PIONEER CX 954 Service Manual
Model Service Manual CD Mechanism Module
SDV-P7/UC CRT2688 CXK6111
AVX-P7300DVD/UC CRT2672
PIONEER CORPORATION 4-1, Meguro 1-Chome, Meguro-ku, Tokyo 153-8654, Japan
PIONEER ELECTRONICS SERVICE INC. P.O.Box 1760, Long Beach, CA 90801-1760 U.S.A.
PIONEER EUROPE NV Haven 1087 Keetberglaan 1, 9120 Melsele, Belgium
PIONEER ELECTRONICS ASIACENTRE PTE.LTD. 253 Alexandra Road, #04-01, Singapore 159936
C PIONEER CORPORATION 2001
K-ZZU. APR. 2001 Printed in Japan
ORDER NO.
CRT2670
DVD MECHANISM MODULE
CX-954
- This service manual describes the operation of the DVD mechanism module incorporated in models
listed in the table below.
- When performing repairs use this manual together with the specific manual for model under repair.
CONTENTS
1. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTIONS ...........................................2
2. MECHANISM DESCRIPTIONS.................................15
3. DISASSEMBLY .........................................................19
2
CX-954
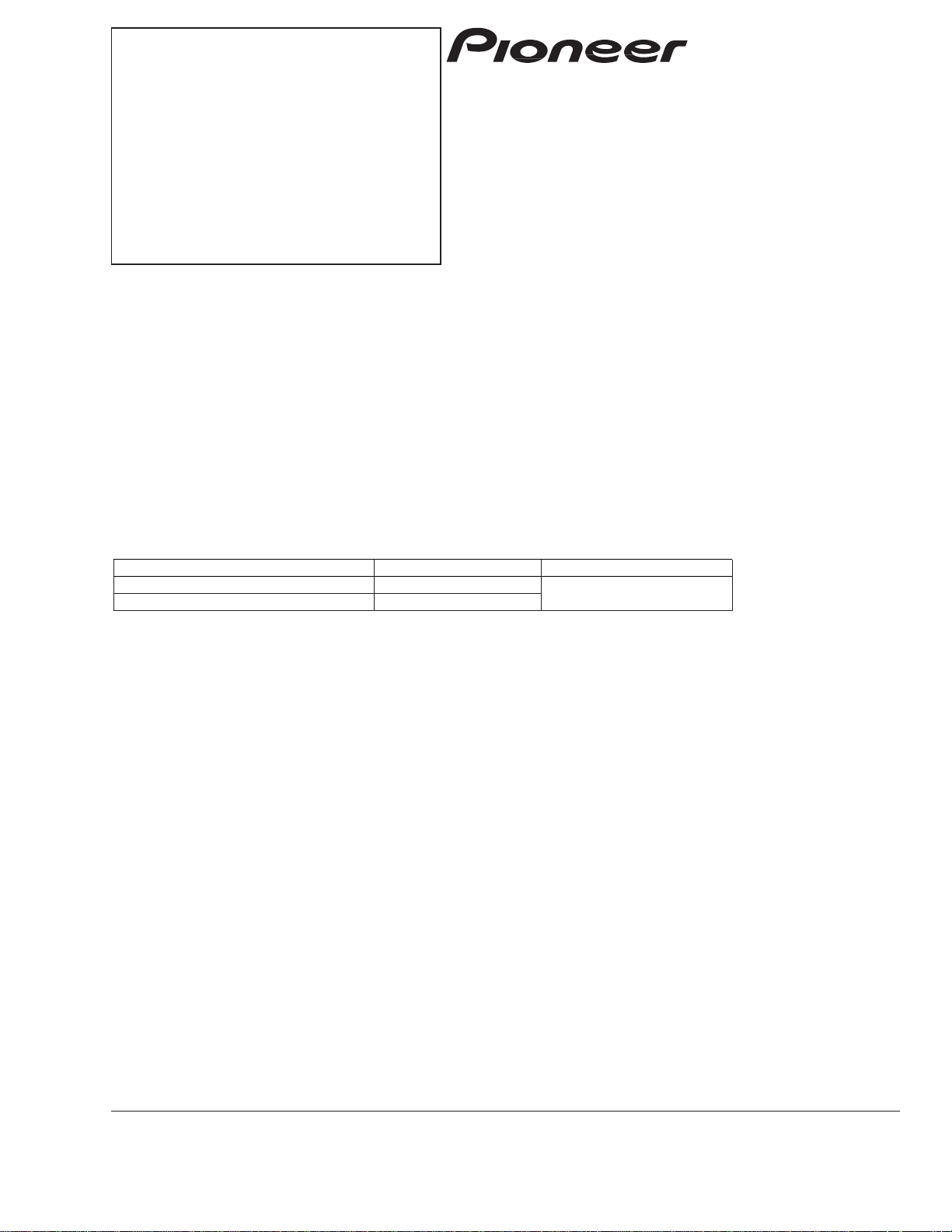
1.1.1 APC circuit
The light output of the laser diode (LD) has a large negatively charged thermal characteristic. The APC circuit is
designed to stabilize the light output at the monitor diode (MD), by controlling the current. AN8702FH contains two
types of APC circuits, one for DVDs and the other for CDs. The LD current can be obtained by dividing the voltage
reading between positions DVDLD1 (CDLD1) and 5V by 15.6 Ω (3.9 Ω x 4 = 15.6 Ω). For DVDs (CDs), it is approximately
26 mA (44mA).
