Philips Optimus 50, Optimus 65, Optimus 80 Instruction Manual

H
Philips Medical Systems DMC GmbH
SERVICE MANUAL
742
UNIT
Converter test kit OPTIMUS
for OPTIMUS 50/65/80 generators Release 3.x
with converters 4512 104 7231 1/2/3
4512 104 91681
DMC Hamburg
Printed in Hamburg, Germany
© 1999 Philips Medical Systems
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
4512 984 22721 REV AA 1
UNIT_ConvTestKit_22721_AA.doc


OPTIMUS CONVERTER TEST KIT
SERVICE MANUAL - UNIT
Converter test kit OPTIMUS Author: A. Duve
for OPTIMUS 50/65/80 generators Release 3.x
with converters 4512 104 7231 1/2/3
Type No: 4512 104 91681
In case there are any questions concerning this manual,
please send this LOPAD via fax to 49/(0)40/5078 2481
File: UNIT_ConvTestKit_22721_AA_BW
List of pages and drawings (LOPAD) Manual Order No: 4512 984 22721
released: 06/2002
0.5 A4 (Orange cardboard)
1
3
5 ... 42 (02.0)
________________________________
6-01 (b/01.0) OPTIMUS RAD
6-1 ... 6-14 (b/01.0) OPTIMUS RAD
________________________________
4512 984 22721 REV AA (02.0) 3
UNIT_ConvTestKit_22721_AA.doc © 1997 Philips Medical Systems
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED


OPTIMUS CONVERTER TEST KIT
TEXT
Contents .......................................................................................5
1. Introduction ..................................................................................7
1.1. Scope of delivery ............................................................................................7
1.2. Tools...............................................................................................................7
2. Generator condition after failure event......................................8
2.1. Special case ................................................................................................... 8
2.2. All other cases ................................................................................................8
2.3. Prerequisites before checking the generator .................................................. 8
3. Check of generator mains supply parts.....................................9
3.1. Condition(s) when the service comes to the site...........................................10
3.1.1. ENF2 tripped, possibly in combination with ENF1 and? mains fuses ....................................10
3.1.2. ENF1 tripped, possibly in combination with mains fuses........................................................10
3.2. Check for open springs at damping resistors................................................ 11
3.3. Check for contacts that are welded at breakers and contactors ................... 11
4. Converter checks (EQ frontal and E2Q rear)...........................12
4.1. Visual converter check..................................................................................12
4.2. Measuring of converter parts ........................................................................12
4.2.1. Rectifier check.........................................................................................................................12
4.2.2. IGBT check .............................................................................................................................13
4.2.3. Overvoltage diode check ........................................................................................................14
4.2.4. Resistor check (PCB versions 4512 108 0862x / 0934x) .......................................................14
4.2.5. Power cable harness check ....................................................................................................15
4.2.6. Resonance capacitor check ....................................................................................................15
5. Check of the high voltage transformer ....................................16
5.1. Analysis ........................................................................................................ 17
6. Visual check of the X-ray tube ..................................................18
7. Interim results ............................................................................18
8. Tube check with Rotor Control part 1 .....................................19
9. kV-driver test ..............................................................................19
10. Tube check with Rotor Control part 2.....................................20
11. Tube and high-voltage cable test with high voltage...............21
Conv_test_OPTIMUS (02.0) 5
UNIT_ConvTestKit_22721_AA.doc © 1999 Philips Medical Systems
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED

CONVERTER TEST KIT OPTIMUS
12. Measuring of primary currents .................................................25
12.1. Measuring of the resonance frequency.........................................................30
12.2. Measurement of kV behavior with an adapted tube......................................31
12.3. Measuring of kV behavior with a non-adapted tube (Optimus 65/80) ...........32
13. Reconditioning of the tube(s) ...................................................33
14. Final system test........................................................................35
APPENDIX
List of checked parts of generator 3x ......................................37
6 (02.0) Conv_test_OPTIMUS
© 1999 Philips Medical Systems UNIT_ConvTestKit_22721_AA.doc
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED

OPTIMUS CONVERTER TEST KIT
1. Introduction
With this document it should be possible to determine which part of kV units of an Optimus generator is still
operational and which part is defective and has to be replaced.
