Page 1
Instructions
Demonstrations
Experiments
Sample Data
Instruction Manual
No. 012-08798A
String Vibrator
WA-9857
Page 2

String Vibr a tor Model No. WA-9 85 7
Contents
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Equipment Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Introductory Activity. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Demonstration 1:
String Density and Wavelength. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Demonstration 2:
Closed Tube Analogy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Experiment 1:
Wave Speed. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Experiment 2:
Standing Waves In Strings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Experiment 1:
Teachers’ Notes–Wave Speed. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Experiment 2:
Teachers’ Notes–Standing Waves In Strings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Safety. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Copyright and Warranty Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Page 3

Model No. WA-9857 String Vibra t or
®
Power Supply
String Vibrator
String Vibrator
Model No. WA-9857
Included Equipment Replacement Part Number
String V ibrator
Power Supply
Wave Cord (3 meters, not pictured)
The demonstrations and experiments described in this manual call for additional equipment. For details,
see the equipment list for each activity.
WA-9857
540-050
SE-9409 (90 m roll)
Introduction
The PASCO scientific WA-9857 String Vibrator drives a string or elastic cord to produce a
standing wave. W ith it, you can study frequency, wavelength, and resonance, as well as the factors
that affect those properties. It is well-suited for classroom demonstrations and hands-on
experiments.
The String Vibrator uses a coil-and-magnet design to vibrate a stainless steel blade, to which you
attach a string or elastic cord. The driving signal and power come from the included power
supply, or (for a variable signal) from an optional signal generator, such as the WA-9867 Sine
Wave Generator.
3
Page 4
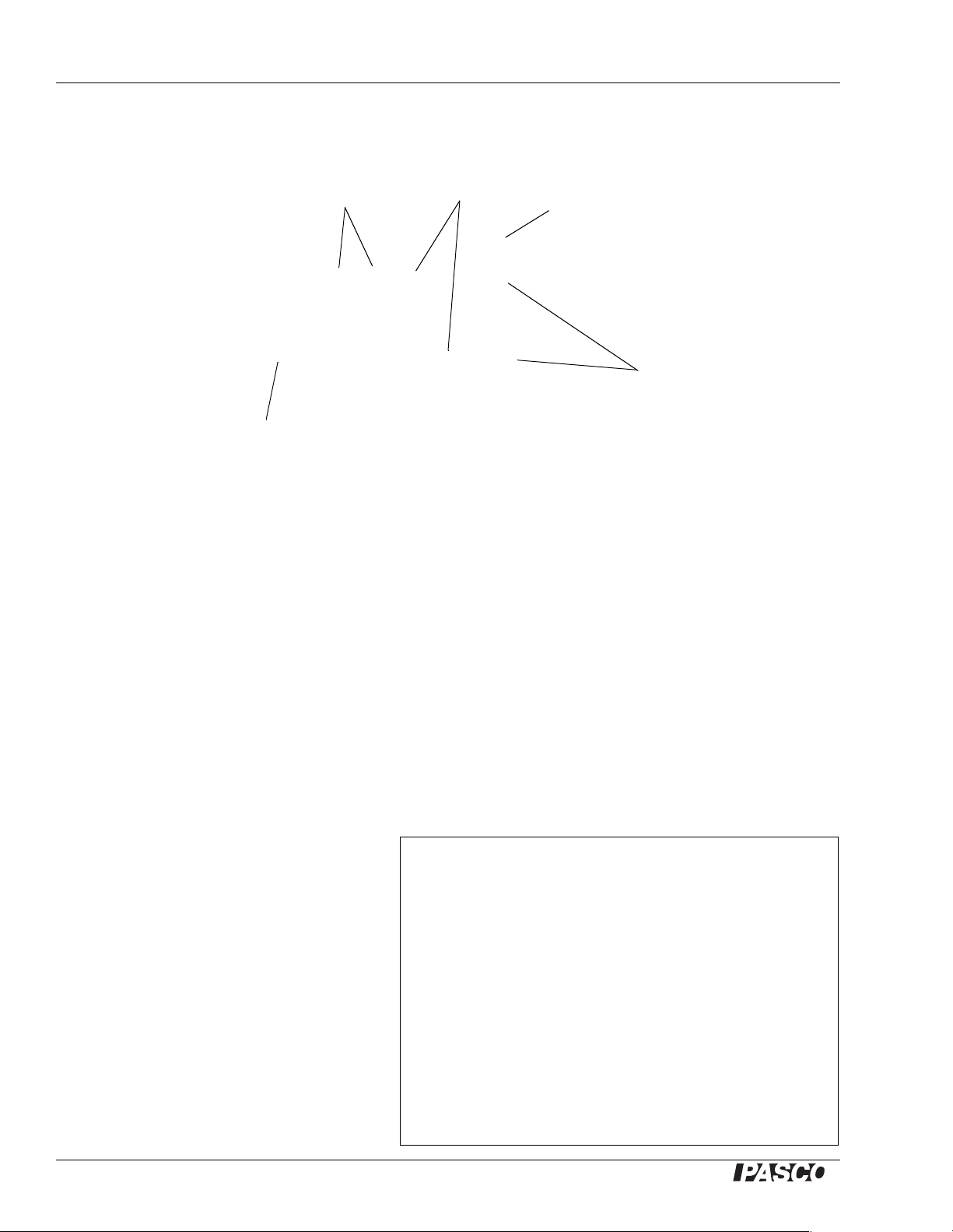
String Vibr a tor Equipment Setup
®
St a cki n g Pin
(one per corner)
Clamping
Surfaces
Power Input
Vibrating
Built-in Rod
Clamp
Equipment Setup
Power
The AC Power supply plugs into the Power Input of the String Vibrator. It drives the String
Vibrator with a constant-frequency, constant-amplitude sine wave. The driving frequency equals
the frequency of the mains power supply (50 or 60 Hz in most countries).
If you would like to dr ive the String Vibrator with a variable signal, you can use any function
generator capable of producing a 10 V amplitude sine wave at up to 1 A, including the following:
• Sine Wave Generator (WA-9867)
• Digital Function Generator (PI-9587)
• 750 or 700 Interface with Power Amplifier II (CI-6552A)
Mounting Options
The String Vibr ator can be fastened to a table in a variety of ways.
C-Clamp
Two recessed Clamping Surfaces on the
String V ibrator allow it to be secured to a
table with a C-clamp. You must use a Cclamp wide enough to accommodate the
thickness of the tabletop plus 3 cm (1¼
inch).
The PASCO Small C-Clamp (SE-7286,
6-pack) can clamp the String Vibrator to
tables up to 5 cm (2¾ inches) thick; the
Large C-Clamp (SE-7285, 6-pack)
accommodates tables up to 7 cm (2¾
inches) thick.
4
Page 5

