.....................................................................................................................88
11.2 Objectives...................................................................................................................88
11.3 Methods......................................................................................................................88
11.4 Steps...........................................................................................................................89
Chapter 12 Virtual Private Network – PPTP..........................................................95
12.1 Demands.....................................................................................................................95
12.2 Objectives...................................................................................................................95
12.3 Methods......................................................................................................................96
12.4 Steps...........................................................................................................................96
12.4.1
12.4.2 Setup PPTP Network Client........................................................................................................97
Setup PPTP Network Server.......................................................................................................96
Chapter 13 Virtual Private Network – L2TP...........................................................99
13.1 Demands.....................................................................................................................99
13.2 Objectives...................................................................................................................99
13.3 Methods......................................................................................................................99
13.4 Steps.........................................................................................................................100
13.4.1 Setup L2TP Network Server.....................................................................................................100
Chapter 14 Content Filtering – Web Filters.........................................................103
14.1 Demands...................................................................................................................103
14.2 Objectives.................................................................................................................104
14.3 Methods....................................................................................................................104
14.4 Steps.........................................................................................................................105
14.5 Setting priorities........................................................................................................110
Chapter 15 Content Filtering – Mail Filters..........................................................113
15.1 Demands...................................................................................................................113
15.2 Objectives.................................................................................................................113
15.3 Methods....................................................................................................................113
15.4 Steps for Anti-Virus...................................................................................................114
15.5 Steps for Anti-Spam..................................................................................................115
III
Page 7

15.6 Steps for SMTP Relay...............................................................................................116
Chapter 16 Content Filtering – FTP Filtering.......................................................117
16.1 Demands...................................................................................................................117
16.2 Objectives.................................................................................................................117
16.3 Methods....................................................................................................................117
16.4 Steps.........................................................................................................................118
Chapter 17 Intrusion Detection Systems.............................................................121
17.1 Demands...................................................................................................................121
17.2 Objectives.................................................................................................................121
17.3 Methods....................................................................................................................121
17.4 Steps.........................................................................................................................122
Chapter 18 Bandwidth Management....................................................................123
18.1 Demands...................................................................................................................123
18.2 Objectives.................................................................................................................124
18.3 Methods....................................................................................................................125
18.4 Steps.........................................................................................................................125
Chapter 19 Load Balancer....................................................................................129
19.1 Demands...................................................................................................................129
19.2 Objectives.................................................................................................................129
19.3 Methods....................................................................................................................130
19.4 Steps.........................................................................................................................130
19.4.1 Outbound Load Balancer..........................................................................................................130
Chapter 20 System Status....................................................................................131
20.1 Demands...................................................................................................................131
20.2 Objectives.................................................................................................................131
20.3 Methods....................................................................................................................131
20.4 Steps.........................................................................................................................131
Chapter 21 Log System........................................................................................134
21.1 Demands...................................................................................................................134
21.2 Objectives.................................................................................................................134
21.3 Methods....................................................................................................................134
21.4 Steps.........................................................................................................................134
21.4.1 System Logs............................................................................................................................134
21.4.2 Syslog & Mail log......................................................................................................................135
Chapter 22 System Maintenance.........................................................................137
22.1 Demands...................................................................................................................137
22.2 Steps for TFTP Upgrade...........................................................................................137
22.3 Steps for Firmware upgrade from Web GUI..............................................................138
IV
Page 8

22.4 Steps for Database Update from Web GUI...............................................................139
22.5 Steps for Factory Reset............................................................................................140
22.5.1 Step for factory reset under web GUI........................................................................................140
22.5.2
22.5.3
Step for NORMAL factory reset................................................................................................140
Steps for EMERGENT factory reset..........................................................................................140
22.6 Save the current configuration..................................................................................141
22.7 Steps for Backup / Restore Configurations...............................................................141
22.8 Steps for Reset password.........................................................................................142
Appendix A Command Line Interface (CLI).....................................................143
A.1 Enable the port of MH-5000......................................................................................143
A.2 CLI commands list (Normal Mode)............................................................................143
A.3 CLI commands list (Rescue Mode)..................................................................................145
Appendix B Troubleshooting............................................................................147
Appendix C System Log Syntax.......................................................................151
Appendix D Glossary of Terms........................................................................158
Appendix E Index..............................................................................................160
Appendix F Version of Software and Firmware..............................................161
V
Page 9
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 1
Quick Start
Chapter 1
Quick Start
This chapter introduces how to quick setup the MH-5000.
MH-5000 is an integrated all-in-one solution that can facilitate the maximum security and the best resource utilization for
the enterprises. It contains a high-performance stateful packet inspection (SPI) Firewall, policy-based NAT, ASIC-based
wire-speed VPN, upgradeable Intrusion Detection System, Dynamic Routing, Content Filtering, Bandwidth
Management, WAN Load Balancer, Anti-Virus, Anti-Spam and other solutions in a single box. It is one of the most
cost-effective all-in-one solutions for enterprises.
1.1 Check Your Package Contents
These are the items included with your MH-5000 purchase. They are the following items
1. MH-5000 x 1
2. Quick Installation Guide x 1
3. CD-ROM Manual / Installation Guide x 1
4. Power Cord x 1
5. Rack mount x 1
6. RS-232 cable x 1
1.2 Five steps to configure MH-5000 quickly
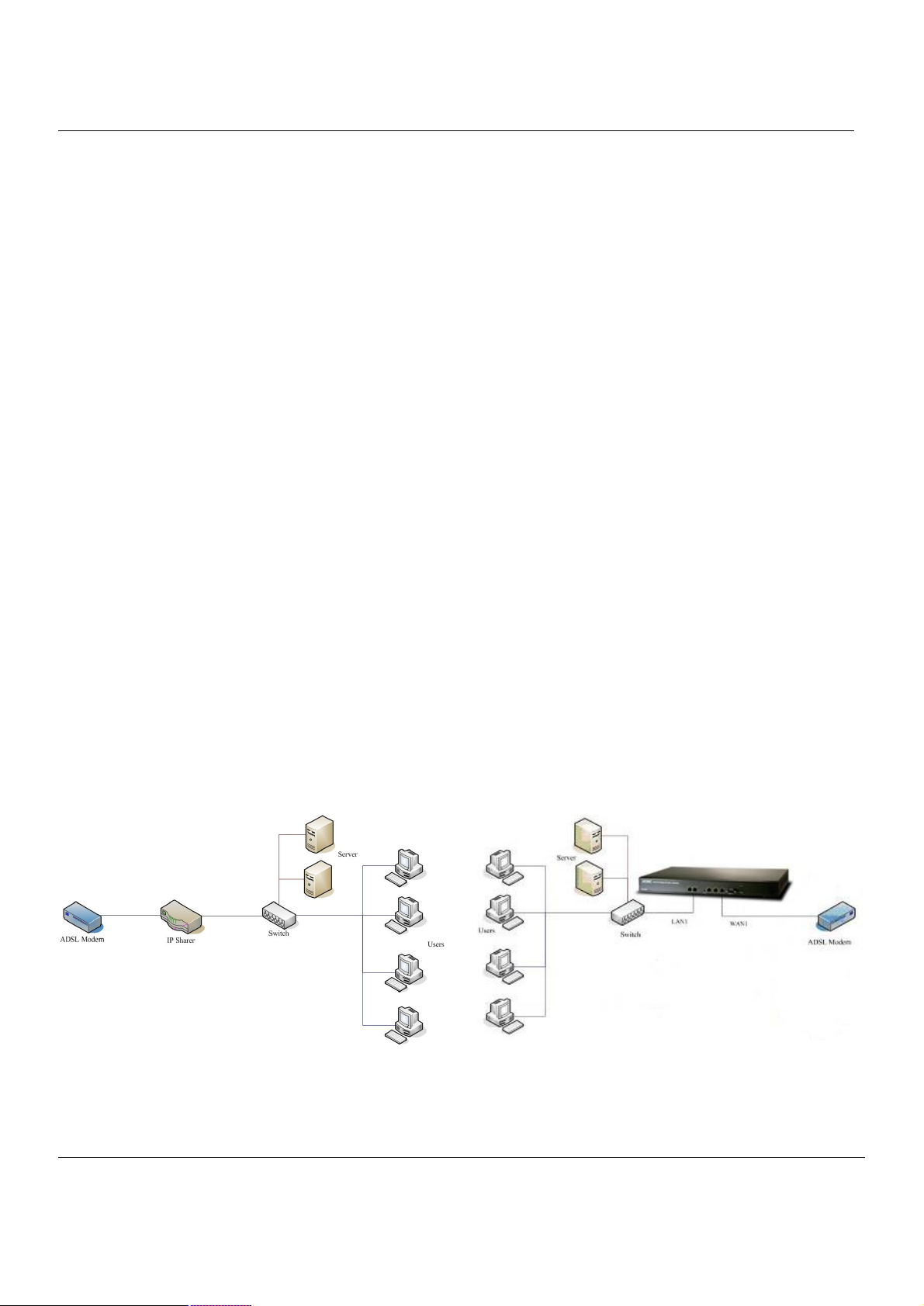
Let’s look at the common network topology without MH-5000 applying like Figure 1-1. This is a topology which is almost
used by all the small/medium business or SOHO use as their internet connectivity. Although that your topology is not
necessarily the same diagram below, but it still can give you a guideline to configure MH-5000 quickly.
Now you can pay attention at the IP Sharer in the diagram. The IP Sharer can provide you with NAT (Network
Address Translation), PAT (Port Address Translation) and other functions.
Figure 1-1 The example before MH-5000 applies on it
Figure 1-2 The example after MH-5000 applies on it
1
Page 10
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 1
Quick Start
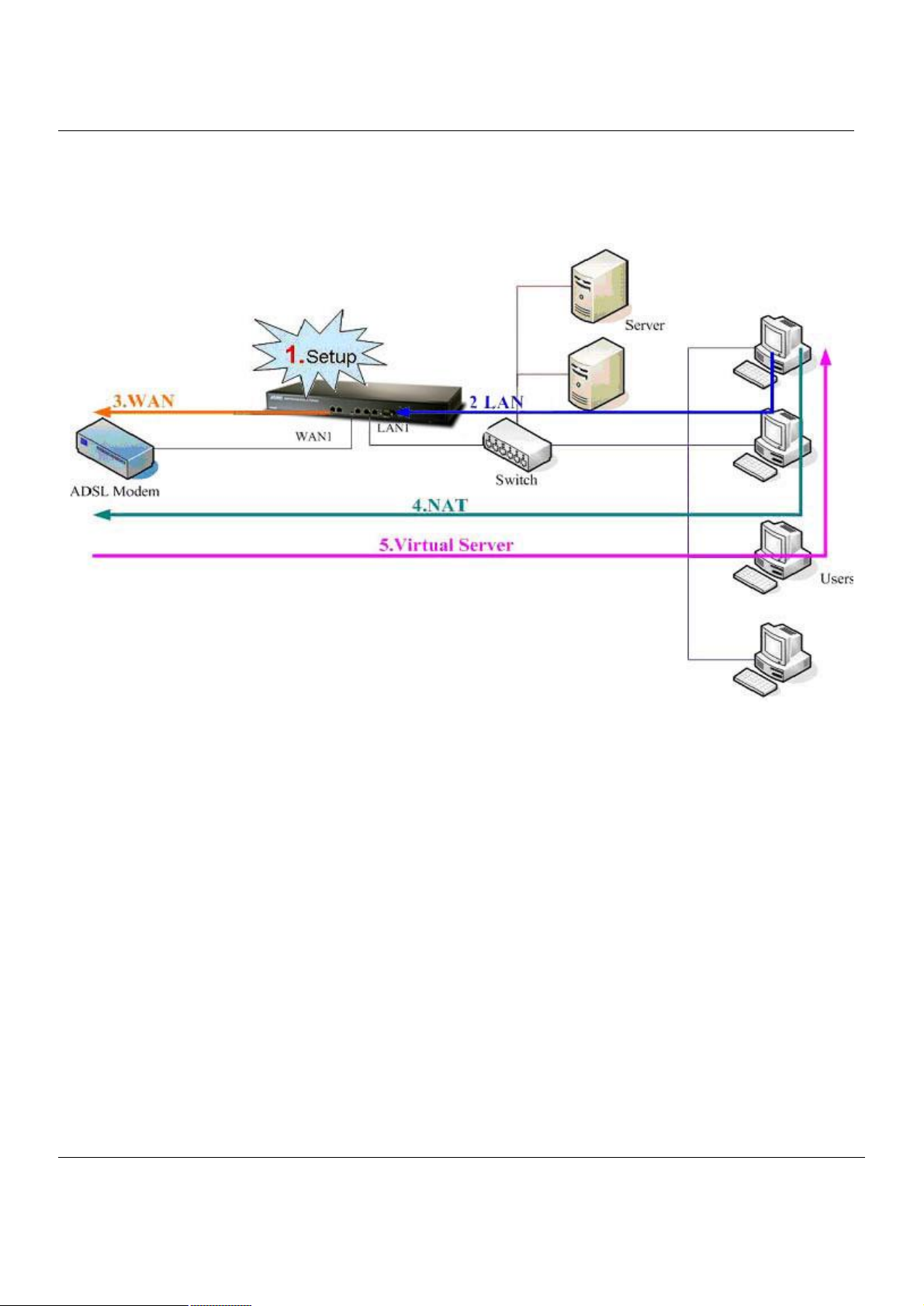
Here we would like to alter the original IP Sharer with the MH-5000 like Figure 1-2. If we hope to have MH-5000 to
replace the IP Sharer, we just need to simply execute the following five steps as Figure 1-3 showed. By these steps, we
hope to build an image to tell you how to let MH-5000 work basically.
Figure 1-3 Five steps to configure MH-5000
As the Figure 1-3 illustrated, with the five-step configurations, MH-5000 will have the same functions with the original IP
Sharer. Please see the following description of the five-step configurations.
1. Setup:
Install three physical lines inclusive of the power cord, outbound link (connected WAN1 port) and inbound direction
(connected LAN1 port). For the details, please refer section 1.3.
Continually, we will connect to the web GUI of MH-5000. So you must make sure that you have a PC which is
located in the same subnet with MH-5000 before this step.
Start up the Internet browser with “http://192.168.1.254” in the address field. And follow with “admin/admin” as the
default user name and password.
Note: The default LAN1 port is (192.168.1.254 / 255.255.255.0). Refer to section 1.5 for more information.
2. LAN:
Configure the LAN1 port of MH-5000. You can refer to section 1.4 for the default network configurations of
MH-5000.
Note: If you were connected from LAN1 port and changed the LAN1 IP address settings of MH-5000. The
network will be disconnected since the IP address is different between your pc and MH-5000 LAN1 port.
3. WAN:
Configure the WAN1 port of MH-5000. You can refer to section 1.4 for the default network configurations of
MH-5000.
3
Page 11

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 1
Quick Start
4. NAT:
Configure the connection of LAN to WAN direction. It will make all the client pc access the internet through
MH-5000. For more information, please refer to section 1.6.1.
5. Virtual Server:
If there is any server located inside the MH-5000. You may hope these servers can provide services outside. So
you should configure the Virtual Server which provides connections of WAN to LAN direction. For more information,
please refer to section 1.6.2.
After you completely finished the above steps, the connectivity function of MH-5000 is probably well-done.
1.3 Wiring the MH-5000
A. First, connect the power cord to the socket at the back panel of the MH-5000 as in
plug the other end of the power adapter to a wall outlet or power strip. The Power LED will turn ON to
indicate proper operation.
Figure 1-4
and then
Figure 1-4 Back panel of the MH-5000
B. Using an Ethernet cable, insert one end of the cable to the WAN port on the front panel of the MH-5000
and the other end of the cable to a DSL or Cable modem, as in Figure 1-5.
C. Computers with an Ethernet adapter can be directly connected to any of the LAN ports using a
cross-over Ethernet cable, as in Figure 1-5.
D. Computers that act as servers to provide Internet services should be connected to the DMZ port using
an Ethernet Cable, as in Figure 1-5.
4
Page 12

