Page 1

Parallels
Virtualization SDK
Programmer's Guide
Copyright © 1999-2011 Parallels Holdings, Ltd. and its affiliates. All
ights reserved. r
Page 2

Parallels Holdings, Ltd.
c/o Parallels International GMbH.
Parallels International GmbH
Vordergasse 49
CH8200 Schaffhausen
Switzerland
Tel: + 41 526320 411
Fax: + 41 52672 2010
www.parallels.com
Copyright © 1999-2011 Parallels Holdings, Ltd. and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
This product is protected by United States and international copyright laws. The product’s underlying
technology, patents, and trademarks are listed at http://www.parallels.com/trademarks.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows Server, Windows NT, Windows Vista, and MS-DOS are registered trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Mac is a registered trademark of Apple, Inc.
All other marks and names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 3

Contents
Getting Started 5
Overview ......................................................................................................................................................5
System Requirements ...................................................................................................................................6
Mac OS X Clients..............................................................................................................................6
Windows Clients ...............................................................................................................................6
Linux Clients.....................................................................................................................................7
Common Network Requirements......................................................................................................7
Parallels C API Concepts 8
Compiling Client Applications.....................................................................................................................8
Mac OS X..........................................................................................................................................8
Windows.......................................................................................................................................... 18
Linux ...............................................................................................................................................19
Handles.......................................................................................................................................................20
Synchronous Functions...............................................................................................................................21
Asynchronous Functions.............................................................................................................................22
Strings as Return Values.............................................................................................................................26
Error Handling............................................................................................................................................28
Parallels C API by Example 30
Obtaining Server Handle and Logging In...................................................................................................31
Host Operations..........................................................................................................................................35
Retrieving Host Configuration Information ....................................................................................36
Managing Parallels Service Preferences..........................................................................................39
Searching for Parallels Servers........................................................................................................42
Managing Parallels Service Users...................................................................................................45
Managing Files In The Host OS......................................................................................................50
Managing Licenses..........................................................................................................................53
Obtaining a Problem Report............................................................................................................56
Virtual Machine Operations........................................................................................................................58
Obtaining the Virtual Machines List ...............................................................................................59
Searching for Virtual Machine by Name.........................................................................................62
Obtaining Virtual Machine Configuration Information...................................................................64
Determining Virtual Machine State.................................................................................................66
Starting, Stopping, Resetting a Virtual Machine.............................................................................69
Suspending and Pausing a Virtual Machine....................................................................................70
Creating a New Virtual Machine.....................................................................................................72
Searching for Virtual Machines.......................................................................................................75
Adding an Existing Virtual Machine...............................................................................................79
Cloning a Virtual Machine..............................................................................................................82
Deleting a Virtual Machine.............................................................................................................84
Modifying Virtual Machine Configuration......................................................................................85
Managing User Access Rights.........................................................................................................99
Working with Virtual Machine Templates....................................................................................101
Events .......................................................................................................................................................110
Receiving and Handling Events.....................................................................................................111
Responding to Parallels Service Questions ...................................................................................114
Performance Statistics...............................................................................................................................121
Obtaining Performance Report......................................................................................................122
Performance Monitoring................................................................................................................125
Page 4
Contents 4
Encryption Plug-in....................................................................................................................................130
Encryption Plug-in Basics.............................................................................................................130
The Encryption API Reference......................................................................................................131
Implementing a Plug-in.................................................................................................................134
Building the Dynamic Library.......................................................................................................140
Plug-in Installation and Usage.......................................................................................................141
Parallels Python API Concepts 142
Package and Modules...............................................................................................................................143
Classes......................................................................................................................................................144
Class Methods...........................................................................................................................................144
Synchronous Methods...................................................................................................................144
Asynchronous Methods.................................................................................................................145
Error Handling.......................................................................................................................................... 147
Parallels Python API by Example 148
Creating a Basic Application....................................................................................................................149
Connecting to Parallels Service and Logging In.......................................................................................152
Host Operations........................................................................................................................................ 155
Retrieving Host Configuration Info...............................................................................................155
Managing Parallels Service Preferences........................................................................................157
Virtual Machine Operations......................................................................................................................158
Obtaining the Virtual Machine List...............................................................................................159
Searching for a Virtual Machine....................................................................................................161
Performing Power Operations.......................................................................................................162
Creating a New Virtual Machine...................................................................................................163
Obtaining Virtual Machine Configuration Data............................................................................165
Modifying Virtual Machine Configuration....................................................................................168
Adding an Existing Virtual Machine.............................................................................................175
Removing an Existing Virtual Machine........................................................................................176
Cloning a Virtual Machine............................................................................................................177
Remote Desktop Access...........................................................................................................................178
Creating a Simple OS Installation Program...................................................................................179
Index 183
Page 5

C HAPTER 1
Getting Started
In This Chapter
Overview............................................................................................................................... 5
System Requirements............................................................................................................ 6
Overview
Parallels Virtualization SDK is a development kit used to create and integrate custom software
solutions with Parallels virtualization products. The SDK provides cross-platform ANSI C and
Python APIs. The SDK can be used to develop software for any hypervisor-based Parallels
virtualization product such as Parallels Server, Parallels Workstation, and Parallels Desktop.
The SDK comprises the following components:
C header files.
Dynamic libraries.
Python package for developing client applications in Python.
Parallels command line tools (prlctl, prlsrvctl) -- a command line utility that can
be used to perform a full range of host and virtual machine operations.
Parallels Virtualization SDK Programmer's Guide (this document).
Parallels C API Reference Guide.
Parallels Python API Reference Guide.
Parallels Command Line Reference Guide.
Page 6

Getting Started 6
System Requirements
Mac OS X Clients
Hardware Requirements
Intel-powered Core™ Duo or Core Solo Mac® Mini, iMac®, MacBook™, MacBook Pro,
MacBook Air, Mac Pro, or Xserve.
Ethernet or WiFi network adapter.
Software Requirements
Mac OS X Tiger 10.4.8 or later.
Mac OS X Leopard 10.5.2 or later.
Parallels Python API requires Python 2.5. Other versions of Python are not officially
supported.
Windows Clients
Hardware Requirements
Intel-compatible x86 (32-bit) or x64 (64-bit) processor.
Ethernet or WiFi network adapter.
Software Requirements
Windows 2000 or higher.
The Parallels Python API requires Python 2.5. Other versions of Python are not officially
supported.
Page 7

Getting Started 7
Linux Clients
Hardware Requirements
Intel-compatible x86 (32-bit) or x64 (64-bit) processor.
Ethernet network adapter.
Software Requirements
Red Hat® Enterprise Linux WS4 (x32, x64).
Red Hat Enterprise Linux AS4 (x32, x64).
Red Hat Enterprise Linux ES4 (x32, x64).
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 (x32, x64)
CentOS 4.x (x32, x64).
CentOS 5.0 (x32, x64).
CentOS 5.1 (x32, x64).
Ubuntu Server 7.10 (x32, x64).
®
SUSE
Linux Enterprise Server 10 SP1 (x32, x64).
Common Network Requirements
Parallels Server
When creating client applications for Parallels Server, your client computer must be able to
establish a network connection with the host computer running the server. The client computer
can be connected to a local area network via a wired or a wireless interface. Clients
communicate with a server via TCP/IP. The server is listening on port 6400. Please make sure
that the port is not blocked by a firewall.
Parallels Desktop and Parallels Workstation
Remote connections to the Parallels Service are not allowed with Parallels Desktop or Parallels
Workstation. With these products, you can run your client applications on the host computer
only.
Page 8

C HAPTER 2
Parallels C API Concepts
In This Chapter
Compiling Client Applications ............................................................................................. 8
Handles.................................................................................................................................. 20
Synchronous Functions......................................................................................................... 21
Asynchronous Functions....................................................................................................... 22
Strings as Return Values....................................................................................................... 26
Error Handling ...................................................................................................................... 28
Compiling Client Applications
Mac OS X
Parallels Virtualization SDK for Mac OS X is provided as a framework. The framework is
installed in the following directory:
/Library/Frameworks/ParallelsVirtualizationSDK.framework
You can use the framework just like any other Apple framework when creating development
projects and compiling applications. Alternately, you can compile and build your applications
without using the framework. In such a case, you will have to specify all the necessary paths to
the SDK source files manually.
When using the framework, the dynamic library, which is supplied with the SDK, will be
directly linked to the application. If you would like to load the dynamic library at runtime, the
Parallels Virtualization SDK includes a convenient dlopen wrapper for this purpose called
SdkWrap. Using the wrapper, you can load and unload the library symbols at any time with one
simple call. Please note that in order to use SdkWrap, you must compile your application
without using the framework. The wrapper source files are located in the Helpers/SdkWrap
directory, which is located in the main SDK installation directory.
The following subsections describe various compilation scenarios in detail and provide code
samples.
Page 9

Parallels C API Concepts 9
Compiling with SdkWrap
When using SdkWrap, your program must contain the following:
The #include "SdkWrap.h" directive. This header file defines the wrapper functions.
The #define SDK_LIB_NAME "libprl_sdk.dylib" directive. This is the name
of the dynamic library included in the SDK.
The SdkWrap_Load(SDK_LIB_NAME) function call that will load the dynamic library
symbols.
The SdkWrap_Unload() function call that will unload the dynamic library when it is no
longer needed.
To compile a program, the following compiler options and instructions must be used:
The DYN_API_WRAP preprocessor macro must be defined.
Full paths to the Headers and the Helpers/SdkWrap directories must be specified.
Both directories are located in the main SDK installation directory.
The SdkWrap.cpp file must be included in the project and must be built together with the
main target.
The libdl library must be linked to the application. This is the standard dynamic linking
interface library needed to load the SDK library.
Using Makefile
The following is a sample Makefile that demonstrates the implementation of the requirements
described above. To compile a program and to build an executable, type make in the Terminal
window. To clean up the project, type make clean. Please note that the SOURCE variable
must contain the name of your source file name.
# Source file name.
# Substitute the file name with your own.
SOURCE = HelloWorld
# Target executable file name.
# Here we are using the same name as the source file name.
TARGET = $(SOURCE)
# Path to the Parallels Virtualization SDK files.
SDK_PATH = /Library/Frameworks/ParallelsVirtualizationSDK.framework
# Relative path to the SdkWrap directory containing
# the SDK helper files. The files are used to load
# the dynamic library.
SDK_WRAP_PATH = Helpers/SdkWrap
OBJS = SdkWrap.o $(SOURCE).o
CXX = g++
CXXFLAGS = -DDYN_API_WRAP -I$(SDK_PATH)/Headers -I$(SDK_PATH)/$(SDK_WRAP_PATH)
LDFLAGS = -ldl
all : $(TARGET)
$(TARGET) : $(OBJS)
$(CXX) -o $@ $(LDFLAGS) $(OBJS)
$(SOURCE).o : $(SOURCE).cpp
$(CXX) -c -o $@ $(CXXFLAGS) $(SOURCE).cpp
Page 10

Parallels C API Concepts 10
SdkWrap.o : $(SDK_PATH)/$(SDK_WRAP_PATH)/SdkWrap.cpp
$(CXX) -c -o $@ $(CXXFLAGS) $(SDK_PATH)/$(SDK_WRAP_PATH)/SdkWrap.cpp
clean:
@rm -f $(OBJS) $(TARGET)
.PHONY : all clean
Using Xcode IDE
If you are using the Xcode IDE, follow these steps to set up your project:
1 Add the SdkWrap.h and the SdkWrap.cpp files to your project.
2 In the Search Paths collection, specify:
a full path to the Helpers/SdkWrap directory (contains the wrapper source files)
a full path to the Headers directory (contains the SDK header files)
a full path to the Libraries directory (contains the dynamic library)
3 In the Preprocessor collection, add the DYN_API_WRAP preprocessor macro.
Example
The following is a complete sample program that demonstrates the usage of the SdkWrap
wrapper. The program loads the dynamic library, initializes the API, and then logs in to the
local Parallels Service. You can copy the entire program into a file on your Mac and try building
and then running it. The program uses a cross-platform approach, so it can also be compiled on
Windows and Linux machines.
#include "SdkWrap.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#ifdef _WIN_
#include <windows.h>
#else
#include <unistd.h>
#endif
PRL_RESULT LoginLocal(PRL_HANDLE &hServer);
PRL_RESULT LogOff(PRL_HANDLE &hServer);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
// Variables for handles.
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE; // job handle
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE; // job result
PRL_HANDLE hServer = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE; // server handle
// Variables for return codes.
PRL_RESULT err = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Log in to Parallels Service.
err = LoginLocal(hServer);
// Log off.
err = LogOff(hServer);
Page 11

Parallels C API Concepts 11
printf( "\nEnd of program.\n\n" );
printf("Press Enter to exit...");
getchar();
exit(0);
}
// Initializes the SDK library and
// logs in to the local Parallels Service.
//
PRL_RESULT LoginLocal(PRL_HANDLE &hServer)
{
// Variables for handles.
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE; // job handle
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE; // job result
// Variables for return codes.
PRL_RESULT err = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Use the correct dynamic library depending on the platform.
#ifdef _WIN_
#define SDK_LIB_NAME "prl_sdk.dll"
#elif defined(_LIN_)
#define SDK_LIB_NAME "libprl_sdk.so"
#elif defined(_MAC_)
#define SDK_LIB_NAME "libprl_sdk.dylib"
#endif
// Load SDK library.
if (PRL_FAILED(SdkWrap_Load(SDK_LIB_NAME)) &&
PRL_FAILED(SdkWrap_Load("./" SDK_LIB_NAME)))
{
fprintf( stderr, "Failed to load " SDK_LIB_NAME "\n" );
return -1;
}
// Initialize the API. In this example, we are initializing the
// API for Parallels Desktop.
// To initialize in the Parallels Workstation mode, pass PAM_WORKSTATION
// as the second parameter.
// To initialize for Parallels Server, pass PAM_SERVER.
// See the PRL_APPLICATION_MODE enumeration for all possible options.
err = PrlApi_InitEx(PARALLELS_API_VER, PAM_DESKTOP, 0, 0);
if (PRL_FAILED(err))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlApi_InitEx returned with error: %s.\n",
prl_result_to_string(err));
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
// Create a server handle (PHT_SERVER).
err = PrlSrv_Create(&hServer);
if (PRL_FAILED(err))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlSvr_Create failed, error: %s",
prl_result_to_string(err));
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
// Log in (asynchronous call).
Page 12

Parallels C API Concepts 12
hJob = PrlSrv_LoginLocal(hServer, NULL, NULL, PSL_NORMAL_SECURITY);
// Wait for a maximum of 10 seconds for
// the job to complete.
err = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(err))
{
fprintf(stderr,
"PrlJob_Wait for PrlSrv_Login returned with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(err));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
// Analyze the result of PrlSrv_Login.
err = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
// First, check PrlJob_GetRetCode success/failure.
if (PRL_FAILED(err))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlJob_GetRetCode returned with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(err));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
// Now check the Login operation success/failure.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
printf("Login job returned with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(nJobReturnCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
else
{
printf( "Login was successful.\n" );
}
return 0;
}
// Logs off the Parallels Service and
// deinitializes the SDK library.
//
PRL_RESULT LogOff(PRL_HANDLE &hServer)
{
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT err = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Log off.
hJob = PrlSrv_Logoff(hServer);
err = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
Page 13

Parallels C API Concepts 13
if (PRL_FAILED(err))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlJob_Wait for PrlSrv_Logoff returned error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(err));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
// Get the Logoff operation return code.
err = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
// Check the PrlJob_GetRetCode success/failure.
if (PRL_FAILED(err))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlJob_GetRetCode failed for PrlSrv_Logoff with
error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(err));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
// Report success or failure of PrlSrv_Logoff.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlSrv_Logoff failed with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(nJobReturnCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
else
{
printf( "Logoff was successful.\n" );
}
// Free handles that are no longer required.
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
// De-initialize the Parallels API, and unload the SDK.
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return 0;
}
Page 14

