Page 1
Instructions for Use
IntelliVue Patient Monitor
MX400/450/500/550/600/700/800
MX400/450/500/550 Release K with Rev. K.1x.xx
MX600/700/800 Release J with Revison J.xx.xx
Patient Monitoring
Page 2

Page 3

1Table of Contents
1 Introduction 13
Safety Information 14
Security Information 15
Introducing the Monitor 16
Devices for Acquiring Measurements 18
Operating and Navigating 27
Operating Modes 36
Understanding Screens 37
Connecting Additional Displays to the Monitor 38
Using the XDS Remote Display 39
Using the Visitor Screen 39
Understanding Profiles 39
Understanding Settings 41
Changing Wave Speeds 42
Freezing Waves 42
Using Labels 44
Entering Measurements Manually 46
Changing Monitor Settings 47
Checking Your Monitor Revision 48
Getting Started 48
Disconnecting from Power 49
Networked Monitoring 50
Using the Integrated PC 50
Using Your Monitor with a Monitor in Companion Mode 52
2 What's New? 55
What's New in Release K.1 (for MX400/450/500/550 only) 55
What's New in Release K.0 55
What's New in Release J.0 56
3 Alarms 59
Visual Alarm Indicators 60
Audible Alarm Indicators 61
Acknowledging Alarms 63
Pausing or Switching Off Alarms 64
Alarm Limits 67
Reviewing Alarms 71
Latching Alarms 72
Testing Alarms 73
Alarm Behavior at Power On 73
3
Page 4

Alarm Recordings 73
4 Patient Alarms and INOPs 75
Patient Alarm Messages 75
Technical Alarm Messages (INOPs) 81
5 Managing Patients and Equipment 105
Patient Concepts 105
Equipment Concepts 105
Managing Patients 106
Managing Equipment 119
Care Groups 126
Information Center Compatibility 132
6 ECG, Arrhythmia, ST and QT Monitoring 133
Skin Preparation for Electrode Placement 133
Connecting ECG Cables 133
Selecting the Primary and Secondary ECG Leads 134
Checking Paced Mode 134
Understanding the ECG Display 134
Monitoring Paced Patients 135
Changing the Size of the ECG Wave 136
Changing the Volume of the QRS Tone 137
Changing the ECG Filter Settings 137
Selecting Positions of Va and Vb Chest Leads (for 6-lead placement) 138
Choosing EASI or Standard Lead Placement 138
About ECG Leads 138
ECG Lead Fallback 139
ECG Lead Placements 139
EASI ECG Lead Placement 145
Capture 12-Lead 146
ECG and Arrhythmia Alarm Overview 149
Using ECG Alarms 151
ECG Safety Information 152
About Arrhythmia Monitoring 154
Switching Arrhythmia Analysis On and Off 154
Choosing an ECG Lead for Arrhythmia Monitoring 155
Atrial Fibrillation Alarm 155
Aberrantly-Conducted Beats 156
Intermittent Bundle Branch Block 156
Understanding the Arrhythmia Display 156
Arrhythmia Relearning 159
Arrhythmia Alarms 160
About ST Monitoring 164
Switching ST or STE On and Off 165
Understanding the ST Display 166
4
Page 5

Updating ST Baseline Snippets 168
Recording ST Segments 168
About the ST Measurement Points 168
ST Alarms 171
STE Alarms 171
Viewing ST Maps 172
About QT/QTc Interval Monitoring 175
QT Alarms 178
Switching QT Monitoring On and Off 179
7 Monitoring Pulse Rate 181
Entering the Setup Pulse Menu 181
System Pulse Source 181
Switching Pulse On and Off 182
Using Pulse Alarms 182
8 Monitoring Respiration Rate (Resp) 185
Lead Placement for Monitoring Resp 185
Understanding the Resp Display 186
Changing Resp Detection Modes 186
Changing the Size of the Respiration Wave 187
Changing the Speed of the Respiration Wave 188
Using Resp Alarms 188
Changing the Apnea Alarm Delay 188
Resp Safety Information 188
9 Monitoring SpO2 191
SpO2 Sensors 191
Applying the Sensor 191
Connecting SpO2 Cables 192
Measuring SpO2 192
SpO2 Signal Quality Indicator (FAST SpO2 only) 193
Assessing a Suspicious SpO2 Reading 194
Changing the Averaging Time 194
Understanding SpO2 Alarms 194
Pleth Wave 200
Perfusion Numeric 200
Perfusion Change Indicator 200
Setting SpO2/Pleth as Pulse Source 200
Setting Up Tone Modulation 201
Setting the QRS Volume 201
Calculating SpO2 Difference 201
10 Monitoring NBP 203
Introducing the Oscillometric NBP Measurement 203
Preparing to Measure NBP 205
5
Page 6

Starting and Stopping Measurements 207
Enabling Automatic Mode and Setting Repetition Time 208
Enabling Sequence Mode and Setting Up The Sequence 208
Choosing the NBP Alarm Source 209
Switching Pulse from NBP On/Off 209
Assisting Venous Puncture 210
Calibrating NBP 210
11 Monitoring Temperature 211
Making a Temp Measurement 211
Calculating Temp Difference 212
12 Monitoring Invasive Pressure 213
Setting up the Pressure Measurement 213
Zeroing the Pressure Transducer 215
Adjusting the Calibration Factor 217
Displaying a Mean Pressure Value Only 217
Changing the Pressure Wave Scale 217
Optimizing the Waveform 217
Using the Wave Cursor 217
Non-Physiological Artifact Suppression 218
Choosing the Pressure Alarm Source 218
Calibrating Reusable Transducer CPJ840J6 219
Calculating Cerebral Perfusion Pressure 221
Calculating Pulse Pressure Variation 221
Measuring IAP 222
Measuring Pulmonary Artery Wedge Pressure 222
Editing the Wedge 223
Identifying the Pressure Analog Output Connector 224
13 Monitoring Cardiac Output 225
Hemodynamic Parameters 226
Using the C.O. Procedure Window 226
Accessing the Setup C.O. and Setup CCO Menus 228
Entering the HemoCalc Window 228
Measuring C. O. Using the PiCCO Method 228
Measuring C.O. Using the Right Heart Thermodilution Method 233
Documenting C.O. Measurements 235
C.O. Injectate Guidelines 235
C.O./CCO Curve Alert Messages 236
C.O./CCO Prompt Messages 238
C.O./CCO Warning Messages 238
C.O./CCO Safety Information 239
14 Monitoring Carbon Dioxide 241
Measurement Principles 242
6
Page 7

Measuring CO2 using M3014A or X2 242
Measuring Mainstream CO2 using M3016A 246
Measuring Microstream CO2 using M3015A/B 248
Setting up all CO2 Measurements 250
Understanding the IPI Numeric 252
15 Monitoring Airway Flow, Volume and Pressure 255
Attaching the Flow Sensor 256
Zero Calibration 258
Automatic Purging 258
Manual Purging 259
Gas Compensation 259
Setting up Spirometry 260
16 Monitoring tcGas 263
Identifying tcGas Module Components 263
Setting the tcGas Sensor Temperature 264
Using the tcGas Site Timer 264
Setting the tcGas Barometric Pressure 265
Remembraning the tcGas Transducer 265
Calibrating the tcGas Transducer 265
Applying the tcGas Transducer 267
Finishing tcGas Monitoring 268
Zeroing the tcGas Relative Heat Power 268
TcGas Corrections 268
17 Monitoring Intravascular Oxygen Saturation 271
Selecting a Measurement Label 272
Preparing to Monitor with the M1021A Wide Module 272
Preparing to Monitor with the M1011A Narrow Module 275
Further Information for Both Modules 277
18 Monitoring EEG 279
EEG Monitoring Setup 279
Using the EEG Impedance/Montage Window 280
About Compressed Spectral Arrays (CSA) 282
Changing EEG Settings 283
EEG Reports 284
EEG Safety Information 284
EEG and Electrical Interference 284
19 Monitoring BIS 285
BIS Monitoring Setup 286
BIS Continuous Impedance Check 288
BIS Cyclic Impedance Check 288
BIS Window 289
7
Page 8

Changing the BIS Smoothing Rate 290
Switching BIS and Individual Numerics On and Off 290
Changing the Scale of the EEG Wave 290
Switching BIS Filters On or Off 290
BIS Safety Information 291
20 Monitoring NMT 293
Stimulation Modes 294
Preparing to Measure NMT 295
Taking NMT Measurements 296
Changing the NMT Measurement Settings 298
Alarms 299
Understanding NMT Numerics 299
21 Guardian Early Warning Scoring 301
Performing the Scoring Procedure 301
Understanding Guardian Early Warning Scoring 303
Viewing EWS Trend Data 304
Using Different Types of Scoring 305
22 Using a Telemetry Device and a Monitor (PIIC only) 307
How Can You Combine Devices? 307
Use Models With Telemetry 309
23 Trends 311
Viewing Trends 311
Setting Up Trends 315
Documenting Trends 319
Trends Databases 319
Screen Trends 320
24 Calculations 325
Viewing Calculations 326
Reviewing Calculations 327
Performing Calculations 327
Entering Values for Calculations 328
Documenting Calculations 329
25 High Resolution Trend Waves 331
Changing the Hi-Res Trend Waves Displayed 331
Hi-Res Trend Wave Scales 331
Hi-Res Trend Waves and OxyCRG 331
Printing Hi-Res Trend Wave Reports 332
Hi-Res Trend Wave Recordings 332
8
Page 9

26 Event Surveillance 333
Levels of Event Surveillance 333
Event Groups 334
Event Episodes 334
Events Pop-Up Keys 335
Event Triggers 336
The Events Database 339
Viewing Events 340
Annotating Events 342
Documenting Events 342
27 ProtocolWatch 349
SSC Sepsis Protocol 349
28 Recording 357
Paper-Strip Recording 357
Electronic Recording 365
29 Printing Patient Reports 369
Starting Report Printouts 369
Stopping Reports Printouts 371
Setting Up Reports 371
Setting Up Individual Print Jobs 372
Checking Printer Settings 373
Printing a Test Report 374
Switching Printers On or Off for Reports 374
Dashed Lines on Reports 374
Unavailable Printer: Re-routing Reports 374
Checking Report Status and Printing Manually 375
Printer Status Messages 375
Sample Report Printouts 376
30 Using the Drug Calculator 381
Accessing the Drug Calculator 382
Performing Drug Calculations 382
Charting Infusion Progress 385
Using the Titration Table 385
Documenting Drug Calculations 386
31 VueLink Modules 387
Connecting an External Device 388
Changing VueLink Waves and Numerics Displayed 388
Viewing the VueLink Device Data Window 389
Using VueLink Screens 389
Switching VueLink On and Off 389
Alarms/INOPs From External Devices 389
9
Page 10

Language Conflict with External Device Drivers 390
32 IntelliBridge EC10 391
Connecting an External Device 391
Changing Waves and Numerics Displayed 392
Viewing the IntelliBridge Device Data Window 392
Using Screens with External Device Data 393
Alarms/INOPs from External Devices 393
33 Using Timers 395
Viewing Timers 395
Timer Setup Pop-up Keys 396
Setting Up Timers 396
Displaying a Timer On The Main Screen 397
Displaying A Clock On The Main Screen 398
34 Respiratory Loops 399
Viewing Loops 399
Capturing and Deleting Loops 400
Showing/Hiding Loops 400
Changing Loops Display Size 400
Using the Loops Cursor 400
Changing Loops Type 401
Setting Up Source Device 401
Documenting Loops 401
35 Laboratory Data 403
Viewing Received Data 403
36 Using Batteries 405
Battery Power Indicators 405
Checking Battery Charge 407
When Battery Lifetime is Expired 407
Replacing a Battery 407
Optimizing Battery Performance 408
Battery Safety Information 409
37 Care and Cleaning 411
General Points 411
Cleaning the Equipment 412
Disinfecting the Equipment 412
Sterilizing the Equipment 413
Cleaning, Sterilizing and Disinfecting Monitoring Accessories 413
Cleaning the SO2 Optical Module 413
Cleaning the Recorder Printhead (M1116B only) 413
Cleaning Batteries and the Battery Compartment 414
10
Page 11

38 Maintenance and Troubleshooting 415
Inspecting the Equipment and Accessories 415
Inspecting the Cables and Cords 416
Maintenance Task and Test Schedule 416
Troubleshooting 417
Returning Equipment for Repair 417
Disposing of the Monitor 417
Disposing of Empty Calibration Gas Cylinders 418
39 Accessories 419
ECG/Resp Accessories 419
NBP Accessories 423
Invasive Pressure Accessories 426
SpO2 Accessories 429
Temperature Accessories 435
Cardiac Output (C.O.) Accessories 436
Mainstream CO2 Accessories 437
Sidestream CO2 Accessories 437
Mainstream CO2 Accessories (for M3016A) 438
Microstream CO2 Accessories 438
Spirometry Accessories 439
tcGas Accessories 439
EEG Accessories 440
BIS Accessories 440
SO2 Accessories for M1021A 440
SO2 Accessories for M1011A 441
NMT Accessories 441
Recorder Accessories 442
Battery Accessories 442
40 Specifications 443
Indications for Use 443
Restricted Availability 444
Use Environment 444
Manufacturer's Information 444
Symbols 445
Installation Safety Information 447
Monitor Mounting Precautions 455
Altitude Setting 456
Monitor Safety Specifications 456
Physical Specifications 457
Environmental Specifications 458
EMC and Radio Regulatory Compliance 462
Monitor Performance Specifications 464
Interface Specifications 470
Display Specifications 474
11
Page 12

M4605A Battery Specifications 475
Measurement Specifications 475
Safety and Performance Tests 495
41 Default Settings Appendix 501
Country-Specific Default Settings 501
Alarm and Measurement Default Settings 508
Alarm Default Settings 508
ECG, Arrhythmia, ST and QT Default Settings 509
Pulse Default Settings 512
Respiration Default Settings 513
SpO2 Default Settings 513
NBP Default Settings 514
Temperature Default Settings 514
Invasive Pressure Default Settings 515
Cardiac Output Default Settings 517
CO2 Default Settings 518
Spirometry Default Settings 518
tcGas Default Settings 519
Intravascular Oxygen Saturation Default Settings 519
SvO2 Default Settings 520
ScvO2 Default Settings 520
EEG Default Settings 520
BIS Default Settings 521
NMT Default Settings 521
VueLink Default Settings 522
Index 523
12
Page 13

1Introduction
These Instructions for Use are for clinical professionals using the IntelliVue MX400/MX450, MX500/
MX550, and MX600/MX700/MX800 patient monitor.
This basic operation section gives you an overview of the monitor and its functions. It tells you how to
perform tasks that are common to all measurements (such as entering data, switching a measurement
on and off, setting up and adjusting wave speeds, working with profiles). The alarms section gives an
overview of alarms. The remaining sections tell you how to perform individual measurements, and
how to care for and maintain the equipment.
Familiarize yourself with all instructions including warnings and cautions before starting to monitor
patients. Read and keep the Instructions for Use that come with any accessories, as these contain
important information about care and cleaning that is not repeated here.
This guide describes all features and options. Your monitor may not have all of them; they are not all
available in all geographies. Your monitor is highly configurable. What you see on the screen, how the
menus appear and so forth, depends on the way it has been tailored for your hospital and may not be
exactly as shown here.
1
MX400/
MX450
In this guide:
•A warning alerts you to a potential serious outcome, adverse event or safety hazard. Failure to
observe a warning may result in death or serious injury to the user or patient.
•A caution alerts you to where special care is necessary for the safe and effective use of the
product. Failure to observe a caution may result in minor or moderate personal injury or damage
to the product or other property, and possibly in a remote risk of more serious injury.
Whenever a monitor's identifier appears to the left of a heading or paragraph, it means that the
information applies to that monitor only. Where the information applies to all models, no distinction is
made.
For installation, repair, testing and troubleshooting instructions, refer to the Service Guide for your
monitor model.
Rx only: U.S. Federal Law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
13
Page 14
1Introduction
Safety Information
The following warnings apply to the monitors in general. Warnings that apply to specific
measurements or procedures can be found in the corresponding chapters.
Electrical Hazards and Interference
WARNING
Grounding: To avoid the risk of electric shock, the monitor must be grounded during operation. If a
three-wire receptacle is not available, consult the hospital electrician. Never use a three-wire to twowire adapter.
Electrical shock hazard: Do not open the monitor or measurement device. Contact with exposed
electrical components may cause electrical shock. Refer servicing to qualified service personnel.
Leakage currents: If multiple instruments are connected to a patient, the sum of the leakage currents
may exceed the limits given in IEC/EN 60601-1, IEC 60601-1-1, UL 60601-1. Consult your service
personnel.
Radio frequency interference: The monitor generates, uses and radiates radio-frequency energy, and
if it is not installed and used in accordance with its accompanying documentation, may cause
interference to radio communications.
Use Environment
WARNING
Explosion Hazard: Do not use in the presence of flammable anesthetics or gases, such as a
flammable anesthetic mixture with air, oxygen or nitrous oxide. Use of the devices in such an
environment may present an explosion hazard.
Positioning Equipment: The monitor should not be used next to or stacked with other equipment.
If you must stack the monitor, check that normal operation is possible in the necessary configuration
before you start monitoring patients.
Environmental Specifications: The performance specifications for the monitors, measurements and
accessories apply only for use within the temperature, humidity and altitude ranges specified in
“Environmental Specifications” on page 458.
Liquid Ingress: If you spill liquid on the equipment, battery, or accessories, or they are accidentally
immersed in liquid, contact your service personnel or Philips service engineer. Do not operate the
equipment before it has been tested and approved for further use.
Prohibited Environments: The monitors are not intended for use in an MRI environment or in an
oxygen-enriched environment (for example, hyperbaric chambers).
14
Page 15

Alarms
WARNING
• Do not rely exclusively on the audible alarm system for patient monitoring. Adjustment of alarm
• Be aware that the monitors in your care area may each have different alarm settings, to suit
Accessories
WARNING
Philips' approval: Use only Philips-approved accessories. Using other accessories may compromise
device functionality and system performance and cause a potential hazard.
Reuse: Never reuse disposable transducers, sensors, accessories and so forth that are intended for
single use, or single patient use only. Reuse may compromise device functionality and system
performance and cause a potential hazard.
1 Introduction
volume to a low level or off during patient monitoring may result in patient danger. Remember
that the most reliable method of patient monitoring combines close personal surveillance with
correct operation of monitoring equipment.
different patients. Always check that the alarm settings are appropriate for your patient before you
start monitoring.
Electromagnetic compatibility: Using accessories other than those specified may result in increased
electromagnetic emission or decreased electromagnetic immunity of the monitoring equipment.
Damage: Do not use a damaged sensor or one with exposed electrical contacts.
Cables and tubing: Always position cables and tubing carefully to avoid entanglement or potential
strangulation.
MR Imaging: During MR imaging, remove all transducers, sensors and cables from the patient.
Induced currents could cause burns.
Security Information
Protecting Personal Information
Protecting personal health information is a primary component of a security strategy. Each facility
using the monitors must provide the protective means necessary to safeguard personal information
consistent with country laws and regulations, and consistent with the facility’s policies for managing
this information. Protection can only be realized if you implement a comprehensive, multi-layered
strategy (including policies, processes, and technologies) to protect information and systems from
external and internal threats.
As per its intended use, the patient monitor operates in the patient vicinity and contains personal and
sensitive patient data. It also includes controls to allow you to adapt the monitor to the patient's care
model. To ensure the patient's safety and protect their personal health information you need a security
concept that includes:
15
Page 16

1Introduction
• Physical security access measures - access to the monitor must be limited to authorized users.
It is essential that you consider physical security measures to ensure that unauthorized users
cannot gain access.
• Operational security measures - for example, ensuring that patients are discharged after
monitoring in order to remove their data from the monitor.
• Procedural security measures - for example, assigning only staff with a specific role the right to
use the monitors.
In addition, any security concept must consider the requirements of local country laws and regulations.
Always consider data security aspects of the network topology and configuration when connecting
patient monitors to shared networks. Your medical facility is responsible for the security of the
network, where sensitive patient data from the monitor may be transferred.
Note: Log files generated by the monitors and measurement modules are used for system
troubleshooting and do not contain patient data.
About HIPAA Rules
If applicable, your facility’s security strategy should include the standards set forth in the Health
Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA), introduced by the United States
Department of Health and Human Services. You should consider both the security and the privacy
rules and the HITECH Act when designing policies and procedures. For more information, please
visit http://www.hhs.gov/ocr/privacy/.
About the EU Directives
If applicable, your facility’s security strategy should include the practices set forth in the Directive on
the protection of individuals with regard to the processing of personal data and on the free movement
of such data (Directive 95/46/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of
24 October 1995). In addition, your facility should also take into account any additional, more
stringent standards put forward by any individual EU countries; that is, Germany, France, and so on.
For more information, please visit http://eur-lex.europa.eu/en/dossier/dossier_27.htm.
Philips Product Security Policy Statement
Additional security and privacy information can be found on the Philips product security web site at
http://www.healthcare.philips.com/main/support/equipment-performance/product-security/
index.wpd
Manufacturer Disclosure Statement for Medical Device Security – MDS2
You can view the Manufacturer Disclosure Statements for Medical Device Security (MDS2) for
specific devices at http://www.healthcare.philips.com/main/support/equipment-performance/
product-security/index.wpd
Introducing the Monitor
16
The IntelliVue MX400/MX450, MX500/MX550, and MX600/MX700/MX800 patient monitor
offers a monitoring solution optimized for the high-end surgical, cardiac, medical and neonatal care
environments. Combining patient surveillance and data management, it allows multi-measurement
monitoring by linking separate modules. The MX600 uses the navigation knob as primary input device
Page 17

1 Introduction
and the MX400/MX450, MX500/MX550, and MX700/MX800 use the touch screen as primary input
device. All monitors have a remote control for convenient access to the five main keys and numeric
data input.
The monitor stores data in trend, event, and calculation databases. You can see tabular trends (vital
signs) and document them on a printer. You can view measurement trend graphs, with up to three
measurements combined in each graph, to help you identify changes in the patient's physiological
condition. You can view fast-changing measurement trends with beat to beat resolution and see up to
four high resolution trend segments. Event surveillance enhances documentation and review of
physiologically significant events by automatically detecting and storing up to 50 user-defined clinical
events over a 24 hour period.
MX600/700/
With the optional Integrated PC, you have computer functionality directly in the monitor. You can use
standard applications (e.g. Web browsers), connect to the hospital network or intranet, and run a
800
second independent display with content from the patient monitor.
An IntelliVue X2 can be connected to your monitor, where it acts as a multi-measurement module,
acquiring measurements for the host monitor. When the X2 is disconnected from the original host
monitor, it continues to monitor the patient as a fully independent, battery powered patient monitor,
eliminating the need for a separate transport monitor. On connection to a new host monitor, the X2
resumes its role as multi-measurement module, ensuring fully continuous monitoring.
Major Parts and Keys
MX400/450/500/550
The MX400/450/500/550 monitors have the same parts, controls and indicators. Here the MX400 is
shown.
1 Color coded alarm lamps
2 Alarms Off lamp
3 Power on/Standby switch with
integrated LED: Green - On/
Standby, Red - Error
4 AC power LED
5 Battery LED
6 Mounting quick-release lever
(when this is pressed the
monitor is not fixed on the
mounting)
7 Service number and serial
number
8 Device type
17
Page 18

1Introduction
MX600/700
1 Color coded alarm lamps
2 Alarms Off lamp
3 Power on/Standby switch with
integrated LED: Green - On/
Standby, Red - Error
4 AC power LED
5 Mounting quick-release lever
(when this is pressed the
monitor is not fixed on the
mounting)
6 Part number and serial number
7 Hardkeys (Silence, Alarms Off,
Main Screen)
8 Navigation knob
MX800
1 Color coded alarm lamps
2 Alarms Off lamp
3 Power on/Standby switch with
4 AC power LED
5 Mounting quick-release lever
6 Part number and serial number
Devices for Acquiring Measurements
integrated LED: Green - On/
Standby, Red - Error
(when this is pressed the
monitor is not fixed on the
mounting)
18
The patient monitor acquires patient measurements using the devices described in this section. You
can also extend the measurement capabilities of your monitor with such devices. Of these
measurement devices, only the X2 has its own power on/standby switch, and can be powered from an
external power supply or a rechargeable battery when not directly connected to the monitor (refer to
the IntelliVue X2 Instructions for Use for details). All the rest take their power exclusively from the
Page 19

monitor, and switch on automatically when you turn on the monitor. A green power-on LED indicates
when they are drawing power from the monitor. A permanently illuminated, or flashing, red LED
indicates a problem with the unit that requires the attention of qualified service personnel.
All symbols used on the front panels are explained in “Symbols” on page 445.
WARNING
When connecting devices for acquiring measurements, always position cables and tubing carefully to
avoid entanglement or potential strangulation.
Flexible Module Rack (M8048A)
1 Introduction
MX600/
MX700/
MX800
The 8-slot flexible module rack (FMS-8) lets you use up to eight plug-in physiological measurement
modules. For the MX800, you can connect two FMSs to use up to 10 measurement modules.
The maximum number of specific module types that can be used simultaneously in an FMS-8 is: five
pressure modules, four temperature modules, four VueLink or IntelliBridge modules (any
combination).
When two FMSs are used, in total a maximum of 10 pressure modules can be used.
Connect the FMS to the monitor via the measurement link cable (MSL). Use the MSL connector on
the left-hand side to connect an additional MMS. Use the connector on the right to connect to the
monitor.
4-Slot Flexible Module Rack (FMS-4)
1 X1 Multi-Measurement Module
2 Multi-Measurement Module
mount
3 Flexible Module Rack FMS-8
4 Power on LED
5 Interruption indicator
MX600/
MX700/
MX800
The 4-Slot flexible module rack (FMS-4) lets you use up to four plug-in physiological measurement
modules.
19
Page 20