Model No. WA-9857 Equipment Setup
®
Rod Clamp
The case of the String Vibrator has a
built-in rod clamp for mounting it either
horizontally or vertically on a rod with
a diameter up to 12.7 mm (1/2 inch).
Slide the rod through the case in the
preferred orientation and tighten the
thumb screw.
The Universal Table Clamp (ME-9472)
and 45 cm Rod (ME-8736) work well in
this application because you can clamp
the rod vertically to the edge of a table.
Permanent Mounting
Two through-holes in the clamping
surfaces allow the String Vibrator to be
mounted permanently on a flat surface.
Place a washer under each screw head
to protect the plastic case.
String Setup
String Selection
The included elastic wave cord works we ll for demonstrations and many la b activities. T he elastic
cord is easy to see, produces good amplitude, and it does not require a hanging mas s to provide
tension, but it does not have constant linear density under tension. For experiments exploring the
relationship between wave speed and string density, it is better to use an inelastic string such as
Braided String (SE-8050) or Yellow Cord (ME-9876).
Attaching the String
If you are using the included elastic
cord, or any other thick cord, pass it
through the grommet, then tie a fr eestanding knot that cannot pass through
the hole when you pull back on the
cord. If the end of the cord is frayed,
trim it to make it easier to thread
through the grommet.
If you are using thin string, thread it
through the grommet at the end of the
blade and tie it in a loop.
5
Page 6
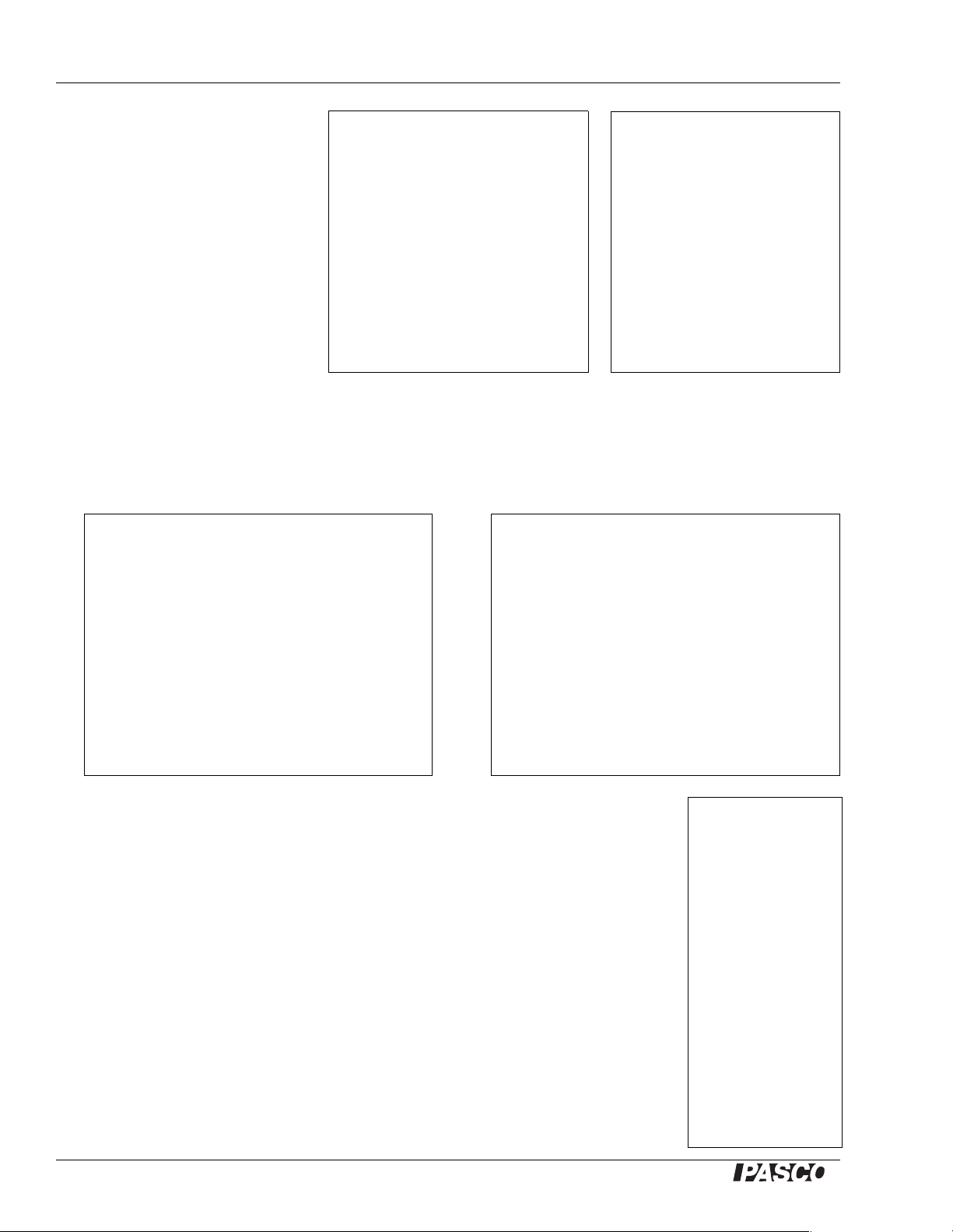
String Vibr a tor Equipment Setup
®
V ert ical Str in g
The vertical arrangement with
the elastic cord makes a good
classroom or lecture
demonstration. It requires a
vertical rod and a horizontal
component at the top of the
rod, such as a Pendulum Clamp
(SE-9443), to attach the elas tic
cord. To adjust the length and
tension, move the top mount
vertically on the rod.
Horizontal String
The pictures below show the horizontal arrangement in two ways. Since the standing waves
produced sometimes vibrate in a plane, it may be necessary to rotate the case for the wave to be
visible.
In the orientation pictured on the left, the wave is visible from above, but
not as easily seen by a student sitti ng out in the c lassroom . As shown on t he
right, the wave is visible from the side, which is most useful for
demonstrations.
Applying Tension to Inelastic String
When you use inelastic string, it is necessary to apply tension. This can be
accomplished with the string oriented horizontally, and with a hanging
mass, a pulley and a table clamp as shown here. The tension on the string is
equal to the weight of the hanging mass.
6
Page 7