Parallels C API Concepts 14
Compiling with Framework
If you are using the ParallelsVirtualizationSDK framework, the program must contain the
following include directive:
#include "ParallelsVirtualizationSDK/Parallels.h"
Parallels.h is the main SDK header file. Please note the framework name in front of the
SDK header file name. This is a common requirement when using a framework.
Note: The difference between the SdkWrap scenario (described in the previous subsection) and
the framework scenario is that Parallels.h must be included when using the framework,
while SdkWrap.h must be included when using SdkWrap. The two files must never be
included together. Please also note that you don't have to load the dynamic library manually in
your program when using the framework.
The only compiler option that must be specified when using the framework is:
-framework ParallelsVirtualizationSDK
Using Makefile
The following sample Makefile can be used to compile a program using the
ParallelsVirtualizationSDK framework:
# Source file name.
# Substitute the file name with your own.
SOURCE = HelloWorld
# Target executable file name.
# Here we are using the same name as the source file name.
TARGET = $(SOURCE)
CXX = g++
LDFLAGS = -framework ParallelsVirtualizationSDK
all : $(TARGET)
$(TARGET) : $(OBJS)
$(CXX) -o $@ $(LDFLAGS) $(OBJS)
$(SOURCE).o : $(SOURCE).cpp
$(CXX) -c -o $@ $(SOURCE).cpp
clean:
@rm -f $(OBJS) $(TARGET)
.PHONY : all clean
Using Xcode IDE
When setting up an Xcode project, the only thing that you have to do is add the
ParallelsVirtualizationSDK framework to the project. No other project modifications are
necessary.
Sample
Page 15

Parallels C API Concepts 15
The following is a complete sample program that demonstrates the usage of the
ParallelsVirtualizationSDK framework.
#include "ParallelsVirtualizationSDK/Parallels.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#ifdef _WIN_
#include <windows.h>
#else
#include <unistd.h>
#endif
PRL_RESULT LoginLocal(PRL_HANDLE &hServer);
PRL_RESULT LogOff(PRL_HANDLE &hServer);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
// Variables for handles.
PRL_HANDLE hServer = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE; // server handle
// Variables for return codes.
PRL_RESULT err = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Log in.
err = LoginLocal(hServer);
// Log off
err = LogOff(hServer);
printf( "\nEnd of program.\n\n" );
printf("Press Enter to exit...");
getchar();
exit(0);
}
// Intializes the SDK library and
// logs in to the local Parallels Service.
//
PRL_RESULT LoginLocal(PRL_HANDLE &hServer)
{
// Variables for handles.
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE; // job handle
// Variables for return codes.
PRL_RESULT err = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Initialize the API. In this example, we are initializing the
// API for Parallels Workstation.
// To initialize in the Parallels Desktop mode, pass PAM_DESKTOP
// as the second parameter.
// To initialize for Parallels Server, pass PAM_SERVER.
// See the PRL_APPLICATION_MODE enumeration for all possible options.
err = PrlApi_InitEx(PARALLELS_API_VER, PAM_DESKTOP, 0, 0);
if (PRL_FAILED(err))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlApi_InitEx returned with error: %s.\n",
prl_result_to_string(err));
PrlApi_Deinit();
Page 16

Parallels C API Concepts 16
return -1;
}
// Create a server handle (PHT_SERVER).
err = PrlSrv_Create(&hServer);
if (PRL_FAILED(err))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlSvr_Create failed, error: %s",
prl_result_to_string(err));
PrlApi_Deinit();
return -1;
}
// Log in (asynchronous call).
hJob = PrlSrv_LoginLocal(hServer, NULL, NULL, PSL_NORMAL_SECURITY);
// Wait for a maximum of 10 seconds for
// the job to complete.
err = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(err))
{
fprintf(stderr,
"PrlJob_Wait for PrlSrv_Login returned with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(err));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
return -1;
}
// Analyze the result of PrlSrv_Login.
err = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
// First, check PrlJob_GetRetCode success/failure.
if (PRL_FAILED(err))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlJob_GetRetCode returned with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(err));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
return -1;
}
// Now check the Login operation success/failure.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
printf("Login job returned with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(nJobReturnCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
return -1;
}
else
{
printf( "Login was successful.\n" );
}
return 0;
}
// Log off the Parallels Service and
// deinitializes the SDK library.
//
Page 17
Parallels C API Concepts 17
PRL_RESULT LogOff(PRL_HANDLE &hServer)
{
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT err = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Log off.
hJob = PrlSrv_Logoff(hServer);
err = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(err))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlJob_Wait for PrlSrv_Logoff returned error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(err));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
return -1;
}
// Get the Logoff operation return code.
err = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
// Check the PrlJob_GetRetCode success/failure.
if (PRL_FAILED(err))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlJob_GetRetCode failed for PrlSrv_Logoff with
error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(err));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
return -1;
}
// Report success or failure of PrlSrv_Logoff.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlSrv_Logoff failed with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(nJobReturnCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
return -1;
}
else
{
printf( "Logoff was successful.\n" );
}
// Free handles that are no longer required.
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
// De-initialize the Parallels API, and unload the SDK.
PrlApi_Deinit();
return 0;
}
Page 18

Parallels C API Concepts 18
Windows
The following steps describe how to set up a project in Microsoft Visual Studio:
1 Create a project of your choice in a usual way and open the project Property Pages
windows.
2 In the C/C++ -> General -> Additional Include Directories section, add the path to the
Include and the Helpers\SdkWrap sub-directories located in the main directory
where you have the SDK installed.
3 Add the following files from the Helpers\SdkWrap subdirectory to the project:
SdkWrap.h
SdkWrap.cpp
These are the helper files that provide a set of methods for loading and unloading dynamic
libraries. You can use the included source code file to customize this functionality if you
wish.
4 Add the following #include directive to your program:
#include "SdkWrap.h"
The standard libraries used by the samples provided in this guide are:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
Page 19

Parallels C API Concepts 19
Linux
The following is a sample make file that can be used to compile Parallels client applications on
Linux:
# set the appropriate path to the SDK headers
SDK_INSTALL_PATH=/usr
OBJS = SdkWrap.o main.o
CXX = g++
CXXFLAGS = -I$(SDK_INSTALL_PATH)/include/parallels-virtualization-sdk
LDFLAGS = -ldl
# Set the current folder name
TARGET = Example
all : $(TARGET)
$(TARGET) : $(OBJS)
$(CXX) -o $@ $(LDFLAGS) $(OBJS)
main.o : main.cpp
$(CXX) -c -o $@ $(CXXFLAGS) main.cpp
SdkWrap.o : $(SDK_INSTALL_PATH)/share/parallels-virtualizationsdk/helpers/SdkWrap/SdkWrap.cpp
$(CXX) -c -o $@ $(CXXFLAGS) $(SDK_INSTALL_PATH)/share/parallelsvirtualization-sdk/helpers/SdkWrap/SdkWrap.cpp
clean:
@rm -f $(TARGET) $(OBJS)
.PHONY : all clean
Page 20

Parallels C API Concepts 20
Handles
The Parallels C API is a set of functions that operate on objects. Objects are not accessed
directly. Instead, references to these objects are used. These references are known as handles.
Handle Types
PRL_HANDLE is the only handle type used in the C API. It is a pointer to an integer and it is
defined in PrlTypes.h.
PRL_HANDLE can reference any type of object within the API. The type of object that
PRL_HANDLE referen ces determines the PRL_HANDLE type. A list of handle types can be
found in the PRL_HANDLE_TYPE enumeration in PrlEnums.h.
A handles' type can be extracted using the PrlHandle_GetType function. A string
representation of the handle type can then be obtained using the handle_type_to_string
function.
Obtaining a Handle
A handle is usually obtained by calling a function that operates on another (we may call it
"parent") handle. For example, a virtual machine handle is obtained by calling a function that
operates on the server handle. A virtual device handle is obtained by calling a function that
operates on the virtual machine handle, and so forth. The Parallels C API Reference guide
contains a description of every available handle and explains how each particular handle type
can be obtained. The examples in this guide also demonstrate how to obtain handles of different
types.
Freeing a Handle
Parallels API handles are reference counted. Each handle contains a count of the number of
references to it held by other objects. A handle stays in memory for as long as the reference
count is greater than zero. A client application is responsible for freeing any handles that are no
longer needed. A handle can be freed using the PrlHandle_Free function. The function
decreases the reference count by one. When the count reaches zero, the object is destroyed.
Failing to free a handle after it has been used will result in a memory leak.
Multithreading
Parallels API handles are thread safe. They can be used in multiple threads at the same time. To
maintain the proper reference counting, the count should be increased each time a handle is
passed to another thread by calling the PrlHandle_AddRef function. If this is not done,
freeing a handle in one thread may destroy it while other threads are still using it.
Example
Page 21

Parallels C API Concepts 21
The following code snippet demonstrates how to obtain a handle, how to determine its type, and
how to free it when it's no longer needed. The code is a part of the bigger example that
demonstrates how to log in to a Parallels Service (the full example is provided later in this
guide).
PRL_HANDLE hServer = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT ret;
ret = PrlSrv_Create(&hServer);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlSvr_Create failed, error: %s",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
return PRL_ERR_FAILURE;
}
// Determine the type of the hServer handle.
PRL_HANDLE_TYPE nHandleType;
PrlHandle_GetType(hServer, &nHandleType);
printf("Handle type: %s\n",
handle_type_to_string(nHandleType));
// Free the handle when it is no longer needed.
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
Synchronous Functions
The Parallels C API provides synchronous and asynchronous functions. Synchronous functions
run in the same thread as the caller. When a synchronous function is called it completes
executing before returning control to the caller. Synchronous functions return PRL_RESULT,
which is a integer indicating success or failure of the operation. Consider the
PrlSrv_Create function. The purpose of this function is to obtain a handle of type
PHT_SERVER. The handle is required to access most of the functionality within the Parallels C
API. The syntax of PrlSrv_Create is as follows:
PRL_RESULT PrlSrv_Create(
PRL_HANDLE_PTR handle
);
The following is an example of the PrlSrv_Create function call:
// Declare a handle variable.
PRL_HANDLE hServer = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
// Call the PrlSrv_Create to obtain the handle.
PRL_RESULT res = PrlSrv_Create(&hServer);
// Examine the function return code.
// PRL_FAILED is a macro that evaluates a variable of type PRL_RESULT.
// A return value of True indicates success; False indicates failure.
if (PRL_FAILED(res))
{
printf("PrlSrv_Create returned error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(res));
exit(ret);
}
Page 22

Parallels C API Concepts 22
Asynchronous Functions
An asynchronous operation is executed in its own thread. An asynchronous function that started
the operation returns to the caller immediately without waiting for the operation to complete.
The results of the operation can be verified later when needed. Asynchronous functions return
PRL_HANDLE, which is a pointer to an integer and is a handle of type PHT_JOB. The handle is
used as a reference to the asynchronous job executed in the background. The general procedure
for calling an asynchronous function is as follows:
1 Register an event handler (callback function).
2 Call an asynchronous function.
3 Analyze the results of events (jobs) within the callback function.
4 Handle the appropriate event in the callback function.
5 Un-register the event handler when it is no longer needed.
The Callback Function (Event Handler)
Asynchronous functions return data to the caller by means of an event handler (or callback
function). The callback function could be called at any time, depending on how long the
asynchronous function takes to complete. The callback function must have a specific signature.
The prototype can be found in PrlApi.h and is as follows:
typedef PRL_METHOD_PTR(PRL_EVENT_HANDLER_PTR) (
PRL_HANDLE hEvent,
PRL_VOID_PTR data
);
The following is an example of the callback function implementation:
static PRL_RESULT OurCallback(PRL_HANDLE handle, void *pData)
{
// Event handler code...
// You must always release the handle before exiting.
PrlHandle_Free(handle);
}
A handle received by the callback function can be of type PHT_EVENT or PHT_JOB. The type
can be determined using the PrlHandle_GetType function. The PHT_EVENT type
indicates that the callback was called by a system event. If the type is PHT_JOB then the
callback was called by an asynchronous job started by the client.
To handle system events within a callback function:
1 Get the event type using PrlEvent_GetType.
2 Examine the event type. If it is relevant, a handle of type PHT_EVENT_PARAMETER can
be extracted using PrlEvent_GetParam.
3 Convert the PHT_EVENT_PARAMETER handle to the appropriate handle type using
PrlEvtPrm_ToHandle.
To handle jobs within a callback function:
Page 23

Parallels C API Concepts 23
1 Get the job type using PrlJob_GetType. A job type can be used to identify the function
that started the job and to determine the type of the result it contains. For example, a job of
type PJOC_SRV_GET_VM_LIST is started by PrlSrv_GetVmList function call,
which returns a list of virtual machines.
2 Examine the job type. If it is relevant, proceed to the next step.
3 Get the job return code using PrlJob_GetRetCode. If it doesn't contain an error,
proceed to the next step.
4 Get the result (a handle of type PHT_RESULT) from the job handle using
PrlJob_GetResult.
5 Get a handle to the result using PrlResult_GetParam. Note that some functions return
a list (ie. there can be more than a single parameter in the result). For example,
PrlSrv_GetVmList returns a list of available virtual machines. In such cases, use
PrlResult_GetParamCount and PrlResult_GetParamByIndex.
6 Implement code to use the handle obtained in step 5.
Note: You must always free the handle that was passed to the callback function before exiting,
regardless of whether you actually used it or not. Failure to do so will result in a memory leak.
The following skeleton code demonstrates implementation of the above steps. In this example,
the objective is to handle events of type PET_DSP_EVT_HOST_STATISTICS_UPDATED
that are generated by a call to function PrlSrv_SubscribeToHostStatistics, and to
obtain the result from a job of type PJOC_SRV_GET_VM_LIST.
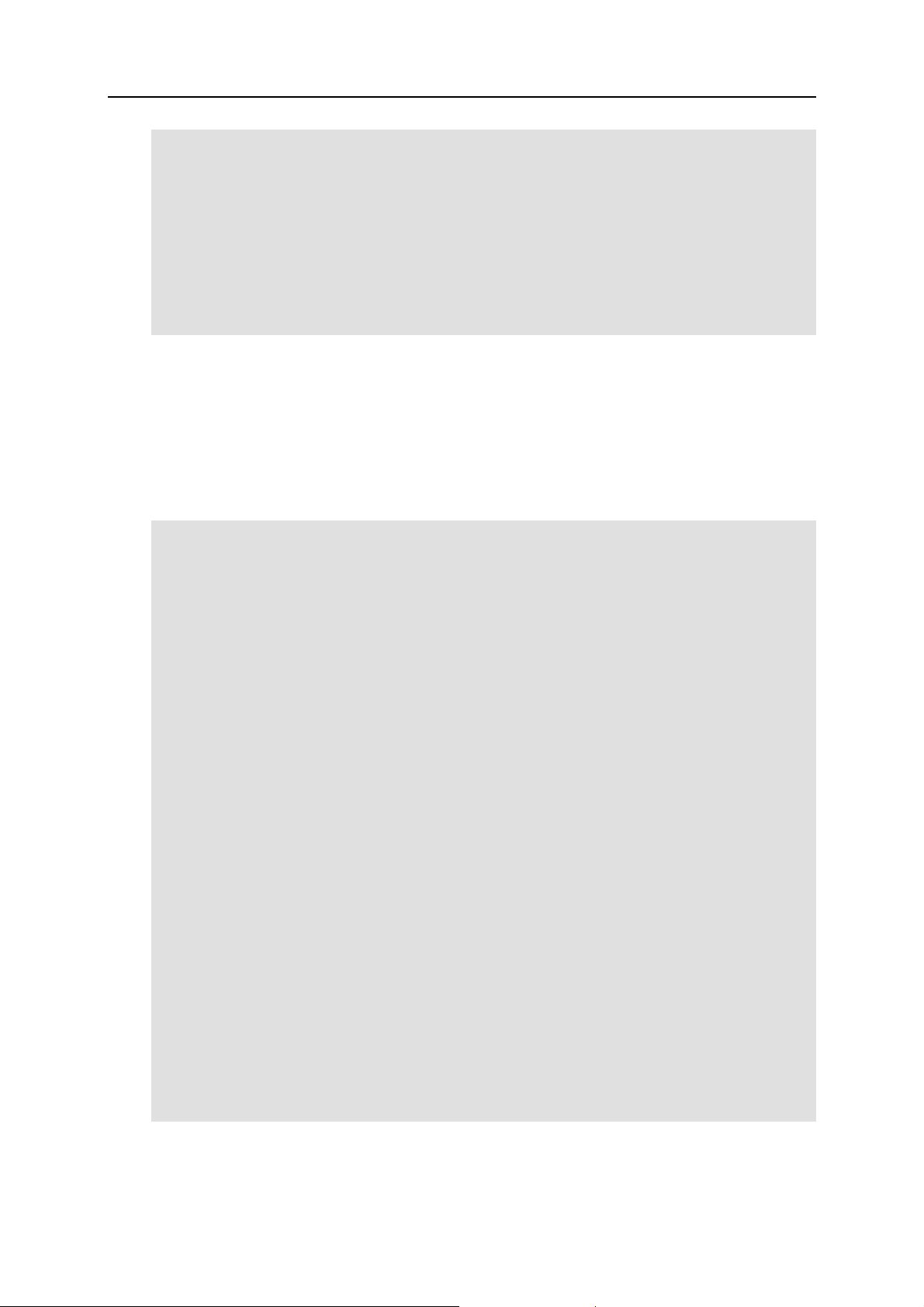
static PRL_RESULT OurCallbackFunction(PRL_HANDLE hHandle, PRL_VOID_PTR
pUserData)
{
PRL_JOB_OPERATION_CODE nJobType = PJOC_UNKNOWN; // job type
PRL_HANDLE_TYPE nHandleType = PHT_ERROR; // handle type
PRL_HANDLE hVm = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE; // virtual machine handle
PRL_HANDLE hParam = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE; // event parameter
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE; // job result
PRL_UINT32 nParamsCount = -1; // parameter count
PRL_UINT32 nParamIndex = -1; // parameter index
PRL_RESULT err = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED; // error
// Check the type of the received handle.
PrlHandle_GetType(hHandle, &nHandleType);
if (nHandleType == PHT_EVENT) // Event handle
{
PRL_EVENT_TYPE EventType;
PrlEvent_GetType(hHandle, &EventType);
// Check if the event type is a statistics update.
if (EventType == PET_DSP_EVT_HOST_STATISTICS_UPDATED)
{
// Get handle to PHT_EVENT_PARAMETER.
PRL_HANDLE hEventParameters = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PrlEvent_GetParam(hHandle, 0, &hEventParameters);
// Get handle to PHT_SYSTEM_STATISTICS.
PRL_HANDLE hServerStatistics = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PrlEvtPrm_ToHandle(hEventParameters, &hServerStatistics);
// Code goes here to extract the statistics data
// using hServerStatistics.
Page 24

