Philips TDA4671-V1 Datasheet

DATA SH EET
Product specification
Supersedes data of June 1993
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1996 Dec 11
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
TDA4671
Picture Signal Improvement (PSI)
circuit
1996 Dec 11 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Picture Signal Improvement (PSI) circuit TDA4671
FEATURES
• Luminance signal delay from 20 to 1100 ns (minimum
step 45 ns)
• Luminance signal peaking with symmetrical overshoots
selectable
• Selectable 2.6 or 5 MHz peaking centre frequency and
degree of peaking (−3, 0, +3 and +6 dB)
• Selectable noise reduction by coring
• Handles negative as well as positive colour-difference
signals
• Selectable Colour Transient Improvement (CTI) to
decrease the colour-difference signal transient times to
those of the high frequency luminance signals
• Selectable 5 or 12 V sandcastle input voltage
• All controls selected via the I
2
C-bus
• Timing pulse generation for clamping and delay time
control synchronized by sandcastle pulse
• Automatic luminance signal delay correction using a
control loop
• Luminance and colour-difference input signal clamping
with coupling capacitor
• 4.5 to 8.8 V supply voltage range
• Minimum of external components.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA4671 delays the luminance signal and improves
colour-difference signal transients. The luminance signal
can also be improved by peaking and noise reduction
(coring).
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
ORDERING INFORMATION
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
P
