Philips TDA9875 Datasheet
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA9875
Digital TV Sound Processor
(DTVSP)
Preliminary specification
Supersedes data of 1997 Mar 20
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1998 Feb 13

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
CONTENTS
1 FEATURES
1.1 Demodulator and decoder section
1.2 DSP section
1.3 Analog audio section
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
2.1 Supported standards
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
4 BLOCK DIAGRAM
5 PINNING
6 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
6.1 Description of the demodulator and decoder
section
6.2 Description of the DSP
6.3 Description of the analog audio section
7 LIMITING VALUES
8 THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
9 CHARACTERISTICS
10 I2C-BUS CONTROL
10.1 Introduction
10.2 Power-up state
10.3 Slave receiver mode
10.4 Slave transmitter mode
10.5 Expert mode
11 I2S-BUS DESCRIPTION
12 EXTERNAL COMPONENTS
13 PACKAGE OUTLINE
14 SOLDERING
14.1 Introduction
14.2 Soldering by dipping or by wave
14.3 Repairing soldered joints
15 DEFINITIONS
16 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
17 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
1998 Feb 13 2

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
1 FEATURES
1.1 Demodulator and decoder section
• Sound IF (SIF) input switch e.g. to select between
terrestrial TV SIF and SAT SIF sources
• SIF AGC with 21 dB control range
• SIF 8-bit Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
• DQPSK demodulation for different standards,
simultaneously with 1-channel FM demodulation
• NICAM decoding (B/G, I and L standard)
• Two-carrier multistandard FM demodulation (B/G, D/K
and M standard)
• Decoding for three analog multi-channel systems (A2,
A2+ and A2*) and satellite sound
• Optional AM demodulation for system L, simultaneously
with NICAM
• Programmable identification (B/G, D/K and M standard)
and different identification times.
1.2 DSP section
• Digital crossbar switch for all digital signal sources and
destinations
• Control of volume, balance, contour, bass, treble,
pseudo stereo, spatial, bass boost and soft-mute
• Plop-free volume control
• Automatic Volume Level (AVL) control
• Adaptive de-emphasis for satellite
• Programmable beeper
• Monitor selection for FM/AM DC values and signals,
with peak detection option
2
• I
S-bus interface for a feature extension (e.g. Dolby
surround) with matrix, level adjust and mute.
1.3 Analog audio section
• Analog crossbar switch with inputs for mono and stereo
(also applicable as SCART 3 input), SCART 1
input/output, SCART 2 input/output and line output
• User defined full-level/−3 dB scaling for SCART outputs
• Output selection of mono, stereo, dual A/B, dual A or
dual B
• 20 kHz bandwidth for SCART-to-SCART copies
• Standby mode with functionality for SCART copies
• Dual audio digital-to-analog converter from
DSP to analog crossbar switch, bandwidth 15 kHz
• Dual audio ADC from analog inputs to DSP
• Two dual audio Digital-to-Analog Converters (DACs) for
loudspeaker (Main) and headphone (Auxiliary) outputs;
also applicable for L, R, C and S in the Dolby Pro Logic
mode with feature extension.
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA9875 is a single-chip Digital TV Sound Processor
(DTVSP) for analog and digital multi-channel sound
systems in TV sets and satellite receivers.
2.1 Supported standards
The multistandard/multi-stereo capability of the TDA9875
is mainly of interest in Europe, but also in Hong
Kong/Peoples Republic of China and South East Asia.
This includes B/G, D/K, I, M and L standard. In other
application areas there exists only subsets of those
standard combinations otherwise only single standards
are transmitted.
M standard is transmitted in Europe by the American
Forces Network (AFN) with European channel spacing
(7 MHz VHF, 8 MHz UHF) and monaural sound.
The AM sound of L/L’ standard is normally demodulated in
the 1st sound IF. The resulting AF signal has to be entered
into the mono audio input of the TDA9875. A second
possibility is to use the internal AM demodulator stage,
however this gives limited performance.
Korea has a stereo sound system similar to Europe and is
supported by the TDA9875. Differences include deviation,
modulation contents and identification. It is based on
M standard.
An overview of the supported standards and sound
systems and their key parameters is given in Table 1.
1998 Feb 13 3
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
2.1.1 ANALOG 2-CARRIER SYSTEMS
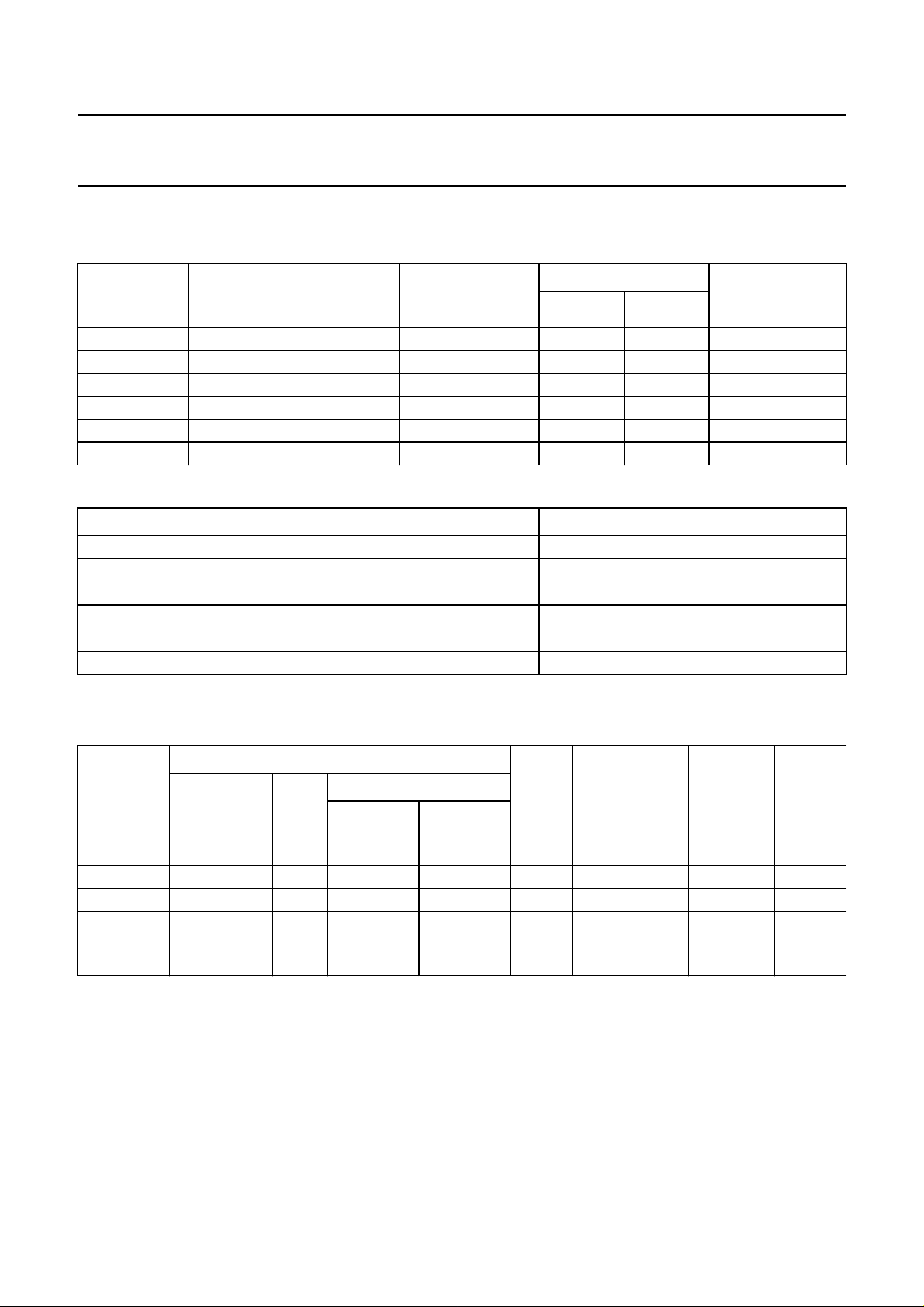
Table 1 Frequency modulation
STANDARD
SOUND
SYSTEM
CARRIER
FREQUENCY
(MHz)
FM DEVIATION
(kHz)
NOM./MAX./OVER
MODULATION BANDWIDTH/
DE-EMPHASIS
SC1 SC2
M mono 4.5 15/25/50 mono − 15/75
M A2+ 4.5/4.724 15/25/50
B/G A2 5.5/5.742 27/50/80
1
⁄2(L + R)1⁄2(L − R) 15/75 (Korea)
1
⁄2(L + R) R 15/50
I mono 6.0 27/50/80 mono − 15/50
D/K A2 6.5/6.742 27/50/80
D/K A2* 6.5/6.26 27/50/80
1
⁄2(L + R) R 15/50
1
⁄2(L + R) R 15/50
Table 2 Identification for A2 systems
PARAMETER A2/A2* A2+ (KOREA)
Pilot frequency 54.6875 kHz = 3.5 × line frequency 55.0699 kHz = 3.5 × line frequency
Stereo identification
frequency
Dual identification frequency
117.5 Hz
274.1 Hz
pilot frequency
= 149.9 Hz
-------------------------------------- 133
pilot frequency
= 276.0 Hz
-------------------------------------- -
57
pilot frequency
=
-------------------------------------- 105
pilot frequency
=
-------------------------------------- -
57
AM modulation depth 50% 50%
2.1.2 2-CARRIER SYSTEMS WITH NICAM
(kHz/µs)
Table 3 NICAM
SC1
SC2
(MHz)
NICAM
DE-EMPHASIS
ROLL-OFF
(%)
STANDARD
FREQUENCY
(MHz)
TYPE
MODULATION
INDEX (%)
NOM/MAX.
DEVIATION
(kHz)
NOM./MAX.
B/G 5.5 FM − 27/50 5.85 J17 40 note 1
I 6.0 FM − 27/50 6.552 J17 100 note 1
D/K 6.5 FM − 27/50 5.85 J17 40 not yet
L 6.5 AM 54/100 − 5.85 J17 40 note 1
Note
1. See
“EBU specification”
or equivalent specification.
NICAM
CODING
defined
1998 Feb 13 4
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
2.1.3 SATELLITE SYSTEMS
An important specification for satellite TV reception is the
“Astra specification”
. The TDA9875 is suited for the reception
of Astra and other satellite signals.
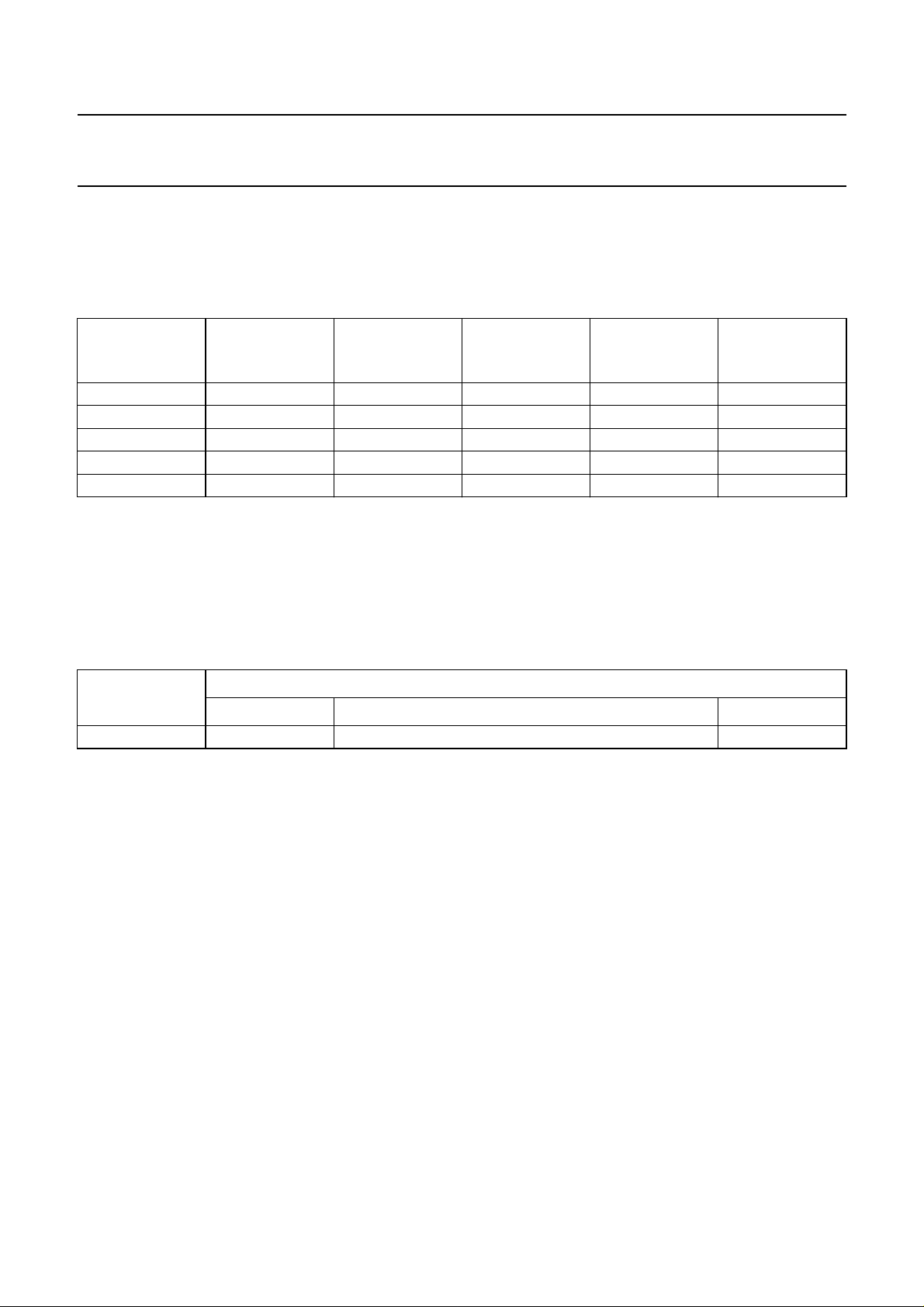
Table 4 FM satellite sound
CARRIER TYPE
Main 6.50
CARRIER
FREQUENCY
(MHz)
(1)
MODULATION
INDEX
0.26 85 mono 15/50
Sub 7.02/7.20 0.15 50 m/st/d
Sub 7.38/7.56 0.15 50 m/st/d
Sub 7.74/7.92 0.15 50 m/st/d
Sub 8.10/8.28 0.15 50 m/st/d
MAXIMUM
FM DEVIATION
(kHz)
MODULATION
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
BANDWIDTH/
DE-EMPHASIS
(kHz/µs)
(1)
15/adaptive
15/adaptive
15/adaptive
15/adaptive
(3)
(3)
(3)
(3)
Notes
1. For other satellite systems, frequencies of, for example, 5.80, 6.60 or 6.65 MHz can also be received. A de-emphasis
of 60 µs, or in accordance with J17, is available.
