Philips PCF1252-0P-F4, PCF1252-0T-F4, PCF1252-5P, PCF1252-5P-F4, PCF1252-5T-F4 Datasheet
...
DATA SH EET
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1996 Jan 23
File under Integrated Circuits, IC11
1998 Apr 16
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
PCF1252-X family
Threshold detector and reset
generator

1998 Apr 16 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Threshold detector and reset generator PCF1252-X family
FEATURES
• Very low current consumption, typically 10 µA
• 10 factory programmed threshold voltages available
covering trip voltages from 4.75 to 2.55 V
•±50 mV trip point accuracy over full temperature range
• Variable RESET delay
• RESET pulse polarity selection
• Defined outputs at 0.6 V (typ.)
• Comparator for second level detection
(e.g. overvoltage detection)
• Advance warning of power fail
• Operating temperature range −40 to +85 °C.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The PCF1252-Xs are low-power CMOS voltage threshold
detectors designed especially for supervision of
microcontroller/microprocessor systems for detection of
power-on/off conditions and generation of a system reset
pulse. The PCF1252-X also provides a POWF (power fail)
output which is activated at a precise factory-programmed
trip point. A system RESET output has a built-in delay with
duration determined by an external capacitor (CCT).
A second comparator (comparator 2) has been included to
enable the possibility of a second monitoring point in the
system.
ORDERING INFORMATION
Note
1. X = 0 to 9; depending on threshold voltage.
BLOCK DIAGRAM
TYPE NUMBER
PACKAGE
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PCF1252-XP
(1)
DIP8 plastic dual in-line package; 8 leads (300 mil) SOT97-1
PCF1252-XT
(1)
SO8 plastic small outline package; 8 leads; body width 3.9 mm SOT96-1
Fig.1 Block diagram.
handbook, full pagewidth
+
−
+
−
COMIN
comparator 2
83
5
PCF1252-X
7
6
1
CT SELECT
RESET
POWF
COMOUT
MGC915
1.30 V
42
comparator 1
DELAY
V
DD
V
SS

1998 Apr 16 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Threshold detector and reset generator PCF1252-X family
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
CT 1 connection for the external capacitor
SELECT 2 select polarity or external reset input
COMIN 3 comparator input
V
SS
4 ground (0 V)
COMOUT 5 comparator output
RESET 6 reset output
POWF 7 power failure signal output
V
DD
8 supply voltage
Fig.2 Pinning diagram.
handbook, halfpage
1
2
3
4
CT
SELECT
COMIN
V
SS
V
DD
POWF
RESET
COMOUT
8
7
6
5
MGC916
PCF1252-X
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION (see Fig.1)
The PCF1252-X contains:
• A precise factory-programmed voltage reference
• Two comparators
• A delay circuit.
The PCF1252-X family is comprised of 10 versions with
different factory-programmed voltage trip-points (V
TRIP
),
see Chapter “Characteristics”.
Supply
The supply voltage (V
DD
) is internally divided before being
compared, via comparator 1, with the internal reference
voltage.
POWF (see Fig.3)
The POWF output is:
• LOW, if VDD is below V
TRIP
• HIGH, if VDD is above V
TRIP
.
Power-on reset (SELECT = LOW)
As V
DD
rises past V
TRIP
, a positive reset pulse is generated
at RESET. The duration of the reset pulse (tR) is
determined by the value of the external capacitor (CCT;
maximum 1 µF, see Fig.8) connected to CT. With no
external capacitor connected, CCT assumes a minimum
value of 100 pF. If SELECT is HIGH, the reset pulse is
inverted.
Power failure
During a power-off condition (V
DD<VTRIP
), POWF goes
LOW. After a time delay (tS), also determined by CCT,
RESET goes HIGH. Any POWF assertion (VDD<V
TRIP
)
will result in a subsequent RESET pulse.
Voltage trip-point
By selecting the voltage trip-point slightly higher than the
minimum operating voltage of the
microcontroller/microprocessor, there is sufficient time for
data storage before the power actually fails.
