
Instructions for Use
IntelliVue Patient Monitor
MX600/MX700/MX800
Release H.0 with Software Revision H.1x.xx
Patient Monitoring

Part Number 453564260091
Printed in Germany 05/11
*453564260091*

1Table of Contents
1 Introduction 13
Introducing the Monitor 13
Devices for Acquiring Measurements 15
Operating and Navigating 24
Operating Modes 31
Understanding Screens 32
Connecting Additional Displays to the Monitor 33
Using the XDS Remote Display 34
Using the Visitor Screen 34
Understanding Profiles 34
Understanding Settings 36
Changing Wave Speeds 37
Freezing Waves 38
Using Labels 39
Entering Measurements Manually 42
Changing Monitor Settings 42
Checking Your Monitor Revision 43
Getting Started 43
Disconnecting from Power 45
Networked Monitoring 45
Using the Integrated PC 46
Using the X2 or MP5 with a Host Monitor 47
2 Alarms 49
Visual Alarm Indicators 50
Audible Alarm Indicators 51
Acknowledging Alarms 53
Pausing or Switching Off Alarms 54
Alarm Limits 56
Reviewing Alarms 60
Latching Alarms 61
Testing Alarms 62
Alarm Behavior at Power On 62
Alarm Recordings 63
3 Patient Alarms and INOPs 65
Patient Alarm Messages 65
Technical Alarm Messages (INOPs) 70
3

4 Managing Patients 95
Admitting a Patient 95
Quick Admitting a Patient 96
Editing Patient Information 97
Discharging a Patient 97
Transferring Patients 98
Data Upload from an MMS 102
Care Groups 105
5 ECG, Arrhythmia, ST and QT Monitoring 111
Skin Preparation for Electrode Placement 111
Connecting ECG Cables 111
Selecting the Primary and Secondary ECG Leads 112
Checking Paced Status 112
Understanding the ECG Display 112
Monitoring Paced Patients 113
Changing the Size of the ECG Wave 114
Changing the Volume of the QRS Tone 115
Changing the ECG Filter Settings 115
Selecting Positions of Va and Vb Chest Leads (for 6-lead placement) 116
Choosing EASI or Standard Lead Placement 116
About ECG Leads 116
ECG Lead Fallback 117
ECG Lead Placements 117
Capture 12-Lead 123
EASI ECG Lead Placement 125
ECG and Arrhythmia Alarm Overview 126
Using ECG Alarms 127
ECG Safety Information 128
About Arrhythmia Monitoring 129
Switching Arrhythmia Analysis On and Off 130
Choosing an ECG Lead for Arrhythmia Monitoring 130
Understanding the Arrhythmia Display 132
Arrhythmia Relearning 134
Arrhythmia Alarms 135
About ST Monitoring 139
Switching ST On and Off 140
Understanding the ST Display 141
Updating ST Baseline Snippets 142
Recording ST Segments 142
About the ST Measurement Points 143
ST Alarms 145
Viewing ST Maps 146
About QT/QTc Interval Monitoring 149
QT Alarms 152
Switching QT Monitoring On and Off 153
4

6 Monitoring Pulse Rate 155
Entering the Setup Pulse Menu 155
System Pulse Source 155
Switching Pulse On and Off 156
Using Pulse Alarms 156
7 Monitoring Respiration Rate (Resp) 159
Lead Placement for Monitoring Resp 159
Understanding the Resp Display 160
Changing Resp Detection Modes 160
Changing the Size of the Respiration Wave 161
Changing the Speed of the Respiration Wave 162
Using Resp Alarms 162
Changing the Apnea Alarm Delay 162
Resp Safety Information 162
8 Monitoring SpO2 165
SpO2 Sensors 165
Applying the Sensor 165
Connecting SpO2 Cables 166
Measuring SpO2 166
SpO2 Signal Quality Indicator (Fast SpO2 only) 167
Assessing a Suspicious SpO2 Reading 168
Changing the Averaging Time 168
Understanding SpO2 Alarms 168
Pleth Wave 171
Perfusion Numeric 171
Perfusion Change Indicator 171
Setting SpO2/Pleth as Pulse Source 172
Setting Up Tone Modulation 172
Setting the QRS Volume 172
Calculating SpO2 Difference 172
9 Monitoring NBP 173
Introducing the Oscillometric NBP Measurement 173
Preparing to Measure NBP 175
Starting and Stopping Measurements 176
Enabling Automatic Mode and Setting Repetition Time 178
Enabling Sequence Mode and Setting Up The Sequence 178
Choosing the NBP Alarm Source 178
Switching Pulse from NBP On/Off 179
Assisting Venous Puncture 179
Calibrating NBP 179
10 Monitoring Temperature 181
Making a Temp Measurement 181
5