Model No. WA-9857 Equipment Setup
®
Bad Node
Good Node
Good Nodes Versus Bad Nodes
Most demonstrations and
experiments involve
adjusting the length, tension
or frequency to produce a
standing wave pattern. It is
tempting to look only at the
amplitude of the wave and
concentrate on making it as
large as possible; but it is
also important to check that
the nodes are “clean” and
well defined, especially the
node at the vibrating blade.
Check the end of the
vibrating blade. There
should be a node at the point
where the cord attaches, as
shown in the first picture to
the right.
An example of a bad node is
shown in the second picture.
The blade rattling against
the plastic case indicates a
bad node.
The method for correcting a bad node depends on the type of experimental setup. With the elastic
cord, the adjustment is usually made to the length and tension simultaneously by moving one of
the end points. With an inelastic string set up with a pulley and a hanging mass, you can adjust the
length of the string by moving String Vibrator, or adjus t the tension by changing the hanging
mass. With either type of string, if you are using a variable-frequency signal generator you can
adjust the driving frequency.
Storage
Pins on the top corners and matching
holes on the bottom corners of the String
Vibrator allow you to stack two or more
units for stora g e.
7
Page 8

String Vibr a tor Introductory Activity
®
Introd uctory Acti vity
Equipme nt R equired Part Nu m ber
String V ibrator
Power Supply
Elastic Wave Cord (1 meter)
Clamp or other device for securing the String Vibrator
WA-9857
Part of WA-9857
Part of WA-9857 (or SE -9409)
SE-7286 or similar
This activity works best with two or more people.
1. Attach the String Vibrator to the table. You’ll be stretching the cord to about 2 m, so leave
enough space.
2. Cut 1 m of elastic cord and attach one end to the vibrating bla d e.
3. Connect the AC power supply to the String V ibrator.
4. Hold the free end of the cord as shown, and slowly increase the tension by pulling it away
from the String Vibrator.
5. Observe the standing wave patterns that occur as you stretch the cord. Note what happens to
the number of segments as you increase the tension. Does increasing the tension cause the
number of segments to increase or decrease?
6. Adjust the tension until the cord vibrates in 4 segments. Then adjust the tension slightly so
that there is a good node at the blade. Maintain that tension for the rest of the activity.
7. Measure the wavelength. (How is the wavelength related to the length of one segment?)
8. Touch the cord at one of the antinodes (the points of maximum vibration). What happens?
9. Touch the cord at one of the nodes. What happens? How is touching the c ord at a node
different from touching it at an antinode?
10. Have a lab partner pinch the cord at the mi ddle node without changing the tension. What
happens to the wavelength?
8
Page 9

Model No. WA-9857 Demonstration 1: String Density and Wavelength
®
Demonstration 1:
String Density and Wavelength
Equipme nt R equired Part Numbe r
String V ibrator
Power Supply
Elastic Wave Cord (50 cm)
Inelastic Cord (80 cm)*
Clamp or other device for securing the St ring Vibrator
Super Pulley
Mounting Rod for Super Pulley
Universal Table Clamp
Mass and Hanger Set, or a ~100 g mass
Opti onal Equipment**
Sine Wave Generator (or equivalent)
Banana Patch Cords
*The recommended inelastic cord (PASCO part ME-9876) has a linear density of 1.5 g/m.
**This demonstration is easier to set up with a Sine Wave Generator (ME-9867), or another ±10 V, 1 A
function generator in place of the fixed-frequency power supply, because it allows you to adjust the driving
frequency instead of the elastic cord length.
WA-9857
Part of WA-9857
Part of WA -9857 (or SE-94 09)
ME-9876 or similar
SE-72 86 or similar
ME-9450
SA-9242
ME-9472 or similar
ME-8967 or similar
WA-9867
SE-9750
Setup
1. Cut approximately 50 cm of the elastic cord and 80 cm of the i nelastic cord. Tie both pieces
together and attach the elastic cord to the blade of the String Vibrator. (Make the knots as
small as possible.)
2. Clamp the pulley at the end of the table, and clamp the String Vibrator about 1 meter away.
Attach a 100 g mass to the end of the inelastic cord, and run the cord over the pulley .
3. Connect the power source to the Strin g Vibrator. If you are using the Sine Wave Generator, set
the frequency at around 50 Hz and turn up the amplitude midway .
9
Page 10

String Vibrator String Density and Wavelength
®
4. Loosen the clamp on the String Vibrator and slide it along the table to adjust the length of the
vibrating part of the inelastic cord. Adjust it so that knot connecting the elastic and inelastic
cords is at a node. (The amplitude may be low, but it will increase after the next steps.)
5. Observe the elastic cord. You want a node to occur at the point where the cord is attached to
the vibrating blade, but that will probably not be the case initially. If you are using the fixedfrequency power supply continue to the next step. If you are using the Sine Wave Generator,
skip to the optional setup section.
6. With a felt-tip pen, mark the elastic cord at the node closest to the blade.
7. Disconnect the power . Adjust the elastic cord so that it is attached to the blade at the poi nt that
you marked. Restore the power connection.
8. Adjust the position of the String Vibrator again so tha t the knot connecting the elastic and
inelastic cords is at a node. Confirm that the connection to the blade is also at a node.
Optional Setup for Variable-frequency Sine Wave Generator
First follow steps 1–5. After you have positioned the String Vibrator so that a node occurs at the
knot, adjust the driving frequency so that another node occurs at the blade. As you adjust the
frequency, adjust the position of the String Vibrator so that the knot stays at a node.
Demonstration
The picture above shows the demonstration using the constant-frequency AC power supply. You
can see that the cord with the higher linear density (the elastic cord) has a smaller wavelength.
Since both have the same frequency, the denser cord must have a lower wave speed.
Further Demonstr ation
Compare the wavelengths of two parallel strings. Tie both strings to the same Str ing Vibrator, but
run them out to separate pulleys. Apply the same tension to both strings, but adjus t the lengths
separately (by moving the pulleys along the edge of the table) to achieve standing waves of
different wavelengths.
10
Page 11

