Page 1

USER
MANUAL
MODEL 1082/I and
1082/144/I
iDSL Modem with
10Base- T Interface
CERTIFIED
An ISO-9001
Certified
Company
Part# 07M1082I-UM
Doc# 03318U2-001
Rev. C
Revised 10/27/06
SALES OFFICE
(301) 975-1000
TECHNICAL SUPPORT
(301) 975-1007
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1.0 Warranty Information ................................................................. 4
1.1 FCC Information ........................................................................... 4
1.2 CE Notice...................................................................................... 4
1.3 Service.......................................................................................... 5
2.0 General Information.................................................................... 6
2.1 Features........................................................................................ 6
2.2 Description.................................................................................... 7
2.3 1082 SNMP Management Solutions............................................. 7
HTTP/HTML Management ........................................................... 7
3.0 PPP Operational Background.................................................... 8
3.1 Applications .................................................................................. 8
4.0 Configuration ............................................................................ 11
4.1 Configuring the Hardware DIP Switches .................................... 11
Configuring DIP Switch S1......................................................... 12
Switches S1-1 and S1-2: Data Rate........................................... 13
Switch S1-5: Asynchronous/Sync Operation.............................. 13
Switches S1-6 and S1-7: System Clock Mode........................... 14
Switch S1-8: Response to RDL Request.................................... 14
Configuring DIP switch “S2” ....................................................... 15
Switches S2-1: 19.2 kbps or 144* kbps
Synchronous Rate Enable.......................................................... 15
Switch S2-2: Front Panel Switch Disable................................... 16
Switches S2-3, S2-6, S2-7 and S2-8: Reserved ........................ 16
5.0 Installation................................................................................. 17
5.1 Connecting DSL Interface........................................................... 17
5.2 Connecting 10Base-T Ethernet Port to PC (DTE)...................... 18
5.3 Connecting 10Base-T Ethernet Port to Hub (DCE).................... 18
5.4 Power Connection ...................................................................... 19
Universal AC Power (100–240VAC)........................................... 19
DC Power................................................................................... 20
6.0 Operation................................................................................... 21
6.1 Power-up .................................................................................... 21
6.2 LED Status Monitors................................................................... 21
6.3 Test Modes................................................................................. 23
Remote Digital Loopback (RDL)/V.52 (BER).............................. 23
A 1082/I Specifications ................................................................ 25
A.1 Transmission Format ................................................................... 25
A.2 Transmission Line ....................................................................... 25
A.3 Clocking ...................................................................................... 25
A.4 Distance ...................................................................................... 25
A.5 Data Rates .................................................................................. 25
A.6 Diagnostics ................................................................................. 25
A.7 LED Status Indicators ................................................................. 25
2
Page 3

A.8 Connectors ................................................................................. 25
A.9 Power .......................................................................................... 25
A.10 Temperature Range .................................................................... 26
A.11 Altitude ........................................................................................ 26
A.12 Humidity ...................................................................................... 26
A.13 Dimensions ................................................................................. 26
A.14 Weight ......................................................................................... 26
B Model 1082/I Factory Replacement Parts
and Accessories ....................................................................... 27
3
Page 4

1.0 WARRANTY INFORMATION
Patton Electronics
components to be free from defects, and will—at our option—repair or
replace the product should it fail within one year from the first date of
shipment.
This warranty is limited to defects in workmanship or materials, and does
not cover customer damage, abuse or unauthorized modification. If this
product fails or does not perform as warranted, your sole recourse shall
be repair or replacement as described above. Under no condition shall
Patton Electronics
product. These damages include, but are not limited to , the f ollo wing: lost
profits, lost savings and incidental or consequential damages arising
from the use of or inability to use this product.
cifically disclaims all other warranties, expressed or implied, and the
installation or use of this product shall be deemed an acceptance of
these terms by the user.
1.1 FCC INFORMATION
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class A digital device, pursuant to P art 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits
are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and,
if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in
which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own
expense. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by
one or more of the following measures:
warrants all Model 1082/I and Model 1082/144/I
be liable for any damages incurred b y the use of this
Patton Electronics
spe-
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected
1.2 CE NOTICE
The CE symbol on your Patton Electronics equipment indicates that it is in
compliance with the Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) directive and
the Low Voltage Directiv e (LVD) of the Union European (EU). A Certificate
of Compliance is available by contacting Patton Technical Support.
4
Page 5

