Philips PCD3359AH, PCD3359AP Datasheet
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
PCD3359A
8-bit microcontroller with DTMF
generator and 128 bytes EEPROM
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1996 Dec 18
File under Integrated Circuits, IC03
1998 May 11

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontroller with DTMF
generator and 128 bytes EEPROM
CONTENTS
1 FEATURES
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
4 BLOCK DIAGRAM
5 PINNING INFORMATION
5.1 Pinning
5.2 Pin descriptions
6 FREQUENCY GENERATOR
6.1 Frequency generator derivative registers
6.2 Melody output (P1.7/MDY)
6.3 Frequency registers
6.4 DTMF frequencies
6.5 Modem frequencies
6.6 Musical scale frequencies
7 EEPROM AND TIMER 2 ORGANIZATION
7.1 EEPROM registers
7.2 EEPROM latches
7.3 EEPROM flags
7.4 EEPROM macros
7.5 EEPROM access
7.6 Timer 2
8 INTERRUPTS
8.1 Derivative interrupt
8.2 Port 0 Wake-up interrupts
PCD3359A
9 TIMING
10 RESET
11 IDLE MODE
12 STOP MODE
13 INSTRUCTION SET RESTRICTIONS
14 OVERVIEW OF PORT AND
POWER-ON-RESET CONFIGURATION
15 SUMMARY OF DERIVATIVE REGISTERS
16 HANDLING
17 LIMITING VALUES
18 DC CHARACTERISTICS
19 AC CHARACTERISTICS
20 PACKAGE OUTLINES
21 SOLDERING
21.1 Introduction
21.2 DIP
21.3 LQFP and SO
22 DEFINITIONS
23 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
1998 May 11 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontroller with DTMF
generator and 128 bytes EEPROM
1 FEATURES
• 8-bit CPU, ROM, RAM, EEPROM and I/O; in a single
28-lead or 32-lead package
• 2-kbyte ROM
• 64-byte RAM
• 128-byte EEPROM
• OTP version available
• Over 100 instructions (based on MAB8048) all of
1 or 2 cycles
• 20 quasi-bidirectional I/O port lines
• 8-bit programmable Timer/event counter 1
• 8-bit reloadable Timer 2
• Three single-level vectored interrupts:
– external
– 8-bit programmable Timer/event counter 1
– derivative; triggered by reloadable Timer 2
• Wake-up via external or Port 0 interrupt
• Two test inputs, one of which also serves as the external
interrupt input
• DTMF, modem, musical tone generator
• Reference for supply and temperature-independent
tone output
• Filtering for low output distortion (CEPT compatible)
• Melody output for ringer application
• Power-on-reset
• Stop and Idle modes
• Supply voltage: 1.8 to 6 V (DTMF tone output and
EEPROM erase/write from 2.5 V)
PCD3359A
• Clock frequency: 1 to 16 MHz (3.58 MHz for DTMF
suggested)
• Operating temperature: −25 to +70 °C
• Manufactured in silicon gate CMOS process.
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
This data sheet details the specific properties of the
PCD3359A. The shared properties of the PCD33xxA
family of microcontrollers are described in the
family”
with this publication.
The PCD3359A is a low voltage microcontroller oriented
towards telephony applications. It includes an on-chip
generator for dual tone multifrequency (DTMF) generator,
modem and musical tones. In addition to dialling,
generated frequencies can be made available as square
waves (P1.7/MDY) for melody generation, providing ringer
operation (in which case the TONE output is disabled).
A wake-up function via Port 0 interrupt facilitates keyboard
interfacing. The PCD3359A can be emulated with the OTP
microcontroller PCD3756A.
The device also incorporates 128 bytes of Electrically
Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EEPROM).
The EEPROM can be used for storing telephone numbers,
particularly for implementing redial functions.
