Page 1

查询ISP1102供应商
ISP1102
Advanced Universal Serial Bus transceiver
Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 Product data
1. General description
The ISP1102 Universal Serial Bus (USB) transceiver is fully compliant with the
Universal Serial Bus Specification Rev. 2.0
USB data at full-speed (12 Mbit/s).
The transceiver allows USB Application Specific ICs (ASICs) and Programmable
Logic Devices (PLDs) with power supply voltages from 1.65 to 3.6 V to interface with
the physical layer of the USB. The transceiver has an integrated 5 V-to-3.3 V voltage
regulator for direct powering via the USB supply line V
integrated voltage detector to detect the presence of the V
When V
protocols.
CC(5.0)
or V
. The ISP1102 can transmit and receive
. The transceiver has an
BUS
voltage (V
BUS
is lost, the D+ and D− pins can be shared with other serial
reg(3.3)
CC(5.0)
).
2. Features
The transceiver is a bi-directional differential interface and is available in HBCC16
and HVQFN14 packages.
The transceiverisideal for use in portable electronic devices, such as mobile phones,
digital still cameras, personal digital assistants and information appliances.
■ Complies with
■ Supports data transfer at full-speed (12 Mbit/s)
■ Integrated 5 V-to-3.3 V voltage regulator for powering via USB line V
■ V
■ VP and VM pins function in bi-directional mode allowing pin count saving for ASIC
■ Used as USB device transceiver or USB host transceiver
■ Stable RCV output during single-ended zero (SE0) condition
■ Two single-ended receivers with hysteresis
■ Low-power operation
■ Supports I/O voltage range from 1.65 to 3.6 V
■ ±12 kV ESD protection (ISP1102W) at D+, D−, V
■ Full industrial operating temperature range from −40 to +85 C
■ Available in HBCC16 and HVQFN14 lead-free and halogen-free packages.
voltage presence indication on pin VBUSDET
BUS
interface
Universal Serial Bus Specification Rev. 2.0
and GND pins
CC(5.0)
BUS
Page 2
Philips Semiconductors
Advanced USB transceiver
3. Applications
■ Portable electronic devices, such as:
◆ Mobile phone
◆ Digital Still Camera (DSC)
◆ Personal Digital Assistant (PDA)
◆ Information Appliance (IA).
4. Ordering information
Table 1: Ordering information
Type number Package
Name Description Version
ISP1102W HBCC16 plastic thermal enhanced bottom chip carrier; 16 terminals;
body 3 × 3 × 0.65 mm
ISP1102BS HVQFN14 plastic thermal enhanced very thin quad flat package; no leads;
14 terminals; body 2.5 × 2.5 × 0.85 mm
ISP1102
SOT639-2
SOT773-1
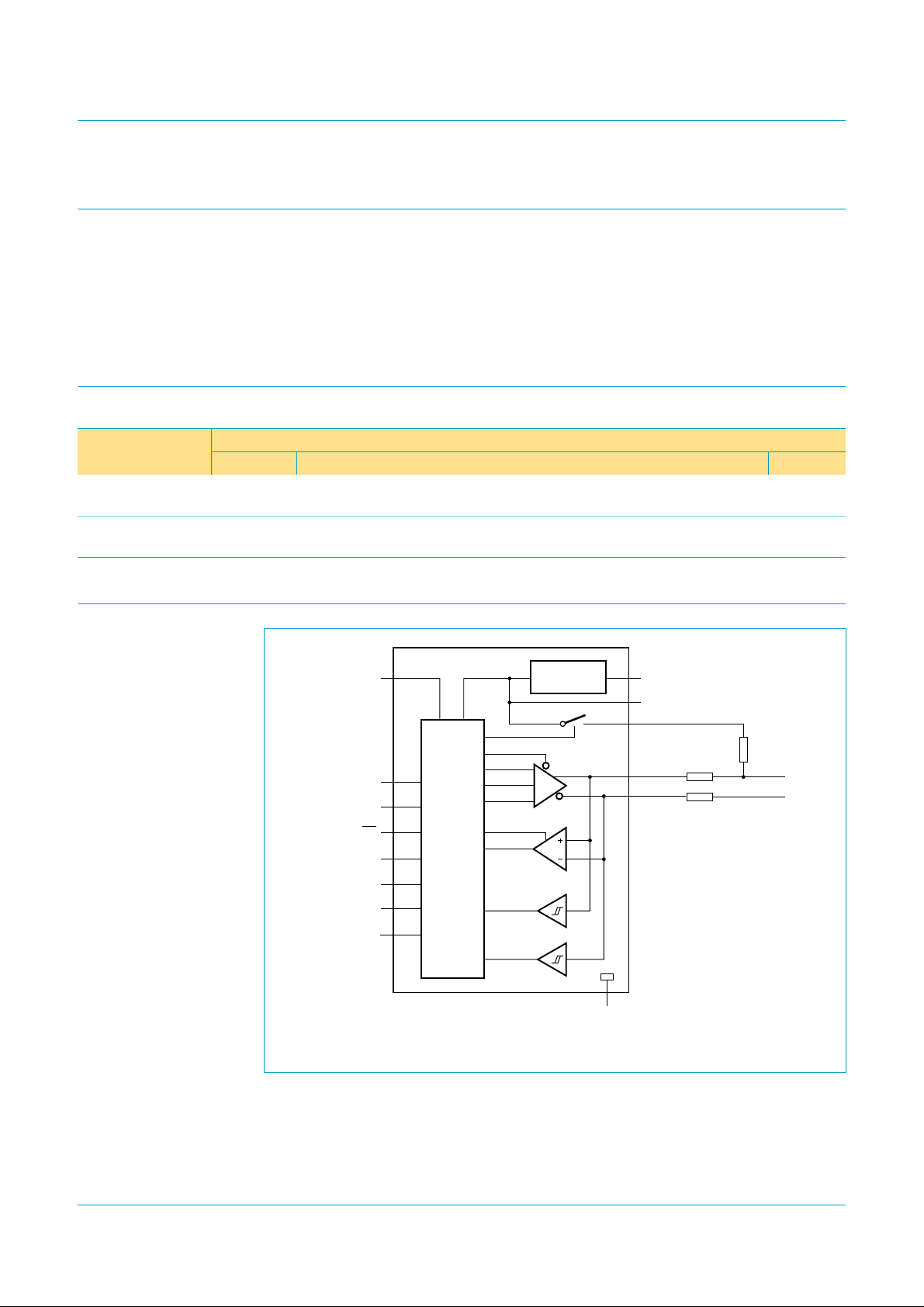
5. Block diagram
V
CC(I/O)
VBUSDET
SOFTCON
OE
RCV
VP/VPO
VM/VMO
SUSPND
LEVEL
SHIFTER
3.3 V
ISP1102
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
004aaa207
GND
V
V
V
pu(3.3)
D+
D−
CC(5.0)
reg(3.3)
33 Ω
33 Ω
(1%)
(1%)
1.5 kΩ
Fig 1. Block diagram.