1Introduction
The maximum number of specific module types that can be used simultaneously in an FMS-4 is: four
pressure modules, four temperature modules, four VueLink or IntelliBridge modules (any
combination).
Connect the FMS to the monitor via the measurement link cable (MSL). Use the MSL connector on
the left-hand side (if you have the appropriate option) to connect an additional MMS. Use the
connector on the back to connect to the monitor.
Measurement Modules
MX500/
MX550
MX600/
MX700/
MX800
You can use up to three plug-in modules in the optional module slots. Available modules are:
• Invasive blood pressure (M1006B)
• Temperature (M1029A)
• Oxygen saturation of arterial blood (SpO
) (M1020B)
2
• Cardiac output (M1012A), and Continuous cardiac output with M1012A Option #C10
• Intravascular Oxygen Saturation - ScvO2 or SvO2 (M1011A)
• Spirometry (M1014A)
• EEG (M1027A)
• NMT (865383)
• IntelliBridge EC10 (865115)
• Recorder (M1116B/C)
You can use up to eight measurement modules with the Flexible Module Rack (M8048A). Available
modules are:
• Invasive blood pressure (M1006B)
• Temperature (M1029A)
• Oxygen saturation of arterial blood (SpO
) (M1020B)
2
• Cardiac output (M1012A), and Continuous cardiac output with M1012A Option #C10
MX500/550/
600/700/800
20
• Transcutaneous gas (M1018A)
• Mixed venous oxygen saturation - SvO
• Intravascular Oxygen Saturation - ScvO
(M1021A)
2
or SvO2 (M1011A)
2
• EEG (M1027A)
• Bispectral Index - BIS (M1034A)
• Spirometry (M1014A)
• NMT (865383)
• VueLink device interface (M1032A)
• IntelliBridge EC10 (865115)
• Recorder (M1116B/C)
You can plug in and unplug modules during monitoring. Insert the module until the lever on the
module clicks into place. Remove a module by pressing the lever upwards and pulling the module out.
A measurement automatically switches on when you plug the module in, and switches off when you
Page 21

unplug it. Reconnecting a module to the same monitor restores its label and measurement settings,
such as alarms limits. If you connect it to a different monitor, the module remembers only its label.
The connector socket on the front of each module is the same color as the corresponding connector
plug on the transducer or patient cable.
Press the Setup key on the module's front to display the measurement's setup menu on the monitor
screen. When the setup menu is open, a light appears above the key. Some modules have a second key.
On the pressure module, for example, it initiates a zeroing procedure.
Example Module (SpO2)
MX500/550/
600/700/800
1 Introduction
1 Module name
2 Setup key LED
3 Setup key to enter setup menu of measurement modules or
external device data window. Some modules have a second
module-specific key next to this one, for example Zero.
4 Connector socket for patient cable/transducer
X1 Multi-Measurement Module (M3001A)
The X1 Multi-Measurement Module (MMS) can simultaneously monitor 3-, 5-, 6- or 10-lead ECG
(including arrhythmia and ST monitoring), respiration, SpO
temperature.
You can connect it to the monitor via a cable or mount it on the left side of the FMS.
, NBP and either invasive pressure or
2
21
Page 22

1Introduction
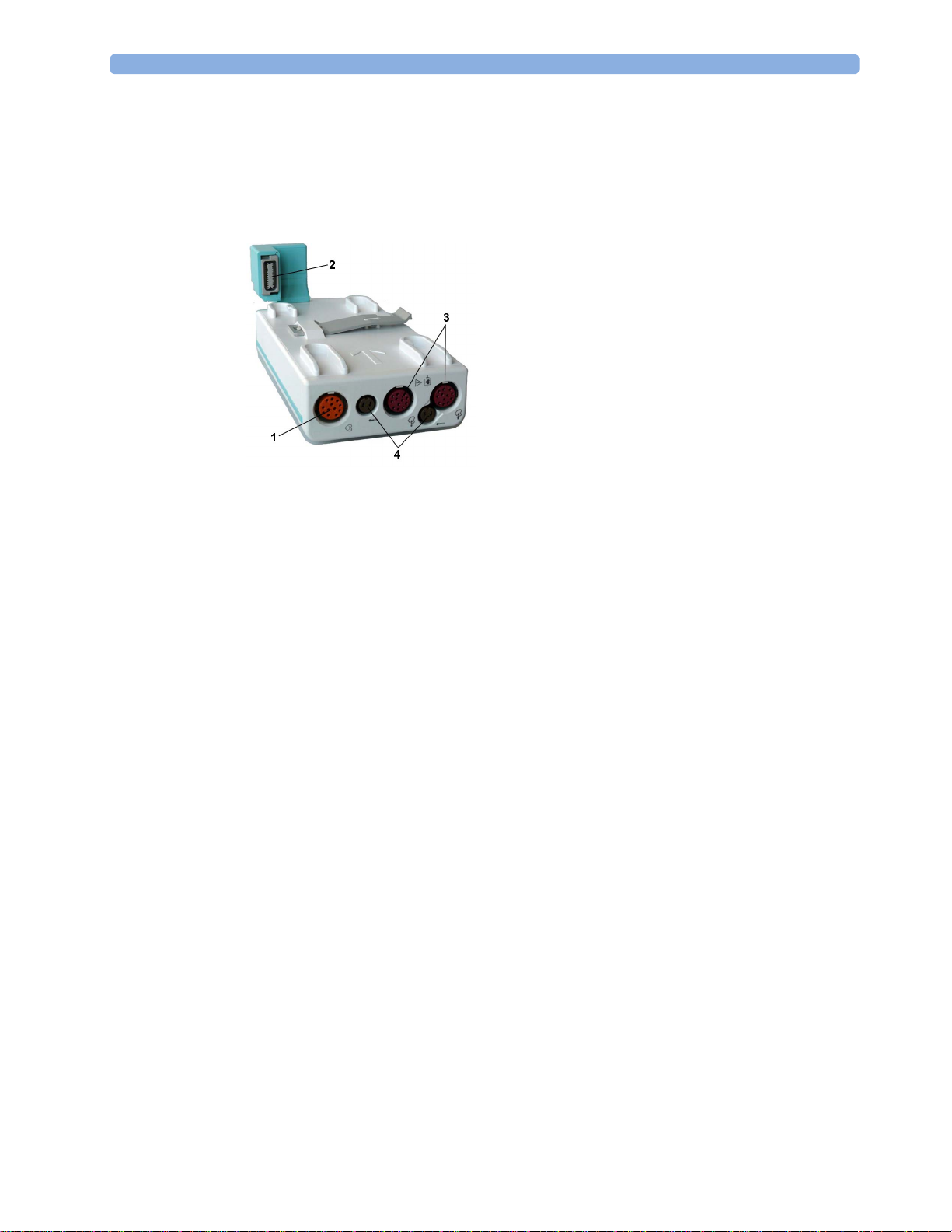
X1 Connectors and Symbols
1 White ECG/Resp connector
X2 Multi-Measurement Module (M3002A)
The X2 Multi-Measurement Module (MMS) can simultaneously monitor 3-, 5-, 6- or 10-lead ECG
(including arrhythmia and ST monitoring), respiration, SpO
temperature, or CO
The X2 has the added capability to operate as a stand-alone monitor, and can be powered by a
rechargeable battery. This makes it particularly suited to transport situations. When the X2 is
disconnected from the original host monitor, it continues to monitor the patient as a stand-alone
monitor running on battery power, eliminating the need for a separate transport monitor. When the
X2 is connected to a new host monitor, it resumes its role as MMS, ensuring fully continuous
monitoring. For details of using the X2 as a stand-alone monitor, refer to the IntelliVue X2
Instructions for Use.
. It has a color touchscreen display.
2
2 Blue SpO
3 Red NBP connector
4 Combined pressure (red) and temperature
connector
2
(brown) connector - connect either invasive
pressure transducer or temperature probe.
You might have a version of the MMS that
does not have this connector.
5 NBP STAT key - starts NBP STAT series
of measurements
or
Zero key - initiates a zero procedure for the
connected pressure transducer when
pressed and held for a second
6 NBP Start/Stop key - starts or stops NBP
measurements
7 Silence: acknowledges all active alarms by
switching off audible alarm indicators and
lamps
, NBP and either invasive pressure and
2
22
When connected to a host monitor (
Companion Mode is indicated), the X2 takes power from the
host, including that required for battery charging. The X2 can also be powered by AC mains when not
connected to a host monitor using the optionally available external power supply (M8023A). See the
IntelliVue X2 Instructions for Use for details.
Page 23

X2 Overview
1 Introduction
1 On/Standby switch
2 Power and battery indicators (see “X2
Controls and Indicators” on page 23)
3 3.5-inch TFT LCD touchscreen QVGA
display
4 Alarm lamps (see “X2 Controls and
Indicators” on page 23)
5 Battery eject button
6 Hard keys (see “X2 Controls and
Indicators” on page 23)
7 Measurement connectors (see “X2 Patient
Connectors, Right Side” on page 24)
8 Battery compartment
X2 Controls and Indicators
1 External power LED. Green when monitor is powered from an external power source.
2 Battery status LED. Yellow when charging. Flashing red when battery is empty.
3 On/Standby LED. Green when monitor is on. Red indicates an error.
4 On/Standby switch. Disabled when X2 is connected to a host monitor
5 Main Screen key: closes all open menus/windows and returns to the main screen.
6 SmartKeys key: brings up SmartKeys on the screen.
7 Alarms key: turns alarms On/Off, or pauses them.
23
Page 24

1Introduction
8
Silence key
9 Active alarm lamp. Red or yellow, depending on alarm level. Blinks until active alarm is
acknowledged.
10 Active INOP alarm lamp in light blue. Blinks until active INOP is acknowledged.
11 Alarms off indicator. When alarms are suspended, the lamp is red (or yellow when yellow alarms
are suspended), and the alarms off symbol is shown.
X2 Patient Connectors, Right Side
1 Pressure (option)
2 Temperature (option)
3 Noninvasive blood pressure
X2 Left Side
4 SpO
5 ECG sync pulse output
6 ECG/Respiration
7 CO
2
(option in place of
2
Pressure and Temperature)
1 Loudspeaker
2 MSL Connector. Connects to the external power
supply or a host monitor via the MSL cable for AC
mains operation, battery charging, and
communication with a network.
24
Page 25

MMS Extensions
The MMS extensions connect to the X1 and X2 MMS and use the MMS settings and power. Trend
data and measurement settings from the measurements in the extensions are stored in the MMS.
WARNING
• The MMS extensions can only function when they are connected to an MMS. If the MMS is
removed during monitoring, the measurements from both the MMS and the extension are lost.
• Measurements from an MMS extension connected to an X2 are not available when the X2 is
running on its own battery power. They are only available when the X2 is powered from AC mains,
when connected to a host monitor or the external power supply (M8023A), or from the Battery
Extension.
To separate an extension from the MMS, press the release lever down, and push the MMS forward.
1 Introduction
M3014A, M3015A, M3015B and M3016A Capnography MMS Extensions
The optional M3014A Capnography extension adds mainstream capnography or sidestream
capnography, and optionally one pressure plus either a pressure or a temperature, Cardiac Output and
Continuous Cardiac Output to the MMS.
M3014A
1 Pressure connectors (red)
2 Temperature connector (brown)
3 Mainstream/sidestream connector CO
4 Cardiac Output connector
2
25
Page 26

1Introduction
The optional M3015A Microstream CO2 extension adds microstream capnography and optionally
either pressure or temperature to the MMS. The optional M3015B Microstream CO
microstream capnography, two pressures and a temperature to the MMS.
M3015A M3015B
1 Pressure connectors (red) - M3015A optional
extension adds
2
MX600/700/
800
2 Temperature connector (brown) - M3015A optional
3 Inlet
4 Microstream connector CO
5 Gas sample outlet
2
The optional M3016A Mainstream CO2 extension adds mainstream capnography and optionally either
pressure or temperature to the MMS.
M3016A
1 Pressure connector (red)
2 Temperature connector (brown)
3 Mainstream/sidestream connector CO
2
(optional)
26
When a capnography extension is connected to an X2 MMS with CO
will be automatically deactivated in favor of the one in the X2. If you prefer to use the CO
, the CO2 from the extension
2
2
measurement on the extension, you can activate it via the measurement selection key (see “Resolving
Label Conflicts” on page 44).
Page 27
The cardiac output measurement in the M3014A is deactivated when the extension is used with an X2
MMS, even if the X2 is connected to an external power supply. The cardiac output measurement is
only available when the X2 is connected to a host monitor.
M3012A Hemodynamic MMS Extension
The M3012A Hemodynamic extension can be connected to the M3001A Multi-Measurement Module
to provide the following additional measurements: Temperature, Pressure, an additional Pressure or
Temperature, and C.O. and CCO measurements.
1 Introduction
1 Cardiac Output (orange; optional)
2 Connection to MMS
3 Pressure connectors (red)
4 Temperature connectors (brown)
The cardiac output measurement is deactivated when the extension is used with an X2 MMS unless the
X2 is connected to a host monitor.
Using MMSs in a Mixed Software Environment
When an MMS is used with monitors having different software revisions, be aware that functionality
set up in a monitor with a newer revision will disappear when the MMS is connected to a monitor with
an older revision without that functionality. For example, if an X2 is used with a revision H monitor
and has been set up to alarm on Afib, this alarm will no longer exist when the X2 is connected to a
revision G monitor. If you work in a mixed software environment, inform yourself about the
differences between revisions by referring to the What's New chapter.
Operating and Navigating
Everything you need to operate the monitor is contained on its screen. Almost every element on the
screen is interactive. Screen elements include measurement numerics, waveforms, screen keys,
information fields, alarms fields and menus. The typical operator's position is in front of the monitor.
The configurability of the monitor means that often you can access the same element in different ways.
For example, you might be able to access an item through its on-screen setup menu, via a hard key, or
via a SmartKey.
27
Page 28
1Introduction
MX400
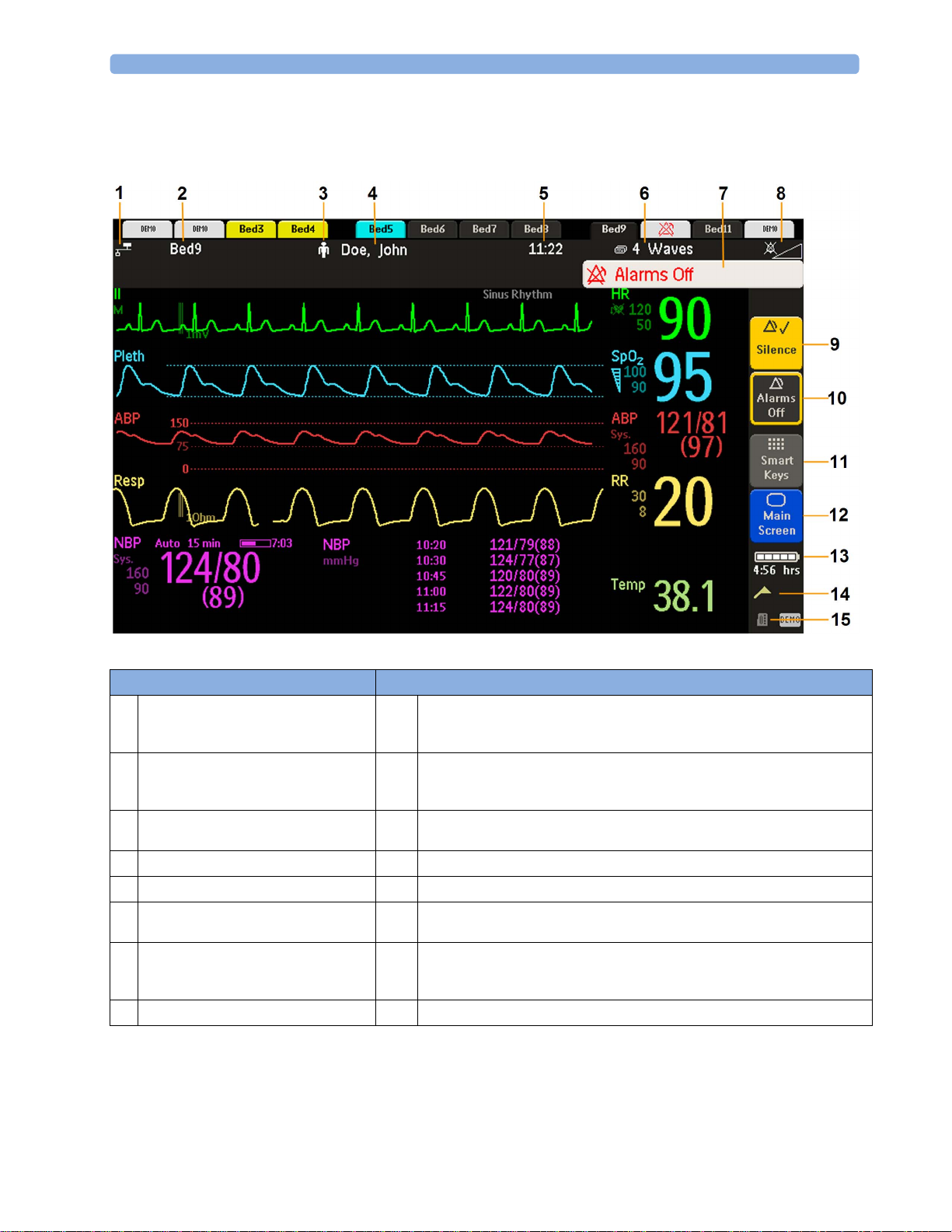
On the MX400, the permanent keys and the key to access the SmartKeys are on the right of the screen.
Monitor information line Other screen elements
network connection indicator
1
(documented in Troubleshooting in the
Service Guide)
bed label - gives access to Equipment
2
window
patient category symbol
3
patient name
4
date and time
5
current screen name/enter Change Screen
6
menu
alarm status area - shows active alarm
7
messages or Alarms Off symbol when
alarms are switched off
alarms off/alarm volume indicator
8
Silence - acknowledges all active alarms by switching off audible alarm indicators
9
and lamps permanently or temporarily, if alarm reminder (ReAlarm) is configured
on.
Pause Alarms or Alarms Off - stops alarms being announced for a set time or
10
switches them off. Select again to immediately switch alarms on again. Can be
configured not to appear here.
SmartKeys -displays a block of SmartKeys. These change according to your
11
monitor's configuration
close all open menus and windows and return to main screen
12
battery indicator with remaining battery time
13
status messages indicator - clicking this area displays any pending status messages
14
measurement selection symbol - opens Measurement Selection window to resolve
15
label conflicts
28
Page 29
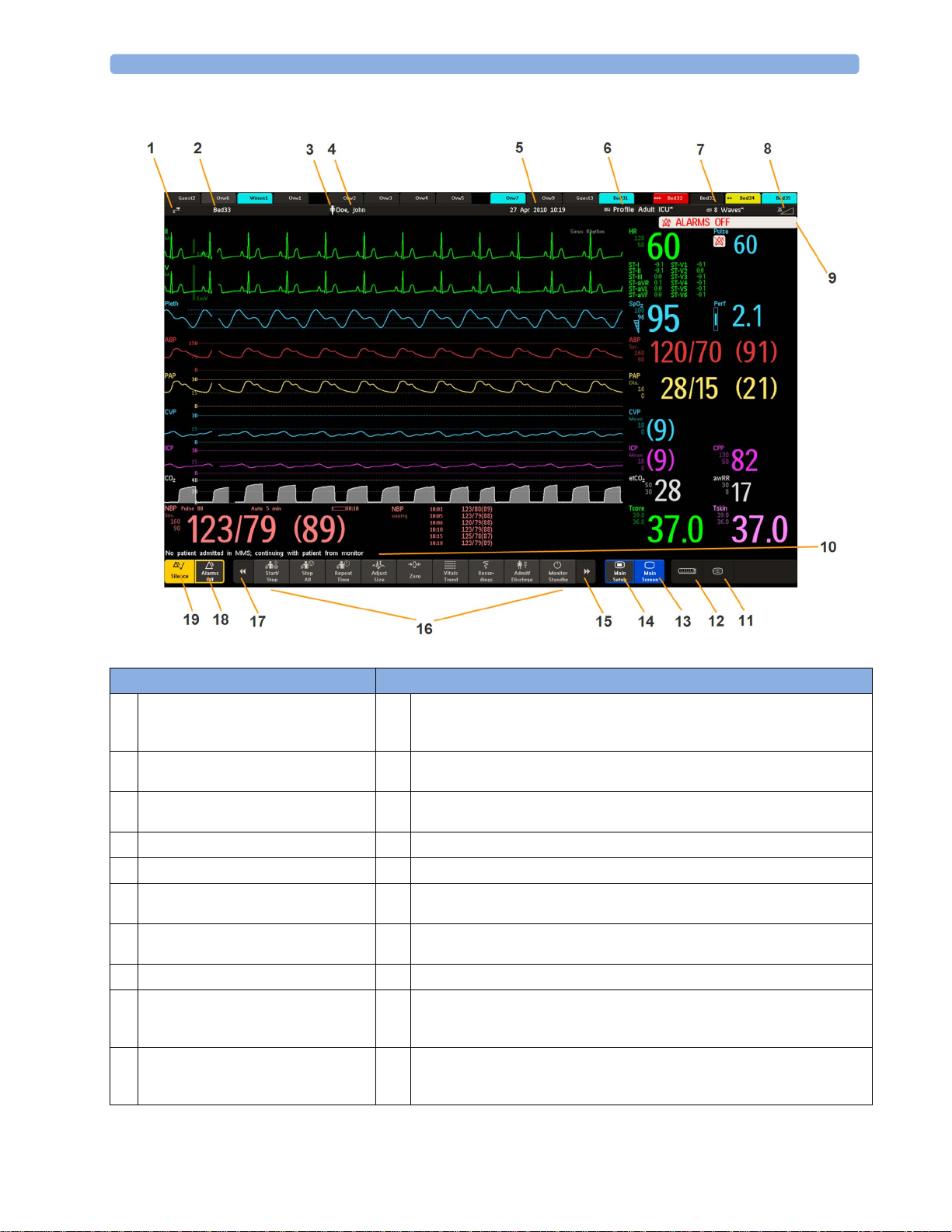
MX450/500/550/600/700/800
1 Introduction
Monitor information line Other screen elements
network connection indicator
1
(documented in Troubleshooting in the
Service Guide)
bed label - gives access to Equipment
2
window
patient category symbol
3
patient name
4
date and time
5
access the Profiles menu or Profile
6
name, depending on configuration
current screen name/enter Change
7
Screen menu
adjust alarm volume/level indicator
8
alarm status area - shows active alarm
9
messages or Alarms Off symbol when
alarms are switched off
The status line shows messages with information and prompts you for possible
10
actions (MX400/450/500/550 do not have a reserved space for this feature).
remote application symbol or iPC symbol (MX600/700/800 only)
11
measurement selection symbol - opens Measurement Selection window to
12
resolve label conflicts
close all open menus and windows and return to main screen
13
enter Main Setup menu
14
scroll right to display more SmartKeys
15
SmartKeys - these change according to your monitor's configuration
16
scroll left to display more SmartKeys
17
Pause Alarms or Alarms Off - stops alarms being announced for a set time or
18
switches them off. Select again to immediately switch alarms on again. Can be
configured not to appear here.
Silence - acknowledges all active alarms by switching off audible alarm indicators
19
and lamps permanently or temporarily, if alarm reminder (ReAlarm) is configured
on.
29
Page 30

