Page 1

10/100/1000Mbps
Intelligent Ethernet Switch
MGSW-2402
User’s Manual
Page 2

Trademarks
Copyright PLANET Technology Corp. 2002.
Contents subject to revision without prior notice.
PLANET is a registered trademark of PLANET Technology Corp. All other trademarks
belong to their respective owners.
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if
not installed and used in accordance with the Instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely
to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference
at his own expense.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference, in
which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Revision
PLANET WEBSwitch User's Manual
FOR MODEL: MGSW-2402
Part No.:
EMMGSW24-1
- 2 -
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. INTROUCTION ........................................................................................................................................4
1.1 C
HECKLIST
1.2 A
BOUT THE SWITCH
1.3 F
EATURES
...............................................................................................................................4
..................................................................................................................4
................................................................................................................................4
2. HARDWARE DESCRIPTION................................................................................................................6
2.1 F
RONT PANEL
2.2 R
EAR PANEL
2.3 H
ARDWARE INSTALLATION
...........................................................................................................................6
.............................................................................................................................6
.........................................................................................................7
3. WEB-BASED MANAGEMENT..............................................................................................................8
3.1 C
ONFIGURATION
3.2 W
EB PAGES
3.3 H
OME
3.4 M
ODULES
3.5 P
ORTS
3.6 S
TATISTICS
....................................................................................................................................9
..................................................................................................................................10
.......................................................................................................................8
.............................................................................................................................8
...............................................................................................................................10
.............................................................................................................................11
3.7 VLAN ..................................................................................................................................11
3.8 TRUNK .................................................................................................................................12
3.9 STP (S
3.10 P
ORT SECURITY
3.11 P
ORT PRIORITY
3.12 P
ORT PRIORITY
PANNING TREE PROTOCOL
....................................................................................................................14
-802.1
- T
........................................................................................................14
P
YPE OF SERVICE
) .........................................................................................13
........................................................................................15
3.13 IGMP ..................................................................................................................................16
3.14 S
TATIC ADDRESS
3.15 B
ROADCAST STORM FILTER
3.16 P
ORT MIRRORING
3.17 IP C
ONFIG
..................................................................................................................16
...................................................................................................17
..................................................................................................................17
............................................................................................................................18
3.18 SNMP..................................................................................................................................19
3.19 S
3.20 U
& R
AVE
PGRADE
...................................................................................................................19
EBOOT
.............................................................................................................................20
4. CONSOLE INTERFACE.......................................................................................................................22
4.1 CONNECT TO PC................................................................................................................22
4.2 M
AIN MENU
............................................................................................................................22
4.2.1. Device settings............................................................................................................................23
4.2.2. Port Settings...............................................................................................................................23
4.2.3. Address Table.............................................................................................................................24
4.2.4. Spanning Tree Protocol..............................................................................................................24
4.2.5 Broadcast Storm Filter.................................................................................................................25
4.2.6. IGMP..........................................................................................................................................25
4.2.7. VLAN Mode (2 modes)...............................................................................................................26
4.2.8. VLAN for CPU (2 VLANs)..........................................................................................................26
4.2.9 Secure IP for Telnet and HTTP...................................................................................................26
4.2.10. Save Current Settings...............................................................................................................27
4.2.11 Factory Default Settings & Reboot System ...............................................................................27
4.2.12 Reboot System ...........................................................................................................................28
4.2.13 Quit............................................................................................................................................28
5. SOFTWARE UPGRADE PROCEDURE.............................................................................................29
APPENDIX A NETWORKING CONNECTION....................................................................................30
APPENDIX B TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS...................................................................................31
- 3 -
Page 4

1. INTROUCTION
1.1 Checklist
Check the contents of your package for following parts:
-- MGSW-2402
-- User's manual CD
-- Power cord
-- 19” rack mount kit
-- RS-232 cable
-- Quick Installation Guide
If any of these pieces are missing or damaged, please contact your dealer immediately, if
possible, retain the carton including the original packing material, and use them against to
repack the product in case there is a need to return it to us for repair.
1.2 About the Switch
The MGSW-2402 Intelligent Switch is designed to provide your network with Ethernet, Fast
Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet connectivity over twisted pair and fiber optic cabling.
Two expansion slots on the front panel of the MGSW-2402 Intelligent Switch further add to the
flexibility of the systems.
The MGSW-2402 Intelligent Switch is a combination of 24x10/100M Ethernet RJ-45 ports and 2
optional module slots.
The two optional modules can be 8-Port 10/100 auto-sensing Intelligent Switch Module, 4-Port
100 Base-FX Intelligent Fiber Module, Gigabit 1000Base-T Intelligent Switch Modules, and
Gigabit 1000Base-SX/LX Intelligent Fiber Modules.
With its build-in Web-based Management, managing and configuring the MGSW-2402
Intelligent Switch becomes easier.
From cabinet management to port-level control and monitoring, you can visually configure and
manage your network via Web Browser, just click your mouse instead of typing cryptic command
strings. However, the MGSW-2402 Intelligent Switch can also be managed via Telnet, Console,
or third-party SNMP Management.
1.3 Features
-- Complies with the IEEE802.3 Ethernet, IEEE802.3u Fast Ethernet , IEEE802.3z and
IEEE802.3ab Gigabit Ethernet standard
-- Provide 2 module slots for 1000Mbps-T or 1000Mbps-SX/LX, 100Mbps-FX, 10/100Mbps-TX
option of modules
-- Features Store-and-Forward mode with wire-speed filtering and forwarding rates
-- Auto-negotiation & Full-duplex/Half-duplex
-- Automatic source address learning and aging
-- Support up to 4K MAC address
-- Support IEEE802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol
-- IEEE802.3x compliant full-duplex flow control
-- Broadcast storm control, runt and CRC Filtering eliminates erroneous packets to optimize the
network bandwidth
-- Support to handle up to 1522 bytes packet
-- LED indicators for simple diagnostics and management
- 4 -
Page 5

-- Internal power supply
-- Auto MDI/ MDI-X on each port
-- Network management configuration:
Web-based management
−
− Console and Telnet Configuration
− SNMP network management
− IEEE 802.1Q Tagging VLAN ( 256 VLAN Group )
− IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol ( STP )
− Port Trunking supported
− IGMP and Sniffer ( Port Mirroring ) supported
− Port Priority - 802.1p & TOS ( Type of Service ) supported
− Static Address Table for manual address addition
− Broadcast Storm Filter function supported
− Firmware upgradeable through TFTP
- 5 -
Page 6

