Philips TDA8547TS Datasheet

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA8547TS
2 × 0.7 W BTL audio amplifier with
output channel switching
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1997 Oct 14
File under Integrated Circuits, IC01
1998 Apr 01

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
2 × 0.7 W BTL audio amplifier with
output channel switching
FEATURES
• Selection between output channels
• Flexibility in use
• Few external components
• Low saturation voltage of output stage
• Gain can be fixed with external resistors
• Standby mode controlled by CMOS compatible levels
• Low standby current
• No switch-on/switch-off plops
• High supply voltage ripple rejection
• Protected against electrostatic discharge
• Outputs short-circuit safe to ground, V
load
• Thermally protected.
APPLICATIONS
and across the
CC
TDA8547TS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA8547TS is a two channel audio power amplifier
for an output power of 2 × 0.7 W with a 16 Ω load at a 5 V
supply. At a low supply voltage of 3.3 V an output power of
0.6 W with an 8 Ω load can be obtained. The circuit
contains two BTL amplifiers with a complementary
PNP-NPN output stage and standby/mute logic.
The operating condition of all channels of the device
(standby, mute or on) is externally controlled by the
MODE pin. With the SELECT pin one of the output
channels can be switched in the standby condition. This
feature can be used for loudspeaker selection and also
reduces the quiescent current consumption.
When only one channel is used the maximum output
power is 1.2 W.
• Telecommunication equipment
• Portable consumer products
• Personal computers
• Motor-driver (servo).
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
CC
I
q
I
stb
P
o
THD total harmonic distortion P
supply voltage 2.2 5 18 V
quiescent current VCC= 5 V; 2 channels − 15 22 mA
= 5 V; 1 channel − 812mA
V
CC
standby current −−10 µA
output power
two channels THD = 10%; R
THD = 10%; R
one channel THD = 10%; R
THD = 10%; R
= 0.4 W − 0.15 − %
o
=8Ω; VCC= 3.3 V 0.5 0.6 − W
L
=16Ω; VCC= 5 V 0.6 0.7 − W
L
=8Ω; VCC=5V 1 1.2 − W
L
=4Ω; VCC= 3.3 V 1 1.2 − W
L
SVRR supply voltage ripple rejection 50 −−dB
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PACKAGE
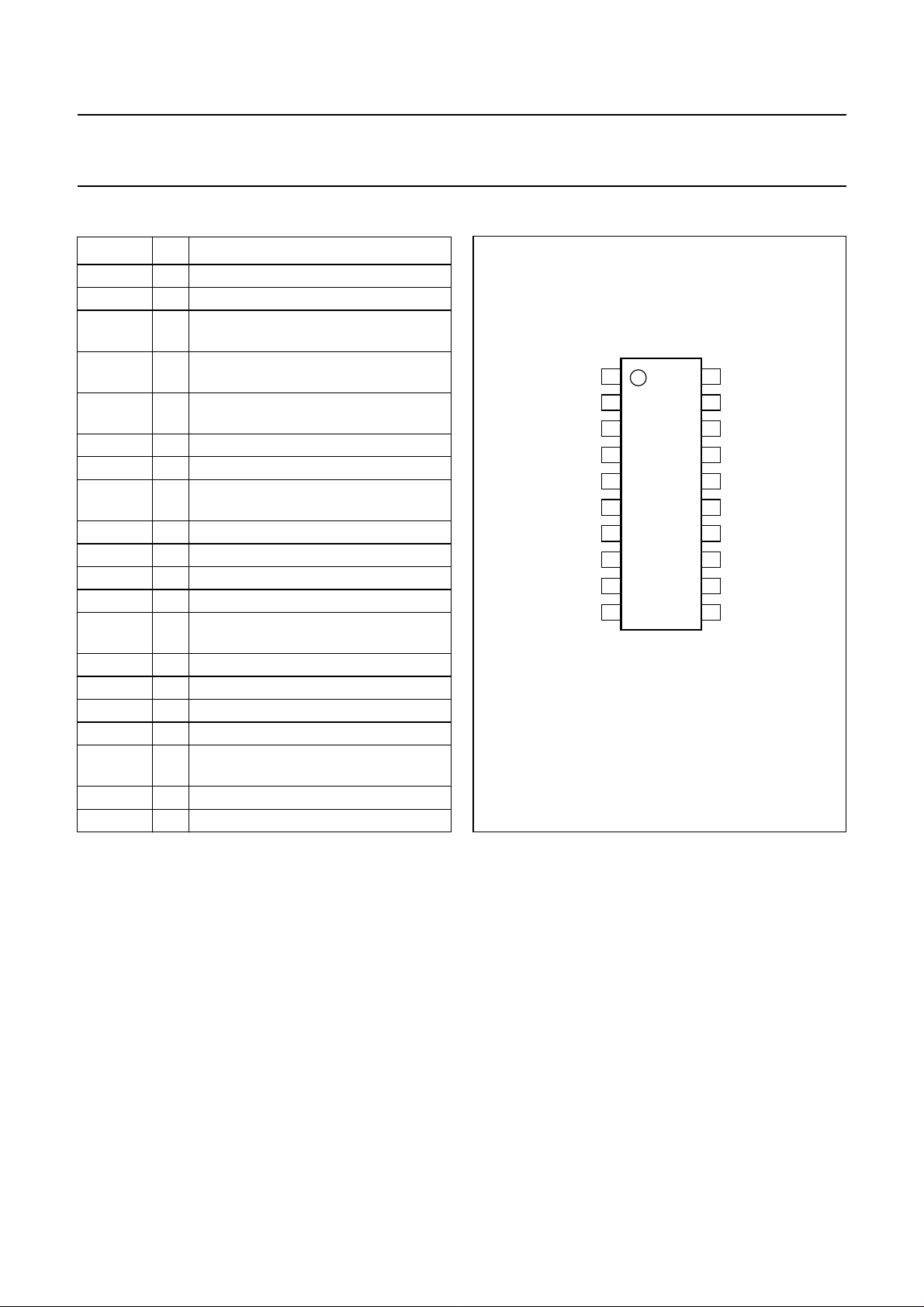