The instruction set is similar to that of the MAB8048 and is
a sub-set of that listed in the
sheet.
data sheet, which should be read in conjunction
“PCD33xxA family”
“PCD33xxA
data
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
PCD3359AP DIP28 plastic dual in-line package; 28 leads (600 mil) SOT117-1
PCD3359AT SO28 plastic small outline package; 28 leads; body width 7.5 mm SOT136-1
PCD3359AH LQFP32 plastic low profile quad flat package; 32 leads; body 7 × 7 × 1.4 mm SOT358-1
Note
1. Please refer to the Order Entry Form (OEF) for this device for the full type number to use when ordering. This type
number will also specify the required program and the ROM mask options.
1998 May 11 3
(1)
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PACKAGE
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
1998 May 11 4
4 BLOCK DIAGRAM
8-bit microcontroller with DTMF
generator and 128 bytes EEPROM
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8
TIMER 2
RELOAD
REGISTER
POWER-ON-RESET
PORT 2
FLIP-FLOP
RESET
GENERATOR
HGF
REGISTER
8
EEPROM
ADDRESS
REGISTER
EEPROM
128 bytes
TONE
FILTER
SINE WAVE
8
LGF
REGISTER
8
EEPROM
TRANSFER
DATA
8
AND PORT
INTERRUPT
CONTROL
REGISTER
derivative
interrupt
MELODY
8
8
INTERRUPT
LOGIC
INTERNAL
CLOCK
FREQ.
30
32
T1
8
ACCUMULATOR
timer interrupt
port 0 interrupt
external interrupt
STOP
IDLE
PORT 1
FLIP-FLOP
TIMER/
EVENT
COUNTER
8
TEMPORARY
REGISTER 2
CE/T0
INTERRUPT INITIALIZE
P2.0 to P2.3
4 7
PORT 2
BUFFER
4
V
POR
8
EEPROM
CONTROL
REGISTER
8
TIMER 2
REGISTER
P1.7/MDY P1.0 to P1.6
PORT 1
BUFFER
8
88
TEMPORARY
REGISTER 1
CONTROL AND TIMING
OSCILLATOR
MEMORY
FLIP-FLOPS
PCD3359A
ARITHMETIC
LOGIC UNIT
DECIMAL
ADJUST
XTAL2XTAL1RESET
RESIDENT ROM
8 kbytes
(PCD3356A)
6 kbytes
(PCD3357A)
2 kbytes
(PCD3359A)
DECODE
BANK
HIGHER
PROGRAM
COUNTER
88
INSTRUCTION
CONDITIONAL
LOWER
PROGRAM
COUNTER
5888 8
8
REGISTER
AND
DECODER
T1
CE/T0
BRANCH
LOGIC
TIMER
CARRY
ACC
RAM
ADDRESS
REGISTER
FLAG
ACC BIT
TEST
PROGRAM
STATUS
WORD
P0.0 to P0.7
PORT 0
BUFFER
PORT 0
FLIP-FLOP
8
MULTIPLEXER
REGISTER 0
REGISTER 1
REGISTER 2
REGISTER 3
REGISTER 4
REGISTER 5
D
REGISTER 6
E
REGISTER 7
C
8 LEVEL STACK
O
(VARIABLE LENGTH)
D
OPTIONAL SECOND
E
REGISTER BANK
DATA STORE
RESIDENT RAM ARRAY
8
MBK811
handbook, full pagewidth
Fig.1 Block diagram.
PCD3359A
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontroller with DTMF
generator and 128 bytes EEPROM
5 PINNING INFORMATION
5.1 Pinning
handbook, halfpage
P0.1
P0.2
P0.3
P0.4
P0.5
P0.6
P0.7
T1
XTAL1
XTAL2
RESET
CE/T0
P1.0
P1.1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
PCD3359A
8
9
10
11
12
13
MBK809
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
1514
P0.0
P2.3
P2.2
P2.1
V
DD
TONE
V
SS
P2.0
P1.7/MDY
P1.6
P1.5
P1.4
P1.3
P1.2
PCD3359A
handbook, full pagewidth
Fig.2 Pin configuration (SOT117-1 and SOT136-1).
P2.2
P2.3
P0.0
n.c.
P0.1
P0.2
P0.3
P0.4
31
n.c.
P0.5
P0.6
P0.7
T1
XTAL1
XTAL2
RESET
32
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
CE/T0
10
P1.0
30
29
PCD3359A
11
12
P1.1
P1.2
28
13
n.c.