2. HARDWARE DESCRIPTION
This product series provide three different running speed – 10Mbps, 100Mbps, and 1000Mbps in
the same switch and automatically distinguish the speed of incoming connection.
This section describes the hardware features of these Switches. For easier management and
control of the switch, familiarize yourself with its display indicators, and ports. Front panel
illustrations in this chapter display the unit LED indicators. Before connecting any network device
to the switch, read this chapter carefully
There are following option module for expansion:
-- 8-Port 10/100 auto-sensing Intelligent Switch Module
-- 4-Port 100 Base-FX Intelligent Fiber Module
-- Gigabit 1000Base-T Intelligent Switch Module
-- Gigabit 1000Base-SX/LX Intelligent Fiber Module
2.1 Front Panel
The Front Panel of the MGSW-2402 Intelligent Switch consists of 24x auto-sensing 10/100Mbps
Ethernet RJ-45 Ports, two optional expansion slots, and Console port. The LED Indicators are
also located on the front panel of the Switch.
MGSW-2402 Switch front panel
LED indicators
MGSW-2402
PWR Green Lit on: Power on
Lit off: power off
Diag. Red Lit on: Alert and problem notice
100 Green Lit on: the port run at 100Mbps
Lit off: the port run at 10Mbps
LNK/ACT Green Lit on: the connection is good.
Blink: The port is receiving or transmitting data
FDX/ COL
Yellow Lit on: the port run at full-duplex
Blink: Half-Duplex/ Collision
Off: Half-duplex or not connected
2.2 Rear Panel
The rear panel of the Switch indicates an AC inlet power socket and an on/off switch which
accepts input power from 100 to 240VAC, 50-60Hz.
MGSW-2402 Switch rear panel
- 6 -
Page 7

Power Notice:
1. The device is a power-required device, it means, it will not work till it is powered. If your
networks should active all the time, please consider using UPS (Uninterrupted Power
Supply) for your device. It will prevent you from network data loss or network downtime.
2. In some area, installing a surge suppression device may also help to protect your switch
from being damaged by unregulated surge or current to the Switch or the power adapter.
2.3 Hardware Installation
2.3.1 Connecting end node or hub or switch
1. Place the Switch on a smooth surface or fasten the mounting brackets with the provided
screws in a standard 19” rack.
2. Connect switch or PC to one port of the Switch using Category 3/4/5 UTP/STP cabling.
3. Connect another switch or PC to the other port of Switch by following the same process
as described in Step2.
Notice:
Cable distance for Switch
The cable distance between Ethernet Switch and hub/PC should not exceed 100 meter
for UTP/STP cable, 220m for 62.5/125 fiber cable and 500m for 50/125 fiber cable.
Make sure the wiring is correct
It can be used Category 3/4/5 cable in 10 Mbps operation. To reliably operate your
network at 100Mbps and 1000Mbps, you must use an Unshielded Twisted-Pair (UTP)
Category 5 cable, or better Data Grade cabling. While a Category 3 or 4 cable may
initially seem to work, it will soon cause data loss.
2.3.2 Connecting to Network Backbone or Server
Connect to the Gigabit Ethernet ports with Category 5 copper cable or fiber optic cable for
uplinking to a network backbone or network server. These ports operate at 1000Mbps in
full-duplex mode. A valid connection is indicated when the Link LED is light. The following
sections describe the function of LEDs on the front panel
- 7 -
Page 8

3. WEB-BASED MANAGEMENT
This chapter describes how to manage the Switch through the at-hand browser like Internet
Browser IE 4.0 or Netscape Communicator 4.x or above. Please check the JAVA applet is
enabled in your browser’s option or preference.
3.1 Configuration
The management function of this interface runs as an unsigned Java applet. As a result, your
browser's security setting should be set as following:
For Netscape 4 or later:
1.Click on Edit
2.Pick up Preferences item
3.Select the Advanced category
4.Make sure Enable Java is checked
5.Make sure Enable JavaScript is checked
ress OK
6.P
For Internet Explorer 4:
1.Click on View
2.Pick up Internet Options
3.Select the Security tab
4.Set Zone to Local Intranet
5.Click Add Sites, click Advanced and add the IP address of the switch to the zone
6.Set the security level to Custom
7.Press the Setting… button
8.Scroll down and set Java permissions to Custom
9.Press the Java Custom Settings button
10.Select the Edit Permissions tab
11.Set Run Unsigned Content to Enable
12.Press OK for all open dialog windows
For Internet Explorer 5:
1.Click on Tools
2.Pick Internet Options
3.Select the Security tab
4.Select Local Intranet (click on the icon)
5.Click on Sites, click Advanced and add the IP address of the switch to the zone
6.Click on Custom Level
7.Scroll down and set Java Permissions to Custom
8.Press the Java Custom Settings button
9.Select the Edit Permissions tab
10.Set Run Unsigned Content to Enable
11.Press OK for all open dialog windows
3.2 Web Pages
The arrangement of the Switch homepage consists of traditional web site hyperlinks
for associated information and Java windows for system management.
Upon connecting to the switch via a web browser (i.e. Netscape Navigator 4.0), Key in
the IP address of the switch or the alias name. The login screen will appear prompting
for an administrator user name and password. Enter the password to access the
switch’s management mode. (or simply hit Enter if password protection is disabled). If
a password box does not appear in the window, it means that the web browser’s
security setting is not correct for the JAVA applet. Section 3.1 outlines the correct
browser settings.
- 8 -
Page 9