2. m/st/d = mono or stereo or dual language sound.
3. Adaptive de-emphasis = compatible to transmitter specification.
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
PACKAGE
TYPE NUMBER
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
TDA9875 SDIP64 plastic shrink dual in-line package; 64 leads (750 mil) SOT274-1
1998 Feb 13 5
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
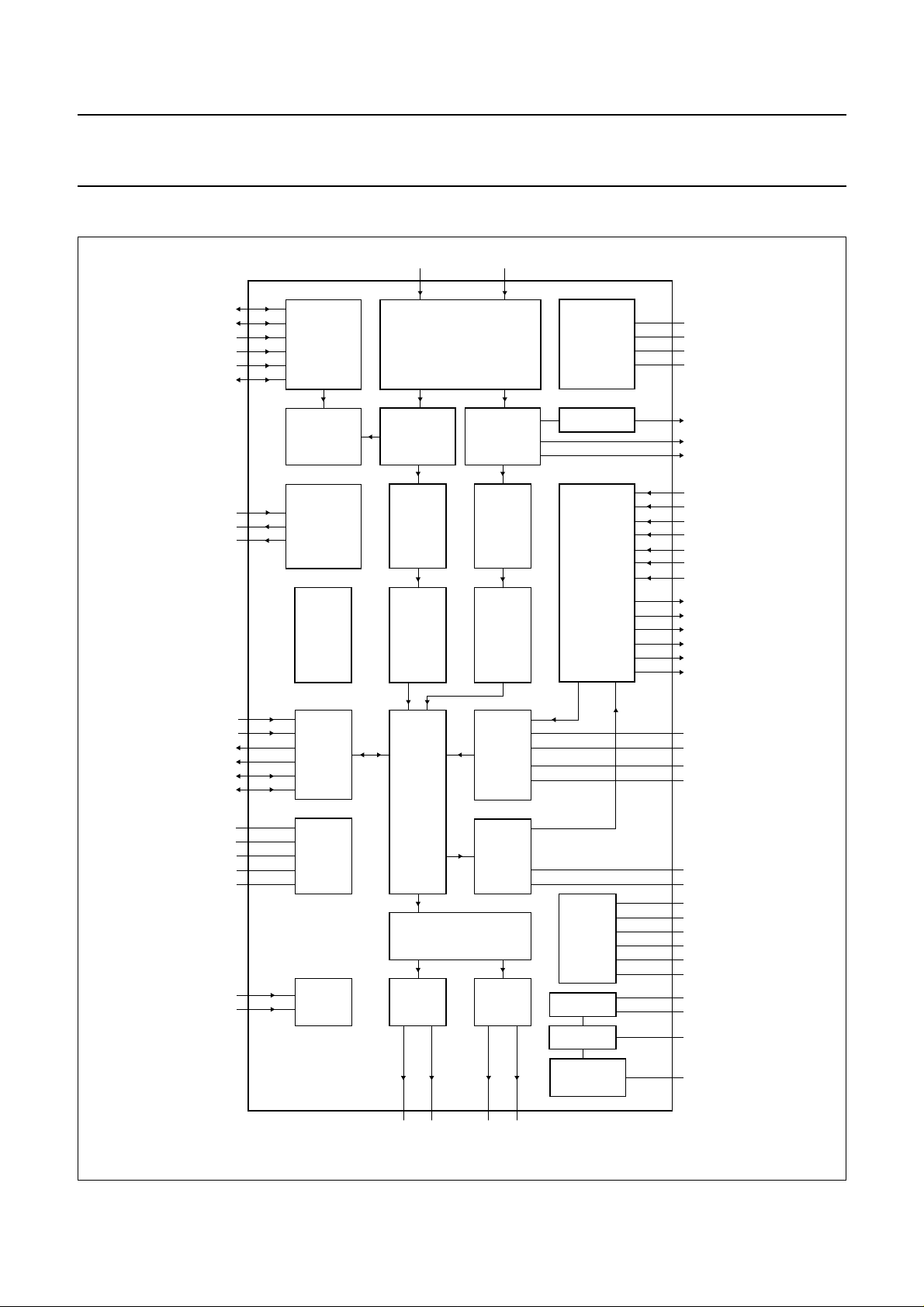
4 BLOCK DIAGRAM
handbook, full pagewidth
ADDR1
ADDR2
SCL
SDA
XTALI
XTALO
SYSCLK
SIF2 SIF1
10 12
9
P1
20
P2
3
13
4
5
18
17
21
I2C-BUS
INTERFACE
IDENTIFICATION
CLOCK
PEAK
DETECTION
INPUT SWITCH
FM (AM)
DEMODULATION
DEMATRIX
LEVEL
ADJUST
AGC, ADC
NICAM
DEMODULATION
NICAM
DECODER
LEVEL
ADJUST
SUPPLY
SOUND IF
(SIF)
TIMING
DETECTION DAC
ANALOG
CROSSBAR
SWITCH
7
V
DDA1
6
V
SSA1
11
V
ref1
8
I
ref
19
V
tune
2
NICAM
1
PCLK
33
SCIR1
34
SCIL1
36
SCIR2
37
SCIL2
31
EXTIR
32
EXTIL
29
MONOIN
47
SCOR1
48
SCOL1
51
SCOR2
52
SCOL2
63
LOR
62
LOL
SDI1
SDI2
SDO1
SDO2
SCK
WS
V
DDD1
V
DDD2
V
SSD1
V
SSD2
CRESET
TEST1
TEST2
27
26
25
24
22
23
15
64
14
49
16
28
30
I2C-BUS
AUDIO
INTERFACE
DIGITAL
SUPPLY
TDA9875
TEST
DIGITAL
SELECT
AUDIO PROCESSING
DAC(2)
61
MOL
MOR60AUXOL58AUXOR
ADC(2)
DAC(2)
DAC(2)
57
SUPPLY
DAC
SUPPLY DAC
REFERENCE
SUPPLY
OPERATIONAL
AMPLIFIERS
42
41
45
44
54
55
38
43
35
46
39
40
59
56
53
50
MGK107
CAPL2
CAPL1
CAPR1
CAPR2
PCAPR
PCAPL
V
DDA2
V
SSA2
V
SSG
V
ref2
V
ref(p)
V
ref(n)
V
DDA3
V
SSA3
V
ref3
V
SSA4
Fig.1 Block diagram.
1998 Feb 13 6
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
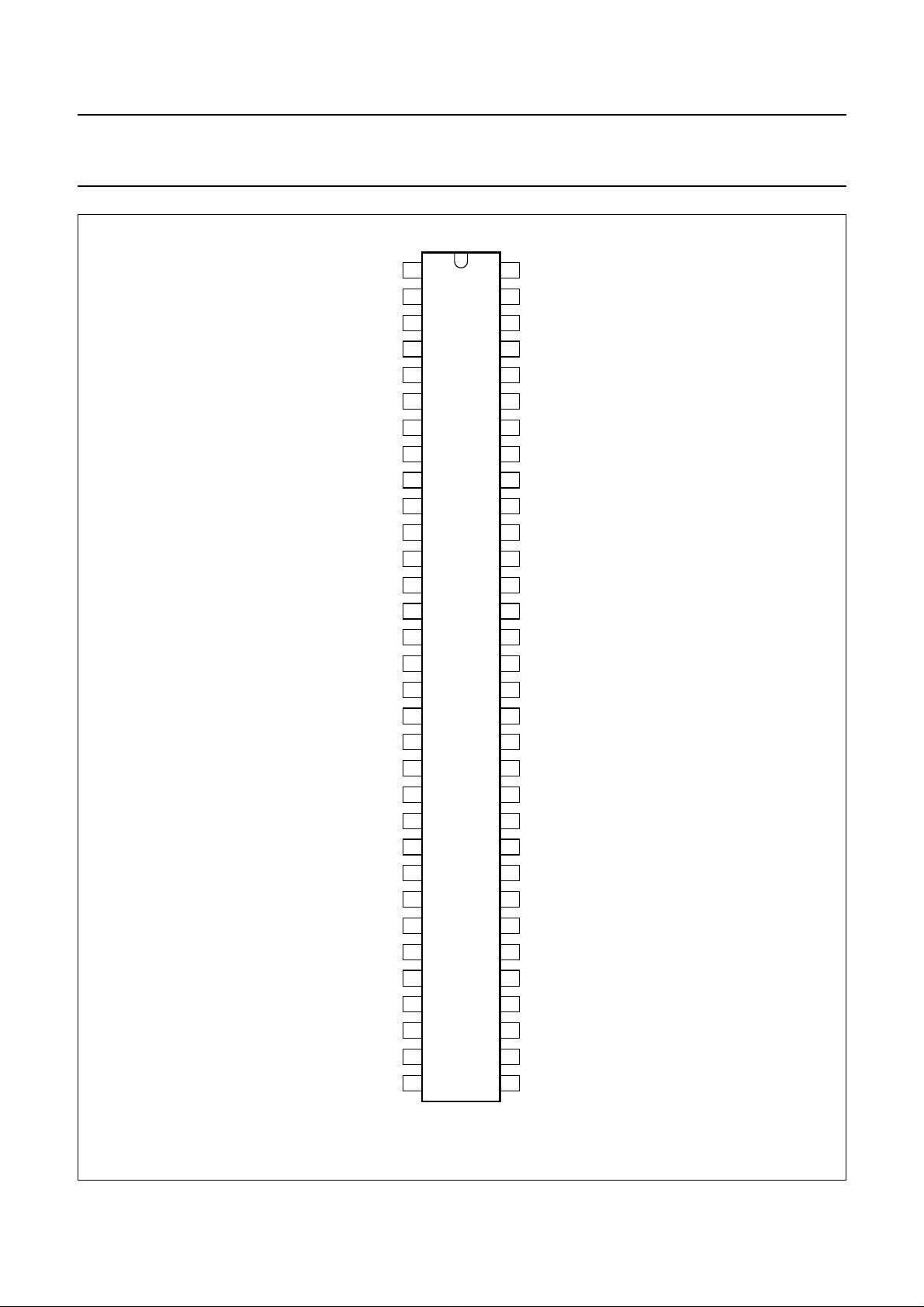
5 PINNING
SYMBOL PIN I/O DESCRIPTION
PCLK 1 O NICAM clock output at 728 kHz
NICAM 2 O serial NICAM data output at 728 kHz
ADDR1 3 I first I
SCL 4 I I
SDA 5 I/O I
V
V
I
ref
SSA1
DDA1
6 supply supply ground 1; analog front-end circuitry
7 supply analog supply voltage 1; analog front-end circuitry
8 − resistor for reference current generator; analog front-end circuitry
P1 9 I/O first general purpose I/O pin
SIF2 10 I sound IF input 2
V
ref1
11 − reference voltage; analog front-end circuitry
SIF1 12 I sound IF input 1
ADDR2 13 I second I
V
V
SSD1
DDD1
14 supply supply ground 1; digital circuitry
15 supply digital supply voltage 1; digital circuitry
CRESET 16 − capacitor for power-on reset
XTALO 17 O crystal oscillator output
XTALI 18 I crystal oscillator input
V
tune
19 O tuning voltage output for crystal oscillator
P2 20 I/O second general purpose I/O pin
SYSCLK 21 O system clock output
SCK 22 I/O I
WS 23 I/O I
SDO2 24 O I
SDO1 25 O I
SDI2 26 I I
SDI1 27 I I
TEST1 28 I first test pin; connected to V
MONOIN 29 I audio mono input
TEST2 30 I second test pin; connected to V
EXTIR 31 I external audio input right channel
EXTIL 32 I external audio input left channel
SCIR1 33 I SCART 1 input right channel
SCIL1 34 I SCART 1 input left channel
V
SSG
35 − ground guards; audio analog-to-digital converter circuitry
SCIR2 36 I SCART 2 input right channel
SCIL2 37 I SCART 2 input left channel
V
V
V
DDA2
ref(p)
ref(n)
38 supply analog supply voltage 2; audio analog-to-digital converter circuitry
39 − positive reference voltage; audio analog-to-digital converter circuitry
40 − reference voltage ground; audio analog-to-digital converter circuitry
2
C-bus slave address modifier
2
C-bus clock
2
C-bus data
2
C-bus slave address modifier
2
S-bus clock
2
S-bus word select
2
S-bus data output 2
2
S-bus data output 1
2
S-bus data input 2
2
S-bus data input 1
for normal operation
SSD1
for normal operation
SSD1
1998 Feb 13 7
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
SYMBOL PIN I/O DESCRIPTION
CAPL1 41 − filter capacitor pin 1; audio analog-to-digital converter, left channel
CAPL2 42 − filter capacitor pin 2; audio analog-to-digital converter, left channel
V
SSA2
CAPR2 44 − filter capacitor pin 2; audio analog-to-digital converter, right channel
CAPR1 45 − filter capacitor pin 1; audio analog-to-digital converter, right channel
V
ref2
SCOR1 47 O SCART 1 output right channel
SCOL1 48 O SCART 1 output left channel
V
SSD2
V
SSA4
SCOR2 51 O SCART 2 output right channel
SCOL2 52 O SCART 2 output left channel
V
ref3
PCAPR 54 − post-filter capacitor pin right channel, audio digital-to-analog converter
PCAPL 55 − post-filter capacitor pin left channel, audio digital-to-analog converter
V
SSA3
AUXOR 57 O headphone (Auxiliary) output right channel
AUXOL 58 O headphone (Auxiliary) output left channel
V
DDA3
MOR 60 O loudspeaker (Main) output right channel
MOL 61 O loudspeaker (Main) output left channel
LOL 62 O line output left channel
LOR 63 O line output right channel
V
DDD2
43 supply supply ground 2; audio analog-to-digital converter circuitry
46 − reference voltage; audio analog-to-digital converter circuitry
49 supply supply ground 2; digital circuitry
50 supply supply ground 4; audio operational amplifier circuitry
53 − reference voltage; audio digital-to-analog converter and operational amplifier
circuitry
56 supply supply ground 3; audio digital-to-analog converter circuitry
59 supply analog supply voltage 3; audio digital-to-analog converter
64 supply digital supply voltage 2; digital circuitry
1998 Feb 13 8
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
handbook, halfpage
PCLK
NICAM
ADDR1
SCL
SDA
V
SSA1
V
DDA1
I
ref
P1
SIF2
V
ref1
SIF1
ADDR2
V
SSD1
V
DDD1
CRESET
XTALO
XTALI
V
tune
P2
SYSCLK
SCK
WS
SDO2
SDO1
SDI2
SDI1
TEST1
MONOIN
TEST2
EXTIR
EXTIL
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
TDA9875
MGK106
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
V
DDD2
LOR
LOL
MOL
MOR
V
DDA3
AUXOL
AUXOR
V
SSA3
PCAPL
PCAPR
V
ref3
SCOL2
SCOR2
V
SSA4
V
SSD2
SCOL1
SCOR1
V
ref2
CAPR1
CAPR2
V
SSA2
CAPL2
CAPL1
V
ref(n)
V
ref(p)
V
DDA2
SCIL2
SCIR2
V
SSG
SCIL1
SCIR1
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
1998 Feb 13 9

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
6 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
6.1 Description of the demodulator and decoder section
6.1.1 SIF
INPUT
Two input pins are provided, SIF1 e.g. for terrestrial TV
and SIF2 e.g. for a satellite tuner. As no specific filters are
integrated, both inputs have the same specification giving
flexibility in application. The selected signal is passed
