Page 1

24
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section
This chapter provides information on transcutaneous monitoring of
oxygen (tcpO
information on preparing the transducer for use, and applying the
transducer to the patient. This chapter includes the following sections:
• Introduction to the tcpO2/tcpCO2 Parameter Module . . . . . . . . 24-2
• Activating the Transducer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24-7
• Preparing the transducer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24-8
• Troubleshooting- Calibration Failure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24-16
• tcpO2/tcpCO2 Alarms and INOP Messages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24-21
• Parameter Settings Transfer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24-24
• Accessories and Ordering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24-25
• Performance Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24-26
• Care and Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24-29
) and of carbon dioxide (tcpCO2). It also provides
2
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section 24-1
Page 2

Introduction to the tcpO2/tcpCO2 Parameter Module
Introduction to the tcpO2/tcpCO2 Parameter Module
What does it
Measure?
How the
tcpO2/
tcpCO2
Measureme
nt Works
Correlation
of
Transcut ane
ous with
Arterial
Blood Gas
Values
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
The tcpO2/tcpCO2 module measures the partial pressure of the oxygen
and carbon dioxide that diffuses transcutaneously (through the skin).
The oxygen measurement is valid for an infant patient who is not under
gas anesthesia. These partial pressures provide a measure of the oxygen
and carbon dioxide levels in the blood.
The tcpO2/tcpCO2 transducer heats the skin. This has the effect of
increasing local blood perfusion so that oxygen and carbon dioxide can
diffuse to the skin surface more easily.
The transducer contains an electrolyte solution which is held in place by
two gas-permeable membranes. The oxygen and carbon dioxide that
diffuses out of the skin passes through these membranes into the
electrolyte solution where electrochemical reactions take place. These
reactions generate electrical signals which are representative of the
amounts of oxygen and carbon dioxide present. The electrical signals
are measured by the module to enable the tcpO
displayed as numerics on the standard display.
Transcutaneous measurements are not capable of replacing arterial
blood gas monitoring. However, transcutaneous monitoring can be used
to reduce the frequency of arterial sampling.
Transcutaneous values are representative of the carbon dioxide and
oxygen levels in the blood. The values at tissue level will not be the
same as those measured arterially because of the transcutaneous nature
of the measurement. However, provided that the transducer is properly
handled by following the procedures described in this chapter, the
transcutaneous values will correlate with (track closely) the arterial
values. For example, a drop in transcutaneous values will usually
indicate that arterial values have dropped as well.
/tcpCO2 values to be
2
Note that transcutaneous values will not always correlate with blood
samples taken from the capillary blood of the heel (heelsticks or
astrups).
24-2 tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section
Page 3

Introduction to the tcpO2/tcpCO2 Parameter Module
For information on “Correlation of transcutaneous with arterial blood gas
values”, see references 5, 6 and 7 in Appendix on Analog Output)
Setting up
the Module
Transducer
Temperature
The optimum application period for the transducer at one site on a patient
is dependent on the transducer temperature and on the sensitivity of the
patient's skin. Before calibrating the transducer, (see the section
Calibrating the tcpO2/tcpCO2 Transducer in this chapter) you should
adjust the transducer temperature and also set the Site Timer.
WarningWarning
The temperature should be selected according to the patient’s age,
weight and physical condition.
Available temperatures for the transducer are 37.0°C, 41.0°C, 41.5°C,
42.0°C, 42.5°C, 43.0°C, 43.5°C, 44.0°C, 44.5°C and 45.0°C. Usually, a higher
transducer temperature results in both a better correlation and also a
shorter time delay between a change in arterial blood gas and its
detection by the transducer. However higher temperatures also increase
the risk of skin burns. A temperature between 42° and 44°C is preferred
by most physicians.
Note—The tcpO
/ tcpCO2 module is equipped with a temperature limiter
2
which prevents the sensor temperature from exceeding 46ºC. If the
temperature limiter fails, the following INOP message is displayed on the
monitor:
• tc EQUIP MALF.
Site Timer The Site Timer helps you to guard against the risk of skin burn by
ensuring that the transducer is used at one site for no longer than a
predefined period. The transducer can be set to operate for any of the
following time periods: 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 or 8 hours. The
selection is visible in the task window next to “Site Time##, and the
time remaining before the Site Timer expires appears next to “Time
Left:”.
Site time settings should be adapted to the patient's skin sensitivity.
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section 24-3
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
Page 4

