Page 1

ISP1582
Hi-Speed Universal Serial Bus peripheral controller
Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 Preliminary data
1. General description
The ISP1582 is a cost-optimized and feature-optimized Hi-Speed Universal Serial
Bus (USB) peripheral controller. It fully complies with
Specification Rev. 2.0
full-speed (12 Mbit/s).
The ISP1582 provides high-speed USB communication capacity to systems based
on microcontrollers or microprocessors. It communicates with a microcontroller or
microprocessor of a system through a high-speed general-purpose parallel interface.
The ISP1582 supports automatic detection of Hi-Speed USB system operation.
Original USB fall-back mode allows thedevice to remain operational under full-speed
conditions. It is designed as a generic USB peripheral controller so that it can fit into
all existing device classes, such as imaging class, mass storage devices,
communication devices, printing devices and human interface devices.
Universal Serial Bus
, supporting data transfer at high-speed (480 Mbit/s) and
The internal generic Direct Memory Access (DMA) block allows easy integration into
data streaming applications.
The modular approach to implementing a USB peripheral controller allows the
designer to select the optimum system microcontroller from the wide variety available.
The ability to reuse existing architecture and firmware investments shortens the
development time, eliminates risk and reduces cost. The result is fast and efficient
development of the most cost-effective USB peripheral solution.
The ISP1582 is ideally suited for many types of peripherals, such as: printers,
scanners, digital still cameras, USB-to-Ethernet links, cable and DSL modems. The
low power consumption during suspend mode allows easy design of equipment that
is compliant to the ACPI™, OnNow™ and USB power management requirements.
The ISP1582 also incorporates features such as SoftConnect™, a reduced
frequency crystal oscillator,andintegrated termination resistors. These features allow
significant cost savings in system design and easy implementation of advanced USB
functionality into PC peripherals.
Page 2

Philips Semiconductors
2. Features
■ Complies fully with:
■ Supports data transfer at high-speed (480 Mbit/s) and full-speed (12 Mbit/s)
■ High performance USB peripheral controller with integrated Serial Interface
■ Automatic Hi-Speed USB mode detection and Original USB fall-back mode
■ Supports sharing mode
■ Supports V
■ High-speed DMA interface
■ Fully autonomous and multiconfiguration DMA operation
■ 7 IN endpoints, 7 OUT endpoints and a fixed control IN/OUT endpoint
■ Integrated physical 8 kbytes of multiconfiguration FIFO memory
■ Endpoints with double buffering to increase throughput and ease real-time data
■ Bus-independent interface with most microcontrollers and microprocessors
■ 12 MHz crystal oscillator with integrated PLL for low EMI
■ Software-controlled connection to the USB bus (SoftConnect™)
■ Low-power consumption in operation and power-down modes; suitable for use in
■ Supports Session Request Protocol (SRP) that complies with
■ Internal power-on and low-voltage reset circuits; also supports software reset
■ Operation over the extended USB bus voltage range (DP, DM and V
■ 5 V tolerant I/O pads at 3.3 V
■ Operating temperature range from −40 °C to +85 °C
■ Available in HVQFN56 halogen-free and lead-free package.
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
◆
Universal Serial Bus Specification Rev. 2.0
◆ Most Device Class specifications
◆ ACPI™, OnNow™ and USB power management requirements.
Engine (SIE), Parallel Interface Engine (PIE), FIFO memory and data transceiver
sensing
BUS
transfer
bus-powered USB devices
On-The-Go
Supplement to the USB Specification Rev. 1.0a
)
BUS
3. Applications
■ Personal digital assistant
■ Digital video camera
■ Digital still camera
■ 3G mobile phone
■ MP3 player
■ Communication device, for example: router and modem
■ Printer
■ Scanner.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 2 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 3

Philips Semiconductors
4. Abbreviations
DMA — Direct Memory Access
EMI — ElectroMagnetic Interference
FS — Full-speed
GDMA — Generic DMA
HS — High-speed
MMU — Memory Management Unit
NRZI — Non-Return-to-Zero Inverted
OTG — On-The-Go
PDA — Personal Digital Assistant
PID — Packet IDentifier
PIE — Parallel Interface Engine
PIO — Parallel Input/Output
PLL — Phase-Locked Loop
SE0 — Single-Ended zero
SIE — Serial Interface Engine
SRP — Session Request Protocol
USB — Universal Serial Bus.
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
5. Ordering information
Table 1: Ordering information
Type
number
ISP1582BS HVQFN56 plastic thermal enhanced very thin quad flat package;
Package
Name Description Version
SOT684-1
no leads; 56 terminals; body 8 × 8 × 0.85 mm
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 3 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 4
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 4 of 66
xxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx x xxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxx xxx xxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxx xxxxxx xx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxx xx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx x x
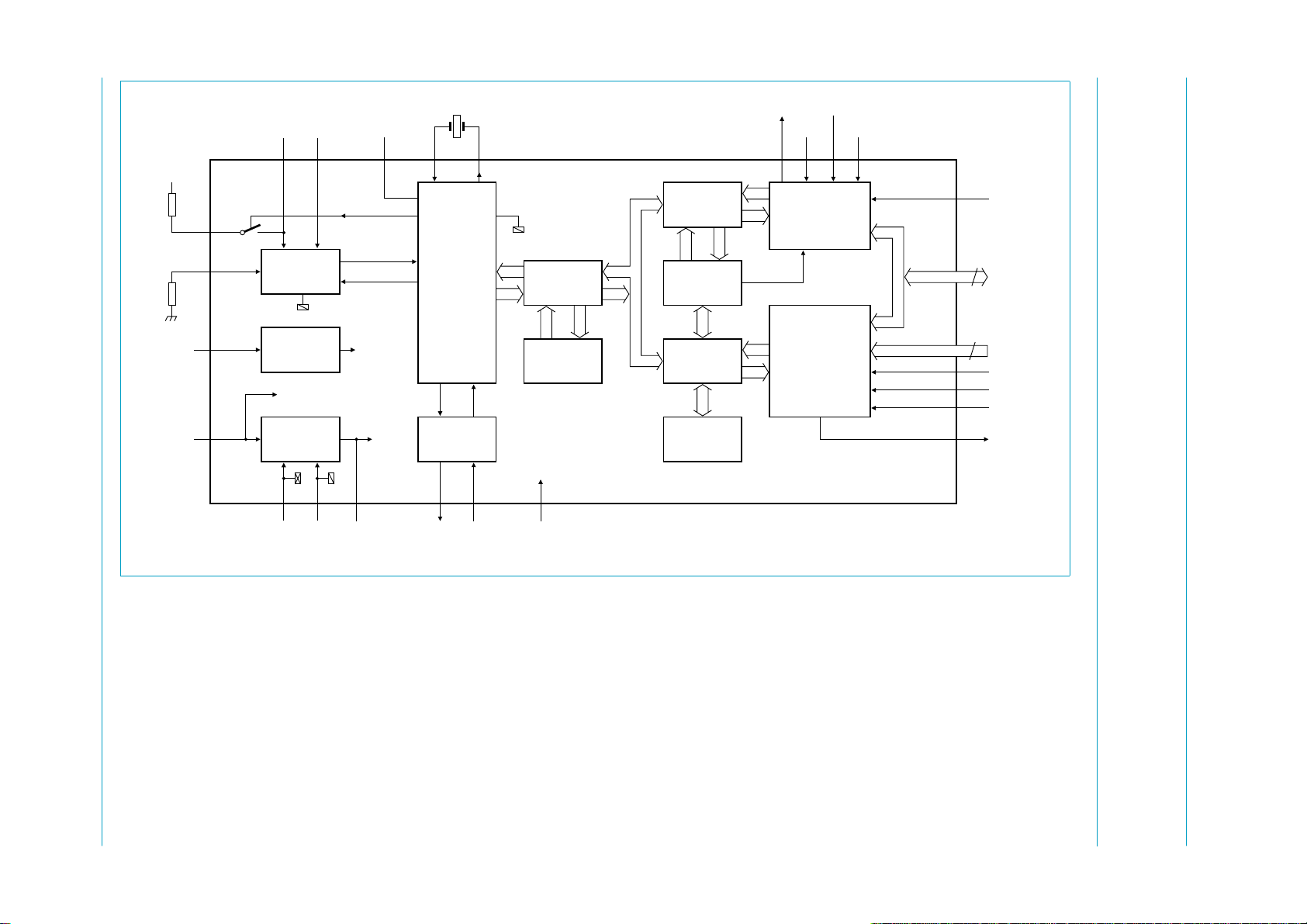
6. Block diagram
Philips Semiconductors
3.3 V
1.5
kΩ
RREF
12.0
kΩ
RESET_N
V
CC
RPU
2
6
7
53, 54
3.3 V
to/from USB
HI-SPEED USB
TRANSCEIVER
POWER-ON
RESET
analog supply
VOLT AGE
REGULATORS
13, 26,
29, 41
12 MHz
DMDP
43495251
V
BUS
XTAL2XTAL1
ISP1582
SoftConnect
MEMORY
MANAGEMENT
UNIT
INTEGRATED
RAM
(8 KBYTES)
I/O pad
supply
21, 34, 4828, 50
V
CC(I/O)
1, 5
V
CC(1V8)
internal
reset
digital
supply
PHILIPS
SIE/PIE
SYSTEM
CONTROLLER
SUSPEND WAKEUPAGNDDGND
5556
DMA
HANDLER
DMA
REGISTERS
MICRO-
CONTROLLER
HANDLER
OTG SRP
MODULE
DREQ DIOR
DACK
9101112
INTERFACE
CONTROLLER
INTERFACE
DIOW
DMA
MICRO-
30 to 33,
35 to 40,
42 to 47
18 to 20,
22 to 25,
27
15
16
17
14
004aaa199
8
EOT
16
8
DATA[15:0
A[7:0
CS_N
RD_N
WR_N
INT
]
]
Fig 1. Block diagram.
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
ISP1582
Page 5
Philips Semiconductors
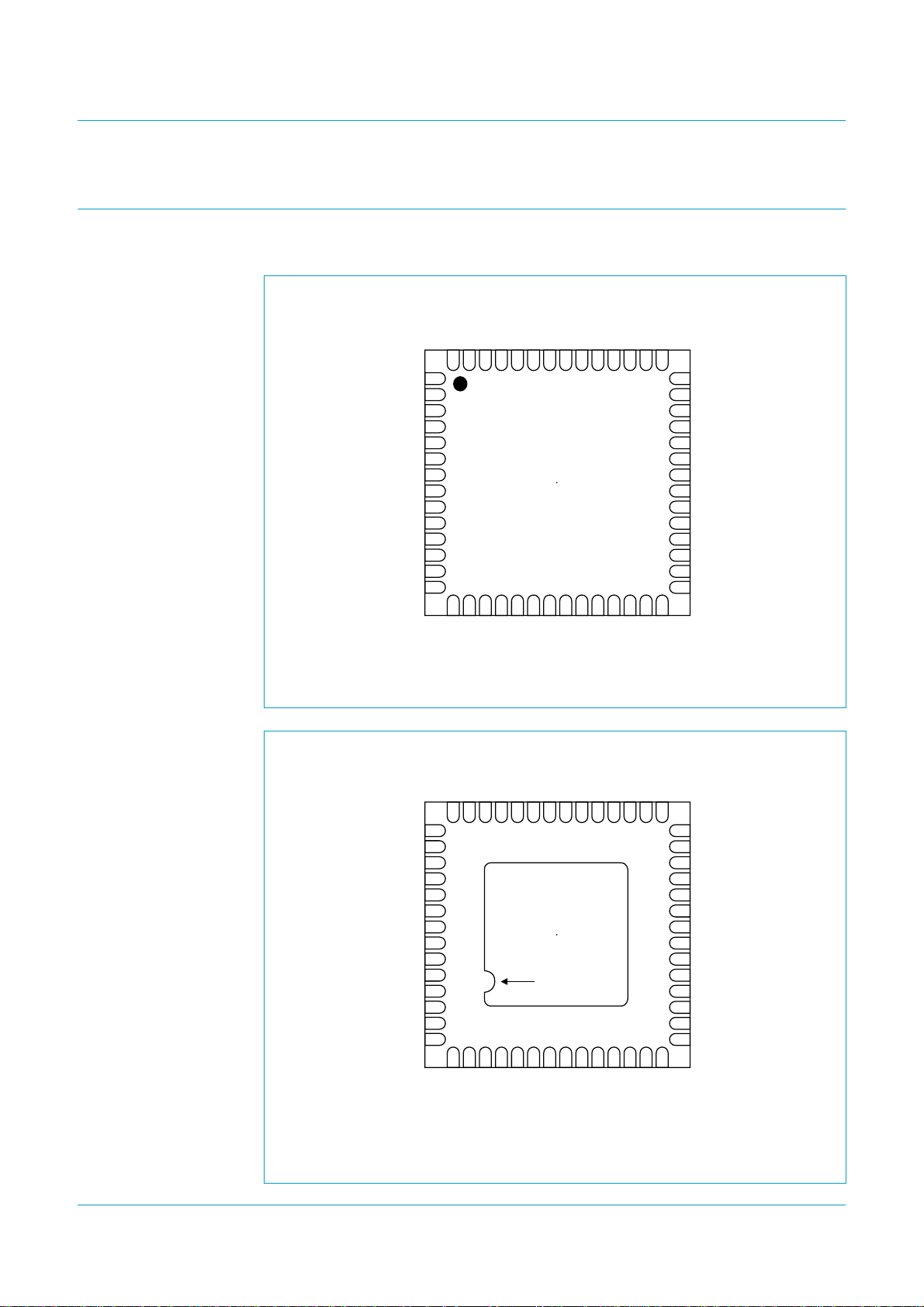
7. Pinning information
7.1 Pinning
AGND
RPU
DP
DM
AGND
RREF
RESET_N
EOT
DREQ
DACK
DIOR
DIOW
DGND
INT
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
BUS
CC(1V8)
CC
CC
XTAL1
V
52
ISP1582BS
19
A1
A0
XTAL2
515349
20
A2
V
WAKEUP
SUSPEND
54
55
56
1 42
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
171518
16
CS_N
RD_N
WR_N
V
V
50
21
A3
CC(I/O)
V
22
CC(I/O)
V
DATA15
474648
24
23
A5
A4
DATA14
DATA13
45
26
25
A6
DGND
DATA12
DATA11
43
44
28
27
A7
CC(1V8)
V
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
ISP1582
DATA10
DGND
DATA9
DATA8
DATA7
DATA6
DATA5
DATA4
V
CC(I/O)
DATA3
DATA2
DATA1
DATA0
DGND
004aaa536
Fig 2. Pin configuration HVQFN56 (top view).
CC(I/O)
A1
A2
A0
V
201822
21
19
GND (exposed die pad)
ISP1582BS
terminal 1
50
52
51
CC
CC
V
XTAL1
XTAL2
CC(1V8)
V
INT
DGND
DIOW
DIOR
DACK
DREQ
EOT
RESET_N
RREF
AGND
DM
DP
RPU
AGND
Bottom View
CS_N
WR_N
RD_N
17
16
15
14 29
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
545653
55
V
WAKEUP
SUSPEND
A3
49
BUS
V
A5
A4
242523
47
48
CC(I/O)
DATA15
V
A6
DGND
26
45
46
DATA13
DATA14
CC(1V8)
A7
V
28
27
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
DATA11
DATA12
DGND
DATA0
DATA1
DATA2
DATA3
V
CC(I/O)
DATA4
DATA5
DATA6
DATA7
DATA8
DATA9
DGND
DATA10
004aaa377
Fig 3. Pin configuration HVQFN56 (bottom view).
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 5 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 6

Philips Semiconductors
7.2 Pin description
Table 2: Pin description
Symbol
AGND 1 - analog ground
RPU 2 A connect to the external pull-up resistor for pin DP; must be
DP 3 A USB D+ line connection (analog)
DM 4 A USB D− line connection (analog)
AGND 5 - analog ground
RREF 6 A connect to the external bias resistor; must be connected to
RESET_N 7 I reset input (500 µs); a LOW levelproducesanasynchronous
EOT 8 I End-of-transfer input (programmable polarity); used in DMA
DREQ 9 O DMA request (programmable polarity) output; when not in
DACK 10 I DMA acknowledge input (programmable polarity); when not
DIOR 11 I DMA read strobe input (programmable polarity); when not in
DIOW 12 I DMA write strobe input (programmable polarity); when not in
DGND 13 - digital ground
INT 14 O interrupt output; programmable polarity (active HIGH or
CS_N 15 I chip select input
RD_N 16 I read strobe input
WR_N 17 I write strobe input
[1]
Pin Type
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
[2]
Description
connected to 3.3 V via a 1.5 kΩ resistor
ground via a 12.0 kΩ±1 % resistor
reset; connect to V
circuit)
TTL; 5 V tolerant
slavemodeonly; when not in use, connect this pin to V
through a 10 kΩ resistor
input pad; TTL; 5 V tolerant
use, connect this pin to ground through a 10 kΩ resistor; see
Table 54 and Table 55
TTL; 4 ns slew-rate control
in use, connect this pin to V
see Table 54 and Table 55
TTL; 5 V tolerant
use, connect this pin to V
Table 54 and Table 55
TTL; 5 V tolerant
use, connect this pin to V
Table 54 and Table 55
TTL; 5 V tolerant
LOW) and signaling (edge or level triggered)
CMOS output; 8 mA drive
input pad; TTL; 5 V tolerant
input pad; TTL; 5 V tolerant
input pad; TTL; 5 V tolerant
for the power-on reset (internal POR
CC
through a 10 kΩ resistor;
CC(I/O)
through a 10 kΩ resistor; see
CC(I/O)
through a 10 kΩ resistor; see
CC(I/O)
CC(I/O)
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 6 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 7