1.1. Scope of delivery
- 2 current transformers
(ratio 1:1000, 20Ω resistors at the secondary coil give a ratio of 50A primary / 1V secondary)
- Test cable with resistor
- Test cable with diode
- Unit Manual Converter R/F
- This documentation
1.2. Tools
- Standard tools
- Extension boards C (96-pin)
- Dual trace oscilloscope with:
- 2 probes for signals
- 1 probe for external triggering
- Multimeter with diode test option
- 1 battery 1.5V D cell (R20) preferred
C cell (R14) or AA cell (R6) possible
Conv_test_OPTIMUS (02.0) 7
UNIT_ConvTestKit_22721_AA.doc © 1999 Philips Medical Systems
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
CONVERTER TEST KIT OPTIMUS
2. Generator condition after failure event
ENF1 and/or ENF2 and/or ENF3 tripped.
Mains fuses might have additionally tripped.
2.1. Special case
ENF3 tripped, possibly in combination with ENF2 and? ENF1 and? mains fuses:
Problem most likely caused by rotor control unit EY (high speed) or EYA (low speed).
Solutions for rotor control problems are not part of this document.
2.2. All other cases
The generator has to be kept in this condition to discover the cause of the problem.
A non-qualified person (e.g. hospital technician not familiar with Optimus) should not be asked to just turn the
fuses back on to prevent further damage.
A qualified person like a Philips field engineer (trained on Optimus) must visit the site.
2.3. Prerequisites before checking the generator
CAUTION!
Do not remove PCB kV-power from the IGBT transistors.
Electrostatic discharge and mobile phone waves can damage and destroy
IGBTs when gate connections are open.
WARNING!
The generator must be switched OFF and must be completely cut
from mains (e.g. room mains switch or earth leakage current
breaker).
All following checks must be made without mains power.
8 (02.0) Conv_test_OPTIMUS
© 1999 Philips Medical Systems UNIT_ConvTestKit_22721_AA.doc
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
OPTIMUS CONVERTER TEST KIT
3. Check of generator mains supply parts
• Measure DC voltage at auxiliary contacts 41-42 of ENK2.
(Converter DC discharging contact, max voltage can be 750VDC.)
If 0V is measured:
the contact is closed (and the converter DC is discharged within 1 minute) -
or
- the contact is open and the converter DC is discharged and safe.
WARNING!
In case one of the ENK2 main contacts is welded the converter
DC discharge time is much longer as the discharging auxiliary
contact ENK2 41-42 cannot be closed.
600VDC discharge time to < 60VDC normally
40 seconds.
With open contact > 11 minutes to be < 60VDC.
• Check if any main contact of contactor ENK2 is welded:
Mechanical check: If snap-on auxiliary contacts or auxiliary contact block cannot be removed from the
main contactor at least one contact is welded.
ENK2 phase 1 1 - 2 contactor ENK2 2422 132 06621
phase 2 3 - 4 + 3 aux. contacts NO 2422 135 04355
phase 3 5 - 6 + 1 aux. contact NC 2422 135 04023
or
successor contactor 2422 132 07381
+ succ. aux. cont. block 2422 135 04464
+ succ. R/C circuit 2422 135 04661
• Record the conditions on last page.
• If contacts have been found to be welded replace contactor, its auxiliary contacts or contact block
+ the R/C circuit.
Conv_test_OPTIMUS (02.0) 9
UNIT_ConvTestKit_22721_AA.doc © 1999 Philips Medical Systems
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
CONVERTER TEST KIT OPTIMUS
3.1. Condition(s) when the service comes to the site
3.1.1. ENF2 tripped, possibly in combination with ENF1 and? mains fuses
Problem might be caused by any of the:
- internal generator units (Optimus RAD + R/F)
or
- external units (Optimus RAD only) connected to breaker ENF2 :T1 :T2 :T3.
Solutions for such a case are not part of this document.
3.1.2. ENF1 tripped, possibly in combination with mains fuses
Problem most likely caused by kV unit malfunction (kV-control, kV-power, converter(s), HV transformer) or
external parts e.g. HV cable(s) or tube.
• Open the cover of the frontal (and rear where present) converter.
• Measure DC at PCB kV-power EQ100 at E2 – C1 (at both converters, see layout drawings attached).
The measured DC must be < 10VDC.
WARNING!
Make sure that the DC voltage in the converter is discharged.
