Philips SAA7184WP, SAA7185BWP Datasheet

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
SAA7184; SAA7185B
Digital Video Encoders
(DENC2-M6)
Preliminary specification
Supersedes data of 1995 Nov 14
File under Integrated Circuits, IC22
1996 Jul 03

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoders (DENC2-M6) SAA7184; SAA7185B
FEATURES
• CMOS 5 V device
• Digital PAL/NTSC encoder
• System pixel frequency 13.5 MHz
• Accepts MPEG decoded data
• 8-bit wide MPEG port
• Input data format Cb, Y, Cr etc. (CCIR 656)
• 16-bit wide YUV input port
• I2C-bus control port or alternatively MPU parallel control
port
• Encoder can be master or slave
• Programmable horizontal and vertical input
synchronization phase
• Programmable horizontal sync output phase
• OVL overlay with Look-Up Tables (LUTs) 8 × 3 bytes
• Colour bar generator
• Line 21 closed caption encoder
• Cross-colour reduction
• Macrovision revision_6 Pay-per-View copy protection
system as option (SAA7184 only). Remark: This device
is protected by U.S. patent numbers 4631603 4577216
and 4819098 and other intellectual property rights.
Use of the Macrovision anticopy process in the device is
licensed for non-commercial home use only. Reverse
engineering or disassembly is prohibited. Please
contact your nearest Philips Semiconductors sales
office for more information.
• DACs operating at 27 MHz with 10-bit resolution
• Controlled rise and fall times of output syncs and
blanking
• Down-mode of DACs
• CVBS and S-Video output simultaneously
• PLCC68 package.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SAA7184 and SAA7185B digital video encoders 2
(DENC2-M6) encode digital YUV video data to an NTSC
or PAL CVBS or S-Video signal.
The circuit accepts CCIR compatible YUV data with
720 active pixels per line in 4:2:2 multiplexed formats,
for example MPEG decoded data. The device includes a
sync/clock generator and on-chip Digital-to-Analog
Converters (DACs).
The circuit is compatible to the DIG-TV2 chip family.
ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE NUMBER
SAA7184WP
SAA7185BWP
1996 Jul 03 2
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PLCC68 plastic leaded chip carrier; 68 leads SOT188-2
PACKAGE

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoders (DENC2-M6) SAA7184; SAA7185B
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
DDA
V
DDD
I
DDA
I
DDD
V
i
V
o(p-p)
R
L
ILE LF integral linearity error −−±2 LSB
DLE LF differential linearity error −−±1 LSB
T
amb
BLOCK DIAGRAM
analog supply voltage 4.75 5.0 5.25 V
digital supply voltage 4.5 5.0 5.5 V
analog supply current − 50 55 mA
digital supply current − 130 170 mA
input signal voltage levels TTL compatible V
analog output signal voltages Y, C and CVBS without load
− 2 − V
(peak-to-peak value)
load resistance 80 −−Ω
operating ambient temperature 0 − +70 °C
MP7
to MP0
VP0
to VP7
RCM1
RCM2
20 to 27
9 to 16
29
30
1,8,19
28,35,
42,62
V
SSD1
V
SSD7
to
SEL_ED
8
8
63 to 66
2 to 5
18
MANAGER
8
DP0
to DP7
SEL_MPU
KEY
DATA
OVL0
to OVL2
31
8
CSN/SA
V
DDD1
RTCI
32 to 34
8
CONTROL
INTERFACE
6168
59 60 58 57 41 40 38 39 36 6 7
A0/SDA
RWN/SCL
DTACK
43
ENCODER
88
clock timing signals
RES
to V
DDD3
17,37,67
internal control bus
XTALI
LLC
XTALO
INTERFACE
CREF
OUTPUT
SYNC
CLK
CDIR
8
RCV1
RCV2
V
V
V
refH
IOA
5547
A
D
SAA7184
SAA7185B
DDA1
to
DDA4
48,50,
54,56
MGC679
53
51
49
52
46
CVBS
Y
CHROMA
V
SSA
V
refL
Fig.1 Block diagram.