1.CIRCUIT DESCRIPTIONS
1.1 Front-end processor (FEP) section (AN8702FH: IC1100)
The IC1100 generates servo signals for focus and tracking operations and increments the RF signal and also controls
the laser power of the pick-up.
The IC contains a focus calculation amplifier, a focus balance adjustment circuit, a three-beam tracking calculation
amplifier, a phase difference tracking detection circuit, a tracking balance adjustment circuit and an envelope detection
circuit for servo controls.
For the RF signal processing the AGC and equalizer functions are contained in the IC as well.
1.1.1 APC circuit
1.1.2 FE generation circuit
1.1.3 TE generation circuit
For CD
For DVD
170mV
180mV
+5V
–
+
–
+
LPC02
LPC2
LPC01
LPC1
+
4
3
+5V
+
2
1
3.9Ω 3.9Ω 3.9Ω
3.9Ω 3.9Ω 3.9Ω
+
3.9Ω
CDLD0
3.9Ω
DVDLD0
CDLD1
DVDLD1
28
10
30
12
CN1100
78LD
78MD
65LD
65MD
CD
LD
+5V
MD
DVD
LD
AN8702FH
PU UNIT
3
CX-954
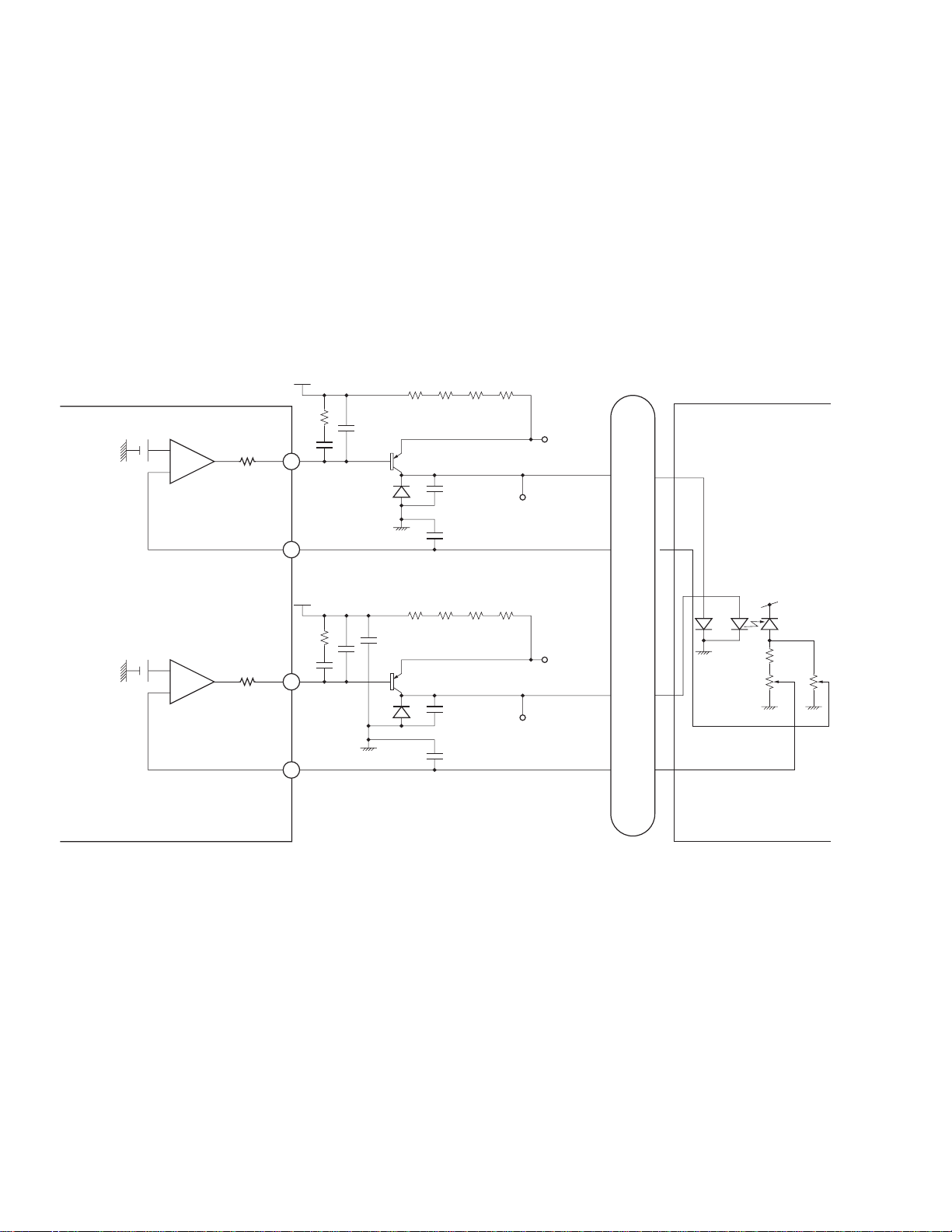
1.1.2 FE generating circuit
Focus error (FE) generating circuit
PU divides the output into four input signals of the FE circuit, B1 through B4. These input signals are fed through the