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Table 2: Pin description
Symbol
[1]
Pin Type
…continued
[2]
Description
A0 18 I bit 0 of the address bus
input pad; TTL; 5 V tolerant
A1 19 I bit 1 of the address bus
input pad; TTL; 5 V tolerant
A2 20 I bit 2 of the address bus
input pad; TTL; 5 V tolerant
[3]
V
CC(I/O)
21 - supply voltage; used to supply voltage to the I/O pads; see
Section 8.14
A3 22 I bit 3 of the address bus
input pad; TTL; 5 V tolerant
A4 23 I bit 4 of the address bus
input pad; TTL; 5 V tolerant
A5 24 I bit 5 of the address bus
input pad; TTL; 5 V tolerant
A6 25 I bit 6 of the address bus
input pad; TTL; 5 V tolerant
DGND 26 - digital ground
A7 27 I bit 7 of the address bus
input pad; TTL; 5 V tolerant
[3]
V
CC(1V8)
28 - regulator output voltage (1.8 V ± 0.15 V); tapped out voltage
from the internal regulator; this regulated voltage cannot
drive external devices; decouple this pin using a 0.1 µF
capacitor; see Section 8.14
DGND 29 - digital ground
DATA0 30 I/O bit0 of bidirectional data bus
bidirectional pad; 4 ns slew-rate control; TTL; 5 V tolerant
DATA1 31 I/O bit1 of bidirectional data bus
bidirectional pad; 4 ns slew-rate control; TTL; 5 V tolerant
DATA2 32 I/O bit2 of bidirectional data bus
bidirectional pad; 4 ns slew-rate control; TTL; 5 V tolerant
DATA3 33 I/O bit3 of bidirectional data bus
bidirectional pad; 4 ns slew-rate control; TTL; 5 V tolerant
[3]
V
CC(I/O)
34 - supply voltage; used to supply voltage to the I/O pads; see
Section 8.14
DATA4 35 I/O bit4 of bidirectional data bus
bidirectional pad; 4 ns slew-rate control; TTL; 5 V tolerant
DATA5 36 I/O bit5 of bidirectional data bus
bidirectional pad; 4 ns slew-rate control; TTL; 5 V tolerant
DATA6 37 I/O bit6 of bidirectional data bus
bidirectional pad; 4 ns slew-rate control; TTL; 5 V tolerant
DATA7 38 I/O bit7 of bidirectional data bus
bidirectional pad; 4 ns slew-rate control; TTL; 5 V tolerant
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 7 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Table 2: Pin description
Symbol
[1]
Pin Type
…continued
[2]
Description
DATA8 39 I/O bit8 of bidirectional data bus
bidirectional pad; 4 ns slew-rate control; TTL; 5 V tolerant
DATA9 40 I/O bit9 of bidirectional data bus
bidirectional pad; 4 ns slew-rate control; TTL; 5 V tolerant
DGND 41 - digital ground
DATA10 42 I/O bit10 of bidirectional data bus
bidirectional pad; 4 ns slew-rate control; TTL; 5 V tolerant
DATA11 43 I/O bit11 of bidirectional data bus
bidirectional pad; 4 ns slew-rate control; TTL; 5 V tolerant
DATA12 44 I/O bit12 of bidirectional data bus
bidirectional pad; 4 ns slew-rate control; TTL; 5 V tolerant
DATA13 45 I/O bit13 of bidirectional data bus
bidirectional pad; 4 ns slew-rate control; TTL; 5 V tolerant
DATA14 46 I/O bit14 of bidirectional data bus
bidirectional pad; 4 ns slew-rate control; TTL; 5 V tolerant
DATA15 47 I/O bit15 of bidirectional data bus
bidirectional pad; 4 ns slew-rate control; TTL; 5 V tolerant
[3]
V
CC(I/O)
48 - supply voltage; used to supply voltage to the I/O pads; see
Section 8.14
V
BUS
49 A USB bus power pin sensing input; used to detect whether
the host is connected or not; it is an output for V
in OTG mode; when V
is not detected, pin RPU is
BUS
BUS
pulsing
internally disconnected from pin DP in approximately 4 ns;
connect a 1 µF electrolytic capacitor and a 1 MΩ pull-down
resistor to ground; see Section 8.12
5 V tolerant
[3]
V
CC(1V8)
50 - regulator output voltage (1.8 V ± 0.15 V); tapped out voltage
from the internal regulator; this regulated voltage can drive
external devices up to 1 mA; decouple this pin using 4.7 µF
and 0.1 µF capacitors; see Section 8.14
XTAL2 51 O crystal oscillator output (12 MHz); connect a fundamental
parallel-resonant crystal; leave this pin open-circuit when
using an external clock source on pin XTAL1; see Table 83
XTAL1 52 I crystal oscillator input (12 MHz); connect a fundamental
parallel-resonant crystal or an external clock source (leaving
pin XTAL2 unconnected); see Table 83
[3]
V
CC
53 - supply voltage (3.3 V ± 0.3 V); this pin supplies the internal
voltage regulator and the analog circuit; see Section 8.14
[3]
V
CC
54 - supply voltage (3.3 V ± 0.3 V); this pin supplies the internal
voltage regulator and the analog circuit; see Section 8.14
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 8 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Table 2: Pin description
Symbol
[1]
Pin Type
…continued
[2]
Description
WAKEUP 55 I wake-up input; when this pin is at the HIGH level, the chip is
prevented from getting into the suspend state and the chip
wakes up from the suspend state; when not in use, connect
this pin to ground through a 10 kΩ resistor
input pad; TTL; 5 V tolerant
SUSPEND 56 O suspend state indicator output; used as a power switch
control output for powered-off application or as a resume
signal to the CPU for powered-on application
CMOS output; 8 mA drive
GND exposed
die pad
[1] Symbol names ending with underscore N (for example, NAME_N) represent active LOW signals.
[2] All outputs and I/O pins can source 4 mA.
[3] Add a decoupling capacitor (0.1 µF) to all the supply pins. For better EMI results, add a 0.01 µF
capacitor in parallel to the 0.1 µF.
- ground supply; down bonded to the exposed die pad
(heatsink); to be connected to DGND during PCB layout
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 9 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 10
Philips Semiconductors
8. Functional description
The ISP1582 is a high-speed USB peripheral controller. It implements the Hi-Speed
USB or the Original USB physical layer and the packet protocol layer. It maintains up
to 16 USB endpoints concurrently (control IN and control OUT, 7 IN and 7 OUT
configurable) along with endpoint EP0 setup, which accesses the setup buffer. The
USB Chapter 9 protocol handling is executed by means of external firmware.
For high-bandwidth data transfer, the integrated DMA handler can be invoked to
transfer data to or from external memory or devices. The DMA interface can be
configured by writing to the proper DMA registers (see Section 9.4).
The ISP1582 supports Hi-Speed USB and Original USB signaling. The USB
signaling speed is automatically detected.
The ISP1582 has 8 kbytes of internal FIFO memory, which is shared among the
enabled USB endpoints.
There are 7 IN endpoints, 7 OUT endpoints and 2 control endpoints that are a fixed
64 bytes long. Any of the 7 IN and 7 OUT endpoints can be separately enabled or
disabled. The endpoint type (interrupt, isochronous or bulk) and packet size of these
endpoints can be individually configured depending on the requirements of the
application. Optional double buffering increases the data throughput of these data
endpoints.
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
The ISP1582 requires 3.3 V power supply. It has 5 V tolerant I/O pads when
operating at V
transceiver.
The ISP1582 operates on a 12 MHz crystal oscillator. An integrated 40× PLL clock
multiplier generates the internal sampling clock of 480 MHz.
= 3.3 V and an internal 1.8 V regulator for powering the analog
CC(I/O)
8.1 DMA interface, DMA handler and DMA registers
The DMA block can be subdivided into two blocks: the DMA handler and the DMA
interface.
The firmware writes to the DMA command register to start a DMA transfer (see
Table 47). The command opcode determines whether a generic DMA or PIO transfer
will start. The handler interfaces to the same FIFO (internal RAM) as used by the
USB core. On receiving the DMA command, the DMA handler directs the data from
the endpoint FIFO to the external DMA device or from the external DMA device to the
endpoint FIFO.
The DMA interface configures the timing and the DMA handshake. Data can be
transferred using either the DIOR and DIOW strobes or by the DACK and DREQ
handshakes. The DMA configurations are set up by writing to the DMA Configuration
register (see Table 52 and Table 53).
For a generic DMA interface, Generic DMA (GDMA) slave mode can be used.
Remark: The DMA endpoint buffer length must be a multiple of 4 bytes.
For details on DMA registers, see Section 9.4.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 10 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors
8.2 Hi-Speed USB transceiver
The analog transceiver directly interfaces to the USB cable through integrated
termination resistors. The high-speed transceiver requires an external resistor
(12.0 kΩ±1 %) between pin RREF and ground to ensure an accurate current mirror
that generates the Hi-Speed USB current drive. A full-speed transceiver is integrated
as well. This makes the ISP1582 compliant to Hi-Speed USB and Original USB,
supporting both the high-speed and full-speed physical layers. After automatic speed
detection, the Philips Serial Interface Engine (SIE) sets the transceiver to use either
high-speed or full-speed signaling.
8.3 MMU and integrated RAM
The Memory Management Unit (MMU) and the integrated RAM provide the
conversion between the USB speed (full-speed: 12 Mbit/s, high-speed: 480 Mbit/s)
and the microcontroller handler or the DMA handler. The data from the USB bus is
stored in the integrated RAM, which is cleared only when the microcontroller has read
or written all data from or to the corresponding endpoint buffer or when the DMA
handler has read or written all data from or to the endpoint buffer. The OUT endpoint
buffer can also be cleared forcibly by setting bit CLBUF in the Control Function
register. A total of 8 kbytes RAM is available for buffering.
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
8.4 Microcontroller interface and microcontroller handler
The microcontroller handler allows the external microcontroller or microprocessor to
access the register set in the Philips SIE as well as the DMA handler. The
initialization of the DMA configuration is done through the microcontroller handler.
8.5 OTG SRP module
The OTG supplement defines a Session Request Protocol (SRP), which allows a
B-device to request the A-device to turn on V
allows the A-device, which may be battery-powered, to conserve power by turning off
V
when there is no bus activity while still providing a means for the B-device to
BUS
initiate bus activity.
Any A-device, including a PC or laptop, can respond to SRP. Any B-device, including
a standard USB peripheral, can initiate SRP.
The ISP1582 is a device that can initiate SRP.
and start a session. This protocol
BUS
8.6 Philips high-speed transceiver
8.6.1 Philips Parallel Interface Engine (PIE)
In the high-speed (HS) transceiver, the Philips PIE interface uses a 16-bit parallel
bidirectional data interface. The functions of the HS module also include bit-stuffing or
destuffing and Non-Return-to-Zero Inverted (NRZI) encoding or decoding logic.
8.6.2 Peripheral circuit
To maintain a constant current driver for HS transmit circuits and to bias other analog
circuits, an internal band gap reference circuit and an RREF resistor form the
reference current. This circuit requires an external precision resistor (12.0 kΩ±1%)
connected to the analog ground.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 11 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors
8.6.3 HS detection
The ISP1582 handles more than one electrical state—full-speed (FS) or high-speed
(HS)—under the USB specification. When the USB cable is connected from the
peripheral to the host controller, the ISP1582 defaults to the FS state until it sees a
bus reset from the host controller.
During the bus reset, the peripheral initiates an HS chirp to detect whether the host
controller supports Hi-Speed USB or Original USB. Chirping must be done with the
pull-up resistor connected and the internal termination resistors disabled. If the HS
handshake shows that there is an HS host connected, then the ISP1582 switches to
the HS state.
In the HS state, the ISP1582 should observe the bus for periodic activity. If the bus
remains inactive for 3 ms, the peripheral switches to the FS state to check for a
Single-Ended Zero (SE0) condition on the USB bus. If an SE0 condition is detected
for the designated time (100 µs to 875 µs; refer to section 7.1.7.6 of the USB
specification Rev. 2.0), the ISP1582 switches to the HS chirp state to perform an HS
detection handshake. Otherwise, the ISP1582 remains in the FS state adhering to the
bus-suspend specification.
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
8.7 Philips Serial Interface Engine (SIE)
The Philips SIE implements the full USB protocol layer. It is completely hardwired for
speed and needs no firmware intervention. The functions of this block include:
synchronization pattern recognition, parallel or serial conversion, bit (de)stuffing,
CRC checking or generation, Packet IDentifier (PID) verification or generation,
address recognition, handshake evaluation or generation.
8.8 SoftConnect
The connection to the USB is established by pulling pin DP (for full-speed devices)
HIGH through a 1.5 kΩ pull-up resistor. In the ISP1582, an external 1.5 kΩ pull-up
resistor must be connected between pin RPU and 3.3 V. Pin RPU connects the
pull-up resistor to pin DP, when bit SOFTCT in the Mode register is set (see Table 20
and Table 21). After a hardware reset, the pull-up resistor is disconnected by default
(bit SOFTCT = 0). The USB bus reset does not change the value of bit SOFTCT.
When the V
the back-drive voltage.
is not present, the SOFTCT bit must be set to logic 0 to comply with
BUS
8.9 System controller
The system controller implements the USB power-down capabilities of the ISP1582.
Registers are protected against data corruption during wake-up following a resume
(from the suspend state) by locking the write access until an unlock code has been
written in the Unlock Device register (see Table 73 and Table 74).
8.10 Output pins status
Table 3 illustrates the behavior of output pins when V
various operating conditions.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 12 of 66
is supplied with VCC in
CC(I/O)
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Table 3: ISP1582 pin status
V
CC
0V V
0V V
0V−> 3.3 V V
3.3 V V
3.3 V V
[1] X: Don’t care.
[2] Dead: The USB cable is plugged-out and V
[3] Plug-out: The USB cable is not present but V
[4] Plug-in: The USB cable is being plugged-in and V
V
CC(I/O)
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
[1]
State Pin
[2]
dead
plug-out
plug-in
[3]
[4]
reset LOW HIGH LOW high-Z high-Z
normal HIGH HIGH LOW high-Z high-Z
CC(I/O)
CC(I/O)
8.11 Interrupt
8.11.1 Interrupt output pin
The Interrupt Configuration register of the ISP1582 controls the behavior of the INT
output pin. The polarity and signaling mode of pin INT can be programmed by setting
bits INTPOL and INTLVL of the Interrupt Configuration register (R/W: 10h); see
Table 24. Bit GLINTENA of the Mode register (R/W: OCh) is used to enable pin INT.
Default settings after reset are active LOW and level mode. When pulse mode is
selected, a pulse of 60 ns is generated when the OR-ed combination of all interrupt
bits changes from logic 0 to logic 1.
RESET_N INT_N SUSPEND DREQ DATA[15:0]
XXXXX
X LOW HIGH high-Z input
X LOW HIGH high-Z high-Z
is not available.
is available.
is available.
CC(I/O)
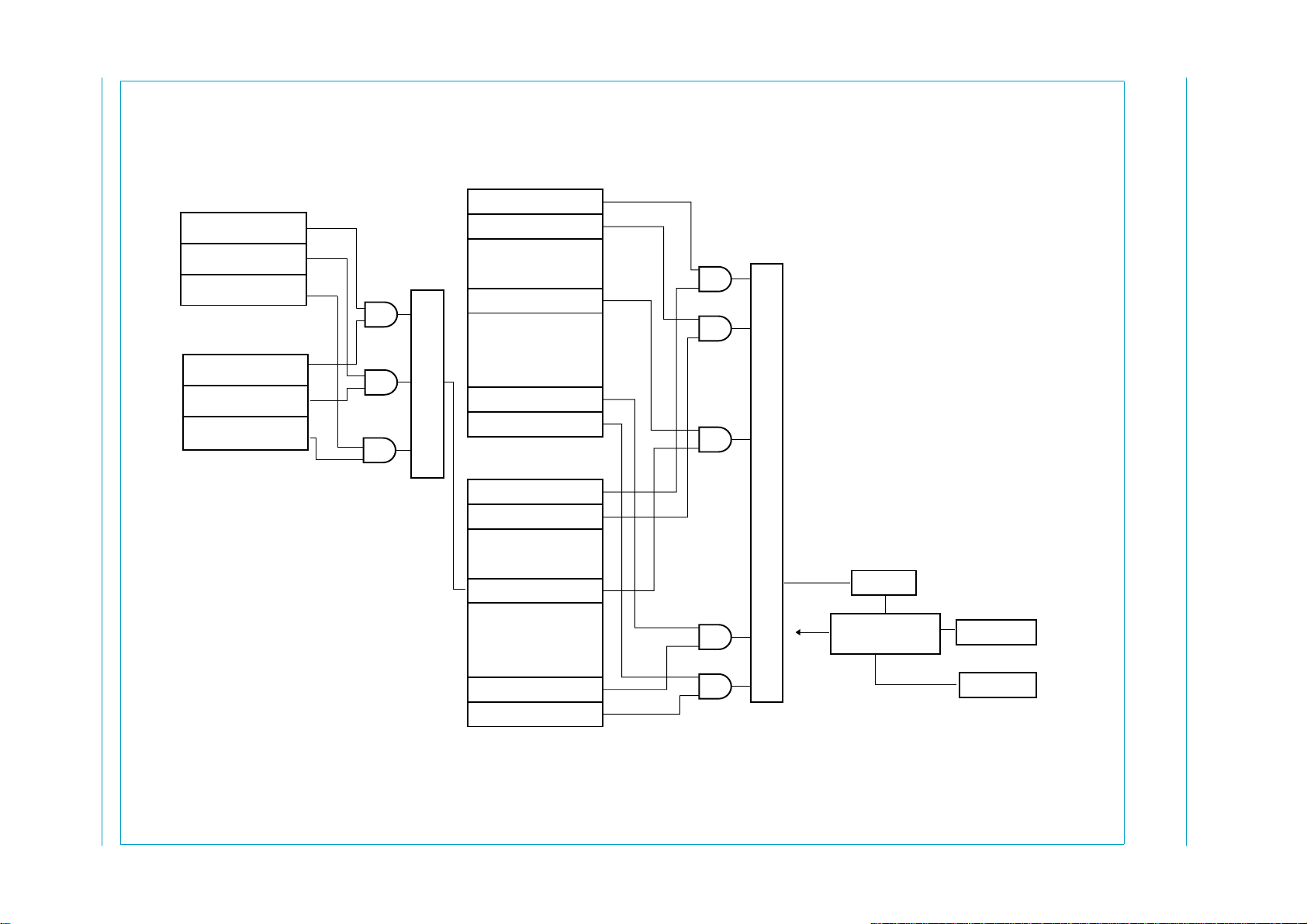
Figure 4 shows the relationship between the interrupt events and pin INT.
Each of the indicated USB and DMA events is logged in a status bit of the Interrupt
register and the DMA Interrupt Reason register, respectively. Corresponding bits in
the Interrupt Enable register and the DMA Interrupt Enable register determine
whether or not an event will generate an interrupt.
Interrupts can be masked globally by means of bit GLINTENA of the Mode register;
see Table 21.
Field CDBGMOD[1:0] of the Interrupt Configuration register controls the generation
of the INT signals for the control pipe. Field DDBGMODIN[1:0] of the Interrupt
Configuration register controls the generation of the INT signals for the IN pipe. Field
DDBGMODOUT[1:0] of the Interrupt Configuration register controls the generation of
the INT signals for the OUT pipe; see Table 25.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 13 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 14
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 14 of 66
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxx x x x xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xx xx
xxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxx x x
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxx
Philips Semiconductors
DMA Interrupt Reason
register
EXT_EOT
INT_EOT
DMA_XFER_OK
IE_EXT_EOT
OR
IE_INT_EOT
IE_DMA_XFER_OK
DMA Interrupt Enable
register
Interrupt Enable register
IEBRESET
IESOF
IEDMA
IEP7RX
IEP7TX
Interrupt register
BRESET
SOF
OR
..........
LE
DMA
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
....................
INT
LATCH
PULSE/LEVEL
GENERATOR
Interrupt Configuration
register
INTPOL
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Fig 4. Interrupt logic.
EP7RX
EP7TX
GLINTENA
Mode register
004aaa275
ISP1582
Page 15
Philips Semiconductors
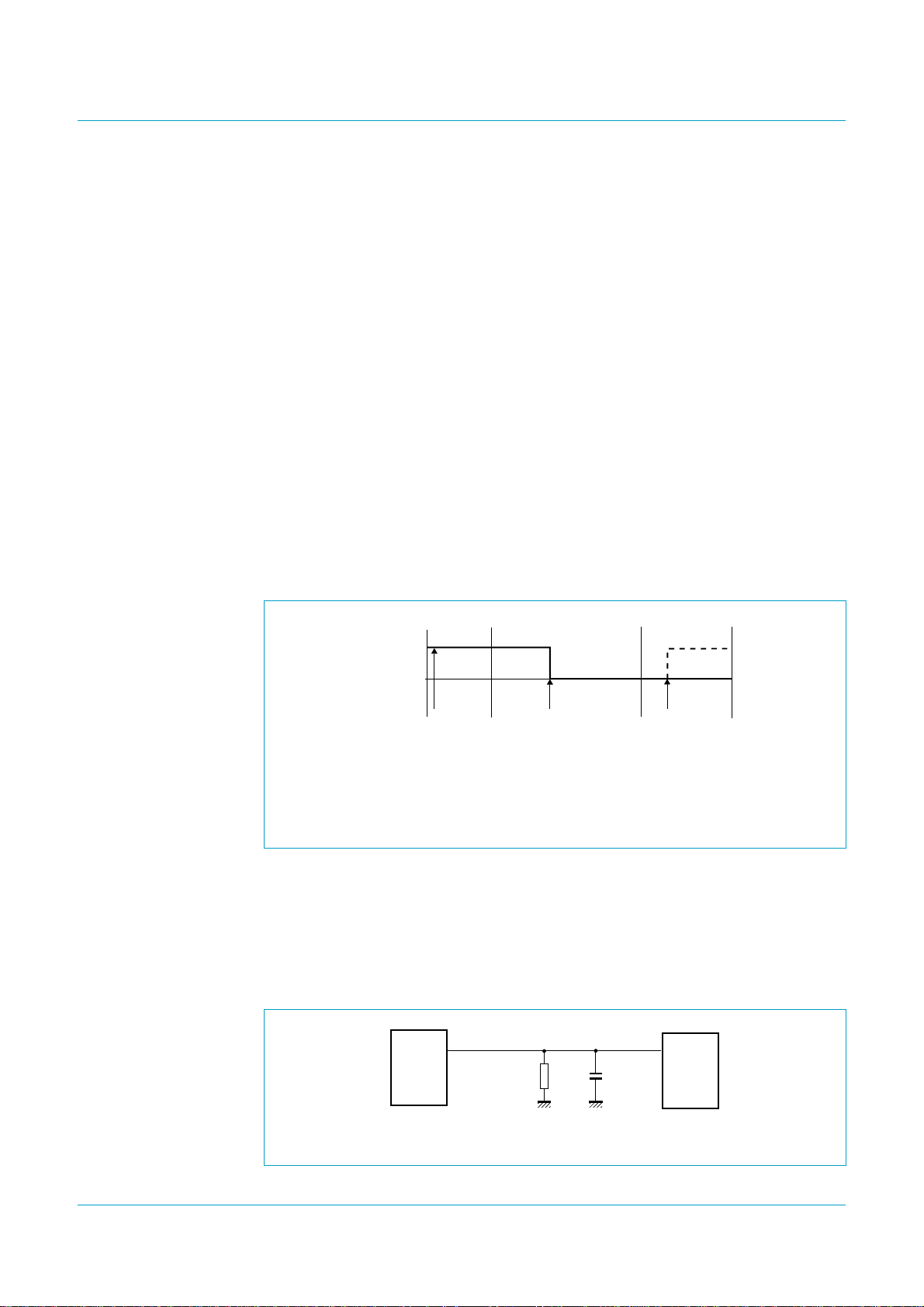
8.11.2 Interrupt control
Bit GLINTENA in the Mode register is a global enable/disable bit. The behavior of this
bit is given in Figure 5.
Event A: When an interrupt event occurs (for example, SOF interrupt) with
bit GLINTENA set to logic 0, an interrupt will not be generated at pin INT. It will,
however, be registered in the corresponding Interrupt register bit.
Event B: When bit GLINTENA is set to logic 1, pin INT is asserted because bit SOF in
the Interrupt register is already set.
Event C: If the firmware sets bit GLINTENA to logic 0, pin INT will still be asserted.
The bold dashed line shows the desired behavior of pin INT.
Deassertion of pin INT can be achieved either by clearing all the Interrupt register or
the DMA Interrupt Reason register, depending on the event.
Remark: When clearing an interrupt event, perform write to all the bytes of the
register.
For more information on interrupt control, see Section 9.2.2, Section 9.2.5 and
Section 9.5.1.
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
8.12 V
Pin V
with bit CLKAON set to logic 0 (clock off option).
To detect whether the host is connected or not, that is V
and a 1 µF electrolytic capacitor must be added to damp the overshoot upon plug-in.
A
INT pin
GLINTENA = 0
(during this time,
an interrupt event
occurs. For example,
SOF asserted.)
Pin INT: HIGH = deassert; LOW = assert (individual interrupts are enabled).
GLINTENA = 1
B
SOF asserted
Fig 5. Behavior of bit GLINTENA.
sensing
BUS
is one of the ways to wake up the clock when the ISP1582 is suspended
BUS
BUS
49
ISP1582
1 MΩ
+
1 µF
C
GLINTENA = 0
SOF asserted
004aaa394
sensing, a 1 MΩ resistor
USB
Connector
004aaa440
Fig 6. Resistor and electrolytic capacitor needed for V
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 15 of 66
sensing.
BUS
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 16
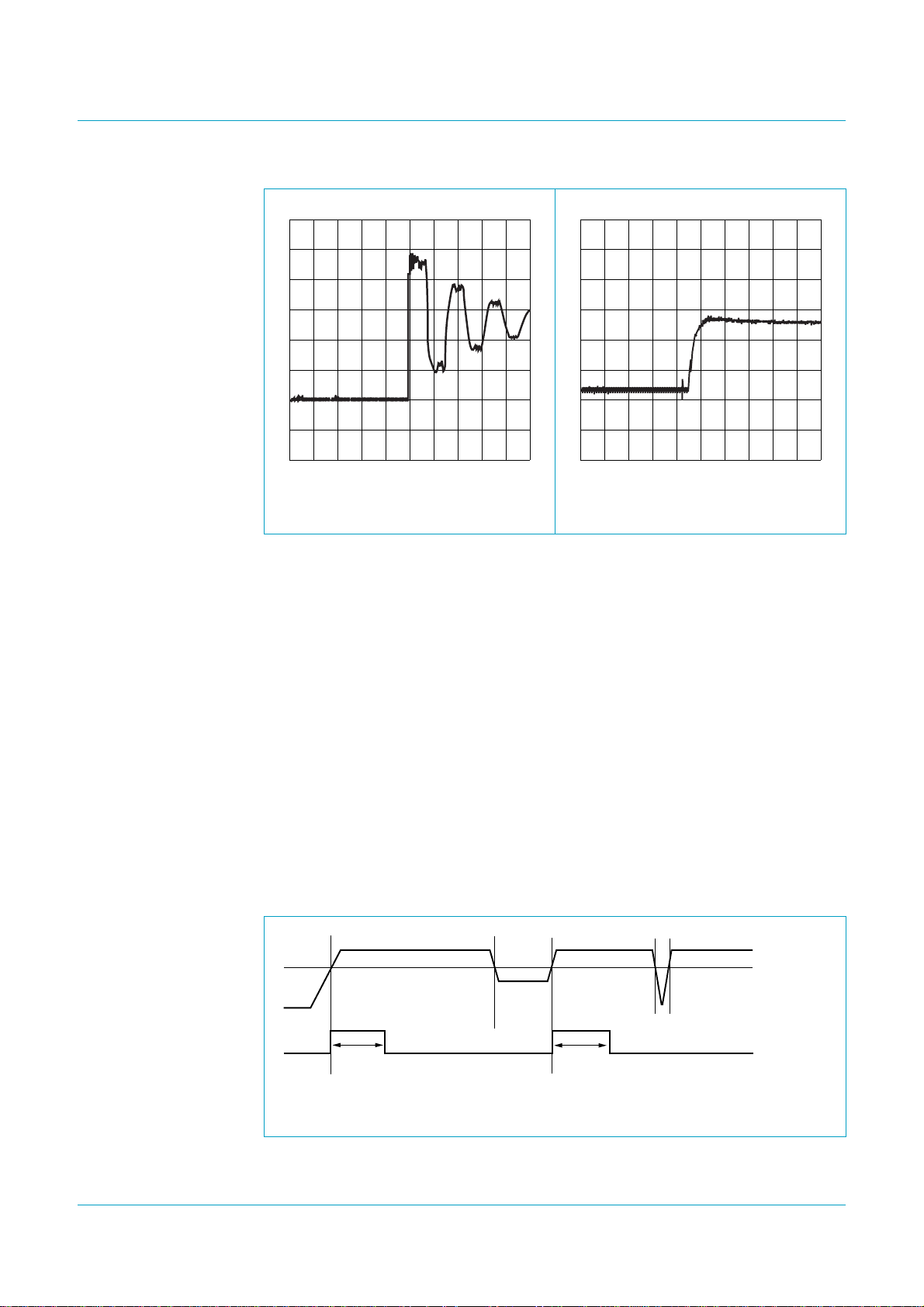
Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
004aaa441 004aaa442
Fig 7. Oscilloscope reading: no resistor
and capacitor in the network.
8.13 Power-on reset
The ISP1582 requires a minimum pulse width of 500 µs.
Pin RESET_N can be either connected to VCC (using the internal POR circuit) or
externally controlled (by the microcontroller, ASIC, and so on). When VCC is directly
connected to pin RESET_N, the internal pulse width t
The power-on reset function can be explained by viewing the dips at t2-t3 and t4-t5
on the V
CC(POR)
t0 — The internal POR starts with a HIGH level.
t1 — The detector will see the passing of the trip level and a delay element will add
another t
PORP
t2-t3 — The internal POR pulse will be generated whenever V
V
for more than 11 µs.
trip
t4-t5 — The dip is too short (< 11 µs) and the internal POR pulse will not react and
will remain LOW.
curve (Figure 9).
before it drops to LOW.
Fig 8. Oscilloscope reading: with
resistor and capacitor in the
network.
will be typically 200 ns.
PORP
CC(POR)
drops below
V
BAT(POR)
V
trip
t0 t1
t
PORP
(1) PORP = power-on reset pulse.
t2
t3
t
PORP
t4
t5
(1)
PORP
004aaa389
Fig 9. POR timing.
Figure 10 shows the availability of the clock with respect to the external POR.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 16 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 17
Philips Semiconductors
Fig 10. Clock with respect to the external POR.
8.14 Power supply
The ISP1582 can be powered by 3.3 V ± 0.3 V, and 3.3 V at the interface. For
connection details, see Figure 11.
If the ISP1582 is powered by VCC= 3.3 V, an integrated 3.3 V-to-1.8 V voltage
regulator provides a 1.8 V supply voltage for the internal logic.
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
POR
EXTERNAL CLOCK
004aaa365
A
Stable external clock is to be available at A.
In sharing mode (that is, when VCC is not present and V
is present), all the I/O
CC(I/O)
pins are in three-state, the interrupt pin is connected to ground, and the suspend pin
is connected to V
ISP1582
CC(I/O)
53, 54
48
34
21
50
28
. See Table 3.
V
CC
V
CC(I/O)
V
CC(I/O)
V
CC(I/O)
V
V
0.01 µF 0.1 µF
CC(1V8)
+
(1)
4.7 µF
CC(1V8)
0.1 µF
0.01 µF
0.01 µF
0.1 µF
0.01 µF
0.1 µF
3.3 V ± 0.3 V
0.1 µF
V
CC
004aaa203
(1) It is mandatory to use a 4.7 µF electrolytic capacitor on V
0.1 µF
CC(1V8)
.
Fig 11. ISP1582 with 3.3 V supply.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 17 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 18
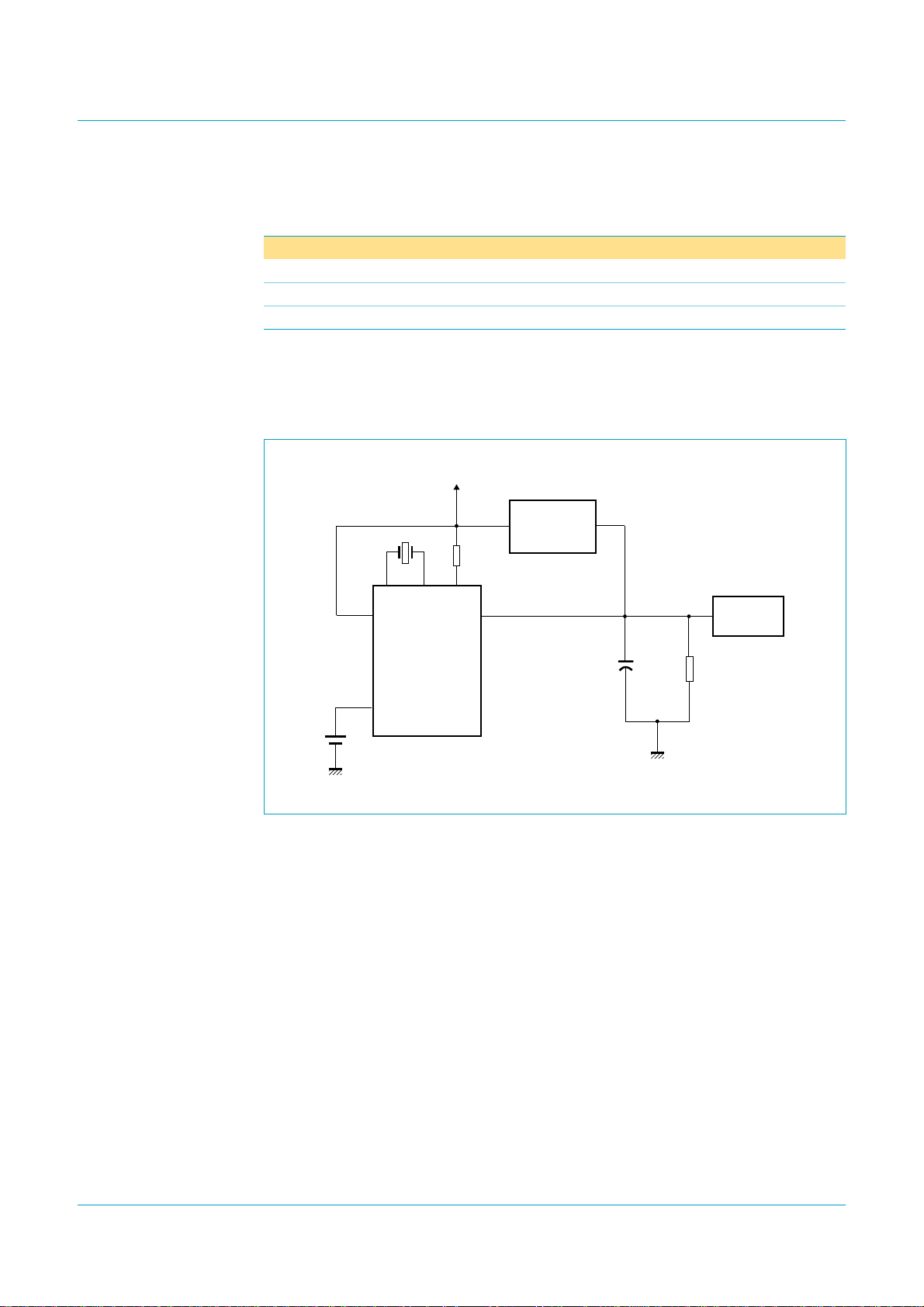
Philips Semiconductors
Table 4 shows power modes in which the ISP1582 can be operated.
Table 4: Power modes
V
CC
V
BUS
self-powered self-powered self-powered
V
BUS
[1] Power supply to the IC (VCC) is 3.3 V. Therefore, if the application is bus-powered, a 3.3 V regulator
[2] V
8.14.1 Power-sharing mode
[1]
[1]
needs to be used.
CC(I/O)=VCC
. If the application is bus-powered, a voltage regulator needs to be used.
V
CC(I/O)
[2]
V
BUS
self-powered power-sharing (hybrid)
To GPIO of processor
for sensing V
BUS
1.5 kΩ
5 V-to-3.3 V
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Power mode
bus-powered
RPU
V
CC
V
CC(I/O)
+
−
ISP1582
V
BUS
004aaa457
1 µF
+
−
V
BUS
USB
1 MΩ
Fig 12. Power-sharing mode.
As can be seen in Figure 12, in power-sharing mode, VCCis supplied by the output of
the 5 V-to-3.3 V voltage regulator. The input to the regulator is from V
BUS
. V
CC(I/O)
is
supplied through the power source of the system. When the USB cable is plugged in,
the ISP1582 goes through the power-on reset cycle. In this mode, OTG is disabled.
The processor will experience continuous interrupt because the default status of the
interrupt pin when operating in sharing mode with the V
overcomethis,implement external V
sensing circuitry.The output from the voltage
BUS
not present is LOW. To
BUS
regulator can be connected to pin GPIO of the processor to qualify the interrupt from
the ISP1582.
Remark: When the core power is removed, the ISP1582 must be reset using the
RESET_N pin. The reset pulse width must be 2 ms.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 18 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 19
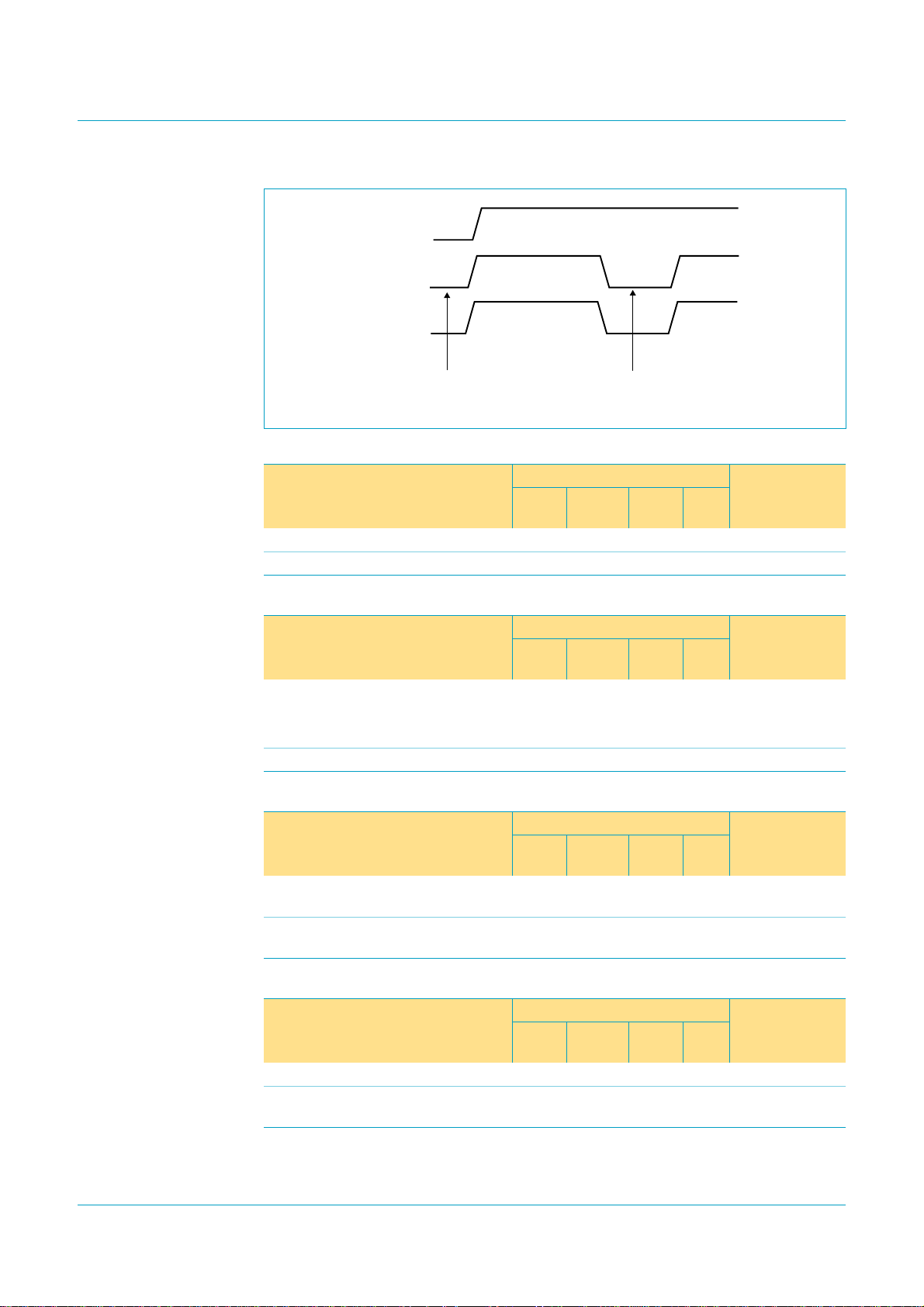
Philips Semiconductors
V
CC(I/O)
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
V
CC
INT
power off
power off
004aaa469
Fig 13. Interrupt pin status during power off in power-sharing mode.
Table 5: Operation truth table for SoftConnect
ISP1582 operation Power supply Bit SOFTCT in
V
CC
V
CC(I/O)
RPU
V
Mode register
BUS
(3.3 V)
Normal bus operation 3.3 V 3.3 V 3.3 V 5 V enabled
Core power is lost 0 V 3.3 V 0 V 0 V not applicable
Table 6: Operation truth table for clock off during suspend
ISP1582 operation Power supply Clockoffduring
V
CC
V
CC(I/O)
RPU
V
BUS
suspend
(3.3 V)
Clock will wake up:
3.3 V 3.3 V 3.3 V 5 V enabled
After resume and
After a bus reset
Core power is lost 0 V 3.3 V 0 V 0 V not applicable
Table 7: Operation truth table for back voltage compliance
ISP1582 operation Power supply Bit SOFTCT in
V
CC
V
CC(I/O)
RPU
V
Mode register
BUS
(3.3 V)
Back voltage is not measured in this
3.3 V 3.3 V 3.3 V 5 V enabled
mode
Back voltage is not an issue because
0 V 3.3 V 0 V 0 V not applicable
core power is lost
Table 8: Operation truth table for OTG
ISP1582 operation Power supply OTG register
V
CC
V
CC(I/O)
RPU
V
BUS
(3.3 V)
SRP is not applicable 3.3 V 3.3 V 3.3 V 5 V not applicable
is
OTG is not possible because V
BUS
0 V 3.3 V 0 V 0 V not applicable
not present and so core power is lost
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 19 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 20
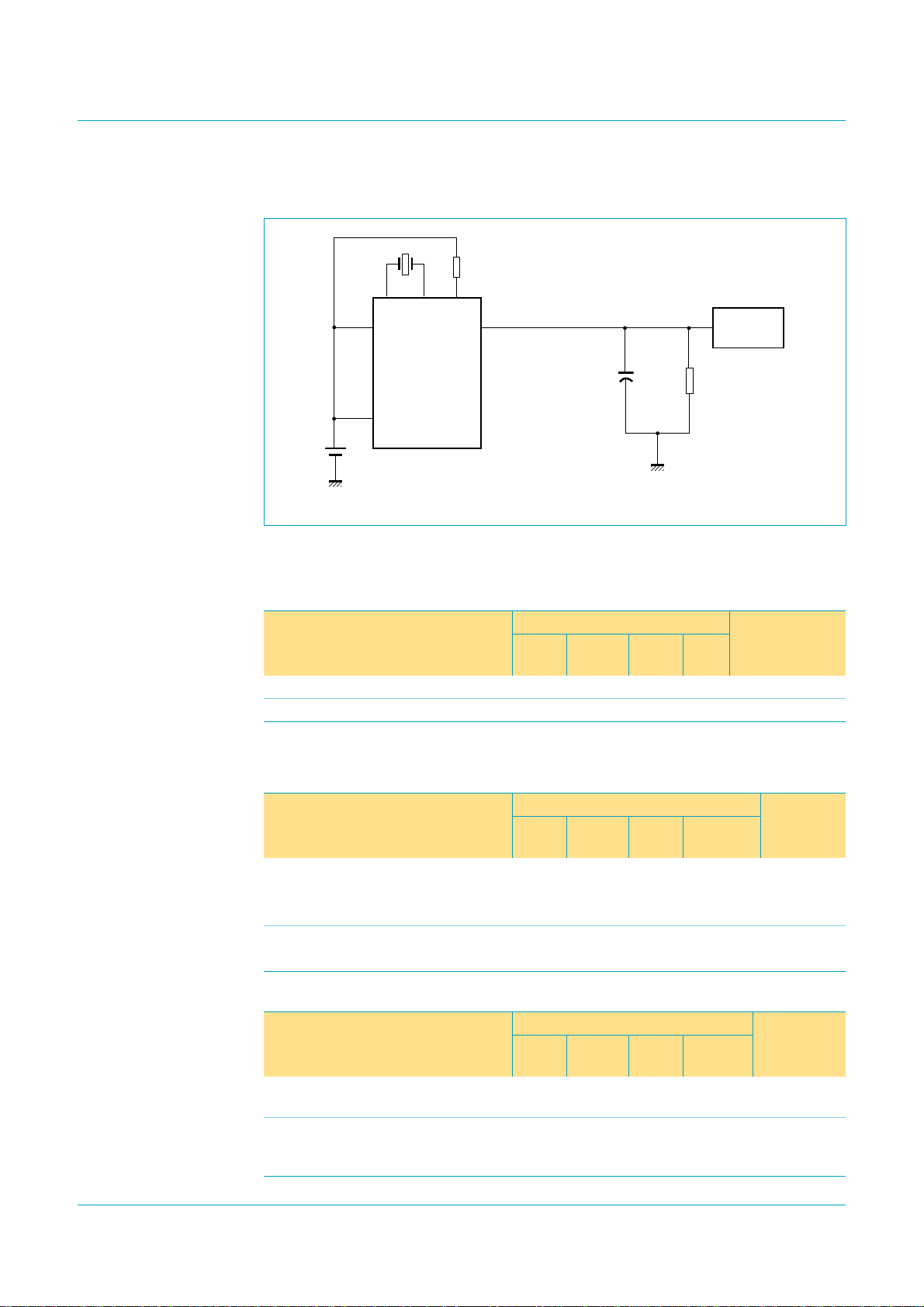
Philips Semiconductors
8.14.2 Self-powered mode
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
1.5 kΩ
RPU
V
CC
V
CC(I/O)
+
−
ISP1582
V
BUS
004aaa460
1 µF
V
BUS
+
−
USB
1 MΩ
Fig 14. Self-powered mode.
In self-powered mode, VCC and V
are supplied by the system. Bit SOFTCT in
CC(I/O)
the Mode register must be always logic 1. See Figure 14.
Table 9: Operation truth table for SoftConnect
ISP1582 operation Power supply Bit SOFTCT in
V
CC
V
CC(I/O)
RPU
(3.3 V)
Normal bus operation 3.3 V 3.3 V 3.3 V 5 V enabled
No pull-up on DP 3.3 V 3.3 V 3.3 V 0 V
[1] When the USB cable is removed, SoftConnect is disabled.
V
Mode register
BUS
[1]
disabled
Table 10: Operation truth table for clock off during suspend
ISP1582 operation Power supply Clock off
during
suspend
Clock will wake up:
V
CC
V
CC(I/O)
RPU
V
BUS
(3.3 V)
3.3 V 3.3 V 3.3 V 5 V enabled
After resume and
After a bus reset
Clock will wake up:
After detecting the presence of V
3.3 V 3.3 V 3.3 V 0 V => 5 V enabled
BUS
Table 11: Operation truth table for back voltage compliance
ISP1582 operation Power supply Bit SOFTCT
in Mode
register
Back voltage is not measured in this
V
CC
V
CC(I/O)
RPU
V
BUS
(3.3 V)
3.3 V 3.3 V 3.3 V 5 V enabled
mode
Back voltage is not an issue because
3.3 V 3.3 V 3.3 V 0 V disabled
pull-up on DP will not be present when
V
is not present
BUS
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 20 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors
Table 12: Operation truth table for OTG
ISP1582 operation Power supply OTG
SRP is not applicable 3.3 V 3.3 V 3.3 V 5 V not
SRP is possible 3.3 V 3.3 V 3.3 V 0 V operational
8.14.3 Bus-powered mode
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
V
CC
V
CC(I/O)
RPU
V
BUS
(3.3 V)
5 V-to-3.3 V
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
V
V
CC
V
BUS
BUS
register
applicable
USB
1 µF
+
−
1 MΩ
1.5 kΩ
V
CC(I/O)
RPU
ISP1582
004aaa462
Fig 15. Bus-powered mode.
In bus-powered mode (see Figure 15), VCCand V
the 5 V-to-3.3 V voltage regulator. The input to the regulator is from V
are supplied by the output of
CC(I/O)
BUS
. On
plugging in of the USB cable, the ISP1582 goes through the power-on reset cycle. In
this mode, OTG is disabled.
Table 13: Operation truth table for SoftConnect
ISP1582 operation Power supply Bit SOFTCT in
V
CC
V
CC(I/O)
RPU
(3.3 V)
Normal bus operation 3.3 V 3.3 V 3.3 V 5 V enabled
Power loss 0 V 0 V 0 V 0 V not applicable
Table 14: Operation truth table for clock off during suspend
ISP1582 operation Power supply Clockoffduring
V
CC
V
CC(I/O)
RPU
(3.3 V)
Clock will wake up:
3.3 V 3.3 V 3.3 V 5 V enabled
After resume and
After a bus reset
Power loss 0 V 0 V 0 V 0 V not applicable
V
V
Mode register
BUS
suspend
BUS
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 21 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors
Table 15: Operation truth table for back voltage compliance
ISP1582 operation Power supply Bit SOFTCT in
Back voltage is not measured in this
mode
Power loss 0 V 0 V 0 V 0 V not applicable
Table 16: Operation truth table for OTG
ISP1582 operation Power supply OTG register
SRP is not applicable 3.3 V 3.3 V 3.3 V 5 V not applicable
Power loss 0 V 0 V 0 V 0 V not applicable
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
V
CC
V
CC(I/O)
RPU
(3.3 V)
3.3 V 3.3 V 3.3 V 5 V enabled
V
CC
V
CC(I/O)
RPU
(3.3 V)
V
V
Mode register
BUS
BUS
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 22 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
9. Register description
Table 17: Register overview
Name Destination Address Description Size
(bytes)
Initialization registers
Address device 00h USB device address and enabling 1 Section 9.2.1
Mode device 0Ch power-down options, global interrupt
enable, SoftConnect
Interrupt Configuration device 10h interrupt sources, trigger mode, output
polarity
OTG device 12h OTG implementation 1 Section 9.2.4
Interrupt Enable device 14h interrupt source enabling 4 Section 9.2.5
Data flow registers
Endpoint Index endpoints 2Ch endpoint selection, data flow direction 1 Section 9.3.1
Control Function endpoint 28h endpoint buffer management 1 Section 9.3.2
Data Port endpoint 20h data access to endpoint FIFO 2 Section 9.3.3
Buffer Length endpoint 1Ch packet size counter 2 Section 9.3.4
Buffer Status endpoint 1Eh buffer status for each endpoint 1 Section 9.3.5
Endpoint MaxPacketSize endpoint 04h maximum packet size 2 Section 9.3.6
Endpoint Type endpoint 08h selects endpoint type: control,
isochronous, bulk or interrupt
DMA registers
DMA Command DMA controller 30h controls all DMA transfers 1 Section 9.4.1
DMA Transfer Counter DMA controller 34h sets byte count for DMA transfer 4 Section 9.4.2
DMA Configuration DMA controller 38h sets GDMA configuration (counter
enable, burst length, data strobing, bus
width)
DMA Hardware DMA controller 3Ch endian type, master or slave selection,
signal polarity for DACK, DREQ, DIOW,
DIOR
DMA Interrupt Reason DMA controller 50h shows reason (source) for DMA interrupt 2 Section 9.4.5
DMA Interrupt Enable DMA controller 54h enables DMA interrupt sources 2 Section 9.4.6
DMA Endpoint DMA controller 58h selects endpoint FIFO,data flow direction 1 Section 9.4.7
1 Section 9.2.2
1 Section 9.2.3
2 Section 9.3.7
1 Section 9.4.3
1 Section 9.4.4
Reference
on page 24
on page 25
on page 27
on page 28
on page 30
on page 31
on page 33
on page 33
on page 34
on page 35
on page 36
on page 37
on page 39
on page 40
on page 41
on page 42
on page 43
on page 45
on page 45
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 23 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 24