through an AGC circuit and then digitized by an 8-bit ADC
operating at 24.576 MHz.
6.1.2 AGC
The gain of the AGC amplifier is controlled from the ADC
output by means of a digital control loop employing
hysteresis. The AGC has a fast attack behaviour to
prevent ADC overloads and a slow decay behaviour to
prevent AGC oscillations. For AM demodulation the AGC
must be switched off. When switched off, the control loop
is reset and fixed gain settings can be chosen from
Table 12 (subaddress 0).
The AGC can be controlled via the I
2
C-bus. Details can be
found in the I2C-bus register definitions (see Chapter 10).
6.1.3 M
IXER
The digitized input signal is fed to the mixers, which mix
one or both input sound carriers down to zero IF. A 24-bit
control word for each carrier sets the required frequency.
Access to the mixer control word registers is via the
I2C-bus. When receiving NICAM programs, a feedback
signal is added to the control word of the second carrier
mixer to establish a carrier-frequency loop.
6.1.4 FM
AND AM DEMODULATION
An FM or AM input signal is fed via a band-limiting filter to
a demodulator that can be used for either FM or AM
demodulation. Apart from the standard (fixed)
de-emphasis characteristic, an adaptive de-emphasis is
available for encoded satellite programs. A stereo decoder
recovers the left and right signal channels from the
demodulated sound carriers. Both the European and
Korean stereo systems are supported.
6.1.5 FM
IDENTIFICATION
The identification of the FM sound mode is performed by
AM synchronous demodulation of the pilot signal and
narrow-band detection of the identification frequencies.
The result is available via the I2C-bus interface. A selection
can be made via the I2C-bus for B/G, D/K and M standard
and for three different modes that represent different
trade-offs between speed and reliability of identification.
6.1.6 NICAM
DEMODULATION
The NICAM signal is transmitted in a DQPSK code at a bit
rate of 728 kbit/s. The NICAM demodulator performs
DQPSK demodulation and feeds the resulting bitstream
and clock signal onto the NICAM decoder and, for
evaluation purposes, to PCLK (pin 1) and NICAM (pin 2).
A timing loop controls the frequency of the crystal oscillator
to lock the sampling rate to the symbol timing of the
NICAM data. The polarity of the control signal is selectable
to support applications in which external circuitry is used to
boost the tuning voltage of the oscillator.
6.1.7 NICAM
DECODER
The device performs all decoding functions in accordance
with the
“EBU NICAM 728 specification”
. After locking to
the frame alignment word, the data is descrambled by
applying the defined pseudo-random binary sequence;
the device will then synchronize to the periodic frame flag
bit C0.
The status of the NICAM decoder can be read out from the
2
NICAM status register by the user (see the I
C-bus
register description in Section 10.4.2). The OSB bit
indicates that the decoder has locked to the NICAM data.
The VDSP bit indicates that the decoder has locked to the
NICAM data and that the data is valid sound data. The C4
bit indicates that the sound conveyed by the FM mono
channel is identical to the sound conveyed by the NICAM
channel. The error byte contains the number of sound
sample errors, resulting from parity checking, that
occurred in the past 128 ms period. The Bit Error Rate
(BER) can be calculated using the following equation;
BER
bit errors
----------------------total bits
error byte 1.74× 10
5–
×≈=
1998 Feb 13 10

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
6.1.8 NICAM AUTO-MUTE
This function is enabled by setting bit AMUTE LOW
subaddress 14 (see Section 10.3.11). Upper and lower
error limits may be defined by writing appropriate values to
two registers in the I2C-bus section (subaddresses 16 and
17; see Sections 10.3.13 and 10.3.14). When the number
of errors in a 128 ms period exceeds the upper error limit
the auto-mute function will switch the output sound from
NICAM to whatever sound is on the first sound carrier
(FM or AM). When the error count is smaller than the lower
error limit the NICAM sound is restored.
The auto-mute function can be disabled by setting bit
AMUTE HIGH. In this condition clicks become audible
when the error count increases; the user will hear a signal
of degrading quality.
A decision to enable/disable the auto-muting is taken by
the microcontroller based on an interpretation of the
application control bits C1, C2, C3 and C4 and, possibly,
any additional strategy implemented by the set maker in
the microcontroller software.
When the AM sound in NICAM L systems is demodulated
in the 1st sound IF and the audio signal connected to the
mono input of the TDA9875, the controlling microcontroller
must implement the switching from NICAM reception to
mono input, if auto-muting is desired.
6.1.9 CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR
A circuit diagram of the external components of the
voltage-controlled crystal oscillator is illustrated in Fig.8
(see Chapter 12).
6.1.10 T
Both test pins are active HIGH, in normal operation of the
device they are wired to V
manufacturing tests only and are not available to
customers. Without external circuitry these pads are pulled
down to LOW level with internal resistors.
EST PINS
. Test functions are for
SSD1
1998 Feb 13 11
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
d
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
1998 Feb 13 12
FM
2
DC
FILTER
from ADC
2
I
2
I
NICAM
ADAPTIVE
DE-EMPHASIS
S1
S2
2
DC
FILTER
2
2
2
FIXED
DE-EMPHASIS
FIXED
DE-EMPHASIS
LEVEL ADJUST
2
LEVEL ADJUST
LEVEL ADJUST
LEVEL ADJUST
LEVEL ADJUST
MATRIX
2 2 2
2
4
6
8
10
book, full pagewidth
DIGITAL
CROSSBAR
SELECT
2
2
2
2
2
MATRIX
MATRIX
MATRIX
MATRIX
MATRIX
AUTOMATIC
VOLUME
LEVEL
VOLUME
SOFT-MUTE
BASS/TREBLE
BEEPER
LEVEL ADJUST AND MUTE
LEVEL ADJUST AND MUTE
LEVEL ADJUST
BASS/TREBLE
SPA TIAL
PSEUDO
VOLUME
BASS BOOST
CONTOUR
SOFT-MUTE
BEEPER
2
2
2
2
2
LS
HP
2
S1
I
2
I
S2
DAC
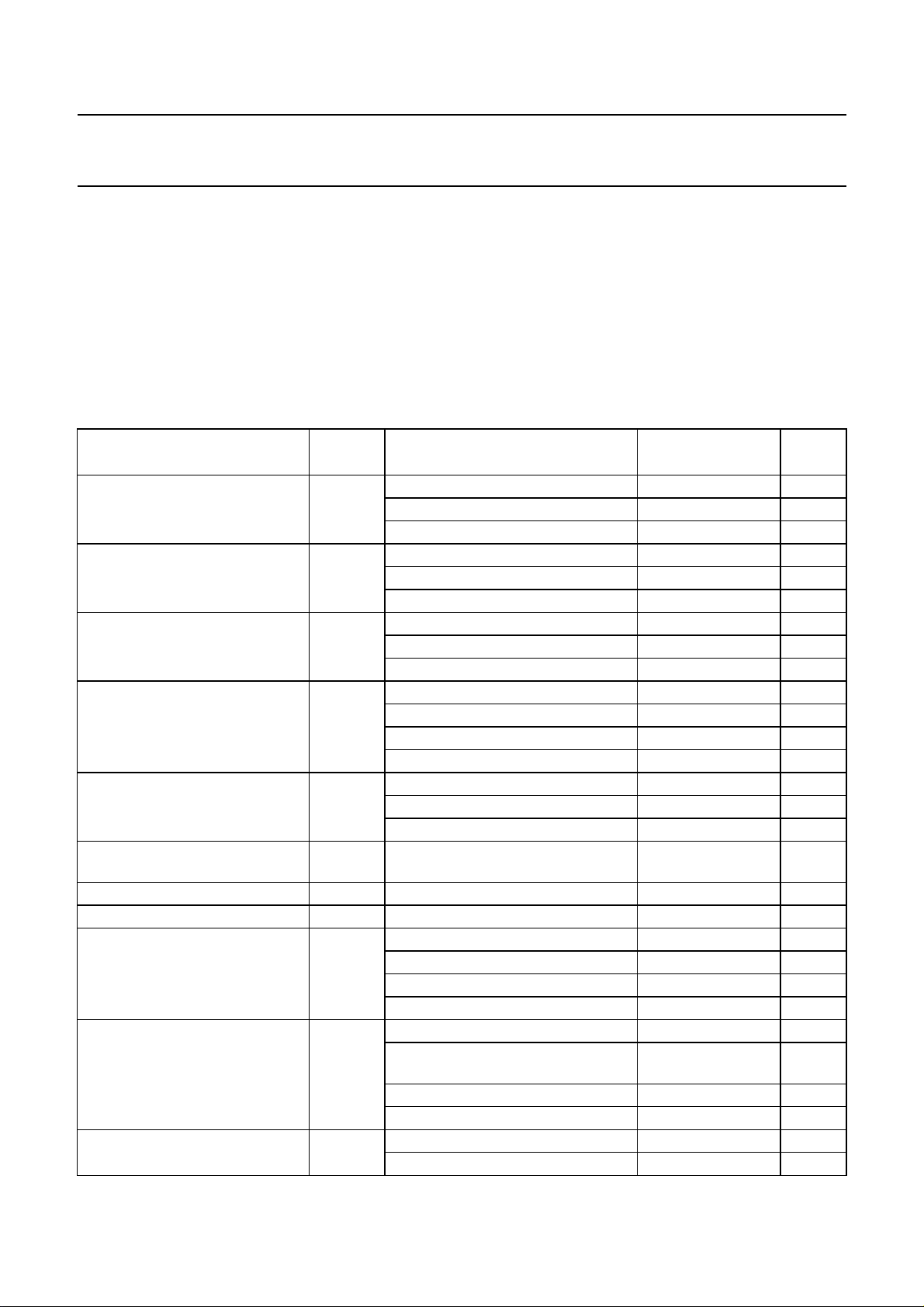
6.2 Description of the DSP
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
2 4
12
Fig.3 DSP data flow diagram.
