Page 1
Model Service Manual CD Mechanism Module
DEH-P630/X1N/UC CRT2648 CXK5500
DEH-P7300R/X1N/EW CRT2649
DEH-P730/X1N/UC CRT2650
DEH-P7350/X1N/ES CRT2651
PIONEER CORPORATION 4-1, Meguro 1-Chome, Meguro-ku, Tokyo 153-8654, Japan
PIONEER ELECTRONICS SERVICE INC. P.O.Box 1760, Long Beach, CA 90801-1760 U.S.A.
PIONEER EUROPE NV Haven 1087 Keetberglaan 1, 9120 Melsele, Belgium
PIONEER ELECTRONICS ASIACENTRE PTE.LTD. 253 Alexandra Road, #04-01, Singapore 159936
C PIONEER CORPORATION 2001
K-ZZA. MAR. 2001 Printed in Japan
ORDER NO.
CRT2624
CD MECHANISM MODULE
CX-977
- This service manual describes the operation of the CD mechanism module incorporated in models
listed in the table below.
- When performing repairs use this manual together with the specific manual for model under repair.
CONTENTS
1. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTIONS ...........................................2
2. MECHANISM DESCRIPTIONS.................................26
3. DISASSEMBLY .........................................................28
Page 2
2
C X-97 7
1. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTIONS
From divisional viewpoint, the CX-977 is roughly divided into four sections, namely, Preamplifier, Servo, Power Supply
and Loading Control.
This LSI realizes eight types of automatic adjustments (controls) through cooperative work between Preamplifier and
Servo unit.
Because the system uses the single power source (+ 5v) specification, reference voltages used in the servo system
(Preamplifier, Servo DSP and Pickup) are all Vref (2.1V).
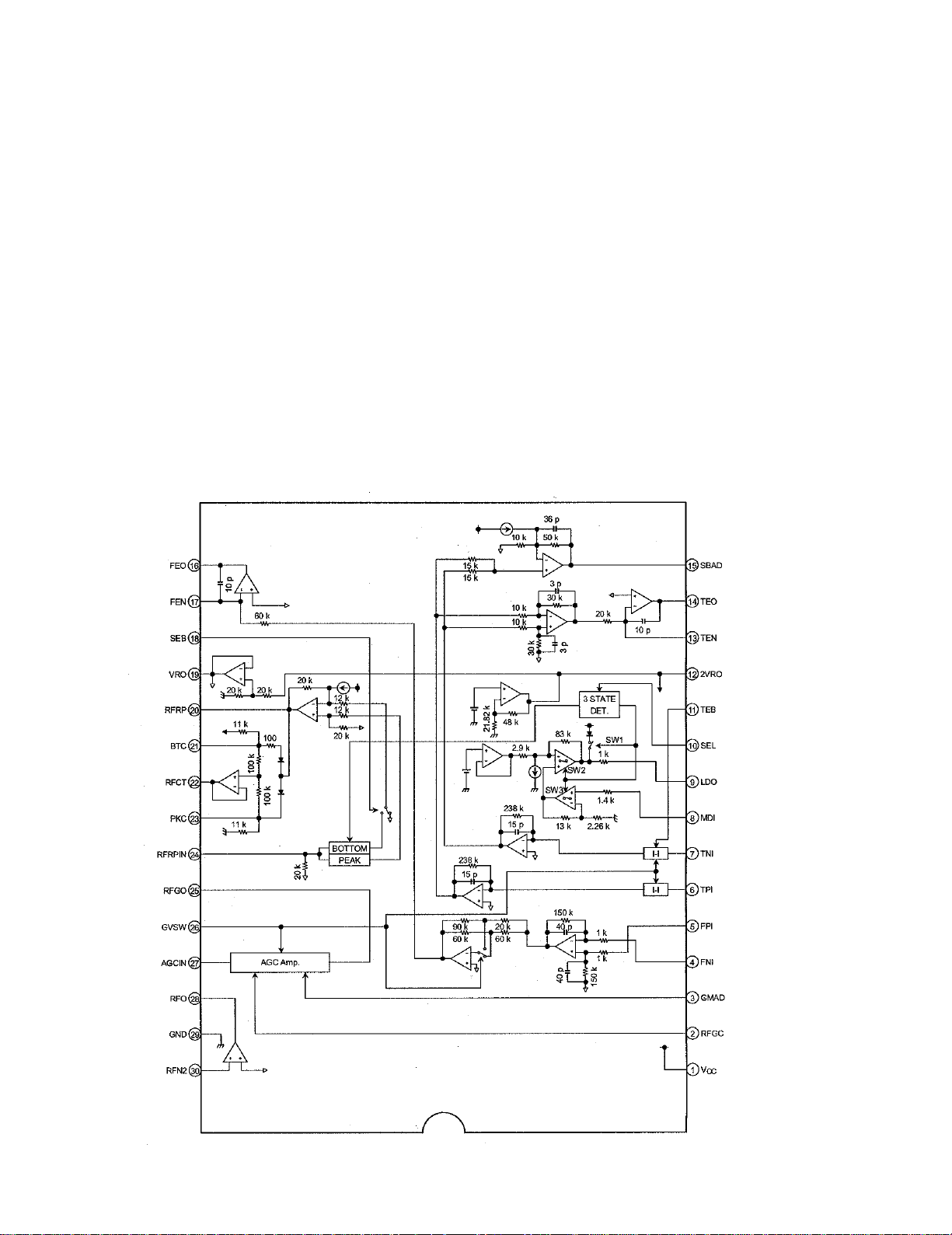
1.1 PREAMPLIFIER (TA2153FN; IC101)
The Preamplifier processes output signals sent from the Pickup and generates signals to supply to each unit of the
next stage, that is, Servo, Demodulator or Control. It also performs power control of Pickup's laser diode. Signals from
the Pickup are I-V-converted by the Preamplifier, which is built-in in Pickup's photo detector, and then added-up by the
RF amplifier to obtain signals such as RF, FE and TE.
Reference voltage, Vref (2.1v), is output from #19 pin of the IC, and 2Vref (4.2v) is supplied to the Servo DSP as the
reference voltage to determine its D range of A/D input.