Introduction to the tcpO2/tcpCO2 Parameter Module
After the selected period of time has expired, an INOP message
“tcCHANGE SITE” is displayed and the INOP tone is sounded. The
Monitor can be configured either to switch off the transducer heating
when the Site Time has expired, or to continue monitoring. This should
be set as required by your hospital's policy, either by your biomedical
engineering department or by the Philips Service Engineer.
Correction for
tcpCO
Section
Values
2
If the choice
Off is available along with the above site times, you can
choose to disable the Site Timer so that no “CHANGE SITE” reminder is
displayed and the transducer monitors (and heats) indefinitely.
Availability of this choice will depend on your hospital's policy and can
be set by your biomedical engineering department or the Philips Service
Engineer.
Transcutaneous pCO
values tend to be higher than arterial values (due
2
to the metabolic processes of the skin and the effect of heating on the
blood under the transducer). This effect can be compensated for by
selecting the Severinghaus correction in a special Configuration Mode
on the monitor. (This has been selected if “corr.” appears under the
value for tcpCO
in the Task Window - consult your biomedical
2
engineering department or the Philips Service Engineer if you wish to
add or remove this correction.)
• The front of the module has two keys:
– The key for parameter setup. A light will appear
O2/CO2
above the key when you are in setup.
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
24-4 tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section
Page 5
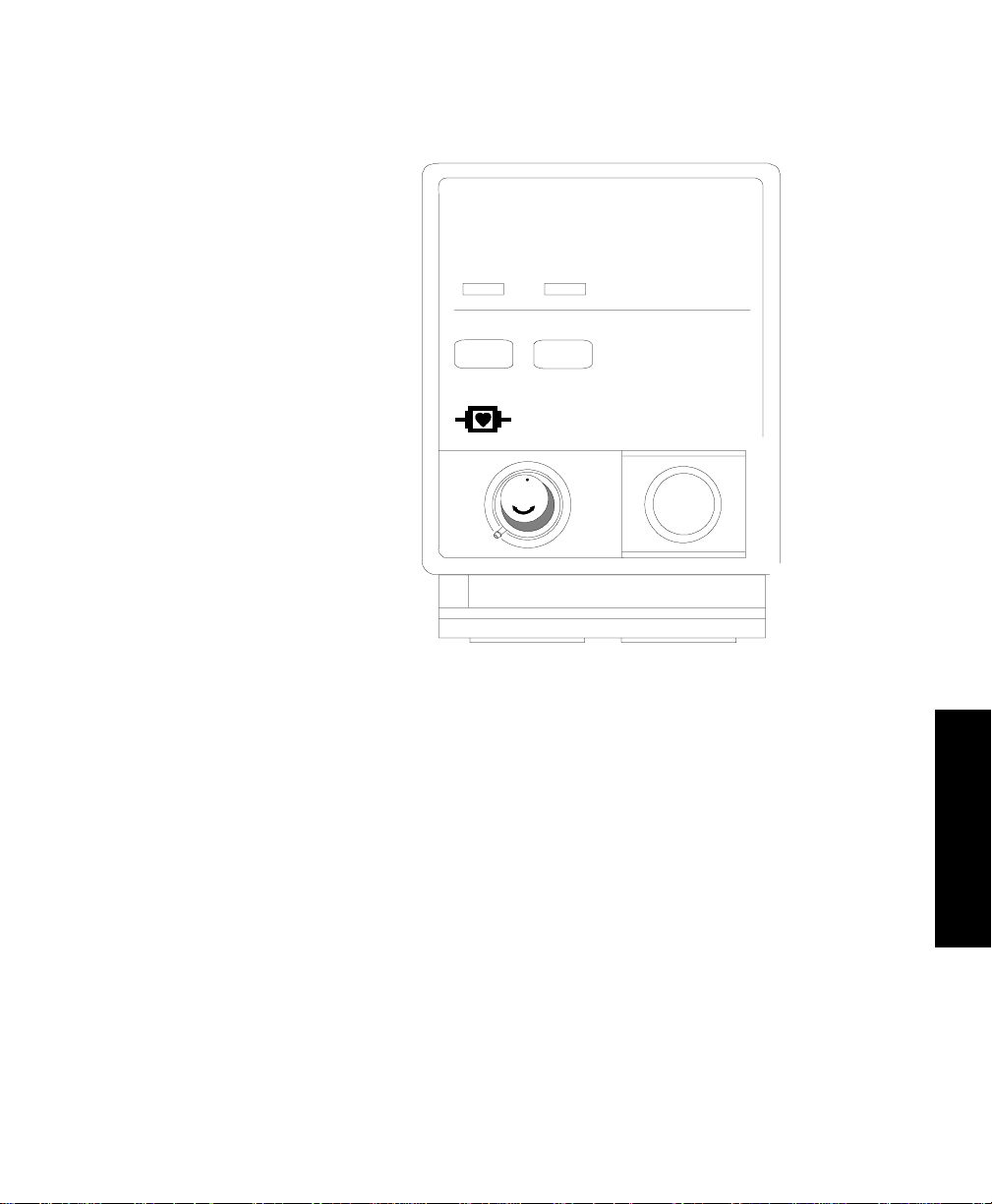
Introduction to the tcpO2/tcpCO2 Parameter Module
– The CAL key to start calibration procedures.
tcpO2 /tcpCO
M1018A
O2 /CO
2
CAL
2
T
80 x 70
The tcpO
Note—The “T” on the front of the module indicates that this module
transfers parameter settings from one monitor to another.
/tcpCO2 Module
2
Symbols to
Indicate Key
Functions
As detailed in the table below, some versions of this module now use
symbols, instead of words, to indicate the function of some keys. If the
monitor’s Reference Manual tells you, for example, to select the CAL key,
you should press the key marked with the corresponding “calibration”
symbol.
The design change also means that you will now find the module’s
product number on the rear of the module’s housing, not on the front.
Although the new modules do not show the letter “T” on the housing, all
modules retain their capability to transfer parameter settings from one
monitor to another.
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section 24-5
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
Page 6