internal resistors and results in (B1 + B3) and (B2 + B4) signals. These signals are then fed into the variable amplifier
for focus balance adjustment, and the FE signal is generated by amplifying the {(B1 + B3) – B2 + B4)} signal.
Numbers and names indicated inside the brackets are identical to those of pins and terminals. Circuits for CDs and
DVDs are identical, except for the input terminals B1 through B4.
B1
CN1100
20
19
17
15
AN8702 FH
60 VIN4
(52 VIN8)
57 VIN1
(49 VIN5)
58 VIN2
(50 VIN6)
59 VIN3
(51 VIN7)
B2
B3
B4
–
+
G4 1–f
G4 1+f
+
–
VHALF
1.65V
22
FEOUT
21 FEN
FEY
RFEN
FEX FE
3 FE
VHALF
MN677061ZY
FBAL7
Control
4
CX-954
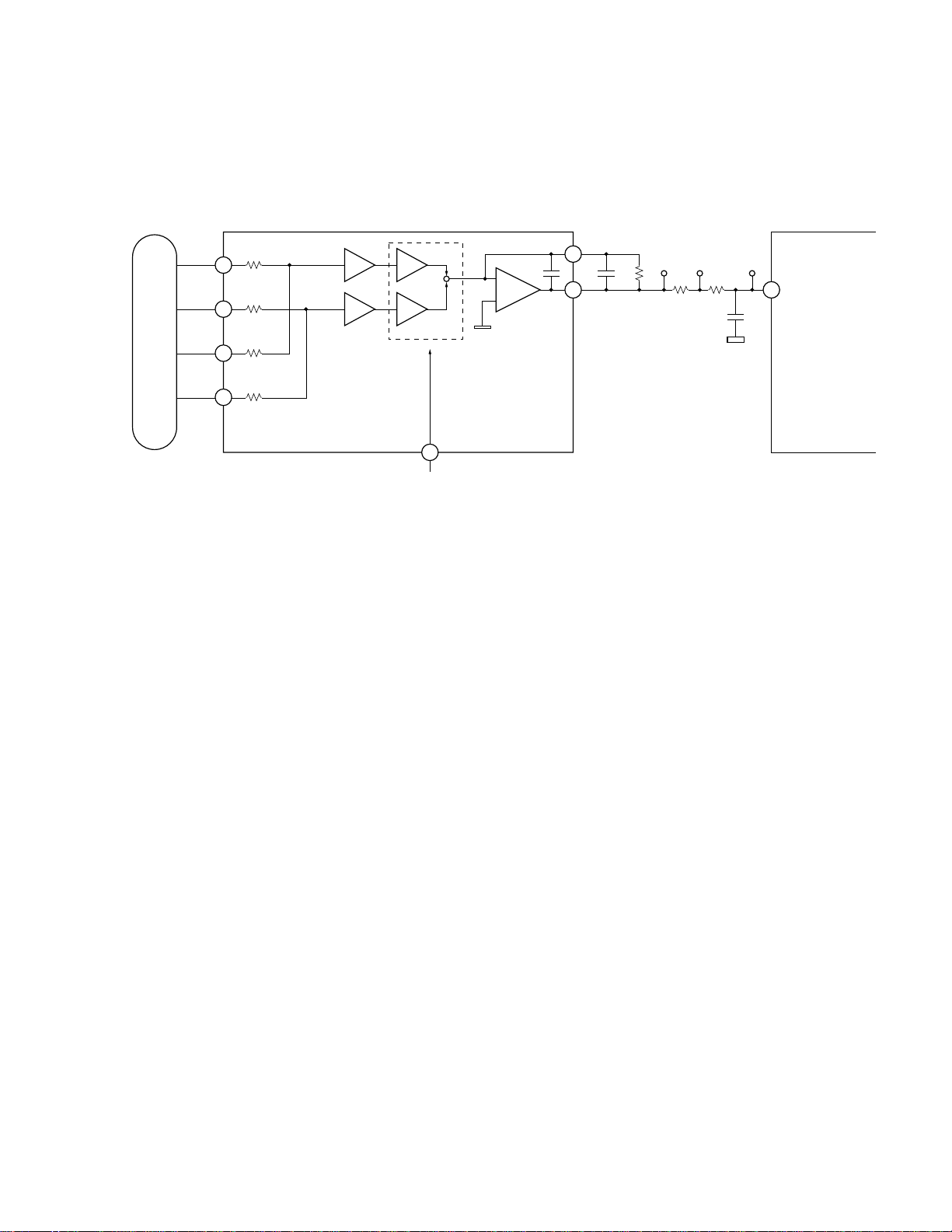
1.1.3 TE generating circuit
• CD (three-beam TE)
Tracking Error (TE) generating circuit
For DVDs, the TE is generated from the difference in phase between (B2 + B4) and (B1 + B3) signals, using the
differential phase method. For CDs, it is generated by amplifying the A + C, after passing through the external resistors
and the variable amplifiers for tracking balance adjustments.
A
C
–
+
14
63 VIN12
21
CN1100
62 VIN11
G4 1+t
G4 1–t
+
–
VHALF 1.65V
18 TEOUT
17 TEN
TEY
RTEN
TEX TE
2 TE
VHALF