Calculating Temp Difference 182
11 Monitoring Invasive Pressure 183
Setting up the Pressure Measurement 183
Zeroing the Pressure Transducer 184
Adjusting the Calibration Factor 186
Displaying a Mean Pressure Value Only 187
Changing the Pressure Wave Scale 187
Optimizing the Waveform 187
Using the Wave Cursor 187
Non-Physiological Artifact Suppression 188
Choosing the Pressure Alarm Source 188
Calibrating Reusable Transducer CPJ840J6 189
Calculating Cerebral Perfusion Pressure 191
Calculating Pulse Pressure Variation 191
Measuring Pulmonary Artery Wedge Pressure 192
Editing the Wedge 193
Identifying the Pressure Analog Output Connector 193
12 Monitoring Cardiac Output 195
Hemodynamic Parameters 195
Using the C.O. Procedure Window 196
Accessing the Setup C.O. and Setup CCO Menus 197
Entering the HemoCalc Window 198
Measuring C. O. Using the PiCCO Method 198
Measuring C.O. Using the Right Heart Thermodilution Method 203
Documenting C.O. Measurements 206
C.O. Injectate Guidelines 206
C.O./CCO Curve Alert Messages 207
C.O./CCO Prompt Messages 209
C.O./CCO Warning Messages 209
C.O./CCO Safety Information 210
13 Monitoring Carbon Dioxide 213
Measurement Principles 214
Measuring CO2 using M3014A or X2 214
Measuring Mainstream CO2 using M3016A 218
Measuring Microstream CO2 using M3015A/B 220
Setting up all CO2 Measurements 222
14 Monitoring Airway Flow, Volume and Pressure 225
Attaching the Flow Sensor 226
Zero Calibration 228
Automatic Purging 228
Manual Purging 229
Gas Compensation 229
6

Setting up Spirometry 230
15 Monitoring tcGas 233
Identifying tcGas Module Components 233
Setting the tcGas Sensor Temperature 233
Using the tcGas Site Timer 234
Setting the tcGas Barometric Pressure 235
Remembraning the tcGas Transducer 235
Calibrating the tcGas Transducer 235
Applying the tcGas Transducer 237
Finishing tcGas Monitoring 238
TcGas Corrections 238
16 Monitoring Intravascular Oxygen Saturation 241
Selecting a Measurement Label 242
Preparing to Monitor with the M1021A Wide Module 242
Preparing to Monitor with the M1011A Narrow Module 246
Further Information for Both Modules 247
17 Monitoring EEG 249
EEG Monitoring Setup 249
Using the EEG Impedance/Montage Window 250
About Compressed Spectral Arrays (CSA) 252
Changing EEG Settings 253
EEG Reports 254
EEG Safety Information 254
EEG and Electrical Interference 255
18 Monitoring BIS 257
BIS Monitoring Setup 257
BIS Continuous Impedance Check 259
BIS Cyclic Impedance Check 260
BIS Window 260
Changing the BIS Smoothing Rate 261
Switching BIS and Individual Numerics On and Off 262
Changing the Scale of the EEG Wave 262
Switching BIS Filters On or Off 262
BIS Safety Information 262
19 Assigning a Telemetry Device and a Monitor to One Patient 265
How Can You Combine Devices? 265
Functions Available When the Telemetry Data Window is Displayed 267
General Telemetry-related Functions 268
Use Models With Telemetry 269
7

20 Trends 271
Viewing Trends 271
Setting Up Trends 274
Documenting Trends 278
Trends Databases 278
Screen Trends 279
21 Calculations 283
Viewing Calculations 284
Reviewing Calculations 285
Performing Calculations 285
Entering Values for Calculations 286
Documenting Calculations 287
22 High Resolution Trend Waves 289
Changing the Hi-Res Trend Waves Displayed 289
Hi-Res Trend Wave Scales 289
Hi-Res Trend Waves and OxyCRG 289
Printing Hi-Res Trend Wave Reports 290
Hi-Res Trend Wave Recordings 290
23 Event Surveillance 291
Levels of Event Surveillance 291
Event Groups 292
Event Episodes 292
Events Pop-Up Keys 293
Event Triggers 294
The Events Database 298
Viewing Events 298
Annotating Events 301
Documenting Events 301
24 ProtocolWatch 309
SSC Sepsis Protocol 309
25 Recording 317
Central Recording 317
Starting and Stopping Recordings 317
Overview of Recording Types 319
All ECG Waves Recordings 319
Creating and Changing Recordings Templates 320
Changing ECG Wave Gain 321
Recording Priorities 321
Recording Strip 321
Reloading Paper 323
Recorder Status Messages 323
8