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Table 17: Register overview
Name Destination Address Description Size
DMA Burst Counter DMA controller 64h DMA burst counter 2 Section 9.4.8
General registers
Interrupt device 18h shows interrupt sources 4 Section 9.5.1
Chip ID device 70h product ID code and hardware version 3 Section 9.5.2
Frame Number device 74h last successfully received
Scratch device 78h allows save or restore of firmware status
Unlock Device device 7Ch reenables register access after suspend 2 Section 9.5.5
Test Mode PHY 84h direct setting of DP and DM states,
…continued
Start-Of-Frame: lower byte (byte 0) is
accessed first
during suspend
internal transceiver test (PHY)
Reference
(bytes)
on page 46
on page 46
on page 48
2 Section 9.5.3
on page 49
2 Section 9.5.4
on page 49
on page 50
1 Section 9.5.6
on page 51
9.1 Register access
Register access depends on the bus width used. The ISP1582 uses a 16-bit bus
access. For single-byte registers, the upper byte (MSByte) must be ignored.
Endpoint specific registers are indexed via the Endpoint Index register. The target
endpoint must be selected before accessing the following registers:
• Buffer Length
• Buffer Status
• Control Function
• Data Port
• Endpoint MaxPacketSize
• Endpoint Type.
Remark: All reserved bits are not implemented. The bus and bus reset values are not
defined. Therefore, writing to these reserved bits will have no effect.
9.2 Initialization registers
9.2.1 Address register (address: 00h)
This register sets the USB assigned address and enables the USB device. Table 18
shows the Address register bit allocation.
Bits DEVADDR will be cleared whenever a bus reset, a power-on reset or a soft reset
occurs. Bit DEVEN will be cleared whenever a power-on reset or a soft reset occurs,
and will be set after a bus reset.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 24 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 25

