Pioneer CX-692 Service manual
Model Service Manual DVD/CD Mechanism Unit
XDV-P9/UC,EW,ES/RC,ES/RD CRT2511 CXK7010
PIONEER CORPORATION 4-1, Meguro 1-Chome, Meguro-ku, Tokyo 153-8654, Japan
PIONEER ELECTRONICS SERVICE INC. P.O.Box 1760, Long Beach, CA 90801-1760 U.S.A.
PIONEER EUROPE N.V. Haven 1087 Keetberglaan 1, 9120 Melsele, Belgium
PIONEER ELECTRONICS ASIACENTRE PTE.LTD. 253 Alexandra Road, #04-01, Singapore 159936
C PIONEER CORPORATION 2000
K-ZZS. MAY 2000 Printed in Japan
ORDER NO.
CRT2533
DVD/CD MECHANISM UNIT
CX-692
- This service manual describes the operation of the DVD/CD mechanism incorporated in models listed
in the table below.
- When performing repairs use this manual together with the specific manual for model under repair.
CONTENTS
1. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTIONS ...........................................2
2. DISASSEMBLY .........................................................20
3. MECHANISM DESCRIPTIONS.................................24
2
C X-692
Q104
PICKUP UNIT
IC103 TA1254AF
45
LDO1
MDI1
44
GND
7
VCC
8
VPS
IC101
3
4
2
1
IM
CPOUT
PICKUP UNIT
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
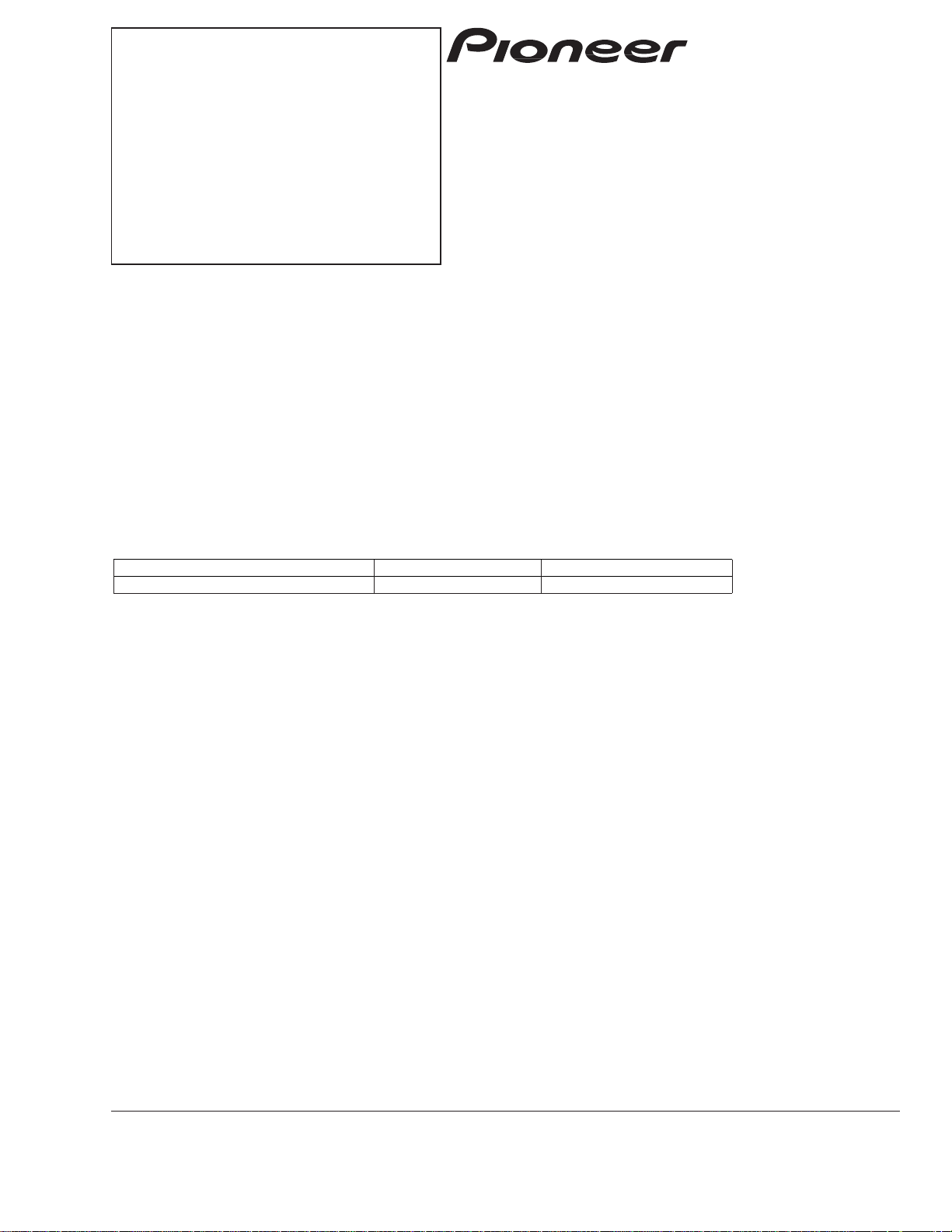
1. Circuit Description
1.1 APC circuit
- APC (Automatic Power Control) circuit
[Fig. 1 CD and Fig. 2 DVD]
Since the optical output of laser beam diodes carries a
large negatived temperature characteristic, necessary
optical power cannot be acquired when driven at a
lower current level. The APC circuit is a circuit to
control the current levels so that the output of the
monitor diode may become constant. By measuring
the voltage occurring between the LD and the drive
transistor, the LD current can be found out and such
current value should be within
±
20% of the value
indicated on the pickup unit flexible P.C. board when
handling the CD and should be 50mA or less when
handling the DVD.