Figure 3-1 : Password Screen
The default user name and password is "root". After the password is entered you will
see the main menu screen.
Figure 3-2: The start up screen of MGSW-2402 Web Page
3.3 Home
The Home page displays the configuration of the MGSW-2402 Intelligent Switch.
System Name An administratively-assigned name of the managed unit
System Location The physical location of this managed unit
System Contact
System Up Time The time last since the managed unit
IP Address The IP address of the managed unit
Subnet Mask The subnet mask of the managed unit
Default Gateway The default Gateway of the managed unit
MAC Address The MAC address of the managed unit
Console The RS232 Console setting of the managed unit
Firmware Version The firmware version of the managed unit
- 9 -
The contact person for this managed unit.
Page 10
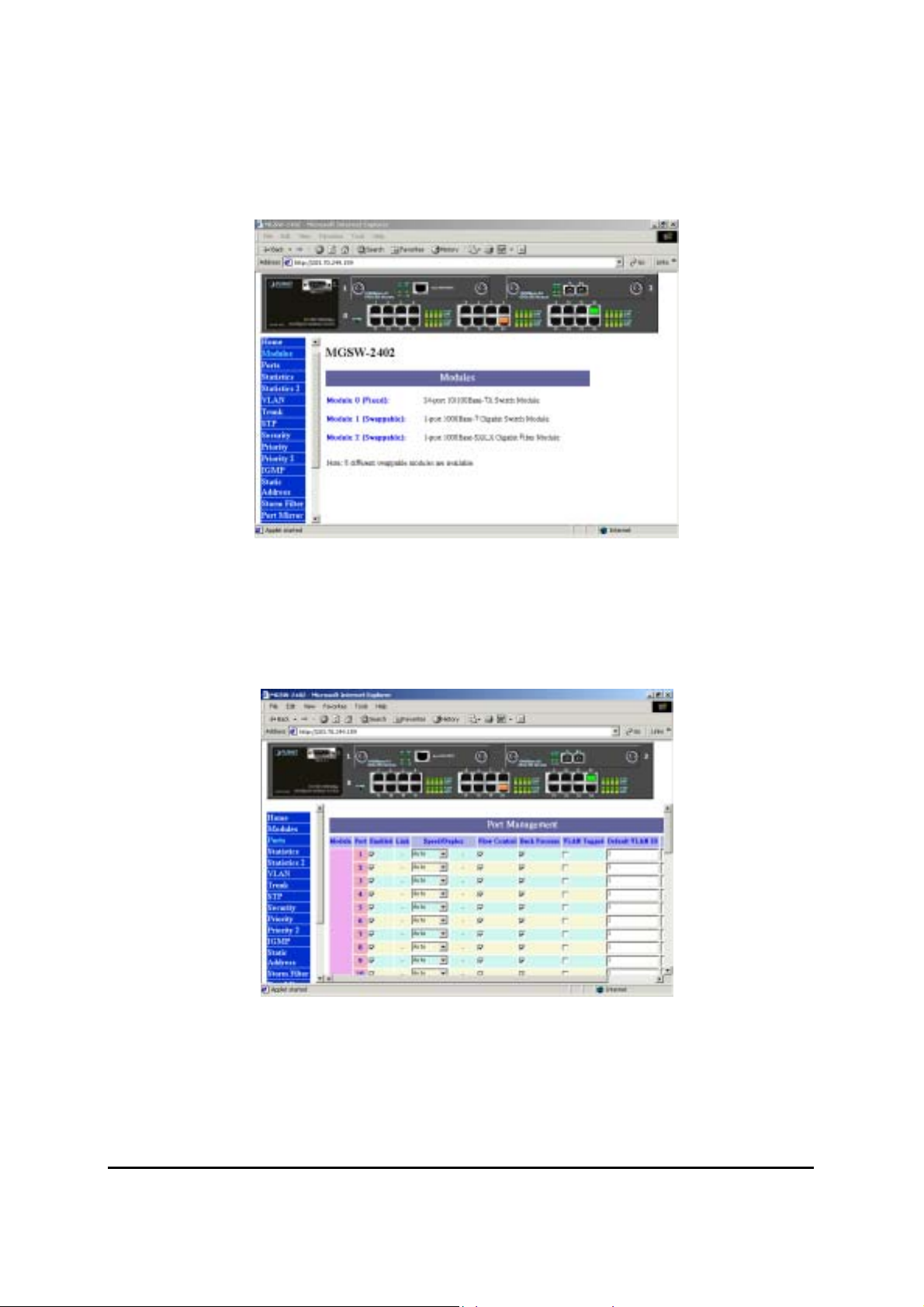
3.4 Modules
Modules page shows the modules that have installed into the MGSW-2402-Slot Intelligent
Switch. There are fixed 24x 10/100 Base-TX ports in Module 0, and another 2 slot ( module 1
and module 2 ) are used for expansion. In the following example, 1-port Gigabit 1000Base-SX
( LX ) Fiber Module, and 4-port 100Base-FX (ST) Fiber Module are installed into the Switch.
Figure 3-3 The Modules Page
3.5 Ports
Inside Ports page, you can enable/disable each port, configure Speed/Duplex for each port, and
assign VLAN ID.
The Port Management table shows the port status of all ports. You can also change some
properties of all ports in this table.
Figure 3-4 The Ports Page
- 10 -
Page 11