16
MONITOR
SELECT
PEAK
DETECTION
1
2
I
C-bus
MGK108

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
6.2.1 LEVEL SCALING
All input channels to the digital crossbar switch (except for
the loudspeaker feedback path) are equipped with a level
adjust facility to change the signal level in a range of
±15 dB. It is recommended to scale all input channels to be
15 dB below full-scale (−15 dB full-scale) under nominal
conditions.
6.2.2 NICAM
PATH
The NICAM path has a switchable J17 de-emphasis.
6.2.3 FM (AM)
PATH
A high-pass filter suppresses DC offsets from the
FM demodulator due to carrier frequency offsets and
supplies the monitor/peak function with DC values and an
unfiltered signal, e.g. for the purpose of carrier detection.
The de-emphasis function offers fixed settings for the
supported standards (50 µs, 60 µs, 75 µs and J17).
An adaptive de-emphasis is available for
Wegener-Panda 1 encoded programs.
A matrix performs the dematrixing of1⁄2(L + R) and
R to L and R signals, of1⁄2(L + R) and1⁄2(L − R) to L and R
signals or of channel 1 and channel 2 to L and R signals.
6.2.4 NICAM
AUTO-MUTE
If NICAM is received and the signal quality becomes poor,
the digital crossbar switch switches automatically to FM
and switches the matrix to channel 1. The automatic
switching between NICAM and channel 1 (FM or AM)
reception depends on the NICAM bit error rate.
The auto-mute function can be disabled via the I2C-bus.
6.2.5 M
ONITOR
This function provides data words from a number of
locations of the signal processing paths to the I2C-bus
interface (2 data bytes). Signal sources include the
FM demodulator outputs, most inputs to the digital
crossbar switch and the inputs to the loudspeaker channel
of the ADC. Source selection and data read-out is
performed via the I2C-bus.
Optionally, the peak value can be measured instead of
simply taking samples. The internally stored peak value is
reset to zero when the data is read via the I2C-bus.
The monitor function may be used, for example, for signal
level measurements or carrier detection.
6.2.6 L
OUDSPEAKER (MAIN) CHANNEL
The matrix provides the following functions; forced mono,
stereo, channel swap, channel 1, channel 2 and spatial
effects.
There are fixed coefficient sets for spatial settings of 30%,
40% and 52%.
The Automatic Volume Level (AVL) function provides a
constant output level of −23 dB full-scale for input levels
between 0 dBFS and −29 dB full-scale. There are some
fixed decay time constants to choose from, i.e. 2, 4 and
8 seconds.
Pseudo stereo is based on a phase shift in one channel via
a 2nd-order all-pass filter. There are fixed coefficient sets
to provide 90 degrees phase shift at frequencies of
150, 200 and 300 Hz.
Volume is controlled individually for each channel ranging
from +24 dB to −83 dB with 1 dB resolution. There is also
a mute position. For the purpose of a simple control
software in the microcontroller, the decimal number that is
2
sent as an I
C-bus data byte for volume control is identical
to the volume setting in dBs (e.g. the I2C-bus data
byte +10 sets the new volume value to +10 dB).
Balance can be realized by independent control of the left
and right channel volume settings.
Contour is adjustable between 0 dB and +18 dB with 1 dB
resolution.
Bass is adjustable between +15 dB and −12 dB with 1 dB
resolution and treble is adjustable between ±12 dB with
1 dB resolution.
For the purpose of a simple control software in the
microcontroller, the decimal number that is sent as an
I2C-bus data byte for contour, bass or treble is identical to
the new contour, bass or treble setting in dBs (e.g. the
I2C-bus data byte +8 sets the new value to +8 dB).
Extra bass boost is provided up to 20 dB with 2 dB
resolution. The implemented coefficient set serves merely
as an example on how to use this filter.
The beeper provides tones in a range from approximately
400 Hz to 30 kHz. The frequency can be selected via the
I2C-bus. The beeper output signal is added to the
loudspeaker and headphone channel signals. The beeper
volume is adjustable with respect to full-scale between
0 dB and −93 dB with a 3 dB step resolution. The beeper
is not effected by mute.
1998 Feb 13 13

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
Soft-mute provides a mute ability in addition to volume
control with a well defined time (32 ms) after which the
soft-mute is completed. A smooth fading is achieved by a
cosine masking.
6.2.7 H
EADPHONE (AUXILIARY) CHANNEL
The matrix provides the following functions; forced mono,
stereo, channel swap, channel 1 and channel 2
(or C and S in Dolby Surround Pro Logic mode).
Volume is controlled individually for each channel in a
range from +24 to −83 dB with 1 dB resolution. There is
also a mute position. For the purpose of a simple control
software in the microcontroller, the decimal number that is
2
sent as an I
C-bus data byte for volume control is identical
to the volume setting in dBs (e.g. the I2C-bus data
byte +10 sets the new volume value to +10 dB).
Balance can be realized by independent control of the left
and right channel volume settings.
Bass is adjustable between +15 dB and −12 dB with 1 dB
resolution and treble is adjustable between ±12 dB with
1 dB resolution.
For the purpose of a simple control software in the
microcontroller, the decimal number that is sent as an
I2C-bus data byte for bass or treble is identical to the new
bass or treble setting in dB (e.g. the I2C-bus data byte +8
sets the new value to +8 dB).
The beeper provides tones in a range from approximately
400 Hz to 30 kHz. The frequency can be selected via the
I2C-bus. The beeper output signal is added to the
loudspeaker and headphone channel signals. The beeper
volume is adjustable with respect to full-scale between
0 dB and −93 dB with a 3 dB step resolution. The beeper
is not effected by mute.
Soft-mute provides a mute ability in addition to volume
control with a well defined time (32 ms) after which the
soft-mute is completed. A smooth fading is achieved by a
cosine masking.
6.2.8 F
EATURE INTERFACE
The feature interface comprises two I2S-bus input/output
ports and a system clock output. Each I2S-bus port is
equipped with level adjust facilities that can change the
signal level in a ±15 dB range in 1 dB steps. Outputs can
be disabled to improve EMC performance.
The I2S-bus output matrix provides the following functions;
forced mono, stereo, channel swap, channel 1 and
channel 2.
One example of how the feature interface can be used in
a TV set is to connect an external Dolby Surround Pro
Logic DSP, such as the SAA7710, to the I
2
S-bus ports.
Outputs must be enabled and a suitable master clock
signal for the DSP can be taken from pin SYSCLK.
A stereo signal from any source will be output on one of
the I2S-bus serial data outputs and the four processed
signal channels will be entered at both I2S-bus serial data
inputs. Left and right could then be output to the power
amplifiers via the Main channel, centre and surround via
the Auxiliary channel.
6.2.9 C
HANNEL FROM THE AUDIO ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL
CONVERTER
The signal level at the output of the ADC can be adjusted
in a range of±15 dB with a 1 dB step resolution. The audio
ADC itself is scaled to a gain of −6 dB.
6.2.10 C
HANNEL TO THE ANALOG CROSSBAR PATH
Level adjust with control positions 0 dB, +3 dB, +6 dB
and +9 dB.
6.2.11 D
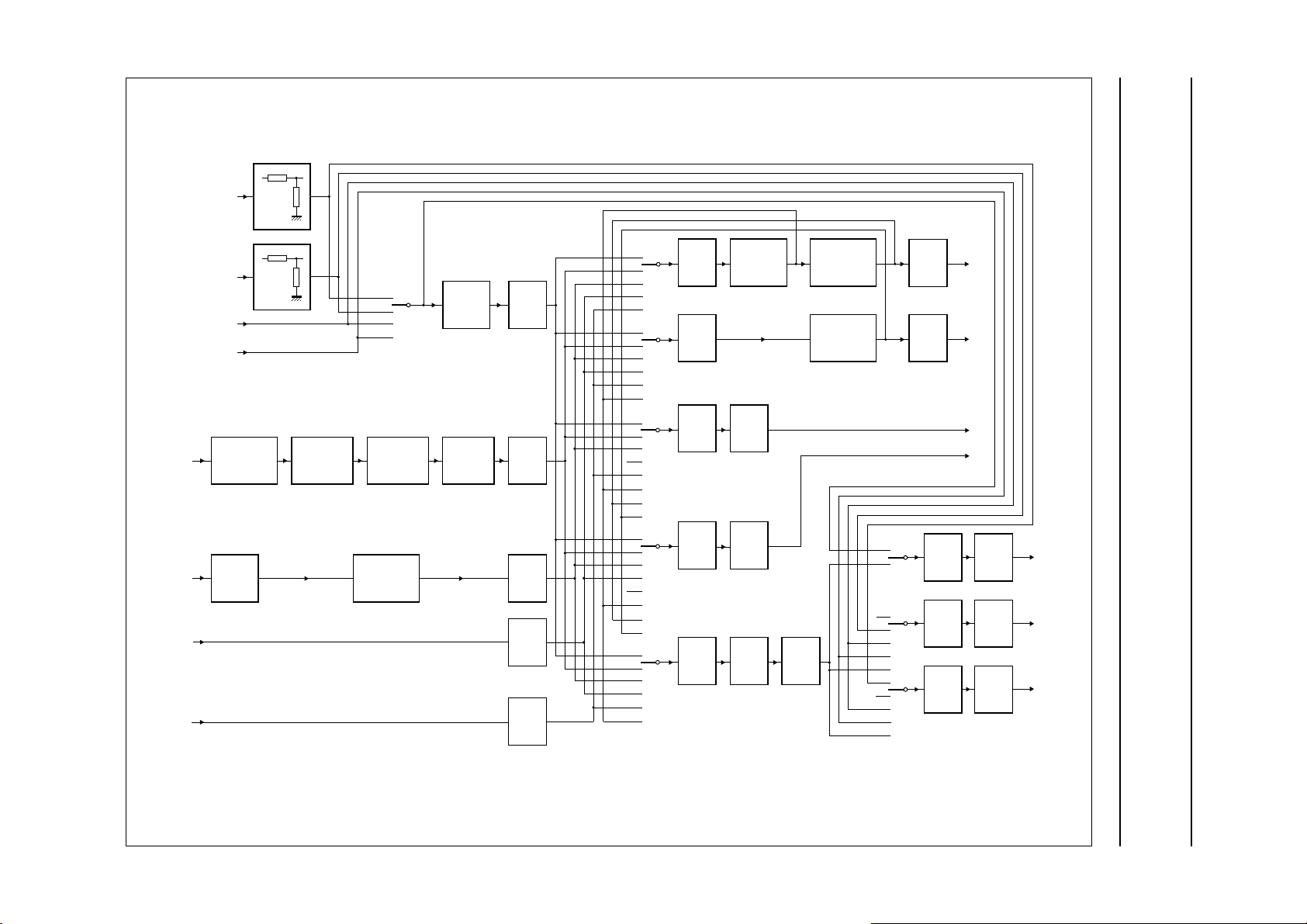
IGITAL CROSSBAR SWITCH (SEE Fig.6)
Input channels to the crossbar switch are from the audio
ADC, I2S1, I2S2, FM path, NICAM path and from the
loudspeaker channel path after matrix and AVL.
Output channels comprise loudspeaker, headphone, I2S1,
I2S2 and the audio DACs for line output and SCART.