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 1
Quick Start
Figure 1-5 Front end of the MH-5000
5
Page 13
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 1
Quick Start
1.4 Default Settings and architecture of MH-5000
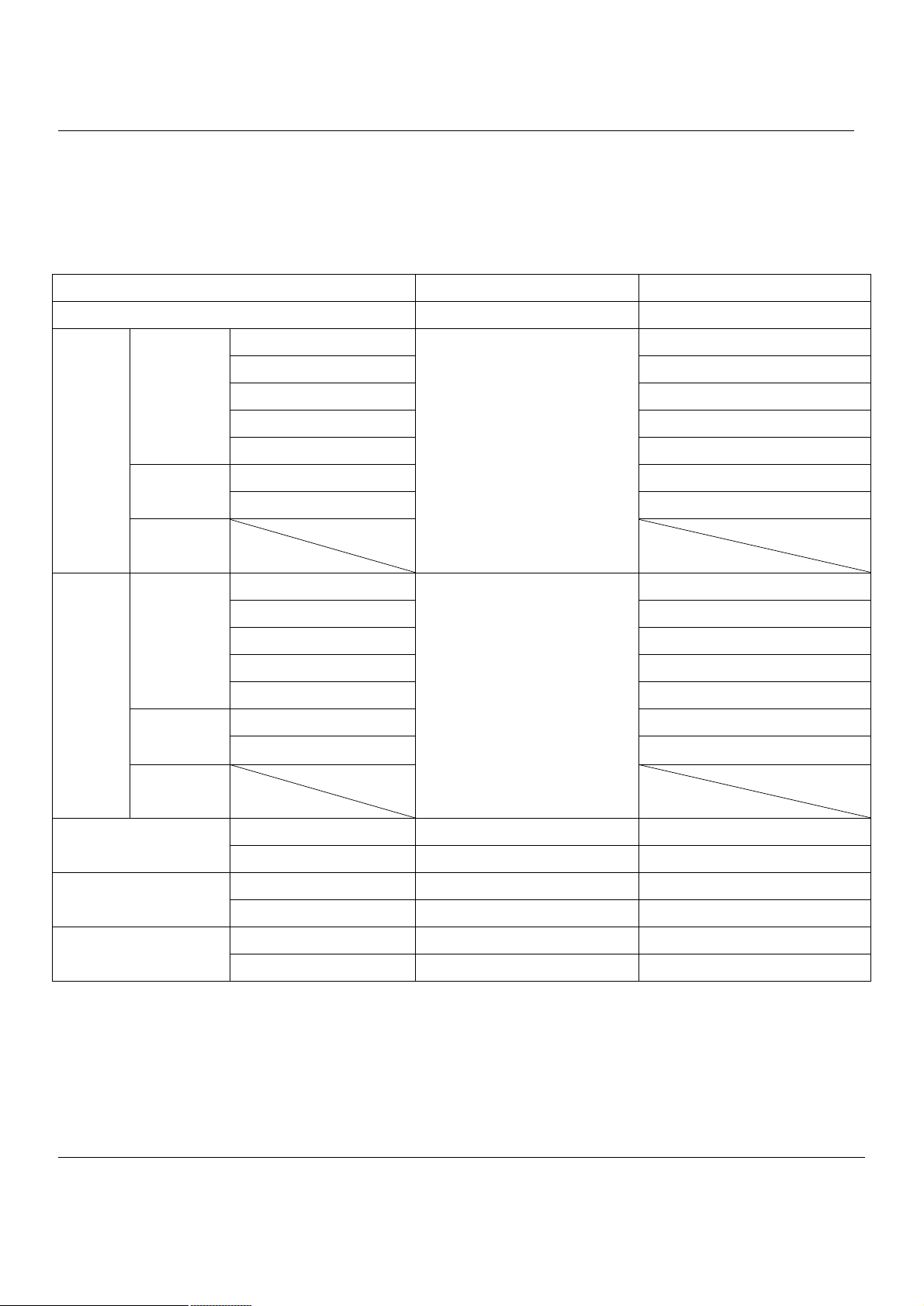
You should have an Internet account already set up and have been given most of the following information as Table 1-1.
Fill out this table when you edit the web configuration of MH-5000.
Items Default value New value
Password: admin
IP Address ____.____.____.____
Subnet Mask ____.____.____.____
WAN1
(Port 1)
WAN2
(Port 2)
DMZ1(Port 3)
Fixed IP
PPPoE
DHCP
Fixed IP
PPPoE
DHCP
Gateway IP ____.____.____.____
Primary DNS ____.____.____.____
Secondary DNS ____.____.____.____
PPPoE Username ____.____.____.____
PPPoE Password ____.____.____.____
IP Address ____.____.____.____
Subnet Mask ____.____.____.____
Gateway IP ____.____.____.____
Primary DNS ____.____.____.____
Secondary DNS ____.____.____.____
PPPoE Username ____.____.____.____
PPPoE Password
IP Address 10.1.1.254 ____.____.____.____
IP Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 ____.____.____.____
Not initialized
Not initialized
____.____.____.____
LAN1(Port 4)
LAN2(Port 5)
IP Address 192.168.1.254 ____.____.____.____
IP Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 ____.____.____.____
IP Address 192.168.2.254 ____.____.____.____
IP Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 ____.____.____.____
Table 1-1 MH-5000 related network settings
6
Page 14
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 1
Quick Start
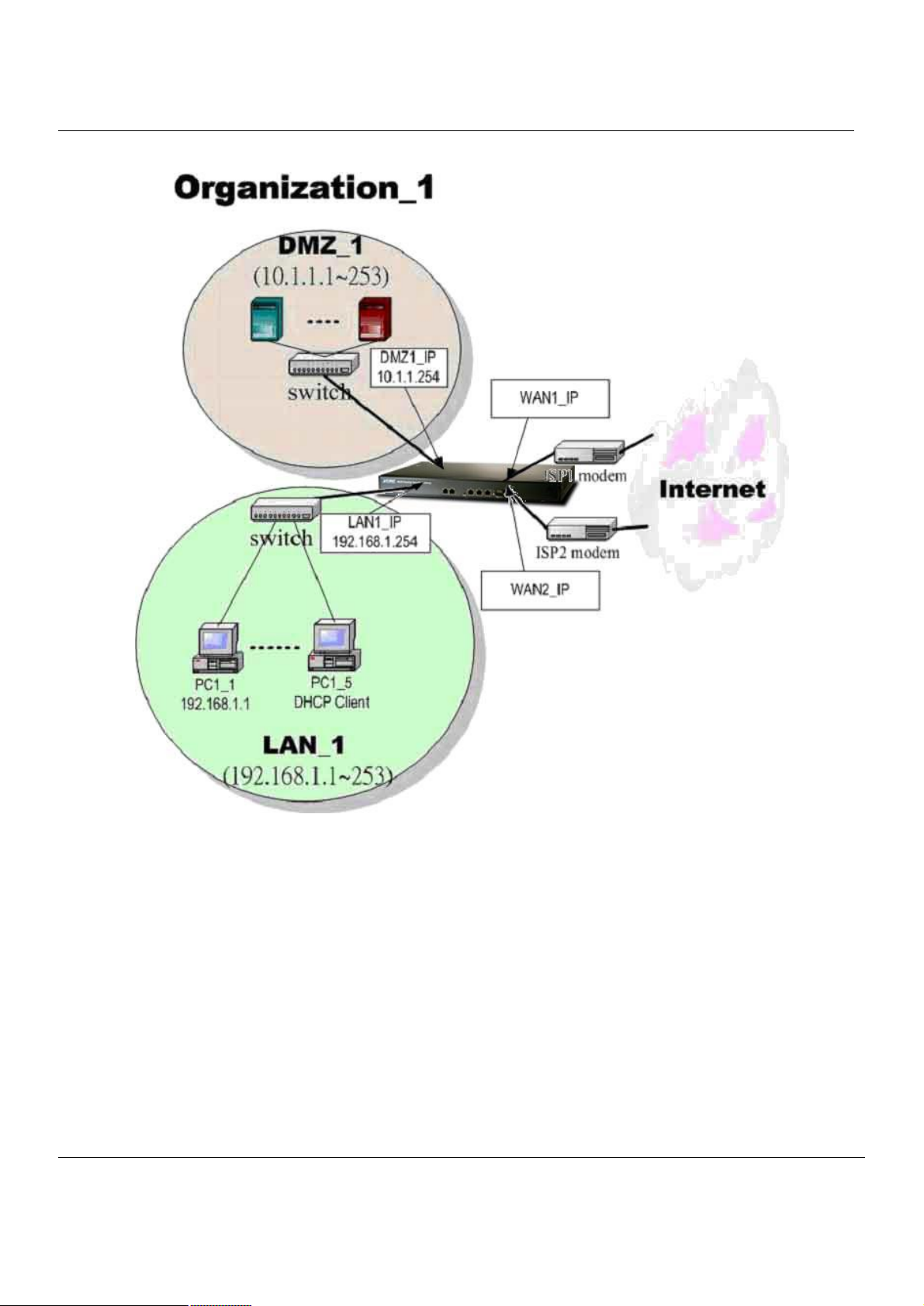
Figure 1-6 The default settings of MH-5000
As the above diagram Figure 1-6 illustrated, this diagram shows the default topology of MH-5000. And you can configure
the MH-5000 by connecting to the LAN1_IP (192.168.1.254) from the PC1_1 (192.168.1.1). In the following sections, we
will teach you how to quickly setup the MH-5000 in the basic appliances.
1.5 Using the Setup Wizard
A computer on your LAN1 must be assigned an IP address and Subnet Mask from the same range as the IP address and
Subnet Mask assigned to the MH-5000, in order to be able to make an HTTPS connection using a web browser. The
MH-5000 is assigned an IP address of 192.168.1.254 with a Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0 by default. The computer
that will be used to configure the MH-5000 must be assigned an IP address between 192.168.1.1 and 192.168.1.253 with
a Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0 to be able to connect to the MH-5000. This address range can be changed later.
7
Page 15
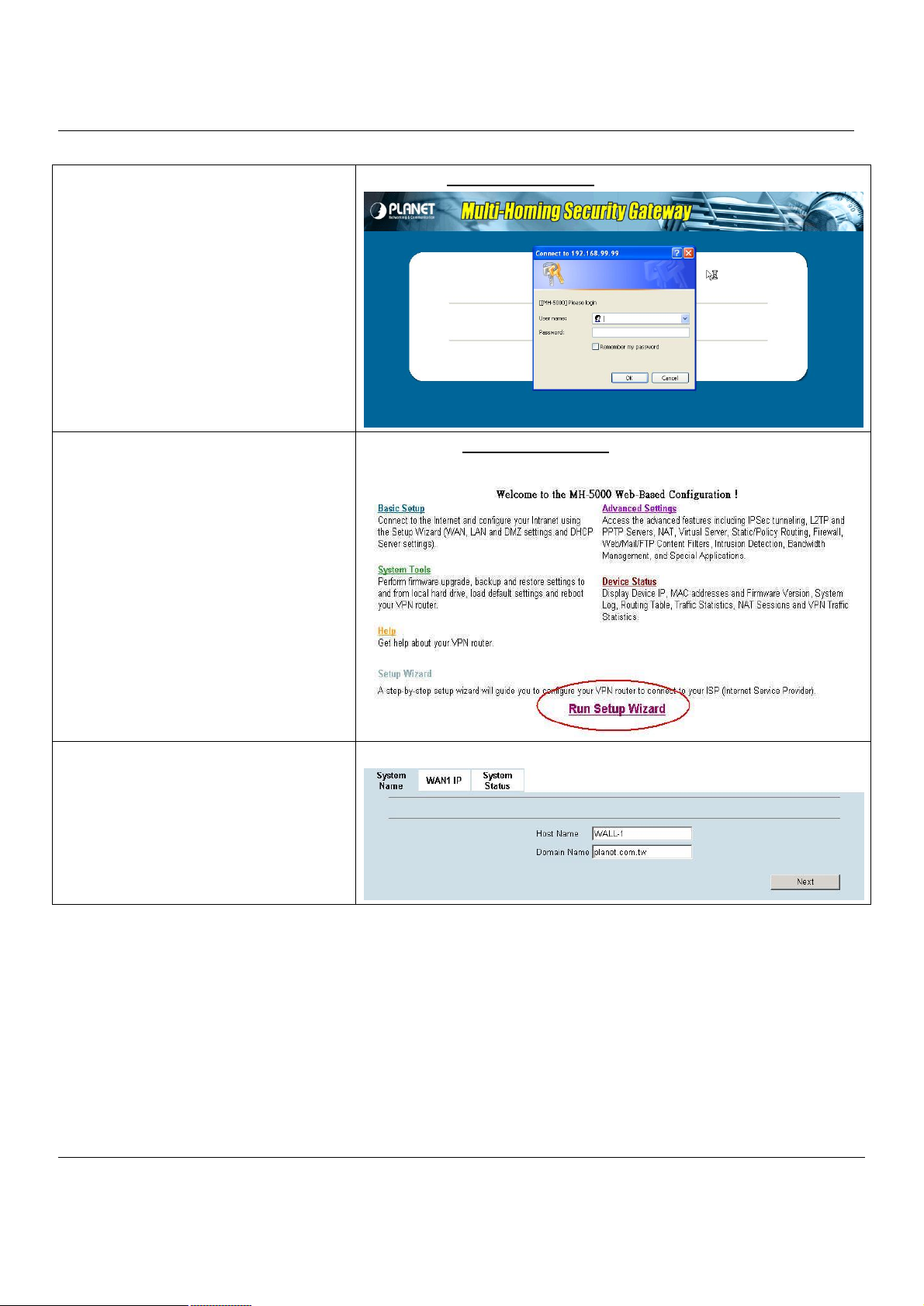
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 1
Quick Start
Step 1. Login
Type “admin” in the account field, “admin” in the
Password field and click Login.
Step 2. Run Setup Wizard
Click the Run Setup Wizard.
Connect to https://192.168.1.254
After login to https://192.168.1.254
BASIC SETUP > Wizard
Step 3. System Name
Enter the Host Name and the Domain
Name, followed by clicking the Next.
BASIC SETUP > Wizard
8
Page 16
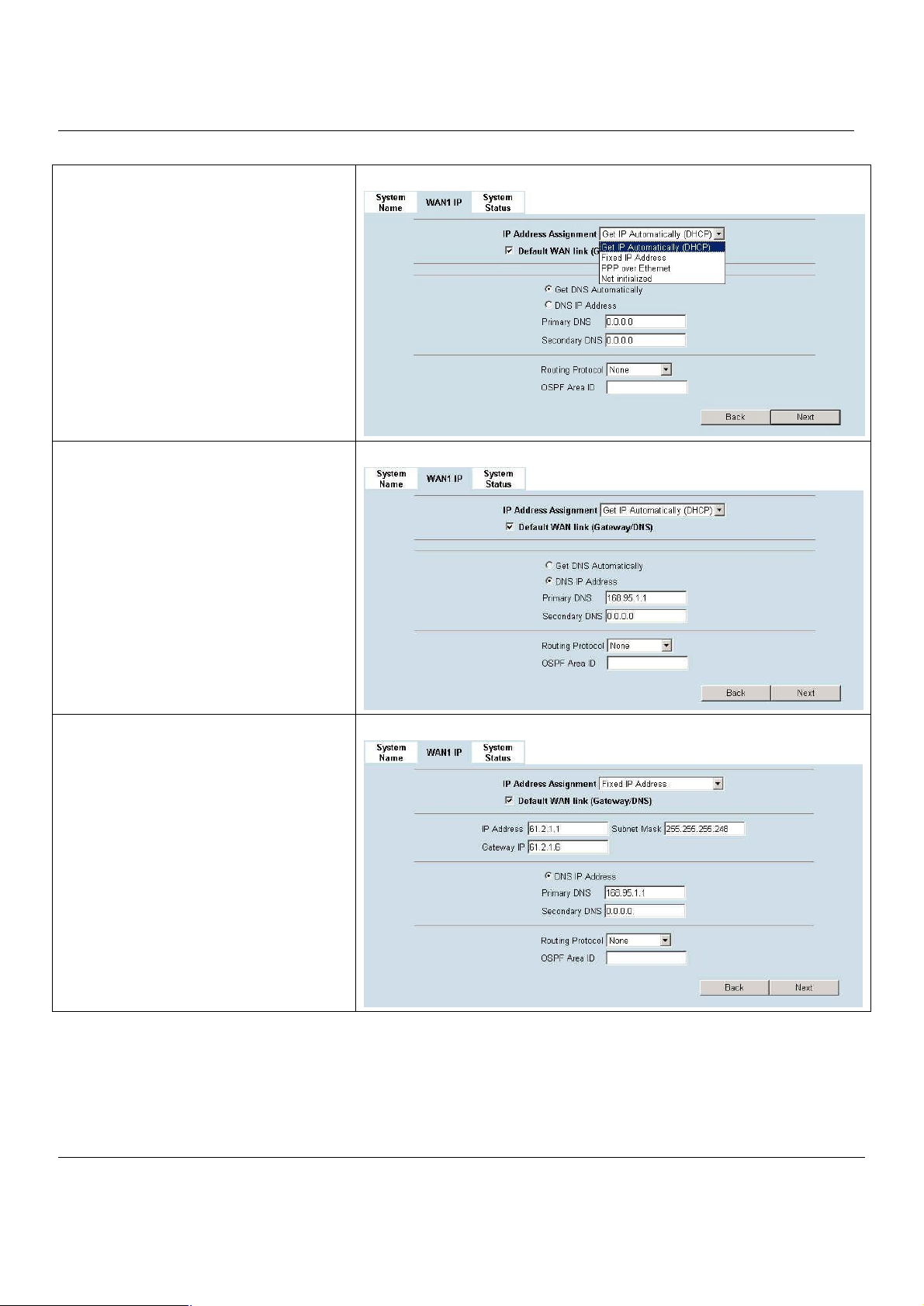
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 1
Quick Start
Step 4. WAN Connectivity
Choose the type of IP Address Assignment
provided by your ISP to access the Internet.
Here we have four types to select. This will
determine how the IP address of WAN1 is
obtained. Click Next to proceed.
Step 4.a — DHCP client
If Get IP Automatically (DHCP) is selected,
MH-5000 will request for IP address, netmask,
and DNS servers from your ISP. You can use
your preferred DNS by clicking the DNS IP
Address and then completing the Primary DNS
and Secondary DNS server IP addresses. Click
Next to proceed.
BASIC SETUP > Wizard > Next
BASIC SETUP > Wizard > Next > DHCP
Step 4.b — Fixed IP
If Fixed IP Address is selected, enter the
ISP-given IP Address, Subnet Mask, Gateway
IP, Primary DNS and Secondary DNS IP. Click
Next to proceed.
BASIC SETUP > Wizard > Next > Fixed IP
9
Page 17
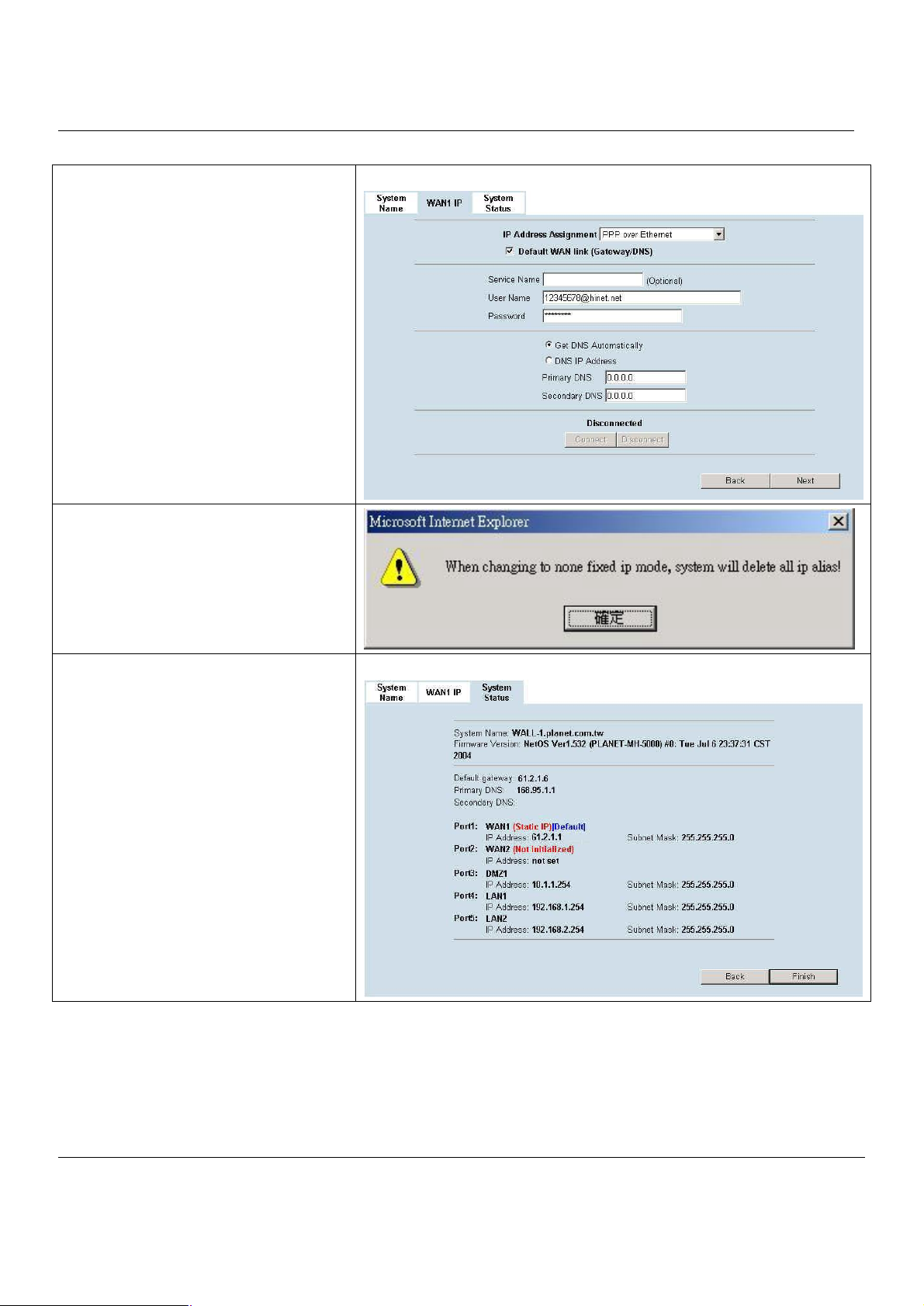
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 1
Quick Start
Step 4.c — PPPoE client
If PPP over Ethernet is selected, enter the
ISP-given User Name, Password and the
optional Service Name. Click Next to proceed.
Step 4.d — Alert Message
Please Note that an alert message box “When
changing to none fixed ip mode, system will
delete all ip alias!” will appear while you change
Get IP Automatically (DHCP) or PPP over
Ethernet but not Fixed IP Address as your WAN
link.
Step 5. System Status
Here we select Fixed IP method in WAN1 port.
Then the MH-5000 provides a short summary of
the system. Please check if anything mentioned
above is properly set into the system. Click
Finish to close the wizard.
BASIC SETUP > Wizard > Next > PPPoE
BASIC SETUP > Wizard > Run Setup Wizard > Next > Next
1.6 Internet Connectivity
After setting up MH-5000 with the wizard, MH-5000 can connect to the ISP. In this chapter, we introduce LAN1-to-WAN1
Connectivity to explain how the computers under LAN1 can access the Internet at WAN1 through MH-5000.
10
Page 18
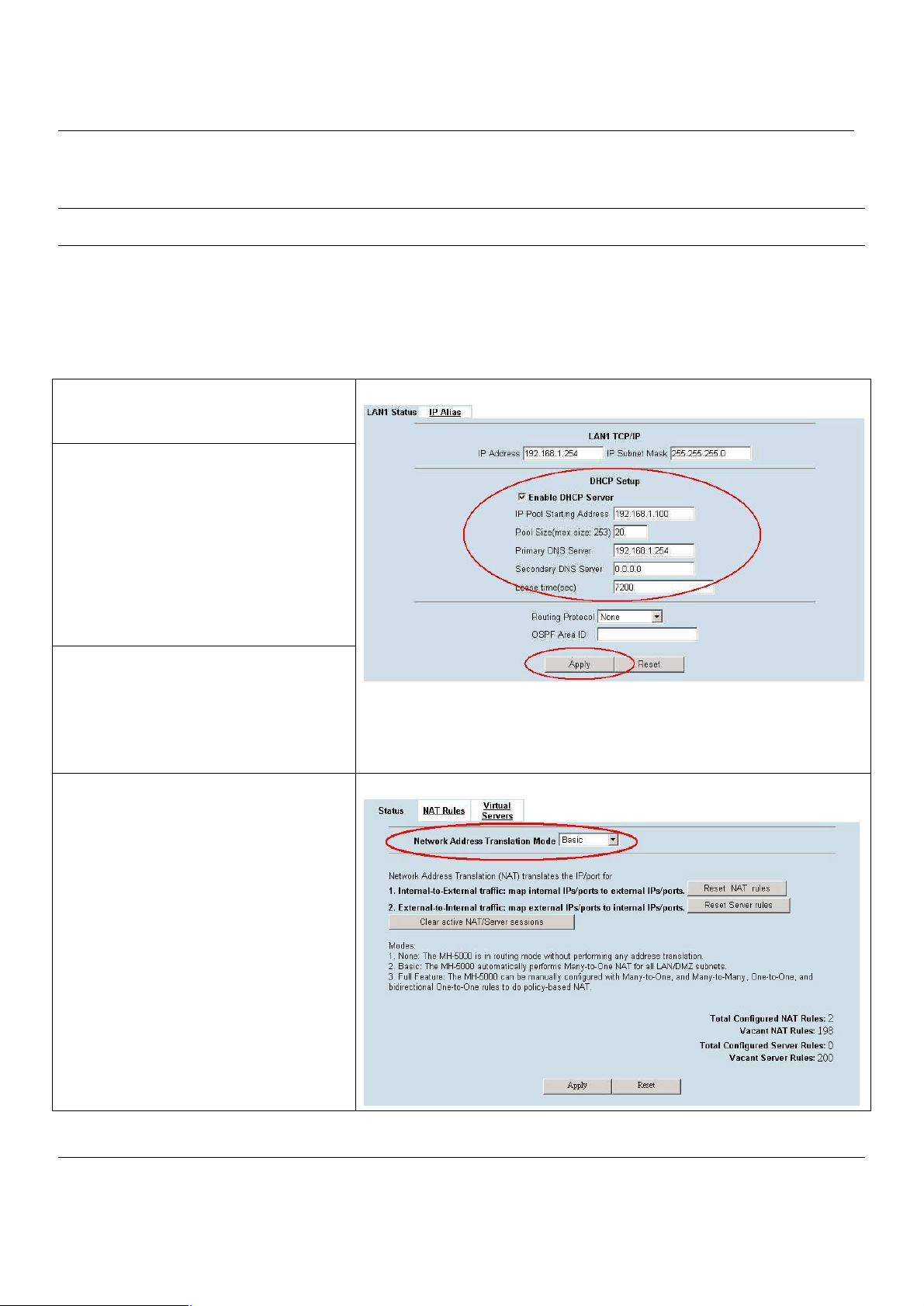
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 1
Quick Start
Subsequently, we introduce WAN1-to-DMZ1 Connectivity to explain how the servers under DMZ1 can be accessed by
the LAN1 users and other Internet users on the WAN1 side.
You MUST press Apply to proceed to the next page. Once applying any changes, the settings are immediately
updated into the flash memory.
1.6.1 LAN1-to-WAN1 Connectivity
The LAN Settings page allows you to modify the IP address and Subnet Mask that will identify the MH-5000 on your LAN.
This is the IP address you will enter in the URL field of your web browser to connect to the MH-5000. It is also the IP
address that all of the computers and devices on your LAN will use as their Default Gateway.
Step 1. Device IP Address
Setup the IP Address and IP Subnet Mask for
the MH-5000.
Step 2. Client IP Range
Enable the DHCP server if you want to use
MH-5000 to assign IP addresses to the
computers under LAN1. Specify the Pool
Starting Address, Pool Size, Primary DNS, and
Secondary DNS that will be assigned to them.
Example: in the figure, the MH-5000 will assign
one IP address from 192.168.1.100 ~
192.168.1.119, together with the DNS server
192.168.1.254, to the LAN1 PC that requests
for an IP address.
Step 3. Apply the Changes
Click Apply to save. Now you can enable the
DHCP clients on your LAN1 PCs to get an IP.
Step 4. Check NAT Status
The default setting of NAT is in Basic Mode.
After completing Step 3, the NAT is
automatically configured related rules to let all
private-IP LAN/DMZ-to-WAN requests to be
translated with the public IP assigned by the
ISP.
BASIC SETUP > LAN Settings > LAN1 Status
Note: The IP Pool Starting Address must be on the same subnet specified in
the IP Address and the IP Subnet Mask field.
For example, the addresses given by the 192.168.1.100 with a pool size of 20
(192.168.1.100 ~ 192.168.1.119) are all within the same range of 192.168.1.254 /
255.255.255.0
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > Status
11
Page 19
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 1
Quick Start
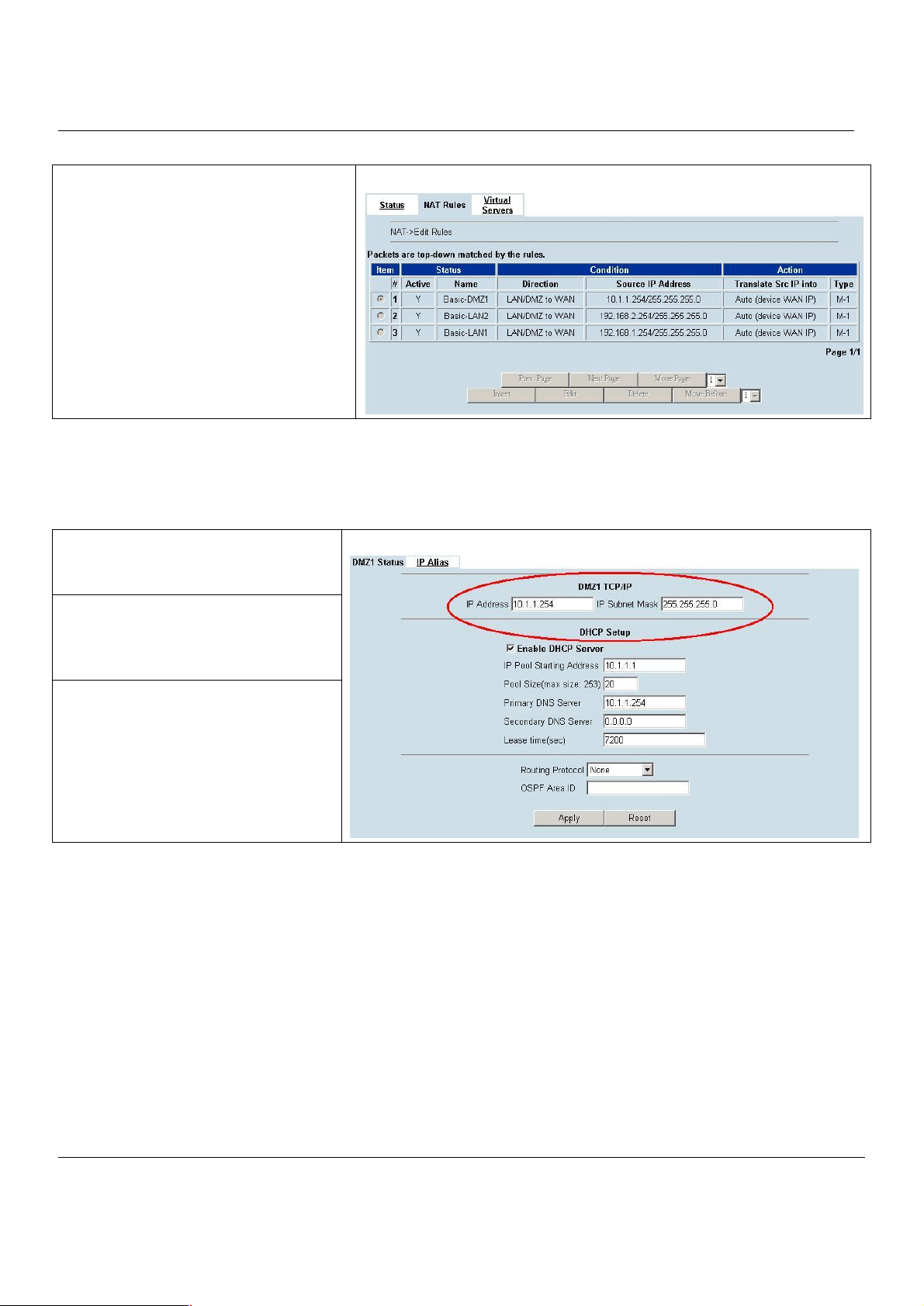
Step 5. Check NAT Rules
The MH-5000 has added the NAT rules as the
right diagram. The rule Basic-LAN1 means that,
when matching the condition (requests of
LAN/DMZ-to-WAN direction with its source IP
falling in the range of 192.168.1.254 /
255.255.255.0), the request will be translated
into a public-source-IP requests, and then be
forwarded to the destinations.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > NAT Rules
1.6.2 WAN1-to-DMZ1 Connectivity
This section tells you how to provide an FTP service with a server installed under your DMZ1 to the public Internet users.
After following the steps, users at the WAN side can connect to the FTP server at the DMZ1 side.
Step 1. Device IP Address
Setup the IP Address and IP Subnet Mask for
the MH-5000 of the DMZ1 interface.
Step 2. Client IP Range
Enable the DHCP server if you want to use
MH-5000 to assign IP addresses to the
computers under DMZ1.
BASIC SETUP > DMZ Settings > DMZ1 Status
Step 3. Apply the Changes
Click Apply to save your settings.
12
Page 20
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 1
Quick Start
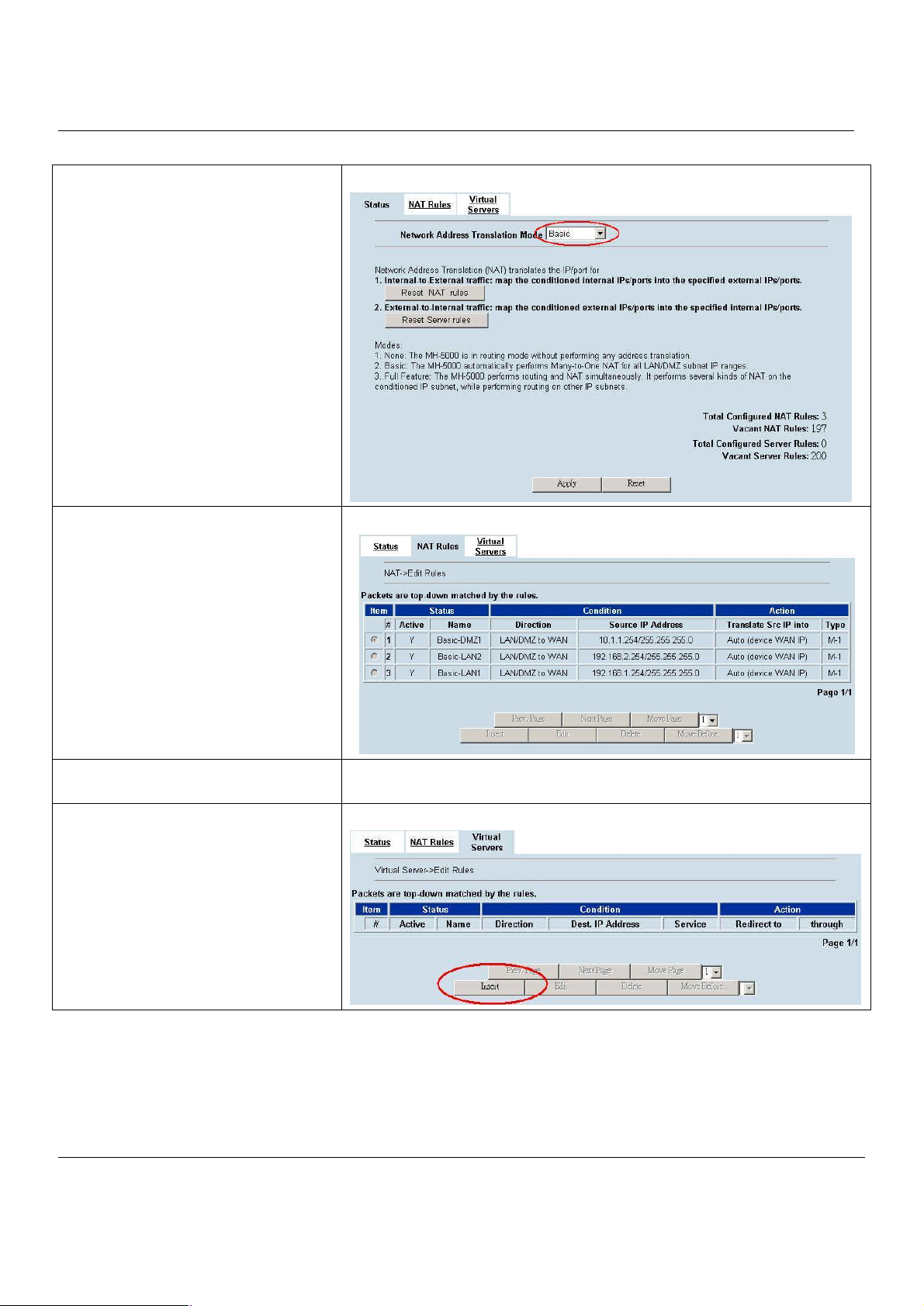
Step 4. Check NAT Status
The default setting of NAT is in Basic Mode.
After applying the Step 3, the NAT is
automatically configured related rules to let
all private-IP LAN/DMZ-to-WAN requests to
be translated with the public IP assigned by
the ISP.
Step 5. Check NAT Rules
The MH-5000 has added the NAT rules as
the right diagram. The rule Basic-DMZ1
(number 1) means that, when matching the
condition (requests of LAN/DMZ-to-WAN
direction with its source IP falling in the range
of 10.1.1.254 / 255.255.255.0), the request
will be translated into a public-source-IP
requests, and then be forwarded to the
destinations.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > Status
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > NAT Rules
Step 6. Setup IP for the FTP
Server
Step 7. Setup Server Rules
Insert a virtual server rule by clicking the
Insert button.
Assign an IP of 10.1.1.5/255.255.255.0 to the FTP server under DMZ1. Assume the
FTP Server is at 10.1.1.5. And it is listening on the well-known port (21).
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > Virtual Servers
13
Page 21
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 1
Quick Start
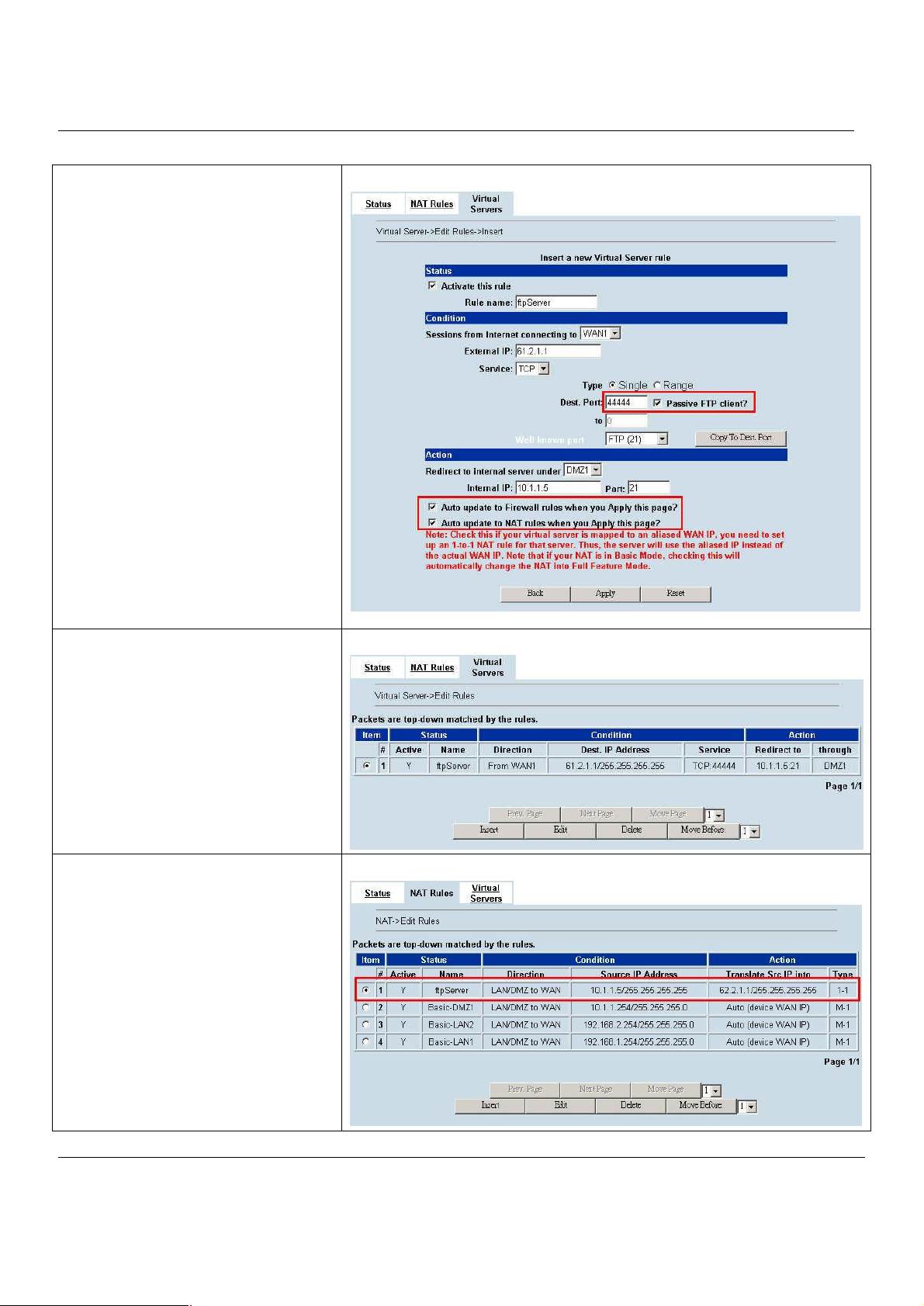
Step 8. Customize the Rule
Customize the rule name as the ftpServer.
For any packets with its destination IP
address equaling to the WAN1 IP (61.2.1.1)
and destination port equaling to 44444.
MH-5000 will translate the packet’s
destination IP/port into 10.1.1.5/21. Check
the Passive FTP client to maximize the
compatibility of the FTP protocol. This is
useful if you want to provide connectivity to
passive FTP clients. For passive FTP clients,
the server at DMZ will return them the private
IP address (10.1.1.5) and the port number for
the clients to connect back for data
transmissions. Since the FTP clients at the
WAN side cannot connect to a private-IP
(ex.10.1.1.5) through the internet. The data
connections would fail. After enabling this
feature, the MH-5000 will translate the private
IP/port into an IP/port of its own. Thus the
problem is gracefully solved. Another point is
to be sure to check “Auto update to Firewall
rules when you Apply this page?” or “Auto
update to NAT rules when you Apply this
page?” Then, the virtual server rule will add
Firewall or NAT rules automatically. Click
Apply to proceed.
Step 9. View the Result
Now any request towards the MH-5000’s
WAN1 IP (61.2.1.1) with dest. port 44444 will
be translated into a request towards 10.1.1.5
with port 21, and then be forwarded to the
10.1.1.5. The FTP server listening at port 21
in 10.1.1.5 will pick up the request.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > Virtual Servers > Insert
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > Virtual Servers
Step 10. View the NAT Rules
In the previous Step 8, we have already
checked “Auto update to Firewall/NAT rules
when you Apply this page”, so it will
automatically add one NAT rule to transfer
the IP address of virtual server when server
responses packet back to the client.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > NAT Rules
14
Page 22
MH-5000 User Manual 0
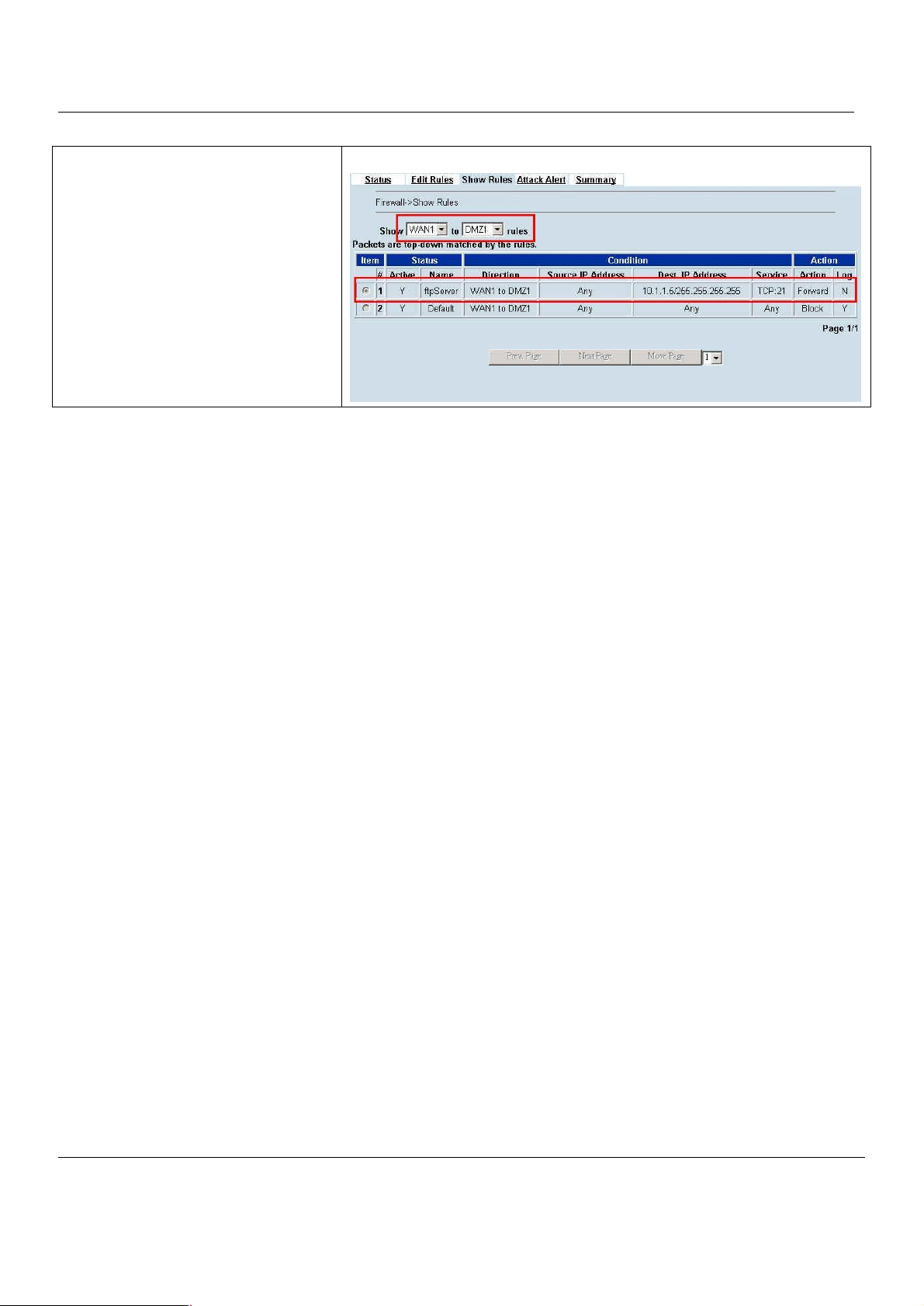
Step 11. View the Firewall Rules
The same as Step 10. When we check “Auto
update to Firewall/NAT rules when you Apply
this page”, it will automatically add one
Firewall rule in the WAN1 to DMZ1 direction.
This firewall rule will let the packets with dest.
IP address/port be matched with virtual
server rule in order to pass through MH-5000.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules
15
Page 23
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 2
System Overview
Chapter 2
System Overview
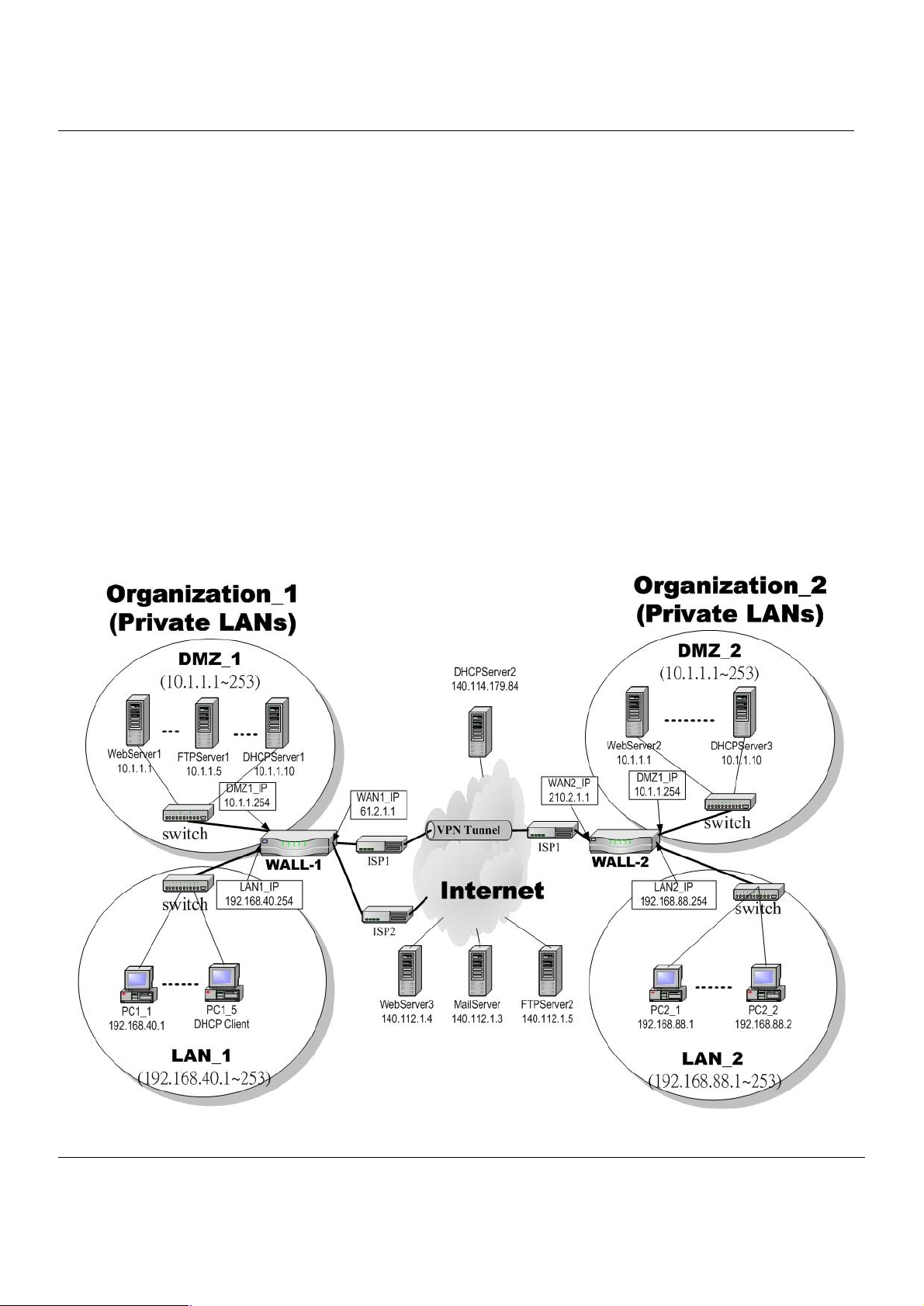
In this chapter, we will introduce the network topology for use with later chapters.
2.1 Typical Example Topology
In this chapter, we introduce a typical network topology for the MH-5000. In Figure 2-1, the left half side is a MH-5000
with one LAN, one DMZ, and one WAN link. We will demonstrate the administration procedure in the later chapters by
using the below Figure 2-1.
The right half side contains another MH-5000 connected with one LAN, one DMZ, and one WAN. You can imagine this is
a branch office of Organization_1. In this architecture, all the users under Organization can access sever reside in the
Internet or DMZ region smoothly. Besides, Organization_1 communicates with Organization_2 with a VPN tunnel
established by the two MH-5000 Multi-Homing Security Gateways. The VPN tunnel secures communications between
Organizations more safely.
We will focus on how to build up the topology using the MH-5000 as the following Figure 2-1. In order to achieve this
purpose, we need to know all the administration procedure.
Figure 2-1 Typical topology for deploying MH-5000
16
Page 24