C X-692
3
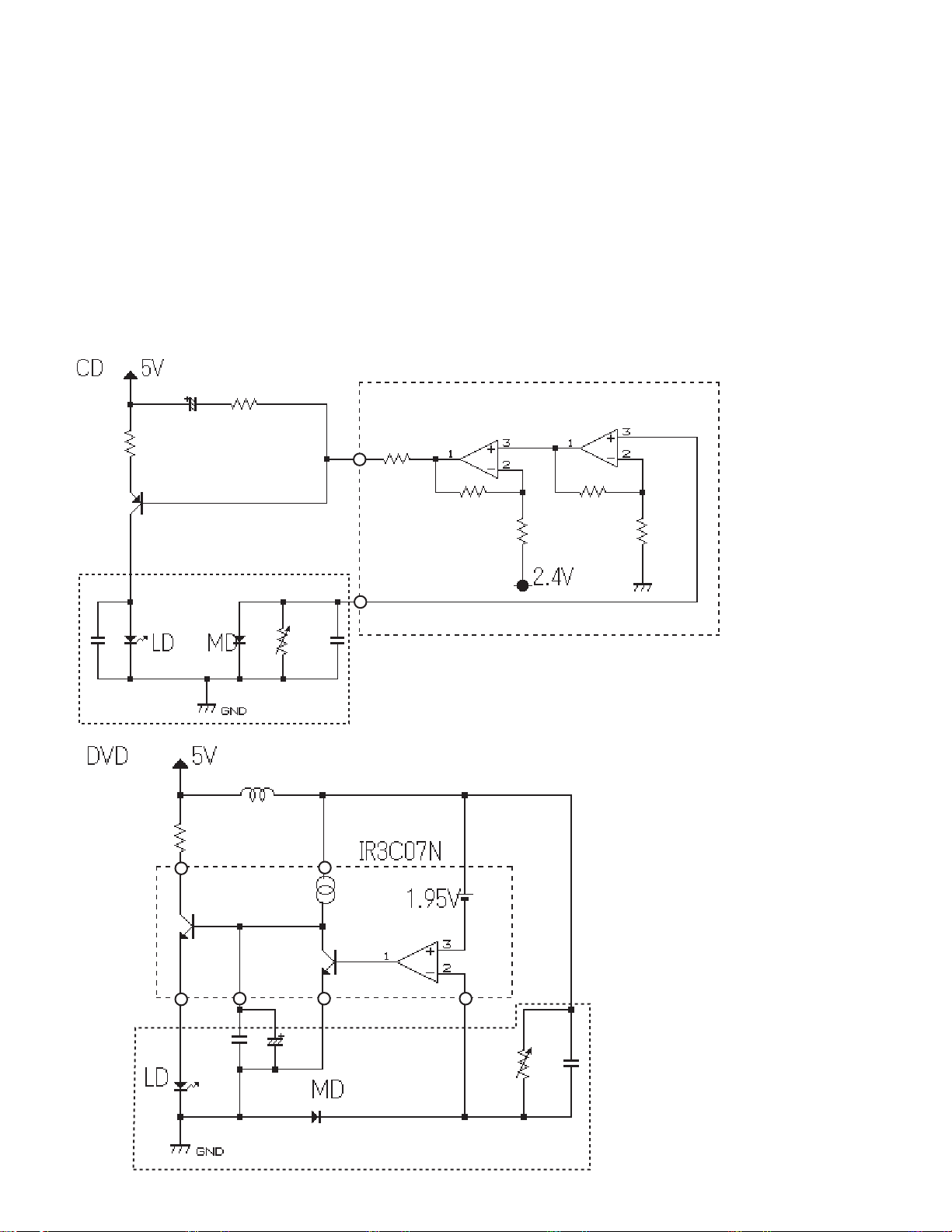
1.2 FOCUS-JUMPING CIRCUIT
Focus-jumping function is a function conforming to
single side 2-layer discs or double-side 2 layer discs.
Fig. 3 below shows the basic movement sequence.
Viewing through the objective lens, the layer on this
side is called Layer 0 (L0) and the layer on the far side is
called the Layer 1 (L1).
Objective lens
RF
FE
Focus
standby level
Focus ON
Vref
GND
Vref
A(Fig.4)
TEST00
B(Fig.4)
IO0
L0=L1
L1=L0
L0 L1
L0
L1
L0
(Layer1) L1
(Layer0) L0
L1
L0
A
B
C
D
E
A
B
C
D
E
Fig. 3
4
C X-692
Described below are the explanations of the basic
movements.
