Philips TPS2.2E Schematic

Colour Television Chassis
18250_000_090210.eps
090504
TPS2.2E
LA
Contents Page Contents Page
1. Revision List 2
2. Technical Specifications, Connections 2
3. Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List 5
4. Mechanical Instructions 9
5. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding 11
6. Alignments 13
7. Circuit Descriptions 14
8. IC Data Sheets 19
9. Block Diagrams
Wiring Diagram 29
Block Diagram 30
10. Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts DrawingPWB
Power board: Adapter
Power Board: Inverter (A02) 3233-34
SSB: D-SUB INPUT (B01) 3552-61
SSB: Video Input & CVBS Output (B02) 3652-61
SSB: Scart (B03) 3752-61
SSB: Tuner (B04) 3852-61
SSB: HDMI Output 1 (B05) 3952-61
SSB: HDMI Output 2 (B06) 4052-61
SSB: Lips & Inverter I/F (B07) 4152-61
SSB: Scaler MST6B885GL-1 (B08) 4252-61
SSB: WT6703F Standby MCU (B09) 4352-61
SSB: Flash ROM & Memory (B10) 4452-61
SSB: Key, IR BD, & Compair I/F (B11) 4552-61
SSB: Panel I/F (B12) 4652-61
SSB: iTV I/F and AOC Hotel (B13) 4752-61
SSB: USB (B14) 4852-61
SSB: Audio/AMP (B15) 4952-61
SSB: Audio I/F and SPDIF Out (B16) 5052-61
SSB: DC-DC Power (B17) 5152-61
IR Board (J) 6263
Keyboard control (E) 6465
(A01) 3133-34
©
Copyright 2009 Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a
retrieval system or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical,
photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of Philips.
Published by QM/EH 0965 BU TV Consumer Care, the Netherlands Subject to modification EN 3122 785 18280
2009-May-29

EN 2 TPS2.2E LA1.
Revision List
1. Revision List
Manual xxxx xxx xxxx.0
• First release.
2. Technical Specifications, Connections
Index of this chapter:
2.1 Technical Specifications
2.2 Directions for Use
2.3 Connections
2.4 Chassis Overview
Notes:
• Figures can deviate due to the different set executions.
• Specifications are indicative (subject to change).
2.1 Technical Specifications
For on-line product support please use the links in. Here is
product information available, as well as getting started, user
manuals, frequently asked questions and software & drivers.
Table 2-1 Described Model Numbers:
Model Number Styling Published in
42PFL3604/12
42PFL3604/60
Note: The given Model Numbers are subject to change.
Click 3122 785 18280
2.2 Directions for Use
Directions for use can be downloaded from the following
websites:
http://www.philips.com/support
http://www.p4c.philips.com
2009-May-29
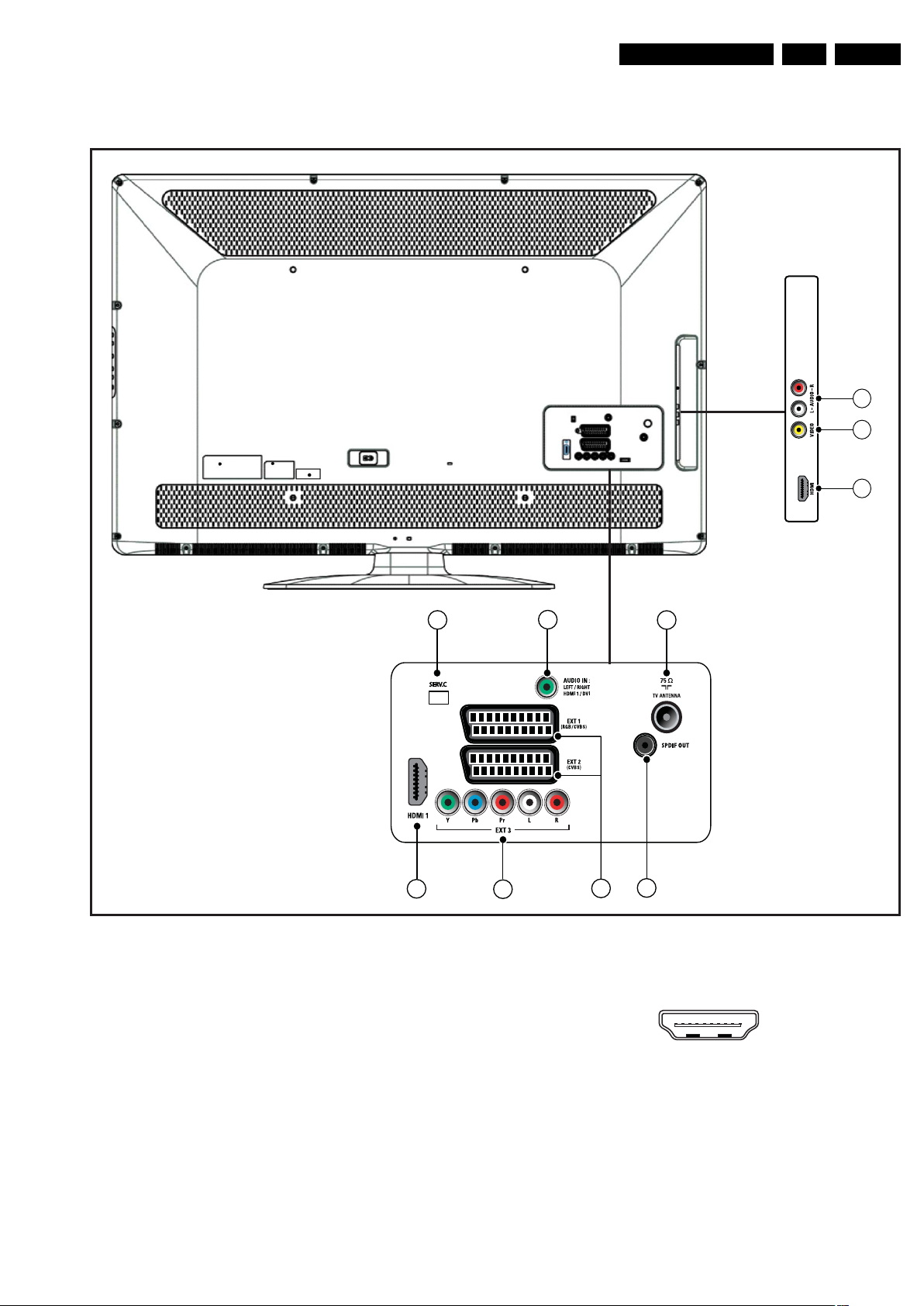
2.3 Connections
18280_001_090420.eps
090515
SERV.C
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
1
2
3
10000_017_090121.eps
090428
19
1
18 2
Technical Specifications, Connections
EN 3TPS2.2E LA 2.
2.3.1 Side Connections
Figure 2-1 Connection overview
Note: The following connector colour abbreviations are used
(acc. to DIN/IEC 757): Bk= Black, Bu= Blue, Gn= Green,
Gy= Grey, Rd= Red, Wh= White, Ye= Yellow.
1 - Cinch: Audio - In
Rd - Audio R 0.5 V
Wh - Audio L 0.5 V
/ 10 kΩ jq
RMS
/ 10 kΩ jq
RMS
2 - Cinch: Video CVBS - In, Audio - In
Ye - Video CVBS 1 V
/ 75 Ω jq
PP
3 - HDMI: Digital Video, Digital Audio - In
Figure 2-2 HDMI (type A) connector
1 -D2+ Data channel j
2 -Shield Gnd H
3 -D2- Data channel j
4 -D1+ Data channel j
5 -Shield Gnd H
6 -D1- Data channel j
7 -D0+ Data channel j
8 -Shield Gnd H
2009-May-29
EN 4 TPS2.2E LA2.
21
20
1
2
10000_001_090121.eps
090121
Technical Specifications, Connections
9 -D0- Data channel j
10 - CLK+ Data channel j
11 - Shield Gnd H
12 - CLK- Data channel j
13 - n.c.
14 - n.c.
15 - DDC_SCL DDC clock j
16 - DDC_SDA DDC data jk
17 - Ground Gnd H
18 - +5V j
19 - HPD Hot Plug Detect j
20 - Ground Gnd H
2.3.2 Rear Connections
4 - Service / UART
1 -Ground Gnd H
2 -UART_TX Transmit k
3 -UART_RX Receive j
5 - Audio - In: Left / Right, HDMI / DVI
Gn - Audio L/R in 0.5 V
/ 10 kW jq
RMS
6 - TV ANTENNA - In
Signal input from an antenna, cable or satellite.
7 - Cinch: S/PDIF - Out
Bk - Coaxial 0.4 - 0.6V
/ 75 W kq
PP
1 -Audio R 0.5 V
2 -Audio R 0.5 V
3 -Audio L 0.5 V
4 -Ground Audio Gnd H
/ 1 kΩ k
RMS
/ 10 kΩ j
RMS
/ 1 kΩ k
RMS
5 -Ground Blue Gnd H
6 -Audio L 0.5 V
7 -Video Blue/C-out 0.7 V
8 -Function Select 0 - 2 V: INT
/ 10 kΩ j
RMS
/ 75 Ω jk
PP
4.5 - 7 V: EXT 16:9
9.5 - 12 V: EXT 4:3 j
9 -Ground Green Gnd H
10 - Easylink P50 0 - 5 V / 4.7 kΩ jk
11 - Video Green 0.7 V
12 - n.c.