The I2S1 and I2S2 outputs also provide digital outputs from
the loudspeaker and headphone channels, but without the
beeper signals.
6.2.12 G
ENERAL
There are a number of functions that can provide signal
gain, e.g. volume, bass and treble control. Great care has
to be taken when using gain with large input signals in
order not to exceed the maximum possible signal swing,
which would cause severe signal distortion. The nominal
signal level of the various signal sources to the digital
crossbar switch should be 15 dB below digital full-scale
(−15 dB full-scale). This means that a volume setting of,
say, +15 dB would just produce a full-scale output signal
and not cause clipping, if the signal level is nominal.
Sending illegal data patterns via the I2C-bus will not cause
any changes of the current setting for the volume, bass,
treble, bass boost and level adjust functions.
1998 Feb 13 14
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
6.2.13 EXPERT MODE
The TDA9875 provides a special expert mode that gives direct write access to the internal Coefficient RAM (CRAM) of
the DSP. It can be used to create user-defined characteristics, such as a tone control with different corner frequencies
or special boost/cut characteristics to correct the low-frequency loudspeaker and/or cabinet frequency responses by
means of the bass boost filter. However, this mode must be used with great care.
More information on the functions of this device, such as filter structures, the number of coefficients per function, their
default values, memory addresses, etc., can be made available on request.
6.2.14 DSP
Table 5 DSP characteristics
Bass control for loudspeaker and
headphone output
Treble control for loudspeaker
and headphone output
Contour for loudspeaker output
Bass boost for loudspeaker
output
Volume control for each separate
channel in loudspeaker and
headphone output
Soft-mute for loudspeaker and
headphone output
Spatial effects yes anti-phase crosstalk positions 30, 40 and 52 %
Pseudo stereo yes 90 degree phase shift at frequency 150, 200 and 300 Hz
Beeper additional to the signal in
the loudspeaker and headphone
channel
AVL
General
CHARACTERISTICS
FUNCTION
EXPERT
MODE
yes
yes
yes
yes
no
no
yes
no
no
PARAMETER VALUE UNIT
control range −12 to +15 dB
step resolution 1 dB
step resolution at frequency 40 Hz
control range −12 to +12 dB
step resolution 1 dB
step resolution at frequency 14 kHz
control range 0 to +18 dB
step resolution 1 dB
step resolution at frequency 40 Hz
control range 0 to +20 dB
step resolution 2 dB
step resolution at frequency 20 Hz
corner frequency 350 Hz
control range −83 to +24 dB
step resolution 1 dB
mute position at step 10101100
processing time 32 ms
beep frequencies see Section 10.3.38
control range 0 to −93 dB
step resolution 3 dB
mute position at step 00100000
step width quasi continuously
AVL output level for an input level
between 0 dB and −29 dB (full-scale)
attack time 10 ms
decay time constant 2, 4 and 8 s
−3 dB lower corner frequency of DSP 10 Hz
−1 dB bandwidth of DSP 14.5 kHz
−23 dB
1998 Feb 13 15
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
FUNCTION
Level adjust I
Level adjust I
outputs
2
S1 and I2S2 inputs
2
S1 and I2S2
EXPERT
MODE
yes
yes
PARAMETER VALUE UNIT
control range −15 to +15 dB
step resolution 1 dB
control range −15 to +15 dB
step resolution 1 dB
mute position at step 00010000
Level adjust analog crossbar path no control positions 0, 3, 6 and 9 dB
Level adjust audio ADC outputs
Level adjust NICAM path
Level adjust FM path
yes
yes
yes
control range +15 to −15 dB
step resolution 1 dB
control range +15 to −15 dB
step resolution 1 dB
control range +15 to −15 dB
step resolution 1 dB
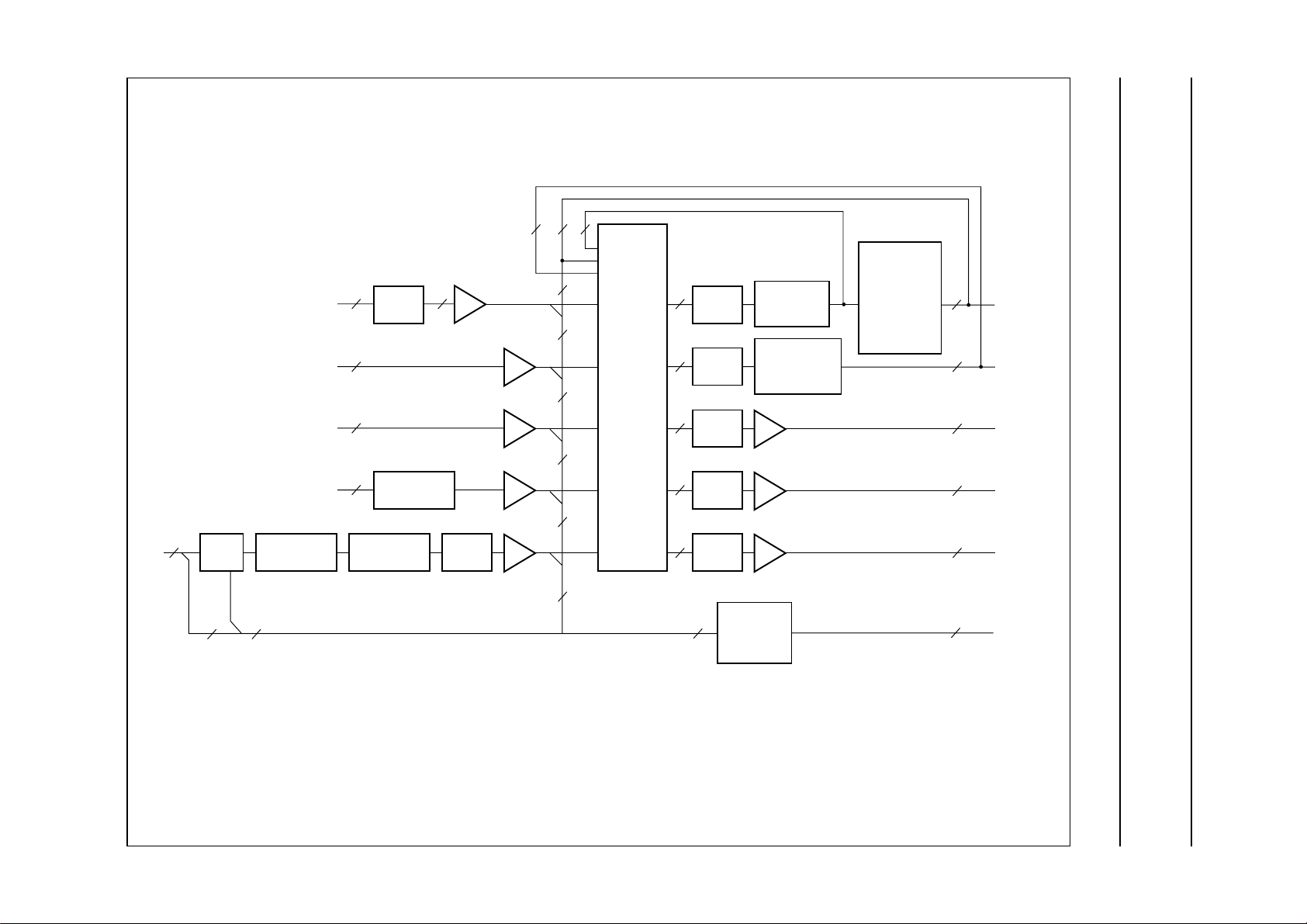
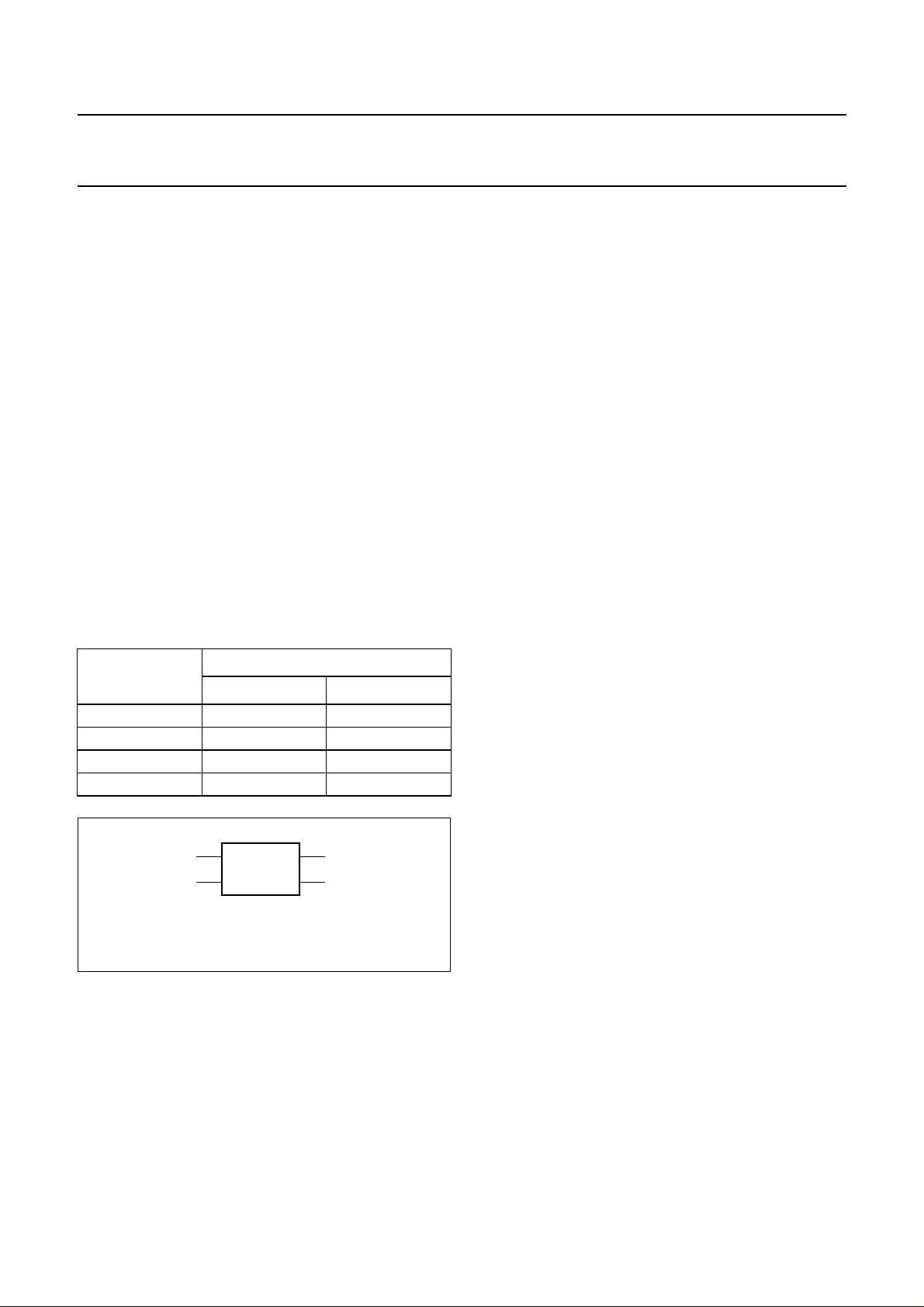
6.3 Description of the analog audio section
handbook, full pagewidth
SCART 1
SCART 2
external
mono
NICAM
I
I
I
I
2
2
2
2
FM
S1
S2
S1
S2
2
−3 dB
2
−3 dB
2
2
D
2
2
2
A
2
2
2
2
2
2
ANALOG
CROSSBAR
SWITCH
DSP
AND
DIGITAL
CROSSBAR
SWITCH
2
2
2
2
2
2
ANALOG
MATRIX
ANALOG
MATRIX
ANALOG
MATRIX
A
D
D
A
D
A
3 dB
2 2
0 dB
3 dB
2
0 dB
3 dB
2
0 dB
2
SCART 1
2
SCART 2
2
Line output
2
Main
2
Auxiliary
MGK109
Fig.4 Block diagram for the audio section.
1998 Feb 13 16
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
6.3.1 ANALOG CROSSBAR SWITCH AND ANALOG MATRIX
(see also Fig.6)
There are a number of analog input and output ports with
the TDA9875. Analog source selector switches are
employed to provide the desired analog signal routing
capability. The analog signal routing is performed by the
analog crossbar switch section. A dual audio ADC
provides the connection to the DSP section and a dual
audio DAC provides the connection from the DSP section
to the analog crossbar switch. The digital signal routing is
performed by a digital crossbar switch.
The basic signal routing philosophy of the TDA9875 is that
each switch handles two signal channels at the same time,
e.g. left and right, language A and B, directly at the source.
Each source selector switch is followed by an analog
matrix to perform further selection tasks, such as putting a
signal from one input channel, say language A, to both
output channels or for swapping left and right channels.
The analog matrix provides the functions given in Table 6
(see also Fig.5).