27
14
P1.3
26
15
P1.4
25
16
P1.5
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
MBK810
P2.1
V
DD
TONE
V
SS
P2.0
P1.7/MDY
P1.6
n.c.
Fig.3 Pin configuration (SOT358-1).
1998 May 11 5
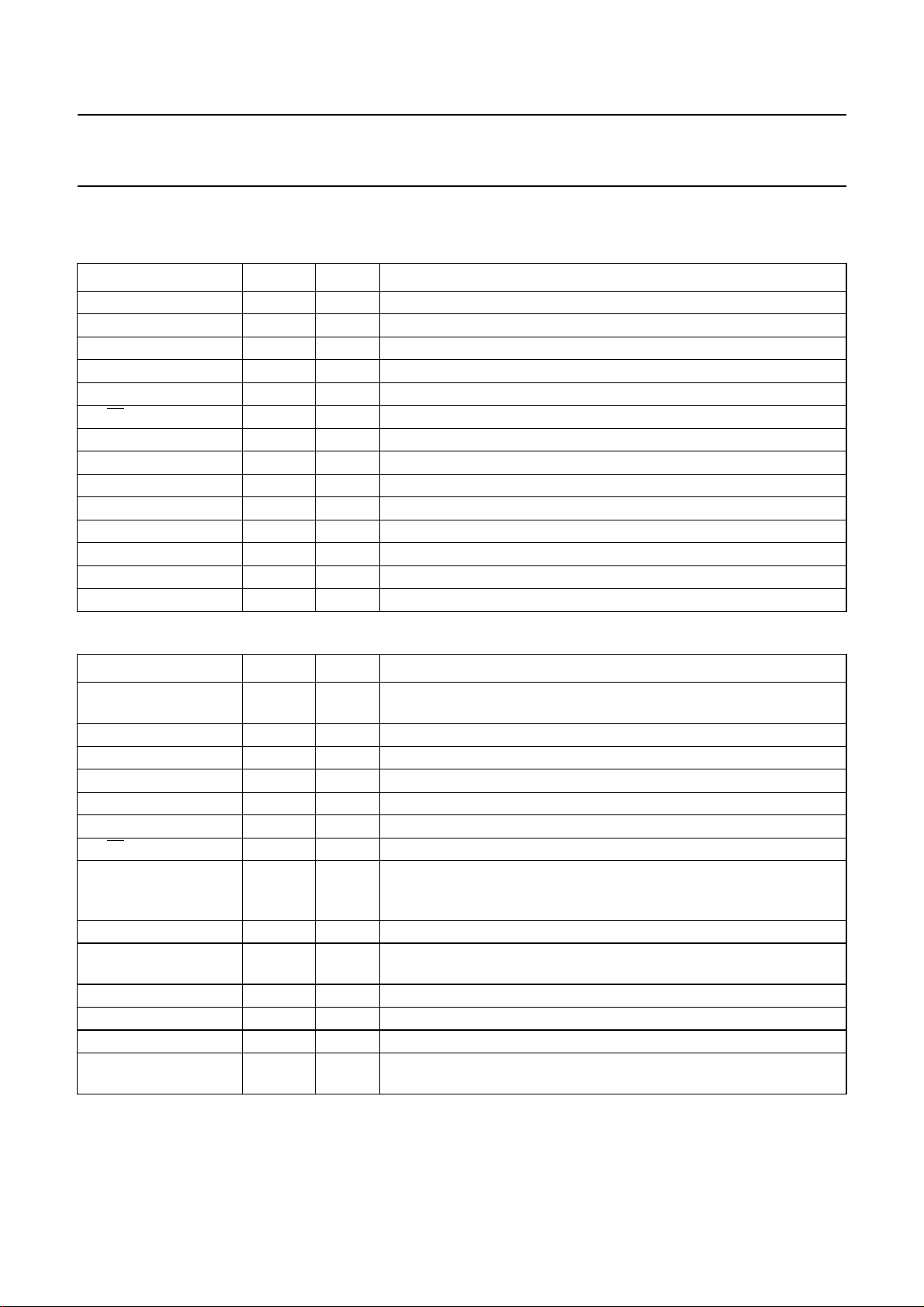
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontroller with DTMF
PCD3359A
generator and 128 bytes EEPROM
5.2 Pin descriptions
Table 1 SOT117-1 and SOT136-1 packages (for information on parallel I/O ports, see Chapter 14)
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION
P0.1 to P0.7 1 to 7 I/O 7 bits of Port 0: 8-bit quasi-bidirectional I/O port; or wake-up interrupts
T1 8 I Test 1 or count input of 8-bit Timer/event counter 1
XTAL1 9 I crystal oscillator or external clock input
XTAL2 10 O crystal oscillator output
RESET 11 I reset input
CE/
T0 12 I Chip Enable or Test 0
P1.0 to P1.6 13 to 19 I/O 7 bits of Port 1: 8-bit quasi-bidirectional I/O port
P1.7/MDY 20 I/O 1 bit of Port 1: 8-bit quasi-bidirectional I/O port; or melody output
P2.0 21 I/O 1 bit of Port 2: 4-bit quasi-bidirectional I/O port
V
SS
TONE 23 O DTMF, modem, musical tone output
V
DD
P2.1 to P2.3 25 to 27 I/O 3 bits of Port 2: 4-bit quasi-bidirectional I/O port
P0.0 28 I/O 1 bit of Port 0: 8-bit quasi-bidirectional I/O port; or wake-up interrupts
22 P ground
24 P positive supply voltage
Table 2 SOT358-1 package(for information on parallel I/O ports, see Chapter14)
SYMBOL PIN TYPE DESCRIPTION
n.c. 1, 13,
17, 28
P0.5 to P0.7 2 to 4 I/O 3 bits of Port 0: 8-bit quasi-bidirectional I/O port; or wake-up interrupts
T1 5 I Test 1 or count input of 8-bit Timer/event counter 1
XTAL1 6 I crystal oscillator or external clock input
XTAL2 7 O crystal oscillator output
RESET 8 I reset input
CE/
T0 9 I Chip Enable or Test 0
P1.0 to P1.6 10 to 12
14 to 16
