Pinnacle Systems Pro Tools TDM - 6.0, Pro Tools LE - 5.3, Pro Tools LE - 5.1, Pro Tools TDM - 5.3, Pro Tools MIX - 5.1 Reference Guide
...Page 1

Pro Tools
Reference Guide
Version 6.0 for TDM or LE Systems on Macintosh
Version 5.3.x for TDM or LE Systems on Windows or Macintosh
Version 5.1.x for MIX or LE Systems on Macintosh
Digidesign
2001 Junipero Serra Boulevard
Daly City, CA 94014-3886 USA
tel: 650·731·6300
fax: 650·731·6399
Technical Support (USA)
tel: 650·731·6100
fax: 650·731·6384
Product Information (USA)
tel: 650·731·6102
tel: 800·333·2137
International Offices
Visit the Digidesign Web site
for contact information
Web Site
www.digidesign.com
Page 2

Copyright
This guide is copyrighted ©2002 by Digidesign, a division of
Avid Technology, Inc. (hereafter “Digidesign”), with all rights
reserved. Under copyright laws, this guide may not be
duplicated in whole or in part without the written consent of
Digidesign.
DIGIDESIGN, AVID and PRO TOOLS are trademarks or
registered trademarks of Digidesign and/or Avid Technology,
Inc. All other trademarks are the property of their respective
owners.
All features and specifications subject to change without
notice.
PN 910610773-00 REV A 012/02
Page 3

Contents
Part I Introduction
Chapter 1. Welcome to Pro Tools
The Pro Tools Guides
Compatibility Information
Digidesign Registration
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Chapter 2. Pro Tools System Configurations
TDM-Equipped Systems
Pro Tools LE Systems
Chapter 3. Pro Tools Concepts
Hard Disk Audio Recording
The Digidesign Audio Engine
Pro Tools Sessions
System Resources
MIDI Concepts
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Chapter 4. Pro Tools Windows
The Mix Window
The Edit Window
The Transport Window
Chapter 5. Keyboard Shortcuts
Global Key Commands
Keyboard Focus
Numeric Keypad Modes
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Contents
iii
Page 4

Part II Sessions & Tracks
Chapter 6. Sessions
Starting Up or Shutting Down Your System
Configuring Pro Tools System Settings
Configuring Pro Tools Hardware Settings
Creating a New Session
Opening a Session
Saving a Session
Creating Custom Session Templates
Closing a Session
Quitting Pro Tools
Sharing Sessions Between Pro Tools TDM Systems and Pro Tools LE Systems
Preferences
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Chapter 7. I/O Setup
The I/O Setup Dialog
Routing Hardware I/O to Pro Tools I/O
Creating and Editing Paths
I/O Settings Files
Default Output, Meter, Audition, and Default Path Order I/O Setup Options
Chapter 8. Tracks
Track Types
Track Controls
Creating Tracks
Hiding Tracks
Assigning Inputs and Outputs to Tracks
Track Priority and Voice Assignment
Setting MIDI Input and Output
Soloing and Muting Tracks
Making Tracks Inactive
Adjusting Track Width
Color Coding Tracks
Grouping Tracks
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Pro Tools Reference Guide
iv
Page 5

Chapter 9. Importing and Exporting Session Data
Importing Audio
Importing Tracks
Importing Tracks and Track Attributes
Loading Audio Files with Drag & Drop
Exporting Audio
Transferring Audio from CD
Conversion Quality
Exporting Pro Tools Tracks as OMF Files
Exporting Session Text
Importing MIDI Files
Exporting MIDI Files
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Chapter 10. File Management and Compatibility
Audio File Management
WAV File Compatibility
Avid File Compatibility
Creating Mac and PC Compatible Sessions
Moving Sessions Between Platforms with MacOpener
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Part III Recording
Chapter 11. Record Setup
Input Connections and Audio Levels
Record Enabling Tracks (Using the Record Enable Button)
Monitoring Modes
Monitoring Latency
Default Track Names
Disk Allocation
Allocating Hard Drive Space for Recording
Record Modes
Recording with the Click
Setting the Default Meter
Chapter 12. Basic Audio Recording
Recording an Audio Track
Record Shortcuts
Recording Multiple Audio Tracks
Record Pause Mode
Recording Additional Takes
Punch Recording Audio
Loop Recording Audio
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Contents
v
Page 6

Auditioning Record Takes
Setting Punch/Loop Points
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
Chapter 13. MIDI Recording
Recording from MIDI Devices
Enabling Input Devices
MIDI Thru
MIDI Input Filter
Input Quantize
Wait for Note
MIDI Merge/Replace
Configuring MIDI Tracks for Recording
Recording to MIDI Tracks
Punch Recording MIDI
Loop Recording MIDI
Recording System Exclusive Data
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Chapter 14. Advanced Recording
QuickPunch Audio Recording
Recording from a Digital Source
Half-Speed Recording and Playback
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Part IV Editing
Chapter 15. Editing Basics
Pro Tools Editing
Track Material
Displaying Region Names and Times
Audio Regions and Waveforms
MIDI Regions and MIDI Data
Playlists
Multiple Undo
The Audio and MIDI Regions Lists
Edit Modes
Zooming
The Universe Window
Timebase Rulers
Main Time Scale
Tick-Based Timing
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 208
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 212
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 213
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
Pro Tools Reference Guide
vi
Page 7

Chapter 16. Playing and Selecting Track Material
Playing Tracks
Scrolling Options
The Scrubber
Separate Edit and Timeline Selections
Selecting Track Material
Playing Selections
Timeline Selections
Playing Edit and Timeline Selections with the Playhead
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 224
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 236
Chapter 17. Working with Regions and Selections
Creating New Regions
Healing a Separation
Placing Regions in Tracks
The Trimmer Tool
The Time Trimmer
Sliding Regions
Nudging
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 253
Shift Command
Quantizing Regions
Locking Regions
Muting/Unmuting Regions
Edit Commands
Duplicate Command
Repeat Command
Merge Paste Command
Editing Stereo and Multichannel Tracks
Processing Audio with AudioSuite Plug-Ins
Waveform Repair with the Pencil Tool
The Smart Tool
Chapter 18. Advanced Editing
Replacing Regions
Repeat Paste To Fill Selection
Compress/Expand Edit To Play . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 269
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 242
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 242
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 246
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 249
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 255
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 256
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 257
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 257
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 260
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 261
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 262
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 262
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 263
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 264
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 265
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 267
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 267
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 269
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
Chapter 19. Fades and Crossfades . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 271
Using Crossfades . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 271
Creating a Crossfade. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 278
Creating Fades at the Beginnings and Ends of Regions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 279
Using AutoFades . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 280
Creating Fades and Crossfades in Batches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 281
Contents
vii
Page 8

Chapter 20. Managing Regions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 283
Stripping Silence from Regions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 283
Inserting Silence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 285
Consolidate Selection Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 286
Managing Regions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 286
Compacting an Audio File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 289
Chapter 21. Conductor Tracks and Memory Locations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 291
Tempo Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 291
Default Tempo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 294
Identify Beat Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 294
Meter Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 297
Renumbering Bars. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 299
Memory Locations and Markers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300
Memory Locations Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 307
Chapter 22. Beat Detective . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 309
About Beat Detective . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 309
Beat Detective Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 310
The Beat Detective Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 311
Beat Detective Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 311
Defining a Beat Detective Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 312
Calculating Tempo with Beat Detective . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 313
Generating Beat Triggers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 314
Generating Bar|Beat Markers with Beat Detective . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 317
DigiGroove Templates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 318
Separating Regions with Beat Detective . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 320
Conforming Regions with Beat Detective . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 322
Edit Smoothing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 325
Detection (Normal) and Collection Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 326
Part V MIDI Editing
Chapter 23. MIDI Editing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 331
The Pencil Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 331
Setting the Grid Value . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 333
Inserting MIDI Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 333
Manually Editing MIDI Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
Continuous Controller Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 340
Program Changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 341
System Exclusive Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 347
Note and Controller Chasing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 347
Pro Tools Reference Guideviii
Page 9

Offsetting MIDI Tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 348
Stuck Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 350
Chapter 24. MIDI Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 351
MIDI Operations Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 351
Select Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 352
Change Velocity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 354
Change Duration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 356
Transpose . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
Quantize . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 358
Groove Quantize . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 363
Restore Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 367
Flatten Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 368
Chapter 25. MIDI Event List. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 369
The MIDI Event List. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 369
Inserting Events in the MIDI Event List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 372
Editing in the MIDI Event List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 374
MIDI Event List Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 376
Part VI Mixing
Chapter 26. Basic Mixing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 379
Mixing Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 379
Metering and Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 379
Audio Signal Flow. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 380
Inserts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 383
Viewing I/O, Inserts, and Sends . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 384
Track Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 385
Track Output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 386
Sends . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 389
Output Windows for Tracks and Sends. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 393
Submixing for Signal Routing and Effects Processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 398
Dither . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 402
Using a Control Surface with Pro Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 404
Chapter 27. Plug-In and Hardware Inserts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 405
Inserting Plug-Ins on Tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 409
The Plug-In Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 410
Hardware I/O Inserts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 416
Connecting and Integrating External Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 417
Contents ix
Page 10

Chapter 28. Automation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 421
Automation Quick Start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 421
Automation Playlists . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 422
Automation Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 423
Automation Preferences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 426
Viewing Automation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 428
Writing Automation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 429
Enabling and Suspending Automation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 432
Deleting Automation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 434
Thinning Automation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 434
Drawing Automation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 435
Editing Automation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 436
Writing Automation to the Start, End or All of a Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 442
Trimming Automation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 444
Creating Snapshot Automation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 445
Chapter 29. Mixdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 449
Recording to Tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 451
Bounce to Disk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 452
Bounce Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 453
Recording a Submix (with Bounce To Disk) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 461
Final Mixdown (with Bounce To Disk) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 462
Mastering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 463
Part VII Surround
Chapter 30. Surround Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 467
Mixing Formats and Surround Formats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 467
Pro Tools Mixing Formats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 468
Speaker Layouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 468
Surround Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 470
Formats and Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 471
Surround Mixing Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 474
Chapter 31. Pro Tools Setup for Surround . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 477
Pro Tools Audio Connections for 5.1 Mixing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 477
Configuring Pro Tools for Multichannel Sessions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 478
Default Selectors in I/O Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 482
5.1 Track Layouts, Routing, and Metering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 482
Pro Tools Reference Guidex
Page 11

Chapter 32. Multichannel Tracks and Signal Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 483
Multichannel Quickstart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 483
Multichannel Audio Tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 483
Multichannel Signal Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 486
Paths in Surround Mixes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 488
Example Paths and Signal Routing for a Surround Mix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 491
Chapter 33. Surround Panning and Mixing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 495
Introduction to Pro Tools Surround Panning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 495
Output Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 496
Standard Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 497
Surround Panner Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 498
Panning Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 500
LFE Faders in Multichannel Panners . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 503
Divergence and Center Percentage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 503
SurroundScope Metering Plug-In . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 506
Part VIII Synchronization
Chapter 34. Synchronization Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 509
Synchronization Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 509
Aspects of Synchronization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 509
Synchronizing Pro Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 510
SMPTE Frame Formats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 513
Working with Film-Originated Material . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 514
Chapter 35. Time Code Synchronization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 519
Pro Tools Synchronization Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 519
Session Setup Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 520
Preparing to Work with SMPTE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 525
Configuring Pro Tools for SMPTE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 526
4% Pull Up and Pull Down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 527
Configuring Pull Up and Pull Down Using SYNC I/O or USD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 533
Putting Pro Tools Online . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 533
Generating Time Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 534
Using MIDI Machine Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 535
Synchronizing a Sequencer to Pro Tools on Macintosh OS 9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 537
Synchronizing a Sequencer to Pro Tools in Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 539
Setting Minimum Sync Delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 539
Remote Track Arming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 540
Synchronizing Pro Tools to an OMS-Compatible Sequencer Using MMC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 540
MIDI Beat Clock. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 542
Contents xi
Page 12

Spotting Regions to SMPTE Frame Locations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 543
Time Stamping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 545
Identifying a Synchronization Point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 547
Troubleshooting Synchronization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 548
Chapter 36. Working with QuickTime Movies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 551
About QuickTime. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 551
QuickTime Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 553
Movie Playback Quality Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 553
Importing a QuickTime Movie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 554
Firewire Playback of QuickTime DV Movies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 555
About the Movie Window. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 557
Setting the Movie Start Time (Movie Offset) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 558
Spotting Audio to a QuickTime Movie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 559
Importing QuickTime Audio (and Other Compressed Video Files) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 560
Bouncing to a New Movie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 561
Appendix A. DSP-Induced Delays in Mixing (TDM Only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 563
Delay Factors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 563
Compensating for Delays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 565
Appendix B. TDM Mixing and DSP Usage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 567
Understand the Benefits of TDM II . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 567
DSP Allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 569
DSP Usage with TDM Mixers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 571
DSP Usage with TDM Plug-Ins. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 579
DSP Usage and I/O Allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 580
Appendix C. Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 581
Backing Up Your Work . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 581
Common Issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 581
Using DigiTest as a Diagnostic Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 582
Performance Factors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 582
Before You Call Digidesign Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 583
Glossary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 585
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 595
Pro Tools Reference Guidexii
Page 13

Part I: Introduction
1
Page 14

2
Page 15

Chapter 1: Welcome to Pro Tools
Welcome to Pro Tools®. Pro Tools integrates
powerful multitrack digital audio and MIDI sequencing features, giving you everything you
need to record, arrange, edit, mix, and master
quality audio for music, video, film, and multimedia.
The Pro Tools Guides
Your Pro Tools System includes the following
guides:
Getting Started Guide Instructions for installing
your Pro Tools system and connecting your studio.
Pro Tools Reference Guide Full details on all
Pro Tools functionality and operations.
(Pro Tools LE systems only include an electronic
PDF version of the Reference Guide.)
Pro Tools Menus Guide Electronic PDF guide to
the Pro Tools on-screen menus.
DigiRack™ Plug-Ins Guide Instructions for using
the DigiRack plug-ins (included with Pro Tools)
for both real-time and file-based audio processing in Pro Tools. (Pro Tools LE systems only include an electronic PDF version of this guide.)
Digidesign Plug-Ins Guide Electronic PDF guide
with instructions for using optional Digidesign
plug-ins for both real-time and file-based audio
processing in Pro Tools.
DigiBase and DigiBase Pro Guide Full details on
using Pro Tools DigiBase databasing and browsers for data and media management. (Pro Tools
LE systems only include an electronic PDF version of this guide.)
Pro Tools MIDI Control Surfaces Guide Electronic PDF guide that includes instructions for
operating Pro Tools with various MIDI control
surfaces.
Expanded Systems Guide (TDM Systems
Only) Instructions for expanding a Pro Tools
TDM system with optional Digidesign cards, or
an expansion chassis.
MachineControl Guide (TDM Systems Only) Instructions for using MachineControl software
for Pro Tools to enable serial communication
with remote audio and video machines.
Keyboard Shortcut Cards Separate electronic
PDFs for Macintosh and Windows that list the
many keyboard shortcuts not shown in the
Pro Tools menus.
Digidesign also provides guides with audio
interfaces, optional dedicated controllers
(such as Control|24 and ProControl) and
other Digidesign options, (such as MIDI
I/O, PRE, and SYNC I/O). Refer to the separate guide provided with the Digidesign
optional product.
Chapter 1: Welcome to Pro Tools 3
Page 16

Conventions Used in These Guides
The Pro Tools guides use the following conventions to indicate menu choices and key commands:
:
Convention Action
File > Save Session Choose Save Session
from the File menu
Control+N Hold down the Control
key and press the N key
Compatibility Information
Digidesign can only assure compatibility and
provide support for hardware and software it
has tested and approved. For a list of Digidesignqualified computers, operating systems, and
third-party devices, refer to the latest compatibility information on the Digidesign Web site
(www.digidesign.com).
Option-click Hold down the Option key
and click the mouse button
Right-click (Windows) Click with the right
mouse button
The following symbols are used to highlight important information:
User Tips are helpful hints for getting the
most from your Pro Tools system.
Important Notices include information that
could affect your Pro Tools session data or
the performance of your Pro Tools system.
Shortcuts show you useful keyboard or
mouse shortcuts.
Cross References point to related sections in
the Pro Tools Guides.
Digidesign Registration
Be sure to complete and return the registration
card included with your Pro Tools system. Registered users will receive periodic software update and upgrade notices. Please refer to the registration card for technical support and
warranty information.
Pro Tools Reference Guide4
Page 17

Chapter 2: Pro Tools System
Configurations
There are two types of Pro Tools systems: TDM
and LE. These refer to both the Pro Tools software and its hardware interfaces, as follows:
• TDM = Pro Tools TDM software for
Pro Tools|HD-series, Pro Tools|24 MIX-series,
or Pro Tools|24 hardware.
• LE = Pro Tools LE software for Digi 002,
Digi 001, Mbox, or Toolbox hardware.
TDM-Equipped Systems
Pro Tools TDM-equipped systems are available
in the following configurations. Each system requires at least one Digidesign audio interface
(sold separately). TDM systems can be expanded
by adding Digidesign cards to increase track
count, add to the amount of possible plug-in
and mixer processing, and connect additional
audio interfaces.
Pro Tools system performance depends on
factors such as computer processor speed,
amount of system memory, and hard drive
performance. Contact your Digidesign
dealer or visit Digidesign’s Web site for the
latest system requirements and compatibility information.
HD-Series Systems
Pro Tools|HD 1
Includes:
• HD Core card
• Pro Tools TDM software
Pro Tools|HD 2
Includes:
• HD Core card
• HD Process card
• Pro Tools TDM software
Pro Tools|HD 3
Includes:
• HD Core card
•Two HD Process cards
• Pro Tools TDM software
Chapter 2: Pro Tools System Configurations 5
Page 18

MIX-Series Systems
Supported Audio Interfaces
Pro Tools|24 MIX
Includes:
•MIX Core card
• Pro Tools TDM software
Pro Tools|24 MIXplus
Includes:
•MIX Core card
• MIX Farm card
• Pro Tools TDM software
Pro Tools|24 MIX3
Includes:
• MIX Core card
•Two MIX Farm cards
• Pro Tools TDM software
Pro Tools|24 System
Pro Tools|24
Includes:
•d24 Audio card
• DSP Farm card
• Pro Tools TDM software
HD-Series Only
The following audio interfaces are compatible
with Pro Tools|HD-series systems:
◆ 192 I/O
◆ 192 Digital I/O
◆ 96 I/O
Pro Tools|HD-series systems require the
use of at least one 192 I/O, 192 Digital
I/O, or 96 I/O.
HD-Series, MIX-Series and Pro Tools|24
The following Digidesign audio interfaces are
supported with Pro Tools|HD-series,
Pro Tools|24 MIX-series and Pro Tools|24 systems:
◆ 888|24 I/O and 882|20 I/O
◆ 1622 I/O
◆ 24-bit ADAT Bridge I/O or original ADAT
Bridge I/O
Audio interfaces that work with HD-series systems require the use of at least one
192 I/O, 192 digital I/O, or 96 I/O.
The original 888 I/O and 882 I/O audio interfaces work with Pro Tools|24 MIX-series and
Pro Tools|24 systems only.
Pro Tools Reference Guide6
Page 19

TDM System Playback, Recording and Voice Limits
The following table lists the audio playback, recording, and voiceable track limits of each type of
Pro Tools TDM system. Playback and recording voices refer to the number of unique simultaneous
playback and record tracks on your system. Total voiceable tracks refers to the maximum number of
audio tracks that can share the available voices on your system. Voice limits are dependant on the session sample rate, and the number of DSP chips dedicated to the system’s Playback Engine. Pro Tools
HD-series systems can open sessions with up to 256 audio tracks (and Pro Tools|24 MIX-series or
Pro Tools|24 systems can open sessions with up to 128 audio tracks), but any audio tracks beyond that
system’s voiceable track limit will be automatically set to Voice Off.
Pro Tools|HD-series systems provide up to 128 Auxiliary tracks (Auxiliary Inputs); Pro Tools|24 MIXseries and Pro Tools|24 systems provide up to 64 Auxiliary Inputs.
All TDM-equipped Pro Tools systems provide a total of 64 internal mix busses. All TDM systems also
provide 5 inserts and 5 sends per track, up to the DSP capacity of your system.
Table 1. Pro Tools|HD-series, Pro Tools|24 MIX-series, and Pro Tools|24 system audio playback, recording and voice
limits
Sample
Core System Type
Pro Tools|HD 1 44.1/48 96 96 112
Expanded Pro Tools|HD 1,
Pro Tools|HD 2,
Pro Tools|HD 3
Pro Tools|24 MIX,
Expanded Pro Tools|24 MIX,
Pro Tools|24 MIXplus,
Pro Tools|24 MIX
Pro Tools|24 44.1/48 32 32 43
Expanded Pro Tools|24 44.1/48 64 64 86
3
Rate
(kHz)
88.2/96 48 48 48
176.4/192 12 12 12
44.1/48 128 128 224
88.2/96 64 64 80
176.4/192 24 24 24
44.1/48 64 64 86
Voices (Mono Tracks of
Simultaneous Playback)
Mono Tracks of
Simultaneous
Recording
Total
Voiceable
Tracks
Chapter 2: Pro Tools System Configurations 7
Page 20