3.6 Statistics
The Statistic page displays the detailed information about each port. You can compare and
evaluate throughput or other port parameters. All screen data is updated automatically and you
can also update the data manually.
Figure 3-5 The Statistics Page
3.7 VLAN
A VLAN ( Virtual LAN ) is a group of switch ports designated by the switch as belonging to the
same broadcast domain. This feature allows workgroup to be defined on the basis of their logical
location instead of their physical location, and does not require recalling.
If a broadcast packet is received from a port, it will forward this broadcast packet only to those
ports belonging to the same VLAN. VLAN classification of every packet is done in the following
way: If the packet is tagged with non-zero VLAN-id field then this is used as the VLAN id.
Otherwise the default VLAN id of the input port is used. You can assign a single switch port to
two or more VLANs.
The factory default VLAN is that all ports belong to the same VLAN group 1.
VLAN also enable you to configure port-based VLANs to help isolate broadcast traffic and
increase security.
Creating VLANs increases network flexibility by allowing you to reassign devices to
accommodate network moves, additions, and changes, eliminating the need to change physical
cabling.
This switch support up to 256 port-based 802.1Q-compatible virtual LANs (VLANs).
- 11 -
Page 12
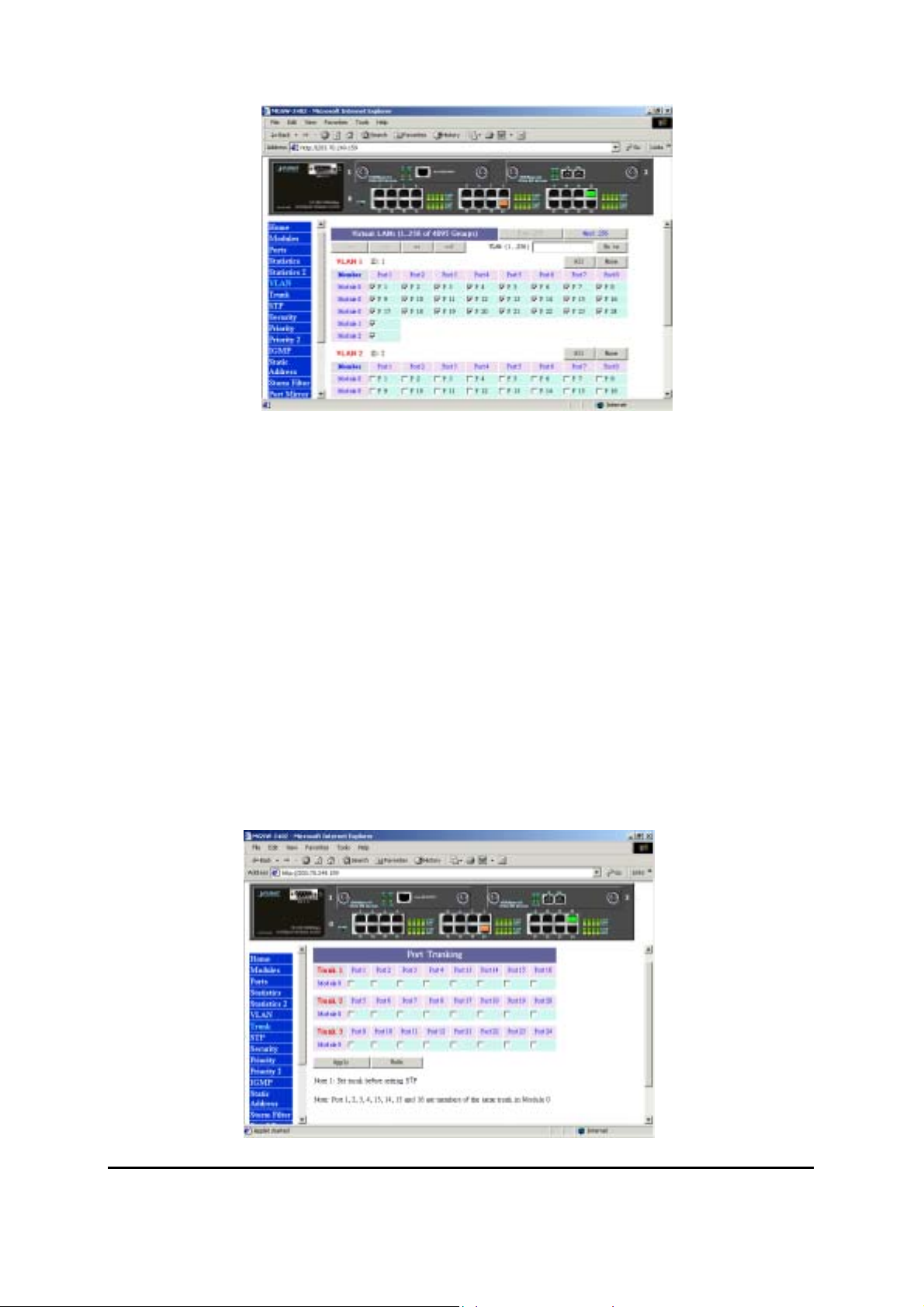
Figure 3-6 The VLAN Page
In the VLAN management window, you will see 2 VLANs in the page. To select a certain VLAN,
you can do the following:
Press ">>" button to display the next two VLANs
Press "<<" button to display the previous two VLANs
Press ">>|" button to display the last two VLANs
Press "|<<" button to display the first two VLANs
Enter the VLAN index in the "VLAN" edit box then press "Go to" button
You can add, edit and remove port members of each VLAN and then finally press "Apply"
button only once to configure the desired VLANs you want.
Note: if you want to set multiple VLANs, we suggest that you set Default VLAN ID for each port
first in Ports page.
3.8 TRUNK
Port trunking is the ability to group several 10/100Base-TX or 100Base-FX ports to increase the
bandwidth between this switch and another compatible switch. This is an inexpensive way to
increase bandwidth. We define port trunking as the ability to group set of ports (up to 8 ) within
the same module into a single logical link. The port trunk acts as a single link between switches.
Multiple trunks may be implemented in this switch, but only one trunk can be created within a
module.
Figure 3-7 The Trunk page
- 12 -
Page 13
You can add, edit and remove port members of each trunk and then press "Apply" button after
you have finished configuring the trunks you need.
( Note: Make sure trunking ports are in the same VLAN group. )
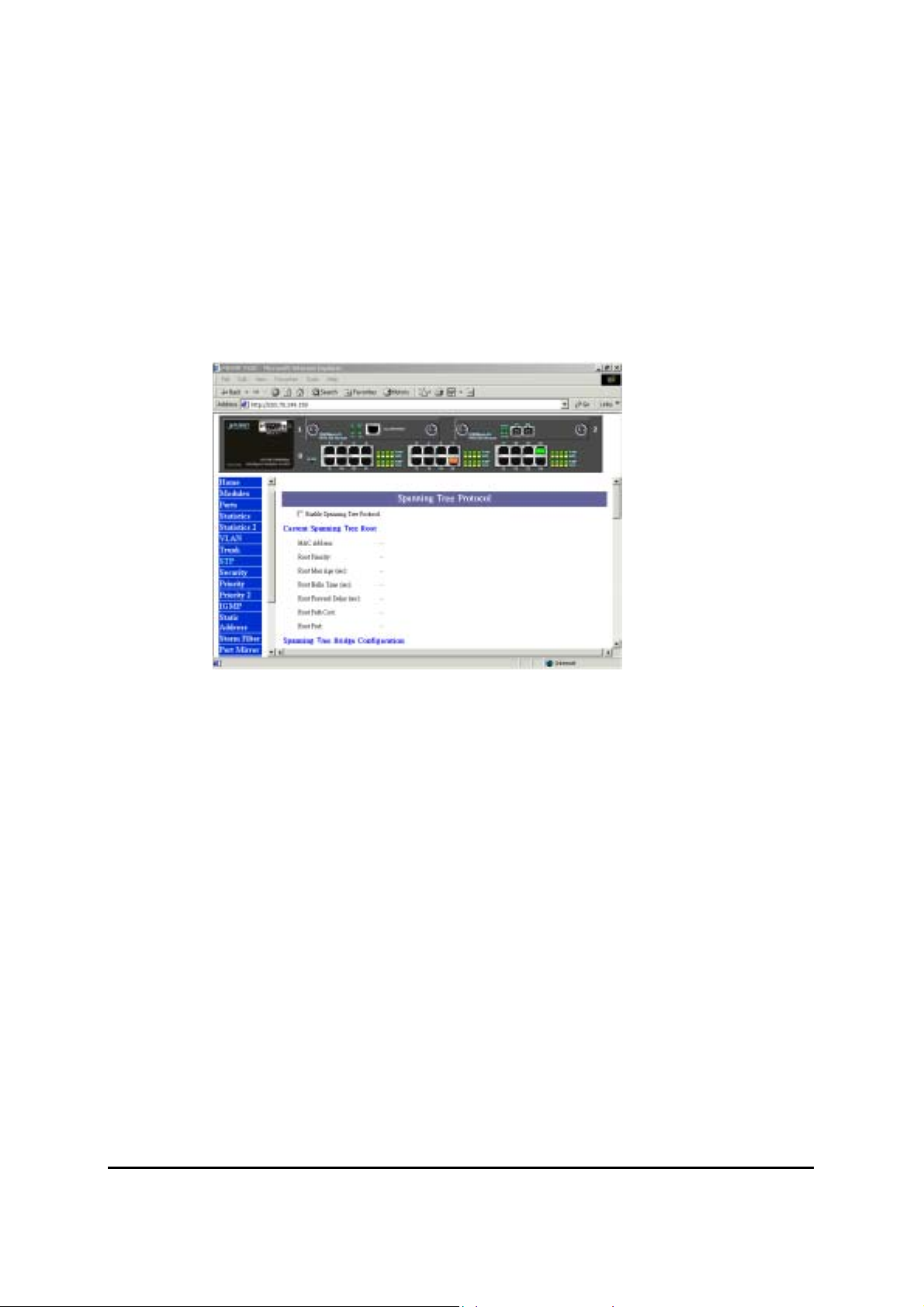
3.9 STP (Spanning Tree Protocol)
Spanning tree is a link management protocol that provides path redundancy while preventing
undesirable loops in the network. For Layer 2 Ethernet network to function properly, only one
active path must exist between two stations.
The spanning-tree algorithm calculates the best loop-free path throughout a switched network.
STP forces redundant data paths into a standby (blocked) state. If a network segment in the
spanning tree fails and a redundant path exists, the spanning-tree algorithm recalculates the
spanning tree topology and activates the standby path.
Figure 3-8 The STP page
If you want to participate in spanning tree, have the "Enable Spanning Tree Protocol"
checkbox selected.
The Current Spanning Tree Root describes the unique root switch information for the instance
of spanning tree.
MAC Address: the MAC address of the root switch
Root Max Age: the amount of time (in seconds) protocol information received on a port is
stored by the root switch
Root Hello Time: how often the root switch broadcasts Hello message to other switches
Root Forward Delay: the amount of time a port will remain in the listening and learning states
before entering the forwarding state
Root Path Cost: the path cost to the root switch from this switch
Root Port: the port providing the best path from the switch to the root switch
The Spanning Tree Bridge Configuration describes this switch information in the spanning
tree.
- 13 -
Page 14