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 2
System Overview
Continually, we will introduce all the needed administration procedure in the following section.
1. Chapter3 Basic Setup
How to configure the WAN/DMZ/LAN port settings..
2. Chapter6 ~ Chapter8 NAT, Routing and Firewall
Introducing the NAT, Routing, Firewall features.
3. Chapter9 ~ Chapter12 VPN Technology Introduction
If you need to build a secure channel with your branch office, or wish to access the inside company resource as
usual while outside your company, the Virtual Private Network (VPN) function can satisfy you.
4. Chapter13 ~ Chapter15 Content Filtering
If you hope to restrict the web contents, mail attachments, or downloaded ftp file from intranet region, try this feature
to fit your requirement.
5. Chapter16 Intrusion Detection System
Use the Intrusion Detection System (IDS) to detect all the potential DoS attacks, worms, hackers from Internet.
6. Chapter17 Bandwidth Management
If you wish to make your inbound/outbound bandwidth utilized more efficiently, you may use the Bandwidth
Management feature to manage your bandwidth.
7. Chapter19 ~ Chapter21 System Maintenance
In this part, we provide some useful skills to help you to justify MH-5000 more securely and steadily.
2.2 Changing the LAN1 IP Address
The default settings of MH-5000 are listing in Table 1-1. However, the original LAN1 setting is
192.168.1.254/255.255.255.0 instead of 192.168.40.254/255.255.255.0 as in Figure 2-1. We will change the LAN1 IP of
the MH-5000 to 192.168.40.254.
We provide two normal ways to configure the LAN1 IP address. One is to configure the LAN1 IP from LAN1 port. The
other way is to configure the LAN1 IP through console.
2.2.1 From LAN1 to configure MH-5000 LAN1 network settings
Step 1. Connect to the MH-5000
Using a network line to connect MH-5000 with
LAN1 port. The PC which connected to MH-5000
must be assigned 192.168.1.X address (LAN1
default IP address is 192.168.1.254/24). Type
https://192.168.1.254
or http://192.168.1.254:8080 to configure the
MH-5000 in the web browser.
Use an IE at 192.168.1.1 to connect to https://192.168.1.254
17
Page 25
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 2
System Overview
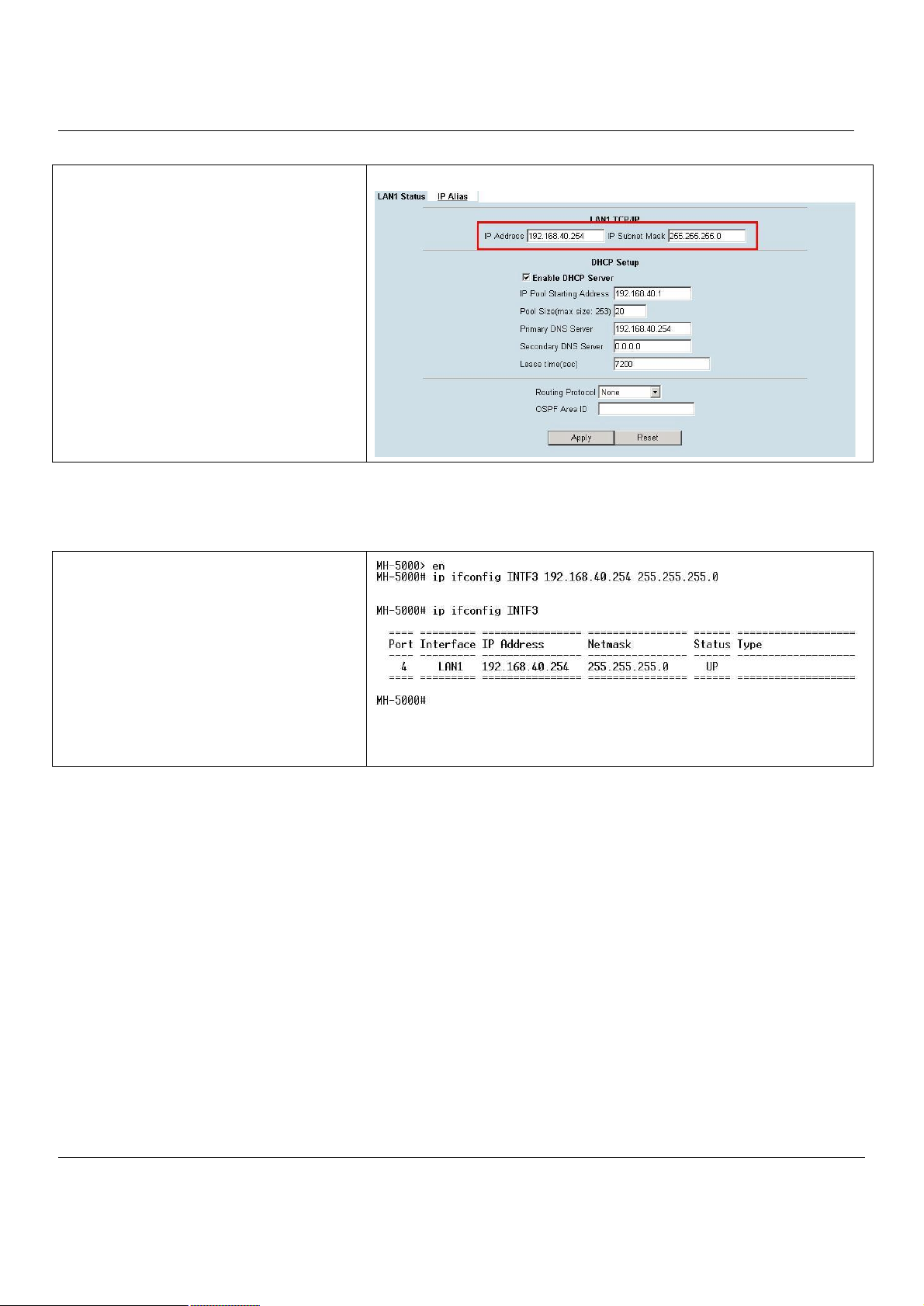
Step 2. Setup LAN1 IP information
Enter the IP Address and IP Subnet Mask with
192.168.40.254 / 255.255.255.0 and click Apply.
Warning: After you apply the changed settings,
the network will be disconnected instantly since
the network IP address you login is changed.
BASIC SETUP > LAN Settings > LAN1 Status
2.2.2 From CLI (command line interface) to configure MH-5000 LAN1 network
settings
Step 1. Use Console port to configure
MH-5000
Use the supplied console line to connect the PC
to the Diagnostic RS-232 socket of the MH-5000.
Start a new connection using the HyperTerminal
with parameters: No Parity, 8 Data bits, 1 stop bit,
and baud rate 9600. Enter admin for user name
and admin for password to login. After logging
into MH-5000, enter the commands “en“ to enter
the privileged mode. Enter the command “ip
ifconfig INTF3 192.168.40.254 255.255.255.0” to
change the IP of the LAN1 interface.
18
Page 26
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 2
Status field:
name of this rule
Condition field:
packet hold? And it will
Action field:
by this rule? What action
will this rule do?
System Overview
2.2.3 The design principle
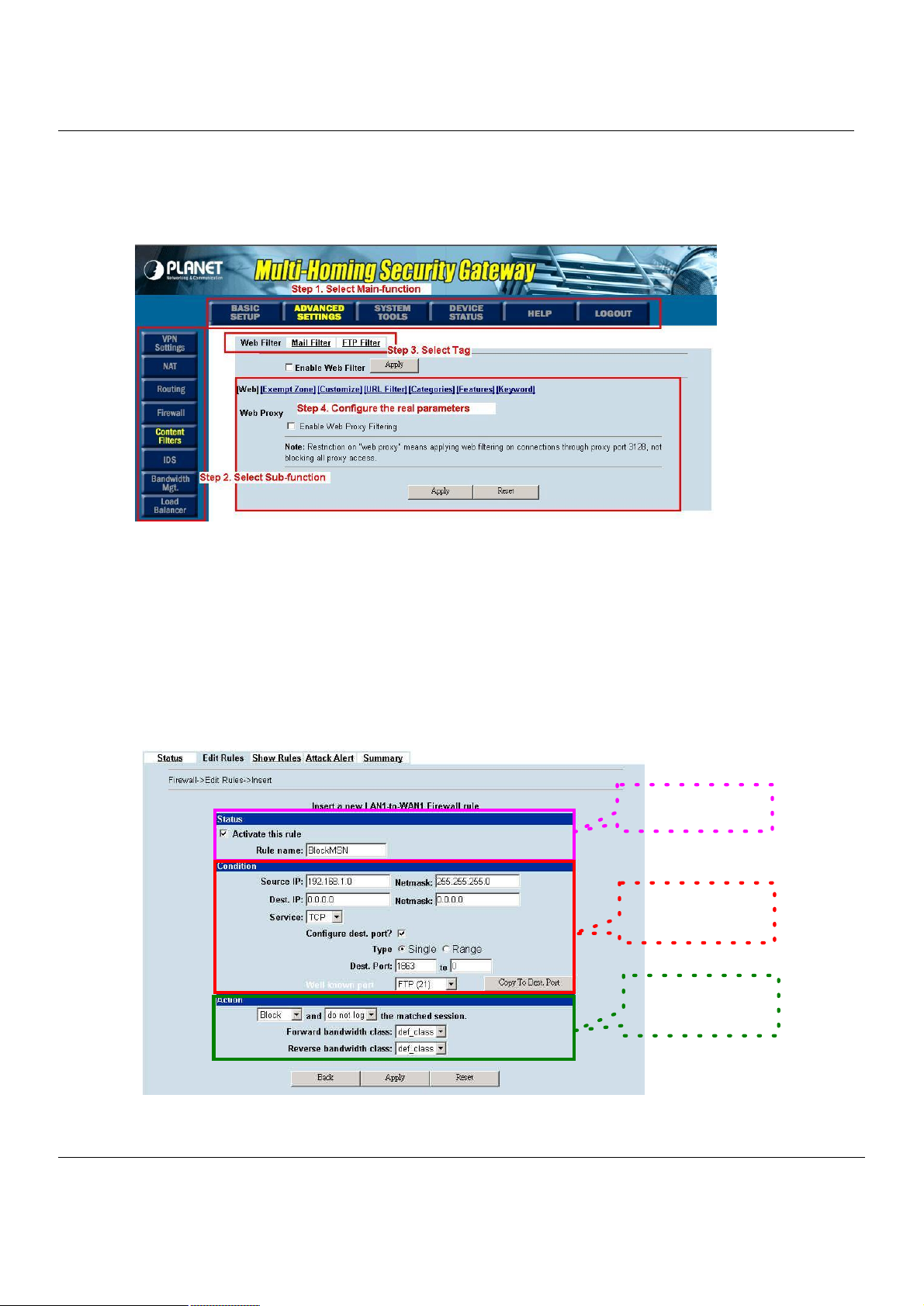
2.2.4 Web GUI design principle
Figure 2-2 You can select the functional area by the sequence in Web GUI
If we want to configure MH-5000, we can follow the sequence as the Figure 2-2 illustrated.
Step1. Select Main-function
Step2. Select Sub-function
Step3. Select Tag
Step4. Configure the real parameters
2.2.5 Rule principle
Describe the status and
What kind of
characteristics does
If the packet is captured
Figure 2-3 The rule configuration is divided into three parts
19
Page 27
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 2
Status field:
Condition field:
Action field:
If the packet is captured by this
do?
If you are not satisfied with the
B
efore button.
System Overview
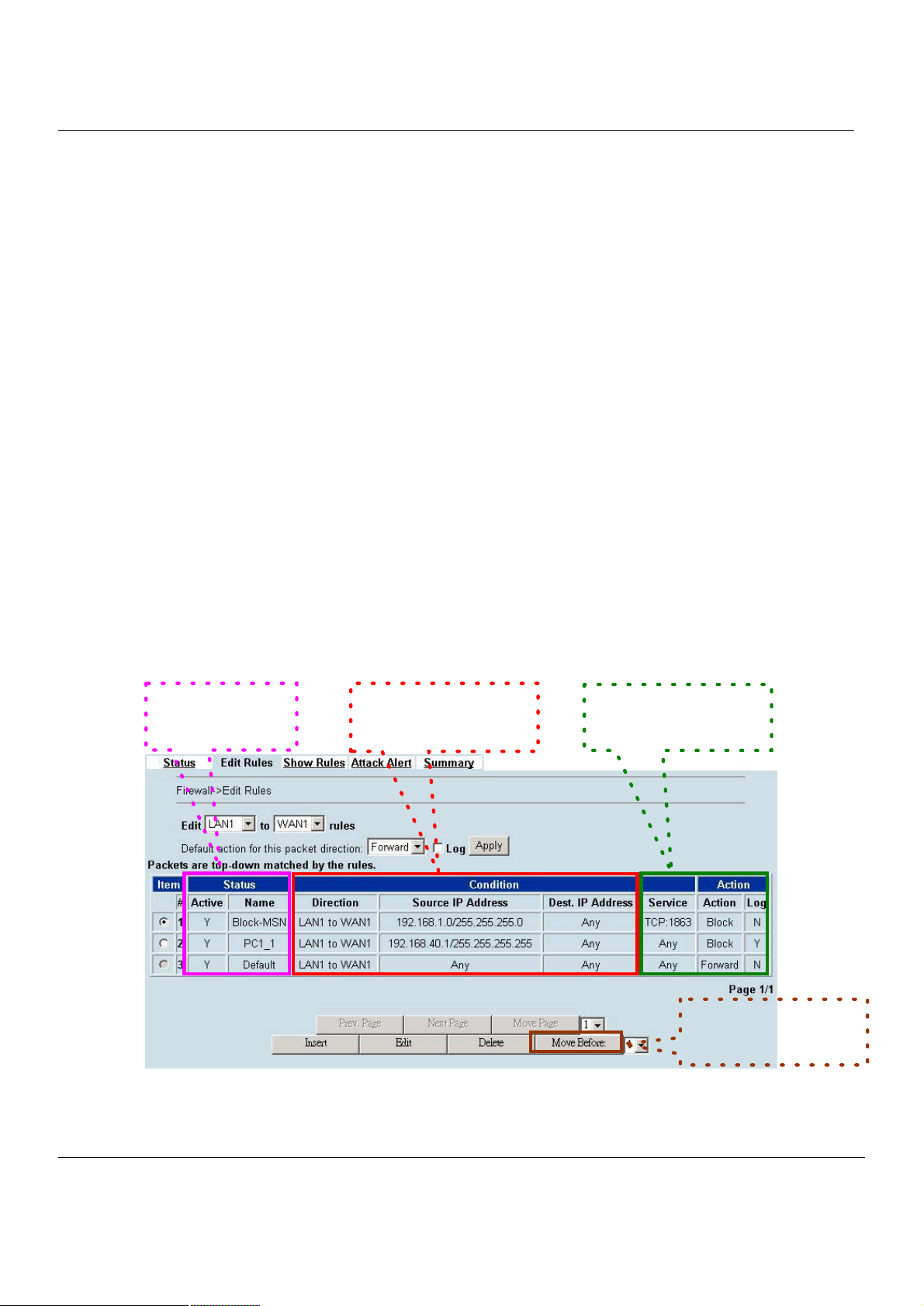
You may find many rules configuration in the MH-5000. They are distributed in the respective feature. These rules
include
1. NAT rule
2. Virtual Server rule
3. Firewall rule
4. Policy route rule
5. Bandwidth management rule
The behavior of each rule is different, and so are their configuration parameters. But the designed principle of each rule is
the same. The configuration is divided into three parts as Figure 2-3 illustrated. You just need to enter the necessary
information onto each part according to your requirement. As for the definitions of the three-part configuration, please
refer to the following description.
1. Status: Describe the status and name of this rule.
Condition
2.
3. Action: If the packet is captured by this rule? What action will this rule do?
As the Figure 2-4 illustrated, the page of the rule edition is also divided into three parts. Their definitions are also the
same as we have discussed in Figure 2-3.
Additionally, please note that there is a button named “Move Before” in the Figure 2-4. If you are not satisfied with the
current rule sequence, you can adjust the rule sequence by using the “Move Before” button.
: What kind of characteristics does packet hold? And it will be captured by this rule.
Describe the status and
name of this rule
What kind of characteristics
does packet hold? And it will
be captured by this rule
rule? What action will this rule
current rule sequence the rule
sequence by using the Move
Figure 2-4 The rules in the page of the rule edition are also divided into three parts.
20
Page 28

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 3
Basic Setup
Chapter 3
Basic Setup
In this chapter, we will introduce how to setup network settings for each port separately
3.1 Demand
1. For the external network, suppose your company uses DSL to connect Internet via fixed-IP. By this way, you
should setup WAN port of the MH-5000 in advance.
2. There are some adjustment within your company, so the original network stucture has been changed. Now, you
should modify the configuration between the internal network (DMZ, LAN).
3. Your company needs more network bandwidth if it is insufficent for your company to connect to the external
network. Suppose there are many public IPs in your commpany. You would like to specify an unique public IP to
a local server.
3.2 Objectives
1. Configure the network settings of the MH-5000 WAN1 port.
2. Configure the network settings of the MH-5000 DMZ1 and LAN1 ports.
3. We hope to assign another IP address to the same WAN port we have configured an existed IP address before.
3.3 Methods
1. Select the Fixed IP Address method in the MH-5000 Basic Setup/WAN settings/WAN1 IP, and then configure the
related account and password in order to connet to the internet.
2. Configure the related network settings in the pages of the MH-5000 Basic Setup / DMZ settings / DMZ1 Status、
Basic Setup / LAN settings / LAN1 Status.
3. Configure the IP alias in WAN1 port.
3.4 Steps
3.4.1 Setup WAN1 IP
Step 1. Setup WAN1 port
Here we select Fixed IP Address method in
WAN1 port. Fill in the IP Address, Subnet Mask,
Gateway IP. And then enter the other DNS IP
Address, Routing Protocol fields. Click Apply to
finish this setting.
BASIC SETUP > WAN Settings > WAN1 IP > Fixed IP Address
21
Page 29
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 3
Basic Setup
IP Address
Assignment
Get IP
Automatically
(DHCP)
FIELD DESCRIPTION Range / Format
Default WAN
link
(Gateway/DNS)
Get DNS
Automatically /
DNS IP Address
Routing
Protocol
OSPF Area ID Specify OSPF area ID number
Default WAN
link
(Gateway/DNS)
When Default WAN link is enabled, all the
packets sent out from MH-5000 will be via
this port.
Get DNS Automatically à Get DNS related
information from DHCP Server
DNS IP Address à manually specify these
Primary and Secondary DNS Server
information
Determine to enable the dynamic routing
protocol, to receive RIP message, to send
out the RIP message if the RIP message is
received or not.
When Default WAN link is enabled. All the
packets sent out from MH-5000 will be via
this port.
Enable/Disable Enabled
Get DNS
Automatically /
DNS IP Address
None,
RIPv1/In,
RIPv1/In+Out,
RIPv2/In,
RIPv2/In+Out,
OSPF
IPv4 format or
digit string (Max
9 bits)
Enable/Disable Enabled
EXAMPLE
Get DNS
Automatically
None
Fixed IP
Address
PPP over
Ethernet
IP Address Specified IP address IPv4 format 61.2.1.1
Subnet Mask Specified subnet mask IPv4 format 255.255.255.248
Gateway IP Default gateway IP address IPv4 format 61.2.1.6
DNS IP
Address:
Primary DNS
Secondary DNS
Routing
Protocol
OSPF Area ID Specify OSPF area ID number
Default WAN
link
(Gateway/DNS)
Service Name ISP vendor (Optional) text string So-Net
Specified Primary and Secondary DNS
Server address
Determine to enable the dynamic routing
protocol, to receive RIP message, to send
out the RIP message if the RIP message is
received or not.
When Default WAN link is enabled. All the
packets sent out from MH-5000 will be via
this port.
IPv4 format
None,
RIPv1/In,
RIPv1/In+Out,
RIPv2/In,
RIPv2/In+Out,
OSPF
IPv4 format or
digit string (Max
9 bits)
Enable/Disable Enabled
Primary DNS:
168.95.1.1
Secondary DNS:
0.0.0.0
None
22
Page 30

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 3
Basic Setup
User Name The user name of PPPoE account text string Hey
Password The password of PPPoE account text string G54688
Get DNS Automatically à Get DNS related
Get DNS
Automatically /
DNS IP Address
information from PPPoE ISP
DNS IP Address à manually specify these
Primary and Secondary DNS Server
information
Get DNS
Automatically /
DNS IP Address
Get DNS
Automatically
Connect /
Disconnect
button
Table 3-1 Detailed information of setup WAN port configuration
Through click Connect or Disconnect
button to connect or disconnect PPPoE link
3.4.2 Setup DMZ1, LAN1 Status
Step 1. Setup DMZ port
Here we are going to configure the DMZ1
settings. Setup IP Address and IP Subnet Mask,
and determine if you would like to enable the
DHCP Server. And then select Routing Protocol.
Click Apply to finish this setting.
Connect /
Disconnect
BASIC SETUP > DMZ Settings > DMZ1 Status
Click Connect
FIELD DESCRIPTION Range / Format
IP Address DMZ port IP address IPv4 format 10.1.1.254
IP Subnet Mask DMZ port IP subnet mask netmask format 255.255.255.0
Enable DHCP Server Enable DMZ port of the DHCP Sever or not Enable/Disable Enabled
IP Pool Starting
Address
Pool Size(max size:
253)
Primary DNS Server
Secondary DNS
Server
Specify the starting address of the DHCP IP address.
Specify the numbers of the DHCP IP address. 1 ~253 20
Specify the Primary DNS Server IP address of the
DHCP information.
Specify the Secondary DNS Server IP address of the
DHCP information.
23
IPv4 format in
the DMZ
address range
IPv4 format 10.1.1.254
IPv4 format 0.0.0.0
EXAMPLE
10.1.1.1
Page 31

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 3
Basic Setup
Lease time(sec) Specify DHCP information lease time greater than 0 7200
None / RIPv1In /
Determine to enable the dynamic routing protocol
Routing Protocol
OSPF Area ID Specify OSPF area ID number
(RIP), to receive RIP message, to send out RIP
message if the message is received or not.
Table 3-2 Configure DMZ network settings
RIPv1In+out /
RIPv2In /
RIPv2In+out /
OSPF
IPv4 format or
digit string (Max
9 bits)
None
N/A
Step 2. Setup LAN port
Here we are going to configure the LAN1 settings.
Setup IP Address and IP Subnet Mask, and
determine if you would like to enable the DHCP
Server. And then select Routing Protocol. Click
Apply to finish this setting.
FIELD DESCRIPTION Range / Format
IP Address LAN1 port IP address IPv4 format 192.168.40.254
IP Subnet Mask LAN1 port IP subnet mask netmask format 255.255.255.0
Enable DHCP Server Enable LAN1 port of the DHCP Sever or not Enable/Disable Enabled
IP Pool Starting
Address
Specify the starting address of the DHCP IP address.
BASIC SETUP > LAN Settings > LAN1 Status
IPv4 format in
the LAN1
address range
EXAMPLE
192.168.40.100
Pool Size(max size:
253)
Primary DNS Server
Secondary DNS
Server
Lease time(sec) Specify DHCP information lease time greater than 0 7200
Specify the numbers of the DHCP IP address. 1 ~253 20
Specify the Primary DNS Server IP address of the
DHCP information.
Specify the Secondary DNS Server IP address of the
DHCP information.
24
IPv4 format 192.168.40.254
IPv4 format 0.0.0.0
Page 32

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 3
Basic Setup
None / RIPv1In /
Determine to enable the dynamic routing protocol
Routing Protocol
OSPF Area ID Specify OSPF area ID number
(RIP), to receive RIP message, to send out RIP
message if the message is received or not.
Table 3-3 Configure LAN network settings
3.4.3 Setup WAN1 IP alias
RIPv1In+out /
RIPv2In /
RIPv2In+out /
OSPF
IPv4 format or
digit string (Max
9 bits)
None
N/A
Step 1. Add WAN1 IP alias
Suppose you apply 8 IP addresses from ISP. The
range of the ISP-given IP address is from
61.2.1.0 to 61.2.1.7. Now you would like to add
three WAN1 IP aliases. Select WAN1 in the
Interface field. Enter the IP alias and Netmask
with 61.2.1.2/255.255.255.248. Key in 3 into the
Alias size field. And then click Apply.
Notice:It’s the same way to set IP alias in DMZ or
LAN.
FIELD DESCRIPTION Range / Format
Interface The interface which we set for the IP alias WAN interfaces WAN1
IP alias The alias IP address IPv4 format
Netmask The netmask of the IP alias netmask format 255.255.255.248
Alias size The size of IP alias address Max 60 3
BASIC SETUP > WAN Settings > IP Alias > Add
EXAMPLE
61.2.1.2
Table 3-4 Add a IP alias record
25
Page 33

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 3
Basic Setup
Step 2. Edit, Delete IP alias record
You can easily add, edit, or delete IP alias
records by the Add, Edit, or Delete button.
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
Prev. Page
Add Insert a new IP alias record. N/A
Edit Edit the properties of the existent record. N/A
If there are more than one IP alias pages, you can press Prev.
Page to back to the previous page.
BASIC SETUP > WAN Settings > IP Alias
N/A
Delete Delete the indicated record. N/A
Next Page
Maximize IP alias
records of MH-5000
If there are more than one action records, you can press Next Page
to go to the next page.
Table 3-5 Show the entered IP alias records
WAN port 60 records
DMZ port 10 records
LAN port 10 records
Table 3-6 IP alias limitation of each port
N/A
26
Page 34

MH-5000 User Manual 0
Step 3. See the IP alias setting in the
“WAN1 IP” page
After entering the IP alias address, it will show the
result in the “WAN1 IP” page.
Warning: If you select Fixed IP Address as your
WAN link type and set any IP alias. When you try
to exchange the WAN link type to other type such
as DHCP, PPPoE. The previous setting IP aliases
will disappear after you apply the new WAN link
setting.
BASIC SETUP > WAN Settings > WAN1 IP > Fixed IP Address
27
Page 35