9397 750 11228
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 2 of 23
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 3

Philips Semiconductors
6. Pinning information
6.1 Pinning
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
SUSPND
1314
pu(3.3)
V
CC(I/O)
V
6
12
CC(5.0)
V
VBUSDET
7
11
reg(3.3)
V
8
9
10
D−
D+
n.c.
004aaa208
VM/VMO
VP/VPO
RCV
OE
Bottom view
SUSPND
5
4
3
2
1
CC(I/O)
V
n.c.
ISP1102W
GND
(exposed diepad)
141516
pu(3.3)
V
SOFTCON
VBUSDET
876
CC(5.0)
V
9
10
11
12
13
D−
D+
n.c.
n.c.
V
reg(3.3)
004aaa209
VP/VPO
RCV
OE
Bottom view
3
2
1
VM/VMO
45
ISP1102BS
GND
(exposed diepad)
SOFTCON
Fig 2. Pin configuration HBCC16. Fig 3. Pin configuration HVQFN14.
6.2 Pin description
Table 2: Pin description
Symbol
OE 1 1 I input for output enable (CMOS level with respect to V
RCV 2 2 O differential data receiver output (CMOS level with respect to V
VP/VPO 3 3 I/O single-ended D+ receiver output VP (CMOS levelwith respect to V
VM/VMO 4 4 I/O single-endedD− receiver output VM (CMOS level with respect to V
SUSPND 5 5 I suspend input (CMOS level with respect to V
[1]
Pin Type Description
HBCC16 HVQFN14
, active LOW);
CC(I/O)
enables the transceiver to transmit data on the USB bus
input pad; push pull; CMOS
driven LOW when input SUSPND is HIGH; the output state of RCV is
CC(I/O)
preserved and stable during an SE0 condition
output pad; push pull; 4 mA output drive; CMOS
forexternal detection of SE0, error conditions, speed of connected device;
this pin also acts as the drive data input VPO; see Table 3 and Table 4
bidirectional pad; push-pull input; three-state output; 4 mA output drive;
CMOS
forexternal detection of SE0, error conditions, speed of connected device;
this pin also acts as the drive data input VMO; see Table 3 and Table 4
bidirectional pad; push-pull input; three-state output; 4 mA output drive;
CMOS
); a HIGH level enables
CC(I/O)
low-power state while the USB bus is inactive and drives output RCV to a
LOW level
input pad; push pull; CMOS
);
CC(I/O)
CC(I/O)
);
);
9397 750 11228
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 3 of 23
Page 4

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
Table 2: Pin description
Symbol
[1]
Pin Type Description
…continued
HBCC16 HVQFN14
n.c. 6 - - not connected
V
CC(I/O)
7 6 - supply voltage for digital I/O pins (1.65 to 3.6 V). When V
connected, the D+ and D− pins are in three-state. This supply pin is totally
independent of V
CC(5.0)
and V
and must never exceed the V
reg(3.3)
voltage.
VBUSDET 8 7 O V
indicator output (CMOS level with respect to V
BUS
> 4.1 V, then VBUSDET = HIGH and when V
V
BUS
CC(I/O)
BUS
VBUSDET = LOW; when SUSPND = HIGH, then pin VBUSDET is pulled
HIGH
output pad; push pull; 4 mA output drive; CMOS
D− 9 8 AI/O negative USB data bus connection (analog, differential)
D+ 10 9 AI/O positive USB data bus connection (analog, differential)
n.c. 11 - not connected
n.c. 12 - not connected
n.c. - 10 - not connected
V
reg(3.3)
13 11 - internal regulator option: regulated supply voltage output (3.0 to 3.6 V)
during 5 V operation; a decoupling capacitor of at least 0.1 µF is required
regulator bypass option: used as a supply voltage input (3.3 V ±10%)
for 3.3 V operation
V
CC(5.0)
V
pu(3.3)
14 12 - internal regulator option: supply voltage input (4.0 to 5.5 V); can be
connected directly to USB line V
regulator bypass option: connect to V
BUS
reg(3.3)
15 13 - pull-up supply voltage (3.3 V ±10%); connect an external 1.5 kΩ resistor
on D+ (full-speed).