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
In response to the standard USB request SET_ADDRESS, the firmware must write
the (enabled) device address to the Address register, followed by sending an empty
packet to the host. The new device address is activated when the device receives
acknowledgment from the host.
Table 18: Address register: bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol DEVEN DEVADDR[6:0]
Reset 00000000
Bus reset 10000000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Table 19: Address register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
7 DEVEN Logic 1 enables the device.
6 to 0 DEVADDR[6:0] This field specifies the USB device address.
9.2.2 Mode register (address: 0Ch)
This register consists of 2 bytes (bit allocation: see Table 20).
The Mode register controls resume, suspend and wake-up behavior, interrupt activity,
soft reset, clock signals and SoftConnect operation.
Table 20: Mode register: bit allocation
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Symbol reserved DMA
CLKON
Reset ------0-
Bus reset ------0-
Access RRRRRRR/WR
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol CLKAON SNDRSU GOSUSP SFRESET GLINTENA WKUPCS PWRON SOFTCT
Reset 00000000
Bus reset 0000unchanged 0 0 unchanged
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Table 21: Mode register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
15 to 10 - reserved
9 DMACLKON 1 — Supply clock to the DMA circuit.
0 — Power save mode; the DMA circuit will stop completely to save
power.
8 VBUSSTAT This bit reflects the V
pin status.
BUS
VBUSSTAT
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 25 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 26

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Table 21: Mode register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
7 CLKAON Clock Always On: Logic 1 indicates that the internal clocks are
always running when in the suspend state. Logic 0 switches off the
internal oscillator and PLL when the device goes into suspend
mode. The device will consume less power if this bit is set to logic 0.
The clock is stopped after a delay of approximately 2 ms, following
which bit GOSUSP is set.
6 SNDRSU Send Resume: Writing logic 1, followed by logic 0 will generate an
upstream resume signal of 10 ms duration, after a 5 ms delay.
5 GOSUSP Go Suspend: Writing logic 1, followed by logic 0 will activate
suspend mode.
4 SFRESET Soft Reset: Writing logic 1, followed by logic 0 will enable a
software-initiated reset to the ISP1582. A soft reset is similar to a
hardware-initiated reset (via pin RESET_N).
3 GLINTENA Global Interrupt Enable: Logic 1 enables all interrupts. Individual
interrupts can be masked by clearing the corresponding bits in the
Interrupt Enable register.
When this bit is not set, an unmasked interrupt will not generate an
interrupt trigger on the interrupt pin. If global interrupt, however, is
enabled while there is any pending unmasked interrupt, an interrupt
signal will be immediately generated on the interrupt pin. (If the
interrupt is set to pulse mode, the interrupt events that were
generated before the global interrupt is enabled may be dropped).
2 WKUPCS Wake up on Chip Select: Logic 1 enables wake-up from suspend
mode through a valid register read on the ISP1582. (A read will
invokethe chip clock to restart. If you write to the register before the
clock gets stable, it may cause malfunctioning).
1 PWRON Pin SUSPEND output control.
…continued
0 — Pin SUSPEND is HIGH when the ISP1582 is in the suspend
state. Otherwise, pin SUSPEND is LOW.
1 — When the device is woken up from the suspend state, there will
be a 1 ms active HIGH pulse on pin SUSPEND. Pin SUSPEND will
remain LOW in all other states.
0 SOFTCT SoftConnect: Logic 1 enables the connection of the 1.5 kΩ pull-up
resistor on pin RPU to the DP line. Bus reset value: unchanged.
When SoftConnect and V
are not present (except in OTG), the USB bus activities
BUS
are not qualified. Therefore, the chip will follow the suspend command to enter
suspend mode (the clock is controlled by bit CLKAON).
When V
is off, the 1.5 kΩ pull-up resister is disconnected from pin DP in
BUS
approximately 4 ns via bit SOFTCT in the Mode register and a suspend interrupt is
set with some latency (debounce and disqualify USB traffic).
When bit SOFTCT is set to logic 0, no interrupt is generated. The firmware can issue
a suspend command, followed by the resetting of bit SOFTCT to suspend the chip.
If OTG is logic 1, the pull-up resistor on pin DP depends on D+ line (V
BUS
sensing
status). Bit DP operates as normal, so the firmware must mask suspend and wake-up
interrupt events. When SRP is completed, the device should clear OTG.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 26 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 27

