Philips TDA8349A Datasheet
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA8349A
Multistandard IF amplifier and
demodulator
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
February 1991
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Multistandard IF amplifier and
TDA8349A
demodulator
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA8349A is a multistandard IF amplifier and demodulator with AGC and AFC functions for television receivers.
The device has a video recognition circuit and a video switch for internal or external video for full SCART applications.
FEATURES
• Full-range gain-controlled wideband IF amplifier up to 60 MHz
• Wide-band video amplifier with good linearity and a class AB output stage to ensure a very low output impedance
• Supply independent video output level
• Small second harmonic IF output
• AGC circuit which operates on top sync level (negative modulation) or on white level (positive modulation) or on top
level (MAC) with reduced sensitivity for high sound carriers
• AFC circuit with an internal 90° phase shift circuit, a sample-and-hold circuit for negatively modulated signals to reduce
video dependent AFC information and an analog or digital output
• Video recognition possibility based on horizontal pulse duty cycles
• Video switch for selection of internal or external video signals
• Wide supply voltage range and ripple rejection
• Requires few external components
• Tuner AGC output for npn and pnp tuners
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
14-17
I
14
V
1-2(RMS)
G
v
V
11-17(p-p)
supply voltage (pin 14) 10.2 12 13.2 V
supply current (pin 14) Vi= 10 mV 40 55 65 mA
IF input sensitivity (RMS value) − 50 80 µV
IF gain control range 66 72 − dB
video output voltage (peak-
1.7 1.9 2.1 V
to-peak value)
S/N signal-to-noise ratio V
V
8-17(p-p)
AFC output voltage swing
=10mV 54 61 − dB
i
10 − 11 V
(peak-to-peak value)
ORDERING AND PACKAGE INFORMATION
EXTENDED
TYPE NUMBER
PINS PIN POSITION MATERIAL CODE
PACKAGE
TDA8349A 20 DIL plastic SOT146
Note
1. SOT146-1; 1996 November 29.
(1)
February 1991 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Multistandard IF amplifier and demodulator TDA8349A
February 1991 3
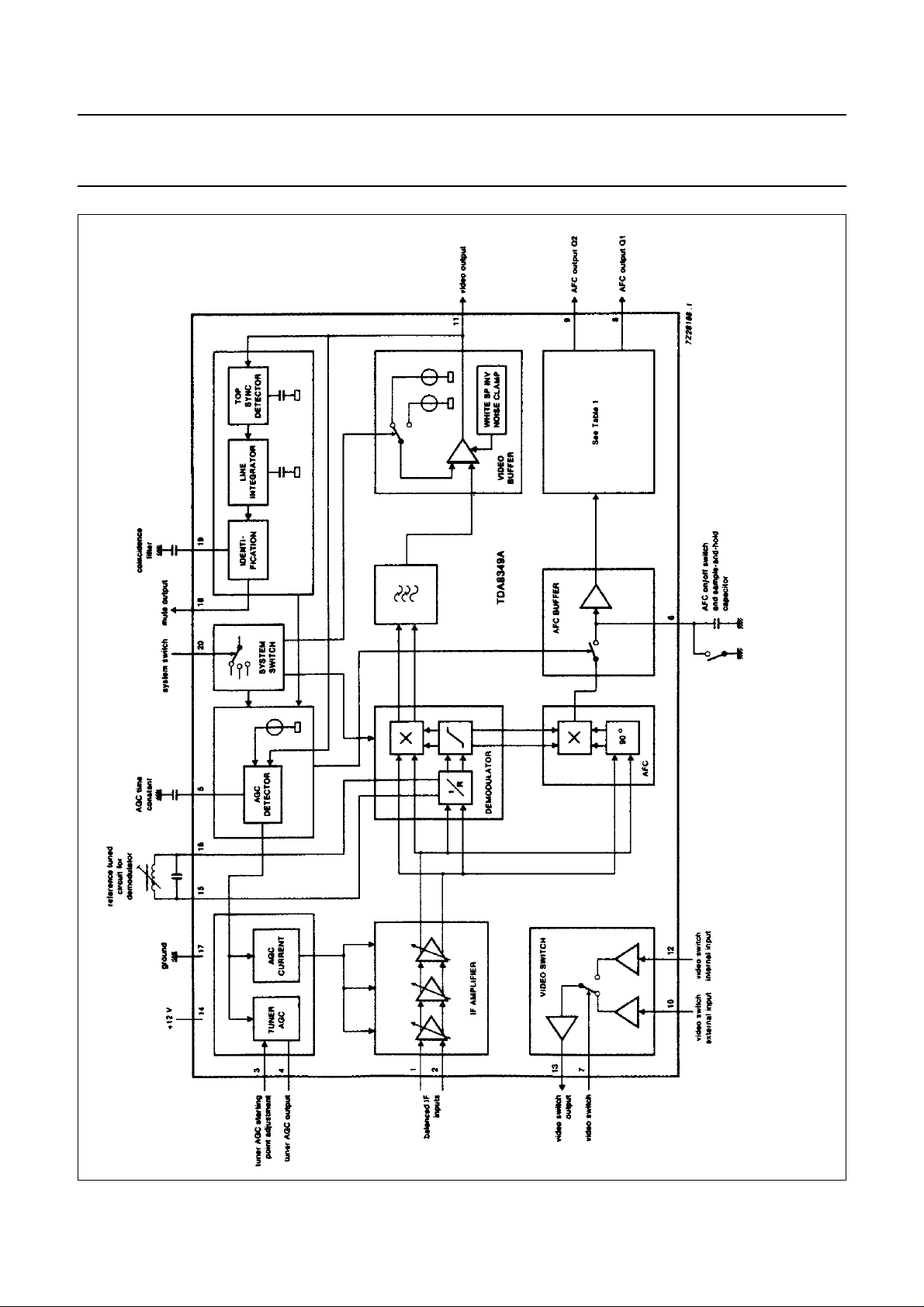
Fig.1 Block diagram.

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Multistandard IF amplifier and demodulator TDA8349A
PINNING
PIN DESCRIPTION
1,2 balanced IF inputs
3 tuner AGC starting point adjustment
4 tuner AGC output
5 AGC time constant
6 AFC on/off switch and sample-and-hold capacitor
7 video switch
8 AFC output Q1
9 AFC output Q2
10 video switch external input
11 video output
12 video switch internal input
13 video switch output
14 positive supply voltage
15,16 reference tuned circuit for demodulator
17 ground
18 mute output
19 coincidence filter
20 system switch
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
General
The IC consists of the following parts as illustrated in Fig.1:
• Gain controlled video IF amplifier
• Quasi-synchronous demodulator