Fig. 1: TA2153FN circuit
Page 3
3
C X-97 7
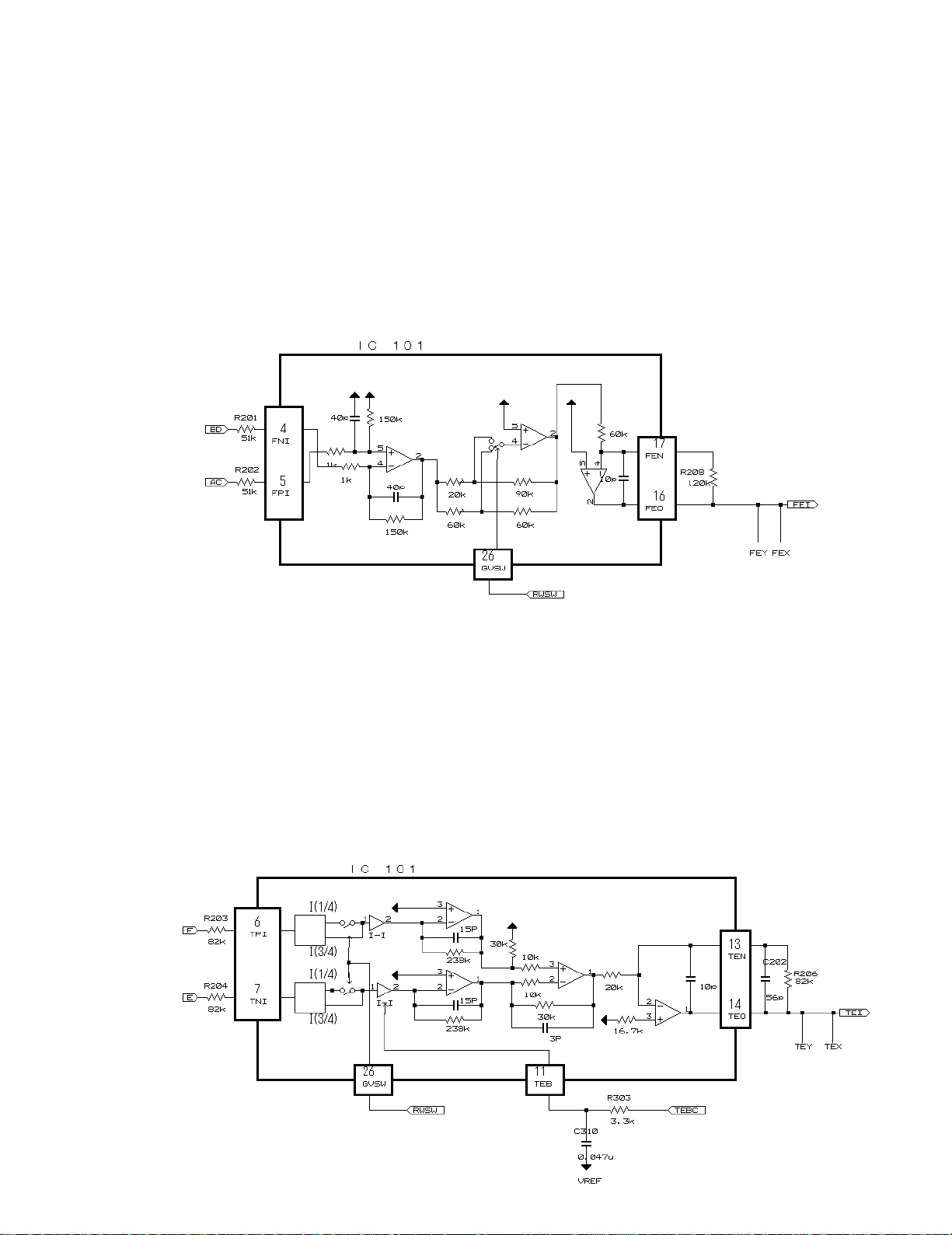
1) Focus Error Amplifier unit
In this sub-unit, outputs from the photo detector, namely, (A+C) and (B+D), are processed in the differential amplifier
and further in the error amplifier, and then, (A+C-B-D) is output as FE signal from #16 pin of IC101 (TA2153FN).
Low frequency component of voltage FE is expressed as:
FE = (A+C-B-D) x (150k/(51k+1k)) x (60k/60k) x (120k/60k) = 5.77 times
In FE output, "S" curve of approximately 1.45 Vpp on the basis of Vref is obtained. The cutoff frequency of the
succeeding amplifier is 11.4 kHz.
2) Tracking Error Amplifier unit
In this sub-unit, outputs from the photo detector, namely, E and F, are processed in the differential amplifier and
further in the error amplifier, and then, (E-F) is output as TE signal from #14 pin of IC101 (TA2153FN).
Low frequency component of voltage TE is expressed as:
TE = (E-F) x 300k/100k x 82k/20k = 5.8 times
In TE output, "TE" waveform of approximately 1.51 Vpp on the basis of Vref is obtained. The cutoff frequency of the
succeeding amplifier is 20 kHz.
Fig. 2: FE circuit
Fig. 3: TE circuit
Page 4
4
C X-97 7
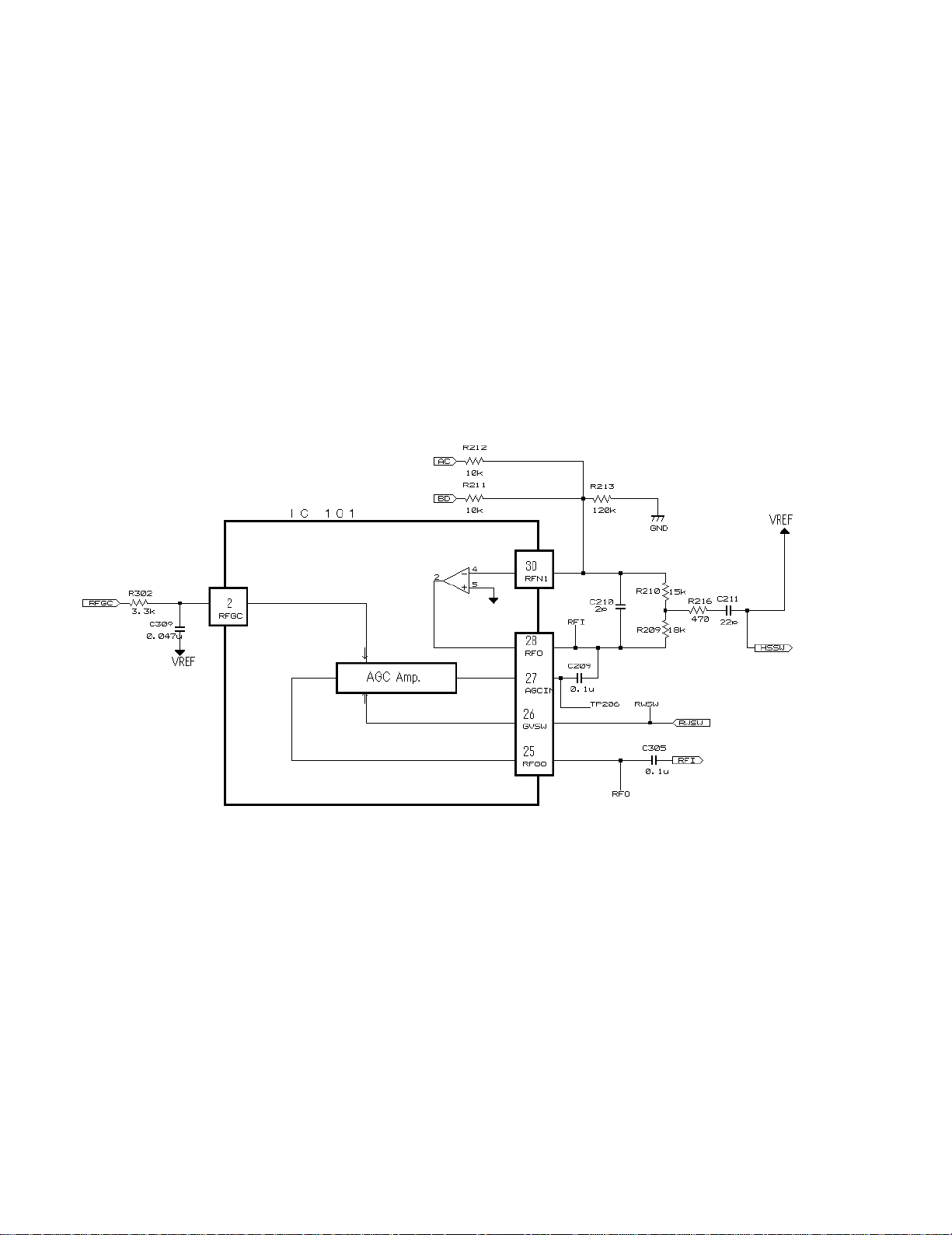
3) RF Amplifier unit
Outputs from the photo detector, namely, (A+C) and (B+D), are added up, amplified and equalized in the Head
Amplifier LSI (TA2153FN). The processed-signals are output to RFI terminal as RF signals (These signals are used to
check eye patterns).
Low frequency component of voltage RFI is expressed as:
RFI = (A+B+C+D) x 5.43
RFI is used for RF Offset Control circuit. These RFI signals so output from #28 pin are AC-coupled outside the unit, and
then re-input to #27 pin and amplified by the RFAGC amplifier to obtain RFO signals.
TA2153FN has built-in function for RFAGC adjustment, as described later, and through such function, the gain of
RFAGC is controlled so that RFO output stays within 1.2 ± 0.3 Vpp range.
Also, RFO signals are used for EFM and RFAGC Adjustment circuit. They are further used to generate RFRP and RFCT
signals, both of which are used for track counting.
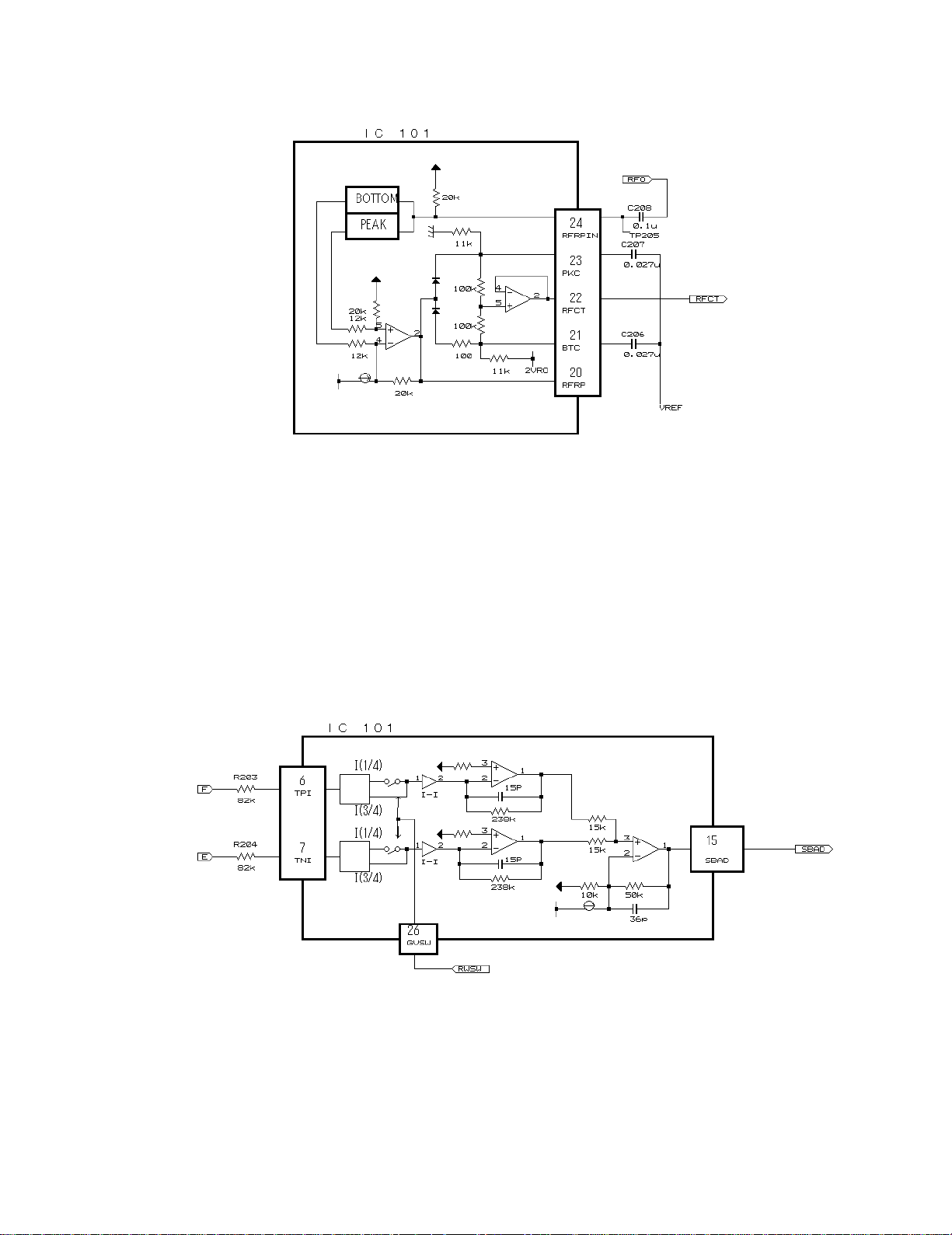