1996 Jul 03 3
l pagewidth

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoders (DENC2-M6) SAA7184; SAA7185B
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN I/O DESCRIPTION
V
SSD1
DP4 to DP7 2 to 5 I/O Upper 4 bits of the data port; if pin 68 (SEL_MPU) is HIGH, the data bus of
RCV1 6 I/O Raster control 1 for video port; depending on the synchronization mode, this
RCV2 7 I/O Raster control 2 for video port; depending on the synchronization mode, this
V
SSD2
VP0 to VP7 9 to 16 I Video port; this is an input for CCIR 656 compatible multiplexed video data. If
V
DDD1
SEL_ED 18 I select encoder data; selects input data either from the MPEG port or from
V
SSD3
MP7 to MP0 20 to 27 I MPEG port; it is an input for CCIR 656 style multiplexed YUV data.
V
SSD4
RCM1 29 O Raster control 1 for MPEG port; this pin provides a VS/FS/FSEQ signal.
RCM2 30 O Raster control 2 for MPEG port; this pin provides an HS pulse for the MPEG
KEY 31 I key signal for OVL (active HIGH)
OVL0 to OVL2 32 to 34 I on-screen display data; this is the index for the internal OVL look-up tables
V
SSD5
CDIR 36 I Clock direction; if the CDIR input is HIGH, the circuit receives a clock signal,
V
DDD2
LLC 38 I/O Line-locked clock; this is the 27 MHz master clock for the encoder. The
CREF 39 I/O Clock reference signal; this is the clock qualifier for DIG-TV2 compatible
XTALO 40 O crystal oscillator output (to crystal)
XTALI 41 I Crystal oscillator input (from crystal). If the oscillator is not used, this pin
V
SSD6
RTCI 43 I Real time control Input; if the clock is provided by the SAA7151B or
AP 44 − test pin (should be connected to digital ground for normal operation)
SP 45 − test pin (should be connected to digital ground for normal operation)
V
refL
V
refH
V
DDA1
1 − digital ground 1
the parallel MPU interface is used. If pin 68 is LOW, then the UV lines of the
video port are used.
pin receives or provides a VS/FS/FSEQ signal.
pin receives or provides an HS/HREF/CBL signal.
8 − digital ground 2
the 16-bit DIG-TV2 format is used, then Y data is input.
17 I digital supply voltage 1
the video port
19 − digital ground 3
28 − digital ground 4
decoder.
35 − digital ground 5
if not LLC and CREF are generated by the internal crystal oscillator.
37 I digital supply voltage 2
direction is set by the CDIR pin.
signals. The polarity is programmable by software.
should be connected to ground.
42 − digital ground 6
SAA7111, RTCI should be connected to the RTCO pin of the decoder to
improve the signal quality.
46 I lower reference voltage input for the DACs
47 I upper reference voltage input for the DACs
48 I analog positive supply voltage 1 for the DACs and output amplifiers
1996 Jul 03 4

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoders (DENC2-M6) SAA7184; SAA7185B
SYMBOL PIN I/O DESCRIPTION
CHROMA 49 O analog output of the chrominance signal
V
DDA2
Y 51 O analog output of the luminance signal
V
SSA
CVBS 53 O analog output of the CVBS signal
V
DDA3
IOA 55 I current input for the output amplifiers (connected via a 15 kΩ resistor to
V
DDA4
RES 57 I Reset input, active LOW. After reset is applied, all outputs are in 3-state input
DTACK 58 O Data acknowledge output of the parallel MPU interface, active LOW,
RWN/SCL 59 I If pin 68 (SEL_MPU) is HIGH, this is the read/write signal of the parallel MPU
A0/SDA 60 I/O If pin 68 (SEL_MPU) is HIGH, this is the address signal of the parallel MPU
CSN/SA 61 I If pin 68 (SEL_MPU) is HIGH, this is the chip select signal of the parallel
V
SSD7
DP0 to DP3 63 to 66 I/O Lower 4 bits of the data port; if pin 68 (SEL_MPU) is HIGH, the data bus of
V
DDD3
SEL_MPU 68 I Select MPU interface input; if it is HIGH, the parallel MPU interface is active,
50 I analog supply voltage 2 for the DACs and output amplifiers
52 − analog ground for the DACs and output amplifiers
54 I analog supply voltage 3 for the DACs and output amplifiers
)
V
DDA
56 I analog supply voltage 4 for the DACs and output amplifiers
mode. The I2C-bus receiver waits for the start condition.
otherwise high impedance.