TDA8547TS SSOP20 plastic shrink small outline package; 20 leads; body width 4.4 mm SOT266-1
1998 Apr 01 2

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
2 × 0.7 W BTL audio amplifier with
output channel switching
BLOCK DIAGRAM
handbook, full pagewidth
IN1−
IN1+
17
16
V
CC1
−
−
+
20 kΩ
TDA8547TS
V
V
CC1
CC2
11
20
18
OUT1−
R
R
−
−
+
3
OUT1+
IN2−
IN2+
SVRR
MODE
SELECT
n.c.
14
15
5
4
6
2, 7, 9, 12, 19
5
20 kΩ
STANDBY/MUTE LOGIC
−
−
+
V
CC2
20 kΩ
20 kΩ
STANDBY/MUTE LOGIC
TDA8547TS
R
R
−
−
+
GND1
13
8
110
GND2
OUT2−
OUT2+
MGK984
Fig.1 Block diagram.
1998 Apr 01 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
2 × 0.7 W BTL audio amplifier with
output channel switching
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
GND1 1 ground, channel 1
n.c. 2 not connected
OUT1+ 3 positive loudspeaker terminal,
channel 1
MODE 4 operating mode select (standby, mute,
operating)
SVRR 5 half supply voltage, decoupling ripple
rejection
SELECT 6 input for selection of operating channel
n.c. 7 not connected
OUT2+ 8 positive loudspeaker terminal,
channel 2
n.c. 9 not connected
GND2 10 ground, channel 2
V
CC2
n.c. 12 not connected
OUT2− 13 negative loudspeaker terminal,
IN2− 14 negative input, channel 2
IN2+ 15 positive input, channel 2
IN1+ 16 positive input, channel 1
IN1− 17 negative input, channel 1
OUT1− 18 negative loudspeaker terminal,
n.c. 19 not connected
V
CC1
11 supply voltage, channel 2
channel 2
channel 1
20 supply voltage, channel 1
handbook, halfpage
GND1
1
n.c.
2
OUT1+
SELECT
OUT2+
MODE
SVRR
n.c.
n.c.
GND2
3
4
5
TDA8547TS
6
7
8
9
10
MGK998
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
TDA8547TS
V
20
CC1
19
n.c.
18
OUT1−
17
IN1−
16
IN1+
15
IN2+
IN2−
14
OUT2−
13
n.c.
12
V
11
CC2
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA8547TS is a 2 × 0.7 W BTL audio power amplifier
capable of delivering 2 × 0.7 W output power to a 16 Ω
load at THD = 10% using a 5 V power supply. Using the
MODE pin the device can be switched to standby and
mute condition. The device is protected by an internal
thermal shutdown protection mechanism. The gain can be
set within a range from 6 to 30 dB by external feedback
resistors.
Power amplifier
The power amplifier is a Bridge-Tied Load (BTL) amplifier
with a complementary PNP-NPN output stage.