4) RFRP and RFCT Signal Circuit unit
RFCT signals are generated through the Head Amplifier (IC101). A RFCT signal is the difference signal that represents
the difference between the peak and bottom level of RF signal. RFRP and RFCT can be monitored at TP203 (#20 pin of
IC101, namely, TA2153FN) and TP204 (#20 pin of IC101) respectively.
Size-comparison among TE, RFRP and RFCT signals is performed by the Hysteresis Comparator in IC201 (TC9495F2),
and through such comparison, track information (TEZC and RFZC signal) is generated. Based on these signals,
information to determine tracking speed of the lens when it moves on the disk is generated. Also based on these
signals, number of tracks is counted.
Fig. 4: RF circuit
Page 5
5
C X-97 7
5) SBAD Signal Circuit unit
In this unit, outputs from the photo detector, namely, E and F are processed through the addition amplifier. That is, E
and F are added together and (E+F) signal is output from #15 pin of IC101 (TA2153FN), as SBAD signal.
This SBAD signal, along with Focus Error signal, is used as one of the conditions that the system uses to internally
judge Focus ON/OFF based on them.
Also, SBAD signal is used to detect defects: defects that may be detected when the Pickup passes a scratch on the
disk, for instance.
Fig. 5: RFRP and RFCT circuit
Fig. 6: SBAD circuit
Page 6
6
C X-97 7
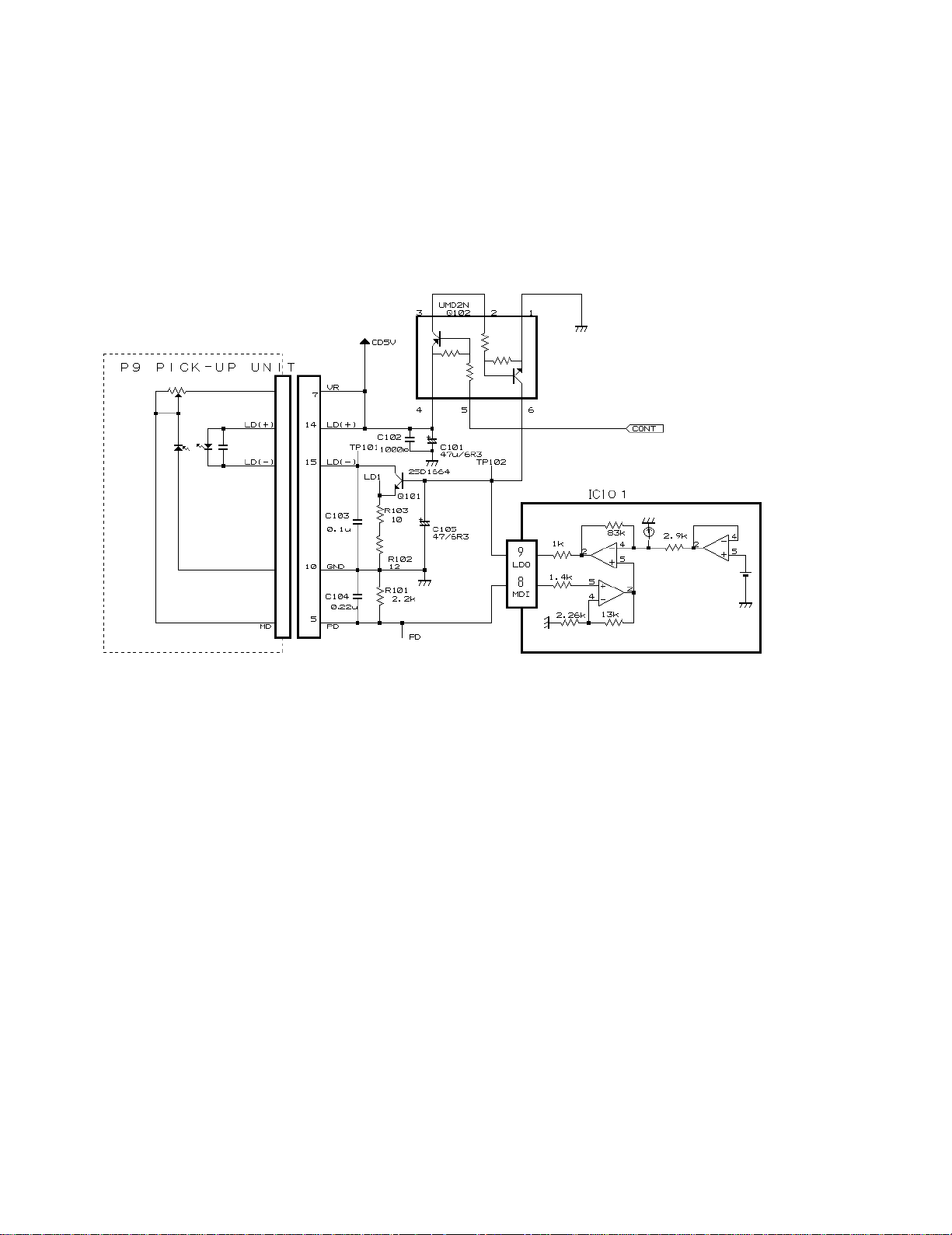
6) APC Circuit unit
If a laser diode is driven at constant current, its optical output comes to have high level negative-characteristics, and
this may cause it out-of-control drive because of the heat. So, driving current must be controlled, through use of a
monitoring diode, so that optical output remains within the specific degree. This is exactly where APC circuit works.
LD current can be obtained by measuring the voltage between LD1 and GND. The value is approximately 35 mA at
room temperature.
Fig. 7: APC circuit
Page 7
7
C X-97 7
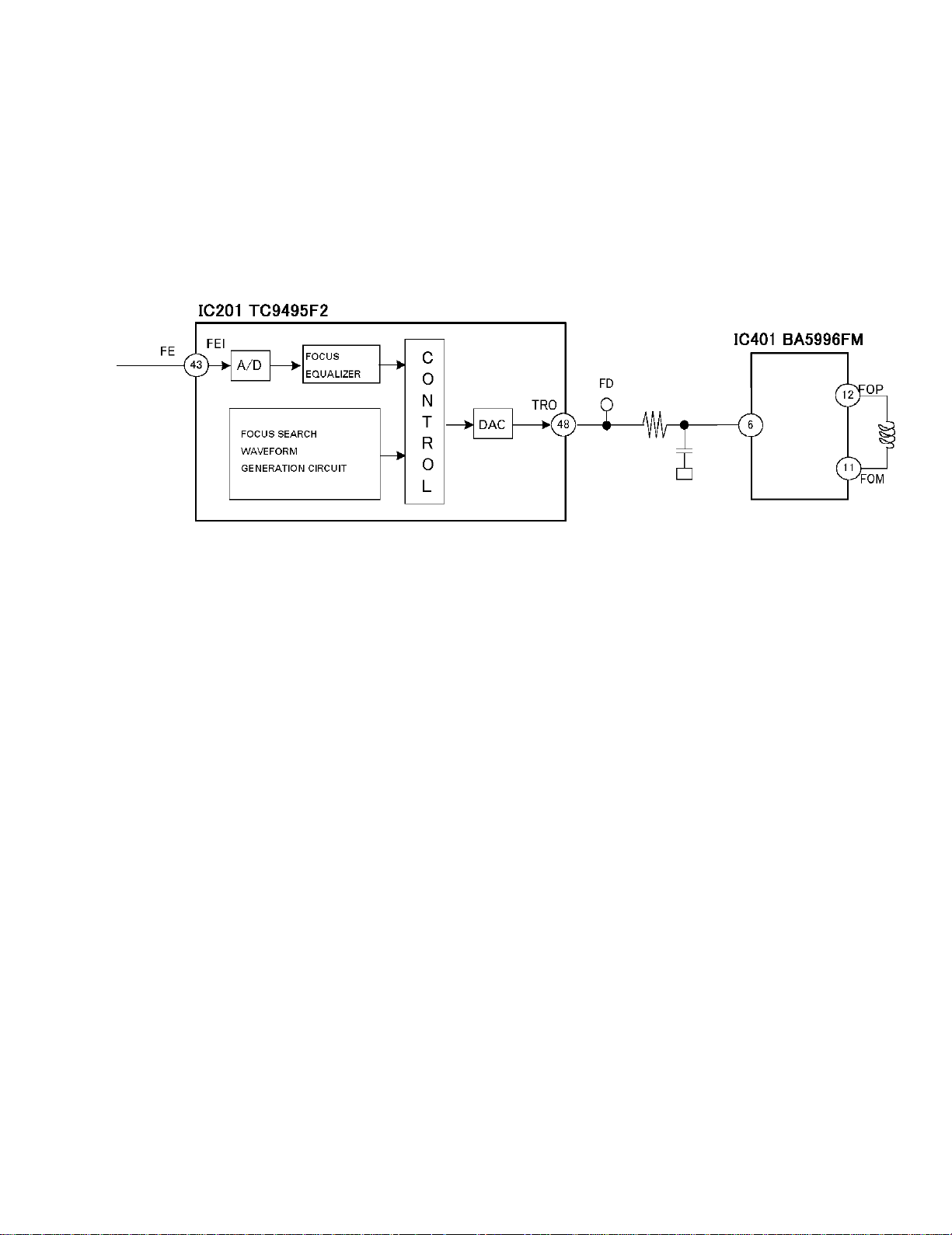
1.2 SERVO DSP (TC9495F2; IC201)
1) Focus Servo system
The main equalizer of the Tracking Servo is comprised with a digital equalizer unit. Fig. 8 shows the block diagram of
the Tracking Servo.
Fig. 8: Block diagram of Focus Servo circuit
Page 8