Parallels C API Concepts 24
PrlHandle_Free(hServerStatistics);
PrlHandle_Free(hEventParameters);
}
}
else if (nHandleType == PHT_JOB) // Job handle
{
// Get the job type.
PrlJob_GetOpCode(hHandle, &nJobType);
// Check if the job type is PJOC_SRV_GET_VM_LIST.
if (nJobType == PJOC_SRV_GET_VM_LIST)
{
// Check the job return code.
PRL_RESULT nJobRetCode;
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hHandle, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "[B]%.8X: %s\n", nJobRetCode,
prl_result_to_string(nJobRetCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hHandle);
return nJobRetCode;
}
err = PrlJob_GetResult(hHandle, &hJobResult);
// if (err != PRL_ERR_SUCCESS), process the error here.
// Determine the number of parameters in the result.
PrlResult_GetParamsCount(hJobResult, &nParamsCount);
// Iterate through the parameter list.
for(nParamIndex = 0; nParamIndex < nParamsCount ; nParamIndex++)
{
// Obtain a virtual machine handle (PHT_VIRTUAL_MACHINE).
PrlResult_GetParamByIndex(hJobResult, nParamIndex, &hVm);
// Code goes here to obtain virtual machine info from hVm.
// Free the handle when done using it.
PrlHandle_Free(hVm);
}
PrlHandle_Free(hJobResult);
}
}
PrlHandle_Free(hHandle);
return PRL_ERR_SUCCESS;
}
Registering / Unregistering an Event Handler
The PrlSrv_RegEventHandler function is used to register an event handler,
PrlSrv_UnregEventHandler is used to unregister an event handler.
Note: When an event handler is registered, it will receive all of the events/jobs regardless of
their origin. It is the responsibility of the client application to identify the type of the event and
to handle each one accordingly.
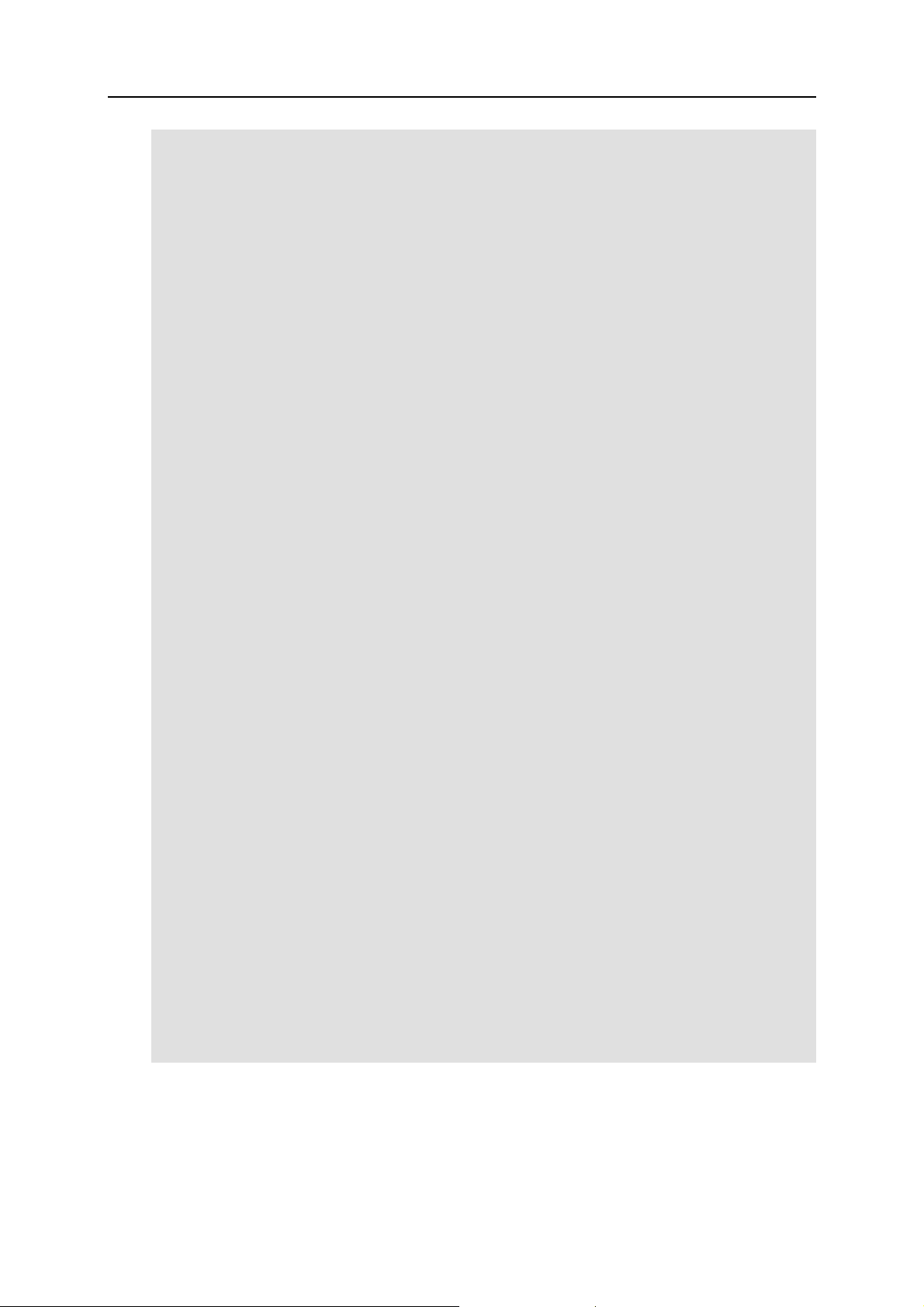
// Register an event handler.
ReturnDataClass rd; // some user-defined class.
PrlSrv_RegEventHandler(hServer, OurCallbackFunction, &rd);
// Make a call to an asynchronous function here.
// OurCallbackFunction will be called by the background thread
Page 25
Parallels C API Concepts 25
// as soon as the job is completed, and code within
// OurCallbackFunction can populate the ReturnDataClass instance.
// For example, we can make the following call here:
hJob = PrlSrv_GetVmList(hServer);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
// Please note that we still have to obtain the
// job object (hJob above) and free it; otherwise
// we will have memory leaks.
// Unregister the event handler when it is no longer needed.
PrlSrv_UnregEventHandler(hServer, OurCallbackFunction, &rd);
Calling Asynchronous Functions Synchronously
It is possible to call an asynchronous function synchronously by using the PrlJob_Wait
function. The function takes two parameters: a PHT_JOB handle and a timeout value in
milliseconds. Once you call the function, the main thread will be suspended and the function
will wait for the asynchronous job to complete. The function will return when the job is
completed or when timeout value is reached, whichever comes first. The following code snippet
illustrates how to call an asynchronous function PrlServer_Login synchronously:
// Log in (PrlSrv_Login is asynchronous).
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PrlSrv_Login(
hServer,
szHostnameOrIpAddress,
szUsername,
szPassword,
0,
0,
0,
PSL_LOW_SECURITY);
// Wait for a maximum of 10 seconds for
// asynchronous function PrlSrv_Login to complete.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 10000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlJob_Wait for PrlSrv_Login returned with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
return -1;
}
// Analyse the result of the PrlServer_Login call.
PRL_RESULT nJobResult;
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobResult);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobResult))
{
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
printf("Login job returned with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(nJobResult));
return -1;
}
else
{
printf("login successfully performed\n");
}
Page 26

Parallels C API Concepts 26
Strings as Return Values
Sting values in the Parallels C API are received by passing a char pointer to a function which
populates it with data. It is the responsibility of the caller to allocate the memory required to
receive the value, and to free it when it is no longer needed. Since in most cases we don't know
the string size in advance, we have to either allocate a chunk of memory large enough for any
possible value or to determine the exact required size. To determine the required buffer size, the
following two approaches can be used:
1 Calling the same function twice: first, to obtain the required buffer size, and second, to
receive the actual string value. To get the required buffer size, call the function passing a
null pointer as a value of the output parameter, and pass 0 (zero) as a value of the variable
that is used to specify the buffer size. The function will calculate the required size and will
populate the variable with the correct value, which you can use to initialize a variable that
will receive the string. You can then call the function again to get the actual string value.
2 It is also possible to use a static buffer. If the length of the buffer is large enough, you will
simply receive the result. If the length is too small, a function will fail with the
PRL_ERR_BUFFER_OVERRUN error but it will populate the "buffer_size" variable with
the required size value. You can then allocate the memory using the received value and call
the function again to get the results.
Consider the following function:
PRL_RESULT PrlVmCfg_GetName(
PRL_HANDLE hVmCfg,
PRL_STR sVmName,
PRL_UINT32_PTR pnVmNameBufLength
);
The PrlVmCfg_GetName function above is a typical Parallels API function that returns a
string value (in this case, the name of a virtual machine). The hVmCfg parameter is a handle to
an object containing the virtual machine configuration information. The sVmName parameter is
a char pointer. It is used as output that receives the virtual machine name. The variable must
be initialized on the client side with enough memory allocated for the expected string. The size
of the buffer must be specified using the pnVmNameBufLength variable.
The following example demonstrates how to call the function using the first approach:
PRL_RESULT ret;
PRL_UINT32 nBufSize = 0;
// Get the required buffer size.
ret = PrlVmCfg_GetName(hVmCfg, 0, &nBufSize);
// Allocate the memory.
PRL_STR pBuf = (PRL_STR)malloc(sizeof(PRL_CHAR) * nBufSize);
// Get the virtual machine name.
ret = PrlVmCfg_GetName(hVmCfg, pBuf, &nBufSize);
printf("VM name: %s\n", pBuf);
// Deallocate the memory.
free(pBuf);
Page 27

Parallels C API Concepts 27
The following example uses the second approach. To test the buffer-overrun scenario, set the
sVmName array size to some small number.
#define MY_STR_BUF_SIZE 1024
PRL_RESULT ret;
char sVmName[MY_STR_BUF_SIZE];
PRL_UINT32 nBufSize = MY_STR_BUF_SIZE;
// Get the virtual machine name.
ret = PrlVmCfg_GetName(hVmCfg, sVmName, &nBufSize);
// Check for errors.
if (PRL_SUCCEEDED(ret))
{
// Everything's OK, print the machine name.
printf("VM name: %s\n", sVmName);
}
else if (ret == PRL_ERR_BUFFER_OVERRUN)
{
// The sVmName array size is too small.
// Get the required size, allocate the memory,
// and try getting the VM name again.
PRL_UINT32 nSize = 0;
PRL_STR pBuf;
// Get the required buffer size.
ret = PrlVmCfg_GetName(hVmCfg, 0, &nSize);
// Allocate the memory.
pBuf = (PRL_STR)malloc(sizeof(PRL_CHAR) * nSize);
// Get the virtual machine name.
ret = PrlVmCfg_GetName(hVmCfg, pBuf, &nSize);
printf("VM name: %s\n", pBuf);
// Dallocate the memory.
free(pBuf);
}
Page 28
Parallels C API Concepts 28
Error Handling
Synchronous Functions
All synchronous Parallels C API functions return PRL_RESULT, which is an integer indicating
success or failure of the operation.
Error Codes for Asynchronous Functions
All asynchronous functions return PRL_HANDLE. The error code (return value) in this case can
be extracted with PrlJob_GetRetCode after the asynchronous job has finished.
Analyzing Return Values
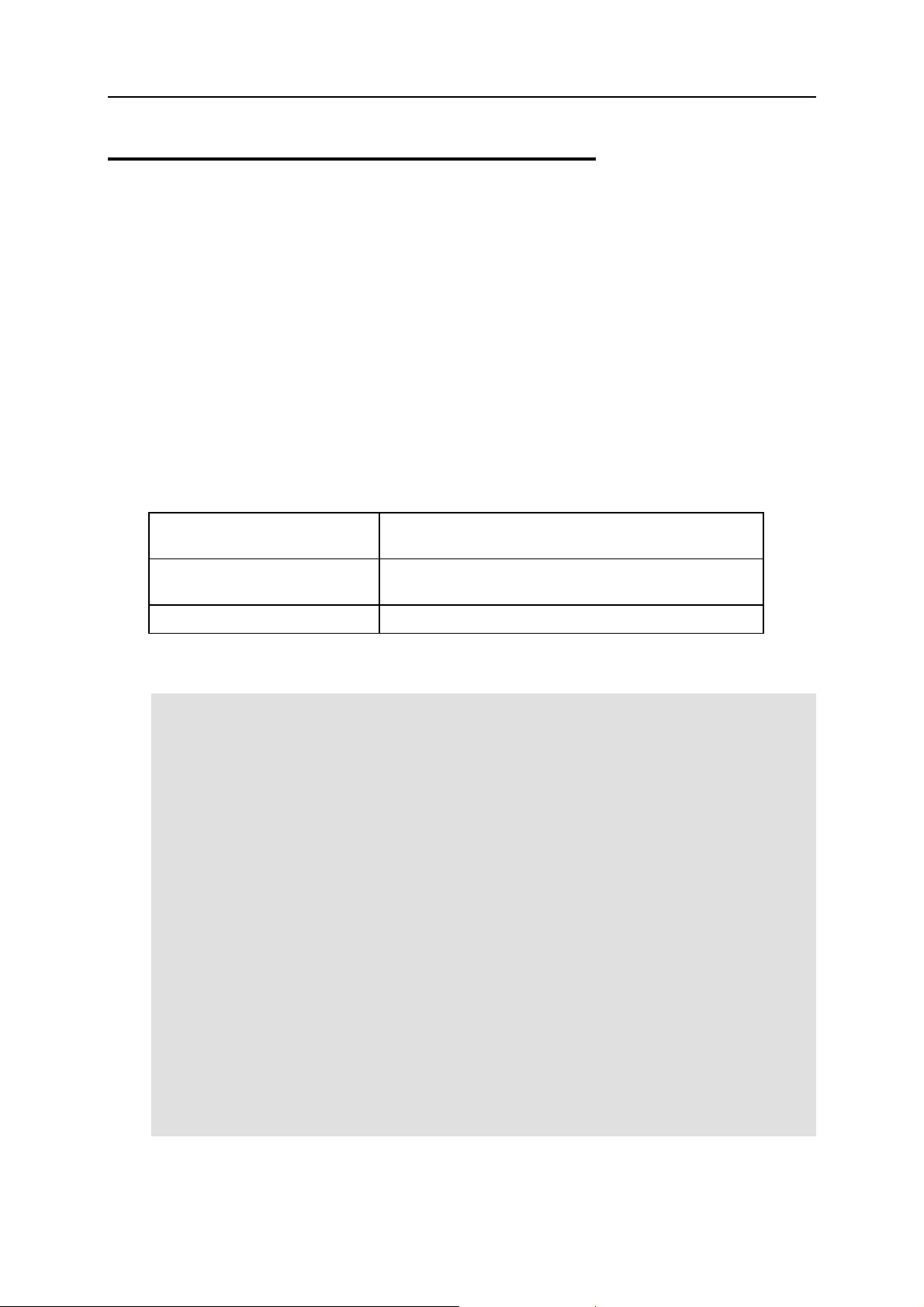
Parallels C API provides the following macros to work with error codes:
PRL_FAILED
Returns True if the return value indicates failure, or False if
the return value indicates success.
PRL_SUCCEEDED
Returns True if the return value indicates success, or False
if the return value indicates failure.
prl_result_to_string
Returns a string representation of the error code.
The following code snippet attempts to create a directory on the host and analyzes the return
value (error code) of asynchronous function PrlSrv_CreateDir.
// Attempt to create directory /tmp/TestDir on the host.
char *szRemoteDir = "/tmp/TestDir";
hJob = PrlSrv_FsCreateDir(hServer, szRemoteDir);
// Wait for a maximum of 5 seconds for asynchronous
// function PrlSrv_FsCreateDir to complete.
PRL_RESULT resWaitForCreateDir = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 5000);
if (PRL_FAILED(resWaitForCreateDir))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlJob_Wait for PrlSvr_FsCreateDir failed with error:
%s\n",
prl_result_to_string(resWaitForCreateDir));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Extract the asynchronous function return code.
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobResult);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobResult))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error creating directory %s. Error returned: %s\n",
szRemoteDir, prl_result_to_string(nJobResult));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
PrlHandle_Free( hJob );
printf( "Remote directory %s was successfully created.\n", szRemoteDir );
Descriptive Error Strings
Page 29
Parallels C API Concepts 29
Descriptive error messages can sometimes be obtained using the PrlJob_GetError
function. This function will return a handle to an object of type PHT_EVENT. In cases where
PrlJob_GetError is unable to return error information,
PrlApi_GetResultDescription can be used. Although it is possible to avoid using
PrlJob_GetError and use PrlJob_GetResultDescription instead, it is
recommended to first use PrlJob_GetError, and if this doesn't return additional descriptive
error information then use PrlApi_GetResultDescription. The reason is that
sometimes errors contain dynamic parameters. The following example demonstrates how to
obtain descriptive error information:
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobResult);
PRL_CHAR szErrBuff[1024];
PRL_UINT32 nErrBuffSize = sizeof(szErrBuff);
PRL_HANDLE hError = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT ret = PrlJob_GetError(hJob, &hError);
// Check if additional error information is available.
if (PRL_SUCCEEDED(ret)) // Additional error information is available.
{
// Additional error information is available.
ret = PrlEvent_GetErrString(hError, PRL_FALSE, PRL_FALSE, szErrBuff,
&nErrBuffSize);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
printf("PrlEvent_GetErrString returned error: %.8x %s\n",
ret, prl_result_to_string(ret));
}
else
{
// Extra error information is available, display it.
printf("Error returned: %.8x %s\n", nJobResult,
prl_result_to_string(nJobResult));
printf("Descriptive error: %s\n", szErrBuff);
}
}
else
{
// No additional error information available, so use
PrlApi_GetResultDescription.
ret = PrlApi_GetResultDescription(nJobResult, PRL_FALSE, PRL_FALSE,
szErrBuff, &nErrBuffSize);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
printf("PrlApi_GetResultDescription returned error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
}
else
{
printf("Error returned: %.8x %s\n", nJobResult,
prl_result_to_string(nJobResult));
printf("Descriptive error: %s\n", szErrBuff);
}
}
// Free handles, return the error code.
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hError);
return nJobResult;
}
Page 30