/ 75 Ω j
PP
13 - Ground Red Gnd H
14 - Ground P50 Gnd H
15 - Video Red/C 0.7 V
/ 75 Ω j
PP
16 - Status/FBL 0 - 0.4 V: INT
1 - 3 V: EXT / 75 Ω j
17 - Ground Video Gnd H
18 - Ground FBL Gnd H
19 - Video CVBS 1 V
20 - Video CVBS/Y 1 V
/ 75 Ω k
PP
/ 75 Ω j
PP
21 - Shield Gnd H
9 - EXT3: Video YPbPr - In, Audio - In
Gn - Video - Y 1 V
Bu - Video - Pb 0.7 V
Rd - Video - Pr 0.7 V
/ 75 W jq
PP
/ 75 W jq
PP
/ 75 W jq
PP
8 - EXT1 - 2: Video RGB/YC - In, CVBS - In/Out, Audio In/Out
Figure 2-3 SCART connector
2.4 Chassis Overview
Refer to 9. Block Diagrams for PWB/CBA locations.
Wh - Audio - L 0.5 V
Rd - Audio - R 0.5 V
/ 10 kW jq
RMS
/ 10 kW jq
RMS
10 - HDMI 1: Digital Video, Digital Audio - In
See 3 - HDMI: Digital Video, Digital Audio - In
.
2009-May-29

Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List
3. Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List
EN 5TPS2.2E LA 3.
Index of this chapter:
3.1 Safety Instructions
3.2 Warnings
3.3 Notes
3.4 Abbreviation List
3.1 Safety Instructions
Safety regulations require the following during a repair:
• Connect the set to the Mains/AC Power via an isolation
transformer (> 800 VA).
• Replace safety components, indicated by the symbol h,
only by components identical to the original ones. Any
other component substitution (other than original type) may
increase risk of fire or electrical shock hazard. Of de set
ontploft!
Safety regulations require that after a repair, the set must be
returned in its original condition. Pay in particular attention to
the following points:
• Route the wire trees correctly and fix them with the
mounted cable clamps.
• Check the insulation of the Mains/AC Power lead for
external damage.
• Check the strain relief of the Mains/AC Power cord for
proper function.
• Check the electrical DC resistance between the Mains/AC
Power plug and the secondary side (only for sets that have
a Mains/AC Power isolated power supply):
1. Unplug the Mains/AC Power cord and connect a wire
between the two pins of the Mains/AC Power plug.
2. Set the Mains/AC Power switch to the “on” position
(keep the Mains/AC Power cord unplugged!).
3. Measure the resistance value between the pins of the
Mains/AC Power plug and the metal shielding of the
tuner or the aerial connection on the set. The reading
should be between 4.5 MΩ and 12 MΩ.
4. Switch “off” the set, and remove the wire between the
two pins of the Mains/AC Power plug.
• Check the cabinet for defects, to prevent touching of any
inner parts by the customer.
picture carrier at 475.25 MHz for PAL, or 61.25 MHz for
NTSC (channel 3).
• Where necessary, measure the waveforms and voltages
with (D) and without (E) aerial signal. Measure the
voltages in the power supply section both in normal
operation (G) and in stand-by (F). These values are
indicated by means of the appropriate symbols.
3.3.2 Schematic Notes
• All resistor values are in ohms, and the value multiplier is
often used to indicate the decimal point location (e.g. 2K2
indicates 2.2 kΩ).
• Resistor values with no multiplier may be indicated with
either an “E” or an “R” (e.g. 220E or 220R indicates 220 Ω).
• All capacitor values are given in micro-farads (μ=× 10
nano-farads (n =× 10
• Capacitor values may also use the value multiplier as the
decimal point indication (e.g. 2p2 indicates 2.2 pF).
• An “asterisk” (*) indicates component usage varies. Refer
to the diversity tables for the correct values.
• The correct component values are listed on the Philips
Spare Parts Web Portal.
3.3.3 Spare Parts
For the latest spare part overview, consult your Philips Spare
Part web portal.
3.3.4 BGA (Ball Grid Array) ICs
Introduction
For more information on how to handle BGA devices, visit this
URL: http://www.atyourservice-magazine.com
“Magazine”, then go to “Repair downloads”. Here you will find
Information on how to deal with BGA-ICs.
BGA Temperature Profiles
For BGA-ICs, you must use the correct temperature-profile.
Where applicable and available, this profile is added to the IC
Data Sheet information section in this manual.
-9
), or pico-farads (p =× 10
. Select
-12
-6
),
).
3.2 Warnings
• All ICs and many other semiconductors are susceptible to
electrostatic discharges (ESD w). Careless handling
during repair can reduce life drastically. Make sure that,
during repair, you are connected with the same potential as
the mass of the set by a wristband with resistance. Keep
components and tools also at this same potential.
• Be careful during measurements in the high voltage
section.
• Never replace modules or other components while the unit
is switched “on”.
• When you align the set, use plastic rather than metal tools.
This will prevent any short circuits and the danger of a
circuit becoming unstable.
3.3 Notes
3.3.1 General
• Measure the voltages and waveforms with regard to the
chassis (= tuner) ground (H), or hot ground (I), depending
on the tested area of circuitry. The voltages and waveforms
shown in the diagrams are indicative. Measure them in the
Service Default Mode with a colour bar signal and stereo
sound (L: 3 kHz, R: 1 kHz unless stated otherwise) and
3.3.5 Lead-free Soldering
Due to lead-free technology some rules have to be respected
by the workshop during a repair:
• Use only lead-free soldering tin. If lead-free solder paste is
required, please contact the manufacturer of your soldering
equipment. In general, use of solder paste within
workshops should be avoided because paste is not easy to
store and to handle.
• Use only adequate solder tools applicable for lead-free
soldering tin. The solder tool must be able:
– To reach a solder-tip temperature of at least 400°C.
– To stabilize the adjusted temperature at the solder-tip.
– To exchange solder-tips for different applications.
• Adjust your solder tool so that a temperature of around
360°C - 380°C is reached and stabilized at the solder joint.
Heating time of the solder-joint should not exceed ~ 4 sec.
Avoid temperatures above 400°C, otherwise wear-out of
tips will increase drastically and flux-fluid will be destroyed.
To avoid wear-out of tips, switch “off” unused equipment or
reduce heat.
• Mix of lead-free soldering tin/parts with leaded soldering
tin/parts is possible but PHILIPS recommends strongly to
avoid mixed regimes. If this cannot be avoided, carefully
clear the solder-joint from old tin and re-solder with new tin.
2009-May-29

EN 6 TPS2.2E LA3.
10000_024_090121.eps
090121
MODEL :
PROD.NO:
~
S
32PF9968/10
MADE IN BELGIUM
220-240V 50/60Hz
128W
AG 1A0617 000001
VHF+S+H+UHF
BJ3.0E LA
Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List
3.3.6 Alternative BOM identification
It should be noted that on the European Service website,
“Alternative BOM” is referred to as “Design variant”.
The third digit in the serial number (example:
AG2B0335000001) indicates the number of the alternative
B.O.M. (Bill Of Materials) that has been used for producing the
specific TV set. In general, it is possible that the same TV
model on the market is produced with e.g. two different types
of displays, coming from two different suppliers. This will then
result in sets which have the same CTN (Commercial Type
Number; e.g. 28PW9515/12) but which have a different B.O.M.
number.
By looking at the third digit of the serial number, one can
identify which B.O.M. is used for the TV set he is working with.
If the third digit of the serial number contains the number “1”
(example: AG1B033500001), then the TV set has been
manufactured according to B.O.M. number 1. If the third digit is
a “2” (example: AG2B0335000001), then the set has been
produced according to B.O.M. no. 2. This is important for
ordering the correct spare parts!
For the third digit, the numbers 1...9 and the characters A...Z
can be used, so in total: 9 plus 26= 35 different B.O.M.s can be
indicated by the third digit of the serial number.
Identification: The bottom line of a type plate gives a 14-digit
serial number. Digits 1 and 2 refer to the production centre (e.g.
AG is Bruges), digit 3 refers to the B.O.M. code, digit 4 refers
to the Service version change code, digits 5 and 6 refer to the
production year, and digits 7 and 8 refer to production week (in
example below it is 2006 week 17). The 6 last digits contain the
serial number.
Figure 3-1 Serial number (example)
3.3.7 Board Level Repair (BLR) or Component Level Repair (CLR)
If a board is defective, consult your repair procedure to decide
if the board has to be exchanged or if it should be repaired on
component level.
If your repair procedure says the board should be exchanged
completely, do not solder on the defective board. Otherwise, it
cannot be returned to the O.E.M. supplier for back charging!
3.3.8 Practical Service Precautions
• It makes sense to avoid exposure to electrical shock.
While some sources are expected to have a possible
dangerous impact, others of quite high potential are of
limited current and are sometimes held in less regard.
• Always respect voltages. While some may not be
dangerous in themselves, they can cause unexpected
reactions that are best avoided. Before reaching into a
powered TV set, it is best to test the high voltage insulation.
It is easy to do, and is a good service precaution.
2009-May-29
3.4 Abbreviation List
0/6/12 SCART switch control signal on A/V
board. 0 = loop through (AUX to TV),
6 = play 16 : 9 format, 12 = play 4 : 3
format
AARA Automatic Aspect Ratio Adaptation:
algorithm that adapts aspect ratio to
remove horizontal black bars; keeps
the original aspect ratio
ACI Automatic Channel Installation:
algorithm that installs TV channels
directly from a cable network by
means of a predefined TXT page
ADC Analogue to Digital Converter
AFC Automatic Frequency Control: control
signal used to tune to the correct
frequency
AGC Automatic Gain Control: algorithm that
controls the video input of the feature
box
AM Amplitude Modulation
AP Asia Pacific
AR Aspect Ratio: 4 by 3 or 16 by 9
ASF Auto Screen Fit: algorithm that adapts
aspect ratio to remove horizontal black
bars without discarding video
information
ATSC Advanced Television Systems
Committee, the digital TV standard in
the USA
ATV See Auto TV
Auto TV A hardware and software control
system that measures picture content,
and adapts image parameters in a
dynamic way
AV External Audio Video
AVC Audio Video Controller
AVIP Audio Video Input Processor
B/G Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 5.5 MHz
BLR Board-Level Repair
BTSC Broadcast Television Standard
Committee. Multiplex FM stereo sound
system, originating from the USA and
used e.g. in LATAM and AP-NTSC
countries
B-TXT Blue TeleteXT
C Centre channel (audio)
CEC Consumer Electronics Control bus:
remote control bus on HDMI
connections
CL Constant Level: audio output to
connect with an external amplifier
CLR Component Level Repair
ComPair Computer aided rePair
CP Connected Planet / Copy Protection
CSM Customer Service Mode
CTI Color Transient Improvement:
manipulates steepness of chroma
transients
CVBS Composite Video Blanking and
Synchronization
DAC Digital to Analogue Converter
DBE Dynamic Bass Enhancement: extra
low frequency amplification
DDC See “E-DDC”
D/K Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 6.5 MHz
DFI Dynamic Frame Insertion
DFU Directions For Use: owner's manual
DMR Digital Media Reader: card reader
DMSD Digital Multi Standard Decoding
DNM Digital Natural Motion

Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List
EN 7TPS2.2E LA 3.