18
P1.7/MDY 19 I/O 1 bit of Port 1: 8-bit quasi-bidirectional I/O port; or melody output
P2.0 to P2.3 20,
24 to 26
V
SS
TONE 22 O DTMF output
V
DD
P0.0 to P0.4 27,
21 P ground
23 P positive supply voltage
29 to 32
− not connected
I/O 7 bits of Port 1: 8-bit quasi-bidirectional I/O port
I/O 4 bits of Port 2: 4-bit quasi-bidirectional I/O port
I/O 5 bits of Port 0: 8-bit quasi-bidirectional I/O port; or wake-up interrupts
1998 May 11 6

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontroller with DTMF
PCD3359A
generator and 128 bytes EEPROM
6 FREQUENCY GENERATOR
A versatile frequency generator section is provided (see
Fig.4). For normal operation, use a 3.58 MHz quartz
crystal or PXE resonator. The frequency generator
includes precision circuitry for dual tone multifrequency
(DTMF) signals, which is typically used for tone dialling
telephone sets.Their frequencies are provided in purely
sinusoidal form on the TONE output or as square waves
on the P1.7/MDY output.
6.1 Frequency generator derivative registers
6.1.1 H
Table 3 gives the addresses, symbols and access types of the High Group Frequency (HGF) and Low Group Frequency
(LGF) Registers.
Table 3 Hexadecimal addresses,symbols, access types and bit symbols of the frequency registers
REGISTER
ADDRESS
IGH AND LOW GROUP FREQUENCY REGISTERS
REGISTER
SYMBOL
11H HGF W H7H6H5H4H3H2H1H0
12H LGF W L7L6L5L4L3L2L1L0
ACCESS
TYPE
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
The TONE output can alternatively issue twelve modem
frequencies for data rates between 300 and 1200 bits/s.
In addition to DTMF and modem frequencies, two octaves
of musical scale in steps of semitones are available.
In case no tones are generated, or the melody function is
used, the TONE output is in 3-state mode.
