Page 1

查询OM6206供应商
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
OM6206
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC17
2001 Nov 14
Page 2

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
CONTENTS
1 FEATURES
2 APPLICATIONS
3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
4 ORDERING INFORMATION
5 BLOCK DIAGRAM
6 PINNING
6.1 Pin functions
6.1.1 R0 to R64: row driver outputs
6.1.2 C0 to C101: column driver outputs
6.1.3 V
6.1.4 V
6.1.5 V
6.1.6 V
6.1.7 V
and V
SS1
, V
DD1
: LCD supply voltage
LCDIN
LCDOUT
LCDSENSE
: ground supply rails
SS2
and V
DD2
DD3
: voltage multiplier output
: voltage multiplier regulation input
: supply voltage rails
6.1.8 T1 to T5: test pins
6.1.9 SDIN: serial data line
6.1.10 SCLK: serial clock line
6.1.11 D/C: mode select
6.1.12 SCE: chip enable
6.1.13 OSC: oscillator
6.1.14 RES: reset
7 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
7.1 Oscillator
7.2 Address counter
7.3 Display data RAM (DDRAM)
7.4 Timing generator
7.5 Display address counter
7.6 LCD row and column drivers
7.7 Addressing
7.7.1 Data structure
8 INSTRUCTIONS
8.1 Initialization
8.2 Reset function
8.3 Function set
8.3.1 PD
8.3.2 V
8.3.3 H
8.4 Display control
8.4.1 D and E
8.5 Set Y-address of RAM
8.6 Set X-address of RAM
8.7 Set high-voltage generator stages
8.8 Bias system
8.9 Temperature control
8.10 Set VOP value
9 LIMITING VALUES
10 HANDLING
11 DC CHARACTERISTICS
12 AC CHARACTERISTICS
13 APPLICATION INFORMATION
13.1 Programming example for the OM6206
13.2 Application diagrams
13.3 Application for COG
13.4 Chip information
14 BONDING PAD INFORMATION
15 DEVICE PROTECTION CIRCUITS
16 TRAY INFORMATION
17 DATA SHEET STATUS
18 DEFINITIONS
19 DISCLAIMERS
2001 Nov 14 2
Page 3

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
1 FEATURES
• Single-chip LCD controller and driver
• 65 row and 102 column outputs
• Display data RAM 65 × 102 bits
• On-chip:
– Configurable 5 (4, 3 and 2) × voltage multiplier
generating V
(external V
LCD
also possible)
LCD
– Generation of intermediate LCD bias voltages
– Oscillator requires no external components
(external clock also possible).
• External reset input pin RES
• Serial interface maximum 4.0 Mbits/s
• CMOS compatible inputs
• Multiplex rate of 1 : 65
• Logic supply voltage range from 2.5 to 5.5 V
(V
to VSS)
DD1
• High-voltage generator supply voltage range from
2.5 to 4.5 V (V
DD2
and V
DD3
to VSS)
• Display supply voltage range from 4.5 to 9.0 V
(V
to VSS)
LCD
• Low power consumption, suitable for battery operated
systems
• Temperature compensation of V
LCD
• Temperature range from −40 to +85 °C
• Slim chip layout, suited for Chip-On-Glass (COG)
applications.
2 APPLICATIONS
• Telecom equipment.
3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The OM6206 is a low-power CMOS LCD controller and
driver, designed to drive a graphic display of 65 rows and
102 columns. All necessary functions for the display are
provided in a single chip, including on-chip generation of
LCD supply and bias voltages, resulting in a minimum of
external components and low power consumption.
TheOM6206interfacesto microcontrollersvia aserial bus
interface.
4 ORDERING INFORMATION
PACKAGE
TYPE NUMBER
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
OM6206U/Z − chip with bumps in tray −
2001 Nov 14 3
Page 4

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
5 BLOCK DIAGRAM
handbook, full pagewidth
V
LCDIN
V
LCDSENSE
V
LCDOUT
T1
T2
T3
T4
T5
V
SS1VSS2
214 to
217,
221,
222
224 to 229
237
230 to 236
218
198
223
220
219
V
DD1VDD2
200 to
213
174 to
179
BIAS
VOLTAGE
GENERATOR
HIGH
VOLTAGE
GENERATOR
181 to
193
V
DD3
REGISTER
C0 to C101
180
COLUMN DRIVERS
DATA LATCHES
DISPLAY DATA RAM
(DDRAM)
65 × 102
ADDRESS COUNTER
DATA
I/O BUFFER
37 to 138
OM6206
R0 to R64
2 to 15, 18 to 36,
139 to 156,
159 to 172
ROW DRIVERS
SHIFT REGISTER
RESET
OSCILLATOR
TIMING
GENERATOR
DISPLAY
ADDRESS
COUNTER
199
1
RES
OSC
195 194 196 197
SDIN SCLK
Fig.1 Block diagram.
2001 Nov 14 4
D/C
SCE
MGT859
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
6 PINNING
SYMBOL PAD DESCRIPTION
R0 to R18 18 to 36 LCD row driver outputs
R19 to R32 2 to 15 LCD row driver outputs
R33 to R50 156 to 139 LCD row driver outputs
R51 to R64 159 to 172 LCD row driver outputs
C0 to C101 37 to 138 LCD column driver outputs
V
SS1
214 to 217,
ground supply 1
221 and 222
V
SS2
V
DD1
V
DD2
V
DD3
V
LCDIN
V
LCDOUT
V
LCDSENSE
200 to 213 ground supply 2
174 to 179 supply voltage 1
181 to 193 supply voltage 2
180 supply voltage 3
224 to 229 LCD supply voltage (V
230 to 236 voltage multiplier output
(V
)
LCD
237 voltage multiplier
regulation input (V
LCD
)
LCD
T1 218 test 1 input
T2 198 test 2 output
T3 223 test 3 input/output
T4 220 test 4 input
T5 219 test 5 input
SCLK 194 serial clock input
SDIN 195 serial data input
D/
C 196 dataor commandselection
input
SCE 197 chip enable (active LOW)
OSC 199 oscillator signal input
RES 1 external reset input (active
LOW)
6.1 Pin functions
6.1.1 R0 TO R64: ROW DRIVER OUTPUTS
These pins output the row signals.
6.1.2 C0 TO C101: COLUMN DRIVER OUTPUTS
These pins output the column signals.
6.1.3 V
The supply rails V
SS1
AND V
SS1
: GROUND SUPPLY RAILS
SS2
and V
must be connected
SS2
together.
6.1.4 V
V
and V
DD2
DD1,VDD2
DD3
AND V
: SUPPLY VOLTAGE RAILS
DD3
are the supply voltage for the internal
voltagegenerator. Bothhave thesame voltageand should
be connected together outside the chip. V
supply voltage for the rest of the chip. V
connected together with V
DD2
and V
DD1
can be
DD1
but in this case
DD3
care must be taken to respect the supply voltage range
(see Chapter 11).
If the internal voltage generator is not used the pins
V
DD2
and V
must be connected to pin V
DD3
DD1
connected to the supply voltage.
)
6.1.5 V
: LCD SUPPLY VOLTAGE
LCDIN
Positive supply voltage for the liquid crystal display. An
external LCD supply voltage can be supplied using
pin V
. In this case, V
LCDIN
has to be left open and
LCDOUT
the internal voltage generator has to be programmed to
zero. If the OM6206 is in Power-down mode, the external
LCD supply voltage has to be switched off.
6.1.6 V
: VOLTAGE MULTIPLIER OUTPUT
LCDOUT
Positive supply voltage for the liquid crystal display. If the
internal voltage generator is used, the two supply rails
V
LCDIN
and V
must be connected together. If an
LCDOUT
external supply is used this pin must be left open.
6.1.7 V
V
LCDSENSE
LCDSENSE
INPUT
is the input of the internal voltage multiplier
: VOLTAGE MULTIPLIER REGULATION
regulation.
If the internal voltage generator is used then V
must be connected to V
voltage is used then V
LCDSENSE
. If an external supply
LCDOUT
can be left open or
connected to ground.
6.1.8 T1 TO T5: TEST PINS
T1, T3, T4 and T5 must be connected to VSS, T2 must be
left open. Not accessible to user.
is used as
or
LCDSENSE
2001 Nov 14 5
Page 6