8
C X-97 7
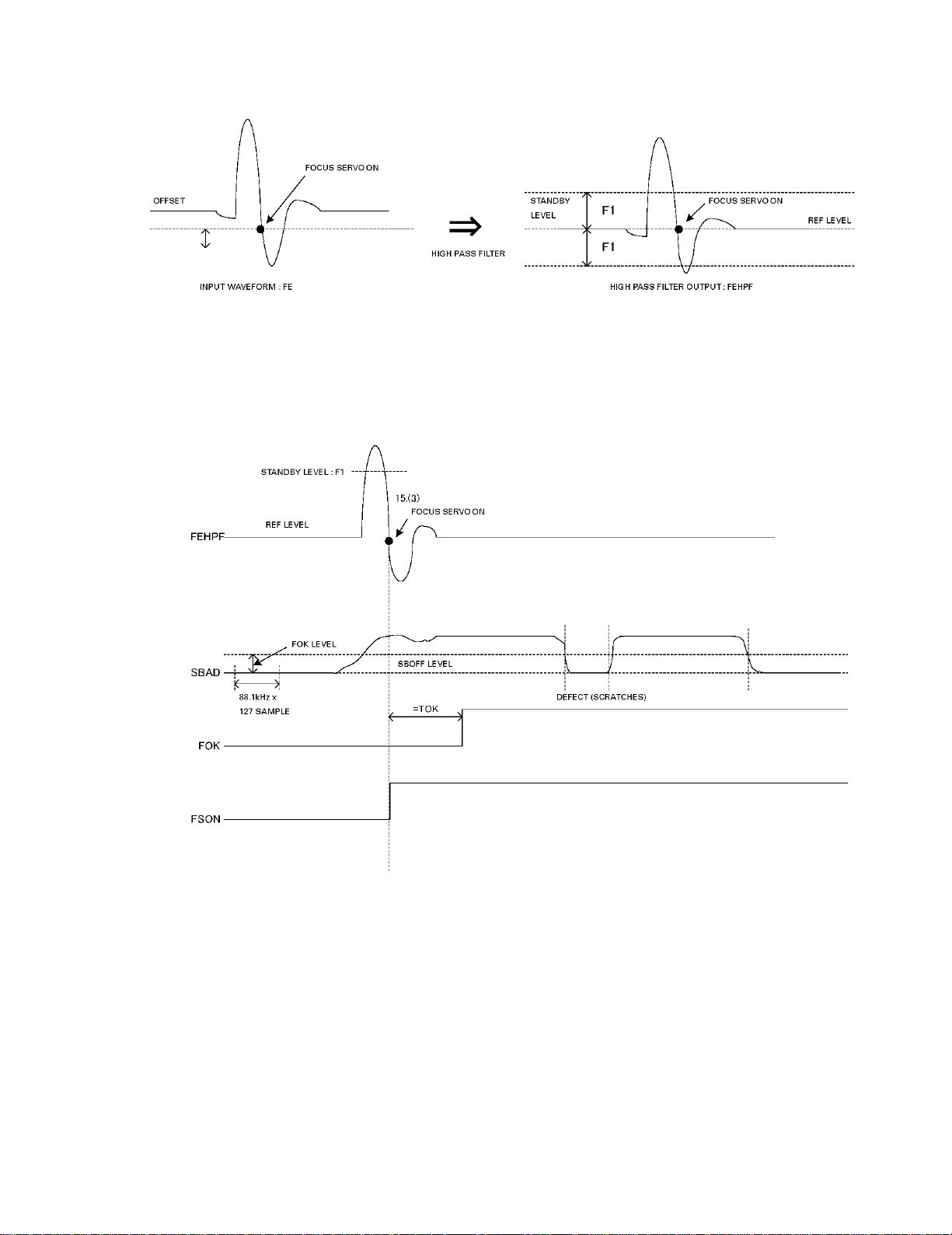
A series of actions of detecting in-focus point and switching on the Focus Servo upon such detection are called "focus
search." In Focus Servo system, the system needs to move the lens to in-focus point so that it performs "Focus Close."
So, the system detects in-focus point moving the lens up and down, which it performs by changing focus search
voltage of a triangle wave. During these operations, the spindle motor maintains offset mode and keeps constant
rotating speed.
The Focus Servo is switched on through three steps shown below.
1. FOK=H
2. The Focus Error signal exceeds "Focus Standby" level threshold
3. The Focus Error signal reaches "Zero Cross"
Here are descriptions of the three steps.
While there is enough distance between the lens and the in-focus point, the system cancels SBAD offset, and defines
this level (distance) as SBOFF. Then, starting from this SBOFF standard, SBAD level moves toward FOK threshold,
reaches it, and finally exceeds the threshold. Upon this passing over the threshold, the condition of the lens becomes
FOK ="H."
As the lens moves up and down, the focus error signal changes at the in-focus point. CD-LSI (IC201) analog/digital-
converts such signal, and then, let the signal pass through the high-pass filter to remove the offset component of the
signal. The signal so processed is called FEHPF signal. When the level of the FEHPF signal (internal signal of the LSI)
exceeds "Focus Standby" level, because it means the lens has come to close to the in-focus point, the system sets the
condition of the lens to "Servo-ON Standby." Finally, the FEHPF signal matches the value of the in-focus point, and the
system triggers ON of the Focus Servo.
Page 9
9
C X-97 7
The microcomputer monitors FOON signal while the system is performing focus search, and starts monitoring of FOK
signal from the point when 40 ms has passed after FOON signal became active (The signal is active when the
condition is "Servo ON." It shows "L" in a test with a probe). If the microcomputer judges that FOK is not active, it
performs necessary actions such as protection.
When, under Test mode, you press the Focus Close button, with the "Mode Select" of the focus set to "Display 01," you
can check Focus Error signals, search-voltage and actual actions of the lens.
Fig. 9: Focus Search Timing
Page 10