3.10 Port Security
Port Security allows you to restrict specific MAC addresses to reside in some port. For example,
a dummy hub is attached to some port for extension, and you just only allow 2 users to access
this port at the same time, you can use the port security window to set the parameters.
Figure 3-9. The Port Security page
To restrict the number of MAC address to reside in a port, you must do the following :
Click the “ Enable “ checkbox for that port. IF the “ Enable “checkbox is uncheck, there is no
MAC address count restriction for that port.
Type the number in the “ Max Allowed MAC Address Count “ edit for that port. The upper
bound of this number is the “ Max Allowed MAC Address Count per port “
Press the “ Press “ button
The “ Used Count “ will tell you how many MAC address residing in the corresponding port now.
Note : A trunked port is not allowed to enable the port security option.
3.11 Port Priority-802.1p
There are two priority queues ( high and low ) on each port. Each port arbitrates between two
transmit queues ( high and low priority ).
The arbitration uses weighted round-robin between the high and low priority queues, and you
can adjust this weight.
- 14 -
Page 15

Figure 3-10. Port Priority – 802.1p page
Programmable Mapping of 802.1p to Internal Priority
The received packets with 802.1q tag are assigned priority according to a flexible and
programmable mapping of the 802.1p user-priority tag (3 bits, value from 0 to 7) to the internal
priority queue. The default is to assign a packet to high priority queue when the 802.1p
user-priority tag is 4 to 7, and to low priority queue when the 802.1p user-priority tag is 0 to 3.
Please check the corresponding mapping checkbox to assign a high priority or uncheck that to
assign a low priority.
3.12 Port Priority- Type of Service
Each port can parse the header of an incoming IPv4 header and identify the Type-Of-Service
byte (TOS field). This is extremely important with the deployment of Microsoft Windows 2000
and the emerging DiffServ standard, which marks Voice-Over-IP and other real-time traffic using
this field. This feature provides Layer 3 QoS.
Figure 3-11. Port Priority – Type of Service
If this function of a port is enabled, then the most significant 6 bits of the TOS (these 6 bits are
also known as the DiffServ Code Point "DSCP" field, value from 0 to 63) are used to assign a
priority to the packet received from this port. Please check the corresponding mapping checkbox
to assign a high priority or uncheck that to assign a low priority.
- 15 -
Page 16

3.13 IGMP
Multicasting is used to support real-time applications such as video conferencing or streaming
audio. IGMP ( Internet Group Management Protocol ) allow you to query for any attached hosts
who want to receive a specific multicast service. The switch looks up the IP Multicast Group
used for this service and adds any port which received a similar request to that group. It then
propagates the service request on to any neighboring multicast switch to ensure that it will
continue to receive the multicast service.
Figure 3-12 The IGMP page
IF you want your switch to support multimedia and IP multicast, enable this option (default is
enabled). When this option is enabled, this switch only directs the multicast data packets to the
ports where needed, saving bandwidth. If " Forward with high priority " option is enabled, then
the IP multicast traffic will have a higher priority than other traffic.
3.14 Static Address
You can lock a certain MAC address ( associated with a host, ) to a certain port. Once a certain
MAC address is locked to a certain port, this MAC address will not receive any packets if it is
moved to another port.
Figure 3-13 The Static Address page
- 16 -
Page 17

Static addresses are manually entered into the Static Address Table.
1. Enter the MAC address in the MAC Address field (ex. 00-00-00-00-00-01) and VLAN ID
(default is 1)
2. Select the Module and Port you want to associate with this entry with from the Port
drop-down box.
3. Click <<Add…<<.
4. Press “ Apply “ button.
Once a certain MAC address is locked to a certain port, this MAC address will not receive any
packets if it is moved to another port. Remove this entry from current static address table to
unlock this MAC address from that port, this MAC address is free again. Press “ Remove All “ to
delete all entries from static address table.
3.15 Broadcast Storm Filter
Storm Filter can avoid any flooded data packets. This feature prevents the bursts of broadcast
traffic. Excessive broadcast packets ( Broadcast Storms ) can be filtered in our managed switch
by enabling the "Broadcast Storm Filtering" option.
Figure 3-14 The Broadcast Storm Filter page
3.16 Port mirroring
Port Mirroring is to mirror traffic ( all frames ) from a specific resource port to a target port. This
help tracking down network errors or erroneous packet transfers without interrupting the flow of
data across the network.
- 17 -
Page 18

3-15 The Port Mirroring page
If you want to monitor all receive and transmit packets of one port. You can do the following:
Choose the monitored port in " Mirror Source Port " choice box in the corresponding mirror
source module. Only one port can be monitored in one module at the same time.
Choose the corresponding target module, port in "Mirror Target Module" and "Mirror Target Port"
choice box.
Click the corresponding "Enabled" check box.
Press "Apply" button
3.17 IP Config
You can change the IP address, subnet mask and default gateway of the managed node. (You
can also do that from RS232 console). Enter the IP address, subnet mask and default gateway
in the corresponding edit box.
Figure 3-16 The IP Config page
If you want to change the user name or password for the managed node, the following steps is
needed:
Click the "Change Password" checkbox
Enter the user name in "Username" edit box
- 18 -
Page 19