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 4
System Tools
Chapter 4
System Tools
This chapter introduces System Management and explains how to implement it.
4.1 Demand
1. Basic configurations for domain name, password, system time, timeout and services.
2. DDNS: Suppose the MH-5000’s WAN uses dynamic IP but needs a fixed host name. When the IP is changed, it
is necessary to have the DNS record updated accordingly. To use this service, one has to register the account,
password, and the wanted host name with the service provider.
3. DNS Proxy: Shorten the time of DNS lookup performed by applications.
4. DHCP Relay: It is to solve the problem that when the DHCP client is not in the same domain with the DHCP
server, the DHCP broadcast will not be received by the server. If the client is in the LAN (192.168.40.X) while the
server is located in the DMZ (10.1.1.4), the server will not receive any broadcast packet from the client.
5. The System Administrator would like to monitor the device from remote side efficiently.
6. Suppose our company applies three ISPs, but there are just two default WAN ports in the MH-5000. You hope to
connect the whole ISP links to the MH-5000.
4.2 Objectives
1. Configure the general properties, such as domain name, password, system time, and connection timeout
correctly. Besides, we can configure the prefered service name as the service name/numeric mapping list.
2. DDNS: By using the DDNS (Dynamic DNS), the MH-5000 will send the request for modification of the
corresponding DNS record to the DDNS server after the IP is changed.
3. DNS Proxy: Reduce the number of DNS requests and the time for DNS lookup.
4. DHCP Relay: Enable the DHCP client to contact with the DHCP server located in different domain and get the
required IP.
5. Through the SNMP manager, we can easily monitor the device status.
6. We hope to customize the interface of MH-5000 to fit our requests.
4.3 Methods
1. Configure the domain name, password, system time, connection timeout and service name.
2. DDNS: Configure the MH-5000 so that whenever the IP of the MH-5000 is changed, it will send requests to the
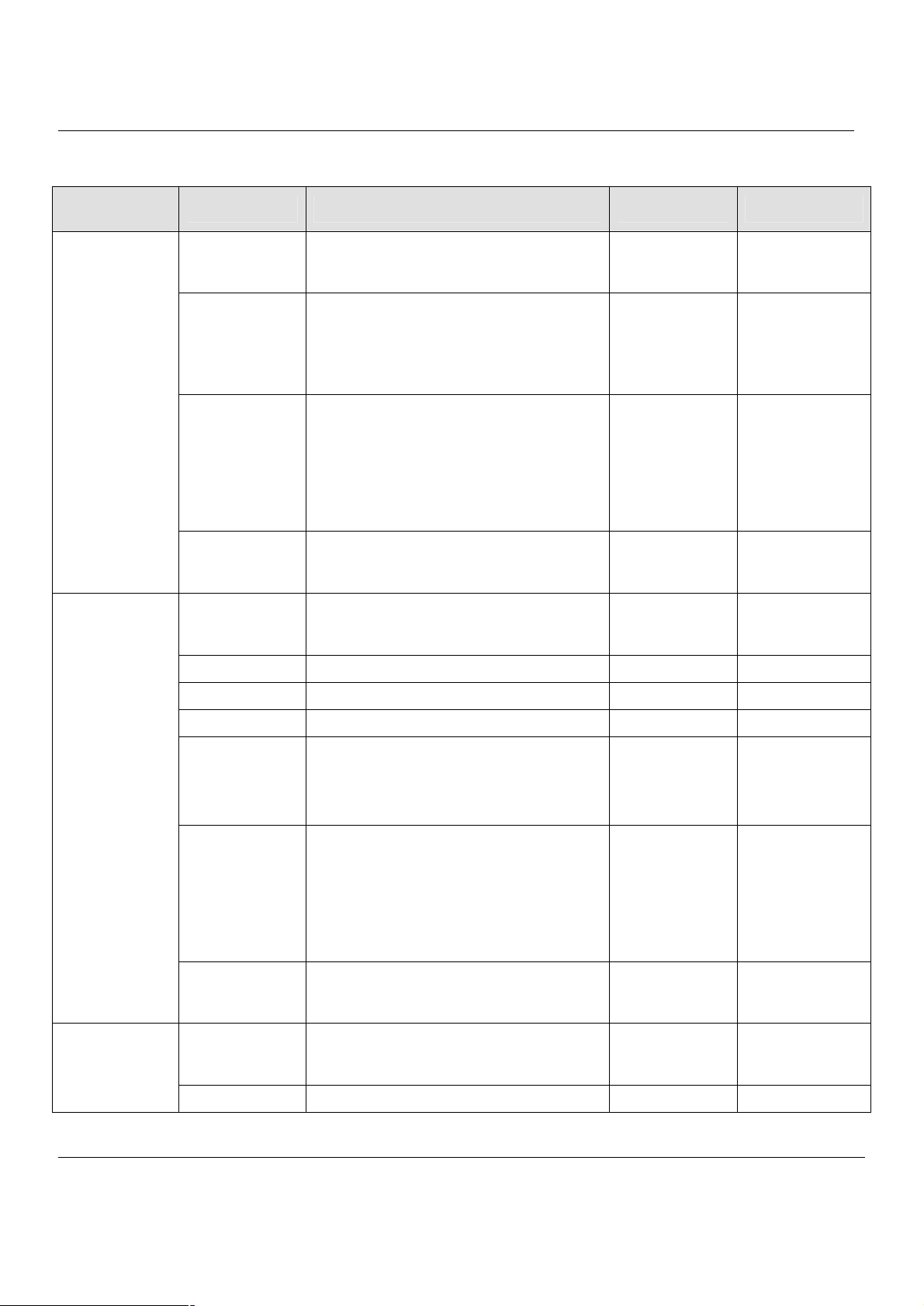
DDNS server to refresh the DNS record. As the following Figure 4-1 demonstrated, the original WALL-1 has
registered WAN1 IP address “61.2.1.1” on the DDNS server (www.dyndns.org). Its domain name address is
“me.dyndns.org”. If the WAN1 IP address is reassigned by the ISP. WALL-1 will update the registered IP address
“61.2.1.1” as the assigned one. This is the base mechanism of the DDNS.
28
Page 36
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 4
System Tools
Figure 4-1 DDNS mechanism chart
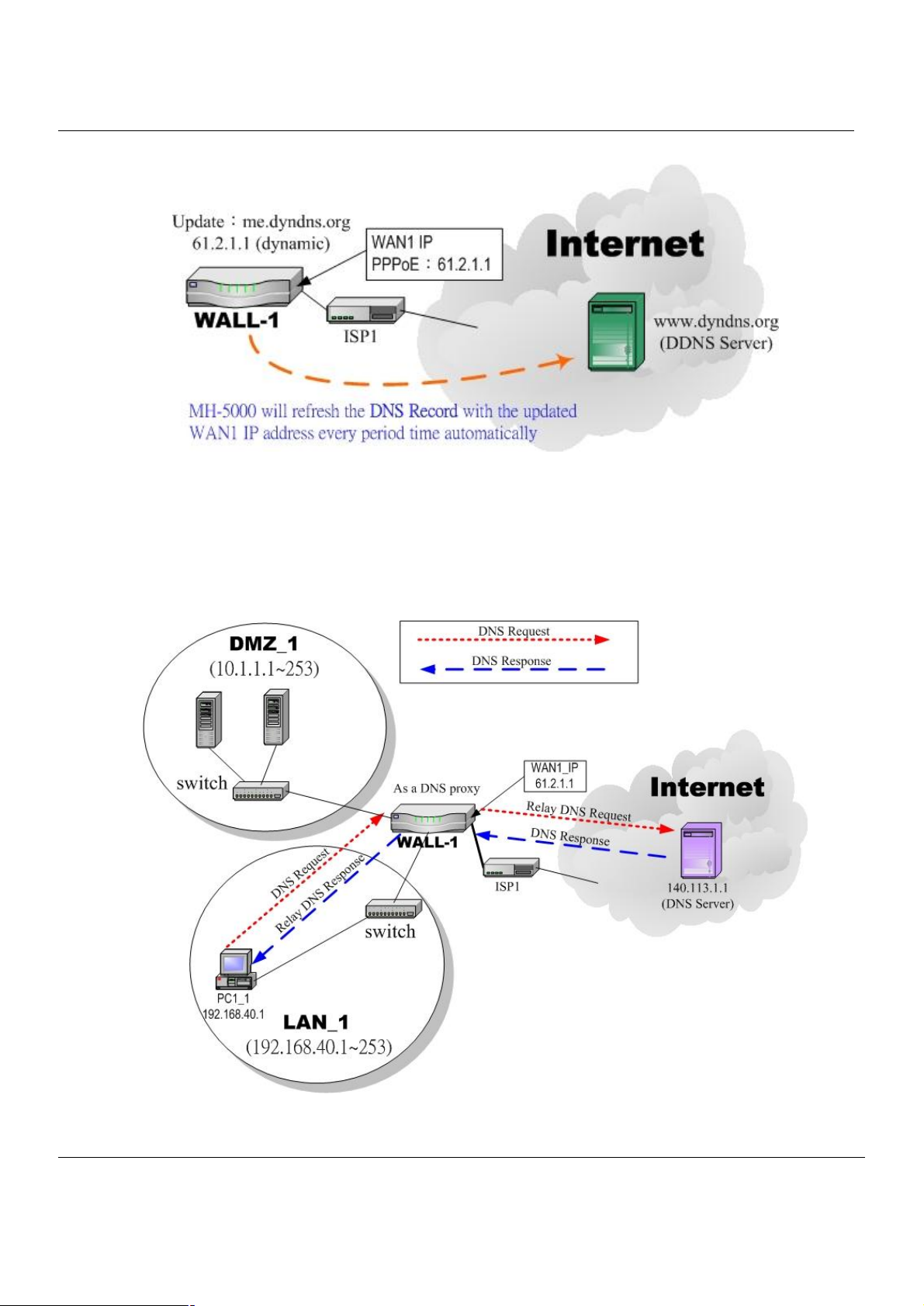
3. DNS Proxy: After activating the DNS proxy mode, the client can set its DNS server to the MH-5000 (that is, send
the DNS requests to the MH-5000). The MH-5000 will then make the enquiry to the DNS server and return the
result to the client. Besides, the caching mechanism performed by the DNS proxy can also help reduce possible
duplicate DNS lookups. As the following Figure 4-2 described. WALL-1 redirects the DNS request from PC1_1 to
the real DNS server (140.113.1.1).
Figure 4-2 DNS Proxy mechanism chart
29
Page 37
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 4
System Tools
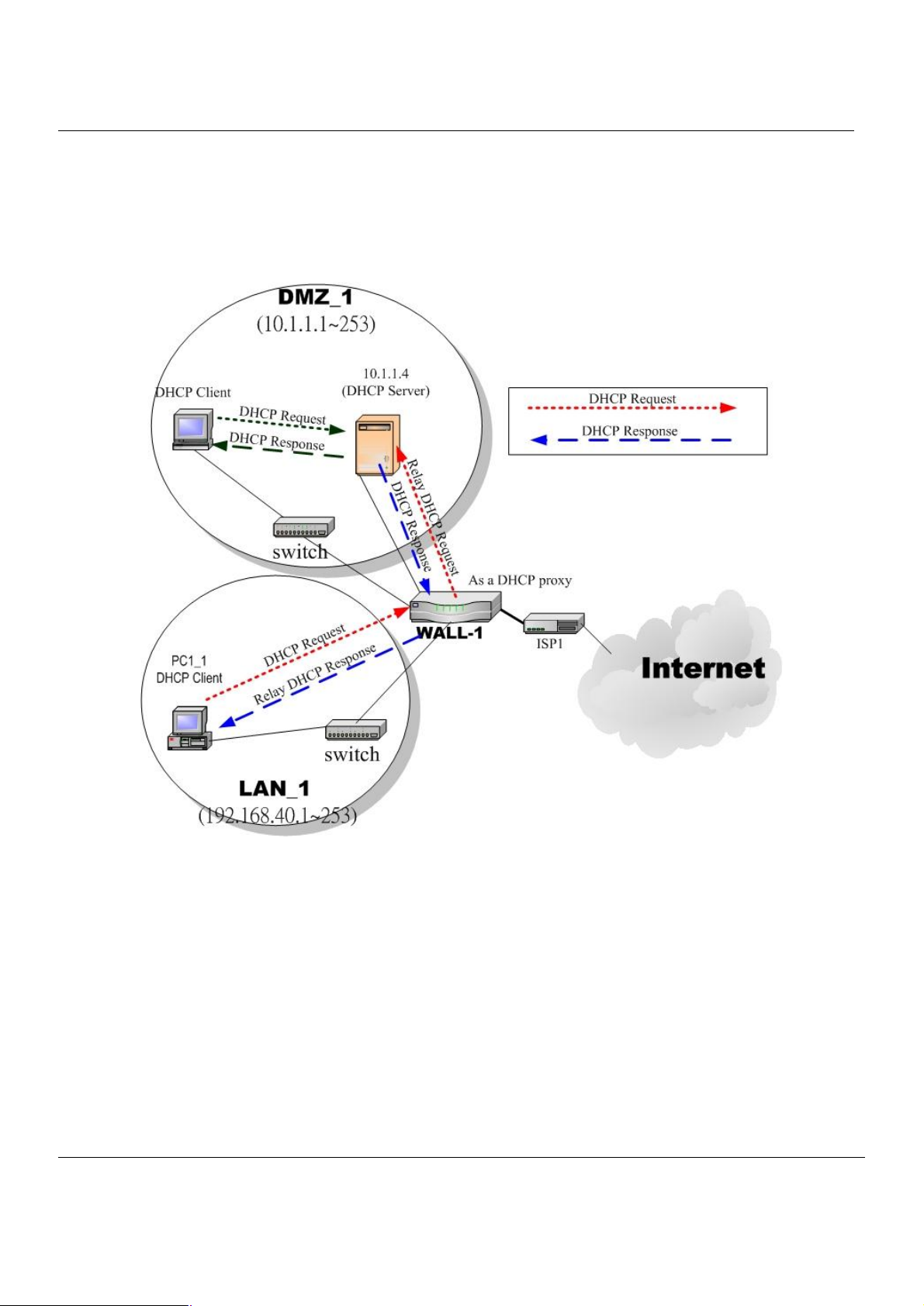
4. DHCP Relay: Activate the DHCP relay mode of MH-5000 so that the MH-5000 will become the relay agent and
relay the DHCP broadcast to the configured DHCP server. As the following Figure 4-3 described, WALL-1
redirects the DHCP request from the preconfigured port (LAN1) to the real DHCP server (10.1.1.4). Besides, in
this diagram, we can find that the PC of DMZ region communicated with the DHCP server directly.
Figure 4-3 DHCP Relay mechanism chart
5. As the following Figure 4-4 demonstrated, there is an embedded snmp agent in the MH-5000. So you can use
SNMP manager to monitor the MH-5000 system status, network status ,etc. from either LAN or internet.
30
Page 38

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 4
System Tools
Figure 4-4 It is efficient to use SNMP Manager to monitor MH-5000 device
6. We can adjust the MH-5000 interface in the SYSTEM TOOLS > Admin Settings > Interface in according to our
preference and requirement (3 WAN, 1 DMZ, 1 LAN). As the following Figure4-5 demonstrated, there are three
ISP connected onto MH-5000. So we must adjust the interface up to 3 WAN ports to fit the current condition.
Figure 4-5 Adjust MH-5000 interface to fit present situation
31
Page 39
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 4
System Tools
4.4 Steps
4.4.1 General settings
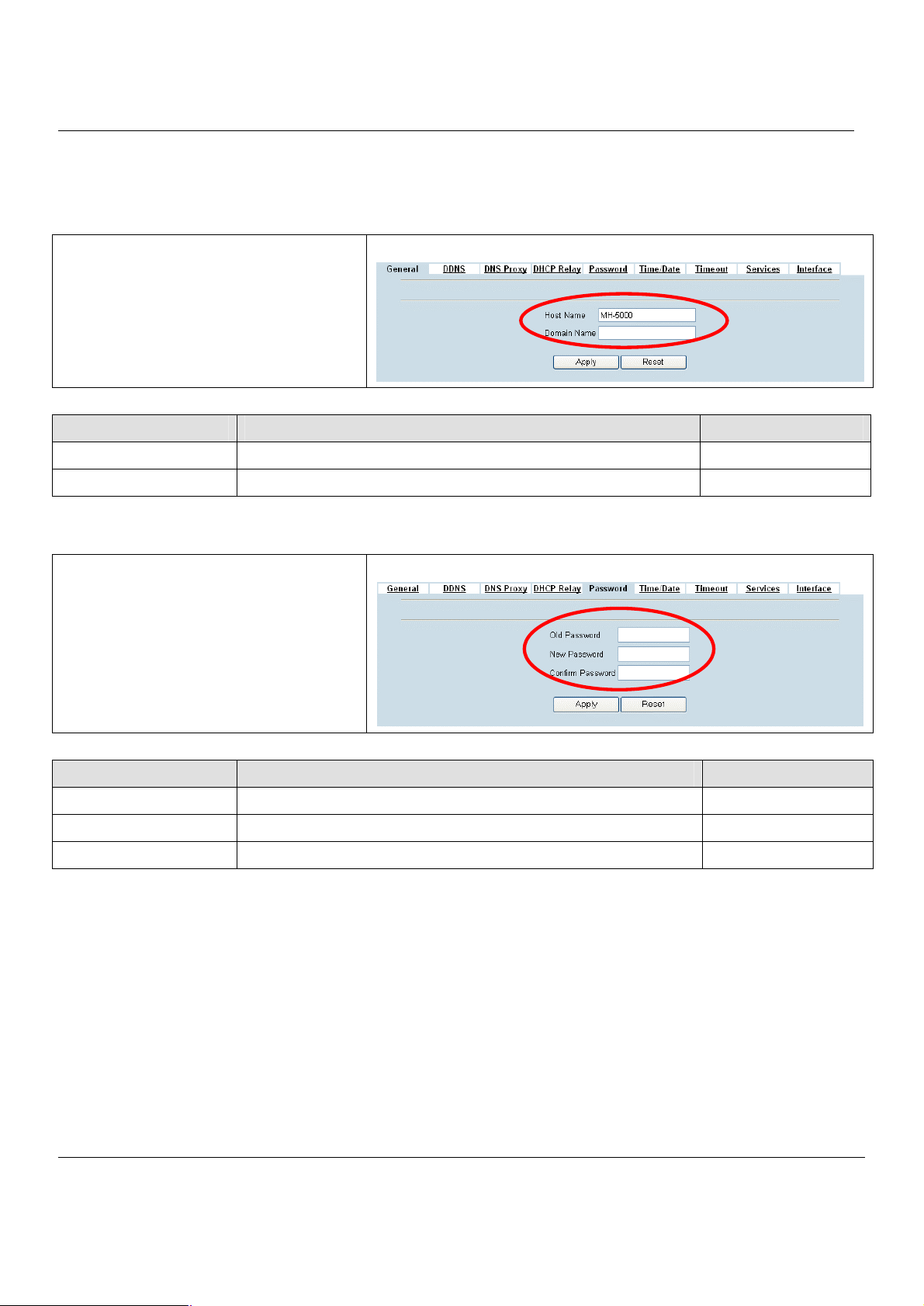
Step 1. General Setup
Enter the Host Name as MH-5000, Domain Name
as the domain name of your company Click
Apply.
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
Host Name The host name of the MH-5000 device MH-5000
Domain Name Fill in the domain name of company Planet.com.tw
Table 4-1 System Tools - General Setup menu
Step 2. Change Password
Enter the current password in the Old Password
field. Enter the new password in the New
Password and retype it in the Confirm Password
field. Click Apply.
SYSTEM TOOLS > Admin Settings > General
SYSTEM TOOLS > Admin Settings > Password
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
Old Password The original password of administrator admin
New Password The new selected password 12345
Confirm Password Double confirm the new selected password 12345
Table 4-2 Enter new password
32
Page 40

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 4
System Tools
Step 3. Setup Time/Date
Select the Time Zone where you are located.
Enter the nearest NTP time server in the NTP
time server address. Note that your DNS must be
set if the entered address requires domain name
lookup. You can also enter an IP address instead.
Check the Continuously (every 3 min) update
system clock and click Apply. The MH-5000 will
immediately update the system time and will
periodically update it. Check the Update system
clock using the time server at boot time and click
Apply if you want to update the clock at each
boot. If you want to manually change the system
time, uncheck the Continuously (every 3 min)
update system clock and proceed by entering the
target date.
SYSTEM TOOLS > Admin Settings > Time/Date
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
Time zone the time zone of your area N/A
NTP time server address Use NTP time server to auto update date/time value tock.usno.navy.mil
Continuously (every 3
min) update system
System will update system date/time value every 3 minutes to NTP
time sever. Enabled
clock
Update system clock
using the time server at
System will update system date/time value to the NTP time server
at boot time.
disabled
boot time
Manual Time Setup Manual setting Time & Date value. N/A
Table 4-3 System Tools – Time Data menu
Step 4. Setup Timeout
Select the target timeout (e.g. 10 min) from the
System Auto Timeout Lifetime. Click the Apply
button. Now the browser will not timeout for the
following 10 minutes after your last touching of it.
SYSTEM TOOLS > Admin Settings > Timeout
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
System Auto Timeout
Lifetime
When system is idle for a specified time, system will force the
people who logins into the system will logout automatically.
10
Table 4-4 System Tools – Timeout menu
33
Page 41

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 4
System Tools
Step 5. Configure Services
We can configure the service name and numeric
port number as the same group, so you can
simply use the domain name for the configuration
in the MH-5000. If you want to add/edit/delete the
service record, just click the below button to
add/edit/delete it.
BUTTON DESCRIPTION
Add Add a service name record
Edit edit an existing service name record
Delete delete an existing service name record
Table 4-5 Setup the service name record
SYSTEM TOOLS > Admin Settings > Services
4.4.2 DDNS setting
Step 1. Setup DDNS
If the IP address of MH-5000 WAN port is
dynamic allocated, you may want to have the
Dynamic DNS mechanism to make your partner
always use the same domain name (like xxx.com)
to connect to you. Select a WAN interface to
update the DDNS record. Here we supply 11
DDNS Service Providers. Fill in the Host Name,
Username, Password supplied by the DDNS web
site. Please refer to the DDNS web site for the
detailed information. Click Apply to activate the
settings.
Before setting the DDNS information in this page.
Make sure that you have registered an account in
the indicated Service Provider. Then you can
enter the related information in the DDNS page.
SYSTEM TOOLS > Admin Settings > DDNS
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
Enable DDNS for WAN1 Enable DDNS feature of MH-5000 Enabled
Interface Assign which public IP address of interface to the DDNS server. WAN1
34
Page 42

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 4
System Tools
The domain address of DDNS server. In the MH-5000, we provide
DHS, DYNDNS, ORAY, CHANGEIP, ADSLDNS, NO-IP,
DNS2GO, DTDNS, 3322, 88IP and HN 11 websites for choice.
Service Provide
If you choose WWW.ORAY.NET as DDNS service provider. It
would register the source IP address which is connected to the
DDNS server. It means that the WAN1 IP address must be public
address.
Hostname The registered Hostname in the DDNS server. abc.vicp.net
Username The registered username in the DDNS server. john
Password The registered password in the DDNS server. 123456
WWW.ORAY.NET
Port
The default port number to connect to WWW.ORAY.NET for free
charge.
Table 4-6 System Tools – DDNS setting page
4.4.3 DNS Proxy setting
Step 1. Setup DNS Proxy
Check the Enable DNS Proxy and click the Apply
to store the settings. From now on, your
LAN/DMZ PCs can use MH-5000 as their DNS
server, as long as the DNS server for MH-5000
has been set in its WAN settings.
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
When the host which resides at the LAN/DMZ region sends a DNS
Request to the DNS server (MH-5000). MH-5000 will request for
Enable DNS Proxy
forwarding it to the assigned DNS server. When there is a response
from assigned DNS server, then MH-5000 will forward it back to the
host of the LAN/DMZ.
Table 4-7 System Tools – DNS Proxy menu
5050
SYSTEM TOOLS > Admin Settings > DNS Proxy
Enabled
4.4.4 DHCP Relay setting
Step 1. Setup DHCP Relay
Check the Enable DHCP Relay. Enter the IP
address of your DHCP server. Here we enter the
DHCP Server address 10.1.1.4. Check the relay
domain of MH-5000 that needs to be relayed.
Namely, check the one where the DHCP clients
are located. And click the Apply button finally.
Notice, the DHCP Server can not be located with
the subnet range of Relay Domain.
SYSTEM TOOLS > Admin Settings > DHCP Relay
35
Page 43

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 4
System Tools
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
When the host of the LAN/DMZ in the MH-5000 internal network
Enable DHCP Relay
DHCP Server Current location of the DHCP server. 10.1.1.4
Relay Domain The locations of the DHCP clients. Enable LAN1
4.4.5 SNMP Control
sends a DHCP request, MH-5000 will forward it automatically to the
specified DHCP server (different subnet from the network segment
of the DHCP client).
Table 4-8 System Tools – DHCP Relay menu
Enabled
Step 1. Setup SNMP Control
Through setting the related information in this
page, we can use SNMP manager to monitor the
system status, network status of MH-5000.
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
Enable SNMP Enable the SNMP function or not. Enabled
System Name The device name of MH-5000. MH-5000.planet.com.tw
System Location The settled location of MH-5000. Office
Contact Info The person who takes charge of the MH-5000. mis
Get community
The community which can get the SNMP information. Here
“community” is something like password.
SYSTEM TOOLS > SNMP Control
public-ro
Set Community
Trusted hosts
Trap community
Trap destination The IP address which will send SNMP trap from the MH-5000. 192.168.1.5
The community which can get the SNMP information. Here
“community” is something like password.
The IP address which can get or set community from the
MH-5000.
The community which will send SNMP trap. Here “community” is
something like password.
36
private-rw
192.168.1.5
trap-comm
Page 44

MH-5000 User Manual 0
4.4.6 Change MH-5000 interface
Step 1. Change Interface definition
The default port settings are 2 WAN ports, 1 DMZ
port and 2 LAN ports. But in order to fit our
requirement. Here we select 3 WAN (port1~3), 1
DMZ (port4), 1 LAN (port5). And then press apply
button to reboot MH-5000. Note that the DMZ and
LAN port IP addresses are going to be 10.1.1.254
and 192.168.1.254 after device finishes reboot.
Besides, there should be at least one WAN
port and one LAN port existing in the
MH-5000. You are not allowed to casually change
the interface to the state which has no LAN port
or WAN port.
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
You can specify WAN / LAN / DMZ for each port by your
Port1 ~ Port5
preference. However, there must be one WAN and one LAN
interface existing in the MH-5000.
SYSTEM TOOLS > Admin Settings > Interface
Port1 : WAN
Port2 : WAN
Port3 : DMZ
Port4 : LAN
Port5 : LAN
Table 4-9 Change the MH-5000 interface setting
37
Page 45
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 5
Remote Management
Chapter 5
Remote Management
This chapter introduces remote management and explains how to implement it.
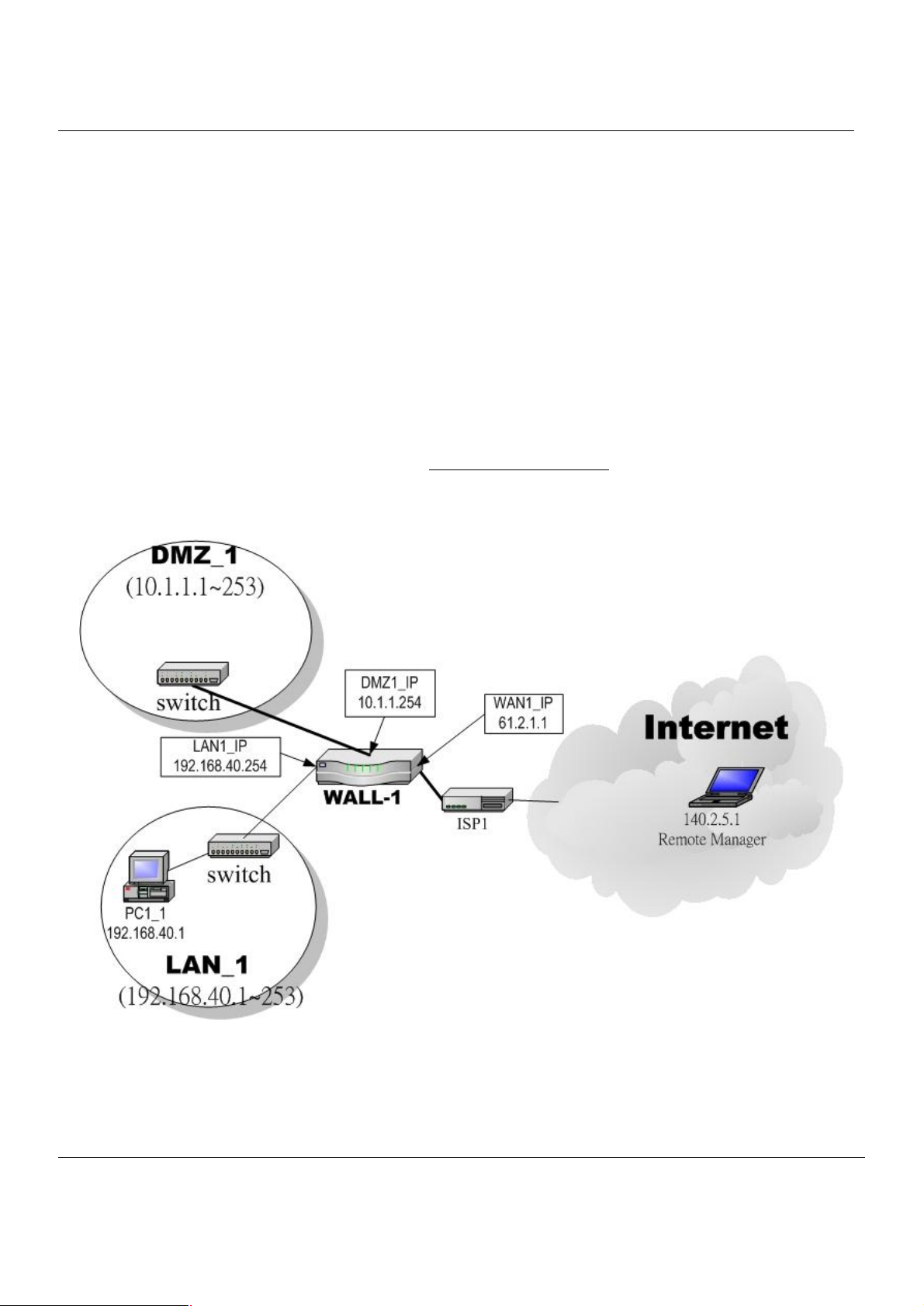
5.1 Demands
Administrators may want to manage the MH-5000 remotely from any PC in LAN_1 with HTTP at port 8080, and from
WAN_PC with TELNET. In addition, the MH-5000 may be more secure if monitored by a trusted host (PC1_1). What is
more, the MH-5000 should not respond to ping to hide itself. The remote management function in MH-5000 devices is
implemented by hidden Firewall rules.
5.2 Methods
1. Only allow management by WAN_PC (140.2.5.1) at the WAN1 side.
2. Administrators can use browsers to connect to http://192.168.40.254:8080 for management.
3. Allow SNMP monitoring by PC1_1 (192.168.40.1) at the LAN1 side.
4. Do not respond to ICMP ECHO packets at the WAN1 side.
Figure 5-1 Some management methods of MH-5000
38
Page 46
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 5
Remote Management
5.3 Steps
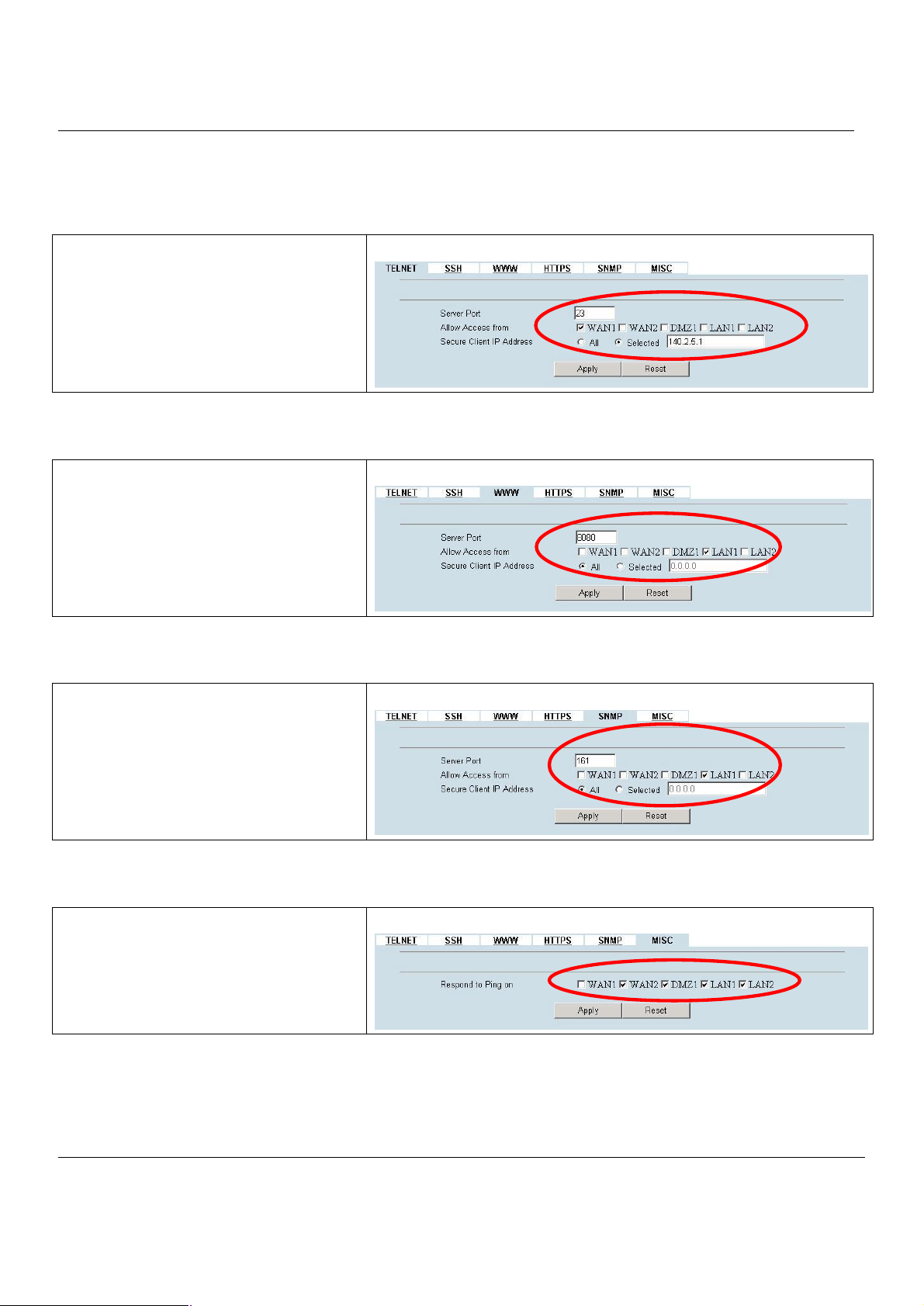
5.3.1 Telnet
Step 1. Setup Telnet
Enter 23 instead of the default 2323 in the Server
Port field. Check the WAN1 checkbox. Click the
Selected of Secure Client IP Address, and then
enter the specified IP address (140.2.5.1) for
accessing MH-5000. And click the Apply.
5.3.2 WWW
Step 1. Setup WWW
Check the LAN1 checkbox, and enter the new
Server Port 8080 that will be accessed by the
user’s browser (http://192.168.40.254:8080).
Here we click All for all no IP range limitation of
clients. And click the Apply button.
5.3.3 SNMP
Step 1. Setup SNMP
Check the LAN1 checkbox. In the Secure Client
Address field. If you prefer indicated specified IP
address. Just click the Selected, and enter the
valid IP address for reading the SNMP MIBs at
the MH-5000. Finally click the Apply button.
SYSTEM TOOLS > Remote Mgt. > TELNET
SYSTEM TOOLS > Remote Mgt. > WWW
SYSTEM TOOLS > Remote Mgt. > SNMP
5.3.4 ICMP
Step 1. Setup ICMP
Uncheck the WAN1 checkbox and make others
checked. Then click the Apply button.
SYSTEM TOOLS > Remote Mgt. > MISC
39
Page 47
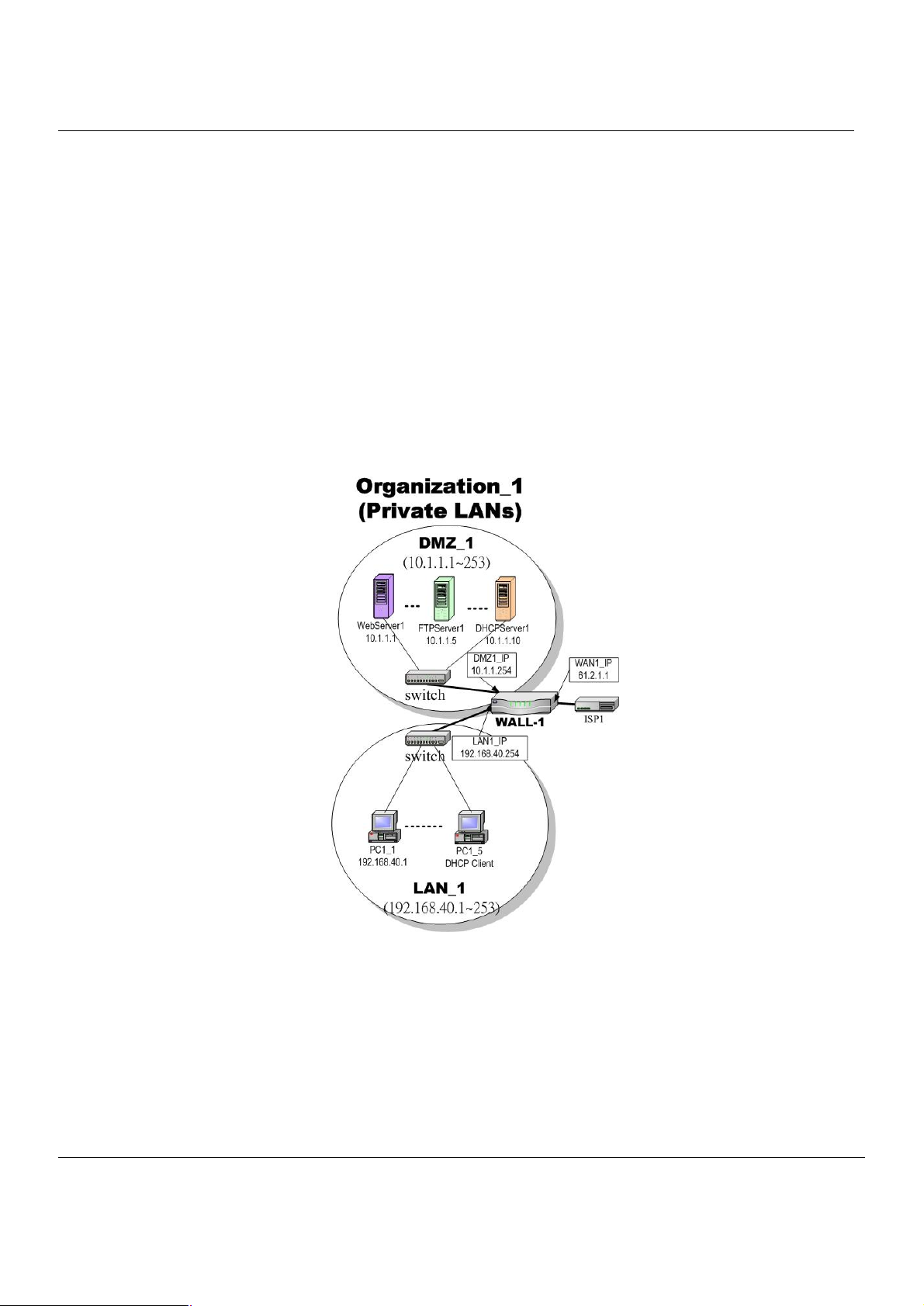
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 6
NAT
Chapter 6
NAT
This chapter introduces NAT and explains how to implement it in MH-5000.
To facilitate the explanation on how MH-5000 implements NAT and how to use it, we zoom in the left part of Figure 1-6
into Figure 6-1.
6.1 Demands
1. The number of public IP address allocated to each Internet subscribers is often very limited compared to the
number of PCs in the LAN1. Additionally, public-IP hosts are directly exposed to the Internet and have more
chances to be cracked by intruders. As the Figure 6-1 illustrated, you hope all the PCs located at LAN1 and
DMZ1 can connect internet through limited IP address (61.2.1.1).
Figure 6-1 All the internal PCs can connect internet through limited WAN IP address by using NAT technology
2. Internet servers provided by your company may open many ports in default that may be dangerous if exposed to
the public Internet. As the Figure 6-2 illustrated, we make the real servers hide behind the MH-5000. And all the
internet clients can still access the service of servers.
40
Page 48