DNR Digital Noise Reduction: noise
reduction feature of the set
DRAM Dynamic RAM
DRM Digital Rights Management
DSP Digital Signal Processing
DST Dealer Service Tool: special remote
control designed for service
technicians
DTCP Digital Transmission Content
Protection; A protocol for protecting
digital audio/video content that is
traversing a high speed serial bus,
such as IEEE-1394
DVB-C Digital Video Broadcast - Cable
DVB-T Digital Video Broadcast - Terrestrial
DVD Digital Versatile Disc
DVI(-d) Digital Visual Interface (d= digital only)
E-DDC Enhanced Display Data Channel
(VESA standard for communication
channel and display). Using E-DDC,
the video source can read the EDID
information form the display.
EDID Extended Display Identification Data
(VESA standard)
EEPROM Electrically Erasable and
Programmable Read Only Memory
EMI Electro Magnetic Interference
EPLD Erasable Programmable Logic Device
EU Europe
EXT EXTernal (source), entering the set by
SCART or by cinches (jacks)
FDS Full Dual Screen (same as FDW)
FDW Full Dual Window (same as FDS)
FLASH FLASH memory
FM Field Memory or Frequency
Modulation
FPGA Field-Programmable Gate Array
FTV Flat TeleVision
Gb/s Giga bits per second
G-TXT Green TeleteXT
H H_sync to the module
HD High Definition
HDD Hard Disk Drive
HDCP High-bandwidth Digital Content
Protection: A “key” encoded into the
HDMI/DVI signal that prevents video
data piracy. If a source is HDCP coded
and connected via HDMI/DVI without
the proper HDCP decoding, the
picture is put into a “snow vision” mode
or changed to a low resolution. For
normal content distribution the source
and the display device must be
enabled for HDCP “software key”
decoding.
HDMI High Definition Multimedia Interface
HP HeadPhone
I Monochrome TV system. Sound
2
I
C Inter IC bus
2
I
D Inter IC Data bus
2
I
S Inter IC Sound bus
carrier distance is 6.0 MHz
IF Intermediate Frequency
IR Infra Red
IRQ Interrupt Request
ITU-656 The ITU Radio communication Sector
(ITU-R) is a standards body
subcommittee of the International
Telecommunication Union relating to
radio communication. ITU-656 (a.k.a.
SDI), is a digitized video format used
for broadcast grade video.
Uncompressed digital component or
digital composite signals can be used.
The SDI signal is self-synchronizing,
uses 8 bit or 10 bit data words, and has
a maximum data rate of 270 Mbit/s,
with a minimum bandwidth of 135
MHz.
ITV Institutional TeleVision; TV sets for
hotels, hospitals etc.
LS Last Status; The settings last chosen
by the customer and read and stored
in RAM or in the NVM. They are called
at start-up of the set to configure it
according to the customer's
preferences
LATAM Latin America
LCD Liquid Crystal Display
LED Light Emitting Diode
L/L' Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 6.5 MHz. L' is Band
I, L is all bands except for Band I
LPL LG.Philips LCD (supplier)
LS Loudspeaker
LVDS Low Voltage Differential Signalling
Mbps Mega bits per second
M/N Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 4.5 MHz
MIPS Microprocessor without Interlocked
Pipeline-Stages; A RISC-based
microprocessor
MOP Matrix Output Processor
MOSFET Metal Oxide Silicon Field Effect
Transistor, switching device
MPEG Motion Pictures Experts Group
MPIF Multi Platform InterFace
MUTE MUTE Line
NC Not Connected
NICAM Near Instantaneous Compounded
Audio Multiplexing. This is a digital
sound system, mainly used in Europe.
NTC Negative Temperature Coefficient,
non-linear resistor
NTSC National Television Standard
Committee. Color system mainly used
in North America and Japan. Color
carrier NTSC M/N= 3.579545 MHz,
NTSC 4.43= 4.433619 MHz (this is a
VCR norm, it is not transmitted off-air)
NVM Non-Volatile Memory: IC containing
TV related data such as alignments
O/C Open Circuit
OSD On Screen Display
OTC On screen display Teletext and
Control; also called Artistic (SAA5800)
P50 Project 50: communication protocol
between TV and peripherals
PAL Phase Alternating Line. Color system
mainly used in West Europe (color
carrier= 4.433619 MHz) and South
America (color carrier PAL M=
3.575612 MHz and PAL N= 3.582056
MHz)
PCB Printed Circuit Board (same as “PWB”)
PCM Pulse Code Modulation
PDP Plasma Display Panel
PFC Power Factor Corrector (or Pre-
conditioner)
PIP Picture In Picture
PLL Phase Locked Loop. Used for e.g.
FST tuning systems. The customer
can give directly the desired frequency
POD Point Of Deployment: a removable
CAM module, implementing the CA
system for a host (e.g. a TV-set)
POR Power On Reset, signal to reset the uP
PTC Positive Temperature Coefficient,
non-linear resistor
PWB Printed Wiring Board (same as “PCB”)
2009-May-29

EN 8 TPS2.2E LA3.
Precautions, Notes, and Abbreviation List
PWM Pulse Width Modulation
QRC Quasi Resonant Converter
QTNR Quality Temporal Noise Reduction
QVCP Quality Video Composition Processor
RAM Random Access Memory
RGB Red, Green, and Blue. The primary
color signals for TV. By mixing levels
of R, G, and B, all colors (Y/C) are
reproduced.
RC Remote Control
RC5 / RC6 Signal protocol from the remote
control receiver
RESET RESET signal
ROM Read Only Memory
RSDS Reduced Swing Differential Signalling
data interface
R-TXT Red TeleteXT
SAM Service Alignment Mode
S/C Short Circuit
SCART Syndicat des Constructeurs
d'Appareils Radiorécepteurs et
Téléviseurs
SCL Serial Clock I
SCL-F CLock Signal on Fast I
SD Standard Definition
SDA Serial Data I
SDA-F DAta Signal on Fast I
2
C
2
C bus
2
C
2
C bus
SDI Serial Digital Interface, see “ITU-656”
SDRAM Synchronous DRAM
SECAM SEequence Couleur Avec Mémoire.
Color system mainly used in France
and East Europe. Color carriers=
4.406250 MHz and 4.250000 MHz
SIF Sound Intermediate Frequency
SMPS Switched Mode Power Supply
SoC System on Chip
SOG Sync On Green
SOPS Self Oscillating Power Supply
SPI Serial Peripheral Interface bus; a 4-
wire synchronous serial data link
standard
S/PDIF Sony Philips Digital InterFace
SRAM Static RAM
SRP Service Reference Protocol
SSB Small Signal Board
STBY STand-BY
SVGA 800 × 600 (4:3)
SVHS Super Video Home System
SW Software
SWAN Spatial temporal Weighted Averaging
Noise reduction
SXGA 1280 × 1024
TFT Thin Film Transistor
THD Total Harmonic Distortion
TMDS Transmission Minimized Differential
Signalling
TXT TeleteXT
TXT-DW Dual Window with TeleteXT
UI User Interface
uP Microprocessor
UXGA 1 600 × 1200 (4:3)
V V-sync to the module
VESA Video Electronics Standards
Association
VGA 640 × 480 (4:3)
VL Variable Level out: processed audio
output toward external amplifier
VSB Vestigial Side Band; modulation
method
WYSIWYR What You See Is What You Record:
record selection that follows main
picture and sound
WXGA 1280 × 768 (15:9)
XTAL Quartz crystal
XGA 1024 × 768 (4:3)
Y Luminance signal
Y/C Luminance (Y) and Chrominance (C)
signal
YPbPr Component video. Luminance and
scaled color difference signals (B-Y
and R-Y)
YUV Component video
2009-May-29

4. Mechanical Instructions
18280_100_090420.eps
090519
Mechanical Instructions
EN 9TPS2.2E LA 4.
Index of this chapter:
4.1 Cable Dressing
4.2 Service Positions
4.3 Assy/Panel Removal
4.4 Set Re-assembly.
4.1 Cable Dressing
Notes:
• Figures below can deviate slightly from the actual situation,
due to the different set executions.