Audio Interfaces for TDM Systems
The following table lists the input and output capabilities of the various audio interfaces for TDMequipped Pro Tools systems. In expanded Pro Tools|HD systems, audio interfaces can be combined
for up to 96 audio inputs and outputs (for example, with one HD Core card, two HD Process cards,
and six I/Os). In expanded Pro Tools|24 MIX systems, audio interfaces can be combined for up to 72
audio inputs and outputs (for example, with one MIX card, five MIX Farm cards, and six 1622 I/Os).
Table 2. Pro Tools TDM system audio interface channel capabilities
Interface Type
192 I/O 16 in/16 out
192 Digital I/O 16 in/16 out 44.1, 48, 88.2,
96 I/O 16 in/16 out 44.1, 48, 88.2, 9624-bit 24-bit 24-bit
888|24 I/O 8 in/8 out 44.1, 48 24-bit 24-bit (or
882|20 I/O 8 in/8 out 44.1, 48 20-bit 20-bit 24-bit
1622 I/O 16 in/2 out 44.1, 48 20-bit 24-bit 24-bit
24-bit ADAT
Bridge I/O
Original ADAT
Bridge I/O
Number of I/O
Channels
(Expansion port
supports up to
16 channels of
additional I/O)
16 in/16 out 44.1, 48 None 24-bit 24-bit
16 in/16 out 44.1, 48 None 20-bit 24-bit (AES
Sample Rates
(kHz)
44.1, 48, 88.2,
96, 176.4, 192
96, 176.4, 192
A/D
Conversion
24-bit 24-bit 24-bit
None None 24-bit
D/A
Conversion
older 20-bit)
Digital I/O
24-bit
or S/PDIF),
or 20-bit
(Optical)
888 I/O 8 in/8 out 44.1, 48 18-bit (or
older 16-bit)
882 I/O 8 in/8 out 44.1, 48 16-bit 16-bit 24-bit
Pro Tools Reference Guide8
18-bit 24-bit
Page 21

Pro Tools LE Systems
Pro Tools LE-based systems are available in the
following configurations:
Digi 002
A Digi 002 system includes:
• Digi 002 combined audio interface and con-
troller
• Pro Tools LE software
Mbox
An Mbox system includes:
• Mbox audio interface
• Pro Tools LE software
Digi ToolBox XP
A Digi ToolBox system includes:
• Audiomedia III PCI card
• Pro Tools LE software
Digi 001
A Digi 001 system includes:
• Digi 001 PCI card
• Digi 001 I/O interface
• Pro Tools LE software
The total processing capacity of a
Pro Tools LE-based system depends on the
processing power of your computer. Contact
your Digidesign dealer or visit Digidesign’s
Web site for the latest system requirements
and compatibility information.
Chapter 2: Pro Tools System Configurations 9
Page 22

Pro Tools LE System Capabilities
The following table lists the playback, recording, and input and output capabilities of each Pro Tools
LE-based system. All Pro Tools LE systems are limited to 32 or 24 mono audio tracks, as noted in
Table 3. If you open a Pro Tools session created on a TDM system containing more than the number
of tracks supported on the LE-based system, audio tracks beyond that system’s voiceable track limit
will be automatically set to Voice Off (Pro Tools 6.0 or higher), or will not open (Pro Tools 5.3.3 or
lower). For example, with a Digi 002, when opening a 64 track session created on a TDM system, only
the audio tracks assigned to the first 32 voices will open; if you save the session using Pro Tools LE,
any audio tracks beyond the available 32 voices will be set to Voice Off (Pro Tools 6.0 or higher) or lost
(Pro Tools 5.3.3 and lower).
All Pro Tools LE systems provide a total of 16 internal mix busses. Pro Tools LE also provides up to 5
inserts and 5 sends per track, depending on your computer’s processing capacity.
Table 3. Pro Tools LE system audio playback, recording, and channel capabilities
System Type
Digi 002 32 up to 18 in/18 out
Digi 001 32 (Pro Tools 6.0 or higher
Mbox 32 (Pro Tools 6.0 or higher
Audiomedia III 32 (Pro Tools 6.0 or higher
Mono Tracks of
Simultaneous Playback
and Pro Tools 5.3.1 or
higher on Windows)
24 (Pro Tools 5.2 or lower)
and Pro Tools 5.3.3 or
higher on Windows)
24 (Pro Tools 5.2)
and Pro Tools 5.3.1 or
higher on Windows)
24 (Pro Tools 5.2 or lower)
Number of I/O
Channels
(at 48 kHz or
lower)
10 in/10 out (at
96 kHz)
up to 18 in/18 out 24-bit 24-bit 24-bit
up to 2 in/2 out 24-bit 24-bit 24-bit
up to 4 in/4 out 18-bit 18-bit 24-bit
A/D
Conversion
24-bit 24-bit 24-bit
D/A
Conversion
Digital
I/O
For details on transferring session material between Pro Tools LE and Pro Tools TDM systems, see
“Sharing Sessions Between Pro Tools TDM Systems and Pro Tools LE Systems” on page 54.
Pro Tools Reference Guide10
Page 23

Chapter 3: Pro Tools Concepts
Pro Tools is based on simple concepts which are
easy to grasp. Many of them you may already be
familiar with. This chapter explains the principals and concepts that form the foundation of
Pro Tools operation and functionality.
Hard Disk Audio Recording
Tape-based recording is a linear medium—you
need to rewind or fast forward a tape to hear a
particular spot in a recording. To rearrange or repeat material in a linear system, you need to rerecord it.
Hard disk recording is a non-linear (or random
access) medium—you can go immediately to
any spot in a recording without having to rewind or fast forward.
Non-linear systems have several advantages.
You can easily rearrange or repeat parts of a recording by making the hard disk read parts of
the recording in a different order and/or multiple times. In addition, this re-arrangement is
nondestructive, meaning that the original recorded material is not altered.
Pro Tools is a non-linear recording system that
lets you rearrange and mix recorded material
nondestructively.
The Digidesign Audio Engine
DAE (or Digidesign Audio Engine) is Digidesign’s real-time operating system for digital recording systems. When you install Pro Tools,
DAE is automatically installed on your system
(and can be accessed from within Pro Tools).
In the same way that a computer’s operating
system provides the foundation for programs
that run on the computer, DAE provides much
of the hard disk recording, digital signal processing, mix automation, and MIDI functionality required by Pro Tools and other products from
Digidesign and its Development Partners.
The DAE Playback Buffer Size determines the
amount of memory allocated within DAE to
manage disk buffers, which affects system performance. For more information, see “DAE Playback Buffer Size” on page 41. The DAE Playback
Buffer Size can be changed in the Playback Engine dialog, discussed below.
Playback Engine Dialog
Pro Tools takes advantage of your computer’s
host processor for certain tasks and optional
host-based DSP processing.
Chapter 3: Pro Tools Concepts 11
Page 24

Pro Tools LE uses host (CPU) processing to provide audio track recording, playback, mixing,
and effects processing. Pro Tools TDM can also
use host processing to run RTAS plug-ins for effects processing. Performance is determined by
your system and its Playback Engine settings.
The Playback Engine dialog lets you set a hardware buffer size and allocate a percentage of
CPU resources for these tasks. For more information, see “Configuring Pro Tools System Settings” on page 39.
Session File
Pro Tools session file icon, Pro Tools 6.0
Pro Tools session file icon, Pro Tools 5.3 or earlier
A session file is the document that Pro Tools cre-
ates when you start a new project. The session
file contains maps of all elements associated
with a project, including audio files, MIDI data,
and all your edit and mix information. You can
make changes to a session and save those
changes in a new session file. This lets you create multiple versions of a project or back up
your editing and mixing work.
Playback Engine dialog for Pro Tools TDM system
The Playback Engine dialog is also where you select the number of voices (and voiceable tracks)
for your system and its sessions. Voice count
choices in the dialog are based on how much
DSP processing you wish to allocate for voicing.
For more information, see “Configuring Pro
Tools System Settings” on page 39.
See also “System Resources” on page 16.
Pro Tools Sessions
When you start a project in Pro Tools, you create
a session. Some basic elements of sessions are explained in this section.
Pro Tools Reference Guide12
Audio File
When you record audio into a Pro Tools session,
audio files are created.
Audio file icon, Pro Tools 6.0
Audio file icon, Pro Tools 5.3 or earlier
Audio files for each session are stored in a folder
named “Audio Files.” Audio files are listed in the
Audio Regions List and can appear in a track. A
section of an audio file can be defined as a region. See “Regions (or Loops)” on page 13.
Page 25

Tracks
Pro Tools tracks are where audio, MIDI, and automation data are recorded and edited.
Audio tracks in the Edit window
MIDI track in the Edit window
Audio and MIDI tracks can be edited into regions or repeated in different locations, to create
loops, re-arrange sections or entire songs, or to
assemble tracks using material from multiple
takes.
Audio tracks can be mono, stereo, or any supported multichannel format (depending on
your type of Pro Tools system). When creating a
new audio track, you can choose from a list of
formats supported by your system.
Regions (or Loops)
Audio region
A region (or loop) is a piece of audio or MIDI data
that may have associated automation data. A region could be a loop, a guitar riff, a verse of a
song, a sound effect, a piece of dialog, or an entire sound file. In Pro Tools, regions are created
from audio or MIDI files, and can be arranged in
audio and MIDI track playlists.
Playlist
Playlist Selector pop-up menu
A playlist is a group of regions arranged on an
audio or MIDI track. Tracks have edit playlists
and automation playlists.
On audio tracks, an edit playlist tells the hard
disk which audio files to read in what order. For
example, you can use the same audio region to
access the same piece of audio multiple times at
different locations and not use additional disk
space. If desired, different versions of the same
original audio can be created to modify the
length, fade-in, fade-out, and effects applied.
A playlist can be made up of a single region or
many separate regions. It can be made up of
similar elements, such as regions from several
different takes of a solo, or dissimilar elements,
such as several sound effects. You can create any
number of edit playlists for a track. This lets you
assemble different versions of performances or
edits on a single audio or MIDI track and choose
between them with a pop-up menu on the track.
Each track has a single set of automation playlists, for volume, pan, mute and each automation-enabled parameter for the insert and send
assignments on that track.
Chapter 3: Pro Tools Concepts 13
Page 26

Figure 1. Rear view of 192 I/O, 16 channels of input and output
Channel
The term channel is used to describe several related components of a Pro Tools system. The
first example of channel refers to a physical input or output of your Pro Tools system.
For example, a 192 I/O audio interface (Figure 1)
provides up to 16 channels of input and output
to a Pro Tools|HD system. An 888|24 I/O audio
interface provides eight channels of analog input and output to a Pro Tools TDM system.
The second use of the term channel refers to a
mixer strip in the Pro Tools Mix window. The
term channel strip refers to the mixer strip of any
track (audio or MIDI track, Auxiliary Input, or
Master Fader) in a session.
Audio and MIDI channel strips have similar
controls, but those controls have slightly different effects. For example, audio and Auxiliary Input channel strip faders control the Pro Tools
mixer, while MIDI channel strip faders send
MIDI volume data (MIDI controller 7).
Figure 2. Channel strip in the Mix window
The term channel also describes a separate
aspect of MIDI operation. See “MIDI Concepts” on page 18.
Pro Tools Reference Guide14
Page 27

Signal Routing
Signal routing options include the following:
Pro Tools provides software-based mixing and
signal routing controls. The Mix window is
where these controls are located. (Some of these
controls can also be accessed from the Edit window, if desired.)
Signal Routing Example
A common signal routing task is to submix multiple tracks to a single channel strip (such as an
Auxiliary Input or a Master Fader) for shared
processing and level control. The following example shows three audio tracks submixed to a
stereo Auxiliary Input.
Stereo
plug-in
Input from
Outputs to
Stereo Bus
path
Stereo
Bus path
Output to
Stereo Output
path
Track I/O Controls The most basic type of signal
routing is track input and output. A track needs
to have an assigned input path to record audio,
and an assigned output path in order to be audible through a hardware output. Signals can also
be routed to or from other tracks in Pro Tools (or
hardware inputs and outputs) using internal
busses.
Auxiliary Inputs and Master Faders Auxiliary Inputs are tracks that can be used as returns, submixers and bus masters. Master Faders are used
as bus and output master level controls. Both
Auxiliary Inputs and Master Faders can have inserts or plug-ins.
Sends Sends route audio to internal busses to
send to other tracks in Pro Tools, or to hardware
outputs.
Plug-Ins and Inserts Software plug-ins and hardware inserts process the audio on their associated track. Plug-in processing occurs completely
within the Pro Tools system. Hardware inserts
utilize audio interface inputs and outputs, for
traditional insert routing to (and from) external
effects and other devices.
Audio Tracks
Submixing to an Auxiliary Input
Auxiliary Input
Paths Pro Tools lets you define a group of multiple inputs, outputs, or busses that have a single
name and (channel) format. These groups comprise the lists of available routing choices in
track I/O Selectors and other menus. Paths can
be very useful for assigning stereo and multichannel I/O routing or sub-paths within a path.
See Chapter 7, “I/O Setup” for more information.
Mixing Formats Sessions can include combinations of mono, stereo, and multichannel format
tracks, busses, inputs, outputs, and inserts.
(Multichannel formats are supported on
Pro Tools HD-series and MIX-series only.)
Chapter 3: Pro Tools Concepts 15
Page 28

System Resources
Track count, plug-in processing, signal path and
routing options, and voice availability are ultimately limited by the combined resources available from the host computer, and from your
Pro Tools hardware.
Pro Tools provides several ways to manage and
conserve resources to maximize the performance of your system. As you begin working
with Pro Tools sessions and tracks, you can take
advantage of the following features to extend
the effectiveness of your available DSP and
other resources:
◆ Pro Tools lets you adjust the performance of
your system by changing system settings (such
as CPU Usage and H/W Buffer Size) that affect its
capacity for processing, playback, and recording. See “Configuring Pro Tools System Settings”
on page 39.
◆ Active and inactive switching lets you selec-
tively toggle items (such as tracks and inserts)
between active (on) and inactive (off). This lets
you precisely allocate DSP and other resources
when developing playlists, tracks, and mixes.
See “Active and Inactive Items” on page 16.
◆ Pro Tools TDM systems and Pro Tools LE 6.0
systems provide flexible voice options for disk
tracks. For more information on voice management and options, see “Voiceable Tracks and
Track Priority” on page 96.
Active and Inactive Items
Pro Tools lets you set certain items (such as audio tracks) as inactive, in order to free up DSP resources and mixer connections.
Items in Pro Tools that can be made inactive (or
active) include the following.
◆ Audio tracks, Auxiliary Inputs, and Master
Faders
◆ Track Inputs and Outputs
◆ Sends
◆ Side-chain inputs
◆ Plug-ins
◆ Hardware inserts
◆ Paths (session-wide)
MIDI tracks cannot be made inactive.
In addition to manually setting Active and Inactive modes, Pro Tools will automatically make
items inactive if there are insufficient or unavailable resources.
When active, items are fully engaged and operational.
When inactive, items are silent and off, although
most associated parameters can still be edited
(changed). Different inactive items affect available system resources in specific ways, as follows:
Plug-Ins When a plug-in is inactive on a track, its
DSP is made available for other plug-ins and
processing. Plug-in assignments can be made inactive manually, or automatically (see “Automatic and Manual Inactive Mode” on page 17).
Paths and Path Assignments When a path or
path assignment is inactive, its mixer resources
are made available for other signal routing purposes in the session. Paths and assignments can
be made inactive manually, or automatically
(see “Automatic and Manual Inactive Mode” on
page 17).
Pro Tools Reference Guide16
Page 29

Tracks For TDM systems (Pro Tools 5.1 and
higher) and Pro Tools LE 6.0 only, when a track
is inactive, its voice is made available for another track. Additionally, when an audio track,
Auxiliary Input, or Master Fader is made inactive, its plug-ins, inserts, sends, and I/O assignments become inactive.
Display of Inactive Items
Automatic and Manual Inactive Mode
Active and Inactive modes are powerful options
for session transfer, and system resource management. Pro Tools provides automatic and
manual Inactive mode switching. You can manually make items inactive (or active) to selectively manage system resources while editing
and mixing.
When items are inactive, their names appear in
italics, and their background becomes dark grey.
When a track is inactive (TDM systems only),
the entire channel strip darkens.
Active Inactive plug-in
Inactive track
Automatically Inactive Items
When opening a session, it is possible that not
all signal paths, plug-ins, or audio interfaces
used in the session will be available as defined
on the current system. Whenever this occurs,
the session will open as it was last saved. All
items that are unavailable, or cannot be loaded
due to insufficient resources, are made inactive.
Manual Inactive Switching
You can manually apply Active or Inactive
modes to manage system resources. By making
an item inactive, its associated resources are
made available elsewhere in the session.
The following are basic instructions for manually making items inactive. Throughout the
Pro Tools Reference Guide, instructions are provided whenever an item can be made inactive.
To toggle an item active or inactive:
■ Command-Control-click (Macintosh) or Con-
trol-Start-click (Windows) the item.
Active and inactive items and tracks
You can apply Active or Inactive modes to all or
all selected tracks using standard Pro Tools modifiers (Option and Option+Shift on the Macintosh, Alt and Alt+Shift in Windows). Side-chain
inputs support direct active and inactive switching, but do not follow switching all or all selected.
Chapter 3: Pro Tools Concepts 17
Page 30

MIDI Concepts
MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is a
communication protocol for musical instruments. This industry standard enables connections between a variety of devices from different
manufacturers. Examples of MIDI-compatible
equipment include synthesizers, sound modules, drum machines, patch bays, effects processors, MIDI interfaces, and sequencers.
MIDI devices are equipped with 5-pin DIN connectors, labeled as either IN, OUT, or THRU.
The MIDI OUT port transmits messages; the
MIDI IN port receives messages; and, MIDI
THRU echoes whatever is received from the IN
port. MIDI devices are connected with MIDI cables that are available at most music stores.
echoed from IN
MIDI Terms
The following are some basic MIDI terms:
MIDI Interface Hardware that lets computers
connect to and communicate with MIDI devices.
MIDI Device Any keyboard, sound module, effects device or other equipment that can send or
receive MIDI information.
MIDI Controller Any MIDI device that transmits
MIDI performance data. These include keyboards, MIDI guitar controllers, MIDI wind instruments, and others. Controllers transmit
MIDI from their MIDI OUT ports.
MIDI Control Surface Any device, such as the
Mackie HUI, that uses a MIDI connection to
send control messages to a software program,
but is not generally used to record MIDI information.
MIDI Sound Source Any MIDI instrument capable of playing back MIDI-triggered sound.
Sound sources receive MIDI from their MIDI IN
ports.
MIDI signal flow
Not all devices will have all three MIDI
ports (IN, OUT and THRU).
A single MIDI cable can transmit a separate set
of messages for each of the 16 channels. These
16 channels correspond to separate MIDI devices or to multiple channels within a single device (if the device is multi-timbral). Each channel
represents a discreet instrument sound; for instance, bass on channel 1, piano on channel 2,
and drums on channel 10. Similar to a multitrack tape recorder, a MIDI sequencer can record
complex arrangements—even using a single
multi-timbral keyboard.
Pro Tools Reference Guide18
Multi-Timbral The capability of playing several
different instrument sounds (such as piano,
bass, and drums) simultaneously on separate
channels. This makes it possible for a single
MIDI sound source to play back entire arrangements.
MIDI Channel Up to 16 channels of MIDI performance data can be transmitted on a single MIDI
cable. The channel number separates the different messages so your sound sources can receive
the right ones.
Program Change Event A MIDI command that
tells a sound source which of its sounds (or
sound patches) to use. The MIDI protocol lets
you choose from a range of 128 patches.
Page 31

Bank Select Message Many devices have more
than 128 patches, which are arranged in banks.
The Bank Select Message is a MIDI command
that specifies the bank of patches from which to
choose.
Local Control A controller setting found on most
MIDI keyboards that lets them play their own
sound source. Disabling “local control” ensures
that a device’s internal sound source is only
played by external MIDI messages.
When using Pro Tools, “local control” should
usually be disabled. When “local control” is off,
your keyboard still transmits data to its MIDI
OUT port.
Continuous Controller Events MIDI instructions
that allow real-time changes to notes that are
currently sounding. These include pitch bend,
modulation, volume, pan, and many others.
System Exclusive Data MIDI data commonly
used for sending and retrieving patch parameter
information for storage purposes.
Common Misconceptions about MIDI
MIDI is not audio. The messages that travel
down a MIDI cable are only numbers that translate to specific instructions. For instance, when
you strike a key on your MIDI keyboard it sends
a message to its MIDI OUT port telling another
device (if connected and set to the same MIDI
channel) to play that particular note.
Signal paths for MIDI instruments
However, to actually hear that second device
(sound source) you’ll need to connect its audio
outputs to a sound system. Your MIDI instruments have two signal paths, one for audio and
another for MIDI.
MIDI does not allow you to use your devices beyond their capabilities. Particular instruments
have their own sound generation, polyphony,
and multi-timbral limitations.
Chapter 3: Pro Tools Concepts 19
Page 32