10
C X-97 7
2) Tracking Servo system
The main equalizer of the Tracking Servo is comprised with a digital equalizer unit. Fig. 10 shows the block diagram of
the Tracking Servo.
Track jump
Track jump is automatically performed with a command issued by the microcomputer. It is performed through Auto-
Sequence function that the LSI has in it.
The CX-977 has two types of track jump as those used for searching. Namely, the "Lens Kick" mode used for 1, 4, 10,
32 and 100 track, and the "Carriage Move" mode used for jumping of more than 1,000 tracks. Under Test mode, you
can use, to check the track position, 1, 32 and 100 jump as Lens Kick jump and Carriage Move jump according to mode
selection.
• Lens Kick jump
A Lens Kick jump is performed when the LSI receives a Lens Kick command from the microcomputer. Direction of
jump and number of tracks are specified by the command. When the LSI receives a Lens Kick command, it applies kick
pulses to the tracking EQ, and the jump occurs.
The LSI controls travelling speed of the lens by referring to the table it holds in it. In such way, the lens travels faster
when there are a good number of tracks to go, while travelling speed gets slower as the number of remaining tracks
decreases.
When track count is completed, Tracking Close is performed. During jump, the LSI observes RFRP signals, and based
on the signals, performs track count. It detects the direction of the jump based on phases of RFRP and TEZI signals.
To prepare for good servo-feed in next time track jump, the system performs operations to increase Tracking Servo's
gain and hysteresis operations for 50 ms after completion of Tracking Close. The system realizes FF/REV actions under
Normal mode by continuously performing single jumps. The speed of FF/REV is approximately 10 to 20 times faster
than "Play" (varies depending on the direction).
Fig. 10: Block diagram of the Tracking Servo
Page 11