Philips Semiconductors
If OTG is logic 0, the status of the pull-up resistor on DP is referred to in Table 22.
Table 22: Status of the chip
V
BUS
On pull-up resistor on DP pull-up resistor on DP is removed;
Off pull-up resistor on DP is removed;
9.2.3 Interrupt Configuration register (address: 10h)
This 1-byte register determines the behavior and polarity of the INT output. The bit
allocation is shown in Table 23. When the USB SIE receives or generates an ACK,
NAK or STALL, it will generate interrupts depending on three Debug mode fields.
CDBGMOD[1:0] — Interrupts for the control endpoint 0
DDBGMODIN[1:0] — Interrupts for the DATA IN endpoints 1 to 7
DDBGMODOUT[1:0] — Interrupts for the DATA OUT endpoints 1 to 7.
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
SoftConnect = on SoftConnect = off
suspend interrupt is immediately set,
regardless of the D+ and D− signals
pull-up resistor on DP is removed;
suspend interrupt is immediately set,
regardless of the D+ and D− signals
suspend interrupt is immediately set,
regardless of the D+ and D− signals
ISP1582
The Debug mode settings for CDBGMOD, DDBGMODIN and DDBGMODOUT allow
you to individually configure when the ISP1582 sends an interrupt to the external
microprocessor. Table 25 lists the available combinations.
Bit INTPOL controls the signal polarity of the INT output: active HIGH or LOW, rising
or falling edge. For level-triggering, bit INTLVL must be made logic 0. By setting
INTLVL to logic 1, an interrupt will generate a pulse of 60 ns (edge-triggering).
Table 23: Interrupt Configuration register: bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol CDBGMOD[1:0] DDBGMODIN[1:0] DDBGMODOUT[1:0] INTLVL INTPOL
Reset 11111100
Bus reset 111111unchanged unchanged
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Table 24: Interrupt Configuration register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
7 to 6 CDBGMOD[1:0] Control 0 Debug Mode: For values, see Table 25
5 to 4 DDBGMODIN[1:0] Data Debug Mode IN: For values, see Table 25
3 to 2 DDBGMODOUT[1:0] Data Debug Mode OUT: For values, seeTable 25
1 INTLVL Interrupt Level: Selects signaling mode on output INT
(0 = level; 1 = pulsed). In pulsed mode, an interrupt
produces a 60 ns pulse. Bus reset value: unchanged.
0 INTPOL Interrupt Polarity: Selects signal polarity on output INT
(0 = active LOW; 1 = active HIGH). Bus reset
value: unchanged.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 27 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 28

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Table 25: Debug mode settings
Value CDBGMOD DDBGMODIN DDBGMODOUT
00h interrupt on all ACK and
NAK
interrupt on all ACK and
NAK
interrupt on all ACK, NYET
and NAK
01h interrupt on all ACK. interrupt on ACK interrupt on ACK and NYET
1Xh interrupt on all ACK and
first NAK
[1] First NAK: the first NAK on an IN or OUT token after a previous ACK response.
[1]
interrupt on all ACK and
first NAK
[1]
interrupt on all ACK, NYET
and first NAK
[1]
9.2.4 OTG register (address: 12h)
The bit allocation of the OTG register is given in Table 26.
Table 26: OTG register: bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol reserved DP BSESSVALID INITCOND DISCV VP OTG
Reset --0- -000
Bus reset --0- -000
Access - - R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Table 27: OTG register: bit description
[1][2][3]
Bit Symbol Description
7 to 6 - reserved
5 DP When set, data-line pulsing is started. The default value of this bit is
logic 0. This bit must be cleared when data-line pulsing is completed.
4 BSESS VALID The device can initiate another V
data-line pulsing and V
pulsing, and before it clears this bit and
BUS
discharge sequence after
BUS
detects a session valid.
This bit is latched to logic 1 once V
exceeds the B-device session
BUS
valid threshold. Once set, it remains at logic 1. To clear this bit, write
logic 1. (The ISP1582 continuously updates this bit to logic 1 when
the B-session is valid. If the B-session is valid after it is cleared, it is
set back to logic 1 by the ISP1582).
0 — It implies that SRP has failed. Toproceed to a normal operation,
the device can restart SRP, clear bit OTG or proceed to an error
handling process.
1 — It implies that the B-session is valid. The device clears bit OTG,
goes into normal operation mode, and sets bit SOFTCT (DP pull-up)
in the Mode register. The OTG host has a maximum of 5 s before it
responds to a session request. During this period, the ISP1582 may
request to suspend. Therefore, the device firmware must wait for
sometime if it wishes to know the SRP result (success—if there is
minimum response from the host within 5 s; failure—if there is no
response from the host within 5 s).
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 28 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 29

Philips Semiconductors
Table 27: OTG register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
3 INIT COND Write logic 1 to clear this bit. The device clears this bit, and waits for
2 DISCV Set to logic 1 to discharge V
1 VP Set to logic 1 to start V
0OTG 1 — Enables the OTG function. The V
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
[1][2][3]
…continued
more than 2 ms to check the bit status. If it reads logic 0, it means
that V
elapsed time is cleared. The device can then start a B-device SRP. If
it reads logic 1, it means that the initial condition of an SRP is
violated. So, the device should abort SRP.
The bit is set to logic 1 by the ISP1582 when initial conditions are not
met, and only writing logic 1 clears the bit. (If initial conditions are not
met after this bit has been cleared, it will be set again).
Remark: This implementation does not cover the case if an initial
SRP condition is violated when this bit is read and data-line pulsing is
started.
starting a new SRP. The discharge can take as long as 30 ms for
V
BUS
logic 0) before starting a session end detection.
16 ms and must be cleared before 26 ms.
bypassed.
0 — Normal operation. All OTG control bits will be masked. Status
bits are undefined.
remains lower than 0.8 V, and DP or DM at SE0 during the
BUS
. The device discharges V
BUS
BUS
before
to be charged less than 0.8 V. This bit must be cleared (write
pulsing. This bit must be set for more than
BUS
sensing functionality will be
BUS
[1] No interrupt is designed for OTG. The V
V
pulsing (see note 2).
BUS
[2] When OTG is in progress, the V
threshold or the OTG host has turned on the V
found during SRP, the device should complete data-line pulsing and V
B_SESSION_VALID detection.
[3] OTG implementation applies to the device with self-power capability. If the device works in sharing
mode, it should provide a switch circuit to supply power to the ISP1582 core during SRP.
BUS
interrupt, however, may assert as a side effect during the
BUS
interrupt may be set because V
supply to the device. Even if the V
BUS
is charged over V
BUS
pulsing before starting the
BUS
BUS
interrupt is
BUS
sensing
Session Request Protocol (SRP):
The ISP1582 can initiate an SRP. The B-device initiates SRP by data-line pulsing
followed by V
pulsing. The A-device can detect either data-line pulsing or V
BUS
BUS
pulsing.
The ISP1582 can initiate the B-device SRP by performing the following steps:
1. Detect initial conditions: read bit INITCOND of the OTG register.
2. Start data-line pulsing: set bit DP of the OTG register to logic 1.
3. Wait for 5 ms to 10 ms.
4. Stop data-line pulsing: set bit DP of the OTG register to logic 0.
5. Start V
pulsing: set bit VP of the OTG register to logic 1.
BUS
6. Wait for 10 ms to 20 ms.
7. Stop V
8. Discharge V
pulsing: set bit VP of the OTG register to logic 0.
BUS
for about 30 ms: optional by using bit DISCV of the OTG register.
BUS
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 29 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 30

Philips Semiconductors
9. Detect bit BSESSVALID of the OTG register for a successful SRP with bit OTG
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
disabled.
The B-device must complete both data-line pulsing and V
Remark: When disabling, OTG data-line pulsing bit DP and V
be cleared by writing logic 1.
9.2.5 Interrupt Enable register (address: 14h)
This register enables or disables individual interrupt sources. The interrupt for each
endpoint can be individually controlled via the associated bits IEPnRX or IEPnTX,
here n represents the endpoint number. All interrupts can be globally disabled
through bit GLINTENA in the Mode register (see Table 20).
An interrupt is generated when the USB SIE receives or generates an ACK or NAK
on the USB bus. The interrupt generation depends on Debug mode settings of bit
fields CDBGMOD[1:0], DDBGMODIN[1:0] and DDBGMODOUT[1:0].
All data IN transactions use the Transmit buffers (TX), which are handled by bits
DDBGMODIN. All data OUT transactions go via the Receive buffers (RX), which are
handled by bits DDBGMODOUT. Transactions on control endpoint 0 (IN, OUT and
SETUP) are handled by bits CDBGMOD.
Interrupts caused by events on the USB bus (SOF, Pseudo SOF, suspend, resume,
bus reset, setup and high-speed status) can also be individually controlled. A bus
reset disables all enabled interrupts except bit IEBRST (bus reset), which remains
unchanged.
pulsing within 100 ms.
BUS
pulsing bit VP must
BUS
The Interrupt Enable register consists of 4 bytes. The bit allocation is given in
Table 28.
Table 28: Interrupt Enable register: bit allocation
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24
Symbol reserved IEP7TX IEP7RX
Reset ------00
Bus Reset ------00
Access - - - - - - R/W R/W
Bit 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Symbol IEP6TX IEP6RX IEP5TX IEP5RX IEP4TX IEP4RX IEP3TX IEP3RX
Reset 00000000
Bus Reset 00000000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Symbol IEP2TX IEP2RX IEP1TX IEP1RX IEP0TX IEP0RX reserved IEP0SETUP
Reset 000000-0
Bus Reset 000000-0
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 30 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 31

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol IEVBUS IEDMA IEHS_STA IERESM IESUSP IEPSOF IESOF IEBRST
Reset 00000000
Bus Reset 0000000unchanged
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Table 29: Interrupt Enable register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
31 to 26 - reserved
25 EP7TX Logic 1 enables interrupt from the indicated endpoint.
24 EP7RX Logic 1 enables interrupt from the indicated endpoint.
23 EP6TX Logic 1 enables interrupt from the indicated endpoint.
22 EP6RX Logic 1 enables interrupt from the indicated endpoint.
21 EP5TX Logic 1 enables interrupt from the indicated endpoint.
20 EP5RX Logic 1 enables interrupt from the indicated endpoint.
19 EP4TX Logic 1 enables interrupt from the indicated endpoint.
18 EP4RX Logic 1 enables interrupt from the indicated endpoint.
17 EP3TX Logic 1 enables interrupt from the indicated endpoint.
16 EP3RX Logic 1 enables interrupt from the indicated endpoint.
15 EP2TX Logic 1 enables interrupt from the indicated endpoint.
14 EP2RX Logic 1 enables interrupt from the indicated endpoint.
13 EP1TX Logic 1 enables interrupt from the indicated endpoint.
12 IEP1RX Logic 1 enables interrupt from the indicated endpoint.
11 IEP0TX Logic 1 enables interrupt from the control IN endpoint 0.
10 IEP0RX Logic 1 enables interrupt from the control OUT endpoint 0.
9 - reserved
8 IEP0SETUP Logic 1 enables interrupt for the setup data received on endpoint 0.
7 IEVBUS Logic 1 enables interrupt for V
6 IEDMA Logic 1 enables interrupt on DMA status change detection.
5 IEHS_STA Logic 1 enables interrupt on detection of a high-speed status
change.
4 IERESM Logic 1 enables interrupt on detection of a resume state.
3 IESUSP Logic 1 enables interrupt on detection of a suspend state.
2 IEPSOF Logic 1 enables interrupt on detection of a Pseudo SOF.
1 IESOF Logic 1 enables interrupt on detection of an SOF.
0 IEBRST Logic 1 enables interrupt on detection of a bus reset.
BUS
sensing.
9.3 Data flow registers
9.3.1 Endpoint Index register (address: 2Ch)
The Endpoint Index register selects a target endpoint for register access by the
microcontroller. The register consists of 1 byte, and the bit allocation is shown in
Table 30.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 31 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 32

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
The following registers are indexed:
• Buffer Length
• Buffer Status
• Control Function
• Data Port
• Endpoint MaxPacketSize
• Endpoint Type.
For example, to access the OUT data buffer of endpoint 1 using the Data Port
register, the Endpoint Index register has to be written first with 02h.
Remark: The Endpoint Index register and the DMA Endpoint Index register must not
point to the same endpoint.
Table 30: Endpoint Index register: bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol reserved EP0SETUP ENDPIDX[3:0] DIR
Reset - - 000000
Bus reset - - 000000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Table 31: Endpoint Index register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
7 to 6 - reserved
5 EP0SETUP Selects the SETUP buffer for endpoint 0.
0 — EP0 data buffer
1 — SETUP buffer.
Must be logic 0 for access to other endpoints than endpoint 0.
4 to 1 ENDPIDX[3:0] Endpoint Index: Selects the target endpoint for register access of
Buffer Length, Control Function, Data Port, Endpoint Type and
MaxPacketSize.
0 DIR Direction bit: Sets the target endpoint as IN or OUT.
0 — target endpoint refers to OUT (RX) FIFO
1 — target endpoint refers to IN (TX) FIFO.
Table 32: Addressing of endpoint 0 buffers
Buffer name EP0SETUP ENDPIDX DIR
SETUP 1 00h 0
Data OUT 0 00h 0
Data IN 0 00h 1
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 32 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 33

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
9.3.2 Control Function register (address: 28h)
The Control Function register performs the buffer management on endpoints. It
consists of 1 byte, and the bit configuration is given in Table 33. The register bits can
stall, clear or validate any enabled data endpoint. Before accessing this register, the
Endpoint Index register must be written first to specify the target endpoint.
Table 33: Control Function register: bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol reserved CLBUF VENDP DSEN STATUS STALL
Reset - - -00000
Bus reset - - -00000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Table 34: Control Function register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
7 to 5 - reserved
4 CLBUF Clear Buffer: Logic 1 clears the RX bufferoftheindexed endpoint; the TX
buffer is not affected. The RX buffer is automatically cleared once the
endpoint is completely read. This bit is set only when it is necessary to
forcefully clear the buffer.
3 VENDP Validate Endpoint: Logic 1 validates the data in the TX FIFO of an IN
endpoint for sending on the next IN token. In general, the endpoint is
automatically validated when its FIFO byte count has reached the
endpoint MaxPacketSize. This bit is set only when it is necessary to
validate the endpoint with the FIFO byte count which is below the
Endpoint MaxPacketSize.
2 DSEN Data Stage Enable: This bit controls the response of the ISP1582 to a
control transfer. When this bit is set, the ISP1582 goes to the data stage;
otherwise, the ISP1582 will NAK the data stage transfer until the firmware
explicitly responds to the setup command.
1 STATUS Status Acknowledge: Only applicable for control IN/OUT.
This bit controls the generation of ACK or NAK during the status stage of
a SETUP transfer. It is automatically cleared when the status stage is
completed, or when a SETUP tokenis received. No interrupt signal will be
generated.
0 — Sends NAK
1 — Sends an empty packet following the IN token (host-to-peripheral) or
ACK following the OUT token (peripheral-to-host).
0 STALL Stall Endpoint: Logic 1 stalls the indexed endpoint. This bit is not
applicable for isochronous transfers.
Remark: ‘Stall’ing a data endpoint will confuse the Data Toggle bit about
the stalled endpoint because the internal logic picks up from where it is
stalled. Therefore, the Data Toggle bit must be reset by disabling and
reenabling the corresponding endpoint (by setting bit ENABLE to logic 0
or logic 1 in the Endpoint Type register) to reset the PID.
9.3.3 Data Port register (address: 20h)
This 2-byte register provides direct access for a microcontroller to the FIFO of the
indexed endpoint. The bit allocation is shown in Table 35.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 33 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 34

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Peripheral-to-host (IN endpoint): After each write action, an internal counter is auto
incremented by two to the next location in the TX FIFO. When all bytes have been
written (FIFO byte count = endpoint MaxPacketSize), the buffer is automatically
validated. The data packet will then be sent on the next IN token. When it is
necessary to validate the endpoint whose byte count is less than MaxPacketSize, it
can be done using the Control Function register (bit VENDP).
Host-to-peripheral (OUT endpoint): After each read action, an internal counter is
auto decremented by two to the next location in the RX FIFO. When all bytes have
been read, the buffer contents are automatically cleared. A new data packet can then
be received on the next OUT token. The buffer contents can also be cleared through
the Control Function register (bit CLBUF), when it is necessary to forcefully clear the
contents.
Remark: The buffer can be automatically validated or cleared by using the Buffer
Length register (see Table 37).
Table 35: Data Port register: bit allocation
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Symbol DATAPORT[15:8]
Reset 00000000
Bus reset 00000000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol DATAPORT[7:0]
Reset 00000000
Bus reset 00000000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Table 36: Data Port register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
15 to 8 DATAPORT[15:8] data (upper byte)
7 to 0 DATAPORT[7:0] data (lower byte)
9.3.4 Buffer Length register (address: 1Ch)
This register determines the current packet size (DATACOUNT) of the indexed
endpoint FIFO. The bit allocation is given in Table 37.
The Buffer Length register is automatically loaded with the FIFO size, when the
Endpoint MaxPacketSize register is written (see Table 41). A smaller value can be
written when required. After a bus reset, the Buffer Length register is made zero.
IN endpoint: When data transfer is performed in multiples of MaxPacketSize, the
Buffer Length register is not significant. This register is useful only when transferring
data that is not a multiple of MaxPacketSize. The following two examples
demonstrate the significance of the Buffer Length register.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 34 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 35

Philips Semiconductors
Example 1: Consider that the transfer size is 512 bytes and the MaxPacketSize is
programmed as 64 bytes, the Buffer Length register need not be filled. This is
because the transfer size is a multiple of MaxPacketSize, and the MaxPacketSize
packets will be automatically validated because the last packet is also of
MaxPacketSize.
Example 2: Consider that the transfer size is 510 bytes and the MaxPacketSize is
programmed as 64 bytes, the Buffer Length register should be filled with 62 bytes just
before the MCU writes the last packet of 62 bytes. This ensures that the last packet,
which is a short packet of 62 bytes, is automatically validated.
Use bit VENDP in the Control register if you are not using the Buffer Length register.
This is applicable only to PIO mode access.
OUT endpoint: The DATACOUNT value is automatically initialized to the number of
data bytes sent by the host on each ACK.
Remark: When using a 16-bit microprocessor bus, the last byte of an odd-sized
packet is output as the lower byte (LSByte).
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Remark: Buffer Length is valid only after an interrupt is generated for the bulk
endpoint.
Table 37: Buffer Length register: bit allocation
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Symbol DATACOUNT[15:8]
Reset 00000000
Bus reset 00000000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol DATACOUNT[7:0]
Reset 00000000
Bus reset 00000000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Table 38: Buffer Length register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
15 to 0 DATACOUNT[15:0] Determines the current packet size of the indexed endpoint
FIFO.
9.3.5 Buffer Status register (address: 1Eh)
This register is accessed using index. The endpoint index must first be set before
accessing this register for the corresponding endpoint. It reflects the status of the
double buffered endpoint FIFO. This register is valid only when the endpoint is
configured to be a double buffer.
Remark: This register is not applicable to the control endpoint.
Table 39 shows the bit allocation of the Buffer Status register.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 35 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 36