1.3 SERVICE
All warranty and non-warranty repairs must be returned freight prepaid
and insured to Patton Electronics. All returns must have a Return Materials Authorization number on the outside of the shipping container. This
number may be obtained from Patton Electronics Technical Service at:
Tel:
(301) 975-1007
E-mail:
URL:
support@patton.com
www.patton.com
Note
Packages received without an RMA number will not be
accepted.
Patton Electronics’ technical staff is also available to answer any questions that might arise concerning the installation or use of your
Model 1082/I or Model 1082/144/I. Technical Service hours:
EST, Monday
through
Friday
.
8AM
to
5PM
5
Page 6

2.0 GENERAL INFORMATION
Thank you for your purchase of this
Patton Electronics
product. This
product has been thoroughly inspected and tested and is warranted for
One Year parts and labor. If any questions or problems arise during
installation or use of this product, please do not hesitate to contact
Patton Electronics Technical Support
at
(301) 975-1007
.
2.1 FEATURES
• Provides MAC Level Data Link (Layer 2) connection between two
peered 10Base-T Ethernet LANs
• Operates transparently to higher level protocols such as TCP/IP, DEC-
net, NETBIOS and IPX
• PPP (Point to Point Protocol, RFC 1661) with Bridge Control Protocol
(RFC 1638)
• Automatically learns, loads and removes MAC addresses
• Point-to-point distances up to 5 miles (all data rates) on 24 AWG
twisted pair
• HTTP/SNMP Manageable as CP (Customer Premises) Unit with
1092ARC CO (Central Office) Rack Card and 1001MC management card
• Internal or receive recovered clocking between units
• LED indicators for 10Base-T Link, DSL Link, Status, No Signal, Error
and T est Mode
• Remote digital loopback, local line loopback diagnostic modes
• Synchronous data rates: 19.2, 32, 56, 64, 128, and 144 kbps
Note
144 kbps data rate is only available on the Model 1082/144/I.
19.2 kbps rate is available on all Model 1082 series modems
except
for the 1082/144/I.
• Full duplex operation over a single twisted pair (2-wires)
• Multi-Rate Symmetric DSL
• Compatible with the popular Patton Model 1092A
• Universal power supply (90–260VAC) or DC power supply (-48VDC)
• Small, Convienent Desktop Unit
• CE Marked
6
Page 7
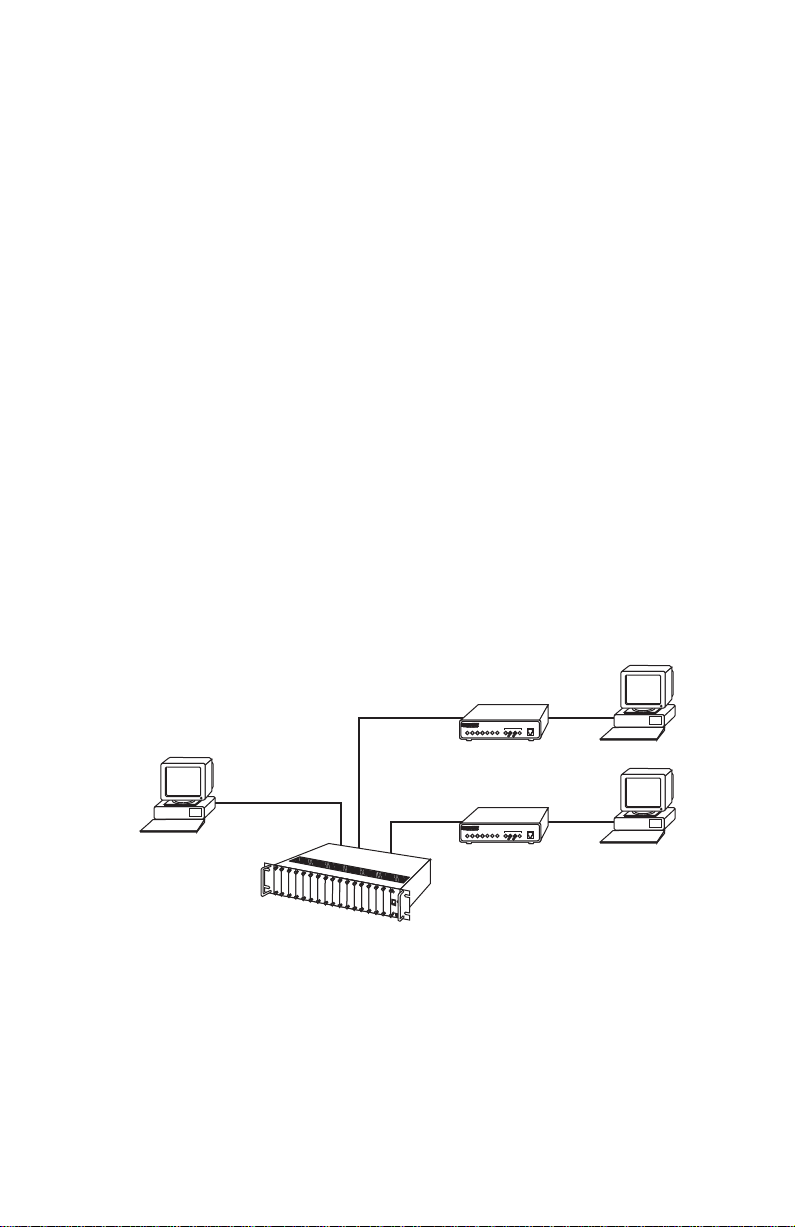
2.2 DESCRIPTION
The Model 1082/I and Model 1082/144/I are Multi Rate iDSL Modems that
provide seamless MAC La y er connectivity between 2 peered 10Base-T
LANs. Now, Enterprise users no longer need to hassle with a bridge and a
CSU/DSU or recurring leased line costs. The 1082 allows users to add additional nodes to a LAN that has reached its maximum distance limits or separate high traffic areas of a LAN. The 1082 connects peered LANs and
automatically forwards and receives LAN broadcasts , m ulti-casts and
frames across a 2-wire DSL span. The Model 1082/I and Model 1082/144/I
support PPP (RFC 1s661) and BCP (RFC 1638).
Both 1082 modems’ features include loopback diagnostics, inband
SNMP/HTTP remote management capabilities using NetLink Plug-andPlay and externally accessible configuration switches. As a symmetric
DSL modem, the1082 offers the same data rates in both directions over
a single pair of regular telephone lines using 2BIQ modulation. The 1082
connects to the DSL line via an RJ-45 jack, and is powered by a universal (90–260VAC) supply or a DC supply (-48VDC).
2.3 1082 SNMP MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS
The Model 1082/I and Model 1082/144/I are SNMP manageable when connected to a rack-mounted Model 1092ARC (see Figure 1). SNMP management is enabled through a 1001MC rack management card located in the
Patton Electronics Rack System.
Model 1082
10Base-T
connection
to 1001MC
Management
Station
Figure 1.
2B1Q
connections to
remote 1082s
Model 1082
Rack-mounted
1092ARCs
Typical application
HTTP/HTML Management
The 1001MC maintains HTML pages that can be viewed through a Web
browser. You can display remote statistics and configure Model 1082
parameters simply by entering the 1001MC’s IP address into the bro wser.
7
Page 8