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
6.1.9 SDIN: SERIAL DATA LINE
Input for the data line.
6.1.10 SCLK: SERIAL CLOCK LINE
Input for the clock signal: up to 4.0 Mbits/s.
6.1.11 D/C: MODE SELECT
Input to select either command or address data input.
6.1.12 SCE: CHIP ENABLE
The enable pin allows data to be clocked in. Signal is
active LOW.
6.1.13 OSC: OSCILLATOR
When the on-chip oscillator is used this input must be
connected to VDD. An external clock signal, if used, is
connected to this input. If theoscillator and external clock
are both inhibited by connecting pin OSC to VSS, the
display is not clocked and may be left in a DC state. To
avoid this the chip should always be put into
Power-down mode before stopping the clock.
6.1.14 RES: RESET
This signal will reset the device and must be applied to
properly initialize the chip. Signal is active LOW.
7 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
7.1 Oscillator
The on-chip oscillator provides the clock signal for the
display system.No external componentsare required and
the OSC input must be connected to VDD. An external
clock signal, if used, is connected to this input.
7.2 Address counter
The address counter assigns addresses to the display
data RAM for writing. The X-address X6to X0 and the
Y-address Y3to Y0 are set separately. After a write
operation, the address counter is automatically
incremented by 1 according to bit V (see Section 7.7).
7.3 Display Data RAM (DDRAM)
The OM6206 contains a 65 × 102 bits static RAM which
stores the display data. The RAM is divided into
eight banks of 102 bytes (8 × 8 × 102 bits) and one bank
of 102 bits (1 × 102 bits). During RAM access, data is
transferred to the RAM via the serial interface. There is a
direct correspondence between X-address and column
output number.
7.4 Timing generator
The timing generator produces the various signals
required to drive the internal circuitry. Internal chip
operation is not affected by operations on the data bus.
7.5 Display address counter
The display is generated by continuously shifting rows of
RAM data to the dot matrix LCD via the column outputs.
The display status (all dots on/off and normal/inverse
video) is set by bits E and D in the command ‘Display
control’ (see Table 2).
7.6 LCD row and column drivers
The OM6206 contains 65 rows and 102 column drivers,
which connect the appropriate LCD bias voltages in
sequence to the displayin accordance with the data tobe
displayed. Figure 2 shows typical waveforms. Unused
outputs should be left unconnected.
2001 Nov 14 6
Page 7