MN677061ZY
TBAL6
ControlAN8702FH
B1
B2
B3
B4
–
+
15
60 VIN4
17
59 VIN3
TGBAL
TGBAL5 TBAL6
19
58 VIN2
20
57 VIN1
TBAL
DIFFERENTIAL
PHASE
DET.
VHALF
1.65V
18
TEOUT
17 TEN
RTEN
TEY TEX
MN677061ZY
TE
2 TE
VHALF
APF/HPF
· DVD (differential phase TE)
5
CX-954
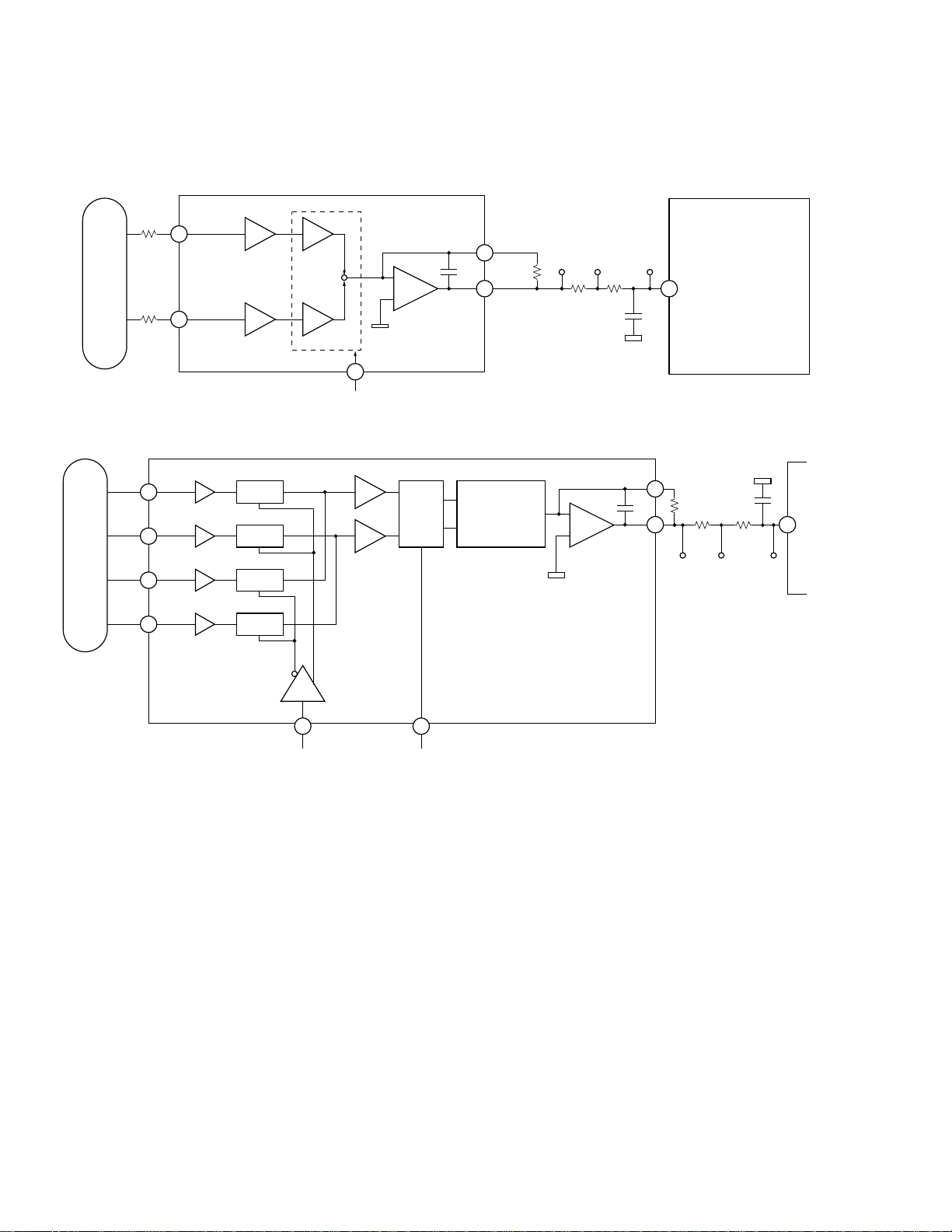
The following procedure is performed for both DVD and CD disks, whenever a focus close command is issued.
1. Measuring and optimizing the signal levels
The lens of PU is initially driven to move away from the disk, and then moved toward the disk. The signal levels of
FE, AS and RFENV are measured at the focal point. Then signal level optimization is conducted for the signals FE
and AS (1 and 2 as shown in the diagram).
Near the disk
Away from the disk
Lens
VHALF
Focal point
FE
RFENV
AS
3
6
7
4
5
1
2
1.2 Servo controller (ADSC) section (MN677061ZYUB: IC1200)
The servo processing section of the IC1200 controls focus, tracking and traverse operations, while the signal
processing section of the IC processes digital signals of the CD-DA and CD-ROM.
A digital signal processor (DSP) is used in the core section of the servo control.
An analog-digital converter, for servo signals as well as the digital-analog converter to output drive values to the driver
for focus and tracking operations, are also contained in the IC.
The PWM converter, which outputs drive values to the driver for spindle and traverse operations, the RF signal data
slicer and PLL as well as the jitter detection circuit, are also included in the IC.
Frame synchronization detection, EFM demodulation, sub-code data processor and the CIRC error correction function
are also included in the CIRC block signal processing section.
1.2.1 Focus close
1.2.2 Tracking close
1.2.3 Track jump
1.2.4 Focus jump
1.2.1 Focus close
FODRV

6
CX-954
2. Closing in the focal point
The lens is then driven away from the disk, taking a measurement for the closing in levels for signals FE and AS.
The focus loop filter is then operated to close in the focal point (3 through 6).
3. Verifying the close in
The closing in of the focal point is verified with signals AS and RFENV (6 and 7).
The signal levels of FE, AS and RFENV, as well as the voltage level of the focus drive, can be verified through the
focus search conducted in the test mode.