Pro Tools Reference Guide20
Page 33

Chapter 4: Pro Tools Windows
Pro Tools provides two complementary ways of
viewing a session: the Mix window and the Edit
window. Pro Tools also allows you to control
the transport and transport-related functions
from the Transport window.
Depending on which version of Pro Tools you
have, the Mix window and Edit window will appear differently.
Pro Tools 6.0
For more information on the main elements of
the Mix window and Edit window, see the page
references provided in Figure 3 on page 22, and
Figure 4 on page 23.
Pro Tools 5.3.x and 5.1.x
For more information on the main elements of
the Mix window and Edit window, see the page
references provided in Figure 5 on page 24, and
Figure 6 on page 25.
The Mix Window
In the Mix window, tracks appear as mixer strips
(or channel strips), with controls for inserts,
sends, input and output assignments, volume,
panning, record-enable, automation mode, and
solo/mute. The following section explains each
of these track controls.
To display the Pro Tools input/output controls,
inserts, sends, and comments, select Display >
Mix Window Shows > All.
To toggle between the Mix and Edit windows: On Macintosh, press Command+Equals (=); on Windows, press Control+Equals (=).
The Edit Window
The Edit window provides a timeline display of
audio, as well as MIDI data and mixer automation for recording, editing and arranging tracks.
As in the Mix window, each track has controls
for record enable, solo, mute and automation
mode.
Systems with the Pro Tools AVoption installed
also provide a timeline display of the movie
track.
To display the input/output controls, inserts,
sends, and comments in the Edit window, select
Display > Edit Window Shows > All. You can
choose to display all of these items, or some of
them.
Chapter 4: Pro Tools Windows 21
Page 34

Show/Hide
Tracks List
(page 90)
Automation
(page 423)
Voice Selec-
tor (page 95)
Output Window
button
(page 387)
Mix Groups
List
(page 101)
Group ID
Indicator
AutoMatch
Indicator
(page 427)
Send with
Send Controls
(page 389)
Plug-In Insert
(page 405)
MIDI Track Program
button (page 342)
Inserts
View
(page 86)
Sends
View
(page 391)
I/O View
(page 86)
Channel Pan
(page 87)
Track
Controls
(page 26)
Channel
Volume
(page 87)
Level Meter
(page 87)
Track Name
(page 89)
Track
Comments
View
(page 88)
Stereo
Audio Track
(page 83)
Figure 3. Pro Tools Mix window (Pro Tools 6.0)
Pro Tools Reference Guide22
Mono
Audio Track
(page 83)
Auxiliary
Input
(page 83)
MIDI
Track
(page 83)
Master
Fader
(page 83)
Page 35

Edit Mode
buttons
(page 205)
Tab to
Transients
(page 232)
Rulers
(page 212)
Show/Hide
Tracks List
(page 90)
Audio Track
(page 83)
Edit Groups
List
(page 101)
Timeline Selections
(page 223)
Commands
Focus
(page 34)
Zoom buttons
(page 208)
Edit tools
(page 26)
Location Indicators
Grid and
Nudge Values
(page 27)
(page 27)
Event Edit Area
(page 27)
Timeline
Audio
Regions
List
(page 202)
Audio
Waveform
View
(page 190)
Volume
Automation
View
(page 190)
MIDI Track
(page 83)
MIDI Velocity View
(page 190)
Selected Region
Figure 4. Pro Tools Edit window (Pro Tools 6.0)
(page 225)
MIDI Notes View
(page 190)
MIDI Regions List
(page 202)
Chapter 4: Pro Tools Windows 23
Page 36

Send with
Send Controls
(page 389)
MIDI Track Program
button (page 342)
Plug-In Insert
(page 405)
Show/Hide
Tracks List
(page 90)
Automation
(page 423)
Output window
button
(page 387)
Group ID
Indicator
Mix Groups
List
(page 101)
AutoMatch
Indicator
(page 427)
Track Name
(page 89)
Track
Comments
View
(page 88)
Stereo
Audio Track
(page 83)
Mono
Audio Track
(page 83)
Auxiliary
Input
(page 83)
Inserts
View
(page 86)
Sends
View
(page 391)
I/O View
(page 86)
Track
Controls
(page 26)
Channel Pan
(page 87)
Channel
Volume
(page 87)
Level Meter
(page 87)
MIDI
Track
(page 83)
Master
Fader
(page 83)
Figure 5. Pro Tools Mix window (Pro Tools 5.3.x and 5.1.x)
Pro Tools Reference Guide24
Page 37

Link Selections
(page 223)
Commands
Focus
(page 34)
Edit Mode
buttons
(page 205)
Zoom buttons
(page 208)
Edit tools
(page 26)
Event Edit Area
(page 27)
Location Indicators
(page 27)
Grid and
Nudge Values
(page 27)
Timeline
b to Transients
(page 232)
Rulers
(page 212)
Show/Hide
Tracks List
(page 90)
Audio Track
(page 83)
MIDI Track
(page 83)
Edit Groups
List
(page 101)
MIDI Velocity View
(page 190)
Selected Region
(page 225)
MIDI Notes View
(page 190)
Audio
Regions
List
(page 202)
Audio
Waveform
View
(page 190)
Volume
Automation
View
(page 190)
MIDI Regions List
(page 202)
Figure 6. Pro Tools Edit window (Pro Tools 5.3.x and 5.1.x)
Chapter 4: Pro Tools Windows 25
Page 38

Track Controls
T
Automation Mode Selector (page 423)
Solo button (page 98)
Mute button (page 98)
Voice Selector (page 95)
Record Enable button (page 136)
Mix window, controls for audio and MIDI tracks,
wide view (Pro Tools 6.0)
Record Enable button (page 136)
Record Enable button
(page 136)
Track Name (page 89)
Playlist Selector (page 199)
Automation Mode Selector
(page 423)
Mute button (page 98)
Voice Selector (page 95)
Track Height Selector (page 192)
Track V iew Selector (page 190)
Solo button (page 98)
Automation Mode Selector (page 423)
Voice Selector (page 95)
Mute button (page 98)
Solo button (page 98)
Mix window, controls for audio and MIDI tracks,
wide view (Pro Tools 5.3.x and 5.1.x)
Track Name (page 89)
rack View Selector (page 190)
Playlist Selector (page 199)
Record Enable button
(page 136)
Solo button (page 98)
Mute button (page 98)
Track Height Selector (page 192)
Automation Mode Selector
(page 423)
Voice Selector (page 95)
Edit window track controls, medium track height
(Pro Tools 6.0)
Edit window track controls, medium track height
(Pro Tools 5.3.x and 5.1.x)
Edit Tools
Trimmer
(page 245)
Zoomer
(page 208)
Selector
(page 217)
Smart Tool
(page 265)
Grabber
(page 226)
Edit tools in Edit window (Pro Tools 6.0)
Trimmer
(page 245)
Zoomer
(page 208)
(page 217)
Smart Tool
(page 265)
Selector
Grabber
(page 226)
(page 264 & page 331)
Edit tools in Edit window (Pro Tools 5.3.x and 5.1.x)
Scrubber
(page 221)
Pencil
(page 264 & page 331)
Scrubber (page 221)
Pencil
Pro Tools Reference Guide26
Page 39

Event Edit Area
The Event Edit Area provides time, pitch, and
other information for the currently selected audio or MIDI data. It also lets you define selections via key entry.
The Start, End, and Length display can be set for
a different Time Scale format (such as Bars:Beats,
or Minutes:Seconds, and so on). For more information, see “Main Time Scale” on page 213.
The Main and Sub display can be set for a different Time Scale format (such as Bars:Beats, or
Minutes:Seconds, and so on). For more information, see “Main Time Scale” on page 213.
Location Indicators (page 218)
Grid value
(page 252)
Nudge value
(page 253)
Cursor Location
(page 217)
Cursor value
(page 217)
Selection
Indicators
(page 28)
Note
Attributes
(page 339)
Pitch
Attack
Velocity
Release
Velocity
Event Edit Area showing MIDI track information
(Pro Tools 6.0)
Selection
Indicators
(page 28)
Note
Attributes
(page 339)
Pitch
Attack Velocity
Release Velocity
Event Edit Area showing MIDI track information
(Pro Tools 5.3.x and 5.1.x)
Location Indicators, Grid/Nudge Values, Current Cursor Display
The Location Indicators, Grid and Nudge values,
and timeline Cursor Location display provide
navigation and editing options.
Edit window display showing MIDI track information
(Pro Tools 6.0)
Location Indicators (page 218)
Nudge value
(page 253)
Cursor Location
(page 217)
Grid value
(page 252)
Cursor value
(page 217)
Edit window display showing MIDI track information
(Pro Tools 5.3.x and 5.1.x)
Chapter 4: Pro Tools Windows 27
Page 40

The Transport Window
Return to Zero Locates to the beginning of the
session.
The Transport window can be set to show basic
transport controls, counters, and MIDI controls.
The counters in the Transport window mirror
the Location Indicators at the top of the Edit
window.
Basic Transport Controls and Counters
Return to Zero
Rewind
Online
Pre-Roll
Post-Roll
Transpor t Master
Transport window showing basic transport controls and
counters (Pro Tools 6.0)
Return to Zero
Rewind
Online
Pre-Roll
Post-Roll
Transpor t Master
Transport window showing basic transport controls and
counters (Pro Tools 5.3.x and 5.1.x)
Online Puts Pro Tools online so that playback
and recording is triggered by an external time
code source.
Fast Forward
Play
Stop
Start, End, and Length
for Timeline Selection
Fast Forward
Play
Stop
Start, End, and Length
for Timeline Selection
Go to End
Record
Go to End
Record
You can press Return (Macintosh) or Enter
on the alpha keyboard (Windows) to locate
to the beginning of the session.
Rewind Rewinds from the current play location.
You can also click repeatedly to rewind incrementally, by an amount based on the Main
Time Scale, as follows:
Rewind Increments
Main Time
Scale Format
Increment Amount
Min:Sec 1 second
Time code 1 frame
Bars:Beats 1 bar
Feet.Frame 1 foot
Sample 1 second
With the Numeric Keypad Mode set to
Transport, you can rewind by pressing 1.
Stop Stops playback or recording.
You can also stop the Transport with the following shortcuts:
• Press the Spacebar.
•With the Numeric Keypad Mode set to Transport, press 0.
Play Starts playback or (if the Record button was
clicked first) recording from the Timeline insertion point.
With the Transport stopped, Control-click Play
(Macintosh) or Right-click Play (Windows) to
toggle Loop Playback mode. When enabled, a
loop symbol appears in the Play button.
Pro Tools Reference Guide28
Page 41

You can also initiate playback with the following shortcuts:
• Press the Spacebar.
•With the Numeric Keypad Mode set to Transport, press 0.
You can play at half-speed with the following
shortcuts:
• Press Shift+Spacebar.
• Shift-click (Macintosh) the Play button.
Fast Forward Fast forwards from the Timeline insertion point. You can also click repeatedly to
fast forward incrementally (by an amount based
on the Main Time Scale).
Fast Forward Increments
Main Time
Scale Format
Min:Sec 1 second
Time code 1 frame
Increment Amount
Record Arms Pro Tools for recording (the button
flashes). Clicking Play then initiates recording.
With the Transport stopped, Control-click
Record (Macintosh) or Right-click Record (Windows) to cycle through the four record modes.
The Record button changes to indicate the currently selected mode: blank for Nondestructive,
“D” for Destructive, a loop symbol for Loop
Record, and “P” for QuickPunch.
You can also begin recording with the following
shortcuts:
• Press F12.
• Press Command+Spacebar (Macintosh) or
Control+Spacebar (Windows).
•With the Numeric Keypad Mode set to Transport, press 3.
To initiate recording at half-speed, press
Command+Shift+Spacebar (Macintosh) or
Control+Shift+Spacebar (Windows).
Bars:Beats 1 bar
Feet.Frame 1 foot
Sample 1 second
With the Numeric Keypad Mode set to
Transport, you can fast forward by pressing
2.
Go to End Locates to the end of the session.
You can press Option+Return (Macintosh)
or Control+Enter on the alpha keyboard
(Windows) to locate to the end of the session.
Pre-Roll During playback or record, specifies the
amount that plays before the play (timeline)
cursor location or beginning of the timeline selection. Pre-roll is particularly useful with punch
recording since it provides you with time to
“catch the beat” before reaching the punch-in
point. To set the pre-roll amount, enter a new
value in this field, or drag the Pre-Roll flag in the
Main Timebase Ruler.
To enable pre-roll, click the Pre-Roll button to
the left of the pre-roll field so it becomes highlighted.
Chapter 4: Pro Tools Windows 29
Page 42

Post-Roll During playback or record, specifies
the amount that plays after the end of a timeline
selection. Post-roll is useful in punch recording
since playback continues after the punch-out
point so you can check for a smooth transition
to previously recorded material. To set the postroll amount, enter a new value in this field, or
drag the Post-Roll flag in the Main Timebase
Ruler.
To enable post-roll, click the Post-Roll button to
the left of the post-roll field so it becomes highlighted.
Start Specifies the beginning of the play or
record range. You can set the start point by entering a location in this field, or by dragging the
corresponding Playback Marker in the Main
Timebase Ruler. For more information, see
“Playback Markers” on page 163.
End Specifies the end of the play or record range.
You can set the end point by entering a location
in this field, or by dragging the corresponding
Playback Marker in the Main Timebase Ruler.
For more information, see “Playback Markers”
on page 163.
Length Specifies the length for the play or record
range. You can set the length by entering a location in this field, or by selecting a range in any
Timebase Ruler.
When the Edit and Timeline selections are
linked, you can drag in a track’s playlist to
set the play and record range.
Transport Master Specifies the “master” for
transport functions. Click this button and
choose from the pop-up menu to select the
Transport Master, which can be set to Pro Tools,
Machine, MMC, or Remote. For information,
see Chapter 35, “Time Code Synchronization.”
MIDI Controls
Wait for Note
Countoff
Click
Meter
Conductor
Transport window showing MIDI controls (Pro Tools 6.0)
Wait for Note
Click
Meter
Conductor
Transport window showing MIDI controls (Pro Tools
5.3.x and 5.1.x)
Wait for Note When selected, recording does not
begin until a MIDI event is received. This ensures that you begin recording when you’re
ready to play, and that the first note, or other
MIDI data, is recorded precisely at the beginning
of the record range.
You can press F11 to turn on Wait for Note,
unless the Operation Preference for “Disable F11 for Wait for Note” is selected.
MIDI Merge
Tempo
Countoff
MIDI Merge
Tempo
Pro Tools Reference Guide30
Page 43

Click When selected, a metronome sounds during playback and recording (as specified by the
settings in the Click/Countoff Options dialog).
Double-click the Click button to open the
Click/Countoff Options dialog.
With the Numeric Keypad Mode set to
Transport, you can press 7 to enable the
Click.
Countoff When selected, Pro Tools counts off a
specified number of measures (indicated in the
button) before playback or recording begins.
Double-click the Countoff button, to open the
Click/Countoff Options dialog.
With the Numeric Keypad Mode set to
Transport, you can press 8 to enable the
Countoff.
MIDI Merge When selected (Merge mode), recorded MIDI data is merged with existing track
material. When deselected (Replace mode), recorded MIDI data replaces existing track material.
Conductor When selected, Pro Tools uses the
tempo map defined in the Tempo Ruler. When
deselected, Pro Tools switches to Manual Tempo
mode and ignores the Tempo Track.
In Manual Tempo mode, you can enter a BPM
value in the tempo field, or tap in the tempo by
clicking the Tap button.
Meter Displays the session’s current meter based
on the play location. Double-click the Meter
button to open the Change Meter window.
Tempo Displays the session’s current tempo
based on the play location. In Manual Tempo
mode, you can enter a BPM value into this field.
In addition, when the tempo field is selected,
you can tap in a tempo from a MIDI controller.
With the Numeric Keypad Mode set to
Transport, you can press 9 to enable MIDI
Merge.
Chapter 4: Pro Tools Windows 31
Page 44

Pro Tools Reference Guide32
Page 45

Chapter 5: Keyboard Shortcuts
Global Key Commands
This section shows keyboard shortcuts that apply to many functions in Pro Tools.
Track Functions
• Changing Automation mode
• Enabling playlists
• Adding plug-ins
• Record enabling, soloing, and muting tracks
• Record safing and solo safing tracks
• Assigning inputs, outputs, and sends
•Toggling volume/peak/delay display
• Clearing meters
• Changing track heights
Command Macintosh Windows
Apply action to all
channel
strips/tracks
Option+
action
Alt+
action
List and Parameter Selection
• Selection of tracks in Show/Hide List
• Enabling of groups in Groups List
• Automation Enable window parameters
• Setting memory location parameters
Command Macintosh Windows
Toggle item and set
all others to same
new state
Toggle item and set
all others to opposite state
Option-click
item
Commandclick item
Alt-click item
Control-click
item
Controls and Editing Tools
◆ Use to move plug-in controls, faders and slid-
ers, the Scrubber, and automation data
Command Macintosh Windows
Fine adjustment of
sliders, knobs, and
breakpoints
Commandclick item
Controlclick item
Apply action to
selected channel
strips/tracks
Option+
Shift+
action
Alt+
Shift+
action
Chapter 5: Keyboard Shortcuts 33
Page 46

Keyboard Focus
The Keyboard Focus in Pro Tools determines
how the alpha keys function. Depending on
which Keyboard Focus is enabled, you can use
the keys on your alpha keyboard to select regions in the Audio or MIDI Regions List, enable
or disable groups, or perform an edit or play
command.
Commands
Key Focus
Groups List
Key Focus
Keyboard Focus buttons (Pro Tools 6.0)
Audio Regions List
Key Focus
MIDI Regions List
Key Focus
You can only enable one Keyboard Focus at a
time. Enabling a Keyboard Focus will disable the
one previously selected.
To set the Keyboard Focus:
■ Click the a–z button for the focus you want to
enable.
– or –
While pressing Command+Option (Macintosh)
or Control+Alt (Windows), press one of the following keys: 1 (Commands), 2 (Audio Regions
List), 3 (MIDI Regions List), or 4 (Groups List).
Commands Focus (All TDM Systems and
Pro Tools LE 6.0 Only) When selected, this pro-
vides a wide range of single key shortcuts from
the alpha keyboard for editing and playing.
With the Commands Focus disabled, you can
still access any of its key shortcuts by pressing
Control (Macintosh) or the Start key (Windows)
along with the key.
An electronic PDF listing of keyboard shortcuts is available in Pro Tools. Choose
Help > Keyboard Shortcuts.
Audio Regions List
Key Focus
Commands
Key Focus
Groups List
Key Focus
MIDI Regions List
Key Focus
Keyboard Focus buttons (Pro Tools 5.3.x and 5.1.x)
Pro Tools Reference Guide34
Audio Regions Focus When selected, audio regions can be located and selected in the Audio
Regions List by typing the first few letters of the
region’s name.
MIDI Regions Focus When selected, MIDI regions can be located and selected in the MIDI
Regions List by typing the first few letters of the
region’s name.
Groups List Focus When selected, Edit and Mix
Groups can be enabled or disabled by typing the
Group ID letter.
Refer to the Keyboard Shortcut Card in
Pro Tools: Choose Help > Keyboard Shortcuts.
Page 47

Numeric Keypad Modes
The Operation preference for Numeric Keypad
Mode determines how the numeric keypad
functions for Transport.
No matter which Numeric Keypad Mode is selected, you can always use the numeric keypad
to select and enter values in the Event Edit Area,
Location Indicators, and Transport fields.
To set the Numeric Keypad Mode:
1 Choose Setups > Preferences and click Opera-
tion.
2 Under the option for Numeric Keypad Mode,
select a keypad mode (Classic, Transport, or
Shuttle), then click Done.
Transport
This mode allows you to set a number of record
and play functions, and also operate the Transport from the numeric keypad.
:
Function Key
Click on/off 7
Countoff on/off 8
MIDI Merge/Replace mode 9
Loop Playback mode on/off 4
Loop Record mode on/off 5
QuickPunch mode on/off 6
Rewind 1
Fast Forward 2
Classic
This mode emulates the way Pro Tools worked
in versions earlier than 5.0. With the Numeric
Keypad Mode set to Classic, you can:
• Play up to two tracks of audio in Shuttle Lock
mode. Press Control (Macintosh) or the Start
key (Windows), followed by 0–9 for different
play speeds. Press Plus or Minus to reverse direction.
• Recall Memory Locations by typing the Memory Location number, followed by a period.
Record 3
Play/Stop 0
With the Numeric Keypad Mode set to Transport, you can also:
• Play up to two tracks of audio in Shuttle Lock
mode. Press Control (Macintosh) or the Start
key (Windows), followed by 0–9 for different
play speeds. Press Plus or Minus to reverse direction.
• Recall Memory Locations by typing period,
the Memory Location number, and period
again.
Chapter 5: Keyboard Shortcuts 35
Page 48
Shuttle
(TDM Systems Only)
Pro Tools offers another form of shuttling, different from that of Shuttle Lock mode. With the
Numeric Keypad Mode set to Shuttle, playback
of the current Edit selection is triggered by pressing and holding the keys on the numeric keypad—playback stops once the keys are released.
Various playback speeds are available in both
forward and reverse. In this mode, pre- and postroll are ignored.
:
Function Key
1x Forward 6
1x Rewind 4
4x Forward 9
4x Rewind 7
1/4x Forward 3
1/4x Rewind 1
1/2x Forward 5+6
1/2x Rewind 5+4
2x Forward 8+9
2x Rewind 8+7
1/16x Forward 2+3
1/16x Rewind 2+1
Loop Selection (1x) 0
With the Numeric Keypad Mode set to Shuttle,
you can also:
• Recall Memory Locations by typing period,
the Memory Location number, and period
again.
Shuttle Lock mode is not available when the
Numeric Keypad Mode is set to Shuttle.
Pro Tools Reference Guide36
Page 49