Table 6 Analog matrix functions
MATRIX OUTPUT
MODE
LEFT OUTPUT RIGHT OUTPUT
1 left input right input
2 right input left input
3 left input left input
4 right input right input
handbook, halfpage
left input
right input
ANALOG
MATRIX
left output
right output
MGK110
Fig.5 Analog matrix.
All switches and matrices are controlled via the I
2
C-bus.
There is one restriction for switching signals at inputs and
outputs for SCART 1 and SCART 2. At these ports, an
input signal cannot be copied to its own output, i.e. it is not
possible to make a copy from SCART 1 input to SCART 1
output.
6.3.2 SCART INPUTS
The SCART specification allows for a signal level of up to
2 V (RMS). Because of signal handling limitations, due to
the 5 V supply voltage of the TDA9875, it is necessary to
have fixed 3 dB attenuators at the SCART inputs to obtain
a 2 V input. This results in a −3 dB SCART-to-SCART
copy gain. If 0 dB copy gain is preferred (with maximum
1.4 V input), there are +3 dB/0 dB amplifiers at the outputs
of SCART 1 and SCART 2 and at the line output.
The input attenuator is realized by an external series
resistor in combination with the input impedance, both of
which form a voltage divider. With this voltage divider the
maximum SCART signal level of 2 V (RMS) is scaled
down to 1.4 V (RMS) at the input pin. If it is known for
certain applications that the input signal level is always
below 1.4 V (RMS), the SCART inputs can be used
without external resistors.
6.3.3 E
XTERNAL AND MONO INPUTS
The 3 dB input attenuators are not required for the external
and mono inputs, because those signal levels are under
control of the TV designer. The maximum allowed input
level is 1.4 V (RMS). By adding external series resistors,
the external inputs can be used as an additional SCART
input.
6.3.4 SCART
OUTPUTS
The SCART outputs employ amplifiers with two gain
settings. The gain can be set to +3 dB or to 0 dB via the
I2C-bus. The +3 dB position is needed to compensate for
the 3 dB attenuation at the SCART inputs should
SCART-to-SCART copies with 0 dB gain be preferred
[under the condition of 1.4 V (RMS) maximum input level].
The 0 dB position is needed, for example, for an
external-to-SCART copy with 0 dB gain.
6.3.5 L
INE OUTPUT
The line output can provide an unprocessed copy of the
audio signal in the loudspeaker channels. This can be
either an external signal that comes from the dual audio
ADC, or a signal from an internal digital audio source that
comes from the dual audio DAC. The line output employs
amplifiers with two gain settings. The +3 dB position is
needed to compensate for the attenuation at the
SCART inputs, while the 0 dB position is needed, for
example, for non-attenuated external or internal digital
signals (see Section 6.3.4).
1998 Feb 13 17

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
6.3.6 LOUDSPEAKER (MAIN) AND HEADPHONE
(AUXILIARY) OUTPUTS
Signals from any audio source can be applied to the
loudspeaker and to the headphone output channels via the
digital crossbar switch and the DSP.
6.3.7 D
UAL AUDIO DAC
The TDA9875 contains three dual audio DACs, one for the
connection from the DSP to the analog crossbar switch
section and two for the loudspeaker and headphone
outputs. Each of the three dual low-noise high-dynamic
range DACs consists of two 15-bit DACs with current
outputs, followed by a buffer operational amplifier.
The audio DACs operate with four-fold oversampling and
noise shaping.
6.3.8 D
UAL AUDIO ADC
There is one dual audio ADC in the TDA9875 for the
connection of the analog crossbar switch section to the
DSP. The dual audio ADC consists of two bitstream
3rd-order sigma-delta audio ADCs and a high-order
decimation filter.
6.3.9 S
TANDBY MODE
The standby mode (subaddress 1, bit 5) disables most
functions and reduces power dissipation. The analog
crossbar switch and the SCART section remains
operational and can be controlled by the I2C-bus to
support copying of analog signals from SCART 1 to
SCART 2 and vice versa.
Unused internal registers may lose their information in
standby mode. Therefore, the device needs to be
initialized on returning to normal operation. This can be
accomplished in the same way as after a power-on reset.
1998 Feb 13 18
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
a
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
1998 Feb 13 19
SCART 1
ndbook, full pagewidth
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
FM/AM
part
NICAM
part
I2S1
2
I
S2
SCART 2
external
mono
FM/AM
DEMODULATOR
NICAM
DECODER
ADAPTIVE
DE-EMPHASIS
SW4
FIXED
DE-EMPHASIS
DE-EMPHASIS
ADC
STEREO
DECODER
LEVEL
ADJUST
LEVEL
ADJUST
LEVEL
ADJUST
LEVEL
ADJUST
LEVEL
ADJUST
SW9
SW5
SW6
SW7
SW8
DIGITAL
MATRIX
DIGITAL
MATRIX
DIGITAL
MATRIX
DIGITAL
MATRIX
DIGITAL
MATRIX
AUTOMATIC
VOLUME
LEVEL
LEVEL
ADJUST
LEVEL
ADJUST
LEVEL
ADJUST
LOUDSPEAKER
PROCESSING
HEADPHONE
PROCESSING
DAC
CHANNEL
CHANNEL
SW3
SW1
SW2
DAC
DAC
ANALOG
MATRIX
ANALOG
MATRIX
ANALOG
MATRIX
Main
Auxiliary
2
I
S1
2
S2
I
BUFFER
0/+3 dB
BUFFER
0/+3 dB
BUFFER
0/+3 dB
Line
SCART 1
SCART 2
MGK111
Fig.6 Audio signal flow diagram.
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
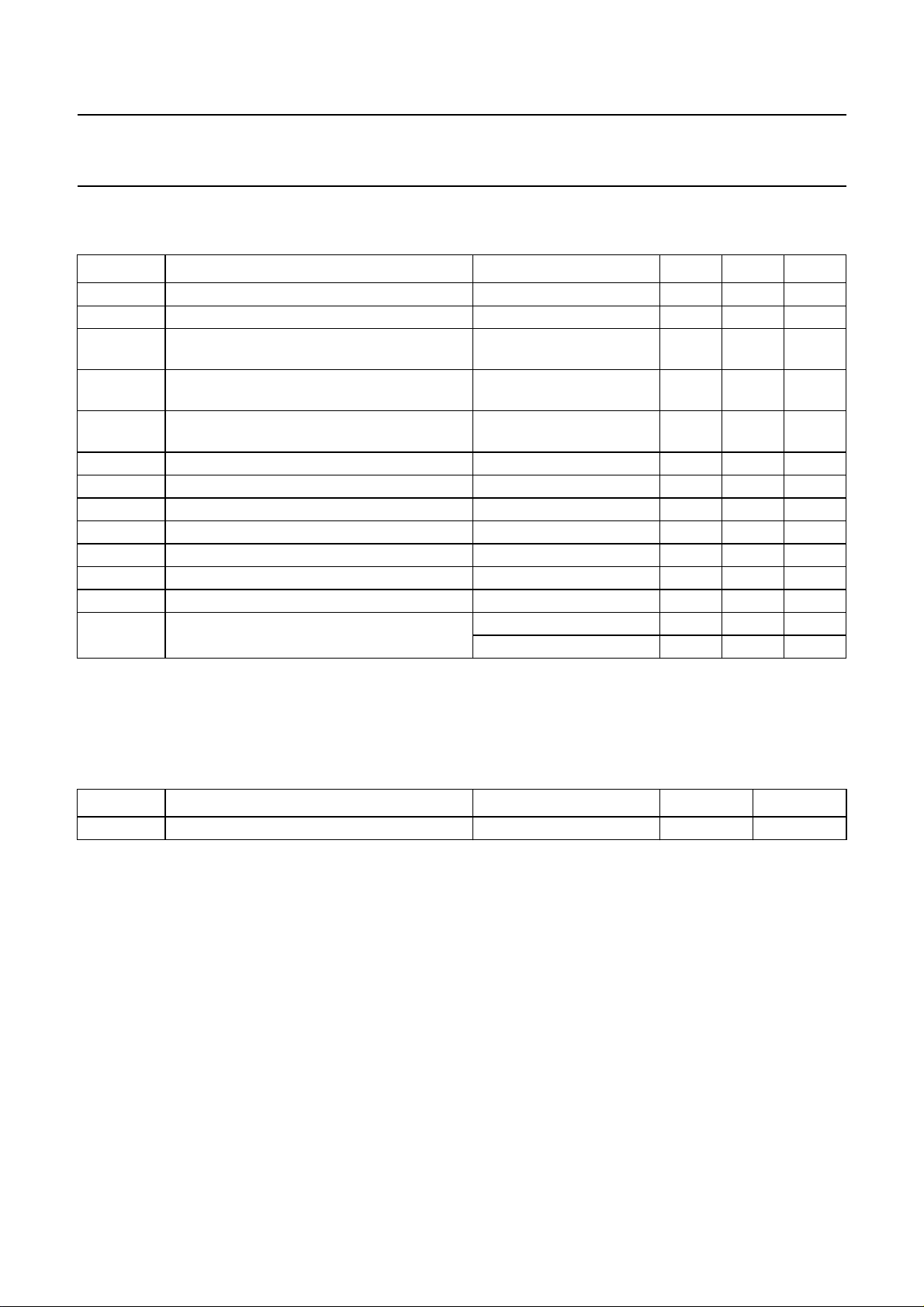
7 LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
DD
∆V
DD
I
IK
I
OK
I
O
I
, I
DDD
SSD
, I
I
DDA
SSA
I
lu(prot)
P/out power dissipation per output − 100 mW
P
tot
T
stg
T
amb
V
es
DC supply voltage −0.5 +6.5 V
voltage differences between two VDD pins − 550 mV
DC input clamping diode current VI< −0.5 V or
−±10 mA
VI>VDD+ 0.5 V
DC output clamping diode current
(output type 4 mA)
DC output source or sink current
VO< −0.5 V or
−±20 mA
VO>VDD+ 0.5 V
−0.5V<VO<VDD+ 0.5 V −±20 mA
(output type 4 mA)