1Introduction
Selecting Screen Elements
Select a screen element to tell the monitor to carry out the actions linked to the element. For example,
select the Patient Identification element to call up the
HR numeric to call up the
menu.
Note that the space between each line of a menu may be configured to wide or narrow to facilitate
your most common method of operation, either touch, remote control or a pointing device such as a
mouse.
Setup ECG menu. Select the ECG wave segment to call up the ECG Lead
Using the Touchscreen
Select screen elements by pressing them directly on the monitor's screen.
Disabling Touchscreen Operation
To temporarily disable touchscreen operation of the monitor, press and hold the Main Screen
permanent key. A padlock will appear on the
Patient Demographics window, or select the
Main Screen permanent key.
Press and hold the Main Screen permanent key again to re-enable the touchscreen operation.
Using a Mouse or Trackball
If you are using a mouse or trackball, select screen elements by clicking on them (press and release the
left mouse button). While you are moving the mouse, a cursor appears and a highlight shows your
current position.
Moving Windows
You can move windows and menus using the Touchscreen or a mouse. To move a window,
1 Select the title of the window and keep your finger on the title, or the mouse button pressed.
2 Move your finger on the Touchscreen, or move the mouse, to move the window.
3 Take your finger off the screen, or release the mouse button, to place the window in the final
position.
The new position is only active until the window or menu is closed. Not all locations on the screen can
be a target position, a window cannot overlap the monitor info line, the alarms and INOPs or the
status line.
Using Keys
The monitor has four different types of keys:
Permanent Keys
A permanent key is a graphical key that remains on the screen all the time to give you fast access to
functions.
30
Page 31

SmartKeys
1 Introduction
Pause Alarms - pauses alarm indicators. Pause duration depends on monitor
configuration. If pause duration is infinite, this key is labeled
Alarms Off.
Select again to immediately re-enable alarm indicators.
Silence - acknowledges all active alarms by switching off audible alarm indicators and
lamps.
Main Screen - close all open menus and windows and return to the main screen.
Main Setup - enter main setup menu.
A SmartKey is a configurable graphical key, normally located at the bottom of the main screen. On
some models, a selection of SmartKeys is displayed by selecting the SmartKeys permanent key on the
right of the main screen.
SmartKeys give you fast access to functions. The selection of SmartKeys available on your monitor
depends on your monitor configuration and on the options purchased. If you have an integrated PC
(iPC) you may also see SmartKeys generated by applications on the iPC.
enter profile menu, or revert to
default profile
change Screen, or revert to default
screen
show BIS Sensor previous Screen
freeze waves quick admit a patient
set alarm limits enter patient demographics menu to
admit/discharge/transfer
change alarm volume end case to discharge a patient
change QRS volume view information for patients in
other beds
enter standby mode - suspends
patient monitoring. All waves and
change screen brightness (not for
independent displays)
numerics disappear from the display.
All settings and patient data
information are retained.
review beat labels (annotate
arrhythmia wave)
change amplitude (size) of ECG
wave
re-learn arrhythmia
enter cardiac output procedure
31
Page 32

1Introduction
- start/stop manual NBP
start NBP STAT measurement
measurement
- start auto series
- stop current automatic
measurement within series
stop automatic or STAT NBP
measurement and measurement
series
start NBP measurement and
stop current NBP measurement
measurement series
start veni puncture (inflate cuff to
set the NBP repeat time
subdiastolic pressure)
access NBP mode selection and
zero invasive pressure transducer
setup, with direct start/stop function
start a delayed recording access pop-up recording keys
access Vital Signs recording function access Select Waves recording
function
set wide automatic alarm limits set narrow automatic alarm limits
access wedge procedure window access the Loops window
review vital signs trend review graph trend
access event surveillance access calculations
access the calculator access the Drug Calculator
gas analyzer - exit standby mode suppress zero for all gas
measurements
unpair equipment and continue
central monitoring with the monitor
unpair equipment and continue
central monitoring with the telemetry
device
access the spirometry data window access ST Map application
start 12-Lead Capture (only available
if Information Center is connected)
access remote applications (if
Application Server is connected)
32
Page 33

1 Introduction
access EEG CSA access the EEG montage
display external device information access timers
access ProtocolWatch set standard or EASI lead placement
Hardkeys
switch CO
pump off new lead setup
2
enter data manually start/stop car seat assessment record
open the
Histogram window open Unit Conversion window
start an NMT measurement cycle stop an NMT measurement cycle
start NMT calibration access patient reports
open the
Equipment window
A hardkey is a physical key on a monitoring device, such as the zero pressure key on the MMS or a
setup key on a module.
Pop-Up Keys
Pop-up keys are task-related graphical keys that appear automatically on the monitor screen when
required. For example, the
Confirm pop-up key appears only when you need to confirm a change.
33
Page 34

1Introduction
Using the Remote Control
The remote control provides you with direct access to five hard keys, a navigation knob and a numeric
keypad:
Hardkeys
1 Silence - acknowledges all active alarms by switching off audible alarm indicators and lamps.
Behavior follows the Silence permanent key configuration.
2 Alarms Off/Pause Alarms - pauses alarm indicators. Behavior follows the Pause Alarms
permanent key configuration.
3 Main Screen - close all open menus and windows and return to the main screen.
4 SmartKeys - display a block of SmartKeys specially configured for remote tasks (see below)
5 Back - go back one step to the previous menu.
6 Enter - mark the end of data entry
Keypad
7 Type numeric data on the keypad and press the Enter key to enter the data on the monitor.
Navigation knob
8 Rotate the knob to highlight screen elements, then press to select the highlighted element.
The remote control can be used with a USB cable connection to the monitor or without a cable using
short range radio. When used without a cable, the remote control must be assigned to the monitor.
The assignment is made in Configuration or Service mode.
34
Page 35

CAUTION
When using a remote control without a cable, it is important that the user knows which remote control
is assigned to which monitor. Use the tethering cable delivered with the remote control to attach it to a
bed rail or IV pole, or label the remote control with the bed or monitor ID.
Using the SmartKeys Key
The SmartKeys hard key on the remote control displays a block of SmartKeys on the monitor screen.
Nine SmartKeys appear in a 3 by 3 matrix which corresponds to the layout of the numeric pad on the
remote control.
1 Introduction
Pressing the 1 key on the remote control selects the top left SmartKey, pressing the 8 key selects the
bottom center SmartKey. The . and the key can be used to select the arrow keys to page up and
down in the available SmartKeys.
The SmartKeys which appear can be configured so that you have the functions available which you
most often need when using the remote control. If no list of SmartKeys has been configured, the
standard SmartKeys will be displayed and you can page through to the key you want.
Using the On-Screen Keyboard
Use this as you would a conventional keyboard. Enter the information by selecting one character after
another. Use the
single characters, or use the
entered and close the on-screen keyboard.
If a conventional keyboard is connected to the monitor, you can use this instead of or in combination
with the on-screen keyboard.
Shift and capital Lock keys to access uppercase letters. Use the Back key to delete
Clr key to delete entire entries. Select Enter to confirm what you have
Using the On-Screen Calculator
You can use the on-screen calculator to perform any of the standard operations for which you would
normally use a handheld calculator.
• To access the on-screen calculator, select the
Calculations followed by Calculator.
Calculator SmartKey, or select Main Setup then
35
Page 36

1Introduction
Operating Modes
When you switch the monitor on, it starts up in monitoring mode. To change to a different mode:
1 Select the Main Setup menu.
2 Select Operating Modes and choose the mode you require.
Your monitor has four operating modes. Some are passcode protected.
• Monitoring Mode: This is the normal, every day working mode that you use for monitoring
patients. You can change elements such as alarm limits, patient category and so forth. When you
discharge the patient, these elements return to their default values. Changes can be stored
permanently only in Configuration Mode. You may see items, such as some menu options or the
altitude setting, that are visible but ‘grayed out’ so that you can neither select nor change them.
These are for your information and can be changed only in Configuration Mode.
• Demonstration Mode: Passcode protected, this is for demonstration purposes only. You must
not change into Demonstration Mode during monitoring. In Demonstration Mode, all stored
trend information is deleted from the monitor’s memory.
• Configuration Mode: Passcode protected, this mode is for personnel trained in configuration
tasks. These tasks are described in the Configuration Guide. During installation the monitor is
configured for use in your environment. This configuration defines the default settings you work
with when you switch on, the number of waves you see and so forth.
• Service Mode: Passcode protected, this is for trained service personnel.
When the monitor is in Demonstration Mode, Configuration Mode, or Service Mode, this is indicated
by a box with the mode name in the center of the Screen and a symbol in the bottom right-hand
corner. Select the mode box in the center of the screen to change to a different mode.
When an X2 is connected to a host monitor (
• The monitor in companion mode will adopt the operating mode of the host monitor.
• You cannot change the operating mode at the monitor in companion mode.
Standby Mode
Standby mode can be used when you want to temporarily interrupt monitoring.
To enter Standby mode,
• select the
•select
The monitor enters Standby mode automatically after the End Case function is used to discharge a
patient.
Standby suspends patient monitoring. All waves and numerics disappear from the display but all
settings and patient data information are retained. A special Standby screen is displayed. This can be
configured to a moving image or a blank screen, or to your own custom image. If a temporary patient
location has been entered at the monitor or at the Information Center, this location will also be
displayed on the Standby screen.
Companion Mode is indicated):
Monitor Standby SmartKey or
Main Setup, followed by Monitor Standby.
36
To resume monitoring,
• Select anything on the screen or press any key.
When monitoring is resumed, alarms are paused for 1 minute to allow time to finish plugging in the
measurement cables.
Page 37

If you connect an X2 that is powered on (and not in Standby) to a host monitor in Standby mode, the
host will leave Standby mode. When connected to a host monitor, with both the host and the monitor
in companion mode in Standby mode, leaving Standby on the monitor in companion mode will also
make the host leave Standby.
Understanding Screens
Your monitor comes with a set of pre-configured Screens, optimized for common monitoring
scenarios such as "OR adult", or "ICU neonatal". A Screen defines the overall selection, size and
position of waves, numerics and other elements on the monitor screen when you switch on. You can
easily switch between different Screens during monitoring. Screens do NOT affect alarm settings,
patient category and so forth.
When you switch from a complex to a less complex Screen layout, some measurements may not be
visible but are still monitored in the background. If you switch to a more complex Screen with, for
example, four invasive pressure waves but you have only two pressures connected to the monitor, the
"missing" two pressures are either left blank or the available space is filled by another measurement.
Switching to a Different Screen
1 To switch to a different Screen, select the current Screen name in the monitor info line, or select
Change Screen SmartKey.
the
1 Introduction
2 Choose the new Screen from the pop-up list.
Changing a Screen's Content
If you do not want to change the entire Screen content, but only some parts of it, you can substitute
individual waves, numerics, high-res waves, or trends. Be aware that these changes cannot be stored
permanently in Monitoring Mode.
To change the selection of elements on a Screen,
1 Select the element you want to change.
2 From the menu that appears, select Change Wave, Change Numeric, or ChangeHiResTrend, and
then select the wave or numeric you want, or select the high-resolution trend wave you want from
the list of available waves.
If you do not see
the numeric beside its wave. Changing the wave will automatically change the numeric.
The changed Screen is shown with an asterisk in the monitor info line.
Change Screen menu, the changed Screen is shown linked to the original Screen and marked
In the
with an asterisk.
Up to three modified Screens can be accessed via the
To recall Screens, either
• select the name of the Screen in the
Change Numeric in the menu, this Screen may be configured to always display
Change Screen menu.
Change Screen menu
or
• use the previous arrow at the top of the
The ten most recently-used Screens including up to three modified Screens can be accessed.
Change Screen menu to move back in the Screen history.
37
Page 38

1Introduction
After a patient discharge, the monitor's default Screen is shown. Modified Screens are still available in
Change Screen menu.
the
If the monitor is switched off and then on again, modified Screens are erased from the monitor's
memory and cannot be recalled. If a modified Screen was the last active Screen when the monitor was
switched off, it is retained (unless
Automat. Default is configured to Yes).
Connecting Additional Displays to the Monitor
You can connect a second display, showing the same Screen as the main display, to your monitor, for
viewing only.
Independent Displays
MX600/700/
800
If you have the optional independent display interface, you can connect a second display which can be
configured and operated individually using standard input devices.
For monitors with multiple displays and multiple input devices, the usage and behavior can be
configured according to specific requirements at installation (for example, use for two independent
operators or tracking of mouse input across two displays). For details refer to the Service Guide.
When two operators are using two displays, the scope of an action depends on the type of operation:
• Patient monitoring operations such as Silence or Pause alarms take effect for the monitor as a
whole, the results will be seen on both displays.
• Display operations such as the
display being operated.
If you are operating two displays with one remote control, to navigate from one display to another:
1 Move the highlight to the Main Screen key and then turn one click further.
The highlighting moves to a special "jump" field at the edge of the Screen.
2 Press the navigation knob on the remote control to confirm; the highlighting will automatically
move to the other display.
The content of each Screen can be changed individually as described in the previous section. If you are
operating two displays, you can choose Screens for both displays from one location:
1 Select Profiles in the monitor info line of the first display,
2 Select Display 1, or Display 2, then select the Screen you want to appear on that display from the
list of available Screens.
Main Screen key and Back hardkey will take effect only on the
38
When two displays are mounted next to each other or one above the other, a special Screen can be
assigned which spans across both displays. The Screen content for these Tall and Wide Screens can
then use the increased area available with two displays. These Screens appear in the Screen list with a
special Tall Screen or Wide Screen symbol.
Certain windows (for example: cardiac output procedure) can only be shown on one display at a time.
If you try to open one of these windows when it is already shown on another display, you will see a
blank gray window with a cross through it.
Page 39

Using the XDS Remote Display
1 Introduction
MX600/700/
Using the IntelliVue XDS solution it is possible to view an independent monitor screen on an external
display. The XDS solution consists of a medical grade PC-based hardware platform, XDS application
800
software and the XDS connectivity option on the monitor. Depending on the configuration you can
also operate the monitor from the external display. The XDS must be connected to the same Local
Area Network (LAN) as the monitor.
It is also possible to use an existing PC, connected to the same LAN, to host the XDS Application
software.
For more details, including limitations and restrictions, refer to the IntelliVue XDS Application
Instructions for Use.
Using the Visitor Screen
If a visitor Screen is configured for your monitor, you can use it to clear the screen of all waves and
numerics but continue to monitor the patient with active alarms and trend storage at the bedside and
Information Center. You can change the name of the visitor Screen in Configuration Mode.
• To activate this Screen, select the Screen name in the monitor info line to open the
menu, then select the name of the visitor Screen configured for your monitor from the list of
available Screens.
To select a Screen with waves and numerics again,
• Select the visitor Screen's name below the clock to open the
different Screen to show waves and numerics again.
Change Screen
Change Screen menu and select a
Understanding Profiles
Profiles are predefined monitor configurations. They let you change the configuration of the whole
monitor so you can adapt it to different monitoring situations. The changes that occur when you
change a complete profile are more far reaching than those made when you change a Screen. Screens
affect only what is shown on the display. Profiles affect all monitor and measurement settings.
The settings that are defined by Profiles are grouped into three categories. Each category offers a
choice of 'settings blocks' customized for specific monitoring situations. These categories are:
• Display (screens)
Each profile can have a choice of many different predefined screens.
If you are using a second display, each display can have its own individual screen selection. When
you change the profile, the screen selection configured for the new profile becomes active.
• Measurement Settings
Each profile can have a choice of different predefined measurement settings. These relate directly
to individual measurements, for example, measurement on/off, measurement color, alarms limits,
NBP alarm source, NBP repeat time, temperature unit (°F or °C), pressure unit (mmHg or kPa).
• Monitor Settings
Each profile can have a choice of different predefined monitor settings. These relate to the
monitor as a whole; for example, display brightness, alarms off/paused, alarm volume, QRS tone
volume, tone modulation, prompt tone volume, wave speed, resp wave speed, pulse source.
39
Page 40

1Introduction
You can change from one complete profile to another or swap individual settings blocks (display/
monitor settings/measurement settings) to change a subset of a profile. Changes you make to any
element within the settings blocks are not saved when you discharge the patient, unless you save them
in Configuration Mode.
Depending on your monitor configuration, when you switch on or discharge a patient the monitor
either continues with the previous profile, or resets to the default profile configured for that monitor.
WARNING
• If you switch to a different profile, the patient category and paced status normally change to the
• If your monitor is configured to show the profile name in the info line at the top of the screen, be
When you leave Demonstration Mode, the monitor uses the default profile.
setting specified in the new profile. However some profiles may be set up to leave the patient
category and paced status unchanged. Always check the patient category, paced status, and all
alarms and settings, when you change profiles.
aware that individual settings may have been changed by other users or by settings synchronization
since the profile was loaded. Hence settings may be different than implied by the profile name.
Swapping a Complete Profile
1 Select Profiles in the monitor info line, or select the Profiles SmartKey.
2 Select the Profile Details pop-up key.
3 In the Profiles menu, select Profile.
4 Choose a profile from the pop-up list.
5 Confirm your selection.
Swapping a Settings Block
1 Select the Profile in the monitor info line.
2 Select the Profile Details pop-up key.
3 In the Profile Details menu, select Display or Measmnt.Settings or Monitor Settings to call up a
list of the settings blocks in each category.
4 Choose a settings block from the pop-up list.
5 Confirm your selection.
Default Profile
Your monitor has a default profile that it uses when you leave Demonstration mode, or when you
discharge a patient. This profile is indicated by a diamond shaped symbol.
Locked Profiles
Some profiles are locked, so that you cannot change them, even in Configuration Mode.
These are indicated by this lock symbol.
40
Page 41

Understanding Settings
Each aspect of how the monitor works and looks is defined by a setting. There are a number of
different categories of settings, including,
Screen Settings, to define the selection and appearance of elements on each individual Screen
Measurement settings, to define settings unique to each measurement, for example, high and low
alarm limits
Monitor settings, including settings that affect more than one measurement or Screen and define
general aspects of how the monitor works, for example, alarm volume, reports and recordings, and
display brightness.
You must be aware that, although many settings can be changed in Monitoring Mode, permanent
changes to settings can only be done in the monitor's Configuration Mode. All settings are reset to the
stored defaults:
• when you discharge a patient
• when you load a Profile
1 Introduction
• when the monitor is switched off for more than one minute (if
Changing Measurement Settings
Each measurement has a setup menu in which you can adjust all of its settings. You can enter a setup
menu:
• via the measurement numeric - select the measurement numeric to enter its setup menu. For
example, to enter the
• via the Setup hardkey (on plug-in modules) - press the Setup hardkey on the module front.
•via the
• via the Measurement Selection key.
This guide always describes the entry method using the setup menu. But you can use any method you
prefer.
Main Setup permanent key - if you want to setup a measurement when the measurement is
switched off, use the
measurement name from the pop-up list. With this permanent key you can access any setup menu
in the monitor.
Setup ECG menu, select the HR (heart rate) numeric.
Main Setup permanent key and select Measurements. Then select the
Switching a Measurement On and Off
When a measurement is off, its waves and numerics are removed from the monitor's screen. The
monitor stops data acquisition and alarming for this measurement. A measurement automatically
switches off if you disconnect its module or MMS. If you disconnect a transducer, the monitor
replaces the measurement numeric with question marks. If you silence the resulting INOP, the
measurement is switched off. Also if you pause or switch off alarms, the measurement may be
switched off completely, depending on your configuration.
Automat. Default is set to Yes).
1 Enter the measurement's setup menu and select the measurement.
2 Select the measurement name to switch between on and off. The screen display indicates the active
setting.
41
Page 42

1Introduction
Switching Numerics On and Off
For some measurements, such as EEG, you can choose which numerics to view on the screen.
In the measurement's setup menu, select the numeric name to toggle between on and off.
For example in the
Setup EEG menu, select the EEG numeric name to toggle between on and off.
Adjusting a Measurement Wave
To quickly adjust wave-related measurement settings (such as speed or size), select the measurement
wave itself. This displays the measurement wave menu, which has only wave-related measurement
settings.
Changing Wave Speeds
Lowering the wave speed compresses the wave and lets you view a longer time period. Increasing the
speed expands the waveform, giving you a more detailed view.
The monitor distinguishes three groups of wave speed settings:
RespiratorySpeed, for all respiratory waves: CO
•
• EEG Speed, for all EEG and BIS waves
Global Speed, for all waves not included in the other two groups.
•
Changing the Wave Group Speed
The wave speed group setting defines the speed of all the waves in the group.
To change the wave speed of a wave speed group,
, anesthetic agents and O
2
2
1 Select Main Setup, then select User Interface
2 Select Global Speed, RespiratorySpeed, or EEG Speed as required
3 Select a value from the list of available speeds.
Changing Wave Speed for a Channel
To change the wave speed of an individual wave channel,
1 Enter the Wave menu for a measurement by selecting its wave.
2 Select Change Speed.
3 To set the speed to the wave group speed, select RespiratorySpeed, EEG Speed, or Global Speed.
To set an individual channel speed, select a numeric value from the list of available speeds. This
overrides the wave group speed setting and set the speed for the individual wave channel on the
monitor Screen. The wave channel speed is independent of the wave (label) depicted in the
channel, if you change the wave, the new wave will retain the set channel speed.
Freezing Waves
You can freeze waves on the screen and measure parts of the wave using cursors. The waves are frozen
with a history of 20 seconds so that you can go back and measure what you have seen.
42
Page 43

Freezing An Individual Wave
To freeze a wave,
1 Enter the Wave menu for the measurement by selecting the wave on the screen.
2 Select Freeze Wave.
The realtime wave is replaced with the frozen wave.
Freezing All Waves
To freeze all waves on the screen,
1 Select the Freeze Waves SmartKey.
All realtime waves are replaced with frozen waves.
Measuring Frozen Waves
To measure a frozen wave,
1 Select the frozen wave.
If you are using touch, this automatically positions the vertical cursor. The cursor can be
repositioned by touching the required point on the wave, or
1 Introduction
2 Using the SpeedPoint or another pointing device or touch: use the right/left arrow keys to move
the vertical cursor.
The vertical cursor moves through the time axis and the current value is displayed next to the
cursor.
3 Use the up/down arrow keys to activate and move the horizontal cursor.
The horizontal cursor measures the wave value, which is displayed above the cursor line. If the
wave is a pressure wave, the cursor value can be stored as a systolic, diastolic or mean pressure
value; if the pressure wave is a PAP wave it can also be stored as a PAWP value; for pressure waves
P, P1 to P8 it can also be stored as an IAP value. The stored value appears in the trend database as
a manually entered value.
Changing The Wave Speed
Lowering the wave speed compresses the wave and lets you view a longer time period. Increasing the
speed expands the waveform, giving you a more detailed view.
To change the wave speed:
1 Select the frozen wave.
2 Select Change Speed.
3 Select a speed from the list.
Updating The Frozen Wave
To update the wave, that is freeze the current wave:
1 Select the frozen wave.
2 Select Freeze Again.
43
Page 44

1Introduction
Releasing Frozen Waves
To release frozen waves,
1 Select a frozen wave.
2 Select Unfreeze Waves.
All frozen waves are released.
Using Labels
Every measurement associated with a monitor is identified by a unique label. You may have more than
one instance of some measurements, for example pressure, being used simultaneously. The monitor
uses the labels to distinguish between them. The default settings defined in the profile (such as
measurement color, wave scale, and alarm settings) are stored within each label. When you assign a
label to a measurement, the monitor automatically applies these default settings to the measurement.
The labels assigned are used throughout the monitor, in reports, recordings, and in trends.
Changing Measurement Labels (e.g. Pressure)
To change a measurement label of a measurement with multiple labels (e.g. invasive pressure or
temperature),
1 Enter the wave menu of the measurement.
2 Select Label.
3 Choose a label from the list.
The monitor automatically applies the scale, color, etc. settings stored in the Profile for the label you
select. You can change scale settings in Monitoring Mode, but color can only be changed in the
monitor's Configuration Mode.
Any labels already being used in the monitor are shown "grayed-out" in the list and cannot be selected.
About Label Sets
Your monitor may be configured to use a Restricted or Full label set. The Full label set provides extra
labels for Pressure and Temp. See the sections on Pressure and Temperature in these Instructions for
Use for more information.
If you connect an MMS from a monitor using a
Restricted label set or an M3/M4 monitor, any additional labels switch to labels available in the target
monitor. This may cause a label conflict with other monitored measurements.
Be aware that connecting a monitor using the
software revisions may affect the availability of measurement information from the additional labels on
the Information Center. See the Information Center documentation and your monitor's Configuration
Guide for information on label set compatibility.
Full label set to an IntelliVue monitor using a
Full label set to an Information Center with certain
Resolving Label Conflicts
Each label must be unique, that is, it can only be assigned once. You cannot monitor two pressures
labeled "ICP" at the same time. If you need to use two identical pressures, you must assign different
labels to them, for example, P and ICP.
Measurement labels are stored in the measurement device (module or MMS). If you try to use two
measurement devices that have identical labels, this causes a label conflict in the monitor.
44
Page 45