26 Printing Patient Reports 325
Starting Report Printouts 325
Stopping Reports Printouts 326
Setting Up Reports 327
Setting Up Individual Print Jobs 328
Checking Printer Settings 329
Printing a Test Report 329
Switching Printers On Or Off for Reports 329
Dashed Lines on Reports 329
Unavailable Printer: Re-routing Reports 330
Checking Report Status and Printing Manually 330
Printer Status Messages 331
Sample Report Printouts 332
27 Using the Drug Calculator 337
Accessing the Drug Calculator 338
Performing Drug Calculations 338
Charting Infusion Progress 340
Using the Titration Table 341
Documenting Drug Calculations 341
28 IntelliBridge EC10 Module 343
Connecting an External Device 343
Changing Waves and Numerics Displayed 344
Viewing the IntelliBridge Device Data Window 344
Using Screens with External Device Data 344
Alarms/INOPs from External Devices 345
Language Conflict with External Device Drivers 345
29 VueLink Modules 347
Connecting an External Device 348
Changing VueLink Waves and Numerics Displayed 348
Viewing the VueLink Device Data Window 349
Using VueLink Screens 349
Switching VueLink On and Off 349
Alarms/INOPs From External Devices 350
Language Conflict with External Device Drivers 350
30 Using Timers 351
Viewing Timers 351
Timer Setup Pop-up Keys 352
Setting Up Timers 352
Displaying a Timer On The Main Screen 353
Displaying A Clock On The Main Screen 354
9

31 Respiratory Loops 355
Viewing Loops 355
Capturing and Deleting Loops 356
Showing/Hiding Loops 356
Changing Loops Display Size 356
Using the Loops Cursor 356
Changing Loops Type 357
Setting Up Source Device 357
Documenting Loops 357
32 Laboratory Data 359
Viewing Received Data 359
33 Care and Cleaning 361
General Points 361
Cleaning the Monitor 362
Disinfecting the Monitor 362
Sterilizing the Monitor 363
Cleaning, Sterilizing and Disinfecting Monitoring Accessories 363
Cleaning the SO2 Optical Module 363
Cleaning the Recorder Printhead (M1116B only) 363
34 Maintenance and Troubleshooting 365
Inspecting the Equipment and Accessories 365
Inspecting the Cables and Cords 366
Maintenance Task and Test Schedule 366
Troubleshooting 367
Disposing of the Monitor 367
Disposing of Empty Calibration Gas Cylinders 367
35 Accessories 369
ECG/Resp Accessories 369
NBP Accessories 372
Invasive Pressure Accessories 375
SpO2 Accessories 376
Temperature Accessories 380
Cardiac Output (C.O.) Accessories 381
Mainstream CO2 Accessories 382
Sidestream CO2 Accessories 382
Mainstream CO2 Accessories (for M3016A) 383
Microstream CO2 Accessories 383
Spirometry Accessories 384
tcGas Accessories 385
EEG Accessories 385
BIS Accessories 385
SO2 Accessories for M1021A 386
10

SO2 Accessories for M1011A 386
Recorder Accessories 386
Battery Accessories 386
36 Specifications 387
Intended Use 387
Manufacturer's Information 387
Symbols 389
Installation Safety Information 390
Monitor Mounting Precautions 393
Altitude Setting 393
Monitor Safety Specifications 393
EMC And Radio Regulatory Compliance 393
Physical Specifications 395
Environmental Specifications 397
Performance Specifications 399
Interface Specifications 401
Measurement Specifications 405
Safety and Performance Tests 424
37 Default Settings Appendix 429
Country-Specific Default Settings 429
Alarm and Measurement Default Settings 436
Alarm Default Settings 436
ECG, Arrhythmia, ST and QT Default Settings 437
Pulse Default Settings 438
Respiration Default Settings 439
SpO2 Default Settings 439
NBP Default Settings 440
Temperature Default Settings 440
Invasive Pressure Default Settings 441
Cardiac Output Default Settings 443
CO2 Default Settings 444
Spirometry Default Settings 444
tcGas Default Settings 445
Intravascular Oxygen Saturation 445
SvO2 Default Settings 446
ScvO2 Default Settings 446
EEG Default Settings 446
BIS Default Settings 447
VueLink Default Settings 447
Index 449
11

12

1
1Introduction
These Instructions for Use are for clinical professionals using the IntelliVue MX600/MX700/MX800
patient monitor.
This basic operation section gives you an overview of the monitor and its functions. It tells you how to
perform tasks that are common to all measurements (such as entering data, switching a measurement
on and off, setting up and adjusting wave speeds, working with profiles). The alarms section gives an
overview of alarms. The remaining sections tell you how to perform individual measurements, and
how to care for and maintain the equipment.
Familiarize yourself with all instructions including warnings and cautions before starting to monitor
patients. Read and keep the Instructions for Use that come with any accessories, as these contain
important information about care and cleaning that is not repeated here.
This guide describes all features and options. Your monitor may not have all of them; they are not all
available in all geographies. Your monitor is highly configurable. What you see on the screen, how the
menus appear and so forth, depends on the way it has been tailored for your hospital and may not be
exactly as shown here.
In this guide:
•A warning alerts you to a potential serious outcome, adverse event or safety hazard. Failure to
observe a warning may result in death or serious injury to the user or patient.
•A caution alerts you to where special care is necessary for the safe and effective use of the
product. Failure to observe a caution may result in minor or moderate personal injury or damage
to the product or other property, and possibly in a remote risk of more serious injury.
Introducing the Monitor
The IntelliVue MX600/MX700/MX800 patient monitor offers a monitoring solution optimized for
the high-end surgical, cardiac, medical and neonatal care environments. Combining patient surveillance
and data management, it allows multi-measurement monitoring by linking separate modules. The
MX600 uses the navigation knob as primary input device and the MX700/MX800 use the touch
screen as primary input device. All monitors have a remote control for convenient access to the five
main keys and numeric data input.
13

