Philips tda1319 DATASHEETS

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA1319T
DCC write amplifier (write 2)
Preliminary specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC01
April 1994
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DCC write amplifier (write 2) TDA1319T
FEATURES
• Bidirectional high current output
drivers
• Single point current setting
• Extra erase current for the auxiliary
channel
• Increased current for auxiliary data
• Low standby power consumption
• Short-circuit protection to ground
• Serial data input
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA1319T has been designed to
drive an inductive recording head
which is suitable for DCC (Digital
Compact Cassette) systems.
The bidirectional current outputs are
controlled by a two-wire serial bus.
The amplitude of the write current can
be set using an external resistor. The
circuit can be switched to the standby
mode to minimize supply current
consumption.
• Reduced RF emission due to slope
control of write current.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
V
I
DD
I
DDO
DD
DDO
supply voltage 4.75 5.0 5.5 V
supply voltage (write outputs) 4.75 5.0 5.5 V
supply current note 1 − 7.5 11 mA
supply current (write outputs) note 2 −−255 mA
note 3 −−365 mA
note 4 −−285 mA
I
sb
T
amb
total standby current note 5 − 23mA
operating ambient temperature −30 − +85 °C
Notes
1. 1 kΩ erase adjust resistor connected between pins 5 and 6, no load at pin 9.
2. Momentary maximum value during write data; see Table 1; IO= 225 mA.
3. Momentary maximum value during erase AUX; see Table 1 and Fig.5; resistor Re connected between pins 5 and 6
(see Fig.7).
4. Momentary maximum value during write AUX; see Table 1; IO= 255 mA.
5. Standby mode; see Table 1; Isb=IDD+I
DDO+Iclamp
.
ORDERING INFORMATION
EXTENDED TYPE
NUMBER
PINS PIN POSITION MATERIAL CODE
PACKAGE
TDA1319T 24 SO24L plastic SOT137-1
April 1994 2
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DCC write amplifier (write 2) TDA1319T
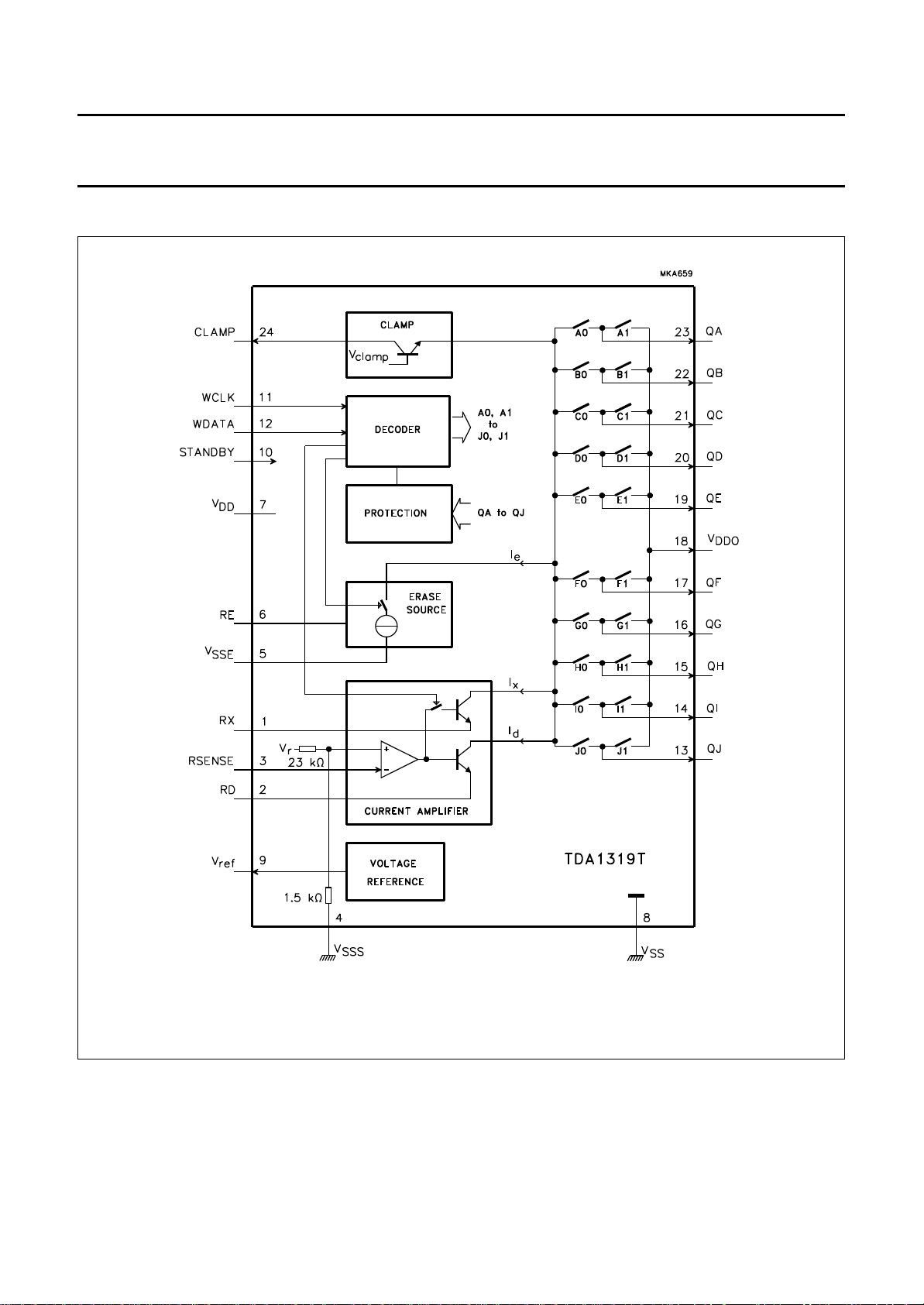
BLOCK DIAGRAM
April 1994 3
Fig.1 Block diagram.