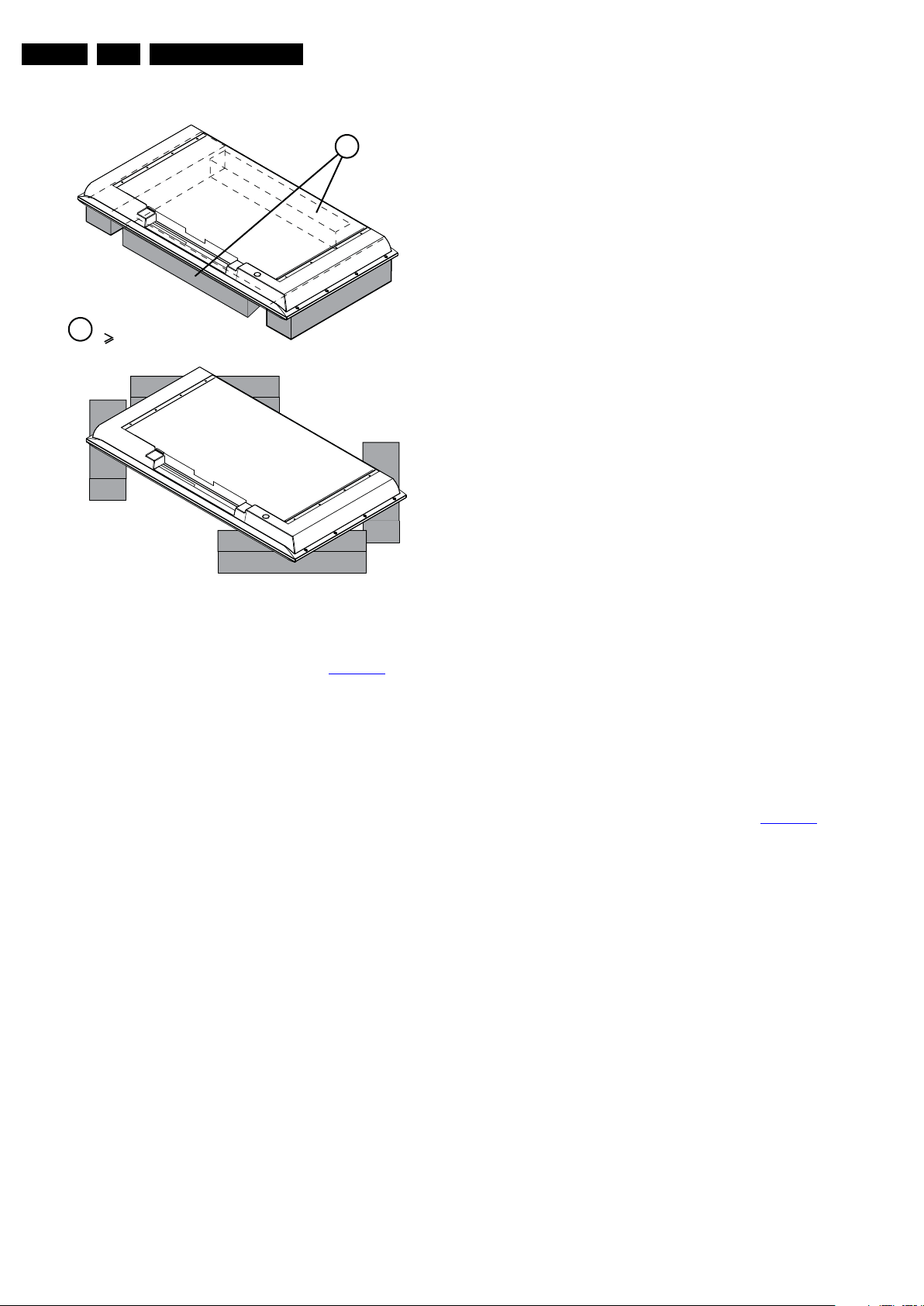
4.2 Service Positions
For easy servicing of this set, there are a few possibilities
created:
• The buffers from the packaging.
• Foam bars (created for Service).
Figure 4-1 Cable dressing
2009-May-29
EN 10 TPS2.2E LA4.
10000_018_090121.eps
090121
1
Required for sets
42"
1
Mechanical Instructions
4.2.1 Foam Bars
4.3.3 Power Supply Unit (PSU)
Caution: it is mandatory to remount all different screws at their
original position during re-assembly. Failure to do so may result
in damaging the PSU.
1. Unplug all connectors.
2. Remove all fixation screws.
3. The PSU can now be taken out of the set.
When defective, replace the whole unit.
4.3.4 Speakers
1. Remove all fixation screws.
2. Take the speakers out together with their casing.
When defective, replace the whole unit.
4.3.5 Keyboard Control Panel
1. Unplug the connector.
2. Remove the cover screws and take out the whole unit.
When defective, replace the whole unit.
4.3.6 IR/LED Board
1. Remove screw and lift the IR Board from the front cover.
2. Unplug the connectors.
When defective, replace the whole unit.
Figure 4-2 Foam bars
The foam bars (order code 3122 785 90580 for two pieces) can
be used for all types and sizes of Flat TVs. See Figure 4-2
details. Sets with a display of 42" and larger, require four foam
bars [1]. Ensure that the foam bars are always supporting the
cabinet and never only the display.
Caution: Failure to follow these guidelines can seriously
damage the display!
By laying the TV face down on the (ESD protective) foam bars,
a stable situation is created to perform measurements and
alignments. By placing a mirror under the TV, the screen can
be monitored.
4.3 Assy/Panel Removal
4.3.1 Rear Cover
Warning: Disconnect the mains power cord before removing
the rear cover.
1. Remove the fixation screws that secure the rear cover.
2. Lift the rear cover from the TV. Make sure that wires and
flat foils are not damaged while lifting the rear cover from
the set.
for
4.3.7 LCD Panel
1. Remove the speakers as described earlier.
2. Unplug the LVDS connector.
3. Remove the fixation screws that fix panel to the subframe.
4. Lift out the subframe.
5. The LCD panel can now be lifted from the front cabinet.
When defective, replace the whole unit.
4.4 Set Re-assembly
To re-assemble the whole set, execute all processes in reverse
order.
Notes:
• While re-assembling, make sure that all cables are placed
and connected in their original position. See Figure 4-1
• Pay special attention not to damage the EMC foams on the
SSB shields. Ensure that EMC foams are mounted
correctly.
.
4.3.2 Small Signal Board (SSB)
Caution: it is mandatory to remount all different screws at their
original position during re-assembly. Failure to do so may result
in damaging the SSB.
1. Release the screws to remove the shielding.
2. Unplug both LVDS connector.
Caution: be careful, as these are very fragile connectors!
3. Unplug all other connectors.
4. Remove the screw near the L- AUDIO- R at the side I/O
cover.
5. Remove the rest of the fixation screws.
6. The SSB can now be taken out of the set.
2009-May-29

Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
18280_200_090420.eps
090518
18280_201_090420.eps
090519
5. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
EN 11TPS2.2E LA 5.
Index of this chapter:
5.1 Service Modes
5.2 Software Upgrading
5.3 Error Codes
5.4 Fault Finding and Repair Tips
5.1 Service Modes
The Customer Service Mode (CSM) is used for communication
between the call centre and the customer, while the Service
Alignment Mode (SAM) offers several features for the service
technician.
This chassis also offers the option of using ComPair, a
hardware interface between a computer and the TV chassis. It
offers the abilities of structured troubleshooting, error code
reading, and software version read-out for all chassis.
5.1.1 Customer Service Mode (CSM)
Purpose
The Customer Service Mode shows error codes and
information on the TV's operation settings.The call centre can
instruct the customer (by telephone) to enter CSM in order to
identify the status of the set.This helps the call centre to
diagnose problems and failures in the TV set before making a
service call.
The CSM is a read-only mode; therefore, modifications are not
possible in this mode.
How to Activate CSM
Key in the code “123654” via the standard RC transmitter.
Note: Activation of the CSM is only possible if there is no (user)
menu on the screen!
– V2.02 is the version and revision
– Y is the vendor code (1 digit):
– Z is the panel revision code(1 digit):
• Codes Displays the lastest 5 error codes (Layer 2) status.
– 000 = No problem
– 011 = I
– 012 = tuner error
• SSB Displays the 12NC of the SSB (Small Signal Board).
• Display Displays the 12NC of the display (LCD Panel).
• PSU Displays the 12NC of PSU (Power Supply Unit).
• NVM version and revision
• PQ Version and revision
• HDCP key Valid or Invalid
• Signal quality/present DTV shows the digital reception
quality, ATV shows whether analog reception is available
• Audio system Mono, Stereo or Dual language
• Video format Displays the received video system (Pal,
Secam, NTSC)
• Standby uP SW version and revision
How to Exit CSM
Press "MENU" on the RC-transmitter.
5.1.2 Service Alignment Mode (SAM)
How to enter
To enter the factory mode, use the following method:
• Press the following key sequence on the remote control
transmitter: "062596" directly followed by the "INFO"
button.
After entering the factory mode, the following screen is visible
on the top and right of the panel.
2
C bus error
Figure 5-1 CSM Menu
How to Navigate
By means of the "CURSOR-DOWN/UP" knob (or the scroll
wheel) on the RC-transmitter, can be navigated through the
menus.
General
• Model Philips Model type number (12 characters
maximum)
• Production serial number Displays the production serial
number of the TV. Note that if an NVM is replaced or is
initialized after corruption, this production code has to be
re-written to NVM. ComPair will foresee a in possibility to
do this.
• Software version
– Format: TPAA.AA V2.XX_Y_Z
– TPS2.2E is the chassis name
Figure 5-2 Factory Mode Menu
How to Navigate
With the up/down cursor keys can be used to navigate through
the menu, while with the Left/Right cursor tha values can be
changed.
2009-May-29
EN 12 TPS2.2E LA5.
10000_036_090121.eps
090121
TO
UART SERVICE
CONNECTOR
TO
UART SERVICE
CONNECTOR
TO
I2C SERVICE
CONNECTOR
TO TV
PC
HDMI
I
2
C only
Optional power
5V DC
ComPair II Developed by Philips Brugge
RC out
RC in
Optional
Switch
Power ModeLink/
Activity
I
2
C
ComPair II
Multi
function
RS232 /UART
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
How to EXIT
Choose "EXIT", and press the "OK" button. Turn “Off” the TV
via the side control key and then turn “On” the TV again.
