Pioneer CX-680 Service manual
Service
Manual
ORDER NO.
CRT2216
CD MECHANISM MODULE
CX-680
-
This Service Manual outlines operations of the CD mechanism module used in the models listed
blow.
-
For repair, use this Service Manual and the Service Manual of the model used in the system.
Model Service manual CD mechanism module CD mechanism unit
DEX-P1R/UC
DEH-P946/ES CRT2206 CXK5101 CXB1699
DEX-P1/ES
DEH-P945R/EW
DEX-P99R/EW
CRT2207 CXK5101 CXB1699
CONTENTS
1. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTIONS ........................................... 2
2. MECHANISM DESCRIPTIONS................................. 15
3. DISASSEMBLY .......................................................... 17
PIONEER ELECTRONIC CORPORATION 4-1, Meguro 1-Chome, Meguro-ku, Tokyo 153-8654, Japan
PIONEER ELECTRONICS SERVICE INC. P.O.Box 1760, Long Beach, CA 90801-1760 U.S.A.
PIONEER ELECTRONIC [EUROPE] N.V. Haven 1087 Keetberglaan 1, 9120 Melsele, Belgium
PIONEER ELECTRONICS ASIACENTRE PTE.LTD. 501 Orchard Road, #10-00, Lane Wheelock Place, Singapore 238880
C PIONEER ELECTRONIC CORPORATION 1998
K-FES. MAY. 1998 Printed in Japan
CX-680
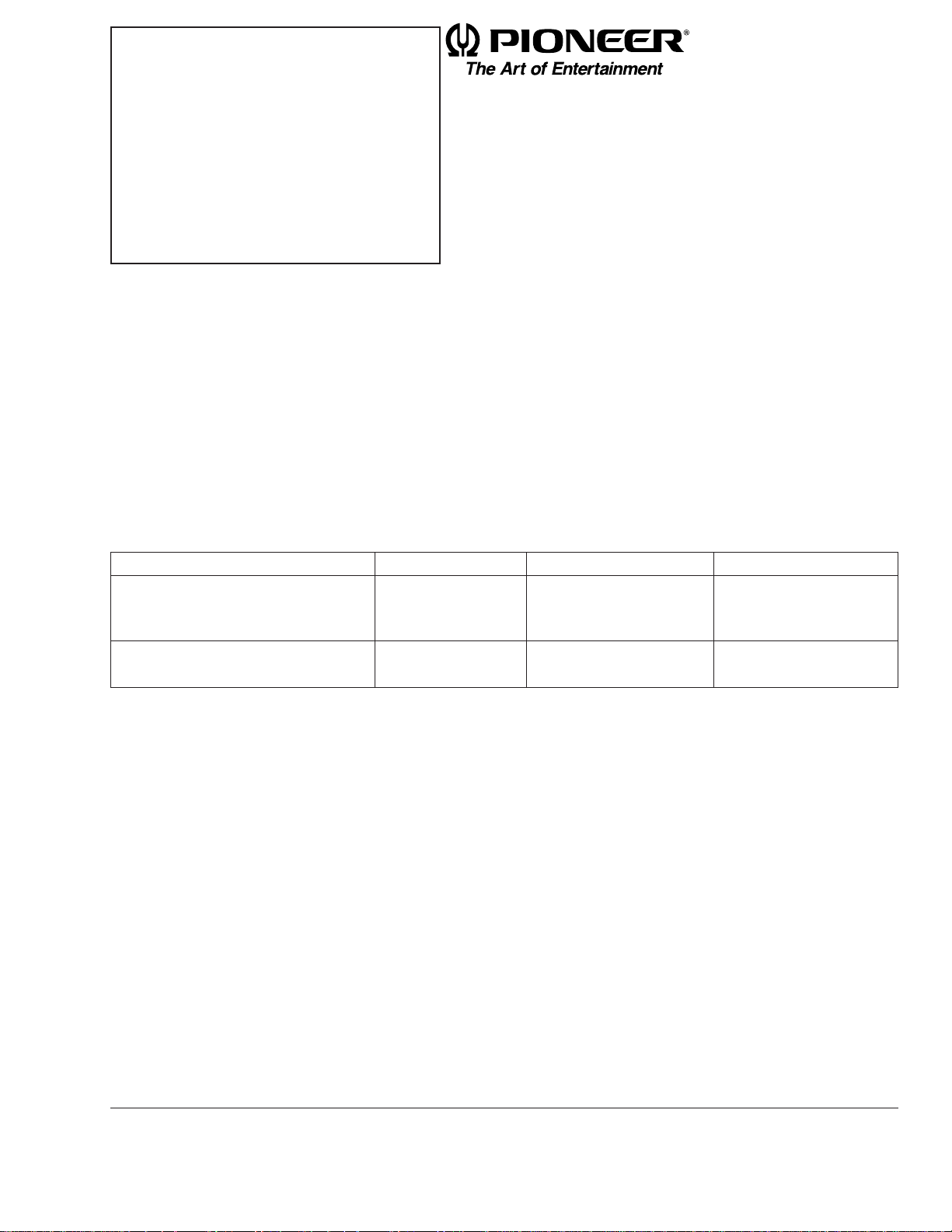
1. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTIONS
1.1 Preamplifier (UPC2572GS: IC101)
The preamplifier processes pickup output signals to
generate signals to be sent to the servo, demodulator, and controller. The preamplifier with built-in
photodetector converts signals from the pickup into
intermediate voltage in the pickup. Then, addition is
made in the RF amplifier (IC101) to obtain RF, FE, TE,
and TE zero cross signals. The system consists of the
UPC2572GS and other components explained below.