The voltage loss on the positive supply line is the
saturation voltage of a PNP power transistor, on the
negative side the saturation voltage of a NPN power
1998 Apr 01 4
transistor. The total voltage loss is <1 V and with a 5 V
supply voltage and a 16 Ω loudspeaker an output power of
0.7 W can be delivered, when two channels are operating.
If only one channel is operating then an output power of
1.2 W can be delivered (5 V, 8 Ω).
MODE pin
The whole device (both channels) is in the standby mode
(with a very low current consumption) if the voltage at the
MODE pin is >(V
− 0.5 V), or if this pin is floating. At a
CC
MODE voltage level of less than 0.5 V the amplifier is fully
operational. In the range between 1.5 V and V
CC
− 1.5 V
the amplifier is in mute condition. The mute condition is
useful to suppress plop noise at the output caused by
charging of the input capacitor.

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
2 × 0.7 W BTL audio amplifier with
output channel switching
SELECT pin
If the voltage at the SELECT pin is in the range between
1.5 V and VCC− 1.5 V, or if it is kept floating, then both
channels can be operational. If the SELECT pin is set to a
LOW voltage or grounded, then only channel 2 can
operate and the power amplifier of channel 1 will be in the
standby mode. In this case only the loudspeaker at
channel 2 can operate and the loudspeaker at channel 1
will be switched off. If the SELECT pin is set to a
HIGH level or connected to VCC, then only channel 1 can
operate and the power amplifier of channel 2 will be in the
standby mode. In this case only the loudspeaker at
channel 1 can operate and the loudspeaker at channel 2
will be switched off. Setting the SELECT pin to a LOW or
Table 1 Control pins MODE and SELECT versus status of output channels
Voltage levels at control pins at V
= 5 V; for other supply voltages see Figs. 14 and 15.
P
CONTROL PIN
MODE SELECT CHANNEL 1 CHANNEL 2
(1)
HIGH
HVP
HVP
HVP
HVP
LOW
(4)
(4)
(4)
/NC
(4)
(5)
/LOW
/LOW
/LOW
(2)
(5)
(5)
(5)
HVP
HVP
HIGH
HVP
LOW
a HIGH voltage results in a reduction of quiescent current
consumption by a factor of approximately 2.
Switching with the SELECT pin during operating is not
plop-free, because the input capacitor of the channel
which is coming out of standby needs to be charged first.
For plop-free channel selecting the device has first to be
set in mute condition with the MODE pin (between 1.5 V
and V
− 1.5 V), then set the SELECT pin to the new
CC
level, after a delay set the MODE pin to a LOW level.
The delay needed depends on the values of the input
capacitor and the feedback resistors. Time needed is
approx. 10 × C1 × (R1 + R2), so approximately 0.6 s. for
the values in Fig.4.
(3)
X
(4)
(2)
/NC
(4)
(2)
/NC
(1)
(4)
(2)
/NC
(5)
TDA8547TS
STATUS OF OUTPUT
CHANNEL
standby standby 0
mute mute 15
on on 15
mute/on standby 8
mute/on mute/on 15
standby mute/on 8
TYP. I
(mA)
q
Notes
1. HIGH = V
pin>VCC
− 0.5 V.
2. NC = not connected or floating.
3. X = don’t care.
4. HVP = 1.5 V < V
5. LOW = V
pin
< 0.5 V.
pin<VCC
− 1.5 V.
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
CC
V
I
I
ORM
T
stg
T
amb
V
Psc
P
tot
supply voltage operating −0.3 +18 V
input voltage −0.3 VCC+ 0.3 V
repetitive peak output current − 1A
storage temperature −55 +150 °C
operating ambient temperature −40 +85 °C
AC and DC short-circuit safe voltage − 10 V
power dissipation − 1.1 W
1998 Apr 01 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
2 × 0.7 W BTL audio amplifier with
TDA8547TS
output channel switching
QUALITY SPECIFICATION
In accordance with
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS VALUE UNIT
R
th(j-a)
“SNW-FQ-611-E”
.