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 6
NAT
Figure 6-2 Internet clients can access the server behind the MH-5000
6.2 Objectives
1. Let PC1_1~PC1_5 connect to the Internet.
2. As the Figure 6-2 illustrated, the clients will connect to the MH-5000. Then MH-5000 will forward the packet to
the real server. So FTPServer1 (10.1.1.5) will be accessed by other Internet users.
6.3 Methods
1. Assign private IP addresses to the PC1_1~PC1_5. Setup NAT at MH-5000 to map those assigned private hosts
under LAN1 to the public IP address WAN_IP at the WAN1 side.
2. Assign a private IP address to the FTPServer1. Setup Virtual Server at MH-5000 to redirect “any connections
towards some port of WAN1” to the port 21 at the FTPServer1.
41
Page 49
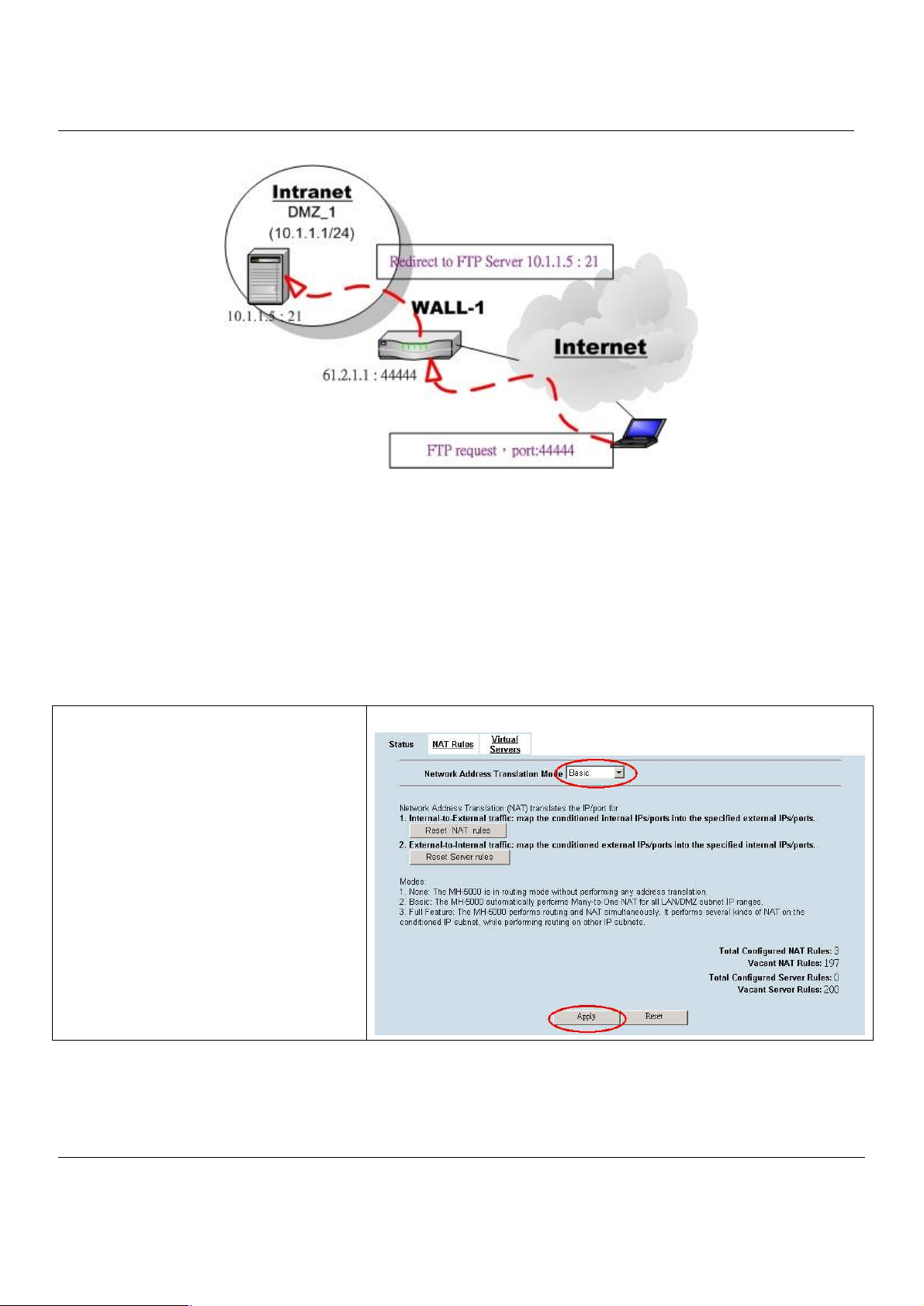
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 6
NAT
Figure 6-3 MH-5000 plays the role as Virtual Server
As the above Figure 6-3 illustrates, the server 10.1.1.5 provides FTP service. But it is located on the DMZ region behind
MH-5000. And MH-5000 will act as a Virtual Server role which redirects the packets to the real server 10.1.1.5. And you
can announce to the internet users that there exists a ftp server IP/port is 61.2.1.1/44444. So, all the internet users will
just connect the 61.2.1.1/44444 to get ftp service.
6.4 Steps
6.4.1 Setup Many-to-one NAT rules
Step 1. Enable NAT
Select the Basic from the list of Network Address
Translation Mode. Click Apply. Now the MH-5000
will automatically set the NAT rules for LAN/DMZ
zones. Namely, all internal networks can
establish connections to the outside world if the
WAN settings are correct.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > Status
42
Page 50

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 6
NAT
FIELD DESCRIPTION Range / Format
Network Address
Translation Mode
Determine what NAT type you are using in your
network topology.
Refer more information in the section 6.5.4.
BUTTON DESCRIPTION
Reset NAT Rules Reset NAT rules to the default status
Reset Server Rules Clear all the Virtual Server rules.
Clear active
NAT/Server sessions
Clear all the active NAT/Virtual Server sessions.
Apply Apply the settings which have been configured.
Reset Clean the filled data and restore the original.
Table 6-1 Determine Network Address Translation Mode
Step 2. Check NAT Rules
As described in the above, the MH-5000 has set
the rules for the LAN/DMZ zones. They all belong
to the Many-to-One (M-1) type that will map many
private addresses to the automatically chosen
public IP address. When the WAN interfaces
change the IP, these rules do not require any
manual modifications for the changed public IP
addresses. The rules will reload the new settings
automatically. Besides, you cannot insert/edit any
rules under the Basic mode.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > NAT Rules
None /
Basic /
Full Feature
EXAMPLE
Basic
Step 3. Switch the NAT Mode
Select the Full Feature from the list of Network
Address Translation Mode. Click Apply. After
applying the setting, the page will highlight a
warning saying that the rules are no more
automatically maintained by the MH-5000. If you
change the LAN/DMZ IP settings, you have to
manually update related rules by yourself.
Otherwise, hosts in your LAN/DMZ cannot
establish connections to the hosts in the WAN
side.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > Status
43
Page 51

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 6
NAT
Step 4. Customize NAT Rules
In the full-feature mode, the rules can be further
customized. Incoming packets from LAN/DMZ
zones are top-down matched by the NAT rules.
Namely, NAT implements first match. Select the
rule item that you want to do with: insert a new
rule before it; delete it; move it before the list-box
chosen item.
Step 5. Insert NAT Rule
Step 5.a — Insert an Many-to-One
Rule
As described in the above, Many-to-One NAT is
the default NAT rule type in the Basic mode. If
you have other alias LAN/DMZ subnets, you can
manually add a Many-to-One NAT rule for them.
First select the Type as Many-to-One, check the
Activate this rule, enter a Rule name for this rule,
enter the private-IP subnet (an IP address with a
netmask) to be translated, and enter the public IP
address for being translated into. You can check
the Auto choose IP from WAN ports. The
MH-5000 will automatically determine which WAN
IP is to be translated into.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > NAT Rules
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > NAT Rules > Insert
Condition
Status
Action
FIELD DESCRIPTION Range / Format
Activate this rule
The NAT rule is enabled or not Enabled /
Disabled
EXAMPLE
Rule name The NAT rule name text string Rule
Source IP /
Netmask
Compared with the incoming packets,
whether Source IP/Netmask is matched or
not.
IPv4 format
192.168.40.0 /
255.255.255.0
Many-to-One /
Type
Determine what NAT method you are using in
the specified NAT rule.
Refer more information in the section 6.5.
Many-to-Many /
One-to-One /
One-to-One
Many-to-One
(bidirectional)
Translated Src
IP (Auto choose
IP from WAN
ports)
Only work in Many-to-One type, the public IP
address will be assigned by the default wan
link.
44
Enabled /
Disabled
Enabled
Enabled
Page 52

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 6
NAT
Space /
Netmask
When NAT type is not Many-to-One, we must
specify IP address / Netmask directly.
Step 5.b — Insert an Many-to-Many
Rule
If your ISP has assigned a range of public IP to
your company, you can tell MH-5000 to translate
the private IP addresses into the pool of public IP
addresses. The MH-5000 will use the first public
IP until MH-5000 uses up all source ports for the
public IP. MH-5000 will then choose the second
public IP from the address pool. Select
Many-to-Many from the Type. Enter the subnet
with an IP address and a netmask. Other fields
are the same with those of Many-to-One rules.
However, the MH-5000 will no longer choose the
device IP for you. It will choose the IP from the
address pool you have entered.
Step 5.c — Insert an One-to-One Rule
Though you may have many public IP address for
translation, you may want to make some private
IP to always use a public IP. In this case, you can
select One-to-One from the Type, and enter the
private-public IP address pair in the Source IP
and the Translated Source IP fields.
IPv4 format N/A
Table 6-2 Add a NAT rule
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > NAT Rules > Insert
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > NAT Rules > Insert
Step 5.d — Insert a One-to-One
(Bidirectional) Rule
The above three modes allow LAN/DMZ-to-WAN
sessions establishment but do not allow
WAN-to-LAN/DMZ sessions. WAN-to-LAN/DMZ
sessions are allowed by Virtual Server rules. You
can make the One-to-One NAT in the above to
incorporate the WAN-to-LAN/DMZ feature by
selecting the One-to-One (Bidirectional) from the
Type. Note that WAN-to-LAN/DMZ traffic will be
blocked by the Firewall in default. You have to
add a Firewall rule to allow such traffic. If you
expect a LAN/DMZ host to be fully accessed by
public Internet users, use this mode. Note that
this mode is extremely dangerous because the
host is fully exposed to the Internet and may be
cracked. Always use Virtual Server rules first.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > NAT Rules > Insert
45
Page 53

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 6
NAT
6.4.2 Setup Virtual Server for the FtpServer1
Step 1. Device IP Address
Setup the IP Address and IP Subnet Mask for the
MH-5000 of the DMZ1 interface.
Step 2. Client IP Range
Enable the DHCP server if you want to use
MH-5000 to assign IP addresses to the
computers under DMZ1. Here we make the
DHCP feature enabled.
Step 3. Apply the Changes
Click Apply to save your settings.
Step 4. Check NAT Status
The default setting of NAT is in Basic Mode. After
applying the Step 3, the NAT is automatically
configured with the rules to let all private-IP
LAN/DMZ-to-WAN requests to be translated with
the public IP assigned by the ISP.
BASIC SETUP > DMZ Settings > DMZ1 Status
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > Status
Step 5. Check NAT Rules
The MH-5000 has added the NAT rules
automatically as right diagram described. The
rule Basic-DMZ1 (number 1) means that, when
matching the condition (requests of
LAN/DMZ-to-WAN direction with its source IP
falling in the range of 10.1.1.254/255.255.255.0),
the request will be translated into a
public-source-IP requests, and then be forwarded
to the destinations.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > NAT Rules
46
Page 54

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 6
NAT
Step 6. Setup IP for the FTP Server
Assign an IP of 10.1.1.1/255.255.255.0 to the
FTP server under DMZ1. Assume the FTP Server
is at 10.1.1.5. And it is listening on the well-known
port (21).
Step 7. Setup Server Rules
Insert a virtual server rule by clicking the Insert
button.
Step 8. Customize the Rule
Customize the rule name as the ftpServer. For
any packets with its destination IP equaling to the
WAN1 IP (61.2.1.1) and destination port equaling
to 44444, ask MH-5000 to translate the packet’s
destination IP/port into 10.1.1.5/21. Check the
Passive FTP client? To maximize the
compatibility of the FTP protocol. This is useful if
you want to provide connectivity to passive FTP
clients. For passive FTP clients, the server will
return them the private IP address and the port
number for them to connect back to do data
transmissions. Since the private IP from them
cannot be routed to our zone, the data
connections would fail. After enabling this feature,
the MH-5000 will translate the private IP/port into
an IP/port of its own. Thus the problem is
gracefully solved. Another point is to be sure to
check “Auto update to Firewall rules when you
Apply this page?” or “Auto update to NAT rules
when you Apply this page?”. Then, the virtual
server rule will add Firewall or NAT rules
automatically. Click Apply to proceed.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > Virtual Servers
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > Virtual Servers > Insert
Status
FIELD DESCRIPTION Range / Format
Activate this rule The Virtual Server rule is enabled or not
Enabled /
Disabled
EXAMPLE
Enabled
Rule name The Virtual Server rule name text string ftpServer
Condition
Sessions from
Internet
connecting to
Which interface does the connected session
come from?
WAN interfaces
WAN1
External IP The public IP address of the Virtual Server. IPv4 format 61.2.1.1
47
Page 55

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 6
NAT
Action
Service
Type Port is Single or Range Single / Range Single
Dest Port
Passive FTP
client
Redirect to
internal server
under
Internal IP
Port
Auto update to
Firewall rules
when you Apply
this page?
The service which is provided by the real
server.
The TCP/UDP port number which is provided
by the real server.
If the Passive FTP client is checked, it will
connect to the internal DMZ FTP server of
MH-5000 when FTP client uses passive
mode. Otherwise, it will not work.
The subnet which is located the virtual server.
The IP address which is actually transferred
to the internal DMZ
The port number which is actually transferred
to the internal DMZ.
If you filled 0 in this field, it means that the
real connected port is the same as the
translated destination port.
If you checked this, it will add the Firewall
rules automatically when you add a virtual
server rule.
TCP / UDP TCP
1 ~65534 44444
Enabled /
Disabled
LAN / DMZ
regions
IPv4 format 10.1.1.5
0 ~ 65534 21
Enabled /
Disabled
Enabled
DMZ1
Enable
Auto update to
NAT rules when
you Apply this
page?
Step 9. View the Result
Now any request towards the MH-5000’s WAN1
IP (61.2.1.1) with port 44444 will be translated
into a request towards 10.1.1.5 with port 21, and
then be forwarded to the 10.1.1.5. The FTP
server listening at port 21 in 10.1.1.5 will pick up
the request.
If you checked this, it will add the NAT rules
automatically when you add a virtual server
rule.
Table 6-3 Add a Virtual Server rule
Enabled /
Disabled
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > Virtual Servers
Enable
48
Page 56

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 6
NAT
Step 10. View the NAT Rules
In the previous step 8, we have already checked
“Auto update to Firewall/NAT rules when you
Apply this page”, so it will automatically add one
NAT rule to transfer the IP address of virtual
server when server responses packet back to the
client.
Step 11. View the Firewall Rules
The same as Step 10. When we have checked
“Auto update to Firewall/NAT rules when you
Apply this page”, it will automatically add one
Firewall rule in the WAN1 to DMZ1 direction. This
firewall rule will let the packets with dest. IP
address/port be matched with virtual server rule in
order to pass through MH-5000.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > NAT > NAT Rules
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules
49
Page 57
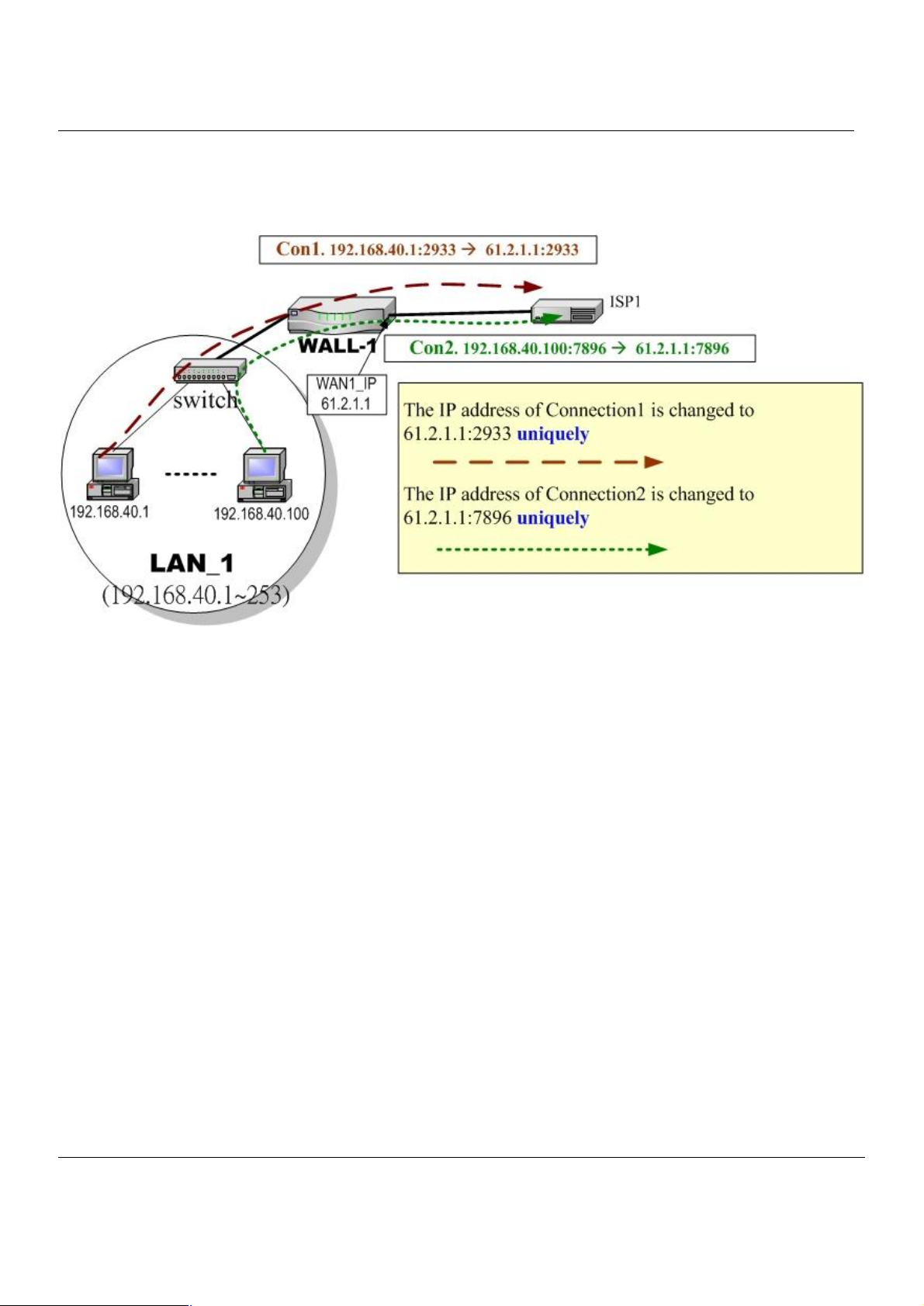
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 6
NAT
6.5 NAT modes introduction
6.5.1 Many-to-One type
Figure 6-4 NAT Many-to-One type
As the above Figure 6-4 illustrated, NAT Many-to-One type means that many local PCs are translated into only one
public IP address when the packets are forwarded out through the MH-5000. Take Connection1 for example. Its IP
address and port are translated from 192.168.40.1:2933 to 61.2.1.1:2933. In the same way, when the packets of
Connection2 are forwarded out, its IP address is still translated to the same public IP address (61.2.1.1:7896).
50
Page 58

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 6
NAT
6.5.2 Many-to-Many type
Figure 6-5 NAT Many-to-Many type
As the above Figure 6-5 illustrated, NAT Many-to-Many type means that many local PCs are translated into multiple
public IP addresses when the packets are forwarded out through the MH-5000. Take Connection1 for example. Its IP
address and port are translated from 192.168.40.1:2933 to 61.2.1.1:2933. Until MH-5000 uses out of all source ports of
the public (61.2.1.1), MH-5000 will then choose the second public IP (such as 61.2.1.2) from the address pool. For
example, Connection2 are forwarded out, the source IP address will be translated into the second public IP address
(61.2.1.2) from the public IP address pools. So the translated IP address (61.2.1.2:7896) is different from Connection1
one (61.2.1.1:2933).
6.5.3 One-to-One type
Figure 6-6 NAT One-to-One type
51
Page 59

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 6
NAT
As the above Figure 6-6 illustrated. NAT One to One type means that each local PC is translated into a unique public IP
address when the packets are forwarded out through the MH-5000. Take Connection1 for example. Its IP address and
port are translated from 192.168.40.1:2933 to 61.2.1.1:2933. But, when the packets of Connection2 are forwards out, the
source IP address is translated to another dedicated public IP address(61.2.1.2:7896).
6.5.4 NAT modes & types
The following three NAT modes are supported by MH-5000 now as the following Table 6-4.
NAT mode Description
None The MH-5000 is in routing mode without performing any address translation.
Basic The MH-5000 automatically performs Many-to-One NAT for all LAN/DMZ subnets.
Full Feature
If you choose Full Feature mode of NAT at Table 6-4, you may need to edit the rule by yourself. Then you must
determine the NAT type in the NAT rule. What meaning does each NAT type represent? How to determine which NAT
type is best choice for you. You can lookup the explanations and suggestions at Table 6-5.
Type Description Usage moment
Many-to-One
Many-to-Many
One-to-One
The MH-5000 can be manually configured with Many-to-One, and Many-to-Many, One-to-One,
and bidirectional One-to-One rules to do policy-based NAT.
Table 6-4 NAT modes overview
Map a pool of private IP addresses to a
single public IP address chosen from the
WAN ports.
Map a pool of private IP addresses to a
subnet range of public IP addresses
chosen from the WAN ports. Only when all
ports of the first public IP are used, it will
then use the next public IP address for
transferring by all private IPs.
Map a single private IP address to a single
public IP address chosen from the WAN
ports.
This was useful when you have multiple
public IPs in the WAN ports. And you
intended to map each local server to a
unique public IP on the WAN port.
If the public IP addresses of your company is insufficient,
and you prefer to increase the node which can connect to
the internet. You can just choose the Many-to-One type to
fit your request.
If the public IP address of your company is not only one
node (ex. you have applied extra-one ISP). You may use
the Many-to-Many type to make the multiple public
addresses sharing the outbound bandwidth. So your
inbound and outbound traffic will be more flexible.
If you wish to specify a unique internal IP address to
transfer a fixed external IP address. You can specify the
One-to-One type.
If you wish to expose the local pc onto the internet, and
open all internet services outside. You can specify the
An internal host is fully mapped to a WAN
One-to-One
(bidirectional)
IP address. Notice that you must add a
firewall rule to forward WAN to LAN/DMZ
traffic.
Table 6-5 The NAT type comparison
52
One-to-One (bidirectional) type. This will make the local
pc you specified fully exposed to the internet. Additionally
you must add a firewall rule to allow WAN to LAN (or
DMZ) traffic forward. Then you can finish the settings. Be
careful to use this type, or it will endanger your network
security.
Page 60
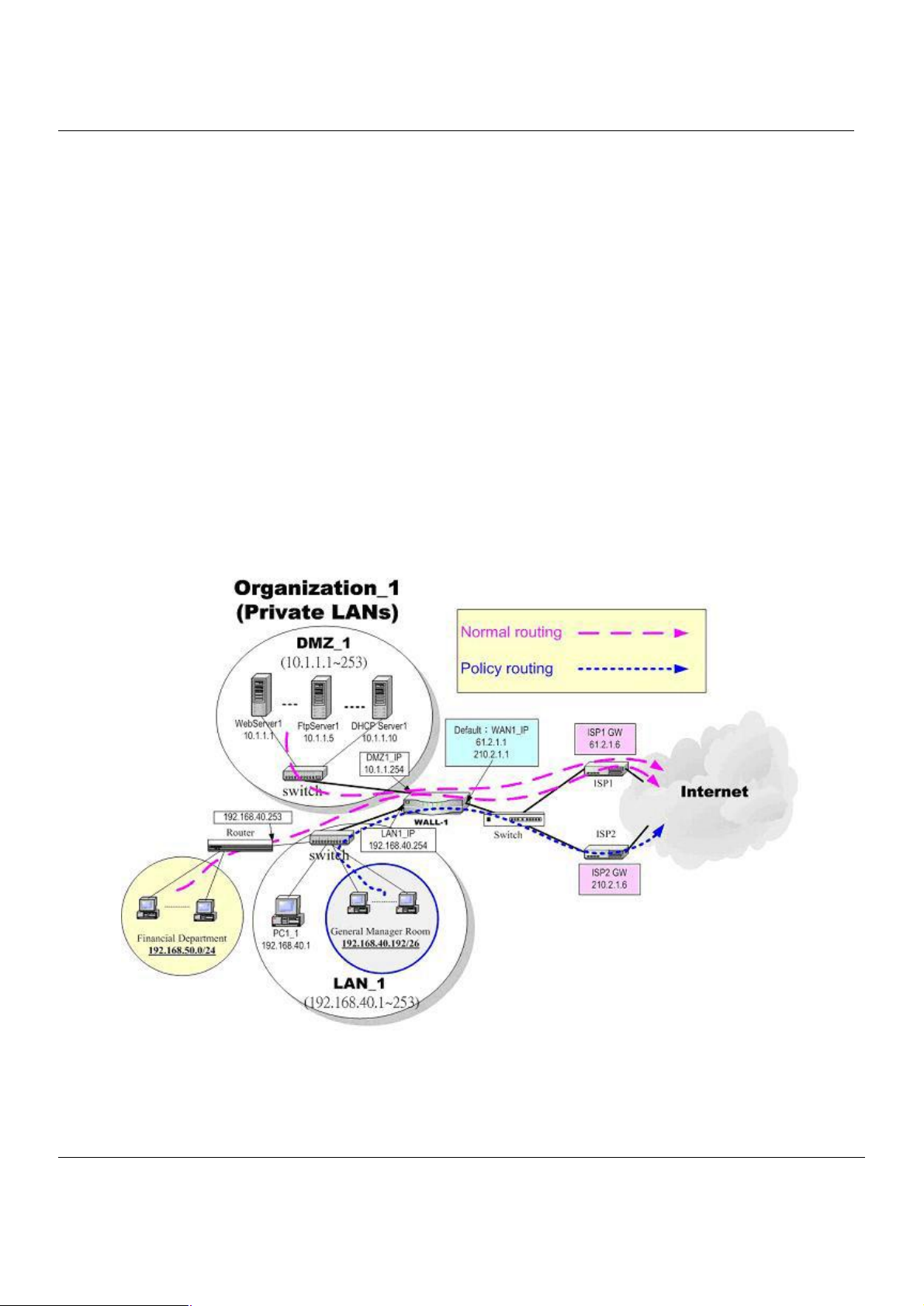
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 7
Routing
Chapter 7
Routing
This chapter introduces how to add static routing and policy routing entries
To facilitate the explanation on how MH-5000 implements routing and how to use it. We zoom in the left part of Figure 2-1
into Figure 7-1 and increase some devices for description.
7.1 Demands
1. There is only one local area (192.168.40.0/24) inside the LAN1 port. Now there is a new financial area
(192.168.50.0/24) in the Figure 7-1. The financial area is connected with a router which is inside the LAN1 port of
MH-5000. So we need to add the configurations for the financial department.
2. Refer to the Figure 7-1 description. The bandwidth subscribed from ISP1 is insufficient so that some important
traffic, say the traffic from PCs belonging to the General-Manager-Room department
(192.168.40.192/255.255.255.192), is blocked by the other traffic. We hope that the employees of
General-Manager-Room can have a dedicated bandwidth to improve the quality of connecting internet.
Figure 7-1 Add policy routing entry for the General-Manager-Room department
53
Page 61
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 7
Routing
7.2 Objectives
1. We need to let MH-5000 knows how to forward the packets which is the destination financial department
(192.168.50.0/24).
2. The network administrator plans to solve the problem by subscribing the second link (ISP2). He hopes that all the
packets from the General-Manager-Room (192.168.40.192/26) will pass through the ISP2 link instead of the
default ISP1 link.
7.3 Methods
1. Add a static routing entry to direct the packets towards 192.168.50.0/24 through the router (192.168.40.253).
2. Add a policy routing entry for the packets coming from General-Manager-Room department (192.168.40.192 /
255.255.255.192) through the ISP2 link.
7.4 Steps
7.4.1 Add a static routing entry
Step 1. Add a static routing rule
Click the Add button to the next process.
Step 2. Fill out the related field
Fill in the Destination and the Netmask field with
192.168.50.0 and 255.255.255.0. Assign the next
hop Gateway as 192.168.40.253 (Router IP
address). Click Add to proceed.
Advanced Settings > Routing > Static Route
Advanced Settings > Routing > Static Route > Add
54
Page 62