2
interface. Otherwise it is the I
interface. Otherwise it is the I
MPU interface. Otherwise it is the I
C-bus serial clock input.
2
C-bus serial data input/output.
2
C-bus slave address select pin. When
LOW slave address = 88H, when HIGH slave address = 8CH.
62 − digital ground 7
the parallel MPU interface is used. If pin 68 is LOW, then the UV lines of the
video port are used.
67 I digital supply voltage 3
2
if not the I
C-bus interface will be used.
1996 Jul 03 5

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoders (DENC2-M6) SAA7184; SAA7185B
handbook, full pagewidth
refL
refH
RWN/SCL
A0/SDA
60
59
DTACK
58
RES
57
DDA4
V
56
IOA
55
DDA3
V
54
CVBS
53
V
52
SSA
DDA2
Y
V
51
50
DDA1
V
CHROMA
49
48
V
V
47
46
SP
45
AP
44
CSN/SA
V
SSD7
DP0
DP1
DP2
DP3
V
DDD3
SEL_MPU
V
SSD1
DP4
DP5
DP6
DP7
RCV1
RCV2
V
SSD2
VP0
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
SAA7184
SAA7185B
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
RTCI
V
SSD6
XTALI
XTALO
CREF
LLC
V
DDD2
CDIR
V
SSD5
OVL2
OVL1
OVL0
KEY
RCM2
RCM1
V
SSD4
MP0
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
VP1
VP2
VP3
VP4
VP5
VP6
VP7
DDD1
V
SEL_ED
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
1996 Jul 03 6
19
SSD3
V
20
MP7
21
MP6
22
MP5
23
MP4
24
MP3
25
MP2
26
MGC678
MP1

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoders (DENC2-M6) SAA7184; SAA7185B
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The digital MPEG-compatible video encoder (DENC2-M6)
encodes digital luminance and chrominance into analog
CVBS and S-Video (Y/C) signals simultaneously. NTSC-M
and PAL B/G standards and sub-standards are also
supported.
The basic encoder function consists of subcarrier
generation and colour modulation plus insertion of
synchronization signals. Luminance and chrominance
signals are filtered in accordance with the standard
requirements of RS-170-A and CCIR 624.
For ease of analog post filtering the signals are twice
oversampled, with respect to the pixel clock, before
digital-to-analog conversion.
For total filter transfer characteristics see Figs 3, 4,
5 and 6. The DACs are realized with full 10-bit resolution.
The encoder provides three 8-bit wide data ports that
serve different applications.
The MPEG port and the video port accept 8 lines
multiplexed Cb-Y-Cr data.
The video port is also able to accommodate DIG-TV2
family compatible 16-bit YUV signals. In this event, the
data port is used for the U/V components.
Alternatively, the data port can accommodate the data of
an 8-bit wide microprocessor interface.
The 8-bit multiplexed Cb-Y-Cr formats are CCIR 656
(D1 format) compatible, but the SAV, EAV etc. codes are
not decoded.
A crystal-stable master clock (LLC) of 27 MHz, which is
twice the CCIR line-locked pixel clock frequency of
13.5 MHz, needs to be supplied externally. A crystal
oscillator input/output pair of pins and an on-chip clock
driver are provided optionally. It is also possible to connect
the Philips Digital Video Decoder (SAA7111 or
SAA7151B) in conjunction with a CREF clock qualifier to
the DENC2-M6 via the RETCI pin (connected to RTCO) of
a decoder. Information concerning the actual subcarrier,
PAL-ID and (with SAA7111) definite subcarrier phase can
be inserted.
The DENC2-M6 synthesizes all necessary internal
signals, colour subcarrier frequency and synchronization
signals, from that clock. The DENC2-M6 is always the
timing master for the MPEG port but can also be
configured as master or slave for the video port.
The IC also contains closed caption and extended data
services encoding (line 21), and supports anti-taping
signal generation in accordance with Macrovision.
It also supports OVL via KEY and 3-bit overlay techniques
using a 24 × 8 LUT.
2
The IC can be programmed via the I
MPU interface, but only one interface configuration can be
active at a time. If the 16-bit video port mode (VP and DP)
is being used, only the I2C-bus interface can be selected.