When the focus-jumping command is issued from the
mechanism controller (IC501:PD5511A), the input to the
focus equalizer is changed over from the AD converter
output (FOO) to the DC hold filter output and DC
holding is effected.
Simultaneously, the focus search drive signals are
output through the TESIO0 pin and the TESIO1 pin. By
the circuit shown in Fig. 4, these signals are made to
apply drive signals to the focusing servo loop which
work to drive the focusing actuator to complete the
layer jump.
FOO
19
FOJ
Q401
Q402
IC402
NJM2904M
IC401
67
43
18
19
IC304
BA6797FM
Focus-jumping circuit
Normal state
While focus-jumping
is in progress
Fig. 4
C X-692
5
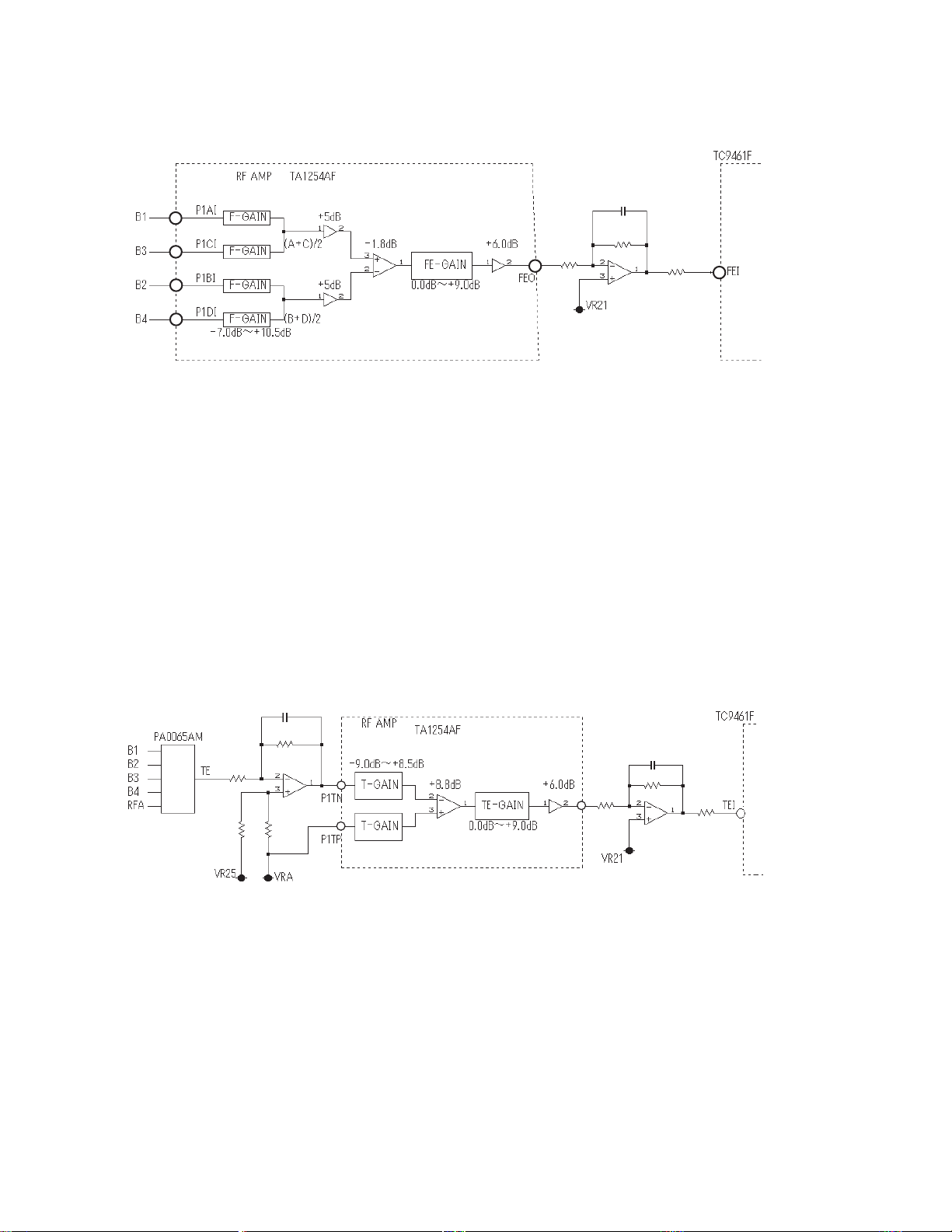
Under normal CD settings: F-GAIN = 0.5dB, FE-GAIN = 3.0dB
Under normal DVD settings: F-GAIN = -4.5dB, FE-GAIN = 6.0dB
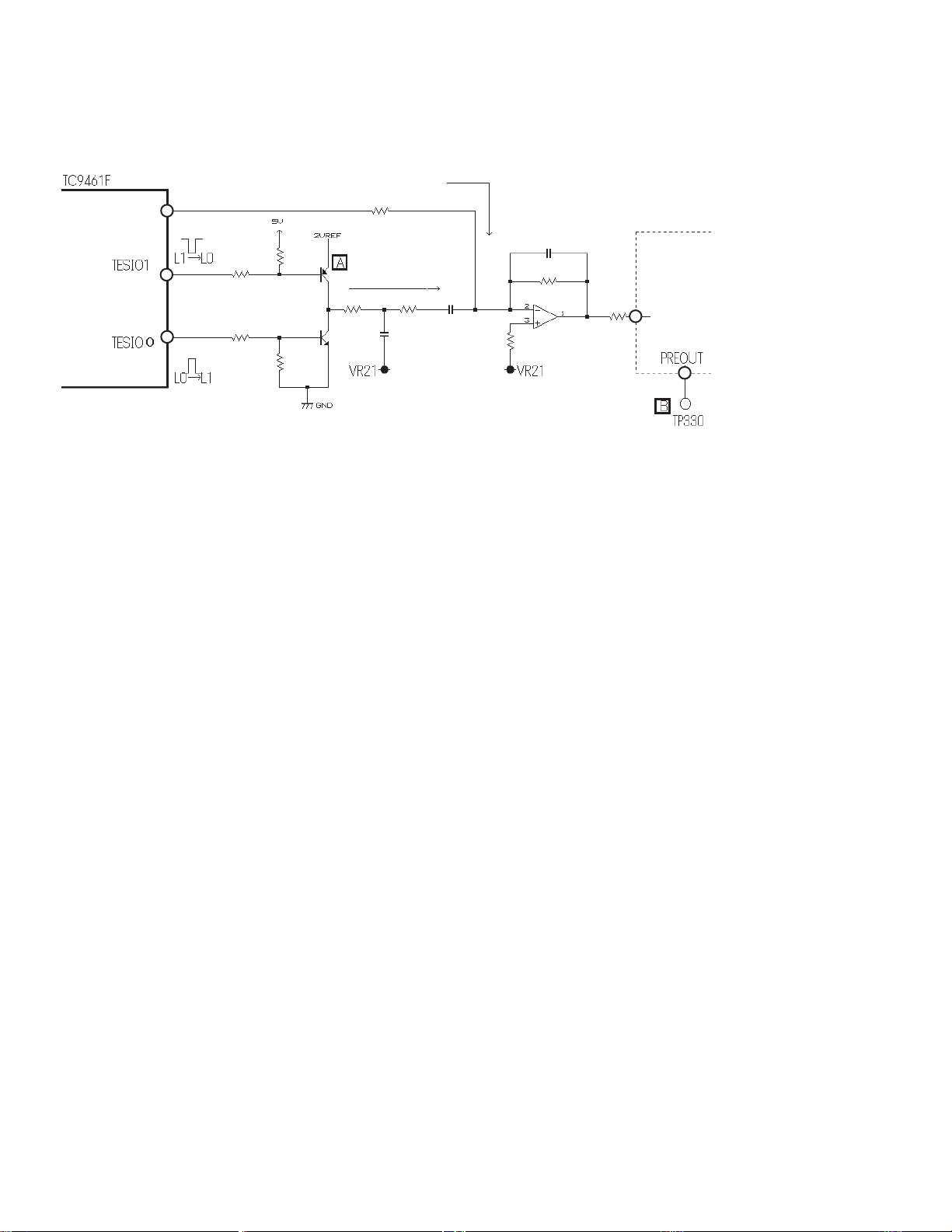
1.4 TRACKING ERROR SIGNAL
GENERATING CIRCUIT
Tracking error signals are being formed by amplifying the RFA
being generated through the B1 - B4 of the pickup unit output
and the RF amplifier (IC103:TA1254AF) by the
TC7WU04FU(IC106,109) and by inputting these signals to the
time difference IC (IC107:PA0065AM). The error signals being
output from the time difference IC are amplified through the OP
amplifier(IC108) and the RF amplifier(IC103) before being input
to the servo DSP (IC401:TC9461F pin41).