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 7
Routing
FIELD DESCRIPTION Range / Format
Type
Destination
Netmask
Gateway The default gateway of this static routing entry record. IPv4 format 192.168.40.253
Step 3. View the result
The static route has been stored. After filling data
completely, view the static routing entries which
have been set.
Determine this static routing entry record is multiple
hosts (Net) or a single host (Host)。
The destination IP address of this static routing entry
record.
The destination IP Netmask of this static routing entry
record.
Table 7-1Add a static routing entry
Advanced Settings > Routing > Static Route
Net / Host Net
IPv4 format 192.168.50.0
IPv4 format 255.255.255.0
EXAMPLE
Step 4. View the routing table
You can notice there is an extra routing entry in
the routing table. The indicated routing entry as
right diagram is produced by static routing rule.
Device Status > System Status > Routing Table
55
Page 63
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 7
Routing
7.4.2 Add a policy routing entry
Step 1. Setup the ISP2 link
We must add an IP alias record to the WAN1 port,
because a new ISP link has been applied. See
section 3.4.3 for the full procedures.
Step 2. Insert a policy routing entry
Click Insert button to add a policy routing entry.
Basic Setup > WAN Settings > IP Alias
Advanced Settings > Routing > Policy Route
Step 3. Fill out the related field
For the General-Manager-Room department, we
need to set an extra policy routing entry for them.
So in the Status region, make sure the Activate
this rule is enabled, and then fill in
GenlManaRoom in the Rule name field. In the
Condition region, we fill 192.168.40.192 in Source
IP field. Fill 255.255.255.192 in the Netmask field.
In the Action region, fill forward to WAN1 with
next-hop gateway 210.2.1.6. After setting as
above, the packets which match the condition,
they will follow the predefined action to forward to
the next hop.
Advanced Settings > Routing > Policy Route > Insert
56
Page 64

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 7
Routing
Status
Condition
FIELD DESCRIPTION Range / Format
Activate this rule The policy routing rule is enabled or not.
Rule name The policy routing rule name. text string
Incoming
packets from
Source IP &
Netmask
Dest IP &
Netmask
Service Verify what is the service of this packet?
Configure src.
port? Type Src.
port
Type
Src. Port
Packets comes from which interface
Verify if the incoming packets belong to the
range of the Source IP/Netmask in the policy
routing rule.
Verify if the incoming packets belong to the
range of the Dest IP/Netmask in the policy
routing rule.
If the service is TCP or UDP, we can choose
to configure or not to configure source port.
If we decide to configure source port, we must
choose the port to be single or range.
If we select single at above field, we just have
to fill a port in the first blank space. If we
select range at above field, we need to fill the
range of the ports.
Enabled /
Disabled
LAN / DMZ
regions
IPv4 format /
IPv4 format
IPv4 format /
IPv4 format
ANY / TCP /
UDP / ICMP
Enabled /
Disabled
Single / Range N/A
1 ~ 65534 N/A
EXAMPLE
Enabled
GenlManaRoo
m
LAN1
192.168.40.192
/
255.255.255.19
2
0.0.0.0 /
0.0.0.0
Any
No
Configure dest.
port? Type Dest.
port
Type
Dest. Port
Forward to
Action
Next-hop
gateway IP
If the service is TCP or UDP, we can choose
to configure or not to configure destination
port.
If we decide to configure destination port, we
must choose the port to be single or range.
If we select single at above field, we just have
to fill a port in the first blank space. If we
select range at above field, we need to fill the
range of the ports.
If the packet is matched to this rule, which
interface does this packet sent out to?
The next gateway IP address of forwarding
interface.
Table 7-2 Add a policy routing entry
Enabled /
Disabled
Single / Range N/A
1 ~ 65534 N/A
WAN interfaces
IPv4 format 210.2.1.6
No
WAN1
57
Page 65

MH-5000 User Manual 0
Step 4. View the result
After filling data completely, view the policy
routing entries which have been set.
Step 5. View the routing table
Finally click the “Routing Table” to see all the
current routing table information.
Advanced Settings > Routing > Policy Route
Device Status > System Status > Routing Table
58
Page 66

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 8
Firewall
Chapter 8
Firewall
This chapter introduces firewall and explains how to implement it.
8.1 Demands
1. Administrators detect that PC1_1 in LAN_1 is doing something that may hurt our company and should instantly
block his traffic towards the Internet.
2. A DMZ server was attacked by SYN-Flooding attack and requires the MH-5000 to protect it.
8.2 Objectives
1. Block the traffic from PC1_1 in LAN1 to the Internet in WAN1.
2. Start the SYN-Flooding protection.
Figure 8-1 Setting up the firewall rule
8.3 Methods
1. Add a LAN1-to-WAN1 Firewall rule to block PC1_1.
2. Start the SYN-Flooding protection by detecting statistical half-open TCP connections.
59
Page 67

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 8
Firewall
8.4 Steps
8.4.1 Block internal PC session (LAN à WAN)
Step 1. Setup NAT
Check the Enable Stateful Inspection Firewall
checkbox, and click the Apply.
FIELD DESCRIPTION Range / Format
Enable Stateful
Inspection Firewall
Block all fragment
packets
BUTTON DESCRIPTION
Reset Rules Reset Firewall rules to the default status
Clear States Clear all the active Firewall states
Enable Firewall feature of MH-5000
Enable this feature will block the fragmented packets
by the firewall of MH-5000. Warning: Enable this
feature will cause problem in some applications.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Status
Enabled /
Disabled
Enabled /
Disabled
EXAMPLE
Enabled
Disabled
Apply Apply the settings which have been configured.
Reset Clean the filled data and restore the original.
Table 8-1 Configure Firewall status
Step 2. Add a Firewall Rule
Select LAN1 to WAN1 traffic direction. The
default action of this direction is to forward all
traffic without logging anything. Click Insert to add
a Firewall block rule before the default rule to stop
the bad traffic.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules
60
Page 68

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 8
Firewall
Step 3. Customize the rule
Check the Activate this rule checkbox. Enter the
rule name as PC1_1, and enter the IP address of
PC1_1 (192.168.40.1 / 255.255.255.255). Select
Block and Log to block and log the matched
traffic. Click the Apply to apply the changes.
Status
FIELD DESCRIPTION Range / Format
Activate this rule Enable the firewall rule for later using
Rule name The name of the Firewall rule text string PC1_1
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules > Insert
Enabled /
Disabled
EXAMPLE
Enabled
Condition
Action
Source IP &
Netmask
Dest IP &
Netmask
Service
Configure dest.
Port?
Type
Dest. Port
Forward / Block
the matched
session
do not log / Log
the matched
session
Compared with the incoming packets,
whether Source IP/Netmask is matched or
not.
Compared with the incoming packets,
whether Dest IP/Netmask is matched or not.
Verified the service of incoming packet is
belong to each TCP、UDP、ICMP.
If the service is TCP or UDP, we can choose
to configure or not to configure destination
port.
If we decide to configure destination port, we
must choose the port to be single or range.
If we select single at above field, we just
have to fill a port in the first blank space. If
we select range at above field, we need to fill
the range of the ports.
If packet is matched the rule condition,
Forward or Block this matched packet?
If packet is matched the rule condition, Log
or Don’t log this matched packet?
IPv4 format /
IPv4 format
IPv4 format /
IPv4 format
TCP / UDP /
ICMP
Enabled /
Disabled
Single / Range N/A
1 ~ 65534 N/A
Forward / Block
log / do not log
192.168.40.1
255.255.255.2
0.0.0.0
0.0.0.0
Any
Disabled
Block
55
log
61
Page 69
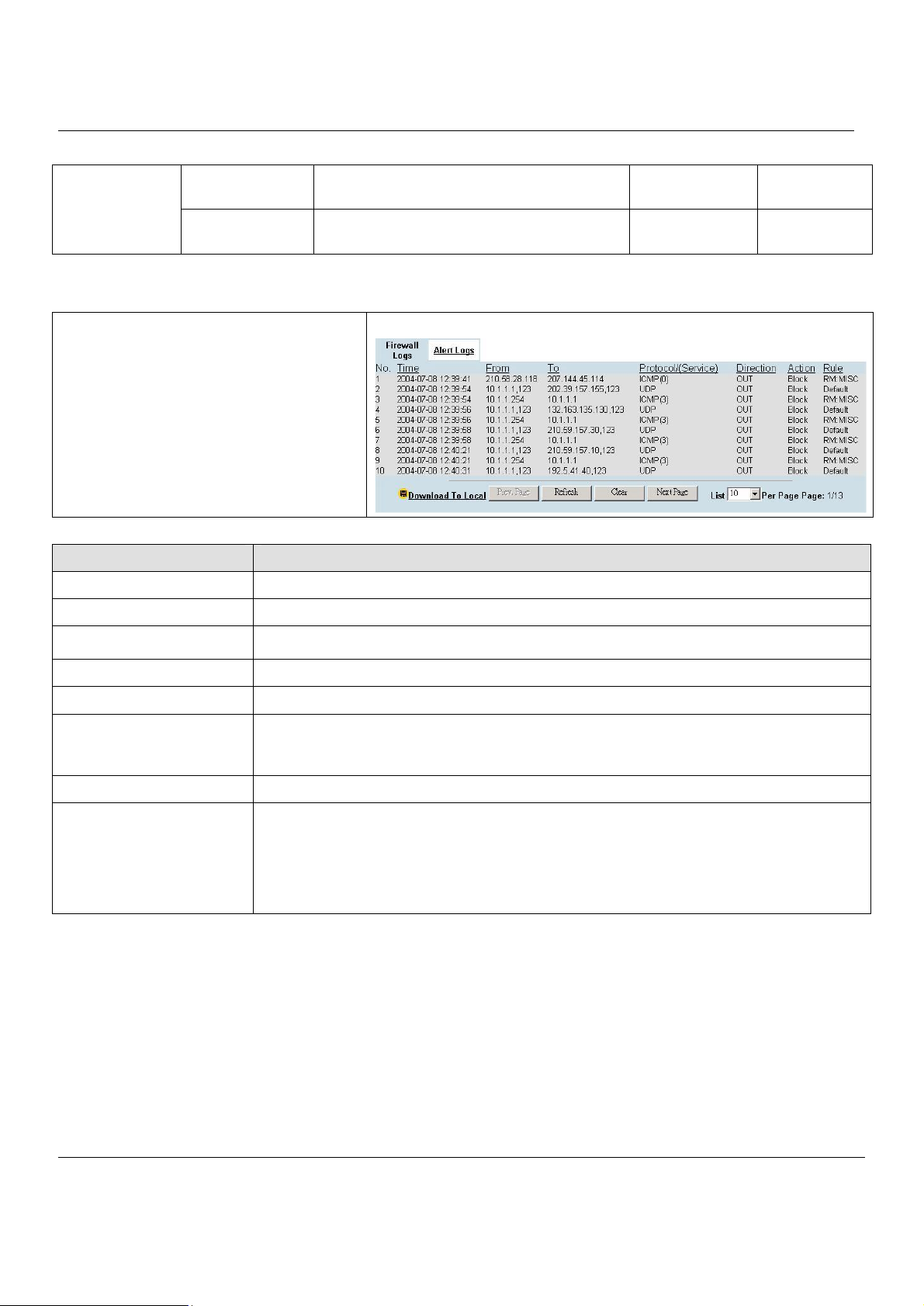
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 8
Firewall
Step 4. View the Firewall Log
You can go to DEVICE Status>Firewall Logs
>Firewall Logs to view the firewall logs. If you
prefer to download these logs, please click the
“Download To Local” button to save the logs to
localhost.
FIELD DESCRIPTION
Time The record time of indicated firewall log.
Forward
bandwidth class
Reverse
bandwidth class
No The indicated firewall log sequence number.
Forward bandwidth class if any. def_class def_class
Reverse bandwidth class if any. def_class def_class
Table 8-2 Insert a Firewall rule
DEVICE Status > Firewall Logs > Firewall Logs
From The source IP address (include port) which the indicated log event come from.
To The destination IP address (include port) for the indicated log event bound.
Protocol/Service The record log is TCP, UDP or ICMP, and which service it will be.
The firewall log direction is OUT or IN. The direction is based on the MH-5000. For
Direction
Action The status of indicated firewall log is Block or Forward.
Rule
example, “OUT WAN1” means the packet is forwarded out through WAN1 to the internet.
“IN LAN1” means the packet is forwarded through LAN1 into intranet.
The log is produced by which firewall rule.
“Default” means the default rule of the selected firewall direction.
“RM XXX” means the log is produced by remote management function (Almost it is the
illegal user who wants to use the Non-Opened remote management functions.
Other condition, it will be marked at the rule number (ex. Rule0, Rule1…).
Table 8-3 Firewall log field description
62
Page 70
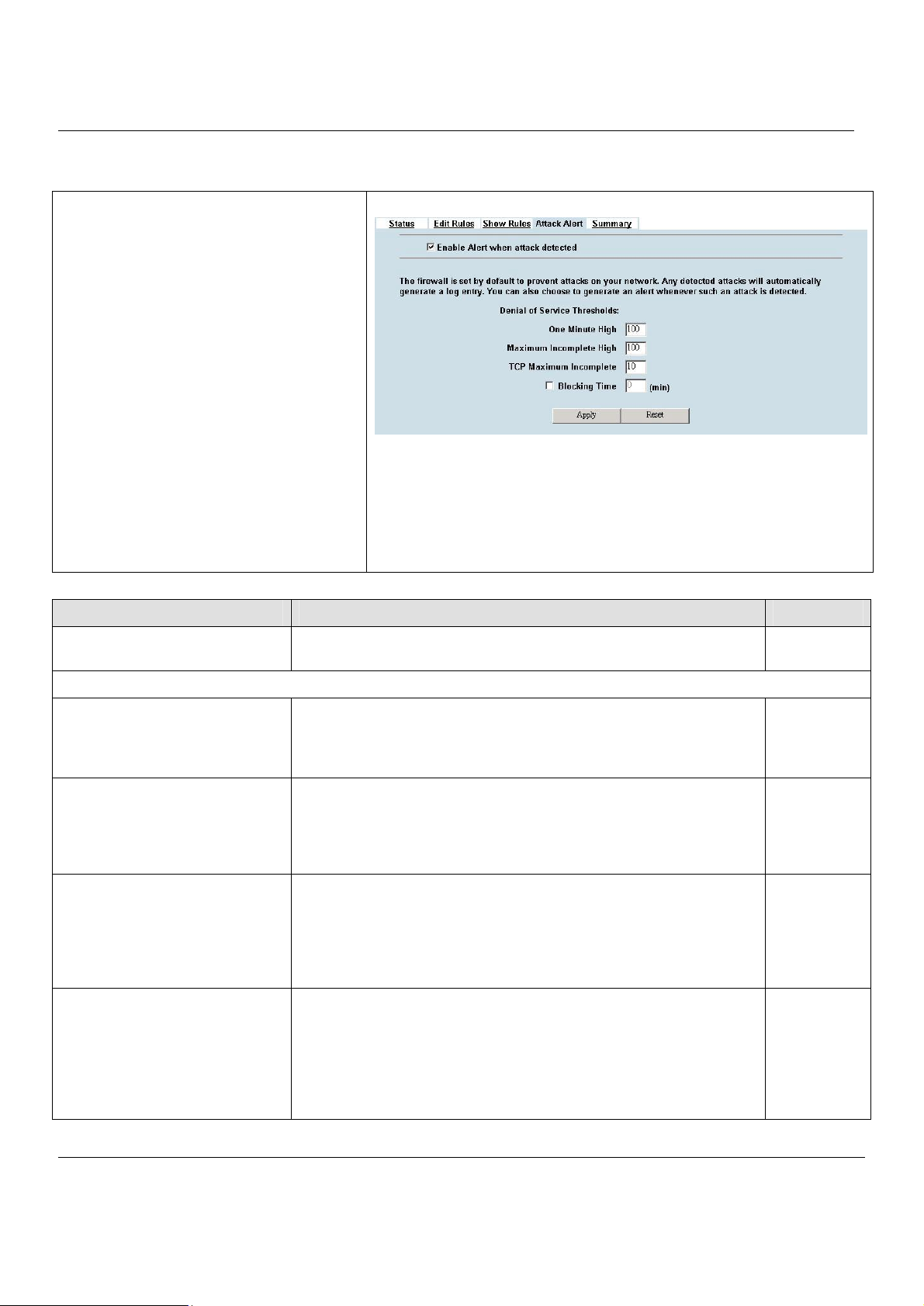
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 8
Firewall
8.4.2 Setup Alert detected attack
Step 1. Setup Attack Alert
With the Firewall enabled, the MH-5000 is already
equipped with an Anti-DoS engine within it.
Normal DoS attacks will show up in the log when
detecting and blocking such traffic. However,
Flooding attacks require extra parameters to
recognize. Check the Enable Alert when attack
detected checkbox. Enter 100 in the One Minute
High means that MH-5000 starts to generate
alerts and delete the half-open states if 100
half-open states are established in the last
minute. Enter 100 in the Maximum Incomplete
High means that MH-5000 starts to generate
alerts and delete half-open states if the current
number of half-open states reaches 100. Enter 10
in the TCP Maximum Incomplete means that
MH-5000 starts to generate alerts and delete
half-open states if the number of half-open states
towards a server (SYN-Flooding attack) reaches
10. Check the Blocking time if you want to stop
the traffic towards the server. During this blocking
time, the server can digest the loading.
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
Enable Alert when attack
Enable the firewall alert to detect Denial of Service (DoS) attack.
detected
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Attack Alert
Enabled
One Minute High
Maximum Incomplete High
TCP Maximum Incomplete
Blocking Time
Denial of Service Thresholds
This is the rate of new half –open sessions that causes the firewall to
start deleting half open sessions. When the rate of new connection
attempts rises above this number, the MH-5000 deletes half-open
sessions as required to accommodate new connection attempts.
This is the number of existing half-open sessions that causes the
firewall to start deleting half-open sessions. When the number of
existing half-open sessions rises above this number, the MH-5000
deletes half-open sessions as required to accommodate new
connection requests.
This is the number of existing half-open TCP sessions with the same
destination host IP address that causes the firewall to start dropping
half-open sessions to the same destination host IP address. Enter a
number between 1 and 999. As a general rule, you should choose a
smaller number for a smaller network, a slower system or limited
bandwidth.
When TCP Maximum Incomplete is reached you can choose if the
next session should be allowed or blocked. If you check Blocking
Time any new sessions will be blocked for the length of time you
specified in the next field (min) and all old incomplete sessions will
be cleared during this period. If you want strong security, it is better
to block the traffic for a short time, as will give the server some time
to digest the loading.
100
100
10
disabled
63
Page 71

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 8
Firewall
(min) Enter the length of Blocking Time in minutes. 0
Table 8-4 Setup the Denial of Service Thresholds of attack alert
64
Page 72

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 9
VPN Technical Introduction
Chapter 9
VPN Technical Introduction
This chapter introduces VPN related technology
9.1 VPN benefit
If you choose to implement VPN technology in your enterprise, then it may bring the following benefits to your company.
1. Authentication
Ensure the data received is the same as the data that was sent and that the claimed sender is in fact the actual sender.
2. Integrity
Ensure that data is transmitted from source to destination without undetected alteration.
3. Confidentiality
Guarantee the intended recipients know what was being sent but unintended parties cannot determine what was sent.
This is almost provided by data encryption.
4. Non-repudiation
The receiver being able to prove that the sender of some data did in fact send the data even though the sender might
later desire to deny ever having sent that data.
9.2 Related Terminology Explanation
9.2.1 VPN
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) logically provides secure communications between sites without the expense of leased
site-to-site lines. A secure VPN is a combination of encryption, tunneling, authentication, and access control used to
transport traffic over the Internet or any insecure TCP/IP networks.
9.2.2 IPSec
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is a standard-based VPN that offers flexible solutions for secure data communications
across a public network like the Internet. IPSec is built around a number of standardized cryptographic techniques to
provide confidentiality, data integrity and authentication at the IP layer.
9.2.3 Security Association
A Security Association (SA) is an agreement between two parties indicating what security parameters, such as keys and
algorithms they will use.
9.2.4 IPSec Algorithms
There are two types of the algorithms in the IPSec, including (1) Encryption Algorithms such as DES (Data Encryption
Standard), and 3DES (Triple DES) algorithms, and (2) Authentication Algorithms such as HMAC-MD5 (RFC 2403), and
HMAC-SHA1 (RFC 2404).
65
Page 73

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 9
VPN Technical Introduction
9.2.5 Key Management
Key Management allows you to determine whether to use IKE (ISAKMP) or manual key configuration in order to setup a
VPN.
Ø IKE Phases
There are two phases to every IKE (Internet Key Exchange) negotiation – phase 1 (Authentication) and phase 2 (Key
Exchange). A phase 1 exchange established an IKE SA and the second one uses that SA to negotiate SAa for IPSec.
In phase 1 you must:
n Choose a negotiation mode
n Authenticate the connection by entering a pre-shared key
n Choose an encryption algorithm
n Choose an authentication algorithm
n Choose a Diffie-Hellman public-key cryptography key group (DH1 or DH2).
n Set the IKE SA lifetime. This field allows you to determine how long IKE SA negotiation should proceed before
it times out. A value of 0 means IKE SA negotiation never times out. If IKE SA negotiation times out, then both
IKE SA and IPSec SA must be renegotiated.
In phase 2 you must:
n Choose which protocol to use (ESP or AH) for the IKE key exchange
n Choose an encryption algorithm
n Choose an authentication algorithm
n Choose whether to enable Perfect Forward Security (PFS) using Diffie-Hellman public-key cryptography
n Choose Tunnel mode or Transport mode
n Set the IPSec SA lifetime. This field allows you to determine how long IPSec SA setup should proceed before
it times out. A value of 0 means IPSec SA never times out. If IPSec SA negotiation times out, then the IPSec
SA must be renegotiated (but not the IKE SA).
Ø Negotiation Mode
The phase 1 Negotiation Mode you select determines how the Security Association (SA) will be established for each
connection through IKE negotiations.
n Main Mode ensures the highest level of security when the communicating parties are negotiating
authentication (phase 1). It uses 6 messages in three round trips (SA negotiation, Diffie-Hellman exchange
and an exchange of nonce (a nonce is a random number)). This mode features identity protection (your
identity is not revealed in the negotiation).
n Aggressive Mode is quicker than Main Mode because it eliminates several steps when the communicating
parties are negotiating authentication (phase 1). However the trade-off is that fast speed limits its negotiating
power and it also does not provide identity protection. It is useful in remote access situation where the address
of the initiator is not known by the responder and both parties want to use pre-shared key authentication.
Ø Pre-Shared Key
A pre-shared key identifies a communicating party during a phase 1 IKE negotiation. It is called “pre-shared” because
you have to share it with another party before you can communicate with them over a secure connection.
66
Page 74

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 9
VPN Technical Introduction
Ø Diffie-Hellman (DH) Key Groups
Diffie-Hellman (DH) is a public-key cryptography protocol that allows two parties to establish a shared secret over an
unsecured communications channel. Diffie-Hellman is used within IKE SA setup to establish session keys. 768-bit
(Group 1 – DH1) and 1024-bit (Group 2 – DH2) Diffie-Hellman groups are supported. Upon completion of the
Diffie-Hellman exchange, the two peers have a shared secret, but the IKE SA is not authenticated. For authentication,
use pre-shared keys.
Ø Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS)
Enabling PFS means that the key is transient. The key is thrown away and replaced by a brand new key using a new
Diffie-Hellman exchange for each new IPSec SA setup. With PFS enabled, if one key is compromised, previous and
subsequent keys are not compromised, because subsequent keys are not derived from previous keys. The
(time-consuming) Diffie-Hellman exchange is the trade-off for this extra security.
This may be unnecessary for data that does not require such security, so PFS is disabled (None) by default in the
MH-5000. Disabling PFS means new authentication and encryption keys are derived from the same root secret (which
may have security implications in the long run) but allows faster SA setup (by bypassing the Diffie-Hellman key
exchange).
9.2.6 Encapsulation
Ø Transport Mode
Transport mode is used to protect upper layer protocols and only affects the data in the IP packets. In Transport mode,
the IP packets contains the security protocol (AH or ESP) located after the original IP header and options, but before any
upper layer protocols contains in the packet (such as TCP and UDP).
With ESP, protection is applied only to the upper layer protocols contained in the packet. The IP header information and
options are not used in the authentication process. Therefore, the originating IP address cannot be verified for integrity
against the data.
With the use of AH as the security protocol, protection is extended forward into the IP header to verify the integrity of the
entire packet by use of portions of the original IP header in the hashing process.
Ø Tunnel Mode
Tunnel mode encapsulates the entire IP packet to transmit it securely. A Tunnel mode is required for gateway services to
provide access to internal system. Tunnel mode is fundamentally an IP tunnel with authentication and encryption. This is
the most common mode of operation. Tunnel mode is required for gateway to gateway and host to gateway
communications. Tunnel mode communication have two sets of IP headers:
n Outside header: The outside IP header contains the destination IP address of the VPN gateway.
n Inside header: The inside IP header contains the destination IP address of the final system behind the VPN
gateway. The security protocol appears after the outer IP header and before the inside IP header.
9.2.7 IPSec Protocols
The ESP and AH protocols are necessary to create a Security Association (SA), the foundation of an IPSec VPN. An SA
is built from the authentication provided by AH and ESP protocols. The primary function of key management is to
establish and maintain the SA between systems. Once the SA is established, the transport of data may commence.
Ø AH (Authentication Header) Protocol
AH protocol (RFC 2402) was designed for integrity, authentication, sequence integrity (replay resistance), and
non-repudiation but not for confidentiality, for which the ESP was designed.
67
Page 75

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 9
VPN Technical Introduction
In applications where confidentiality is not required or not sanctioned by government encryption restrictions, an AH can
be employed to ensure integrity. This type of implementation does not protect the information from dissemination but will
allow for verification of the integrity of the information and authentication of the originator.
Ø ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) Protocol
The ESP protocol (RFC 2406) provides encryption as well as some of the services offered by AH. ESP authenticating
properties are limited compared to the AH due to the non-inclusion of the IP header information during the authentication
process. However, ESP is sufficient if only the upper layer protocols need to be authenticated.
An added feature of the ESP is payload padding, which further protects communications by concealing the size of the
packet being transmitted.
9.3 Make VPN packets pass through MH-5000
Step 1. Enable IPSec
If we need to setup MH-5000 between the existed
IPSec / PPTP / L2TP connections. We need to
open up the Firewall blocking port of MH-5000 in
advance. Here we provide a simple way. You can
through enable the IPSec / PPTP / L2TP pass
through checkbox on this page. Then the VPN
connections of IPSec / PPTP / L2TP will pass
through MH-5000. As well as MH-5000 will play
the middle forwarding device role.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > Pass Through
68
Page 76
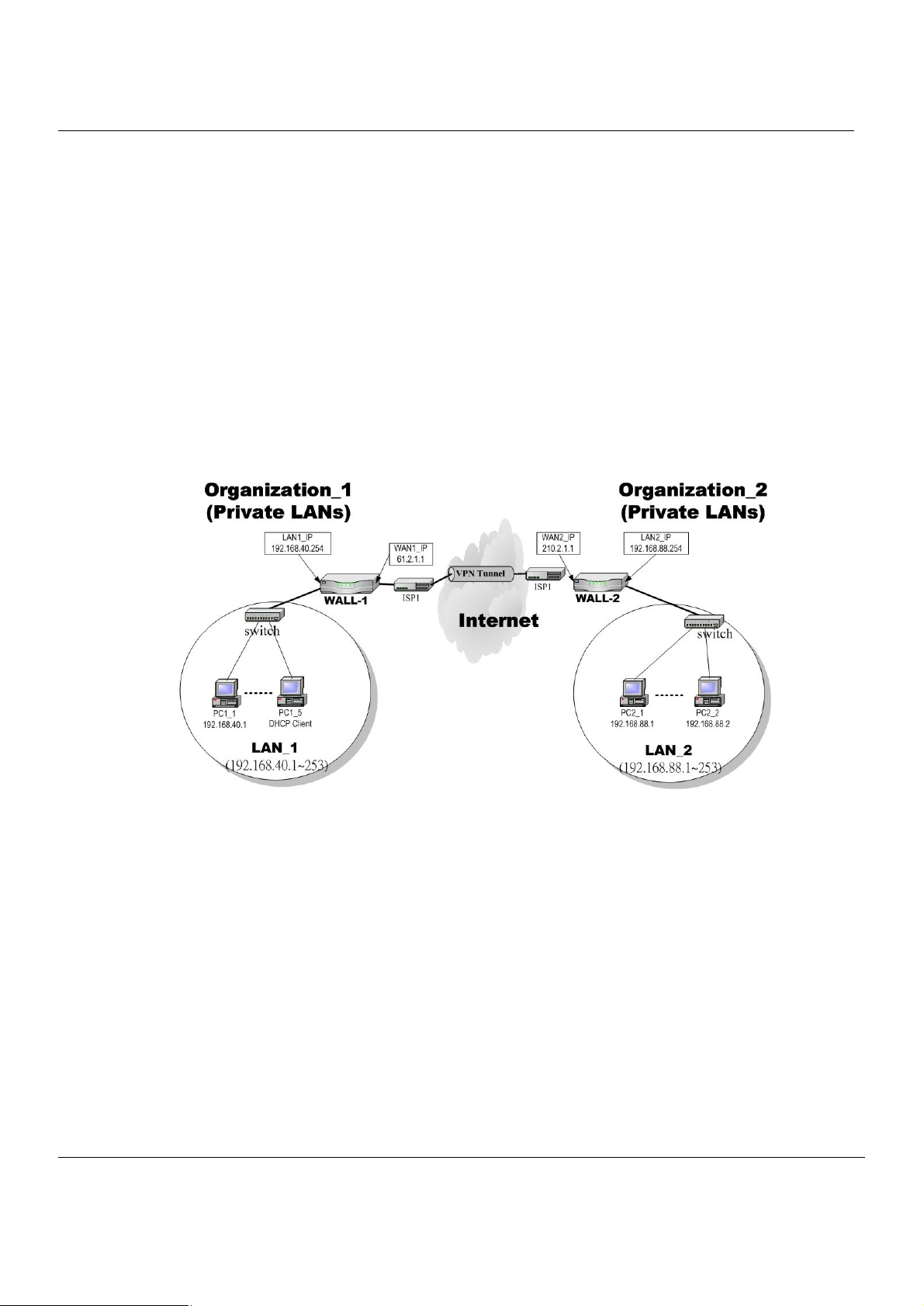
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
This chapter introduces IPSec VPN and explains how to implement it.
As described in the Figure 2-1, we will extend to explain how to make a VPN link between LAN_1 and LAN_2 in this
chapter. The following Figure 10-1 is the real structure in our implemented process.
10.1 Demands
1. When a branch office subnet LAN_1 wants to connect with another branch office subnet LAN_2 through the
public Internet instead of the expensive private leased lines, VPN can provide encryption and authentication to
secure the tunnel that connects these two LANs.
Figure 10-1 Organization_1 LAN_1 is making VPN tunnel with Organization_2 LAN_2
10.2 Objectives
1. Let the users in LAN_1 and LAN_2 share the resources through a secure channel established using the public
Internet.
10.3 Methods
1. Separately configure WALL-1 and WALL-2 which are the edge gateways of LAN_1 and LAN_2 respectively. You
have to determine a key management method between IKE (Internet Key Exchange) and Manual Key. The
following table compares the settings between IKE and Manual Key. In the following, we will describe them
separately.
69
Page 77