10 (02.0) Conv_test_OPTIMUS
© 1999 Philips Medical Systems UNIT_ConvTestKit_22721_AA.doc
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED

OPTIMUS CONVERTER TEST KIT
3.2. Check for open springs at damping resistors
EN :R1 safety resistor 47Ω 100W 4512 100 45441
:R2
:R3
• Record the conditions on sheet of appendix.
• Check for open springs at damping resistors.
Springs might be open if all breakers are ON when the service comes to the site.
In this case the generator must have been switched ON after all fuses and breakers were reactivated.
Short-circuit in the converter or its mains rectifier/filter could have happened.
Springs can be resoldered. If the springs have to be resoldered, use as little solder as possible.
• Check that the ceramic resistor bodies do not have cracks. In case of cracks the springs must be
resoldered.
3.3. Check for contacts that are welded at breakers and contactors
• Switch OFF breakers ENF1 and ENF2.
ENF1 L1 – T1 automatic circuit-breaker ENF1 Optimus 50 2422 129 15514
L2 – T2 or successor 2422 129 16291
L3 – T3
Optimus 65/80 2422 129 15513
or successor 2422 129 16292
ENF2 L1 – T1 automatic circuit-breaker ENF2 Optimus 50/65/80 2412 129 00341
L2 – T2 or successor 2422 129 16288
L3 – T3
ENK1 phase 1 2 – 1 contactor ENK1 Optimus 50 2422 132 06625
phase 2 4 – 3 or successor 2422 132 07382
phase 3 6 – 5 + R/C circuit 2422 135 04662
Optimus 65/80 2422 132 06624
or successor 2422 132 07383
+ R/C circuit 2422 135 04662
• Record the conditions of the breakers in the appendix.
• Check for contacts that are welded at breakers and contactors.
If contacts have been found to be welded replace breaker(s) and/or contactor(s).
• Remove the converter mains lines (frontal and rear converter) from contactor ENK1 :1 :3 :5.
Measure with an ohmmeter each line against the others (of each converter).
There should be no short-circuit, the meter should display 2MΩ ±5% after at least 20 seconds
(filter resistors).
Conv_test_OPTIMUS (02.0) 11
UNIT_ConvTestKit_22721_AA.doc © 1999 Philips Medical Systems
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