The system uses a single power source (+5 V). Therefore, the reference voltage of IC101 and the reference
voltage of the power unit and servo circuit are REFO
(+2.5 V). REFO is obtained from REFOUT of servo LSI
(IC201: UPD63702GF) via a buffer, and is output from
Pin 19 of IC101. This REFO is used as reference for all
measurements.
Note: Do NOT short-circuit REFO and GND during
measurement.
EFM-IN
AGC-OUT
C AGC
RF-IN
RF-OUT
RF-
C1.3T
C2.3T
Vcc
LDON
X12
DC shift
Mirror circuit
X3
X2
FE
BAL
TE
BAL
120kΩ
FE-BAL
38
TE-BAL
37
ASY
36
EFM-OUT
35
C.DEF
34
DEFECT
33
RFOK
32
MIRR
31
3T-OUT
30
C.FE
29
FE-OUT
28
FE-
27
GND
26
TE-
25
TE-OUT1
24
TE-OUT2
23
DET-IN
22
DET-OUT
21
VREF-INVREF-OUT
20
1
AGC
2
Detection
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
10
C
11
B
12
D
13
F
14
E
15
PD
16
LD
17
APC
18
19
DEFECT circuit
Vcc
RF
envelope
Peak
Bottom
3T detection
BAL
FE
Control
FE
Control
EFM comparator
Vcc
Phase detection
BAL
HPF
Peak
Bottom
DC shift
1) Automatic Power Control (APC) circuit
Laser diode has negative temperature characteristics
with great optical output when the diode is driven
with constant current. Therefore, current must be
controlled by a monitor diode to ensure constant output. Thus functions the APC circuit. LD current can be
obtained by measuring the voltage between LD1 and
GND. The current value is approximately 35 mA.
C124
0.1µF
CONT
Fig. 1 Block Diagram of UPC2572GS
Pickup unit
Vcc (5V)
LD MD
15
Q101
2SD1664
LD1
R101
10Ω
R102
12Ω
Q102 UMD2N
R112
Vr
2.2kΩ
5
C101
(100µF/6.3V)
5V
PD
C104
0.33µF
LD
16
17
16kΩ
1kΩ
18
5V
UPC2572GS
2.5V
150kΩ
1kΩ
5V
Fig. 2 APC Circuit
2
CX-680
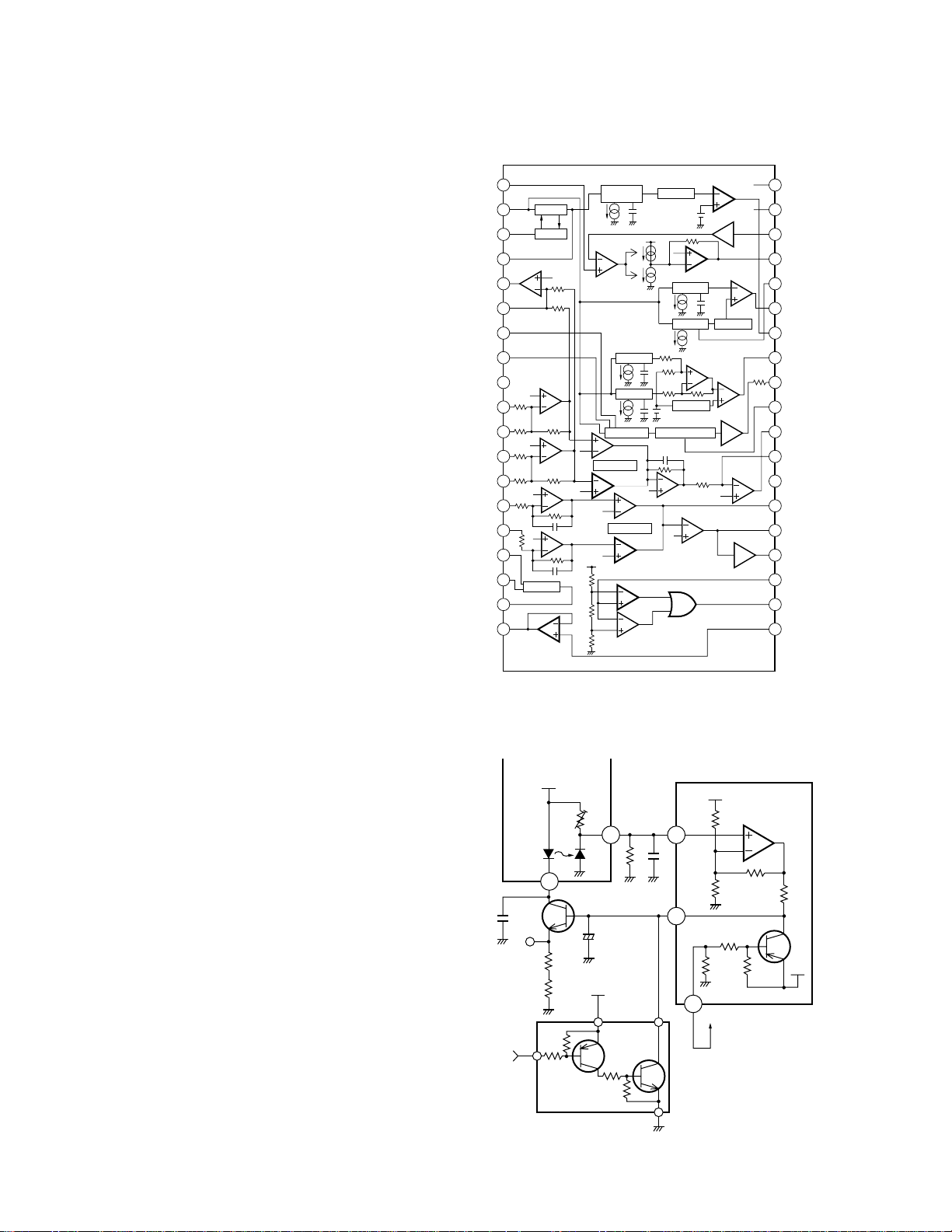
2) RF amplifier and RF AGC amplifier
Photodetector outputs (A+C and B+D) are added, amplified and equalized in IC101, and output to the RFI
terminal as RF signal. (Eye pattern can be checked at
this terminal.)