Enter the same password in "Password" and "Confirm Password" edit box
Press the "Apply" button
You should reboot system to let your settings take effect if you have changed one of the IP
address, subnet mask and default gateway.
3.18 SNMP
You can manage the Switch using third-party’s SNMP ( Simple Network Management Protocol )
agent. Access rights to the SNMP agent are controlled by community strings.
To set system name, system location and system contact, you can type the desired text string in
the corresponding edit box.
Figure 3-17 The SNMP page
3.19 Save & Reboot
If you want to reboot system, click the "Reboot System" checkbox then press the "Apply" button
next to the checkbox. Please wait a moment (about 15 seconds) then continue to operate this
home page.
- 19 -
Page 20

Figure 3-18 Save & Reboot page
3.20 Upgrade
You can on-line upgrade the firmware of the managed unit. The following steps is needed to
upgrade the firmware:
Use HTTP or FTP to download the new version firmware from our website.
Enter password in the "Password" edit box.
Enter the file downloaded in the "File Path" edit box. (You can use "Browse" button to select the
file.)
Press the "Upgrade" button.
After you have successfully upgraded the new firmware, please reboot the system so that the
new firmware will take effect.
Figure 3-19 Upgrade page
- 20 -
Page 21

- 21 -
Page 22

4. CONSOLE INTERFACE
4.1 CONNECT TO PC
RS-232 serial cable
Prepare a RS-232 serial cable. Attach the 9-pin female connector to the male connector on
the switch. Plug the other side of this cable to your PC.
Hyper Terminal
In Windows 95/98/2000/XP,launch “HyperTerminal”, create a new connection, and adjust
settings as below:
4.2 Main Menu
The main menu displays all the sub-menus that are available. Striking Enter, at a highlighted
option, will confirm the choice of the specified sub-menu. As shown in Figure 4-2, there are
thirteen menu items to choose from:
-- Device Settings
-- Port settings
-- Address Table
-- Spanning Tree Protocol
-- Broadcast Storm Filter
-- IGMP
-- VLAN Mode (2 modes)
-- VLAN for CPU (2 VLANs)
-- Secure IP for Telnet and HTTP
-- Save Current Settings
-- Factory Default Settings & Reboot System
-- Reboot System
-- Quit
- 22 -
Page 23

Figure 4-1 The Main Menu of Console Management
4.2.1. Device settings
This menu contains system parameters to display and configure the switch to your network.
Menu items are:
-- Version (RO): display the firmware version of MGSW-2402
-- MAC Address (RO): display the MAC Address of MGSW-2402
-- System Up Time (RO): display the work time of MGSW-2402
-- System Name: display and change the system name of this Switch
-- System Location: display and set the location of this Switch
-- System Contact: display and set the administrator of this Switch
-- IP Address: display and set the IP address of MGSW-2402
-- Subnet Mask: display and set the Subnet Mask of MGSW-2402
-- Default Gateway: display and set the gateway of MGSW-2402
-- Change User/Password: allow to set the User name and password, default value is root
-- Console Login Enabled: provide enable or disable Console login MGSW-2402
-- Quit: logout on MGSW-2402
Figure 4-2: Device settings
4.2.2. Port Settings
Select any one port, the menu contains ten items for port management will shown up as
below:
-- Link (RO): display the link state(UP/DOWN) of per port on MGSW-2402
-- Speed/Duplex (RO): display the Speed/Duplex of the device connect to the port
-- Port Enabled: allow enable or disable the port of MGSW-2402
- 23 -
Page 24

-- Speed/Duplex: allow set Auto- negotiation,100Mbps-full/half duplex,10Mbps-full/half
duplex
-- Flow Control: allow enable or disable flow control on each port
-- Back Pressure: allow enable or disable Back Pressure on each port
-- VLAN Tagged: allow enable or disable VLAN Tagged on each port
-- Default VLAN ID: allow set VLAN ID 1~4095 on each port
-- Note: set and display the information of each port
-- Quit: back to previous menu
Figure 4-3: Port Settings
4.2.3. Address Table
This menu contains four items for MAC address record on each working port
-- All
-- Module
-- Module Port
-- Quit
Figure 4-4: Address Table
4.2.4. Spanning Tree Protocol
This menu contains three items to enable or disable STP:
-- Enable
-- Disable
-- Quit
- 24 -
Page 25