C HAPTER 3
Parallels C API by Example
In This Chapter
Obtaining Server Handle and Logging In............................................................................. 31
Host Operations..................................................................................................................... 35
Virtual Machine Operations.................................................................................................. 58
Events.................................................................................................................................... 110
Performance Statistics........................................................................................................... 121
Encryption Plug-in................................................................................................................ 130
Page 31

C HAPTER 4
Obtaining Server Handle and Logging In
The following steps are required in any client application using the Parallels C API:
1 Load the Parallels Virtualization SDK library using the SdkWrap_Load function.
2 Initialize the API using the PrlApi_InitEx function. The API must be initialized
properly for the given Parallels product, such as Parallels Server, Parallels Workstation,
Parallels Desktop, etc. The initialization mode is determined by the value of the nAppMode
parameter passed to the PrlApi_InitEx function. The value must be one of the
enumerators from the PRL_APPLICATION_MODE enumeration.
3 Create a server handle using the PrlSrv_Create function.
4 Call PrlSrv_LoginLocal or PrlSrv_Login to login to the Parallels Virtualization
Service (or simply Parallels Service). Parallels Service is a combination of processes
running on the host machine that comprise the Parallels virtualization product. The first
function is used when the client program and the target Parallels Service are running on the
same host. The second function (PrlSrv_Login) is used to log in to a remote Parallels
Service. Please note that remote login is supported in Parallels Server-based virtualization
products only.
If the above steps are executed without errors, the handle created in step 3 will reference a
server object (a handle of type PHT_SERVER) identifying the Parallels Service. A handle to a
valid server object is required to access most of the functionality within the Parallels C API. The
PrlSrv_LoginLocal function (step 4) establishes a connection with a specified Parallels
Service and performs a login operation using the specified credentials. The function operates on
the server object created in step 3. Upon successful login, the object can be used to perform
other operations.
To end the session with the Parallels Service, the following steps must be performed before
exiting the application:
1 Call PrlSrv_Logoff to log off the Parallels Service.
2 Free the server handle using PrlHandle_Free.
3 Call PrlApi_Deinit to de-initialize the library.
4 Call SdkWrap_Unload to unload the API.
Example
The following sample functions demonstrates how to perform the steps described above.
// Intializes the SDK library and
// logs in to the local Parallels Service.
// Obtains a handle of type PHT_SERVER identifying
// the Parallels Service.
PRL_RESULT LoginLocal(PRL_HANDLE &hServer)
Page 32

Parallels C API by Example 32
{
// Variables for handles.
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE; // job handle
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE; // job result
// Variables for return codes.
PRL_RESULT err = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Use the correct dynamic library depending on the platform.
#ifdef _WIN_
#define SDK_LIB_NAME "prl_sdk.dll"
#elif defined(_LIN_)
#define SDK_LIB_NAME "libprl_sdk.so"
#elif defined(_MAC_)
#define SDK_LIB_NAME "libprl_sdk.dylib"
#endif
// Load SDK library.
if (PRL_FAILED(SdkWrap_Load(SDK_LIB_NAME)) &&
PRL_FAILED(SdkWrap_Load("./" SDK_LIB_NAME)))
{
fprintf( stderr, "Failed to load " SDK_LIB_NAME "\n" );
return -1;
}
// Initialize the API. In this example, we are initializing the
// API for Parallels Workstation.
// To initialize in the Parallels Desktop mode, pass PAM_DESKTOP
// as the second parameter.
// To initialize for Parallels Server, pass PAM_SERVER.
// See the PRL_APPLICATION_MODE enumeration for all possible options.
//
err = PrlApi_InitEx(PARALLELS_API_VER, PAM_WORKSTATION, 0, 0);
if (PRL_FAILED(err))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlApi_InitEx returned with error: %s.\n",
prl_result_to_string(err));
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
// Create a server handle (PHT_SERVER).
err = PrlSrv_Create(&hServer);
if (PRL_FAILED(err))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlSvr_Create failed, error: %s",
prl_result_to_string(err));
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
// Log in (asynchronous call).
hJob = PrlSrv_LoginLocal(hServer, NULL, NULL, PSL_NORMAL_SECURITY);
// Wait for a maximum of 10 seconds for
// the job to complete.
err = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(err))
{
fprintf(stderr,
"PrlJob_Wait for PrlSrv_Login returned with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(err));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
Page 33

Parallels C API by Example 33
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
// Analyze the result of PrlSrv_Login.
err = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
// First, check PrlJob_GetRetCode success/failure.
if (PRL_FAILED(err))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlJob_GetRetCode returned with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(err));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
// Now check the Login operation success/failure.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
printf("Login job returned with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(nJobReturnCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
else
{
printf( "Login was successful.\n" );
}
return 0;
}
// Log off the Parallels Service and
// deinitializes the SDK library.
//
PRL_RESULT LogOff(PRL_HANDLE &hServer)
{
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT err = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Log off.
hJob = PrlSrv_Logoff(hServer);
err = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(err))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlJob_Wait for PrlSrv_Logoff returned error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(err));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
Page 34

Parallels C API by Example 34
// Get the Logoff operation return code.
err = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
// Check the PrlJob_GetRetCode success/failure.
if (PRL_FAILED(err))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlJob_GetRetCode failed for PrlSrv_Logoff with
error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(err));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
// Report success or failure of PrlSrv_Logoff.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlSrv_Logoff failed with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(nJobReturnCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
else
{
printf( "Logoff was successful.\n" );
}
// Free handles that are no longer required.
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
// De-initialize the Parallels API, and unload the SDK.
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return 0;
}
Page 35

C HAPTER 5
Host Operations
This chapter describes the common tasks that can be performed on the host.
In This Chapter
Retrieving Host Configuration Information.......................................................................... 36
Managing Parallels Service Preferences............................................................................... 39
Searching for Parallels Servers ............................................................................................. 42
Managing Parallels Service Users......................................................................................... 45
Managing Files In The Host OS............................................................................................ 50
Managing Licenses ............................................................................................................... 53
Obtaining a Problem Report..................................................................................................56
Page 36

Parallels C API by Example 36
Retrieving Host Configuration Information
The Parallels C API provides a set of functions to retrieve detailed information about a host
machine. This includes:
CPU(s) - number of, mode, model, speed.
Devices - disk drives, network interfaces, ports, sound.
Operating system - type, version, etc.
Memory (RAM) size.
This information can be used when modifying Parallels Service preferences, setting up devices
inside virtual machines, or whenever you need to obtain information about the resources
available on the physical host.
To retrieve this information, first obtain a handle of type PHT_SERVER_CONFIG and then use
its functions to get information about a particular resource. The following sample function
demonstrates how it is accomplished. The function accepts the hServer parameter which is a
server handle. For the example on how to obtain a server handle, see Obtaining Server Handle
and Logging In (p. 31).
PRL_RESULT GetHostConfig(PRL_HANDLE hServer)
{
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hHostConfig = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// An asynchronous call that obtains a handle
// of type PHT_SERVER_CONFIG.
hJob = PrlSrv_GetSrvConfig(hServer);
// Wait for the job to complete.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Analyze the result of PrlSrv_GetSrvConfig.
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Get the job return code.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Get job result.
ret = PrlJob_GetResult(hJob, &hJobResult);
Page 37

Parallels C API by Example 37
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Get the PHT_SERVER_CONFIG handle.
ret = PrlResult_GetParam(hJobResult, &hHostConfig);
PrlHandle_Free(hJobResult);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Obtain the individual configuration setting.
printf("\nHost Configuration Information: \n\n");
// Get CPU count.
PRL_UINT32 nCPUcount = 0;
ret = PrlSrvCfg_GetCpuCount(hHostConfig, &nCPUcount);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hHostConfig);
return -1;
}
printf("CPUs: %d\n", nCPUcount);
// Get host OS type.
PRL_HOST_OS_TYPE nHostOsType;
ret = PrlSrvCfg_GetHostOsType(hHostConfig, &nHostOsType);
// if (PRL_FAILED(ret)) { handle the error... }
printf("OS Type: %d\n", nHostOsType);
// Get host RAM size.
PRL_UINT32 nHostRamSize;
ret = PrlSrvCfg_GetHostRamSize(hHostConfig, &nHostRamSize);
// if (PRL_FAILED(ret)) { handle the error... }
printf("RAM: %d MB\n", nHostRamSize);
// Get the network adapter info.
// First get the net adapter count.
PRL_UINT32 nNetAdaptersCount = 0;
ret = PrlSrvCfg_GetNetAdaptersCount(hHostConfig,
&nNetAdaptersCount);
// if (PRL_FAILED(ret)) { handle the error... }
// Now iterate through the list and get the info
// about each adapter.
printf("\n");
for (PRL_UINT32 i = 0; i < nNetAdaptersCount; ++i)
{
printf("Net Adapter %d\n", i+1);
// Obtains a handle of type PHT_HW_NET_ADAPTER.
PRL_HANDLE phDevice = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
ret = PrlSrvCfg_GetNetAdapter(hHostConfig, i, &phDevice);
// Get adapter type (physical, virtual).
Page 38

Parallels C API by Example 38
PRL_HW_INFO_NET_ADAPTER_TYPE nNetAdapterType;
ret = PrlSrvCfgNet_GetNetAdapterType(phDevice,
&nNetAdapterType);
printf("Type: %d\n", nNetAdapterType);
// Get system adapter index.
PRL_UINT32 nIndex = 0;
ret = PrlSrvCfgNet_GetSysIndex(phDevice, &nIndex);
printf("Index: %d\n\n", nIndex);
}
PrlHandle_Free(hHostConfig);
return 0;
}
Page 39

Parallels C API by Example 39
Managing Parallels Service Preferences
Parallels Service preferences is a set of parameters that control its default behaviour. Some of
the important parameters are:
Memory limits for the Parallels Service itself.
Memory limits and recommended values for virtual machines.
Virtual network adapter information.
Default virtual machine directory (the directory where all new virtual machines are created
by default).
Communication security level.
Parallels Service preferences are managed using the PHT_DISP_CONFIG handle which is
obtained using the PrlSrv_GetCommonPrefs function. For the complete list of functions
provided by the PHT_DISP_CONFIG object, see the Parallels C API Reference guide.
The following sample function demonstrates how to obtain a handle of type
PHT_DISP_CONFIG and how to use its functions to retrieve and modify some of the Parallels
Service preferences. The function accepts the hServer parameter which is a server handle. For
the example on how to obtain a server handle, see Obtaining Server Handle and Logging In (p.
31).
PRL_RESULT GetSetServicePrefs(PRL_HANDLE hServer)
{
// Variables for handles.
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hDispConfig = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
// Variables for return codes.
PRL_RESULT ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// An asynchronous call that obtains a handle
// of type PHT_DISP_CONFIG.
hJob = PrlSrv_GetCommonPrefs(hServer);
// Wait for the job to complete.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Analyze the result of PrlSrv_GetCommonPrefs.
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Get the job return code.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
Page 40

Parallels C API by Example 40
return -1;
}
// Get job result.
ret = PrlJob_GetResult(hJob, &hJobResult);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Get the PHT_DISP_CONFIG handle.
ret = PrlResult_GetParam(hJobResult, &hDispConfig);
PrlHandle_Free(hJobResult);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Get the default virtual machine directory.
char sDefaultDir[1024];
PRL_UINT32 nBufSize = sizeof(sDefaultDir);
ret = PrlDispCfg_GetDefaultVmDir(hDispConfig,
sDefaultDir, &nBufSize);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hDispConfig);
return -1;
}
printf("Parallels Service Preferences \n\n");
printf("Default VM Directory: %s\n", sDefaultDir);
// Get the recommended virtual machine memory size.
PRL_UINT32 nMemSize = 0;
ret = PrlDispCfg_GetRecommendMaxVmMem(hDispConfig, &nMemSize);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hDispConfig);
return -1;
}
printf("Recommended VM memory size: %d\n", nMemSize);
// Modify some of the Parallels Service preferences.
// Begin edit.
hJob = PrlSrv_CommonPrefsBeginEdit(hServer);
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hDispConfig);
return -1;
}
// Get the "begin edit" operation success code.
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
Page 41

Parallels C API by Example 41
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hDispConfig);
return -1;
}
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(nJobReturnCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hDispConfig);
return -1;
}
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
// Modify the recommended virtual machine memory size.
nMemSize = 512;
ret = PrlDispCfg_SetRecommendMaxVmMem(hDispConfig, nMemSize);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hDispConfig);
return -1;
}
// Commit the changes.
hJob = PrlSrv_CommonPrefsCommit(hServer, hDispConfig);
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hDispConfig);
return -1;
}
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hDispConfig);
return -1;
}
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(nJobReturnCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hDispConfig);
return -1;
}
printf("The recommended VM memory size changed to: %d\n", nMemSize);
PrlHandle_Free(hDispConfig);
return 0;
}
Page 42