supply voltage (pins 1 and 5) 4.5 5 8.8 V
I
P(tot)
total supply current 31 41 52 mA
t
d(Y)
Y signal delay time 20 − 1130 ns
V
i(VBS)(p-p)
composite Y input signal (peak-to-peak value,
pin 16)
− 450 640 mV
V
i(CD)(p-p)
colour-difference input signal
(peak-to-peak value)
±(R − Y) on pin 3 − 1.05 1.48 V
±(R − Y) on pin 7 − 1.33 1.88 V
G
Y
gain of Y channel −−1−dB
G
CD
gain of colour-difference channel − 0 − dB
T
amb
operating ambient temperature 0 − 70 °C
TYPE
NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
TDA4671 DIP18 plastic dual in-line package; 18 leads (300 mil) SOT102-1
1996 Dec 11 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Picture Signal Improvement (PSI) circuit TDA4671
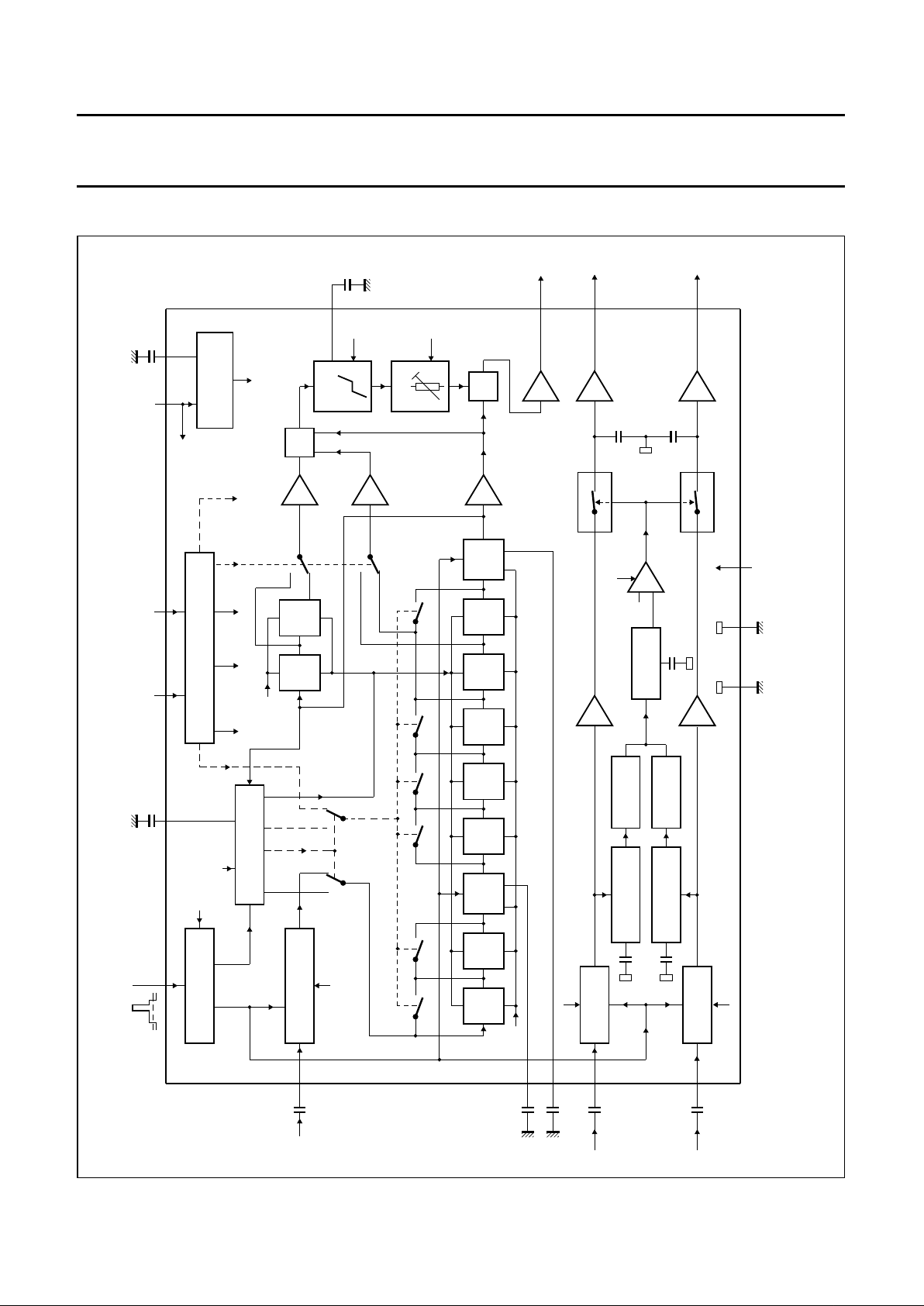
BLOCK DIAGRAM
handbook, full pagewidth
MED746
BLACK
LEVEL
CLAMP
180
ns
90
ns
45
ns
90
ns
100
ns
BLACK
LEVEL
CLAMP
450
ns
180
ns
control signal
100 nF13100 nF
14
10 nF
3
BLACK LEVEL
CLAMP
−(R − Y)
DIFFERENTIATOR
DIFFERENTIATOR
10 nF
7
BLACK LEVEL
CLAMP
−(B − Y)
V
ref
V
ref
V
ref
FULL-WAVE
RECTIFIER
FULL-WAVE
RECTIFIER
HIGH-PASS
FILTER
+1
−0.5
5 MHz
2.6 MHz
100
ns
90
ns
5 MHz
2.6 MHz
−0.5
V
ref
V
ref
DELAY TIME
CONTROL
BK
SANDCASTLE PULSE
DETECTOR
BLACK LEVEL
CLAMP
sandcastle
5 V/12 V
CTI
on/off
coring
on/off
peaking
frequency
degree of
peaking
I
2
C-BUS RECEIVER
9 10
Y delay
BK
BK, H + V
16
17
I
2
C-BUS
V
ref
V
ref
100 nF
Y
8 18 5
V
P2
= 5 to 8 V
100 nF
2
sandcastle
pulse
SDA
SCL
CORING
PEAKING
CORING
I
2
C-BUS
I
2
C-BUS
I
2
C-BUS
100
nF
100 nF
15
V
P1
= 5 to 8 V
V
ref
GENERATION
1
−(R − Y)
−(B − Y)
Y
11
12
4
6
storage
capacitors
analog switch
analog switch
V
T
comparator
TDA4671
+
+
Fig.1 Block diagram.