In order to prevent oscillations around the voltage
trip-point, a small hysteresis has been included, resulting
in a power-on switching point that is higher than the
voltage trip-point (minimum of 15 mV). The voltage
trip-point refers to the value at which power-off is signalled.
COMIN
Input to the second comparator (comparator 2).
When used in conjunction with an external voltage divider,
this allows a second point in the system to be monitored.
This input has no built-in hysteresis. When not in use
connect to V
DD
. COMOUT will be LOW or HIGH
depending on the voltage at COMIN:
• COMOUT = HIGH, if voltage at COMIN is above the
switch point VSP (typically 1.30 V).
• COMOUT = LOW, if voltage at COMIN is below the
switch point VSP (typically 1.30 V).

1998 Apr 16 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Threshold detector and reset generator PCF1252-X family
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
HANDLING
Inputs and outputs are protected against electrostatic discharge in normal handling. However, to be totally safe, it is
desirable to take normal handling precautions appropriate to handling MOS devices (see
“Handling MOS Devices”
).
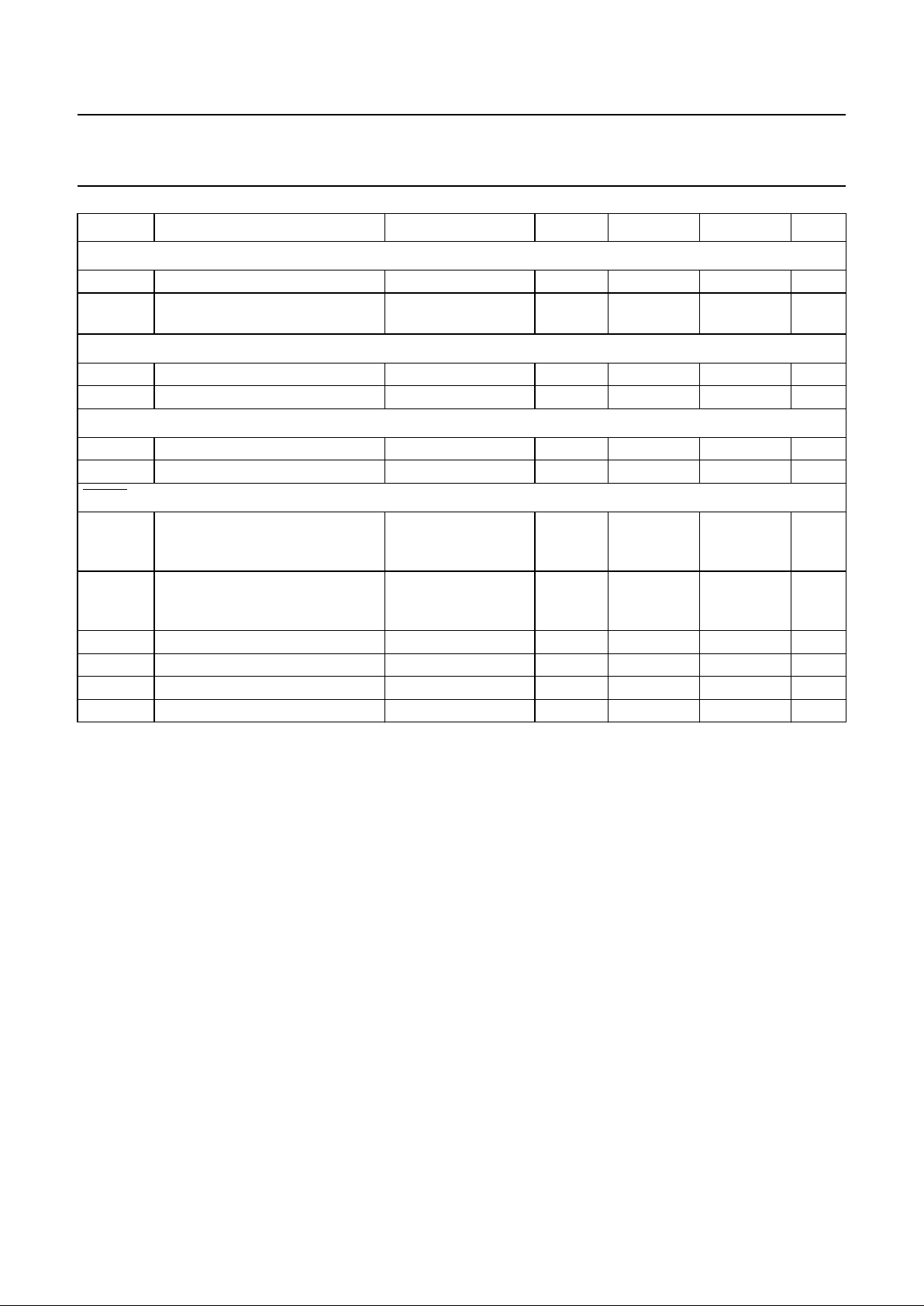
CHARACTERISTICS
V
DD
= 2.4 to 6.0 V; VSS=0V; T
amb
= −40 to +85 °C; (see Fig.3); unless otherwise specified.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
DD
supply voltage −0.5 +7.0 V
V
I
input voltage −0.5 VDD+ 0.5 V
I
I
DC clamp-diode current all pins: VI< −0.5 V
or VI>VDD+ 0.5 V
− 20 mA
I
O
output current − 20 mA
P
tot
total power dissipation − 150 mW
T
stg
storage temperature −65 +100 °C
T
amb
operating ambient temperature −40 +85 °C
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
DD
supply voltage 2.4 − 6.0 V
V
TRIP
Voltage trip-point: T
amb
=25°C; note 1
PCF1252-0 4.70 4.75 4.80 V