A number of possibilities are provided for setting the
different video parameters such as:
black and blanking level control
colour subcarrier frequency
black variable burst amplitude etc.
During reset (RES = LOW) and after reset is released, all
digital I/O stages are set to the input mode. A reset forces
the control interfaces to abort any running bus transfer and
to set register 3AH to contents 1FH, register 61H to
contents 06H, and registers 6CH and 7AH to contents
00H. All other control registers are not influenced by a
reset.
Data manager
Real time arbitration on the data stream to be encoded is
performed in the data manager.
Depending on the hardware conditions (signals on pins
SEL_ED, KEY, OVL2 to OVL0, MP7 to MP0, VP7 to VP0
and DP7 to DP0) and different software programming,
either data from the MP port, from the VP port or from the
OVL port, is selected to be encoded to CVBS and Y/C
signals.
Optionally, the OVL colour look-up tables located in this
block can be read out in a pre-defined sequence
(8 steps per active video line) thereby achieving, for
example, a colour bar test pattern generator without the
need for an external data source. The colour bar function
is only under software control.
Encoder
IDEO PATH
V
The encoder generates luminance and colour subcarrier
output signals, suitable for use as CVBS or separate Y/C
signals, from the Y, U and V baseband signals.
C-bus or via the 8-bit
1996 Jul 03 7

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoders (DENC2-M6) SAA7184; SAA7185B
The luminance gain and offset are modified (offset being
programmable within a certain range to enable different
black level set-ups). After the signals have been inserted,
a fixed synchronization level in accordance with standard
composite synchronization schemes and blanking level,
(also programmable in a certain range to allow for
manipulations with Macrovision anti-tapping) additional
insertion of AGC super white pulses (programmable in
height) is supported.
In order to enable easy analog post filtering, luminance is
interpolated from a 13.5 MHz data rate to a 27 MHz data
rate, thereby providing luminance in a 10-bit resolution.
This filter is also used to define smoothed transients for
synchronization pulses and blanking period. The transfer
characteristics of the luminance interpolation filter are
illustrated in Figs 5 and 6.
The chrominance gain is modified (programmable
separately for U and V), a standard dependent burst is
inserted before baseband colour signals are interpolated
from a 6.75 MHz data rate to a 27 MHz data rate. One of
the interpolation stages can be bypassed, thereby
providing a higher colour bandwidth, which can be used for
the Y/C output. The transfer characteristics of the
chrominance interpolation filter are illustrated in
Figs 3 and 4.
The amplitude of the inserted burst is programmable within
a certain range, suitable for standard signals and for
special effects. Colour in a 10-bit resolution is provided on
the subcarrier after the succeeding quadrature modulator.
The numeric ratio between Y and C outputs is in
accordance with set standards.
C
LOSED CAPTION ENCODER
Using the closed caption encoder circuit, data in
accordance with the specification of closed caption or
extended data service, delivered by the control interface,
can be encoded (line 21). Two dedicated pairs of bytes
(two bytes per field) are possible, each pair preceded by
run-in clocks and framing code.
The actual line number where data is to be encoded, can
be modified within a certain range.
The data clock frequency is in accordance with the
definition for NTSC-M standard 32 times horizontal line
frequency.
Data LOW at the output of the DACs corresponds to 0 IRE,
data HIGH at the output of the DACs corresponds to
approximately 50 IRE.
It is also possible to encode closed caption data for 50 Hz
field frequencies at 32 times horizontal line frequency.
Output interface
In the output interface, encoded Y and C signals are
converted from digital to analog in a 10-bit resolution and
then combined into a 10-bit CVBS signal. Also, in front of
the summation point, the luminance signal can be fed
through a further filter stage (optional), thereby
suppressing components in the subcarrier frequency
range. Thus, a type of cross colour reduction is provided,
which is useful in a standard TV set with CVBS input.
The slopes of the synchronization pulses are not affected
with any active cross colour reduction.
Three different filter characteristics or bypass are
available, see Fig.5.
The CVBS output occurs with the same processing delay
as the Y and C outputs. Absolute amplitudes at the input
of the DAC for CVBS is reduced by
and C DACs to make maximum use of conversion ranges.