1996 Dec 11 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Picture Signal Improvement (PSI) circuit TDA4671
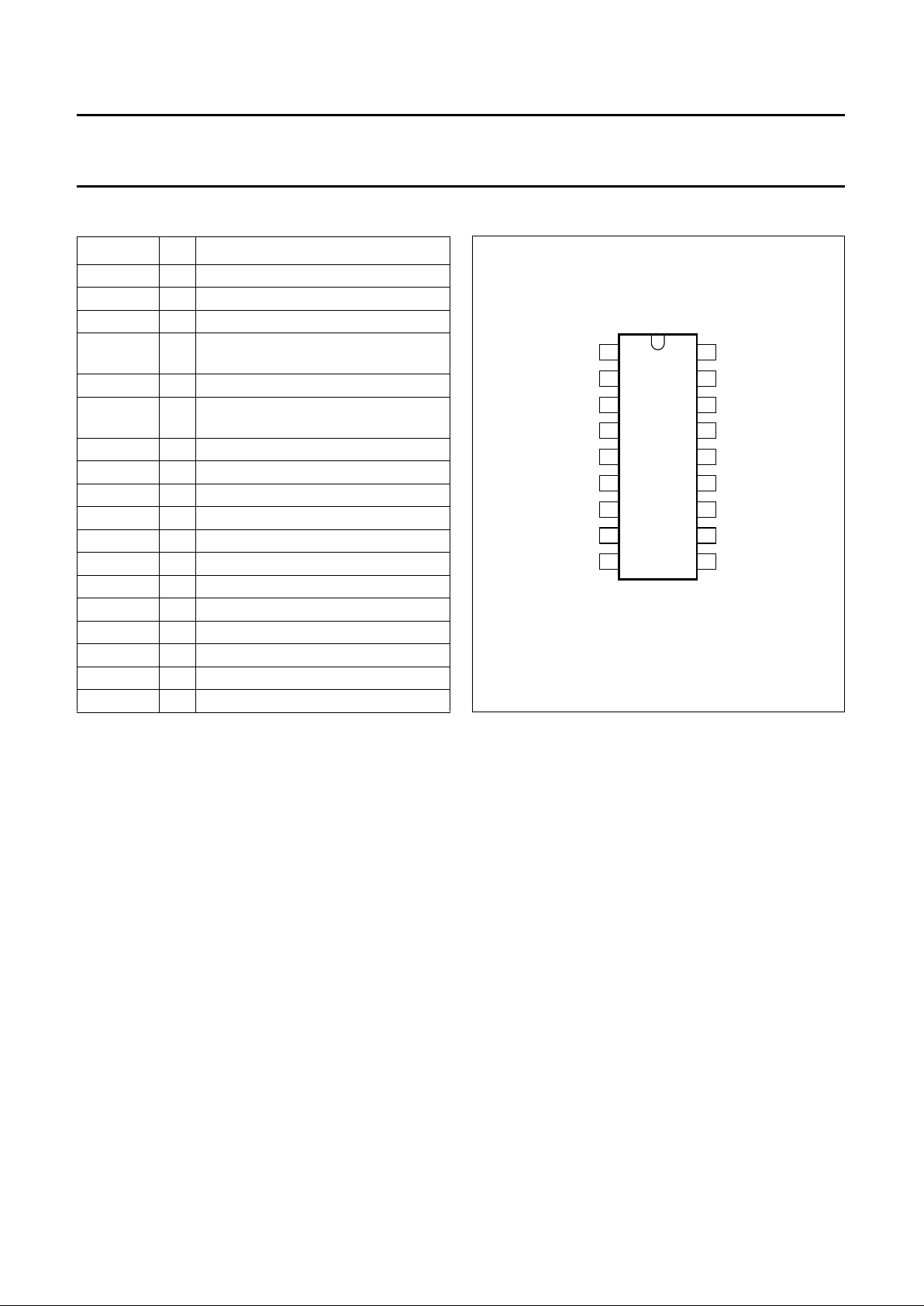
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
V
P1
1 positive supply voltage 1
C
DL
2 capacitor of delay time control
V
i(R − Y)
3 ±(R − Y) colour-difference input signal
V
o(R − Y)
4
±(R − Y) colour-difference output
signal
V
P2
5 positive supply voltage 2
V
o(B − Y)
6
±(B − Y) colour-difference output
signal
V
i(B − Y)
7 ±(B − Y) colour-difference input signal
GND2 8 ground 2 (0 V)
SDA 9 I
2
C-bus serial data input/output
SCL 10 I
2
C-bus serial clock input
C
COR
11 coring capacitor
V
oY
12 delayed luminance output signal
C
CLP1
13 black level clamping capacitor 1
C
CLP2
14 black level clamping capacitor 2
C
ref
15 capacitor of reference voltage
V
iY
16 luminance input signal
SAND 17 sandcastle pulse input
GND1 18 ground 1 (0 V)
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
handbook, halfpage
TDA4671
MED747
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
V
P1
V
P2
C
DL
GND2
SDA
V
i(R − Y)
V
o(R − Y)
V
o(B − Y)
V
i(B − Y)
GND1
SAND
V
iY
V
oY
C
ref
C
CLP2
C
CLP1
C
COR
SCL

1996 Dec 11 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Picture Signal Improvement (PSI) circuit TDA4671
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA4671 contains luminance signal processing and
colour-difference signal processing. The luminance signal
section comprises a variable, integrated luminance delay
line with luminance signal peaking and a noise reduction
by coring.
The colour-difference section consists of a transient
improvement circuit to decrease the rise and fall times of
the colour-difference signal transients. All functions and
parameters are controlled via the I2C-bus.
Y-signal path
The video and blanking signal is AC-coupled to the input
pin 16. Its black porch is clamped to a DC reference
voltage to ensure the correct operating range of the
luminance delay stage.
The luminance delay line consists of all-pass filter sections
with delay times of 45, 90, 100, 180 and 450 ns
(see Fig.1). The luminance signal delay is controlled via
the I
2
C-bus in steps of 45 ns in the range of 20 to 1100 ns,