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DCC write amplifier (write 2) TDA1319T
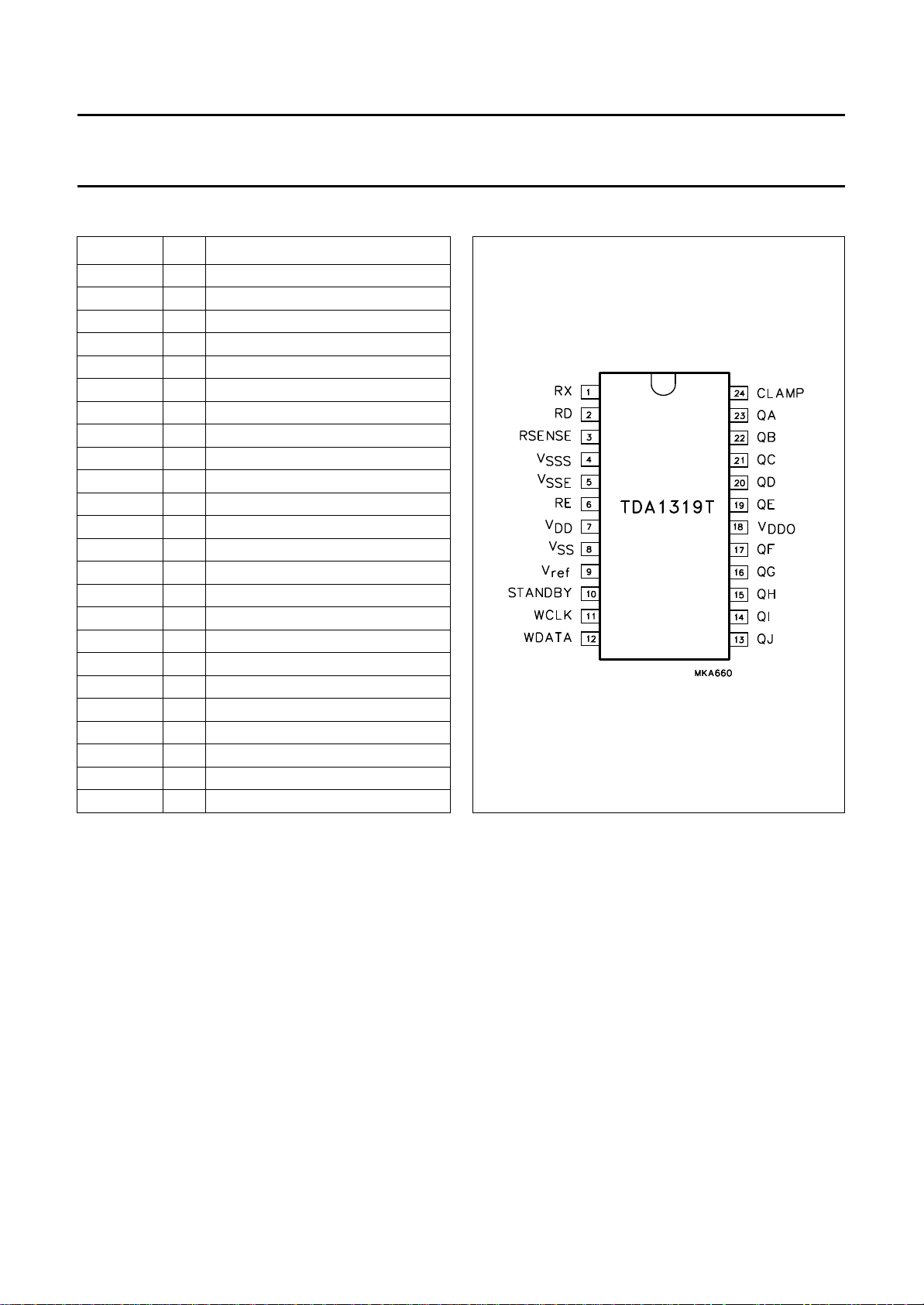
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
RX 1 auxiliary current adjust resistor
RD 2 data current adjust resistor
RSENSE
V
SSS
V
SSE
RE 6 erase current adjust resistor
V
DD
V
SS
V
ref
STANDBY 10 standby mode control input
WCLK 11 write clock input
WDATA 12 write data input
QJ 13 write pulse output
QI 14 write pulse output
QH 15 write pulse output
QG 16 write pulse output
QF 17 write pulse output
V
DDO
QE 19 write pulse output
QD 20 write pulse output
QC 21 write pulse output
QB 22 write pulse output
QA 23 write pulse output
CLAMP 24 clamp current output
3 sense voltage positive input
4 sense voltage ground
5 erase current source ground
7 supply voltage
8 ground
9 reference voltage output
18 supply voltage (write outputs)
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
April 1994 4

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
DCC write amplifier (write 2) TDA1319T
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA1319T is designed to drive the nine elements of
the multichannel recording head (as used in a DCC
recorder) by forcing a current through the selected path. A
brief functional description of each block (see Fig.1) is
given below.