Outputs of all DACs can be set together, via software
control, to minimum output voltage for either purpose.
Synchronization
The synchronization of the DENC2 is able to operate in
two modes; slave mode and master mode.
In the slave mode, the circuit accepts synchronization
pulses at the bidirectional RCV1 port. The timing and
trigger behaviour, related to the video signal on VP
(and DP, if used), can be influenced by programming the
polarity and on-chip delay of RCV1. The active slope of
RCV1 defines the vertical phase and, as an option, the
odd/even and colour frame phase to be initialized. It can
also be used to set the horizontal phase.
If the horizontal phase is not to be influenced by RCV1, a
horizontal pulse needs to be applied at pin RCV2. Timing
and trigger behaviour can also be influenced for RCV2.
If there are missing pulses at RCV1 and/or RCV2, the time
base of the DENC2-M6 will become free-running, thus an
arbitrary number of synchronization slopes may miss, but
no additional pulses must occur (such as with wrong
phase).
If the vertical and horizontal phase is derived from RCV1,
RCV2 can be used for horizontal or composite blanking
input or output.
15
⁄16 with respect to Y
1996 Jul 03 8

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoders (DENC2-M6) SAA7184; SAA7185B
In the master mode, the time base of the circuit is
continuously free-running. At the RCV1 port, the IC can
output:
• A vertical sync signal (VS) with 3 or 2.5 lines duration, or
• An odd/even signal which is LOW in odd fields, or
• A field sequence signal (FSEQ) which is HIGH in the first
of 4 respectively 8 fields.
The IC can provide a horizontal pulse with programmable
start and stop phase at the RCV2 port. This pulse can be
inhibited in the vertical blanking period to build up, for
example, a composite blanking signal.
The phase of the output pulses at RCV1 or RCV2 are
referenced to the VP port, polarity of both signals is
selectable.
The DENC2-M6 isalways the timing master for the source
at the MP input. The IC provides two signals for
synchronizing this source:
1. At the RCM1 port the same signals as at RCV1
(as output) are available.
2. At RCM2 the IC provides a horizontal pulse with
programmable start and stop phase.
The start and end of the active part can be programmed.
The active part of a field always starts at the beginning of
a line if the standard blanking option SBLBN is not set.
Control interface
DENC2-M6 contains two control interfaces, an I
2
C-bus
slave transceiver and an 8-bit parallel microprocessor
interface. The interfaces cannot be used simultaneously.
The I2C-bus interface is a standard slave transceiver,
supporting 7-bit slave addresses and 400 kbits/s
guaranteed transfer rate. It uses 8-bit subaddressing with
an auto-increment function. All registers are write only,
except one status byte which can be read.
The parallel interface is defined by:
D7 to D0 data bus
CS active LOW chip select signal
RW read/write signal, LOW for a write cycle
DTACK 680xx style data acknowledge (handshake),
active-LOW
A0 register select, LOW selects address, HIGH selects
data.
The parallel interface uses two registers, one
auto-incremental containing the current address of a
control register (equals subaddress with I2C-bus control),
and one containing actual data. The currently addressed
register is mapped to the corresponding control register.
The status byte can be read (optionally) via a read access
to the address register, no other read access is provided.
Input levels and formats
DENC2-M6 accepts digital YUV data with levels (digital
codes) in accordance with CCIR 601.
Deviating amplitudes in the colour difference signals can
be compensated for by independent gain control setting,
while the gain for luminance is set to predefined values,
distinguishable for 7.5 IRE set-up or without set-up.
The MPEG port accepts only 8-bit multiplexed CCIR 656
compatible data.
2
If the I
C-bus interface is used, the VP port can
accommodate both formats, 8-bit multiplexed Cb-Y-Cr
data on the VP lines, or the 16-bit DTV2 format with the Y
signal on the VP lines and the UV signal on the DP port.
Reference levels are measured with a colour bar,
100% white, 100% amplitude and 100% saturation.
Two I2C-bus slave addresses can be selected
(pin SEL_MPU must be LOW):
88H: pin 61 = LOW
8CH: pin 61 = HIGH.