3.0 PPP OPERATIONAL BACKGROUND
PPP is a protocol used for multi-plexed transport over a point-to-point
link. PPP operates on all full duplex media, and is a symmetric peer-topeer protocol, which can be broken into three main components:
• A standard method to encapsulate datagrams over serial links
• A Link Control Protocol (LCP) to establish, configure, and test the
data-link connection
• A family of Network Control Protocols (NCPs) to establish and config-
ure different network layer protocols
In order to establish communications over a point-to-point link, each end
of the PPP link must first announce its capabilities and agree on the
parameters of the link’s operation. This exchange is facilitated through
LCP Configure-Request packets.
Once the link has been established and optional facilities have been
negotiated, PPP will attempt to establish a network protocol. PPP will
use Network Control Protocol (NCP) to choose and configure one or
more network layer protocols. Once each of the network layer protocols
have been configured, datagrams from the established network layer
protocol can be sent over the link. The link will remain configured for
these communications until explicit LCP or NCP packets close the link
down, or until some external event occurs.
The PPP Bridging Control Protocol (BCP), defined in RFC 1638, configures and enables/disables the bridge protocol on both ends of the pointto-point link. BCP uses the same packet exchange mechanism as the
Link Control Protocol (LCP). BCP is a Network Control Protocol of PPP,
bridge packets may not be exchanged until PPP has reached the network layer protocol phase.
3.1 APPLICATIONS
In situations where a routed network requires connectivity to a remote Ethernet network, the interface on a router can be configured as a PPP IP Half
Bridge. The serial line to the remote bridge functions as a Virtual Ethernet
interface, eff ectiv ely e xtending the routers serial port connection to the
remote network. The bridge device sends bridge packets (BPDU’s) to the
router's serial interface. The router will receive the layer three address information and will forward these pack ets based on its IP address .
8
Page 9