Pin function is controlled by input SOFTCON:
is not
CC(I/O)
); when
< 3.6 V, then
reg(3.3)
SOFTCON = LOW — V
floating (high impedance); ensures zero
pu(3.3)
pull-up current
SOFTCON = HIGH — V
= 3.3 V; internally connected to V
pu(3.3)
reg(3.3)
SOFTCON 16 14 I software controlled USB connection input; a HIGH level applies 3.3 V to
pin V
, which is connected to an external 1.5 kΩ pull-up resistor; this
pu(3.3)
allows USB connect or disconnect signalling to be controlled by software
input pad; push pull; CMOS
GND exposed
die pad
[1] Symbol names with an overscore (e.g. OE) indicate active LOW signals.
9397 750 11228
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 4 of 23
exposed
die pad
- ground supply; down bonded to the exposed die pad (heatsink); to be
connected to the PCB ground
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors
7. Functional description
7.1 Function selection
Table 3: Function table
SUSPND OE D+, D− RCV VP/VPO VM/VMO Function
L L driving/
L H receiving
H L driving inactive
H H high-Z
[1] Signal levels on the D+ and D− pins are determined by other USB devices and external pull-up or
pull-down resistors.
[2] In the suspend mode (SUSPND = HIGH), the differential receiver is inactive and the output RCV is
always LOW. Out-of-suspend (K) signalling is detected via the single-ended receivers VP/VPO and
VM/VMO.
receiving
[1]
Advanced USB transceiver
active VPO input VMO input normal driving
(differential receiver
active)
[1]
active VP output VM output receiving
[2]
VPO input VMO input driving during suspend
(differential receiver
inactive)
inactive
[2]
VP output VM output low-power state
ISP1102
7.2 Operating functions
Table 4: Driving function using differential input data interface (pin OE=L)
VM/VMO VP/VPO Data
L L SE0
L H differential logic 1
H L differential logic 0
H H illegal state
Table 5: Receiving function (pin
D+, D− RCV VP/VPO VM/VMO
differential logic 0 L L H
differential logic 1 H H L
SE0 RCV*
[1] RCV* denotes the signal level on output RCV just before the SE0 state occurs. This level is stable
during the SE0 period.
OE=H)
[1]
LL
7.3 Power supply configurations
The ISP1102 can be used with different power supply configurations, which can be
changed dynamically. Table 7 provides an overview of the power supply
configurations.
Normal mode — V
V
are connected.
reg(3.3)
For 5 V operation, V
is connected. V
CC(I/O)
is connected to a 5 V source (4.0 to 5.5 V). The internal
CC(5.0)
is connected only, or V
CC(5.0)
CC(5.0)
and
voltage regulator then produces 3.3 V for the USB connections.
9397 750 11228
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 5 of 23
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 6

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
For 3.3 V operation, both V
CC(5.0)
and V
are connected to a 3.3 V source
reg(3.3)
(3.0 to 3.6 V).
V
is independently connected to a voltage source (1.65 to 3.6 V), depending on
CC(I/O)
the supply voltage of the external circuit.
Sharing mode — V
is connected only; V
CC(I/O)
CC(5.0)
and V
are not connected.
reg(3.3)
In this mode, the D+ and D− pins are made three-state and the ISP1102 allows
external signals of up to 3.6 V to share the D+ and D− lines. The internal circuits of
the ISP1102 ensure that virtually no current (maximum 10 µA) is drawn via the
D+ and D− lines. The power consumption through pin V
drops to the low-power
CC(I/O)
(suspended) state level.
Pins VBUSDET and RCV are driven LOW to indicate this mode. The VBUSDET
function is ignored during the suspend mode of the ISP1102.
Some hysteresis is built into the detection of V
Table 6: Pin states in the sharing mode
Pin Sharing mode
V
CC(5.0)
V
reg(3.3)
V
CC(I/O)
V
pu(3.3)
D+, D− high impedance
VP/VPO, VM/VMO
[1]
RCV L
VBUSDET L
OE, SUSPND, SOFTCON high impedance
not present
not present
1.65 to 3.6 V input
high impedance (off)
L
reg(3.3)
lost.
[1] VP/VPO and VM/VMO are bidirectional pins.
Table 7: Power supply configuration overview
V
CC(5.0)
Configuration Special characteristics
connected normal mode not connected sharing mode D+, D− and V
VBUSDET driven LOW
high impedance;
pu(3.3)
9397 750 11228
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 6 of 23
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 7

Philips Semiconductors
7.4 Power supply input options
The ISP1102 has two power supply input options.
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
Internal regulator — pin V
is used to supply the internal circuitry with 3.3 V (nominal). The V
is connected to 4.0 to 5.5 V. The internal regulator
CC(5.0)
reg(3.3)
pin becomes
a 3.3 V output reference.
Regulator bypass — pins V
CC(5.0)
and V
are connected to the same supply.
reg(3.3)
The internal regulator is bypassed and the internal circuitry is supplied directly from
pin V
. The voltage range is 3.0 to 3.6 V to comply with the USB specification.
reg(3.3)
The supply voltage range for each input option is specified in Table 8.
Table 8: Power supply input options
Input option V
Internal
regulator
Regulator
bypass
CC(5.0)
supply input for internal
regulator (4.0 to 5.5 V)
connected to V
with maximum voltage
drop of 0.3 V
(2.7 to 3.6 V)
reg(3.3)
V
reg(3.3)
voltage reference output
(3.3 V, 300 µA)
supply input
(3.0 V to 3.6 V)
V
CC(I/O)
supply input for digital
I/O pins (1.65 V to 3.6 V)
supply input for digital
I/O pins (1.65 V to 3.6 V)
9397 750 11228
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 7 of 23
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors
8. Electrostatic discharge (ESD)
8.1 ESD protection
For HBCC package, the pins that are connected to the USB connector (D+, D−,
V
measurement is limited by the test equipment. Capacitors of 4.7 µF connected from
V
protection (see Figure 4).