Decoder
The IC is controlled by the 32-bit wide serial dataword
which is clocked in at WDATA (pin 12). The clock
frequency (WCLK, pin 11) is 3.072 MHz with a clock
period of 325 ns. The write pulses are made available at
the outputs QA to QJ (see Fig.4). The timing sequence of
the write pulses is illustrated in Fig.5.
The operating mode of the IC can be set by the first 3 bits
of data (see Fig.5). The signals TCH0 to TCH7 and
TERAUX determine the direction of the write current.
When TCHn is HIGH, the current flows as indicated in
Fig.4. When TCHn is LOW current flows in the opposite
direction. The various modes of operation are given in
Table 1. The standby mode can also be forced by setting
the STANDBY input (pin 10) HIGH.
Current amplifier
The write current at the outputs is regulated by the current
amplifier. The value of the current I
external resistor Rd, connected between pin 2 and V
can be set using an
d
SS
(see Fig.9). The current through Rd also flows at the
outputs. The current amplifier regulates the voltage across
Rd, which is measured between RSENSE and V
SSS
(pins 3 and 4), to a value of 150 mV (see Chapter
“Characteristics”). This force-sense technique eliminates
the influence of parasitic series impedances.
The output of the current amplifier is internally switched to
the output pins QA to QJ. During AUX write (outputs QA
and QB active) an additional current Ix is added to the write
current. This current can be controlled by a resistor R
x
connected between RX (pin 1) and VSS. RX must be
6.7 × Rd for 1.2 dB current increase.
During the erase mode of the auxiliary channel
(TERAUX = HIGH; see Table 1) it is possible to let an
additional output current Ie flow through QA and QB
(pins 23 and 22). This extra current can be adjusted with
an external resistor Re connected between pins 6 and 5.
Pin 5 must be externally connected to ground. A typical
value of the extra current can be calculated from the
response curve of Fig.7.
Voltage reference
A reference voltage is available at pin 9. This voltage is
derived from a bandgap reference source and can be used
to modify the voltage sensed by the current amplifier, e.g.
for external temperature compensation.
Outputs
Each channel is selected in sequence. Depending on the
dataword, the current is directed forward or reversed
through the heads. The outputs that are not selected are
kept floating to prevent any incorrect current flow. A
simplified schematic of one output stage is illustrated in
Fig.3. In the HIGH state (one of the switches A1 to J1 is
closed) the output is internally connected to a fixed voltage
(see Chapter “Characteristics”). In the LOW state
V
OH
(one of the switches A0 to J0 is closed) the output is
connected to the current amplifier. The voltage developed
across the output pin pairs must not exceed a certain
value, otherwise the lower switch transistor (Fig.3) will
become saturated.
Clamp circuit
During the periods that the head elements are not
selected, the clamp circuit accommodates the write
current. This current is directed through an external
resistor from pin 24 to the supply, in order to have less
dissipation in the IC. The clamping results in a constant
current being drawn from the supply and therefore reduces
emission of interferences (the DC level at pin 24 must not
fall lower than 1.8 V).
Standby
The circuit is in the standby mode when TDAPLB = 1 and
TAUPLB = 1 (see Table 1 and Fig.6), or when a HIGH
level is applied to pin 10. After a HIGH-to-LOW transition
at pin 10, the IC will remain in the standby mode until
TDAPLB = 0 or TAUPLB = 0. When the IC is in the
standby mode, the current amplifier is switched off to
minimize the power consumption, switches A to J are
open-circuit and the voltage reference and the erase
source are switched off.
Protection
The IC is immediately switched to standby mode when a
short-circuit to ground at an output pin is detected
< 0.5 V; see Fig.6, “SHORT”). When the short-circuit
(V
o
condition is removed, the IC will resume operation. The
state of the decoder is not affected by a “SHORT”.
April 1994 5
 Loading...
Loading...