PCF1252-1 4.50 4.55 4.60 V
PCF1252-2 4.20 4.25 4.30 V
PCF1252-3 4.00 4.05 4.10 V
PCF1252-4 3.70 3.75 3.80 V
PCF1252-5 3.50 3.55 3.60 V
PCF1252-6 3.20 3.25 3.30 V
PCF1252-7 3.00 3.05 3.10 V
PCF1252-8 2.70 2.75 2.80 V
PCF1252-9 2.50 2.55 2.60 V
I
DD
supply current T
amb
=25°C;
VDD=V
TRIP
+ 0.5 V;
COMIN = VDD;
see Figs. 4 and 5
− 10 15 µA
∆V
TRIP
voltage trip-point temperature
coefficient
note 2 −±100 × 10−6±400 × 10−6mV/K
V
hys
voltage trip-point hysteresis 15 30 50 mV
1998 Apr 16 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Threshold detector and reset generator PCF1252-X family
Notes
1. Long time stability of COMIN switch point VSP and voltage trip point V
TRIP
: within 10 years of continuous operation
at V
DD(max)
and an average operating temperature of 55 °C the drift of VSP will not exceed ±10 mV. The maximum
drift for V
TRIP
will not exceed (±V
TRIP(typ)/VSP(typ)
) 10 mV.
2. Values given per degree Kelvin; tested on a sample basis.
3. Conformance to these specifications is only guaranteed if the slew rate of VDD is less than 25 V/ms.
COMIN
V
SP
COMIN switch point T
amb
=25°C; note 1 1.28 1.30 1.32 V
∆V
SP
COMIN switch point temperature
coefficient
note 2 −±0.1 ±0.5 mV/K
SELECT
V
IL
LOW level input voltage −− 0.3V
DD
V
V
IH
HIGH level input voltage 0.7V
DD
−−V
SELECT and COMIN
I
LI
LOW level leakage input current −− −1.0 µA
I
LI
HIGH level leakage input current −− 1.0 µA
POWF, RESET and COMOUT
I
O
output sink current VO= 0.4 V;
VDD= 2.4 V;
see Fig.6
13 − mA
I
O
output source current VO= 2.0 V;
VDD= 2.4 V;
see Fig.7
−0.75 −2 − mA
t
R
reset time CCT= 1 nF; note 3 400 1000 2000 µs
t
S
save time CCT= 1 nF; note 3 40 100 200 µs
t
R/tS
reset to save time ratio − 10 −
C
int
CT internal capacitance − 100 − pF
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
 Loading...
Loading...