Under normal CD settings: T-GAIN = -9.0dB, TE-GAIN = 0.0dB
Under normal DVD settings: T-GAIN = -9.0dB, TE-GAIN = 6.0dB
IC103
55
53
54
52
21
IC105
NJM3404AM
IC401
38
IC107
2
8
4
10
6
19
IC108
NJM3404AM
IC103
46
47
20
TEO
IC108
NJM3404AM
41
IC401
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
1.3 FOCUS ERROR AMPLIFIER
6
C X-692
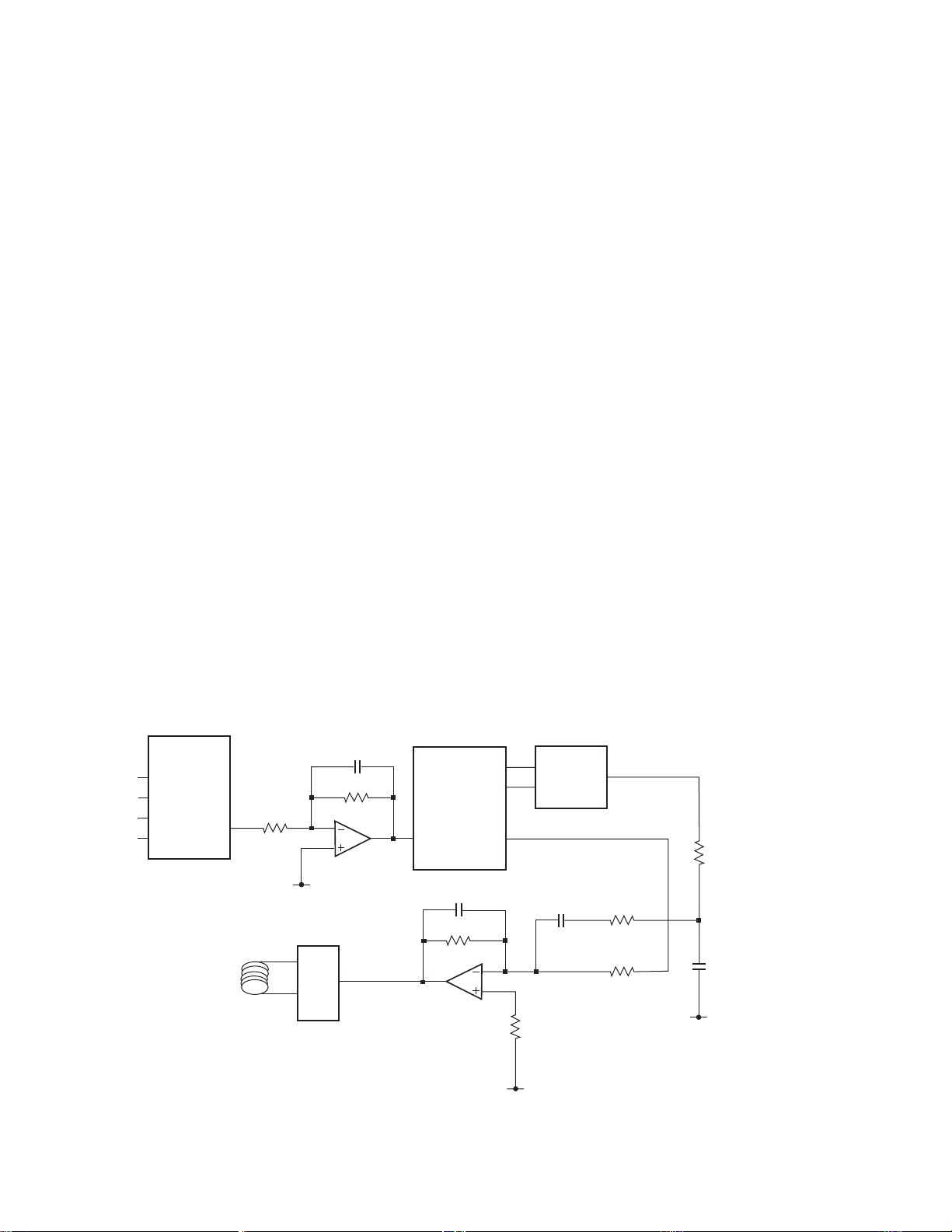
1.5 SERVO SYSTEMS
1.5.1 FOCUSING SERVO SYSTEM
The main equalizer for the focusing servo system is
being provided inside the servo DSP (IC401:TC9461F).
Fig. 7 shows the block diagram of the focusing servo
system.
With the focusing servo system, it is necessary to move
the leans into inside the focusing range to make focus
closing. For this purpose, the lens is moved up and
down by the focus search voltage of the chopping wave
to find out the focusing point. Also, while this
movement is in progress, the SPDL motor is being
kicked to maintain its speed to the preset speed.
The servo DSP works to monitor the FEI signals and the
SBAD signals (upper envelope of the RF) to issue
commands to execute automatic focus closing
movement at the optimum point. Focus closing is
executed when the following conditions are being
satisfied:
1) When the lens moves from "Near" -> "Far" as against
the disc
2) When the FEI signal level exceeds the prescribed
STANDBY level
3) When the FE becomes "0" (FE = "0", at the reference
voltage of 2.1V)
When the SBAD stays beyond the SBREF level
continuously for 32mS after focus closing, the servo LSI
recognizes the focus closed state to raise the FOK port
of the microcomputer to the "H" level.
While if the SBAD stays below the SBREF level
continuously for 12mS after focus closing, the servo LSI
recognizes that the focus is lost to activate the resetting
process.
Meanwhile, the reference voltages for the
aforementioned SBREF level and STANDBY level
coincide the offset levels for respective signals (FEI and
SBAD) for the POWER ON state and for the LD OFF
(CONT = "L") state.
Fig. 8 shows the series of movements relevant to focus
searching and focus closing.
While a 2-layer disc of DVD is being handled, since the
reflectance is low, the focusing error signals will not
exceed the STANDBY level and focus closing is not
workable. In such case, the FE level will be raised
through the OEIC and F-GAIN to start movement to
make the closing motion once again. Since this
movement is not valid under the test mode, it is so
designed that the gain settings for 2-layer DVD discs
can be worked out manually.