Patton
1082/I
Bridge
Ethernet LAN
Patton 1082/C
connected to a router
PEC device with
serial interface
Figure 2.
Cisco router with serial interface, configured as PPP Half-Bridge
Figure 2 shows a typical Cisco router with a serial interface configured
as a PPP Half Bridge. The router serial interface uses a remote device
that supports PPP bridging to function as a node on the remote Ethernet
network. The serial interface on the Cisco will have an IP address on the
same Ethernet subnet as the bridge.
For example, the customer site is assigned the addresses 192.168.1.0/
24 through 192.168.1.1/24. The address 192.168.1.1/24 is also the
default gateway for the remote network. The above settings remove any
routing/forwarding intelligence from the CPE. The associated Cisco configuration will set serial interface (s0) to accommodate half bridging for
the above example.
Authentication is optional under PPP. In a point-to-point leased-line link,
incoming customer facilities are usually fixed in nature , therefore authentication is generally not required. If the foreign device requires authentication via PAP or CHAP, the PPP software will respond with default PeerID consisting of the units Ethernet MAC address and a password which
consists of the unit’s Ethernet MAC address.
Some networking systems do not define network numbers in packets
sent out over a network. If a packet does not have a specific destination
network number, a router will assume that the packet is set up for the
local segment and will not forward it to any other sub-network. However,
in cases where two devices need to communicate over the wide-area,
bridging can be used to transport non-routable protocols.
9
Page 10

Figure 3.
Transparent bridging between two routers over a serial interface
Figure 3 illustrates transparent bridging between two routers over a
serial interface (s0). Bridging will occur between the two Ethernet interfaces on router A (e0 and e1) and the two Ethernet interfaces on router B
(e0 and e1).
10
Page 11

4.0 CONFIGURATION
The Model 1082/I and Model 1082/144/I each are equipped with 16 DIP
switches that enable configuration of the unit for a wide variety of applications. This section describes switch locations and e xplains the different
configurations.
4.1 CONFIGURING THE HARDWARE DIP SWITCHES
Using a small flat-tip screwdriver , remov e the protectiv e co v er located on
the underside of the Model 1092 (see Figure 4).
10BTDSL
Link
Model 1194E Single Mode Fiber - Quad G.703/G.704 Modem
G.703/G.704 Test Modes
NSStatus
511E
TMER
511/RDL
Normal
511
NetLink 10BastT iDSL Modem
511E/RBL
Figure 4.
Removing the cover to access DIP switches S1 and S2
11
Page 12

12
ON
S1 S2
1234ON5678
1234ON5678
S1
S2
S1
Switch toggle
ON
1234
5678
Push toggle up
for ON position
Push toggle
down for
OFF position
1234ON5678
S1
Figure 5.
DIP switches S2 and S2
Figure 5 shows the orientation of the DIP switches in the “ON” and “OFF”
positions.
Configuring DIP Switch S1
DIP switch S1 is where you configure the data rate, asynchronous or
synchronous data format, transmit clock source, and response to RDL
request. The following table summarizes default positions of DIP
switches S1-1 through S1-8. Detailed descriptions of each switch follow
the table.
S1 Summary Table
Position Function Factory Default
S1-1 Data Rate On
S1-2 Data Rate Off
}
64K Sync
S1-3 Reserved On
S1-4 Reserved On
S1-5 Async/Sync Data Format Off
Async/Sync
S1-6 Tx Clock Source On
Internal Clock
S1-7 Tx Clock Source On
}
S1-8 Response to RDL Request On Enable
12
Page 13