Parallels C API by Example 42
Searching for Parallels Servers
This topic applies to Parallels Server only.
If you have multiple Parallels Servers running on your network and don't know their exact
locations and/or connection parameters, you can search for them using the
PrlSrv_LookupParallelsServers function. The function returns the information as a
list of handles of type PHT_SERVER_INFO, each containing the information about an
individual Parallels Server. The information includes host name, port number, version of the OS
that a host is running, Parallels Server version number, and the global ID (UUID). This
information can then be used to establish a connection with the Parallels Server of interest (you
will have to know the correct user name and password in addition to the returned parameters).
The PrlSrv_LookupParallelsServers function can be executed asynchronously using
the callback functionality or it can be used synchronously. To use the function asynchronously,
you must implement a callback function first. The callback function pointer must then be passed
to the PrlSrv_LookupParallelsServers as a parameter. During the search operation,
the callback function will be called for every Parallels Server found and a handle of type
PHT_SERVER_INFO containing the Parallels Server information will be passed to it.
Searching an entire local area network can take a significant time, so using a callback is the
recommended approach.
To use the PrlSrv_LookupParallelsServers function synchronously, pass a null
pointer instead of the callback function pointer, and use PrlJob_Wait to wait for the job to
complete. The returned job object will contain a list of PHT_SERVER_INFO objects.
Note: The PrlSrv_LookupParallelsServers function can be executed without being
logged in to a Parallels Service. For example, if you are writing an application with a user
interface, you can search the network for available Parallels Servers and present the list to the
user so that he/she can select a server to connect to.
The following sample functions demonstrate how to search local network for Parallels Servers.
The first sample function calls the PrlSrv_LookupParallelsServers function
synchronously. The second function takes an asynchronous approach.
PRL_RESULT SearchServersSynch()
{
// Variables for handles.
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE; // job handle
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE; // job result
PRL_HANDLE hHostConfig = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE; // PHT_SERVER_CONFIG
// Variables for return codes.
PRL_RESULT ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Search for Parallels servers.
hJob = PrlSrv_LookupParallelsServers(
1000, // timeout
NULL, // callback function (not used)
NULL // user object pointer (not used)
);
// Wait for the job to complete.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 10000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
Page 43

Parallels C API by Example 43
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s. \n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
return -1;
}
// Analyze the result of PrlSrv_LookupParallelsServers.
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Get the job return code.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Get job result.
ret = PrlJob_GetResult(hJob, &hJobResult);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Get the number of objects returned.
PRL_UINT32 nCount = 0;
PrlResult_GetParamsCount(hJobResult, &nCount);
// Iterate and a obtain handle to each object.
for (PRL_UINT32 i = 0; i < nCount ; ++i)
{
PRL_HANDLE hParam = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PrlResult_GetParamByIndex(hJobResult, i, &hParam);
PRL_CHAR sBuf[1024];
PRL_UINT32 nBufSize = sizeof(sBuf);
// Get the host name.
ret = PrlSrvInfo_GetHostName(hParam, sBuf, &nBufSize);
if (PRL_SUCCEEDED(ret))
{
printf("Found Parallels Server: %s\n", sBuf);
}
else
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s \n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
}
PrlHandle_Free(hParam);
}
}
In the following example, the PrlSrv_LookupParallelsServers is called
asynchronously. In order to that, we first have to implement a callback function (we'll call it
ourCallback):
Page 44

Parallels C API by Example 44
static PRL_RESULT ourCallback(PRL_HANDLE hEvent, PRL_VOID_PTR pUserData)
{
printf("%s: ", pUserData);
// Get the host name.
PRL_UINT32 nBufSize = 1024;
PRL_CHAR sBuf[nBufSize];
PrlSrvInfo_GetHostName(hEvent, sBuf, &nBufSize);
// Get the other server properties and process them here, if needed...
// The handle must be freed.
PrlHandle_Free(hEvent);
return rc;
}
The PrlSrv_LookupParallelsServers function can now be called as follows:
hJob = PrlSrv_LookupParallelsServers(
1000,
&ourCallback,
(PRL_VOID_PTR)("callback"));
Page 45

Parallels C API by Example 45
Managing Parallels Service Users
This topic applies to Parallels Server only.
Parallels Service doesn't have its own user database. It performs user authentication against the
host operating system user database. However, it has a user registry where the user information
that relates to Parallels Service operations is kept. The information includes user UUID
(Universally Unique ID), user name, the name and path of the virtual machine directory for the
user, and two flags indicating if a user is allowed to modify server preferences and use
management console application. A new user record is created in the registry for every user as
soon as he/she logs in to a Parallels Service for the very first time.
There are two API handles that are used to obtain information about Parallels Service users and
to modify some of the user profile parameters. These handles are PHT_USER_INFO and
PHT_USER_PROFILE. Both handles are containers that contain information about a user. The
difference between the two is PHT_USER_PROFILE is used to obtain information about
currently logged in user while PHT_USER_INFO is used to obtain information about a
specified user. There are also some differences in the type of the information provided.
Getting the information about the currently logged in user
The information about the currently logged in user can be retrieved using functions of the
PHT_USER_PROFILE handle. The following sample demonstrates how to obtain the handle
and how to use its functions to retrieve user information. The sample also shows how to set up a
default virtual machine directory for the user. Parallels Service automatically assigns a default
virtual machine directory (the directory where new virtual machines are created) for every new
user. If needed, a user can specify a different directory for his/her virtual machines. At the time
of this writing, this is the only property of the Parallels Service user profile that can be
modified. Every user profile modification must begin with the
PrlSrv_UserProfileBeginEdit function call and end with the
PrlSrv_UserProfileCommit call. These two functions are used to prevent collisions with
other clients trying to modify the same user profile at the same time.
PRL_RESULT UserProfileSample(const PRL_HANDLE &hServer)
{
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hUserProfile = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Get user info from the server.
hJob = PrlSrv_GetUserProfile(hServer);
// Wait for the job to complete.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Analyze the result of PrlSrv_GetUserProfile.
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
Page 46

Parallels C API by Example 46
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Check the job return code.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Get job result.
ret = PrlJob_GetResult(hJob, &hJobResult);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Get the user profile handle (PHT_USER_PROFILE) from
// the result.
ret = PrlResult_GetParam(hJobResult, &hUserProfile);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJobResult);
return -1;
}
// Free job result handle.
PrlHandle_Free(hJobResult);
// See if the user is allowed to modify
// the Parallels server preferences.
PRL_BOOL bCanChange = PRL_FALSE;
ret = PrlUsrCfg_CanChangeSrvSets(hUserProfile, &bCanChange);
printf("Can modify server preferences: %d\n", bCanChange);
// See if the user is allowed to use management
// console application.
ret = PrlUsrCfg_CanUseMngConsole(hUserProfile, &bCanChange);
printf("Can use management console: %d\n", bCanChange);
// Get the default virtual machine folder
// for the user.
PRL_CHAR sBufFolder[1024];
PRL_UINT32 nBufSize = sizeof(sBufFolder);
ret = PrlUsrCfg_GetDefaultVmFolder(hUserProfile, sBufFolder, &nBufSize);
// If sBufFolder contains an empty string then this user
// does not have a default virtual machine folder and is
// currently using the default virtual machine folder set
// for this Parallels server. If this is the case, retrieve
// that folder.
if (sBufFolder == "")
{
ret = PrlUsrCfg_GetVmDirUuid(hUserProfile, sBufFolder, &nBufSize);
}
printf("VM folder: %s\n", sBufFolder);
// Modify the name and location of the virtual
// machine folder.
// This operation must begin with the
// PrlSrv_UserProfileBeginEdit that marks the
Page 47

Parallels C API by Example 47
// beginning of the operation. This is done to
// prevent collisions with other sessions trying to
// modify the same profile at the same time.
hJob = PrlSrv_UserProfileBeginEdit(hServer);
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Analyze the result of PrlSrv_UserProfileBeginEdit.
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Check the job return code.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Set the new virtual machine folder.
// The folder must already exist on the server.
ret = PrlUsrCfg_SetDefaultVmFolder(hUserProfile,
"/Users/Shared/Parallels/JDoe");
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hUserProfile);
return -1;
}
// Finally, commit the changes to the server.
hJob = PrlSrv_UserProfileCommit(hServer, hUserProfile);
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Analyze the result of PrlSrv_UserProfileCommit.
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Check the job return code.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
PrlHandle_Free(hUserProfile);
}
Getting the information about a particular user
Page 48

Parallels C API by Example 48
The information about a particular Parallels Service user can be obtained using the functions of
the PHT_USER_INFO handle. The handle can be obtain using one of the following functions:
PrlSrv_GetUserInfo or PrlSrv_GetUserInfoList. The first function takes the user
UUID as an input parameter and returns a single handle of type PHT_USER_INFO containing
the user information. The second function returns information about all users that exist in the
Parallels Service user registry. The information is returned as a list of handles of type
PHT_USER_INFO.
The following sample uses the PrlSrv_GetUserInfoList function to obtain information
about all users in the Parallels Service user registry. It then iterates through the returned list of
PHT_USER_INFO handles and retrieves information about individual users.
PRL_RESULT UserInfoSample(const PRL_HANDLE &hServer)
{
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hUserInfo = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Get user info from the Parallels Service.
hJob = PrlSrv_GetUserInfoList(hServer);
// Wait for the job to complete.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Analyze the result of PrlSrv_GetUserInfoList.
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Check the job return code.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Get job result.
ret = PrlJob_GetResult(hJob, &hJobResult);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Get parameter count (the number of PHT_USER_INFO
// handles in the result set).
PRL_UINT32 nParamCount = 0;
ret = PrlResult_GetParamsCount(hJobResult, &nParamCount);
// Iterate through the list obtaining
Page 49

Parallels C API by Example 49
// a handle of type PHT_USER_INFO for
// each user.
for (PRL_UINT32 i = 0; i < nParamCount; ++i)
{
ret = PrlResult_GetParamByIndex(hJobResult, i, &hUserInfo);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Get user UUID.
PRL_CHAR sBufID[1024];
PRL_UINT32 nBufSize = sizeof(sBufID);
ret = PrlUsrInfo_GetUuid(hUserInfo, sBufID, &nBufSize);
printf("UUID: %s\n", sBufID);
// Get user name.
PRL_CHAR sBufName[1024];
nBufSize = sizeof(sBufName);
PrlUsrInfo_GetName(hUserInfo, sBufName, &nBufSize);
printf("Name: %s\n", sBufName);
// Get default virtual machine folder
// for the user.
PRL_CHAR sBufFolder[1024];
nBufSize = sizeof(sBufFolder);
PrlUsrInfo_GetDefaultVmFolder(hUserInfo, sBufFolder, &nBufSize);
printf("VM folder: %s\n", sBufFolder);
// See if the user is allowed to modify
// the Parallels server preferences.
PRL_BOOL bCanChange = PRL_FALSE;
PrlUsrInfo_CanChangeSrvSets(hUserInfo, &bCanChange);
printf("Can modify server preferences: %d\n\n", bCanChange);
PrlHandle_Free(hUserInfo);
}
PrlHandle_Free(hJobResult);
}
Page 50

Parallels C API by Example 50
Managing Files In The Host OS
The following file management operations can be performed using the Parallels C API on the
host machine:
Obtaining a directory listing.
Creating directories.
Automatically generate unique names for new file system entries.
Rename file system entries.
Delete file system entries.
The file management functionality can be accessed through the PHT_SERVER handle. The file
management functions are prefixed with "PrlSrv_Fs".
Obtaining the host OS directory listing
The directory listing is obtained using the PrlSrv_FsGetDirEntries function. The
function returns a handle of type PHT_REMOTE_FILESYSTEM_INFO containing the
information about the specified file system entry and its immediate child entries (if any). The
child entries are returned as a list of handles of type PHT_REMOTE_FILESYSTEM_ENTRY
which is included in the PHT_REMOTE_FILESYSTEM_INFO object. The sample function
below demonstrates how to obtain a listing for the specified directory. On initial call, the
function obtains a list of child entries (files and sub-directories) for the specified directory and is
then called recursively for each file system entry returned. On completion, the entire directory
tree will be displayed on the screen.
// Obtains the entire directory tree in the host OS
// starting at the specified path.
// The "levels" parameter specifies how many levels should the
// function traverse down the directory tree.
PRL_RESULT GetHostDirList(PRL_HANDLE hServer, PRL_CONST_STR path, int levels)
{
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hParentDirectory = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hChildElement = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Get directory list from the host.
// The second parameter specifies the absolute
// path for which to get the directory listing.
hJob = PrlSrv_FsGetDirEntries(hServer, path);
// Wait for the job to complete.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Analyze the result of PrlSrv_FsGetDirEntries.
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
Page 51

Parallels C API by Example 51
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Check the job return code.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Get job result.
ret = PrlJob_GetResult(hJob, &hJobResult);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Get a handle to the parent directory.
// This is the directory that we specified in the
// PrlSrv_FsGetDirEntries call above.
ret = PrlResult_GetParam(hJobResult, &hParentDirectory);
PrlHandle_Free(hJobResult);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Get parameter count (the number of child entries).
PRL_UINT32 nParamCount = 0;
ret = PrlFsInfo_GetChildEntriesCount(hParentDirectory, &nParamCount);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Iterate through the list obtaining
// a handle of type PHT_REMOTE_FILESYSTEM_ENTRY
// for each child element of the parent directory.
for (PRL_UINT32 i = 0; i < nParamCount; ++i)
{
// Get a handle to the child element.
ret = PrlFsInfo_GetChildEntry(hParentDirectory, i, &hChildElement);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
continue;
}
// Get the filesystem element name.
PRL_CHAR sBuf[1024];
PRL_UINT32 nBufSize = sizeof(sBuf);
ret = PrlFsEntry_GetAbsolutePath(hChildElement, sBuf, &nBufSize);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hChildElement);
continue;
}
printf("%s\n", sBuf);
PrlHandle_Free(hChildElement);
Page 52

Parallels C API by Example 52
// Recursive call. Obtains directory listing for
// the entry returned in this iteration.
if (levels > 0 || levels <= -1)
{
int count = levels - 1;
GetHostDirList(hServer, sBuf, count);
}
}
PrlHandle_Free(hParentDirectory);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return PRL_ERR_SUCCESS;
}
Page 53

Parallels C API by Example 53
Managing Licenses
The Parallels license information can be retrieved using the PrlSrv_GetLicenseInfo
function. The function returns a handle of type PHT_LICENSE containing the license details.
The handle provides a set of functions to retrieve the details. To install or update a license, use
the PrlSrv_UpdateLicense function.
The following sample function demonstrates how to obtain license information and how to
install a new license.
PRL_RESULT UpdateLicenseSample(PRL_HANDLE hServer)
{
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hLicense = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hUpdateLicense = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Get the license info from the Parallels Service.
hJob = PrlSrv_GetLicenseInfo(hServer);
// Wait for the job to complete.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Analyze the result of PrlSrv_GetUserInfoList.
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Check the job return code.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Get job result.
ret = PrlJob_GetResult(hJob, &hJobResult);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Get parameter from job result.
ret = PrlResult_GetParam(hJobResult, &hLicense);
PrlHandle_Free(hJobResult);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
Page 54

Parallels C API by Example 54
// Get company name.
PRL_CHAR sCompany[1024];
PRL_UINT32 nCompanyBufSize = sizeof(sCompany);
ret = PrlLic_GetCompanyName(hLicense, sCompany, &nCompanyBufSize);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hLicense);
return -1;
}
printf("Company: %s\n", sCompany);
// Get user name.
PRL_CHAR sUser[1024];
PRL_UINT32 nUserBufSize = sizeof(sUser);
ret = PrlLic_GetUserName(hLicense, sUser, &nUserBufSize);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hLicense);
return -1;
}
printf("User: %s\n", sUser);
// Get license key.
PRL_CHAR sKey[1024];
PRL_UINT32 nKeyBufSize = sizeof(sKey);
ret = PrlLic_GetLicenseKey(hLicense, sKey, &nKeyBufSize);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hLicense);
return -1;
}
printf("Key: %s\n", sKey);
// See license type.
PRL_BOOL isTrial = PRL_TRUE;
ret = PrlLic_IsTrial(hLicense, &isTrial);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hLicense);
return -1;
}
printf("Trial: %d\n", isTrial);
PrlHandle_Free(hLicense);
// Update the license info.
// Here, we use the same license information that we
// retrieved earlier. Normally, you would use the
// information that you received from
// your Parallels product distributor.
hUpdateLicense = PrlSrv_UpdateLicense(hServer, sKey,
sUser, sCompany);
// Wait for the job to complete.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hUpdateLicense, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
PrlHandle_Free(hUpdateLicense);
}
Page 55