B1
B2
B3
B4
RF AMP
IC103
TA1254AF
55
53
54
52
21
FEO
2
3
1
VR21
SERVO DSP
IC401
TC9461F
FEI
FOO
38
43
IC105
NJM3404AM
F.JUMP
CIRCUIT
2
3
1
VR21
VR21
F ACT.
16
17
19
DRIVER
IC304
BA6797FM
IC402
NJM2904M
Fig. 7
7
C X-692
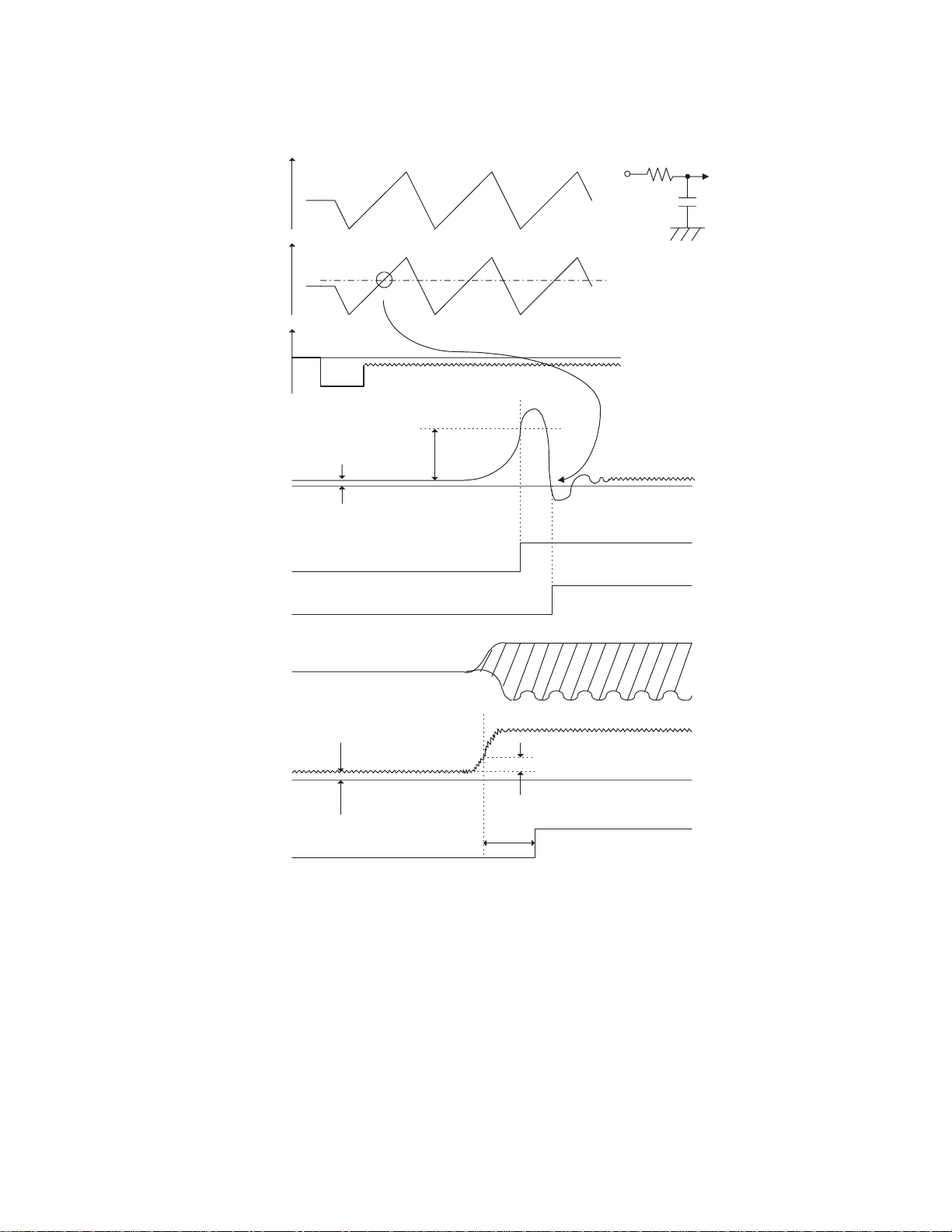
1) Focus searching
F
±
Focusing point
Near
Far
Relative
distance between
the lens and the disc
0
EC
2) Focus closeing
Normally,focus closing is made at this point
H
L
CLOSE
OPEN
STANDBY
Close
(Inside the servo LSI)
(Inside the servo LSI)
Offsetting
SBREF
FOK
RF
SBAD
FOK
(Inside the servo LSI)
H
L
FOK = 32mS
Monitor
R=100kΩ
C= 0.016µF
Offsetting
STANDBY
(Reference voltage at 2.1V)
ECR(Reference voltage at 2.5V)
(Reference voltage at 2.1V)
Fig. 8
8
C X-692
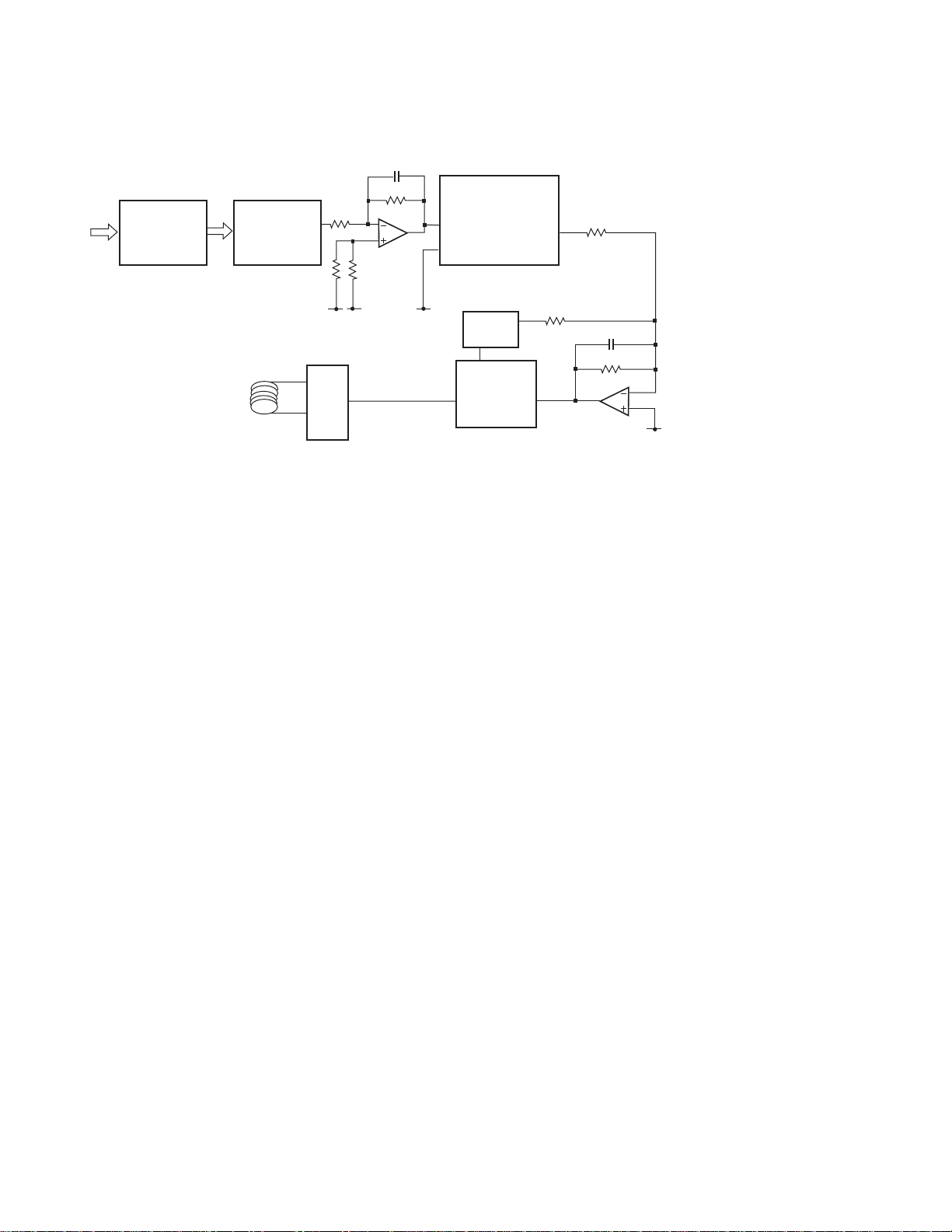
1.5.2 TRACKING SERVO SYSTEM
The main equalizer for the tracking servo system is being provided
inside the TC9461F(IC401). Fig. 9 shows the block diagram of the
tracking servo system.
Tracking closing and tracking jumping movements are being made
automatically by the auto-sequencing function incorporated inside
the servo DSP (IC401:TC9461F) after the LSI receives the command
from the microcomputer(IC501:PD5511A). This system is being
equipped with the lens kick mode which is to be used for jumping
of 255 tracks or less and the feed kick mode which is to be used for
jumping of 512 tracks or more as the track jumping means to use
for searching. Also, tracking closing movements are being
realized by the zero-track jumping command under the lens kick
mode. Under the test mode, 14 types of jumps, namely, 1, 4, 8,
16, 32, 64, 100, 255, 512, 1,000, 4,095, 4,096, 16,384 and 32760 can
be used for checking by making the mode selection accordingly.
Under the normal mode, jumps of:
CD: 1, 2, 4, 8, 10, 16, 32, 64 and 100
DVD: 1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 12, 16, 32, 64, 100 and 255
are available for lens kicks.
2
3
1
T.BAL
CIRCUIT
T ACT.