Model No. WA-9857 Demonstration 2: Closed Tube Analogy
®
Demonstration 2:
Closed Tube Analogy
Equipme nt R equired Part Numbe r
String V ibrator
Power Supply
Elastic Wave Cord (50 cm)
Black Thread (50 cm)
Clamp or other device for securing the St ring Vibrator
Super Pulley
Mounting Rod for Super Pulley
Universal Table Clamp
Mass and Hanger Set*
Opti onal Equipment*
Sine Wave Generator (or equivalent)
Banana Patch Cords
*With a Sine Wave Generator (ME-9867), or another a ±10 V, 1 A function generator in place of the fixedfrequency power supply, this demonstration is easier to set up, and requires only a single mass of about
150 g rather than an adjustable set of masses.
WA-9857
Part of WA-9857
Part of WA -9857 (or SE-94 09)
ME-9875 or similar
SE-72 86 or similar
ME-9450
SA-9242
ME-9472 or similar
ME-8967 or similar
WA-9867
SE-9750
Setup
1. Cut approximately 50 cm of elastic cord and 50 cm of black thread. Tie both pieces together
and attach the elastic cord to the blade of the String Vibrator . (Make the knots as small as
possible.)
2. Clamp the pulley at the end of the table, and clamp the String Vibrator to the table about 70
cm away. Hang a 150 g mass on the thread over the pulley .
3. Connect the power source to the Strin g Vibrator. If you are using the Sine Wave Generator, set
the frequency to around 50 Hz, and turn up the amplitude midway.
11
Page 12

String Vibr a tor Closed Tube Analogy
®
4. Adjust the hanging mass (or the driving frequency) so that there is a node at the blade and an
anti-node at the knot connecting the thread and the elastic cord.
Demonstration
This demonstration is analogous to sound produced by a pipe with one open end and one closed
end. Notice that the segment with the anti-node on the end is a quarter wavelength, where the
other segments are half wavelengths.
A dark background placed behind the wave can hide how this is done; the white elastic cord
shows up very well, but the black thread disappears when the String Vibrator is running.
12
Page 13

Model No. WA-9857 String Vibra t or
®
Experiment 1:
Wave Speed
Equipme nt R equired Part Numbe r
String V ibrator
Power Supply
Elastic Wave Cord (50 cm)
Universal Table Clamps (qty. 2)
45 cm Rods (qty. 2)
Force Sensor
Voltage Sensor
Computer Interface(s) and software,
compatible with sensors
Balance
Tape Measure
WA-9857
Part of WA-9857
Part of WA -9857 (or SE-94 09)
ME-9472 or similar
ME-8736 or similar
CI-6746, CI-6537, or P S-2104
CI-6503 or PS-2115
Various, see PASCO catalog
SE-8765A or similar
SE-8712A or similar
Introduction
In this experiment you will deter mine the wave speed in a stretched string using three methods.
First, you will calculate the speed based on the wavelength and frequency of a standing wave in
the string. Next, you will calculate the speed based on the linear density and tension of the string.
Finally, you will measure the time for a single pulse to travel a known distance, and calculate the
speed of the pulse.
Procedure
1. Use rods and clamps to connect the Force Sens or and String Vibrator to the table as shown.
13
Page 14

String Vibr a tor Wave Speed
®
l
2. Cut about 1 m of elastic cord. Measure its exact unstretched length. Measure the mass using a
balance. Calculate the Unstretched Linear Density (mass/length).
(If your balance is not precise enough to measure 1 meter of cord, measure the mass and
length of a much longer piece of cord, and use those measurements to calculate the linear
density.)
3. Attach the cord to the blade of the String Vibrator. Tie a short loop in the other end and slip it
onto the hook on the Force Sensor .
4. Plug in the AC power supply, and connect it to the String Vibrator.
5. Move the force sensor or String V ibrator to adjust the tension in the cord so that it vibrates in
three or four segments. As you adjust the tension, check the end of the vibrating blade; there
should be a node at the point where the cord attaches to the blade. It is more important to have
a good node at the blade than to have the largest possible amplitude.
6. Record the number of segments
Tension
You will use the force sensor to measure the tension of the cord.
1. Set the sample rate to 100 Hz.
2. Unhook the cord from the force sensor and zero (or tare) the sensor. Reattach the cord.
3. Record data for a few seconds.
4. Find the average force. This is the tension (F) of the cord.
Wave Speed Calculated from Wavelength and Frequency
1. Meas u re t he stretched length of the cord (L) from the force sensor hook to the Str ing Vibrator
blade. Use this measurement and the number of wave segments to calculate the wavelength,
λ. Hint: one wavelength is two segments.
2. The speed of the wave (v) is related to the wavelength (λ) and the frequency (f) by
(eq. 1) v = λ f
Calculate the speed of the wave.
(f = 60.0 Hz in the U.S., f = 50.0 Hz in most other countries.)
14
Page 15

Model No. WA-9857 Experiment 1: Wave Speed
®
v
F
µ
---=
Stretched Linear Density µ
Unstretched Length()
Stretched Length()
----------------------------------------------------
Unstretched Linear Density()×==
Wave Speed Calculated from Tension and String Density
You can also calculate the wave speed from the tension (F) and the linear density (µ) of the cord
with:
(eq. 2)
The linear density is the ma ss per unit le ngth of the cord when it is stretched. This will be less than
the value that you calculated for the unstretched cord. You will now calculate the stretched linear
density.
1. Unhook the cord from the Force Sensor and measure its unstretched length (from the String
Vibrator blade to the loop on the other end).
2. Calculate the stretched density using the formula:
3. Calculate the speed of the wave from your values of F and µ.
Speed of a Single Pulse
Another way to find the wave speed is to measure the speed of a single pulse. You will use the
force sensor and the voltage sensor, to time a pulse traveling down the cord.
1. Unplug the power supply from the String Vibrator. Connect the voltage sensor to the power
input of the String Vi brator.
2. Set the sampling rates of force sensor and the voltage sensor to 1000 Hz.
3. To activate the wave, pluck the string vertically as close as possible to the force sensor (as
shown in the picture). Notice that when the pulse reaches the String Vibrator, it makes the
blade move up and down; this motion moves a magnet inside a coil, which generates a
voltage spike that the voltage sensor will measure.
15
Page 16