The ISP1102W can withstand ±12 kV using the Human Body Model and ±5 kV using
the Contact Discharge Method as specified in
and GND) have a minimum of ±12 kV ESD protection. The ±12 kV
CC(5.0)
to GND and V
reg(3.3)
Advanced USB transceiver
to GND are required to achieve this ±12 kV ESD
CC(5.0)
IEC 61000-4-2
.
ISP1102
HIGH VOLTAGE
DC SOURCE
R
C
1 MΩ
charge current
limit resistor
100 pF
C
S
capacitor
storage
R
D
1500 Ω
discharge
resistance
DEVICE UNDER
A
B
4.7 µF
Fig 4. Human Body ESD test model.
Note: For HVQFN package, the pins that are connected to the USB connector (D+,
D−, V
and GND) have a minimum of ±7 kV ESD protection.
CC(5.0)
8.2 ESD test conditions
A detailed report on test set-up and results is available on request.
TEST
V
CC(5.0)
V
4.7 µF
GND
reg(3.3)
004aaa145
9397 750 11228
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 8 of 23
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
9. Limiting values
Table 9: Absolute maximum ratings
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134).
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Unit
V
CC(5.0)
V
CC(I/O)
V
I
I
lu
V
esd
T
stg
supply voltage −0.5 +6.0 V
I/O supply voltage −0.5 +4.6 V
DC input voltage −0.5 V
CC(I/O)
+ 0.5 V
latch-up current VI= −1.8 to +5.4 V - 100 mA
electrostatic discharge voltage pins D+, D−, V
GND; I
<3µA for HBCC
LI
CC(5.0)
and
[1][2]
−12000 +12000 V
package
pins D+, D−, V
GND; I
<3µA for HVQFN
LI
CC(5.0)
and
[2]
−7000 +7000 V
package
all other pins; I
<1µA
LI
[2]
−2000 +2000 V
storage temperature −40 +125 °C
[1] Testing equipment limits measurement to only ±12 kV. Capacitors needed on V
[2] Equivalent to discharging a 100 pF capacitor via a 1.5 kΩ resistor (Human Body Model).
CC(5.0)
and V
(see Section 8).
reg(3.3)
10. Recommended operating conditions
Table 10: Recommended operating conditions
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
V
CC(5.0)
V
CC(I/O)
V
I
V
I(AI/O)
T
amb
supply voltage 4.0 5.0 5.5 V
I/O supply voltage 1.65 - 3.6 V
input voltage 0 - V
CC(I/O)
V
input voltage on AI/O pins pins D+ and D− 0 - 3.6 V
ambient temperature −40 - +85 °C
11. Static characteristics
Table 11: Static characteristics: supply pins
V
combinations; T
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
V
I
I
I
I
= 4.0 to 5.5 V or V
CC(5.0)
reg(3.3)
CC
CC(I/O)
CC(idle)
CC(I/O)(static)
= 3.0 to 3.6 V; V
reg(3.3)
=−40 to +85°C; unless otherwise specified.
amb
regulated supply voltage output internal regulator option;
operating supply current transmitting and receiving at
= 1.65 to 3.6 V; V
CC(I/O)
≤ 300 µA
I
load
12 Mbit/s; C
= 50 pF on
L
= 0 V; see Table 8 for valid voltage level
GND
[1][2]
3.0 3.3 3.6 V
[3]
- 48mA
pins D+ and D−
operating I/O supply current transmitting and receiving at
[3]
- 12mA
12 Mbit/s
supply current during full-speed
idle and SE0
idle: VD+> 2.7 V,VD−< 0.3 V;
SE0: V
< 0.3 V, VD−< 0.3 V
D+
[4]
- - 300 µA
static I/O supply current idle, SE0 or suspend - - 20 µA
9397 750 11228
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 9 of 23
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
Table 11: Static characteristics: supply pins
V
combinations; T
= 4.0 to 5.5 V or V
CC(5.0)
= 3.0 to 3.6 V; V
reg(3.3)
=−40 to +85°C; unless otherwise specified.
amb
…continued
= 1.65 to 3.6 V; V
CC(I/O)
= 0 V; see Table 8 for valid voltage level
GND
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
I
CC(susp)
I
CC(I/O)(sharing)
I
Dx(sharing)
V
CC(5.0)th
suspend supply current SUSPND = HIGH
sharing mode I/O supply current V
sharing mode load current on
pins D+ and D−
supply voltage detection
threshold
not connected - - 20 µA
CC(5.0)
V
not connected;
CC(5.0)
SOFTCON = LOW;
= 3.6 V
V
Dx
1.65 V ≤ V
CC(I/O)
supply lost - - 3.6 V
≤ 3.6 V
[4]
--20µA
--10µA
supply present 4.1 - - V
V
CC(5.0)hys
supply voltage detection
V
CC(I/O)
= 1.8 V - 70 - mV
hysteresis
V
CC(I/O)th
I/O supply voltage detection
threshold
V
reg(3.3)
= 2.7 to 3.6 V
supply lost - - 0.5 V
supply present 1.4 - - V
V
CC(I/O)hys
I/O supply voltage detection
V
reg(3.3)
= 3.3 V - 0.45 - V
hysteresis
V
reg(3.3)th
regulated supply voltage
detection threshold
1.65 V ≤ V
2.7 V ≤ V
CC(I/O)
reg(3.3)
≤ V
reg(3.3)
≤ 3.6 V
;
supply lost - - 0.8 V
[5]
2.4 - - V
V
reg(3.3)hys
regulated supply voltage
supply present
V
= 1.8 V - 0.45 - V
CC(I/O)
detection hysteresis
[1] I
[2] The minimum voltage is 2.7 V in the suspend mode.
[3] Maximum value characterized only, not tested in production.