Part II: Sessions & Tracks
37
Page 50

38
Page 51

Chapter 6: Sessions
This chapter covers the basics of starting a
project in Pro Tools, including how to set up
and save a Pro Tools session.
Starting Up or Shutting Down Your System
To ensure that the components of your
Pro Tools system communicate properly with
each other, you need to start them in a particular order.
Start up your Pro Tools system in this order:
1 For TDM systems with an expansion chassis,
turn on the chassis.
2 Turn on any external hard drives. Wait ap-
proximately ten seconds for them to spin up to
speed.
3 Turn on any MIDI interfaces, MIDI devices, or
synchronization peripherals.
4 Lower the volume of all output devices in
your system.
5 For TDM systems, turn on your Pro Tools au-
dio interfaces. Wait at least fifteen seconds for
your system hardware to initialize.
6 Turn on your computer.
Shut down your Pro Tools system in this order:
1 Quit Pro Tools and any other running applica-
tions.
2 Turn off or lower the volume of all output de-
vices in your system.
3 Turn off your computer.
4 For TDM systems, turn off audio interfaces.
5 For TDM systems with an expansion chassis,
turn off the chassis.
6 Turn off any MIDI interfaces, MIDI devices, or
synchronization peripherals.
7 Turn off any external hard drives.
Configuring Pro Tools System
Settings
Pro Tools allows you to adjust the performance
of your system by changing system settings that
affect its capacity for processing, playback, and
recording.
In most cases, the default settings for your system provide optimum performance, but you
may want to adjust them to accommodate large
or processing-intensive Pro Tools sessions.
7 Launch Pro Tools or any third-party audio or
MIDI applications.
Chapter 6: Sessions 39
Page 52

Hardware Buffer Size
The Hardware Buffer Size (H/W Buffer Size) controls the size of the hardware cache used to handle host-based tasks such as Real-Time AudioSuite (RTAS) plug-in processing.
◆ Lower Hardware Buffer Size settings reduce
monitoring latency, and are useful when you are
recording live input.
◆ Higher Hardware Buffer Size settings allow for
more audio processing and effects, and are useful when you are mixing and using more RTAS
plug-ins.
◆ Lower CPU Usage Limit settings limit the ef-
fect of Pro Tools processing on other CPU-intensive tasks, such as screen redraws, and are useful
when you are experiencing slow system response, or when running other applications at
the same time as Pro Tools.
◆ Higher CPU Usage Limit settings allocate
more processing power to Pro Tools, and are
useful for playing back large sessions or using
more real-time plug-ins.
Increasing the CPU Usage Limit may slow
down screen responses on slower computers.
In addition to causing slower screen response and monitoring latency, higher
Hardware Buffer Size settings can affect the
accuracy of plug-in automation, mute data,
and timing for MIDI tracks.
To change the Hardware Buffer Size:
1 Choose Setups > Playback Engine.
2 From the H/W Buffer Size pop-up menu, select
the audio buffer size, in samples.
3 Click OK.
CPU Usage Limit
The CPU Usage Limit controls the percentage of
CPU resources allocated to Pro Tools host processing tasks.
With Pro Tools 5.3.3 and earlier, the maximum
CPU Usage Limit is 85 percent.
With Pro Tools 6.0, the maximum CPU Usage
Limit is 85 percent for single-processor computers, and 99 percent for multi-processor computers. (The 99 percent setting dedicates one entire
processor to Pro Tools.)
To change the CPU Usage Limit:
1 Choose Setups > Playback Engine.
2 From the CPU Usage Limit pop-up menu, se-
lect the percentage of CPU processing you want
to allocate to Pro Tools.
3 Click OK.
Number of Voices
(TDM Systems Only)
On TDM systems, the Number of Voices setting
lets you control the number of available voices
and how those voices are allocated to DSPs in
your system. For example, the default number
of voices on a Pro Tools HD 1 system is 48
voices, using one DSP (at sample rates of
44.1 kHz or 48 kHz).
Changing the number of voices affects
DSP usage, the total number of voiceable
tracks, and overall system performance.
Depending on the current sample rate and the
number of TDM cards in your system, you will
have different choices for voice count. For voice
limits on different HD systems, see “TDM System Playback, Recording and Voice Limits” on
page 7.
Pro Tools Reference Guide40
Page 53

To change the Voice Count:
1 Choose Setups > Playback Engine.
Playback Engine dialog (Pro Tools 6.0)
Playback Engine dialog (Pro Tools 5.1.3)
Default Sample Rate
The Sample Rate setting appears as the default
sample rate when you create a new session.
(This setting is available only when there is no
session open.)
The Sample Rate setting can affect the
number of available voices on TDM systems.
To change the default Sample Rate:
1 Choose Setups > Playback Engine.
2 Select the sample rate from the Sample Rate
pop-up menu.
3 Click OK.
You can change the sample rate when creating a new Pro Tools session by selecting a
different sample rate in the New Session dialog. (
See “Creating a New Session” on
page 46.)
2 Select the number of voices and DSPs to allo-
cate for voicing by selecting a value from the
Number of Voices pop-up menu (Pro Tools 5.3
and later), or by clicking a value under Playback
Engine (Pro Tools 5.1.3).
• Select higher voice numbers when your
Digidesign cards are the only PCI cards in
your computer, or when you are using an
expansion chassis to run higher track
counts.
• Select medium voice numbers when your
Digidesign cards are in an expansion chassis, or when you are using other PCI cards
along with Digidesign cards.
• Select minimum voice numbers if you are
using high-bandwidth PCI cards (such as
video capture cards) along with your
Digidesign cards.
3 Click OK.
DAE Playback Buffer Size
The DAE Playback Buffer Size determines the
amount of memory DAE uses to manage disk
buffers, which affects system performance.
◆ Lower DAE Playback Buffer Size settings can
improve playback and recording initiation
speed. However, a lower setting can make it difficult for slower hard drives to play or record
tracks reliably.
◆ Higher DAE Playback Buffer Size settings can
allow for a higher density of edits in a session.
However, a higher setting can cause a time lag to
occur before playback or recording begins. It can
also cause a time lag to occur when you are editing during playback.
Chapter 6: Sessions 41
Page 54

To change the DAE Playback Buffer Size
(Pro Tools 5.3 and later):
1 Choose Setups > Playback Engine.
2 Choose File > Set Playback Buffer Size.
Playback Engine dialog (Pro Tools 6.0)
2 From the DAE Playback Buffer pop-up menu,
select a buffer size. Memory requirements for
each setting are shown at the bottom of the
Playback Engine dialog box.
3 Click OK.
4 If Pro Tools needs more system memory for
the DAE Playback Buffer, it will prompt you to
restart your computer.
To change the DAE Playback Buffer Size
(Pro Tools 5.1.3):
1 Launch DAE. If Pro Tools is already running,
switch to the DAE application.
DAE Playback Buffer Size dialog (Pro Tools 5.1.3)
3 Select a buffer size.
4 Click OK.
5 Quit Pro Tools if it is running, or quit the DAE
application. The new buffer setting will take effect when you launch Pro Tools again.
System Memory Allocation
(Pro Tools 6.0 TDM Systems Only)
When you start your computer, Pro Tools automatically reserves a portion of system memory
for the DAE Playback Buffer. This reserved memory is unavailable to other applications, even if
Pro Tools is not running.
You can set Pro Tools to reserve only the minimum amount of required memory, so that system memory is available to other applications.
To minimize system memor y allocation:
1 Choose Setups > Playback Engine.
2 Select the “Minimize System Memory Alloca-
tion” option.
3 Click OK.
4 Restart your computer.
Pro Tools Reference Guide42
Page 55

Configuring Pro Tools
Hardware Settings
Pro Tools allows you to configure the signal
routing, digital I/O format, default sample rate,
clock source, and other hardware-based settings
depending on your system configuration.
The following section outlines the configuration of a Pro Tools|HD system with one or more
HD interfaces (with one or more MIX-series interfaces attached).
To configure a Pro Tools MIX-series,
Pro Tools|24, or Pro Tools LE system, refer
to the
Getting Started Guide that came with
that system.
Configuring Pro Tools|HD
Hardware
On TDM systems, you configure Hardware settings for each audio interface connected to your
system. For example, Pro Tools|HD-series systems can have 192 I/O, 192 Digital I/O, or
96 I/O audio interfaces connected to HD Core
and HD Process cards in the system. Those audio
interfaces can have additional interfaces attached (including older Digidesign audio interfaces, or Legacy I/Os, such as the 888|24 I/O,
882|20 I/O or 1622 I/O). For more information,
see Chapter 2, “Pro Tools System Configurations.”
Configuring Hardware Setup
The Main page of the Hardware Setup dialog is
where you define which physical inputs and
outputs on your audio interface are routed to
available inputs and outputs in Pro Tools.
Hardware Setup dialog for 192 I/O (Main page)
Additional pages are available to configure other
controls for each audio interface (such as setting
operating levels). For details, refer to the Getting
Started Guide for your system, or to the guide for
your audio interface.
Hardware Setup dialog for 192 I/O (Analog In page)
You can identify audio interface connections at any time by selecting the interface
name in the Peripherals list, then clicking
Identify. All the LEDs on the interface front
panel will illuminate.
To configure audio interfaces on an HD system:
1 Choose Setups > Hardware Setup.
2 From the Peripherals list, select the Digidesign
audio interface connected to the first card in
your system. This will be the interface at the top
of the list.
3 Click the Main tab.
Chapter 6: Sessions 43
Page 56

4 From the Clock Source pop-up menu, select
the appropriate clock source for the system. In
most cases, you will use Internal. The other
choices are for resolving Pro Tools to external
clock sources. Depending on your audio interface, Clock Source options can include:
AES/EBU [Encl], S/PDIF, Optical [Encl], AES/EBU
1–8, TDIF, ADAT, and Word Clock (optional
Word Clock rates are available when operating
at higher sample rates).
5 From the Ext. Clock Output pop-up menu, se-
lect the appropriate clock output to send to devices attached to your audio interface.
6 Select which digital I/O port on your audio in-
terface enclosure is active under Digital Format.
Choices include: AES/EBU, S/PDIF, and Optical
(S/PDIF). Selecting Optical (S/PDIF) resets the
Optical I/O port (which is, by default, eight
channels of ADAT I/O) to two channels of
S/PDIF Optical I/O.
7 For S/PDIF compatibility with Tascam DA-30
DAT recorders select the Tascam option under
S/PDIF Format.
8 For the 96 I/O, click the Meters pop-up menu
and select whether to meter the input or output
signal.
9 From the Input and Output pop-up menus, se-
lect the physical ports (such as Analog 1–2 or
Optical 1–2), that will be routed to the corresponding Pro Tools input and output channels
(such as Ch 1–2 or Ch 3–4), listed on the left side
of the Main page.
Inputs and outputs of similar format are differentiated in the input and output channel popup menus. For example, the AES/EBU inputs
and outputs in the 192 I/O enclosure are listed
as AES/EBU [Encl], while the AES/EBU inputs
and outputs on the factory-installed Digital I/O
card are listed (in pairs) as AES/EBU 1–2,
AES/EBU 3–4, AES/EBU 5–6, and AES/EBU 7–8.
For 192 I/Os equipped with the optional
Digital I/O Card, the additional AES/EBU I/O
ports on the optional card are listed as AES/EBU
9–10, AES/EBU 11–12, AES/EBU 13–14, and
AES/EBU 15–16.
10 Click other tabs (such as Analog In and Ana-
log Out) for additional configuration options
specific to the audio interface. These include:
• On the 96 I/O, configuring the operating
levels of analog inputs and outputs (+4 dBu
or –10 dB).
• On the 192 I/O analog input, setting the
input connector, input trim (A or B), and
Soft Limit.
• On the 192 I/O, configuring the two sets of
trims for inputs and outputs.
• On the 192 I/O, configuring inputs and
outputs on any optional A/D card, D/A
card, or Digital I/O cards installed in the
unit.
For more information on Hardware Setup
controls for each HD audio interface, refer
to the Getting Started with HD Guide or the
guide for that audio interface.
11 Repeat the above steps for each additional
HD-series audio interface.
Use the Up and Down Arrow keys to scroll
though peripherals in the Peripherals list.
12 Repeat the above steps for any Legacy I/Os
connected to the HD-series audio interfaces in
your system. Before you can configure a Legacy
I/O, it must first be initialized in Hardware Setup
(See “Initializing MIX-Series Peripherals” on
page 45.)
13 Click OK.
Pro Tools Reference Guide44
Page 57

Initializing MIX-Series Peripherals
Configuring I/O Setup
Before you can configure a Legacy I/O, it must
first be initialized in Hardware Setup.
To initialize a Legacy I/O on an HD system:
1 Start up your Pro Tools system. See “Starting
Up or Shutting Down Your System” on page 39.
2 Make sure to lower the volume of your output
devices. Very loud digital noise may be emitted
before the Legacy I/O is initialized.
3 Turn on your Legacy I/O.
4 From the Peripherals list, choose the primary
audio interface (the interface to which your Legacy I/O is connected).
5 In the Main page of the Hardware Setup dia-
log, select the Legacy I/O option under Port Settings.
6 In the Peripherals list, “No Interface” is listed
twice, directly below the primary audio interface. Click the first “No Interface.” An Interface
pop-up menu appears in the Hardware Setup dialog, listing supported I/O choices.
7 From the Interface pop-up menu, select the
type of Legacy I/O you connected.
8 Set the External Clock Output on the HD in-
terface to 256x, which is the required clock
speed for Legacy I/Os.
The I/O Setup dialog provides a graphical representation of the signal routing for each connected audio interface, with controls to route
physical ports on the audio interface to
Pro Tools inputs and outputs. These controls
mirror the routing controls found in the Hardware Setup dialog—changes made to physical
routing in one dialog are always reflected in the
other. The I/O Setup dialog also lets you label
and map Pro Tools input, output, insert, and
bus signal paths. For more information on paths,
path labeling, and path mapping, see Chapter 7,
“I/O Setup.”
Routing a Pro Tools Output Pair to
Multiple Destinations
Pro Tools channel pairs can be routed to multiple outputs on an audio interface through the
Hardware Setup dialog. For example, if you assign both Analog 1–2 and Analog 3–4 interface
outputs to Pro Tools Output pair 1–2, when you
send a signal to Pro Tools Outputs 1–2, that signal will be routed simultaneously to both pairs
of output ports on your audio interface.
This lets you send the same signal (such as a stereo pair, a stem mix, or a multichannel mix) to
multiple destinations (such as multiple mastering devices).
After you select an audio interface, the Main
page updates with controls that can be configured. Refer to the guide for your audio interface
for details on each control.
9 Repeat the above steps for each additional
Legacy I/O.
For more information on Hardware Setup
controls for each Legacy audio interface, refer to the guide that came with the interface.
To select multiple output por ts for a Pro Tools
output channel pair:
1 Choose Setups > Hardware Setup.
2 From the Peripherals list, select an interface.
3 Click the Main tab.
4 Select an output pair from an Output pop-up
menu.
Chapter 6: Sessions 45
Page 58

5 Control-click (Macintosh) or Start-click (Win-
dows) the same pop-up menu a second time to
choose an additional output pair.
The output name updates with a plus sign (“+”)
before it to indicate that multiple output ports
are selected. In the pop-up menu, each physical
port pair assigned to that Pro Tools output pair
is indicated by a check mark.
When you record a new audio track, the track is
saved as a new audio file to the Audio Files
folder. You can also import other audio files into
the session, and work with them as well.
Typical session folder
For details on allocating audio tracks to different
hard drive locations, including shared media
volumes, see “Disk Allocation” on page 141.
Hardware Setup dialog for 192 I/O, Main page
6 Repeat the above steps to select additional
output destinations. The only limit to output
choices is the number of outputs available in
your system.
Pro Tools output pairs can also be routed to
multiple audio interface outputs in the
I/O Setup dialog. For more information, see
“Routing Hardware I/O to Pro Tools I/O” on
page 69.
Creating a New Session
The first step in beginning a Pro Tools project is
creating a new session. When you do this,
Pro Tools automatically creates a new folder
named for your session. Within this folder is the
session file and two subfolders, an Audio Files
folder, and a Fade Files folder.
The Audio Files folder contains all audio recorded or converted during the session. The
Fade Files folder contains any crossfaded audio
data generated by the session.
To create a new session:
1 Choose File > New Session.
New Session dialog
2 Choose the drive where you want to save the
session. The session should be saved on a dedicated audio drive.
Pro Tools Reference Guide46
Page 59

3 Select “Enforce Mac/PC Compatibility” (Mac-
intosh) if you want to create session and audio
files that can be used in either Macintosh or
Windows versions of Pro Tools. See “Creating
Mac and PC Compatible Sessions” on page 130
for more information.
To use Japanese or non-ASCII characters in
track and region names, or track comments,
deselect the option for “Enforce Mac/PC
Compatibility” when creating a new session.
If you save a session copy with the “Enforce
Mac/PC Compatibility” option enabled, all
Japanese and non-ASCII characters will be
lost.
Choosing Bit Depth and Sample Rate
When choosing a bit depth or sample rate for
your session, consider the disk space your selection will require. 24-bit audio files occupy about
50 percent more disk space than 16-bit audio
files. 192 kHz audio files occupy about four
times the space as 44.1 kHz audio files.
Bit depth and sample rate also have an effect on
the amount of mixing power available in a session. On TDM systems, fewer mixer channels
are available with 24-bit sessions and with sessions at higher sample rates (see Appendix B,
“TDM Mixing and DSP Usage”). On LE systems,
24-bit sessions require more processing power as
well.
4 Select the audio file format for the session.
For optimum compatibility between Windows
and Macintosh sessions, set the file type to
WAV. Sound Designer II (SD II) files are not supported on Windows systems, and Pro Tools prevents you from choosing SD II as the file type if
Enforce Mac/PC Compatibility is selected (or
the session is on a PC).
5 Select the bit depth (16 bit or 24 bit) and the
sample rate.
6 Select the I/O Settings to use for the session.
Several pre-configured I/O Settings are included
with your system, or you can select a custom I/O
Setting that you have created. See Chapter 7,
“I/O Setup” for more information.
7 Name the Session.
8 Click Save.
It is not possible to combine different bit depths
within a single Pro Tools session; files of different bit depths must be converted and imported
into the session.
Chapter 6: Sessions 47
Page 60

Opening a Session
When you open a session, Pro Tools looks in the
session folder for audio and fade files linked to
the session.
To open an existing session:
1 Choose File > Open Session.
2 Locate the session you want to open and click
Open.
Opening a Session that Contains Unavailable Resources
Pro Tools prompts you when opening a session
that contains unavailable voices, I/O paths, DSP
resources, or plug-ins. This is common when
transferring sessions to systems with different
Digidesign hardware.
Opening a session with unavailable resources
The dialog contains a summary of the missing
session components. To save a text file containing a more detailed report, along with the resulting action, click OK.
The following will occur when opening a session with unavailable items:
Open Session dialog
Pro Tools Reference Guide48
With Pro Tools TDM Systems:
◆ Any tracks beyond the maximum number of
available voices on the current system are made
inactive.
With Pro Tools LE 6.0:
◆ Any tracks beyond the maximum number of
available voices on the current system are set to
voice off.
With Pro Tools LE 5.3.x and earlier:
◆ Any tracks beyond the maximum number of
available voices on the current system are removed from the session. If the session is saved,
the removed tracks are lost.
Page 61

With all Pro Tools Systems:
◆ Inserts assigned to unavailable plug-ins are
made inactive.
◆ Inputs, outputs, and sends that are assigned to
unavailable paths are made inactive.
Saving a Session
You should save regularly while working on
your session to ensure that your work is preserved on your hard drive.
Speeding up Saves by Reducing the
Disk Cache Size
(Mac OS 9 Only)
Saving the Session File with a New Name
To save a copy of the current session with a new
name or to a different hard drive location, you
can use the Save Session As command. Because
the Save Session As command closes the current
session and lets you keep working on the renamed copy, it is useful if you are experimenting and want to save successive versions of the
session.
By working this way, you can quickly retrace
your steps if you want to go back to an earlier
version of your session. The Save Session As
command saves a new version of the session file
only—not duplicate versions of the audio or
fade files.
To speed up session saves and disk bounces, it is
recommended that you reduce the Cache Size
for your Macintosh to 512K (in the Control
Panel > Memory dialog).
Saving the Session File
The Save Session command saves the changes
you have made to your session and writes them
over the previously saved version of the session
file. The Save Session command cannot be undone.
To save a session:
■ Choose File > Save Session.
Revert to Saved Command
If you have made changes to a session since you
last saved it, you can discard the changes and revert to its previously saved state.
To revert to the last saved version of a session:
■ Choose File > Revert to Saved.
To save a session with a new name:
1 Choose File > Save Session As.
2 Enter a new name for your session.
3 Click Save.
The renamed session file is saved in the session
folder along with the original session. Any new
audio files that you record in your renamed session will be placed into the same Audio Files
folder that was created for your original session.
Chapter 6: Sessions 49
Page 62