BIT SYMBOLS
6.1.2 MELODY AND PORT INTERRUPT CONTROL REGISTER (MDYCON)
The Melody and Port Interrupt Control Register has two functions: bit 0 defines the behaviour of the melody output; bits
4 to 7 individually enable/disable specific pairs of Port 0 interrupts. MDYCON is a R/W register.
Table 4 Melody and Port Interrupt Control Register (address 13H)
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
EPI3 EPI2 EPI1 EPI0 0 0 0 EMO
Table 5 Description of MDYCON bits
BIT SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
7 to 4 EPI3 to EPI0 Enable Port 0 interrupts. Bits 7 to 4 individually enable/disable specific pairs of Port 0
interrupts; see Table 6 and Section 8.2 for details.
3to1 − These bits are set to a logic 0.
0 EMO Enable Melody Output. If bit EMO = 0, then P1.7/MDY is a standard port line and the
TONE output is enabled. If bit EMO = 1, then P1.7/MDY is the melody output and the
TONE output is disabled (3-state). EMO = 1 does not inhibit the port instructions for
P1.7/MDY. Therefore, the state of both port line and flip-flop may be read in and the port
flip-flop may be written by port instructions. However, the port flip-flop of P1.7/MDY
must remain set to avoid conflicts between melody and port outputs. When the HGF
contents are zero while EMO = 1, P1.7/MDY is in the logic HIGH state.
1998 May 11 7
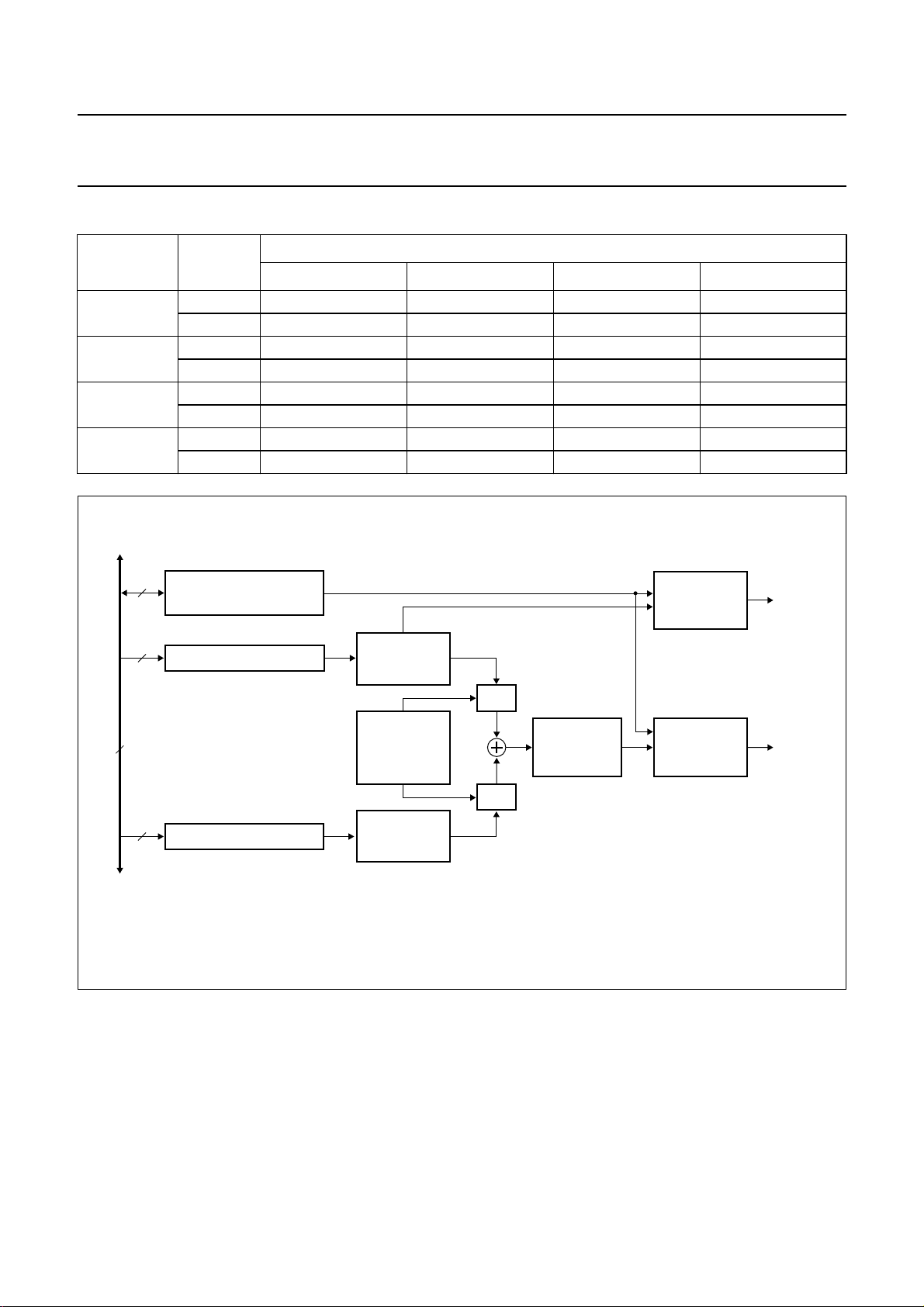
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontroller with DTMF
PCD3359A
generator and 128 bytes EEPROM
Table 6 Port0 Interrupts control bits
BIT STATE
P0.0 AND P0.1 P0.2 AND P0.3 P0.4 AND P0.5 P0.6 AND P0.7
EPI0 1 enabled −−−
0 disabled −−−
EPI0 1 − enabled −−
0−disabled −−
EPI0 1 −−enabled −
0 −−disabled −
EPI0 1 −−−enabled
0 −−−disabled
handbook, full pagewidth
8
MELODY AND PORT
INTERRUPT
CONTROL REGISTER
INTERRUPTS
square wave
PORT/MELODY
OUTPUT LOGIC
P1.7/
MDY
8
8
INTERNAL BUS
8
Fig.4 Block diagram of the frequency generator and melody output (P1.7/MDY) section.
HGF REGISTER
LGF REGISTER
DIGITAL
SINE WAVE
SYNTHESIZER
SWITCHED