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
ROW0
R0(t)
ROW1
R1(t)
COL0
C0(t)
COL1
C1(t)
V
LCD
V3 − V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
SS
LCD
2
3
4
5
SS
LCD
2
3
4
5
SS
LCD
2
3
4
5
SS
LCD
2
3
4
5
SS
frame n frame n + 1
V
state1
V
state2
(t)
(t)
V
− V
LCD
V
state1
V
state2
V
(t) = C1(t) to R0(t).
state1
V
(t) = C1(t) to R1(t).
state2
(t)
(t)
0 V
V3 − V
V
LCD
V3 − V
V
LCD
0 V
V3 − V
2
SS
− V
2
2
2
012345678... ... 64 012345678... ... 64
Fig.2 Typical LCD driver waveforms.
2001 Nov 14 7
V4 − V
0 V
VSS − V
V4 − V
− V
LCD
V4 − V
0 V
VSS − V
V4 − V
− V
LCD
MGT860
5
5
LCD
5
5
LCD
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
DDRAM
bank 0
top of LCD
bank 1
bank 2
bank 3
bank 7
bank 8
LCD
Fig.3 DDRAM to display mapping.
2001 Nov 14 8
MGT861
Page 9
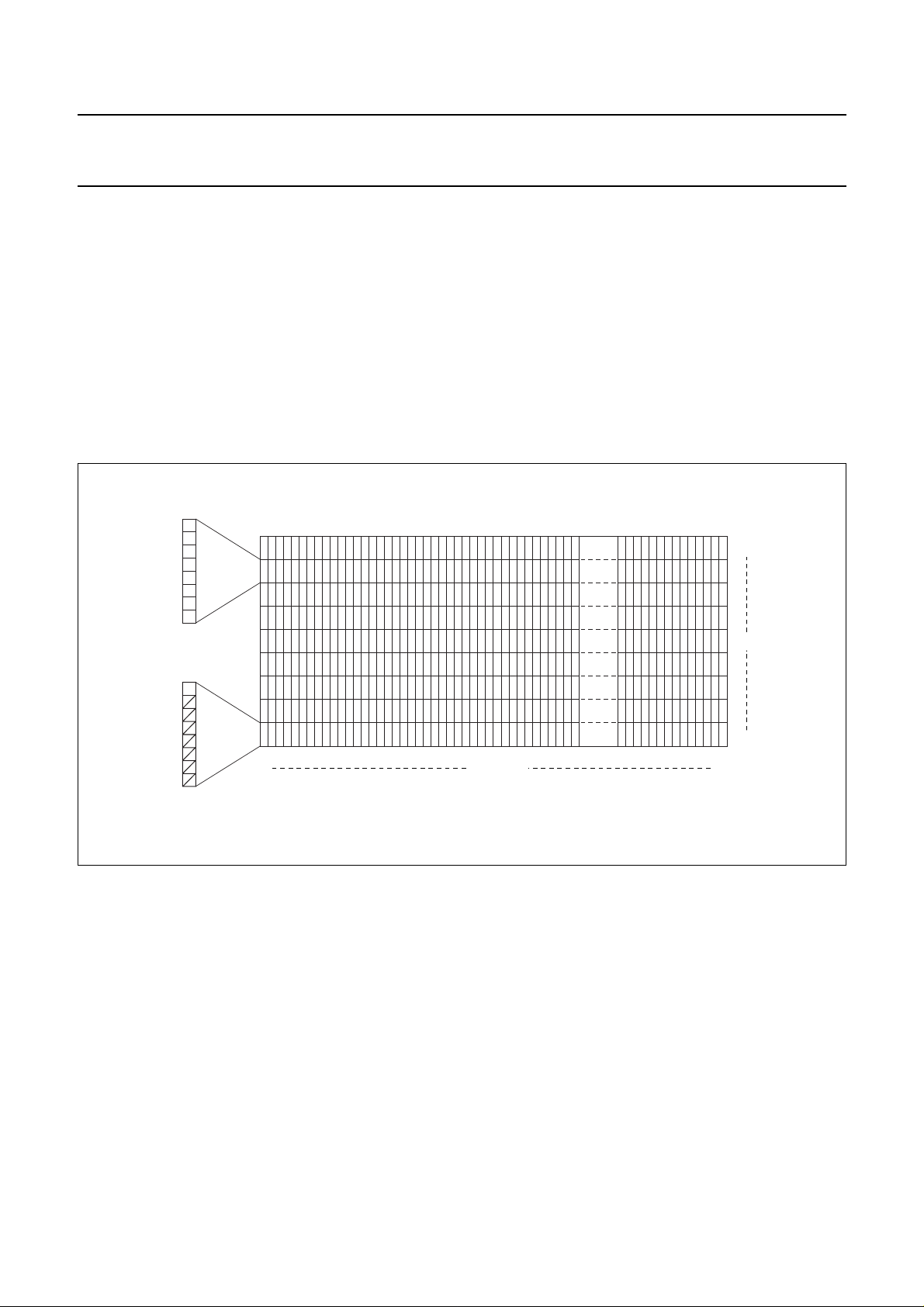
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
7.7 Addressing
Data is downloaded in bytes into the RAM matrix of
OM6206 as indicated in Figs.3, 4, 5 and 6.
The display RAM has a matrix of 65 × 102 bits. The
columns are addressed by the address pointer. The
address ranges are: X from 0 to 101 (1100101)
and Y from 0 to 8(1000). Addressesoutside theseranges
are not allowed.
In vertical addressing mode (bit V = 1) the Y-address
increments after each byte (see Fig.6).
7.7.1 DATA STRUCTURE
handbook, full pagewidth
LSB
MSB
After the last Y-address (Y = 8) Y wraps
around to 0 and X increments to addressthe next column.
In horizontal addressing mode (bit V = 0) the X-address
increments after each byte (see Fig.5). After the last
X-address (X = 101) X wraps around to 0 and
Y increments to address the next row.
After the very last address (X = 101, Y = 8) the address
pointers wrap around to address X = 0, Y = 0.
0
Y-address
LSB
MSB
0 101X-address
Fig.4 RAM format, addressing.
8
MGT862
2001 Nov 14 9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
handbook, full pagewidth
handbook, full pagewidth
09
110
2
3
4
5
6
7
8 917
0 101X-address
0
Y-address
8
MGT 863
Fig.5 Sequence of writing data bytes into RAM with vertical addressing (V = 1).
012
102 103 104
204 205 206
306 307 308
408 409 410
510 511 512
612 613 614
714 715 716
816 817 818 917
0 101X-address
0
Y-address
8
MGT864
Fig.6 Sequence of writing data bytes into RAM with horizontal addressing (V = 0).
8 INSTRUCTIONS
The instruction format is divided into two modes:
• If D/C (mode select) is set LOW, the current byte is
interpreted as command byte (see Table 1).
• If D/C is set HIGH, the following bytes are stored in the
display data RAM. After every data byte the address
counter is incremented automatically.
Thelevel ofthe D/C signalis readduringthe lastbit ofdata
byte.
2001 Nov 14 10
Every instruction canbe sent in anyorder to the OM6206.
The MSBof a byte istransmitted first (seeFig.7). Figure 8
shows one possible command stream, used to set up the
LCD driver.
The serialinterface isinitialized whenSCE isHIGH. In this
state SCLK clock pulses have no effect and no power is
consumedby the serialinterface. Anegative edgeon SCE
enablesthe serialinterfaceand indicatesthe startofa data
transmission.
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
handbook, halfpage
MSB (DB7) LSB (DB0)
Fig.7 General format of data stream.
handbook, full pagewidth
bias systemfunction set (H = 1)
Fig.8 Serial data stream, example.
Figures 9 and 10 show the serial bus protocol:
• When SCE is HIGH, SCLK clock signals are ignored.
During the HIGH time of SCE, the serial interface is
initialized (see Fig.11)
• SDIN is sampled at the positive edge of SCLK
• D/C indicates, whether the byte is a command
(D/C = LOW) or RAM data(D/C = HIGH); it is read with
the eighth SCLK pulse
datadata
MGT865
set V
OP
temperature control
X-addressY-addressdisplay controlfunction set (H = 0)
MGT866
• If SCE stays LOW after the last bit of a
command/data byte, theserial interface expects bit 7of
the next byte at the next positive edge of SCLK (see
Fig.11)
• A reset pulse with RES interrupts the transmission.
No data are written into the RAM. The registers are
cleared. If SCE is LOW after the positive edge of RES,
the serial interface is ready to receive bit 7 of a
command/data byte (see Fig.11).
handbook, full pagewidth
SCE
D/C
SCLK
SDIN
DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
Fig.9 Serial bus protocol for transmission of one byte.
2001 Nov 14 11
MGT867
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
handbook, full pagewidth
SCE
D/C
SCLK
SDIN DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 DB7DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
Fig.10 Serial bus protocol for transmission of several bytes.
handbook, full pagewidth
SCE
D/C
RES
SCLK
SDIN DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0 DB7DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
Fig.11 Serial bus reset function (SCE).
DB6 DB5
MGT868
DB6 DB5
MGT869
handbook, full pagewidth
SCE
RES
D/C
SCLK
SDIN DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB7DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
Fig.12 Serial bus interrupt function (RES).
2001 Nov 14 12
DB6 DB5 DB4
MGT870
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
Table 1 Instruction set
INSTRUCTION DESCRIPTION
PIN COMMAND BYTE
C DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
D/
(H=0or1)
NOP no operation LOW 00000000
Function set power down control; entry
LOW00100PDVH
mode; extended instruction set
control (H)
D
D
D
D
D
D
Write data writes data to display RAM HIGH D
7
6
5
4
3
2
D
1
0
(H=0)
Reserved do not use LOW 000001XX
Display control sets display configuration LOW 00001D0E
Set HIGHor LOW
V
programming range select LOW 0001000PRS
LCD
program range
V
OP
Set Y-address of
RAM
Set X-address of
RAM
sets Y-address of RAM;
0 ≤ Y ≤ 8
sets X-address of RAM;
0 ≤ X ≤ 101
LOW0100Y
LOW 1 X
X
6
X
5
3
X
4
3
Y
2
X
2
Y
1
X
1
Y
0
X
0
(H=1)
Reserved do not use LOW 00000001
do not use LOW 0000001X
Temperature
control
HVgen stages multiplication of high-voltage
set Temperature Coefficient
(TCx)
LOW000001TC
LOW000010S
1TC0
1
S
0
generator voltage (Sx)
Bias system set Bias System (BSx) LOW00010BS
2BS1
BS
0
Reserved do not use (reserved for test) LOW 0 1 XXXXXX
Set V
OP
write V
to register LOW 1 V
OPx
OP6VOP5VOP4VOP3VOP2VOP1VOP0
Table 2 Explanations for symbols in Table 1
BIT BIT VALUE DESCRIPTION RESET STATE
PD 0 chip is active 1
1 chip is in Power-down mode
V 0 horizontal addressing 0
1 vertical addressing
H 0 use basic instruction set 0
1 use extended instruction set
D and E 00 display blank 00
10 normal mode
01 all display segments on
11 inverse video mode
PRS 0 V
1V
programming range LOW 0
LCD
programming range HIGH
LCD
2001 Nov 14 13
Page 14