1996 Jul 03 9
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoders (DENC2-M6) SAA7184; SAA7185B
Table 1 CCIR signal component levels
SIGNAL IRE DIGITAL LEVEL CODE
016
Y
100 235
bottom peak 16
Cb
top peak 240
bottom peak 16
Cr
top peak 240
Table 2 8-bit multiplexed format (similar to CCIR 656)
TIME 0 1 2 2 4 5 6 7
Sample Cb
0
Y
0
Cr
0
Y
1
Cb
Luminance pixel number 0 1 2 3
Colour pixel number 0 2
straight binary50 126
straight binarycolourless 128
straight binarycolourless 128
2
Y
2
Cr
2
Y
3
Table 3 16-bit multiplexed format (DTV2 format)
TIME 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Sample Y line Y
Sample UV line Cb
0
0
Y
Cr
1
0
Y
Cb
2
2
Luminance pixel number 0 1 2 3
Colour pixel number 0 2
Y
Cr
3
2
1996 Jul 03 10

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital Video Encoders (DENC2-M6) SAA7184; SAA7185B
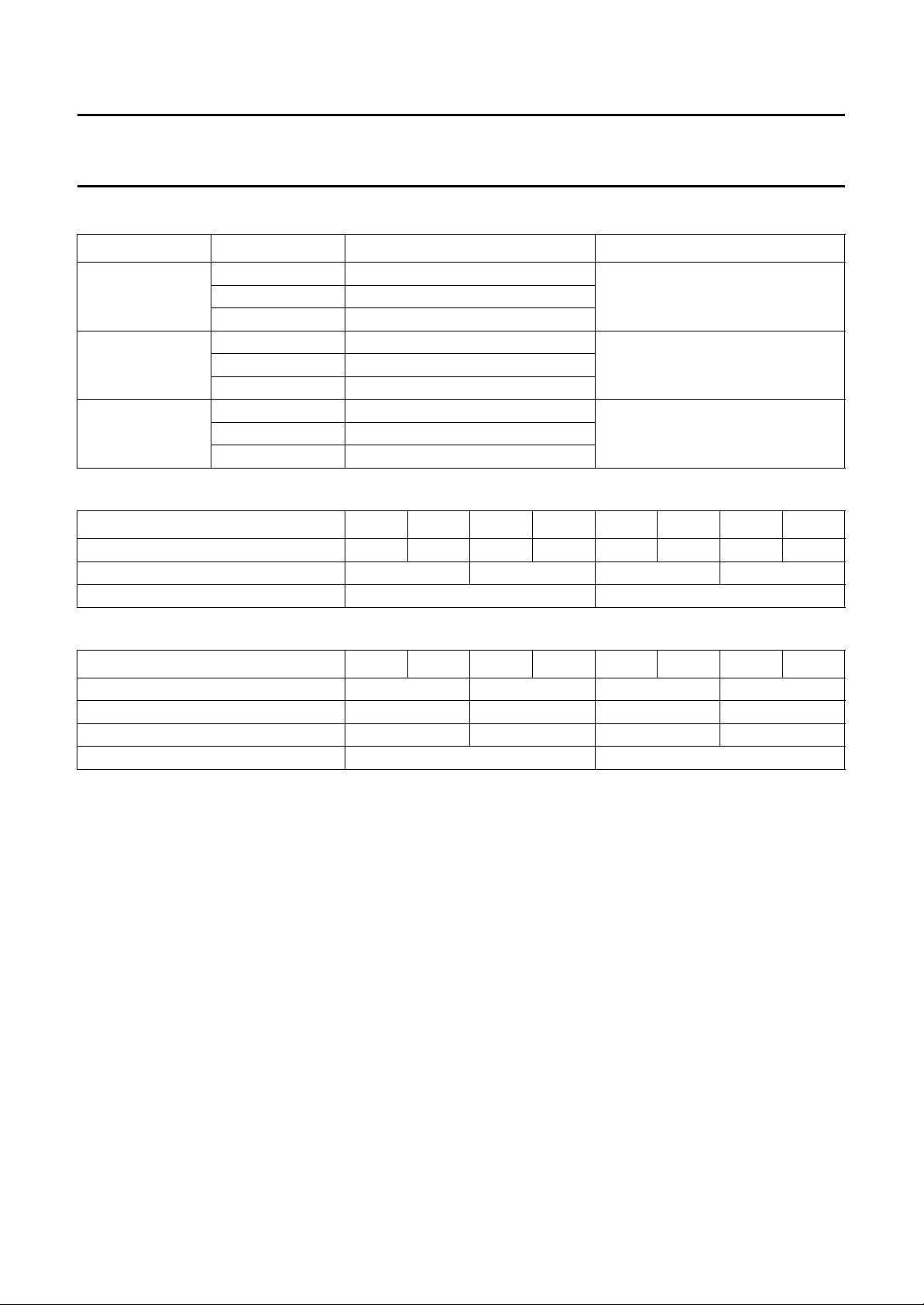
DATA BYTE (note 1)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
SUB
ADDRESS
↓↓
↓↓
REGISTER FUNCTION
Null 00 00000000
Null 39 00000000
Input port control 3A CBENB 0 0 V656 VY2C VUV2C MY2C MUV2C
OVL LUT Y0 42 OVLY07 OVLY06 OVLY05 OVLY04 OVLY03 OVLY02 OVLY01 OVLY00
OVL LUT U0 43 OVLU07 OVLU06 OVLU05 OVLU04 OVLU03 OVLU02 OVLU01 OVLU00
Bit allocation map
Table 4 Slave receiver (slave address 88h or 8Ch)
1996 Jul 03 11
OVL LUT V0 44 OVLV07 OVLV06 OVLV05 OVLV04 OVLV03 OVLV02 OVLV01 OVLV00