1 Introduction
Measurement selection key with question marks indicating a label conflict.
Depending on your configuration, the monitor will either
• resolve the conflict automatically, by assigning a new, generic label to the most recently connected
conflicting label (e.g. a second FAP label could be changed to ABP)
•display the
• take no action, you must enter the
Measurement Selection window automatically for you to resolve the conflict
Measurement Selection window and resolve the conflict.
All the currently available measurement devices, for example MMSs, MMS extensions, measurement
modules, Gas analyzers, devices connected to a host monitor and manually entered measurements
(marked ), are depicted in the
Measurement Selection window.
De-activated devices are grayed-out (here
the Temp measurement on the left)
Any measurement labels causing a label conflict are shown in red. If a measurement device is
connected but currently unavailable, for example, because it was deactivated due to a label conflict, the
device is shown "grayed-out".
When an X2 is connected to a host monitor, the measurement selection window looks like this:
X2 connected to a host monitor
WARNING
When an X2 with an active measurement, say SpO2, is connected to a host monitor with the same
measurement already active, the SpO
Deactivated INOP is displayed. The measurement can only be reactivated if the X2 is disconnected
measurement on the X2 is deactivated and the Meas.
2
from the host monitor. The label conflict can be resolved on the host monitor like any other label
conflict.
45
Page 46

1Introduction
To resolve a label conflict:
1 Select the measurement selection key or select Main Setup, then Meas. Selection to display the
Measurement Selection window.
2 Select the device whose label you want to correct.
3 Use the measurement selection pop-up keys to resolve the conflict. Select either:
Change Label: to assign a different label to the conflicting label.
–
–
Activate: to activate the highlighted measurement and deactivate the blinking measurement.
This requires confirmation.
–
De- Activate: to disable the conflicting device. It retains its label for future use but becomes
invisible to the monitor, as though it had been unplugged. When the device has been
deactivated the question marks under the measurement selection key will be replaced by XXX.
Setup <Measurement Label>: to enter the Setup menu for the measurement and change the
–
conflicting device's label to a different label.
Modify Driver (VueLink/IntelliBridge only): - to modify the device driver setup to disable the
–
conflicting device's label.
Label Compatibility
When a new measurement is introduced, or new labels for an existing measurement, these labels will
not be shown on older Information Centers, and consequently not on the Overview screen sourced
from the Information Center.
When a patient is transferred from a monitor with these new labels to one with an older software
revision, the labels will be replaced with a generic label for that measurement. The settings for that
generic label will then be used.
If it is critical that the measurement labels are available at the Information Center and after transfers,
the older monitors and the Information Center must be upgraded to the appropriate software revision.
Entering Measurements Manually
You can enter values into the monitor that have been measured with other equipment or manually (for
example, manual temperatures, lab values). These values are then stored in the database, included in
trends and reports, and passed on to the Information Center and central charting systems. There is no
alarm functionality for manually entered measurements.
To enter values,
1 Select the Enter Values SmartKey or select Main Setup then select Enter MeasValues.
2 Select the measurement you want to enter values for. The Edit window will open.
3 If the measurement is switched off, switch it on by selecting the label.
4 Select Value and enter the value.
5 Select Date/Time to enter the date and time for the value. The default is always the current date
and time.
6 For compound labels, for example ABPs, ABPd and ABPm, select the Format field to select
whether all values are required or a single value.
46
7 Select Save.
When a manually entered value has been configured to display as a numeric on the screen, you can also
enter a new value for this measurement by selecting the numeric, then selecting
Enter MeasValues.
Page 47

1 Introduction
Manually entered measurement values are marked with a * on the display, in trends, and so forth. Each
measurement has a defined measurement interval after which a value becomes invalid (no value is then
displayed). Values can be entered up to two hours after they have been measured or up to the
measurement interval, if this is shorter.
The list of measurement labels which appears in the
Configuration Mode.
Enter Measurement Values window is set in
Switching Manually Entered Measurements On and Off
To switch a manually entered measurement on or off,
1 Select the Enter Values SmartKey or select Main Setup then select Enter MeasValues.
2 Select the measurement you want to switch on or off.
3 Select the measurement label field to switch between On and Off.
Changing Monitor Settings
To change monitor settings such as brightness, or QRS tone volume, select the Main Setup permanent
key and then select
Adjusting the Screen Brightness
To adjust the brightness:
1 Select the Brightness SmartKey.
User Interface to enter a submenu where you can change these settings.
2 Select the appropriate setting for the screen brightness. 10 is the brightest, 1 is the least bright.
Optimum is suitable for most monitoring locations and optimizes power usage for battery
powered monitors.
The MX400/450/500/550 monitors can be configured to automatically adapt the screen brightness to
the ambient light conditions. The range within which this adaptation is made is determined by the
setting made with the
Your monitor may be configured with a lower brightness for Standby mode and also (for battery
powered monitors) for transport to conserve battery power. These settings can only be changed in the
monitor's Configuration Mode.
If you are using a monitor with an external display, the
brightness of this display. Refer to the documentation supplied with the external display for
instructions.
Brightness SmartKey.
Setting the Date and Time
1 Select the Date, Time screen element from the monitor's info line to enter the Date, Time menu.
2 Select, in turn, the Year, Month, Day, Hour (in 24 hour format, only) and Minute as necessary.
Select the correct values from the pop-up list.
3 Select Store Date, Time to change the date and time.
If your monitor is connected to an Information Center, the date and time are automatically taken from
this. Once it is set, the internal clock retains the setting even when you switch off the monitor.
Brightness SmartKey does not adjust the
47
Page 48

1Introduction
WARNING
Changing the date or time will affect the storage of trends and events.
Checking Your Monitor Revision
1 Select Main Setup then select Revisions to open the Monitor Revision menu.
2 Select the correct device from the device pop-up keys.
3 From the Monitor Revision menu, select the monitor component for which you need revision
information.
Getting Started
Once you understand the basic operation principles, you can get ready for monitoring. We also
recommend working through the E-Learning Education Programs for self-training before using the
monitor (available at the Philips Learning Center, english only).
Inspecting the Monitor
WARNING
If the monitor or mounting hardware is mechanically damaged, or if it is not working properly, do not
use it for any monitoring procedure on a patient. Contact your service personnel.
1 Before you start to make measurements, carry out the following checks on the monitor including
all connected MMSs, modules, or MMS extensions.
– Check for any mechanical damage.
– Check all the external cables, plug-ins and accessories.
2 Plug the power cord into the AC power source.
3 Check all the functions of the instrument that you need to monitor the patient, and ensure that the
instrument is in good working order.
Setting up the Modules
1 Decide which measurements you want to make.
2 Connect the required modules, MMSs, or MMS extensions.
3 Check that you have the correct patient cables and transducers plugged in. The connectors are
color-coded to the patient cables and transducers for easy identification.
Switching On
Press the power on/standby switch on the monitor for one second. The monitor performs a self test
during which all lamps will light up and a tone will be sounded, and is then ready to use. If you see a
message such as
measurement.
48
CO₂ Sens Warmup wait until it disappears before starting to monitor that
Page 49

Connected devices usually take their power from the monitor. External devices such as gas monitors
and those connected via VueLink/IntelliBridge have their own power switches.
Power On/Power Off Behavior
The general rules determining the behavior of the monitor when connected to, or disconnected from
power are as follows:
• A monitor that was switched on prior to a temporary power loss switches on again when power is
restored.
• A monitor that was switched off prior to a temporary power loss remains off when power is
restored.
• When AC mains power is lost, a battery powered monitor continues to run without interruption
on battery power.
• An MMS switches on automatically when connected to a running host monitor.
• When an X2 is disconnected from a running host monitor, the X2 continues to run without
interruption on battery power.
Starting Monitoring
1 Introduction
After you switch on the monitor,
1 Admit your patient to the monitor.
2 Check that the profile, alarm limits, alarm and QRS volumes, patient category and paced status and
so forth are appropriate for your patient. Change them if necessary.
3 Refer to the appropriate measurement chapter for further details of how to perform the
measurements you require.
WARNING
During MR imaging, remove all transducers, sensors and cables from the patient. Induced currents
could cause burns.
Disconnecting from Power
The On/Standby switch does not disconnect the monitor from the ac power source. To disconnect,
unplug the power cable.
Monitoring After a Power Failure
• A monitor that was switched on prior to a temporary power loss switches on again when power is
restored.
• A monitor that was switched off prior to a temporary power loss remains off when power is
restored.
If the monitor is without power for less than one minute, monitoring will resume with all active
settings unchanged.
If the monitor is without power for more than one minute, the behavior depends on your
configuration.
49
Page 50

1Introduction
If Automat. Default is set to Yes, the default profile will be loaded when power is restored. If
Automat. Default is set to No, all active settings are retained, if power is restored within 48 hours. The
Automat. Default setting is made in Configuration Mode.
Networked Monitoring
You can connect your monitor to an Information Center on a network, using one of the optional
interfaces:
• Standard wired LAN
• Wireless LAN
• IntelliVue Instrument Telemetry System (IIT).
WARNING
Only connect patient monitors to networks that conform to the network installation instructions
provided by Philips for your system.
It is possible to assign additional monitoring equipment and a telemetry device to the same patient,
resulting in the information from multiple devices being combined in one sector at the Information
Center. (See “When Multiple Equipment is Used for One Patient” on page 122 and “Using a
Telemetry Device and a Monitor (PIIC only)” on page 307.)
If your monitor is connected to a network, a network symbol is displayed in the upper left corner next
to the bed label. To see details about the Care Group, the monitoring equipment, and technical
information about the network, select the bed label in the monitor info line.
Be aware that some network-based functions may be limited for monitors on wireless networks in
comparison to those on wired networks.
Printout functionality and data export are not guaranteed when using a standard hospital network.
Using the Integrated PC
MX600/
MX700/
MX800
If your monitor has the optional integrated PC (iPC), you can run applications on the iPC. The
applications display data on the monitor's display (or on a second independent display) that is
generated on and retrieved from the iPC or externally.
For details about applications, refer to the IntelliVue XDS Application Instructions for Use.
The monitor runs independently of the iPC, and vice versa.
WARNING
• Some clinical applications may show data from another patient. Be aware that some of the data on
your patient monitor display may not always be from your patient.
• Applications running on the iPC cannot act as a primary alarming device and cannot be relied
upon for alarm notification. There may be no audible or visible indications apart from what is
shown on the screen and any data shown may be delayed.
50
Page 51

CAUTION
When you install any software on the iPC you are responsible for ensuring that the resulting system
complies with all relevant local regulations.
Starting the iPC
Your monitor may be configured to have the iPC start up automatically when the monitor is switched
on. If not:
1 Select Main Setup then Internal PC.
2 In the Internal PC menu, select Switch PC on to start the iPC.
Viewing the iPC Desktop on the Monitor Display
If the Desktop is not displayed on the monitor display:
1 Select the iPC key , or
2 Select Main Setup, Internal PC, then Show PC Window.
1 Introduction
To hide the Desktop again, select
There are special iPC screens available that use the full height of the screen for the iPC Desktop. The
monitoring screen content is then arranged on the right side of the screen. Such iPC screens may be
loaded automatically when the iPC key is selected. In this case the
Previous Screen key, to give you a fast and easy method to switch back and forth between the iPC
screen and the regular screen.
Main Screen.
Adjusting the iPC Audio Volume
The Audio from the iPC is normally configured to be off. However, your monitor may have the iPC
audio configured on for use with specific PC applications.
WARNING
Always minimize the iPC audio volume or mute it completely when it is not needed for an iPC
application. This will avoid iPC tones distracting from or masking tones from the monitor.
Using Input Devices with the iPC and Monitor
You can connect input devices such as a mouse, trackball and keyboard to the rear of the patient
monitor (using the left hand row of USB connectors) and use them for input to the monitor.
Correspondingly you can connect input devices to the rear of the patient monitor (using the right
hand row of USB connectors) or to the front USB connector and use them for the iPC. Input devices
connected to the iPC can also be shared with the patient monitor. Sharing input devices and
touchscreen input requires a specific software application; refer to the IntelliVue XDS Application
Instructions for Use for details.
Main Screen key is replaced by a
If the iPC is switched off when input devices are shared, any input devices connected to it will not be
available for use with the monitor.
51
Page 52

1Introduction
Shutting the iPC Down
The iPC will be shut down automatically when the monitor is switched off.
If you want to shut down the iPC when the monitor is on,
1 Select Main Setup then Internal PC.
2 In the Internal PC menu, select Switch PC off.
If there is a problem with the shutdown, and you need to switch off the iPC manually,
1 Select Main Setup then Internal PC.
2 In the Internal PC menu, select Force PC off to force the iPC to power down.
Special Situations at Shutdown
• If you switch the monitor off and then on again immediately, the iPC will continue running and
will not be shut down.
• In some situations, shutting down the iPC can take a little time. The monitor will go into Standby
mode until the shutdown is complete. By touching the touchscreen, you can bring the monitor
back into operating mode. If you do this, the iPC will restart when the shutdown is complete.
• If the shutdown cannot be completed within a certain time, a window will open giving the reason:
for example, that a file has not been saved, or that updates are being installed. You can then decide
whether to wait (for example, in the case of the updates) or to take action (for example by saving
the unsaved file). You will also have the option to force shutdown, if necessary.
Using Your Monitor with a Monitor in Companion Mode
When you connect an X2 in companion mode to a host monitor, an integrated system is formed for
monitoring a single patient. The following general observations and considerations apply to such a
system:
• The host monitor is the "master" of the system, and you have full control over all the system's
operation only via the host monitor.
• Functions you can operate on a monitor in companion mode are restricted to measurements
originating in that device. If you try to operate controls that are disabled, you are prompted by the
message
• Depending on how it is configured, your host monitor can determine whether the user interface of
a connected monitor in companion mode is completely disabled or not, and what is displayed on
the screen (a standard main screen, or a blank screen indicating
This is controlled by two monitor settings that are applied to the monitor in companion mode on
connection. You can change the settings in Configuration Mode.
• Global settings such as line frequency, QRS sound and ECG lead colors from the host monitor,
are applied to the monitor in companion mode on connection. When disconnected from the host,
the monitor in companion mode re-applies its own global settings.
• No audible alarms are available on a monitor in companion mode when connected to a host
monitor. The only visual alarm indication is provided by the alarm lamps which are controlled by
the host monitor. Alarms become active again as soon as the monitor in companion mode is
disconnected from the host monitor.
Not available in Companion Mode.
Companion Mode).
52
Page 53

1 Introduction
• The host monitor is the master of all ADT information. ADT operations on the monitor in
companion mode are disabled, and any pending actions on the monitor in companion mode (for
example, admit or end case) are canceled.
• The date and time of the monitor in companion mode is synchronized with that of the host
monitor.
• An X2 switches on automatically when connected to a running host monitor.
• When an X2 is disconnected from a running host monitor, the X2 continues to run without
interruption on battery power.
• When an X2 is used with host monitors having different software revisions, be aware that
functionality set up in a monitor with a newer revision will disappear when the X2 is connected to
a monitor with an older revision without that functionality. For example, if an X2 is used with a
revision H monitor and has been set up to alarm on Afib, this alarm will no longer exist when the
X2 is connected to a revision G monitor. If you work in a mixed software environment, inform
yourself about the differences between revisions by referring to the What's New chapter.
• Event surveillance in the monitor in companion mode is disabled. Main Setup menu operations
and SmartKeys are disabled. While connected to a host monitor, no new events are detected in the
monitor in companion mode, and no events are deleted. There is no transfer of stored events from
the monitor in companion mode to the host monitor. After disconnection from the host monitor,
event surveillance is enabled again in the monitor in companion mode, and new events are
detected.
53
Page 54

1Introduction
54
Page 55

2
2What's New?
This section lists the most important new features and improvements to the monitor and its user
interface introduced with each release. Further information is provided in other sections of this book.
You may not have all of these features, depending on the monitor configuration purchased by your
hospital.
What's New in Release K.1 (for MX400/450/500/550 only)
MX500/MX550
In this release the MX500/MX550 patient monitors join the IntelliVue monitor family. The monitors
are optimized for transport within the hospital environment.
The MX500 has a 12-inch display and the MX550 has a 15-inch display. Both models have three
integrated plug-in module slots for up to three measurement modules, or the IntelliBridge interface
module (865115), or recorder module (M1116B/C). The MX500/550 have the option to be operated
with a single, user-replaceable battery.
EC10 IntelliBridge Interface Board
MX400/450/
500/550
The functionality of the IntelliBridge EC10 plug-in module - interfacing data from a connected
external device into the monitor - is now available in an embedded board. The connector for the
optional interface board is accessed at the rear of the monitor.
Wireless Remote Control
MX400/450/
500/550
The remote control, previously only available with a USB cable connection, can now also be used
wirelessly, with a short-range radio connection, as with the models MX600-800.
What's New in Release K.0
MX400/MX450
In this release the MX400/MX450 patient monitors join the IntelliVue monitor family. The monitors
are optimized for transport within the hospital environment. The MX400 has a 9-inch display and the
MX450 has a 12-inch display. Both monitors can optionally be equipped with an integrated recorder
and have the option to be operated with a single user-replaceable battery.
55
Page 56

2What's New?
What's New in Release J.0
Flexible, Patient-oriented Workflow (with PIIC iX only)
With the IntelliVue Information Center iX, more flexible, patient-oriented workflows are supported
for admitting, tracking and transferring patients. This allows you to adapt monitor use to the patient
data flow models in your specific facility and department.
Managing Patients
When the patient monitor is connected to an IntelliVue Information Center iX, an extended
comparison of patient data allows more intelligent admission and transfer procedures. A
key can be used to search through the patient lists at the Information Center and other connected
systems and take over the corresponding data found.
Flexible Transfer
A transfer can be initiated in the unit at the monitor, on patient arrival or patient departure, or centrally
at the Information Center.
Managing Equipment
When used together with an Information Center iX, extended equipment management functionality is
now available. Depending on how equipment is used in your facility, there are various ways to
associate devices with patients, beds or monitors.
Find Patient
Additionally there are mechanisms to automatically free up equipment that is no longer used. Using the
Equipment window you have an overview of all equipment being used for a patient, together with
new
patient and caregiver data.
New NMT Module
A new NMT module enables the evaluation of muscle relaxation of patients under Neuromuscular
Block by measuring the strength of muscle reaction after electrically stimulating the dedicated motor
nerve.
Alarm Functionality Enhancements
• Pause Yellow Alarms (with PIIC iX only) - up until now, the Pause Alarms / Alarms Off key
switched off or paused all red and yellow alarms. Now an alarm priority configuration setting is
available to have only yellow alarms affected.
Pause Alarms / Alarms Off not allowed - when the alarm priority is set to Not Allowed, alarms
•
can no longer be switched off or paused. The
Pause Alarms / Alarms Off key can be removed from the screen - a configuration setting removes
•
the permanent key from the screen to avoid unintentional switching off of alarms. Alarms can still
be switched off or paused, in the
• Alarms paused after Standby mode - alarms are automatically paused for 1 minute after Standby
mode to allow time for patient connection.
Alarms menu, under Main Setup.
Pause Alarms / Alarms Off key is disabled.
Capture 12-Lead ECG Enhancements (with PIIC iX only)
The existing 12-Lead ECG capture functionality has been extended to offer:
• Download of analysis results from the IntelliVue Information Center.
• Download of 12-Lead captures from the IntelliVue Information Center for review at the patient
monitor.
56
Page 57

• Analysis results included in reports and additional report selections with ST Map.
• Remote operation of the 12-Lead Export function at the IntelliVue Information Center.
• Remote operation of the 12-Lead Lock/Unlock function at the IntelliVue Information Center.
• New filter settings that are used as a default for future 12-Lead captures.
New "End Afib" and "End Irregular HR" Alarms
The end of an atrial fibrillation or irregular HR phase is announced with an ** End AFIB or **End
Irregular HR
alarm. The delay time before the alarm is announced can be configured.
Information Line Changes
Patient Category is now displayed as a symbol in front of the patient name and cannot be changed
from the Information line. Paced Mode is no longer displayed in the Information line; it appears next
to the HR numeric.
Depending on your configuration, you will see the current Profile name, and/or the Screen name in
the Information line. The Profiles menu has been simplified in Monitoring and Configuration Mode.
Sepsis Protocol Configurability
2What's New?
The SSC Sepsis protocol can now be configured, to customize it for the specific treatment measures
used in your facility. This can include changes to limits for measured or manually entered values,
changes to the Severe Sepsis Screening criteria, and changes to the recommendations in the Sepsis
Resuscitation Bundle and the Sepsis Management Bundle.
Integrated Pulmonary Index for Microstream CO2
An Integrated Pulmonary Index (IPI) numeric is provided, that is an indication of the patient's overall
ventilatory status based on four measurement parameters: etCO
, awRR, pulse rate and SpO2.
2
Cardiac Output (transpulmonary method) - Changes to Calculation Basis for Extravascular Lung Water Index and Preload Indexes
EVLWI is now calculated using Ideal Body Weight (IBW). ITBVI and GEDVI are calculated using
Ideal Body Surface Area (IBSA). IBW and IBSA are based on the patient category, gender and height
that are entered for the patient.
Improved Visibility of Gridlines in Overlapping Waves
Visibility of the gridlines for overlapping waves has been improved, and you can now configure
gridlines to be shown in white, if you prefer, in a thin or thick style.
Timeout for "Aged" Numerics
NBP and SpO2 numerics from intermittent measurements can be configured to be grayed out or to
disappear from the screen after a set time. This avoids older numerics being misinterpreted as current
data. The time can be set individually for SpO
and NBP in Configuration mode.
2
57
Page 58

2What's New?
58
Page 59

3Alarms
The alarm information here applies to all measurements. Measurement-specific alarm information is
discussed in the sections on individual measurements.
The monitor has two different types of alarm: patient alarms and INOPs.
Patient Alarms
Patient Alarms are red and yellow alarms. A red alarm indicates a high priority patient alarm such as a
potentially life threatening situation (for example, asystole). A yellow alarm indicates a lower priority
patient alarm (for example, a respiration alarm limit violation). Additionally there are short yellow
alarms, most of which are specific to arrhythmia-related patient conditions (for example, ventricular
bigeminy).
INOPs
INOPs are technical alarms, they indicate that the monitor cannot measure or detect alarm conditions
reliably. If an INOP interrupts monitoring and alarm detection (for example,
places a question mark in place of the measurement numeric and an audible indicator tone will be
sounded. INOPs without this audible indicator indicate that there may be a problem with the reliability
of the data, but that monitoring is not interrupted.
3
Leads Off), the monitor
Most INOPs are light blue, however there are a small number of INOPs which are always yellow or
red to indicate a severity corresponding to red and yellow alarms. The following INOPs can also be
configured as red or yellow INOPs to provide a severity indication:
ECG Leads Off
•
• NBP Cuff Overpress
• Cuff Not Deflated
• Occlusion
• <SpO₂ Label> No Pulse
• <Press Label> No Pulse
• Tele Disconnected
• Battery Empty / Replace Battery
All monitors in a unit should have the same severity configured for these INOPs.
59
Page 60