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
BIT BIT VALUE DESCRIPTION RESET STATE
TC1and TC
S
and S
BS
V
1
OP6
to BS
2
to V
0
OP0
0
0
00 V
01 V
10 V
11 V
temperature coefficient 0 00
LCD
temperature coefficient 1
LCD
temperature coefficient 2
LCD
temperature coefficient 3
LCD
00 2× voltage multiplier 00
01 3× voltage multiplier
10 4× voltage multiplier
11 5× voltage multiplier
− bias system 000
− V
programming 0000000
LCD
8.1 Initialization
Immediately following power-on, all internal registers as
well asthe RAMcontent are undefined.A RESpulse must
be applied.
Reset isaccomplished byapplying an externalreset pulse
(active LOW) at pin RES. When reset occurs within the
specified time, all internal registers are reset however the
RAM isstill undefined. Thestate afterreset is describedin
Section 8.2.
RES input must be ≤0.3VDDwhen VDD reaches V
(or higher) within a maximal time t
after VDD going
VHRL
DD(min)
HIGH (see Fig.16).
8.2 Reset function
After reset the LCD driver has the following state:
• Power-down mode (PD = 1)
• Horizontal addressing (V = 0)
• Normal instruction set (H = 0)
• Display blank (E andD=0)
• Address counter X6to X0= 0, Y3to Y0=0
• Temperature control (TC1and TC0=0)
• Bias system (BS2to BS0=0)
• V
is equal to 0 V and the high-voltage generator is
LCD
switched off (V
OP6
to V
= 0 and PRS = 0)
OP0
• After power-on, RAM data are undefined, the reset
signal does not change the content of the RAM
• All LCD outputs at VSS (display off).
8.3 Function set
8.3.1 PD
When PD = 1 the chip is in Power-down mode:
• All LCD outputs at VSS (display off)
• Bias generator and V
generator off; V
LCD
LCD
can be
disconnected
• Oscillator off (external clock possible)
• Serial bus: command, function etc.
• RAM contents not cleared; RAM data can be written
• V
discharged to VSS in Power-down mode.
LCD
8.3.2 V
When V = 0, the horizontal addressing is selected. The
data is written into the DDRAM as shown in Fig.6.
When V = 1, the vertical addressing is selected. Thedata
is written into the DDRAM as shown in Fig.5.
8.3.3 H
When H = 0 the commands ‘display control’, ‘set
Y-address’, ‘set X-address’ and ‘set the PRS bit’(LOW or
HIGH range of the high-voltage generator) can be
performed; when H = 1 the others can be executed. The
commands ‘write data’ and ‘function set’can be executed
in both cases.
8.4 Display control
8.4.1 D AND E
The bits D and E select the display mode (see Table 2).
2001 Nov 14 14
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
8.5 Set Y-address of RAM
Y3to Y0 define the Y-address vector address of the display RAM.
Table 3 X/Y-address range
Y
3
Y
2
Y
1
Y
0
00000 0to101
00011 0to101
00102 0to101
00113 0to101
01004 0to101
01015 0to101
01106 0to101
01117 0to101
10008; note 2 0 to 101
BANK
(1)
ALLOWED X-RANGE
Notes
1. Display RAM.
2. Only the MSB is accessed.
8.6 Set X-address of RAM
The X-address points to the columns. The range of X is
0 to 101 (65H).
8.7 Set high-voltage generator stages
TheOM6206 incorporatesa softwareconfigurable voltage
multiplier. After reset (RES) the voltagemultiplier is set to
2 × V
. Other voltage multiplier factors are set via the
DD2
command ‘HVgen stages’ (see Tables 1 and 2).
Table 4 Programming the required bias system
BS
2
BS
1
BS
0
0007 1:100
0016 1:80
0105 1:65 or 1:65
0114 1:48
1003 1:40 or 1:34
1012 1:24
1101 1:18 or 1:16
1110 1:10 or 1:9 or 1:8
8.8 Bias system
The bias voltage levels are set in the ratio of
R-R-nR-R-R giving a bias system. Different
1
------------ n4+
multiplex rates require different factors n (see Table 4).
This is programmed by BS
to BS0. For multiplex rate
2
1 : 65 the optimum bias value n is given by:
n653–5.062 5===
resulting in a
1
/9bias system.
n RECOMMENDED MULTIPLEX RATE
(1)
2001 Nov 14 15
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
Table 5 LCD bias voltage
SYMBOL BIAS VOLTAGES BIAS VOLTAGE FOR1⁄9 BIAS
V1 V
LCD
V2
V3
V4
V5
V6 V
SS
8.9 Temperature control
n3+
------------ n4+
n2+
------------ n4+
2
------------ n4+
1
------------ n4+
V
V
LCD
SS
8
⁄9× V
7
⁄9× V
2
⁄9× V
1
⁄9× V
LCD
LCD
LCD
LCD
Due to the temperature dependency of the liquid crystals viscosity the LCD controlling voltage V
must be increased
LCD
with lower temperature to maintain optimal contrast. There are four temperature coefficients available in the OM6206
(see Fig.13). The coefficients are selected by the two bits TC1and TC0. Table 6 shows the typical values of the
temperature coefficients. The coefficients are proportional to the programmed V
(1) TC0.
(2) TC1.
(3) TC2.
(4) TC3.
handbook, halfpage
V
LCD
(V)
T
cut
MGT871
at reference temperature.
LCD
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
T (°C)
Fig.13 Temperature coefficients behaviour.
2001 Nov 14 16
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
8.10 Set VOP value
The operation voltage V
can be set by software. The
LCD
generated voltage is dependent on the programmed
voltage at reference temperature (T
), the programmed
cut
Temperature Coefficient (TC) and the operating
temperature (T).
The voltage at reference temperature can be calculated
as:
abV
V
LCD Tcut()
×+=
OP
The voltage at operating temperature can be calculated
as:
V
LCD(T)
V
LCD(Tcut)
TT
–()TC×+=
cut
Two overlapping V
command ‘set HIGH or LOW program range VOP’.
For the LOW range (bit PRS = 0) component a = a1 and
for the HIGH range (bit PRS = 1) component a = a2. The
steps in both ranges are equal to b.
It should be noted that the charge pump is turned off if
bits V
OP6
to V
OP0
Fig.14).
(2)
For multiplexer rate 1 : 65 the optimum operation voltage
of the liquid can be calculated as:
165+
---------------------------------------
21
×
(3)
V
LCD
ranges are selectable via the
LCD
and bit PRS are all set to zero (see
× 6.85 Vth×==
V
1
–
----------
th
65
The parameters are explained in Table 6.
Themaximum voltagethat canbegenerated isdepending
on the V
voltage and the display load current.
DD2
where V
material used.
is the threshold voltage of the liquid crystal
th
Table 6 Typical values for parameters for the high-voltage generator programming
SYMBOL VALUE UNIT
a
1
a
2
2.94 (PRS = 0) V
6.75 (PRS = 1) V
b 0.03 V
T
cut
27
(4)
°
C
Table 7 Temperature coefficients
BIT
NAME
TC
1
TC
0
TC0 0 0 −0.00 × 10−3× V
TC1 0 1 −0.76 × 10
TC2 1 0 −1.05 × 10
TC3 1 1 −2.10 × 10
−3
−3
−3
× V
× V
× V
LCD(Tcut)
LCD(Tcut)
LCD(Tcut)
LCD(Tcut)
VALUE UNIT
V/°C
V/°C
V/°C
V/°C
2001 Nov 14 17
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
handbook, full pagewidth
V
LCD
(V)
b
a
2
a1 + b
a
1
charge pump off
00
01 02
V
to V
OP6
to be programmed (00H to 7FH), programming ranges LOW and HIGH.
OP0
As theprogramming range forthe internally generatedV
03 04 05 06
LOW (PRS = 0) HIGH (PRS = 1)
. . . 5F 6F 7F 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 . . . 5F 6F 7F
Fig.14 VOP programming at T = T