1Introduction
The monitor stores data in trend, event, and calculation databases. You can see tabular trends (vital
signs) and document them on a printer. You can view measurement trend graphs, with up to three
measurements combined in each graph, to help you identify changes in the patient's physiological
condition. You can view fast-changing measurement trends with beat to beat resolution and see up to
four high resolution trend segments. Event surveillance enhances documentation and review of
physiologically significant events by automatically detecting and storing up to 50 user-defined clinical
events over a 24 hour period.
With the optional Integrated PC, you have computer functionality directly in the monitor. You can use
standard applications (e.g. Web browsers), connect to the hospital network or intranet, and run a
second independent display with content from the patient monitor.
An IntelliVue X2 or MP5 can be connected to your monitor, where it acts as a multi-measurement
module, acquiring measurements for the host monitor. When the X2 or MP5 is disconnected from the
the original host monitor, it continues to monitor the patient as a fully independent, battery powered
patient monitor, eliminating the need for a separate transport monitor. On connection to a new host
monitor, the X2 or MP5 resumes its role as multi-measurement module, ensuring fully continuous
monitoring.
Major Parts and Keys
MX600/700:
1 Color coded alarm lamps
2 Alarms Off lamp
3 Power on/Standby switch with
integrated LED: Green - On/
Standby, Red - Error
4 AC power LED
5 Mounting quick-release lever
(when this is pressed the
monitor is not fixed on the
mounting)
6 Part number and serial number
7 Hardkeys (Silence, Alarms Off,
Main Screen)
8 Navigation knob
14

MX800:
1 Introduction
1 Color coded alarm lamps
2 Alarms Off lamp
3 Power on/Standby switch with
integrated LED: Green - On/
Standby, Red - Error
4 AC power LED
5 Mounting quick-release lever
(when this is pressed the
monitor is not fixed on the
mounting)
6 Part number and serial number
Devices for Acquiring Measurements
The patient monitor acquires patient measurements using the devices described in this section. You
can also extend the measurement capabilities of your monitor with such devices. Of these
measurement devices, only the X2 has its own power on/standby switch, and can be powered from an
external power supply or a rechargeable battery when not directly connected to the monitor (refer to
the IntelliVue X2 Instructions for Use for details). All the rest take their power exclusively from the
monitor, and switch on automatically when you turn on the monitor. A green power-on LED indicates
when they are drawing power from the monitor. A permanently illuminated, or flashing, red LED
indicates a problem with the unit that requires the attention of qualified service personnel.
All symbols used on the front panels are explained in “Symbols” on page 389.
WARNING
When connecting devices for acquiring measurements, always position cables and tubing carefully to
avoid entanglement or potential strangulation.
Flexible Module Rack (M8048A)
The 8-slot flexible module rack (FMS-8) lets you use up to eight plug-in physiological measurement
modules. For the MX800, you can connect two FMSs to use up to 10 measurement modules.
The maximum number of specific module types that can be used simultaneously in an FMS-8 is: five
pressure modules, four temperature modules, four VueLink or IntelliBridge modules (any
combination).
15

1Introduction
Connect the FMS to the monitor via the measurement link cable (MSL). Use the MSL connector on
the left-hand side to connect an additional MMS. Use the connector on the right to connect to the
monitor.
4-Slot Flexible Module Rack (FMS-4)
The 4-Slot flexible module rack (FMS-4) lets you use up to four plug-in physiological measurement
modules.
1 X1 Multi-Measurement Module
2 Multi-Measurement Module
mount
3 Flexible Module Rack FMS-8
4 Power on LED
5 Interruption indicator
The maximum number of specific module types that can be used simultaneously in an FMS-4 is: four
pressure modules, four temperature modules, four VueLink or IntelliBridge modules (any
combination).
Connect the FMS to the monitor via the measurement link cable (MSL). Use the MSL connector on
the left-hand side (if you have the appropriate option) to connect an additional MMS. Use the
connector on the back to connect to the monitor.
Measurement Modules
You can use up to eight measurement modules with the Flexible Module Rack (M8048A). Available
modules are:
• Invasive blood pressure (M1006B)
• Temperature (M1029A)
• Oxygen saturation of arterial blood (SpO
• Cardiac output (M1012A), and Continuous cardiac output with M1012A Option #C10
• Transcutaneous gas (M1018A)
• Mixed venous oxygen saturation - SvO
• Intravascular Oxygen Saturation - ScvO
16
) (M1020B)
2
(M1021A)
2
or SvO2 (M1011A)
2