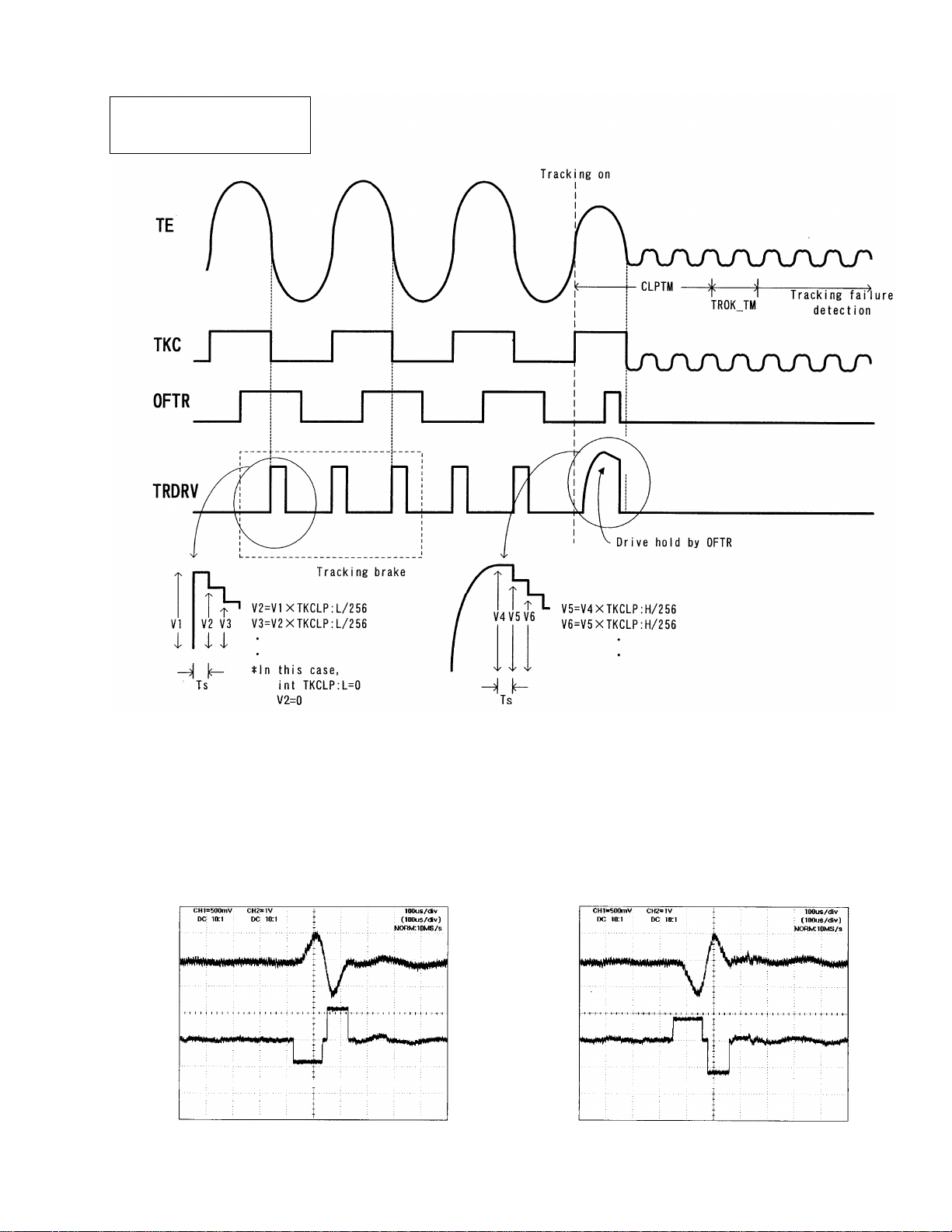
1.2.2 Tracking close
The following procedure is performed for both DVD and CD disks, whenever a tracking close command is issued.