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Table 39: Buffer Status register: bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol reserved BUF1 BUF0
Reset ------00
Bus reset ------00
Access ------RR
Table 40: Buffer Status register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
7 to 2 - reserved
1 to 0 BUF[1:0] 00 — The buffers are not filled.
01 — One of the buffers is filled.
10 — One of the buffers is filled.
11 — Both the buffers are filled.
9.3.6 Endpoint MaxPacketSize register (address: 04h)
This register determines the maximum packet size for all endpoints except control 0.
The register contains 2 bytes, and the bit allocation is given in Table 41.
Each time the register is written, the Buffer Length registers of all endpoints are
reinitialized to the FFOSZ field value. Bits NTRANS control the number of
transactions allowed in a single microframe (for high-speed isochronous and interrupt
endpoints only).
Table 41: Endpoint MaxPacketSize register: bit allocation
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Symbol reserved NTRANS[1:0] FFOSZ[10:8]
Reset - - -00000
Bus reset - - -00000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol FFOSZ[7:0]
Reset 00000000
Bus reset 00000000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 36 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 37

Philips Semiconductors
Table 42: Endpoint MaxPacketSize register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
15 to 13 - reserved
12 to 11 NTRANS[1:0] Number of Transactions. HS mode only.
10 to 0 FFOSZ[10:0] FIFO Size: Sets the FIFO size, in bytes, for the indexed endpoint.
Table 43: Programmable FIFO size
NTRANS[1:0] FFOSZ[10:0] Non-isochronous Isochronous
0h 08h 8 bytes 0h 10h 16 bytes 0h 20h 32 bytes 0h 40h 64 bytes 0h 80h 128 bytes 0h 100h 256 bytes 0h 200h 512 bytes 2h 400h - 3072 bytes
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
00 — 1 packet per microframe
01 — 2 packets per microframe
10 — 3 packets per microframe
11 — reserved.
These bits are applicable only for isochronous or interrupt
transactions.
Applies to both high-speed and full-speed operations (see
Table 43).
Each programmable FIFO can be independently configured via its Endpoint
MaxPacketSize register (R/W: 04h), but the total physical size of all enabled
endpoints (IN plus OUT) must not exceed 8192 bytes.
9.3.7 Endpoint Type register (address: 08h)
This register sets the endpoint type of the indexed endpoint: isochronous, bulk or
interrupt. It also serves to enable the endpoint and configure it for double buffering.
Automatic generation of an empty packet for a zero-length TX buffer can be disabled
using bit NOEMPKT. The register contains 2 bytes, and the bit allocation is shown in
Table 44.
Table 44: Endpoint Type register: bit allocation
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Symbol reserved
Reset -------Bus reset -------Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 37 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 38

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol reserved NOEMPKT ENABLE DBLBUF ENDPTYP[1:0]
Reset - - -00000
Bus reset - - -00000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Table 45: Endpoint Type register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
15 to 5 - reserved
4 NOEMPKT No Empty Packet: Logic 0 causes the ISP1582 to return a null
length packet for the IN token after the DMA IN transfer is
complete. For ATA mode or the IN DMA transfer, which does not
require a null length packet after DMA completion, set to logic 1 to
disable the generation of the null length packet.
3 ENABLE Endpoint Enable: Logic 1 enables the FIFO of the indexed
endpoint. The memory size is allocated as specified in the
Endpoint MaxPacketSize register. Logic 0 disables the FIFO.
Remark: ‘Stall’ing a data endpoint will confuse the Data Toggle bit
on the stalled endpoint because the internal logic picks up from
where it has stalled. Therefore, the Data Toggle bit must be reset
by disabling and reenabling the corresponding endpoint (by setting
bit ENABLE to logic 0 or logic 1 in the Endpoint Type register) to
reset the PID.
2 DBLBUF Double Buffering: Logic 1 enables double buffering for the
indexed endpoint. Logic 0 disables double buffering.
1 to 0 ENDPTYP[1:0] Endpoint Type: These bits select the endpoint type as follows.
00 — not used
01 — Isochronous
10 — Bulk
11 — Interrupt.
9.4 DMA registers
The Generic DMA (GDMA) transfer can be done by writing the proper opcode in the
DMA Command register. The control bits are given in Table 46.
GDMA read/write (opcode = 00h/01h) for Generic DMA slave mode
Depending on the MODE[1:0] bit set in the DMA configuration register, either the
DACK signal or the DIOR/DIOW signals strobe the data. These signals are driven by
the external DMA controller.
GDMA (slave) mode can operate in either counter mode or EOT-only mode.
In counter mode, bit DIS_XFER_CNT in the DMA Configuration register must be set
to logic 0. The DMA Transfer Counter register must be programmed before any DMA
command is issued. The DMA transfercounter is set by writing from the LSByte to the
MSByte (address: 34h to 37h). The DMA transfer count is internally updated only
after the MSByte has been written. Once the DMA transfer is started, the transfer
counter starts decrementing and on reaching 0, bit DMA_XFER_OK is set and an
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 38 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 39

Philips Semiconductors
interrupt is generated by the ISP1582. If the DMA master wishes to terminate the
DMA transfer, it can issue an EOT signal to the ISP1582. This EOT signal overrides
the transfer counter and can terminate the DMA transfer at any time.
In EOT-only mode, DIS_XFER_CNT has to be set to logic 1. Although the DMA
transfer counter can still be programmed, it will not have any effect on the DMA
transfer. The DMA transfer will start once the DMA command is issued. Any of the
following three ways will terminate this DMA transfer:
• Detecting an external EOT
• Detecting an internal EOT (short packet on an OUT token)
• Resetting the DMA.
There are three interrupts programmable to differentiate the method of DMA
termination: bits INT_EOT, EXT_EOT and DMA_XFER_OK in the DMA Interrupt
Reason register. For details, see Table 58.
Table 46: Control bits for GDMA read/write (opcode = 00h/01h)
Control bits Description Reference
DMA Configuration register
MODE[1:0] Determines the active read/write data strobe signals. Table 52
WIDTH Selects the DMA bus width: 8 or 16 bits.
DIS_XFER_CNT Disables the use of the DMA Transfer Counter.
DMA Hardware register
EOT_POL Selects the polarity of the EOT signal. Table 54
ENDIAN[1:0] Determines whether the data is to be byte swapped or
ACK_POL,
DREQ_POL,
WRITE_POL,
READ_POL
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
normal. Applicable only in 16-bit mode.
Select the polarity of the DMA handshake signals.
Remark: The DMA bus defaults to three-state, until a DMA command is executed. All
the other control signals are not three-state.
9.4.1 DMA Command register (address: 30h)
The DMA Command register is a 1-byte register (for bit allocation, see Table 47) that
initiates all DMA transfer activity on the DMA controller. The register is write-only:
reading it will return FFh.
Remark: The DMA bus will be in three-state until a DMA command is executed.
Table 47: DMA Command register: bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol DMA_CMD[7:0]
Reset 11111111
Bus reset 11111111
Access WWWWWWWW
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 39 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 40

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Table 48: DMA Command register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
7 to 0 DMA_CMD[7:0] DMA command code; see Table 49.
Table 49: DMA commands
Code Name Description
00h GDMA Read Generic DMA IN token transfer (slave mode only): Data is transferred from the external
DMA bus to the internal buffer. Strobe: DIOW by external DMA controller.
01h GDMA Write Generic DMA OUT token transfer (slave mode only): Data is transferred from the internal
buffer to the external DMA bus. Strobe: DIOR by external DMA controller.
02h to 0Dh - reserved
0Eh Validate Buffer Validate Buffer (for debugging only): Request from the microcontroller to validate the
endpoint buffer following a DMA to USB data transfer.
0Fh Clear Buffer Clear Buffer: Request from the microcontroller to clear the endpoint buffer after a USB to
DMA data transfer.
10h - reserved
11h Reset DMA Reset DMA: Initializes the DMA core to its power-on reset state.
Remark: When the DMA core is reset during the Reset DMA command, the DREQ, DACK,
DIOW and DIOR handshake pins will be temporarily asserted. This can confuse the external
DMA controller. To prevent this, start the external DMA controller only after the DMA reset.
12h - reserved
13h GDMA Stop GDMA stop: This command stops the GDMA data transfer. Any data in the OUT endpoint
that is not transferred by the DMA will remain in the buffer.The FIFO data for the IN endpoint
will be written to the endpoint buffer. An interrupt bit will be set to indicate the completion of
the DMA Stop command.
14h to FFh - reserved
9.4.2 DMA Transfer Counter register (address: 34h)
This 4-byte register sets up the total byte count for a DMA transfer (DMACR). It
indicates the remaining number of bytes left for transfer. The bit allocation is given in
Table 50.
For IN endpoint — As there is a FIFO in the ISP1582 DMA controller, some data
may remain in the FIFO during the DMA transfer. The maximum FIFO size is 8 bytes,
and the maximum delay time for the data to be shifted to endpoint buffer is 60 ns.
For OUT endpoint — Data will not be cleared for the endpoint buffer until all the data
has been read from the DMA FIFO.
If the DMA counter is disabled in the DMA transfer, it will still decrement and rollover
when it reaches zero.
Table 50: DMA Transfer Counter register: bit allocation
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24
Symbol DMACR4 = DMACR[31:24]
Reset 00000000
Bus reset 00000000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 40 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 41

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Bit 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Symbol DMACR3 = DMACR[23:16]
Reset 00000000
Bus reset 00000000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Symbol DMACR2 = DMACR[15:8]
Reset 00000000
Bus reset 00000000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol DMACR1 = DMACR[7:0]
Reset 00000000
Bus reset 00000000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Table 51: DMA Transfer Counter register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
31 to 24 DMACR4, DMACR[31:24] DMA transfer counter byte 4 (MSB)
23 to 16 DMACR3, DMACR[23:16] DMA transfer counter byte 3
15 to 8 DMACR2, DMACR[15:8] DMA transfer counter byte2
7 to 0 DMACR1, DMACR[7:0] DMA transfer counter byte 1 (LSB)
9.4.3 DMA Configuration register (address: 38h)
This register defines the DMA configuration for GDMA mode. The DMA Configuration
register consists of 2 bytes. The bit allocation is given in Table 52.
Table 52: DMA Configuration register: bit allocation
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Symbol reserved
Reset 00000000
Bus Reset 00000000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol DIS_
XFER_CNT
Reset 00000001
Bus Reset 00000001
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
reserved MODE[1:0] reserved WIDTH
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 41 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 42

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Table 53: DMA Configuration register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
15 to 8 - reserved
7 DIS_XFER_CNT Logic 1 disables the DMA Transfer Counter (see Table 50). The
transfer counter can be disabled only in GDMA (slave) mode.
6 to 4 - reserved
3 to 2 MODE[1:0] These bits only affect the GDMA slave handshake signals.
00 — DIOW slave strobes data from the DMA bus into the
ISP1582; DIOR slave puts data from the ISP1582 on the DMA
bus
01 — DACK slave strobes data from the DMA bus into the
ISP1582; DIOR slave puts data from the ISP1582 on the DMA
bus
10 — DACK slave strobes data from the DMA bus into the
ISP1582 and also puts data from the ISP1582 on the DMA bus.
(This mode is applicable only to the 16-bit DMA; this mode
cannot be used for the 8-bit DMA.)
11 — reserved.
1 - reserved
0 WIDTH This bit selects the DMA bus width for the GDMA slave.
0 — 8-bit data bus
1 — 16-bit data bus.
[1]
[1] The DREQ pin will only be driven only after you perform a write access to the DMA Configuration
register (that is, after you have configured the DMA Configuration register).
9.4.4 DMA Hardware register (address: 3Ch)
The DMA Hardware register consists of 1 byte. The bit allocation is shown in
Table 54.
This register determines the polarity of the bus control signals (EOT, DACK, DREQ,
DIOR and DIOW) and DMA mode (master or slave). It also controls whether the
upper and lower parts of the data bus are swapped (bits ENDIAN[1:0]) for GDMA
(slave) mode.
Table 54: DMA Hardware register: bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol ENDIAN[1:0] EOT_POL reserved ACK_POL DREQ_
POL
Reset 00000100
Bus reset 00000100
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
WRITE_
POL
READ_
POL
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 42 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 43

Philips Semiconductors
Table 55: DMA Hardware register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
7 to 6 ENDIAN[1:0] These bits determine whether the data bus is swapped between the
5 EOT_POL Selects the polarity of the End-Of-Transfer input; used in GDMA
4 - reserved; must be set to logic 0.
3 ACK_POL Selects the DMA acknowledgment polarity.
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
internal RAM and the DMA bus. This only applies for GDMA (slave)
mode.
00 — Normal data representation
16-bit bus: MSB on DATA[15:8], LSB on DATA[7:0]
01 — Swapped data representation
16-bit bus: MSB on DATA[7:0], LSB on DATA[15:8]
10 — reserved
11 — reserved.
Remark: While operating with the 8-bit data bus, bits ENDIAN[1:0]
should be always set to logic 00.
(slave) mode only.
0 — EOT is active LOW
1 — EOT is active HIGH.
0 — DACK is active LOW
1 — DACK is active HIGH.
2 DREQ_POL Selects the DMA request polarity.
0 — DREQ is active LOW
1 — DREQ is active HIGH.
1 WRITE_POL Selects the DIOW strobe polarity.
0 — DIOW is active LOW
1 — DIOW is active HIGH.
0 READ_POL Selects the DIOR strobe polarity.
0 — DIOR is active LOW
1 — DIOR is active HIGH.
9.4.5 DMA Interrupt Reason register (address: 50h)
This 2-byte register shows the source(s) of DMA interrupt. Each bit is refreshed after
a DMA command has been executed.An interrupt source is cleared by writing logic 1
to the corresponding bit. When reading, AND the value of the bits in this register with
the value of the corresponding bits in the DMA Interrupt Enable register.
The bit allocation is given in Table 56.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 43 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 44

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Table 56: DMA Interrupt Reason register: bit allocation
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Symbol TEST3 reserved GDMA_
STOP
Reset ---000-0
Bus reset ---000-0
Access R R R R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol reserved
Reset -------Bus reset -------Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Table 57: DMA Interrupt Reason register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
15 TEST3 This bit is set when the DMA transfer for a packet(OUTtransfer)
terminates before the whole packet has been transferred. This
bit is a status bit, and the corresponding mask bit of this register
is always logic 0. Writing any value other than logic 0 has no
effect.
14 to 13 - reserved
12 GDMA_STOP When the GDMA_STOP command is issued to the DMA
Command registers, it means the DMA transfer has
successfully terminated.
11 EXT_EOT Logic 1 indicates that an external EOT is detected. This is
applicable only in GDMA (slave) mode.
10 INT_EOT Logic 1 indicates that an internal EOT is detected; see Table 58.
9 - reserved
8 DMA_XFER_OK Logic 1 indicates that the DMA transfer has been completed
(DMA Transfer Counter has become zero). This bit is only used
in GDMA (slave) mode.
7 to 0 - reserved
EXT_EOT INT_EOT reserved DMA_
XFER_OK
Table 58: Internal EOT-functional relation with bit DMA_XFER_OK
INT_EOT DMA_XFER_OK Description
1 0 During the DMA transfer, there is a premature termination
with short packet.
1 1 DMA transfer is completed with short packet and the DMA
transfer counter has reached 0.
0 1 DMA transfer is completed without any short packet and the
DMA transfer counter has reached 0.
Table 59 shows the status of the bits in the DMA Interrupt Reason register when the
corresponding bits in the Interrupt register is set.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 44 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 45

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Table 59: Status of the bits in the DMA Interrupt Reason register
Status EXT_EOT INT_EOT DMA_XFER_OK
IN full 1 0 1 0
IN short 1 0 1 0
OUT full 1 0 1 0
OUT short 1 1
[1] 1 indicates that the bit is set and 0 indicates that the bit is not set. A bit is set when the corresponding
EOT condition is met. For example; EXT_EOT is set if external EOT conditions are met (pin EOT
active), regardless of other EOT conditions. If multiple EOT conditions are met, the corresponding
interrupt bits are set.
[2] If both EXT_EOT and DMA_XFER_OK conditions are met in DMA for an IN endpoint, the EXT_EOT
interrupt is not set.
[3] The value of INT_EOT may not be accurate if an external or internal transfer counter is programmed
with a value that is lower than the transfer that the host requests. To terminate an OUT transfer with
INT_EOT, the external or internal DMA counter should be programmed as a multiple of the full-packet
length of the DMA endpoint. When a short packet is successfully transferredbyDMA,INT_EOT is set.
[3]
9.4.6 DMA Interrupt Enable register (address: 54h)
This 2-byte register controls the interrupt generation of the source bits in the DMA
Interrupt Reason register. The bit allocation is given in Table 60.The bit description is
given in Table 57.
Logic 1 enables the interrupt generation. After a bus reset, interrupt generation is
disabled, with the values turning to logic 0.
[1][2]
Counter enabled Counter disabled
10
Table 60: DMA Interrupt Enable register: bit allocation
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Symbol TEST4 reserved IE_GDMA_
STOP
Reset - - -00000
Bus reset - - -00000
Access R - - R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol reserved
Reset 00000000
Bus reset 00000000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
IE_EXT_
EOT
IE_INT_
EOT
reserved IE_DMA_
XFER_OK
9.4.7 DMA Endpoint register (address: 58h)
This 1-byte register selects a USB endpoint FIFO as a source or destination for DMA
transfers. The bit allocation is given in Table 61.
Table 61: DMA Endpoint register: bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol reserved EPIDX[2:0] DMADIR
Reset ----0000
Bus reset ----0000
Access ----R/WR/WR/WR/W
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 45 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 46