CAPACITOR
BANDGAP
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
DIGITAL
SINE WAVE
SYNTHESIZER
DAC
DAC
SWITCHED
CAPACITOR
LOW-PASS
FILTER
RC LOW-PASS
FILTER/OUTPUT
LOGIC
MGB823
TONE
1998 May 11 8

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
-
8-bit microcontroller with DTMF
generator and 128 bytes EEPROM
6.2 Melody output (P1.7/MDY)
The melody output (P1.7/MDY) is very useful for
generating musical notes when a purely sinusoidal signal
is not required, such as for ringer applications.
If bit EMO = 1 in the Melody and Port Interrupt Control
Register the TONE output is disabled (3-state) and a
square wave with the frequency defined by the HGF
contents is output on line P1.7/MDY. The square wave
(duty cycle =12⁄23or 52%) will include the attenuated
harmonics of the base frequency, which is defined by the
contents of the HGF register (Table 3). However, even
higher frequency notes may be produced since the
low-pass filtering on the TONE output is not applied to the
P1.7/MDY output. This results in the minimum decimal
value x in the HGF register (see equation in Section 6.3)
being 2 for the P1.7/MDY output, rather than 60 for the
TONE output. A sinusoidal TONE output is produced at the
same time as the melody square wave, but due to the
filtering, the higher frequency sine waves with x < 60 will
not appear at the TONE output.
Since the melody output is shared with P1.7, the port
flip-flop of P1.7 has to be set HIGH before using the
melody output. This is to avoid conflicts between melody
and port outputs. The melody output drive depends on the
configuration of port P1.7/MDY; see Chapter 14, Table 25.
6.3 Frequency registers
The two frequency registers HGF and LGF define two
frequencies. From these, the digital sine synthesizers
PCD3359A
together with the Digital-to-Analog Converters (DACs)
construct two sine waves. Their amplitudes are precisely
scaled according to the bandgap voltage reference. This
ensures tone output levels independent of supply voltage
and temperature.