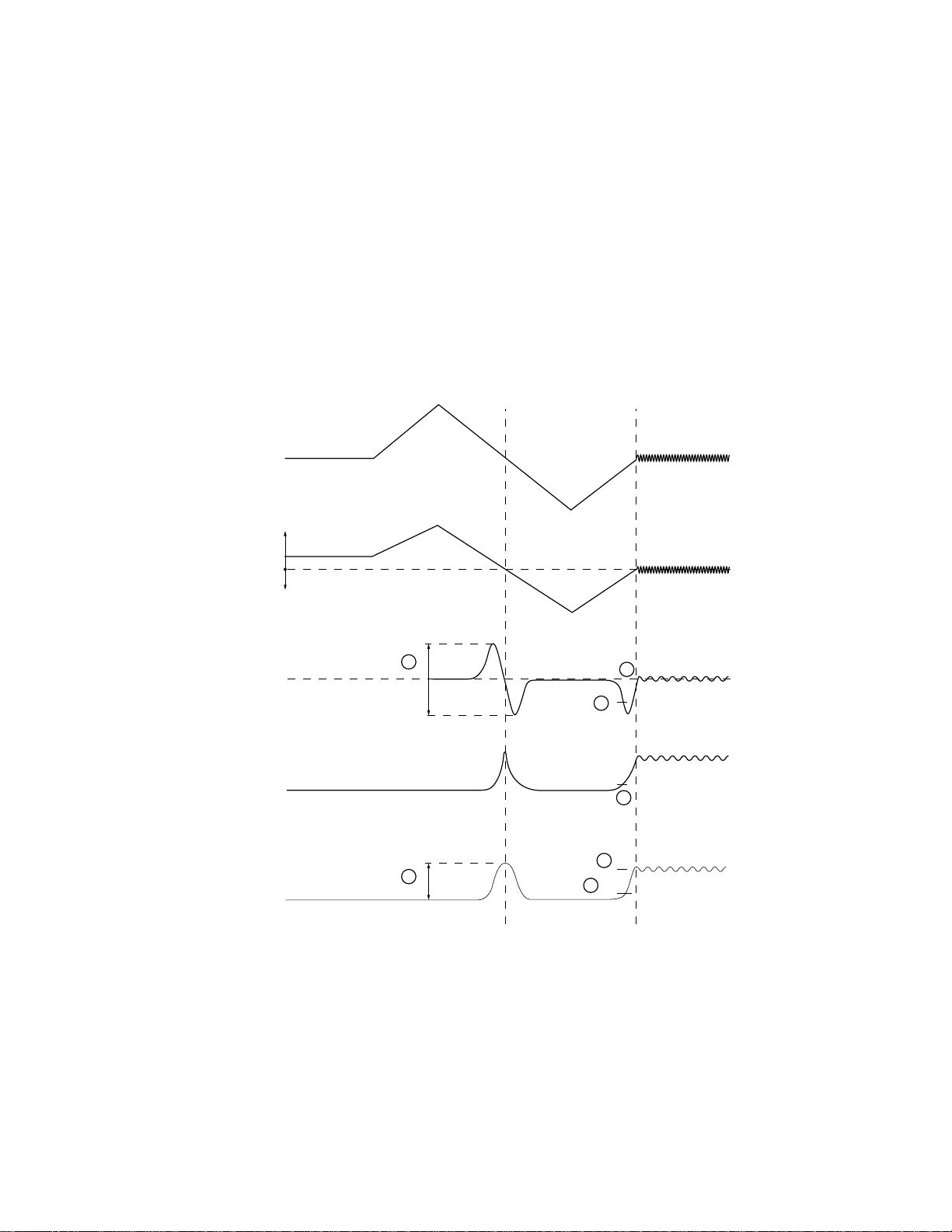
1. Tracking brake
A half cycle of the track crossing signal is measured. If the measured cycle falls within the specified range, then a
brake pulse signal is output. The direction of the brake pulse output is determined from the phase relationship of
signals OFTR and TKC (signal resulting from the conversion of the TE signal to a binary signal). Vibration control
of the lens, with respect to the disk, is verified and if the control is carried out satisfactorily, the brake pulse output
will be terminated, moving on to the closing in of the focal point. The brake pulse is output, and if the conditions
for the closing in of the focal point are not established within 30msec., the brake pulse output will be terminated.
Monitoring will continue for a maximum of 70msec., before moving on to the closing in of the focal point.
2. Closing in the tracking
The tracking drive hold process is conducted with the OFTR signal.
3. Verifying the closing in
The track jump is counted to determine whether the number of track jumps within a specified time interval falls
within the specified number of track jumps or not. Verification of the close in reaches time out at 7msec., and a
retry will take place automatically for as many times as specified.
1.2.3 Track jump
Three methods are available with this system, which are selected according to the number of target transition
tracks. The methods are the interval jump, multi-jump and transverse seek.
1. Interval jump
Since track jumps are conducted repeatedly on a single track a detailed seek is possible. This method is used
when the target track is near, or for seeking a neighboring track.
2. Multi-jump
Both edges of the TKC, of the track cross signal, are counted. Transition, by the number of specified track counts,
is carried out.
3. Traverse seek
The transition speed is controlled by taking a measurement of the track cross signal's TKC time. The vibration of
the pick up, which occurs during transition, is held within minimum values.