11
C X-97 7
Fig. 11: Lens Kick
Page 12

12
C X-97 7
• Carriage Move jump
A Carriage Move jump is performed when the LSI receives a Carriage Move command from the microcomputer.
Direction of move and number of tracks are specified by the command. When the LSI receives a Carriage Move
command, it makes the Tracking Servo "Open," applies kick signals to the Carriage EQ and make the carriage motor
drive. Thus, a track jump occurs.
The profile of the kick signals so applied to the EQ has the specific constant given to it at the starting-up of the jump
operations. So, as the number of remaining tracks decreases, voltage is lowered so that travelling speed of the
carriage becomes slower. In this way, by reducing speed just before the jump terminates, the servo-feed at the end of
the jump is improved.
Also, to prepare for good servo-feed in next time track jump, every time a jump is completed, the system performs
operations to increase the gain of the Tracking Servo and hysteresis operations for 60 ms after the completion of the
jump.
Fig. 12: Carriage Move
Page 13

13
C X-97 7
• Hysteresis operations
In certain operation, such as Setup or jump, servo-feed tends to be deteriorated during operations. Hysteresis is the
operation to keep stable feed to servo-loop under such conditions. It acts in such manner that it holds a TE signal
when each beam spot comes to off-track position, so that convergence of the Tracking Servo can be improved.
Fig. 13: Hysteresis operations
Page 14

14
C X-97 7
3) Carriage Servo system
The Carriage Servo inputs low-frequency-component output (lens position information) of the tracking equalizer into
the carriage equalizer, then, after it has earned certain amount of gain, it outputs a drive signals from the LSI. Further,
such drive signals are applied to the carriage motor via the driver.
Specifically, the system works as follows. That is, entire body of the pickup needs to move to the forward direction
when the lens offset reaches certain level during Play. So, the gain of the equalizer is set in such manner that the
equalizer constantly outputs higher voltage than the starting-up voltage of the carriage motor when such condition
occurs. Practically, the system satisfies such requirement in such manner that the Servo LSI outputs the drive voltage
only when the equalizer's output exceeds the specific level of threshold.
To minimize power consumption, and to stabilize operations, the level of threshold is pre-set slightly higher than the
starting-up voltage of the motor. Waveforms of output of this drive voltage take pulse shape.
Fig. 14: Block diagram of Carriage Servo circuit
Page 15

15
C X-97 7
4) Spindle Servo system
Fig.16 shows the block diagram of the Spindle Servo.
Fig. 16: Block diagram of the Spindle Servo circuit
Fig. 15: Carriage signal waveform
Page 16

16
C X-97 7
Spindle Servo has the following modes
• CLV Servo mode
This is the mode the system uses for such span as "after Focus Close and before it applies brake to the motor to stop
the disk." Before Tracking Close and during normal Play, the system operates under this mode.
During this mode, the system performs synchronous detection in EFM demodulation block in the CD-LSI (IC201) so
that the disk keeps predefined rotating speed. To realize synchronous detection before Tracking Close the system
adopts such method that it applies to PLL circuit the same speed control by VCO that is performed in the LSI.
On the other hand, as to speed control after Tracking Close, control by VCO is muted and the method is switched to
speed/phase control through the master clock (a ceramic oscillator).
• Offset Servo mode
(a) After the kick is over in the setup, this mode is turned on until changing to rough servo mode.
(b) When focus is lost during play, this mode is turned on until the focus is restored.
Both of the above are used for maintaining the disc rotation rate near to the specified rate.
• Brake mode
The mode is for use to stop the spindle motor.
Brake Sequence starts up when the microcomputer sends the command to CD-LSI. Then, the LSI, watching disk's
rotating speed, sets the flag when it detects that the speed comes to approximately one twentieth (1/20). On the other
hand, the microcomputer, also monitoring such flag, switches off the servo when it caches the flag.
In case the microcomputer cannot catch such flag within the specific period after starting-up of the Brake Sequence, it
changes the mode to Stop, and monitoring FG pulses, keep the mode until it confirms that the speed has become
slow.
In case such change to Stop mode occurs at Eject time, the microcomputer moves the operations to Eject operations
after Timeout time elapses.
• Stop mode
This is the mode used for Power-On and Eject operations. Drive's output is "0."
Page 17

17
C X-97 7
1.3 AUTOMATIC ADJUSTMENT FUNCTION
In this CX-977 system, all circuit adjustments are automatically performed in CD-LSI (IC201: TC9495F2). Adjustments
are automatically performed every time a disk is inserted into the unit, or a CD mode is selected through the Source
Key.
1) Automatic TE offset/FE offset adjustment
This is the adjustment performed at POWER ON time. It adjusts both TE and FE amp- offsets of the Preamplifier to the
target value defined for each signal (TE and FE), using Vref as the reference. The target values are (TE, FE) = (0, 0) [V]
Adjustments are performed as follows.
(1) Servo LSI reads each offset value under the condition of "Laser Diode is OFF."
(2) The LSI, based on the value so read, calculates the voltage to be reversed, and assigns the revised value to the
location specified for use for such adjustment.
If you want to observe changes of voltage to examine actual offset voltage shown as error (focus error or tracking
error), you cannot see such changes, even after adjustment, because such adjustment is made inside the digital filter.
2) Automatic Tracking Balance (T, BAL) adjustment
This is the control that eliminates the difference between pickup's Ech and Fch output by changing the gain in the
Preamplifier. In practice, the LSI realizes the control in such manner that it makes a TE waveform vertically symmetric
against the Servo Reference level.
Adjustments are performed as follows.
(1) After Focus Close
(2) The system switches on the spindle servo.
(3) The LSI fetches the level of TE signal and the level of TE offset, and based on these values, calculates the TE center
value.
(4) The LSI changes RF amp's gain so that such center value comes to close to the Servo Reference level.
Fig. 17: Offset adjustment
Page 18

18
C X-97 7
Servo Reference level is set as follows.
In case offset adjustment is made, the level is set to:
The level of TEI input (i.e. TF offset level) at "Servo = OFF."
In case offset adjustment is not made, the level is equal to:
Vref level.
In this case, the adjustment is repeated several times to improve adjustment accuracy.
Fig. 18: Tracking Balance Adjustment
Page 19