5.2 Software Upgrading
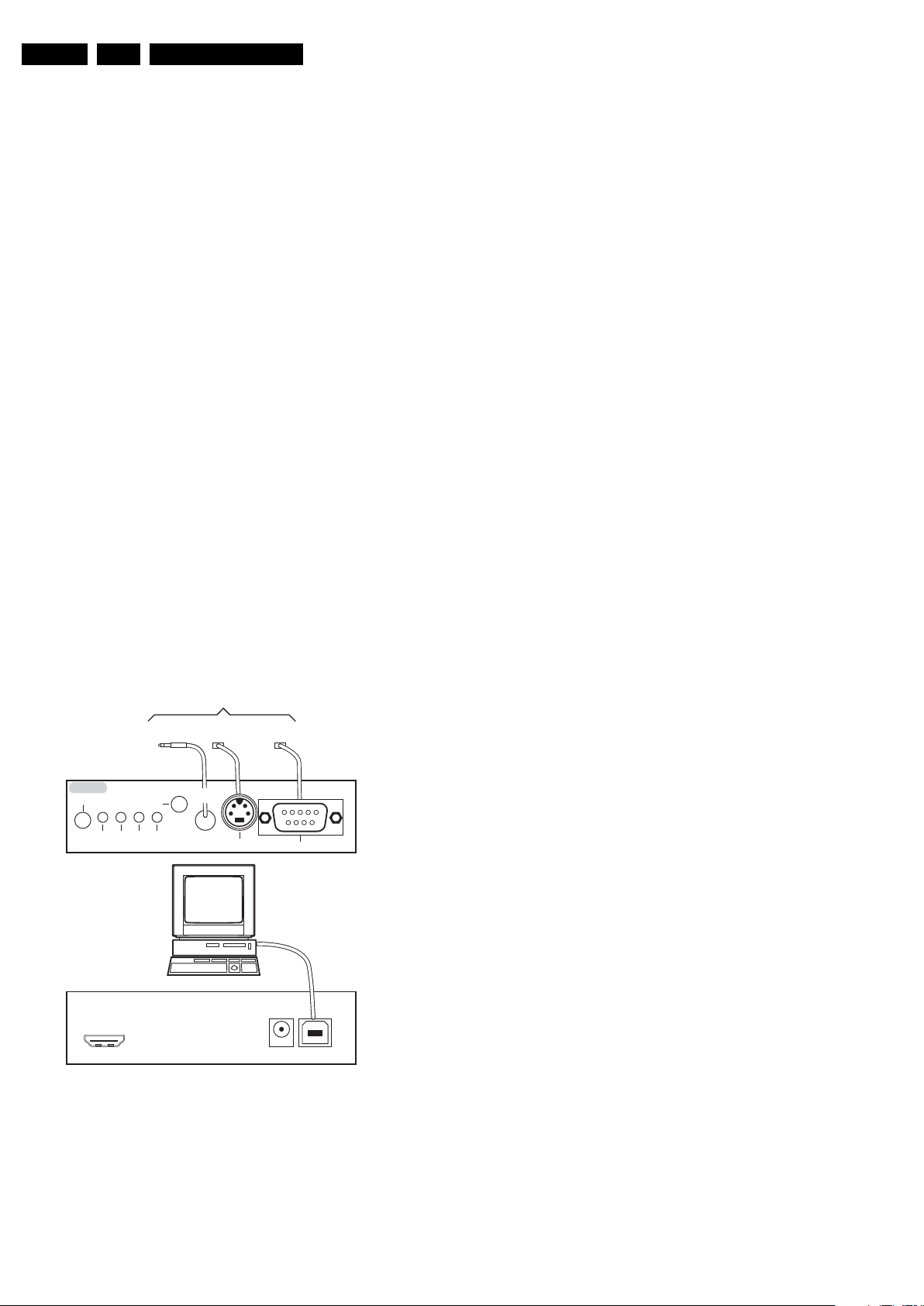
5.2.1 ComPair
Introduction
ComPair (Computer Aided Repair) is a Service tool for Philips
Consumer Electronics products. and offers the following:
1. ComPair helps to quickly get an understanding on how to
repair the chassis in a short and effective way.
2. ComPair allows very detailed diagnostics and is therefore
capable of accurately indicating problem areas. No
knowledge on I
because ComPair takes care of this.
3. ComPair speeds up the repair time since it can
automatically communicate with the chassis (when the uP
is working) and all repair information is directly available.
4. ComPair features TV software up possibilities.
Specifications
ComPair consists of a Windows based fault finding program
and an interface box between PC and the (defective) product.
The ComPair II interface box is connected to the PC via an
USB cable. For the TV chassis, the ComPair interface box and
the TV communicate via a bi-directional cable via the service
connector(s).
The ComPair fault finding program is able to determine the
problem of the defective television, by a combination of
automatic diagnostics and an interactive question/answer
procedure.
2
C or UART commands is necessary,
How to Order
ComPair II order codes:
• ComPair II interface: 3122 785 91020.
• Programming software can be downloaded from the Philips
Service portal.
• ComPair UART interface cable for TPS2.2x xx.
(using JST PHR-3, 2 mm pitch connector):
3122 785 90630.
Note: While having problems, contact the local support desk.
5.3 Error Codes
The error code buffer contains all errors detected since the last
time the buffer was erased. The buffer is written from left to
right. When an error occurs that is not yet in the error code
buffer, it is displayed at the left side and all other errors shift one
position to the right.
5.4 Fault Finding and Repair Tips
5.4.1 Speakers
Make sure that the volume is set to minimum during
disconnecting the speakers in the ON-state of the TV. The
audio amplifier can be damaged by disconnecting the speakers
during ON-state of the set!
5.4.2 Tuner
Attention: In case the tuner is replaced, always check the tuner
options.
How to Connect
This is described in the chassis fault finding database in
ComPair.
Figure 5-3 ComPair II interface connection
Caution: It is compulsory to connect the TV to the PC as
shown in the picture above (with the ComPair interface in
between), as the ComPair interface acts as a level shifter. If
one connects the TV directly to the PC (via UART), ICs will be
blown!
2009-May-29
6. Alignments
18290_200_090330.eps
090416
Alignments
EN 13TPS2.2E LA 6.
Index of this chapter:
6.1 General Alignment Conditions
6.2 CVI (YPbPr) source Auto Colour Adjust
6.3 White Balance Adjustment
6.4 Serial Number Definition
Note: The Service Alignment Mode (SAM) are described in
chapter 5. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
Menu navigation is done with the CURSOR UP, DOWN, LEFT
or RIGHT keys of the remote control transmitter.
6.1 General Alignment Conditions
Perform all electrical adjustments under the following
conditions:
• Power supply voltage: 220 - 240 V
• Connect the set to the mains via an isolation transformer
with low internal resistance.
• Allow the set to warm up for approximately 15 minutes.
• Measure voltages and waveforms in relation to correct
ground.
Caution: It is not allowed to use heatsinks as ground.
• Test probe: Ri > 10 MΩ, Ci < 20 pF.
• Use an isolated trimmer/screwdriver to perform
alignments.
/ 50 ± 3 Hz.
AC
6.2 CVI (YPbPr) source Auto Colour Adjust
6.2.1 Equipment Requirements
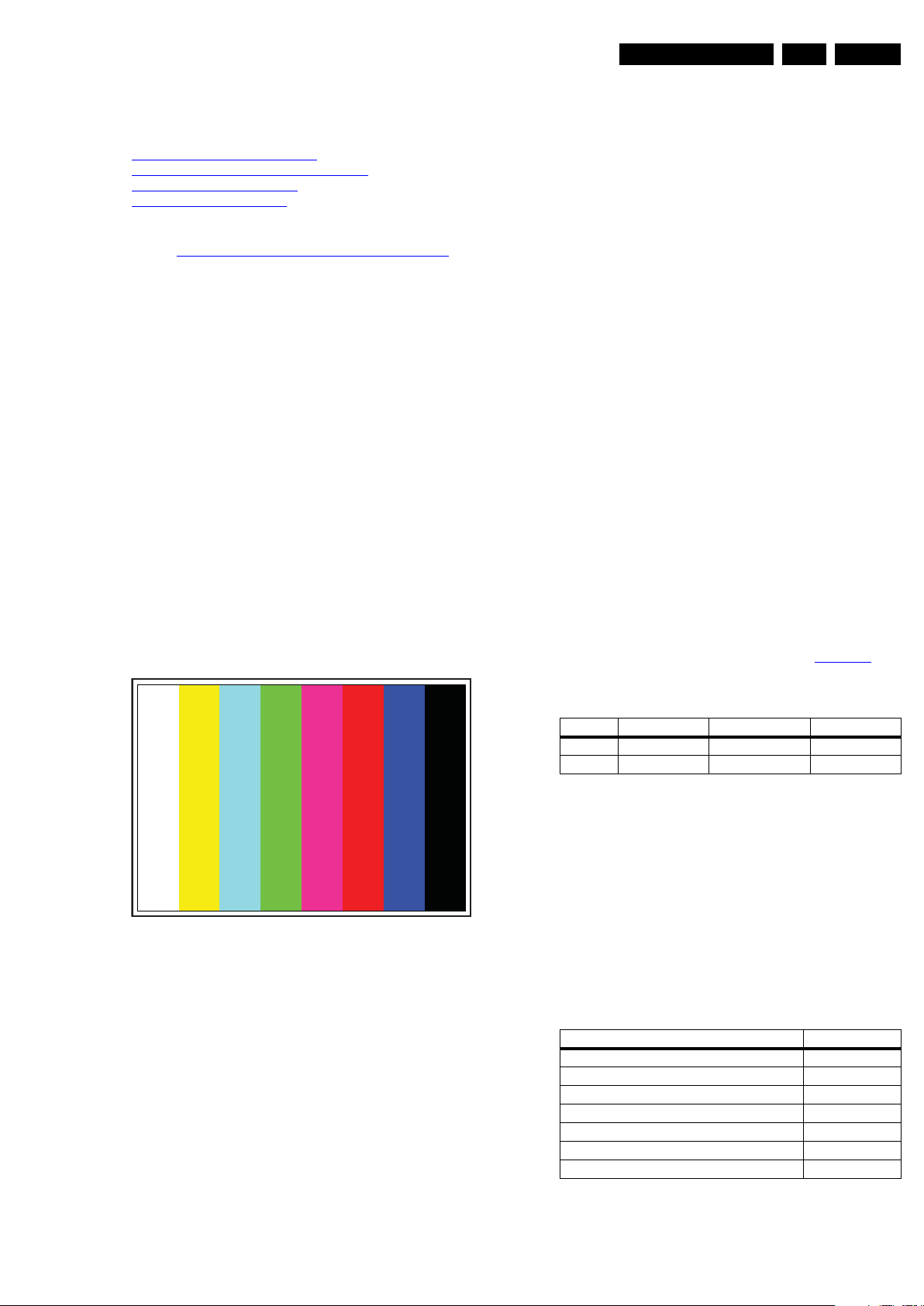
Quantum Data Pattern Generator 802G or 802R or 882. Apply
576i, and the pattern TVBAR100 shown as below.