Note
When setting the 1082 for SNMP Management, the DTE rate
switches (S1-1,S1-2, and S2-1) must be also set to the ON position. Therefore, to set a 1082 unit SNMP Mangagement mode, the
following switches ha v e to be at the ON position, S1-1, S1-2, S2-1.
Switches S1-1 and S1-2: Data Rate
Use switches S1-1 and S1-2 to configure the asynchronous or synchronous data rate of the Model 1082/I and Model 1082/144/I. Each setting
represents one synchronous data rate and one asynchronous data rate.
S1-1 S1-2 Sync Data Rate Async. Data Rate
On On 32 kbps Reserved
Off On 56 kbps Reserved
On Off 64 kbps Reserved
Off Off 128 kbps (see note) 0–38.4 kbps
Off Off 144 kbps or 19.2 kbps (see note) Reserved
Note
The Model 1082/I can also operate at the 19.2 kbps synchronous rate, and the Model 1092/144/I can also operate at the 144
kbps synchronous rate. To operate at these rates, set Switches
S1-1 and S1-2 both to the OFF position and Switch S2-1 to the
ON position (see “Configuring DIP switch “S2”” on page 152 for
a description of Switch S2-1).
If the S2-1 switch is positioned in the OFF position, the 128 kbps
sync data rate/0–38.4 kbps async data rate option is selected.
Switch S1-3 and S1-4: Must be set to the ON position (Reserved).
S1-3 Setting S1-4 Setting
On Reserved On Reserved
Switch S1-5: Asynchronous/Sync Operation
Use Switch S1-5 to configure the Model 1082 for async/sync operation.
Switch S1-5 must be set in the Off position. There is no other valid setting.
S1-5 Setting
Off Async/Sync
13
Page 14

Switches S1-6 and S1-7: System Clock Mode
Use Switches S1-6 and S1-7 to configure the 1082/I or Model 1082/144/
I for internal, or receive recover clock mode.
S1-6 S1-7 Clock Mode Description
On On Internal System clock generated internally
On Off Receive Recover System clock derived from the
received line signal
Off Off Hardware Reset
A pair of Model 1082/Is communicate synchronously
across the twisted pair line connection. Therefore,
you
must set these switches whether your application is
async or sync
. For Sync or Async applications, please
configure one Model 1082/I for internal clock mode and
Important
the other Model 1082/I for receive recover clock mode.
Switch S1-8: Response to RDL Request
Use Switch S1-8 to allow Model 1082/I and Model 1082/144/I to enter the
Remote Digital Loopback diagnostic test when requested to do so by the
far end Model 1082/I and Model 1082/144/I. F or example, when switch S18 is set to “ON”, it will enter RDL mode (See section 6.3, “Test Modes” on
page 23) when requested to do so by the remote Model 1082/I and Model
1082/144/I.
S1-8 Setting
On Response to RDL Request Enabled
Off Response to RDL Request Disabled
Note
The Remote Digital Loopback (RDL) will not work for 144 kbps.
You must first set the units to 128 kbps or slower to use the RDL.
14
Page 15

Configuring DIP switch “S2”
Use the eight DIP switches in S2 to enable 19.2 kbps or 144* kbps synchronous operation and set the loopback modes. The following table
summarizes default positions of DIP switches S2-1 through S2-8.
Detailed descriptions of each switch follow the table.
S2 Summary Table
Position Function Factory Default
S2-1
19.2 or 14
4* k
bps Enable
Off
S2-2 Front Panel Switch Disable Off
S2-3 Reserved Off
S2-4 Reserved Off
S2-5 Reserved Off
S2-6 Reserved On
S2-7 Reserved Off
S2-8 Reserved
Off
Switches S2-1: 19.2 kbps or 144* kbps Synchronous Rate Enable
Use switch S2-1 to allow the Model 1082/I and Model 1082/144/I to operate at the 19.2 kbps
synchronous
data rate, or to enable the Model 1082/
144/I to operate at the 144* kbps synchronous data rate.
S2-1 Activation Description
Off Disabled Synchronous data rate is 32–128 kbps as
defined by switches S1-1 and S1-2
On Enabled Model 1082/I operates at synchronous 19.2 kbps
data rate (see note). The Model 1082/144/I oper-
ates at 144 kbps synchronous data rate (see note)
Note
To operate at 19.2 kbps or 144 kbps, set switches S1-1 and S1-2
to the OFF position and switch S2-1 to ON (see section “Configuring DIP Switch S1” on page 12).
* 144 kbps data rate is only available on the Model 1082/144/I.
19.2 kbps rate is available on all Model 1082 series modems
for the 1082/144/I.
except
15
Page 16