Low-frequency components of voltage RFI is:
RFI = (A + B + C + D) x 3.22
where R111 is offset resistor to keep RFI signal within
the output range of the preamplifier. RFI signal is
goes under AC coupling, and is input to Pin 4 (RFIN
terminal).
IC101 contains an RF AGC circuit. RFO output from
Pin 2 is maintained to a constant level (1.2 ±0.2 Vp-p).
The RFO signal is used in the EFM, DFCT, and MIRR
circuits.
3) EFM circuit
The EFM circuit converts RF signal into digital signals of “0” and “1.” RFO signal after AC coupling is
input to Pin 1, and supplied to the EFM circuit.
Asymmetry caused during manufacturing of discs
cannot be eliminated solely by AC coupling. Therefore, the system controls the reference voltage ASY
of the EFM comparator by using the fact that probability to generate “0” and “1” is 50% in EFM signal.
This reference voltage ASY is generated by output
from the EFM comparator through L.P.F. EFM signal
is output from Pin 35. As signal level, amplification is
2.5 Vp-p around REFO.
Q103
2SK303
3
4) DFCT (defect) circuit
DFCT signal detects mirror defect in discs, and is output from Pin 33. The system outputs “H” when a mirror defect is detected.
If disc is soiled, the system determines it as lack of
mirror. Therefore, the system inputs the DFCT signal
output to the HOLD terminal of servo LSI. Focus and
tracking servo drives change to Hold status only
when DFCT output is in “H” so that performance of
the system upon detection of defect can be improved.
5) RFOK circuit
The RFOK circuit outputs signal to show the timing of
focus closing servo, as well as the status of focus
closing during playback. The signal is output from
Pin 32. The system inputs the RFOK signal output to
the RFOK terminal of servo LSI. The servo LSI issues
Focus Close command. The system outputs signal in
“H” during focus closing and playback.