Parallels C API by Example 55
Page 56

Parallels C API by Example 56
Obtaining a Problem Report
If you are experiencing a problem with a virtual machine, you can obtain a problem report from
the Parallels Service. The report can then be sent to the Parallels technical support for
evaluation. A problem report contains technical data about your Parallels product installation,
log data, and other technical details that can be used to determine the source of the problem and
to develop a solution. The following example demonstrates how to obtain the report.
PRL_RESULT GetProblemReport(PRL_HANDLE hServer)
{
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Get problem report from the host.
hJob = PrlSrv_GetProblemReport(hServer);
// Wait for the job to complete.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Analyze the result of PrlSrv_GetProblemReport.
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Check the job return code.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Get job result.
ret = PrlJob_GetResult(hJob, &hJobResult);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Get the string containing the report data.
// First, get the required buffer size.
PRL_UINT32 nBufSize = 0;
ret = PrlResult_GetParamAsString(hJobResult, NULL, &nBufSize);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJobResult);
return -1;
}
Page 57

Parallels C API by Example 57
// Second, initialize the buffer and get the report.
char* sReportData =(PRL_STR)malloc(nBufSize);
ret = PrlResult_GetParamAsString(hJobResult, sReportData, &nBufSize);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJobResult);
return ret;
}
printf("%s", sReportData);
PrlHandle_Free(hJobResult);
free(sReportData);
return 0;
}
Page 58

C HAPTER 6
Virtual Machine Operations
This chapter describes the common tasks that can be performed on virtual machines.
In This Chapter
Obtaining the Virtual Machines List..................................................................................... 59
Searching for Virtual Machine by Name .............................................................................. 62
Obtaining Virtual Machine Configuration Information........................................................ 64
Determining Virtual Machine State ...................................................................................... 66
Starting, Stopping, Resetting a Virtual Machine................................................................... 69
Suspending and Pausing a Virtual Machine.......................................................................... 70
Creating a New Virtual Machine .......................................................................................... 72
Searching for Virtual Machines............................................................................................ 75
Adding an Existing Virtual Machine .................................................................................... 79
Cloning a Virtual Machine.................................................................................................... 82
Deleting a Virtual Machine................................................................................................... 84
Modifying Virtual Machine Configuration........................................................................... 85
Managing User Access Rights.............................................................................................. 99
Working with Virtual Machine Templates............................................................................ 101
Page 59

Parallels C API by Example 59
Obtaining the Virtual Machines List
Any virtual machine operation begins with obtaining a handle of type
PHT_VIRTUAL_MACHINE identifying the virtual machine. Once a handle identifying a virtual
machine is obtained, its functions can be used to perform a full range of virtual machine
operations. This sections describes how to obtain a list of handles, each identifying an individual
virtual machines registered with a Parallels Service. If you would like to search for unregistered
virtual machines on the host computer, please refer to the Searching for Virtual Machines section
(p. 75).
The steps that must be performed to obtain the virtual machine list are:
1 Log in to the Parallels Service and obtain a handle of type PHT_SERVER. See Obtaining
Server Handle and Logging In (p. 31) for more info and code samples.
2 Call PrlSrv_GetVmList. This is an asynchronous function that returns a handle of type
PHT_JOB.
3 Call PrlJob_GetResults passing the PHT_JOB object obtained in step 2. This
function returns a handle of type PHT_RESULT containing the virtual machine list.
4 Free the job handle using PrlSrv_GetVmList as it is no longer needed.
5 Call PrlResult_GetParamsCount to determine the number of virtual machines
contained in the PHT_RESULT object.
6 Call the PrlResult_GetParamByIndex function in a loop passing an index from 0 to
the total virtual machine count. The function obtains a handle of type
PHT_VIRTUAL_MACHINE containing information about an individual virtual machine.
7 Use functions of the PHT_VIRTUAL_MACHINE object to obtain the virtual machine
information. For example, use PrlVmCfg_GetName to obtain the virtual machine name.
8 Free the virtual machine handle using PrlHandle_Free.
9 Free the result handle using PrlHandle_Free.
The following sample function implements the steps described above.
PRL_RESULT GetVmList(PRL_HANDLE hServer)
{
// Variables for handles.
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE; // job handle
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE; // job result
// Variables for return codes.
PRL_RESULT ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Get the list of the available virtual machines.
hJob = PrlSrv_GetVmList(hServer);
// Wait for a maximum of 10 seconds for PrlSrv_GetVmList.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 10000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
fprintf(stderr,
"PrlJob_Wait for PrlSrv_GetVmList returned with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
Page 60

Parallels C API by Example 60
return ret;
}
// Check the results of PrlSrv_GetVmList.
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlJob_GetRetCode returned with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return ret;
}
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlSrv_GetVmList returned with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return ret;
}
// Get the results of PrlSrv_GetVmList.
ret = PrlJob_GetResult(hJob, &hJobResult);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlJob_GetResult returned with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return ret;
}
// Handle to the result object is available,
// job handle is no longer needed, so free it.
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
// Iterate through the results (list of virtual machines returned).
PRL_UINT32 nParamsCount = 0;
ret = PrlResult_GetParamsCount(hJobResult, &nParamsCount);
printf("\nVirtual Machines:\n");
for (PRL_UINT32 i = 0; i < nParamsCount; ++i)
{
PRL_HANDLE hVm = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE; // virtual machine handle
// Get a handle to the result at index i.
PrlResult_GetParamByIndex(hJobResult, i, &hVm);
// Now that we have a handle of type PHT_VIRTUAL_MACHINE,
// we can use its functions to retrieve or to modify the
// virtual machine information.
// As an example, we will get the virtual machine name.
char szVmNameReturned[1024];
PRL_UINT32 nBufSize = sizeof(szVmNameReturned);
ret = PrlVmCfg_GetName(hVm, szVmNameReturned, &nBufSize);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
printf("PrlVmCfg_GetName returned with error (%s)\n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
}
else
{
printf(" (%d) %s\n\n", i+1, szVmNameReturned);
}
Page 61

Parallels C API by Example 61
// Free the virtual machine handle.
PrlHandle_Free(hVm);
}
return PRL_ERR_SUCCESS;
}
Page 62

Parallels C API by Example 62
Searching for Virtual Machine by Name
This section contains am example of how to obtain a handle of type
PHT_VIRTUAL_MACHINE identifying the virtual machine using the virtual machine name as a
search parameter. We will use the sample as a helper function in the later section of this guide
that demonstrate how to perform operations on virtual machines. The sample is based on the
code provided in the Obtaining the Virtual Machine List section (p. 59).
// Obtains a handle of type PHT_VIRTUAL_MACHINE using the
// virtual machine name as a search parameter.
// Parameters
// hServer: A handle of type PHT_SERVER.
// sVmName: The name of the virtual machine.
// hVm: [out] A handle of type PHT_VIRTUAL_MACHINE
// identifying the virtual machine.
PRL_RESULT GetVmByName(PRL_HANDLE hServer, PRL_STR sVmName, PRL_HANDLE &hVm)
{
PRL_HANDLE hResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT nJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
// Get a list of available virtual machines.
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PrlSrv_GetVmList(hServer);
PRL_RESULT ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 10000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
return ret;
}
// Check the results of PrlSrv_GetVmList.
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobResult);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobResult))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
return ret;
}
// Get the results of PrlSrv_GetVmList.
ret = PrlJob_GetResult(hJob, &hResult);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
return ret;
}
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
// Iteratre through the results (list of virtual machines returned).
PRL_UINT32 nParamsCount = 0;
ret = PrlResult_GetParamsCount(hResult, &nParamsCount);
for (PRL_UINT32 i = 0; i < nParamsCount; ++i)
{
// Get a handle to result i.
PrlResult_GetParamByIndex(hResult, i, &hVm);
Page 63

Parallels C API by Example 63
// Get the name of the virtual machine for result i.
char vm_name[1024];
PRL_UINT32 nBufSize = sizeof(vm_name);
ret = PrlVmCfg_GetName(hVm, vm_name, &nBufSize);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return PRL_ERR_FAILURE;
}
// If the name of the virtual machine at this index is equal to
sVmName,
// then this is the handle we need.
if (strcmp(sVmName, vm_name) == 0)
{
PrlHandle_Free(hResult);
return PRL_ERR_SUCCESS;
}
// It's not the virtual machine being searched for, so free the handle
to it.
PrlHandle_Free(hVm);
}
// The specified virtual machine was not found.
PrlHandle_Free(hResult);
return PRL_ERR_NO_DATA;
}
Page 64

Parallels C API by Example 64
Obtaining Virtual Machine Configuration Information
The virtual machine configuration information is obtained using functions of the
PHT_VM_CONFIGURATION object. The functions are prefixed with PrlVmCfg_. To use the
functions, a handle of type PHT_VM_CONFIGURATION must first be obtained from the virtual
machine object (a handle of type PHT_VIRTUAL_MACHINE) using the PrlVm_GetConfig
function. The following example shows how to obtain the virtual machine name, guest
operating system type and version, RAM size, HDD size, and CPU count. To obtain the virtual
machine handle (hVm input parameter), use the helper function described in the Searching for
Virtual Machine by Name section (p. 62).
PRL_RESULT GetVmConfig(PRL_HANDLE hVm)
{
PRL_RESULT ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Obtain the PHT_VM_CONFIGURATION handle.
PRL_HANDLE hVmCfg = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
ret = PrlVm_GetConfig(hVm, &hVmCfg);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return ret;
}
// Get the virtual machine name.
PRL_STR szVmName;
PRL_UINT32 nVmNameSize = 0;
// Call once with NULL (PRL_INVALID_HANDLE) to get the size
// of the buffer to allocate for the VM name.
PrlVmCfg_GetName(hVmCfg, PRL_INVALID_HANDLE, &nVmNameSize);
// Allocate memory for the VM name.
szVmName = (PRL_STR)malloc(nVmNameSize);
// Get the virtual machine name.
PrlVmCfg_GetName(hVmCfg, szVmName, &nVmNameSize);
printf("Virtual machine name: %s\n", szVmName);
free(szVmName);
// Get the OS type.
PRL_UINT32 nOsType = 0;
PrlVmCfg_GetOsType(hVmCfg, &nOsType);
char* sOsTypeName;
switch (nOsType)
{
case PVS_GUEST_TYPE_WINDOWS:
sOsTypeName = "Windows";
printf("OS Type: %s\n", PVS_GUEST_TYPE_NAME_WINDOWS);
break;
case PVS_GUEST_TYPE_LINUX:
printf("OS Type: %s\n", PVS_GUEST_TYPE_NAME_LINUX);
break;
case PVS_GUEST_TYPE_MACOS:
printf("OS Type: %s\n", PVS_GUEST_TYPE_NAME_MACOS);
break;
case PVS_GUEST_TYPE_FREEBSD:
printf("OS Type: %s\n", PVS_GUEST_TYPE_NAME_FREEBSD);
Page 65

Parallels C API by Example 65
break;
default:
printf("OS Type: %s: %d\n", "Other OS Type: ", nOsType);
}
// Get the OS version.
PRL_UINT32 nOsVersion = 0;
PrlVmCfg_GetOsVersion(hVmCfg, &nOsVersion);
printf("OS Version: %s\n", PVS_GUEST_TO_STRING(nOsVersion));
// Get RAM size.
PRL_UINT32 nRamSize = 0;
PrlVmCfg_GetRamSize(hVmCfg, &nRamSize);
printf("RAM size: %dMB\n", nRamSize);
// Get default HDD size.
PRL_UINT32 nDefaultHddSize = 0;
PrlVmCfg_GetDefaultHddSize(nOsVersion, &nDefaultHddSize);
printf("Default HDD size: %dMB\n", nDefaultHddSize);
// Get CPU count.
PRL_UINT32 nCpuCount = 0;
PrlVmCfg_GetCpuCount(hVmCfg, &nCpuCount);
printf("Number of CPUs: %d\n", nCpuCount);
return PRL_ERR_SUCCESS;
}
Page 66

Parallels C API by Example 66
Determining Virtual Machine State
To determine the current state of a virtual machine, first obtain a handle to the virtual machine
as described in the Obtaining a List of Virtual Machines section (p. 59). Then use the
PrlVmCfg_GetState function to obtain a handle of type PHT_VM_INFO and call the
PrlVmInfo_GetState function to obtain the state information. The function returns the
virtual machine state as an enumerator from the VIRTUAL_MACHINE_STATE enumeration
that defines every possible state and transition applicable to a virtual machine. The following
table lists the available states and transitions:
Enumerator State/Transition Description
VMS_UNKNOWN
State Unknown or unsupported state.
VMS_STOPPED
VMS_STARTING
VMS_RESTORING
VMS_RUNNING
VMS_PAUSED
VMS_SUSPENDING
VMS_STOPPING
VMS_COMPACTING
VMS_SUSPENDED
VMS_SNAPSHOTING
VMS_RESETTING
VMS_PAUSING
VMS_CONTINUING
State Virtual machine is stopped.
Transition Virtual machine is starting.
Transition Virtual machine is being restored from a
snapshot.
State Virtual machine is running.
State Virtual machine is paused.
Transition Virtual machine is going into "suspended"
mode.
Transition Virtual machine is stopping.
Transition The Compact operation is being performed
on a virtual machine.
State Virtual machine is suspended.
Transition A snapshot of the virtual machine is being
taken.
Transition Virtual machine is being reset.
Transition Virtual machine is going into the "paused"
mode.
Transition Virtual machine is being brought back up
from the "paused" mode.
VMS_MIGRATING
VMS_DELETING_STATE
VMS_RESUMING
Transition Virtual machine is being migrated.
Transition Virtual machine is being deleted.
Transition Virtual machine is being resumed from the
"suspended" mode.
The following example demonstrates how obtain state/transition information for the specified
virtual machine.
PRL_RESULT GetVMstate(PRL_HANDLE hVm)
{
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hVmInfo = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
Page 67

Parallels C API by Example 67
// Obtain the PHT_VM_CONFIGURATION handle.
PRL_HANDLE hVmCfg = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
ret = PrlVm_GetConfig(hVm, &hVmCfg);
// Obtain a handle of type PHT_VM_INFO containing the
// state information. The object will also contain the
// virtual machine access rights info. We will discuss
// this functionality later in this guide.
hJob = PrlVm_GetState(hVmCfg);
// Wait for the job to complete.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Analyze the result of PrlVm_GetState.
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Check the job return code.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Get job result.
ret = PrlJob_GetResult(hJob, &hJobResult);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Get the PHT_VM_INFO handle.
ret = PrlResult_GetParam(hJobResult, &hVmInfo);
PrlHandle_Free(hJobResult);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Get the virtual machine state.
VIRTUAL_MACHINE_STATE vm_state = VMS_UNKNOWN;
ret = PrlVmInfo_GetState(hVmInfo, &vm_state);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hVmInfo);
return -1;
}
printf("Status: ");
switch (vm_state) {
case VMS_UNKNOWN:
printf("Unknown state\n");
Page 68

Parallels C API by Example 68
break;
case VMS_STOPPED:
printf("Stopped\n");
break;
case VMS_STARTING:
printf("Starting...\n");
break;
case VMS_RESTORING:
printf("Restoring...\n");
break;
case VMS_RUNNING:
printf("Running\n");
break;
case VMS_PAUSED:
printf("Paused\n");
break;
case VMS_SUSPENDING:
printf("Suspending...\n");
break;
case VMS_STOPPING:
printf("Stopping...\n");
break;
case VMS_COMPACTING:
printf("Compacting...\n");
break;
case VMS_SUSPENDED:
printf("Suspended\n");
break;
default:
printf("Unknown state\n");
}
printf("\n");
PrlHandle_Free(hVmCfg);
PrlHandle_Free(hVmInfo);
return 0;
}
Page 69