String Vibr a tor Wave Speed
®
v
L
∆t
-----=
4. Start recording data just before you pluck the string, then immediately stop recording.
5. V iew the force and voltage data on a graph, and find the elapsed time, ∆t, between the sudden
decrease in tension and the change in voltage.
6. Calculate the pulse speed:
(eq. 3)
Conclusions
You have calculated the wave speed using three methods.
1) Compare your results. Are the similar? If they deviate from one another, can you explain
why?
2) Which method do you think is the most accurate? Explain why.
Further Investigation
Repeat this experiment with a different length of cord (you will find that the tension to achieve a
standing wave will be different). Before you measure v using the three methods, predict how the
results will differ from your initial findings.
16
Page 17

Model No. WA-9857 String Vibra t or
®
L =
L = l
l
3
2
L = l
1
2
Experiment 2:
Stand ing Waves In Str ings
Equipme nt R equired Part Numbe r
String V ibrator
Power Supply
Inelastic Braided String
Clamp or other device of securing the String Vibrator
Super Pulley
Mounting Rod for Super Pulley
Universal Table Clamp
Mass and Hanger Set
Balance
Tape Measure
WA-9857
Part of WA-9857
SE-80 50 or similar
SE-72 86 or similar
ME-9450
SA-9242
ME-9472 or similar
ME-8967 or similar
SE-8765A or similar
SE-8712A or similar
Purpose
The general appearance of waves can be shown by means of standing waves in a string. This type
of wave is very important because most of the vi brations of extended bodies, such as the prong s of
a tuning fork or the strings of a piano, are standing waves. The purpose of this experiment is to
study how the speed of the wave in a vibrating string is affected by the stretching force and the
frequency of the wave.
Theory
Standing waves (stationary waves) are produced by the
interference of two traveling waves, both of which have the
same wavelength, speed and amplitude, but travel in
opposite directions through the same medium. The necessary conditions for the production of
standing waves can be met in the case of a stretched string by having waves set up by some vibrating
body, reflected at the end of the string and then interfering with the oncoming waves.
A stretched string has many natural modes of vibration (three examples are shown above). If the
string is fixed at both ends then there must be a node at each end. It may vibrate as a single
segment, in which case the length (L) of the string is equal to 1/2 the wavelength (λ) of the wave.
It may also vibrate in two segments with a node at each end and one node in the middle; then the
wavelength is equal to the length of the string. It may also vibrate with a larger integer number of
segments. In every case, the length of the string equals some integer number of half wavelengths.
If you drive a stretched string at an a rbitrary frequency, you will probably not see any particular
mode; many modes will be mixed together. But, if the tension and the string's length are correctly
17
Page 18

String Vibrator Standing Waves In Strings
®
v
F
µ
---=
L
String
String
Vibrator
Hanging
Mass
Pulley
λ
2L
n
------= n 123…,,,=
adjusted to the frequency of the driving vibrator, one vibrational mode will occur at a much
greater amplitude than the other modes.
For any wave with wavelength λ and frequency f, the speed, v , is
(eq. 1) v = λ f
The speed of a wave on a string is also given by
(eq. 2)
where F is the tension in the string and µ is the linear density (mass/length) of the string.
In this experiment, standing waves are set
up in a stretched string by the vibrations of
an electrically-driven String Vibrator. The
arrangement of the apparatus is shown to
the right. The tension in the st r ing equals
the weight of the masses suspended over
the pulley . You can alter the tension by
changing the masses.
L is the length of the string and n is the number of segments. (Note that n is not the number of
nodes). Since a segment is 1/2 wavelength then
(eq. 3)
Setup
1. Measure the exact length of a piece of string several meters long. Measure the mass of the
string and calculate the linear density, µ (mass/length).
(If your balance is not precise enough to measure that length of string, use a much longer
piece of string to calculate the linear density.)
2. As shown in the picture,
clamp the String Vibrator
and pulley about 100 cm
apart. Attach the string to
the vibrating blade, run it
over the pulley, and hang
about 100 g of mass from
it. Cut off the excess string.
3. Measure from the knot where the string attaches to the String Vibrator to the top of the pulley .
This is distance L. (L is not the total length of the string that you measured in step 1.)
4. Connect the AC power supply to the String V ibrator.
18
Page 19