OVL LUT Y7 57 OVLY77 OVLY76 OVLY75 OVLY74 OVLY73 OVLY72 OVLY71 OVLY70
OVL LUT U7 58 OVLU77 OVLU76 OVLU75 OVLU74 OVLU73 OVLU72 OVLU71 OVLU70
OVL LUT V7 59 OVLV77 OVLV76 OVLV75 OVLV74 OVLV73 OVLV72 OVLV71 OVLV70
Chrominance phase 5A CHPS7 CHPS6 CHPS5 CHPS4 CHPS3 CHPS2 CHPS1 CHPS0
Gain U 5B GAINU7 GAINU6 GAINU5 GAINU4 GAINU3 GAINU2 GAINU1 GAINU0
Gain V 5C GAINV7 GAINV6 GAINV5 GAINV4 GAINV3 GAINV2 GAINV1 GAINV0
Gain U MSB, black level 5D GAINU8 0 BLCKL5 BLCKL4 BLCKL3 BLCKL2 BLCKL1 BLCKL0
Gain V MSB, blanking level 5E GAINV8 0 BLNNL5 BLNNL4 BLNNL3 BLNNL2 BLNNL1 BLNNL0
Null 60 00000000
Standard control 61 0 DOWN INPI1 YGS RTCE SCBW PAL FISE
Burst amplitude 62 DECTYP BSTA6 BSTA5 BSTA4 BSTA3 BSTA2 BSTA1 BSTA0
Subcarrier 0 63 FSC07 FSC06 FSC05 FSC04 FSC03 FSC02 FSC01 FSC00
Subcarrier 1 64 FSC15 FSC14 FSC13 FSC12 FSC11 FSC10 FSC09 FSC08
Subcarrier 2 65 FSC23 FSC22 FSC21 FSC20 FSC19 FSC18 FSC17 FSC16
Subcarrier 3 66 FSC31 FSC30 FSC29 FSC28 FSC27 FSC26 FSC25 FSC24
Line 21 odd 0 67 L21O07 L21O06 L21O05 L21O04 L21O03 L21O02 L21O01 L21O00
Line 21 odd 1 68 L21O17 L21O16 L21O15 L21O14 L21O13 L21O12 L21O11 L21O10
Line 21 even 0 69 L21E07 L21E06 L21E05 L21E04 L21E03 L21E02 L21E01 L21E00
Line 21 even 1 6A L21E17 L21E16 L21E15 L21E14 L21E13 L21E12 L21E11 L21E10
Encoder control, CC line 6B MODIN1 MODIN0 PCREF SCCLN4 SCCLN3 SCCLN2 SCCLN1 SCCLN0
RCV port control 6C SRCV11 SRCV10 TRCV2 ORCV1 PRCV1 CBLF ORCV2 PRCV2
 Loading...
Loading...