Q104
UN2111
SCONT
CN101
7
13
REFO (+2.5V)
10
A+C
11
B+D
12
13
10kΩ
10kΩ
10kΩ
10kΩ
R111
27kΩ
20kΩ
20kΩ
CWX2165
20kΩ
32
RFOK
(CXK5121)
C106
0.01µF
+5V
2
1
R104
8.2kΩ
C128
33P
C122
0.1µF
RFI
20kΩ
RF
ENVELOPE
HPF
RFIN
C105
47pF
R105
6.8kΩ
C125 3pF
6 54 3 21
9.3kΩ
9.3kΩ
R123
10K
C107
4.7µF/35V
DETECT
(RF AGC)
AGC
VDC
Fig. 3 RF AMP, RF AGC, EFM, DFCT, RFOK Circuit
PEAK
UPC2572GS
Vcc
DEFECT
×12
ASY
35
36
33
34
RFO
EFM
R107 8.2kΩ
R106 18kΩ
C110
0.1µF
DEFECT
C112 0.047µF
BOTTOM
C111 3300pF
3
CX-680
CN101
R117
16kΩ
R116
16kΩ
14
15
9
11
31kΩ
31kΩ
50pF
63kΩ
C123
4.7nF
R114
10kΩ
R113
10kΩ
TBAL
C115
120pF
R109
68kΩ
R115
1kΩ
C126
15nF
TEY
4R
R
F
E
23
TEC
C116
6.8nF
TE VCA
gm=1/17kΩ
63kΩ
37
24
5pF
TOFST
R110
130kΩ
50pF
25
REFO (+2.5V)
gm CONDUCTANCE
UPC2572GS
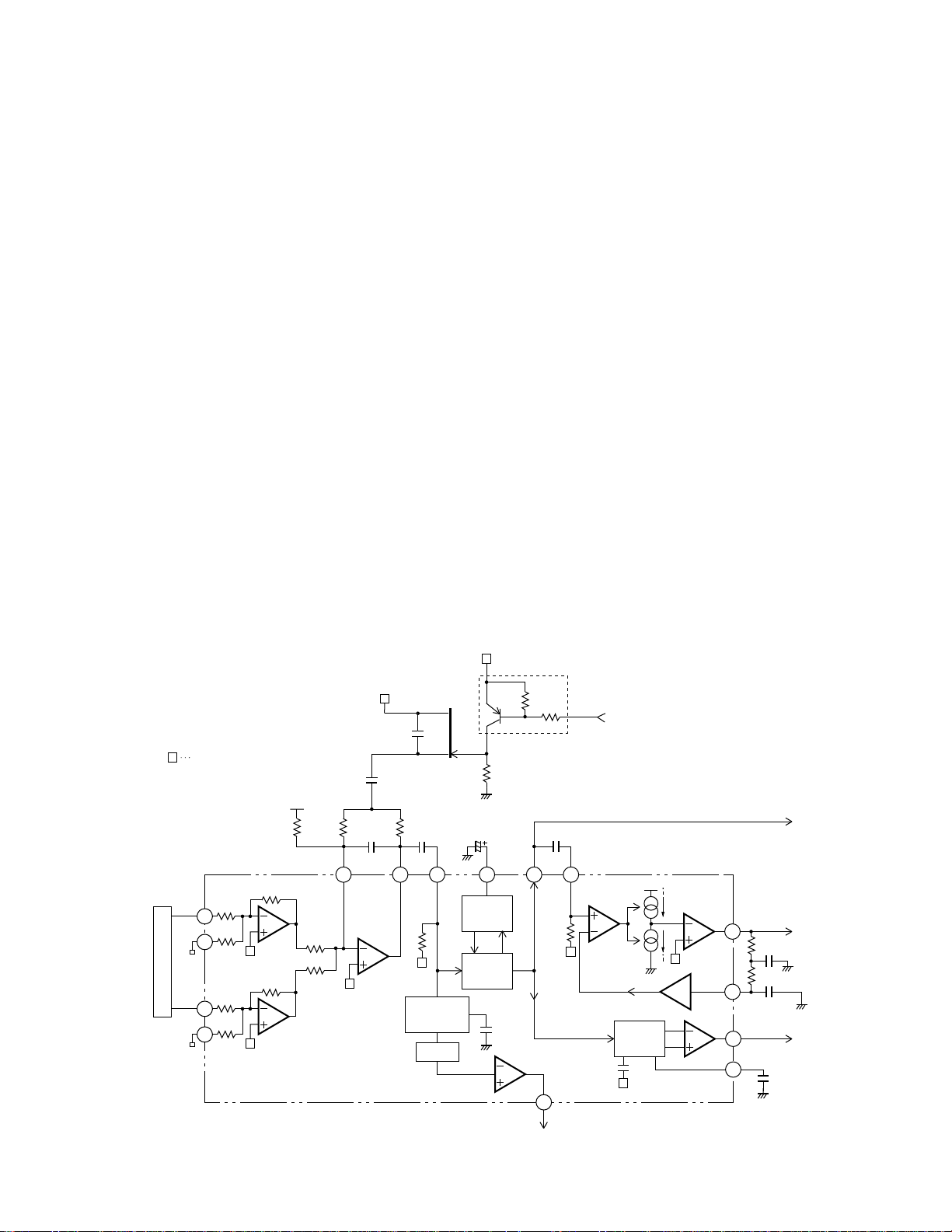
6) Focus-error amplifier
The system outputs photodetector output (A+C and
B+D) as FE signal (A+C-B-D) from Pin 28 via the difference amplifier, then via the error amplifier.