allows valuesabove the maximumallowed V
LCD
cut
.
MGT878
(9.0 V) the
LCD
user has toensure while setting the VOPvalue and selectingthe Temperature Coefficient (TC), that under allconditions
and including all tolerances the V
remains below 9.0 V.
LCD
9 LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134); notes 1 and 2.
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
V
V
V
I
I
P
DD1
DD2,
LCD
i
SS
, I
I
tot
, V
DD3
O
supply voltage 1 −0.5 +6.5 V
supply voltages 2 and 3 −0.5 +4.5 V
supply voltage LCD −0.5 +9.0 V
all input voltages −0.5 VDD+ 0.5 V
ground supply current −50 +50 mA
DC input or output current −10 +10 mA
total power dissipation − 300 mW
P/out power dissipation per output − 30 mW
T
stg
storage temperature −65 +150 °C
Notes
1. Stresses above those listed under limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device.
2. Parameters are valid over operating temperature range unless otherwise specified. All voltages are with respect to
VSS unless otherwise specified.
2001 Nov 14 18
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
10 HANDLING
Inputs and outputs are protected against electrostatic discharge in normal handling. However, to be totally safe, it is
desirable to take normal precautions appropriate to handling MOS devices (see
11 DC CHARACTERISTICS
VDD= 2.5 to 5.5 V; VSS=0V; V
= 4.5 to 9.0 V; T
LCD
= −40 to +85 °C; unless otherwise specified.
amb
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
V
V
DD1
DD2
DD3
supply voltage 1 2.5 − 5.5 V
,
supply voltages 2 and 3 LCD voltage internally
generated (voltage generator
enabled)
V
LCDIN
input supply voltage LCD LCD voltage externally supplied
(voltage generator disabled)
V
LCDOUT
output supply voltage LCD LCD voltage internally
generated (voltage generator
enabled); note 1
I
DD(tot)
total supply current normal mode; VDD= 2.8 V;
V
= 7.6 V; no serial clock;
LCD
T
=25°C; no display load;
amb
4 × charge pump; note 2
Power-down mode;with internal
I
LCDIN
supply current from
external V
LCD
or external V
VDD= 2.8 V; V
serial clock; T
LCD
LCD
amb
; note 3
= 7.6 V; no
=25°C; no
display load; notes 2 and 4
Logic
V
IL
V
IH
I
L
LOW-level input voltage V
HIGH-level input voltage 0.7VDD− V
leakage current VI=VDDor V
SS
Column and row outputs
R
col
output resistance of
V
= 7.6 V − 12 20 kΩ
LCD
columns C0 to C101
R
row
output resistance of
V
= 7.6 V − 12 20 kΩ
LCD
rows R0 to R64
V
col
bias tolerance voltage of
columns C0 to C101
V
row
bias tolerance voltage of
rows R0 to R64
LCD supply voltage generator
∆V
LCD
tolerance of internally
generated V
LCD
VDD= 2.8 V; V
serial clock; T
LCD
amb
=25°C;
= 7.6 V; no
display load is 10 µA; notes 5
and 6
TC0 V
temperature
LCD
note 7 − 0 × 10−3V
coefficient 0
“Handling MOS devices”
).
2.5 − 4.5 V
4.5 − 9.0 V
4.5 − 9.0 V
− 200 300 µA
− 1.5 −µA
− 30 −µA
SS
− 0.3VDDV
DD
V
−1 − +1 µA
−100 0 +100 mV
−100 0 +100 mV
−300 0 +300 mV
LCD
− V/°C
2001 Nov 14 19
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
TC1 V
TC2 V
TC3 V
Notes
1. Themaximum possibleV
2. Internal clock.
3. During Power-down mode, all static currents are switched off.
4. If external V
5. Tolerancedepends on thetemperature; typicalnull at T
temperate range limit; maximum tolerance is proportional to V
6. For TC1 to TC3.
7. VDD= 2.8 V; no serial clock; T
temperature
LCD
note 7 −−0.76 × 10−3V
coefficient 1
temperature
LCD
note 7 −−1.05 × 10−3V
coefficient 2
temperature
LCD
note 7 −−2.10 × 10−3V
coefficient 3
voltage thatmay begenerated isdependent onvoltage, temperatureand (display)load.
LCD
, the display load current is not transmitted to IDD.
LCD
= −20 to +70 °C; display load = 10 µA.
amb
− V/°C
LCD
− V/°C
LCD
− V/°C
LCD
=27°C; maximumtolerance valuesare measured atthe
amb
.
LCD
12 AC CHARACTERISTICS
VDD= 2.5 to 5.5 V; VSS=0V; V
= 4.5 to 9.0 V; T
LCD
= −40 to +85 °C; unless otherwise specified.
amb
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
f
osc
f
ext
f
frame
t
VHRL
t
RW
oscillator frequency VDD= 2.8 V; T
= −20 to +70 °C223867kHz
amb
external clock frequency 20 38 67 kHz
frame frequency f
VDDHIGH to RES LOW time see Fig.16 0
osc
or f
= 38 kHz; note 1 − 73 − Hz
ext
(2)
− 1 µs
RES LOW pulse width see Fig.16 100 −−ns
Serial bus timing characteristics; see Fig.15
f
SCLK
t
CYC
t
PWH1
t
PWL1
t
S2
t
H2
t
PWH2
t
H5
t
S3
t
H3
t
S4
t
H4
clock frequency VDD= 3.0 V ±10%; note 3 0 − 4 MHz
SCLK clock cycle time 250 −−ns
SCLK pulse width HIGH 100 −−ns
SCLK pulse width LOW 100 −−ns
SCE setup time 60 −−ns
SCE hold time 100 −−ns
SCE HIGH time 100 −−ns
SCE start hold time note 4 100 −−ns
D/C setup time 100 −−ns
D/C hold time 100 −−ns
SDIN setup time 100 −−ns
SDIN hold time 100 −−ns
Notes
f
1.
f
frame
ext
=
--------- 520
2001 Nov 14 20
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
2. RES may be LOW before VDD goes HIGH.
3. All signal timing is based on 20% to 80% of VDD and a maximum rise and fall time of 10 ns.
4. tH5is the time from the previous SCLK positive edge(irrespective of the state of SCE) to the negative edge of SCE.
handbook, full pagewidth
SCE
D/C
SCLK
SDIN
t
S2
t
t
S4
t
S3
PWL1
t
H3
t
PWH1
t
H4
Fig.15 Serial interface timing.
t
H2
(tH5)
t
CYC
t
S2
t
PWH2
t
H5
MGT872
handbook, full pagewidth
V
DD
RES
V
DD
RES
t
RW
t
VHRL
t
RW
Fig.16 Reset timing.
2001 Nov 14 21
t
RW
t
RW
MGT873
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
13 APPLICATION INFORMATION
13.1 Programming example for the OM6206
Table 8 Programming example
STEP
DISPLAY OPERATION
D/C DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
SERIAL BUS BYTE
1 start
SCE is going LOW
2 000100001 function set:
PD = 0 and V = 0; select
extended instruction set
(H=1)
3 010010000 set V
: VOP is set to
OP
a +16 × b [V]
4 000100000 function set:
PD = 0 and V = 0; select
normal instruction set
(H=0)
5 000001100 display control: set
normal mode
(D=1andE=0)
6 100011111 data write: Yand X are
initialized to 0 by default,
so they are not set here
MGT144
7 100000101 data write
MGT145
8 100000111 data write
MGT146
9 100000000 data write
MGT146
10100011111 data write
MGT148
11100000100 data write
MGT149
2001 Nov 14 22
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
STEP
C DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
D/
DISPLAY OPERATION
12100011111 data write
SERIAL BUS BYTE
MGT151
13000001101 display control: set
inverse video mode
(D=1andE=1)
MGT152
14010000000 set X-address of RAM:
set address to ‘0000000’
MGT152
15100000000 data write
MGT874
13.2 Application diagrams
handbook, full pagewidth
(1) 6 if external oscillator is used.
Fig.17 Application diagram: internal charge pump is used and a single supply VDD.
LCD
(65 × 102 pixels)
102 column drivers33 row drivers 32 row drivers
OM6206
DD2
DD3VDD1
V
V
(1)
5
C
I/O
V
DD
VDD
SS1VSS2VLCDSENSE
V
C
VLCD
V
SS
LCDOUTVLCDIN
V
MGT875
2001 Nov 14 23
Page 24