The jump switching settings for both DVDs and CDs are shown below:
Target transition Type of jumps
1~10 Interval jump
11~100 Multi-jump
101~500 Combination of multi-jump and interval jump
501~ Traverse seek
Waveforms of the tracking jumps are shown next page:
7
CX-954
TE
TD
Tracking–on process
Interval jump (one track)
External circumference jump Internal circumference jump
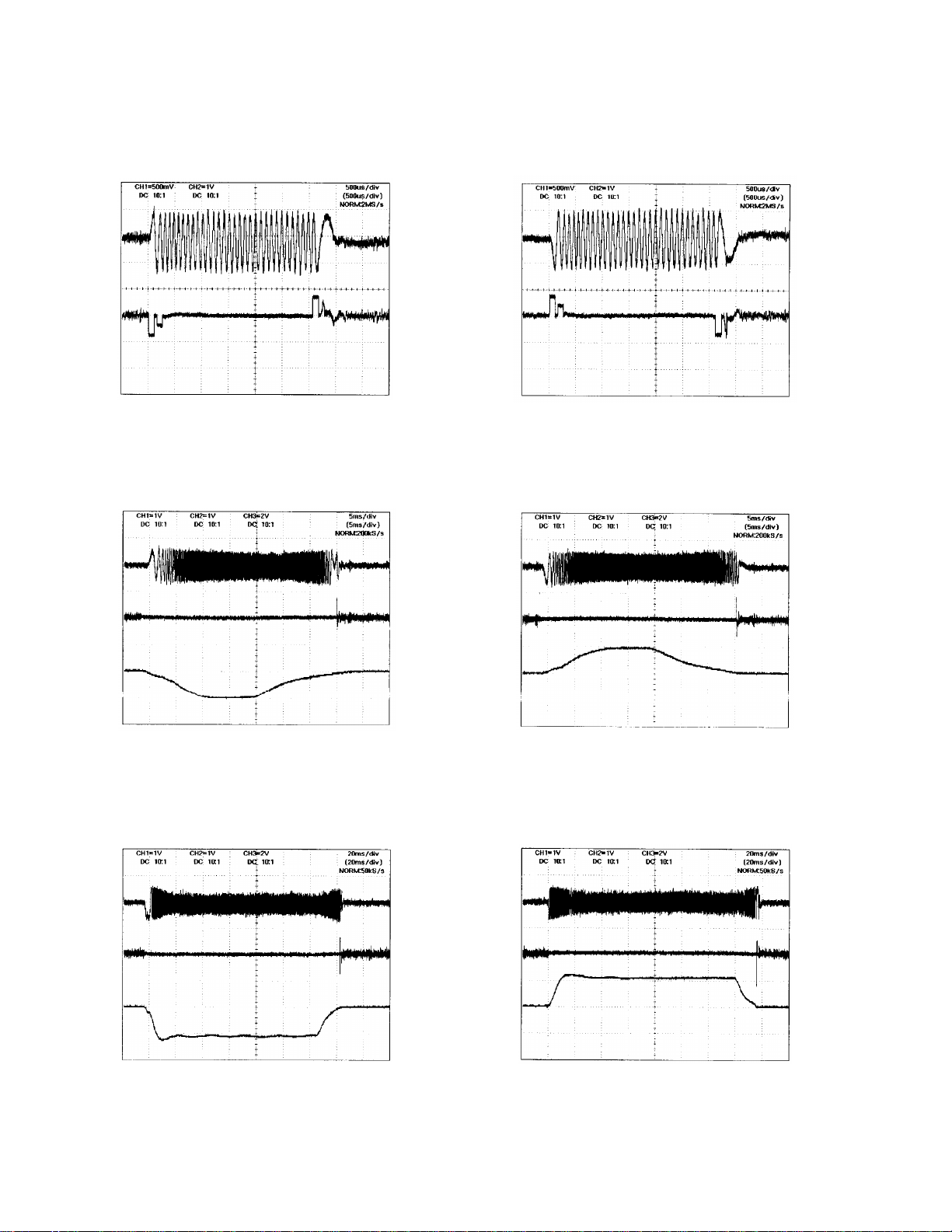
8
CX-954
Traverse seek (501 tracks)
External circumference jump Internal circumference jump
Multi-jump (32 tracks)
External circumference jump Internal circumference jump
TE
TD
TE
TD
CO±
Traverse seek (5,000 tracks)
External circumference jump Internal circumference jump
TE
TD
CO±
 Loading...
Loading...