Saving a Copy of the Session
To save a copy of the current session along with
its audio files and fade files, you can use the Save
Session Copy In command. In addition, you can
specify a session file format, audio file format,
bit depth, and sample rate for the session copy.
Using the Save Session Copy In command is the
only way to change the sample rate of a session.
When you Save Session Copy with a lower
bit rate, Dither (and Noise Shaping) may be
applied. See the following table:
Dither and Noise Shaping with Save Session Copy In
Save
Bit Rate Conversion
Session
Copy
Save Session Copy In dialog
Unlike the Save Session As command, Save Session Copy In does not close the original session,
so subsequent edits are made to the original session. Session copies can be used to archive important sessions, or as a means to prepare sessions for transfer to another Pro Tools system.
Save Session Copy In saves only the audio being
used in the session. Any audio that was recorded
or imported and then later removed from the
session will not be included in the new session
copy.
24-bit to 16-bit
(Dither and Noise
Shape)
24-bit to 8-bit
(Noise Shape Only)
16-bit to 8-bit
(Noise Shape Only)
Yes
No
No
For more information about using Dither with
the Save Session Copy In command, see
“Dither” on page 402.
Session Format
You can save the session copy in the following
formats:
• Latest (Pro Tools 5.1 or later)
• Pro Tools 5 Session
• Pro Tools 4 24-Bit Session
• Pro Tools 4 16-Bit Session
• Pro Tools 3.2 Session
Use Latest if you are working with Pro Tools
software 5.1 or higher.
When saving sessions to versions earlier than
5.1, multichannel tracks and multi-mono plugins are lost. In this case, make sure to first separate the tracks and plug-ins to individual mono
tracks.
Pro Tools Reference Guide50
Page 63

Session Parameters
Audio File Type
The higher the quality of sample rate conversion you choose, the longer Pro Tools will take
to process the audio file.
You can save the session to reference WAV or
AIFF audio files. On the Macintosh, you can also
save the session to reference SD II audio files (at
sample rates up to 48 kHz).
SD II sessions are not supported with
Pro Tools for Windows, or with sample
rates higher than 48 kHz. You cannot set
the session audio file type to SD II on the
Macintosh if Enforce Mac/PC Compatibility is selected, or if the sample rate of the
destination session is greater than 48 kHz.
Using Mixed File Types
A session can use mixed audio file types. If your
original session has mixed file types, they are
not converted to a different file type unless you
specify that they be converted. However, when
using mixed file types, audio performance will
be reduced (due to additional file handling required for some file formats).
Bit Depth
You can save the new session at 16-bit or 24-bit
depth. If your session is in a different bit depth,
audio files are converted to the new session bit
depth, and copied to the location you specify.
Sample Rate
You can save the new session at sample rates of
44.1 kHz or 48 kHz (on Mbox, Digi 001 and
MIX-series systems) and at sample rates up to
96 kHz (on Digi 002) or 192 kHz (on HD-series
systems). If your session is at a different sample
rate, audio files are converted to the new session
sample rate, and copied to the location you
specify.
Enforce Mac/PC Compatibility
This setting forces Macintosh or Windows versions of Pro Tools to create sessions and audio
files that are usable on both platforms. For more
information, see “Creating Mac and PC Compatible Sessions” on page 130.
Items to Copy
All Audio Files
When this option is selected, all audio files are
copied to the new location.
This setting is automatically selected if you are
changing the bit depth or sample rate of the session.
All (Non-Native) Audio Files
This name of this option varies depending on
the audio file type you select. If you are changing the audio file type of the session, this option
ensures that all files in the copied session are
converted to the selected file type. Use this option to avoid the reduced performance of a session with mixed file types.
This option is automatically selected if you are
changing bit depth or sample rate, or copying a
session on the Macintosh from SD II format to
AIFF or WAV format with Enforce Mac/PC Compatibility selected.
Chapter 6: Sessions 51
Page 64

Don’t Copy Fade Files
When this option is selected, Fade Files are not
copied to the new session Fade Files folder.
When the session is launched, the Find Files dialog will prompt you to locate Fade Files. You
can either locate the existing fades using the
find file dialog, or Skip All to let Pro Tools recreate the fades from the session document.
Session Plug-In Settings Folder
When this option is selected, the session’s PlugIn Settings folder is copied to the new location.
The references to these plug-in settings in the
session are redirected to point to the copied settings files.
3 Set the Audio File Type to AIFF, WAV, or SD II.
If the audio files need to be compatible with either Macintosh or Windows, select AIFF or WAV.
4 Set the Sample Rate and Bit Depth for the ses-
sion.
5 Select “Enforce Mac/PC Compatibility” if you
want to create session and audio files that can be
used in either Macintosh or Windows versions
of Pro Tools. See “Creating Mac and PC Compatible Sessions” on page 130 for more information.
6 Select the Items to Copy to the new session.
7 Click Save.
Root Plug-In Settings Folder
When this option is selected, the contents of the
root-level Plug-In Settings Folder are copied into
a folder named Place in Root Settings Folder, indicating that these files will need to be moved to
the root level plug-in settings folder on the destination system before you can use them. The
references to these settings files in the session
are not redirected to point to the copied files.
Movie/Video Files
When this option is selected, session movie files
(QuickTime video files or AVoption or
AVoption XL video files) are copied to the new
location, and session references are updated to
point to the copied movie files.
To save a session copy in a new location:
1 Choose File > Save Session Copy In.
2 In the Save Session Copy dialog, choose a des-
tination and enter a name for the new session
file.
Creating Custom Session Templates
You can create custom session documents that
are pre-configured to the track setups, mixer setups, window arrangements, and zoom level
memory locations that you use most frequently.
Doing this will save you the trouble of having to
create your studio setup from scratch every time
you start a new session.
Creating Macintosh Templates
On the Macintosh, you can create a session template by saving a session file as a Stationery Pad
document. Once a session is saved as a Stationery Pad, it acts as a template that you can open
and then resave as a normal session.
To create a custom session template on the
Macintosh:
1 Create a session and arrange its elements as
desired. In addition to track setup, you can also
define parameters such as signal routings, insert
and send configurations, Mix and Edit window
views, Ruler settings, and Preference settings.
Pro Tools Reference Guide52
Page 65

2 Choose File > Save Session As.
3 Name the session and click Save.
4 Close the session.
Creating Windows Templates
In Windows, you can create a session template
by making a session file a Read Only document.
5 Locate the session file that you just saved.
6 Click once on the file to select it.
7 Choose File > Get Info > General Information.
Saving a session as a Stationery Pad (Macintosh)
8 Select the Stationery Pad option to save the
file as a template, then close the information
window.
To use this template, double-click it or open it
with the Open Session command if you are already running Pro Tools. You can create several
custom templates for studio setups that you frequently use.
To create a custom session template in Windows:
1 Create a session and arrange Pro Tools as de-
sired. You can also define the parameters within
these windows, such as signal routings, insert
and send configurations, track views, Ruler settings, and Preference settings.
2 Choose File > Save Session As.
3 Name the session and click Save.
4 Close the session.
5 Locate the session file that you just saved.
6 Right-click the file and choose Properties.
7 Under Attributes, deselect Archive and select
Read Only.
When you open a session saved as a Stationery
Pad, Pro Tools gives you the option of editing
the template or starting a new session using the
template settings. If you choose New Session,
Pro Tools will create a new folder containing a
copy of your session template and Audio and
Fades folders.
Making a session a Read Only file (Windows)
8 Click OK.
Chapter 6: Sessions 53
Page 66

To use this template, double-click it or open it
with the Open Session command. When you
first save the session, Pro Tools will ask you to
give the session a new name. Your original session template will remain unchanged.
To modify the session template, you will need to
reopen its Properties, deselect the Read Only option and select the Archive option, make your
modifications, then change it back to a Read
Only file.
Sharing Sessions Between
Pro Tools TDM Systems and
Pro Tools LE Systems
Pro Tools makes it easy to share sessions between Pro Tools LE and TDM-equipped systems.
There are some important differences between
the two types of systems that can affect how session material is transferred.
Differences between TDM and LE systems
Feature TDM Systems LE Systems
Closing a Session
Because Pro Tools allows you to work on just
one session at a time, you must close the current
session if you want to work on another. The
Close Session command closes your current
Pro Tools session but leaves the Pro Tools application open. You can save your work using the
Save Session or Save Session As command before
closing the current session.
To close a session:
■ Choose File > Close Session.
Quitting Pro Tools
Although Pro Tools will warn you before allowing you to quit without saving changes, you
should generally save your work before quitting.
To quit Pro Tools on the Macintosh:
■ Choose Pro Tools > Quit Pro Tools
(Pro Tools 6.0) or File > Quit (Pro Tools 5.3.x
and earlier).
To exit Pro Tools in Windows:
■ Choose File > Exit.
Number of
Audio Tracks
Number of
Mix Busses
Inserts per
Track
Sends per
Track
up to 256
(HD-series)
up to 128
(MIX-series)
64 busses 16 busses
up to 5 inserts up to 5 inserts
up to 5 sends up to 5 sends
up to 32
(Pro Tools 6.0
on all systems,
Pro Tools 5.3.1
and later on
Windows)
up to 24
(Pro Tools 5.3.x
and earlier on
Macintosh,
Pro Tools 5.1.x
and earlier on
Windows)
When opening a TDM session in Pro Tools LE,
the following rules apply:
With Pro Tools LE 6.0 and later (all systems) or
Pro Tools 5.3.1 and later (Windows):
◆ Any tracks beyond the first 32, as well any in-
active tracks, are set to voice off.
◆ Multichannel surround tracks are removed
from the session.
Pro Tools Reference Guide54
Page 67

◆ Any assignments to busses beyond 16 are
made inactive.
◆ Unavailable input and output paths are made
inactive.
◆ TDM plug-ins with RTAS equivalents are re-
tained; those without equivalents are made inactive.
With Pro Tools LE 5.3.x and earlier (Macintosh)
or Pro Tools LE 5.1.x and earlier (Windows):
◆ Any tracks beyond the first 24, as well any in-
active tracks, are removed from the session.
◆ Multichannel surround tracks are removed
from the session.
◆ Any assignments to busses beyond 16 are
made inactive.
◆ Unavailable input and output paths are made
inactive.
◆ TDM plug-ins with RTAS equivalents are re-
tained; those without equivalents are made inactive.
Preferences
The Preferences dialog has several tabbed pages
in which you can specify your preferred settings
for various session parameters. Each new session
will use these preferences.
Display Preferences
Edit Window Follows Bank Selection If you are
using a supported control surface with
Pro Tools, this option scrolls the Edit window to
display the selected bank of tracks when you
switch banks on the control surface, ensuring
that the current bank is viewable on-screen.
Show Meters in Sends View When the Sends
View is displaying individual send controls, you
can select this option to show send level meters.
Deselecting this option can help speed up
screen redraws and processing.
Mix Window Follows Bank Selection If you are
using a supported control surface with
Pro Tools, this option scrolls the Mix window to
display the selected bank of tracks when you
switch banks on the control surface, ensuring
that the current bank is viewable on-screen.
Draw Grids in Edit Window Adds grid lines to the
Edit window. Grid line resolution is based on
the zoom level of the Edit window.
Draw Waveforms Rectified Displays audio waveform data in rectified view. In this view, audio
waveforms are displayed so that their positive
and negative waveform excursions (the portions
Chapter 6: Sessions 55
Page 68

that fall above and below the center line) are
summed together and viewed as a single positive-value signal. This view allows more waveform detail to be seen in either normal or reduced track height views. It can be particularly
useful when editing volume automation data,
since it depicts waveform levels as starting at the
bottom of the track.
Recompute Invalid Overviews Prompts Pro Tools
to look for missing or corrupted overview data
(the data used to create waveform displays)
when it opens sessions. If Pro Tools finds that
overview data is missing or corrupted, it will recreate one or more overviews for the session. This
may take some time if there are many tracks in
the session. If you suspect that overview data for
a session has become corrupted, or if you import
audio files which have no overview data into a
session, make sure this preference is enabled for
the session, save and close the session, then reopen it. Pro Tools will recreate any overviews for
the session when it opens.
Edit Window Color Coding
Edit Window Color Coding determines how colors are assigned to the waveform display in the
Edit window.
None Turns off color assignment to the waveform display of tracks in the Edit window.
Tracks and MIDI Channels Assigns a color to the
waveform display of each track in the Edit window according to its voice number and MIDI
channel assignment.
Tracks and MIDI Devices Assigns a color to the
waveform display of each track in the Edit window according to its voice number and MIDI device type.
Groups Assigns a color to the waveform display
of each track in the Edit window according to its
group ID. If groups are suspended using the Suspend Groups command, all waveforms will be
displayed in black.
Edit Window Default Length This option allows
you to set a default length for the Edit window
in hours, minutes, seconds, and frames. This is
useful if you want to assemble a session of a particular length or leave extra room to expand the
Edit window’s work area in your session. There
is a 13 hour maximum limit for the length of a
Pro Tools session.
Zoom Toggle Track Height Sets the default track
height when the Zoom Toggle function is used
to zoom in on a selection.
Pro Tools Reference Guide56
Peak Hold Options
These options determine how long the peak indicators on track meters stay lit after a peak is
detected.
3-Second Peak Hold When this option is selected, track meters display the last peak level
for three seconds.
Infinite Peak Hold When this option is selected,
track meters display the last peak level until you
click them to clear them.
No Peak Hold When this option is selected, track
meters do not hold the peak level.
Page 69

Operation Preferences
Latch Record Enable Buttons When this option
is deselected, it prevents multiple audio tracks
from being record-enabled. Record-enabling an
audio track takes any other audio track out of
record-enabled mode.
Latch Solo Buttons When this option is deselected, it prevents multiple tracks from being soloed. Soloing a track mutes any track that is soloed.
Link Mix and Edit Group Enables When this option is selected, it links enabling and disabling
of Mix and Edit groups. For example, enabling
Group A in the Edit Window automatically enables Group A in the Mix window.
Timeline Insertion Follows Playback This option
causes the screen’s play cursor to update its location to the point where playback stops.
Edit Insertion Follows Scrub/Shuttle When selected, the edit cursor automatically locates to
the point where scrubbing stops.
Support Background Record Applications Allows
other audio recording applications to run in the
background concurrently with Pro Tools. Files
recorded in the background can be imported
into Pro Tools, and then trimmed and viewed
while recording continues.
Sends Default to –INF Sets the initial fader level
of newly-created Sends to –∞ (no audible signal
level).
Audio During Fast Forward/Rewind When selected, audio is audible during fast-forward or rewind.
Limit Pull Ups to NTSC/PAL Film Standards This
option, which is selected by default, filters the
list of available Pull Up rates that appears in the
Session Setup window.
Use F11 Key for Wait for Note When this option
is selected, pressing the F11 Function key puts
MIDI recording in Wait for Note mode.
Numeric Keypad Mode
Numeric Keypad Mode determines how the numeric keypad functions. You can always use the
numeric keypad to select and enter values in the
Event Edit Area, Location Indicators, and Transport fields.
Classic Emulates the way Pro Tools worked in
versions earlier than 5.0. With the Numeric Keypad Mode set to Classic, you can play up to two
tracks of audio in Shuttle Lock mode. Press Control (Macintosh) or the Start key (Windows), followed by 0–9 for different play speeds. Press Plus
(+) or Minus (–) to reverse direction. Recall
Memory Locations by typing the Memory Location number, followed by period (.).
Transport Allows you to set a number of record
and play functions, and also operate the Transport from the numeric keypad. With the Numeric Keypad Mode set to Transport, you can
play up to two tracks of audio in Shuttle Lock
mode. Press Control (Macintosh) or the Start
Chapter 6: Sessions 57
Page 70

key (Windows), followed by 0–9 for different
play speeds. Press Plus (+) or Minus (–) to reverse
direction. Recall Memory Locations by typing
period (.), the Memory Location number, and
period (.) again.
Shuttle (TDM Only) Selects a type of shuttling
different from that of Shuttle Lock mode. With
the Numeric Keypad Mode set to Shuttle, playback is triggered by pressing and holding the
keys on the numeric keypad—playback stops
once the keys are released. Various playback
speeds are available in both forward and reverse.
You can also recall Memory Locations by typing
period (.), the Memory Location number, and
period (.) again.
AutoSave
This preference determines how the AutoSave
feature functions.
Enable Session File Auto Backup When this option is selected, Pro Tools automatically saves
backups of your Pro Tools session file while you
work. Use the Keep and Backup Every fields to
specify the total number of incremental backups
that are kept and how often the session is saved.
Online Options
Record Online at Time Code (or ADAT)
Lock When this option is selected, online re-
cording begins as soon as Pro Tools receives and
locks to time code or ADAT sync.
Record Online at Insertion/Selection When this
option is selected, online recording begins at the
Edit cursor location. Recording continues until
Pro Tools stops receiving time code. If you make
a selection, Pro Tools records online for the
length of the selection.
Open Ended Record Allocation
This preference determines how much of your
available hard drive space is allocated for recording.
Use All Available Space When selected, the
drive’s entire available space is allocated. This
can sometimes slow down the recording process
for hard drives that use certain file systems, including HFS+ and NTFS.
Limit To Sets the maximum allowable recording
duration. This can help reduce the time it takes
to begin recording by allocating only a portion
of your hard drive. The number of minutes specified is allocated for each record-enabled track.
You may find it necessary to experiment with
this number to achieve the desired performance
for recording.
Machine Control
These preferences determine how a connected
transport responds to Pro Tools.
Machine Chases Memory Location When selected, navigating to a specific location in a session with a Memory Location causes a connected transport to chase to that location.
Machine Follows Edit Insertion/Scrub When selected, navigating to a specific location in a session by moving the selection point or by scrubbing a track will cause a connected transport to
chase to that location.
Machine Cues Intelligently When selected, if you
navigate to a cue point that is more than 10 seconds from the current location, Pro Tools will
command a connected transport to shuttle to
the new location at full speed to within 10 seconds of the cue point. Cueing will then slow to
normal speed until the point is reached. This
significantly speeds up tape cueing.
Pro Tools Reference Guide58
Page 71
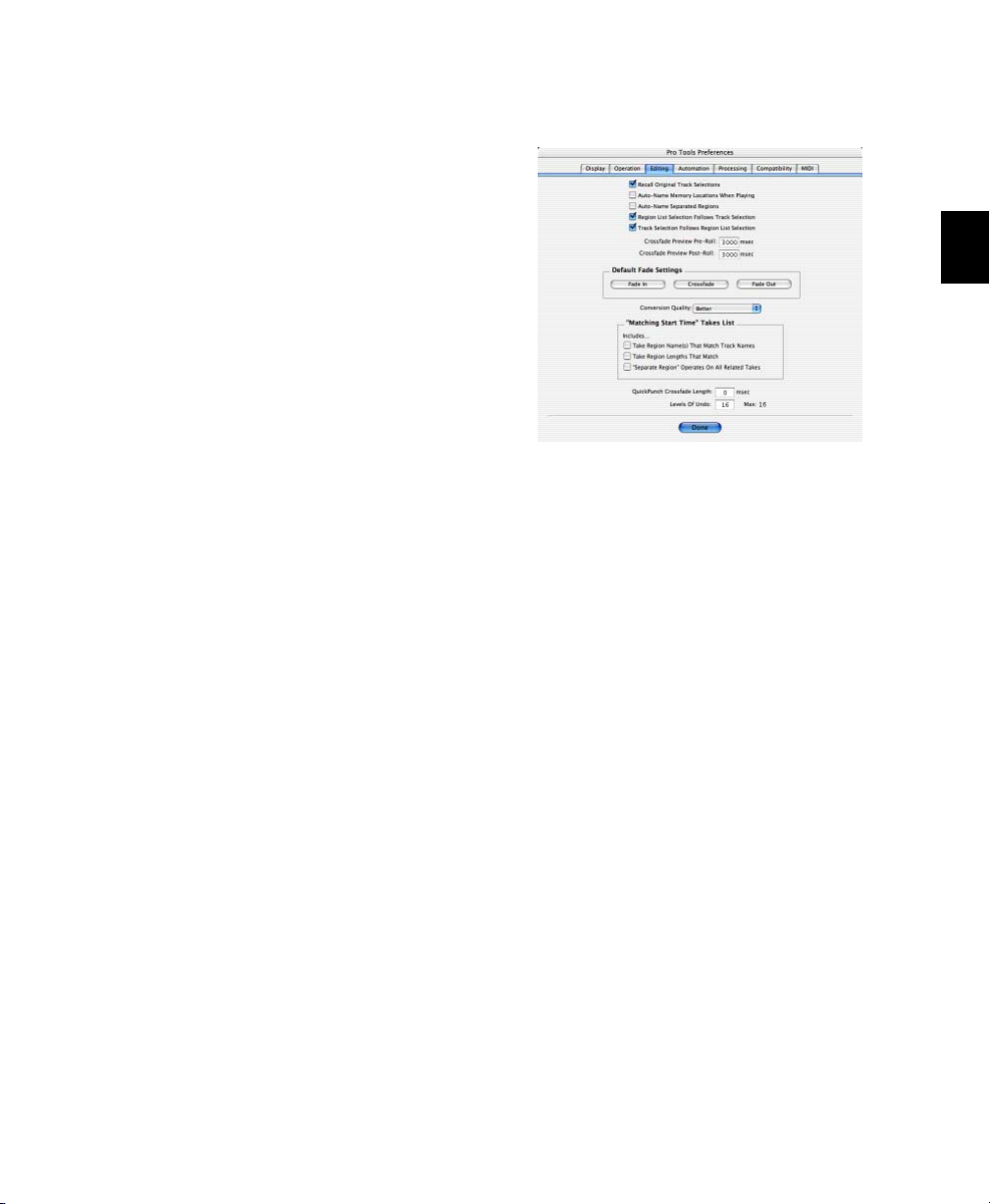
Stop at Shuttle Speed Zero Causes Pro Tools to
send a Stop command whenever you stop shuttling. This is useful if you have a machine that
requires an explicit stop command to park correctly.
Remote Mode (9-pin Deck Emulation)
(TDM Systems Only)
Punch In Frame Offset Sets an offset (in frames)
to compensate for punch in timing advances or
delays.
Punch Out Frame Offset Sets an offset (in frames)
to compensate for punch out timing advances
or delays.
Editing Preferences
Delay After Play Command Sets an offset (in
frames) to compensate for lockup time of external machines.
Ignore Track Arming Sets Pro Tools to ignore incoming track arming (record enable) commands. This is useful if you are using a master
controller to arm tracks on other machines, but
you don’t want to arm tracks in Pro Tools.
Auto Regions Fade In/Out Length Sets a default
length for fade-ins and fade-outs automatically
applied to region boundaries. Using automatic
fade-ins and fade-outs saves you the trouble of
editing to zero-crossings or creating numerous
rendered fades in order to eliminate clicks or
pops in playback. Autofades are not written to
disk. Value range is from 0–10 ms for the Auto
Region Fade In/Out Length. A value of zero (the
default) means that no auto-fading will occur.
The Auto Fade value is saved with the session,
and is automatically applied to all free-standing
region boundaries until you change it.
Calibration Reference Level Sets a default calibration reference level in dB when Pro Tools is
in Calibration mode.
Recall Original Track Selections When this option is selected, Memory Locations that recall a
selection also recall the track in which the selection was made.
Auto-Name Memory Locations When
Playing When this option is selected, Pro Tools
gives new memory locations default names
based on their time location in the session. The
time units currently chosen in the Display
menu determine the units for the names.
Auto-Name Separated Regions When this option
is selected, Pro Tools automatically names
newly separated regions by appending a number
to the region’s name.
Region List Selection Follows Track
Selection When this option is selected, selecting
a region in a track also selects it in the Regions
List.
Track Selection Follows Regions List
Selection When this option is selected, selecting
a region in the Regions List causes Pro Tools to
highlight that region’s occurrence in a track.
Chapter 6: Sessions 59
Page 72