• Video amplifier/buffer with white spot clamp/inverter and
noise clamp
• AGC circuit which operates either on top sync level
(negative modulation) or on white level (positive
modulation) or on top level (MAC)
• AFC circuit with sample-and-hold circuit for negatively
modulated signals, on/off switch and a digital or analog
output (switchable)
• Circuit for switching between positive and negative
modulation
• Video recognition circuit for sound muting and tuning
indication
• Video switch which facilitates selection between two
different video signals, with different gain settings
IF amplifier
The IF amplifier consists of three AC coupled differential
gain stages with adjustable feedback in the emitter. The
AC coupling allows simple biasing, cascades can be used
and no DC feedback is required. This provides a control
range above 70 dB with good linearity. The minimum input
signal to obtain the nominal output amplitude is
50 µV RMS.
Demodulator
The demodulator is a quasi-synchronous circuit that
employs passive carrier regeneration and a tuned circuit
for selectivity. The regenerated carrier signal is limited by
a clamping circuit before it is fed to the demodulator.
Switching between positive and negative modulation is
achieved by the system switch which provides currents to
the demodulator in a positive or negative direction.
Video amplifier
The video amplifier based on the feedback principle
improves the linearity of the video output buffer. It has an
internal bandgap reference to ensure a stable video output
at different supply voltages and temperatures. This
February 1991 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Multistandard IF amplifier and demodulator TDA8349A
bandgap also reduces the supply ripple on the video
output to values less than −30 dB. The video amplifier has
a typical bandwidth of 10 MHz which allows application for
all new video standards with bandwidths of up to 10 to
12 MHz. The video output signal has an amplitude of
2 V (p-p). White spot protection comprises a white spot
clamp system combined with a delayed-action inverter
which is also highly resistant to high sound carriers. A
switchable DC shift for positively modulated IF signals
ensures correct signal handling. This switching is obtained
via pin 20, which is the same pin used for switching the
demodulation polarity in the demodulator.
The circuit also has a noise clamp which prevents the
video output becoming less than ±400 mV below the top
sync level at noise peaks. The output buffer of the video
amplifier consists of a class A/B circuit which can handle
large source as well as large sink currents. This makes the
circuit more flexible in several applications with one or
more ceramic filters connected to this output buffer.
AGC control circuit
This converts the AGC detector voltage (pin 5) into a
current signal which controls the gain of the IF amplifier. It
also provides a tuner AGC control output from pin 4,
current limiting is incorporated to prevent internal damage.