Introduction to the tcpO2/tcpCO2 Parameter Module
Symbol Name Function Which Modules?
Cal calibrate SvO
Mainstream CO
(M1021A), tcpO2/tcpCO2 (M1018A)
2
(M1016A)
2
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
24-6 tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section
Page 7

Activating the Transducer
Follow the 24 hour activation procedure if:
• the electrolyte in your transducer has dried out (this occurs when
the transducer has been out of use for a long period),
• or you are about to use a new transducer (new transducers are
shipped dry).
Activate by following the Remembraning the Transducer procedure, then
leave the transducer in a safe place for 24 hours, unplugged from the
module and with the cap on. Remembrane the transducer again just
before carrying out the calibration procedure.
Activating the Transducer
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section 24-7
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
Page 8

Preparing the transducer
Preparing the transducer
There are three steps to preparing a transducer for application to a
patient.
First, remembrane the transducer.
Then, calibrate the transducer (first checking the module settings
- Site Time, Transducer Temp and Alarm Limits).
Finally, prepare a site and apply the transducer to your patient.
The procedure for carrying out these steps is described in the following
three sections. Each section gives guidelines on when you should carry
out each step. Follow the procedures carefully to ensure best results.
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
1. Remembrane the
tcpO2/
tcpCO2
Transducer
With normal use, the membranes will last approximately 1 week before
a change is required. Change the membrane on the transducer if:
• you are about to use a new transducer,
• the transducer is to be used with a new patient,
• the membranes of the transducer are damaged (scratched or
wrinkled),
• the transducer has been used for 5 days continuously,
• the transducer has been in storage for up to 28 days,
• you have a transducer which must be remembraned after
activating for 24 hours (see previous page, Activating the
Transducer), or
• calibration has failed twice.
1. Check that you have the Philips tc Accessory Kit containing an Oring remover, absorbent paper, electrolyte solution and membrane
replacers.
24-8 tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section
Page 9

Preparing the transducer
2. Unscrew the protection cap from the transducer, then hook the Oring remover under both O-rings to remove them.
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section 24-9
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
Page 10

Preparing the transducer
3. Remove both of the clear plastic membranes using your fingers.
4. Clean the transducer head with absorbent paper. Make sure you
clean the groove in the head and also the rim around the head to
remove any old electrolyte - all of the old electrolyte must be
removed to ensure a successful calibration and reliable
measurements.
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
24-10 tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section
Page 11

Preparing the transducer
5. Apply electrolyte solution to the transducer head (approximately
two drops). Break any air bubbles in the electrolyte using the nozzle
of the solution container.
6. Press the transducer head downwards into an unused membrane
replacer until the replacer retracts as far as it can and a click is
heard. Discard the used replacer.
7. Remove any surplus electrolyte solution on the outside of the
membranes with a soft tissue.
8. Examine the transducer carefully to ensure that the new
membranes are secured by two O-rings on the transducer. If any air
bubbles are visible under the membranes, repeat this procedure - air
bubbles will cause incorrect readings.
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section 24-11
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
Page 12

Preparing the transducer
Provided that you do not need to activate the transducer for 24 hours
(see the section Activating the Transducer on page 20-7), the
transducer is now ready to be calibrated and can be placed in the
calibration chamber on the front of the module - see the next section.
2.
Calibrating
the tcpO2/
tcpCO2
System
Section
Module Setup
Calibration of your tcpO
• you have just fitted a new membrane,
• you have just changed the transducer operating temperature, or,
• the INOP message tc CAL REQUIRD appears on the screen.
Note—To maintain accuracy, the tcpO
calibrated regularly, even if the CMS, V24 or V26 monitor does not
prompt you to do so.
-->
tcpO2/tcpCO2
/tcpCO2 system is required if:
2
/tcpCO2 transducer should be
2
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
24-12 tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section
Calibration of your tcpO
/tcpCO2 system is recommended if:
2
• the accuracy of the measurement is in doubt,
• you are about to start a new monitoring period, or
• you are about to change the measurement site, or
• at least six hours have elapsed since the last calibration
Page 13

Preparing the transducer
1. Check that you have a tcpO2/tcpCO2 module (inserted at the
extreme left position in the rack for best accessibility) and a Philips
Calibration Unit (15210B). The Calibration Unit must have a gas
cylinder inserted in the rear and a pressure indicator reading that is
above the out-of-gas zone (black on 15210B and red on Radiometer
TCC3 Calibration Unit).
2. Check that the transducer is plugged into the module and that the
transducer is inserted into the calibration chamber on the front of
the module (swing the flap back and insert the transducer, then
swing the flap over the transducer).
V24 Monitor with 15210B Calibration Unit
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section 24-13
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
Page 14

Preparing the transducer
.
.
V24 Monitor with Radiometer TCC3 Calibration Unit
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
24-14 tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section
3. Press , followed by to bring up
the tcpO
screen by pressing on the front of the module.)
Module Setup
/tcpCO2 Setup Task Window. (You can also reach this
2
tcpO2/tcpCO2
O2/CO2
4. Check the module settings as displayed on the screen - Transducer
Temp., Site Time and Alarm Limits. You can change any of these
values by pressing the appropriate softkeys (see the CMS, V24 or
V26).
5. Fit the gas tubing from the Calibration Unit into the inlet on the
side of the calibration chamber (the other end of the tubing must
be fitted into the Calibration Unit).
6. If you are using a 15210B Calibration Unit, turn the timer control
dial on the Calibration Unit clockwise as far as you can and press
Start Calibr
on the Monitor. If you are using a Radiometer
TCC3 Calibration Unit, press the button with the green arrow on
the front of the calibration unit once, then press
Start Calibr
on the monitor.(You can also start the calibration by pressing the
CAL key on the front of the module until the light above the key
Page 15

