WCS-SIF-01
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan 49083
Training & Maintenance Manual
ISSUED: November, 2006
Supersedes: June, 2006
Pneumatic Spotwelding
Control Systems
Training & Maintenance Manual
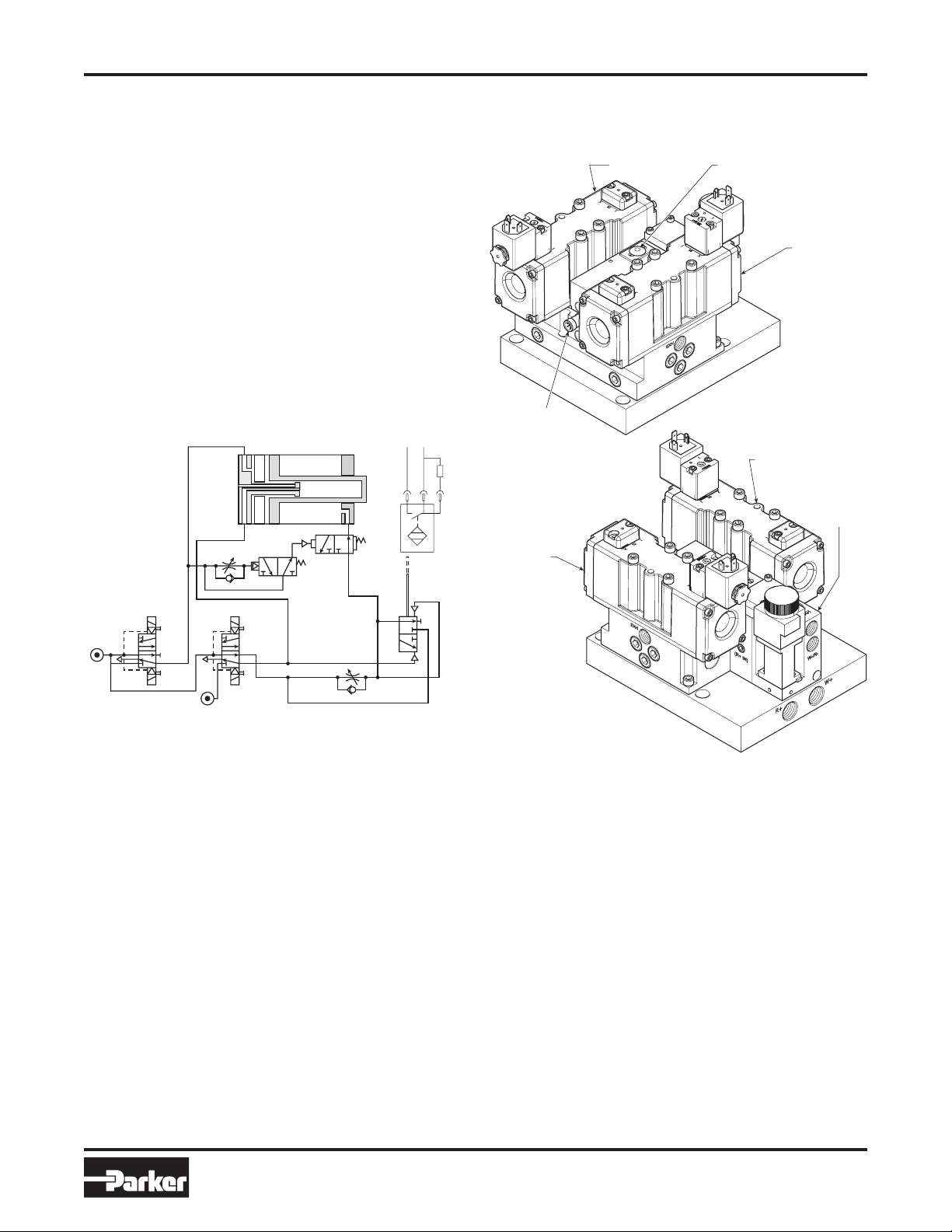
WCS-SIF-01
Pneumati
c
Front View
Back View
Weld Stroke
Valve
Retract
(Pre-Stroke)
Valve
Feedback
Sensor
Flow
Control
Weld Stroke
Valve
Quick
Exhaust
(Air
Operated)
Retract
(Pre-Stroke)
Valve
WR-
ANSI (3 Ported Cylinder Option)
Inductive Sensor / Connection: Turck
Connection Diagram Inductive Sensor
1 Brown +24 VDC Power Supply
3 Blue 0 V Power Supply
4 Black Switch Wire
W+R+
Pw
Pr
Retract (Pre-Stroke)
Valve
Weld Stroke
Valve
14 4 2 12
14 4 2 12
1
pnp
+3-
4
Description & Operation
General Description of Spotwelding Units
The spotwelding system is an integrated pneumatic
controlled circuit that is specifically designed to increase
production throughput, while improving weld quality and
reducing decibel noise level.
Each unit consists of 2 independent, 2 position, directional
control valves for retract (pre-stroke) and weld stroke. Each
valve is dual pressure, with single solenoid / spring assist
return or double solenoid available. Also included with each
unit is a proportional / quick dump valve, a feedback sensor
for initiating the welding process, and a flow control for
metering the impact speed of the weld tips.
Training & Maintenance Manual
General Operation of
Spotwelding Units – 3 ported guns
Spotwelding systems control both retract (pre-stroke) and
weld stroke motions. When a 3 ported cylinder is used, the
control block functions as follows:
1. The pre-stroke (retract) valve is energized, allowing
the weld cylinder to extend under full line pressure by
actuating the quick exhaust valve and moving to its
predetermined position prior to welding.
2. The quick exhaust valve time is adjusted by the knob
on top of the unit. To start, the white line on the dial
is set at top dead center. Turn knob clockwise to set
quick exhaust valve open time. Continuing to turn knob
clockwise will lengthen time until it reaches a full 360°
rotation, which covers the complete timing range.
3. The weld stroke valve is then energized using a selected
weld schedule pressure. The closure speed of the weld
tips is controlled by the use of an adjustable flow control,
thus creating “low impact”.
4. Immediately following weld tip contact with the sheet
metal, two actions take place.
a. The proportional / quick dump valve that senses
pressure allows the front end of the cylinder to exhaust
(by-passing the flow control), providing weld schedule
pressure instantly.
b. The proportional / quick dump valve also actuates a
feedback sensor to start the weld cycle.
5.
Once the weld cycle is complete, the weld stroke valve
is de-energized, allowing the weld tips to open under
full pressure.
6. The retract (pre-stroke) valve is then de-energized,
allowing the weld cylinder to open completely under
full line pressure.
Note: Dual pressure is provided to the control block. Line
(high) pressure is used for both retract stroke and weld
stroke open. Weld schedule pressure is used for weld stroke
close. Dual pressure provides for weld tips to be closed for
tip dressing using any pressures available, from as low as
5 PSIG to maximum line pressure.
2
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics
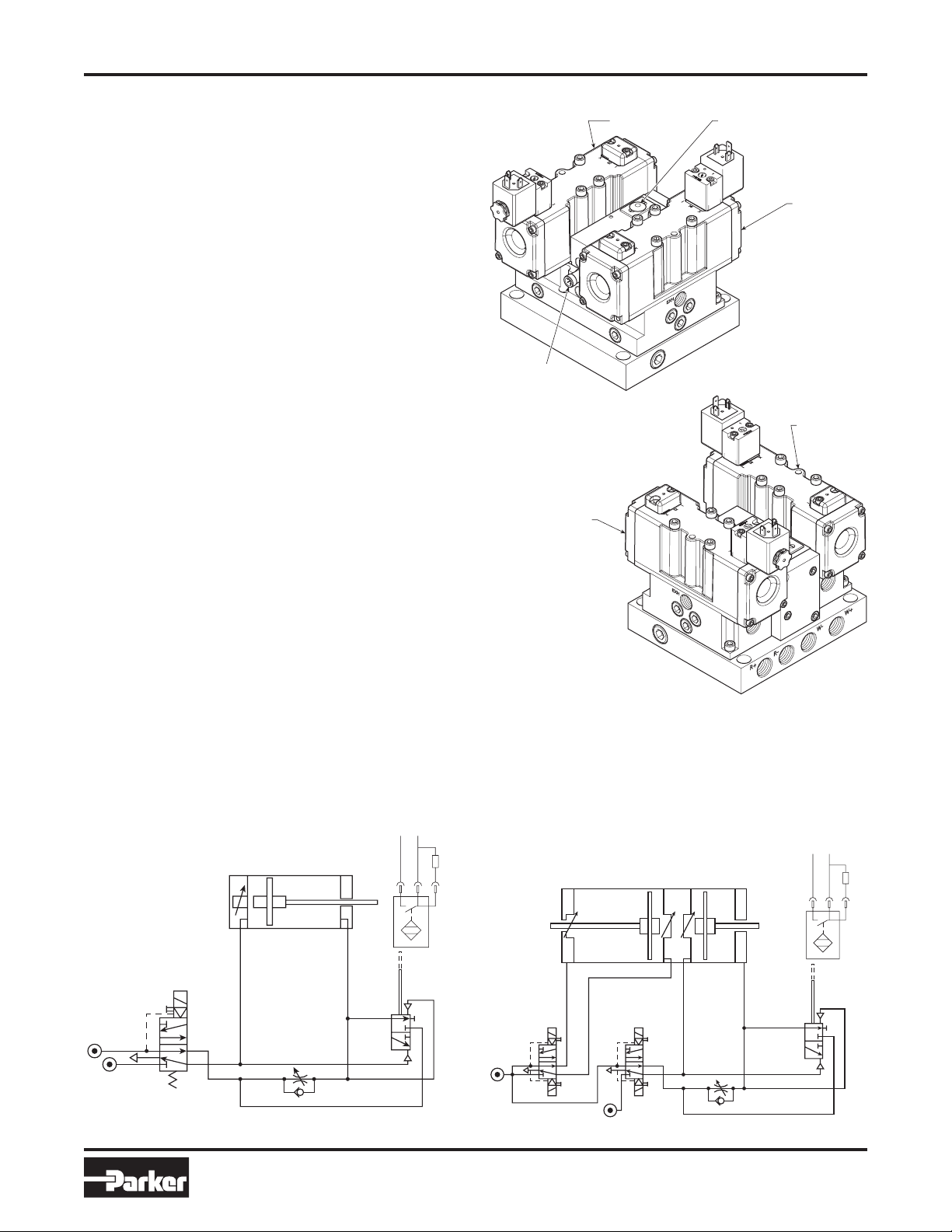
WCS-SIF-01
Pneumati
c
W-
Pw
Pr
ANSI (2 Ported Cylinder Option)
Inductive Sensor / Connection: Turck
Connection Diagram Inductive Sensor
1 Brown +24 VDC Power Supply
3 Blue 0 V Power Supply
4 Black Switch Wire
W+
1
pnp
+3-
4
W-
ANSI (4 Ported Cylinder Option)
Inductive Sensor / Connection: Turck
Connection Diagram Inductive Sensor
1 Brown +24 VDC Power Supply
3 Blue 0 V Power Supply
4 Black Switch Wire
W+R-
R+
Pw
Pr
1
pnp
+3-
4
Front View
Back View
Weld Stroke
Valve
Retract
(Pre-Stroke)
Valve
(4 Ported
Gun Only)
Feedback
Sensor
Flow
Control
Weld Stroke
Valve
Retract
(Pre-Stroke)
Valve
(4 Ported
Gun Only)
Description & Operation
General Operation of
Spotwelding Units – 2 and 4 ported guns
Spotwelding systems control both retract (pre-stroke) and
weld stroke motions. When a 4 ported cylinder is used, the
control block functions as follows:
1. The retract (pre-stroke) valve is energized, allowing
the weld cylinder to extend under full line pressure and
moving to its predetermined position prior to welding.
2. The weld stroke valve is then energized using a selected
weld schedule pressure. The closure speed of the weld
tips is controlled by the use of an adjustable flow control,
thus creating “low impact”.
3. Immediately following weld tip contact with the sheet
metal, two actions take place.
a. The proportional / quick dump valve that senses
pressure allows the front end of the cylinder to exhaust
(by-passing the flow control), providing weld schedule
pressure instantly.
b. The proportional / quick dump valve also actuates a
feedback sensor to start the weld cycle.
4.
Once the weld cycle is complete, the weld stroke valve is deenergized, allowing the weld tips to open under full pressure.
5.
The retract (pre-stroke) valve is then de-energized, allowing
the weld cylinder to open completely under full line pressure.
Training & Maintenance Manual
Note: Dual pressure is provided to the control block. Line
(high) pressure is used for both retract stroke and weld stroke
open. Weld schedule pressure is used for weld stroke close.
Dual pressure provides for weld tips to be closed for tip
dressing using any pressures available, from as low as
5 PSIG to maximum line pressure. 2 ported guns perform
the same steps as above, except that the retract (pre-stroke)
portion of the cylinder does not exist. Steps 2–4 only apply.
3
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics
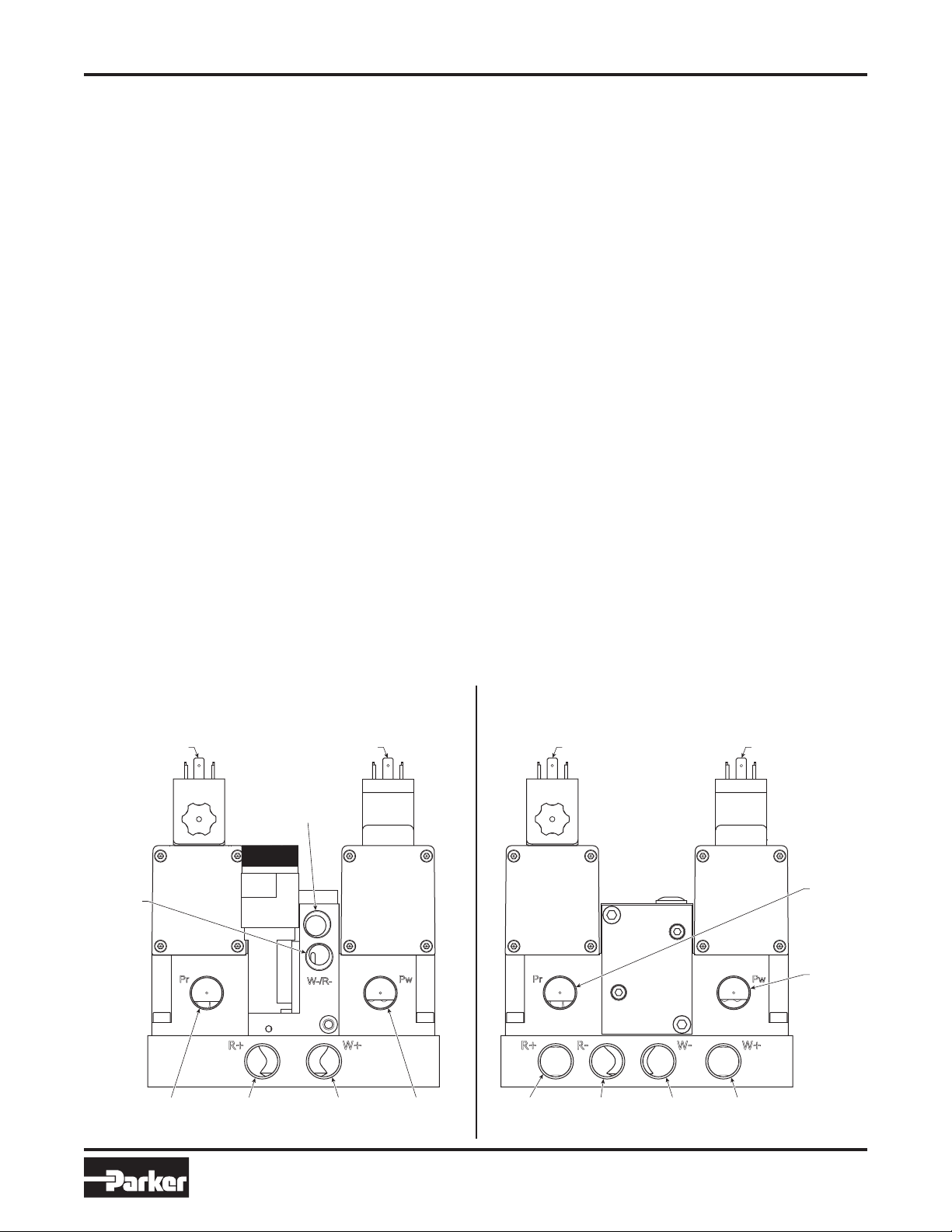
WCS-SIF-01
Pneumati
c
3 Ported Installation 4 Ported Installation
Weld Stroke
Connector(s)
Exhaust
High
Pressure
Inlet
Retract
Extend
Weld
Extend
Weld
Pressure
Inlet
Weld
Return
High
Pressure
Inlet
Weld
Pressure
Inlet
Weld Stroke
Connector(s)
Retract
(Pre-Stroke)
Connector(s)
Retract
(Pre-Stroke)
Connector(s)
Retract
Extend
Weld
Extend
Weld
Return
Retract
Return
Installation & Setup Instructions
Installation – Air and Electrical
A. Installing Weld Block with Existing Equipment
1. Shut off air supply to weld gun and turn power off to cell.
2. Disconnect air hoses from existing weld block ports. This
will vary depending on weld gun type, and whether the
existing weld block is single or dual pressure.
Note: If the current weld block is mounted directly to the
cylinder, then only the inlet port hoses will be disconnected.
3. Disconnect solenoid connectors from valves. Be sure
to note which connectors are being used for pre-stroke
(retract) valves and weld stroke valves.
4. Remove current weld block from gun.
B. Installing Weld Block on New Equipment
5.
Mount weld block spotwelding system to robot using (4) M8
screws and torque to 130 to 145 in. lbs (14.7 to 16.4 Nm).
6. Connect all air hoses to weld block (see schematic on
pages 2 or 3).
Note: An additional air hose may be necessary for the
inlet, since this unit is dual pressure. If so, connect the
already existing hose to the Pw port (pressure weld).
This hose should be supplying scheduled pressures from
a proportional regulator. Connect the additional hose
before the proportional regulator using a T-fitting so that
full line pressure is being used. This hose should be
connected to the Pr port (pressure retract).
7. Connect the solenoid cables to the proper valves.
Connect an M12 sensor cable to the feedback sensor on
the unit. The other end of this cable should be wired to
the PLC controller.
Training & Maintenance Manual
8. Turn air supply and power on.
9. Check for air leaks. The weld cylinder should be in the
home position (completely open). If not, check that all
air hoses are connected to the correct ports. Verify that
all solenoids are de-energized, and valve overrides are
unactuated. Once this is done, verify the function of the
weld block, by actuating the weld block valves using the
manual overrides. Press and hold the retract (pre-stroke)
valve manual override. The weld cylinder should move to
the weld stroke position. Press and hold the weld stroke
valve manual override [still holding the retract (pre-stroke)
override]. The weld cylinder should now close. Release
the weld stroke override and the retract (pre-stroke)
override. The weld cylinder will return to home position.
Note: The weld stroke portion of the cylinder will move
slower than the pre-stroke. This is due to the regulated
pressure being used, as well as the flow control.
Adjusting the speed of the cylinder will be covered in the
Setup Instructions. Repeat this process, now energizing
the solenoids. The cylinder should perform the same. If
not, verify that the solenoid connectors are located on the
proper valves. Once the unit has been properly installed,
the following setup procedure can be used to ensure that
the Parker weld system is used to its fullest potential.
Wiring
Refer to valve Instruction Sheet for proper wiring connections.
Available at: www.parker.com/pneumatic (see B6 and ISO
size 2 valves Installation and Service Instructions).
4
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics
WCS-SIF-01
Pneumati
c
Open
Flow Control
Close
Flow Control
5mm
Allen Wrench
Required For
Flow Control
Adjustment
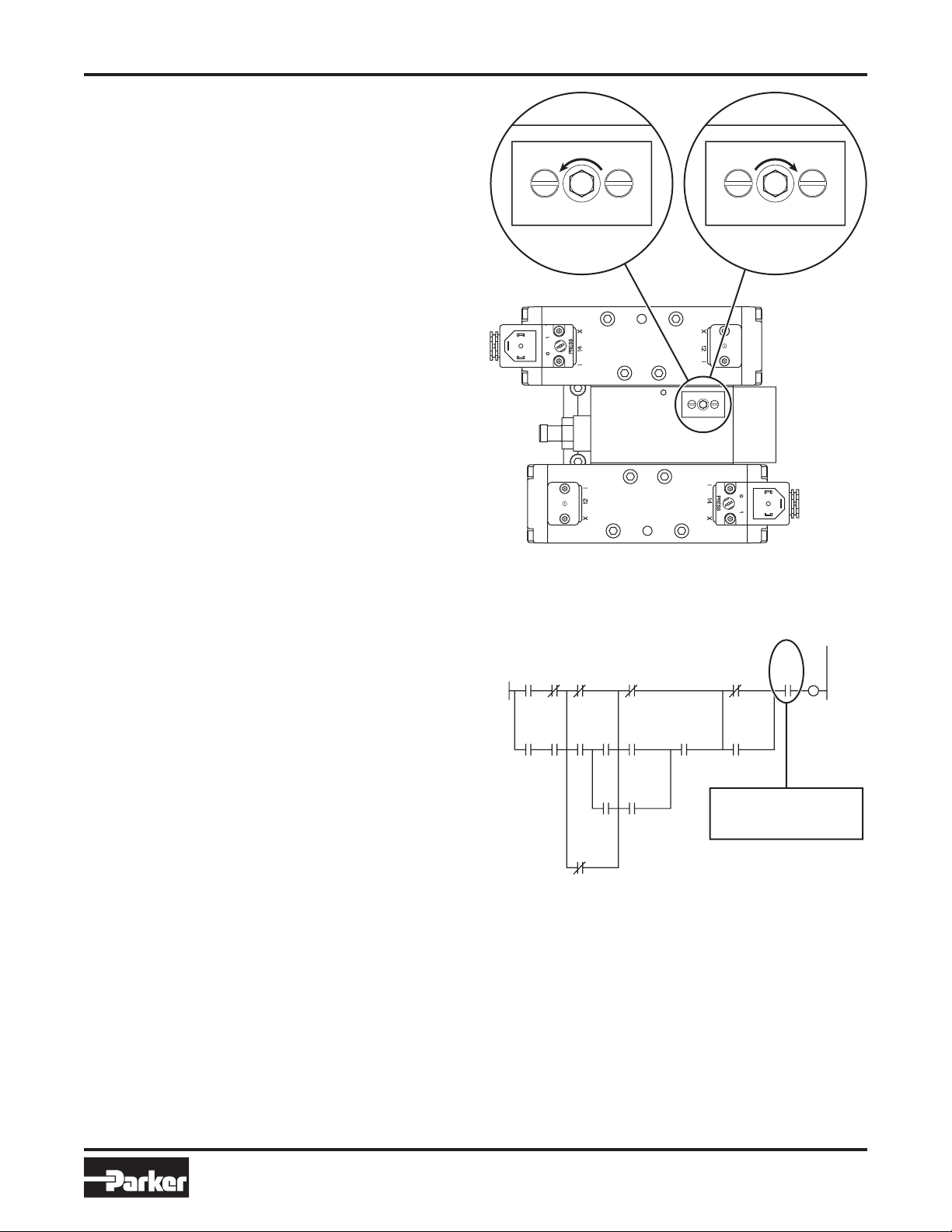
Electrical Changes (Sample):
GUN PR
ESS
TEACHI
NG
M005
00061
CUT CA RE-WEL
BLE CH D(PB)
ECKING
M052 M03C P1-M00F
K2 STR
OKE CH
ANGE
P1-M00F
TEACHI
NG
P1-M00F
GUN PR
ESS
M005
CUT CA RE-WEL
BLE CH D(PB)
ECKING
M052
RE-WEL
D(PB)
WELD R
EADY S
ENSOR
X024 1022 WELD START
M00B M03C
CHECK
MODE/P
ROGRAM
P1-L04B
STROKE
CHANG
E TIME
T015
AUTO R
E-WELD
M05B
RE-WEL
D
M00B
MANUAL
WELD
P1-L058
Insert contact on the
WELD START rung of
the Robot PLC program.
Installation & Setup Instructions
Setup
Below are the step by step setup procedures for properly
setting the flow control and feedback sensor.
How to Set the Flow Control Properly
Begin by turning the flow control clockwise until it stops. If
this is done properly, then the weld stroke should move
extremely slow or not at all.
Note: As stated in the Installation procedure, the pre-stroke
valve must be actuated prior to the weld stroke valve in order
for the weld cylinder to move correctly.
Slowly (1/4 to 1/2 turn at a time) begin to open the flow
control by turning counterclockwise. The weld tips should
now close upon actuation of the valves. At this point, you
should begin to hear a second exhaust coming from the
weld unit once the weld tips have made contact. This
second exhaust is the air from the front side of the cylinder
bypassing the flow control. As you continue to speed up the
weld stroke by turning the flow control, the delay between
the tips closing and the second exhaust will get shorter.
Also, check the feedback sensor while this is occurring. The
indicator light from the sensor should illuminate when you
hear the second exhaust. This is the key to determining the
proper setting of the flow control. The optimum setting for
each weld block will be different for each gun, based on the
bore size and weld stroke used. Continue to open the flow
control, allowing the weld tips to close faster until:
Training & Maintenance Manual
1. You have reached an impact speed you are happy with.
2. You have reached an acceptable decibel noise level.
3. You see that the second exhaust and feedback sensor
illumination occur “just” as the weld tips contact.
Note:
This is a judgement call. If the flow control is set
too far open, then the weld block could result in welding
misfire causing the gun to fire before the weld tips close
fully. The reason this would occur is because the flow
control has been opened so much that all the air on the
front side of the cylinder has exhausted before the tips fully
close, thus negating the “low impact” benefit of the system.
To guarantee proper performance, find the setting where
the exhaust / illumination occurs “just” as the tips close,
and then adjust the flow control 1/2 turn clockwise.
How to Set the Feedback Sensor Properly
The purpose of the feedback sensor is to provide an input
signal at the exact moment that full weld pressure has been
obtained at the weld tips. Traditionally this is achieved using
squeeze time. An experienced weld / electrical engineer
is needed to place the feedback sensor input into the PLC
program. The location of this input will vary depending on
the PLC manufacturer. Consult the robot manufacturer for
the proper input location.
Above is a sample PLC program where the feedback sensor
was placed during a typical install. The location of the input
should be right before the weld start command. Once the input
has been placed into the program, disconnect the sensor cable
from the feedback sensor. This will allow you to determine
whether or not the input was placed in the correct spot.
Perform a trial run. If on the first weld, the weld tips close
and the robot stops, then the sensor input has been located
correctly in the program. If the robot continues to run, despite
the cable being disconnected, then the sensor input is not
correct. Review the location and then try the trial run again.
Note: The weld block should perform the same whether the
robot is in manual or automatic mode.
5
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics

WCS-SIF-01
Pneumati
c
Specifications
Training & Maintenance Manual
Pneumatic System
with Low Impact and
Rapid Approach Control
Description
Pneumatic valve block for use with pneumatic weld
gun cylinders. The block has an integrated low impact
system and is provided with two solenoid operated
“Namur” or ISO size 2 valves. One valve for the retract
(pre-stroke) and one for the weld stroke. The valves
can be of the single solenoid type or the double
solenoid type. The block is available for different
constructions of cylinders:
DH / WH = 3 Ported Cylinders
DP / WP = 2 and 4 Ported Cylinders
Ordering Code: See pages 7 – 13.
Dimensions: See pages 15 – 18.
Applications
The Spotwelding System can be used with any
Pneumatic Spot Weld Cylinder.
Mounting
The weld block can either be mounted on the side of
the robot or directly to the cylinder. See pages 10 – 12
for bolt hole patterns for robot mount. Consult Parker
for cylinder mount application.
Technical Data
Medium .......................... Compressed air, filtered to
40µ and dried to a dewpoint
of 37°F (3°C), lubricated
or non-lubricated. Once
lubricated air is applied, this
must be maintained.
Working Pressure ..........37 to 145 PSIG (2.5 to 10 bar)
WH Series Air Operated
Quick Exhaust ..........40 to 115 PSIG (2.7 to 7.9 bar)
Ambient Temperature ...... 41°F to 120°F (5°C to 49°C)
Weight –
DP ................................................. 12.0 lbs (5.4 kgs)
DH ................................................... 7.0 lbs (3.2 kgs)
WP (with Baseplate) ...................... 14.0 lbs (6.4 kgs)
WH (with Baseplate) ...................... 18.0 lbs (8.2 kgs)
Pneumatic Valve
24 VDC
Operating Voltage Solenoids
Power Consumption .....................................4.8W
Class of Protection ....................... IP65 (with plug
mounted)
Connector ............................ M12, 22mm, 30mm,
Auto (ISO 2 only)
120 VAC
Operating Voltage Solenoids
Frequency ............................................50 / 60 Hz
Power Consumption ..................... 7.8 VA / 6.3 VA
Class of Protection ....................... IP65 (with plug
mounted)
Connector ............................ M12, 22mm, 30mm,
Auto (WP / WH only)
Proximity Sensor
24 VDC
Supply Voltage ................................10 to 30 VDC
Rated Operational Current ........................200mA
Degree of Protection .....................................IP67
Ambient Temperature Range ....... -13°F to 158°F
(-25°C to 70°C)
Switching Indication ................... By LED (Yellow)
Output ..............................................PNP or NPN
120 VDC (Consult factory for availability)
Supply Voltage .............................. 20 to 140 VAC
Frequency ......................................... 50 or 60 Hz
Supply Voltage Indication ........... By LED (Green)
Rated Operational Current .......................400 mA
Degree of Protection .....................................IP67
Ambient Temperature Range ...... -13°F to 158°F
(-25°C - +70°C)
Switching Indication ................. By LED (Orange)
....24 VDC +10/-15%
...120 VAC +10/-15%
Service Kits: See page 9.
6
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics

WCS-SIF-01
Pneumati
c
Training & Maintenance Manual
Ordering Information
Model Number Index – B6 Namur Valves (2 and 4 Ported Guns)
Valve Valve Block Valve Block
Valve Block Operators Operators Port
Series Block Sensor Retract Valve Weld Stroke Valve Voltage Type
DP A 1 S S D N
DP B6 NAMUR
(2 or 4
Cylinder
Ports
Note: NAMUR valves mounted on
valve block have BSPP porting.
A Valve Block
w/Base Plate
X Valve Block
for Base Plate
Less Base Plate
1 PNP
Sensor24 VDC
S Single
Solenoid
D Double
Solenoid
X Valve
Block w/o
Pre-Stroke
Valve
Model Selection Examples
Valve Block Only ...............................................DPX1SSDN
S Single
D Double
X Valve
Solenoid
Solenoid
Block w/o
Weld Stroke
Valve
Valve Block with Base .......................................DPA1SSDN
Model Number Index – B6 Namur Valves (3 Ported Guns)
Valve Valve Block Valve Block
Valve Block Operators Operators Port
Series Block Sensor Retract Valve Weld Stroke Valve Voltage Type
A 120VAC
22mm Coil
B 120VAC
30mm Coil
D 24VDC
22mm Coil
E 24VDC
30mm Coil
F 24VDC M12
Connector
X Without
Valves
N NPT
G BSPP
DH G 1 S S D N
DH B6 NAMUR
(3 Cylinder
Ports
Note: NAMUR valves mounted on
valve block have BSPP porting.
4 Valve Block
High Pressure
Quick Exhaust
Mounted
(w/o base)
G Valve Block
High Pressure
Quick Exhaust
Mounted
(w/Base)
1 PNP
Sensor24 VDC
S Single
Solenoid
D Double
Solenoid
X Valve
Block w/o
Pre-Stroke
Valve
S Single
D Double
X Valve
Solenoid
Solenoid
Block w/o
Weld Stroke
Valve
A 120VAC
22mm Coil
B 120VAC
30mm Coil
D 24VDC
22mm Coil
E 24VDC
30mm Coil
F 24VDC M12
Connector
X Without
Valves
N NPT
G BSPP
Model Selection Examples
Valve Block with Quick Exhaust (w/o Base) ..... DH41SSDN
Valve Block with Quick Exhaust (w/ Base) ...... DHG1SSDN
7
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics

WCS-SIF-01
Pneumati
c
Training & Maintenance Manual
Ordering Information
Model Number Index – ISO Size 2 Cylinder & Base Plate Mountable (2 and 4 Ported Guns)
Valve Valve Block Valve Block
Valve Block Operators Operators Port
Series Block Sensor Retract Valve Weld Stroke Valve Voltage Type
WP A 1 S S F N
A Valve Block
w/Base Plate
X Valve Block
w/o Base Plate
WP ISO 2
(2 or 4
Cylinder
Ports)
1 PNP Sensor-
24 VDC
Model Number Index – ISO Size 2
Valve Valve Block Valve Block
Valve Block Operators Operators Port
Series Block Sensor Retract Valve Weld Stroke Valve Voltage Type
S Single
Solenoid
D Double
Solenoid
X Valve
Block w/o
Pre- Stroke
Valve
S Single
D Double
X Valve
Solenoid
Solenoid
Block
w/o
Weld
Stroke
Valve
B 120VAC 30mm Square 3-Pin ISO 4400
E 24VDC 30mm Square 3-Pin ISO 4400
F 24VDC M12 Euro
H 120VAC 5-Pin Mini Auto Straight (GM)
J 120VAC 5-Pin Mini Auto Straight (Ford)
K 120VAC 5-Pin Mini Auto Straight (Chrysler)
M 24VDC 4-Pin M12 Micro Auto Straight (GM)
N 24VDC 4-Pin M12 Micro Auto Straight (Ford)
P 24VDC 4-Pin M12 Micro Auto Straight (Chrysler)
Q 24VDC 5-Pin Mini Auto Straight (GM)
R 24VDC 5-Pin Mini Auto Straight (Ford)
S 24VDC 5-Pin Mini Auto Straight (Chrysler)
X Without Valves
Cylinder & Base Plate Mountable
N NPT
G BSPP
(3 Ported Guns)
WH B 1 S S F N
WH ISO 2
(3 Cylinder
Ports)
4 Valve Block Quick
B Valve Block w/Base Plate
G Valve Block w/Base Plate
H Valve Block w/Base Plate
Y Valve Block Less Base
Z Valve Block Less Base
1 PNP Sensor-
24 VDC
Exhaust Mounted
(Cylinder Mount)
(Air Operated High Flow
Quick Exhaust)
(High Pressure Quick
Exhaust)
(Solenoid Operated High
Flow Quick Exhaust)
Plate (Air Operated High
Flow Quick Exhaust)
Plate (Solenoid Operated
Quick Exhaust)
S Single
Solenoid
D Double
Solenoid
X Valve
Block w/o
Pre-Stroke
Valve
8
S Single
Solenoid
D Double
Solenoid
X Valve
Block
w/o
Weld
Stroke
Valve
E 24VDC 30mm Square 3-Pin ISO 4400
F 24VDC M12 Euro
M 24VDC 4-Pin M12 Micro Auto Straight (GM)
N 24VDC 4-Pin M12 Micro Auto Straight (Ford)
P 24VDC 4-Pin M12 Micro Auto Straight (Chrysler)
Q 24VDC 5-Pin Mini Auto Straight (GM)
R 24VDC 5-Pin Mini Auto Straight (Ford)
S 24VDC 5-Pin Mini Auto Straight (Chrysler)
X Without Valves
N NPT
G BSPP
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics

WCS-SIF-01
Pneumati
c
Training & Maintenance Manual
Ordering Information
Model Number Index – ISO Size 2 Manifold Mountable (2 and 4 Ported Guns)
Valve Valve Block Valve Block
Valve Block Operators Operators Port
Series Block Sensor Retract Valve Weld Stroke Valve Voltage Type
WP J 1 X X X N
WP ISO 2
(2 or 4
Cylinder
Ports)
J Valve Block (Standard)
ISO 2 Manifold Mountable
Plug-In
M Valve Block (Standard)
ISO 2 Manifold Mountable
Non Plug-In
1 PNP Sensor-
24 VDC
Model Number Index – ISO Size 2
Valve Valve Block Valve Block
Valve Block Operators Operators Port
Series Block Sensor Retract Valve Weld Stroke Valve Voltage Type
X Valve
Block w/o
Pre-Stroke
Valve
X Valve Block
Manifold Mountable
w/o
Weld
Stroke
Valve
X Without
Valves
(3 Ported Guns)
N NPT
G BSPP
WH ISO 2
(3 Cylinder
Ports)
WH K 1 X X X N
1 PNP Sensor-
K Valve Block ISO Manifold
Mountable Plug-In
(Air Operated High Flow
Quick Exhaust)
L Valve Block ISO Manifold
Mountable Plug-In
(Solenoid Operated High
Flow Quick Exhaust)
N Valve Block ISO Manifold
Mountable Non Plug-In
(Air Operated High Flow
Quick Exhaust)
P Valve Block ISO Manifold
Mountable Non Plug-In
(Solenoid Operated High
Flow Quick Exhaust)
24 VDC
X Valve
Block w/o
Pre-Stroke
Valve
X Valve Block
w/o
Weld
Stroke
Note: ISO Size 2 manifold mountable weld units cannot be ordered
with valves or manifold bases. See pages 10 and 11 for valve and
manifold base ordering information.
Valve
9
X Without
Valves
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics
N NPT
G BSPP

WCS-SIF-01
Pneumati
c
H2
H2
H2
Training & Maintenance Manual
Ordering Information
Model Number Index – 5599-1 CNOMO - Size 2
Enclosure / Automotive
Basic Operator / Pilot Source / Overrides / Lead Voltage & Wiring Engineering
Series Function Mounting Pilot Exhaust Lights Length Frequency Options Level
H2 E WX H B L 49 — C
5599-1
Basic Series
ISO 5599-1
Size 2
5599-1
Operator / Function
2 Double Solenoid, 2-Position
E Single Solenoid, 2-Position -
Air Return, Spring Assist
5599-1
Mounting
WX Valve
Less Base
5599-1
Pilot Source /
Pilot Exhaust
H #5 Port / Vented
5599-1
Overrides / Lights
B Non-Locking, Flush,
Push - w/o Light
G* Non-Locking, Flush,
Push - w/ Light
* Apply to Voltage Code “19” &
Enclosure / Lead Length “6”.
5599-1
Enclosure /
Lead Length
6* 2-Pin M12 Euro
Connector with
CNOMO Operator
L 3-Pin 30mm
DIN 43650A with
CNOMO Operator
*
Only available with
Voltage / Wiring “19000FC”.
5599-1
Automotive
Wiring Options
Blank None
000F* SAE / Ford
* Required with Enclosure “6” Only.
5599-1
Voltage & Frequency
Code
19* 24
49 24
*
LED & Surge Suppression.
Only Available with Enclosure “6”.
AC
60Hz 50Hz
5599-1
Engineering
Level
C Current
DC
Model Number Index – 5599-1 AUTO - Size 2
Enclosure / Automotive
Basic Operator / Pilot Source / Overrides / Lead Voltage & Automotive Wiring Engineering
Series Function Mounting Pilot Exhaust Lights Length Frequency Enclosure Options Level
H2 E WX H G 2 B9 000 F C
5599-1
Basic Series
ISO 5599-1
Size 2
5599-1
Operator / Function
2 Double Solenoid,
2-Position
E Single Solenoid,
2-Position - Air Return,
Spring Assist
Mounting
WX Valve
Less
Base
5599-1
Overrides / Lights
G* Non-Locking, Flush,
Push - w/ Light
5599-1
Pilot Source /
Pilot Exhaust
H #5 Port / Vented
5599-1
5599-1
Enclosure /
Lead Length
2 4-Pin M12 Micro
Straight Connector
3 5-Pin Mini
Automotive
Straight Connector
5599-1
Automotive
Wiring Options
C Chrysler
F SAE / Ford
G General Motors
5599-1
Voltage & Frequency
Code
B9* 24 LED & Sup
* Solenoid is Blue color.
AC
60Hz 50Hz
Engineering
C Current
DC
Surge Sup
5599-1
Level
Light &
Model Number Index – 5599-2 Size 2
Enclosure /
Basic Operator / Pilot Source / Overrides / Lead Voltage & Engineering
Series Function Mounting Pilot Exhaust Lights Length Frequency Level
H2 E VX H G 0 B9 C
5599-2
Basic Series
ISO 5599-2
Size 2
5599-2
Operator / Function
2 Double Solenoid, 2-Position
E Single Solenoid, 2-Position -
Air Return, Spring Assist
5599-2
Mounting
VX Valve
Less Base
H #5 Port / Vented
Overrides / Lights
G Non-Locking, Flush,
Push - w/ Light
BOLD OPTIONS ARE MOST POPULAR
5599-2
Pilot Source /
Pilot Exhaust
5599-2
10
Enclosure / Lead Length
0 None, Remote Pilot Valve
or Valve Less Base
5599-2
Voltage & Frequency
Code
B9* 24 LED & Sup
* Solenoid is Blue color.
AC
60Hz 50Hz
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics
5599-2
Engineering
C Current
DC
Surge Sup
5599-2
Level
Light &