1 Introduction
• Recorder (M1116B)
• VueLink device interface (M1032A)
• IntelliBridge EC10
• EEG (M1027A)
• Bispectral Index - BIS (M1034A)
• Spirometry (M1014A)
You can plug in and unplug modules during monitoring. Insert the module until the lever on the
module clicks into place. Remove a module by pressing the lever upwards and pulling the module out.
A measurement automatically switches on when you plug the module in, and switches off when you
unplug it. Reconnecting a module to the same monitor restores its label and measurement settings,
such as alarms limits. If you connect it to a different monitor, the module remembers only its label.
The connector socket on the front of each module is the same color as the corresponding connector
plug on the transducer or patient cable.
Press the Setup key on the module's front to display the measurement's setup menu on the monitor
screen. When the setup menu is open, a light appears above the key. Some modules have a second key.
On the pressure module, for example, it initiates a zeroing procedure.
Example Module (SpO2)
1 Module name
2 Setup key LED
3 Setup key to enter setup menu of measurement modules or
external device data window. Some modules have a second
module-specific key next to this one, for example Zero.
4 Connector socket for patient cable/transducer
X1 Multi-Measurement Module (M3001A)
The X1 Multi-Measurement Module (MMS) can simultaneously monitor 3-, 5-, 6- or 10-lead ECG
(including arrhythmia and ST monitoring), respiration, SpO
temperature.
You can connect it to the monitor via a cable or mount it on the left side of the FMS.
, NBP and either invasive pressure or
2
17

1Introduction
X1 Connectors and Symbols
1 White ECG/Resp connector
X2 Multi-Measurement Module (M3002A)
The X2 Multi-Measurement Module (MMS) can simultaneously monitor 3-, 5-, 6- or 10-lead ECG
(including arrhythmia and ST monitoring), respiration, SpO
temperature, or CO
. It has a color touchscreen display.
2
2 Blue SpO
3 Red NBP connector
4 Combined pressure (red) and temperature
connector
2
(brown) connector - connect either invasive
pressure transducer or temperature probe.
You might have a version of the MMS that
does not have this connector.
5 NBP STAT key - starts NBP STAT series
of measurements
OR
Zero key - initiates a zero procedure for the
connected pressure transducer when
pressed and held for a second
6 NBP Start/Stop key - starts or stops NBP
measurements
7 Silence: acknowledges all active alarms by
switching off audible alarm indicators and
lamps
, NBP and either invasive pressure and
2
18

1 Introduction
The X2 has the added capability to operate as a stand-alone monitor, and can be powered by a
rechargeable battery. This makes it particularly suited to transport situations. When the X2 is
disconnected from the original host monitor, it continues to monitor the patient as a stand-alone
monitor running on battery power, eliminating the need for a separate transport monitor. When the
X2 is connected to a new host monitor, it resumes its role as MMS, ensuring fully continuous
monitoring. For details of using the X2 as a stand-alone monitor, refer to the IntelliVue X2 Instructions
for Use.
X2 Overview
When connected to a host monitor (
Companion Mode is indicated), the X2 takes power from the
host, including that required for battery charging. The X2 can also be powered by AC mains when not
connected to a host monitor using the optionally available external power supply (M8023A). See the
IntelliVue X2 Instructions for Use for details.
1 On/Standby switch
2 Power and battery indicators (see “X2
Controls and Indicators” on page 20)
3 3.5-inch TFT LCD touchscreen QVGA
display
4 Alarm lamps (see “X2 Controls and
Indicators” on page 20)
5 Battery eject button
6 Hard keys (see “X2 Controls and
Indicators” on page 20)
7 Measurement connectors (see “X2 Patient
Connectors, Right Side” on page 21)
8 Battery compartment
19

1Introduction
X2 Controls and Indicators
1 External power LED. Green when monitor is powered from an external power source.
2 Battery status LED. Yellow when charging. Flashing red when battery is empty.
3 On/Standby LED. Green when monitor is on. Red indicates an error.
4 On/Standby switch. Disabled when X2 is connected to a host monitor
5 Main Screen key: closes all open menus/windows and returns to the main screen.
6 SmartKeys key: brings up SmartKeys on the screen.
7 Alarms key: turns alarms On/Off, or pauses them.
8 Silence key
9 Active alarm lamp. Red or yellow, depending on alarm level. Blinks until active alarm is
acknowledged.
10 Active INOP alarm lamp in light blue. Blinks until active INOP is acknowledged.
11 Alarms off indicator. When alarms are suspended, the lamp is red, and the alarms off symbol is
shown.
20