thermal resistance from junction to ambient in free air 110 K/W
2.0
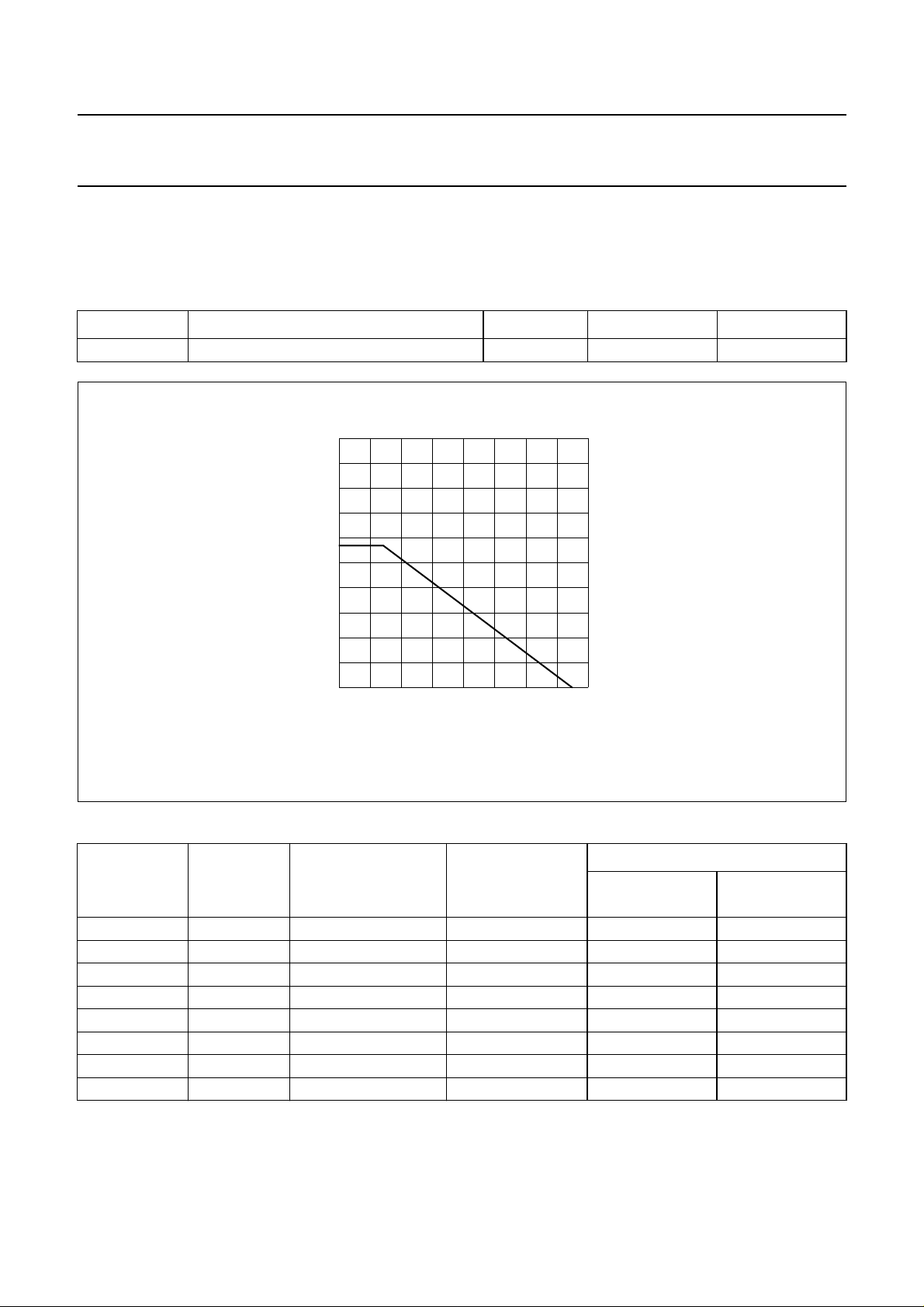
handbook, halfpage
P
(W)
1.6
1.2
0.8
MGK987
0.4
0
0 40 80 160
120
T
amb
(°C)
Fig.3 Power derating curve.
Table 2 Maximum ambient temperature at different conditions
CONTINUOUS SINE WAVE DRIVEN
V
(V)
CC
R
(Ω)
L
APPLICATION
P
(W)
o
(1)
P
max
(W)
3.3 4 1 channel 1.2 0.58 86
3.3 4 2 channels 2 × 1.2 1.12 27
3.3 8 1 channels 0.6 0.3 117
3.3 8 2 channels 2 × 0.6 0.60 84
5 8 1 channel 1.2 0.67 76
5 8 2 channels 2 × 1.2 1.33 −
5 16 1 channel 0.7 0.35 112
5 16 2 channels 2 × 0.7 0.70 73
T
amb(max)
(°C)
Note
1. At THD = 10%.
1998 Apr 01 6
 Loading...
Loading...