Philips SAA7212H-C1 Datasheet
DATA SH EET
Preliminary specification
Supersedes data of 1998 Feb 18
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
1998 Sep 07
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
SAA7212
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder

1998 Sep 07 2
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
FEATURES
General features
• Single external Synchronous DRAM organized
as1M×16 interfacing at 81 MHz. Due to efficient
memory use in MPEG decoding, more than 1 Mbit
available for graphics
• Fast 16-bit data + 8-bit address interface with external
controller on 27 MHz. Sustained data rate to external
SDRAM ≤9 Mbytes/s in bursts of 128 bytes
• Dedicated input for audio and video in PES or ES in byte
wide. Data input rate: ≤9 Mbytes/s in byte mode.
Accompanying strobe signals distinguish between audio
and video data
• Dedicated compressed data input compatible with the
VLSI VES2020/2030 demultiplexers; video is received
in byte format and audio serially
• Audio and/or video can also be input via the CPU
interface in PES/ES in 8 or 16-bit parallel format up to a
peak data rate of 9 Mbytes/s
• Single 27 MHz external clock for time base reference
and internal processing. Internal system time base at
90 kHz can be synchronized via CPU port. All required
decoding and presentation clocks are generated
internally
• Flexible memory allocation under control of the external
CPU enables optimized partitioning of memory for
different tasks
• Boundary scan testing implemented
• External SDRAM self test
• Supply voltage 3.3 V
• Package QFP160.
CPU related features
• 16 bits data, 8 bits address, or 16 bits multiplexed bus.
Motorola 68xxx and Intel x 86 compatible.
• Support fast DMA transfer
• Flexible bidirectional interface to external SDRAM.
Minimum sustained rate is 9 Mbytes/s
• Enhanced block mover allows 3 D data move in the
external SDRAM. Picture move/Graphic bit maps
construction can be done with minimum CPU support.
MPEG2 system features
• Parsing of MPEG2 PES and MPEG1 packet streams
• Double system time clock counters
• Stand-alone or supervised audio/video synchronization
• Processing of errors flagged by channel decoding
section
• Support for retrieval of PES header.
MPEG2 video features
• Decoding of MPEG2 video up to main level, main profile
• Output picture format: CCIR-601 4:2:2 interlaced
pictures. Picture format 720 × 576 at 50 Hz or 720 × 480
at 60 Hz
• Support of constant and variable bit rates up to
15 Mbits/s
• Stand-alone or CPU controlled mode for
decoding/display processes
• Stand-alone mode can be used by applications requiring
still pictures manipulations
• Output interface at 8-bit wide, 27 MHz UYVY
multiplexed bus
• Horizontal and vertical pan and scan allows the
extraction of a window from the coded picture
• Flexible horizontal scaling from 0.5 up to 4 allows easy
aspect ratio conversion including support
for 2.21 : 1 aspect ratio movies. In case of shrinking an
anti-aliasing pre-filter is applied
• Vertical scaling with fixed factors 0.5, 1 or 2. Factor 0.5,
realizing picture shrink. Factor 2 can be used for
up-conversion of pictures with 288 (240) lines or less.
• Vertical down-scaling with 0.75 factor, realizing letter
box conversion
• Horizontal and vertical scaling can be combined to scale
pictures to
1
⁄4 their original size, thus freeing up screen
space for graphic applications like electronic program
guides
• Non full screen MPEG pictures will be displayed in a box
of which position and background colour are adjustable
by the external microcontroller
• Nominal video input buffer size for ml@mp 2.7 Mbit
• Video output may be slaved to internally (master)
generated or externally (slave) supplied HV
synchronization signals. The position of active video is
programmable. Display phase is not affected by MPEG
timebase changes.

1998 Sep 07 3
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
• Video output direct connectable to SAA718x encoder
family
• Various trick modes under control of external
microcontroller in stand-alone mode:
– Freeze field/frame on I or P pictures; restart on I
picture
– Freeze field on B pictures; restart on the next I or P
picture.
– Scanning and decoding of I or I + P pictures in a IBP
sequence
– Single step mode
– Repeat/skip field for time base correction.
MPEG2 audio features
• Decoding of 2 channels, layer I and II MPEG audio.
Support for mono, stereo, intensity stereo and dual
channel mode.
• Constant and variable bit rates up to 448 kbit/s
• Supported audio sampling frequencies: 48, 44.1, 32, 24,
22.05 and 16 kHz
• CRC error detection
• 3 decoding modes for dual channel streams: decoding
of CH1 only, decoding of CH2 only and decoding of both
CH1 and CH2
• Storage of last 54 bytes in ancillary data field
• Dynamic Range Control (DRC) at output
• Independent channel volume control and programmable
inter channel crosstalk through a baseband audio
processing unit
• Muting possibility via external controller. Automatic
muting in case of errors or data lack.