19
C X-97 7
3) Focus/Tracking AGC
This is the control that automatically adjusts servo loop gain of the Focus Servo and Tracking Servo.
The adjustment is performed in the following manner.
(1) The system (microcomputer) injects a disturbance into servo loop.
(2) Then, caused by such injection, error signals (FE and TE) are generated, and the system samples such error signals
through BPF.
(3) Then, inside the LSI, comparison of the difference of phase between the error signal and the disturbance is
performed.
(4) Finally, the system adjusts the gain so that the difference of phase accords to the target value preset by the
microcomputer.
4) FE Bias automatic adjustment
The task of this adjustment is to maximize RFI level by optimizing the focus point during Play. The adjustment is
performed by examining RFRP level and phase-difference as of the time when a disturbance to generate focus errors
is injected into focus loop.
Steps of the adjustment are shown below.
(1) A disturbance is injected into focus loop based on the command issued by the microcomputer. (The session is
performed in the Servo LSI.)
(2) In the LSI, level of RFRP signal is detected.
(3) Also in the LSI, the relation between such RFRP signal and the disturbance is examined, and through such
examination the degree and direction of focus misalignment is detected.
(4) Then, the system substitutes the detected-result for the value in the "Bias Adjustment" item (field).
Fig. 19: Loop gain adjustment
Page 20

20
C X-97 7
As to this FE Bias automatic adjustment, as similar to cases of automatic gain control, the system repeats a series of
adjustments several times to maximize accuracy of adjustments.
5) RF Level automatic adjustment (RFAGC)
The aim of this adjustment is to adjust the variance of signals' level (RFO signals), which may be caused by
mechanical factors or those factors derived from the disk, and keeps such variant levels to the specific value so that
stable and accurate signal transfer can be secured. The adjustment is realized by varying amplifier-gains between RFI
and RFO.
The following steps are taken.
(1) Based on the peak and bottom value of RFRP level inside the Servo LSI, RFRP 's PP level is calculated.
(2) The system compares this PP level with the standard level and catches the difference between the two. Then, based
on this difference, it sets such amount of amplifier-gain, inside the LSI, as it needs to accord RFO signals with the
target RFO level, so that RF amp's gain can be controlled.
Fig. 20: FE Bias adjustment
Page 21

21
C X-97 7
These adjustments are performed in the following timing.
Just before the completion of Setup (i.e. just before "Play")
After restoration of correct focus, in case focus point comes to out of focus.
6) Gain adjustment at Preamplifier-Stage
This adjustment increases the gain of entire RFAMP (FE, TE and RE amp.) by +13 dB through the specific setting on
GVSW terminal. The adjustment occurs in such occasion that the lens is stained, or there is remarkably little reflection
(light), during CD-RW replay operations, for instance.
The adjustment is performed as follows.
During Setup operations, if the system judges that there is remarkably little reflection of the disk, it switches the value
of GVSW terminal from "H" to "L." Then, the gain of entire RFAMP increases by 13 dB.
For reference, if the system so changes the gain, it performs Setup operations over again form the beginning.
7) Comments for initial values of the foregoing adjustments
In principle, every and each automatic adjustment uses previous adjustment-value as the initial value unless
microcomputer's power is switched off (That is, unless backup power is switched off.) (There are several exceptions.)
In case backup power is switched off, or the value of CVSW terminal is "L," default initial value is used instead of such
previous adjustment-value.
8) Function to display coefficient of the adjustment-result
In some automatic adjustments (FE Offset/TE Offset, Tracking Balance, Focus/Tracking AGC, FE Bias and RF AGC) you
can display the result of the adjustment, that is, display the coefficient, under Test mode, to confirm the result. Below,
details of coefficient-display function for each automatic adjustment are shown.
(1) FE Offset/TE Offset adjustment
Standard value = 32 (Value "32" indicates that no adjustment was required, and this value-definition applies to
every case described in this section.) The unit of value representation of coefficient is 46 mV.
Example: Coefficient of FE offset = 35
35 - 32 = 3 3 x 46 mV = 138 mV
This means, that FE offset before the adjustment was 138 mV.
Fig. 21: RF level adjustment
Page 22

22
C X-97 7
(2) T. BAL (Tracking Balance) adjustment
Standard value = 32
Coefficient = 33 to 63 ------ TE: Top side - Bottom side < 0
Coefficient = 31 to 0 ------ TE: Top side - Bottom side >0
Every time the value moves by "1" misalignment changes by approximately 0.71 to 4.97 %.
Maximum misalignment of minus side (<0) = When coefficient is 63
This is the misalignment of [TYP - 45 %].
Maximum misalignment of plus side (>0) = When coefficient is 0
This is the misalignment of [TYP + 45 %].
(3) Focus/Tracking AGC adjustment
Standard value: Focus/Tracking = 32 The unit of value representation of coefficient is approximately 0.375 dB.
Example: Coefficient of AGC = 48
48 - 32 = 16 16 x 0.375 dB = 6 dB
The meaning is, the system performed adjustment of "+6 dB" (i.e. 2 times).
In other words, servo-loop's gain before adjustment was "1/2 times" (a half) so the system doubled the entire
gain to obtain the target value.
4) FE Bias adjustment
Standard value = 32 The unit of value representation of coefficient is approximately 21.5 mV.
Example: Coefficient of FE Bias = 35
35 - 32 = 3 3 x 21.5 mV = 64.5 mV
Thus, you can see that misalignment of FE Bias before the adjustment was "+ 64.5 mV."
5) RF Level adjustment (RFAGC)
Standard value = 32
Coefficient = 33 to 63 …… Adjustment of level-variance is being made to the direction of raising RF level
(Direction of increasing gain)
Coefficient = 31 to 0 …… Adjustment of level-variance is being made to the direction of lowering RF level
(Direction of decreasing gain)
Every time the value move by "1" gain changes by approximately 0.07 to 0.15 dB.
Maximum gain = When coefficient is 63
This is the gain of [TYP - 2.69 dB].
Minimum gain = When coefficient is 0
This is the gain of [TYP - 3.93 dB].
1.4 POWER SUPPLY AND LOADING CONTROL SECTION
CX-977 uses power sources of two systems. One is the VD (8.3 ± 0.5V) supplied by the motherboard. This system of
power source ("Drive system" power source) is supplied to the 4-CH CD Driver IC and the 5V Regulator IC. The second
is V+5 power source ("Control system" power source).
ON/OFF switching of the CD driver, except those for Load and Eject, is controlled by the microcomputer through
"CONT" control terminal. ON/OFF switching of 5V is controlled through "CD5VON" control terminal. As to ON/OFF
switches of the loading drive (Load/Eject), there is no control terminal specifically provided for such use. However,
"LOEJ," which is an input signal, performs similar task. Also, at LCO Output part, switching of LOADING and
CARRIAGE mode is performed through "CLCONT."
Page 23

23
C X-97 7
Fig. 22: Block diagram of circuits in Power supply/Loading system
Fig. 23: Switching of LOADING/CARRIAGE mode
CLCONT
Loading Mode Loading Mode
Carriage Mode
Page 24

24
C X-97 7
LOAD/EJECT actions are controlled through condition-changes of four switches, namely, the Clamp switch on the
mechanical unit and three switches on the Control unit (Combination of ON/OFF conditions of each one of these 4
switches is called "status" as a whole). That is, DSCSNS voltage changes according to ON/OFF conditions of these
switches, and controls are performed through such change of voltage. Accordingly, to control this voltage, the
microcomputer judges each status (A to E) using its A/D port. Also, it judges whether the disk is 8cm-disk or 12cm-disk
through such change of status, too.
Fig. 24 shows each status and Fig. 25 shows transition of status.
Fig. 24: DSCSNS status
DETECTION SWITCH STATUS AT THE TIME OF LOAD EJECTION
STATUS A B C D E
SW1(S903) ON OFF OFF OFF ON
SW2(S905) OFF OFF ON ON OFF
SW3(S904) OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
SW4(S902) OFF OFF OFF OFF ON
MECH. STATUS NO DISK CLAMP
Page 25