Parallels C API by Example 69
Starting, Stopping, Resetting a Virtual Machine
Note: When stopping or resetting a virtual machine, please be aware of the following important
information:
Stopping a virtual machine is not the same as performing a guest operating system shutdown
operation. When a virtual machine is stopped, it is a cold stop (i.e. it is the same as turning off
the power to a physical computer). Any unsaved data will be lost. However, if the OS in the
virtual machine supports ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface) then you can set
the second parameter of the PrlVm_Stop function to PRL_FALSE in which case, the ACPI
will be used and the machine will be properly shut down.
Resetting a virtual machine is not the same as performing a guest operating system restart
operation. It is the same as pressing the "Reset" button on a physical box. Any unsaved data will
be lost.
The following sample function demonstrates how start, stop, and reset a virtual machine.
PRL_RESULT StartStopResetVm(PRL_HANDLE hVm, VIRTUAL_MACHINE_STATE action)
{
PRL_RESULT ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
if (action == VMS_RUNNING)
{
// Start the virtual machine.
hJob = PrlVm_Start(hVm);
printf("Starting the virtual machine... \n");
}
else if (action == VMS_STOPPED)
{
// Stop the virtual machine.
hJob = PrlVm_Stop(hVm, PRL_TRUE);
printf("Stopping the virtual machine... \n");
}
else if (action == VMS_RESETTING)
{
// Reset the virtual machine.
hJob = PrlVm_Reset(hVm);
printf("Resetting the virtual machine... \n");
}
else
{
printf ("Invalid action type specified \n");
return PRL_ERR_FAILURE;
}
PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 10000);
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
printf ("Error: %s\n", prl_result_to_string(nJobReturnCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return PRL_ERR_FAILURE;
}
return PRL_ERR_SUCCESS;
}
Page 70

Parallels C API by Example 70
Suspending and Pausing a Virtual Machine
Suspending a Virtual Machine
When a virtual machine is suspended, the information about its state is stored in non-volatile
memory. A suspended virtual machine can resume operating in the same state it was in at the
point it was placed into a suspended state. Resuming a virtual machine from a suspended state is
quicker than starting a virtual machine from a stopped state.
To suspend a virtual machine, obtain a handle to the virtual machine, then call
PrlVm_Suspend.
The following example will suspend a virtual machine called Windows XP - 01.
const char *szVmName = "Windows XP - 01";
// Get a handle to virtual machine with name szVmName.
PRL_HANDLE hVm = GetVmByName((char*)szVmName, hServer);
if (hVm == PRL_INVALID_HANDLE)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Virtual machine \"%s\" was not found.\n", szVmName);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
exit(-1);
}
PRL_RESULT nJobResult;
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PrlVm_Suspend(hVm);
PRL_RESULT ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAIL(ret))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlJob_Wait for PrlVm_Suspend failed. Error: %s",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
exit(-1);
}
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobResult);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobResult))
{
fprintf(stderr, "PrlVm_Suspend failed with error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(nJobResult));
PrlHandle_Free(hVm);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
A suspended virtual machine can be stopped completely (placed into a "stopped" state) using
the PrlVm_DropSuspendedState function.
Pausing a Virtual Machine
Page 71

Parallels C API by Example 71
Pausing a virtual machine will pause execution of the virtual machine. This can be achieved
using PrlVm_Pause. PrlVm_Pause takes two parameters: a h andle to the virtual machine,
and a boolean value indicating if ACPI should be used. The above example could be modified
to pause a virtual machine by replacing the line:
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PrlVm_Suspend(hVm);
with:
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PrlVm_Pause(hVm, PRL_FALSE);
It would also be necessary to change the error messages accordingly.
Resuming / Continuing a Virtual Machine
A suspended or paused virtual machine can be restarted using PrlVm_Start. Alternatively,
PrlVm_Resume can be used to resume execution of a suspended virtual machine.
Dropping Suspended State
A suspended virtual machine can be shut down using PrlVm_DropSuspendedState. If
this is used, any unsaved data will be lost.
Page 72

Parallels C API by Example 72
Creating a New Virtual Machine
The first step in creating a new virtual machine is to create a blank virtual machine and register
it with the Parallels Service. A blank virtual machine is the equivalent of a hardware box with
no operating system installed on the hard drive. Once a blank virtual machine is created and
registered, it can be powered on and an operating system can be installed on it.
In this section, we will discuss how to create a typical virtual machine for a particular OS type
using a sample configuration. By using this approach, you can easily create a virtual machine
without knowing all of the little details about configuring a virtual machine for a particular
operating system type.
The steps involved in creating a typical virtual machine are:
1 Obtain a new handle of type PHT_VIRTUAL_MACHINE using the PrlSrv_CreateVm
function. The handle will identify our new virtual machine.
2 Obtain a handle of type PHT_VM_CONFIGURATION by calling the PrlVm_GetConfig
function. The handle is used for manipulating virtual machine configuration settings.
3 Set the default configuration parameters based on the version of the OS that you will later
install in the virtual machine. This step is performed using the
PrlVmCfg_SetDefaultConfig function. You supply the version of the target OS, and
the function will generate the appropriate configuration parameters automatically. The OS
version parameter value is specified using predefined macros. The names of the macros are
prefixed with PVS_GUEST_VER_. You can find the macro definitions in the C API
Reference guide or in the PrlOses.h file. In addition to the OS information, the
PrlVmCfg_SetDefaultConfig function allows to specify the physical host
configuration which will be used to connect the virtual devices inside a virtual machine to
their physical counterparts. The devices include floppy disk drive, CD drive, serial and
parallel ports, sound card, etc. To connect the available host devices, obtain a handle of type
PHT_SERVER_CONFIG (physical host configuration) using the
PrlSrv_GetSrvConfig function. The handle should then be passed to
PrlVmCfg_SetDefaultConfig together with OS information and other parameters. If
you don't want to connect the devices, set the hSrvConfig parameter to
PRL_INVALID_HANDLE.
4 Choose a name for the new virtual machine and set it using the PrlVmCfg_SetName
function.
5 Modify some of the default configuration parameters if needed. For example, you may want
to modify the hard disk image type and size, the amount of memory available to the
machine, and the networking options. You will have to obtain an appropriate handle for the
type of the parameter that you would like to modify and call one of its functions to perform
the modification. The code sample below shows how to modify some of the default values.
6 Create and register the new machine using the PrlVm_Reg function. This step will create
the necessary virtual machine files on the host and register the machine with the Parallels
Service. The directory containing the virtual machine files will have the same name as the
virtual machine name. The directory will be created in the default location for this Parallels
Service. If you would like to create the virtual machine directory in a different location, you
may specify the desired parent directory name and path.
Page 73

Parallels C API by Example 73
The following sample demonstrates how to create a new virtual machine. The sample assumes
that the client program has already obtained a server object handle (hServer) and performed
the login operation.
PRL_HANDLE hVm = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hVmCfg = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT nJobRetCode;
PRL_RESULT ret;
// Obtain a new virtual machine handle.
ret = PrlSrv_CreateVm(hServer, &hVm);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Error handling goes here...
return ret;
}
// Get the host config info.
hJob = PrlSrv_GetSrvConfig(hServer);
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 10000);
// Check the return code of PrlSrv_GetSrvConfig.
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n", prl_result_to_string(nJobRetCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hVm);
return nJobRetCode;
}
// Get a handle to the object containing the result of PrlSrv_GetSrvConfig,
// and then get a hosts configuration handle from it.
ret = PrlJob_GetResult(hJob, &hResult);
PRL_HANDLE hSrvCfg = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PrlResult_GetParam(hResult, &hSrvCfg);
// Free job and result handles.
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hResult);
// Now that we have the host configuration data,
// we can set the default configuration for the new virtual machine.
ret = PrlVm_GetConfig(hVm, &hVmCfg);
ret = PrlVmCfg_SetDefaultConfig(
hVmCfg, // VM config handle.
hSrvCfg, // Host config data.
PVS_GUEST_VER_WIN_2003, // Target OS version.
PRL_TRUE); // Create and connect devices.
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n", prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hSrvCfg);
PrlHandle_Free(hVmCfg);
PrlHandle_Free(hVm);
return ret;
}
PrlHandle_Free(hSrvCfg);
// Set the virtual machine name.
ret = PrlVmCfg_SetName(hVmCfg, "My Windows Server 2003");
// The following two calls demonstrate how to modify
Page 74

Parallels C API by Example 74
// some of the default values of the virtual machine configuration.
// These calls are optional. You may remove them to use the default values.
//
// Set RAM size for the machine to 256 MB.
ret = PrlVmCfg_SetRamSize(hVmCfg, 256);
// Set virtual hard disk size to 20 GB.
// First, get the handle to the hard disk object using the
// PrlVmCfg_GetHardDisk function. The index of 0 is used
// because the default configuration has just one virtual hard disk.
// After that, use the handle to set the disk size.
PRL_HANDLE hHDD = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
ret = PrlVmCfg_GetHardDisk(hVmCfg, 0, &hHDD);
ret = PrlVmDevHd_SetDiskSize(hHDD, 20000);
// Create and register the machine with the Parallels Service.
// This is an asynchronous call. Returns a job handle.
hJob = PrlVm_Reg(hVm, // VM handle.
"", // VM root directory (using default).
PRL_TRUE); // Using non-interactive mode.
// Wait for the operation to complete.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 10000);
// Check the return code of PrlVm_Reg.
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n", prl_result_to_string(nJobRetCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hVmCfg);
PrlHandle_Free(hVm);
return nJobRetCode;
}
// Delete handles.
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hVmCfg);
PrlHandle_Free(hVm);
Page 75

Parallels C API by Example 75
Searching for Virtual Machines
A host computer may have virtual machines on its hard drive that are not currently registered
with the Parallels Service. This can happen when a virtual machine is removed from the
Parallels Service registry but its files are kept on the drive, or when a virtual machine files are
manually copied to the drive from another computer. Parallels C API provides the
PrlSrv_StartSearchVms function that can be used to find such virtual machines on the
specified host at the specified location on the hard drive. The function accepts a string
containing a directory name and path and searches the directory and all its subdirectories for
unregistered virtual machines. It then returns a list of PHT_FOUND_VM_INFO handles, each
containing information about an individual virtual machine that it finds. You can then decide
whether you want to keep the machine as-is, register it, or remove it from the hard drive.
Since the search operation may take a long time (depending on the size of the specified
directory tree), the PrlSrv_StartSearchVms function should be executed using the
callback functionality (p. 22). The callback function will be called for every virtual machine
found and a single instance of the PHT_FOUND_VM_INFO handle will be passed to it. As we
discussed earlier in this guide (p. 22), a callback function can receive two types of objects: jobs
(PHT_JOB) and events (PHT_EVENT). In this instance, the information is passed to the
callback function as an event of type PET_DSP_EVT_FOUND_LOST_VM_CONFIG. To
following steps are involved in processing the event inside the callback function:
1 Determine the type of the event using the PrlHandle_GetType function. If it is
PET_DSP_EVT_FOUND_LOST_VM_CONFIG then the data passed to the callback
function contains information about an unregistered virtual machine. If not, then the event
was generated by some other function and contains the data relevant to that function.
2 Use the PrlEvent_GetParam function to obtain a handle of type
PHT_EVENT_PARAMETER (this is a standard event processing step).
3 Use the PrlEvtPrm_ToHandle function to obtain a handle of type
PHT_FOUND_VM_INFO containing the virtual machine information.
4 Use functions of the PHT_FOUND_VM_INFO object to determine the location of the virtual
machine files, the virtual machine name, guest OS version, and some other information.
The following is an implementation of the steps above:
static PRL_RESULT callback(PRL_HANDLE hEvent, PRL_VOID_PTR pUserData)
{
PRL_RESULT ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_HANDLE_TYPE nHandleType;
PrlHandle_GetType(hEvent, &nHandleType);
// If this is a job, release the handle and exit.
// Normally, we would process this, if we were after
// a job.
if (nHandleType == PHT_JOB)
{
PrlHandle_Free(hEvent);
return 0;
}
// If it's not a job, then it is an event (PHT_EVENT).
// Get the type of the event received.
PRL_EVENT_TYPE eventType;
PrlEvent_GetType(hEvent, &eventType);
Page 76

Parallels C API by Example 76
// Check the event type. If it's what we are looking for, process it.
if (eventType == PET_DSP_EVT_FOUND_LOST_VM_CONFIG)
{
PRL_UINT32 nParamsCount = 0;
// this will receive the event parameter handle.
PRL_HANDLE hParam = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
// The PrlEvent_GetParam function obtains a handle of type
// PHT_EVENT_PARAMETER.
ret = PrlEvent_GetParam(hEvent, 0, &hParam);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
fprintf(stderr, "[4]%.8X: %s\n", ret,
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hParam);
PrlHandle_Free(hEvent);
return ret;
}
PRL_HANDLE hFoundVmInfo = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
ret = PrlEvtPrm_ToHandle(hParam, &hFoundVmInfo);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
fprintf(stderr, "[9]%.8X: %s\n", ret,
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hParam);
PrlHandle_Free(hEvent);
return ret;
}
// Get the virtual machine name.
PRL_CHAR sName[1024];
PRL_UINT32 nBufSize = sizeof(sName);
ret = PrlFoundVmInfo_GetName(hFoundVmInfo, sName, &nBufSize);
printf("VM name: %s\n", sName);
// Get the name and path of the virtual machine directory.
PRL_CHAR sPath[1024];
nBufSize = sizeof(sPath);
ret = PrlFoundVmInfo_GetConfigPath(hFoundVmInfo, sPath, &nBufSize);
printf("Path: %s\n\n", sPath);
PrlHandle_Free(hFoundVmInfo);
PrlHandle_Free(hEvent);
return 0;
}
// The received event handler MUST be freed.
PrlHandle_Free(hEvent);
}
To begin the search operation, place the following code into your main program:
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Register the event handler.
PrlSrv_RegEventHandler(hServer, &callback, NULL);
// Create a string list object and populate it
// with the name and path of the directory to search.
PRL_HANDLE hStringList = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
ret = PrlApi_CreateStringsList(&hStringList );
ret = PrlStrList_AddItem(hStringList, "/Users/Shared/Parallels/");
Page 77

Parallels C API by Example 77
// Begin the search operation.
hJob = PrlSrv_StartSearchVms(hServer, hStringList);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
In order for the callback function to be called, your program should have a global loop (the
program never exits on its own). The callback function will be called as soon as the first virtual
machine is found. If there are no unregistered virtual machines in the specified directory tree,
then the function will never be called as a PET_DSP_EVT_FOUND_LOST_VM_CONFIG event
(it will still be called at least once as a result of the started job and will receive the job object but
this and possibly other callback invocations are irrelevant in the context of this example).
Receiving the search results synchronously
It is also possible to use this function synchronously using the PrlJob_Wait function (p. 22).
In this case, the information is returned as a list of PHT_FOUND_VM_INFO objects contained
in the job object returned by the PrlSrv_StartSearchVms function. The following
example demonstrates how to call the function and to process results synchronously.
PRL_RESULT SearchVMsSample(PRL_HANDLE hServer)
{
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hFoundVmInfo = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Create a string list object and populate it
// with the name and path of the directory to search.
PRL_HANDLE hStringList = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PrlApi_CreateStringsList(&hStringList );
PrlStrList_AddItem(hStringList, "/Users/Shared/Parallels/");
// Begin the search operation.
hJob = PrlSrv_StartSearchVms(hServer, hStringList);
// Wait for the job to complete.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Analyze the result of PrlSrv_StartSearchVms.
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Check the job return code.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Get job result.
ret = PrlJob_GetResult(hJob, &hJobResult);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
Page 78

Parallels C API by Example 78
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Iterate through the returned list obtaining a
// handle of type PHT_FOUND_VM_INFO in each iteration containing
// the information about an individual virtual machine.
PRL_UINT32 nIndex, nCount;
PrlResult_GetParamsCount(hJobResult, &nCount);
for(nIndex = 0; nIndex < nCount ; nIndex++)
{
PrlResult_GetParamByIndex(hJobResult, nIndex, &hFoundVmInfo);
// Get the virtual machine name.
PRL_CHAR sName[1024];
PRL_UINT32 nBufSize = sizeof(sName);
ret = PrlFoundVmInfo_GetName(hFoundVmInfo, sName, &nBufSize);
printf("VM name: %s\n", sName);
// Get the name and path of the virtual machine directory.
PRL_CHAR sPath[1024];
nBufSize = sizeof(sPath);
ret = PrlFoundVmInfo_GetConfigPath(hFoundVmInfo, sPath, &nBufSize);
printf("Path: %s\n\n", sPath);
PrlHandle_Free(hFoundVmInfo);
}
PrlHandle_Free(hJobResult);
PrlHandle_Free(hStringList);
}
Page 79