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
Same “Local Address” means the local LAN subnet; “Remote Address” means the remote LAN subnet; “My
Difference The “Pre-Shared Key” must be the same at
IKE Manual Key
IP Address” means the WAN IP address of the local VPN gateway while the “Peer’s IP Address”
means the WAN IP address of the other VPN gateway.
The types and keys of “Encryption” and
both MH-5000s.
Table 10-1 Compared IKE and Manual Key methods
“Authenticate” must be set the same on both
MH-5000s. However, the “Outgoing SPI” at
WALL-1 must equal to “Incoming SPI” at WALL-2,
and the “Outgoing SPI” at WALL-2 must equal to
“Incoming SPI” at WALL-1.
10.4 Steps
In the following we will separately explain the ways to set up a secure DES/MD5 tunnel with IKE and Manual key.
10.4.1 DES/MD5 IPSec tunnel: the IKE way
At WALL-1:
At the first, we will install the IPSec properties of WALL-1.
Step 1. Enable IPSec
Check the Enable IPSec checkbox and click
Apply.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
Enable IPSec Enable IPSec feature of MH-5000 Enabled
BUTTON DESCRIPTION
Apply Apply the settings which have been configured.
Table 10-2 Enable the IPSec feature
70
Page 78
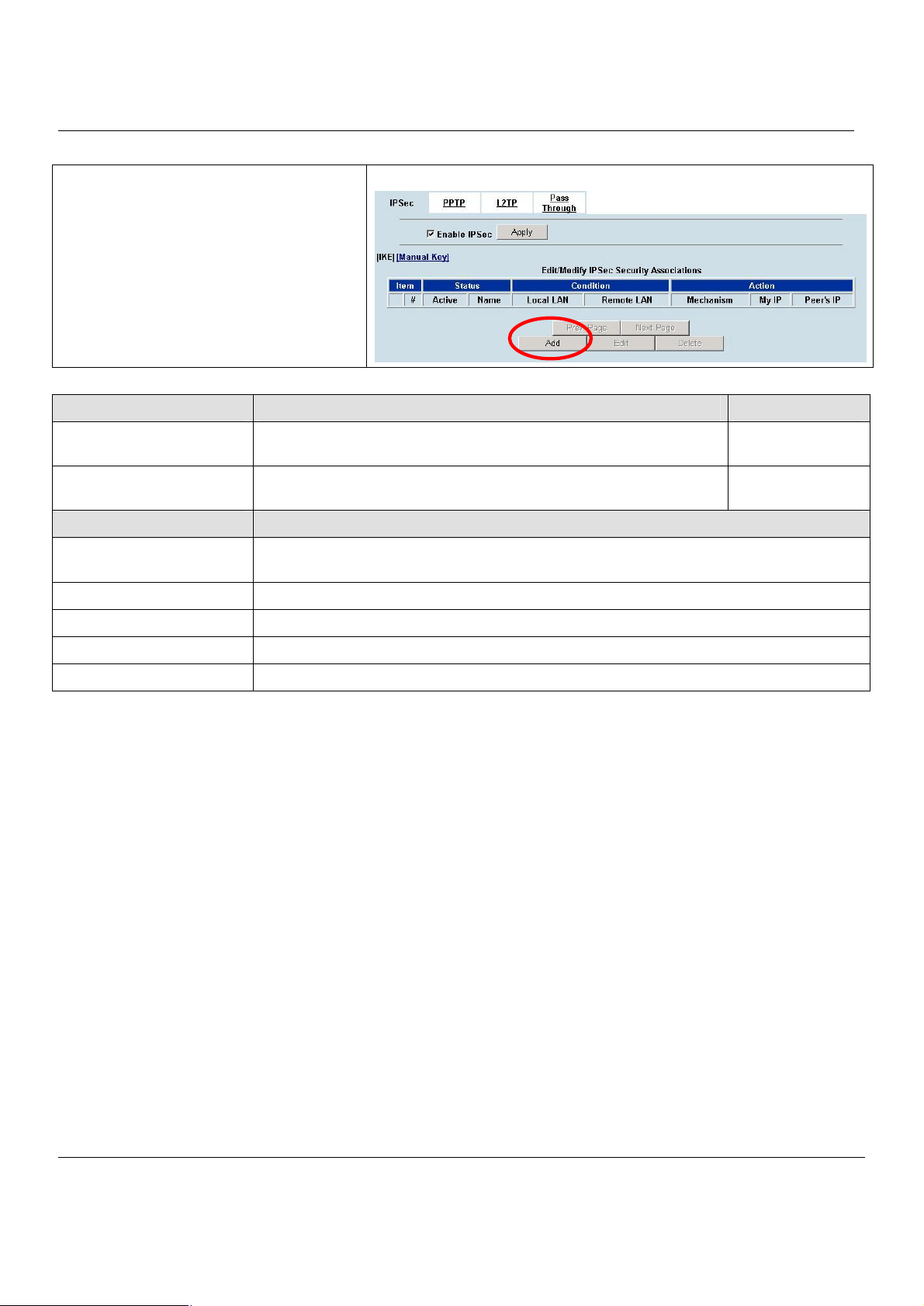
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
Step 2. Add an IKE rule
Click the IKE hyperlink and click Add to add a
new IPSec VPN tunnel endpoint.
FIELD DESCRIPTION EXAMPLE
IKE
Manual Key
BUTTON DESCRIPTION
Prev. Page If there are more than one action pages, you can press Prev. Page to back to the previous
Next Page
Add
Use the IKE (Internet Key Exchange) method to negotiate the key
used in building IPSec tunnel.
Use the key which you have been designated to build IPSec tunnel in
peer VPN device.
page.
If there are more than one action pages, you can press Next Page to go to the next page.
Insert a new IPSec rule.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > IKE
Selected
Non selected
Edit
Delete
Edit the properties of the indicated IPSec rule.
Delete the indicated IPSec rule.
Table 10-3 Add an IPSec policy rule
71
Page 79

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
Step 3. Customize the rule
Check the Active checkbox. Enter a name for this
rule like IKErule. Enter the Local IP Address
(192.168.40.0/255.255.255.0) and the Remote IP
Address (192.168.88.0/255.255.255.0). Select
the Outgoing Interface of this Multi-Homing
Security Gateway. Enter the public IP of the
opposite-side VPN gateway (210.2.1.1) in the
Peer’s IP Address. Click the ESP Algorithm and
select Encrypt and Authenticate (DES, MD5).
Enter the Pre-Shared Key as 1234567890. Click
the Apply button to store the settings. Note, In the
Action region. It should choose either ESP
Algorithm or AH Algorithm, or system will show
error message. If you hope to set the detailed
item of IKE parameter. Click the Advanced button
in this page. Otherwise it is ok to just leave the
value default.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > IKE > Add
Self local IP
Address
The opposite
side IP
Condition
Status
FIELD DESCRIPTION Range / Format
EXAMPLE
Active This field will activate this IPSec policy rule Enable/Disable Enabled
IKE Rule Name The name of this IPSec policy text string IKErule
Local Address
Type
Determine the method to connect to the
remote side of VPN by using the local
subnet or the local single host.
Subnet Address
/ Single
Address
Subnet Address
IP Address The local IP address IPv4 format 192.168.40.0
Prefix
Len/Subnet
The local IP Netmask
IPv4 format 255.255.255.0
Mask
Remote
Address Type
Determine the method to connect to the
local side of VPN by using the remote
subnet or the remote single host.
Subnet Address
/ Single
Address
Subnet Address
IP Address The remote IP address IPv4 format 192.168.88.0
Prefix
Len/Subnet
The remote IP Netmask
IPv4 format 255.255.255.0
Mask
72
Page 80
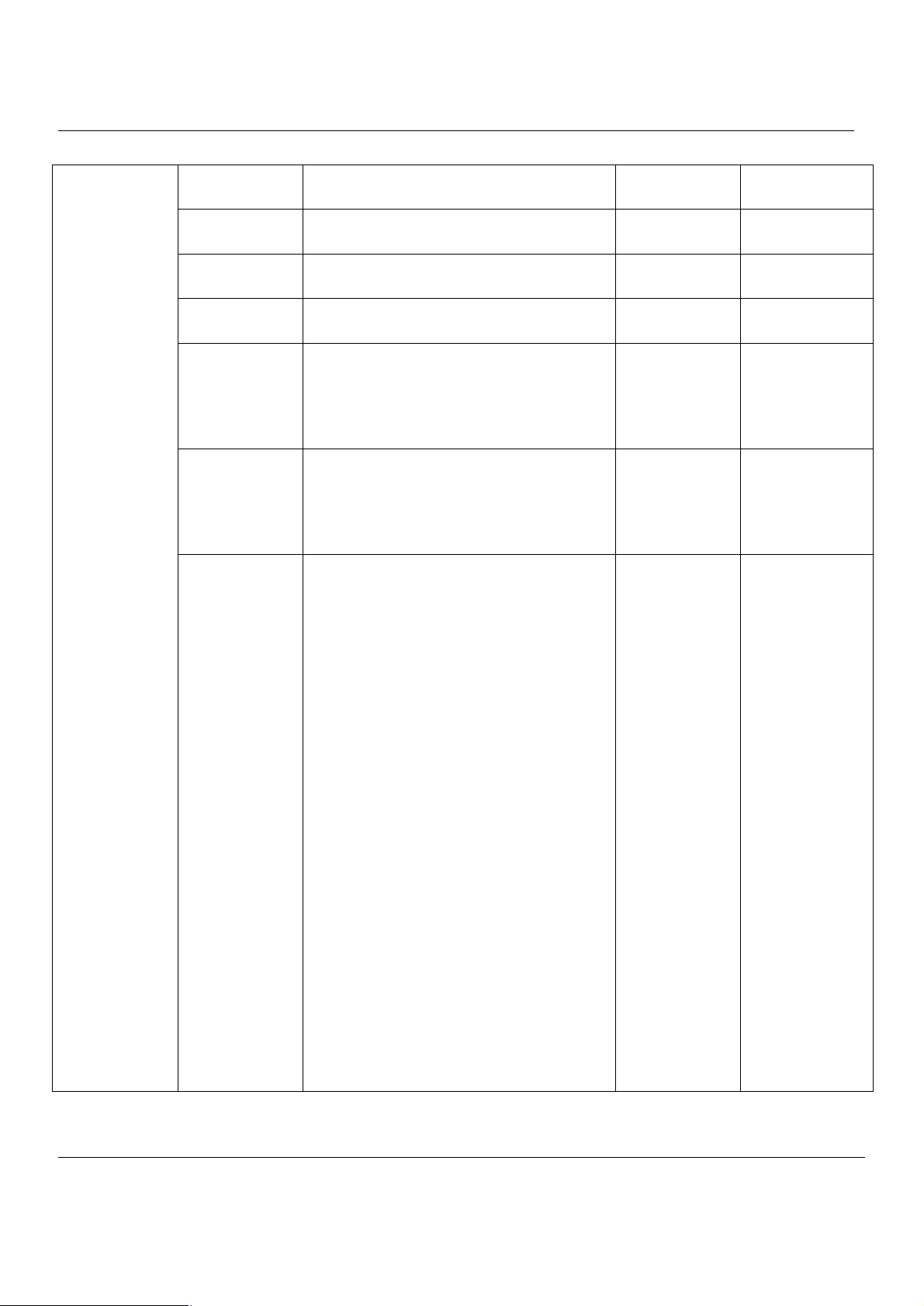
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
Action
Negotiation
Mode
Encapsulation
Mode
Outgoing
Interface
Peer’s IP
Address
My Identifier
Peer’s Identifier
ESP Algorithm
Choose Main or Aggressive mode, see
Chapter 9 for details.
Choose Tunnel or Transport mode, see
Chapter 9 for details.
The WAN interface you are going to build
IPSec tunnel with.
The IP address of remote VPN device. The
IP address may be fixed (Static) or dynamic.
Fill your information in this field. The filled
information will be provided for the IPSec
tunnel establishment.
Fill the information of peer VPN device in
this field. The filled information will be
provided for the IPSec tunnel establishment.
ESP Algorithm may be grouped by the items
of the Encryption and Authentication
Algorithms or execute separately.
We can select below items, the Encryption
and Authentication Algorithm combination or
the below item Authentication Algorithm
singly.
Here Encryption Algorithms include
DES(64 bits), 3DES(192 bits) and
AES(128/192/256 bits)
Authentication Algorithms include
MD5(128 bits) and SHA1(160 bits)
Main /
Aggressive
Tunnel /
Transport
WAN interfaces
Static IP /
Dynamic IP
IP Address /
FQDN (domain
name) /
User FQDN
(mail box)
IP Address /
FQDN (domain
name) /
User FQDN
(mail box)
Encrypt and
Authenticate
(DES, MD5) /
Encrypt and
Authenticate
(DES, SHA1) /
Encrypt and
Authenticate
(3DES, MD5) /
Encrypt and
Authenticate
(3DES, SHA1) /
Encrypt and
Authenticate
(AES, MD5) /
Encrypt and
Authenticate
(AES, SHA1) /
Encrypt only
(DES) /
Encrypt only
(3DES) /
Encrypt only
(AES) /
Authenticate
only (MD5) /
Authenticate
only (SHA1)
Main
Tunnel
WAN1
Static IP
210.2.1.1
IP Address
IP Address
Encrypt and
Authenticate
(DES, MD5)
73
Page 81

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
AH Algorithm Select Authentication Algorithm
Pre-Shared Key
Table 10-4 Related field explanation of adding an IPSec policy rule
Step 4. Detail settings of IPSec IKE
In this page, we will set the detailed value of IKE
parameter. Fill in the related field as Table 10-5
indicated to finish these settings.
The key which is pre-shared with remote
side.
Authenticate
(MD5) /
Authenticate
(SHA1)
text string 1234567890
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > IKE > Add >
Advanced
Disabled
Condition
Action
FIELD DESCRIPTION Range / Format EXAMPLE
Utilize this field to select some packets which
Transport Layer
Protocol
Enable Replay
Detection
Negotiation
Mode
Pre-Shared Key
are specified protocol (ANY, TCP, UDP). If
the packets are not the specified protocol will
not be allowed to pass through IPSec tunnels.
Whether is the “Replay Detection” enabled? NO / YES NO
Phase1
View only, it is set previously and can not be
edited again.
View only, it is set previously and can not be
edited again.
74
ANY / TCP / UDP TCP
Can not be edited Main
Can not be edited 1234567890
Page 82

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
Encryption
Algorithm
SA Life Time
Key Group
Encapsulation
Active Protocol
Choose a type of encryption and
authentication algorithm combination.
Set the IKE SA lifetime. A value of 0 means
IKE SA negotiation never times out. See
Chapter 9 for details.
Choose a Diffie-Hellman public-key
cryptography key group
Phase2
View only, it is set previously and can not be
edited again.
View only, it is set previously and can not be
edited again.
Encrypt and
Authenticate (DES,
MD5) /
Encrypt and
Authenticate (DES,
SHA1) /
Encrypt and
Authenticate (3DES,
MD5) /
Encrypt and
Authenticate (3DES,
SHA1)
0 ~ 9999999999
sec/min/hour
DH1 / DH2 / DH5 DH2
Can not be edited Tunnel
Can not be edited ESP
Encrypt and
Authenticate
(DES、MD5)
28800 sec
Encryption
Algorithm
Choose a type of encryption and
authentication algorithm combination or
singly.
Encrypt and
Authenticate (DES,
MD5) /
Encrypt and
Authenticate (DES,
SHA1) /
Encrypt and
Authenticate (3DES,
MD5) /
Encrypt and
Authenticate (3DES,
SHA1) /
Encrypt and
Authenticate (AES,
MD5) /
Encrypt and
Authenticate (AES,
SHA1) /
Encrypt only (DES) /
Encrypt only (3DES) /
Encrypt only (AES) /
Authenticate only
(MD5) / Authenticate
only (SHA1)
Encrypt and
Authenticate
(DES、MD5)
75
Page 83
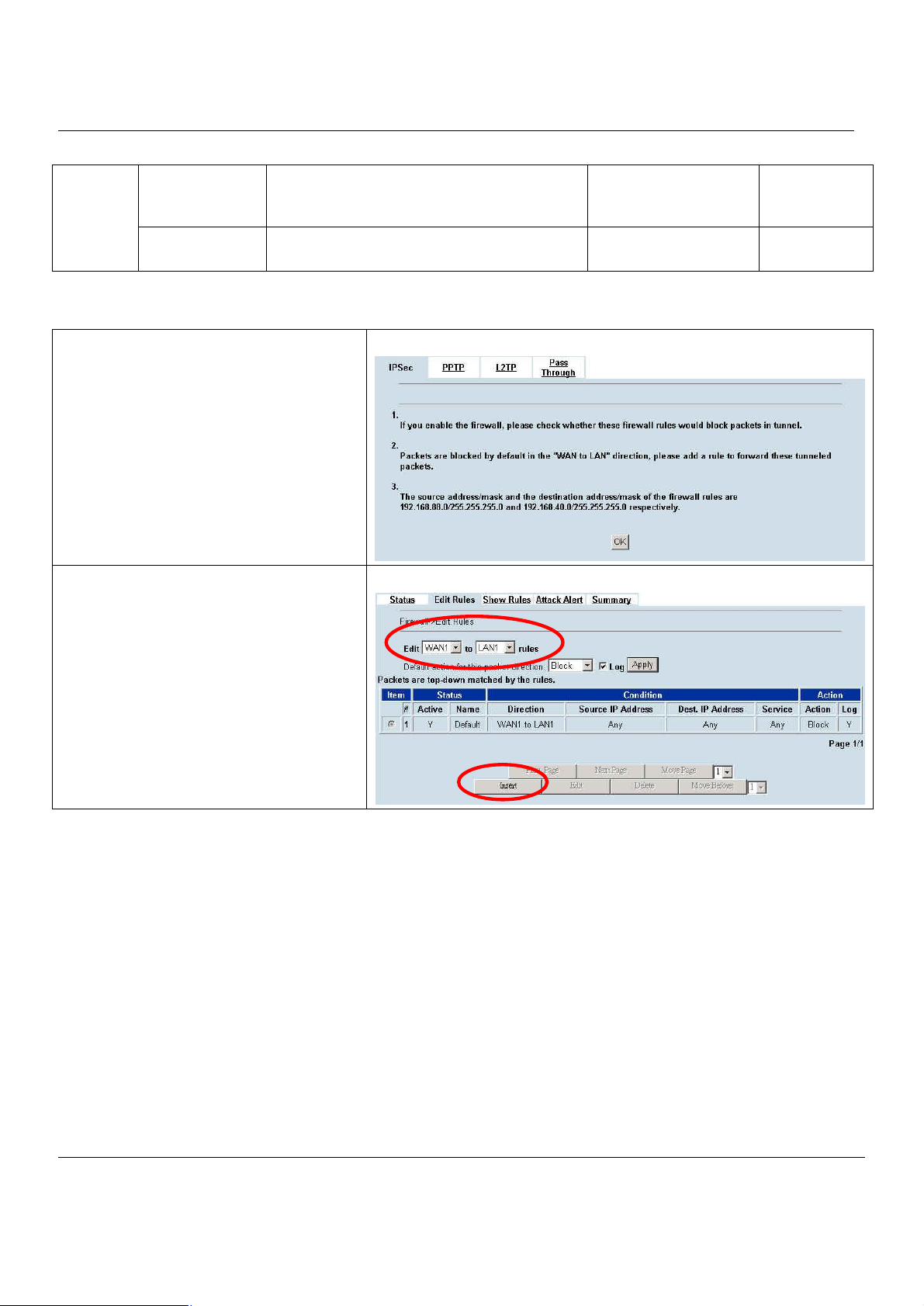
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
SA Life Time
Set the IPSec SA lifetime. A value of 0 means
IKE SA negotiation never times out. See
Chapter 9 for details.
Perfect Forward
Secrecy(PFS)
Enabling PFS means that the key is transient.
This extra setting will cause more security.
Table 10-5 Setup Advanced feature in the IPSec IKE rule
Step 5. Remind to add a Firewall rule
After finishing IPSec rule settings, we need to add
a firewall rule. Here system shows a window
message to remind you of adding a firewall rule.
Just press the OK button to add a firewall rule.
Step 6. Add a Firewall rule
Beforehand, please make sure that the Firewall is
enabled. Select WAN1-to-LAN1 to display the
rules of this direction. The default action of this
direction is Block with Logs. We have to allow the
VPN traffic from the WAN1 side to enter our LAN1
side. So we click the Insert button to add a
Firewall rule before the default rule.
0 ~ 9999999999
sec/min/hour
28800 sec
None / DH1 / DH2 /
DH5
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > IKE > Add
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules
DH1
76
Page 84

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
Step 7. Customize the Firewall rule
Check the Activate this rule. Enter the Rule Name
as AllowVPN, Source IP as 192.168.88.0, and
Dest. IP as 192.168.40.0. Click Apply to store this
rule.
Step 8. View the result
Here we have a new rule before the default
firewall rule. This rule will allow packets from
192.168.88.0 / 255.255.255.0 pass through
MH-5000. And accomplish the VPN tunnel
establishment.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules > Insert
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules
At WALL-2:
Here we will install the IPSec properties of WALL-2. Note that the “Local Address” and “Remote address” field are
opposite to the WALL-1, and so are “My IP Address” and “Peer’s IP Address” field.
Step 1. Enable IPSec
Check the Enable IPSec checkbox and click
Apply.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec
77
Page 85

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
Step 2. Add an IKE rule
Click the IKE hyperlink and click Add to add a
new IPSec VPN tunnel endpoint.
Step 3. Customize the rule
Check the Active checkbox. Enter a name for this
rule like IKErule. Enter the Local IP Address
(192.168.88.0/255.255.255.0) and the Remote IP
Address (192.168.40.0/255.255.255.0). Select
the Outgoing interface of this Multi-Homing
Security Gateway. Enter the public IP of the
opposite-side VPN gateway (61.2.1.1) in the
Peer’s IP Address. Click the ESP Algorithm and
select Encrypt and Authenticate (DES, MD5).
Enter the Pre-Shared Key as 1234567890. Click
the Apply button to store the settings. Note, in the
Action region, you should choose either ESP
Algorithm or AH Algorithm, or system will show
error message.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > IKE
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > IKE > Add
Self local IP
Address
The opposite
side IP
78
Page 86
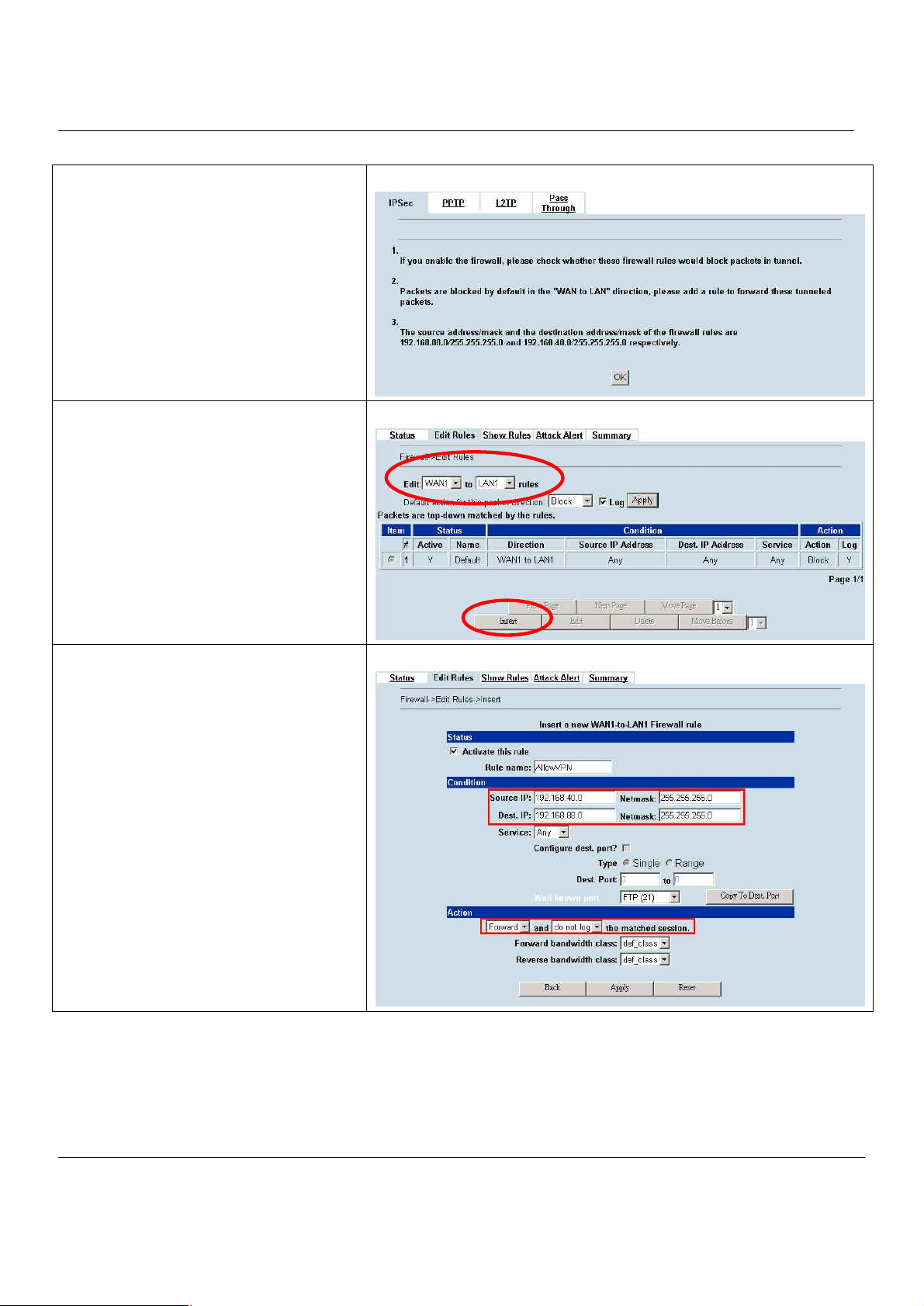
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
Step 4. Remind to add a Firewall rule
After finishing IPSec rule settings, we need to add
a firewall rule. Here system shows a window
message to remind you of adding a firewall rule.
Just press the OK button to add a firewall rule.
Step 5. Add a Firewall rule
Same as at WALL-1. We need to add an extra
firewall rule to allow IPSec packets to come from
internet. So here we select WAN1-to-LAN1
direction, and click Insert button.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > IKE > Add
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules
Step 6. Customize the Firewall rule
Check the Activate this rule. Enter the Rule Name
as AllowVPN, Source IP as 192.168.40.0, and
Dest. IP as 192.168.88.0. Click Apply to store this
rule.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules > Insert
79
Page 87

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
Step 7. View the result
Now we have inserted a new rule before the
default firewall rule. Any packets from
192.168.40.0/24 to 192.168.88.0/24 will be
allowed to pass through the MH-5000 and
successfully access the 192.168.88.0/24 through
the VPN tunnel.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules
10.4.2 DES/MD5 IPSec tunnel: the Manual-Key way
In the previous section, we have introduced IKE method. Here we will introduce another method using Manual-Key
way instead of IKE to install WALL-1.
At WALL-1:
At the first, we will use the Manual-Key way to install the IPSec properties of WALL-1.
Step 1. Enable IPSec
Check the Enable IPSec checkbox and click
Apply.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec
Step 2. Add a Manual Key rule
Click the Manual Key hyperlink and click Add to
add a new IPSec VPN tunnel endpoint.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > Manual Key
80
Page 88

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
Step 3. Customize the rule
Same as those in IKE. But there is no pre-shared
key in the manual-key mode. Enter the Key for
encryption, such as 1122334455667788. Enter
the Key for authentication, such as
11112222333344445555666677778888.
Additionally, the Outgoing SPI and Incoming SPI
have to be manually specified. Enter 2222 and
1111 respectively to the Outgoing SPI and the
Incoming SPI. Click Apply to store the rule.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > Manual Key > Add
Status
Condition
FIELD DESCRIPTION Range / Format EXAMPLE
Active This field will activate this IPSec policy rule Enable / Disable Enabled
Manual Key
Rule Name
Local Address
Type
The name of this IPSec policy text string
Determine the method to connect to the
remote side of VPN by using the local subnet
or the local single host.
Subnet Address /
Single Address
ManualKeyrul
e
Subnet
Address
IP Address The local IP address IPv4 format 192.168.40.0
PrefixLen /
Subnet Mask
Remote Address
Type
The local IP Netmask IPv4 format 255.255.255.0
Determine the method to connect to the local
side of VPN by using the remote subnet or
the remote single host.
Subnet Address /
Single Address
Subnet
Address
IP Address The remote IP address IPv4 format 192.168.88.0
PrefixLen /
Subnet Mask
The remote IP Netmask IPv4 format 255.255.255.0
81
Page 89

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
Action
Outgoing
Interface
Peer’s IP
Address
Outgoing SPI
Incoming SPI
Encapsulation
Mode
ESP –
Encryption /
Authentication
The WAN interface you are going to build
IPSec tunnel with.
The IP address of remote site device, like
MH-5000 Multi-Homing Security Gateway.
The Outgoing SPI (Security Parameter Index)
value.
The Incoming SPI (Security Parameter Index)
value.
Choose Tunnel or Transport mode, see
Chapter 9 for details.
Select the Encryption (DES, 3DES, AES or
Null) and Authentication (MD5, SHA1 or
NULL) Algorithm combination. And enter the
key either hex or string form separately.
Notice: You can not select both Encryption
and Authentication “NULL” type.
WAN interfaces WAN1
IPv4 format 210.2.1.1
hex(600 ~ 600000) /
dec(1500 ~ 6300000)
hex(600 ~ 600000) /
dec(1500 ~ 6300000)
Transport / Tunnel Tunnel
Encryption:
DES(64bits) /
3DES(192bits) /
AES(128, 192,
256bits) / NULL
Authentication:
MD5(128bits) /
SHA1(160bits) /
NULL
Input format:
hex{0-9,a-f,A-F}/
str{text string}
hex: 2222
hex: 1111
ESP –
Encryption
(DES) /
Authentication
(MD5)
AH Authentication
Step 4. Detail settings of IPSec Manual
Key
For the detailed setting in the Manual Key. We
can press the Advanced button in the previous
page. Then set the parameter separately.
Use the Authentication method only. And
enter the key either hex or string form.
Table 10-6 Add a IPSec Manual Key rule
MD5(128bits) /
SHA1(160bits)
Input format:
hex{0-9,a-f,A-F}/
str{text string}
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > Manual Key > Add
> Advanced
Disabled
82
Page 90