Model No. WA-9857 Experiment 2: Standing Waves In Strings
®
v
Fµ
F
µ
---=
% Deviation =
v
Fµvλf
–
v
λf
----------------------
100%×
Procedure
1. Adjust the tension by adding to or subtracting from the hanging mass so that the string
vibrates in 2 segments. Adjust the tension further to achieve a “clean” node at the center. Also
check the end of the vibrating blade; the point where the string attaches should be a node. It is
more important to have a good node at the blade than it is to have the largest amplitude
possible. However, it is desirable to have the largest amplitude possible while keeping a good
node.
2. Record the hanging mass, m (do not forget to include the mass of the hange r). How much
uncertainty is there in your value? By how much can you change the hanging mass before you
see an effect? Record the uncertainty.
Analysis Method 1
1. Calculate the tension (including the uncertainty) in the string.
Tension = F = mg
2. Calculate the speed (including uncertainty) of the wave from your observed values of tension
(F) and linear density (µ).
Record your calculated value with the uncertainty and the correct number of significant
figures.
3. Calculate the speed from the wavelength (λ) and frequency (f).
vλf = λ f
(In the U.S. f = 60.0 Hz. In most other countries f = 50.0 Hz.)
4. Compare the two values of speed. What is the difference? How does the difference compare
to the uncertainty that you determined in step 2?
5. Calculate the percentage by which vFµ deviates from vλf.
6. Repeat the Procedure and this analysis for standing waves of three and four segments.
Analysis Method 2
1. Repeat the Procedure for standing waves of 3, 4, 5, etc. segments. Get as many as you can.
Record the mass, m, (including uncertainty) and the number of segments, n, in a table.
19
Page 20

String Vibrator Standing Waves In Strings
®
F 4µf2L
2
1
n
2
-----
=
% Deviation
Measured Accepted–
Accepted
----------------------------------------------------
100%×=
2. For every value of mass, calculate the tension (including uncertainty) in the string.
Tension = F = mg
3. Make a graph of F versus n. Describe in words the shape of the graph.
4. For every value of n, calculate 1/n2. Make a graph of F versus 1/n2. Does the graph look
linear?
5. Find the slope (including uncertainty) of the best fit line through this data.
6. Combine equations 1, 2, and 3 (from the Theory section), and show that the tension can be
written as:
Thus the slope of an F versus 1/n2 graph is 4µf2L2.
7. Use the slope from your graph to calculate the density, µ, of the string. Also calculate the
uncertainty of µ.
8. Compare this measured value of density to the accepted value. (You calculated the accepted
value of µ from the mass and length of the st ring). What is the difference? How does the
difference to compare the uncertainty that you calculated in step 7?
9. Calculate the percent deviation of the measured value of µ fr om the accepted value of µ.
Further Investigations
1. Hang a mass on the string with a value that is about halfway between the masses that
produced standing waves of 3 and 4 segments. The string should show no particular mode.
Place a “bridge” so that you can see the exact fundamental (n = 1) between the String
V ibr ator and the bride. What is the wavelength?
Slide the bridge away from String Vibrator until the string vibrates in 2 segments. How does
the wavelength of the two-segment wave compare to the wavelength of the previous onesegment wave?
2. If a strobe is available, observe the standing wave on a string with the strobe light. Draw a
20
Why is a standing wave created only when the bridge is at certain locations? What are these
locations called?
diagram explaining the motion of the string.
Page 21

Model No. WA-9857 String Vibra t or
®
Experiment 1:
Teachers’ Notes–Wave Speed
Equipment Notes
Clamps
Instead of table clamps and rods, you can use two C-clamps to fasten the String Vibrator and force
sensor to the table. Use a block or book to elevate the force sensor a few centimeters above the
surface of the table. Be careful when applying clamping pressure to the force se nsor.
Balance
The density of the elastic wave cord is about 1.5 g/m , so it’s best to use a balance readable to 0.01
g. If you have a less-precise balance, have a long piece of cord available for students to measure
the length and mass of.
Sensors and Interface
This experiment calls for simultaneous data collection from a f or ce sensor and a voltage sensor.
There are several sensor options available; contact Technical Support, or see the PASCO website
and catalog for more information. One convenient combination of equipment (which was used for
the sample data below) is:
• PASPORT Force Sensor (PS-2104)
• PASPORT Voltage/Current Sensor (PS-21 15)
• PowerLink interface (PS-2001)
• DataStudio
®
software
Because of the variety of equipment that may be used, the instructions here do not go into detail
about collecting data. Students should be prepar ed to use the sensors, interface and software to:
• Set up the hardware and software to collect data from voltage and force sensors (sensor setup)
• Change the sampling rate of the s ensors
• Record data (data collection)
• Display the data in a graph (display windows: adding an input)
• Find the average value of a data set (Statistics)
In DataStudio, click on the Help menu, select search, and look up the underlined terms in the
index for detailed instructions.
Procedure Notes and Sample Data
The cord will stretch by a factor of about 2. If you don’t have enough lab space to accommodate
that length of cord, start with a shorter piece.
Unstretched Length (without knots) = 1.354 m
Mass = 5.74 g
Unstretched Linear Density = 4.24 × 10-3 kg/m
21
Page 22