[4] Excluding any load current and V
[5] When V
includes the pull-up resistor current via pin V
load
or Vsw source current to the 1.5 kΩ and 15 kΩ pull-up and pull-down resistors (200 µA typ.).
pu(3.3)
< 2.7 V, the minimum value for V
CC(I/O)
.
pu(3.3)
= 2.0 V for supply present condition.
reg(3.3)th
Table 12: Static characteristics: digital pins
V
= 1.65 to 3.6 V; V
CC(I/O)
GND
=0V; T
=−40 to +85°C; unless otherwise specified.
amb
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
V
= 1.65 to 3.6 V
CC(I/O)
Input levels
V
IL
V
IH
LOW-level input voltage - - 0.3V
HIGH-level input voltage 0.6V
CC(I/O)
-- V
CC(I/O)
V
Output levels
V
OL
V
OH
LOW-level output voltage IOL= 100 µA - - 0.15 V
= 2 mA - - 0.4 V
I
OL
HIGH-level output voltage IOH= 100 µAV
= 2 mA V
I
OH
− 0.15 - - V
CC(I/O)
− 0.4 - - V
CC(I/O)
Leakage current
I
LI
input leakage current
[1]
−1-+1µA
9397 750 11228
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 10 of 23
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
Table 12: Static characteristics: digital pins
V
= 1.65 to 3.6 V; V
CC(I/O)
GND
=0V; T
amb
…continued
=−40 to +85°C; unless otherwise specified.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Capacitance
C
IN
Example 1: V
input capacitance pin to GND - - 10 pF
= 1.8 V ± 0.15 V
CC(I/O)
Input levels
V
IL
V
IH
LOW-level input voltage - - 0.5 V
HIGH-level input voltage 1.2 - - V
Output levels
V
OL
V
OH
Example 2: V
LOW-level output voltage IOL= 100 µA - - 0.15 V
= 2 mA - - 0.4 V
I
OL
HIGH-level output voltage IOH= 100 µA 1.5 - - V
= 2 mA 1.25 - - V
I
OH
= 2.5 V ± 0.2 V
CC(I/O)
Input levels
V
IL
V
IH
LOW-level input voltage - - 0.7 V
HIGH-level input voltage 1.7 - - V
Output levels
V
OL
V
OH
Example 3: V
LOW-level output voltage IOL= 100 µA - - 0.15 V
= 2 mA - - 0.4 V
I
OL
HIGH-level output voltage IOH= 100 µA 2.15 - - V
= 2 mA 1.9 - - V
I
OH
= 3.3 V ± 0.3 V
CC(I/O)
Input levels
V
IL
V
IH
LOW-level input voltage - - 0.9 V
HIGH-level input voltage 2.15 - - V
Output levels
V
OL
V
OH
LOW-level output voltage IOL= 100 µA - - 0.15 V
= 2 mA - - 0.4 V
I
OL
HIGH-level output voltage IOH= 100 µA 2.85 - - V
= 2 mA 2.6 - - V
I
OH
[1] If V
CC(I/O)
≥ V
, then the leakage current will be higher than the specified value.
reg(3.3)
Table 13: Static characteristics: analog I/O pins D+ and D−
V
= 4.0 to 5.5 V or V
CC(5.0)
= 3.0 to 3.6 V; V
reg(3.3)
GND
=0V; T
=−40 to +85°C; unless otherwise specified.
amb
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Input levels
Differential receiver
V
DI
V
CM
differential input sensitivity |V
differential common mode
− V
I(D+)
| 0.2 - - V
I(D−)
includes VDI range 0.8 - 2.5 V
voltage
9397 750 11228
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 11 of 23
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
Table 13: Static characteristics: analog I/O pins D+ and D−
V
= 4.0 to 5.5 V or V
CC(5.0)
= 3.0 to 3.6 V; V
reg(3.3)
GND
=0V; T
…continued
=−40 to +85°C; unless otherwise specified.
amb
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Single-ended receiver
V
IL
V
IH
V
hys
LOW-level input voltage - - 0.8 V
HIGH-level input voltage 2.0 - - V
hysteresis voltage 0.4 - 0.7 V
Output levels
V
OL
V
OH
LOW-level output voltage RL= 1.5 kΩ to 3.6 V - - 0.3 V
HIGH-level output voltage RL=15kΩ to GND
[1]
2.8 - 3.6 V
Leakage current
I
LZ
OFF-state leakage current −1- +1µA
Capacitance
C
IN
transceiver capacitance pin to GND - - 20 pF
Resistance
Z
DRV
Z
INP
R
SW
driver output impedance steady-state drive
input impedance 10 - - MΩ
internal switch resistance at
pin V
pu(3.3)
[2]
34 39 44 Ω
--10Ω
Termination
V
TERM
termination voltage for
upstream port pull-up (R
)
pu
[3][4]
3.0 - 3.6 V
[1] V
OH(min)=Vreg(3.3)
[2] Includes external resistors of 33 Ω±1% on both pins D+ and D−.
[3] This voltage is available at pins V
[4] The minimum voltage is 2.7 V in the suspend mode.
− 0.2 V.
reg(3.3)
and V
pu(3.3)
.
