Philips PXT2222A Datasheet
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS
DATA SH EET
ook, halfpage
M3D109
PXT2222A
NPN switching transistor
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1997 May 05
1999 Apr 14
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
NPN switching transistor PXT2222A
FEATURES
• High current (max. 600 mA)
PINNING
PIN DESCRIPTION
• Low voltage (max. 40 V).
APPLICATIONS
• General purpose switching and linear amplification.
DESCRIPTION
handbook, halfpage
NPN switching transistor in a SOT89 plastic package.
PNP complement: PXT2907A.
MARKING
TYPE NUMBER MARKING CODE
PXT2222A p1P
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
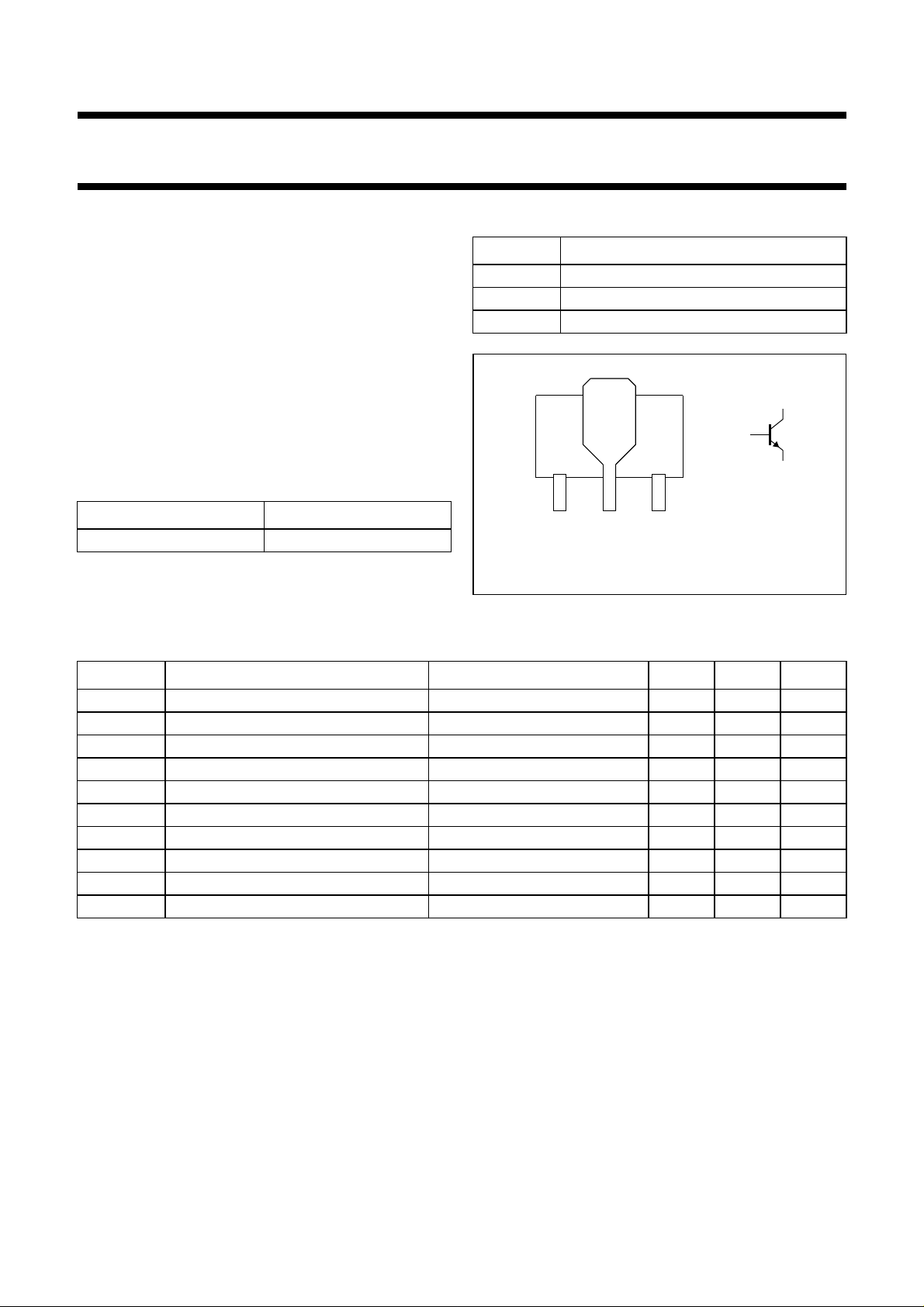
1 emitter
2 collector
3 base
2
3
1
123
Bottom view
MAM296
Fig.1 Simplified outline (SOT89) and symbol.