3 Alarms
Alarm Delays
There is a delay between a physiological event at the measurement site and the corresponding alarm
indication at the monitor. This delay has two components:
• The general measurement delay time is the time between the occurrence of the
physiological event and when this event is represented by the displayed numerical values.
This delay depends on the algorithmic processing and, for certain measurements (SpO
BIS), on the configured averaging time. The longer the averaging time configured, the longer the
time needed until the numerical values reflect the physiological event.
• The time between the displayed numerical values crossing an alarm limit and the alarm
indication on the monitor. This delay is the sum of the alarm delay configured for the specific
measurement plus the system alarm delay. The system alarm delay is the processing time the
system needs for any alarm on the monitor to be indicated after the measurement has triggered the
alarm. See the performance specifications in the Specifications chapter for the system alarm delay
specification.
, EEG and
2
The alarm delay configured for a specific measurement is normally a fixed time. For SpO
possible to configure a Smart Alarm Delay that is calculated using an intelligent algorithm. See “Smart
Alarm Delays” on page 195 in the SpO
Multiple Alarms
If more than one alarm is active, the alarm messages are shown in the alarm status area in succession.
An arrow symbol next to the alarm message informs you that more than one message is active.
The monitor sounds an audible indicator for the highest priority alarm. If more than one alarm
condition is active in the same measurement, the monitor announces the most severe. Your monitor
may be configured to increase alarm indicator volume automatically during the time when the alarm is
not acknowledged.
Visual Alarm Indicators
WARNING
• No alarms are available on an X2 when connected to a host monitor (Companion Mode is
indicated). Alarms become active again as soon as the X2 is disconnected from the host monitor.
• Alarm fields and other visual alarm indicators are disabled on an X2 when connected to a host
monitor. The only visual alarm indication is provided by the alarm lamps, which are controlled by
the host monitor.
chapter for more details.
2
it is also
2
Alarm Message
An alarm message text appears in the alarm status area at the top of the screen indicating the source of
the alarm. If more than one measurement is in an alarm condition, the message changes every two
seconds, and has an arrow ( ) at the side. The background color of the alarm message matches the
alarm priority: red for red alarms, yellow for yellow alarms, light blue for standard INOPs, red for red
INOPs and yellow for yellow INOPs. The asterisk symbols (
alarm priority:
not have a symbol, red and yellow INOPs have exclamation marks beside the alarm message:
red INOPs and
60
*) beside the alarm message match the
*** for red alarms, ** for yellow alarms, * for short yellow alarms. Standard INOPs do
!!! for
!! for yellow INOPs.
Page 61

3 Alarms
Depending on how your monitor is configured, it may display alarm limit violation messages:
• in text form, for example
• in numeric form, for example
deviation from the alarm limit, and the second number shows the currently set limit.
Flashing Numeric
The numeric of the measurement in alarm flashes.
Bright Alarm Limits
If the alarm was triggered by an alarm limit violation, the corresponding alarm limit on the monitor
screen is shown more brightly if
screen.
Alarm Lamp
A lamp on the monitor's front panel flashes. The alarm lamp is divided into two sections. The right
one flashes for a patient alarm, except for short yellow alarms where the lamp will light for
approximately six seconds. The color is yellow or red corresponding to the highest priority patient
alarm currently present. The left one lights continuously for a light blue INOP and flashes for yellow
or red INOPs as follows:
INOP Lamp Color On Off
** SpO₂ Low or
**Pulse xxx>yyy where the first number shows the maximum
Show ALarmLimits is enabled and there is sufficient room on the
Yellow 1.0 seconds 1.0 seconds
Red 0.25 seconds 0.25 seconds
If only patient alarms are present, and no INOPs, the patient alarms will use both left and right
sections to flash (for red and yellow alarms) or light for approximately six seconds (for short yellow
alarms). If only INOPs are present, and no patient alarms, red and yellow INOPs will use both left and
right sections to flash but light blue INOPs will always light continuously in the left section only.
MX400/450/
500/550
If the screen brightness is configured to automatically adapt to ambient light conditions, the alarm
lamps will also adapt their brightness accordingly.
Nurse Call Systems
If configured to do so, red, yellow and light blue alarms are indicated on any device connected to the
nurse call relay.
Audible Alarm Indicators
The audible alarm indicators configured for your monitor depend on which alarm standard applies in
your hospital. Audible alarm indicator patterns are repeated until you acknowledge the alarm by
switching it off or pausing it, or until the alarm condition ceases (if audible alarm indication is set to
non-latching).
61
Page 62

3 Alarms
WARNING
• Do not rely exclusively on the audible alarm system for patient monitoring. Adjustment of alarm
volume to a low level or off during patient monitoring may result in patient danger. Remember
that the most reliable method of patient monitoring combines close personal surveillance with
correct operation of monitoring equipment.
• No audible alarm indicators are available on an X2 when connected to a host monitor
Companion Mode is indicated). Alarms become active again as soon as the X2 is disconnected
(
from the host monitor.
Alarm Tone Configuration
The audible alarm indicators of your monitor are configurable. In the monitor's Configuration Mode,
you can:
• increase the alarm volume of unacknowledged alarms at regular intervals
• change the interval between alarm sounds (ISO/IEC Standard alarms only)
• change the base volume of the red and yellow alarm tones and the INOP tones
• change the alarm sound to suit the different alarm standards valid in different countries.
T raditional Audible Alarms (HP/Agilent/Philips/Carenet)
• Red alarms and red INOPs: A high pitched sound is repeated once a second.
• Two-star yellow alarms and yellow INOPs: A lower pitched sound is repeated every two seconds.
• One-star yellow alarms (short yellow alarms): The audible indicator is the same as for yellow
alarms, but of shorter duration.
• Standard INOPs: an INOP tone is repeated every two seconds.
ISO/IEC Standard Audible Alarms
• Red alarms and red INOPs: A high pitched tone is repeated five times, followed by a configurable
pause.
• Two-star yellow alarms and yellow INOPs: A lower pitched tone is repeated three times, followed
by a configurable pause.
• One-star yellow alarms (short yellow alarms): The audible indicator is the same as for yellow
alarms, but of shorter duration.
• Standard INOPs: a lower pitched tone is repeated twice, followed by a pause.
Changing the Alarm Tone Volume
• The alarm volume symbol at the top right of the monitor screen gives you an indication of the
current volume.
62
To change the volume, select the volume symbol and then select the required volume from the
pop-up selection.
Page 63

• If you want to see a numerical indication of the current alarm volume on a scale from zero to 10,
or change the setting, select the
The volume scale pops up. The current setting is indented. To change the setting, select the
required number on the scale. Any settings that are inactive ("grayed out") have been disabled in
the monitor's Configuration Mode.
• When the alarm volume is set to zero (off), the alarm volume symbol reflects this.
If you switch the alarm volume off, you will not get any audible indication of alarm conditions.
There is no alarm volume indication on the screen of an X2 when connected to a host monitor
Companion Mode is indicated).
(
Alarm Volume SmartKey.
Minimum Volume for No Central Monitoring INOP
If your monitor is connected to an Information Center, and the connection is interrupted, the INOP
message
ensure that this INOP, and any other active alarm, is not overlooked, the INOP and alarm tones may
be configured to have a minimum volume. In this case, INOP and alarm tones will sound even if the
monitor alarm volume is set to zero.
No Central Monit. will appear within 30 seconds, accompanied by an INOP tone. To help
3 Alarms
Minimum Volume for Severe Yellow or Red INOPs
Severe yellow or red INOPs require action to ensure the well-being of the patient. Therefore the
minimum volume for the INOP tone is set to at least alarm volume 8, irrespective of the current alarm
volume setting. The INOP tone will sound even if the monitor alarm volume is set to zero.
The severe INOPs for which this applies are:
Cuff Not Deflated (configurable to yellow or red)
NBP Cuff Overpress (configurable to yellow or red)
!! Insert Battery - X2 (yellow)
Battery Empty / Replace Battery - (configurable to light blue, yellow or red)
Power Loss Tone
When power is lost - no power is available via the power cable or battery (where available) - a buzzer
will sound, if so configured. The tone can be silenced by pressing the On/Off power switch.
Acknowledging Alarms
To acknowledge all active alarms and INOPs, select the Silence permanent key. This switches off the
audible alarm indicators and alarm lamps.
63
Page 64

3 Alarms
Alternatively, you can acknowledge alarms by pressing the Silence hardkey on the MMS or on the
SpeedPoint. The hardkeys follow the behavior configured for the permanent key.
A check mark beside the alarm message indicates that the alarm has been acknowledged . If the
monitor is configured to re-alarm, a dashed check mark will be shown .
If the condition that triggered the alarm is still present after the alarm has been acknowledged, the
alarm message stays on the screen with a check mark symbol beside it, except for NBP alarms and
alarms from other intermittent measurements. When such an alarm is acknowledged the alarm
message disappears.
If the alarm condition is no longer present, all alarm indicators stop and the alarm is reset.
Switching off the alarms for the measurement in alarm, or switching off the measurement itself, also
stops alarm indication.
Acknowledging Disconnect INOPs
Acknowledging an INOP that results from a disconnected transducer switches off the associated
measurement, unless the monitor is configured to not allow this. The only exception is ECG/Resp:
acknowledging a disconnect INOP for ECG leads does not switch off the ECG and Resp
measurements. Acknowledging a disconnect INOP at the Information Center switches off the audible
INOP indicator but does not switch off the measurement.
Unplugging an MMS or a plug-in module automatically switches off its measurements.
Alarm Reminder
If Alarm Reminder is configured on for your monitor, you will get an audible reminder of alarm
conditions that remain active after you have acknowledged the alarm. This reminder may take the form
of a repetition of the alarm tone for a limited time, or an unlimited repetition of the alarm tone (this is
the same as a new alarm).
yellow and red INOPs.
In Configuration Mode, you can set the interval between silencing the alarm and sounding the
reminder tone to one, two, or three minutes.
The alarm reminder behavior at the Information Center is different to that at the monitor. Refer to the
Information Center Instructions for Use for further information.
Alarm Reminder is not available for standard, light blue INOPs but for
Pausing or Switching Off Alarms
If you want to temporarily prevent alarms from sounding, for example while you are moving a patient,
you can pause alarms. Depending on your monitor configuration, alarms are paused for one, two, or
three minutes, or infinitely. Infinite alarm pause is equivalent to switching the alarms off.
To view the alarm pause setting chosen for your unit,
1 Select Main Setup, Alarms, then Alarm Settings
64
2 Check the Alarms Off setting.
This setting can only be changed in Configuration Mode.
Page 65

3 Alarms
There are some settings made in Configuration Mode that can affect the availability of the pause
alarms functionality.
•The
Pause Alarms / Alarms Off permanent key can be removed from the screen to avoid
unintentional switching off of alarms. The corresponding hardkey on the SpeedPoint or
Navigation Point is then also disabled. In this case you can only pause alarms or switch alarms off
permanently in the
•The
Pause Alarms / Alarms Off permanent key and the corresponding hardkey can be
configured to pause or switch off red and yellow alarms, yellow alarms only, or not to function at
all. If they are configured not to function, you cannot pause alarms or switch alarms off
permanently at all.
When the alarms off priority is set to
Pause Yellow / Yellow Al. Off key.
the
To Pause All Alarms
• Select the Pause Alarms permanent key. If your monitor is configured to infinite pause time, the
permanent key is labeled
• Or press the Alarms hardkey on the SpeedPoint or Navigation Point. The hardkey follows the
behavior configured for the permanent key.
Depending on the configuration, you may need to select
Alarms menu, under Main Setup.
Yellow Only, the Pause Alarms / Alarms Off key becomes
Alarms Off, and selecting it switches alarms off.
Confirm to complete the change.
To Switch All Alarms Off
You can only switch alarms off permanently if your monitor is configured to allow infinite alarms
pause and the permanent key is labeled
• Select the
Alarms Off (or Yellow Al. Off) permanent key.
Alarms Off (or Yellow Al. Off).
• Or press the Alarms hardkey on the SpeedPoint or Navigation Point. The hardkey follows the
behavior configured for the permanent key.
Depending on the configuration, you may need to select
Confirm to complete the change.
To Switch Individual Measurement Alarms On or Off
1 Select the measurement numeric to enter its setup menu.
2 Select Alarms to switch between on and off.
The alarms off symbol is shown beside the measurement numeric.
65
Page 66

3 Alarms
While Alarms are Paused or Off
When red alarms are paused or off:
• The red Alarms Paused lamp on the monitor front panel is lit.
In the alarm field, the monitor displays the message
the alarms paused symbol or the alarms off symbol.
When yellow alarms are paused or off:
• The yellow Alarms Paused lamp on the monitor front panel is lit.
In the alarm field, the monitor displays the message
together with the alarms paused symbol or the alarms off symbol.
For red and yellow alarms:
Alarms Paused Alarms Off
• No alarms are sounded and no alarm messages are shown.
• INOP messages are shown but no INOP tones are sounded.
The only exceptions are the INOPs
to empty, missing and malfunctioning batteries.
These INOPs switch the alarms on, and the INOP tones are sounded, even if alarms are paused or
off. You need to remove the INOP condition first before you can switch the alarm tones off again.
Al. Paused x:yy or Alarms Off, together with
YellowPaused x:yy or Yellow Alarms Off,
Cuff Not Deflated, NBP Cuff Overpress and INOPs relating
• The nurse call relay is not active.
If a disconnect INOP is present and alarms are paused or switched off, the measurement in question
may be switched off, depending on monitor configuration.
Restarting Paused Alarms
To manually switch on alarm indication again after a pause, select the permanent key Pause Alarms (or
Alarms Off) again.
Alarm indication starts again automatically after the pause period expires. If the monitor is configured
to stay paused infinitely, you must select
Alarms Off again to restart alarm indication.
Resetting Arrhythmia Alarm Timeout s
To reset the timeout period, either
• select the
•select
Alarms Off or Pause Alarms permanent key and then reselect it, or
Reset Alarming in the Review Alarms window or the Alarm Messages window.
Extending the Alarm Pause Time
If your monitor has extended alarm pause enabled, you can extend the alarm pause time. Use this to
prevent alarms being indicated, for example, while you are washing a patient or carrying out a
procedure. Only extend the alarm pause time when you are sure that clinical personnel are available to
monitor the patient's condition closely.
66
Page 67

To extend the alarm pause time to five or 10 minutes,
1 Select one of the alarm fields. This calls up the Alarm Messages window.
2 Select either the pop-up key PauseAl. 5 min or the pop-up key PauseAl. 10 min. Each time you
select one of these pop-up keys, the Alarm Pause Time is reset to five (or 10) minutes.
Alarm Settings for Unattended Monitoring
When monitoring patients that are not continuously attended, use appropriate alarm settings to
optimize monitoring:
• Always leave alarms switched on when the patient is unattended.
3 Alarms
• Recommended configuration: Use one of the temporary settings for the
Infinite, and make sure that the AlarmOffReminder and the Alarm Reminder are switched on
(these settings are made in Configuration mode).
• Set alarm limits so that alarms will be triggered for those changes in the patient condition that you
want to be advised of. Setting limits to very high or low values can render the alarm system useless.
• Use available notification routes, such as a nurse call system or the connection to an Information
Center, or at least select an appropriate alarm volume to ensure that alarms are recognized.
Alarm Limits
The alarm limits you set determine the conditions that trigger yellow and red limit alarms. For some
measurements (for example, BIS and SpO
alarm limit to 100 switches the high alarm off, or setting the low alarm limit to 0 switches it off. In
these cases, the alarms off symbol is not displayed.
WARNING
Be aware that the monitors in your care area may each have different alarm settings, to suit different
patients. Always check that the alarm settings are appropriate for your patient before you start
monitoring.
Alarms Off setting, not
), where the value ranges from 100 to 0, setting the high
2
Viewing Individual Alarm Limits
You can usually see the alarm limits set for each measurement next to the measurement numeric on
the main screen.
If your monitor is not configured to show the alarm limits next to the numeric, or if the numeric is so
small that the limits cannot be displayed, you can see them in the appropriate measurement setup
menu. Select the measurement numeric to enter the menu and check the limits.
67
Page 68

3 Alarms
Viewing All Alarm Limits
The Alarm Limits overview window lists the currently set alarm limits for all measurements. If an
Apnea alarm delay time is set, this is also shown. The alarms off symbol is shown beside the
measurement label of any measurement whose alarm switched off.
To open the
then select the
Alarm Limits window, either select any alarm field to open the Alarm Messages window,
Alarm Limits pop-up key, or select the Alarm Limits SmartKey, if configured.
1 Measurement labels, with alarms off symbol where appropriate
2 Current alarm limits
3 Graphic view of current yellow and red alarm limits and currently monitored measurement value.
Off indicates the measurement is switched off
•Select
Show ST Limits to expand the list of ST leads and view the currently set alarm limits.
Selecting
Hide ST Limits hides the list again.
You can use the pop-up keys that open with the
All Al. On/All Al. Off
–
– All Lim. Narrow/All Lim. Wide to set narrow or wide alarm AutoLimits for all measurements.
Print Limits/Record Limits to print a list of all current alarm limit settings on a connected
–
printer or recorder.
These pop-up keys are not available in the window for changing individual alarm limits which you
access by selecting the measurement label in the
Changing Alarm Limits
Set limits so that alarms will be triggered for those changes in the patient condition that you want to be
advised of. Setting limits to very high or low values can render the alarm system useless.
To change individual measurement alarm limits using the measurement's Setup Menu,
1 In the measurement's setup menu, select the alarm limit you want to change. This calls up a list of
available values for the alarm limit.
68
Alarm Limits window to perform common tasks:
Alarm Limits window.
Page 69

3 Alarms
2
Select a value from the list to adjust the alarm limit.
Alternatively, you can use the keys in the measurement alarm limits window, which you access by
selecting the measurement label in the
Alarm Limits window.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Parameter label
High red alarm limit (view only)
High yellow alarm limit field. Select to open a pop-up list of high alarm limits
Alarms On/Off key - select to switch between alarms on or off
Preview Alarm AutoLimits for a measurement before applying
Select to apply wide AutoLimits
Select to apply narrow AutoLimits
Low yellow alarm field. Select to open a pop-up list of low alarm limits
Low red alarm (view only)
Graphic view of alarm limits with currently measured value
15-min trend, showing alarm limits and monitored measurement values
To change alarm limits,
1 Enter the Alarm Limits window.
2 Using touch: to set the high alarm limit, select the high yellow alarm field to open a pop-up list of
high alarm limits. Select a limit from the list. Repeat to set the low yellow alarm field.
Using a SpeedPoint or Navigation Point: position the cursor in the high yellow alarm field,
then press the knob inwards. Rotate the knob to the left or right to adjust the limit. Press the knob
again to set the displayed limit. Repeat to set the low yellow alarm limit.
69
Page 70

3 Alarms
If you set the yellow alarm limit outside the red alarm limit, the monitor will automatically adapt the
red alarm limit.
When an ST measurement is in the alarm limits window there are also two pop-up keys available
labeled
Alarm Limits can also be changed at the IntelliVue Information Center iX.
All ST Narrow/All ST Wide. With these keys you can set Auto Limits for all ST Leads.
About Automatic Alarm Limits
The monitor can automatically set alarm limits suited to your individual patient, using the Automatic
Alarm Limits function (AutoLimits). This tells the monitor to adapt the alarm limits of selected
measurements to the measured vital signs within a defined safe limit. The monitor calculates safe
AutoLimits for each patient based on the measured values from the last 12 seconds.
The wide and narrow limits have a fixed relationship to the measured value within the nonpathological range. Outside of this range, no auto limits are calculated. To set values outside of the
non-pathological range, limits must be changed manually, based on the clinician's judgment about the
specific patient.
1 Wide alarm limits
2 Narrow alarm limits
3 Alarm Limits
4 Measurement value
Limits Narrow sets limits close to the currently measured values for situations where it is critical for
you to be informed about small changes in your patient's vital signs.
Limits Wide sets limits further away from the currently measured values for situations where small
changes are not so critical.
Use the keys in the measurement alarm limits window to apply AutoLimits for individual
measurements. These keys are not available if AutoLimits have been disabled for the measurement in
the monitor's Configuration Mode.
AutoLimits are not available for all measurements. The list of measurements for which AutoLimits can
be used is defined in the monitor's Configuration mode.
Use the measurement alarm limits window to check AutoLimits before you apply them to ensure that
they are appropriate for your individual patient and their clinical condition. Once applied, AutoLimits
are shown on the monitor screen just like manually-set alarm limits. If the AutoLimits are not
appropriate for your patient, you must set alarm limits manually. The limits remain unchanged until
you set them again or change them manually.
Documenting Alarm Limits
The alarm limits pop-up keys appear with the Alarm Limits and measurement alarm limits windows.
70
Page 71

3 Alarms
• Select the Print Limits pop-up key to print an overview of all alarm limits on a connected printer.
• Select the
Record Limits pop-up key to send a recording of the alarm limits to a recorder.
Reviewing Alarms
You can see which alarms and INOPs are currently active in the respective alarms and INOPs fields at
the top of the screen.
To see the currently active alarms and INOPs listed in one place, select any of the alarm status areas on
the monitor screen. The
All alarms are erased from the
change to Demonstration Mode.
Alarm Messages Window
The Alarm Messages window shows all the currently active alarms and INOPs sorted by priority,
beginning at the top with the most recent. INOPs are shown on the left hand side and patient alarms
are shown on the right hand side. Any active red alarms are shown first, followed by yellow alarms.
Acknowledged alarms or INOPs are shown with the check mark symbol.
Alarm Messages window pop-up keys appear when the window is opened. If alarm pause
The
extension is disabled, the pause pop-up keys are inactive ("grayed-out"). Selecting the
pop-up key opens the
If you do not immediately understand an INOP or alarm message, refer to its help text.
Alarm Messages window pops up.
Review Alarms window.
Alarm Messages window when you discharge a patient, or if you
Review Alarms
•In the
Alarm Messages window, select the message. This calls up a help window with an
explanation of the message and, where appropriate, a suggested solution for the problem.
• If the alarm or INOP was generated in a device other than the monitor (for instance, in an MMS
or FMS), this source is specified at the end of the help text.
Review Alarms Window
The Review Alarms window contains a list of the most recent alarms and INOPs with date and time
information.
If configured to do so, each alarm is shown with the alarm limit active when the alarm was triggered
and the maximum value measured beyond this limit. The
monitor was switched on (after being switched off for longer than 1 minute) and any actions related to
switching device alarms on and off, entering or leaving Standby mode, silencing alarms or changing the
ECG source.
When you select an item from the list, you can get additional information about that item. If you select
a high or low limit alarm in the list, the
you select an alarm resulting from an event alarm notification, the
event will open. If you select an alert other than a high or low alarm, a help text window opens with
more information. This is the same as the help text window that opens in the
window. Some items in the list are simply log items not related to a patient alert as such (for example,
Alarms On or Alarms Off). You cannot see any further information if you select one of these items.
When you close these windows you will return to the
Review Alarms window also shows when the
Graphical Trends window will open to provide further data. If
Event Episode window for that
Alarm Messages
Review Alarms window.
The information in the
Review Alarms window is deleted when a patient is discharged, and when you
leave Demonstration Mode.
71
Page 72

3 Alarms
The Review Alarms window pop-up keys appear when the window is opened. If alarm pause
extension is disabled, the pause pop-up keys are inactive. Selecting the
opens the
Alarm Messages window.
Latching Alarms
The alarm latching setting for your monitor defines how the alarm indicators behave when you do not
acknowledge them. When alarms are set to non-latching, their indicators end when the alarm condition
ends. Switching alarm latching on means that visual and/or audible alarm indications are still displayed
or announced by the monitor after the alarm condition ends. The indication lasts until you
acknowledge the alarm.
Viewing the Alarm Latching Settings
To see the alarm latching setting for your monitor
1 In the monitor's Main Setup menu, select Alarms.
2 Select Alarm Settings, and see the Visual Latching and Audible Latching settings.
This setting can only be changed in Configuration Mode. You should be aware of the settings chosen
for your unit. There are three possible choices each for visual and audible latching, red only, red and
yellow, and off. These choices can be combined to give the following settings:
Active Alarms pop-up key
Visual Latching Audible Latching
Red&Yellow Red&Yellow
Red&Yellow Red Only
Red&Yellow Off
Red Only Red Only
Red Only Off
Off Off
Alarm Latching Behavior
Red & Yellow Measurement
Alarms
Alarm has not
been
acknowledged.
Alarm has been
acknowledged.
Alarm condition
still present.
Alarm condition
no longer present.
Alarm condition
still present.
Alarm condition
no longer present.
Non-latching alarms Visual and audible latching Visual latching, audible
Alarm tone on. Alarm lamp on.
Alarm message. Flashing
numerics.
All audible and visual alarm
indicators automatically stop.
Alarm tone off. Alarm lamp off.
Alarm message. Flashing
numerics. Audible alarm
reminder (if configured).
Audible and visual alarm
indicators automatically stop.
Alarm tone on. Alarm lamp
on. Alarm message. Flashing
numerics.
Alarm tone on.
Alarm lamp on.
Alarm message.
Flashing numerics.
Alarm tone off. Alarm lamp
off. Alarm message. Flashing
numerics. Audible alarm
reminder (if configured).
Audible and visual alarm
indicators automatically stop.
non-latching
Alarm tone on. Alarm lamp
on. Alarm message. Flashing
numerics.
Alarm message. Flashing
numerics.
Audible alarm indicators
automatically stop.
Alarm tone off. Alarm lamp
off. Alarm message. Flashing
numerics. Audible alarm
reminder (if configured).
Audible and visual alarm
indicators automatically stop.
72
Page 73