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
FIELD DESCRIPTION Range / Format EXAMPLE
Utilize this field to select some packets which
Condition
Transport Layer
Protocol
are specified protocol (ANY, TCP, UDP). If
the packets are not the specified protocol will
not be allowed to pass through IPSec tunnels.
Action
Enable Replay
Detection
Whether is the “Replay Detection” enabled?
Table 10-7 Setup Advanced feature in the IPSec Manual Key rule
Step 5. Remind to add a Firewall rule
After finishing IPSec rule settings, we need to add
a firewall rule. Here system shows a window
message to remind you of adding a firewall rule.
Just press the OK button to add a firewall rule.
ANY / TCP / UDP ANY
NO / YES NO
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > Manual Key > Add
Step 6. Add a Firewall rule
Same as that in IKE method. Please make sure
that the Firewall is enabled. Select
WAN1-to-LAN1 to display the rules of this
direction. The default action of this direction is
Block with Logs. We have to allow the VPN traffic
from the WAN1 side to enter our LAN1 side. So
we click the Insert button to add a Firewall rule
before the default rule.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules
83
Page 91
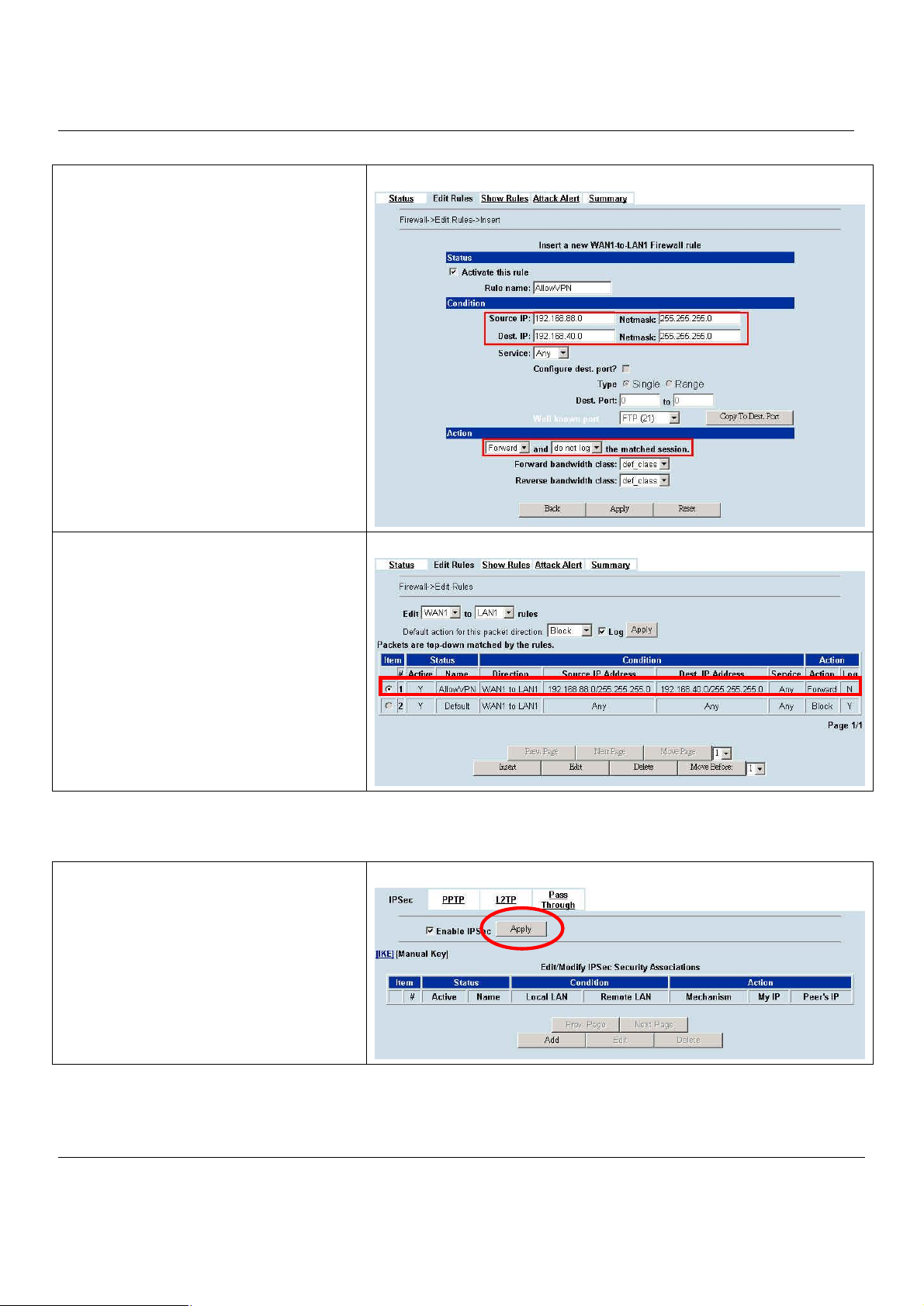
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
Step 7. Customize the Firewall rule
Check the Activate this rule. Enter the Rule Name
as AllowVPN, Source IP as 192.168.88.0, and
Dest. IP as 192.168.40.0. Click Apply to store this
rule.
Step 8. View the result
Here we have a new rule before the default
firewall rule. This rule will allow packets from
192.168.88.0 / 255.255.255.0 pass through
MH-5000. And accomplish the VPN tunnel
establishment.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules > Insert
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules
At WALL-2:
Second, we will use the Manual-Key way to install the IPSec properties of WALL-1.
Step 1. Enable IPSec
Check the Enable IPSec checkbox and click
Apply.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec
84
Page 92
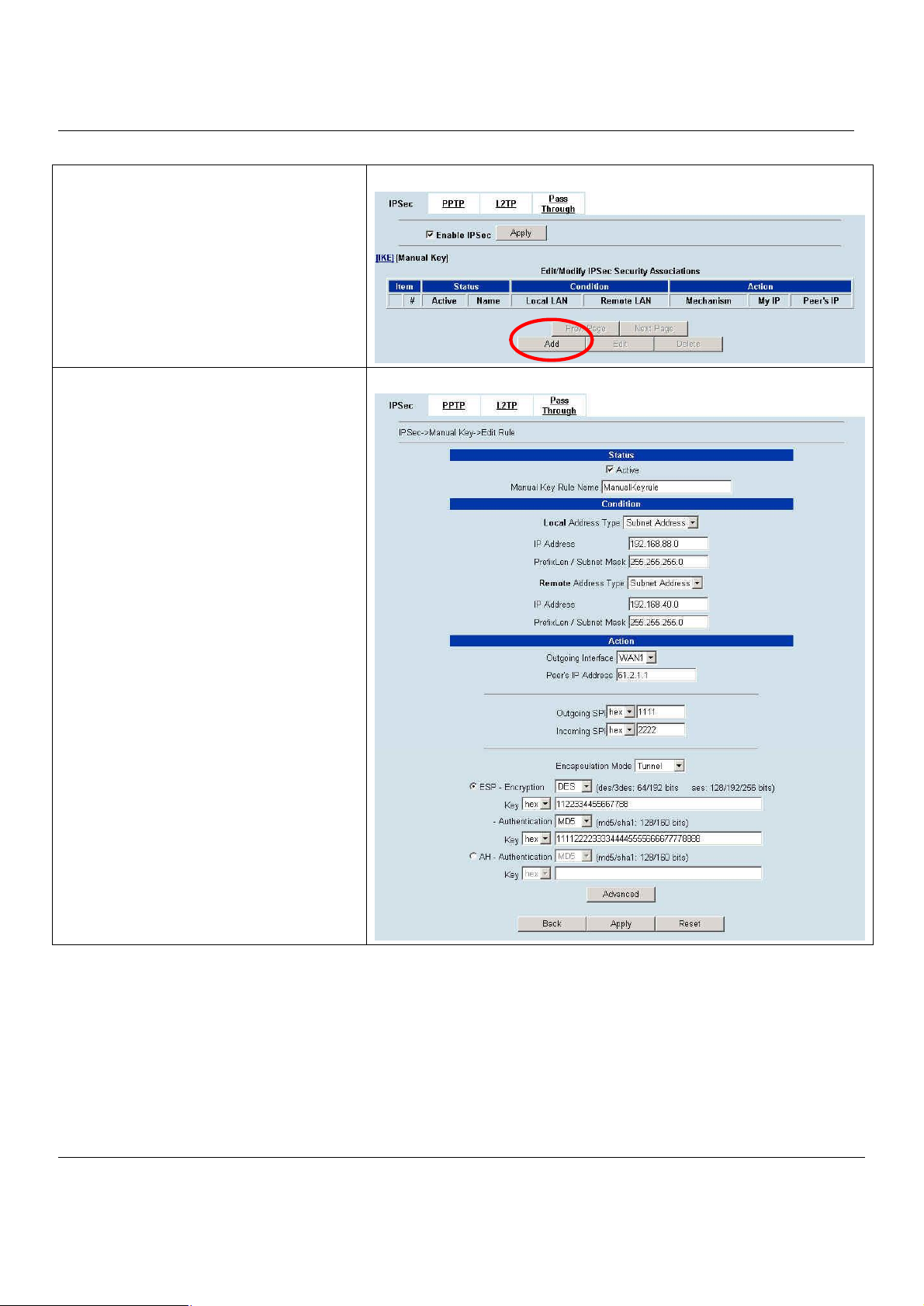
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
Step 2. Add a Manual Key rule
Click the Manual Key hyperlink and click Add to
add a new IPSec VPN tunnel endpoint.
Step 3. Customize the rule
Similar to those in WALL-1, except that you
should interchange the Local IP Address with
Remote IP Address in the Condition part and the
Outgoing SPI with the Incoming SPI in the Action
part. Besides, set the Peer’s IP Address with the
WAN1 IP address of WALL-1.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > Manual Key
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > Manual Key > Add
85
Page 93
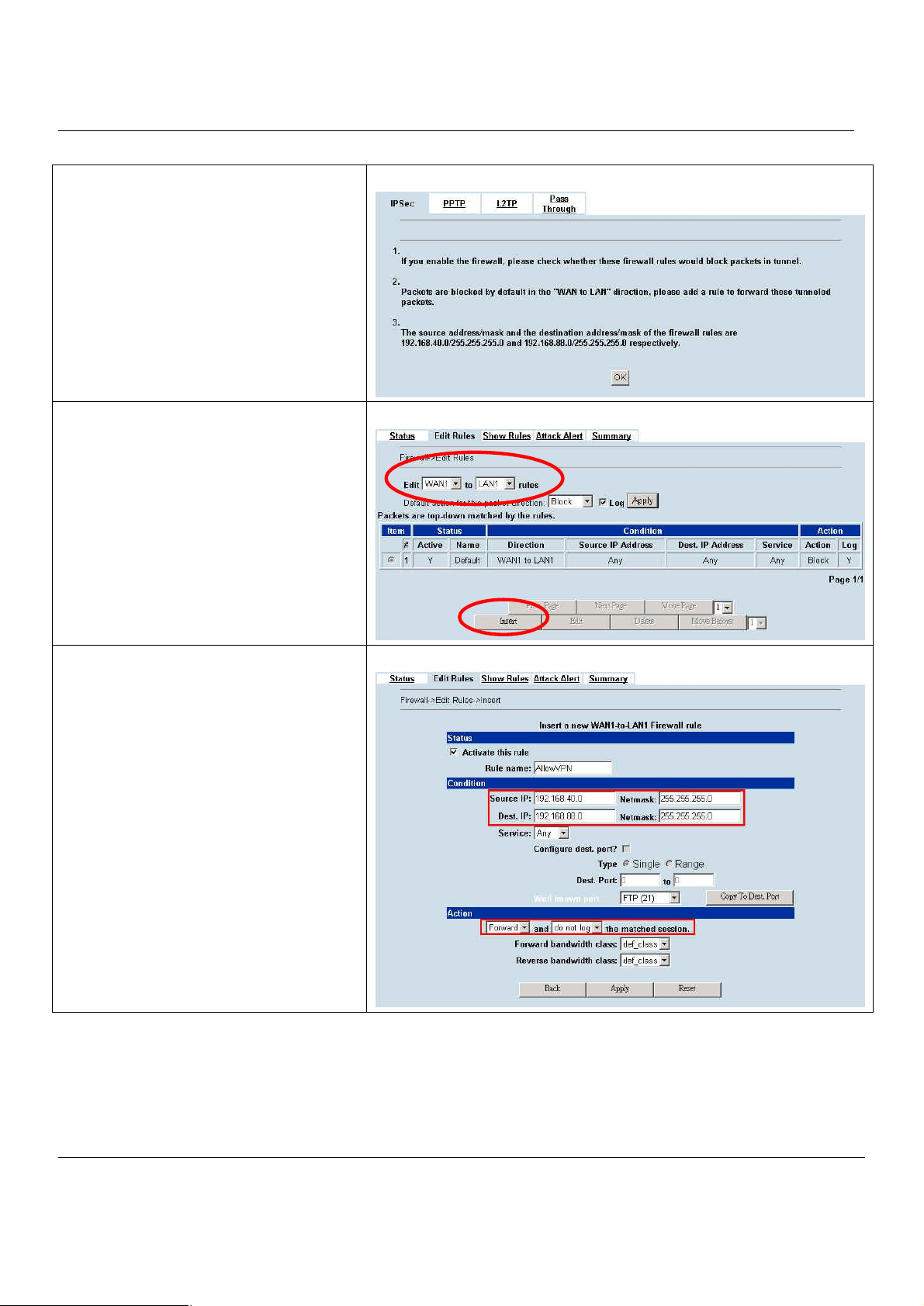
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 10
Virtual Private Network – IPSec
Step 4. Remind to add a Firewall rule
After finishing IPSec rule settings, we need to add
a firewall rule. Here system shows a window
message to remind you of adding a firewall rule.
Just press the OK button to add a firewall rule.
Step 5. Add a Firewall rule
Same as that in IKE method. Please make sure
that the Firewall is enabled. Select
WAN1-to-LAN1 to display the rules of this
direction. The default action of this direction is
Block with Logs. We have to allow the VPN traffic
from the WAN1 side to enter our LAN1 side. So
we click the Insert button to add a Firewall rule
before the default rule.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > Manual Key > Add
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules
Step 6. Customize the Firewall rule
Check the Activate this rule. Enter the Rule Name
as AllowVPN, Source IP as 192.168.40.0, and
Dest. IP as 192.168.88.0. Click Apply to store this
rule.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules > Insert
86
Page 94

MH-5000 User Manual 0
Step 7. View the result
Now we have inserted a new rule before the
default firewall rule. Any packets from
192.168.40.0/24 to 192.168.88.0/24 will be
allowed to pass through the MH-5000 and
successfully access the 192.168.88.0/24 through
the VPN tunnel.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules
87
Page 95

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 11
Virtual Private Network –Dynamic IPSec
Chapter 11
Virtual Private Network –Dynamic IPSec
This chapter introduces Dynamic IPSec VPN and explains how to implement it.
As described in the Figure 2-1, we will extend to explain how to make a dynamic VPN link between LAN_1 and LAN_2 in
this chapter. The following Figure 11-1 is the real structure in our implemented process.
11.1 Demands
1. When a branch office subnet LAN_1 wants to connect with another branch office subnet LAN_2 through the public
Internet instead of the expensive private leased lines, VPN can provide encryption and authentication to secure the tunnel
that connects these two LANs. If the remote VPN peer has a dynamically assigned IP address (DHCP or PPPoE) like
Organization_2, we have to use the Dynamic IPSec for the tunnel connection.
Figure 11-1 Organization_1 LAN_1 is making dynamic VPN tunnel with Organization_2 LAN_2
11.2 Objectives
1. Let the users in LAN_1 and LAN_2 share the resources through a secure channel established using the dynamic IPSec
VPN.
11.3 Methods
1. Separately configure WALL-1 and WALL-2 which are the edge gateways of LAN_1 and LAN_2 respectively.
88
Page 96
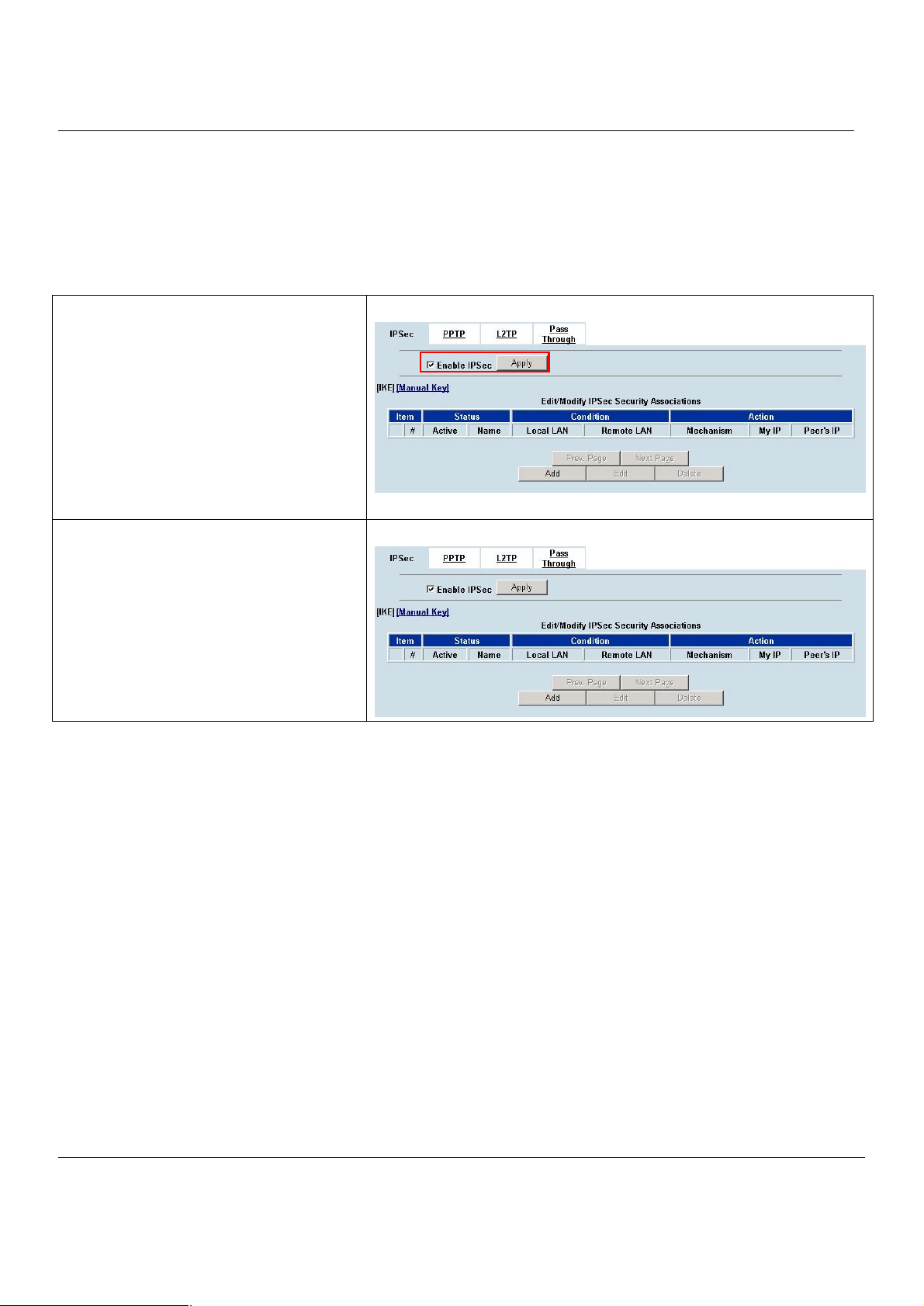
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 11
Virtual Private Network –Dynamic IPSec
11.4 Steps
In the following we will separately explain how to set up a secure DES/MD5 tunnel with the dynamic remote gateway IP
address type.
At WALL-1:
At the first, we will install the IPSec properties of WALL-1. For the related explanation, please refer to Chapter 9 and
Chapter 10.
Step 8. Enable IPSec
Check the Enable IPSec checkbox and click
Apply.
Step 9. Add an IKE rule
Click the IKE hyperlink and click Add to add a
new IPSec VPN tunnel endpoint.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > IKE
89
Page 97

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 11
side IP Address
Virtual Private Network –Dynamic IPSec
Step 10. Customize the rule
Check the Active checkbox. Enter a name for this
rule like IKErule. Enter the Local IP Address
(192.168.40.0/255.255.255.0) and the Remote IP
Address (192.168.88.0/255.255.255.0). Select
the Outgoing Interface of this Device. Select
Dynamic IP in the Peer’s IP Address. Be sure to
select Aggressive mode for the dynamic remote
gateway address type. Click the ESP Algorithm
and select Encrypt and Authenticate (DES, MD5).
Enter the Pre-Shared Key as 1234567890. Click
the Apply button to store the settings. Note, In the
Action region. It should choose either ESP
Algorithm or AH Algorithm, or system will show
error message. If you hope to set the detailed
item of IKE parameter. Click the Advanced button
in this page. Otherwise it is ok to just leave the
value default.
Note that Peers Identifier must NOT be IP
Address type in the Dynamic IP type. So, you
have to select FQDN (domain name) or user
FQDN (mailbox) as the Peer’s Identifier.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > IKE > Add
Self local IP
Address
The opposite
90
Page 98
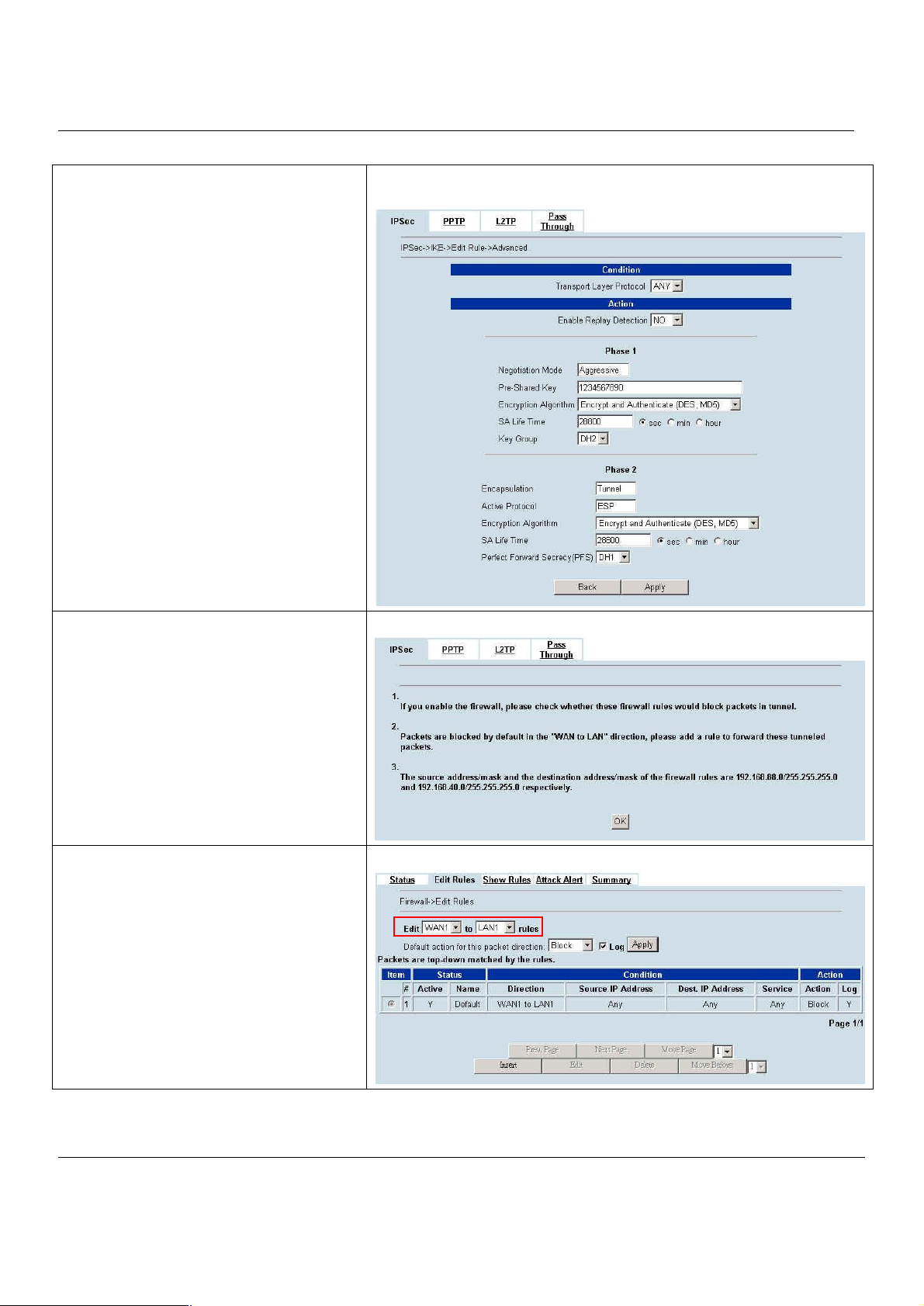
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 11
Virtual Private Network –Dynamic IPSec
Step 11. Detail settings of IPSec IKE
In this page, we will set the detailed value of IKE
parameter. For the related field, please refer to
Table 10-5 indicated.
Step 12. Remind to add a Firewall rule
After finishing IPSec rule settings, we need to add
a firewall rule. Here system shows a window
message to remind you of adding a firewall rule.
Just press the OK button to add a firewall rule.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > IKE > Add >
Advanced
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > IKE > Add
Step 13. Add a Firewall rule
Beforehand, please make sure that the Firewall is
enabled. Select WAN1-to-LAN1 to display the
rules of this direction. The default action of this
direction is Block with Logs. We have to allow the
VPN traffic from the WAN1 side to enter our LAN1
side. So we click the Insert button to add a
Firewall rule before the default rule.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules
91
Page 99
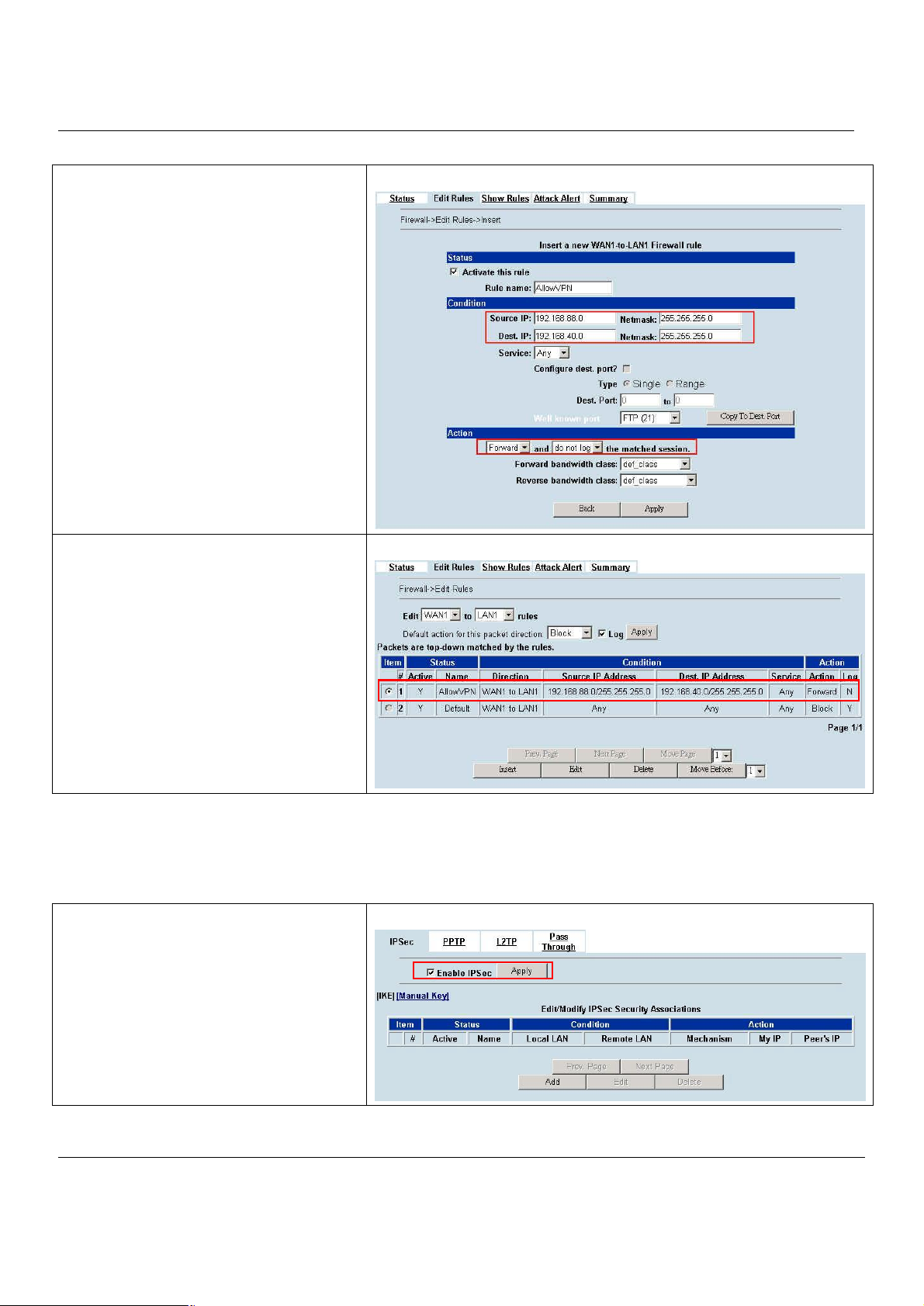
MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 11
Virtual Private Network –Dynamic IPSec
Step 14. Customize the Firewall rule
Check the Activate this rule. Enter the Rule Name
as AllowVPN, Source IP as 192.168.88.0, and
Dest. IP as 192.168.40.0. Click Apply to store this
rule.
Step 15. View the result
Here we have a new rule before the default
firewall rule. This rule will allow packets from
192.168.88.0 / 255.255.255.0 pass through
MH-5000. And accomplish the VPN tunnel
establishment.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules > Insert
ADVANCED SETTINGS > Firewall > Edit Rules
At WALL-2:
Here we will install the IPSec properties of WALL-2. Note that the “Local Address” and “Remote address” field are opposite
to the WALL-1, and so are “My IP Address” and “Peer’s IP Address” field.
Step 16. Enable IPSec
Check the Enable IPSec checkbox and click
Apply.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec
92
Page 100

MH-5000 User Manual Chapter 11
side IP Address
Virtual Private Network –Dynamic IPSec
Step 17. Add an IKE rule
Click the IKE hyperlink and click Add to add a
new IPSec VPN tunnel endpoint.
Step 18. Customize the rule
Check the Active checkbox. Enter a name for this
rule like IKErule. Enter the Local IP Address
(192.168.88.0/255.255.255.0) and the Remote IP
Address (192.168.40.0/255.255.255.0). Be sure
to select Aggressive mode to match the WALL-1
settings. Select the Outgoing interface of this
Device. Enter the public IP of the opposite-side
VPN gateway (61.2.1.1) in the Peer’s IP Address.
Click the ESP Algorithm and select Encrypt and
Authenticate (DES, MD5). Enter the Pre-Shared
Key as 1234567890. Select User FQDN
(mailbox) and enter planet.com.tw in My Identifier
field. Click the Apply button to store the settings.
Note, in the Action region, you should choose
either ESP Algorithm or AH Algorithm, or system
will show error message.
Note that one of the Peer’s IP Addresses is Static
IP, and the other must be the Dynamic IP while
using Dynamic IPSec VPN type to establish the
VPN tunnel.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > IKE
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > IKE > Add
Self local IP
Address
The opposite
Step 19. Remind to add a Firewall rule
After finishing IPSec rule settings, we need to add
a firewall rule. Here system shows a window
message to remind you of adding a firewall rule.
Just press the OK button to add a firewall rule.
ADVANCED SETTINGS > VPN Settings > IPSec > IKE > Add
93
 Loading...
Loading...