Preparing the transducer
.
comes on and a tone sounds. In addition, a calibration can be
restarted by pressing .)
Start Calibr
7. Wait for “...tcpO
“...tcpO
/tcpCO2 calibration complete” in the task window (the
2
/tcpCO2 calibration running” to be replaced by
2
calibration process generally takes 3 to 10 minutes but may take up
to 20 minutes). For 15210B Calibration Units: If the timer control
dial has not reached the start position when “...tcpO
/tcpCO2
2
calibration complete” is displayed, you can save gas by turning the
dial counter-clockwise to the start position. For Radiometer TCC3
Calibration Units: If the green light on the front of the Calibration
Unit is still flashing when “...tcpO
/tcpCO2 calibration complete” is
2
displayed, you can save gas by pressing the button with the green
arrow again.
When calibration is complete, the transducer is ready to be applied to a
patient - see the next section. The Site Timer will start when you remove
the transducer from the calibration chamber.
Apply the transducer to your patient as soon as possible after the
“...calibration complete” message appears on the screen. If you wait
longer than 30 minutes, the heat supply to the transducer is automatically
switched off in order to prevent the electrolyte from drying out. This
means that a new calibration will be required.
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section 24-15
Page 16

Preparing the transducer
Trouble-
shooting-
Calibration
Failure
If the calibration is unsuccessful, the message “...tcpO
/tcpCO2
2
transducer or Cal Unit malf” is displayed in the task window. In
addition, the CAL FAILED INOP message for tc, tcpO
or tcpCO2
2
appears in the upper left corner of the screen. Perform each of the
following steps in the order specified until calibration is successful:
1. Check the Calibration Unit, then recalibrate, remembering to turn
on the gas supply on the Calibration Unit. (If the pressure
indicator reading is in the out of gas zone, there is insufficient gas
in the cylinder. The gas tubing must be firmly connected to the
Calibration Unit and to the calibration chamber on the module.)
2. If Step 1 is unsuccessful, check whether you need to activate the
transducer (necessary if the electrolyte has dried out or if you
have a new transducer, see page 24-6). Then remembrane the
transducer ensuring that you:
a. remove the old membranes, and
b. clean the transducer head thoroughly.
Then calibrate a second time.
3. If Step 2 is unsuccessful, calibrate again. (A second calibration
may be required in order to stabilize the electrochemical system
in the transducer.)
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
24-16 tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section
4. Only if the above steps are unsuccessful (you have activated and
remembraned the transducer and calibration has still failed twice),
replace the transducer.
Page 17

Preparing the transducer
3. Applying
the
Transducer
to the
Patient
To apply the transducer to your patient, use the following procedure:
1. Check that you have the Philips Fixation Kit containing a box of
fixation rings and contact fluid.
2. Select a measuring site and clean the skin with alcohol solution. (To
optimize the measurement, select a site with high capillary density
and blood flow, thin epidermis and no cardiovascular disorders.
Most physicians use the abdomen, chest and back.)
3. Take a fixation ring from the box and peel off the protection film
to reveal the sticky surface.
4. Apply the fixation ring to clean and dry skin by pressing the ring
onto the site with a finger, first in the center and then around the
outside to ensure a good seal. (A good seal between the fixation ring
and the skin is essential for good results.)
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section 24-17
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
Page 18