All INOPs are non-latching. See “Yellow Arrhythmia Alarms” on page 160 for information on onestar yellow alarms latching behavior.
Testing Alarms
When you switch the monitor on, a selftest is started. You must check that the alarms lamps light, one
after the other, and that you hear a single tone. This indicates that the visible and audible alarm
indicators are functioning correctly. For further testing of individual measurement alarms, perform the
measurement on yourself (for example SpO
that appropriate alarm behavior is observed.
or CO2) or use a simulator. Adjust alarm limits and check
2
Alarm Behavior at Power On
If the monitor is switched off for longer than one minute and then switched on again (or after a loss of
power lasting longer than one minute, or when a patient is discharged), the monitor can be configured
to:
• restore the alarm settings from the monitor's configured default Profile,
• restore the most recently used alarm settings, or
3 Alarms
• switch the alarms off.
After any of these situations, you should check that the alarm settings are appropriate for your patient
and monitoring situation, and if necessary, select the correct Profile and patient category.
If power is lost for less than one minute, the alarm on/off condition prior to the power loss is
restored.
Alarm Recordings
You can set up your monitor so that it automatically triggers alarm recordings locally or at the
Information Center, or if configured, to a printer as a realtime report.
1 Press the Main Setup SmartKey.
2 Select Alarms from the Main Setup menu.
3 Select Alarm Recording from the Alarms menu to open the Alarm Recordings menu.
4 Select a measurement from those listed for which you want to change the alarm condition that
triggers an alarm recording. This opens a pop-up list.
5 For the desired measurement(s), choose the alarm condition to trigger an alarm recording:
Red Only: an alarm recording will automatically be triggered when the measurement enters a red
alarm condition.
Red&Yellow: both yellow and red alarms will trigger an alarm recording.
Off: disables automatic alarm recording.
Refer to the "Recording" chapter for details of how to set up a recording.
73
Page 74

3 Alarms
74
Page 75

4Patient Alarms and INOPs
This chapter lists patient alarms alphabetically, and technical alarms (INOPs) arranged by the source of
the INOP and then alphabetically, irrespective of their priority. All alarms and INOPs are listed here;
the ones which can appear on your monitor will depend on the model and the individual options.
Patient Alarm Messages
The measurement labels and abbreviations for pressure, temperature, SpO2, and anesthetic agent
alarms are explained in the individual chapters.
Some alarms may be shown at the Information Center in shortened form, when transferred through
IntelliVue Instrument Telemetry. These shortened alarm texts are included in the list and identified
with the note "at Information Center".
4
Refer to your IntelliBridge Device Driver Instructions for Use for patient alarms from connected
external devices.
Refer to your Gas Module Instructions for Use for patient alarms and INOPs from the gas modules.
Refer to your IntelliVue TcG10 Instructions for Use for patient alarms and INOPs from the TcG10.
Alarm Message From Condition Indication
* AFIB ECG/Arrhythmia Atrial fibrillation waveform detected yellow alarm lamp, short yellow
alarm tone
*** Apnea
*** Apnea x:yy
*** Apnea >10 min
*** Asystole ECG No QRS detected for a period > the asystole
** awRR High CO
** awRR Low CO
** BIS High BIS The Bispectral Index value has exceeded the
** BIS Low BIS The Bispectral Index value has dropped below
, Resp,
CO
2
Spirometry
, Resp, AGM The airway respiration rate has exceeded the
2
, Resp, AGM The airway respiration rate has dropped below
2
Respiration has stopped for longer than the
preset apnea time. "x:yy" denotes the Apnea
duration in minutes and seconds
alarm threshold
high alarm limit.
the low alarm limit.
high alarm limit.
the low alarm limit.
numeric flashes, red alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes, red alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes and high limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes and low limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes and high limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes and low limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
75
Page 76

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
Alarm Message From Condition Indication
***Brady/P xxx<yyy
***Brady xxx < yyy
** CCO High
Press, SpO
2
ECG
CCO Continuous Cardiac Output or CC Index is
** CCI High
** CCO Low
CCO Continuous Cardiac Output or CC Index is
** CCI Low
** CPP High CPP The CPP value has exceeded the high alarm
** CPP Low CPP The CPP value has fallen below the low alarm
*** Desat
SpO
2
*** Desat xx < yy
** EC10 Alarm
EC10 IntelliBridge A yellow (**) or red (***) patient alarm is
*** EC10 Alarm
at Information Center
* End AFIB ECG/Arrhythmia Atrial fibrillation no longer detected for the
* End Irregular HR ECG/Arrhythmia Irregular HR no longer detected for the
** etCO₂ High CO
** etCO₂ Low CO
** etO₂ High O
** etO₂ Low O
* Event
, AGM The end tidal CO2 high alarm limit has been
2
, AGM The end tidal CO2 value has fallen below the
2
, AGM The end tidal O2 high alarm limit has been
2
, AGM The end tidal O2 value has fallen below the low
2
Event surveillance An event has occurred and the event
** Event
*** Event
at Information center
* Event:<Event Group>
Event surveillance An event has occurred and the event
** Event:<Event
Group>
*** Event:<Event
Group>
This is the alternative alarm message for ***
Extreme Brady, when the alarm text setting
is Enhanced.
Heart rate < the extreme bradycardia alarm
limit. xxx denotes the lowest measured value;
yyy is the extreme bradycardia limit.
above the high alarm limit.
below the low alarm limit.
limit.
limit.
The SpO2 value has fallen below the
desaturation alarm limit. xx denotes the lowest
measured value, and yy is the desaturation limit.
present on the IntelliBridge module. Check the
monitor display for more detailed alarm
information.
configured Afib end delay time
configured irregular HR end delay time.
exceeded.
low alarm limit.
exceeded.
alarm limit.
notification is configured to alarm. Check on
the monitor for more details on event group.
notification is configured to alarm.
numeric flashes and alarm limit is
highlighted, red alarm lamp, alarm
tone
numeric flashes and high alarm
limit is highlighted, yellow alarm
lamp, alarm tone
numeric flashes and low alarm limit
is highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes and high limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes and low limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes, red alarm lamp,
alarm tone
(on monitor) yellow or red alarm
lamp; the alarm text is defined by
the IntelliBridge device driver
yellow alarm lamp, short yellow
alarm tone
yellow alarm lamp, short yellow
alarm tone
numeric flashes and high limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes and low limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes and high limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes, and low limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
(on monitor) event group name
flashes, yellow or red alarm lamp
and alarm tone
event group name flashes, yellow or
red alarm lamp and alarm tone
76
Page 77

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
Alarm Message From Condition Indication
*** Extreme Brady ECG Heart rate < the extreme brady alarm limit. numeric flashes and alarm limit is
highlighted, red alarm lamp, alarm
tone
*** Extreme Tachy ECG Heart rate > the extreme tachy alarm limit. numeric flashes and alarm limit is
highlighted, red alarm lamp, alarm
tone
* HR High
** HR High
* HR Low
** HR Low
** IPI Low CO
* Irregular HR ECG/Arrhythmia Consistently irregular rhythm (irregular R-R
** <iTemp Label> High
** <iTemp Label> Low
* Missed Beat ECG/Arrhythmia No beat detected for > 1.75*(the averaged R-R
* More Alarms
** More Alarms
*** More Alarms
* Multiform PVCs ECG/Arrhythmia Two different shaped Vs detected, each
** NBP High NBP The measured NBP value is above the high
** NBP Low NBP The measured NBP value is below the low
* Non-Sustain VT ECG/Arrhythmia A run of PVCs < the V-Tach run limit and
ECG Heart rate > the high HR alarm limit numeric flashes and high limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone. If configured to short
yellow, the sound switches off after
5 seconds if Arrhythmia is switched
on.
ECG Heart rate < the low HR alarm limit numeric flashes and low limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone. If configured to short
yellow, the sound switches off after
5 seconds if Arrhythmia is switched
on.
2
iTemp The temperature value has exceeded the high
iTemp The temperature value has dropped below the
other assigned
devices
The IPI value has fallen below the low alarm
limit.
intervals).
alarm limit.
low alarm limit.
interval), or no beat detected for > one second
if HR > 120 (For non-paced patients only).
There is more than one physiological alarm of
the corresponding severity active on the devices
that monitor this patient. For details, check the
information displayed at the Information
Center.
occurring at least twice within the last 300 beats
and at least once within the last 60 beats.
alarm limit.
s, d, or m after the label indicates whether the
systolic, diastolic or mean pressure has crossed
the limit.
alarm limit.
s, d, or m after the label indicates whether the
systolic, diastolic or mean pressure has crossed
the limit.
ventricular heart rate > the V-Tach HR limit
numeric flashes, and low limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
short yellow audible alarm
numeric flashes and high limit is
high-lighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes and low limit is
high-lighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
short yellow audible alarm
yellow or red alarm lamp and alarm
tone
numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
short yellow audible alarm
numeric flashes and high limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes and low limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
short yellow audible alarm
77
Page 78

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
Alarm Message From Condition Indication
* OtherMon Alarm
** OtherMon Alarm
*** OtherMon Alarm
* Pacer Not Capt ECG/Arrhythmia
* Pacer Not Pacing ECG/Arrhythmia
* Pair PVCs ECG/Arrhythmia Two ventricular beats between two non-
* Pause ECG/Arrhythmia No beat detected for a period > the pause
*** <Press Label>
Disconnect
*** <Press Label> High PRESS The measured pressure value is above the
** <Press Label> High PRESS The measured pressure value is above the high
*** <Press Label> Low PRESS The measured pressure value is below the
** <Press Label> Low PRESS The measured pressure value is below the low
** Pulse High PRESS, SpO
** Pulse Low PRESS, SpO
* PVCs/min High ECG/Arrhythmia PVCs detected within a minute > the alarm
** QTc High ECG/QT QTc value has exceeded the QTc high limit for
** ΔQTc High ECG/QT ΔQTc value has exceeded the ΔQTc high limit
another assigned
monitor
Another monitor used for the patient is in an
alarm condition. Check the detailed alarm
information at the Information Center.
No beat detected for > 1.75*(the averaged R-R
(paced patients
only)
interval) with detected pace pulse(s). (For paced
patients only).
No beat and pace pulse detected for >
(paced patients
only)
1.75*(the averaged R-R interval). (For paced
patients only).
ventricular beats.
threshold.
PRESS The pressure is non-pulsatile and the mean
pressure is continuously less than 10 mmHg
(1.3 kPa). This alarm occurs only with arterial
pr es su re s ( P, A BP, AR T, Ao , BA P, FAP, PA P,
UAP, P1, P2, P3, P4).
extreme high alarm limit.
s, d, or m after the label indicates whether the
systolic, diastolic or mean pressure has crossed
the limit.
alarm limit.
s, d, or m after the label indicates whether the
systolic, diastolic or mean pressure has crossed
the limit.
extreme low alarm limit.
s, d, or m after the label indicates whether the
systolic, diastolic or mean pressure has crossed
the limit.
alarm limit.
s, d, or m after the label indicates whether the
systolic, diastolic or mean pressure has crossed
the limit.
The pulse rate has exceeded the high alarm
2
limit.
The pulse rate has dropped below the low
2
alarm limit.
limit
more than 5 minutes
for more than 5 minutes
yellow or red alarm lamp and alarm
tone
numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
short yellow audible alarm
numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
short yellow audible alarm
numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
short yellow audible alarm
numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
short yellow audible alarm
numeric flashes, red alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes, high limit is
highlighted, red alarm lamp, alarm
tone
numeric flashes, high limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes and low limit is
highlighted, red alarm lamp, alarm
tone
numeric flashes and low limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes and high limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes and low limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
short yellow audible alarm
numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
78
Page 79

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
Alarm Message From Condition Indication
* R-on-T PVCs ECG/Arrhythmia For HR < 100, a PVC with R-R interval < 1/3
the average interval followed by a
compensatory pause of 1.25*(the average R-R
interval), or two such Vs without compensatory
pause occurring within 5 minutes of each other.
(When HR > 100, 1/3 R-R interval is too short
for beat detection)
** RR High RESP The respiration rate has exceeded the high
alarm limit.
** RR Low RESP The respiration rate has dropped below the low
alarm limit.
* Run PVCs High ECG/Arrhythmia A run of > 2 PVCs. numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
** <SO₂ Label> High SvO
/SO
2
2
The the measured intravascular oxygen
saturation has exceeded the high limit.
** <SO₂ Label> Low SvO
/SO
2
2
The measured intravascular oxygen saturation
has fallen below the low limit.
** <SpO₂ Label> High SpO
2
The arterial oxygen saturation has exceeded the
high alarm limit.
** <SpO₂ Label> Low SpO
2
The arterial oxygen saturation has fallen below
the low alarm limit.
**ST Multi <n>,<n> ECG/ST Two contiguous ST leads <n> and <n> have
exceeded elevation or depression limits for
more than 60 seconds. The limit violations for
both leads must be with respect to same limit;
either both above the high limit or both below
the low limit.
**ST Multi
at Information Center
ECG/ST The ST depression or elevation is outside of
the limit in two or more leads. Check on the
monitor
**STE <n>,<n> ECG/ST Two contiguous leads <n> and <n> are above
their respective STE limits
** ST-<n> High ECG/ST The ST elevation in lead <n> is higher than the
limit. Lead is not contiguous with any other
lead.
** ST-<n> Low ECG/ST The ST depression in lead <n> is lower than
the limit. Lead is not contiguous with any other
lead.
* SVT ECG/Arrhythmia A run of supraventricular beats > the SVT run
limit and heart rate > the SVT HR limit.
numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
short yellow audible alarm
numeric flashes and high limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes and low limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
short yellow audible alarm
numeric flashes and high alarm
limit is highlighted, yellow alarm
lamp, alarm tone
numeric flashes and low alarm limit
is highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes and high limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes and low limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
(on monitor) numeric flashes,
yellow alarm lamp, alarm tone
numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes and high alarm
limit is highlighted, yellow alarm
lamp, alarm tone
numeric flashes and low alarm limit
is highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
79
Page 80

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
Alarm Message From Condition Indication
***Tachy/P xxx>yyy
or
***Tachy xxx > yyy
** Tblood High C.O. The blood temperature value has exceeded the
** Tblood Low C.O. The blood temperature value has fallen below
** tcpO₂ High
** tcpCO₂ High
** tcpO₂ Low
** tcpCO₂ Low
* Tele Alarm
** Tele Alarm
*** Tele Alarm
** <Temp Label> High TEMP The temperature has exceeded the high alarm
** <Temp Label> Low TEMP The temperature has fallen below the low alarm
* T-Mon Alarm
** T-Mon Alarm
*** T-Mon Alarm
** TOFcnt High NMT TOFcnt value has exceeded the high alarm
* Vent Bigeminy ECG/Arrhythmia A dominant rhythm of N, V, N, V (N =
*** Vent Fib/Tach ECG Fibrillatory waveform (sinusoidal wave between
* Vent Rhythm
** Vent Rhythm
* Vent Trigeminy ECG/Arrhythmia A dominant rhythm of N, N, V, N, N, V (N =
*** VTach ECG, Arrhythmia A run of PVCs ≥ the V-Tach run limit and
** VueLink Alarm
*** VueLink Alarm
at Information Center
Press, SpO2,
ECG
This is the alternative alarm message for ***
Extreme Tachy when the alarm text setting
is Enhanced.
Heart rate >the extreme tachycardia alarm
limit. xxx denotes the highest measured value;
yyy is the tachycardia limit.
high alarm limit.
the low alarm limit.
tcGas The tcpO
or tcpCO2 value has exceeded the
2
high alarm limit.
tcGas The tcpO
or tcpCO2 value has fallen below
2
the low alarm limit.
an assigned
telemetry device
A telemetry device used for the patient is in an
alarm condition. Check the detailed alarm
information at the Information Center.
limit.
limit.
an assigned
transport monitor
A transport monitor used for the patient is in
an alarm condition. Check the detailed alarm
information at the Information Center.
limit
supraventricular beat, V=ventricular beat)
2 – 10 Hz) for 4 consecutive seconds.
ECG/Arrhythmia A dominant rhythm of adjacent Vs > the vent
rhythm limit and ventricular heart rate < the V-
Tach HR limit.
supraventricular beat, V = ventricular beat).
heart rate > the V-Tach HR limit.
VueLink A yellow (**) or red (***) patient alarm is
present on the VueLink module. Check the
monitor display for more detailed alarm
information.
numeric flashes, alarm limit is
highlighted, red alarm lamp, alarm
tone
numeric flashes, high alarm limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes, low alarm limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes, high alarm limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes, low alarm limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
yellow or red alarm lamp and alarm
tone
numeric flashes and high limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes and low limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
yellow or red alarm lamp and alarm
tone
numeric flashes and high limit is
highlighted, yellow alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
short yellow audible alarm
numeric flashes, red alarm lamp,
alarm tone
numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
short yellow audible alarm
numeric flashes, yellow alarm lamp,
short yellow audible alarm
numeric flashes, red alarm lamp,
alarm tone
(on monitor) yellow or red alarm
lamp; the alarm text is defined by
the VueLink device driver
80
Page 81

Technical Alarm Messages (INOPs)
If an INOP interrupts monitoring and alarm detection, the measurement numeric will be replaced
-?-. If an INOP may lead to unreliable measurement values, a ? appears next to the numeric.
by
4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
The measurement labels and abbreviations for pressure, temperature, SpO
messages are explained in the individual measurement chapters.
Monitor INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
Bad MSL
INOP tone
Central: Tele Only
INOP tone
Check Alarm Lamps
INOP tone
Check DrugSettings
INOP tone
!!Check ECG Source
Yellow tone
!! Check Equipment
INOP tone/Yellow tone
Check Flex Texts
INOP tone
Check Keyboard
INOP tone
Check Main Board 2
INOP tone
Check Monitor Func
INOP tone
Check Monitor Temp
INOP tone
Check Mouse
INOP tone
Check MSL Voltage
INOP tone
Check Network Conf
INOP tone
!! Check Pairing
Yellow tone
!!Check Patient ID
Yellow tone
1) An MMS with an incompatible software revision is connected to the monitor. This combination
does not allow monitoring, OR
2) You cannot use this combination of monitor, MMS and cable. Switch off the monitor and contact
your service personnel.
System connectivity via telemetry device is limited (No alarms, only local numerics) when in
companion mode and host monitor does not have system connectivity. Only telemetry device
parameters can be displayed at central station.
Perform a visual check of the alarm lamp to establish whether there is a problem. Contact your service
personnel to check the internal connections to the alarm lamps.
There was a problem loading the drug settings. Check that the settings are complete and correct.
The telemetry device and the monitor both have valid ECG signals. Unpair the telemetry device and
the monitor if they are no longer used for the same patient.
There is an equipment status dispute relating to one or more of the devices assigned to this patient. See
the Equipment window for details.
Check the names of the monitor menus, for example the labels for screens, profiles, event or trend
group names, before you resume monitoring. If they are unexpected, there may be a problem with the
monitor software. Contact your service personnel.
Perform a visual and functional check of the keyboard. Contact your service personnel.
There is a problem with the second main board in the monitor. Contact your service personnel.
Potential problem with alarm lamps, display or interfaces detected. Contact your service personnel.
The temperature inside the monitor is too high. Check that the monitor ventilation is not obstructed.
If the situation continues, contact your service personnel.
Perform a visual and functional check of the mouse input device. Contact your service personnel.
There is a problem with the voltage of the Measurement Link (MSL). Contact your service personnel.
The monitor is receiving network topology information from more than one source, e.g. the Database
Server and an Application Server. Contact your service personnel.
There is a problem with device pairing. Check that the monitor and telemetry device are correctly
paired.
There is a mismatch between patient data in two connected devices. Resolve the mismatch to allow
settings and data synchronization.
, and VueLink INOP
2
81
Page 82

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
Check Screen Res.
INOP tone
Check Settings
INOP tone
Check SpeedPoint
INOP tone
Check Touch Input
INOP tone
Check Waves
INOP tone
Chk ECG Sync Cable
INOP tone
Chk IndepDsp Cable The monitor cannot communicate with the D80 Intelligent Display. Check the MSL coupling cable.
Chk <Measurement
Label>Settings
Chk MSL Connection
INOP tone
Internal.Comm.Malf
INOP tone
MCC Reversed
INOP tone
MCC Unsupported
INOP tone
Meas. Deactivated An X2 or MP5 has been connected to a host monitor (companion mode) and all derived
!!More Bed Alarms
!!!More Bed Alarms
at Information Center
More INOPs
!! More INOPs
!!! More INOPs
MSL Power High The power consumption of the devices connected to the Measurement Link (MSL) cable is too high.
MSL Power Off
INOP tone
MSL Power Overload
INOP tone
The Screen you have selected uses a resolution which is not supported by the display. The monitor will
show a generic Screen instead until you select a different Screen.
Contact your service personnel if you want the Screen deleted from the Profile(s) to avoid this in
future.
If this INOP appears, check the monitor and patient settings before you resume monitoring. If the
settings are unexpected, there may be a problem with the monitor software. Contact your service
personnel.
Perform a visual and functional check of the SpeedPoint input device. Contact your service personnel.
Perform a visual and functional check of the touch input device. Contact your service personnel.
The options purchased with this monitor may not support the number of waves required to show the
selected Screen, so some waves or high resolution trends are missing from the Screen. Select a
different Screen with fewer waves.
Contact your service personnel if you want the Screen deleted from the Profile(s) to avoid this in
future.
The ECG Sync is detecting an invalid signal, or the ECG Sync cable is disconnected.
The end with the gray connector must be connected to the Intelligent Display.
Synchronization of the settings for the measurement cited, has failed. Check that settings are
appropriate for your patient.
Check that the MSL cable is properly connected. If this is the case, try using another MSL cable, to
check if your cable is defective. If this does not help, the device connected via the MSL cable may be
defective, contact your service personnel.
There is a problem with I2C Bus communication in the monitor. Contact your service personnel.
The MSL coupling cable is reversed. Connect the end with the gray connector to the Intelligent
Display.
An MSL coupling cable has been connected to a device which does not support MSL coupling.
measurements have been deactivated and/or measurements with a label conflict. The measurements
can only be reactivated by disconnecting the measurement device from the host monitor.
The monitor is associated with a telemetry device and is sending data to the Information Center via
the telemetry device. There are currently more alarms at the bedside than can be transmitted to the
Information Center.
There is more than one technical alarm of the corresponding severity active on the devices that
monitor this patient. For details check the information displayed at the Information Center.
If this situation continues, the MSL will be switched off. Contact your service personnel.
The power consumption of the devices connected to the Measurement Link (MSL) cable was too high
for too long and the MSL has been switched off. Contact your service personnel.
The power consumption of the devices connected to the Measurement Link (MSL) cable is much too
high or there has been a short circuit. The MSL has been switched off. Contact your service personnel.
82
Page 83

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
No Central Monit.
INOP tone
No ECG at Central The ECG measured with the monitor ECG is not being sent to the Information Center via the
OtherMon INOP
!! OtherMon INOP
!!! OtherMon INOP
Rem.AlarmDev.Malf.
INOP tone
Settings Malfunct
INOP tone
Speaker Malfunct
INOP tone
SRR Incompatible
INOP tone
SRR Interference
INOP tone
SRR Invalid Chan
INOP tone
SRR Malfunction
INOP tone
TAAP Disabled
INOP tone
Tele Config Unsupp
INOP tone
Tele ECG Malfunct.
Numeric is displayed with a -?INOP tone
Tele Equip Malf
INOP tone
Tele Incompatible SRR-enabled telemetry device is not supported by this central software revision. Please check
Tele INOP
!! Tele INOP
!!! Tele INOP
Tele Unsupported
INOP tone
TimeExpired:<Timer
Label>
INOP tone
T-Mon INOP
!! T-Mon INOP
!!! T-Mon INOP
INOP tone
TransportEquipment The equipment is ready for transport. See the Equipment window for details.
There is a problem with the communication to the network. Central monitoring is currently not
possible (no patient alarms or information). Check the connection. In case the connection is via a
telemetry device, the current telemetry use model does not support central monitoring. Contact your
service personnel.
telemetry device.
Another monitor assigned to the patient (e.g. a transport monitor) is in an INOP condition. Check the
detailed INOP information at the Information Center and resolve the INOP condition(s) at the other
monitor.
There is a problem with the connection to the remote alert device. Contact your service personnel to
check the remote alert device and its connections.
The monitor cannot use the predefined settings for monitoring. Contact your service personnel.
Contact your service personnel to check the speaker and the connection to the speaker.
The short range radio component has compatibility problems. Contact your service personnel.
The short range radio connection has interference from another device. Try using another channel.
The channel configuration of the Short Range Radio is invalid. Check channel and channel mask
configuration.
Malfunction in the short range radio device. If the INOP persists contact your service personnel.
The currently selected telemetry configuration on the monitor does not allow connection of telemetry
devices to the monitor.
Telemetry Workflow configuration not supported. Check revision and configuration of monitor and
central.
Contact your service personnel.
The ECG in the Telemetry device is faulty.
The telemetry device has a malfunction. Disconnect and reconnect the telemetry device. If the INOP
reappears, replace the telemetry device.
configuration.
A telemetry device assigned to the patient is in an INOP condition. Check the detailed INOP
information at the Information Center and resolve the INOP condition(s) at the telemetry device.
This telemetry device is not supported for direct connection to the monitor.
The time has expired for the timer indicated in the INOP text. Clearing the timer clears the INOP.
A transport monitor assigned to the patient is in an INOP condition. Check the detailed INOP
information at the Information Center and resolve the INOP condition(s) at the transport monitor.
83
Page 84