Low-frequency components of voltage FEY is:
FEY=(A+C–B–D)X X X
20kΩ 90kΩ R108
10kΩ 68.8kΩ 17.2kΩ
: (FE level of pickup unit x 5.02)
An S curve equivalent to approximately 1.6 Vp-p is
obtained at FE output (Pin 28) by using REFO as reference. The cut-off frequency of the amplifier of the
last layer is 12.4 kHz.
7) Tracking-error amplifier
Outputs E and F from the photodetector are output as
TE signal (E-F) from Pin 24 via the difference amplifier, then via the error amplifier.
Low-frequency components of voltage TEY is:
TEY=(E–F) X X
: (TE level of pickup unit x 5.36)
TE waveforms equivalent to approximately 1.5 Vp-p
are obtained at TE output (Pin 24) by using REFO as
reference. The cut-off frequency of the amplifier of
the last layer is 19.5 kHz.
63kΩ R109
31kΩ+16kΩ 17kΩ
REFO (+2.5V)
gm CONDUCTANCE
A+C
10kΩ
7
10
10kΩ
11
B+D
13
12
CN101
10kΩ
13
10kΩ
UPC2572GS
Fig. 4 Focus-error amplifier
20kΩ
20kΩ
FE VCA
gm=1/68.8kΩ
F.BAL
9.3kΩ
9.3kΩ
38
REFO
65
RFO
R
50pF
27
90kΩ
17.2kΩ
C114
390pF
R108
33kΩ
FE
28
FE
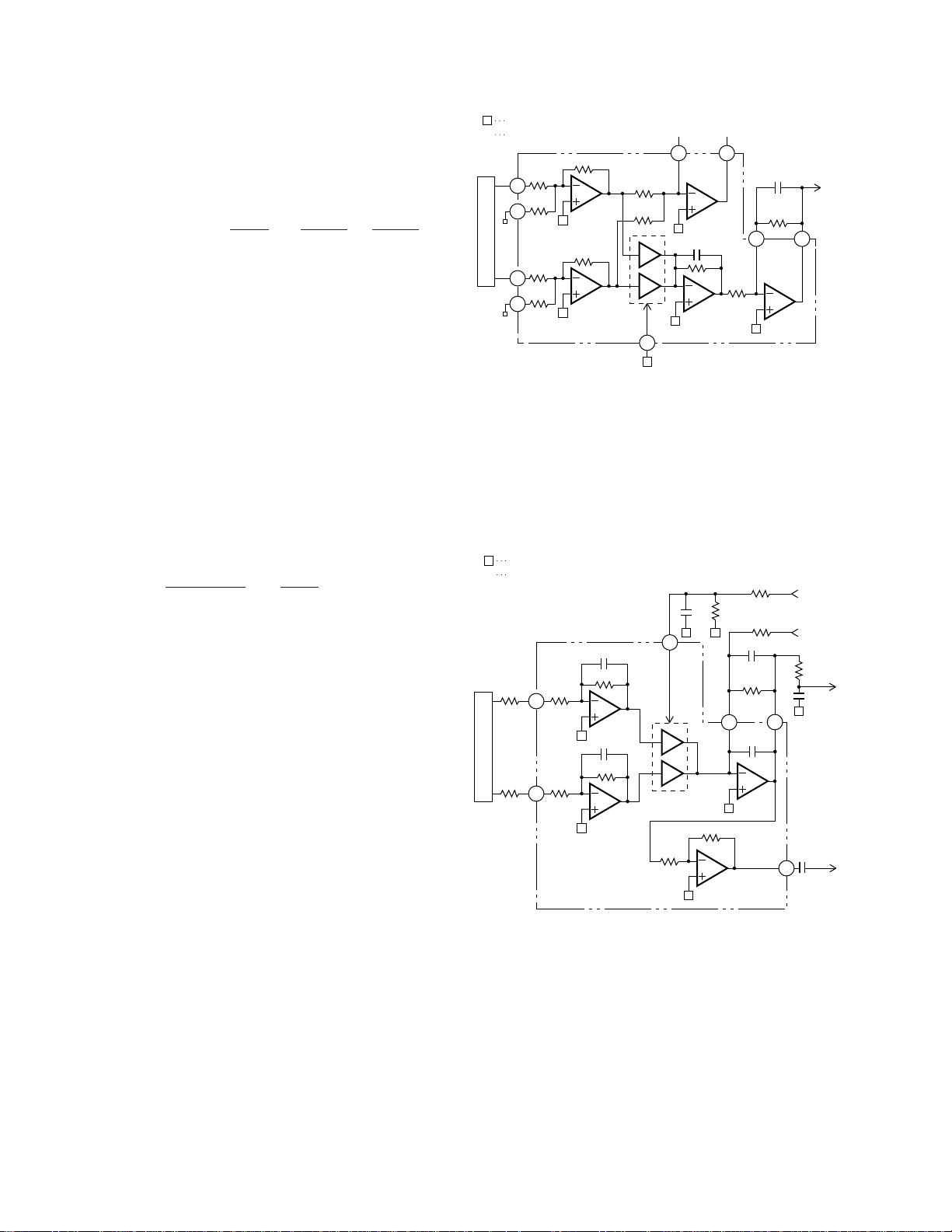
8) Tracking zero-cross amplifier
Tracking zero-cross signal (TEC signal) is generated
by amplifying TE waveforms (voltage at Pin 24) by a
factor of four. The signal is used for detecting the
zero-cross point of tracking error in the servo LSI
UPD63702GF. The purposes of detecting the zerocross point are as follows:
(1) To be used for counting tracks for carriage move
and track jump.
(2) To be used for detecting the direction of lens
movement when tracking is closed. (To be used in
the tracking brake circuit mentioned later.)
The frequency range of TEC signal is from 500 Hz
to 19.5 kHz.
Voltage TEC = TE level x 4
In other words, the TEC signal level is calculated as 6
Vp-p. This level exceeds the D range of the operation
amplifier, resulting in the signal to clip. However,
there shall be no problem, since the servo LSI uses
only zero-cross point.
4
Fig. 5 Tracking-error amplifier,
Tracking zero-cross amplifier
RFO
PEAK HOLD
BOTTOM HOLD
MIRROR
1
A
0
False MIRR caused by dirt
True MIRR
OFF TRACK
Dirt, etc.
B
C
Z
Ø
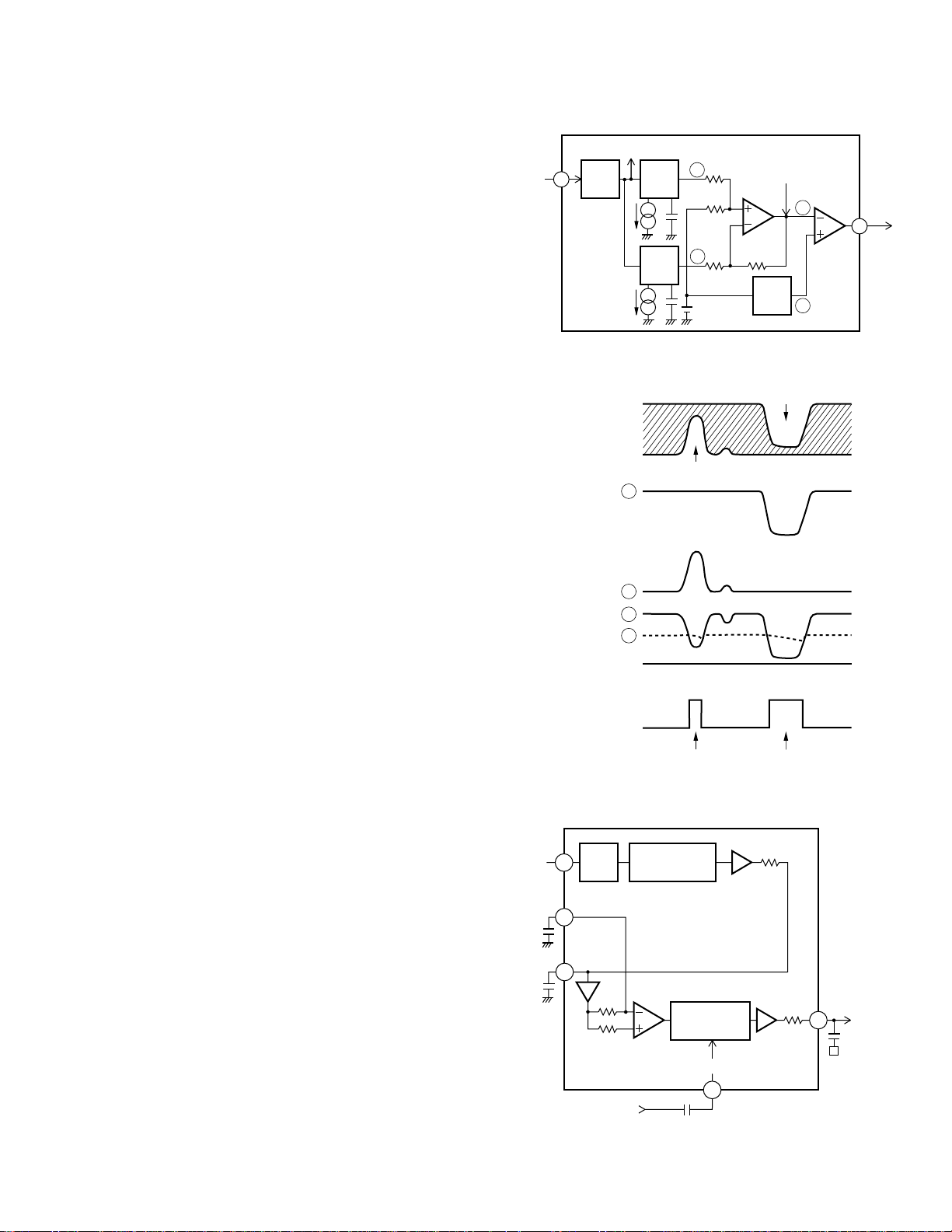
9) MIRR (mirror) circuit
MIRR
COMP
DC
shift
PeakAGC
Bottom
RFO
Detection
A
1.5V
UPC2572GS
(Peak) – (Bottom)
4
31
RFIN
B
Z
C
MIRR signal shows ON and OFF track information.
The signal is output from Pin 31.
The status of MIRR signal is as follows:
Laser beam ON track: MIRR = “L”
Laser beam OFF track: MIRR = “H”
The signal is used in the brake circuit mentioned later.
CX-680
Fig.6 MIRR Circuit
10) 3T OUT circuit
The system detects flickering of RF signal when disturbance is input to the focus servo loop, and outputs
the difference of phase between FE signal and RFlevel fluctuation signal from Pin 30. The resulting signal is obtained through L.P.F. with a fc of 40 Hz. This