WCS-SIF-01
Pneumati
c
H2
Training & Maintenance Manual
Ordering Information
Manifold and Subbase Kit Ordering Code
Mounting Base Style / Enclosures / Wiring Engineering Factory
Basic Series Port Size Lead Length Options Level Designator
PS4111 55 A — C P
0 None, No Electrical Plug - 5599-1
7† 3-Pin Mini Connector in Base
8*† 4-Pin M12 Micro Connector in Base
9† 5-Pin Mini Connector in Base
A 6" Leads
C Terminal Block
J‡ Circuit Board, Single Address
M‡ Circuit Board, Double Address
T* SAM Gen 3.0 Wiring
* Valve Voltage Code “B9” Only.
† Must Specify Valve Auto Wiring Option “C”,
“F”, or “G”.
‡ Not Available with Subbase Kits.
Mounting Base Style / Port Size
H2
17 Subbase: 1/2 NPT Side Ports
18* Subbase: 1/2 BSPP Side Ports
57 Manifold: 1/2 NPT End Port
58* Manifold: 1/2 BSPP, End Ports
* BSPP ISO 1179 Specifications.
Enclosures / Lead Length
Wiring Options
Blank None
C Chrysler
F SAE / Ford
G General Motors
Engineering
Level
C Current
Subbase Kits Manifold Kits
H2 H2
Automotive Connectors
Mounted in 1/2" Conduit Port
• 3-Pin - Wired for Single Solenoid
• 4-Pin / 5-Pin - Wired for Double Solenoid
Automotive Connectors
Mounted in Individual Manifold Conduit Cover
• 3-Pin - Wired for Single Solenoid
• 4-Pin / 5-Pin - Wired for Double Solenoid
11
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics

WCS-SIF-01
Pneumati
c
Ordering Information
How To Order Add-A-Fold
Assemblies
1. List Add-A-Fold Assembly call out. This automatically
includes the end plate kit assembly.
2. List complete Valve and Base model number. List left to
right, LOOKING AT THE CYLINDER PORTS on the #12
end of the manifold. The left most station is station 1.
Training & Maintenance Manual
Station 1
#14 End
#12 End
Station 2
Add-A-Fold Assembly Model Number
Valve End Plate Port Number of
Series Type Type Stations
AA H2 S 0 02
Valve Series
H2 Right & Left
End Plate
Example
Application requires a 2-Station manifold with weld block and
valves, and requires isolation between station 1 and 2 for port
#3 galley only.
Item Qty. Part No.
01 1 AAH2E002
02 1 H22VXHG0B9C ................................... Station 1 & 2
03 2 PS411157MCP .................................... Station 1 & 2
04 1 WPJ1XXXN .................................................Station 2
05 1 H2EVXHG0B9C ..........................................Station 2
06 1 PS3632P .....
Galley 3 Isolation Between Station 1 & 2
End Plate Type
D† 25-Pin
E† 19-Pin
G† M23, 12-Pin
S Standard -
Non-collective Wiring
† Collective Wiring Module
Included.
Example:
2-Station Manifold with (2) H2 Valves
On Manifold Bases
Port Type
0 NPT
1 BSPP “G”
NOTE: Construct manifold assemblies from left to right while looking at
the cylinder ports.
Number of
Stations
02
* Only Available
with 2-Station
Manifold when
Used in Welding
Applications.
12
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics

WCS-SIF-01
Pneumati
c
Training & Maintenance Manual
Ordering Information
Model Number Index – Generation 3.0
Basic Valve Manifold / Engineering
Series Series Protocol Subbase Stations Power I/O Options Level
S3 H2 D 2 D 0 C
Basic Series
S3 Serial Generation 3.0
Valve Series
H2 Size 2 ISO 5599-2 Valves
Notes:
1. Not available with single subbase option.
2. 2 inputs come standard with subbase or manifold options.
3. 2 additional auxiliary inputs can be ordered by selecting this option.
Protocol
D DeviceNet
TM
Subbase Stations
1 1 - Station Manifold
2 2 - Station Manifold
5 Single Subbase
Manifold /
2
2
2
Power I/O
A 2 In / 4 Out, Bus Power
B 2 In / 4 Out, Ext. Power
C 4 In / 4 Out, Bus Power
D 4 In / 4 Out, Ext Power
E Subbase, Bus Power
F Subbase, Ext. Power
Options
0 None
1
1
1,3
1,3
Engineering Level
C Current
13
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics

WCS-SIF-01
Pneumati
c
11 12
2
4
5
10
10
115 to 130 in. lb.
Torque (4)
15 to 18 in. lb.
Torque (4)
3
3
7
3
Bore
Hand Tight
Torque
Hand Tight
Torque
4 to 6 in. lb.
Torque (2)
115 to 130 in. lb.
Torque (4)
115 to 130 in. lb.
Torque (4)
85 to 100 in. lb.
Torque (2)
85 to 100 in. lb.
Torque (2)
6
8
Not Shown
9
Bore
11 12
2
4
5
10
10
115 to 130 in. lb.
Torque (4)
15 to 18 in. lb.
Torque (4)
3
3
7
3
Bore
Hand Tight
Torque
Hand Tight
Torque
4 to 6 in. lb.
Torque (2)
115 to 130 in. lb.
Torque (4)
115 to 130 in. lb.
Torque (4)
85 to 100 in. lb.
Torque (2)
85 to 100 in. lb.
Torque (2)
6
8
Not Shown
9
Bore
Training & Maintenance Manual
Components
Replacement Components
Item Kit Number Description Item Kit Number Description
1 6505953
2 3534400 Quick Exhaust Kit - High Pressure 9 3087800 PNP 24 VDC Sensor Kit
3 3538600 High Flow Quick Exhaust Kit 10 See page 10
4 PRTF10
5 WHQE49
6 3059500 Flow Control Kit 13
7 3059900 Check Valve Kit — — —
DP/DH Weld Block Sleeve Kit (1 pc.) (Not Shown)
Air Operated Timer for High Flow Quick Exh.
Sol. Oper. Kit for High Flow Quick Exh. 24VDC
8 3087900 Sensor Valve Kit
ISO 2 Replacement Valve for WP/WH Weld Blocks
11 PS2828A49P 24 VAC 30mm Coil Kit
12 PS2828619P 24 VDC M12 Euro Coil Kit
Contact Parker
Lightly grease with provided lubricant.
Lightly grease with provided lubricant.
Inspect for nicks, scratches, and surface imperfections.
Inspect for nicks, scratches, and surface imperfections.
If present, reduced service life is probable and future
If present, reduced service life is probable and future
replacement should be planned.
replacement should be planned.
Clean with lint-free cloth.
Clean with lint-free cloth.
B6 Replacement Valve for DP/DH Weld Blocks
ISO 2 Weld Block - Exploded View
14
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics

WCS-SIF-01
Pneumati
c
100% ED
100% ED
0 1
0 1
139.8
(5.50)
125
(4.92)
7.3
(0.29)
258.7
(10.19)
136
(5.35)
9
(0.35)
50.7
(2.00)
127.3
(5.01)
102
(4.02)
28
(1.10)
44.8
(1.76)
28
(1.10)
58.8
(2.31)
11.5
(0.45)
81.5
(3.21)
29.5
(1.16)
15
(0.59)
33
(1.30)
0 1
0 1
100% ED
100% ED
113.6
(4.47)
258.7
(10.19)
50.7
(2.00)
58
(2.28)
83.2
(3.28)
85.5
(3.37)
42.7
(1.68)
12.5
(0.49)
11.5
(0.45)
21
(0.83)
B6 Series Dimensions
DH Series – 3 Ported Guns Dimensions
Training & Maintenance Manual
DP Series – 2 and 4 Ported Guns Dimensions
mm
(inches)
15
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics

WCS-SIF-01
Pneumati
c
170.5
(6.71)
248.65
(9.79)
192.3
(7.57)
67
(2.64)36(1.42)
34.5
(1.36)
136
(5.35)
100.2
(3.94)
15
(0.59)
55
(2.17)
76
(2.99)
79.25
(3.12)
88
(3.46)
9
(0.35)
136
(5.35)
12.75
(0.50)
145
(5.71)
(R + IN)
Pr Pw
R+ W+
W-/R-
EXH
X I12
X I12
XI 14
10
PRESS
XI 14
10
PRESS
WH Series – For 3 Ported Gun Dimensions
WH ISO Size 2 Cylinder & Base Plate
Mountable
Training & Maintenance Manual
mm
(inches)
16
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics

WCS-SIF-01
WH Series – For 3 Ported Gun Dimensions
WP ISO Size 2 Cylinder & Base Plate
Mountable
Training & Maintenance Manual
79.25
(3.12)
XI 14
10
PRESS
X I12
170.5
(6.71)
PRESS
10
X I12
XI 14
216.31
(8.52)
192.3
(7.57)
88
(3.46)
12.75
(0.50)
145
(5.71)
(0.35)
Pr Pw
55
(2.17)
(0.59)
R+ R-
15
32
(1.26)30(1.18)30(1.18)38(1.50)
34.5
(1.36)
W+W-
101.5
(4.00)
136
9
(5.35)
mm
(inches)
Pneumatic
17
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics

WCS-SIF-01
Pneumati
c
X I12
X14
10
PRESS
58
(2.28)
109.5
(4.31)
31.5
(1.24)
16.1
(0.63)
63
(2.48)32(1.26)
88.8
(3.49)
46.5
(1.83)
146.7
(5.78)
80.7
(3.18)
187.5
(7.38)
208.7
(8.22)
X I12
X14
10
PRESS
W-/R-
88.8
(3.49)
113.5
(4.47)
46.5
(1.83)
146.7
(5.78)
80.7
(3.18)
187.5
(7.38)
208.7
(8.22)
16.1
(0.63)
63
(2.48)32(1.26)
58
(2.28)
31.5
(1.24)
WP Series – For 2 & 4 Ported Gun Dimensions
WH ISO Size 2 Manifold Mountable
Training & Maintenance Manual
WP ISO Size 2 Manifold Mountable
mm
(inches)
18
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics

WCS-SIF-01
Pneumati
c
!
!
!
Maintenance, Troubleshooting & Warnings
Training & Maintenance Manual
Scheduled Maintenance
Silencer – Periodic maintenance of the exhaust mufflers may
be required. The frequency of maintenance depends on the
environment and condition of the air supply.
Cautions
• Filtrate the inlet air to protect the weld block against
contaminating matter typically found in compressed air
systems (i.e. rust, water, compressor oil, or other foreign
particles). A standard 40 micron filter is recommended.
If liquid aerosols, both water and oil, and submicron
particulate matter need to be removed from your air system,
then a coalescing filter is required.
• The inlet compressed air must be filtered, regulated, and
periodically maintained to ensure maximum operating
performance and warranty.
Weld Block Troubleshooting
Always verify that air and electrical are connected properly
per Installation Instructions on page 4. At startup, cylinder
should be open fully with no electrical signal to solenoids.
All air lines, filters, regulators, tubing, hoses, fittings and
electrical cables should be in good working condition as
specified in automotive plant maintenance schedule.
1. Cylinder does not extend / retract.
• Does the cylinder move using manual overrides?
– If yes, then check electrical conditions.
Check the following:
• Solenoid connections
• Coils – replace if necessary
• PLC program
–
If no, does the cylinder move freely with air turned off?
• If no, then cylinder should be repaired / replaced.
• If yes, is the flow control open?
– If no, open flow control. See Setup Instructions
on page 5.
– If yes, verify with gauges that there is pressure
on back side of cylinder when valve shifts. There
is a possibility that the metering of exhaust
air on the front side of the cylinder, due to the
flow control, is creating a “Joe Block” effect
occurring between the piston face and cylinder.
Contact Parker Representative for assistance.
– If yes, replace valves on System
2. Cylinder tips close too fast / slow.
• Adjust flow control. See Setup Instructions on page 5.
• Quick Exhaust only – Adjust air timer on quick exhaust.
• Check muffler for proper operation. If covered with
weld slag, then replace muffler.
3. Weld gun does not fire weld.
• Is cable connected to sensor?
– If no, connect to sensor
– If yes, is cable connected to PLC?
• If no, wire to controller
• If yes, check PLC program on location of weld
signal to start weld. Also verify feedback sensor
is operating properly.
4. Weld gun fires before tips are closed
• Adjust flow control so that weld tips close slower. See
Setup Instructions on page 5.
• Is sensor input in the PLC correct? See Setup
Instructions on page 5.
Warnings
WARNING
To avoid unpredictable system behavior that can cause personal
injury and property damage:
• Disconnect electrical supply (when necessary) before installation,
servicing, or conversion.
• Disconnect air supply and depressurize all air lines connected
to this product before installation, servicing, or conversion.
• O pe ra te within the m anufacturer’s sp ecified pre ss ur e,
temperature, and other conditions listed in these instructions.
• Medium must be moisture-free if ambient temperature is below
freezing.
• Service according to procedures listed in these instructions.
• Installation, service, and conversion of these products must be
performed by knowledgeable personnel who understand how
pneumatic products are to be applied.
After installation, servicing, or conversion, air and electrical
•
supplies (when necessary) should be connected and the product
tested for proper function and leakage. If audible leakage is present,
or the product does not operate properly, do not put into use.
• Warnings and specifications on the product should not be
covered by paint, etc. If masking is not possible, contact your
local representative for replacement labels.
FAILURE OR IMPROPER SELECTION OR IMPROPER USE OF
THE PRODUCTS AND/OR SYSTEMS DESCRIBED HEREIN OR
RELATED ITEMS CAN CAUSE DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY AND
PROPERTY DAMAGE.
This doc ument an d other informat ion from Pa rke r Hannif in
Corporation, its subsidiaries and authorized distributors provide
product and/or system options for further investigation by users having
technical expertise. It is important that you analyze all aspects of your
application, including consequences of any failure and review the
information concerning the product or systems in the current product
catalog. Due to the variety of operating conditions and applications
for these products or systems, the user, through its own analysis
and testing, is solely responsible for making the final selection of the
products and systems and assuring that all performance, safety and
warning requirements of the application are met.
The products described herein, including without limitation, product
features, specifications, designs, availability and pricing, are subject
to change by Parker Hannifin Corporation and its subsidiaries at any
time without notice.
EXTRA COPIES OF THESE INSTRUCTIONS ARE AVAILABLE FOR
INCLUSION IN EQUIPMENT / MAINTENANCE MANUALS THAT UTILIZE
THESE PRODUCTS. CONTACT YOUR LOCAL REPRESENTATIVE.
19
WARNING
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics

WCS-SIF-01
Pneumati
c
Training & Maintenance Manual
Offer of Sale
The items described in this document and other documents or descriptions provided by Parker Hannifin Corporation, its subsidiaries and its authorized
distributors, are hereby offered for sale at prices to be established by Parker Hannifin Corporation, its subsidiaries and its authorized distributors. This
offer and its acceptance by any customer (“Buyer”) shall be governed by all of the following Terms and Conditions. Buyer’s order for any such item, when
communicated to Parker Hannifin Corporation, its subsidiaries or an authorized distributor (“Seller”) verbally or in writing, shall constitute acceptance
of this offer.
1. Terms and Conditions of Sale: All descriptions, quotations, proposals, offers,
acknowledgments, acceptances and sales of Seller’s products are subject to and
shall be governed exclusively by the terms and conditions stated herein. Buyer’s
acceptance of any offer to sell is limited to these terms and conditions. Any terms
or conditions in addition to, or inconsistent with those stated herein, proposed by
Buyer in any acceptance of an offer by Seller, are hereby objected to. No such
additional, different or inconsistent terms and conditions shall become part of the
contract between Buyer and Seller unless expressly accepted in writing by Seller.
Seller’s acceptance of any offer to purchase by Buyer is expressly conditional upon
Buyer’s assent to all the terms and conditions stated herein, including any terms
in addition to, or inconsistent with those contained in Buyer’s offer. Acceptance
of Seller’s products shall in all events constitute such assent.
2. Payment: Payment shall be made by Buyer net 30 days from the date of
delivery of the items purchased hereunder. Amounts not timely paid shall bear
interest at the maximum rate permitted by law for each month or portion thereof
that the Buyer is late in making payment. Any claims by Buyer for omissions or
shortages in a shipment shall be waived unless Seller receives notice thereof
within 30 days after Buyer’s receipt of the shipment.
3. Delivery: Unless otherwise provided on the face hereof, delivery shall be made
F.O.B. Seller’s plant. Regardless of the method of delivery, however, risk of loss
shall pass to Buyer upon Seller’s delivery to a carrier. Any delivery dates shown are
approximate only and Seller shall have no liability for any delays in delivery.
4.
Warranty: Seller warrants that the items sold hereunder shall be free from
defects in material or workmanship for a period of 18 months from date of shipment
from Parker Hannifin Corporation. THIS WARRANTY COMPRISES THE SOLE
AND ENTIRE WARRANTY PERTAINING TO ITEMS PROVIDED HEREUNDER.
SELLER MAKES NO OTHER WARRANTY, GUARANTEE, OR REPRESENTATION
OF ANY KIND WHATSOEVER. ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, INCLUDING BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR PURPOSE, WHETHER
EXPRESS, IMPLIED, OR ARISING BY OPERATION OF LAW, TRADE USAGE,
OR COURSE OF DEALING ARE HEREBY DISCLAIMED.
NOTWITHSTANDING THE FOREGOING, THERE ARE NO WARRANTIES
WHATSOEVER ON ITEMS BUILT OR ACQUIRED WHOLLY OR PARTIALLY,
TO BUYER’S DESIGN OR SPECIFICATIONS.
5. Limitation of Remedy: SELLER’S LIABILITY ARISING FROM OR IN ANY
WAY CONNECTED WITH THE ITEMS SOLD OR THIS CONTRACT SHALL
BE LIMITED EXCLUSIVELY TO REPAIR OR REPLACEMENT OF THE ITEMS
SOLD OR REFUND OF THE PURCHASE PRICE PAID BY BUYER, AT
SELLER’S SOLE OPTION. IN NO EVENT SHALL SELLER BE LIABLE FOR ANY
INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL OR SPECIAL DAMAGES OF ANY KIND OR
NATURE WHATSOEVER, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO LOST PROFITS
ARISING FROM OR IN ANY WAY CONNECTED WITH THIS AGREEMENT
OR ITEMS SOLD HEREUNDER, WHETHER ALLEGED TO ARISE FROM
BREACH OF CONTRACT, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, OR IN TORT,
INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, NEGLIGENCE, FAILURE TO WARN OR
STRICT LIABILITY.
6. Changes, Reschedules and Cancellations: Buyer may request to modify the
designs or specifications for the items sold hereunder as well as the quantities
and delivery dates thereof, or may request to cancel all or part of this order,
however, no such requested modification or cancellation shall become part of
the contract between Buyer and Seller unless accepted by Seller in a written
amendment to this Agreement. Acceptance of any such requested modification
or cancellation shall be at Seller’s discretion, and shall be upon such terms and
conditions as Seller may require.
7. Special Tooling: A tooling charge may be imposed for any special tooling,
including without limitations, dies, fixtures, molds and patterns, acquired to
manufacture items sold pursuant to this contract. Such special tooling shall be
and remain Seller’s property notwithstanding payment of any charges by Buyer.
In no event will Buyer acquire any interest in apparatus belonging to Seller which
is utilized in the manufacture of the items sold hereunder, even if such apparatus
has been specially converted or adapted for such manufacture and notwithstanding
any charges paid by Buyer. Unless otherwise agreed, Seller shall have the right
to alter, discard or otherwise dispose of any special tooling or other property in
its sole discretion at any time.
8. Buyer’s Property: Any designs, tools, patterns, materials, drawings, confidential
information or equipment furnished by Buyer, or any other items which become
Buyer’s property, may be considered obsolete and may be destroyed by Seller
after two (2) consecutive years have elapsed without Buyer placing an order
for the items which are manufactured using such property. Seller shall not
be responsible for any loss or damage to such property while it is in Seller’s
possession or control.
9. Taxes: Unless otherwise indicated on the face hereof, all prices and charges
are exclusive of excise, sales, use, property, occupational or like taxes which
may be imposed by any taxing authority upon the manufacture, sale or delivery
of the items sold hereunder. If any such taxes must be paid by Seller or if Seller
is liable for the collection of such tax, the amount thereof shall be in addition to
the amounts for the items sold. Buyer agrees to pay all such taxes or to reimburse
Seller therefore upon receipt of its invoice. If Buyer claims exemption from any
sales, use or other tax imposed by any taxing authority, Buyer shall save Seller
harmless from and against any such tax, together with any interest or penalties
thereon which may be assessed if the items are held to be taxable.
10. Indemnity For Infringement of Intellectual Property Rights: Seller shall
have no liability for infringement of any patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade
dress, trade secrets or similar rights except as provided in this Part 10. Seller
will defend and indemnify Buyer against allegations of infringement of U.S.
patents, U.S. trademarks, copyrights, trade dress and trade secrets (hereinafter
“Intellectual Property Rights”). Seller will defend at its expense and will pay the
cost of any settlement or damages awarded in an action brought against Buyer
based on an allegation that an item sold pursuant to this contract infringes the
Intellectual Property Rights of a third party. Seller’s obligation to defend and
indemnify Buyer is contingent on Buyer notifying Seller within ten (10) days after
Buyer becomes aware of such allegations of infringement, and Seller having sole
control over the defense of any allegations or actions including all negotiations
for settlement or compromise. If an item sold hereunder is subject to a claim
that it infringes the Intellectual Property Rights of a third party, Seller may, at
its sole expense and option, procure for Buyer the right to continue using said
item, replace or modify said item so as to make it noninfringing, or offer to accept
return of said item and return the purchase price less a reasonable allowance
for depreciation. Notwithstanding the foregoing, Seller shall have no liability for
claims of infringement based on information provided by Buyer, or directed to
items delivered hereunder for which the designs are specified in whole or part
by Buyer, or infringements resulting from the modification, combination or use
in a system of any item sold hereunder. The foregoing provisions of this Part 10
shall constitute Seller’s sole and exclusive liability and Buyer’s sole and exclusive
remedy for infringement of Intellectual Property Rights.
If a claim is based on information provided by Buyer or if the design for an item
delivered hereunder is specified in whole or in part by Buyer, Buyer shall defend
and indemnify Seller for all costs, expenses or judgements resulting from any
claim that such item infringes any patent, trademark, copyright, trade dress, trade
secret or any similar right.
11. Force Majeure: Seller does not assume the risk of and shall not be liable for
delay or failure to perform any of Seller’s obligations by reason of circumstances
beyond the reasonable control of Seller (hereinafter “Events of Force Majeure”).
Events of Force Majeure shall include without limitation, accidents, acts of God,
strikes or labor disputes, acts, laws, rules or regulations of any government or
government agency, fires, floods, delays or failures in delivery of carriers or
suppliers, shortages of materials and any other cause beyond Seller’s control.
12. Entire Agreement/Governing Law: The terms and conditions set forth
herein, together with any amendments, modifications and any different terms
or conditions expressly accepted by Seller in writing, shall constitute the entire
Agreement concerning the items sold, and there are no oral or other representations
or agreements which pertain thereto. This Agreement shall be governed in all
respects by the law of the State of Ohio. No actions arising out of sale of the
items sold hereunder or this Agreement may be brought by either party more
than two (2) years after the cause of action accrues.
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
8676 E. M89
P.O. Box 901
Richland, MI 49083 USA
Tel: (269) 629-5000
Fax: (269) 629-5385
WCS-SIF-01 11/06 5M IGS Printed in U.S.A.
20
Customer/Technical Service
Tel: (269) 629-5575
Fax: (269) 629-5385
Web site: www.parker.com/pneumatics
E-mail: PDNMKTG@parker.com
Parker Hannifin Corporation
Pneumatic Division
Richland, Michigan
www.parker.com/pneumatics
 Loading...
Loading...