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
handbook, full pagewidth
LCD
(65 × 102 pixels)
102 column drivers33 row drivers 32 row drivers
OM6206
DD2
DD3VDD1
V
V
(1)
5
I/O
V
DD2
V
DD1
C
C
VDD2
VDD1
SS1VSS2VLCDSENSE
V
C
V
SS
VLCD
LCDOUTVLCDIN
V
MGT876
(1) 6 if external oscillator is used.
Fig.18 Application diagram: internal charge pump is used and two separate supplies V
handbook, full pagewidth
LCD
(65 × 102 pixels)
102 column drivers33 row drivers 32 row drivers
DD1
and V
DD2
.
OM6206
DD2
DD3VDD1
V
V
(1)
5
C
I/O
V
DD
VDD
SS1VSS2VLCDSENSE
V
V
SS
V
LCDOUTVLCDIN
V
LCDIN
MGT877
(1) 6 if external oscillator is used.
Fig.19 Application diagram: external supply V
2001 Nov 14 24
LCDIN
is used.
Page 25

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
The required minimumvalue for the externalcapacitors in
an application with the OM6206 are:
• C
• C
VLCD
VDD
> 100 µF
, C
VDD1
and C
VDD2
>1µF
Higher capacitor values are recommended for ripple
reduction.
13.3 Application for COG
The pinning of the OM6206 is optimized for single plane
wiring e.g.for Chip-On-Glass (COG)display modules with
display size of 65 × 102 pixels.
14 BONDING PAD INFORMATION
COORDINATES
(1)
SYMBOL PAD
xy
RES_B 1 −3870 +935
row32 2 −4270 +935
row31 3 −4340 +935
row30 4 −4410 +935
row29 5 −4480 +935
row28 6 −4550 +935
row27 7 −4620 +935
row26 8 −4690 +935
row25 9 −4760 +935
row24 10 −4830 +935
row23 11 −4900 +935
row22 12 −4970 +935
row21 13 −5040 +935
row20 14 −5110 +935
row19 15 −5180 +935
dummy pad 16 −5320 +935
dummy pad 17 −5355 −935
row0 18 −5005 −935
row1 19 −4935 −935
row2 20 −4865 −935
row3 21 −4795 −935
row4 22 −4725 −935
row5 23 −4655 −935
row6 24 −4585 −935
row7 25 −4515 −935
row8 26 −4445 −935
row9 27 −4375 −935
To reduce the sensitivity of a reset to ESD/EMC
disturbances for a chip-on-glass application, it is strongly
recommended to implement on the glass (indium track
resistance) a series input resistance in the reset line
(recommended minimum value of 8 kΩ).
13.4 Chip information
TheOM6206 ismanufactured inn-well CMOStechnology.
The substrate is on VSS potential.
COORDINATES
(1)
SYMBOL PAD
xy
row10 28 −4305 −935
row11 29 −4235 −935
row12 30 −4165 −935
row13 31 −4095 −935
row14 32 −4025 −935
row15 33 −3955 −935
row16 34 −3885 −935
row17 35 −3815 −935
row18 36 −3745 −935
col0 37 −3605 −935
col1 38 −3535 −935
col2 39 −3465 −935
col3 40 −3395 −935
col4 41 −3325 −935
col5 42 −3255 −935
col6 43 −3185 −935
col7 44 −3115 −935
col8 45 −3045 −935
col9 46 −2975 −935
col10 47 −2905 −935
col11 48 −2835 −935
col12 49 −2765 −935
col13 50 −2695 −935
col14 51 −2625 −935
col15 52 −2555 −935
col16 53 −2485 −935
col17 54 −2415 −935
col18 55 −2345 −935
2001 Nov 14 25
Page 26