12. Dynamic characteristics
Table 14: Dynamic characteristics: analog I/O pins D+ and D−
V
combinations; T
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Driver characteristics
t
t
FRFM differential rise/fall time
V
= 4.0 to 5.5 V or V
CC(5.0)
FR
FF
CRS
= 3.0 to 3.6 V; V
reg(3.3)
=−40 to +85°C; unless otherwise specified.
amb
= 1.65 to 3.6 V; V
CC(I/O)
rise time CL= 50 to 125 pF;
10% to 90% of |V
see Figure 5
fall time CL= 50 to 125 pF;
90% to 10% of |V
see Figure 5
excluding the first transition
matching (t
output signal crossover
voltage
FR/tFF
)
from Idle state
excluding the first transition
from Idle state; see Figure 6
OH
OH
− VOL|;
− VOL|;
= 0 V; see Table 8 for valid voltage level
GND
4 - 20 ns
4 - 20 ns
90 - 111.1 %
[1]
1.3 - 2.0 V
9397 750 11228
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 12 of 23
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
Table 14: Dynamic characteristics: analog I/O pins D+ and D−
V
combinations; T
= 4.0 to 5.5 V or V
CC(5.0)
= 3.0 to 3.6 V; V
reg(3.3)
=−40 to +85°C; unless otherwise specified.
amb
CC(I/O)
= 1.65 to 3.6 V; V
…continued
GND
= 0 V; see Table 8 for valid voltage level
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Driver timing
t
PLH(drv)
t
PHL(drv)
t
PHZ
t
PLZ
t
PZH
t
PZL
driver propagation delay
(VPO, VMO to D+, D−)
driver propagation delay
(VPO, VMO to D+, D−)
driver disable delay
OE to D+, D−)
(
driver disable delay
OE to D+, D−)
(
driver enable delay
OE to D+, D−)
(
driver enable delay
OE to D+, D−)
(
LOW-to-HIGH; seeFigure 6
and Figure 9
HIGH-to-LOW; see Figure 6
and Figure 9
HIGH-to-OFF; see Figure 7
and Figure 10
LOW-to-OFF; seeFigure 7
and Figure 10
OFF-to-HIGH; see Figure 7
and Figure 10
OFF-to-LOW; see Figure 7
and Figure 10
--18ns
--18ns
--15ns
--15ns
--15ns
--15ns
Receiver timings
Differential receiver
t
PLH(rcv)
t
PHL(rcv)
propagation delay
(D+, D− to RCV)
propagation delay
(D+, D− to RCV)
LOW-to-HIGH; seeFigure 8
and Figure 11
HIGH-to-LOW; see Figure 8
and Figure 11
--15ns
--15ns
Single-ended receiver
t
PLH(se)
propagation delay
(D+, D− to VP/VPO,
LOW-to-HIGH; seeFigure 8
and Figure 11
--18ns
VM/VMO)
t
PHL(se)
propagation delay
(D+, D− to VP/VPO,
HIGH-to-LOW; see Figure 8
and Figure 11
--18ns
VM/VMO)
[1] Characterized only, not tested. Limits guaranteed by design.
9397 750 11228
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 13 of 23
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 14

Philips Semiconductors
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
1.65 V
logic input
tFR, t
V
OH
V
OL
LR
90 %
10 %
90 %
tFF, t
10 %
LF
MGS963
0 V
V
OH
V
OL
differential
data lines
0.9 V
t
PLH(drv)
V
CRS
Fig 5. Rise and fall times. Fig 6. Timing of VPO and VMO to D+ and D−.
0.9 V
t
PHL(drv)
V
CRS
MGS964
1.65 V
logic input
0 V
V
OH
V
OL
differential
data lines
0.9 V
t
PZH
t
PZL
V
CRS
0.9 V
t
PHZ
t
PLZ
V
−0.3 V
OH
V
+0.3 V
OL
MGS966
2.0 V
differential
data lines
0.8 V
V
OH
logic output
V
OL
V
CRS
t
PLH(rcv)
t
PLH(se)
0.9 V
V
CRS
t
PHL(rcv)
t
PHL(se)
0.9 V
Fig 7. Timing of OE to D+ and D−. Fig 8. Timing of D+ and D− to RCV, VP/VPO and
VM/VMO.
MGS965
9397 750 11228
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 14 of 23
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors
13. Test information
V
pu(3.3)
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
D.U.T.
1.5 kΩ
test point
D+/D−
004aaa037
33 Ω
C
15 kΩ
L
Load capacitance CL= 50 pF (minimum or maximum timing)
Fig 9. Load on pins D+ and D−.
test point
V = 0 V for t
V=V
reg(3.3)
PZH
for t
and t
PZL
PHZ
and t
D.U.T.
33 Ω
PLZ
500 Ω
50 pF
V
MBL142
Fig 10. Load on pins D+ and D− for enable and disable times.
test point
D.U.T.
25 pF
MGS968
Fig 11. Load on pins VM/VMO, VP/VPO and RCV.
9397 750 11228
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 15 of 23
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors
14. Package outline
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
HBCC16: plastic thermal enhanced bottom chip carrier; 16 terminals; body 3 x 3 x 0.65 mm
terminal 1
index area
e
4
D
e
1
D
h
e
59
B
A
E
y
e
E
e
h
2
1
detail X
C
b
f
b
2
v
M
w
M
b
1
b
3
v
M
w
M
C
y
SOT639-2
ACCB
v
M
ACCB
w
M
v
M
ACCB
w
M
ACCB
1/2 e
4
113
1/2 e
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
A
max.
0.8
OUTLINE
VERSION
A
0.10
0.05
1bA2
0.7
0.6
UNIT
mm
SOT639-2 MO-217
b
0.33
0.33
0.27
0.27
IEC JEDEC JEITA
Fig 12. Package outline HBCC16.
16
3
e
3
0 2.5 5 mm
b
b
1
0.38
0.32
3
2
0.38
0.32
X
D
D
h
3.1
1.45
2.9
1.35
REFERENCES
3.1
2.9
scale
E
E
h
1.45
1.35
0.5
2.5
e
1
2.5
e
e
2
2.45
A
2
A
e
3
4
2.45
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
A
1
we
v
0.23
0.17
f
0.08
yy
0.1 0.05 0.2
ISSUE DATE
01-11-13
03-03-12
1
9397 750 11228
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 16 of 23
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors
HVQFN14: plastic thermal enhanced very thin quad flat package; no leads;
14 terminals; body 2.5 x 2.5 x 0.85 mm
A
D
B
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
SOT773-1
terminal 1
index area
L
E
terminal 1
index area
A
A
E
e
1
b
1/2 e
e
4
3
h
1
14
D
h
7
11
v
M
ACCB
w
M
8
e
e
2
10
1
detail X
y
C
1
c
C
y
X
0 2.5 5 mm
scale
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.075 mm maximum per side are not included.