Preparing the transducer
5. Place 3 to 5 drops of contact fluid in the center of the ring.
6. Remove the transducer from the chamber (the Site Timer on the
screen will start) and align the arrow on the transducer either with
or opposite the tab on the ring.
7. Turn the transducer a quarter-turn clockwise to fasten it to the
ring.
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
24-18 tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section
8. Wait 10 to 20 minutes for readings to stabilize. (The tcpO
tcpCO
numerics are displayed on the standard display.)
2
and
2
Page 19

Preparing the transducer
r
Restarting the
Site Timer
• The Site Timer is automatically restarted after the transducer has
been calibrated and removed from the calibration chamber
(calibration is recommended whenever the site is changed).
• You can restart the Site Timer up to 2 hours after the time period
has expired. (After this 2 hour period a calibration is required.)
Press to enter the Site Timer task window. Confirm
Site Time
your required time.
When changing the application site after a measuring period, some users
leave the fixation rings in position. This allows the transducer to be
quickly moved from site to site.
Note— During the initial 3 minutes of use, tcpO
/tcpCO2 alarms are
2
suspended to eliminate false alarms. During this period, the
“STABILIZING” INOP message is displayed for tc, tcpO
or tcpCO2. After
2
the transducer has been attached to the skin, the instrument reading will
slowly assume a steady value. The reading will stabilize as soon as the
measurement site is warmed up and local hyperemization is completed;
usually 10 to 20 minutes for the tcpO
tcpCO
The tcpO
.
2
/tcpCO2 Setup Task Window indicates the amount of remaining
2
reading and 3 to 7 minutes for
2
time before the Site Timer expires. At the end of the site time the INOP
message “CHANGE SITE” is displayed and the INOP tone is sounded. The
Monitor will switch off the transducer heating or will continue
monitoring, depending on how the Monitor has been configured.
WarningWarning
• Prolonged continuous monitoring may increase the risk of
undesirable changes in skin characteristics, such as
irritation, reddening, blistering or burns. If the Site Timer is
Section
Off (disabled) or automatic heating switch-off has been
disabled, the transducer will heat indefinitely while on a
patient. Ensure that the site is changed in accordance with
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
standard medical procedures in your hospital.
• Always unscrew the transducer from the fixation ring before
removing the fixation ring from the skin.
• When defibrillating a patient, it is important to either:
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section 24-19
Page 20

Preparing the transducer
– remove the transducer before defibrillating, or
– remembrane and calibrate the transducer after
defibrillating
Caution
• All specified transducers (but not membranes) are protected
against the effects of the discharge of a defibrillator.
• To avoid transducer damage, remove it from the patient during
high frequency surgical procedures.
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
24-20 tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section
Page 21

tcpO2/tcpCO2 Alarms and INOP Messages
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Alarms and INOP Messages
The tcpO2/tcpCO2 alarm messages are rated in order of severity:
** Yellow
INOP message
Alarm tone = a single tone repeated every second
INOP tone = a single beep repeated every 2 seconds.
Physiological Alarms
Alarm Message Condition Visual Indication
tcpO2 90>80 tcpO
above high alarm limit tcpO2 numeric blinks.
2
Yellow alarm lamp.
tcpO2 40<50 tcpO
below low alarm limit tcpO2 numeric blinks.
2
Yellow alarm lamp.
tcpCO2 60>50 tcpCO
above high alarm limit tcpCO2 numeric blinks.
2
Yellow alarm lamp.
tcpCO2 20<30 tcpCO
below low alarm limit tcpCO2 numeric blinks.
2
Yellow alarm lamp.
Audible
Indication
Alarm tone
Alarm tone
Alarm tone
Alarm tone
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section 24-21
Page 22