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
SYMBOL PAD
COORDINATES
xy
col19 56 −2275 −935
col20 57 −2205 −935
col21 58 −2135 −935
col22 59 −2065 −935
col23 60 −1995 −935
col24 61 −1925 −935
col25 62 −1785 −935
col26 63 −1715 −935
col27 64 −1645 −935
col28 65 −1575 −935
col29 66 −1505 −935
col30 67 −1435 −935
col31 68 −1365 −935
col32 69 −1295 −935
col33 70 −1225 −935
col34 71 −1155 −935
col35 72 −1085 −935
col36 73 −1015 −935
col37 74 −945 −935
col38 75 −875 −935
col39 76 −805 −935
col40 77 −735 −935
col41 78 −665 −935
col42 79 −595 −935
col43 80 −525 −935
col44 81 −455 −935
col45 82 −385 −935
col46 83 −315 −935
col47 84 −245 −935
col48 85 −175 −935
col49 86 −105 −935
col50 87 +35 −935
col51 88 +105 −935
col52 89 +175 −935
col53 90 +245 −935
col54 91 +315 −935
col55 92 +385 −935
col56 93 +455 −935
col57 94 +525 −935
(1)
SYMBOL PAD
COORDINATES
xy
col58 95 +595 −935
col59 96 +665 −935
col60 97 +735 −935
col61 98 +805 −935
col62 99 +875 −935
col63 100 +945 −935
col64 101 +1015 −935
col65 102 +1085 −935
col66 103 +1155 −935
col67 104 +1225 −935
col68 105 +1295 −935
col69 106 +1365 −935
col70 107 +1435 −935
col71 108 +1505 −935
col72 109 +1575 −935
col73 110 +1645 −935
col74 111 +1715 −935
col75 112 +1785 −935
col76 113 +1925 −935
col77 114 +1995 −935
col78 115 +2065 −935
col79 116 +2135 −935
col80 117 +2205 −935
col81 118 +2275 −935
col82 119 +2345 −935
col83 120 +2415 −935
col84 121 +2485 −935
col85 122 +2555 −935
col86 123 +2625 −935
col87 124 +2695 −935
col88 125 +2765 −935
col89 126 +2835 −935
col90 127 +2905 −935
col91 128 +2975 −935
col92 129 +3045 −935
col93 130 +3115 −935
col94 131 +3185 −935
col95 132 +3255 −935
col96 133 +3325 −935
(1)
2001 Nov 14 26
Page 27

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
COORDINATES
(1)
SYMBOL PAD
xy
col97 134 +3395 −935
col98 135 +3465 −935
col99 136 +3535 −935
col100 137 +3605 −935
col101 138 +3675 −935
row50 139 +3815 −935
row49 140 +3885 −935
row48 141 +3955 −935
row47 142 +4025 −935
row46 143 +4095 −935
row45 144 +4165 −935
row44 145 +4235 −935
row43 146 +4305 −935
row42 147 +4375 −935
row41 148 +4445 −935
row40 149 +4515 −935
row39 150 +4585 −935
row38 151 +4655 −935
row37 152 +4725 −935
row36 153 +4795 −935
row35 154 +4865 −935
row34 155 +4935 −935
row33 156 +5005 −935
dummy pad 157 +5355 −935
dummy pad 158 +5320 +935
row51 159 +5180 +935
row52 160 +5110 +935
row53 161 +5040 +935
row54 162 +4970 +935
row55 163 +4900 +935
row56 164 +4830 +935
row57 165 +4760 +935
row58 166 +4690 +935
row59 167 +4620 +935
row60 168 +4550 +935
row61 169 +4480 +935
row62 170 +4410 +935
row63 171 +4340 +935
row64 172 +4270 +935
COORDINATES
(1)
SYMBOL PAD
xy
dummy pad 173 +4050 +935
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
DD1
DD1
DD1
DD1
DD1
DD1
DD3
DD2
DD2
DD2
DD2
DD2
DD2
DD2
DD2
DD2
DD2
DD2
DD2
DD2
174 +3890 +935
175 +3810 +935
176 +3730 +935
177 +3650 +935
178 +3570 +935
179 +3490 +935
180 +3250 +935
181 +3090 +935
182 +3010 +935
183 +2930 +935
184 +2850 +935
185 +2770 +935
186 +2690 +935
187 +2610 +935
188 +2530 +935
189 +2450 +935
190 +2370 +935
191 +2290 +935
192 +2210 +935
193 +2130 +935
SCLK 194 +1890 +935
SDIN 195 +1650 +935
DC_B 196 +1410 +935
SCE_B 197 +1170 +935
T2 198 +930 +935
OSC 199 +690 +935
V
SS2
V
SS2
V
SS2
V
SS2
V
SS2
V
SS2
V
SS2
V
SS2
V
SS2
V
SS2
V
SS2
V
SS2
200 +530 +935
201 +450 +935
202 +370 +935
203 +290 +935
204 +210 +935
205 +130 +935
206 +50 +935
207 −30 +935
208 −110 +935
209 −190 +935
210 −270 +935
211 −350 +935
2001 Nov 14 27
Page 28

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
COORDINATES
(1)
SYMBOL PAD
xy
V
SS2
V
SS2
V
SS1
V
SS1
V
SS1
V
SS1
212 −430 +935
213 −510 +935
214 −670 +935
215 −750 +935
216 −830 +935
217 −910 +935
T1 218 −1150 +935
T5 219 −1630 +935
T4 220 −2030 +935
V
SS1
V
SS1
221 −2110 +935
222 −2190 +935
T3 223 −2270 +935
V
LCDIN
V
LCDIN
V
LCDIN
V
LCDIN
V
LCDIN
V
LCDIN
V
LCDOUT
V
LCDOUT
V
LCDOUT
V
LCDOUT
V
LCDOUT
V
LCDOUT
V
LCDOUT
V
LCDSENSE
224 −2510 +935
225 −2590 +935
226 −2670 +935
227 −2750 +935
228 −2830 +935
229 −2910 +935
230 −3070 +935
231 −3150 +935
232 −3230 +935
233 −3310 +935
234 −3390 +935
235 −3470 +935
236 −3550 +935
237 −3630 +935
Alignment marks
Circle 1 −5185 −910
Circle 2 +5185 −910
Circle 3 +4160 +910
Circle 4 −4160 +910
Table 9 Bonding pad dimensions
NAME DIMENSION
Pad pitch 70 µm
Pad size, aluminium 62 × 100 µm
Bump dimensions 50 × 90 × 17.5 (±5) µm
Wafer thickness (including
maximum 430 µm
bumps)
Wafer thickness (without
typical 380 µm
bumps)
Note
1. Allx/y coordinates(in µm) arereferencedto thecentre
of the chip (see Fig.20).
2001 Nov 14 28
Page 29