Switch S2-2: Front Panel Switch Disable
Use switch S2-2 to enable or disable the front panel toggle switches.
S2-2 Setting
On Disable the front panel switches
Off Enable the front panel switches
Switches S2-3, S2-6, S2-7 and S2-8: Reserved
16
Page 17

5.0 INSTALLATION
When the Model 1082 has been properly configured, it may be connected to the DSL twisted pair interface, the 10Base-T Ethernet Interface, and the power source. This section describes these connections.
Interface connector
ON
Power Interface
OFF|O
DSL interface
Made in the USA
DSL
Power input
connector
Model 1194E Single Mode Fiber - Quad G.703/G.704 Modem
G.703/G.704 Test Modes
Figure 6.
Power
Model 1082/I or Model 1082/144/I rear view
511E
Made in the USA
DSL
Interface
5.1 CONNECTING DSL INTERFACE
The Model 1082 supports communication between 10Base-T Hubs or
Workstations at distances to 5 miles (8 km) over 24 AWG (.5mm) twisted
pair wire. There are two requirements for installing the Model 1082:
• These units operate as a pair. Both units at the end of the twisted pair
DSL span must be set for the same DTE rate.
• To function properly, the Model 1082 needs one twisted pair of metallic
wire. This twisted pair must be unconditioned, dry, metallic wire,
between 19 (.9mm) and 26 AWG (.4mm) (the higher number gauges
will limit distance). Standard dial-up telephone circuits, or leased circuits that run through signal equalization equipment, or standard, flat
modular telephone type cable, are not acceptable.
17
Page 18

The RJ-45 connector on the Model 1082’s twisted pair interface is polarity insensitive and is wired for a two-wire interface. The signal/pin relationships are shown in Figure 7 below.
Figure 7.
Model 1082/I twisted pair line interface
5.2 CONNECTING 10BASE-T ETHERNET PORT TO PC (DTE)
The 10Base-T interface is configured as DTE (Data Terminal Equipment). If the Model 1088 is to to connect to another DTE device such as
a 10Base-T network interface card, construct a 10Base-T crossover
cable and connect the wires as shown in Figure 8.
10Base-T Port
RJ-45 Pin No.
1 (TD+)
2 (TD-)
3 (RD+)
6 (RD-)
Figure 8.
Connecting 10Base-T Ethernet port to PC
10Base-T DTE
RJ-45 Pin No.
1 (TD+)
2 (TD-)
3 (RD+)
6 (RD-)
5.3 CONNECTING 10BASE-T ETHERNET PORT TO HUB (DCE)
The 10Base-T interface is configured as DTE (Data Terminal Equipment), just like a 10Base-T network interface card in a PC. Therefore, it
“expects” to connect to a 10Base-T Hub using a straight-through RJ-45
cable. Figure 9 shows how to construct a cable to connect the 10Base-T
interface to a 10Base-T Hub.
10Base-T Port
RJ-45 Pin No.
1 (TD+)
2 (TD-)
10Base-T Hub
RJ-45 Pin No.
1 (TD+)
2 (TD-)
3 (RD+)
6 (RD-)
Figure 9.
3 (RD+)
6 (RD-)
Connecting the 10Base-T interface to a 10Base-T Hub
18
Page 19

5.4 POWER CONNECTION
Universal AC Power (100–240VAC)
The Model 1082/I uses a 5VDC, 2A universal input 100–240VAC, power
supply (center pin is +5V). The universal input power supply has a male
IEC-320 power entry connector. This power supply connects to the
Model 1082/I by means of a barrel jack on the rear panel. Many international power cords are available for the universal power supply. Please
refer to Appendix B for country-specific power cords.
The Model 1082/I powers up as soon as it is plugged into an AC outlet.
The Model 1082/I does not have a power switch.
19
Page 20

DC Power
The 36-60 VDC DC to DC adapter is supplied with the DC v ersion of the
Model 1082. The black and red leads plug into a DC source (nominal
48VDC) and the barrel power connector plugs into the barrel power supply jack on the rear panel of the 1082. (See Figure 10).
To Power
Supply Jack
Barrel power connector
WARNING
SWITCHING POWER SUPPLY
MODEL : SYD1106-0505
INPUT : 36-60V 0.2A MAX
OUTPUT : +5V 1.0A
S/N: G01234567890
MADE IN CHINA BY SUNNY
OUTPUT POWER : 5W MAX
-Vin
To -48VDC
Source
+Vin
Figure 10.
Power adapter
There are no user-serviceable parts in the power supply
section of the Model 1082/I. Contact Patton Electronics
Technical support at +1 (301) 975-1007, via our web site
at www.patton.com, or by E-mail at
support@patton.com, for more information.
Black lead (-V)
Red lead (+V)
20
Page 21