signal is used for automatic adjustment of FE bias.
RFIN
C108
0.027µF
C109
100pF
UPC2572GS
4
C1.3T
7
C2.3T
8
AGC
H.P.F
10kΩ
10kΩ
Fig. 7 MIRR Circuit
Differential
rectification
3T LEVEL ENVELOPE
DETECTOR
Phase detection
Phase
comparison
FE signal
29
FEY
C113
10nF
Fig. 8 3T OUT Circuit
1kΩ
L.P.F
+
120kΩ
8
3T-OUT
30
3T detection
C117
0.033µF
5
CX-680
1.2 Servo (UPD63702AGF: IC201)
The servo consists of mainly two parts. The first part
is the servo processing unit to equalize error signals
and control track jump, carriage move, in focus, etc.
The second part is the signal processing unit to perform data decoding, error correction, and interpolation.
The system converts FE and TE signals from analog
to digital in IC201, then outputs drive signals of the
focus, tracking, and carriage systems via the servo
block. The EFM signal input from the preamplifier is
decoded by the signal processing unit, and eventually output as audio signal after conversion into analog
from digital signals via the DA converter (IC201 contains audio DAC). Then, the system generates error
signal for the spindle servo in the decoding process,
sends the signal to the spindle servo to generate
drive signal for spindle.
After that, drive signals for focus, tracking, carriage,
and spindle are amplified in IC301 and BA6797FM,
and supplied to respective actuators and motors.