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Table 62: DMA Endpoint register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
7 to 4 - reserved
3 to 1 EPIDX[2:0] selects the indicated endpoint for DMA access
0 DMADIR 0 — Selects the RX/OUT FIFO for DMA read transfers
1 — Selects the TX/IN FIFO for DMA write transfers.
The DMA Endpoint register must not reference the endpoint that is indexed by the
Endpoint Index register (2Ch) at any time. Doing so would result in data corruption.
Therefore, if the DMA Endpoint register is unused, point it to an unused endpoint. If
the DMA Endpoint register, however, is pointed to an active endpoint, the firmware
must not reference the same endpoint on the Endpoint Index register.
9.4.8 DMA Burst Counter register (address: 64h)
Table 63 shows the bit allocation of the register.
Table 63: DMA Burst Counter register: bit allocation
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Symbol reserved BURSTCOUNTER[12:8]
Reset - - -00000
Bus reset - - -00000
Access - - - R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol BURSTCOUNTER[7:0]
Reset 00000010
Bus reset 00000010
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Table 64: DMA Burst Counter register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
15 to 13 - reserved
12 to 0 BURSTCOUNTER[12:0] This register defines the burstlength.The counter must
be programmed to be a multiple of two in 16-bit mode.
The value of the burst counter should be programmed
such that the buffer counter is a factor of the burst
counter.
For IN endpoint — When the burst counter equals 2,
in GDMA mode, DREQ will drop at every DMA read or
write cycle.
9.5 General registers
9.5.1 Interrupt register (address: 18h)
The Interrupt register consists of 4 bytes. The bit allocation is given in Table 65.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 46 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 47

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
When a bit is set in the Interrupt register, it indicates that the hardware condition for
an interrupt has occurred. When the Interrupt register content is nonzero, the INT
output will be asserted corresponding to the Interrupt Enable register. On detecting
the interrupt, the external microprocessor must read the Interrupt register and mask it
with the corresponding bits in the Interrupt Enable register to determine the source of
the interrupt.
Each endpoint buffer has a dedicated interrupt bit (EPnTX, EPnRX). In addition,
various bus states can generate an interrupt: resume, suspend, pseudo SOF, SOF
and bus reset. The DMA controller only has one interrupt bit: the source for a DMA
interrupt is shown in the DMA Interrupt Reason register.
Each interrupt bit can be individually cleared by writing logic 1. The DMA Interrupt bit
can be cleared by writing logic 1 to the related interrupt source bit in the DMA
Interrupt Reason register and writing logic 1 to the DMA bit of the Interrupt register.
Table 65: Interrupt register: bit allocation
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24
Symbol reserved EP7TX EP7RX
Reset -----000
Bus reset -----000
Access -----R/WR/WR/W
Bit 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Symbol EP6TX EP6RX EP5TX EP5RX EP4TX EP4RX EP3TX EP3RX
Reset 00000000
Bus reset 00000000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Symbol EP2TX EP2RX EP1TX EP1RX EP0TX EP0RX reserved EP0SETUP
Reset 000000-0
Bus reset 000000-0
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W - R/W
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol VBUS DMA HS_STAT RESUME SUSP PSOF SOF BRESET
Reset 00000000
Bus reset 0000000unchanged
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Table 66: Interrupt register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
31 to 26 - reserved
25 EP7TX Logic 1 indicates the endpoint 7 TX buffer as interrupt source.
24 EP7RX Logic 1 indicates the endpoint 7 RX buffer as interrupt source.
23 EP6TX Logic 1 indicates the endpoint 6 TX buffer as interrupt source.
22 EP6RX Logic 1 indicates the endpoint 6 RX buffer as interrupt source.
21 EP5TX Logic 1 indicates the endpoint 5 TX buffer as interrupt source.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 47 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 48

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Table 66: Interrupt register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
20 EP5RX Logic 1 indicates the endpoint 5 RX buffer as interrupt source.
19 EP4TX Logic 1 indicates the endpoint 4 TX buffer as interrupt source.
18 EP4RX Logic 1 indicates the endpoint 4 RX buffer as interrupt source.
17 EP3TX Logic 1 indicates the endpoint 3 TX buffer as interrupt source.
16 EP3RX Logic 1 indicates the endpoint 3 RX buffer as interrupt source.
15 EP2TX Logic 1 indicates the endpoint 2 TX buffer as interrupt source.
14 EP2RX Logic 1 indicates the endpoint 2 RX buffer as interrupt source.
13 EP1TX Logic 1 indicates the endpoint 1 TX buffer as interrupt source.
12 EP1RX Logic 1 indicates the endpoint 1 RX buffer as interrupt source.
11 EP0TX Logic 1 indicates the endpoint 0 data TX buffer as interrupt source.
10 EP0RX Logic 1 indicates the endpoint 0 data RX buffer as interrupt source.
9 - reserved
8 EP0SETUP Logic 1 indicates that a SETUP token was received on endpoint 0.
7 VBUS Logic 1 indicates V
6 DMA DMA status: Logic 1 indicates a change in the DMA Status
register.
5 HS_STAT High speed status: Logic 1 indicates a change from full-speed to
high-speed mode (HS connection). This bit is not set, when the
system goes into full-speed suspend.
4 RESUME Resume status: Logic 1 indicates that a status change from
suspend to resume (active) was detected.
3 SUSP Suspend status: Logic 1 indicates that a status change from
active to suspend was detected on the bus.
2 PSOF Pseudo SOF interrupt: Logic 1 indicates that a pseudo SOF or
µSOF was received. Pseudo SOF is an internally generated clock
signal (full-speed: 1 ms period, high-speed: 125 µs period)
synchronized to the USB bus SOF or µSOF.
1 SOF SOF interrupt: Logic 1 indicates that a SOF or µSOF was
received.
0 BRESET Bus reset: Logic 1 indicates that a USB bus reset was detected.
When bit OTG in the OTG register is set, BRESET will not be set,
instead, this interrupt bit will report SE0 on DP and DM for 2 ms.
…continued
is turned on.
BUS
9.5.2 Chip ID register (address: 70h)
This read-only register contains the chip identification and the hardware version
numbers. The firmware should check this information to determine the functions and
features supported. The register contains 3 bytes, and the bit allocation is shown in
Table 67.
Table 67: Chip ID register: bit allocation
Bit 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Symbol CHIPID[15:8]
Reset 00010101
Bus reset 00010101
Access RRRRRRRR
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 48 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 49

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Symbol CHIPID[7:0]
Reset 10000010
Bus reset 10000010
Access RRRRRRRR
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol VERSION[7:0]
Reset 00110000
Bus reset 00110000
Access RRRRRRRR
Table 68: Chip ID register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
23 to 16 CHIPID[15:8] chip ID: lower byte (15h)
15 to 8 CHIPID[7:0] chip ID: upper byte (82h)
7 to 0 VERSION[7:0] version number (30h)
9.5.3 Frame Number register (address: 74h)
This read-only register contains the frame number of the last successfully received
Start-Of-Frame (SOF). The register contains 2 bytes, and the bit allocation is given in
Table 69. In case of 8-bit access, the register content is returned lower byte first.
Table 69: Frame Number register: bit allocation
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Symbol reserved MICROSOF[2:0] SOFR[10:8]
Power Reset - -000000
Bus Reset - -000000
Access RRRRRRRR
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol SOFR[7:0]
Power Reset 00000000
Bus Reset 00000000
Access RRRRRRRR
Table 70: Frame Number register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
15 to 14 - reserved
13 to 11 MICROSOF[2:0] microframe number
10 to 0 SOFR[10:0] frame number
9.5.4 Scratch register (address: 78h)
This 16-bit register can be used by the firmware to save and restore information. For
example, the device status before it enters the suspend state. The bit allocation is
given in Table 71.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 49 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 50

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Table 71: Scratch register: bit allocation
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Symbol SFIRH[7:0]
Reset 00000000
Bus reset 00000000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol SFIRL[7:0]
Reset 00000000
Bus reset 00000000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Table 72: Scratch register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
15 to 8 SFIRH[7:0] Scratch firmware information register (higher byte)
7 to 0 SFIRL[7:0] Scratch firmware information register (lower byte)
9.5.5 Unlock Device register (address: 7Ch)
To protect the registers from getting corrupted when the ISP1582 goes into suspend,
the write operation is disabled if bit PWRON in the Mode register is set to logic 0. In
this case, when the chip resumes, the Unlock Device command must be first issued
to this register before attempting to write to the rest of the registers. This is done by
writing unlock code (AA37h) to this register.
The bit allocation of the Unlock Device register is given in Table 73.
Table 73: Unlock Device register: bit allocation
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
Symbol ULCODE[15:8] = AAh
Reset not applicable
Bus reset not applicable
Access WWWWWWWW
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol ULCODE[7:0] = 37h
Reset not applicable
Bus reset not applicable
Access WWWWWWWW
Table 74: Unlock Device register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
15 to 0 ULCODE[15:0] Writing data AA37h unlocks the internal registers and FIFOs
for writing, following a resume.
When bit PWRON in the Mode register is logic 1, the chip is powered. In such a case,
you do not need to issue the Unlock command because the microprocessor is
powered and therefore, the RD_N, WR_N and CS_N signals maintain their states.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 50 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 51

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
When bit PWRON is logic 0, the RD_N, WR_N and CS_N signals are floating
because the microprocessor is not powered. To protect the ISP1582 registers from
being corrupted during suspend, register write is locked when the chip goes into
suspend. Therefore, you need to issue the Unlock command to unlock the ISP1582
registers.
9.5.6 Test Mode register (address: 84h)
This 1-byte register allows the firmware to set pins DP and DM to predetermined
states for testing purposes. The bit allocation is given in Table 75.
Remark: Only one bit can be set to logic 1 at a time. This must be implemented for
the Hi-Speed USB logo compliance testing.
Table 75: Test Mode register: bit allocation
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Symbol FORCEHS reserved FORCEFS PRBS KSTATE JSTATE SE0_NAK
Reset 0- -00000
Bus reset 0- -00000
Access R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Table 76: Test Mode register: bit description
Bit Symbol Description
[1]
7 FORCEHS logic 1
disables the chirp detection logic.
6 to 5 - reserved.
4 FORCEFS logic 1
disables the chirp detection logic.
3 PRBS logic 1
random pattern.
2 KSTATE writing logic 1
1 JSTATE writing logic 1
0 SE0_NAK writinglogic 1
state. The device only responds to a valid high-speed IN token
with a NAK.
[1] Either FORCEHS or FORCEFS should be set at a time.
[2] Of the four bits (PRBS, KSTATE, JSTATE and SE0_NAK), only one bit should be set at a time.
forces the hardware to high-speed mode only and
[1]
forces the physical layer to full-speed mode only and
[2]
sets pins DP and DM to toggle in a predetermined
[2]
sets pins DP and DM to the K state.
[2]
sets pins DP and DM to the J state.
[2]
sets pins DP and DM to a high-speed quiescent
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 51 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 52

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
10. Limiting values
Table 77: Absolute maximum ratings
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134).
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Unit
V
CC
V
CC(I/O)
V
I
I
lu
V
esd
T
stg
[1] The maximum value for 5 V tolerant pins is 6 V.
supply voltage −0.5 +4.6 V
I/O pad supply voltage −0.5 +4.6 V
input voltage
latch-up current VI< 0 or VI>V
CC
[1]
−0.5 VCC+ 0.5 V
- 100 mA
electrostatic discharge voltage ILI<1µA −2000 +2000 V
storage temperature −40 +125 °C
11. Recommended operating conditions
Table 78: Recommended operating conditions
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Unit
V
CC
V
CC(I/O)
V
I
V
I(AI/O)
V
O(pu)
T
amb
supply voltage 3.0 3.6 V
I/O pad supply voltage V
CC
V
CC
V
input voltage range VCC= 3.3 V 0 5.5 V
input voltage on analog I/O pins
0 3.6 V
DP and DM
open-drain output pull-up voltage 0 V
CC
V
ambient temperature −40 +85 °C
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 52 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 53

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
12. Static characteristics
Table 79: Static characteristics; supply pins
VCC= 3.3 V±0.3 V; V
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Supply voltage
V
CC
I
CC
I
CC(susp)
supply voltage 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
operating supply current VCC= 3.3 V
suspend supply current VCC= 3.3 V - 160 - µA
I/O pad supply voltage
V
CC(I/O)
I
CC(I/O)
I
CC(I/O)(susp)
I/O pad supply voltage V
operating supply current V
suspend supply current V
Regulated supply voltage
V
CC(1V8)
regulated supply voltage with voltage
GND
=0V; T
=−40°Cto+85°C; typical values at T
amb
high-speed - 45 60 mA
full-speed - 17 25 mA
= 3.3 V
CC(I/O)
high-speed - 430 500 µA
full-speed - 180 120 µA
= 3.3 V - 5 10 µA
CC(I/O)
converter
=25°C; unless otherwise specified.
amb
CC
V
CC
V
CC
1.65 1.8 1.95 V
V
Table 80: Static characteristics: digital pins
V
CC(I/O)=VCC
; V
GND
=0V; T
=−40°C to +85°C; unless otherwise specified.
amb
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Input levels
V
IL
V
IH
LOW-level input voltage - - 0.3V
HIGH-level input voltage 0.7V
CC(I/O)
-- V
CC(I/O)
V
Output levels
V
OL
V
OH
LOW-level output voltage IOL= rated drive - - 0.15V
HIGH-level output voltage IOH= rated drive 0.8V
CC(I/O)
-- V
CC(I/O)
V
Leakage current
I
LI
[1] This value is applicable to transistor input only. The value will be different if internal pull-up or pull-down resistors are used.
input leakage current
[1]
−5- +5 µA
Table 81: Static characteristics: OTG detection
V
CC(I/O)=VCC
; V
GND
=0V; T
=−40°C to +85°C; unless otherwise specified.
amb
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Charging and discharging resistor
R
PD
R
PU
discharging resistor 684.8 843.5 1032 Ω
charging resistor 551.9 666.7 780.6 Ω
Comparator levels
V
V
BVALID
V
SESEND
valid detection V
BUS
V
B-session end detection V
BUS
= 3.3 V ± 0.3 V 2.0 - 4.0 V
CC(I/O)
= 3.3 V ± 0.3 V 0.2 - 0.8 V
CC(I/O)
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 53 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 54

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Table 82: Static characteristics: analog I/O pins DP and DM
VCC= 3.3 V±0.3 V; V
GND
=0V; T
=−40°Cto+85°C; unless otherwise specified.
amb
[1]
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Input levels
V
DI
V
CM
V
SE
V
IL
V
IH
differential input sensitivity |V
differential common mode voltage includes VDI range 0.8 - 2.5 V
single-ended receiver threshold 0.8 2.0 V
LOW-level input voltage - - 0.8 V
HIGH-level input voltage 2.0 - - V
I(DP)
− V
| 0.2 - - V
I(DM)
Schmitt-trigger inputs
V
V
V
th(LH)
th(HL)
hys
positive-going threshold voltage 1.4 - 1.9 V
negative-going threshold voltage 0.9 - 1.5 V
hysteresis voltage 0.4 - 0.7 V
Output levels
V
OL
V
OH
LOW-level output voltage RL= 1.5 kΩ to 3.6 V - - 0.4 V
HIGH-level output voltage RL=15kΩ to GND 2.8 - 3.6 V
Leakage current
I
LZ
OFF-state leakage current 0 < VI< 3.3 V −10 - +10 µA
Capacitance
C
IN
transceiver capacitance pin to GND - - 10 pF
Resistance
Z
DRV
Z
INP
driver output impedance steady-state drive 40.5 - 49.5 Ω
input impedance 10 - - MΩ
[1] Pin DP is the USB positive data pin and pin DM is the USB negative data pin.
13. Dynamic characteristics
Table 83: Dynamic characteristics
VCC= 3.3 V±0.3 V; V
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Reset
t
W(RESET_N)
pulse width on pin RESET_N crystal oscillator running 500 - - µs
Crystal oscillator
f
XTAL
R
S
C
L
crystal frequency - 12 - MHz
series resistance - - 100 Ω
load capacitance - 18 - pF
External clock input
V
IN
t
J
input voltage 1.65 1.8 1.95 V
external clock jitter - - 500 ps
δ clock duty cycle 45 50 55 %
, t
t
r
f
rise time and fall time - - 3 ns
GND
=0V; T
=−40°Cto+85°C; unless otherwise specified.
amb
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 54 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 55

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Table 84: Dynamic characteristics: analog I/O pins DP and DM
VCC= 3.3 V±0.3 V; V
Figure 25; unless otherwise specified.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Driver characteristics
Full-speed mode
t
FR
t
FF
rise time CL=50pF;
fall time CL=50pF;
FRFM differential rise time and fall time
matching (t
V
CRS
output signal crossover voltage
High-speed mode
t
HSR
t
HSF
high-speed differential rise time with captive cable 500 - - ps
high-speed differential fall time with captive cable 500 - - ps
Data source timing
Full-speed mode
t
FEOPT
t
FDEOP
source EOP width see Figure 16
source differential data-to-EOP
transition skew
Receiver timing
Full-speed mode
t
JR1
receiver data jitter tolerance to
next transition
t
JR2
receiver data jitter tolerance for
paired transitions
t
FEOPR
t
FST
receiver SE0 width accepted as EOP; see Figure 16
width of SE0 during differential
transition
GND
FR/tFF
=0V; T
)
=−40°Cto+85°C; CL= 50 pF; RPU= 1.5 kΩ on DP to V
amb
10 % to 90 % of |V
90 % to 10 % of |V
see Figure 16
see Figure 17
see Figure 17
rejected as EOP; see Figure 18
OH
OH
− VOL|
− VOL|
[1]
[1][2]
[2]
[2]
[2]
[2]
[2]
[2]
; test circuit of
TERM
4 - 20 ns
4 - 20 ns
90 - 111.11 %
1.3 - 2.0 V
160 - 175 ns
−2 - +5 ns
−18.5 - +18.5 ns
−9 - +9 ns
82--ns
--14ns
[1] Excluding the first transition from the idle state.
[2] Characterized only, not tested. Limits guaranteed by design.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 55 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 56

Philips Semiconductors
T
PERIOD
+3.3 V
differential
data lines
0 V
T
is the bit duration corresponding with the USB data rate.
PERIOD
crossover point
differential data to
SE0/EOP skew
N × T
PERIOD
+ t
DEOP
Full-speed timing symbols have a subscript prefix ‘F’, low-speed timing symbols have a prefix 'L'.
Fig 16. Source differential data-to-EOP transition skew and EOP width.
T
PERIOD
+3.3 V
crossover point
extended
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
source EOP width: t
receiver EOP width: t
EOPT
EOPR
mgr776
differential
data lines
0 V
T
is the bit duration corresponding with the USB data rate.
PERIOD
t
JR
N × T
Fig 17. Receiver differential data jitter.
Fig 18. Receiver SE0 width tolerance.
consecutive
transitions
PERIOD
+3.3 V
differential
data lines
0 V
+ t
JR1
N × T
paired
transitions
PERIOD
+ t
JR2
t
t
FST
JR1
V
IH(min)
mgr872
t
JR2
mgr871
9397 750 13699
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 56 of 66
Page 57