The amplitude of the Low Group Frequency sine wave is
attenuated by 2 dB compared to the amplitude of the High
Group Frequency sine wave. The two sine waves are
summed and then filtered by an on-chip switched
capacitor and RC low-pass filters. These guarantee that all
DTMF tones generated fulfil the CEPT recommendations
with respect to amplitude, frequency deviation, total
harmonic distortion and suppression of unwanted
frequency components.
The value 00H in a frequency register stops the
corresponding digital sine synthesizer. If both frequency
registers contain 00H, the whole frequency generator is
shut off, resulting in lower power consumption.
The frequency of the sine wave generated ‘f’ is dependent
on the crystal frequency ‘f
in the frequency registers (HGF and LGF). The variables
are related by the equation:
f
=
f
The frequency limitation given by x ≥ 60 is due to the
low-pass filters which would attenuate higher frequency
sine waves.
xtal
-------------------------------23 x 2+()[]
; where 60 ≤ x ≤ 255.
’ and the decimal value ‘x’ held
xtal
1998 May 11 9
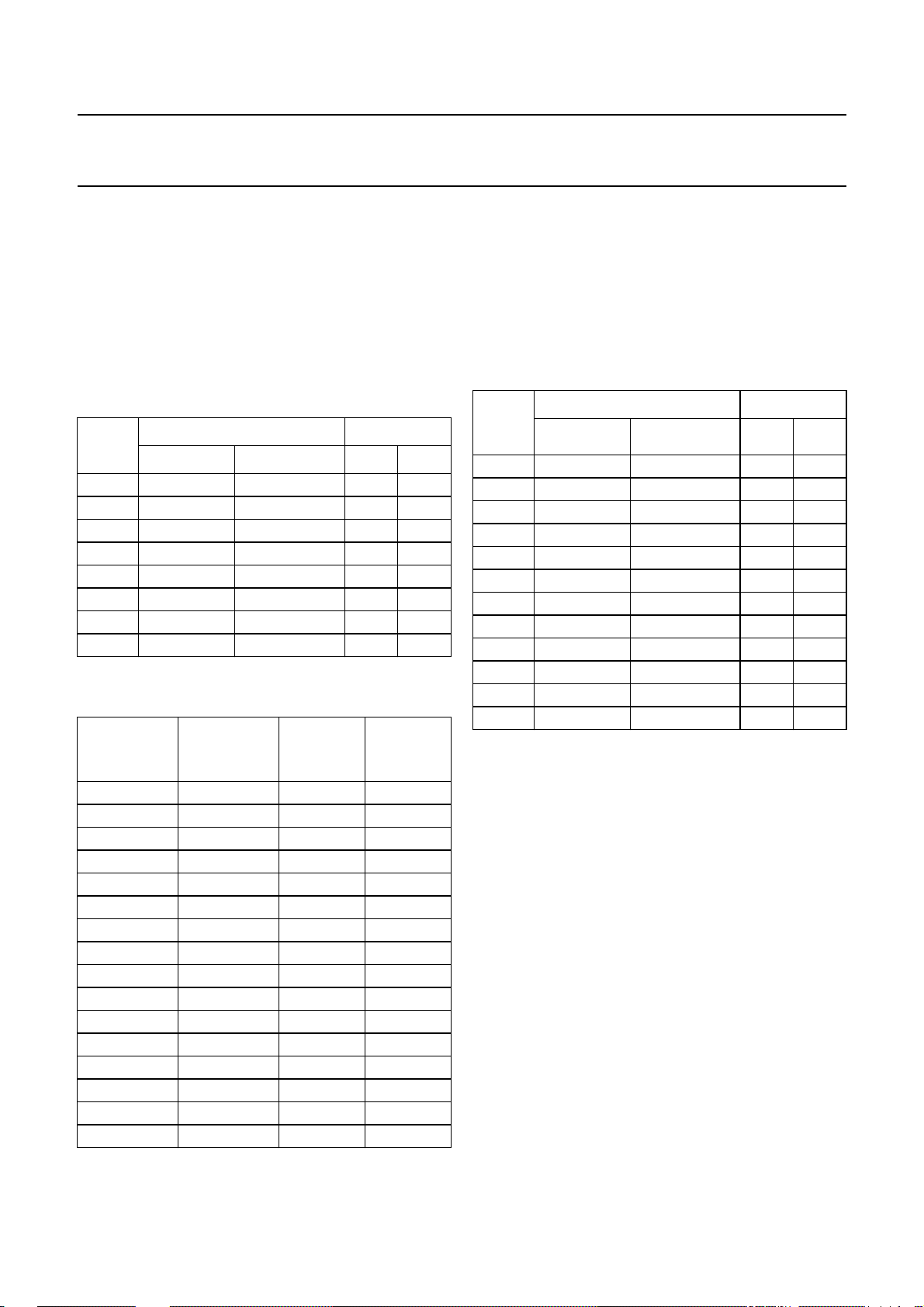
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
8-bit microcontroller with DTMF
generator and 128 bytes EEPROM
6.4 DTMF frequencies
Assuming an oscillator frequency f
DTMF standard frequencies can be implemented as
shown in Table 7.