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
Unsupported LAN
INOP tone
User I/F Malfunct
INOP tone
There is a problem with the communication to the network and central monitoring is currently not
possible. Check the connection. If the INOP persists, switch off the monitor and contact your service
personnel.
Perform a visual and functional check of all the monitor input devices. Contact your service personnel.
Battery INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
Batt 1 Missing
Batt 2 Missing
INOP tone
During this INOP, alarms cannot
be paused or switched off.
Batt Empty
!!Batt Empty
!!!Batt Empty
INOP tone, battery LED flashes
During this INOP, alarms cannot
be paused or switched off.
Batt Extensn Malf
INOP tone
Batt Incompat
INOP tone
Batt Low
INOP tone
Batt Malfunction
INOP tone, battery LED flashes
During this INOP, alarms cannot
be paused or switched off unless
the monitor is connected to
mains power.
Batteries Empty
!!Batteries Empty
!!!Batteries Empty
Batt 1 Empty
!!Batt 1 Empty
!!!Batt 1 Empty
Batt 2 Empty
!!Batt 2 Empty
!!!Batt 2 Empty
INOP tone, battery LED flashes
During this INOP, alarms cannot
be paused or switched off.
Batteries Incompat
Batt 1 Incompat
Batt 2 Incompat
INOP tone
Batteries Low
Batt 1 Low
Batt 2 Low
INOP tone
The monitor requires two batteries but can detect only one battery. Insert the missing battery
immediately.
The estimated remaining battery-powered operating time is less than 10 minutes. Replace the battery
immediately.
If the condition persists and the monitor is not connected to mains power, this INOP is re-issued two
minutes after you acknowledge it.
There is a hardware error in the Battery Extension. Contact your service personnel.
The battery cannot be used with this monitor. Replace with the correct battery as specified in this
book.
The estimated battery-powered operating time remaining is less than 20 minutes.
The monitor cannot determine the battery status. If this INOP persists, replace the faulty battery. If
the condition persists and the monitor is not connected to mains power, this INOP is re-issued two
minutes after you acknowledge it.
Place the battery in a different monitor or in a battery charger. If the same INOP is shown, contact
your service personnel.
The estimated remaining battery-powered operating time of the indicated battery or batteries is less
than 10 minutes. Replace the batteries immediately.
If the condition persists and the monitor is not connected to mains power, this INOP is re-issued two
minutes after you acknowledge it.
The indicated battery or batteries cannot be used with this monitor. Replace with the correct battery or
batteries as specified in this book.
The estimated battery-powered operating time remaining is less than 20 minutes.
84
Page 85

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
Batteries Malfunct
Batt 1 Malfunction
Batt 2 Malfunction
INOP tone, battery LED flashes
During this INOP, alarms cannot
be paused or switched off unless
the monitor is connected to
mains power.
Charge Batt 1 now
Charge Batt 2 now
INOP tone
Charger Malfunct
INOP tone, battery LED may
flash
Check Batt Temp
INOP tone
Chk MSL Connection Check the MSL connection between X2/MP2 and the battery extension for damage or loose
ExtBat Empty
!!ExtBat Empty
!!!ExtBat Empty
INOP tone, battery LED flashes
During this INOP, alarms cannot
be paused or switched off.
ExtBat Incompat The battery in the battery extension cannot be used. Replace with the correct battery as specified in
ExtBat Low The estimated battery-powered operating time remaining is less than 20 minutes.
ExtBat Malfunction
INOP tone, battery LED flashes
During this INOP, alarms cannot
be paused or switched off unless
the monitor is connected to
mains power.
ExtBat Missing There is no battery in the Battery Extension
!! Insert Battery
Severe yellow INOP tone
During this INOP, alarms cannot
be paused or switched off.
MSL Power High The power consumption of the devices connected to the Battery Extension is too high. If this
MSL Power Off The power consumption of the devices connected to the Battery Extension was too high for too long.
The monitor cannot determine the battery status. If this INOP persists, replace the faulty battery or
batteries. If the condition persists and the monitor is not connected to mains power, this INOP is reissued two minutes after you acknowledge it.
Place the batteries in a different monitor or in a battery charger. If the same INOP is shown, contact
your service personnel.
Battery must be charged. Connect the monitor to mains power or exchange the battery.
There is a problem with the battery charger in the monitor. Connect the monitor to mains power and
contact your service personnel.
The temperature of one or both batteries is too high. Check that ventilation openings (if applicable)
are not blocked and monitor is not exposed to heat.
connections. Check also if a second X1 or X2 has been connected accidentally (e.g. in companion
mode).
The estimated battery-powered operating remaining time is less than 10 minutes. Replace the battery in
the battery extension immediately.
If the condition persists and the monitor is not connected to mains power, this INOP is re-issued two
minutes after you acknowledge it.
this book.
The monitor cannot determine the status of the battery in the battery extension. If this INOP persists,
replace the faulty battery in the battery extension. If the condition persists and the monitor is not
connected to mains power or a host monitor, this INOP is re-issued two minutes after you
acknowledge it.
X2/MP2 only: There is no battery in the battery compartment. You cannot operate the monitor on
AC mains or battery extension while the battery compartment is open (not sealed with a battery). Load
a battery immediately.
situation continues, the Battery Extension will be switched off. Contact your service personnel.
The Battery Extension has been switched off. Contact your service personnel.
MMS, MMS Extensions and FMS INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
FMS Unplugged
INOP tone
Make sure that the Flexible Module Rack is connected to the monitor. All FMS measurements are off
while the FMS is unplugged.
85
Page 86

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
FMS Unsupported
INOP tone
MMS Ext. Unplugged
INOP tone
MMS Ext. Unpowered
INOP tone
MMS Ext. Unsupp
INOP tone
MMS Ext.Equip Malf
INOP tone
MMS Unplugged
INOP tone
MMS Unsupported
INOP tone
MMS/FMS Unsupportd
INOP tone
No PPV from FMS The measurement device does not supply a beat-to-beat arterial pressure value. Contact your service
No PPV from MMS The measurement device does not supply a beat-to-beat arterial pressure value. Contact your service
The Flexible Module Rack is not supported by your monitor. Contact your service personnel.
The MMS extension has been disconnected from the Multi-Measurement Module.
The MMS extension cannot operate while the Multi-Measurement Module is running on battery
power.
The MMS extensions not supported by your monitor. Contact your service personnel.
Loss of communication between the Multi-Measurement Module and the MMS extension. Contact
your service personnel.
Make sure that the Multi-Measurement Module is connected to the monitor. All MMS measurements
are off while the MMS is unplugged.
The Multi-measurement Module is not supported by your monitor. Contact your service personnel.
The Multi-Measurement module is not supported by the monitor. Contact your service personnel.
personnel.
personnel.
Display INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
Indep.Dsp Malfunc. There is a problem with the Independent Display. Check the MSL coupling cable then contact your
service personnel.
Indep.Dsp NotSupp. The monitor does not support a second main display. The monitor software is incompatible. Contact
your service personnel.
Intell.Dsp Malf. There is a problem with the Intelligent Display. Check the MSL coupling cable then contact your
service personnel.
Intell.Dsp Missing The monitor has lost contact with the connected Intelligent Display. Contact your service personnel.
Intell.Dsp Unsupp. The monitor does not support the connected Intelligent Display. The monitor software is
incompatible.
ECG, Arrhythmia, QT and ST INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
C Lead Off
HR Numeric is replaced
by -?- for 10 seconds.
INOP tone
Cannot Analyze ECG The arrhythmia algorithm cannot reliably analyze the ECG data. Check the ECG signal quality of the
The C electrode (AAMI: V electrode) has become detached from the patient or the lead set has been
changed. Reattach the electrode or select New Lead Setup in the Setup ECG menu to confirm the
new lead set.
selected primary and secondary leads. If necessary, improve lead position or reduce patient motion.
If you have arrhythmia analysis on, and you are not getting a reliable HR because the signal is below a
minimum amplitude, unstable, or contains artifact, and you have tried to improve the system
performance by choosing another lead and changing electrodes, you should consider turning
arrhythmia analysis off.
86
Page 87

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
Cannot Analyze QT The QT algorithm cannot generate a valid QT value for more than 10 minutes, or 1 minute in the
initial phase.
Cannot Analyze ST The ST algorithm cannot generate a valid ST value. Possible causes are large variations in the measured
ST values for consecutive beats, or ventricular paced beats. Review the ECG signal quality and the ST
measurement points.
If the patient has a ventricular pacemaker, ST analysis is not possible.
Cannot Analyze STE The STE algorithm cannot generate valid ST elevation values. Possible causes are large variations in
the measured ST values for consecutive beats, or ventricular paced beats. Review the ECG signal
quality and the ST measurement points.
ECG Equip Malf
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<ECG Lead> Lead Off
!! <ECG Lead> Lead Off
!!! <ECG Lead> Lead Off
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
ECG Leads Off
!! ECG Leads Off
!!!ECG Leads Off
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
ECG Noisy Elec <ECG
Lead>
ECG Noisy Signal
INOP tone
ECG Out Equip Malf
INOP tone
!!ECG/Ar AlarmsOff All ECG alarms have been switched off, or the HR alarm source is not ECG. To resume ECG alarm
ECG/Arrh AlarmsOff
!!ECG/Ar AlarmsOff
LA Lead Off
Numeric is replaced by -?- for
10 seconds.
INOP tone
LL Lead Off
Numeric is replaced by -?- for
10 seconds.
INOP tone
RA Lead Off
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
RL Lead Off
Numeric is replaced by -?- for
10 seconds.
INOP tone
Some ECG AlarmsOff This message appears (if configured to do so) when the on/off settings of the yellow arrhythmia
Contact your service personnel.
The ECG hardware is faulty.
Not all the required leads for ECG monitoring are connected. Check the ECG connections and make
sure that the electrode indicated by <ECG lead> [RA, LA, LL, RL, V or C] electrodes is attached. In
EASI mode, all 5 electrodes must be connected.
Check that all of the required ECG leads are attached, and that none of the electrodes have been
displaced. The INOP may also be caused by a saturated or overloaded ECG amplifier.
The ECG signal from the named ECG electrodes [RA, LA, LL, RL, V (or C)] is noisy. Check the ECG
connections and make sure that the electrode indicated is attached.
The ECG signal is too noisy. Check that the electrodes are properly placed and have not dried out.
Remove any possible sources of signal noise (such as power cords) from the area around the cable and
the patient.
The ECG signal may be saturated or overloaded.
There is a problem with the device connected to the ECG Out connector. Contact your service
personnel.
generation, switch ECG alarms on or select ECG as the alarm source.
All ECG alarms have been switched off, or the HR alarm source is not ECG. To resume ECG alarm
generation, switch ECG alarms on or select ECG as the alarm source.
The LA electrode has become detached from the patient or the lead set has been changed. Reattach
the electrode or select New Lead Setup in the Setup ECG menu to confirm the new lead set.
The LL electrode has become detached from the patient or the lead set has been changed. Reattach the
electrode or select New Lead Setup in the Setup ECG menu to confirm the new lead set.
The RA electrode has become detached from the patient or the lead set has been changed. Reattach
the electrode or select New Lead Setup in the Setup ECG menu to confirm the new lead set.
The RL electrode has become detached from the patient or the lead set has been changed. Reattach
the electrode or select New Lead Setup in the Setup ECG menu to confirm the new lead set.
alarms differ from the current Profile.
87
Page 88

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
V Lead Off
Numeric is replaced by -?- for
10 seconds.
INOP tone
The V electrode (IEC: C electrode) has become detached from the patient or the lead set has been
changed. Reattach the electrode or select New Lead Setup in the Setup ECG menu to confirm the
new lead set.
Pulse INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
Pulse Not Alarming
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
Pulse has no alarming because the system pulse is measured by an external device. Select another pulse
source to enable pulse alarming.
Resp INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
Resp Equip Malf
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
Resp Erratic
Numeric is replaced by -?-
Resp Leads Off
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
Contact your service personnel. The RESP hardware is faulty.
The monitor has detected too many artifacts in the measured Resp signal. Check that the RA and LL
electrodes are correctly attached and have not dried out.
Not all the required leads for Resp monitoring are attached. Make sure that the RA and LL leads are
attached.
NBP INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
!! Cuff Not Deflat
!!!Cuff Not Deflat
Numeric is displayed with a -?Severe yellow/red INOP tone
During this INOP, alarms cannot
be paused or switched off.
!! Cuff Overpress
!!!Cuff Overpress
Numeric displayed with a -?Severe yellow/red INOP tone
During this INOP, alarms cannot
be paused or switched off.
NBP Deactivated
INOP tone
NBP Equip Malf
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
Remove the cuff from the patient. Make sure that the tubing is not kinked or twisted and that the
correct patient category is selected. Try repeating the measurement.
You can silence the INOP, but the INOP message remains visible until the next NBP measurement is
started or the Stop All SmartKey is selected.
[Adult or pediatric patients: The NBP cuff pressure has exceeded 15 mmHg (2 kPa) for more than
3minutes.
Neonatal patients: The NBP cuff pressure has exceeded 5 mmHg (0.7 kPa) for more than 90 seconds.]
The NBP cuff pressure exceeds the overpressure safety limits. Remove the cuff from the patient. Make
sure that the tubing is not kinked or twisted and that the correct patient category is selected. Try
restarting the measurement.
You can silence this INOP, but the INOP message remains visible until the next measurement is
started or the Stop All SmartKey is selected.
The NBP measurement label in the measurement device has been deactivated by deactivating the label
in the Measurement Selection window. The measurement automatically disappears from the
display. To switch the measurement on again, reactivate the measurement label in the Measurement
Selection window.
Remove the cuff from the patient. The NBP hardware is faulty. Contact your service personnel.
You can silence this INOP, but the INOP message remains visible until the next measurement is
started or the Stop All SmartKey is selected.
88
Page 89

INOP Message, Indication What to do
NBP Interrupted
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
NBP Measure Failed
Numeric may be displayed with
a-?INOP tone
Check the tubing and cuff for leakages or kinks. Check that you are using the correct cuff size and
placement, and that the correct patient category is selected. Try restarting the measurement.
If the INOP occurs repeatedly, contact your service personnel.
You can silence this INOP, but the INOP message remains visible until the next measurement is
started or the Stop All SmartKey is selected.
This INOP arises when the measurement needed longer than the maximum time for inflation,
deflation or the total measurement.
Check that you are using the correct cuff size and placement, and that the correct patient category is
selected. Try restarting the measurement.
You can silence this INOP, but the INOP message remains visible until the next measurement is
started or the Stop All SmartKey is selected.
Check the condition and suitability of the patient for NBP monitoring. Use another cuff to continue
measuring.
Temperature INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
T1, T2, T3, T4 INOPs See <Temp Label> INOPs
Tamb INOPs See <Temp Label> INOPs
Tart INOPs See <Temp Label> INOPs
Tcereb INOPs See <Temp Label> INOPs
Tcore INOPs See <Temp Label> INOPs
<Temp Label>
Deactivated
INOP tone
<Temp Label> Equip Malf
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<Temp
Label>NoTransducer
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<Temp Label> Overrange
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<Temp Label> Unplugged
INOP tone
Tesoph INOPs See <Temp Label> INOPs
Tnaso INOPs See <Temp Label> INOPs
Trect INOPs See <Temp Label> INOPs
Tskin INOPs See <Temp Label> INOPs
Ttymp INOPs See <Temp Label> INOPs
A Temp measurement label in the measurement device has been deactivated, either by connecting a
Pressure transducer in the shared Press/Temp socket, or by deactivating the label in the
Measurement Selection window.
The measurement automatically disappears from the display.
To switch the measurement on again, either reconnect a Temp transducer or reactivate the
measurement label in the Measurement Selection window.
Contact your service personnel.
The temperature hardware is faulty.
Make sure the TEMP probe is connected to the MMS or module.
If you silence this INOP, the measurement will be switched off.
Try changing the application site of the transducer.
[The temperature is less than -1°C, or greater than 45°C.]
A Temp measurement label has been deactivated, either by unplugging a module, or by deactivating
the label in the Measurement Selection window.
The measurement automatically disappears from the display.
To switch the measurement on again, either replug the module or reactivate the measurement label in
the Measurement Selection window.
4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
89
Page 90

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
Tven INOPs See <Temp Label> INOPs
Tvesic INOPs See <Temp Label> INOPs
SpO2 INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
<SpO₂ Label> Chk Sensor The condition of the signal at the SpO
Check proper application of the sensor in accordance with the Instructions for Use. If the INOP
persists, consider exchanging the sensor.
<SpO₂ Label> Deactivated
INOP tone
The SpO
in the Measurement Selection window. The measurement automatically disappears from the
measurement label in the measurement device has been deactivated by deactivating the label
2
display. To switch the measurement on again, reactivate the measurement label in the Measurement
Selection window.
<SpO₂ Label> Equip Malf
Numeric is replaced by -?-
The MMS or module is faulty. Unplug and replug the MMS or module. If the INOP persists, contact
your service personnel.
INOP tone
<SpO₂ Label> Erratic
Numeric is replaced by -?-
Check the sensor placement. Try another adapter cable and sensor. If the INOP persists, contact your
service personnel.
INOP tone
<SpO₂ Label>
Extd.Update
The update period of displayed values is extended due to an NBP measurement on the same limb or
an excessively noisy signal.
Numeric is replaced by -?(questionable numeric)
<SpO₂ Label>Interference
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<SpO₂ Label> Low Perf
Numeric is replaced by -?-
There is too much interference, caused by a high level of ambient light and/or electrical interference.
Cover the sensor to minimize ambient light. If the INOP persists, make sure that the sensor cable is
not damaged or positioned too close to power cables.
Accuracy may be compromised due to very low perfusion. Stimulate circulation at sensor site. If INOP
persists, change the measurement site.
(questionable numeric)
<SpO₂ Label> No Pulse
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<SpO₂ Label> No Sensor
Numeric is replaced by -?-
Check the perfusion at measurement site. If necessary, stimulate circulation or change measurement
site. If the INOP is due to NBP measurement on the same limb, wait until the NBP measurement is
finished.
Make sure the SpO
sensor is connected. If the INOP persists, try another adapter cable and sensor. If
2
you silence this INOP, the measurement will be switched off.
INOP tone
<SpO₂ Label> NoisySignal
Numeric is replaced by -?-
Excessive patient movement or electrical interference is causing irregular pulse patterns. Try to reduce
patient movement or to relieve the cable strain on the sensor.
INOP tone
<SpO₂ Label> Poor Signal
Numeric is replaced by -?-
The signal condition of the SpO
measurement is poor and measurement accuracy may be
2
compromised. If the INOP persists, consider changing the application site or using another sensor.
(questionable numeric)
<SpO₂ Label> Pulse?
The detectable pulsations of the SpO
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<SpO₂ Label> Searching
Numeric unavailable
<SpO₂ Label> Sensor Malf
Numeric is replaced by -?-
SpO
is analyzing the patient signal to derive Pulse, SpO2 and Perf values. Please wait until the search
2
analysis is complete.
The SpO
sensor or adapter cable is faulty. Try another adapter cable and sensor. If the INOP persists,
2
contact your service personnel.
INOP tone
sensor is not as expected. Accuracy may be compromised.
2
signal are outside the specified pulse rate range.
2
90
Page 91

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
<SpO₂ Label> Sensor Off
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<SpO₂ Label>
Unkn.Sensor
Numeric is replaced by -?-
<SpO₂ Label> Unplugged
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<SpO₂ Label> Upgrade
Numeric is replaced by -?Numeric is unavailable
The SpO2 sensor is not properly applied to the patient. Apply the sensor following the instructions
supplied by the manufacturer.
The connected sensor or adapter cable is not supported by the SpO
sensors and cables.
An SpO
the label in the Measurement Selection window.
The measurement automatically disappears from the display.
To switch the measurement on again, either replug the module or reactivate the measurement label in
the Measurement Selection window.
The SpO
measurement label has been deactivated, either by unplugging a module, or by deactivating
2
measurement is currently in upgrade mode. Monitoring is not possible in this mode.
2
measurement. Use only specified
2
Pressure INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
ABP INOPs See <Press Label> INOPs
Ao INOPs See <Press Label> INOPs
ART INOPs See <Press Label> INOPs
BAP INOPs See <Press Label> INOPs
CPP Chk Sources
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
CPP Chk Units
Numeric is replaced by -?-
CPP Disabled CPP has been disabled, either in the setup in Configuration mode, or by loading settings with CPP
CVP INOPs See <Press Label> INOPs
FAP INOPs See <Press Label> INOPs
IC1 / IC2 INOPs See <Press Label> INOPs
ICP INOPs See <Press Label> INOPs
LAP INOPs See <Press Label> INOPs
P / P1 / P2 / P3 / P4 INOPs See <Press Label> INOPs
PAP INOPs See <Press Label> INOPs
PPV bad <Press Label>
Signal
PPV bad Signal
at Information Center
PPV Chk Sources The arterial pressure source selected for PPV is unplugged or switched off. When this INOP has
<Press Label> Artifact
Numeric questionable
Not all measurements or values required to perform the calculation are available. Check the
measurement sources.
The monitor has detected a conflict in the units used for this calculation. Check the unit settings.
disabled. This can happen when changing from a pediatric or neonatal profile to an adult profile, as the
default profile settings have the CPP measurement disabled in the adult profile and enabled in the
pediatric and neonatal profiles. Enable CPP in the current profile to clear the INOP.
The arterial pressure source selected for PPV is not providing a pulsatile signal.
The arterial pressure source selected for PPV is not providing a pulsatile signal.
displayed for 1 minute PPV will be switched off.
A non-physiological event (flush or blood sample) is detected. A resulting limit alarm or non-pulsatile
INOP will be suppressed.
91
Page 92

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
<Press Label> Deactivated
INOP tone
<Press Label> Equip Malf
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<Press Label> No Pulse
Pulse numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<Press Label> No
Transducer
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<Press Label> Noisy
Signal
Pulse numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<Press Label> Overrange
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<Press Label> Reduce
Size
<Press Label> Unplugged
INOP tone
<Press Label>
Zero+Check Cal
Numeric is replaced by -?-
RAP INOPs See <Press Label> INOPs
UAP INOPs See <Press Label> INOPs
UVP INOPs See <Press Label> INOPs
A Pressure measurement label in the measurement device or extension has been deactivated, either by
connecting a Temp transducer in the shared Press/Temp socket, or by deactivating the label in the
Measurement Selection window.
The measurement automatically disappears from the display.
To switch the measurement on again, either reconnect a Pressure transducer or reactivate the
measurement label in the Measurement Selection window.
Contact your service personnel.
The pressure hardware is faulty.
This INOP can only arise when a pressure is selected as the pulse source. It occurs when the pulse rate
being measured is less than 25 beats per minute or the amplitude is less than three mmHg.
Check the catheter and connections to the patient.
Make sure that the pressure transducer is connected to the measurement device or module.
If you silence this INOP, the measurement will be switched off.
This INOP can only arise when a pressure is selected as the pulse source. It occurs when the pulse
detector finds a pulse rate above 350 bpm. This is usually caused by movement artifact or electrical
interference.
Make sure that the measurement has been properly prepared and zeroed, and that the transducer is
level with the heart. If this INOP persists, try another transducer.
Possible causes are a measured pressure outside the allowed pressure range, or a broken wire to the
transducer.
Increase the scale for the pressure wave.
A Pressure measurement label has been deactivated, either by unplugging a module, or by deactivating
the label in the Measurement Selection window.
The measurement automatically disappears from the display.
To switch the measurement on again, either replug the module or reactivate the measurement label in
the Measurement Selection window.
Perform a zero and check the calibration of the transducer.
CO2 INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
CO₂ Auto Zero
Numeric is replaced by -?if the Autozero lasts >15 sec,
INOP tone sounds.
CO₂ Cal Failed
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
92
The automatic zero calibration is in progress. This typically takes 10 seconds. During this time the CO
values may not be updated, or they may be replaced by -?-. Wait until the zero calibration is complete
to resume monitoring.
Make sure that the Cal cell was changed between CAL1 and CAL2. Repeat the calibration. If the
INOP reappears, try another transducer. If the INOP persists, contact your service personnel.
2
Page 93