X2 Patient Connectors, Right Side
Showing symbols version (international) - English version has text labels
1 Introduction
1 Pressure (option)
2 Temperature (option)
3 Noninvasive blood pressure
X2 Left Side
4 SpO
5 ECG sync pulse output
6 ECG/Respiration
7 CO
1 Loudspeaker
2 MSL Connector. Connects to the external power
2
(option in place of Pressure and Temperature)
2
supply or a host monitor via the MSL cable for AC
mains operation, battery charging, and
communication with a network.
MMS Extensions
The MMS extensions connect to the X1 and X2 MMS and use the MMS settings and power. Trend
data and measurement settings from the measurements in the extensions are stored in the MMS.
WARNING
• The MMS extensions can only function when they are connected to an MMS. If the MMS is
removed during monitoring, the measurements from both the MMS and the extension are lost.
• Measurements from an MMS extension connected to an X2 are not available when the X2 is
running on its own battery power. They are only available when the X2 is powered from AC mains,
when connected to a host monitor or the external power supply (M8023A), or from the Battery
Extension.
To separate an extension from the MMS, press the release lever down, and push the MMS forward.
21

1Introduction
M3014A, M3015A, M3015B and M3016A Capnography MMS Extensions
The optional M3014A Capnography extension adds mainstream capnography or sidestream
capnography, and optionally one pressure plus either a pressure or a temperature, Cardiac Output and
Continuous Cardiac Output to the MMS.
M3014A
1 Pressure connectors (red)
2 Temperature connector (brown)
3 Mainstream/sidestream connector CO
4 Cardiac Output connector
2
22

1 Introduction
The optional M3015A Microstream CO2 extension adds microstream capnography and optionally
either pressure or temperature to the MMS. The optional M3015B Microstream CO
extension adds
2
microstream capnography, two pressures and a temperature to the MMS.
M3015A M3015B
1 Pressure connectors (red) - M3015A optional
2 Temperature connector (brown) - M3015A optional
3 Inlet
4 Microstream connector CO
2
5 Gas sample outlet
The optional M3016A Mainstream CO
extension adds mainstream capnography and optionally either
2
pressure or temperature to the MMS.
M3016A
1 Pressure connectors (red)
2 Temperature connector (brown)
3 Mainstream/sidestream connector CO
(optional)
2
When a capnography extension is connected to an X2 MMS with CO
will be automatically deactivated in favor of the one in the X2. If you prefer to use the CO
, the CO2 from the extension
2
2
measurement on the extension, you can activate it via the measurement selection key (see “Resolving
Label Conflicts” on page 40).
23