DC VDD or VSS current per digital supply pin −±100 mA
DC VDD or VSS current per analog supply pin −±50 mA
latch-up protection 100 − mA
total power dissipation − 1.3 W
storage temperature −55 +125 °C
operating ambient temperature −20 +70 °C
electrostatic handling note 1 2000 − V
note 2 200 − V
Notes
1. Human body model: C = 100 pF; R = 1.5 kΩ.
2. Machine model: C = 200 pF; L = 0.75 µH; R = 0 Ω.
8 THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS VALUE UNIT
R
th j-a
thermal resistance from junction to ambient in free air 31 K/W
1998 Feb 13 20
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
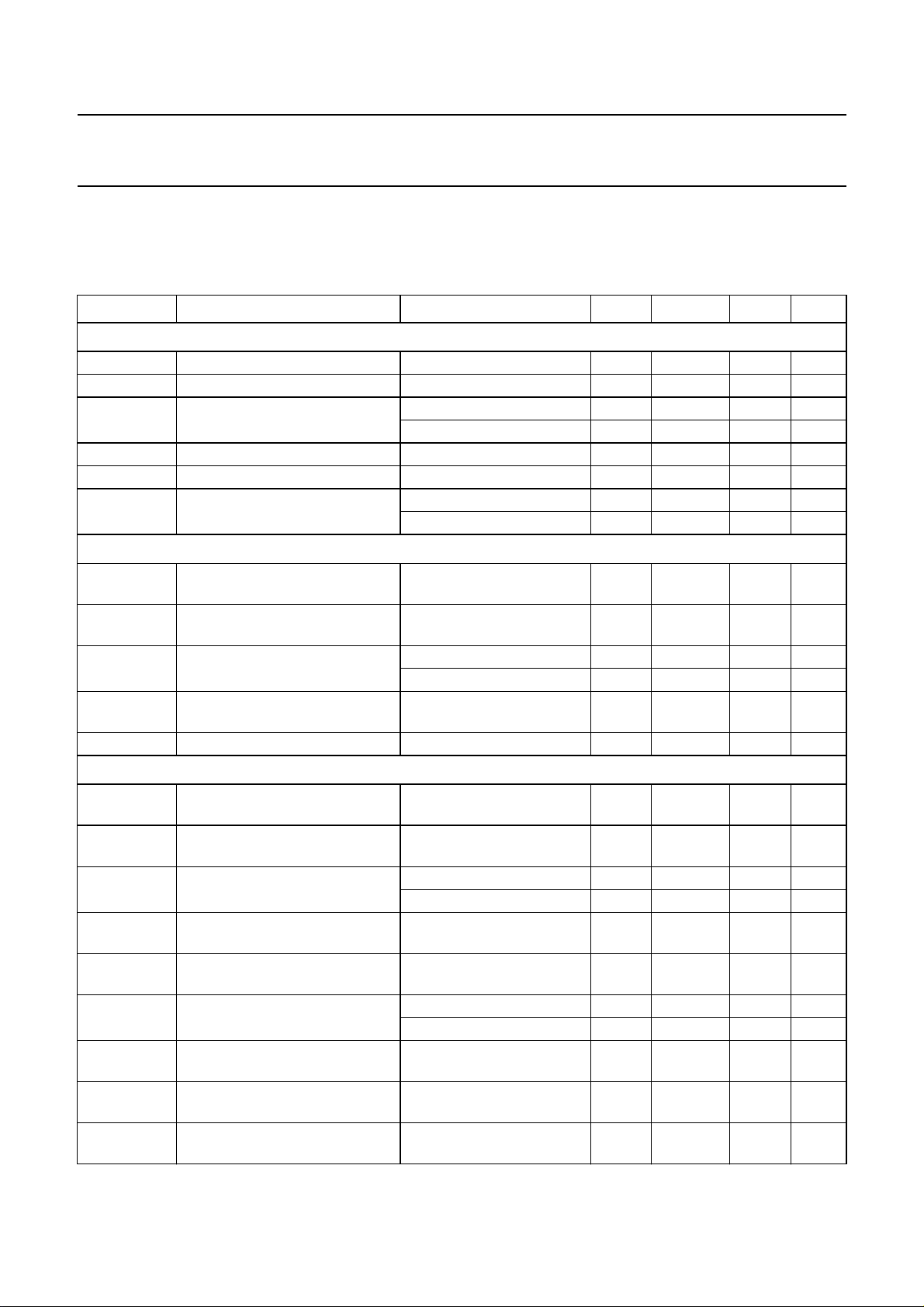
9 CHARACTERISTICS
V
=5V; T
DD
parameters in accordance with system A2; NICAM in accordance with
resistance for AF inputs; unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Digital supplies
V
DDD1
V
SSD1
I
DDD1
V
DDD2
V
SSD2
I
DDD2
Demodulator supplies and references
V
DDA1
V
SSA1
I
DDA1
V
ref1
I
ref1(sink)
Audio supplies and references
V
DDA2
V
SSA2
I
DDA2
V
DDA3
V
SSA3
I
DDA3
V
SSA4
V
SSG
V
ref2
=25°C; settings in accordance with B/G standard; FM deviation ±50 kHz; f
amb
“EBU specification”
= 1 kHz; FM sound
mod
; 1 kΩ measurement source
digital supply voltage 1 4.75 5.0 5.5 V
digital supply ground 1 − 0.0 − V
digital supply current 1 V
=5.5V 6580 95mA
DDD1
V
=5.0V 5570 85mA
DDD1
digital supply voltage 2 4.75 5.0 5.5 V
digital supply ground 2 − 0.0 − V
digital supply current 2 V
analog supply voltage for
=5.5V 5065 80mA
DDD2
V
=5.0V 4555 65mA
DDD2
4.75 5.0 5.5 V
demodulator part
analog ground for demodulator
− 0.0 − V
part
analog supply current for
demodulator part
analog reference voltage for
V
=5.5V 2026 31mA
DDA
V
=5.0V 1924 28mA
DDA
referenced to V
DDA1/VSSA1
35 50 65 %
demodulator part
V
sink current 170 220 260 µA
ref1
analog supply voltage for audio
4.75 5.0 5.5 V
ADC part
analog ground for audio ADC
− 0.0 − V
part
analog supply current for audio
ADC part
analog supply voltage for audio
V
= 5.5 V 11 14 17 mA
DDA
V
=5.0V 1013 16mA
DDA
4.75 5.0 5.5 V
DAC part
analog ground for audio DAC
− 0.0 − V
part
analog supply current for audio
DAC part
analog ground for operational
V
= 5.5 V; digital silence 9 12 14 mA
DDA
V
= 5.0 V; digital silence 8 11 13 mA
DDA
− 0.0 − V
amplifier
ground, guard rings for
− 0.0 − V
analog-to-digital circuitry
reference voltage for audio
referenced to V
DDA2/VSSA2
− 50 − %
ADCs
1998 Feb 13 21
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
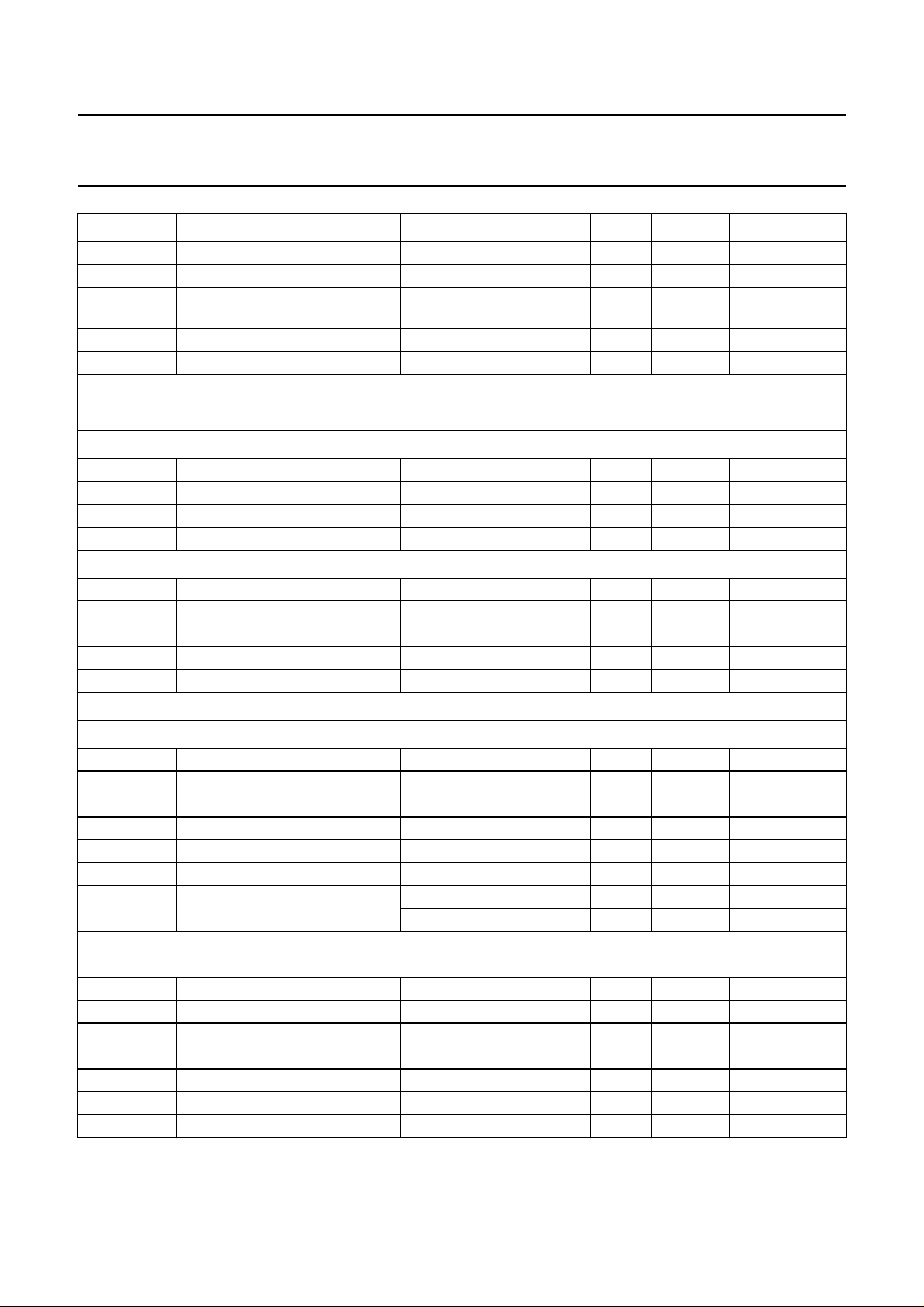
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Z
Vref2-VDDA2
Z
Vref2-VSSA2
V
ref3
Z
Vref3-VDDA3
Z
Vref3-VSSA3
Digital inputs and outputs
I
NPUTS
CMOS level input, high drive, pull-down (pins TEST1 and TEST2)
V
IL
V
IH
C
i
Z
i
CMOS level input, hysteresis, high drive, pull-up (pin CRESET)
V
IL
V
IH
V
hys
C
i
Z
i
INPUTS/OUTPUTS
impedance V
impedance V
reference voltage for audio DAC
ref2
ref2
to V
to V
DDA2
SSA2
referenced to V
DDA3/VSSA3
− 20 − kΩ
− 20 − kΩ
− 50 − %
and operational amplifier
impedance V
impedance V
ref3
ref3
to V
to V
DDA3
SSA3
− 20 − kΩ
− 20 − kΩ
LOW level input voltage −− 1.6 V
HIGH level input voltage 3.0 −−V
input capacitance −− 10 pF
input impedance − 50 − kΩ
LOW level input voltage −− 1.6 V
HIGH level input voltage 3.0 −−V
hysteresis voltage − 0.33V
DDD
− V
input capacitance −− 10 pF
input impedance − 50 − kΩ
I2C-bus level input with Schmitt trigger, open-drain output stage (pins SCL and SDA)
V
IL
V
IH
V
HYS
I
LI
C
i
V
OL
C
L
LOW level input voltage −− 1.6 V
HIGH level input voltage 3.0 −−V
hysteresis voltage − 0.33V
DDD
− V
input leakage current −− ±10 µA
input capacitance −− 10 pF
LOW level output voltage −− 0.5 V
load capacitance active pull-up −− 400 pF
passive pull-up −− 200 pF
TTL/CMOS level, high drive, 4 mA 3-state output stage, pull-up (pins PCLK, NICAM, ADDR1, ADDR2, P1, P2, SCK,
WS, SDO1, SDO2, SDI1 and SDI2)
V
IL
V
IH
C
i
V
OL
V
OH
C
L
Z
i
LOW level input voltage −− 0.8 V
HIGH level input voltage 2.0 −−V
input capacitance −− 10 pF
LOW level output voltage IOL=3mA −− 0.5 V
HIGH level output voltage IOH= −3 mA 2.9 −−V
load capacitance active pull-up −− 50 pF
input impedance − 50 − kΩ
1998 Feb 13 22
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
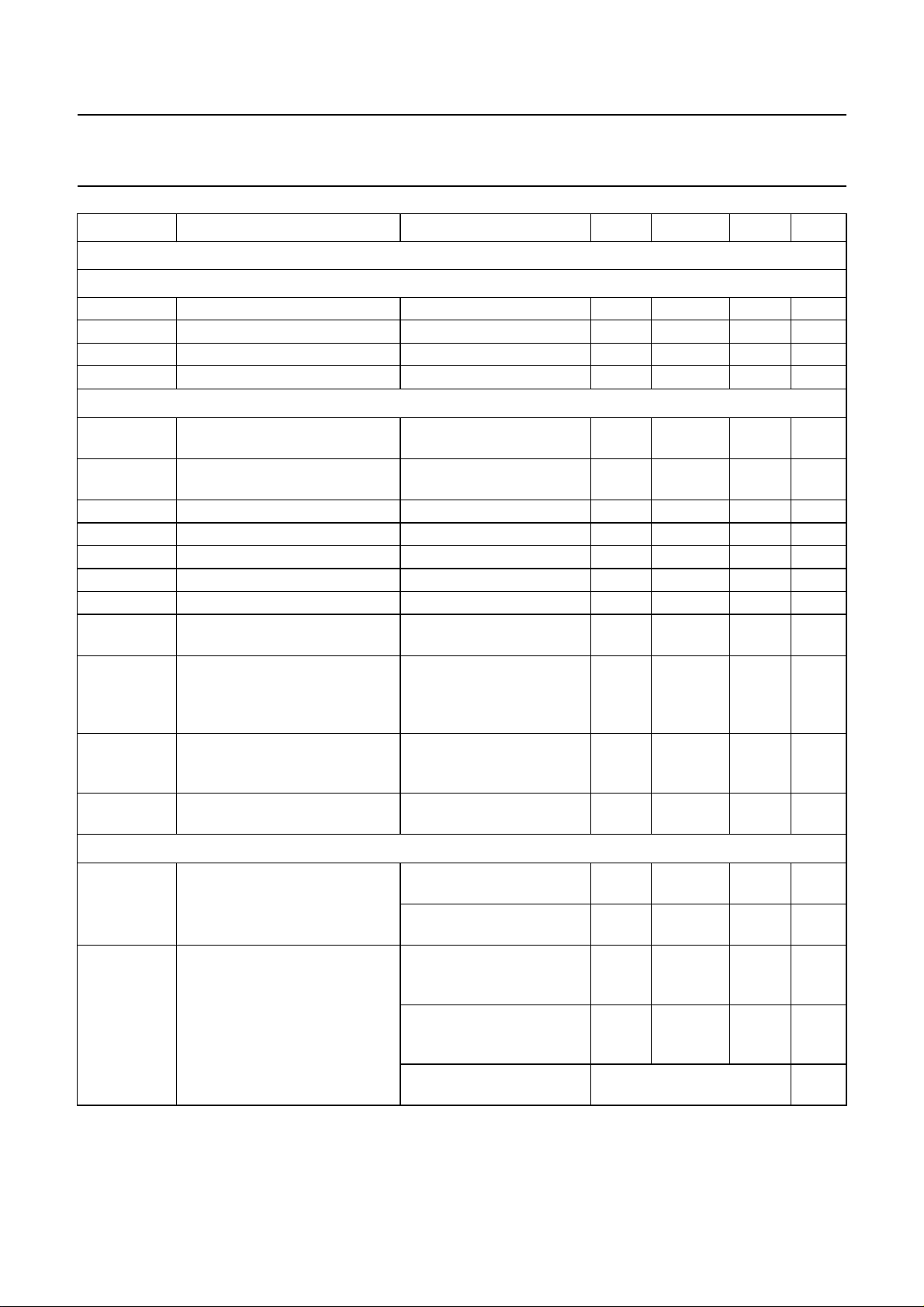
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
OUTPUTS
4 mA 3-state output stage (pin SYSCLK)
V
OL
V
OH
C
L
I
LIZ
SIF1 and SIF2 analog inputs
V
SIFmax(rms)
V
SIFmin(rms)
AGC AGC range − 21 − dB
f
i
R
i
C
i
∆f
FM
∆f
FM(FS)
C/N
FM
C/N
N
α
ct
LOW level output voltage IOL=2mA −− 0.5 V
HIGH level output voltage IOH= −2 mA 2.9 −−V
load capacitance −− 50 pF
3-state leakage current Vi= 0 to V
maximum composite SIF input
DDD
−− ±10 µA
− 250 − mV
voltage (RMS value)
minimum composite SIF input
− 21 − mV
voltage (RMS value)
input frequency 4 − 9.2 MHz
input resistance 10 13 16 kΩ
input capacitance − 7.5 11 pF
FM deviation B/G standard; THD < 1% 100 −−kHz
FM deviation full-scale level terrestrial FM; level adjust
150 −−kHz
0dB
FM carrier C/Nc ratio NFM bandwidth = 6 MHz;
white noise for
S/N = 40 dB;
“CCIR468”
− 77 −
;
dB
FM
------------- Hz
quasi peak
NICAM carrier C/Nc ratio Nc bandwidth = 6 MHz;
bit error rate = 10−3;
white noise
crosstalk attenuation input
fi= 4 to 9.2 MHz 50 −−dB
− 66 −
dB
----------
Hz
N
channel
Demodulator performance
THD + N total harmonic distortion plus
noise
from FM source to any
output; Vo= 1 V (RMS)
from NICAM source to any
output; V
= 1 V (RMS)
o
S/N signal-to-noise ratio SC1 from FM source to any
output; V
= 1 V (RMS),
o
TIMPOL bit HIGH
SC2 from FM source to any
output; V
= 1 V (RMS),
o
TIMPOL bit HIGH
NICAM source;
= 1 V (RMS)
V
o
1998 Feb 13 23
− 0.3 0.5 %
− 0.1 0.3 %
61 65 − dB
57 60 − dB
NICAM in accordance with
“EBU specification”
; note 2
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
B
−3
α
ct
α
cs(stereo)
α
AM
DEP
D
S/N
AM
IDENTIFICATION FOR FM SYSTEMS
mod
p
C/N
p
hys
tun
f
ident
t
ident(on)
t
ident(off)
−3 dB bandwidth from FM source to any
14.5 15 − kHz
output
from NICAM source to any
14.5 15 − kHz
output
crosstalk attenuation from SIF1 or SIF2 to any
65 70 − dB
output
stereo channel separation 40 45 − dB
AM suppression for FM AM: 1 kHz,
50 −−dB
30% modulation; reference:
1 kHz, 50 kHz deviation
de-emphasis 50 µs, 60 µs, 75 µs, J17,
adaptive de-emphasis
AM demodulation SIF level 100 mV (RMS);
− 36 − dB
54% AM; 1 kHz AF;
“CCIR468”
; quasi peak
pilot modulation for identification 25 50 75 %
pilot sideband C/N for
identification start
− 32 −
dB
------ Hz
hysteresis −− 2dB
identification window B/G stereo
slow mode 116.85 − 118.12 Hz
medium mode 116.11 − 118.89 Hz
fast mode 114.65 − 120.46 Hz
B/G dual
slow mode 273.44 − 274.81 Hz