tcpO2/tcpCO2 Alarms and INOP Messages
Technical
Alarms
INOP messages appear when the monitor cannot measure or process
signals properly or when the measuring site is to be changed. For
transcutaneous gas measurements all INOP messages except CHANGE
SITE and CHECK TIME relate to equipment-related problems but you
must check the patient's condition first. If the INOP message is
accompanied by an audible alarm, it can be silenced with the
Silence/Reset
key.
INOP Messages
INOP Message Condition Visual Indication
tc UN-PLUGGED Parameter switched on and
unplugged from rack. Silencing
tcpO
/tcpCO2
2
numerics display -?-.
the alarm switches the
parameter off.
tc EQUIP MALF Malfunction in the transducer or
module.
tcpO
/tcpCO2
2
numerics display -?-.
Prompt message
appears in task
window.
tc NO TRANSDUC No transducer is connected to
the tcpO
/tcpCO2 module.
2
tcpO
/tcpCO2
2
numerics display -?-.
Silencing the alarm switches the
parameter off.
Audible
Indication
INOP tone
INOP tone
INOP tone
tc CHANGE SITE Site Timer has timed out tcpO
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
24-22 tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section
/tcpCO2
2
numerics may
display -?- depending
on configuration.
Prompt message
appears in task
window.
INOP tone
Page 23

tcpO2/tcpCO2 Alarms and INOP Messages
INOP Message Condition Visual Indication
tc CAL FAILED
1
Calibration failed due to out of
range or unstable signal during
calibration.
tcpO2/tcpCO2
numerics display -?-.
Prompt message
appears in task
window.
tc CAL REQUIRD Calibration is required before
applying the transducer to the
patient
2
tcpO2/tcpCO2
numerics display -?-.
Prompt message
appears in task
window.
tc CAL RUNNING The tcpO
running.
/tcpCO2 calibration is
2
Numerics display -?-.
Prompt message
appears in task
window.
tc STABILIZING The transducer has not yet
reached the selected
temperature and/or skin
hyperemization is not yet
complete.
tcpO
/tcpCO2
2
numeric is displayed
with ? to indicate
that values are
unstable.
Audible
Indication
INOP tone
INOP tone
None
None
tc CHECK TIME Site Timer due to time out (15
minutes or less)
1
See “Troubleshooting - Calibration Failure” earlier in this chapter or the
CMS, V24 or V26 User’s Guide.
2
Possible module or transducer malfunction if calibration in progress.
None None
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section 24-23
Page 24

Parameter Settings Transfer
Parameter Settings Transfer
The following parameter settings can be transferred with tcpO2/tcpCO2
modules. For more information on Parameter Settings Transfer, refer to
“Parameter Settings Transfer,” Chapter 3.
Setting Name Meaning
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
Section
Alarm limits tcpO
and tcpCO2 high and low alarm limits
2
Site Time setting Period transducer will be active at one site
Transducer temperature Temperature to which transducer is heated
Recalibration of the tcpO
/tcpCO2 system is required if the module has
2
been transferred.
24-24 tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section
Page 25

Accessories and Ordering
Accessories and Ordering
You can order parts and accessories from Philips supplies at
www.medical.philips.com or consult your local Philips representative for
details.
Warning Reuse: Never reuse disposable transducers, sensors, accessories
and so forth that are intended for single use, or single patient use
only.
Philips’ approval: Use only Philips-approved accessories.
Packaging: Do not use a sterilized accessory if its packaging is
damaged.
This symbol indicates that the specified transducer (but not
its membranes) is designed to have special protection
against electric shocks (particularly regarding allowable
leakage currents), and is defibrillator proof.
Description Part No.
12x tc Accessory Kit (O-ring remover, absorbent paper, electrolyte solution, replacement membrane)
tc Application Kit (4x25 disposable fixation rings, 4x20ml contact fluid)
Calibration gas - 6 gas bottles 15210-60010
Calibration gas - 6 gas bottles (Europe and Japan only) 15210-64010
Replacement tubing (5 tubes) M2205A
tcpO2/CO2 transducer M1918A
Calibration unit 15210B
Radiometer TCC3 calibration unit (available from Radiometer) n/a
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module Section 24-25
15209-60010
15209-60020
Section
tcpO2/tcpCO2 Module
 Loading...
Loading...