Figure 4-5: Spanning Tree
4.2.5 Broadcast Storm Filter
This menu contains three items to enable or disable Broadcast Storm Filter:
-- Enable
-- Disable
-- Quit
Figure 4-6: Broadcast Storm Filter
4.2.6. IGMP
This menu contains three items to enable or disable IGMP:
-- Enable
-- Disable
-- Quit
Figure 4-7: IGMP
- 25 -
Page 26
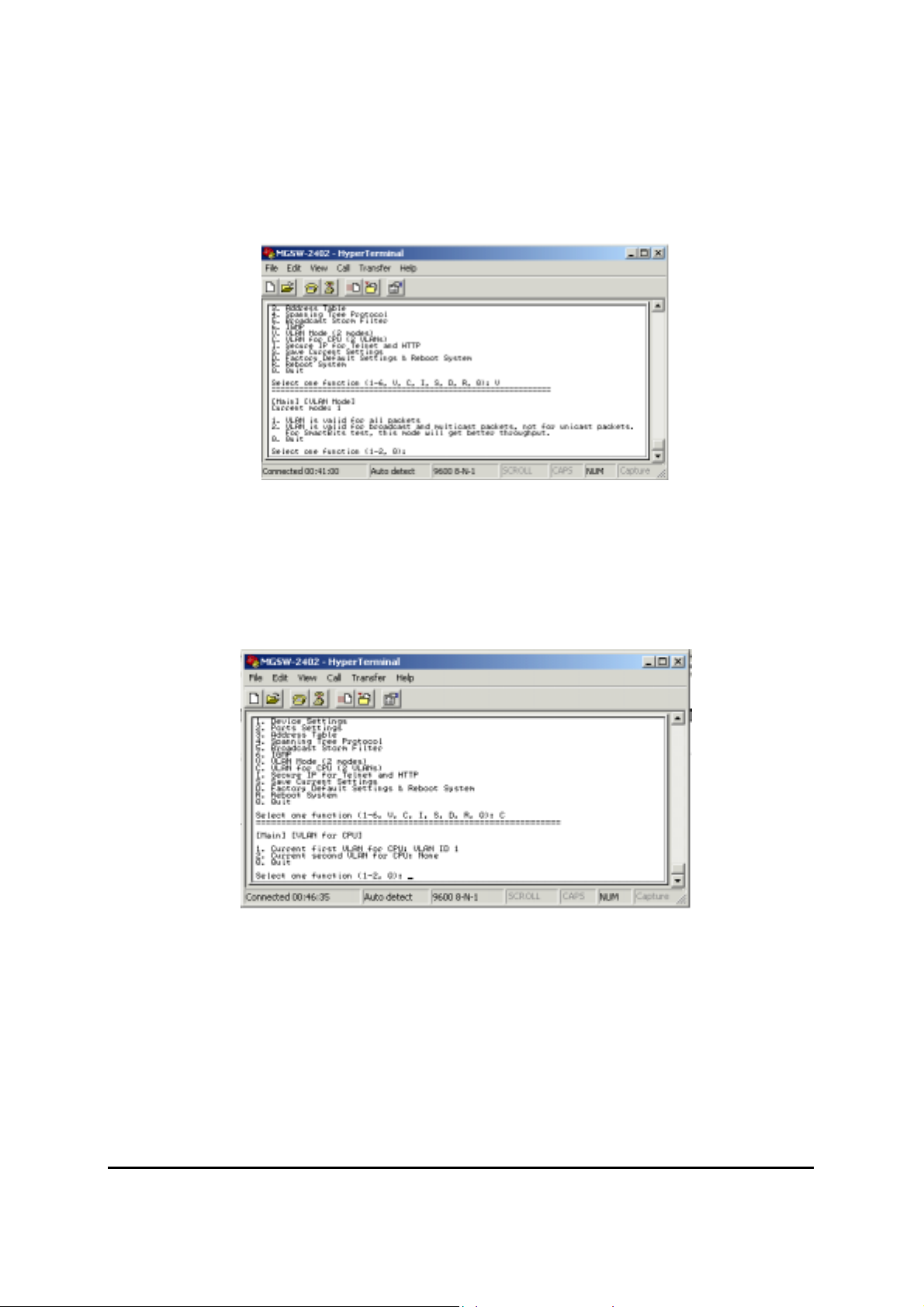
4.2.7. VLAN Mode (2 modes)
This menu contains two items for 2 VLAN mode selection:
-- VLAN is valid for all packets Disable
-- VLAN is valid for broadcast and multicast packets, not for unicast packets.
-- Quit
Figure 4-8: VLAN Mode( 2 modes)
4.2.8. VLAN for CPU (2 VLANs)
This menu contains two items for 2 VLANs for CPU:
-- Current first VLAN for CPU: VLAN ID 1
-- VLAN for CPU: None
-- Quit
Figure 4-9: VLAN for CPU( 2 VLANs)
Current second
4.2.9 Secure IP for Telnet and HTTP
This menu contains seven items for Secure IP setting:
-- Secure IP for Telnet: Disabled(default value)
-- Secure IP for HTTP: Disabled (default value)
-- Secure IP 1:
-- Secure IP 2:
-- Secure IP 3:
-- Secure IP 4:
-- Quit
- 26 -
Page 27
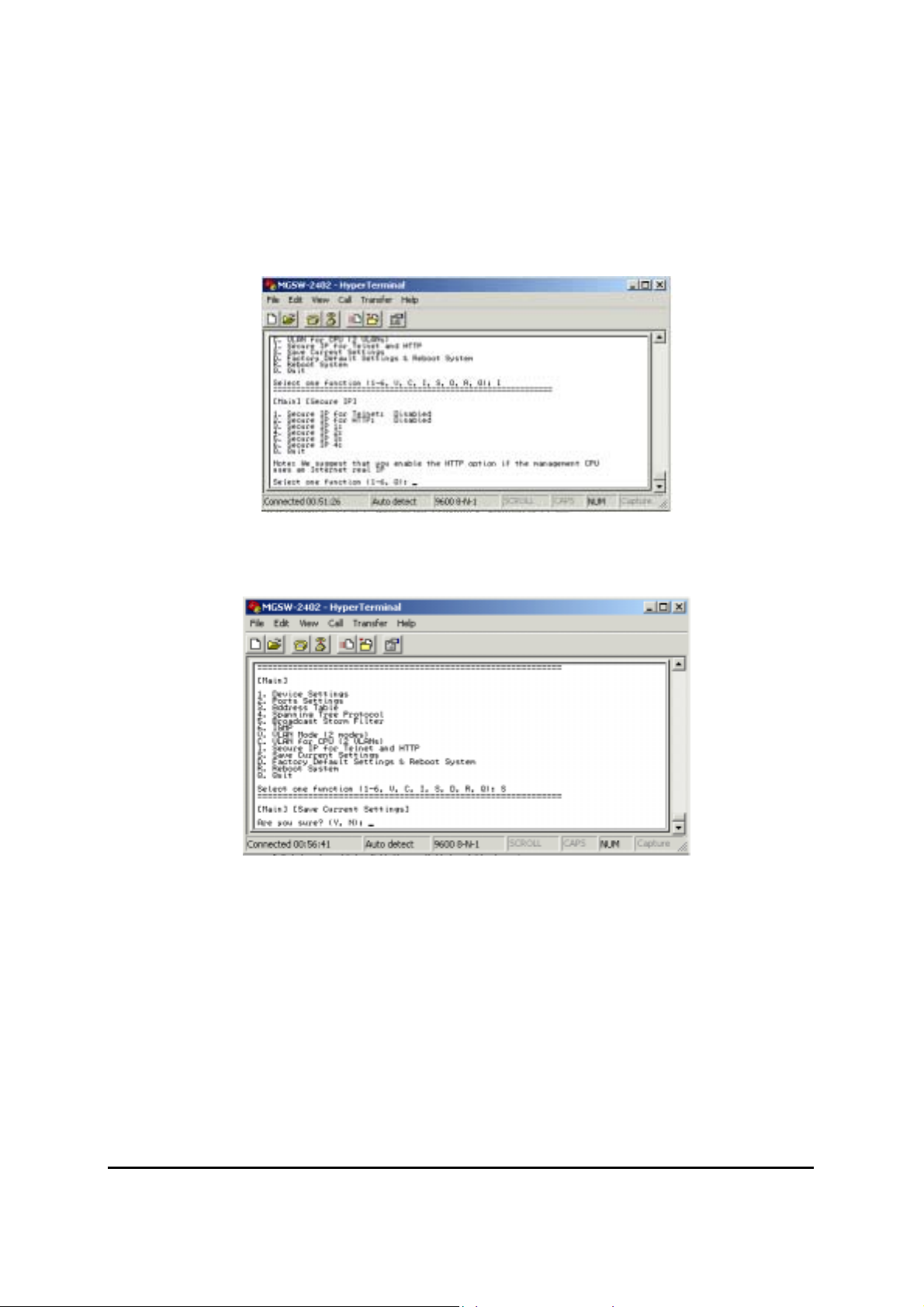
4.2.9.1 Secure IP for Telnet:
disable allow any PC login in MGSW-2402 by Telnet , enable allow the PC of secure IP
login in MGSW-2402.
4.2.9.2 Secure IP for HTTP:
disable allow any PC login in MGSW-2402 by HTTP, enable allow PC of secure IP login in
MGSW-2402.
4.2.9.3 Secure IP 1.2.3.4:
allow to set 4 Secure IP address of 4 PCs
4.2.10. Save Current Settings
Figure 4-10: Secure IP for Telnet and HTTP
This menu provide save current settings of this Switch.
Figure 4-11: Save Current Settings
4.2.11 Factory Default Settings & Reboot System
This menu provide restore to the default settings of this Switch
- 27 -
Page 28