6.0 OPERATION
When the Model 1082/I and Model 1082/144/I have been properly configured and installed, it should operate transparently. This sections describes
power-up, LED status monitors , and the b uilt-in loopbac k test modes.
6.1 POWER-UP
Before applying power to the Model 1082/I or Model 1082/144/I, please
read section 5.4, “Power Connection” on page 19 and ensure that the
unit is connected to the appropriate power source.
6.2 LED STATUS MONITORS
The Model 1082/I and Model 1082/144/I feature six front panel LEDs that
monitor connections on the DSL and 10Base-T links, signaling, error and
test modes. (See Figure 11 for front panel location of each LED).
Descriptions of each LED follow in Table 1 on page 22.
NetLink™ 10Base-T iDSL Model
Link
DSL
10BT NS ER TM
511E/RDL
Normal
511/RDL
Figure 11.
DSL NS
10BTTMER
Model 1082/I or 1082/144/I front panel LED locations
Loopback
switch
21
Page 22

Table 1:
LED status monitor indications
LED Description
DSL Link (Active Green) Solid green (On) indicates that the end to
end DSL Framer Link is up , signifying that the link across
the DSL span is active. The DSL Link LED is Off when the
link is down.
Status Blinks yellow from one to elev en times to indicate system
status. Each pulse pattern is separated by a 2 second “off”
period. Greater pulse patterns have higher priority (buff er
saturation has greater priority than an empty MAC table).
Valid system statuses are:
1 pulse—system status is okay
•
•
2 pulses—no MAC entries in the MAC Address Table
3 pulses—Clear to Send (CTS) or Carrier Detect (DCD)
•
from base unit are not asserted
•
4 pulses—IM1/I buffer is saturated
5 pulses—WAN receive frame(s) too large
•
•
6 pulses—WAN receive frame(s) not octet aligned
•
7 pulses—WAN receive frame(s) aborted
8 pulses—Detected WAN receive frame(s) with CRC
•
•
9 pulses—Detected LAN receive frame(s) too large
10 pulses—Detected LAN receive frame(s) not octet
•
aligned
•
11 pulses—Detected LAN receive frame(s) with bad
CRC
10BT Link (Active green) Solid green indicates that the 10Base-T
Ethernet interface has detected a valid SQE heartbeat, signifying a valid 10Base-T connection
NS (Active red) Solid red indicates that the Digital Signal Proces-
sors (DSPs) are not linked
ER (Active red) Flashing red indicates CRC errors on DSL
(framer) side if DSL Link is active or if bit errors are received
during loop/BER test
ER flashes once, to indicate a CRC error (during normal
operation) or bit errors (during Remote Loopback 511/511E
tests)
TM (Active yellow) Solid yellow indicates an Active Test Mode.
The unit may be placed in test mode by the local user or by
the remote user.
22
Page 23

Table 2:
LED configurations
LOCAL REMOTE
10Base-T DSL Status NS ER TM 10Base-T DSL Status NS ER TM
Power ON G* off F on off off G* off F ONoff off
DSL Link G* G F off off off G* off F off off off
Link Brk G* off F off off off G* off F off off off
Brk+ 10s G* off F ON off off G* off F ONoff off
RDL G* G F off off ON G* off F off off ON
RDL+511 G* off F off off ON G* off F off off ON
With DTE Connected With DTE Connected
Mark G* G F off off off G* G F off off off
Space G* G F off off off G* G F off off off
Data G* G F off off off G* G F off off off
G=GREEN
O=ORANGE
ON= ON
off= OFF
Brk+10s = 10 Seconds following Link Break
G*=Green if a valid 10Base-T connection is detected.
F=Flashing
Link Brk = DSL Link Broken
6.3 TEST MODES
The Model 1082/I and Model 1082/144/I has a built-in proprietary loopback test mode, plus a built-in V.52 BER test pattern generator , for evaluating the condition of the modems and the communication link. These
tests can be activated physically from the front panel, or via the interf ace.
Remote Digital Loopback (RDL)/V.52 (BER)
The Remote Digital Loopback (RDL) test checks the performance of both
the local and remote Model 1082s, and the communication link between
them. Any characters sent to the remote Model 1082 in this test mode
will be returned back to the originating device (see Figure 7, below). For
example, characters typed on the keyboard of the local terminal will
appear on the local terminal screen after having been passed to the
remote Model 1082 and looped back.
Remote 1082Local 1082
RDL initiated
Figure 12.
Remote digital loop
23
Page 24