String Vibrator Teachers’ Notes–Wave Speed
®
v
F
µ
--- 70.2 m/s==
Tension
F = 10.4 N
Wave Speed Calculated from Wavelength and Frequency
Stretched Length = L = 2.343 m
Number of segments = 4
λ = 1.172 m
f = 60.0 Hz
v = λ f = 70.2 m/s
Wave Speed Calculated from Tension and String Density
The unstretched length measured in this part of the experiment will be le ss than the unstretched
length measured initially because of the knots tied in the ends.
Unstretched Length (with knots) = 1.162 m
µ = 2.11 × 10-3 kg/m
Speed of a Single Pulse
The sudden decrease in tension may appear on the graph as a sudden decrease or increase in force,
depending on whether the force sensor is set up to register tension as a positive or negative force .
22
Page 23

Model No. WA-9857 Experiment 2: Teachers’ Notes–Standing Waves In Strings
®
Be sure to measure from the sudden force change, not the relatively slow variation that may occur
before the actual pluck. It may be helpful to repeat the measurement a few times and take the
average value.
-2
∆t = 3.4 × 10
s
v = L/∆t = 68.8 m/s
Conclusions
1) In the sample data above, all three calculations of v were within 5% of each other. (The first
two calculations were exactly equal, but that is not typical.) With a sample rate of 1000 Hz,
the uncertainty of the pulse timing measurement was about 1 ms, or 3% of ∆t, which would
account for much of the 5% deviation obs er ved.
2) The method based on frequency and wavelength was probably the most accurate because it
involved only one measurement, length, which was probably accurate to within a few
millimeters (or about 0.1%). The frequency of the AC power is usually very close to its
nominal value, so you can ignore its uncertainty. You can also use the voltage sensor plugged
into the output of the pow er supply to measure the frequency. Do not attempt to measure the
voltage directly from the wall.
Experiment 2:
Teachers’ Notes–Standing Waves In Strings
The density of the recommended string is about 0.266 g/m, so it’ s best to use a balance readable to
0.01 g. If you have a less-precise balance, have a long piece of string available for students to
measure the length and mass of.
Standing waves of n = 1, 2 and 3 are fairly easy to achieve. Standing waves of n ≥ 4 may require
mass adjustments of 1 g or less. You can make these adjustments by adding pieces of paper to the
hanging mass. It will suffice to estimate the mass to within 0.5 g.
Analysis Method 1
L = 0.987 m
f = 60.0 Hz
µ = 2.66 × 10-4 kg/m
Number of
Segments
1 380 10 120 118 1.7%
295260.59.21.3%
Hanging
Mass (g)
Uncertainty
(g)
vFµ (m/s) v
(m/s) % Deviation
λ
f
34113939.51.3%
4 22.5 1 29 29.6 2.0%
51412323.73.0%
6 9 1 20 19.7 1.5%
23
Page 24

String Vibrator Teachers’ Notes–Standing Waves In String s
®
F
vs.
n
F
vs. 1/
n
2
Slope = 3.74 ± 0.01 N
4µf2L
2
3.74 0.01 N±=
µ
3.74 0.01 N±()
4f
2L2
-------------------------------------- 2.67 0.01±()
10
4–
× kg/m==
% Deviation
2.67 10
4–
× kg/m 2.66 10
4–
× kg/m–
2.66 10
4–
× kg/m
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
100%× 0.4%==
Analysis Method 2
f = (60.0 ± 0.1) Hz
L = (0.987 ± 0.001 m)
This result differs from the direct measurement of linear density by 0.01 × 10-4 kg/m. It is within
the estimated uncertainty.
24
Page 25

Model No. WA-9857 String Vibra t or
Safety
Read the instructions before using this
product. Students should be super vised by
their instructors. When using this pr oduct,
follow the instructions in this ma nual a nd all
local safety guidelines that apply to you.
Technical Support
For assistance with any P ASC O product,
contact PASCO at:
Address: P ASCO scientif ic
10101 Foothills Blvd.
Roseville, CA 95747-7100
Phone: (916) 786-3800
(800) 772-8700
Fax: (916) 786-3292
Web: www.pasco.com
Email: techsupp@pasco.com
Copyright and Warranty Information
Copyright Notice
The PASCO scientific 012-08798A String
Vibrator Instruction Manual is copyrighted
and all rights reserved. However, permiss ion
is granted to non-profit educational
institutions for reproduction of any part of
this manual, providing the reproductions are
used only for their laboratories and are not
sold for profit. Reproduction under any ot her
circumstances, without the written consent
of PASCO scientific, is prohibited.
Limited Warranty
For a description of the product warranty , see
the PASCO catalog.
Authors:Jon Hanks
Alec Ogston
Page 26

 Loading...
Loading...