SYMBOL P ARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
CBO
V
CEO
V
EBO
I
C
I
CM
I
BM
P
tot
T
stg
T
j
T
amb
collector-base voltage open emitter − 75 V
collector-emitter voltage open base − 40 V
emitter-base voltage open collector − 6V
collector current (DC) − 600 mA
peak collector current − 800 mA
peak base current − 200 mA
total power dissipation T
≤ 25 °C; note 1 − 1.25 W
amb
storage temperature −65 +150 °C
junction temperature − 150 °C
operating ambient temperature −65 +150 °C
Note
2
1. Device mounted on a printed-circuit board, single-sided copper, tinplated, mounting pad for collector 6 cm
For other mounting conditions, see
“Thermal considerations for SOT89 in the General Part of associated Handbook”.
.
1999 Apr 14 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
NPN switching transistor PXT2222A
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS VALUE UNIT
R
th j-a
R
th j-s
Note
1. Device mounted on a printed-circuit board, single-sided copper, tinplated, mounting pad for collector 6 cm2.
For other mounting conditions, see
CHARACTERISTICS
=25°C unless otherwise specified.
T
j
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
I
CBO
I
EBO
h
FE
V
CEsat
V
BEsat
C
c
C
e
f
T
F noise figure I
thermal resistance from junction to ambient note 1 100 K/W
thermal resistance from junction to soldering point 20 K/W
“Thermal considerations for SOT89 in the General Part of associated Handbook”.
collector cut-off current IE= 0; VCB=60V − 10 nA
I
= 0; VCB= 60 V; T
E
= 125 °C − 10 µA
amb
emitter cut-off current IC= 0; VBE=5V − 10 nA
DC current gain IC= 0.1 mA; VCE= 10V 35 −
= 1 mA; VCE=10V 50 −
I
C
I
= 10 mA; VCE=10V 75 −
C
collector-emitter saturation
voltage
= 10 mA; VC=10V; T
I
C
I
= 150 mA; VCE=1V 50 −
C
I
= 150 mA; VCE= 10 V 100 300
C
= 500 mA; VCE=10V 40 −
I
C
IC= 150 mA; IB=15mA − 300 mV
I
= 500 mA; IB=50mA − 1V
C
= −55 °C35 −
amb
base-emitter saturation voltage IC= 150 mA; IB= 15 mA 0.6 1.2 V
I
= 500 mA; IB=50mA − 2V
C
collector capacitance IE=ie= 0; VCB= 10 V; f = 1 MHz − 8pF
emitter capacitance IC=ic= 0; VEB= 500 mV; f = 1 MHz − 25 pF
transition frequency IC= 20 mA; VCE= 10 V; f = 100 MHz 300 − MHz
= 200 µA; VCE=5V; RS=2kΩ;
C
− 4dB
f = 1 kHz; B = 200 Hz
Switching times (between 10% and 90% levels); (see Fig.2)
t
on
t
d
t
r
t
off
t
s
t
f
turn-on time I
delay time − 15 ns
rise time − 20 ns
turn-off time − 250 ns
storage time − 200 ns
fall time − 60 ns
= 150 mA; I
Con
I
= −15 mA
Boff
1999 Apr 14 3
=15mA;
Bon
− 35 ns
 Loading...
Loading...