Do not
send a 511 test pattern from the test equipment
when you connect external test equipment to the 1082.
Important
Activating RDL can be done in two ways:
1. Move the front panel toggle switch to appropriate position.
2. Set remote loopback from SNMP screen (when used with 1092ARC
Rack Card)
Note Remote loopback cannot be activated until approximately 45
seconds after the two modems have linked to each other.
Note The Remote Digital Loopback (RDL) will not work for 144 kbps.
You must first set the units to 128 kbps or slower to use the RDL.
To use the V .52 BER tests with the Remote Digital Loopbac k tests, do the
following:
1. Locate the 511/RDL toggle switch on the front panel of the 1082/I
and move it DOWN. This initiates the RDL and sends a 511 pattern
into the loop. If any errors are present, the local modem’s red “ER”
LED will blink continually.
2. If the above test indicates no errors are present, move the V.52 toggle switch UP, activating the 511E/RDL test with errors present. If
the test is working properly, the local modem's red “ER” LED will
blink approximately once per second. A successful 511E/RDL test
will confirm that the link is in place, and that the Model 1082’s built-in
“511” generator and detector are working properly.
24
Page 25

APPENDIX A
1082/I Specifications
A.1 TRANSMISSION FORMAT
Synchronous or asynchronous
A.2 TRANSMISSION LINE
Single unconditioned twisted pair
A.3 CLOCKING
Internal or receive loopback
A.4 DISTANCE
2-Wire Distance Table in miles (km)
Data Rate
19 (.9) 22 (.6) 24 (.5) 6 (.4)
All rates 10.8 (17.2) 7.2 (11.5) 5.0 (8.0) 3.4 (5.5)
A.5 DATA RATES
Synchronous 19.2, 32, 56, 64, and 128 kbps, (and 144 kbps on 1082/144
only); Asynchronous 0–38.4 kbps
A.6 DIAGNOSTICS
V.52 compliant bit error rate pattern (511/511E pattern) generator and
detector with error injection mode; Local Line Loopback and Reomote Digital Loopback, activated by front panel switches or via serial interface.
A.7 LED STATUS INDICATORS
DSL, 10Base-T, Status, NS (no signal), ER (error) and TM (test Mode)
A.8 CONNECTORS
RJ-45 on line side; shielded RJ-45 on Ethernet port
A.9 POWER
100–253 VAC, 50–60 Hz (universal input option); 48 VDC (optional),
5 watts
AWG Wire Gauge (mm)
25
Page 26

A.10 TEMPERATURE RANGE
32–122°F (0–50°C)
A.11 ALTITUDE
0–15,000 feet (0–4,572 meters)
A.12 HUMIDITY
5–95% non-condensing
A.13 DIMENSIONS
4.125W x 1.625H x 6.0D in. (10.5W x 4.1W x 15.2D cm)
A.14 WEIGHT
2.01 lbs. (1.0 kg)
26
Page 27

APPENDIX B
MODEL 1082/I FACTORY REPLACEMENT PARTS AND ACCESSORIES
Model # Description
1082/I 10Base-T, DSL Modem
1082/144/I 10Base-T DSL modem with maximum data rate of 144 kbps
48V-PSM DC Power Supply Module
08055DCUI 100-240VAC (+5V ±5% reg. DC/2A) Universal Input Adapter
0805EUR European Power Cord CEE 7 (“A”)
0805UK United Kingdom Power Cord (“D”)
0805US American Power Cord (“K”)
0805AUS Australia/New Zealand Power Cord (“C”)
0805DEN Denmark Power Cord (“E”)
0805FR France/Belgium Power Cord (“F”)
0805IN India Power Cord (“G”)
0805IS Israel Power Cord (“H”)
0805JAP Japan Power Cord (“J”)
0805SW Switzerland Power Cord (“L”)
07M1082 User Manual
27
Page 28

Notes
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
Copyright © 1998, 2001, 2006
Patton Electronics Company
All Rights Reserved.
28
 Loading...
Loading...