(1)
A
UNIT
mm
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT773-1 - - - - - -- - -
max.
A
0.05
0.00
1
D
1.45
1.15
h
(1)
E
E
h
2.6
1.45
2.4
1.15
REFERENCES
b
0.30
0.18
D
2.6
0.2
2.4
IEC JEDEC JEITA
(1)
c
e
e
1
1.5
0.51
L
2
0.35
1
0.25
0.1v0.05
ye
w
0.05 0.1
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
y
1
ISSUE DATE
02-07-05
Fig 13. Package outline HVQFN14.
9397 750 11228
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 17 of 23
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors
15. Packaging
The ISP1102W (HBCC16 package) is delivered on a Type A carrier tape, see
Figure 14. The tape dimensions are given in Table 15.
The reel diameter is 330 mm. The reel is made of polystyrene (PS) and is not
designed for use in a baking process.
The cumulative tolerance of 10 successive sprocket holes is ±0.02 mm. The camber
must not exceed 1 mm in 100 mm.
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
Type A
4
Type B
4
P1
A0
direction of feed
A0
P1
direction of feed
K0
dth
W
B0
W
elongated
sprocket hole
B0
Fig 14. Carrier tape dimensions.
Table 15: Type A carrier tape dimensions for the ISP1102W
Dimension Value Unit
A0 3.3 mm
B0 3.3 mm
K0 1.1 mm
P1 8.0 mm
W 12.0 ±0.3 mm
K0
MLC338
16. Soldering
16.1 Introduction to soldering surface mount packages
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology. A more in-depth account
of soldering ICs can be found in our
Packages
9397 750 11228
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 18 of 23
(document order number 9398 652 90011).
Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC packages. Wavesoldering can still
be used for certain surface mount ICs, but it is not suitable for fine pitch SMDs. In
these situations reflow soldering is recommended. In these situations reflow
soldering is recommended.
16.2 Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of fine solder particles, flux and
binding agent) to be applied to the printed-circuit board by screen printing, stencilling
or pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement. Driven by legislation and
environmental forces the worldwide use of lead-free solder pastes is increasing.
Several methods exist for reflowing; for example, convection or convection/infrared
heating in a conveyor type oven. Throughput times (preheating, soldering and
cooling) vary between 100 and 200 seconds depending on heating method.
Typical reflow peak temperatures range from 215 to 270 °C depending on solder
paste material. The top-surface temperature of the packages should preferably be
kept:
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
• below 220 °C (SnPb process) or below 245 °C (Pb-free process)
– for all BGA and SSOP-T packages
– for packages with a thickness ≥ 2.5 mm
– for packages with a thickness < 2.5 mm and a volume ≥ 350 mm3 so called
thick/large packages.
• below 235 °C (SnPb process) or below 260 °C (Pb-free process) forpackages with
a thickness < 2.5 mm and a volume < 350 mm3 so called small/thin packages.
Moisture sensitivity precautions, as indicated on packing, must be respected at all
times.
16.3 Wave soldering
Conventional single wave soldering is not recommended for surface mount devices
(SMDs) or printed-circuit boards with a high component density, as solder bridging
and non-wetting can present major problems.
To overcome these problems the double-wave soldering method was specifically
developed.
If wave soldering is used the following conditions must be observed for optimal
results:
• Use a double-wave soldering method comprising a turbulent wave with high
upward pressure followed by a smooth laminar wave.
• For packages with leads on two sides and a pitch (e):
– larger than or equal to 1.27 mm, the footprint longitudinal axis is preferred to be
parallel to the transport direction of the printed-circuit board;
– smaller than 1.27 mm, the footprint longitudinal axis must be parallel to the
transport direction of the printed-circuit board.
The footprint must incorporate solder thieves at the downstream end.
9397 750 11228
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 19 of 23
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors
• For packages with leads on four sides, the footprint must be placed at a 45° angle
During placement and before soldering, the package must be fixed with a droplet of
adhesive. The adhesive can be applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the adhesive is cured.
Typical dwell time of the leads in the wave ranges from 3 to 4 seconds at 250 °C or
265 °C, depending on solder material applied, SnPb or Pb-free respectively.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal of corrosive residues in
most applications.
16.4 Manual soldering
Fix the component by first soldering two diagonally-opposite end leads. Use a low
voltage (24 V or less) soldering iron applied to the flat part of the lead. Contact time
must be limited to 10 seconds at up to 300 °C.
When using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be soldered in one operation within
2 to 5 seconds between 270 and 320 °C.
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
to the transport direction of the printed-circuit board. The footprint must
incorporate solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
16.5 Package related soldering information
Table 16: Suitability of surface mount IC packages for wave and reflow soldering
methods
Package
BGA, LBGA, LFBGA, SQFP, SSOP-T
TFBGA, VFBGA
DHVQFN, HBCC, HBGA, HLQFP, HSQFP,
HSOP, HTQFP, HTSSOP, HVQFN, HVSON,
SMS
PLCC
LQFP, QFP, TQFP not recommended
SSOP, TSSOP, VSO, VSSOP not recommended
PMFP
[1] For more detailed information on the BGA packages refer to the
[2] All surface mount (SMD) packages are moisture sensitive. Depending upon the moisture content, the
[3] These transparent plastic packages are extremely sensitive to reflow soldering conditions and must
[4] These packages are not suitable for wave soldering. On versions with the heatsink on the bottom
[1]
Soldering method
Wave Reflow
[3]
,
not suitable suitable
not suitable
[5]
, SO, SOJ suitable suitable
[8]
(AN01026); order a copy from your Philips Semiconductors sales office.
maximum temperature (with respect to time) and body size of the package, there is a risk that internal
or external package cracks may occur due to vaporization of the moisture in them (the so called
popcorn effect). For details, refer to the Drypack information in the
Circuit Packages; Section: Packing Methods
on no account be processed through more than one soldering cycle or subjected to infrared reflow
soldering with peak temperature exceeding 217 °C ± 10 °C measured in the atmosphere of the reflow
oven. The package body peak temperature must be kept as low as possible.
side, the solder cannot penetrate between the printed-circuit board and the heatsink. On versions with
the heatsink on the top side, the solder might be deposited on the heatsink surface.
not suitable not suitable
.