this ensures that the maximum delay difference between
the luminance and colour-difference signals is ±22.5 ns.
An automatic luminance delay time adjustment in an
internal control loop (with the horizontal frequency as a
reference) is used to correct changes in the delay time,
due to component tolerances. The control loop is
automatically enabled between the burst key pulses of
lines 16 (330) and 17 (331) during the vertical blanking
interval. The control voltage is stored in capacitor C
DL
connected to pin 2.
The peaking section is using a transversal filter circuit with
selectable centre frequencies of 2.6 and 5.0 MHz.
It provides selectable degrees of peaking of −3, 0, +3 and
+6 dB and noise reduction by coring, which attenuates the
high-frequency noise introduced by peaking.
The output buffer stage ensures a low-ohmic VBS output
signal on pin 12 (<160 Ω). The gain of the luminance
signal path from pin 16 to pin 12 is unity.
An oscillation signal of the delay time control loop is
present on output pin 12 instead of the VBS signal. It is
present during the vertical blanking interval of the burst key
pulses in lines 16 (330) to 18 (332). This sync should not
be applied for synchronization.
Colour-difference signal paths
The colour-difference input signals (on pins 3 and 7) are
clamped to a reference voltage.
Each colour-difference signal is fed to a transient detector
and to an analog signal switch with an attached voltage
storage stage.
The transient detectors consist of differentiators and
full-wave rectifiers. The output voltages of both transient
detectors are added and then compared. The comparator
controls both following analog signal switches
simultaneously.
The analog signal switches are in open position at a
certain value of transient time; the held value (held by
capacitors) is then applied to the outputs. The switches
close to rapidly accept the actual signal levels at the end
of these transients. The improved transient time is
approximately 100 ns long independent of the input
transient time.
Colour-difference paths are independent of the input
signal polarity and have a nominal unity gain.
The CTI functions are switched on and off via the I
2
C-bus.
 Loading...
Loading...