Crossfade Preview Pre-Roll This option specifies
the amount of pre-roll to be added when you are
auditioning crossfades in the Fades dialog.
Crossfade Preview Post-Roll This option specifies the amount of post-roll to be added when
you are auditioning crossfades in the Fades dialog.
“Matching Start Time” Takes List
When you Command-click (Macintosh) or Control-click (Windows) a region in a track,
Pro Tools displays a list of regions whose time
stamp matches the current cursor location. The
following preferences determine which regions,
or takes, appear in this list:
Default Fade Settings
Fade In Selects the default envelope shape for
fade-ins.
Crossfade Selects the default envelope shape for
crossfades.
Fade Out Selects the default envelope shape for
fade-outs.
Conversion Quality Selects the sample rate conversion quality. Sample rate conversion is used
in a variety of Pro Tools processes including
converting and importing audio files of different formats into a session, and bouncing and
saving tracks to a different sample rate or bit
depth. The higher the quality of sample rate
conversion you choose, the longer Pro Tools
will take to process the audio file.
Take Region Names That Match Track
Names When this option is selected, only re-
gions that share the same root name with the
track and playlist appear in the Takes List popup menu.
Take Region Lengths That Match When this option is selected, only regions that match the
length of the current selection appear in the
Takes List pop-up menu.
“Separate Region” Operates On All Related
Takes When this option is selected, editing a re-
gion with the Separate Region command also affects all other related takes with the same User
Time Stamp. This option helps you compare different sections from a group of related takes.
QuickPunch Crossfade Length Specifies a default
length for crossfades created by QuickPunch recording. Crossfades occur before the punch in
and after the punch out.
Levels Of Undo Sets the maximum number of actions (up to 16) that can be undone with the
multiple undo feature. Setting this to a lower
number can speed up the performance of slower
computers.
Pro Tools Reference Guide60
Page 73

Automation Preferences
Faders Move During Playback When this option
is selected, on-screen faders move if automation
has been written for them. When this option is
deselected, on-screen faders do not move, but
automation still functions. Deselecting this option can help speed up screen redraws and processing.
Mutes Follow Groups When this option is selected, muting a track that belongs to a Mix
group mutes all members of the group. When
this option is deselected, tracks are muted individually. You can also mute individual group
members by Control-clicking (Macintosh) or
Right-clicking (Windows) their Mute buttons.
Solos Follow Groups When this option is selected, soloing a track that belongs to a Mix
group solos all members of the group. When
this option is deselected, tracks are soloed individually. You can also solo individual group
members by Control-clicking (Macintosh) or
Right-clicking (Windows) their Solo buttons.
Send Mutes Follow Groups When this option is
selected, muting a Send on a track that belongs
to a Mix group mutes the corresponding Send
(A–E) on all members of the group. When this
option is deselected, Sends are muted individually. You can also mute individual group members by Control-clicking (Macintosh) or Rightclicking (Windows) their Solo buttons.
Smooth and Thin Data After Pass When this option is selected, Pro Tools automatically
smooths and then applies the specified amount
of thinning to the automation data created in
an automation pass. (See “Thinning Automation” on page 434.)
Write Switches To Touch After Pass (TDM Systems Only) When this option is selected, after
an automation pass in Auto Write mode,
Pro Tools automatically switches to Auto Touch
mode. On TDM systems, you can choose to stay
in Auto Write mode by deselecting this option.
Write Switches to Touch After Pass does not
affect Trim mode. In Trim mode, tracks do
not automatically change from Trim/Auto
Write to Trim/Auto Touch after an automation pass.
Send Levels Follow Groups When this option is
selected, adjusting the level of a Send on a track
that belongs to a Mix group adjusts the level of
the corresponding Send (A–E) on all members of
the group. When this option is deselected, Send
levels are adjusted individually. You can also adjust individual group members by Control-dragging (Macintosh) or Start-dragging (Windows)
their Send level faders.
LFEs Follow Groups When this option is selected, adjusting an LFE control of a track or
send that belongs to a Mix group adjusts the LFE
controls of all members of the group. When this
option is deselected, LFE controls are adjusted
individually. You can also adjust individual
group members by Control-dragging (Macintosh) or Start-dragging (Windows) their LFE
controls. With send-based LFEs, grouping affects only that Send (A–E) on other tracks.
Chapter 6: Sessions 61
Page 74

Degree of Thinning Specifies the amount of thinning performed on automation data when you
use the Tin Automation command, or if you
have selected the Smooth and Thin Data After
Pass option. (See “Thinning” on page 426.)
Touch Timeout If you are writing automation in
Auto Touch mode and you stop moving a nontouch sensitive control, Pro Tools continues to
write automation for the Touch Timeout value.
After the Touch Timeout period, writing of automation stops and the automation data returns
to its previous automation value at the rate specified in the AutoMatch Time setting.
AutoMatch Time If you are writing automation
in Auto Touch mode, when you release a fader
or control, writing of automation stops and the
automation data returns to its previous automation value. The rate of return to the previous
value is the AutoMatch Time. See “AutoMatch”
on page 426.
Amount of memory to reserve for automation recording Allocates memory for automation. See
“Setting the Automation Buffer Size” on
page 427 for details.
Processing Preferences
AudioSuite Dither
Use AudioSuite Dither When selected, applies
dither to specific AudioSuite processing tasks,
such as Gain and Normalize.
Dither Plug-In Specifies the plug-in used for
dither processing when the Use AudioSuite
Dither option is selected.
Edit Settings When a Digidesign dither plug-in
is used, allows you to apply either normal or
noise-shaping dither.
Pro Tools Reference Guide62
Page 75
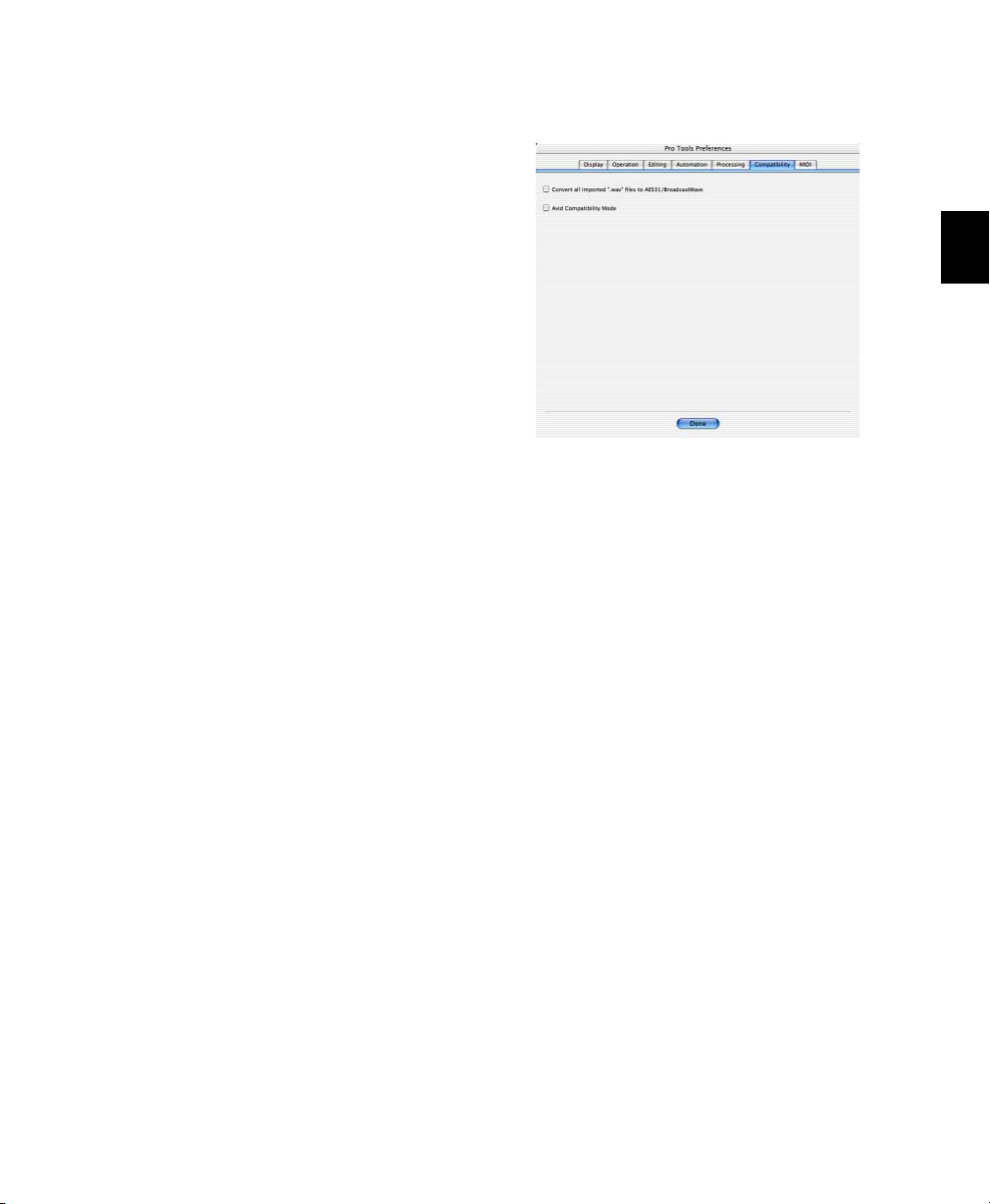
Bit Depth
16-, 18-, 20-, and 24-Bit allows you to select a bit
depth for the dithered audio.
AudioSuite Buffer Size
Audio Suite Buffer Size sets the size of the memory buffer used for audio processing and previewing with AudioSuite plug-ins. Generally,
choosing a smaller buffer speeds up AudioSuite
audio previewing functions. Choosing a larger
buffer speeds up AudioSuite processing functions. Set the buffer according to your current
task. Before auditioning an AudioSuite plug-in,
set the buffer to Mini or Small. When you process a file, set it to Large or Jumbo.
TC/E
TC/E Plug-In Allows you to choose the plug-in
used for Time Compression and Expansion
when you edit audio with the Time Trimmer
tool. The Time Trimmer works by using Time
Compression/Expansion to match an audio region to the length of another region, a tempo
grid, a video scene, or other reference point.
Default Settings Specifies the default settings
used by the chosen Time Compression/Expansion plug-in.
Compatibility Preferences
Convert All Imported “WAV” Files To
AES31/BroadcastWave When selected, this op-
tion applies to all newly imported .WAV files,
making them compliant with the AES31/EBU
Broadcast standard.
Avid Compatibility Mode When selected, ensures
that all imported OMF media files are treated as
Read-Only and prevents destructive editing processes such as those used by the Pencil and Time
Trimmer tools and AudioSuite processing.
Chapter 6: Sessions 63
Page 76
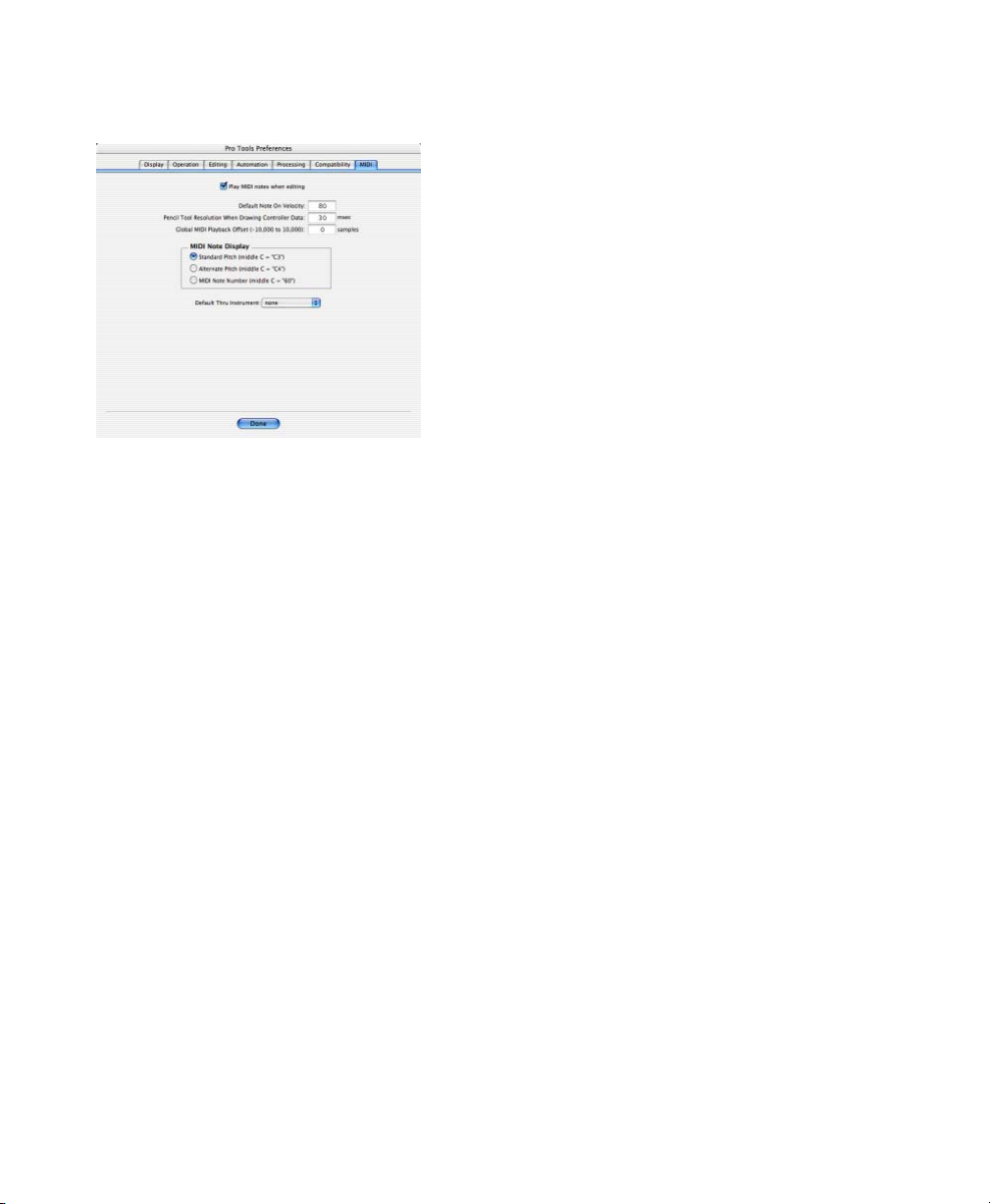
MIDI Preferences
Play MIDI Notes When Editing When selected,
causes MIDI notes to sound when you insert
them with the Pencil or drag them with the
Grabber.
Default Note On Velocity Sets the default Note On
velocity for MIDI notes inserted in the Edit window and the MIDI Event List.
Pencil Tool Resolution Sets the default resolution
for MIDI controller data created with the Pencil.
Setting this to a lower resolution helps avoid
creating controller data that is unnecessarily
dense. The value range is from 1 to 100 milliseconds.
Global MIDI Playback Offset Sets an offset in samples to compensate for MIDI latency. Entering a
value here has the same effect as setting an offset with the MIDI Track Offset command (Windows > MIDI Track Offset). Offset values can be
positive (later) or negative (earlier).
MIDI Note Display Sets the reference for middle
C as C3, C4, or MIDI note number 60.
Default Thru Instrument Sets the default MIDI
Thru instrument from your available MIDI instruments.
Pro Tools Reference Guide64
Page 77

Chapter 7: I/O Setup
The I/O Setup dialog provides tools to label, format, and map Pro Tools input, output, insert,
bus, and SampleCell signal paths for each session. (SampleCell paths are available only on
MIX-series systems with TDM-equipped SampleCell cards.)
A signal path is a logical grouping of multiple
inputs, outputs or busses that has a single name
and (channel) format. In Pro Tools, paths are
similar to stems, known to the film and video industries (see “Stems and Stem Mixes” on
page 67). The I/O Setup dialog lets you define
and name paths according to the needs of each
project.
On HD-series systems, the I/O Setup Dialog provides a graphical representation of the signal
routing for each connected audio interface, with
controls to route physical ports to Pro Tools inputs and outputs. These controls mirror the
routing controls found in the Hardware Setup
dialog—changes made to physical routing in
one dialog are always reflected in the other.
Each Pro Tools system can have a different
I/O Setup configuration, determined by:
• Whether it is a Pro Tools LE system or a
Pro Tools TDM system
• Whether it is an HD-series, MIX-series, or
Pro Tools|24 system
• On TDM systems, the number and types of
audio interfaces
• On TDM systems, the mixer plug-in currently
installed
Each Pro Tools session retains its path configurations as I/O Settings. The I/O Settings saved
with the session are loaded automatically when
the session is opened. Unavailable items (including hardware, paths, or required resources)
remain in the session as inactive items (see “Active and Inactive Paths” on page 75).
When you create a new session, you can specify
a default I/O Setup configuration, including
presets for stereo or multichannel mixing formats (multichannel mixing requires an HD-series or MIX-series system).
The I/O Setup dialog also lets you save and import I/O Settings files.
Chapter 7: I/O Setup 65
Page 78

Paths in Sessions
Paths and I/O Setup
In sessions, audio is routed using the track Input, Output, Insert, Plug-in, and Send Selectors.
These selectors let you assign tracks to hardware
outputs and inputs, internal busses, and other
Pro Tools signal paths.
Paths comprise the lists of available signal routing choices in track input, output, insert and
send selectors.
Track Input Selectors
The signal routing choices available in a session
are defined in the I/O Setup dialog.
I/O Setup dialog Output paths on a Digi 001 system
Track Input and Output Selectors
Pro Tools Reference Guide66
I/O Setup dialog Output paths on an HD system
Page 79

Main Paths and Sub-Paths
Default Settings Files
Paths in the I/O Setup dialog include main paths
and sub-paths.
Stereo main path
mono sub-path
mono sub-path
Main and sub-paths in the I/O Setup Channel Grid
Main Paths
Main paths are logical groupings of inputs, inserts, busses, or outputs. For example, a master
stereo output path could be named Main Out.
Path names in a stereo path are often appended
with “.L” and “.R” for left and right.
Sub-Paths
A sub-path represents a signal path within a
main path. For example, a default stereo output
path consists of two mono sub-paths, left and
right. Mono tracks and sends can be routed to
either mono sub-path of the stereo output path.
It is especially useful to define and name
sub-paths for complex mixing setups, such
as a 5.1 Surround mix.
Default I/O Settings
A default I/O Settings file is installed automatically by Pro Tools, so you have a set of default
paths that will get you started, without the need
to configure the I/O Setup dialog. You can then
customize your I/O Setup configuration at any
time, according to the needs of each project (see
“The I/O Setup Dialog” on page 68).
The default Stereo settings file is available on all
Pro Tools systems, and provides stereo main
paths, each with its own mono sub-paths.
Multichannel settings files are available for
Pro Tools HD-series and MIX-series systems.
These settings provide specialized path definitions for surround mixing. See “Configuring
Pro Tools for Multichannel Sessions” on
page 478.
Default Path Names
Default names for input, output, and insert
paths are based on the type of system (LE systems) or the type and number of interfaces
(TDM systems) you are using.
Stems and Stem Mixes
The use of stems and stem mixes originated in
the post production industry as a method to organize and manage elements of a mix by type or
content.
For example, a film mix often requires a stem
mix for Foley, a stem mix for sound effects, a
stem mix for dialog, and another for music. The
dialog stem, for example, would contain all the
dialog elements mixed relative to each other.
The dialog stem can then be mixed with the
other stems during the final mix of the scene or
reel. The final mix is simplified by the ability to
control the level of each stem, rather than the
multitude of individual tracks that comprise a
typical film mix.
In Pro Tools, you can work with main and subpaths as you would stem mixes. These can be assigned as needed, including the ability to assign
multiple outputs to individual tracks and sends.
For more information, see “Multiple Output Assignments” on page 387.
Chapter 7: I/O Setup 67
Page 80