The relationships between telephone keyboard symbols,
DTMF frequency pairs and the frequency register contents
are given in Table 8.
Table 7 DTMF standard frequencies and their
implementation; value = LGF, HGF contents
VALUE
(HEX)
FREQUENCY (Hz) DEVIATION
STANDARD GENERATED (%) (Hz)
DD 697 697.90 0.13 0.90
C8 770 770.46 0.06 0.46
B5 852 850.45 −0.18 −1.55
A3 941 943.23 0.24 2.23
7F 1209 1206.45 −0.21 −2.55
72 1336 1341.66 0.42 5.66
67 1477 1482.21 0.35 5.21
5D 1633 1638.24 0.32 5.24
Table 8 Dialling symbols, corresponding DTMF
frequency pairs and frequency register contents
TELEPHONE
KEYBOARD
SYMBOLS
DTMF FREQ.
PAIRS
(Hz)
0 (941, 1336) A3 72
1 (697, 1209) DD 7F
2 (697, 1336) DD 72
3 (697, 1477) DD 67
4 (770, 1209) C8 7F
5 (770, 1336) C8 72
6 (770, 1477) C8 67
7 (852, 1209) B5 7F
8 (852, 1336) B5 72
9 (852, 1477) B5 67
A (697, 1633) DD 5D
B (770, 1633) C8 5D
C (852, 1633) B5 5D
D (941, 1633) A3 5D
• (941, 1209) A3 7F
# (941, 1477) A3 67
= 3.58 MHz, the
xtal
LGF
VALUE
(HEX)
HGF
VALUE
(HEX)
PCD3359A
6.5 Modem frequencies
Again assuming an oscillator frequency f
the standard modem frequencies can be implemented as
in Table 9. It is suggested to define the frequency by the
HGF register while the LGF register contains 00H,
disabling Low Group Frequency generation.
Table 9 Standard modem frequencies and their
implementation
HGF
FREQUENCY (Hz) DEVIATION
VALUE
(HEX)
9D 980
82 1180
8F 1070
79 1270
80 1200
45 2200
76 1300
48 2100
5C 1650
52 1850
4B 2025
44 2225
MODEM GENERATED (%) (Hz)
(1)
(1)
(2)
(2)
(3)
(3)
(4)
(4)
(1)
(1)
(2)
(2)
978.82 −0.12 −1.18
1179.03 −0.08 −0.97
1073.33 0.31 3.33
1265.30 −0.37 −4.70
1197.17 −0.24 −2.83
2192.01 −0.36 −7.99
1296.94 −0.24 −3.06
2103.14 0.15 3.14
1655.66 0.34 5.66
1852.77 0.15 2.77
2021.20 −0.19 −3.80
2223.32 −0.08 −1.68
Notes
1. Standard is V.21.
2. Standard is Bell 103.
3. Standard is Bell 202.
4. Standard is V.23.
= 3.58 MHz,
xtal
1998 May 11 10
 Loading...
Loading...