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
13.1 Register access timing
Table 85: Register access timing parameters: separate address and data buses
V
CC(I/O)=VCC
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit
Reading
t
RLRH
t
AVRL
t
RHAX
t
RLDV
t
RHDZ
t
RHSH
t
SLRL
Writing
t
WLWH
t
AVWL
t
WHAX
t
DVWH
t
WHDZ
t
WHSH
t
SLWL
General
T
cy(RW)
= 3.3 V; V
RD_N LOW pulse width >t
GND
=0V; T
=−40°Cto+85°C.
amb
RLDV
-ns
address set-up time before RD_N LOW 0 - ns
address hold time after RD_N HIGH 0 - ns
RD_N LOW to data valid delay - 26 ns
RD_N HIGH to data outputs three-state delay 0 15 ns
RD_N HIGH to CS_N HIGH delay 0 - ns
CS_N LOW to RD_N LOW delay 2 - ns
WR_N LOW pulse width 15 - ns
address set-up time before WR_N LOW 0 - ns
address hold time after WR_N HIGH 0 - ns
data set-up time before WR_N HIGH 11 - ns
data hold time after WR_N HIGH 5 - ns
WR_N HIGH to CS_N HIGH delay 0 - ns
CS_N LOW to WR_N LOW delay 2 - ns
read/write cycle time 50 - ns
T
cy(RW)
t
SLWL
CS_N
t
SLRL
]
A[7:0
t
RLDV
RD_N
WR_N
]
t
AVRL
t
AVWL
]
t
RLRH
t
WLWH
t
DVWH
(read) DATA[15:0
(write) DATA[15:0
Fig 19. Register access timing: separate address and data buses.
t
WHDZ
t
WHSH
t
t
WHAX
t
RHSH
RHAX
t
RHDZ
004aaa276
9397 750 13699
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 57 of 66
Page 58

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
13.2 DMA timing
Table 86: GDMA (slave) mode timing parameters
V
CC(I/O)=VCC
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit
T
cy1
t
su1
t
d1
t
h1
t
w1
t
w2
t
d2
t
h2
t
h3
t
su2
t
su3
t
a1
= 3.3 V; V
GND
=0V; T
=−40°Cto+85°C.
amb
read/write cycle time 75 - ns
DREQ set-up time before first DACK on 10 - ns
DREQ on delay after last strobe off 33.33 - ns
DREQ hold time after last strobe on 0 53 ns
DIOR/DIOW pulse width 39 600 ns
DIOR/DIOW recovery time 36 - ns
read data valid delay after strobe on - 20 ns
read data hold time after strobe off - 5 ns
write data hold time after strobe off 1 - ns
write data set-up time before strobe off 10 - ns
DACK set-up time before DIOR/DIOW assertion 0 - ns
DACK deassertion after DIOR/DIOW deassertion 0 30 ns
(2)
DREQ
t
DACK
DIOR/DIOW
(read) DATA[15:0
(write) DATA[15:0
su1
(1)
t
su3
(1)
]
]
t
w1
t
d2
t
su2
t
h2
T
cy1
t
w2
t
h3
DREQ is continuously asserted until the last transfer is done or the FIFO is full.
Data strobes: DIOR (read) and DIOW (write).
(1) Programmable polarity: shown as active LOW.
(2) Programmable polarity: shown as active HIGH.
Fig 20. GDMA (slave) mode timing (bits MODE[1:0] = 00).
t
h1
t
d1
t
a1
MGT500
9397 750 13699
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 58 of 66
Page 59

Philips Semiconductors
(2)
DREQ
DACK
(1)
t
su1
t
su3
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
t
w1
T
cy1
t
d1
t
h1
t
d2
DIOR/DIOW
(read) DATA[15:0
(write) DATA[15:0
(1)
t
h2
]
t
su2
]
t
h3
DREQ is asserted for every transfer.
Data strobes: DIOR (read) and DACK (write).
(1) Programmable polarity: shown as active LOW.
(2) Programmable polarity: shown as active HIGH.
Fig 21. GDMA (slave) mode timing (bits MODE[1:0] = 01).
(2)
DREQ
t
w1
t
d2
t
su2
t
w2
t
h2
t
h3
DACK
DIOR/DIOW
(read) DATA[15:0
(write) DATA[15:0
t
su1
(1)
(1)
]
]
HIGH
t
a1
MGT502
T
cy1
t
h1
t
d1
MGT501
DREQ is continuously asserted until the last transfer is done or the FIFO is full.
Data strobe: DACK (read/write).
(1) Programmable polarity: shown as active LOW.
(2) Programmable polarity: shown as active HIGH.
Fig 22. GDMA (slave) mode timing (bits MODE[1:0] = 10).
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 59 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 60

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
RD_N, WR_N
(1) Programmable polarity: shown as active LOW.
Remark: EOT should be valid for 36ns (minimum) when RD_N/WR_N is active.
Fig 23. EOT timing in generic processor mode.
14. Application information
EOT
DREQ
(1)
CPU
36 ns (min)
t
h1
address 8
data
read strobe
write strobe
chip select
004aaa378
ISP1582
A[7:0]
16
DATA[15:0]
RD_N
WR_N
CS_N
15. Test information
The dynamic characteristics of the analog I/O ports DP and DM were determined
using the circuit shown in Figure 25.
004aaa206
Fig 24. Typical interface connections for generic processor mode.
test point
D.U.T
15 kΩ
C
L
50 pF
MGT495
In full-speed mode, an internal 1.5 kΩ pull-up resistor is connected to pin DP.
Fig 25. Load impedance for pins DP and DM (full-speed mode).
9397 750 13699
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 60 of 66
Page 61

Philips Semiconductors
16. Package outline
HVQFN56: plastic thermal enhanced very thin quad flat package; no leads;
56 terminals; body 8 x 8 x 0.85 mm
A
D
terminal 1
index area
B
E
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
SOT684-1
A
A
1
detail X
c
e
1
D
D
4.45
4.15
1/2 e
h
h
e
15 28
L
14
E
h
1
terminal 1
index area
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
(1)
A
UNIT
mm
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.075 mm maximum per side are not included.
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT684-1 MO-220 - - -- - -
max.
1
A
0.05
0.00
56
(1)
c
b
1
0.30
0.18
D
8.1
0.2
7.9
IEC JEDEC JEITA
b
(1)
E
E
h
4.45
8.1
4.15
7.9
REFERENCES
29
1/2 e
42
43
0 2.5 5 mm
0.5
e
6.5
C
y
1
y
X
ISSUE DATE
01-08-08
02-10-22
v
M
ACCB
w
M
e
2
scale
e
e
6.5
L
2
0.5
0.3
1
y
1
w
0.1v0.05
C
ye
0.05 0.1
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
Fig 26. HVQFN56 package outline.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 61 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 62

Philips Semiconductors
17. Soldering
17.1 Introduction to soldering surface mount packages
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology. A more in-depth account
of soldering ICs can be found in our
Packages
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all surface mount IC packages. Wave
soldering can still be used for certain surface mount ICs, but it is not suitable for fine
pitch SMDs. In these situations reflow soldering is recommended. In these situations
reflow soldering is recommended.
17.2 Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of fine solder particles, flux and
binding agent) to be applied to the printed-circuit board by screen printing, stencilling
or pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement. Driven by legislation and
environmental forces the worldwide use of lead-free solder pastes is increasing.
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit
(document order number 9398 652 90011).
Several methods exist for reflowing; for example, convection or convection/infrared
heating in a conveyor type oven. Throughput times (preheating, soldering and
cooling) vary between 100 and 200 seconds depending on heating method.
Typical reflow peak temperatures range from 215 to 270 °C depending on solder
paste material. The top-surface temperature of the packages should preferably be
kept:
• below 225 °C (SnPb process) or below 245 °C (Pb-free process)
– for all BGA, HTSSON..T and SSOP..T packages
– for packages with a thickness ≥ 2.5 mm
– for packages with a thickness < 2.5 mm and a volume ≥ 350 mm3 so called
thick/large packages.
• below 240 °C (SnPb process) or below 260 °C (Pb-free process) for packages with
a thickness < 2.5 mm and a volume < 350 mm3 so called small/thin packages.
Moisture sensitivity precautions, as indicated on packing, must be respected at all
times.
17.3 Wave soldering
Conventional single wave soldering is not recommended for surface mount devices
(SMDs) or printed-circuit boards with a high component density, as solder bridging
and non-wetting can present major problems.
To overcome these problems the double-wave soldering method was specifically
developed.
If wave soldering is used the following conditions must be observed for optimal
results:
• Use a double-wave soldering method comprising a turbulent wave with high
upward pressure followed by a smooth laminar wave.
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 62 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 63

Philips Semiconductors
• For packages with leads on two sides and a pitch (e):
• For packages with leads on four sides, the footprint must be placed at a 45° angle
During placement and before soldering, the package must be fixed with a droplet of
adhesive. The adhesive can be applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the adhesive is cured.
Typical dwell time of the leads in the wave ranges from 3 to 4 seconds at 250 °C or
265 °C, depending on solder material applied, SnPb or Pb-free respectively.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal of corrosive residues in
most applications.
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
– larger than or equal to 1.27 mm, the footprint longitudinal axis is preferred to be
parallel to the transport direction of the printed-circuit board;
– smaller than 1.27 mm, the footprint longitudinal axis must be parallel to the
transport direction of the printed-circuit board.
The footprint must incorporate solder thieves at the downstream end.
to the transport direction of the printed-circuit board. The footprint must
incorporate solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
17.4 Manual soldering
Fix the component by first soldering two diagonally-opposite end leads. Use a low
voltage (24 V or less) soldering iron applied to the flat part of the lead. Contact time
must be limited to 10 seconds at up to 300 °C.
When using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be soldered in one operation within
2 to 5 seconds between 270 and 320 °C.
17.5 Package related soldering information
Table 87: Suitability of surface mount IC packages for wave and reflow soldering
methods
Package
BGA, HTSSON..T
SSOP..T
DHVQFN, HBCC,HBGA,HLQFP,HSO,HSOP,
HSQFP, HSSON, HTQFP, HTSSOP, HVQFN,
HVSON, SMS
PLCC
LQFP, QFP, TQFP not recommended
SSOP, TSSOP, VSO, VSSOP not recommended
CWQCCN..L
[1]
[3]
[3]
, TFBGA, USON, VFBGA
[5]
, SO, SOJ suitable suitable
, LBGA, LFBGA, SQFP,
[8]
, PMFP
[9]
, WQCCN..L
[8]
Soldering method
Wave Reflow
not suitable suitable
not suitable
not suitable not suitable
[2]
[4]
[5][6]
[7]
suitable
suitable
suitable
[1] For more detailed information on the BGA packages refer to the
(AN01026); order a copy from your Philips Semiconductors sales office.
[2] All surface mount (SMD) packages are moisture sensitive. Depending upon the moisture content, the
maximum temperature (with respect to time) and body sizeofthepackage, there is a risk that internal
or external package cracks may occur due to vaporization of the moisture in them (the so called
popcorn effect). For details, refer to the Drypack information in the
Circuit Packages; Section: Packing Methods
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 63 of 66
.
(LF)BGA Application Note
Data Handbook IC26; Integrated
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 64

Philips Semiconductors
[3] These transparent plastic packages are extremely sensitive to reflow soldering conditions and must
[4] These packages are not suitable for wave soldering. On versions with the heatsink on the bottom
[5] If wave soldering is considered, then the package must be placed at a 45° angle to the solder wave
[6] Wave soldering is suitable for LQFP, QFP and TQFP packages with a pitch (e) larger than 0.8 mm; it
[7] Wave soldering is suitable for SSOP, TSSOP, VSO and VSOP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or
[8] Image sensor packages in principle should not be soldered. They aremountedinsockets or delivered
[9] Hot bar soldering or manual soldering is suitable for PMFP packages.
18. Revision history
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
on no account be processed through more than one soldering cycle or subjected to infrared reflow
soldering with peak temperature exceeding 217 °C ± 10 °C measured in the atmosphere of the reflow
oven. The package body peak temperature must be kept as low as possible.
side, thesoldercannotpenetrate between the printed-circuit board and theheatsink.Onversions with
the heatsink on the top side, the solder might be deposited on the heatsink surface.
direction. The package footprint must incorporate solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
is definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.65mm.
larger than 0.65 mm; it is definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than
0.5 mm.
pre-mounted on flex foil. However, the image sensor package can be mounted by the client on a flex
foil by using a hot bar soldering process. The appropriate soldering profile can be provided on
request.
Table 88: Revision history
Rev Date CPCN Description
03 2004xxxx - Preliminary data (9397 750 13699)
Modifications:
• Globally changed V
to the same value as VCC.
CC(I/O)
• Table 2 “Pin description”: updated pin description for EOT, DACK, DIOW and DIOR; also
removed table note 3.
• Section 8.14.1 “Power-sharing mode”: added Remark.
• Section 9.5.4 “Scratch register (address: 78h)”: updated the bus reset value.
02 20040629 - Preliminary data (9397 750 12979)
01 20040223 - Preliminary data (9397 750 11496)
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 64 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 65

Philips Semiconductors
19. Data sheet status
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
Level Data sheet status
I Objective data Development This data sheet contains data from the objective specification for product development. Philips
II Preliminary data Qualification This data sheetcontainsdata from thepreliminary specification.Supplementarydata will be published
III Product data Production This data sheet contains data from the product specification. Philips Semiconductors reserves the
[1] Please consult the most recently issued data sheet before initiating or completing a design.
[2] The product status of the device(s) described in this data sheet may have changed since this data sheet was published. The latest information is available on the Internet at
URL http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.
[3] For data sheets describing multiple type numbers, the highest-level product status determines the data sheet status.
[1]
Product status
20. Definitions
Short-form specification — The data in a short-form specification is
extracted from a full data sheet with the same type number and title. For
detailed information see the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting values definition — Limiting values given are in accordance with
the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device.
These are stress ratings only and operation of the device at these or at any
other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the
specification is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods
may affect device reliability.
Application information — Applications that are described herein for any
of these products are for illustrative purposes only. Philips Semiconductors
make no representation or warranty that such applications will be suitable for
the specified use without further testing or modification.
[2][3]
Definition
Semiconductors reserves the right to change the specification in any manner without notice.
at a laterdate. Philips Semiconductors reserves therightto change the specification without notice,in
order to improve the design and supply the best possible product.
right to make changesat any time in order to improve the design, manufacturingandsupply. Relevant
changes will be communicated via a Customer Product/Process Change Notification (CPCN).
customers using or selling these products for use in such applications do so
at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips Semiconductors for any
damages resulting from such application.
Right to make changes — Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to
make changes in the products - including circuits, standard cells, and/or
software - described or contained herein in order to improve design and/or
performance. When the product is in full production (status ‘Production’),
relevant changes will be communicated via a Customer Product/Process
Change Notification (CPCN). Philips Semiconductors assumes no
responsibility or liability for the use of any of these products, conveys no
licence or title under any patent, copyright, or mask work right to these
products, andmakes norepresentationsor warrantiesthat these productsare
free frompatent, copyright, or maskwork right infringement, unlessotherwise
specified.
22. Trademarks
21. Disclaimers
Life support — These products are not designed for use in life support
appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these products can
reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips Semiconductors
ACPI — is an open industry specification for PC power management,
co-developed by Intel Corp., Microsoft Corp. and Toshiba
OnNow — is a trademark of Microsoft Corp.
SoftConnect — is a trademark of Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V.
Contact information
For additional information, please visit http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.
For sales office addresses, send e-mail to: sales.addresses@www.semiconductors.philips.com. Fax: +31 40 27 24825
9397 750 13699
Preliminary data Rev. 03 — 25 August 2004 65 of 66
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004. All rights reserved.
Page 66

Philips Semiconductors
Contents
ISP1582
Hi-Speed USB peripheral controller
1 General description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
3 Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
4 Abbreviations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
5 Ordering information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
6 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
7 Pinning information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
7.1 Pinning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
7.2 Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
8 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
8.1 DMA interface, DMA handler and DMA
registers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
8.2 Hi-Speed USB transceiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
8.3 MMU and integrated RAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
8.4 Microcontroller interface and
microcontroller handler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
8.5 OTG SRP module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
8.6 Philips high-speed transceiver . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
8.6.1 Philips Parallel Interface Engine (PIE) . . . . . . 11
8.6.2 Peripheral circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
8.6.3 HS detection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
8.7 Philips Serial Interface Engine (SIE). . . . . . . . 12
8.8 SoftConnect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
8.9 System controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
8.10 Output pins status. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
8.11 Interrupt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
8.11.1 Interrupt output pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
8.11.2 Interrupt control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
8.12 V
sensing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
BUS
8.13 Power-on reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
8.14 Power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
8.14.1 Power-sharing mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
8.14.2 Self-powered mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
8.14.3 Bus-powered mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
9 Register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
9.1 Register access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
9.2 Initialization registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
9.2.1 Address register (address: 00h) . . . . . . . . . . . 24
9.2.2 Mode register (address: 0Ch). . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
9.2.3 Interrupt Configuration register (address: 10h) 27
9.2.4 OTG register (address: 12h). . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
9.2.5 Interrupt Enable register (address: 14h). . . . . 30
9.3 Data flow registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
9.3.1 Endpoint Index register (address: 2Ch) . . . . . 31
9.3.2 Control Function register (address: 28h) . . . . 33
9.3.3 Data Port register (address: 20h) . . . . . . . . . . 33
9.3.4 Buffer Length register (address: 1Ch) . . . . . . 34
9.3.5 Buffer Status register (address: 1Eh) . . . . . . . 35
9.3.6 Endpoint MaxPacketSize register (address:
04h). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
9.3.7 Endpoint Type register (address: 08h) . . . . . . 37
9.4 DMA registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
9.4.1 DMA Command register (address: 30h) . . . . 39
9.4.2 DMA Transfer Counter register (address: 34h) 40
9.4.3 DMA Configuration register (address: 38h) . . 41
9.4.4 DMA Hardware register (address: 3Ch). . . . . 42
9.4.5 DMA Interrupt Reason register (address: 50h) 43
9.4.6 DMA Interrupt Enable register (address: 54h) 45
9.4.7 DMA Endpoint register (address: 58h). . . . . . 45
9.4.8 DMA Burst Counter register (address: 64h). . 46
9.5 General registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
9.5.1 Interrupt register (address: 18h). . . . . . . . . . . 46
9.5.2 Chip ID register (address: 70h) . . . . . . . . . . . 48
9.5.3 Frame Number register (address: 74h) . . . . . 49
9.5.4 Scratch register (address: 78h) . . . . . . . . . . . 49
9.5.5 Unlock Device register (address: 7Ch). . . . . . 50
9.5.6 Test Mode register (address: 84h) . . . . . . . . . 51
10 Limiting values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
11 Recommended operating conditions . . . . . . 52
12 Static characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
13 Dynamic characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
13.1 Register access timing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
13.2 DMA timing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
14 Application information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
15 Test information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
16 Package outline. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
17 Soldering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
17.1 Introduction to soldering surface mount
packages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
17.2 Reflow soldering. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
17.3 Wave soldering. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
17.4 Manual soldering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
17.5 Package related soldering information. . . . . . 63
18 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
19 Data sheet status. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
20 Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
21 Disclaimers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
22 Trademarks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2004.
Printed in The Netherlands
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior
written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or
contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed without notice. No
liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication
thereof does not convey nor imply any license under patent- or other industrial or
intellectual property rights.
Date of release: 25 August 2004 Document order number: 9397 750 13699
 Loading...
Loading...