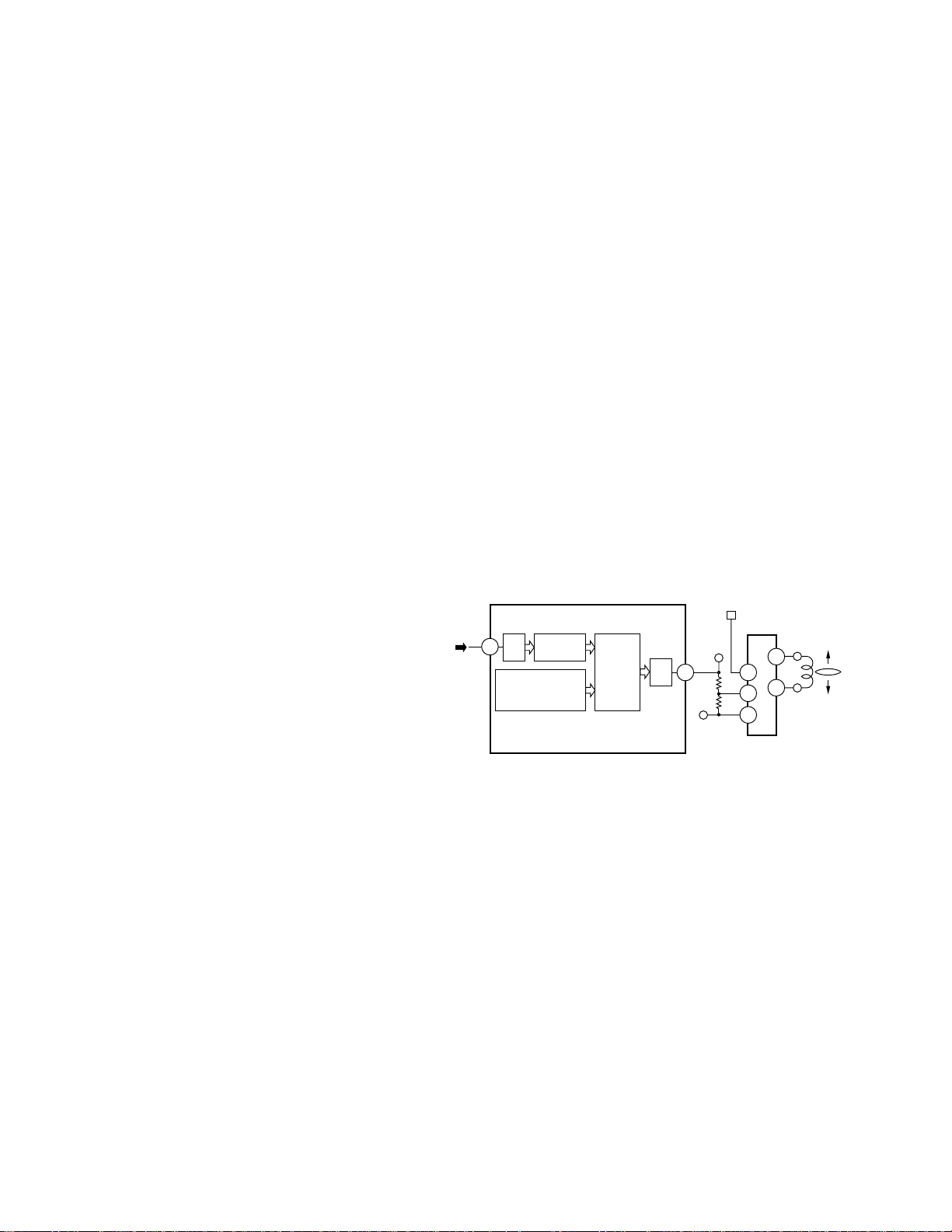
1) Focus servo system
The main equalizer of focus servo is located in the
UPD63702AGF. Fig. 9 shows block diagram of the focus servo.
For the focus servo system, the lens must be positioned within the focusing range in order to perform
focus closing. To achieve this, the system moves the
lens upward/downward by focus-search voltage of
triangular waveform to detect the focusing point.
During searching, the system kicks the SPDL motor
to maintain rotation speed to set speed.
The servo LSI monitors FE and RFOK signals so that
focus closing is performed automatically at an appropriate point.
Focus closing is performed when the following four
conditions are satisfied:
(1) When the lens moves nearer to the disc.
(2) RFOK = “H”
(3) FZD signal (in IC) is latched to “H.”
(4) FE = 0 (REFO as reference)
FOCUS
ERROR
76
IC 201 UPD63702AGF
DIGITAL
A/D
EQUALIZER
FOCUS SEARCH
TRIANGULAR WAVE
GENERATOR
CONTROL
DAC
D/A
64
Fig. 9 Focus servo block diagram
R302
20kΩ
FIN
FD
R301
30kΩ
IC301
BA6797FM
16
20
17
19
18
DRIVER
FO
FO
+
LENS
6
 Loading...
Loading...