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
ndbook, full pagewidth
.
.
.
.
.
.
DD1
V
DD2
V
SS2
SS1
dummy bump
R51
R64
dummy bump
DD3
V
SCLK
SDIN
D/C
SCE
T2
OSC
V
V
(1)
y
alignment mark
x
0,0
(1)
alignment mark
OM6206
R33
.
.
.
.
.
.
R50
C101
.
.
.
.
.
.
C76
C75
.
.
.
.
.
.
C50
C49
.
.
.
MGT887
dummy bumpdummy bump
10.94 mm
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in theAcrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to forcelandscape pages to berotated correctly when browsing throughthe pdf in the Acrobatreader. white to forcelandscape pages to be ...
2001 Nov 14 29
T1
T5
T4
SS1
V
T3
LCDIN
V
LCDOUT
V
LCDSENSE
V
RES
row 32
.
.
.
.
.
.
row 19
dummy bump
.
.
.
C25
C24
.
.
.
.
.
.
pad 237
pad 1
(1)
alignment mark
(1)
mm
2.14
C0
R18
.
.
.
.
.
.
R0
alignment mark
Fig.20 Bonding pad locations.
(1) The alignment marks are circles with a diameter of 100 µm.
Page 30

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
15 DEVICE PROTECTION CIRCUITS
SYMBOL PAD INTERNAL CIRCUIT
V
DD1
174 to 179
MGT879
V
SS1
V
DD2
V
DD3
V
SS1
V
SS2
V
LCDIN
V
LCDSENSE
V
LCDOUT
181 to 193
180
214 to 217, 221, 222
200 to 213
224 to 229
237
230 to 236
page
MGT879
MGT883
MGT879
MGT880
V
V
SS1
V
V
SS1
V
V
SS2
SS1
SS1
SS2
T2 198
T3 223
2001 Nov 14 30
MGT882
V
V
DD1
SS1
Page 31

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
SYMBOL PAD INTERNAL CIRCUIT
SDIN 195
SCLK 194
SCE 197
D/
C 196
OSC 199
RES 1
T1 217
T4 218
T5 220
R0 to R64 2 to 15,18 to 36,139 to 156,
159 to 172
C0 to C101 37 to 138
alfpage
MGT884
1 per block
V
V
DD1
SS1
V
LCDIN
MGT881
V
SS1
2001 Nov 14 31
Page 32

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
16 TRAY INFORMATION
handbook, full pagewidth
x
y
H
F
G
A
E
C
D
B
MGT885
Fig.21 Tray details.
handbook, halfpage
OM6206
MGT886
The orientation of the IC in a pocket is indicated by the position of the IC type name on the die surface with respect to the chamfer on the upper left
corner of the tray. Refer to the bonding pad location diagram for the orientating and position of the type name on the die surface.
Fig.22 Tray alignment.
2001 Nov 14 32
Page 33

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
Table 10 Tray dimensions
DIMENSIONS DESCRIPTION VALUE
A pocket pitch; in the x direction 13.77 mm
B pocket pitch; in the y direction 4.45 mm
C pocket width; in the x direction 11.04mm
D pocket width; in the y direction 2.24mm
E tray width; in the x direction 50.8 mm
F tray width; in the y direction 50.8 mm
G distance from cut corner to pocket centre 11.63 mm
H distance from cut corner to pocket centre 5.41 mm
x number of pockets in the x direction 3
y number of pockets in the y direction 10
2001 Nov 14 33
Page 34

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
17 DATA SHEET STATUS
PRODUCT
DATA SHEET STATUS
Objective data Development This data sheet contains data from the objective specification for product
Preliminary data Qualification This data sheet contains data from the preliminary specification.
Product data Production This data sheet contains data from the product specification. Philips
(1)
STATUS
(2)
development. Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to change the
specification in any manner without notice.
Supplementary data will be published at a later date. Philips
Semiconductors reserves the right to change the specification without
notice, in order to improve the design and supply the best possible
product.
Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes at any time in order
to improve the design, manufacturing and supply. Changes will be
communicated according to the Customer Product/Process Change
Notification (CPCN) procedure SNW-SQ-650A.
DEFINITIONS
Notes
1. Please consult the most recently issued data sheet before initiating or completing a design.
2. The product status of the device(s) described in this data sheet may have changed since this data sheet was
published. The latest information is available on the Internet at URL http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.
18 DEFINITIONS
Short-form specification The data in a short-form
specification is extracted from a full data sheet with the
same type number and title. For detailed information see
the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting valuesdefinition Limitingvalues givenare in
accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System
(IEC 60134). Stress above one or more of the limiting
values may cause permanent damage to the device.
These are stress ratings only and operation of the device
atthese orat anyotherconditions abovethose givenin the
Characteristics sectionsof the specification isnot implied.
Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may
affect device reliability.
Application information Applications that are
described herein for any of these products are for
illustrative purposes only. Philips Semiconductors make
norepresentation orwarrantythat suchapplications willbe
suitable for the specified use without further testing or
modification.
19 DISCLAIMERS
Life support applications These products are not
designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or
systems where malfunction of these products can
reasonably beexpected toresult inpersonal injury.Philips
Semiconductorscustomers usingorselling theseproducts
for use in such applications do so at their own risk and
agree to fully indemnify Philips Semiconductors for any
damages resulting from such application.
Right to make changes Philips Semiconductors
reserves the right to make changes, without notice, in the
products, including circuits, standard cells, and/or
software, described or contained herein in order to
improve design and/or performance. Philips
Semiconductors assumes no responsibility or liability for
theuse ofany oftheseproducts, conveysnolicence ortitle
under any patent, copyright, or mask work right to these
products,and makesno representationsor warrantiesthat
these products are free from patent, copyright, or mask
work right infringement, unless otherwise specified.
Bare die All die are tested and are guaranteed to
comply with all data sheet limits up to the point of wafer
sawing for a period of ninety (90) days from the date of
Philips' delivery. If there are data sheet limits not
guaranteed, these will be separately indicated in the data
sheet. There are no post packing tests performed on
individual die or wafer. Philips Semiconductors has no
control of third party procedures in the sawing, handling,
packing or assembly of the die. Accordingly, Philips
Semiconductors assumes no liability for device
functionality or performance of the die or systems after
third party sawing, handling, packing or assembly of the
die. It is the responsibility of the customer to test and
qualify their application in which the die is used.
2001 Nov 14 34
Page 35

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
65 × 102 pixels matrix LCD driver OM6206
NOTES
2001 Nov 14 35
Page 36

Philips Semiconductors – a w orldwide compan y
Contact information
For additional information please visit http://www.semiconductors.philips.com. Fax: +31 40 27 24825
For sales offices addresses send e-mail to: sales.addresses@www.semiconductors.philips.com.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2001
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document doesnot formpart of any quotation or contract, isbelieved to be accurate and reliable and may bechanged
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Printed in The Netherlands 403506/01/pp36 Date of release: 2001 Nov 14 Document order number: 9397 750 07746
SCA73
 Loading...
Loading...