• Generation of ‘beeps’ with programmable tone height,
duration and amplitude
• Serial two channel digital audio output with 16, 18, 20 or
22 bits per sample, compatible either to I
2
S or Japanese
formats. Output can be set to high-impedance mode via
the external controller.
• Serial SPDIF audio output. Output can be set to
high-impedance mode.
• Clock output 256 or 384 × fs for external DA converter.
Output can be set to high-impedance mode.
• Audio FIFO in external SDRAM. Programmable buffer
size, at least 64 kbit is available.
• Synchronization modes: PTS controlled, PTS free
running, software controlled, buffer controlled
• PTS register can be set via external controller
• Programmable processing delay compensation
• Software controlled stop and restart functions.
Graphics features
• Graphics are presented in boxes independent of video
format
• Screen arrangement of boxes is determined by display
list mechanism which allows for multiple boxes,
background loading, fast switching, scrolling and fading
of regions
• Support of 2, 4, 8-bit/pixel in fixed bit maps format or
coded in accordance to the DVB variable/run length
standard for region based graphics
• Display colours are obtained via colour look up tables.
CLUT output is YUVT at 8-bit for each signal component
thus enabling 16 M different colours and 6-bit for T
which gives 64 mixing levels with video,
(T = transparency).
• Bit-map table mechanism to specify a sub set of entries
if the CLUT is larger than required by the coded bit
pattern. Supported bit-map tables are 16 to 256,
4 to 256 and 4 to 16.
• Graphics boxes may not overlap vertically. If 256 entry
CLUT has to be down loaded, a vertical separation of
1 line is mandatory.
• Optimized memory utilization in MPEG video decoding
allows for a storage capacity of 1.2 Mbit for graphics bit
maps. Flexibility in memory control enables larger
capacity in a lot of applications. Moreover variable
length/run length encoding makes better use of
available memory capacity for graphics bit maps thus
making full screen graphics at 8-bit/pixel feasible.
• Fast CPU access (9 Mbytes/s) enables full 1.2 Mbit bit
map update within 20 ms
• Internal support for fast block moves in external SDRAM
• Graphics mechanism can be used for signal generation
in the vertical blanking interval. Useful for teletext, wide
screen signalling, closed caption, etc.
• Support for a single down loadable cursor of 1k pixel
with programmable shape. Supported shapes are
8 × 128 pixels, 16 × 64 pixels, 32 × 32 pixels,
64 × 16 pixels and 128 × 8 pixels.
• Cursor colours obtained via 4 entry CLUT with YUVT at
6,4,4 respectively 2 bits. Mixing of cursor with
video + graphics in 4 levels.
• Cursor can be moved freely across the screen without
overlapping restrictions.

1998 Sep 07 4