6.3 White Balance Adjustment
6.3.1 Equipment Requirements
Color analyzer.
.
6.3.2 Input requirements
For SZ factory:
• Signal Type: RF signal
1. Set to PAL D/K system, frequency=184.25MHz ( for
China model ) with white pattern of 100%.
2. Set to PAL B/G system, frequency=64.25MHz ( for AP
model ) with white pattern of 100%.
• Input Signal Strength: 10mV (80 dBuV) terminal voltage.
• Input Injection Point: TV Tuner input.
For FQ factory:
• Signal Type: CVI (YPbPr)
1. Using Quantum Data Pattern Generator 802G or 802R
or 882.
2. Set to 576i with white pattern of 100% (flat patten).
6.3.3 Alignment Request in the center of the screen
1. Apply full white pattern, select smart setting to be
"PERSONAL".
2. Adjust Brightness = 50, Contrast = 50, and Color = 50.
3. Adjusting SCALER GAIN R G B to reach W/D and
luminance in factory mode as below.
4. Enter factory mode menu: press numeric keys "MENU" +
"1999" key (FAC mode menu).
5. Adjust Color Temp in the factory Mode OSD by adjusting
GAIN R xxx G xxx B xxx in factory modeFigure 6-1
.
Figure 6-1 Colour bar pattern
6.2.2 Alignment method
1. Select source as "YPbPr".
2. Set Smart picture as "Personal" and adjust Brightness to
50, Contrast to 50, and Colour to 50.
3. Access to factory OSD first, then to enable AUTO-COLOR
to get HD ADC OFFSET and HD ADC GAIN. Check 32
Gray scales can be distinguishable.
6.2.3 Process
1. Press "MENU" key.
2. Press digit "1999" to enter factory mode.
3. Press UP/DOWN to move curser to "AUTO COLOR".
4. Press RIGHT to do "ADC GAIN" and "ADC OFFSET".
5. Choose "EXIT" and press "OK".
Table 6-1 White D alignment values
Cool Normal Warm
x (center) 0.278±0.015 0.289 ± 0.015 0.314±0.015
y (center) 0.278±0.015 0.291 ± 0.015 0.319±0.015
Notes:
• R/G/B Gain value <= 124 to avoid satsuation at 32-grey
pattern.
• At TV Luminance at Normal >= 400cd/m2 when contrast
and brightness and color are 100%.
• These group settings about color temp are also applied
automatically into HDMI1/CVI(for SZ factory)/SIDE
AV/TV(for FQ factory). That means TV/HDMI/CVI use the
same setting.
6.4 Serial Number Definition
Table 6-2 BOM Code
Panel Supplier Code
AU 1
CPT 2
LPL (LG) 3
QDI 4
CMO 5
HSD 6
SVA 7
2009-May-29

EN 14 TPS2.2E LA7.
7. Circuit Descriptions
Index of this chapter:
7.1 General Description
7.2 Main Supply
7.3 MST9B885GL
Notes:
•Only new circuits (circuits that are not published recently)
are described.
• Figures can deviate slightly from the actual situation, due
to different set executions.
• For a good understanding of the following circuit
descriptions, please use the wiring, block and circuit
diagrams. Where necessary, you will find a separate
drawing for clarification.
7.1 General Description
This chassis supports PC digital input (via HDMI connector) up
to 1920 × 1080 60Hz mode for Full HD panel. It supports
ATV(RF) PAL and SECAM. Besides that it supports CVBS and
also YPbPr signal input from SDTV to HDTV (480i/p, 576i/p,
720p, 1080i/p) and also HDMI signal input from SDTV to HDTV
(480i/p, 576i/p, 720p, 1080i/p).
This chassis uses M-STAR MST9B885GL-1 which has
embedded ADC for HD(YPbPr)/VGA input, digital port for
HDMI/DVI decoder digital data input, SD ADC for CVBS/YC
input, video decoder, audio demodulator, audio decoder, TT
decoder, microcontroller, OSD engine and up/down scaler.
M-STAR MST9B885GL-1 is a high performance and fully
integrated IC for multi-function chassis with resolutions up to
Full HD. It is a multi-standard TV video and audio decoder.
MST9B885GL-1 supports all NTSC/PAL/SECAM standards
video decoder, Nicam/A2/FM stereo & SAP demodulation
audio decoder, LVDS transmitter, and TV decoder.
The MST9B885GL-1 embeds the 3D motion de-interlace to
generate very smooth picture quality for motion video. The 3D
comb filter also renders rich details for still image. The special
color processing engine provides favorite and natural color for
TV. To enrich the features of ATV, MST9B885GL-1 has an
built-in HDMI receiver to support digital signal in HDMI/DVI with
HDCP function, integrated with high bandwidth VGA ADC, high
resolution Video/Audio ADC, 90 dB Audio DAC and 10-bit
Video DAC.
Circuit Descriptions
2009-May-29
Circuit Descriptions
LG-S710D
PC Audio
Component
Audio
Component
MST9B885GL-1
CVBS
CVBS1 AUL3, AUR3
SIF0
DDR
230MHz
SPI Flash
ROM/2M
24C32
NVRAM
I2C
LVDS
LCD Panel
1366 × 768
SP
ComPair
UART
Cloning
(iTV-1)
12P
(4P)
(7P)
IR Board
Key
Board
LIPS
Y, Pb, Pr
AV IN (Side)
AUL0, AU R0
AUL1, AUR1
24C02
HDMI
TPA3124
2×(2P)
5 W, 16 Ω L-R Speaker
Remark: Reserve only for iTV
WT6703
STDBY MCU
HDMI
TM26
1
RGB / CVBS
SCART 1
CVBSOUT/audio out
24C02
HDMI
HDMI
SCART 2
CVBSOUT/audio out
CVBS
18280_203_090420.eps
090518
EN 15TPS2.2E LA 7.
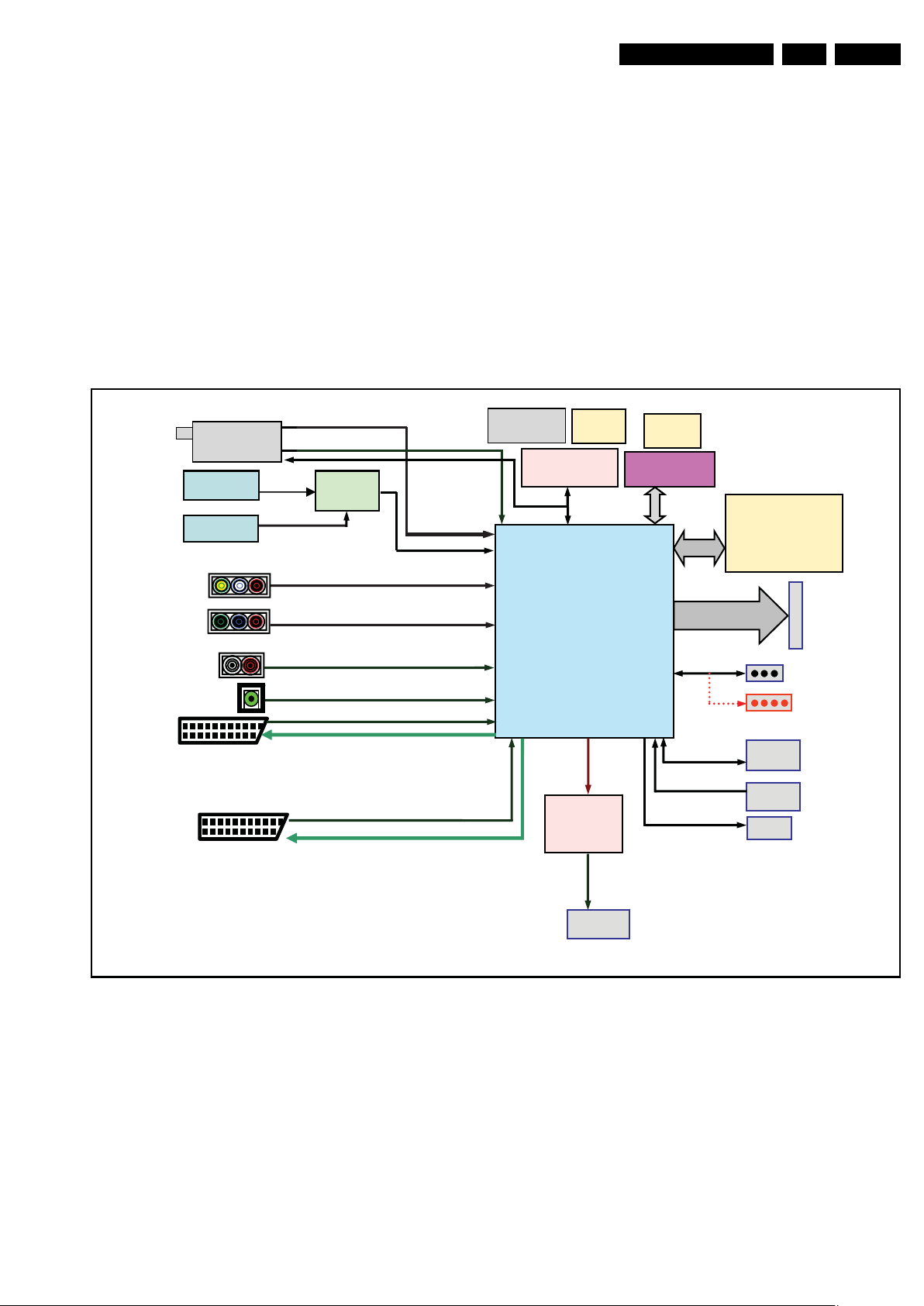
7.1.1 Block Diagram
The tuner supports PAL\SECAM RF signal by region, For TV
signal, MST9B885GL-1 embeds analog video demodulator,
decodes the CVBS signal generated from tuner for further
video processing. And the SIF signal is also delivered to
MST9B885GL-1 for audio demodulator and further audio
processing. The AL3 platform supports different sources:
• Tuner: PAL / SECAM
• HDMI IN: HDMI input (TV digital interface support HDCP)
with digital audio / PC DVI input
• HDMI SIDE: HDMI input (TV digital interface support
HDCP) with digital audio / PC DVI input
• EXT1( SCART IN / OUT 1): RGB / CVBS with audio input
and CVBS with audio line out
• EXT2( SCART IN / OUT 2): CVBS with audio input and
CVBS with audio line out
• EXT3: YPbPr component video input (RCA jack) with audio
R/L (RCA jack)
• Side AV: AV input (CVBS, RCA jack) with audio R/L (RCA
jack)
• SPDIF (Digital audio) OUT: RCA jack
• PC AUDIO IN: 3.5 mini-jack
All the input source video signals will be delivered to
MST9B885GL-1 for further video processing and audio signal
will be delivered to MST9B885GL-1 for further audio
processing. MUX selects input source and digitalizes/
processes audio signal, then transformed by audio DAC and
output to audio amplifier TPA3124. The MST9B885GL-1
supports LVDS signaling, connects these LVDS signal to panel
for displaying image. The TPS2.2E LA is designed with
IPS/MVA panel, LVDS interface.