Figure 4-12: Factory Default Settings & Reboot System
4.2.12 Reboot System
This menu provide reboot the Switch
4.2.13 Quit
HIS MENU PROVIDE LOGOUT OUT THE SWITCH
T
Figure 4-13: Reboot System
Figure 4-14: Quit
- 28 -
Page 29

5. SOFTWARE UPGRADE PROCEDURE
The application software is field upgradable. The upgrade procedure and the required equipment
is described in the following section.
Note that once the system is up, it is controlled by an executing application image residing in the
flash memory. No software upgrade is possible during this mode. The upgrade can only be done
when the system is resetting. To initiate this sequence, the user must set the “boot mode”
configuration parameter to “Boot from Net” during normal operation, and then perform a “reset”.
When the Boot-from-NET option is set, Bootstrap can start the system with an image residing on a
TFTP server on the network. In such a setup, a console terminal is connected to the console port,
and a TFTP server in the network is connected to one of the Ethernet ports. A network can be as
simple as an Ethernet Hub.
The upgrade procedure is as follow:
1. Use HTTP or FTP to download the new version firmware from our website.
2. Enter password in the "Password" edit box.
3. Enter the file downloaded in the "File Path" edit box. (You can use "Browse" button to select
the file.)
4. Press the "Upgrade" button.
Note: After you have successfully upgraded the new firmware, please reboot the system so that
the new firmware will take effect.
- 29 -
Page 30
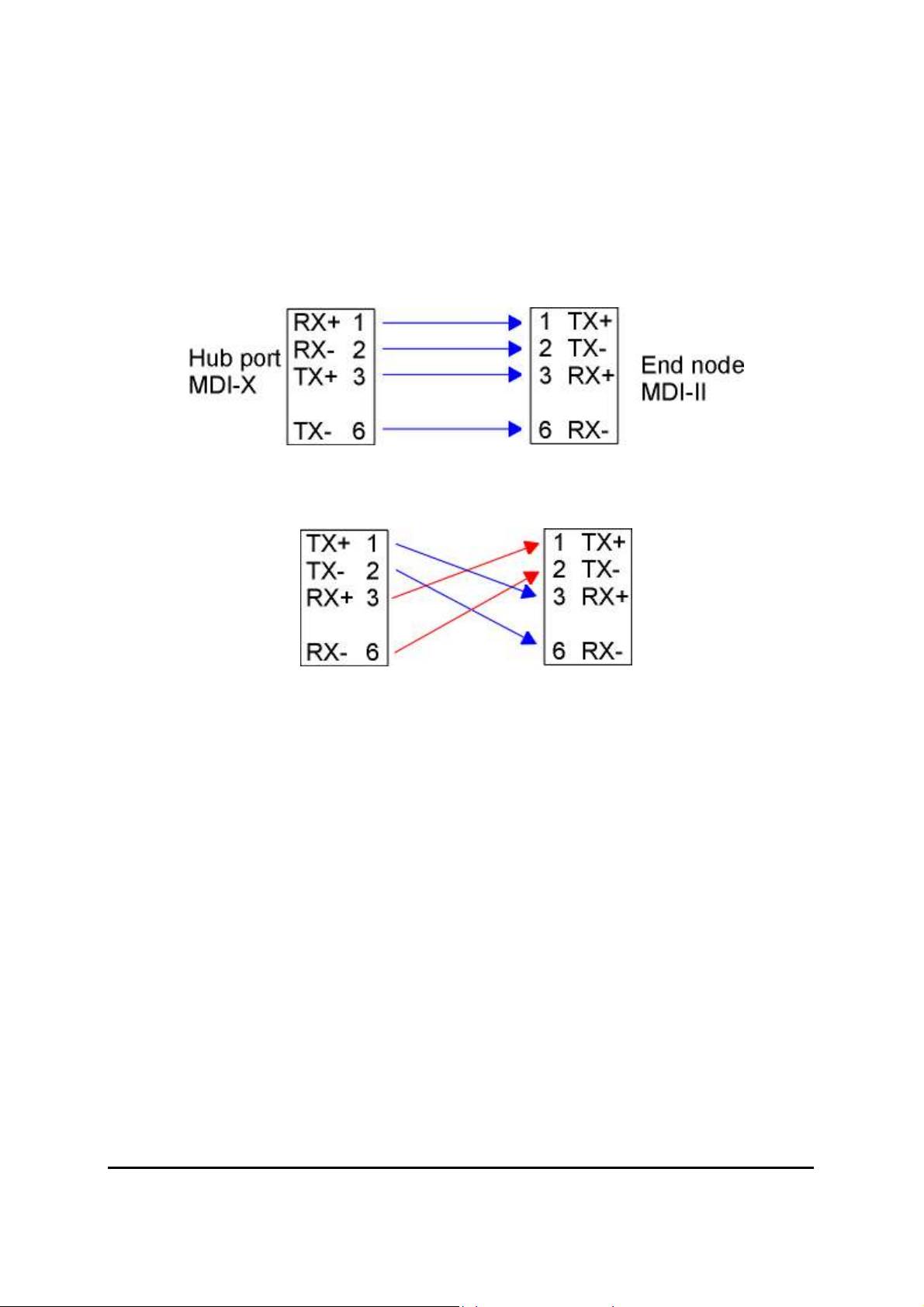
APPENDIX A NETWORKING CONNECTION
When attaching an end-station to the device, a standard straight-through CAT5 cable may be used,
even when the end-station is attached via a patch panel. However, when attaching another switch
or attaching workstations via hubs, a crossover cable will need to be used. Please see the
following wire diagrams for examples of both cable types.
Figure A-1: Straight-Through Cable
Figure A-2: Crossover Cable
- 30 -
Page 31

APPENDIX B TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Standard
IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u, IEEE802.3z, IEEE802.3ab,IEEE802.1Q,IEEE802.1d
Interface
RJ-45 10/100M Ethernet Port 24 - front
RS232 Male connector 1 - front
Slide-in Slot 2 - front
Indicator
Diag LED 1 per unit
Port LEDs
100M 1 per port
LNK/ACT 1 per port
FDX/COL 1 per port
Power
Input 100-240VAC 50-60Hz
Environment
Temperature Operating 0 degree to 45 degree C
Humility Operating 10 to 90 % RH
EMI
FCC Class A, CE Mark
Safety
cUL,UL
Dimensions
440mm x 226mm x 66.5mm
PWR LED 1 per unit
- 31 -
 Loading...
Loading...