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
APPLICATIONS
• Tbf.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SAA7212 is an MPEG2 source decoder which combines audio decoding and video decoding. Additionally to these
basic MPEG functions it also provides means for enhanced graphics and/or on-screen display (OSD). Due to an
optimized architecture for audio and video decoding, maximum capacity in external memory and processing power from
the external CPU is available for graphics support.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
ORDERING INFORMATION
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
DD
functional supply voltage 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
I
DD(tot)
total supply current; VDD= 3.3 V − tbf − mA
f
clk
device clock frequency −30 ppm 27.0 +30 ppm MHz
TYPE NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
SAA7212H QFP160 plastic quad flat package; 160 leads (lead length 1.95 mm);
body 28 × 28 × 3.4 mm; high stand-off height
SOT322-1
1998 Sep 07 5
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
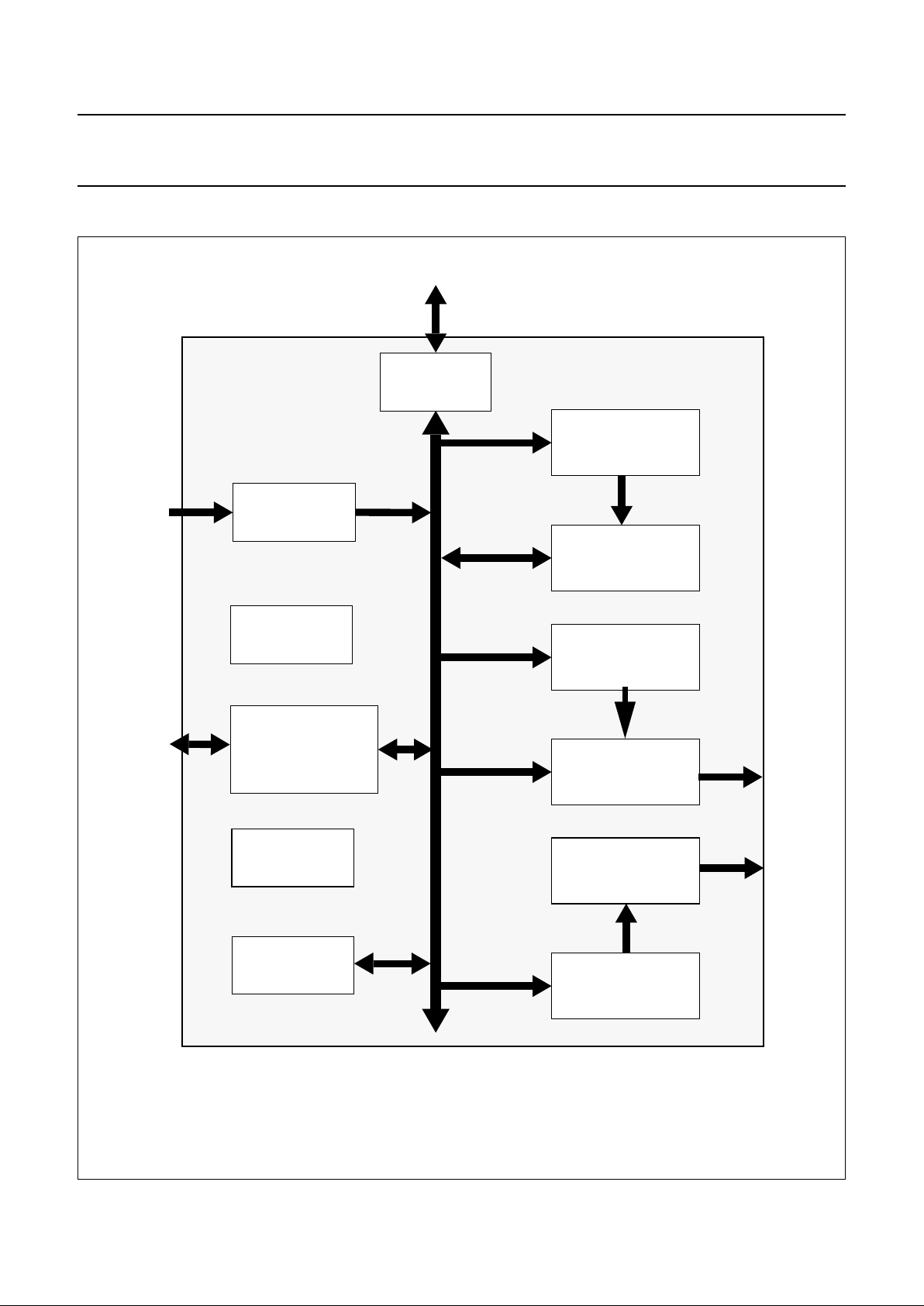
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Fig.1 Block diagram.
Memory
interface
Audio/video
interface
SDRAM
to/from
to
digital
encoder
Display
to
audio
DAC
Decoder
Audio
System time
base unit
Graphics
unit
CPU
unit
external
Decoder
Video
Clock
JTAG
generation
buffer and sync
Video input
from
Demux
buffer and sync
Audio input
Host interface
SDRAM access
unit
1998 Sep 07 6
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Integrated MPEG AVG decoder SAA7212
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
MUX 1 multiplexed/non multiplexed bus
CPU_TYPE 2 Intel/Motorola selection
DMA_ACK 3 DMA acknowledge
DMA_REQ 4 DMA request
DMA_DONE 5 DMA end
DMA_RDY 6 DMA ready
V
SS
7 ground for pad ring
CS 8 chip select.
DS 9 data strobe
AS 10 address strobe
RWN 11 read/write
DTACK 12 data acknowledge
V
DD
13 3.3 V supply for pad ring
IRQ 0 14 individually maskable interrupts
IRQ 1 15 individually maskable interrupts
V_REQ 16 compressed video data request
A_REQ 17 compressed audio data request
V
SS
18 ground for pad ring
V
SSCO
19 ground for core logic
V
DDCO
20 3.3 V supply for core logic
DATA 0 21 CPU data interface
DATA 1 22 CPU data interface
DATA 2 23 CPU data interface
DATA 3 24 CPU data interface
V
DD
25 3.3 V supply for pad ring
DATA 4 26 CPU data interface
DATA 5 27 CPU data interface
DATA 6 28 CPU data interface
DATA 7 29 CPU data interface
V
SS
30 ground for pad ring
DATA 8 31 CPU data interface
DATA 9 32 CPU data interface
DATA 10 33 CPU data interface
DATA 11 34 CPU data interface
V
DD
35 3.3 V supply for pad ring
DATA 12 36 CPU data interface
DATA 13 37 CPU data interface
DATA 14 38 CPU data interface
DATA 15 39 CPU data interface
V
SS
40 ground for pad ring
 Loading...
Loading...