medium mode 272.07 − 276.20 Hz
fast mode 270.73 − 277.60 Hz
total identification time ON slow mode −− 2s
medium mode −− 1s
fast mode −− 0.5 s
total identification time OFF slow mode −− 2s
medium mode −− 1s
fast mode −− 0.5 s
Analog audio inputs
M
ONO INPUT
V
i(nom)(rms)
nominal level input voltage
note 3 − 500 − mV
(RMS value)
V
i(clip)(rms)
clipping level input voltage
THD < 3%; note 4 1250 1400 − mV
(RMS value)
R
i
input resistance note 4 28 35 42 kΩ
1998 Feb 13 24
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
SCART AND EXTERNAL INPUTS
V
i(nom)(rms)
V
i(clip)(rms)
R
i
Analog audio outputs
L
OUDSPEAKER (MAIN) AND HEADPHONE (AUXILIARY) OUTPUTS
V
o(clip)(rms)
R
o
R
L(AC)
R
L(DC)
C
L
V
offset(DC)
α
mute
G
ro(main,aux
PSRR
main,aux
SCART OUTPUTS AND LINE OUTPUT
V
o(nom)(rms)
V
o(clip)(rms)
R
o
R
L(AC)
R
L(DC)
C
L
V
offset(DC)
α
mute
nominal level input voltage at
input pin (RMS value)
−3 dB divider with external
15 kΩ resistor;
− 350 − mV
notes 3 and 5
clipping level input voltage at
input pin (RMS value)
−3 dB divider with external
15 kΩ resistor; THD < 3%;
1250 1400 − mV
notes 4 and 5
input resistance note 4 28 35 42 kΩ
clipping level output voltage
THD < 3% 1400 −−mV
(RMS value)
output resistance 150 250 375 Ω
AC load resistance 10 −−kΩ
DC load resistance 10 −−kΩ
output load capacitance − 10 12 nF
static DC offset voltage − 30 70 mV
mute suppression nominal input signal from
80 −−dB
any source; fi= 1 kHz;
note 3
) roll-off gain at 14.5 kHz for Main
from any source −3 −2 − dB
and Auxiliary channels
power supply ripple rejection for
Main and Auxiliary channels
f
= 70 Hz;
ripple
V
= 100 mV (peak);
ripple
C
=47µF;
Vref
40 45 − dB
signal from I2S-bus
nominal level output voltage
+3 dB amplification; note 3 − 500 − mV
(RMS value)
clipping level output voltage
THD < 3% − 1400 − mV
(RMS value)
output resistance 150 250 375 Ω
AC load resistance 10 −−kΩ
DC load resistance 10 −−kΩ
output load capacitance −− 2.5 nF
static DC offset voltage output amplifiers at +3 dB
− 30 50 mV
position
mute suppression nominal input signal from
80 −−dB
any source; fi= 1 kHz;
note 3
1998 Feb 13 25
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
B
line
PSRR
line
Audio performance
THD + N total harmonic distortion plus
S/N signal-to-noise ratio reference voltage
α
ct
α
cs
G
A
line bandwidth from SCART, external,
Auxiliary and mono
sources; −3 dB bandwidth
from DSP sources;
−3 dB bandwidth
power supply ripple rejection f
= 70 Hz;
ripple
V
= 100 mV (peak);
ripple
C
=47µF;
Vref
signal from I2S-bus
noise
V
fi= 1 kHz; bandwidth
i=Vo
= 1 V (RMS);
20 Hz to 15 kHz; note 1
from any analog audio
input to I
from I
2
S-bus
2
S-bus to any
analog audio output
SCART-to-SCART copy − 0.1 0.3 %
SCART-to-Main copy − 0.2 0.5 %
V
= 1.4 V (RMS);
o
fi= 1 kHz;
“CCIR468”
;
quasi peak; note 1
from any analog audio
input to I
from I
2
S-bus
2
S-bus to any
analog audio output
SCART-to-SCART copy 78 90 − dB
SCART-to-Main copy 73 77 − dB
crosstalk attenuation between any analog input
pairs; fi= 1 kHz
between any analog output
pairs; f
=10kHz
i
channel separation between left and right of
any input pair
between left and right of
any output pair
from SCART-to-SCART with
−3 dB input voltage divider
output amplifier in +3 dB
position;
R
=15kΩ±10%
ext
output amplifier in 0 dB
position;
R
=15kΩ±10%
ext
from external input to
=15kΩ±10%; note 1 −1.5 0 +1.5 dB
R
ext
loudspeaker
20 −−kHz
14.5 −−kHz
40 45 − dB
− 0.1 0.3 %
− 0.1 0.3 %
73 77 − dB
78 90 − dB
70 −−dB
65 −−dB
65 −−dB
60 −−dB
−1.5 0 +1.1 dB
−4.5 −3.0 −1.9 dB
1998 Feb 13 26
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
VCXO and clock generation
VCXO
Crystal input
C
i
V
bias(DC)
Crystal output
V
osc(p-p)
V
bias(DC)
G
m
C
o
CRYSTAL SPECIFICATION (FUNDAMENTAL MODE)
f
xtal
C
L
C
1
C
0
Φ
pull
R
R
R
N
∆T temperature range −20 +25 +70 °C
X
J
X
D
X
A
input capacitance −− 10 pF
DC bias voltage Ri= 100 kΩ 3.5 3.63 3.7 V
oscillation amplitude
− 1.4 − V
(peak-to-peak value)
DC bias voltage 2.0 2.4 2.8 V
mutual conductance at
24.576 MHz
16.6 17.6 18.8
mA
---------
V
output capacitance −− 10 pF
crystal frequency − 24.576 − MHz
load capacitance − 20 − pF
series capacitance − 20 − fF
parallel capacitance −− 7pF
pulling sensitivity CL changed from
18 to 16 pF
− 25 −
10
----------pF
6–
equivalent series resistance at nominal frequency −− 30 Ω
equivalent series resistance of
2R
−−Ω
R
unwanted mode
adjustment tolerance −− ±30 10
drift across temperature range −− ±30 10
ageing −− ±5
−6
−6
10
-----------
year
6–
1998 Feb 13 27

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital TV Sound Processor (DTVSP) TDA9875
Notes to the characteristics
1. ADC level adjust = +6 dB, all other level adjusts = 0 dB, if external −3 dB divider is used set output buffer gain to
+3 dB, tone control to 0 dB, AVL off and volume control to 0 dB.
2. Due to companding, the quantization noise of the NICAM system limits signal-to-noise ratio to 62 dB
(unweighted; RMS value).
3. Definition of nominal levels:
The full-scale level for analog audio signals is VFS= 1.4 V (RMS). The nominal level at the digital crossbar switch is
defined at −15 dB (full-scale).
a) Audio input nominal levels:
SCART: 350 mV (at pin); −12 dB (full-scale)
external, mono: 500 mV; −9 dB (full-scale)
b) FM/AM path nominal (maximum) levels:
system M: 15 kHz deviation; −23.7 dB (full-scale)
system B/G, D/K, I: 27 kHz deviation; −18.6 dB (full-scale)
SAT stereo (maximum): 50 kHz deviation; −13.3 dB (full-scale)
SAT mono (maximum): 85 kHz deviation; −8.7 dB (full-scale)
AM: 54% modulation; full-scale SIF ADC; −20 dB (full-scale)
c) NICAM path nominal (maximum) levels:
system B/G: −18.2 dB (full-scale)
system I: −22.8 dB (full-scale)
maximum level: 0.0 dB (full-scale).
4. If the supply voltage for the TDA9875 is switched off, because of the ESD protection circuitry, all audio input pins are
short-circuited. To avoid a short-circuit at the SCART inputs a 15 kΩ resistor (−3 dB divider) has to be used.
5. The SCART specification allows a signal level of up to 2 V (RMS). Because of signal handling limitations due to the
5 V supply voltage for the TDA9875, there is a need for fixed 3 dB attenuators at the SCART inputs. To achieve
SCART-to-SCART copies with 0 dB gain, there are +3 dB/0 dB amplifiers at the outputs of SCART 1 and SCART 2
and at the line output. The attenuator is realized by an internal resistor that works together with an external series
resistor as a voltage divider. With this voltage divider the maximum SCART input signal level of 2 V (RMS) is scaled
down to 1.4 V (RMS) at the input pin. To avoid clipping, the +3 dB gain must not be used if the SCART input signal
is larger than 1.4 V (RMS).
1998 Feb 13 28
 Loading...
Loading...