Figure 7-1 System architecture
2009-May-29
EN 16 TPS2.2E LA7.
18280_204_090420.eps
090518
TUNER
DDR
CLASS D
Flash
MCU
FFC
Scaler
HDMI
Scart
Component
AV Input
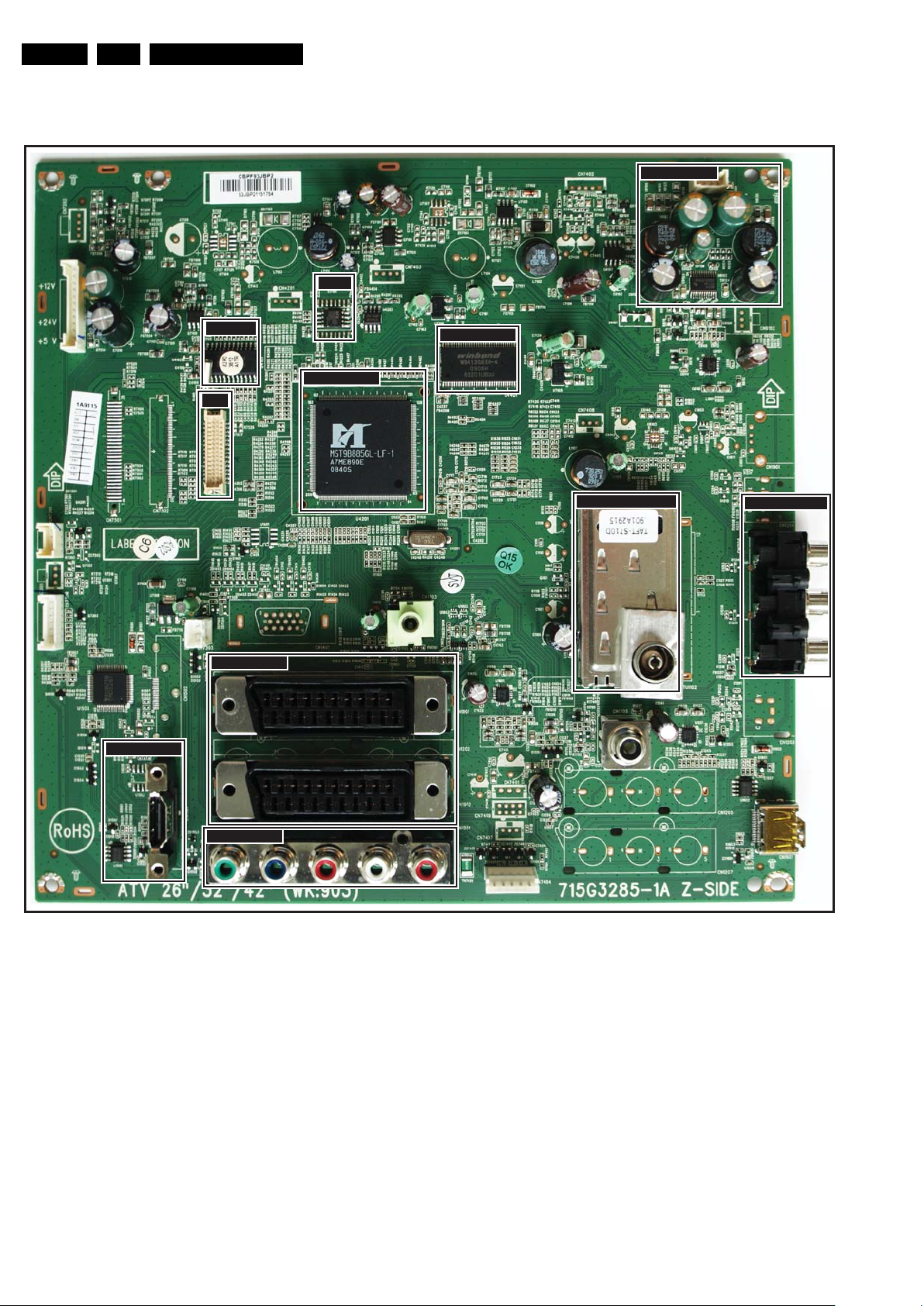
7.1.2 SSB Cell Layout
Circuit Descriptions
Figure 7-2 SSB top view
2009-May-29
7.2 Main Supply
18280_205_090420.eps
090518
3V3_SW
(WT6703F)
1V2
3V3
2V6
(MST9A885GL)
(SD RAM)
(DDR)
(MST9A885GL)
(MST9A885GL)
(DVR601RT)
(MST9A885GL)
3V3_HD_SW
(TMDS261)
+3V3_STBY
+5V_STBY
USB5V
USB5V
(HDMI SWITCH)
TUNER
VDDP
AVDD_MPLL
AVDDA
(MST9A885GL)
(MST9A885GL)
VDDC
(MST9A885GL)
AVDD_VIF1
AVDD_MemPLL
AVDD_AU
AVDD_USB2
AVDD_VIF5
AVDD_VIF2
(MST9A885GL)
(MST9A885GL)
(MST9A885GL)
(MST9A885GL)
(MST9A885GL)
(MST9A885GL)
VDDM
(STMPS2171STR)
(MST9A885GL)
(STMPS2171STR)
USB5V
+24V 5V2
Panel_PWR
SI4835
SI4835
+24V_SW
SC4525A
+24V_AMP
5V_SW
2V5V21+
5V_SW
)D3213APT()D3213APT(
(SPEAKER)
Panel_PWR
Panel_PWR
Panel_PWR
3V3
3V3_SW
TPS62203
SC4524B
SC4524B
SI4835
SI4835
SI4835
SI4835
SC4525A
AME1117
AME1117
AME1117
SC4524B
(M24C32)
AIC1084PE
Circuit Descriptions
EN 17TPS2.2E LA 7.
Figure 7-3 Power Diagram
2009-May-29

EN 18 TPS2.2E LA7.
7.3 MST9B885GL
7.3.1 Instruction
The MST9B885GL-1 is a high performance and fully integrated
IC for multi-function LCD monitor/TV with resolutions up to full
HD (1920 × 1080). It is configured with an integrated tripleADC/PLL, an integrated DVI/HDCP/HDMI receiver, a multistandard TV video and audio decoder, a video de-interlacer, a
scaling engine, the MStar ACE-3 color engine, an on-screen
display controller, an 8-bit MCU and a built-in output panel
interface. By use of external frame buffer, 3-D video decoding
and processing are fulfilled for high-quality TV applications. To
further reduce system costs, the MST9B885GL-1 also
integrates intelligent power management control capability for
green-mode requirements and spread-spectrum support for
EMI management.