1Introduction
The cardiac output measurement in the M3014A is deactivated when the extension is used with an X2
MMS, even if the X2 is connected to an external power supply. The cardiac output measurement is
only available when the X2 is connected to a host monitor.
M3012A Hemodynamic MMS Extension
The M3012A Hemodynamic extension can be connected to the M3001A Multi-Measurement Module
to provide the following additional measurements: Temperature, Pressure, an additional Pressure or
Temperature, and C.O. and CCO measurements.
1 Cardiac Output (orange; optional)
2 Connection to MMS
3 Pressure connectors (red)
4 Temperature connectors (brown)
The cardiac output measurement is deactivated when the extension is used with an X2 MMS unless the
X2 is connected to a host monitor.
Operating and Navigating
Everything you need to operate the monitor is contained on its screen. Almost every element on the
screen is interactive. Screen elements include measurement numerics, waveforms, screen keys,
information fields, alarms fields and menus.
The configurability of the monitor means that often you can access the same element in different ways.
For example, you might be able to access an item through its on-screen setup menu, via a hard key, or
via a SmartKey.
24
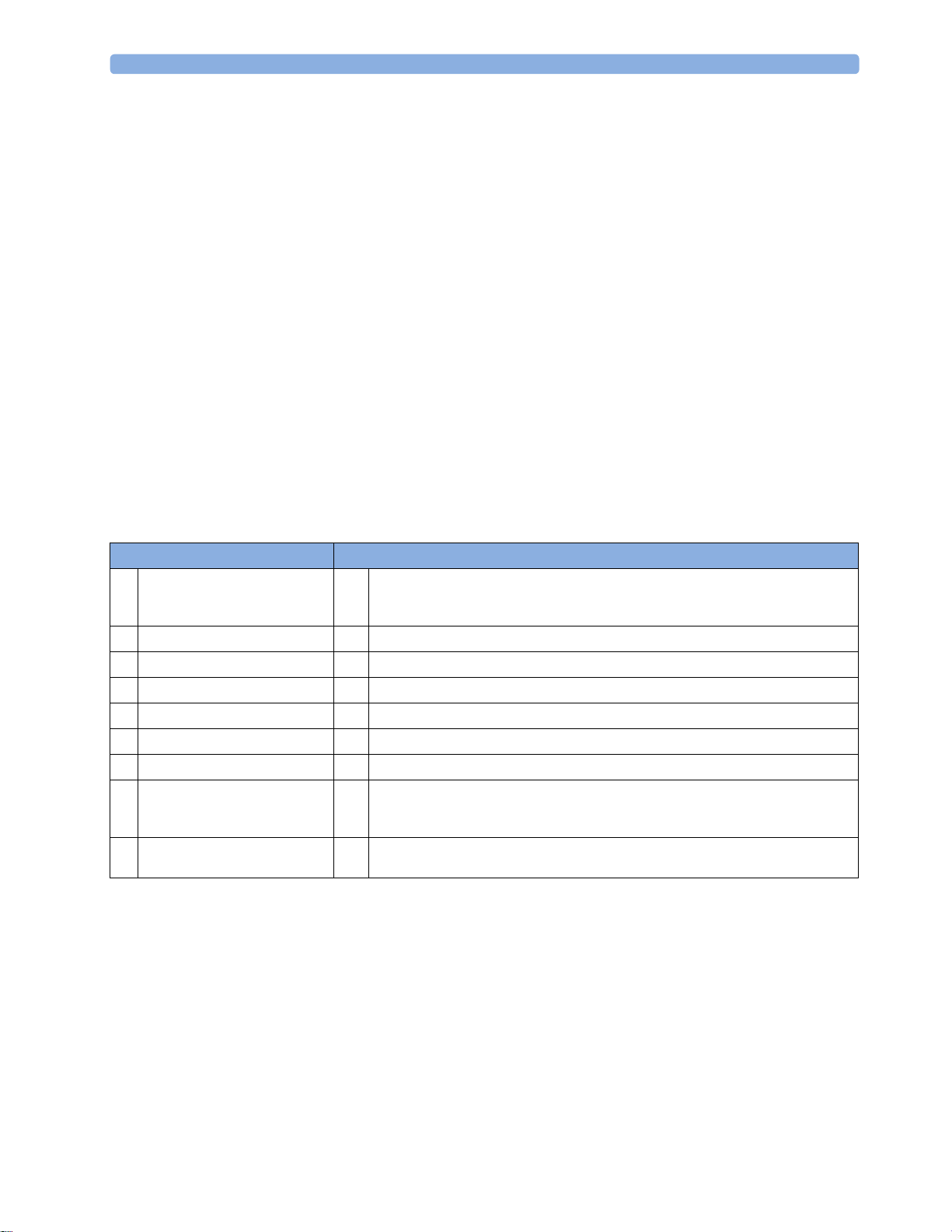
1 Introduction
Monitor information line Other screen elements
network connection indicator
1
(documented in Information
Center Instructions for Use)
bed label
2
patient identification
3
patient category
4
paced status
5
date and time
6
access the Profiles menu
7
current screen name/enter
8
Change Screen menu
adjust alarm volume/level
9
indicator
alarm status area - shows active alarm messages
10
status line - shows information messages and prompting you for action
11
close all open menus and windows and return to main screen
12
enter Main Setup menu
13
scroll right to display more SmartKeys
14
SmartKeys - these change according to your monitor's configuration
15
scroll left to display more SmartKeys
16
Pause Alarms - pauses alarm indicators. Pause duration depends on monitor
17
configuration. If pause duration is infinite, this key is labeled Alarms Off. Select again
to immediately re-enable alarm indicators.
Silence - acknowledges all active alarms by switching off audible alarm indicators and
18
lamps permanently or temporarily, if alarm reminder (ReAlarm) is configured on.
Selecting Screen Elements
Select a screen element to tell the monitor to carry out the actions linked to the element. For example,
select the Patient Identification element to call up the
HR numeric to call up the
menu.
Setup ECG menu. Select the ECG wave segment to call up the ECG Lead
Patient Demographics window, or select the
Note that the space between each line of a menu may be configured to wide or narrow to facilitate
your most common method of operation, either touch, remote control or a pointing device such as a
mouse.
25

1Introduction
Using the Touchscreen
Select screen elements by pressing them directly on the monitor's screen.
Disabling Touchscreen Operation
To temporarily disable touchscreen operation of the monitor, press and hold the Main Screen
permanent key. A padlock will appear on the
Main Screen permanent key.
Press and hold the
Main Screen permanent key again to re-enable the touchscreen operation.
Using a Mouse or Trackball
If you are using a mouse or trackball, select screen elements by clicking on them (press and release the
left mouse button). While you are moving the mouse, a cursor appears and a highlight shows your
current position.
Moving Windows
You can move windows and menus using the Touchscreen or a mouse. To move a window,
1 Select the title of the window and keep your finger on the title, or the mouse button pressed.
2 Move your finger on the Touchscreen, or move the mouse, to move the window.
3 Take your finger off the screen, or release the mouse button, to place the window in the final
position.
The new position is only active until the window or menu is closed. Not all locations on the screen can
be a target position, a window cannot overlap the monitor info line, the alarms and INOPs or the
status line.
Using Keys
The monitor has four different types of keys:
Permanent Keys
A permanent key is a graphical key that remains on the screen all the time to give you fast access to
functions.
26
Pause Alarms - pauses alarm indicators. Pause duration depends on monitor
configuration. If pause duration is infinite, this key is labeled
Select again to immediately re-enable alarm indicators.
Silence - acknowledges all active alarms by switching off audible alarm indicators and
lamps.
Main Screen - close all open menus and windows and return to the main screen.
Main Setup - enter main setup menu.
Alarms Off.