The I/O Setup Dialog
The I/O Setup dialog defines Pro Tools input, output, insert, and bus paths. Routing I/O ports to
Pro Tools inputs and outputs can also be done here.
Expand/Collapse
Main and Sub-Paths
Active/Inactive
Status
Options
Path Type Tabs
Path Name column
Path For mat Selector
Figure 7. I/O Setup dialog on a Pro Tools|HD system with a 96 I/O
To open the I/O Setup dialog:
1 Make sure your audio interfaces are enabled
and configured properly in the Hardware Setup.
2 Choose Setups > I/O Setup.
Closing the I/O Setup Dialog
You can click Cancel at any time to close the
I/O Setup dialog. When you click OK, Pro Tools
checks several settings for routing validity (to
prevent feedback loops). If there are any over-
To open the Input, Output, Insert, Bus or
SampleCell page in the I/O Setup dialog:
■ Click the corresponding tab at the top of the
I/O Setup dialog.
lapping or invalid settings, you will be required
to correct them before the I/O Setup dialog will
close. For more information, see “Initializing
I/O Setup” on page 75.
Channel Grid
Input and Output
Selectors
Path Tools
Pro Tools Reference Guide68
Page 81

I/O Setup Dialog Controls
This section provides an overview of the controls in the I/O Setup dialog.
Path Type Tabs Select the type of I/O to configure. Choices are Inputs, Outputs, Inserts, Busses,
or SampleCell. (SampleCell paths are available
only on MIX-series systems with TDM-equipped
SampleCell cards.)
Input and Output Selectors Select the physical
ports on your audio interface to route to
Pro Tools inputs and outputs. Ports are selectable in channel pairs. Available ports for each
displayed interface are based on Hardware Setup
settings; for example, if the AES/EBU inputs and
outputs of an interface are enabled in Hardware
Setup, they are available for routing in I/O
Setup. The functionality provided with the Input and Output Selector is the same as that provided on the Main page of the Hardware Setup
dialog.
Path Name Column Shows paths that are available for selection, including the name of each
defined path.
Show Original Setup Appears in the I/O Setup dialog in certain session transfer situations. For
details on this feature, see “Show Original Setup
and Show Current Setup” on page 77.
Options Provide pop-up menus to set paths or
orders for Meter, Audition (Regions List previewing), Default Output (for new tracks), and
Default Path Order. See “Default Output, Meter,
Audition, and Default Path Order I/O Setup Options” on page 80.
Routing Hardware I/O to
Pro Tools I/O
The I/O Setup dialog lets you define which
physical ports on your I/O peripheral are routed
to available inputs and outputs in Pro Tools.
The Input and Output Selectors in the I/O Setup
dialog serve as a patchbay that allows you to
route any of the physical inputs or outputs to
your Pro Tools mixer.
Expand/Collapse Shows or hides the sub-paths
associated with a main path.
Active/Inactive Status Shows and changes the
active/inactive status of each path.
Path Format Selector Shows and selects the
type/format (such as Mono, Stereo, Quad, or
5.1) of each defined path.
Channel Grid Maps paths to specific interfaces
and channels.
Path Tools Customize the I/O Setup configuration. Buttons include: New Path, New Sub-Path,
Delete Path, and Default.
I/O Channel Selector pop-up menu
Chapter 7: I/O Setup 69
Page 82

To configure I/O routing in I/O Setup:
1 Choose Setups > I/O Setup.
2 Click the Input or Output tab to display the
corresponding path type.
3 Click the Input or Output Selector for the first
interface channel pair, located below the first
audio interface icon.
4 From the pop-up menu, select a physical port
pair (such as Analog 1–2), to route to a Pro Tools
channel pair (such as A 1–2) in the Path Name
column on the left.
5 Repeat the above step for additional channel
pairs.
6 Click OK.
Routing a Pro Tools Output Pair to
Multiple Destinations
Pro Tools channel pairs can be routed to multiple outputs on an audio interface through the
I/O Setup dialog. For example, if you assign both
Analog 1–2 and Analog 3–4 interface outputs to
Pro Tools Output pair 1–2, when you send a signal to Pro Tools Outputs 1–2, that signal will be
routed simultaneously to both pairs of output
ports on your audio interface.
This lets you send the same signal (such as a stereo pair, a stem mix, or a multichannel mix) to
multiple destinations (such as multiple mastering devices).
To route a Pro Tools output channel pair to
multiple audio interface output ports:
1 Choose Setups > I/O Setup.
2 Click the Output tab.
3 Click the Output Selector for an interface
channel pair, just below an audio interface icon.
4 From the pop-up menu, select a physical port
pair (such as Analog 1–2) to route to the corresponding Pro Tools channel pair (such as A 1–2)
in the Path Name column on the left.
5 Control-click (Macintosh) or Start-click (Win-
dows) the same Output Selector and select an
additional output pair from the same pop-up
menu.
The output name updates with a plus sign (“+”)
before it to indicate that multiple output ports
are selected. In the pop-up menu, each physical
port pair assigned to that Pro Tools output pair
is indicated by a check mark.
6 Repeat the above steps to select additional
output destinations. The only limit to output
choices is the number of outputs available in
your system.
0utput path assignments cannot overlap.
See “Valid Paths and Requirements” on
page 75 for details.
Pro Tools outputs pairs can also be routed to
multiple audio interface outputs in the Hardware Setup dialog. For more information, see
“Routing a Pro Tools Output Pair to Multiple
Destinations” on page 45.
Pro Tools Reference Guide70
Page 83

Creating and Editing Paths
The I/O Setup dialog lets you create and customize signal path definitions.
Paths can be:
• Renamed, for easier identification after
changing or renaming audio interfaces
• Remapped, to or from different sources or destinations
•Deactivated (or reactivated) to manage unavailable or unnecessary I/O resources
• Deleted
In addition, you can import and export your
I/O Setup configurations as I/O Settings files, as
well as set default path parameters.
The following table lists the available path attributes for each path type.
Path Options by Type
Path Type Path Options (Attributes)
Input Names, formats, and source
channel (analog or digital audio
interface, or CPU input)
Output Names, formats, and destination
(audio interface output channel or
internal send bus)
Insert Names, formats and destination
(audio interface channels)
Creating a Default Main or Sub-Path
You can set an I/O Setup path type to its default
path configuration at any time.
To restore default paths and pathnames:
1 Choose Setups > I/O Setup.
2 Click the Input, Output, Insert, Bus, or Sam-
pleCell tab to display the corresponding path
type.
3 Click Default.
Pro Tools creates all possible stereo main paths.
Mono sub-paths are also auto-created for every
stereo main path. These default path names appear in a session’s track Input and Output Selectors.
Default stereo output paths
To optimize Pro Tools DSP resources, it is
best to create mono sub-paths for Outputs
and Busses, rather than mono main paths.
Bus Names and formats
SampleCell
(MIX-series
only)
Input names
Chapter 7: I/O Setup 71
Page 84

Creating New Paths
You can create new main path and sub-paths
with custom names, format, and mapping. Custom path names appear in a session’s track Input
and Output Selectors.
To create a new path:
1 Choose Setups > I/O Setup.
7 Click OK to close the I/O Setup dialog. If there
are any overlapping or identically named paths,
you will be instructed to correct them before the
I/O Setup dialog will close. For more information, see “Initializing I/O Setup” on page 75.
Multichannel paths and mixing are explained in Chapter 31, “Pro Tools Setup for
Surround.”
2 Click the Input, Output, Insert, Bus, or Sam-
pleCell tab to display the corresponding path
type.
3 Click New Path, or press Command+N (Mac-
intosh) or Control+N (Windows).
– or –
Select a main path and click New Sub-Path.
4 Double-click in the Name field and enter a
name for the path. Press Tab to move to the next
editable field, or press Return (Macintosh) or Enter (Windows) to set the new path name.
5 Choose a format from the Path Format Selec-
tor (mono, stereo, or multichannel).
Path Format Selector
6 Repeat the previous steps to configure other
path types (Input, Output, Insert, Bus, or SampleCell).
Selecting and Arranging Paths
Individual and multiple paths can be selected in
the I/O Setup dialog Path Name column. Selected paths and sub-paths can be moved higher
or lower in the Path Name column to change
their menu order in track Input and Output Selectors. Paths can also be deleted. Sub-paths follow their main paths when they are moved in
the I/O Setup dialog.
To select a main path or sub-path:
■ Click the path name.
Selecting paths in the I/O Setup dialog
To select multiple main paths or sub-paths:
■ Shift-click the path names.
To select all paths and sub-paths:
■ Option-click (Macintosh) or Alt-click (Win-
dows) any path name.
To rearrange paths:
■ Drag one or more path names up or down.
Pro Tools Reference Guide72
Page 85

Resetting Paths
TDM Audio Interface Names
The Default button in the I/O Setup dialog provides two primary functions:
•Creates new, default paths up to the capacity
of your system’s available audio interfaces and
resources. See “Creating a Default Main or
Sub-Path” on page 71.
• Resets selected path names to matching or
corresponding paths in the current I/O Setup
configuration. For example, if you change
modes on Digi 001, or replace an audio interface on a Pro Tools HD-series or MIX-series
system, you can use the Default switch to update your I/O Setup definitions with the new
hardware configuration.
On TDM systems, audio interface names
can be customized. See “TDM Audio Interface Names” on page 73.
To reset path names:
■ Click Default.
If there are matching paths available with the
new system configuration, existing paths will be
updated to include new audio interfaces (TDM
systems), or I/O mode selection (Digi 001 only).
Resetting Mix Busses (TDM Only)
With TDM-equipped Pro Tools systems, audio
interface names can be customized in the
I/O Setup dialog. The I/O Setup dialog then
bases default path names on the custom names.
To rename an audio interface in the I/O Setup
dialog:
■ Double-click the text above an interface, enter
a new interface name, and press Return (Macintosh) or Enter (Windows).
Interface name
Interface name
Deleting Paths
Path definitions can be deleted from the current
session to reflect changes to your hardware
setup, or to clean up track selector menus by removing unwanted or unnecessary path definitions. After deleting a path, any tracks or send
assignments to that path are reset to No Output.
Pro Tools 5.3 and later supports up to 64 mix
busses for TDM systems. However, when you
open a session created with Pro Tools 5.0.1 or
earlier, only 32 busses are initially available.
To make 64 busses available in sessions created
with Pro Tools 5.0.1 or earlier:
1 Open the I/O Setup dialog.
2 Click the Bus tab in the upper left.
3 Click Default.
To delete a main path or sub-path:
1 In the I/O Setup dialog, select the path you
want to delete.
2 Click Delete Path.
To delete all paths:
1 Option-click (Macintosh) or Alt-click (Win-
dows) any path name.
2 Click Delete Path.
Chapter 7: I/O Setup 73
Page 86
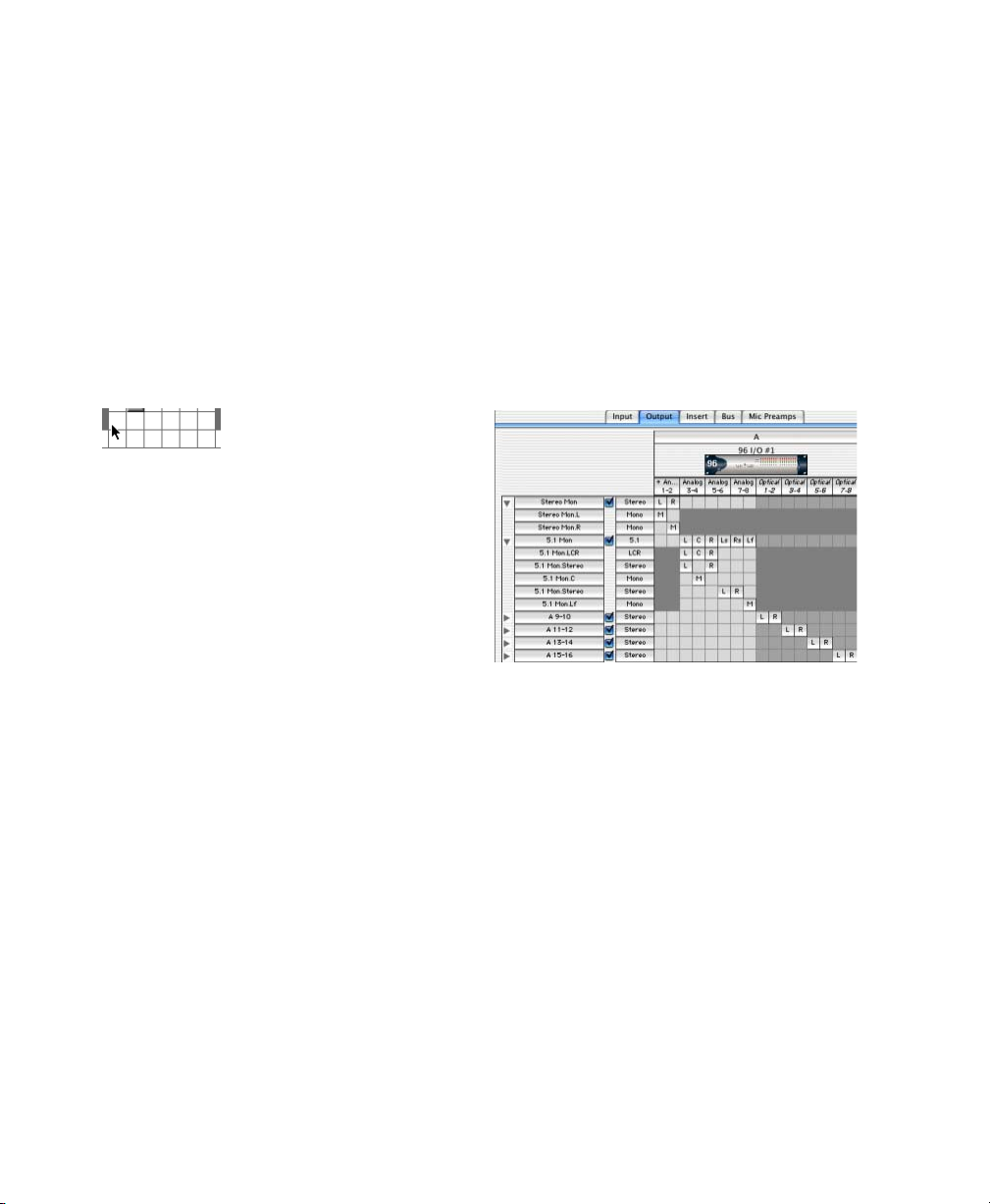
Channel Mapping
Once a path has been created and formatted, it
can be mapped to specific audio interface, bus,
or SampleCell channels in the Grid.
To map channels:
1 Select a main or sub-path.
2 In the row for the selected path, click in the
Grid column under an audio interface and
channel. Other channels for the path type, if
any, fill to the right.
Mapping channels
For example, when mapping a new stereo path,
clicking in the path row under output channel 1
fills both channel 1 and 2 (left to 1, right to 2).
To remap channels in a path, see “Remapping
Channels” on page 74.
Channel Mapping and Surround Mixer
(Pro Tools HD-Series and MIX-Series Systems
Only)
When mapping multichannel paths, the left
channel (L) is mapped first to the clicked Grid
box, and remaining channels fill immediately to
the right according to the default path order. Because some multichannel mixing formats use
unique track layouts, Pro Tools lets you set the
default format in the I/O Setup dialog (see “Default Output, Meter, Audition, and Default Path
Order I/O Setup Options” on page 80).
Customized Output paths for a 5.1 mix
Remapping Channels
You can move the individual assignments to different channels, to reorder the path’s definition
(for example, changing a multichannel map to
L-R-C-Sub-LS-RS).
To remap channels in a path:
■ Drag the channel to the new location in the
Grid. Other channel assignments will move
(shuffle) to accommodate dragged channels.
Pro Tools Reference Guide74
Page 87

Channel Shuffling
Minimum Path Definitions
Moving a signal from right to left results in a
shuffle of other signals after the new destination
channel. Moving a signal from left to right shuffles any and all signals after the new destination
channel and leave the previous channel empty.
Changing a path’s format erases any current channel mapping.
Sub-Paths Follow Main Paths
When a main path is remapped, its sub-paths (if
any) will remap automatically to maintain consistent routing. For example, remapping a stereo
path to different hardware outputs results in
any of its sub-paths moving with it.
Initializing I/O Setup
To set the current I/O Setup configuration:
■ Click OK in the I/O Setup dialog.
All paths must be valid before the I/O Setup configuration can be applied.
Valid Paths and Requirements
While configuring the I/O Setup window, certain rules apply for path definition and channel
mapping.
Though it is possible to set up invalid mappings
in the Channel Grid, Pro Tools will not accept
an I/O Setup configuration unless all paths meet
the path definition and channel mapping requirements described below.
All paths must have a name, be of a specific format, and have a valid I/O mapping.
Overlapping Channels and Valid Paths
Channel mapping follows certain rules regarding overlapping paths.
◆ There can be no partial or complete overlaps
between any two main Output paths, any two
Insert paths, or any two main Bus paths.
◆ A newly-created Output or Bus path must ei-
ther be completely independent of other maps
(not mapped to any other available I/O interface/channels), or it must be a sub-path completely contained within a larger path (for
example, an LCR sub-path within a larger 5.1
path).
◆ Output and Insert paths can overlap in I/O
Setup, but only one or the other can be used at
any given time in a session. (Inputs and SampleCell paths, however, can be routed to multiple
tracks.)
Active and Inactive Paths
Pro Tools paths can be Active (on) or Inactive
(off, or unavailable). You can manually switch
paths between Active or Inactive on a track-bytrack or session-wide basis. In addition,
Pro Tools sets paths to Inactive automatically
when I/O is unavailable.
Track Path Assignments Track input, output,
and bus path assignments can be switched to Inactive using the corresponding selector on the
track. This leaves track playlists intact, while disconnecting that particular track from the output
or bus path. Use this to remove a track from a
signal path.
Chapter 7: I/O Setup 75
Page 88

Session-Wide Path Assignments Paths can be
globally activated or deactivated in the
I/O Setup window. Use this to turn off a signal
path on any and all tracks currently assigned to
it. Pro Tools also sets unavailable paths to inactive. Paths can be unavailable when hardware or
other system resources are unavailable, such as
when opening a session saved on a different system.
Track Path Assignments
(Mix and Edit Windows)
To toggle a track path assignment to be Active or
Inactive:
■ In the Mix or Edit window, Command-Con-
trol-click (Macintosh) or Control-Start-click
(Windows) the track’s Input, Output, Insert, or
Send Selector.
Toggling Multiple Paths
If a track has only one main output assignment,
you can Command-Control-click (Macintosh)
or Control-start-click (Windows) the track’s
Output Selector to toggle the main output to inactive. When there are multiple assignments,
the track selector will be displayed for you to
specify the input, output, insert, or bus path.
If a Send (A
–E) has multiple output assignments
and one of those is toggled, then all of the output assignments for that Send (A
–E) will be tog-
gled.
Session-Wide Path Assignments
(I/O Setup Dialog)
Paths can be globally configured for Active or
Inactive status in the I/O Setup Dialog.
Inactive track path assignments are indicated
with an asterisk (*) in the track selector menu.
(Paths set to globally inactive in the I/O Setup
window are listed in italics.)
Toggling All or All Selected
The Option (Macintosh) and Alt (Windows)
modifiers apply the path toggle to all tracks. The
Option+Shift (Macintosh) or Alt+Shift (Windows) modifiers apply the path toggle to all selected tracks. However, Pro Tools will only apply the change to identical path assignments, if
any, in the current track or tracks. Toggling multiple tracks only affects tracks that have the
same path assignment as the one you are explicitly toggling.
Pro Tools Reference Guide76
Display of Active and Inactive Status
Unhighlighted (Italics) Indicates the path is inac-
tive.
Highlighted (Non-Italics) Indicates the path is active.
Highlighted (Italics) Indicates the path is active,
but there are not enough system resources available.
Active
Inactive
Active and inactive path settings in I/O Setup
Page 89

To globally activate or deactivate a path:
1 Choose Setup > I/O Setup.
2 Select a path type using the tabs at the top of
the window.
3 Set the Active/Inactive control for the path.
Any track path assignment can also be deactivated on a track-by-track basis. See “Active and Inactive Paths” on page 75
Inactive paths are displayed in italics in the
track path selectors.
Active and inactive paths in a track Output Selector
Hardware Setup and Session Transfer
Sessions created in Pro Tools 5.1 and later store
the type and order of audio interfaces connected
and active when the session was last saved.
Unavailable I/O
When opening a session, Pro Tools checks to see
if the hardware configuration has changed since
the session was last saved. If the current hardware configuration differs from that saved in the
session, paths associated with the unavailable
I/O are made inactive.
Remapping
Remapping occurs when a session’s original
I/O Setup does not match that of the current
system and session paths are remapped to current hardware.
Systems of equivalent I/O capability are
remapped directly. For example, a session
tracked to a Pro Tools HD-series system through
two 192 I/O audio interfaces would include 32
input paths spread across the two 16-channel
interfaces. If the session is taken to a different
Pro Tools system that has a 96 I/O audio interface (a 16-channel I/O unit) and a 1622 Audio
Interface (a 16-channel I/O unit) connected to
its Legacy Port. When the session is first opened
on the second system, Pro Tools will map the 32
input paths to the inputs of the two interfaces.
When hardware is unavailable to a session being
opened, assignments can either be replaced using the remap option, or opened as Inactive.
Any tracks left assigned to an unavailable path
will not be audible. This can be beneficial, however, when you want to reassign tracks into your
system’s mix one at a time.
See “Active and Inactive Paths” on page 75
for more information.
Show Original Setup and Show Current Setup
When a session is opened that contains path
definitions for unavailable I/O modules, the
I/O Setup dialog lists those paths in italics.
The Show Original Setup button displays the audio interfaces used in the original session. This
temporary display lets you check the original
I/O configuration for reference while configuring the session for your system.
Chapter 7: I/O Setup 77
Page 90