Circuit Descriptions
2009-May-29
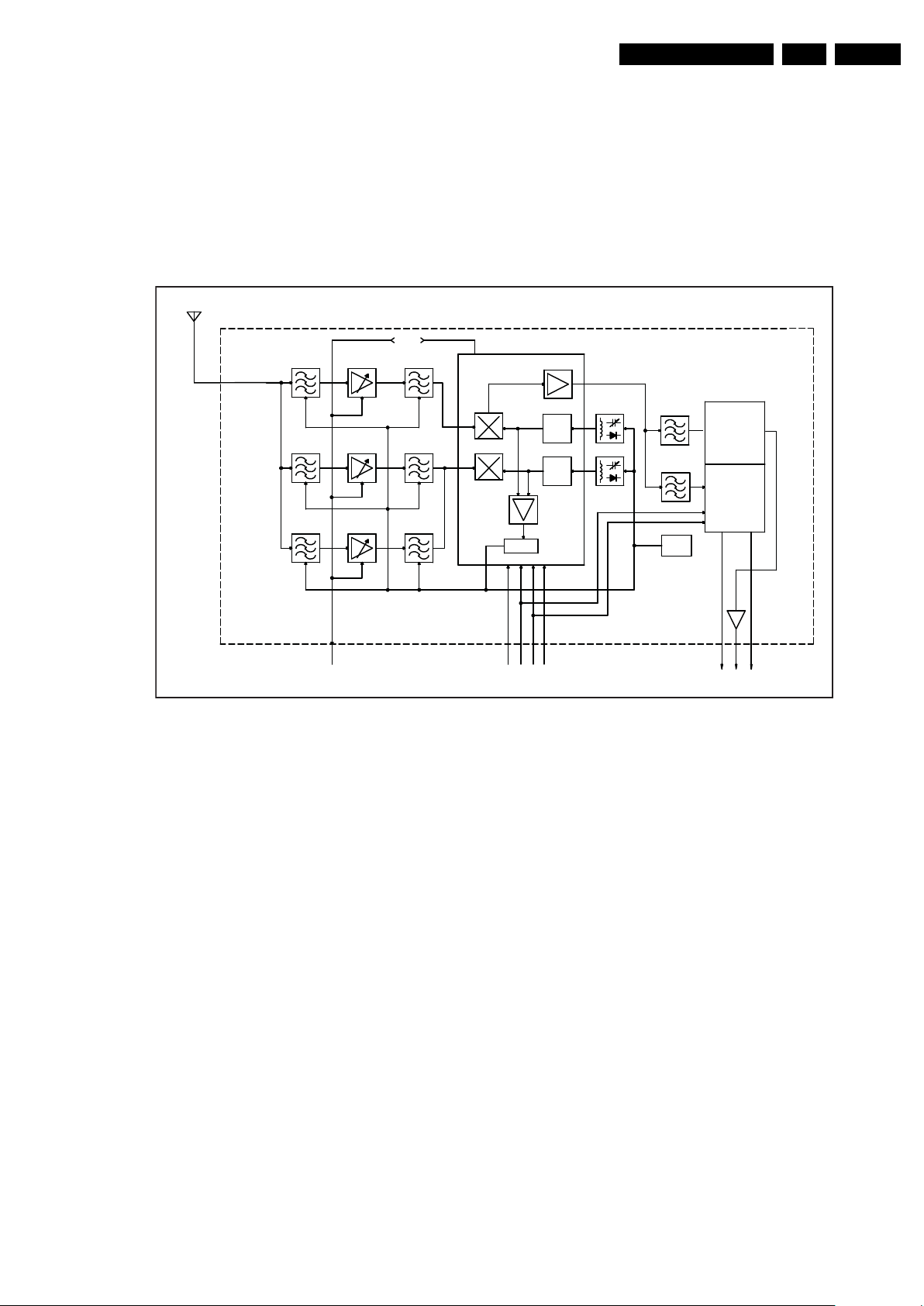
8. IC Data Sheets
18250_300_090210.eps
090318
SIF
VIDEO
AUDIO
RF AGC
+5V
SCL
SDA
AS
LOW BAND
HIGH BAND
MID BAND
RF AGC
PLL
MIXER & OSC & PLL
UHF
OSC
VHF
OSC
IF
VT
DC/DC
VIF PLL
DEMODULATOR
SOUND
DEMODULATOR
SAW
SAW
V
ANT IN. (RF IN)
IF
IF
S
This section shows the internal block diagrams and pin
configurations of ICs that are drawn as “black boxes” in the
electrical diagrams (with the exception of “memory” and “logic”
ICs).
8.1 TAFT-S710D (IC TU1101)
IC Data Sheets
EN 19TPS2.2E LA 8.
Figure 8-1 Internal block diagram
2009-May-29
EN 20 TPS2.2E LA8.
Pin 1
13
14
17
18
21
23
25
27
28
30
32
34
36
39
41
43
15
16
19
20
22
24
26
29
31
33
35
37
38
40
42
44
45
46
47
48
50
51
52
49
REXT
HSYNC1
VSYNC1
VCLAMP
REFP
REFM
BI N1P
RIN1P
BI N0P
GI N0 P
RIN0P
AVDD_33
HSYNC0
VSYNC2
SOGIN1
GI N1 P
VCOM2
VCOM3
SOGIN0
GND
VSYNC0
BI N2P
SOGIN2
GI N2 P
RIN2P
C1
Y1
C0
Y0
CVBS3
CVBS2
CVBS1
VCOM1
AVDD_33
CVB SOUT1
CVB SOUT0
GND
GPIOL[0]
GPIOL[1]
GPIOL[4]
XOUT
AVDD_MPLL
GND_VIFPLL
VR27
VR12
1
2
3
4
5
7
9
11
6
8
10
12
53
54
55
56
57
59
61
63
58
60
62
64
GND_RXS
SIFP
SIFM
VI FM
VIFP
AVDD_RXV
TAFC
AVDD_TAGC
GND_ TAGC
TAGC
AVDD_AU
777881
8
2
85
87
8991929496
98
100
1
0
3
105
1
07
7980838486
88
909395
979
9
101102
1
0
4
106
108
1
0
9
1
1
0
111
112114
115
1
16
113
A
U
V
AG
AVDD_A U
LI NE_IN_ 0L
L
I
NE_I N_
0
R
LI NE_
I
N
_
1L
L
I
NE_
IN_1
R
A
U
CO
M
LINE_I N_3
L
LI NE_I
N
_M
O
N
O
L
INE_
O
UT_
3
R
LI
N
E
_OU
T
_2
R
L
I
NE_OU
T
_1
R
LINE_OUT_0R
GP
IO
D
[0]
LI NE_IN_ 2L
L
I
NE_I N_2R
L
I
NE_I
N_3
R
L
I
N
E
_
OUT
_
3L
L
IN
E
_
O
UT_
2
L
L
INE_
O
UT_
1
L
L
I
N
E
_
OUT
_
0L
GP
IO
D[ 1
]
GPI OD[ 2 ]
GN
D
VDDC
WRZ
RD
Z
AL
E
BADR[ 1 ]
BADR[ 0 ]
RA
S
Z
VDDC
GND
AVDD
_
MI
CASZ
WE
Z
MADR[1
1
]
MADR[ 10]
656667
6869
717375707274
7
6
11
7
118
119
120
121123
125
1
27
122
1
2
4
126
128
MADR[ 9]
MADR[ 8]
MADR[ 7]
M
AD
R[
6
]
MADR[ 5]
MADR[ 4]
MADR[ 1]
MADR[ 3]
MADR[ 2]
M
AD
R
[0
]
180
179
176
175
172
170
168
166
165
163
161
159
157
154
152
150
178
177
174
173
171
169
167
164
162
160
158
156
155
153
151
149
148
147
146
145
143
142
141
144
192
191
190
189
188
186
184
182
187
185
183
181
140
139
138
137
136
134
132
130
135
133
131
129
244
243
240
2
39
236
234232
230
229
227
225
2
23
221
2
1
8216
214
2
4
2
241
238
2
3
7
235
233
231
228226
2242222
2
0
219
2
17
2
1
5
21
3
2
1
2
2
1
1
210
209
20
7
2
06
205
208
DDCD_SCL
DDCD_SDA
H
PLU
G
RX2P
RX2N
GND
RX0P
RX0N
AVDD_3
3
2
5
6
25
5
254253
2
5
2250
248
246
2
5
1
24
9
247
2
45
2
0
4
203
202
201
200
198
196
19
4
19
9
197
1
9
5
19
3
AUVRP
AVDD_RXS
GND
G
ND
DI [7]
DI [6]
DI [5]DI [4]
VDDP
DI [3]
DI [2]
DI [1]
DI [0]
VD
D
P
PWM2
PWM3
RXCKN
RXCKP
RX1
N
VDDC
ICLK
GPI OT[ 0 ]
A
U
VRM
GND
CVBS0
VCOM0
AV
D
D_M
I
PWM 0
SAR2
SAR0
GND
SPI_SCZ
SPI_SCK
GND
SAR3
SAR1
VDDC
SPI_SDO
SPI_SDI
USB20_DM
AVDD _USB
USB20_REXT
MVREF
MCLKE
MCLK
MCLKZ
DQM1
DQS1
MDATA[15]
MDATA[11]
MDATA[10]
AVDD_MI
MDATA[3]
MDATA[2]
GND
MDATA[1]
MDATA[0]
AVDD_MI
DQS0
DQM0
INT
DDCA_SCL
DDCA_SDA
DDCR_SCL
DDCR_SDA
PWM 1
GPIOR[0]
G
PI O
D
[3]
GPI OD[ 5 ]
GP
IO
D[ 7
]
GP
IO
D
[
4
]
G
PI O
D
[6]
V
D
DP
AVDD
_
MI
PLL
GND_RXV
GND
USB20_DP
VDDP
GND
IRIN
VDDP
USB_DM
USB_VBUS
USB_DP
USB_CID
GPIOB[0]
GPIOB[1]
RX1P
GND
XIN
MDATA[9]
MDATA[8]
AVDD_MI
MDATA[7]
MDATA[6]
MDATA[5]
MDATA[4]
MDATA[14]
MDATA[13]
MDATA[12]
AVDD_MI
GPIOL[2]
GPIOL[3]
A
D[0]
AD[
1
]
AD
[2
]
A
D[3]
GND
V
DDP
LVB0M
LVB0P
LVB1M
LVB1P
LVB2M
L
VB
2
P
LVBCKM
LVBCKP
L
VB3
M
LVB3P
AVDD_MI
GND
VDDP
LVA0M
LVA0P
LVA1M
LVA1P
LVA2M
LVA2P
LVACKM
LVACKP
LVA3M
LVA3P
VDDC
GND
HWRESET
GPI OE[ 2 ]
GPI OE[ 0 ]
G
PI O
E
[
1
]
GPI OE[ 3]
NC
NC
NC
NC
18280_301_090420.eps
090519
MST9B885
GL-1
8.2 MST9B885GL-1-LF (IC U4201)
IC Data Sheets
XXXXXXXX
XXX
XX
2009-May-29
Figure 8-2 Pin configuration
 Loading...
Loading...