The AGC starting point is adjusted by a voltage between 3
and 5 V for pnp tuners and between 7 and 9 V for npn
tuners via pin 3.
AGC circuit
A new AGC system has been designed for the AGC. It will
be a top sync-detector for negatively modulated signals
and a top white level AGC for positively modulated signals.
For optimal flexibility reasons the load and unload currents
of the AGC are chosen such that both, a relatively fast set,
as well as a set with a low tilt are possible for positive (L)
and negative (B/G) modulated signals. For this reason a tilt
ratio between positive (L) and negative (B/G) of
approximately 3:1 has been chosen. This means that in a
fast set the choice of a typical tilt for negatively modulated
signals of 2% will obtain a typical tilt for positively
modulated signals (L) of 6%. For a digital set which
requires a small tilt the choice of tilt can be a factor of 5 or
10 smaller by increasing the AGC capacitor.
The chosen AGC currents:
MODE UNLOAD CURRENT LOAD CURRENT TILT AT 2.2 µF
B/G 50 µA 1.5 mA typ. 0.5% (line tilt)
L 500 nA (note 1) 1.5 mA typ. 1.5% (field tilt)
MAC(positive) 200 nA 1.5 mA typ. 1.2% (frame tilt)
MAC(negative) 500 nA 1.5 mA typ. 1.5% (field tilt)
Note
1. As long as no signal has been identified by the identification detector the unload current will be 50 µA.
Switching between the first three modes can be achieved
by the system switch. This is a 3-level switch which when
grounded selects B/G; open or 5 V selects L, and with pin
20 connected to VCC selects positively modulated MAC.
The IC operates in a fourth mode if the identification
capacitor at pin 19 is connected to VCC, it can be used for
negatively modulated MAC.
During channel switching a situation can occur that
requires the AGC to increase the gain more than for
example 50 dB. If this increase of gain has to be done for
a positively modulated (L) signal, it will be achieved by the
500 nA load current and is therefore extremely slow.
Because the identification information can be used to
indicate that the signal is too small, in this event the
identification circuit will mute, it is possible to increase the
positive unload current to the same value as that used for
negatively modulated signals. This switching is fully
automatic and cannot be switched off.
AFC circuit
The AFC circuit consists of a demodulator stage which is
fed with signals 90° out of phase. A very accurate internally
realized 90° phase shift circuit makes it possible to use the
demodulator IF regenerator tuned circuit for tuning the
AFC circuit. To prevent video ripple on the AFC output
voltage a sample-and-hold circuit is used for negatively
modulated signals. The output signal of the demodulator is
sampled during sync level of the video signal and will be
stored with the aid of an external capacitor.
February 1991 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Multistandard IF amplifier and demodulator TDA8349A
This sample-and-hold circuit is not used in the L mode, but
it will function as a low-pass filter in this mode and
therefore also reduces the video dependency of the AFC.
A gain stage amplifies the voltage swing by 5 times. The
output of the AFC circuit will be an inverse analog output
on pin 8 when pin 9 is connected to a voltage above 8 V. If
pin 9 is connected to a voltage above 10 V the output will
be a normal analog output. Normally pins 8 and 9 together
unloaded during the sync pulse. The maximum voltage at
this internal capacitor is a value for the main frequency of
the video signal. By changing the value of an external
capacitor it is possible to influence the speed and
sensitivity of the recognition circuit. It is possible to gain
sensitivity performance at disturbed signals by increasing
the value of the external capacitor, however this will
reduce the speed of the identification circuit.
provide digital AFC information.
Video switch circuit
Video recognition circuit
For full scart functions it is necessary to implement a
second mute function for non-video signals in the whole
television concept. This is realized in this IF-IC. With an
internal sync separator and an internal integrator it is
possible to achieve a very sensitive identification circuit,
which measures the mean frequency of the input signal.
This is normally approximately 16 kHz. The integrator
The video switch also provides application for full SCART
functions. The circuit has two inputs, one output and a
control pin. The switch selects either internal or external
video signals. A × 2 gain stage for the external input
provides an equal output level for internal or external video
from the SCART. The crosstalk of the unwanted signal is
better than −50 dB and the total signal handling meets all
the requirements for SCART specifications.
capacitor will be loaded during the whole line time and
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum System (IEC 134)
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
P
T
T
14-17
tot
stg
amb
supply voltage (pin 14) −0.5 13.2 V
total power dissipation − 1.2 W
storage temperature range −25 +150 °C
operating ambient temperature range −25 + 75 °C
February 1991 6
 Loading...
Loading...