[4]
[5][6]
[7]
(LF)BGA Application Note
Data Handbook IC26; Integrated
suitable
suitable
suitable
[2]
9397 750 11228
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 20 of 23
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors
[5] If wave soldering is considered, then the package must be placed at a 45° angle to the solder wave
direction. The package footprint must incorporate solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
[6] Wave soldering is suitable for LQFP, QFP and TQFP packages with a pitch (e) larger than 0.8 mm; it
is definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.65mm.
[7] Wave soldering is suitable for SSOP and TSSOP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than
0.65 mm; it is definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.5 mm.
[8] Hot bar soldering or manual soldering is suitable for PMFP packages.
17. Revision history
Table 17: Revision history
Rev Date CPCN Description
03 20030902 - Product data (9397 750 11228)
Modifications:
• Added HVQFN14 package information
• Section 2: updated
• Added pad details to Table 2
• Section 7.3: updated the first line under Normal mode
• Table 6: added a table note
• Section 8.1: updated the first paragraph and added a note
• Table 9: updated info on V
02 20030106 - Product data (9397 750 10397)
01 20000524 - Objective data
and added a table note.
esd
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
9397 750 11228
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 21 of 23
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors
18. Data sheet status
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
Level Data sheet status
I Objective data Development This data sheet contains data from the objective specification for product development. Philips
II Preliminary data Qualification This data sheet contains data from the preliminary specification. Supplementary data will be published
III Product data Production This data sheet contains data from the product specification. Philips Semiconductors reserves the
[1] Please consult the most recently issued data sheet before initiating or completing a design.
[2] The product status of the device(s) described in this data sheet may have changed since this data sheet was published. The latest information is available on the Internet at
URL http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.
[3] For data sheets describing multiple type numbers, the highest-level product status determines the data sheet status.
[1]
Product status
19. Definitions
Short-form specification — The data in a short-form specification is
extracted from a full data sheet with the same type number and title. For
detailed information see the relevant data sheet or data handbook.
Limiting values definition — Limiting values given are in accordance with
the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device.
These are stress ratings only and operation of the device at these or at any
other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the
specification is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods
may affect device reliability.
Application information — Applications that are described herein for any
of these products are for illustrative purposes only. Philips Semiconductors
make no representation or warranty that such applications will be suitable for
the specified use without further testing or modification.
[2][3]
Definition
Semiconductors reserves the right to change the specification in any manner without notice.
at a later date. Philips Semiconductors reservesthe right to change the specification without notice, in
order to improve the design and supply the best possible product.
right to make changes at any time in order to improve the design, manufacturing and supply.Relevant
changes will be communicated via a Customer Product/Process Change Notification (CPCN).
20. Disclaimers
Life support — These products are not designed for use in life support
appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these products can
reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips Semiconductors
customers using or selling these products for use in such applications do so
at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips Semiconductors for any
damages resulting from such application.
Right to make changes — Philips Semiconductors reserves the right to
make changes in the products - including circuits, standard cells, and/or
software - described or contained herein in order to improve design and/or
performance. When the product is in full production (status ‘Production’),
relevant changes will be communicated via a Customer Product/Process
Change Notification (CPCN). Philips Semiconductors assumes no
responsibility or liability for the use of any of these products, conveys no
licence or title under any patent, copyright, or mask work right to these
products, and makes no representations or warrantiesthat these products are
free from patent, copyright, or mask workright infringement, unless otherwise
specified.
Contact information
For additional information, please visit http://www.semiconductors.philips.com.
For sales office addresses, send e-mail to: sales.addresses@www.semiconductors.philips.com. Fax: +31 40 27 24825
9397 750 11228
Product data Rev. 03 — 02 September 2003 22 of 23
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003. All rights reserved.
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors
Contents
1 General description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
3 Applications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
4 Ordering information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
5 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
6 Pinning information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
6.1 Pinning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
6.2 Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
7 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
7.1 Function selection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
7.2 Operating functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
7.3 Power supply configurations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
7.4 Power supply input options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
8 Electrostatic discharge (ESD). . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
8.1 ESD protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
8.2 ESD test conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
9 Limiting values. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
10 Recommended operating conditions. . . . . . . . 9
11 Static characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
12 Dynamic characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
13 Test information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
14 Package outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
15 Packaging. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
16 Soldering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
16.1 Introduction to soldering surface mount
packages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
16.2 Reflow soldering. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
16.3 Wave soldering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
16.4 Manual soldering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
16.5 Package related soldering information . . . . . . 20
17 Revision history. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
18 Data sheet status. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
19 Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
20 Disclaimers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
ISP1102
Advanced USB transceiver
© Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. 2003.
Printed in The Netherlands
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior
written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation or
contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed without notice. No
liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication
thereof does not convey nor imply any license under patent- or other industrial or
intellectual property rights.
Date of release: 02 September 2003 Document order number: 9397 750 11228
 Loading...
Loading...