SmartKeys
1 Introduction
A SmartKey is a configurable graphical key, located at the bottom of the main screen. It gives you fast
access to functions. The selection of SmartKeys available on your monitor depends on your monitor
configuration and on the options purchased. If you have an integrated PC (iPC) you may also see
Smartkeys generated by applications on the iPC.
enter profile menu, or revert to
default profile
show BIS Sensor previous Screen
freeze waves quick admit a patient
set alarm limits enter patient identification menu to
change alarm volume end case to discharge a patient
change QRS volume view information for patients in
enter standby mode - suspends
patient monitoring. All waves and
numerics disappear from the display.
All settings and patient data
information are retained.
change Screen, or revert to default
screen
admit/discharge/transfer
other beds
change screen brightness (not for
independent displays)
review beat labels (annotate
arrhythmia wave)
change amplitude (size) of ECG
wave
- start/stop manual NBP
measurement
- start auto series
- stop current automatic
measurement within series
start NBP measurement and
measurement series
start veni puncture (inflate cuff to
subdiastolic pressure)
access patient reports zero invasive pressure transducer
re-learn arrhythmia
enter cardiac output procedure
start NBP STAT measurement
stop automatic or STAT NBP
measurement and measurement
series
stop current NBP measurement
set the NBP repeat time
27

1Introduction
start a delayed recording access pop-up recording keys
access Vital Signs recording function access Select Waves recording
function
set wide automatic alarm limits set narrow automatic alarm limits
access wedge procedure window access the Loops window
review vital signs trend review graph trend
access event surveillance access calculations
access the calculator access the Drug Calculator
gas analyzer - exit standby mode suppress zero for all gas
measurements
unpair equipment and continue
central monitoring with the monitor
unpair equipment and continue
central monitoring with the telemetry
device
access the spirometry data window access ST Map application
start 12-Lead Capture (only available
if Information Center is connected)
access remote applications (if
Application Server is connected)
access EEG CSA access the EEG montage
display external device information access timers
access ProtocolWatch set standard or EASI lead placement
switch CO
pump off new lead setup
2
28
enter data manually start/stop car seat assessment record
open the
Histogram window open Unit Conversion window

Hardkeys
A hardkey is a physical key on a monitoring device, such as the zero pressure key on the MMS or a
setup key on a module.
Pop-Up Keys
Pop-up keys are task-related graphical keys that appear automatically on the monitor screen when
required. For example, the
Confirm pop-up key appears only when you need to confirm a change.
Using the Remote Control
1 Introduction
The remote control provides you with direct access to five hard keys, a navigation knob and a numeric
keypad:
Hardkeys
1 Silence - acknowledges all active alarms by switching off audible alarm indicators and lamps.
Behavior follows the Silence permanent key configuration.
2 Alarms Off/Pause Alarms - pauses alarm indicators. Behavior follows the Pause Alarms
permanent key configuration.
3 Main Screen - close all open menus and windows and return to the main screen.
4 SmartKeys - display a block of SmartKeys specially configured for remote tasks (see below)
5 Back - go back one step to the previous menu.
29

1Introduction
Keypad
6 Type numeric data on the keypad and press the Enter key to enter the data on the monitor.
Navigation knob
7 Rotate the knob to highlight screen elements, then press to select the highlighted element.
The remote control can be used with a USB cable connection to the monitor or without a cable using
short range radio. When used without a cable, the remote control must be assigned to the monitor.
The assignment is made in Configuration or Service mode.
CAUTION
When using a remote control without a cable, it is important that the user knows which remote control
is assigned to which monitor. Use the tethering cable delivered with the remote control to attach it to a
bed rail or IV pole, or label the remote control with the bed or monitor ID.
Using the SmartKeys Key
The SmartKeys hard key on the remote control displays a block of SmartKeys on the monitor screen.
Nine SmartKeys appear in a 3 by 3 matrix which corresponds to the layout of the numeric pad on the
remote control.
Pressing the 1 key on the remote control selects the top left SmartKey, pressing the 8 key selects the
bottom center SmartKey. The . and the key can be used to select the arrow keys to page up and
down in the available SmartKeys.
The SmartKeys which appear can be configured so that you have the functions available which you
most often need when using the remote control. If no list of SmartKeys has been configured, the
standard SmartKeys will be displayed and you can page through to the key you want.
Using the On-Screen Keyboard
30
Use this as you would a conventional keyboard. Enter the information by selecting one character after
another. Use the
single characters, or use the
entered and close the on-screen keyboard.
If a conventional keyboard is connected to the monitor, you can use this instead of or in combination
with the on-screen keyboard.
Shift and capital Lock keys to access uppercase letters. Use the Back key to delete
Clr key to delete entire entries. Select Enter to confirm what you have
 Loading...
Loading...