CONVERTER TEST KIT OPTIMUS
4. Converter checks (EQ frontal and E2Q rear)
4.1. Visual converter check
• Check the converter visually.
The entire converter chassis must be replaced if cracks are visible at the white IGBT body
(looking through the converter cage grid) or if the kV-power PCB Q100 is bent towards the cover plate.
4.2. Measuring of converter parts
Use an ohmmeter which has a diode test feature.
• Check the polarity of the meter (for ohm and diode testing):
Anode of diode symbol on meter = positive voltage >>
Cathode of diode symbol on meter = negative voltage >>
PLUS (see measurement)
MINUS (tables)
Ω = Normal ohm measurements
¨ = Diode test option of meter
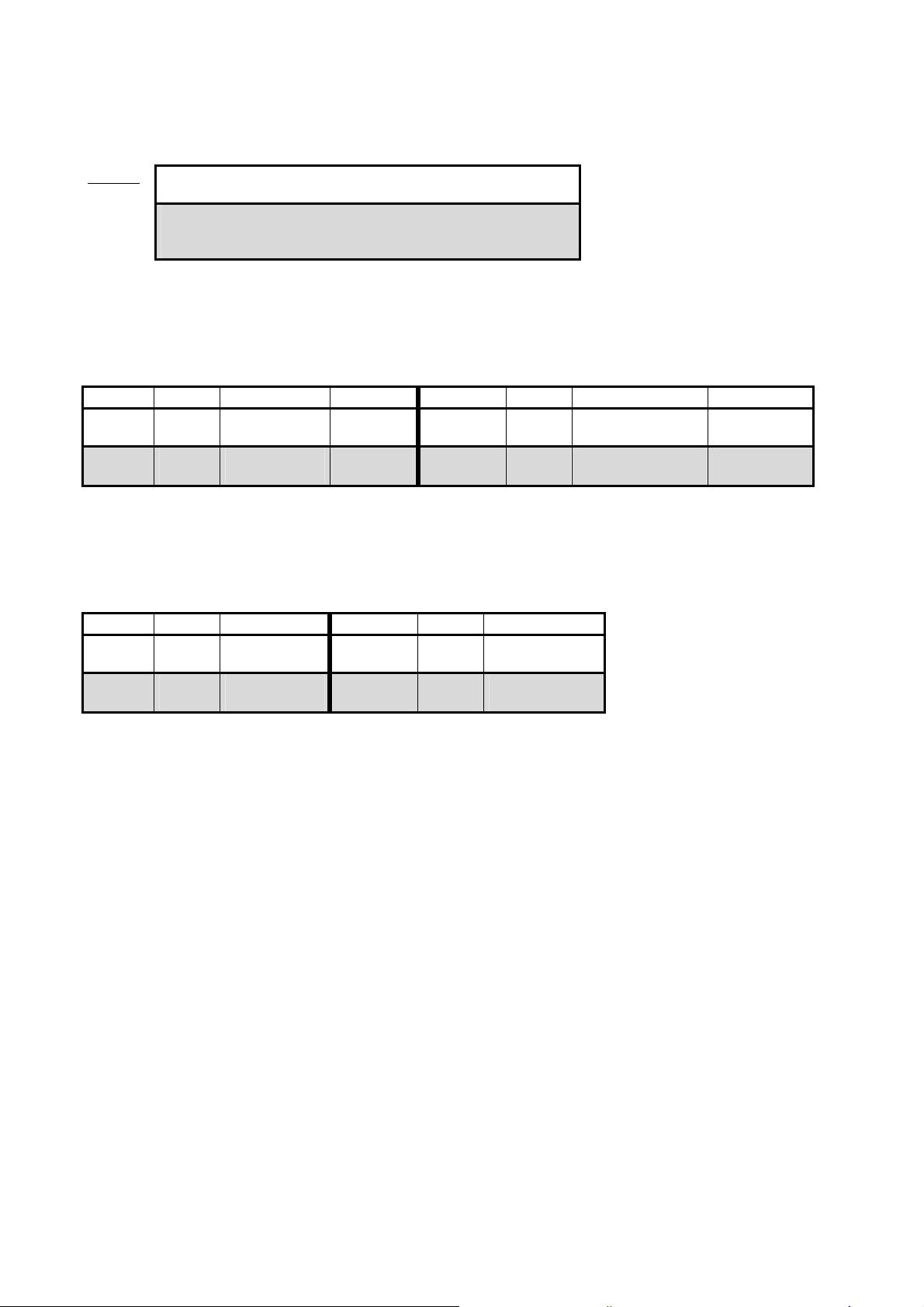
4.2.1. Rectifier check
• Open the right side of the converter(s) to get access to the mains rectifier.
L1 ⊘ ⊘ –
L2 ⊘ ⊘ –
L3 ⊘ ⊘ +
MINUS PLUS ¨ PLUS MINUS ¨
L1 / L2 / L3 ⊘ ⊘ – ⊘ + L1 / L2 / L3 ⊘ ⊘ – ⊘ +
450mV ±10%
• Record the conditions in the appendix.
Rectifier EQV5 layout
∞
∞
450mV ±10%
12 (02.0) Conv_test_OPTIMUS
© 1999 Philips Medical Systems UNIT_ConvTestKit_22721_AA.doc
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
OPTIMUS CONVERTER TEST KIT
4.2.2. IGBT check
Legend
typical values when part is OK
typical values of defective parts
If at least one test fails the converter must be exchanged.
Proceed with chapter 5.
The table below shows results of IGBT emitter - collector measurement.
Converter working OK and completely assembled.
Q100 kV-power PCB 4512 108 0862x / 0934x
MINUS PLUS
E1
E2,3,4
C1
C2,3,4
Ω
21.5 - 22kΩ
¨
∞
PLUS MINUS
E1
E2,3,4
C1
C2,3,4
Ω
16.5kΩ ±10%
¨
300mV ±10%
Ex Cx
0 Ω
< 200mV
Ex Cx
The table below shows values of IGBT gate - emitter resistances.
Converter working OK and completely assembled.
Q100 kV-power PCB 4512 108 0862x / 0934x
MINUS PLUS
G1
G2,3,4
E1
E2,3,4
Gx Ex
Ω
3.8kΩ ±10%
0Ω
PLUS MINUS
G1
G2,3,4
E1
E2,3,4
Gx Ex
4.2kΩ ±10%
• Record the conditions in the appendix.
Ω
0Ω
0Ω
< 200mV
Conv_test_OPTIMUS (02.0) 13
UNIT_ConvTestKit_22721_AA.doc © 1999 Philips Medical Systems
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
 Loading...
Loading...