25
C X-97 7
LOAD EJECTION OPERATING STATUS TRANSITION DIAGRAM
A
Fig. 25: Transition of loading actions in correlation to status-change
LOADING
12cm
B
A
C
D
E
A/D A B C D C B E
CLCONT
LOEJ
MOTOR STOP LOAD STOP
12cm RECOGNITION CHECK
LOAD/CARRIAGE SWITCHING
8cm
B
C
D
E
A/D A B C B A or B B E
CLCONT
LOEJ
MOTOR STOP LOAD STOP
8cm RECOGNITION CHECK
DEAD ZONE LOAD/CARRIAGE SWITCHING
EJECT
12cm
B
A
C
D
E
A/D E B C D C
CLCONT
LOEJ
MOTOR STOP EJECT STOP
CARRIAGE/LOAD SWITCHING
8cm
B
A
C
D
E
A/D E B A or B B C
CLCONT
LOEJ
MOTOR STOP EJECT STOP
A
CARRIAGE/LOAD SWITCHING
DEAD ZONE
Page 26

26
C X-97 7
- Loading actions
1. When a disk is inserted, SW Arm L and R rotate. Due to the rotation of Arm L, SW1 is switched from ON to OFF and
the Load Carriage Motor starts.
2. If the disk is 12cm-disk, when it is carried to the position shown with the dotted line in the drawing, SW 3 switches
to ON due to such rotation of Arm L. Then, the microcomputer judges that the disk is 12cm-disk.
3. In case of 8cm-disk, the disk cannot reach such dotted line position, and from such limitation of approach, the
microcomputer judges that the disk is 8cm-disk and simply triggers clamp actions.
(Movement of SW Arm L and R are connected together. So, if pushing force is fed to only one arm, the distance
between tow arms cannot be widened beyond the specific degree, because the coupling part is locked in such case.)
- Disk centering mechanism
1. In case of 12cm-disk, the 12cm-Disk Detection Arm rotates, and with such rotation, it raises the Centering Arms to
retreat the arms from disk's trace. The disk passes through under the arms, and at the inner part, it is centered.
2. In case of 8cm-disk, it is just centered at the position where its edge touches the front portion of the Centering Arm.
2. MECHANISM DESCRIPTIONS
Page 27

27
C X-97 7
- Clamp actions
1. When centering of 12 or 8cm-disk onto the Spindle is completed, the Detection Arm starts driving.
2. Then, the Detection Arm, via the Detection Reversion Arm, triggers driving of the Plunging Rack, which is on the
Mode Switching Arm unit, in order to engage the rack with the 2-Stage Gear.
3. With such engaging, the Mode Switching Arm rotates, and with the rotation, slides the Clamp-Up Lever and pushes
down the Clamp Arm. At the same time, the Mode Switching Arm slides the Loading-Up lever, and separates the
Loading Arm from the disk. Also, the Loading-Up Lever rotates the Mechanics Lock Arm, releases the Mechanics
Lock, and switches on the Clamp SW. Now, at this position (the position where the disk is situated when the Clamp
SW is switched on), clamping actions are completed.
4. Then, upon the completion of clamping actions, the Plunging Rack lets the Pickup Lock Arm start rotating, and this
Pickup Lock Arm, with such rotation, feeds the Pickup to Feed Screw's screw portion. Now, Carriage actions start.
- Eject actions
1. Eject actions start when the Pickup is fed to the position inner than "Home SW ON" point in the internal
circumference of the circle, caused by backward rotation of the Load Carriage Motor. Eject actions follow the
foregoing procedures (steps taken in loading, centering and clamping actions), but each action in those steps is
performed in reversed manner.
2. In case of 12cm-disk, Eject is completed when SW3 completes its condition- transition of OFF → ON → OFF.
3. For 8cm-disk, Eject is completed when SW2 completes its condition-transition of OFF → ON → OFF.
Page 28

28
C X-97 7
- How to hold the Mechanical Unit
1.Hold the top and bottom frame.
2.Do not squeeze top frame's front portion too tight,
because it is fragile.
- How to remove the Top and Bottom Frame
1.When the disk is "clamp" state, unlock Spring A (6
pieces) and Spring B (2 pieces), and unscrew screws
(4 pieces).
2.Unlock each 1 of pawl at the both side of the frame,
then remove the top frame.
3.Remove the Carriage Mechanical part in such way
that; you remove the mechanical part from 3 pieces
of Damper while slowly pulling up the part.
4.Now, the top frame has been removed, and under
this state, fix the genuine Connector again, and eject
the disk.
(Caution)
When you reassemble the Carriage Mechanical part,
apply a bit of alcohol to Dampers.
- How to remove the Guide Arm Assy
1.Unlock the spring (1 piece) at the right side of the
assembly.
2.Unscrew screws (2 pieces), then remove the Screw
Gear Bracket.
3.Shift the Guide Arm Assy to the left and slowly rotate
it to the upper direction.
4.When the Guide Arm Assy rotates approximately 45
degree, shift the Assy to the right side direction and
remove it.
Top Frame
Bottom Frame
Damper
Spring
Screw Gear Bracket
Guide Arm
Assy
Carriage
Mechanical
Part
Do not squeeze.
3. DISASSEMBLY
Page 29

29
C X-97 7
- How to remove the Control Unit
1.Give jumper-solder treatment to the Flexible Wire of
the Pickup unit, then remove the wire from the
Connector.
2.Remove all 4 points of solder-treatment on the Lead
Wire. Also, unscrew the screw(1 piece).
3.Then, Remove the Control unit.
(Caution)
Be careful not to damage SW when you reassemble
the Control Unit into the device.
- How to remove the Loading Arm Assy
1.Unlock the spring (1 piece) and remove the E ring (1
piece) of the Fulcrum Shaft.
2.Shift the arm to the left side direction and unlock pins
(2 pieces).
- How to remove the Pickup Unit
1.Unscrew 2 pieces of screws, then remove the Pulley
Cover.
2.Remove the Feed Screw unit from the pawl of the
Feed Screw Guide (The pawl is located inside the
guide).
3.Remove the belt from the Pulley, then remove the
Pickup unit.
(Caution)
Make sure not to stain the belt with grease when you
fix the belt.
Control Unit
Jumper-Solder
Solder
Loading Arm Assy
Pickup Unit
Pulley Cover
Feed Screw Guide
Belt
Grease Application
Grease Application
Grease Application
Page 30

C X-97 7
- How to remove the Load Carriage Motor Assy
1.Unscrew the screw (1 piece).
2.Remove the Load Carriage Motor Assy.
- How to remove the Clamp Arm Assy
1.Unlock springs (3 pieces).
2.Remove the Clamp-Up Lever.
3.Remove the Assy in such way that; you shift the Assy
to the left side direction while you rotate it to the
upper direction slowly.
- How to remove the Spindle Motor
1.Unscrew 2 pieces of screws. Then you can remove
the motor.
Load Carriage
Motor Assy
Clamp-Up Lever
Spindle Motor
Clamp Arm Assy
Spring
Spring
Spring
Grease Application
 Loading...
Loading...