INOP Message, Indication What to do
CO₂ Cal Mode
numeric displays current
CO
2
Currently no calibration is running. Accuracy can be checked by placing the transducer on the two cells
of the calstick and starting calibration. To start monitoring, leave Cal. Mode.
CO2 value for accuracy check
CO₂ Cal Running
Wait until calibration is finished.
Numeric is replaced by -?-
CO₂ Check Cal
Numeric is replaced by -?-
The CO
and, if necessary, recalibrate the transducer.
value is outside the measurement range. Perform an accuracy check for both calstick cells
2
INOP tone
CO₂ Chk Adapter
Numeric is replaced by -?-
Check that the sensor is connected to the airway adapter, clean the airway adapter, if necessary.
Perform a zero calibration. If the INOP persists, contact your service personnel.
INOP tone
CO₂ Deactivated
INOP tone
The CO
in the Measurement Selection window. The measurement automatically disappears from the
measurement label in the measurement device has been deactivated by deactivating the label
2
display. To switch the measurement on again, reactivate the measurement label in the Measurement
Selection window.
CO₂ Equip Malf
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
CO₂ No Sensor
from M3014A
The Measurement Extension is faulty. Unplug and replug the Multi-Measurement Module with
Extension. If you are using the mainstream method, unplug and replug the transducer or try another
transducer. If the INOP persists, contact your service personnel.
There is no CO
off.
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
CO₂ No Tubing
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
!! CO₂ Occlusion
!!! CO₂ Occlusion
Either the sample line is disconnected, or an incorrect line is attached. Check the connection. If
necessary, connect another sample line (Use only the approved accessories).
If you silence this INOP, the measurement will be switched off.
The sample line or exhaust tube is blocked. Check the tubing, then disconnect and reconnect the
sample line. If the INOP persists, connect a new sample line.
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
CO₂ Overrange
Numeric is replaced by -?-
The CO
service personnel.
value is higher than the measurement range. If you suspect a false high value, contact your
2
INOP tone
CO₂ Pump Off
Numeric is replaced by -?-.
CO₂ Purging
Numeric is replaced by -?-
The pump has been switched off for fifteen minutes. To switch it on again, select Pump On in the
Setup CO₂ menu.
The Filterline is being purged to remove an occlusion in the line or airway adapter. If the occlusion is
removed, the INOP will disappear. If not, the INOP CO₂ Occlusion is displayed.
INOP tone
CO₂ Sens Warmup
Wait until the sensor reaches operating temperature and the INOP disappears.
Numeric is replaced by -?Microstream CO
: INOP tone
2
Mainstream CO2: no INOP tone
CO₂ Upgrade FWNumeric is replaced by -?-
The software in the Measurement Extension does not match the software in the MMS. Contact your
service personnel.
INOP tone
CO₂ Wait Cal2
Numeric is replaced by -?-
CO₂ Zero Failed
Numeric is replaced by -?-
Calibration on the first calstick cell is complete. Place the transducer on the other calstick cell and start
the CAL2 calibration cycle.
An error occurred during the last zero calibration. Check the airway adapter and clean, if necessary.
Perform another zero calibration. If the INOP persists, contact your service personnel.
INOP tone
CO₂Change Scale The CO
wave is clipped. Select a more appropriate wave scale to display the whole wave.
2
4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
sensor connected. If you silence this INOP the CO2 measurement will be switched
2
93
Page 94

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
CO₂NoTransducer
from mainstream CO
(except
2
There is no CO
calibrated. If you silence this INOP the CO
transducer connected. If you replace the transducer, the new transducer must be
2
measurement will be switched off.
2
M3014A)
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
CO₂Zero Running Wait until zero calibration is finished.
CO₂ZeroRequired
Perform zero calibration for the CO2 sensor. If the INOP persists, contact your service personnel.
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
IPI Check Pat. Age For Adult patients: a date of birth has been entered that results in a calculated patient age of less than
12 years. Enter correct date of birth or, if patient is pediatric, correct patient category.
For pediatric patients: either no date of birth has been entered (it is required for calculation of IPI for
pediatric patients) or the calculated age is below 1 year or above 12 years. Check that correct date of
birth is entered.
IPI Check Sources The IPI numeric cannot be provided as one or more of the measurement sources required for IPI is
not available. Check availability of etCO
, awRR, SpO2, and pulse rate.
2
IPI Neo Patient ? Check patient category. The IPI numeric is not available for neonatal patients.
SO2 INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
<SO₂ Label> Cal Failed
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<SO₂ Label>Cal Required
Numeric is replaced by -?-
The calibration failed. Check the catheter-to-Optical-Module connection. Manually restart the
calibration. Try another catheter and Optical Module. If the catheter is already inserted, perform an in-
vivo calibration.
There is no valid calibration data in the Optical Module. Perform either a pre-insertion or an in-vivo
calibration.
INOP tone
<SO₂ Label> Cal. Mode
Numeric is replaced by -?-
Pre-insertion calibration is complete, but the catheter tip is still inside the optical reference. The
catheter is now ready for insertion.
INOP tone
<SO₂ Label> Cannot Meas
Numeric is replaced by -?-
The signal is out of the normal range, and no oxygen saturation can be derived. Perform an in-vivo
calibration. If the INOP persists, try another Optical Module and catheter.
INOP tone
<SO₂ Label>Config Error
Numeric is replaced by -?-
The Optical Module has been configured to SaO
menu to reconfigure to venous saturation mode.
Mode. Use Change to Venous in the setup
2
INOP tone
<SO₂ Label> Conn
OptMod
The Optical Module was disconnected during data storage. Reconnect the Optical Module for at least
20 seconds.
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<SO₂ Label> Equip Malf
Numeric is replaced by -?-
The SO
SvO
/SvO2 Module or Optical Module is faulty. Unplug and replug the Optical Module and SO2/
2
module. Exchange the modules. If the INOP persists, contact your service personnel.
2
INOP tone
<SO₂ Label> Incompat.
The SO
Module or Optical Module is not supported. Contact your service personnel.
2
INOP tone
<SO₂ Label> In-Vivo Cal The in-vivo calibration is not yet complete. Lab values must be stored to the Optical Module to
complete the calibration. Either continue with the next steps of the current calibration or recall the
previous calibration.
94
Page 95

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
<SO₂ Label>Light Intens
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<SO₂ Label> Low Light
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<SO₂ Label> No OptMod
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<SO₂ Label> OptMod Malf The Optical Module memory is faulty, and calibration data cannot be stored for transport or during
<SO₂ Label> Pre-Ins Cal
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<SO₂ Label> Unplugged
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<SO₂ Label> Upgrade
INOP tone
<SO₂ Label> Warmup
Numeric is replaced by -?-
The intensity changed considerably since the last light intensity calibration. This may indicate that the
catheter tip is positioned against a blood vessel wall or that there is low blood flow. Reposition the
catheter (and perform a Light Intensity Calibration).
The optical signal levels are too low. Check that the catheter is either in the optical reference or
inserted into the patient. Check the catheter-to-Optical Module connection. If INOP persists, try
another catheter and Optical Module.
Connect the Optical Module. If the INOP persists, try another Optical Module. Silencing this INOP
switches the measurement off.
power failure. If this capability is needed, use another Optical Module.
The pre-insertion calibration is running. This typically takes one minute. During this time alarms are
switched off. Wait until the calibration is complete.
Measurement switched on and SO
The SO
Monitoring is not possible in this mode.
The Optical Module has not yet reached the operating temperature. Wait a few minutes until warm-up
is finished.
module is currently in upgrade mode.
2
/SvO2 module unplugged from the rack.
2
C.O. INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
C.O. Deactivated
INOP tone
C.O. Equip Malf
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
C.O. Unplugged
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
CCI No BSA
CCI numeric unavailable
INOP tone
CCO BadPressSignal
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
CCO No Calibration
Numeric is replaced by -?-
CCO No <Press Label>
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone may sound
The Cardiac Output measurement label in the measurement device has been deactivated by
deactivating the label in the Measurement Selection window. The measurement automatically
disappears from the display. To switch the measurement on again, reactivate the measurement label in
the Measurement Selection window.
There is a problem with the C.O. hardware. Contact your service personnel.
Plug in the C.O. module. Silencing this INOP switches off the measurement.
CCI cannot be calculated because the patient's body surface area is unknown. Enter the patient weight
and height to provide the BSA for CCI calculation.
The arterial pressure wave can currently not be used for pulse contour calculation for CCO or CCI
measurement. Possible causes are air bubbles in the tubing or a physiological condition, for example
severe arrhythmia.
The CCO measurement is currently not calibrated.
CCO/CCI cannot be calculated. Make sure that the pressure chosen in the Setup CCO menu under
CCO from matches the pressure measured with the arterial catheter for CCO measurement. A
pressure from an external device cannot be used. Select another pressure label, either ABP, Ao, ART,
BA P, FA P, or UA P.
95
Page 96

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
CCO No Press
at Information Center
CCO Not Supported
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
CCO Overrange
CCI Overrange
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
CCO Press Invalid
at Information Center
CCO <Press Label> Invalid
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone may sound
CCO PressOverrange
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
CCO PulseOverrange
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
CCO Recalibrate
Numeric is replaced by -?-
CCO/Tbl NoTransduc
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
Tblood Overrange
Numeric is replaced by -?-
TbloodNoTransducer
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
CCO/CCI cannot be calculated. Make sure that the pressure chosen in the Setup CCO menu under
CCO from matches the pressure measured with the arterial catheter for CCO measurement. A
pressure from an external device cannot be used. Select another pressure label, either ABP, Ao, ART,
BA P, FA P, or UA P.
A catheter for transpulmonary C.O. measurements has been unplugged and replaced with a Right
Heart C.O. catheter, or the measurement mode has been changed manually. Silencing this INOP
switches the measurement off.
The measured CCO or CCI value is not within the specified range for CCO/CCI measurement.
The arterial pressure selected for pulse contour calculation for CCO is available but currently invalid.
Make sure the pressure transducer is connected and the zero calibration is valid.
The arterial pressure selected for pulse contour calculation for CCO is available but currently invalid.
Make sure the pressure transducer is connected and the zero calibration is valid.
The mean value of the arterial pressure values used for pulse contour calculation for CCO is below
0mmHg or above 300mmHg.
The pulse rate of the pressure used for pulse contour calculation for CCO is below 30 bpm or above
240 bpm.
The most recent CCO or CCI calibration was made over 8 hours ago or the arterial pressure
measurement used for CCO calculation has been zeroed after the CCO calibration was performed.
You should recalibrate CCO or CCI with transpulmonary C.O. measurements at least every 8 hours or
when the hemodynamic condition of the patient has changed. The pressure measurement must be
zeroed before a CCO calibration.
No transducer attached to the module or catheter disconnected.
Tblood out of range 17°C - 43°C.
No transducer attached to the module or catheter disconnected.
tcGas INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
<tcGas Label> Cal Failed
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<tcGas Label> Cal
Running
Numeric displays first -?-, then
numeric is displayed with a ?
<tcGas Label>
CalRequired
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
96
A calibration failed. Check the calibration unit, gas pressure, and tubing connections, then restart the
calibration. If the calibration has failed more than once, remembrane the transducer and restart the
calibration. If this INOP persists, contact your service personnel.
Wait until the tcpO
Calibration is required before applying the transducer to the patient.
Insert a membraned transducer into the calibration chamber on the module, connect the calibration
unit to the calibration chamber, open the gas valve and start the calibration. If this INOP occurs
during a calibration, there may be a module or transducer malfunction: contact your service personnel.
/tcpCO2 calibration is finished.
2
Page 97

INOP Message, Indication What to do
<tcGas Label> Change
Site
If Heat Switch Off is
configured to Yes, numeric is
replaced by -?INOP tone
<tcGas Label> Check
Time
<tcGas Label> Equip Malf
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<tcGas
Label>NoTransducer
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
<tcGas Label> Stabilizing
A ? appears next to the label
<tcGas Label> Unplugged
Numeric is replaced by -?INOP tone
Site Timer has timed out. Change the application site to avoid skin burns. To reset the Site Timer,
either calibrate and change the measurement site, or change the measurement site and reset the Site
Timer manually by selecting the appropriate site time from the Setup tcGas menu.
Site Timer due to time out in 15 minutes or less.
There is a malfunction in the transducer or module. Connect another transducer. If this INOP persists,
contact your service personnel.
No transducer is connected to the tcpO
measurement.
The transducer has not yet reached the selected temperature and/or skin hyperemization is not yet
finished. This INOP will disappear within three minutes.
The measurement is switched on but the module is unplugged.
The measurement automatically disappears from the display. Silencing this INOP switches off the
measurement.
4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
/tcpCO2 module. Silencing the alarm switches off the
2
EEG INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
EEG Equip Malf
INOP tone
EEG Impedance High
EEG1 ImpedanceHigh
EEG2 ImpedanceHigh
EEG Line Noise
EEG1 Line Noise
EEG2 Line Noise
EEG Muscle Noise
EEG1Muscle Noise
EEG2Muscle Noise
EEG Unplugged
INOP tone
EEG1 Lead Off <n>
EEG2 Lead Off <n>
[n = electrode]
EEG1 Lead Off
EEG2 Lead Off
at Information Center
EEG1 Leads Off
EEG2 Leads Off
EEG1 Overrange
EEG2 Overrange
EEGNoTransducer
INOP tone
The EEG hardware is faulty. Contact your service personnel.
The signal electrode in one or both channels exceeds the user-selected impedance limit, or the
impedance of a single electrode exceeds the limit. Check the impedance. If the impedance is too high,
reconnect the electrodes according to the EEG monitoring setup guidelines. If the INOP persists,
contact your service personnel.
Excessive line noise has been detected in either channel EEG1 or EEG2, or in both EEG channels.
Keep all cables together and away from metallic bodies, other cables & radiated fields.
Too much power above 30 Hz has been detected in channel EEG1 or EEG2, or both.
Check the Electrode-to-Skin Impedance and reposition the electrode away from possible muscle
activity, if necessary.
Plug in module. Silencing this INOP switches off the measurement.
Reconnect specified electrode.
One or more electrodes are not connected. Check in the EEG Impedance / Montage window on
the monitor which electrode(s) are affected and reconnect the electrodes.
Two or more electrodes are not connected. Check in the EEG Impedance / Montage window
which electrodes are affected and reconnect the electrodes.
Input signal is too high in one or both channels. This is usually caused by interfering signals such as
line noise or electrosurgery.
The trunk cable is disconnected from the EEG plug-in module. Reconnect the trunk cable. Silencing
this INOP switches the measurement off.
97
Page 98

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
BIS INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
BIS Cable Incompat
INOP tone
BIS Cable Usage
INOP tone
BIS DSC Disconnect
INOP tone
BIS DSC Incompat.
INOP tone
BIS DSC Malfunct Electrocautery used during self-test OR malfunction in the DSC hardware.
BIS DSC Upgrade
INOP tone
BIS Electr. Disc.
INOP tone
BIS Engine Disconn
INOP tone
BIS Engine Incomp.
INOP tone
BIS Engine Malfunc
INOP tone
BIS Equip Malf
INOP tone
BIS High Impedance
INOP tone may sound
BIS ImpedanceCheck
INOP tone may sound
BIS IsoelectricEEG No discernible EEG activity is detected for longer than one minute.
BIS Lead Off
INOP tone may sound
BIS Overcurrent
INOP tone
The semi-reusable sensor cable connected is unknown or not supported by your software revision.
Replace it with a Philips-supported sensor cable.
The semi-reusable sensor cable has exceeded the maximum number of uses. Replace the cable.
DSC is not properly connected OR either DSC or BIS engine may be faulty.
Make sure that the DSC is properly connected to the BIS Engine. If INOP persists, replace DSC with
a known good one of the same type.
If INOP persists replace BIS engine.
Silencing this INOP switches the measurement off.
DSC is not supported by the BIS engine or new DSC connected to an old BIS engine. A software
upgrade may be required. Contact your service personnel.
Make sure not to use electrocautery during the self-test procedure. Disconnect and reconnect the DSC
to the BIS engine. If the INOP persists, replace the DSC or contact your service personnel.
DSC update currently being carried out. This INOP will disappear when the DSC update is finished.
Do not disconnect the DSC during the update. No action is needed.
One or more electrodes are not connected to the semi-reusable sensor cable. Check all electrode
connections.
BIS engine not connected OR Module Cable defective.
Make sure that the Module Cable is properly connected. If INOP persists, replace the Module Cable.
Silencing this INOP switches the measurement off.
BIS engine software is not supported. A software upgrade may be required. Contact your service
personnel.
MP20/30 - BIS engine not supported.
Malfunction in the BIS engine hardware. Disconnect and reconnect the BIS engine. If the INOP
persists, replace BIS engine.
There is a malfunction in the BIS hardware. Unplug and replug the BIS module. If the INOP persists,
contact your service personnel.
Impedance of one or more electrode(s) is above the valid range, most often caused by bad skin
preparation. Check the sensor montage and press the electrode pads firmly. If this INOP persists,
replace the sensor(s) in question using correct skin preparation.
If INOP persists, contact your service personnel.
The Cyclic Impedance check is running. It will stop automatically if all impedances are within the valid
range. If any electrodes do not pass the impedance test, check the sensor montage and press the
electrode pads firmly.
To manually stop the Cyclic Impedance Check, select Sensor Check off in the Setup BIS menu.
Check the patient. Check that the electrodes are properly connected.
One or more electrodes have no skin contact and therefore impedances cannot be measured. Check
the sensor montage and press the electrode pads firmly.
If this INOP persists, replace the sensor(s) in question, using correct skin preparation.
Unplug and replug the BIS module or, f or the MP20/MP30, disconnect and reconnect the BISx from
the Interface board. If the INOP persists, contact your service personnel.
98
Page 99

INOP Message, Indication What to do
BIS Sensor Disconn
INOP tone
BIS Sensor Incomp.
INOP tone
BIS Sensor Malfunc
INOP tone
BIS Sensor Usage
INOP tone
BIS SQI < 15%
INOP tone
BIS Unplugged
INOP tone
BISx Disconnected
INOP tone
BISx Incompatible
INOP tone
BISx Malfunction
INOP tone
The sensor is not properly connected to the patient interface cable (PIC) and/or the PIC is not
properly connected to the DSC or BISx, or the sensor or PIC or DSC or BISx may be faulty.
Check all the connections.
Disconnect and reconnect the sensor, PIC, DSC, BISx.
If the INOP persists, replace the sensor.
If the INOP persists, replace PIC. If INOP persists, contact your service personnel.
Silencing this INOP switches the measurement off.
Unsupported sensor connected or sensor type unknown or not supported by your software revision.
Replace the sensor, using only Philips supported sensors.
Malfunction in the sensor hardware, most often caused by liquids permeating into the connectors OR
patient interface cable (PIC) or DSC or BISx may be faulty.
Replace the sensor. Manually initiate a Cyclic Impedance Check. Make sure all electrodes pass the test.
Make sure that the both sides of the PIC connector (between PIC and sensor) are dry. If you are not
sure that the connector is dry, replace the PIC until it has dried. If this INOP persists, contact your
service personnel.
Excessive sensor usage. Replace sensor.
A Cyclic Impedance Check will start automatically.
If the signal quality is below 15%, no BIS numerics can be derived.
This may occur as a result of artifacts such as those generated from motion or the presence of
electrocautery devices. Make sure the sensor is properly attached to the patient. Manually initiate a
Cyclic Impedance Check. Make sure all electrodes pass the test. Make sure the patient is completely
relaxed (even small motions of the facial muscles affect the signal quality).
Plug in the BIS module. Silencing this INOP switches off the measurement.
The BISx is not connected to the BIS module or the BIS interface board. Silencing this INOP switches
the measurement off.
The BISx software is not compatible with the BIS module or with the MP20/MP30 monitor software.
A software upgrade may be required. Contact your service personnel.
The BISx is faulty. Disconnect and reconnect it to the module or BIS interface board. If the INOP
persists, replace the BISx.
MP20/MP30 - Malfunction on interface board. If the INOP persists, contact your service personnel.
4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
Spirometry INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
AWFChange Scale Airway flow signal exceeds range of selected scale. Adjust scale to display complete wave.
AWPChange Scale Airway pressure signal exceeds range of selected scale. Adjust scale to display complete wave.
AWVChange Scale Airway volume signal exceeds range of selected scale. Adjust scale to display complete wave.
Spiro Alarms Suppr Alarming is suppressed for the spirometry module.
SPIRO Cannot Meas Measurement is at its limit, e.g. ambient pressure out of range.
Spiro Gas Compens? Gas compensation is set to Gas Analyzer but not all gases necessary for compensation are
measured by a gas monitor. Some of the fall-back values provided by the user are used. Measurement
accuracy might be reduced.
Spiro Incompatible Module revision not compatible with the host monitor software revision. Contact your service
personnel.
Spiro Malfunction Module failure detected. Contact your service personnel.
Spiro No Breath No breath was detected for more than 25 seconds. Breath derived numerics are not available.
Spiro No Sensor No sensor detected. Make sure the correct sensor is attached to the breathing circuit.
99
Page 100

4 Patient Alarms and INOPs
INOP Message, Indication What to do
Spiro Patient Cat. Mismatch of patient size configured in the host monitor and sensor type plugged into the module.
Check the instructions on selecting the correct sensor in the chapter on “Spirometry”.
Spiro Purge Failed The purge operation could not be completed successfully. Check for kinked sensor tubings, hard
occlusions and make sure that the pump is running and all valves are switching.
Spiro Purging A purge operation is in progress - no data update on the screen. Wait until purge is complete.
Spiro Unkn. Sensor An unknown sensor ID code was detected. Use only the sensors listed in the “Accessories” chapter.
Spiro Upgrade The module is running a firmware upgrade. Wait until upgrade is completed before resuming
monitoring.
NMT INOPs
INOP Message, Indication Explanation
NMT Alarm Suppress NMT alarms are suppressed until the TOF count reaches zero for the first time.
NMT Cable Disconn
INOP tone
NMT Cable Unknown
INOP tone
NMT Cal Failed The NMT calibration cycle failed. Check that the sensor and the electrodes are placed properly, then
NMT Cal Running An NMT calibration is running. Wait until the calibration is complete.
No patient cable is connected to the NMT measurement module. Silencing this INOP switches the
NMT measurement off.
The patient cable connected to the NMT module is not supported or cannot be identified. Replace it
with a supported cable.
start another calibration. Ensure that patient's arm is kept still before and during the calibration cycle.
If calibration fails again, replace the patient cable. If INOP persists, contact your service personnel.
NMT Cannot Measure
INOP tone
NMT Equip Malfunct
INOP tone
NMT Impedance High The impedance of the NMT stimulation electrodes has exceeded the allowed limit. Check that the
NMT Incompatible
INOP tone
NMT Lead Off
INOP tone
NMT Neo Patient?
INOP tone
NMT Noisy Signal
INOP tone
NMT Overcurrent
INOP tone
NMT Overrange The signal from the acceleration sensor is out of the measurement range. Check that the acceleration
NMT Sensor Malfunc
INOP tone
NMT Upgrade
INOP tone
NMT is unable to reliably derive measurement values. Check that the sensor and the electrodes are
placed properly and start another measurement. If this INOP persists, try another patient cable.
There is a problem with the NMT hardware. Unplug the NMT measurement module then plug it in
again. If the INOP persists contact your service personnel.
electrodes are placed properly, have firm skin contact and have not dried out.
This version of the NMT measurement module is not supported, or the module firmware is
incomplete and needs to be upgraded. Contact your service personnel.
One or both NMT stimulation electrodes have become detached from the patient. Check that both
electrodes have firm skin contact, that the electrodes are placed properly and that the lead wires are
connected.
The NMT measurement does not support neonatal patients. Check the patient category.
The NMT signal is too noisy to derive measurement values reliably. If electrosurgery is currently being
used, repeat the NMT measurement after it has stopped.
The current through the NMT stimulation electrodes is too high. Check that that the patient cable is
not visibly damaged. Disconnect and reconnect the patient cable. If this INOP persists, replace the
cable and/or module.
sensor is positioned properly. If this INOP persists, try another patient cable.
There is a problem with the acceleration sensor of the NMT patient cable. Disconnect and reconnect
the patient cable. If this INOP persists, replace the cable.
An NMT module firmware upgrade is in progress. NMT monitoring is currently not possible. Wait
until the upgrade has completed and this INOP is no longer displayed. Do not unplug the module or
switch off power.
100
 Loading...
Loading...