Once a session has been opened with unavailable I/O retained, you can then reassign tracks
to available I/O paths.
To redefine the paths, see “Creating and
Editing Paths” on page 71.
I/O Settings Files
I/O Settings can be managed when transferring
sessions, and when developing I/O Setup configurations over the course of multiple sessions
and projects.
Importing and Exporting I/O Settings
Files
You can export and import I/O Setup configurations as I/O Settings files. This lets you save settings for different projects, import settings for
reconfiguring I/O Setup, and manage path definitions and signal routing setups.
Exporting I/O Settings
To export and save an I/O Setup configuration:
1 Click Export Settings.
2 Name and save the settings file.
Defaults, Settings Files, and Last Used Settings for New Sessions
When creating new sessions, you can set the session’s I/O Setup configuration using the following options:
Default I/O Setups The Pro Tools Installer provides factory presets for stereo and surround I/O
Setups (surround mixing is only supported on
Pro Tools HD-series and MIX-series systems).
See “Factory I/O Settings Files” on page 79 for
more information.
Custom Presets You can store and recall custom
presets using the export and import features of
the I/O Setup dialog.
Last Used The most recent (or, last used)
I/O Setup configuration is saved as a Last Used
settings file. See “Last Used I/O Settings” on
page 79 for more information.
Default I/O Settings at First Launch
The first time you create a session, you can
choose default Stereo Mix or Surround Mix settings, depending on your system and installation choices. See “Factory I/O Settings Files” on
page 79.
To start sessions with a blank or empty
I/O Setup dialog, you can create and export
an I/O Settings file in which all definitions
have been deleted.
Importing I/O Settings
I/O Settings can be imported before you open a
session, or you can import settings into a session
that is already open. When you import I/O Settings, you can choose to delete any unused path
definitions before importing the new paths, or
leave unused path definitions intact and add the
new paths to the current I/O Setup configuration.
To import I/O Settings:
1 Click Import Settings in the I/O Setup dialog.
2 Select an I/O settings file in the Import Set-
tings dialog and click Import.
Pro Tools Reference Guide78
Page 91

3 A dialog appears asking whether you want to
delete existing paths. Do one of the following:
• Click Yes to remove any unused paths and
add the imported paths to the current I/O
Setup configuration. Any I/O assignments
and automation data associated with the
unused paths are also deleted.
• Click No to add the imported paths to the
current I/O Setup configuration.
If the import results in overlapping paths, the
new paths will appear in the I/O Setup dialog as
Inactive. (See “Active and Inactive Paths” on
page 75.)
After importing I/O Settings, you can then reassign path routing definitions in the I/O Setup dialog by remapping, renaming, and deleting
paths. (See “Creating and Editing Paths” on
page 71.)
Stereo Mix Settings File
The Stereo Mix preset consists of all possible stereo and mono paths for your session.
Using the “Stereo Mix” preset has the same
effect as clicking Default for every individual tab in I/O Settings. See “Creating and
Editing Paths” on page 71 for details.
Specifically, the Stereo Mix preset will create the
maximum number paths of each type, as determined by the available system’s I/O Setup and
hardware configuration.
Surround Mix Settings File (TDM Systems Only)
The Surround Mix provides additional, surround-specific Output and Bus presets. See “Surround Mix Settings Files” on page 479 for more
information.
Last Used I/O Settings
If any changes are made to the I/O Setup dialog
during a session, these changes are saved to the
Last Used settings file when the I/O Setup dialog
is closed (by clicking OK).
Changes to I/O Setup are saved along with the
current session. User Presets files will not contain recent changes unless you export an updated settings file.
The Last Used settings are available as a choice
when creating or opening sessions, in addition
to the factory presets described below.
Factory I/O Settings Files
Pro Tools provides I/O Settings files for Stereo
and Surround mixing. These files provide generic main and sub-path definitions for either
mixing format.
About Direct Out Mode
Direct Outputs mode, as found in older versions
of Pro Tools, has been replaced by the default
mono sub-paths available through all valid I/O
in the I/O Setup dialog.
The Default switch creates main Output paths
with appropriate mono sub-paths. These subpaths provide discrete monophonic routing.
When a session is opened that was saved in Direct Outputs mode, Pro Tools maps all the output assignments to equivalent mono sub-paths
(as available). See “Hardware Setup and Session
Transfer” on page 77 for more information on
remapping.
To convert a session so that it emulates Direct
Outs mode, use the Auto Assign Ascending Outputs feature:
Chapter 7: I/O Setup 79
Page 92
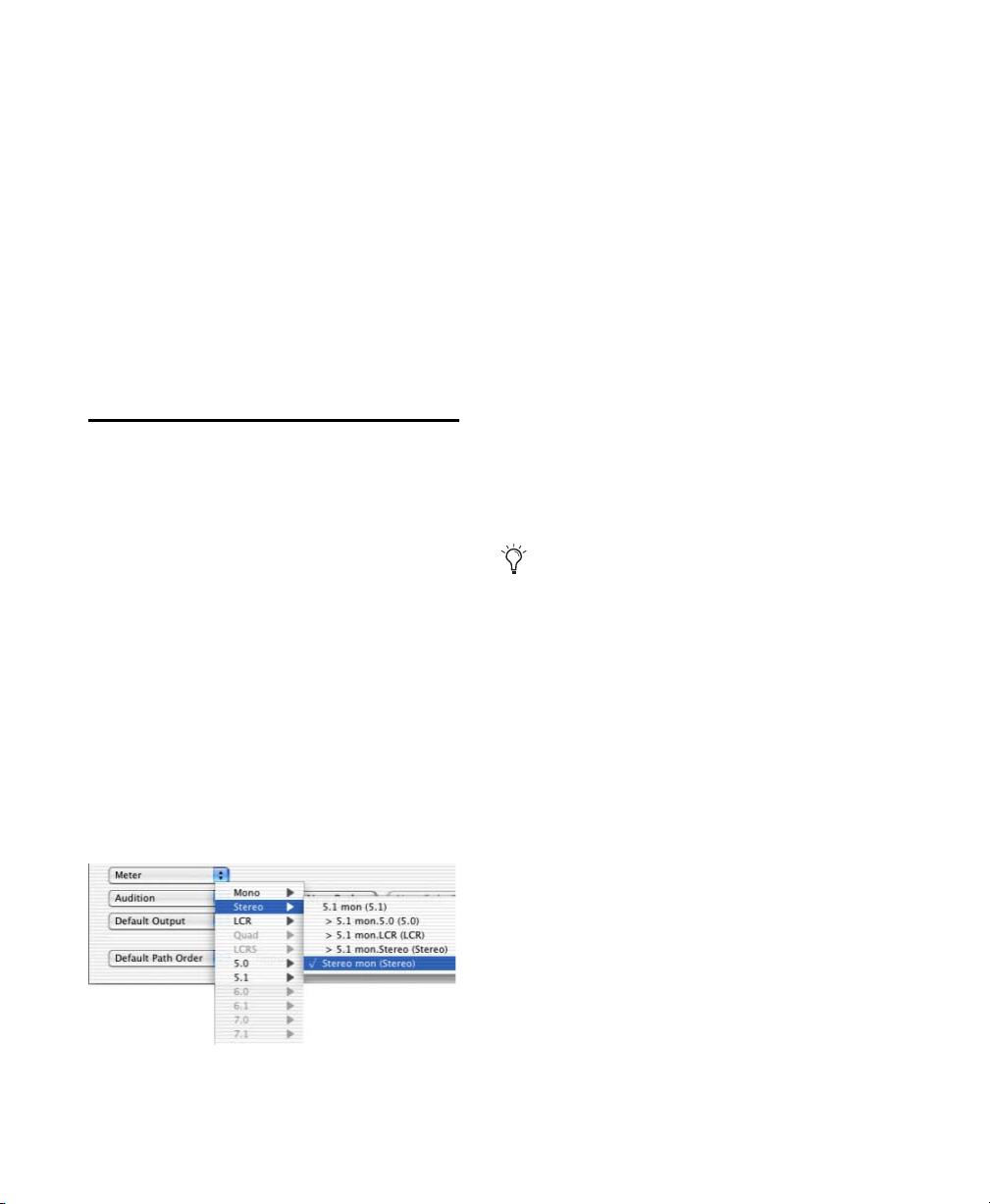
To auto assign track outputs for Direct Out:
1 Make sure that all tracks are visible if desired
(because the hidden tracks will not be affected).
2 Select all desired tracks (Shift-click each track
name).
3 Command-Option-click (Macintosh) or Con-
trol-Alt-click (Windows) the Output Selector of
the left-most track and assign it to the sub-path
for Output #1. All visible tracks will be auto-assigned to unique mono sub-path outputs in ascending order.
Default Output, Meter, Audition, and Default Path Order I/O Setup Options
Pro Tools systems have additional I/O Setup features. These include default signal routing for
metering and auditioning, and default track layout for multichannel mix formats.
Default Output Path
You can specify the default Output path assignment for new tracks, in each available format.
Audition Path
The Audition path is the output path through
which files and regions are previewed (listened
to) in the Regions List.
To audition regions in the Regions List:
■ Option-click (Macintosh) or Alt-click (Win-
dows) the region in the list.
Using the Default Audition Path
When you audition a file or region in the Regions List, Pro Tools routes the audio output
through the Audition path. Pro Tools assigns a
default Audition path to the first available main
Output path of the corresponding format. You
can also select a different Audition Path in the
I/O Setup dialog.
On TDM systems with more than one audio
interface, you can only select the first audio
interface as an audition path.
Configuring Audition Paths
You can specify the monitoring outputs for Regions List auditioning using the Audition paths
menu.
To specify a default Output in I/O Setup window:
■ Select a format and Output path from the de-
fault Output Selector.
Selecting default Output paths
Pro Tools Reference Guide80
Audition Path Main Menu The main menu consists of all path format choices available on the
current system (Mono and Stereo on all systems,
LCR and greater on surround-capable systems).
Audition Path Submenus Each path format
choice has a submenu listing Output paths of
that given format. (The mono submenu lists
Output paths of any format.)
Page 93

To configure Audition Paths:
■ Select a path from the Audition path menu or
submenus.
Selecting an Audition path
Auditioning Discrete Signals in Multichannel
Items
In the Audio Regions List, multichannel regions
are auditioned through the current Audition
path. Signals can be auditioned “in-place,” or
through all outputs, as described below.
Audition In-Place
When auditioning a mono component of a
multichannel region, that mono component
will by default be auditioned in-place. That is, it
will play out the corresponding speaker channel
of its parent multichannel region.
To audition through all channels of the main
audition path:
■ Shift-Option-click (Macintosh) or Shift-Alt-
click (Windows) on the signal in the Regions
List.
Default Path Order
(TDM Systems Only)
The Default Path Order Selector lets you select
the default track layout you want Pro Tools to
follow when creating and mapping 5.1-format
main or sub-paths in the I/O Setup dialog.
This setting does not affect existing path definitions or metering—it only specifies channel
mapping in new 5.1-format paths.
To choose a Default Path Order:
■ Select the channel mapping from the Default
Path Order menu.
Default Path Order Selector
To audition in-place:
1 In the Regions List, make sure the stereo or
multichannel region is in expanded view (showing .L, .R, and other component channels).
2 Option-click (Macintosh) or Alt-click (Win-
dows) the region for the desired channel.
Audition to All Outputs
Mono regions can be routed equally to all outputs of the parent region’s Audition path.
For more information about multichannel mixing, see Chapter 31, “Pro Tools Setup for Surround.”
Meter Path Selector
(ProControl Only)
The Meter Path Selector determines the path
displayed across the ProControl Output meters.
See the latest ProControl documentation for
more details.
Chapter 7: I/O Setup 81
Page 94

Pro Tools Reference Guide82
Page 95

Chapter 8: Tracks
This chapter covers basic track management
tasks such as creating and deleting tracks, assigning voices and output channels, and grouping tracks.
Track Types
In a Pro Tools session, you can have several different types of tracks. These can include audio
tracks, Auxiliary Input tracks, MIDI tracks, and
Master Fader tracks, and QuickTime Movie
tracks. On Macintosh systems, sessions can have
AVoption or AVoption XL Movie tracks.
QuickTime Movie track features are described in Chapter 36, “Working with
QuickTime Movies.”
Audio Tracks, Auxiliary Input Tracks,
and Master Fader Tracks
Pro Tools provides mono, stereo, and multichannel format audio tracks, Auxiliary Inputs,
and Master Faders.
Audio Tracks
Audio tracks contain arrangements of recorded
(or imported) audio files. Audio tracks can be
mono, stereo, or multichannel format (multichannel tracks are supported on Pro Tools HDseries and MIX-series systems only).
Auxiliary Input Tracks
Auxiliary Input tracks can be used as effects
sends, destinations for an alternate mix, as a
bounce destination, as inputs to monitor or process audio (such as audio from MIDI sources),
and for many other audio routing tasks.
Chapter 8: Tracks 83
Page 96

Master Fader Tracks
Master Fader tracks control the overall level of
the audio tracks that are routed to the session’s
main output paths. For example, you could
have 24 tracks in a session with channels 1–8
routed to Analog Output 1–2, channels 9–16 to
Analog Output 3–4, and channels 17–24 to Analog Output 5–6. You could then create three
master faders, one to control each of these output pairs.
MIDI Tracks
MIDI tracks store MIDI note, instrument, and
controller data. You cannot select a track format
when you create a MIDI track, because audio
does not pass through it.
Multichannel Tracks (Pro Tools HD-Series and
MIX-Series Systems Only)
A multichannel track is a single channel strip
that plays multiple channels of audio (from 3–8
channels at a time). This allows Pro Tools to
support multichannel mixing formats including
3+1, 5.1, 6.1, and others.
For more information on surround mixing with
Pro Tools, see the following chapters:
• Chapter 31, “Pro Tools Setup for Surround”
• Chapter 32, “Multichannel Tracks and
Signal Routing”
• Chapter 33, “Surround Panning and Mixing”
Audio Track/Channel Strip
Track Formats
Mono Tracks
A mono audio track, Auxiliary Input, or Master
Fader track controls volume, and, in some cases,
panning, for a single channel of audio. A mono
track uses a single voice.
Stereo Tracks
A stereo audio track, Auxiliary Input, or Master
Fader track is a single channel strip that plays
two channels of audio as a stereo pair. Stereo
tracks use two voices.
Each audio track has its own set of controls for
volume, pan, output window, record enable, automation mode, solo, mute, comments, and
voice assignment.
With slight variations, audio track channel
strips in the Mix window look like the tracks
shown in the following figures.
Audio tracks can be added to a session with the
New Track command.
Pro Tools Reference Guide84
Page 97

Inserts
Inserts
Sends
Input/Output selectors
Automation Mode selector
Pan Sliders
Pan Indicators
Solo/Mute buttons
Voice Selector
Open Output window
Record Enable button
Volume Fader
Level Meters
Group ID
Track Type indicator
Volume/Peak/Delay indicator
Track Name
Track Comment
Stereo audio track channel strip (Pro Tools 6.0)
Sends
Input/Output selectors
Volume/Peak/Delay indicator
Pan indicator
Automation Mode selector
Record Enable/Solo/Mute/Voice
Pan slider
Open Output window
Group ID
Volume Fader
Level Meter
Track Type indicator
Track Name
Track Comment
Mono audio track channel strip (Pro Tools 5.1.3)
Chapter 8: Tracks 85
Page 98

MIDI Track/Channel Strip
Each MIDI track has its own set of controls for
volume, pan, record enable, automation mode,
solo, mute, MIDI patch assignment (program
change), and MIDI channel assignment.
MIDI tracks can be added to a session with the
New Track command.
MIDI Input selector
MIDI Output selector
Automation Mode selector
MIDI Pan slider
MIDI Pan indicator
Solo/Mute buttons
Program Change
Record Enable
MIDI Volume Fader
MIDI Velocity Meter
Group ID
Track Type indicator
MIDI Volume indicator
Track Name
MIDI Channel
Automation
Record Enable/Program/Solo/Mute
MIDI Pan
MIDI Volume Fader
MIDI Velocity Meter
Track Name
MIDI channel strip (Pro Tools 5.1.3)
Track Controls
Input/Output Selectors
The I/O View shows Input and Output Selectors
on audio and MIDI tracks.
Track Comment
MIDI channel strip (Pro Tools 6.0)
Pro Tools Reference Guide86
Input Selector
Output Selector
(or MIDI Device/Channel Selector)
Pan Slider
Pan Indicator
Inputs/Outputs View (Pro Tools 6.0)
Input Selector
Output Selector
(or MIDI Device/Channel Selector)
Level/Peak/Channel Delay Indicator
Pan Indicator
Inputs/Outputs View (Pro Tools 5.1.3)
Page 99

To show the I/O View:
■ Select Display > Edit Window Shows (or Mix
Windows Shows) > I/O View.
In Pro Tools 6.0, channel strips in the Mix
window always display Input and Output
Selectors as well as volume and pan values,
so there is no I/O View display option for the
Mix window.
Pan Indicator
The Pan Indicator displays the current pan setting of a track. Pan values range from <100 (full
left) to 100> (full right). Pan controls are only
available for stereo tracks or for mono tracks
routed to a stereo output.
Pan Slider
For details on Input and Output Selectors, see
“Assigning Inputs and Outputs to Tracks” on
page 92.
Volume/Peak/Channel Delay Indicator
The Volume indicator on an audio track has
three display modes: Volume, Peak, and Channel Delay.
To toggle the Volume indicator display:
■ Command-click (Macintosh) or Control-click
(Windows) the indicator to toggle it between
the following modes:
Volume Indicator Shows the current volume, or
input level of a track as set by the track Volume
fader.
Peak Indicator Functions as a headroom indicator based on the last peak playback level. To reset the peak counter, click anywhere in the
meter. Values range from +6 dB (highest level
signal), to –∞ (no signal).
Channel Delay Indicator Shows the total delay, in
samples, incurred on the track from the use of
any TDM plug-ins on that channel.
The Pan slider controls the balance of a track between the assigned output pair. It only appears
if you are using stereo tracks or mono tracks
routed to a stereo output.
The Pan slider on a MIDI track is effective only if
you are controlling a sound module that supports MIDI panning.
Volume Fader
The Volume fader controls the volume of a track
when it is in playback, and the monitor level of
the track when it is in record. You can link the
record and monitor levels by enabling the Operation Preference for “Link Record and Play Faders.”
The volume fader on a MIDI track is effective
only if you are controlling a sound module that
supports MIDI volume.
Track Level Meter
On audio tracks, level meters indicate the level
of the signal being recorded or played back from
the hard drive. Green indicates nominal levels;
Yellow indicates pre-clipping (–6 dB below full
scale); and Red indicates clipping. When a track
is record-enabled, these meters indicate record
levels.
On MIDI tracks, the level meter shows the MIDI
velocity of the most recent MIDI event.
Chapter 8: Tracks 87
Page 100

Pre- and Post-Fader Metering
You can globally set audio track level meters to
indicate pre-or post-fader levels by selecting or
de-selecting Operations > Pre-Fader Metering.
When pre-fader metering is selected, the level
meters show levels independent of fader position. With post-fader metering, the level meters
respond to fader position.
Peak Hold
If clipping occurs, the topmost LED will stay lit
(red). In addition, Pro Tools meters provide a
peak hold feature with three options: 3 Second
Peak Hold, Infinite Peak Hold, or No Peak Hold.
To enable Wide Meters View:
■ Command-Option-Control-click the track
level meters in either the Mix window or the
Edit window.
To choose a peak hold setting:
■ Choose Setups > Preferences, click Display,
and select a Peak Hold option.
To clear a meter:
You can clear a meter’s clipping or peak hold indicator by clicking anywhere on the meter.
To clear all meters:
■ Option-click (Macintosh) or Alt-click (Win-
dows) any meter.
Wide Meters View
(Pro Tools 6.0 Only)
Wide Meters View expands the width of the
level meters for tracks in both the Mix and Edit
windows. Wide Meters View can make the track
level meters easier to read.
Wide Meters View, Mix and Edit windows
To disable Wide Meters View:
■ Command-Option-Control-click the track
level meters a second time in either the Mix
window or the Edit window.
Track Comments View
Comments View shows any comments entered
in the Track Name/Comments dialog. You can
type directly in the Comments area for each
track when it is displayed.
To display the Comments View:
■ Select Display > Mix Window Shows (or Edit
Window Shows) > Comments.
For details on adding comments to tracks, see
“Naming Tracks” on page 89.
Pro Tools Reference Guide88
 Loading...
Loading...