26
27
25
DRIVER
IC304
BA6797FM
SERVO DSP
IC401
TC9461F
44
TRO
TEI
41
6
5
7
RF AMP
IC103
TA1254AF
20
46
47
TEO
P1TN
P1TP
VR21
VR21
VR25
VR21
IC108
NJM3404AM
47
TE IC
IC107
PA0065AM
B1
B2
B3
B4
RFA
IC106,109
TC7WU04FU
19
Fig. 9
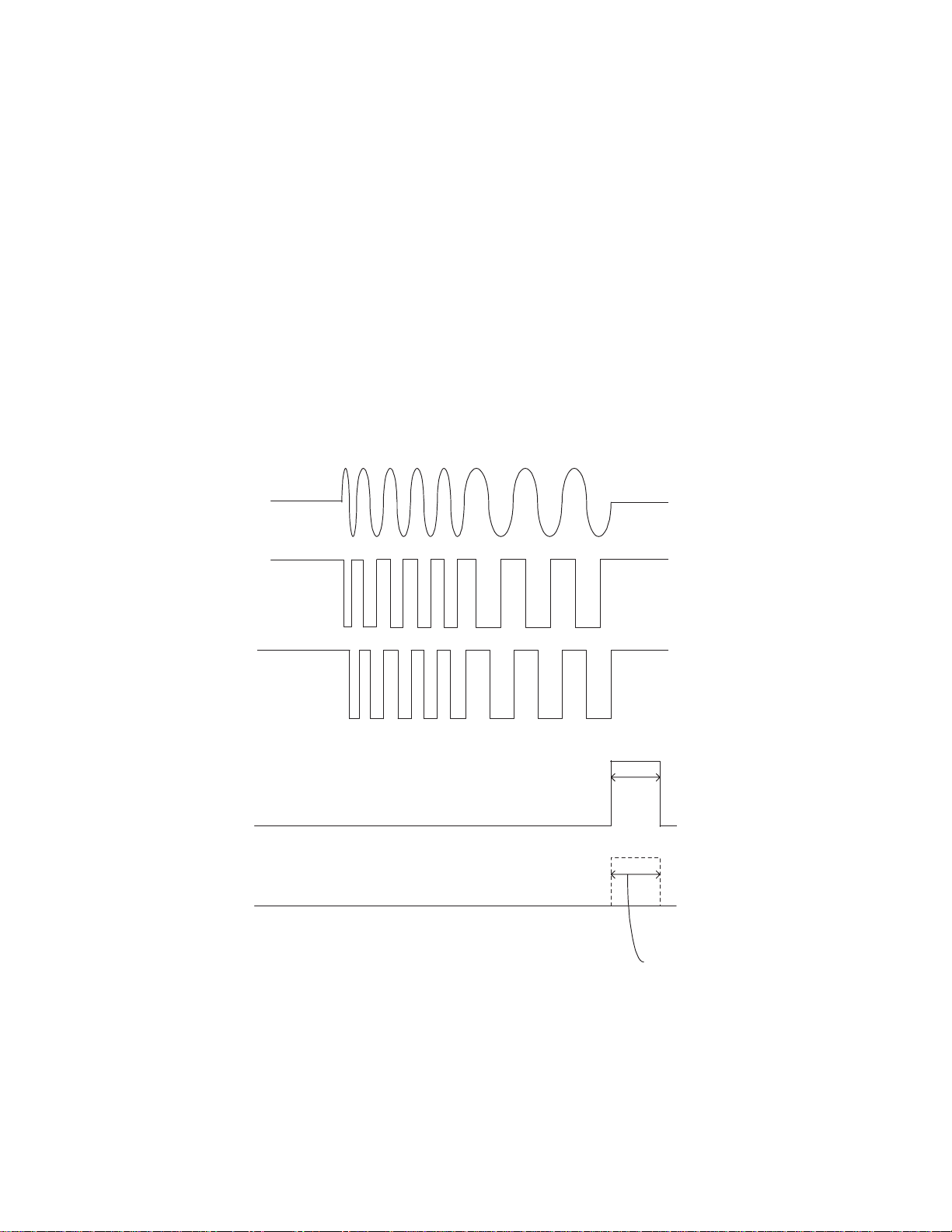
9
C X-692
Lens kick mode jumping
The lens kick mode jumping is being executed by the
lens kick command being issued by the
microcomputer(IC501:PD5511A).The jumping direction
and the number of jumping tracks (1 - 255) are being
designated by the command. Receiving the lens kick
command, the LSI applies the kick pulse to the front
stage of the tracking EQ to execute the jumping. At
this time, the LSI works to control the moving speed of
the lens referring to the table carrying inside the LSI.
By this function, when the number of remaining tracks
is still large, the speed is raised, while the speed is
lowered as the number of remaining tracks decreases
to facilitate taking-in action by the servo when the jump
has been finished. While jumping is in progress, the
track counting is being made in observation of the RFRP
signals. Also, the jumping direction is being detected
by the phases of the RFRP and the TEZ1.
Meanwhile, when a track jumping has been finished, in
order to stabilize the taking-in action by the servo, the
tracking servo gain will be raised for about 2 to 3mS
after a jump has been finished, or with some jumps,
hysteresis movements are being employed.
8 track jumping
Equalizer
Hysteresis
TE
RFZC
(IC401's internal signals
being formed by the RFRP)
TEZC
(IC401's internal signals
being formed by the TEI)
GAIN UP
NORMAL
ON
OFF
2-3mS
The hysteresis ON for 2mS to 3mS
for 100 or 255 track jumping only
Fig. 10
 Loading...
Loading...