Parallels C API by Example 79
Adding an Existing Virtual Machine
A host may have virtual machines that are not registered with the Parallels Service. This can
happen if a virtual machine was previously removed from the Parallels Service registry or if the
virtual machine files were manually copied from a different location. If you know the location
of such a virtual machine, you can easily register it with the Parallels Service using the
PrlSrv_RegisterVm function. The function accepts a server handle, name and path of the
directory containing the virtual machine files, and registers the machine.
Note: The PrlSrv_RegisterVm function does NOT generate new MAC addresses for the
virtual network adapters that already exist in the virtual machine. If the machine is a copy of
another virtual machine then you should set new MAC addresses for its network adapters after
you register it. The example at the end of this section demonstrates how this can be
accomplished. For more information on modifying an existing virtual machine, please see the
Modifying Virtual Machine Configuration section (p. 85).
The following sample function demonstrates how to add an existing virtual machine to the
Parallels Service. The function takes a handle of type PHT_SERVER and a string specifying the
name and path of the virtual machine directory. It registers the virtual machine with the Service
and then modifies the MAC address of every virtual network adapter installed in it.
PRL_RESULT RegisterExistingVM(PRL_HANDLE hServer, PRL_CONST_STR sVmDirectory)
{
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobRetCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Register the virtual machine.
hJob = PrlSrv_RegisterVm(
hServer,
sVmDirectory,
PRL_TRUE); // Using non-interactive mode.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 10000);
// Check the return code of PrlSrv_RegisterVm.
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
printf("PrlSrv_RegisterVm returned error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(nJobRetCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
// Obtain the virtual machine handle from the job object.
// We will use the handle later to modify the virtual machine
// configuration.
PRL_HANDLE hVm = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
ret = PrlJob_GetResult(hJob, &hJobResult);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return ret;
}
ret = PrlResult_GetParam(hJobResult, &hVm);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
Page 80

Parallels C API by Example 80
{
// Handle the error...
return ret;
}
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hJobResult);
printf("Virtual machine '%s' was successfully registered.",
sVmDirectory);
// The following code will generate and set a new MAC address
// for every virtual network adapter that exists in the virtual machine.
// This step is optional and should normally be performed when the virtual
// machine is a copy of another virtual machine.
PRL_HANDLE hJobBeginEdit = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobCommit = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
// Begin the virtual machine editing operation.
hJobBeginEdit = PrlVm_BeginEdit(hVm);
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJobBeginEdit, 10000);
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJobBeginEdit, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n", prl_result_to_string(nJobRetCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJobBeginEdit);
return nJobRetCode;
}
// Obtain a handle of type PHT_VM_CONFIGURATION containing the
// virtual machine configuration data.
PRL_HANDLE hVmCfg = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
ret = PrlVm_GetConfig(hVm, &hVmCfg);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return ret;
}
// Determine the number of the network adapters
// installed in the machine.
PRL_UINT32 nCount = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
ret = PrlVmCfg_GetNetAdaptersCount(hVmCfg, &nCount);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return ret;
}
// Itereate through the adapter list.
PRL_HANDLE hNetAdapter = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
for (PRL_UINT32 i = 0; i < nCount; ++i)
{
ret = PrlVmCfg_GetNetAdapter(hVmCfg, i, &hNetAdapter);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return ret;
}
// Automatically generate new MAC address for the current adapter.
// The address will be updated in the configuration object.
ret = PrlVmDevNet_GenerateMacAddr(hNetAdapter);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
Page 81

Parallels C API by Example 81
return ret;
}
}
// Commit the changes to the virtual machine.
hJobCommit = PrlVm_Commit(hVm);
// Check the results of the commit operation.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJobCommit, 10000);
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJobCommit, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Commit error: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(nJobRetCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJobCommit);
return nJobRetCode;
}
PrlHandle_Free(hNetAdapter);
PrlHandle_Free(hVm);
PrlHandle_Free(hVmCfg);
PrlHandle_Free(hJobCommit);
PrlHandle_Free(hJobBeginEdit);
return 0;
}
Page 82

Parallels C API by Example 82
Cloning a Virtual Machine
A new virtual machine can also be created by cloning an existing virtual machine. The machine
will be created as an exact copy of the source virtual machine and will be automatically
registered with the Parallels Service. The cloning operation is performed using the
PrlVm_Clone function. The following parameters must be specified when cloning a virtual
machine:
1 A valid handle of type PHT_VIRTUAL_MACHINE containing information about the source
virtual machine.
2 A unique name for the new virtual machine (the name is NOT generated automatically).
3 The name of the directory where the virtual machine files should be created (or an empty
string to create the files in the default directory).
4 A boolean value specifying whether to create the new machine as a valid virtual machine or
as a template. PRL_TRUE indicates to create a template. PRL_FALSE indicates to create a
virtual machine. See the Working with Virtual Machine Templates (p. 101) section for more
virtual machine info and examples.
The source virtual machine must be registered with the Parallels Service before it can be cloned.
The following sample function demonstrates how to clone an existing virtual machine. When
testing a function, the hVm parameter must contain a valid handle of type
PHT_VIRTUAL_MACHINE (the source virtual machine to clone). On completion, the new
virtual machine should appear in the list of registered virtual machines.
PRL_RESULT CloneVmSample(PRL_HANDLE hVm)
{
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Declare and populate variables that
// will be used as input parameters
// in the function that clones a VM.
// Virtual machine name.
// Get the name of the original VM and use
// it in the new virtual machine name. You can
// use any name that you like of course.
char vm_name[1024];
PRL_UINT32 nBufSize = sizeof(vm_name);
PRL_HANDLE hVmCfg = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
ret = PrlVm_GetConfig(hVm, &hVmCfg);
ret = PrlVmCfg_GetName(hVmCfg, vm_name, &nBufSize);
char new_vm_name[1024] = "Clone of ";
strcat(new_vm_name, vm_name);
// Name of the target directory on the
// host.
// Empty string indicates that the default
// directory should be used.
PRL_CHAR_PTR new_vm_root_path = "";
// Virtual machine or template?
// The cloning functionality allows to create
// a new virtual machine or a new template.
// True indicates to create a template.
// False indicates to create a virtual machine.
Page 83

Parallels C API by Example 83
// We are creating a virtual machine.
PRL_BOOL bCreateTemplate = PRL_FALSE;
// Begin the cloning operation.
hJob = PrlVm_Clone(hVm, new_vm_name, new_vm_root_path, bCreateTemplate);
// Wait for the job to complete.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
printf("Error: (%s)\n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hVmCfg);
return -1;
}
// Analyze the result of PrlVm_Clone.
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hVmCfg);
return -1;
}
// Check the job return code.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
// Handle the error...
printf("Error: (%s)\n",
prl_result_to_string(nJobReturnCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hVmCfg);
return -1;
}
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hVmCfg);
return 0;
}
Page 84

Parallels C API by Example 84
Deleting a Virtual Machine
If a virtual machine is no longer needed, it can be removed. There are two options for removing
a virtual machine:
1 Un-register the virtual machine using PrlVm_Unreg. This will remove the virtual
machine from the list of the virtual machines registered with the Service. Once a virtual
machine has been unregistered it is not possible to use it. The directory containing the
virtual machine files will remain on the hard drive of the host computer, and the virtual
machine can later be re-registered and used.
2 Delete the virtual machine using PrlVm_Delete. The virtual machine will be
unregistered, and the directory (or just some of its files that you can specify) will be deleted.
The following example demonstrates un-registering a virtual machine. Note that this example
makes use of a function called GetVmByName that can be found in the Obtaining a List of
Virtual Machines section.
const char *szVmName = "Windows XP - 02";
// Get a handle to virtual machine with name szVmName.
PRL_HANDLE hVm = GetVmByName((char*)szVmName, hServer);
if (hVm == PRL_INVALID_HANDLE)
{
fprintf(stderr, "VM \"%s\"was not found.\n", szVmName);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
// Unregister a virtual machine.
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PrlVm_Unreg(hVm);
PRL_RESULT ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 10000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
printf("PrlJob_Wait failed for PrlVm_Unreg. Error returned: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hVm);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobResult);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobResult))
{
printf("PrlVm_Unreg failed. Error returned: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(nJobResult));
PrlHandle_Free(hVm);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
return -1;
}
The following example demonstrates deleting a virtual machine and deleting config.pvs
within the virtual machine directory:
// Delete a virtual machine and a specified file.
PRL_HANDLE hDeviceList = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PrlApi_CreateStringsList(&hDeviceList);
PrlStrList_AddItem(hDeviceList, "/Users/Shared/Parallels/WinXP02/config.pvs");
hJob = PrlVm_Delete(hVm, hDeviceList);
PrlHandle_Free(hDeviceList);
Page 85

Parallels C API by Example 85
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 10000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
printf("PrlJob_Wait failed for PrlVm_Unreg. Error returned: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(ret));
PrlHandle_Free(hVm);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobResult);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobResult))
{
printf("PrlVm_Delete failed. Error returned: %s\n",
prl_result_to_string(nJobResult));
PrlHandle_Free(hVm);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
PrlHandle_Free(hServer);
PrlApi_Deinit();
SdkWrap_Unload();
return -1;
}
To delete the virtual machine and the virtual machine directory (all files belonging to the virtual
machine), omit the line:
PrlStrList_AddItem(hDeviceList, "/Users/Shared/Parallels/WinXP02/config.pvs");
from the above example. Note that this operation is irreversible.
Modifying Virtual Machine Configuration
The Parallels C API provides a complete set of functions to modify the configuration parameters
of an existing virtual machine. You can find the list of the available functions in the Parallels C
API Reference guide by looking at the PHT_VM_CONFIGURATION group. Most of the get/set
functions in the group allow to obtain and modify the virtual machine configuration parameters.
Some parameters are handled as objects and require extra steps in getting or setting them. The
following subsections describe how to modify the most common configuration parameters and
provide code samples. The samples assume that:
you've already obtained a handle to the server object and logged on to the Parallels Service.
you've already obtained a handle to the virtual machine that you would like to modify.
Note: All operations on virtual machine devices (adding, modifying, removing) must be
performed on a stopped virtual machine. An attempt to modify the device configuration on a
running machine will result in error.
Page 86

Parallels C API by Example 86
PrlVm_BeginEdit and PrlVm_Commit Functions
All virtual machine configuration changes must begin with the PrlVm_BeginEdit and end
with the PrlVm_Commit call. These two functions are used to detect collisions with other
clients trying to modify the configuration settings of the same virtual machine.
When PrlVm_BeginEdit is called, the Parallels Service timestamps the beginning of a
configuration change(s) operation. It does not lock the machine, so other clients can make
changes to the same virtual machine at the same time. The function will also automatically
update your local virtual machine object with the current virtual machine configuration
information. This is done in order to ensure that your local object contains the changes that
might have have happened since you obtained the virtual machine handle.
When you are done making the changes, you must call the PrlVm_Commit function. The first
thing that the function will do is verify that the virtual machine configuration has not been
modified by other client(s) since you called the PrlVm_BeginEdit function. If it has been,
your changes will be rejected and PrlVm_Commit will return with error. In such a case, you
will have to reapply your changes. In order to do that, you will have to get the latest
configuration using the PrlVm_GetConfig function, compare your changes with the latest
changes, and make a decision about merging them. Please note that PrlVm_GetConfig
function will update the configuration data in your current virtual machine object and will
overwrite all existing data, including the changes that you've made to it. Furthermore, the
PrlVm_BeginEdit function will also overwrite all existing data (see above). If you don't
want to loose your data, save it locally before calling PrlVm_GetConfig or
PrlVm_BeginEdit.
The following example demonstrates how to use the PrlVm_BeginEdit and
PrlVm_Commit functions:
PRL_HANDLE hJobBeginEdit = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobCommit = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT nJobRetCode = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
// Timestamps the beginning of the "transaction".
// Updates the hVm object with current configuration data.
hJobBeginEdit = PrlVm_BeginEdit(hVm);
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJobBeginEdit, 10000);
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJobBeginEdit, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n", prl_result_to_string(nJobRetCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJobBeginEdit);
return nJobRetCode;
}
// The code modifying configuration parameters goes here...
// Commits the changes to the virtual machine.
hJobCommit = PrlVm_Commit(hVm);
// Check the results of the commit operation.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJobCommit, 10000);
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJobCommit, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Commit error: %s\n", prl_result_to_string(nJobRetCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJobCommit);
return nJobRetCode;
Page 87

Parallels C API by Example 87
}
Obtaining a PHT_VM_CONFIGURATION handle
Before you can use any of the virtual machine configuration management functions, you have to
obtain a handle of type PHT_VM_CONFIGURATION. The handle is obtained from the virtual
machine object as shown in the following example:
PRL_HANDLE hVmCfg = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
ret = PrlVm_GetConfig(hVm, &hVmCfg);
Once you have the handle, you can use its functions to manipulate the virtual machine
configuration settings. As usual, don't forget to free the handle when it is no longer needed.
Page 88

Parallels C API by Example 88
Name, Description, Boot Options
The virtual machine name and description modifications are simple. They are performed using a
single call for each parameter:
// Modify VM name.
ret = PrlVm_GetConfig(hVm, &hVmCfg);
ret = PrlVmCfg_SetName(hVmCfg, "New Name1");
// Modify VM description.
ret = PrlVmCfg_SetDescription(hVmCfg, "My updated VM");
To modify the boot options (boot device priority), first make the
PrlVmCfg_GetBootDevCount call to determine the number of the available devices. Then
obtain a handle to each device by making the PrlVmCfg_GetBootDev call in a loop. To
place a device at the specified position in the boot device priority list, use the
PrlBootDev_SetSequenceIndex function passing the device handle and the index (0 first boot device, 1 - second boot device, and so forth).
The following sample illustrates how to make the above modifications.
PRL_HANDLE hJobBeginEdit = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobCommit = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT nJobRetCode = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
// Timestamp the beginning of the transaction.
hJobBeginEdit = PrlVm_BeginEdit(hVm);
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJobBeginEdit, 10000);
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJobBeginEdit, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n", prl_result_to_string(nJobRetCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJobBeginEdit);
return nJobRetCode;
}
// Modify VM name.
ret = PrlVmCfg_SetName(hVmCfg, "New Name1");
// Modify VM description.
ret = PrlVmCfg_SetDescription(hVmCfg, "My updated VM");
// Modify boot options.
// Set boot device list as follows:
// 0. CD/DVD drive.
// 1. Hard disk.
// 2. Network adapter.
// 3. Floppy disk drive.
// Remove all other devices (if any) from the
// boot devices list for this VM.
// Device count.
PRL_UINT32 nDevCount;
// A handle identifying the device.
PRL_HANDLE hDevice = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
// Device type.
PRL_DEVICE_TYPE devType;
// Get the total number of devices.
ret = PrlVmCfg_GetBootDevCount(hVmCfg, &nDevCount);
// Iterate through the device list.
Page 89

Parallels C API by Example 89
// Get a handle for each available device.
// Set an index for a device in the boot list.
for (int i = 0; i < nDevCount; ++i)
{
ret = PrlVmCfg_GetBootDev(hVmCfg, i, &hDevice);
ret = PrlBootDev_GetType(hDevice, &devType);
if (devType == PDE_OPTICAL_DISK)
{
PrlBootDev_SetSequenceIndex(hDevice, 0);
}
if (devType == PDE_HARD_DISK)
{
PrlBootDev_SetSequenceIndex(hDevice, 1);
}
else if (devType == PDE_GENERIC_NETWORK_ADAPTER)
{
PrlBootDev_SetSequenceIndex(hDevice, 2);
}
else if (devType == PDE_FLOPPY_DISK)
{
PrlBootDev_SetSequenceIndex(hDevice, 3);
}
else
{
PrlBootDev_Remove(hDevice);
}
}
// Commit the changes.
hJobCommit = PrlVm_Commit(hVm);
// Check the results of the commit operation.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJobCommit, 10000);
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJobCommit, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Commit error: %s\n", prl_result_to_string(nJobRetCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJobCommit);
return nJobRetCode;
}
RAM Size
The size of the memory available to the virtual machine is performed using the
PrlVmCfg_SetRamSize function. The first parameter is the virtual machine handle and the
second parameter is the new RAM size in megabytes:
PrlVmCfg_SetRamSize(hVmCfg, 512);
Page 90

Parallels C API by Example 90
Hard Disks
Modifying the size of the existing hard disk image
A virtual machine may have more than one virtual hard disk. To select a disk that you would
like to modify, first retrieve the list of the available disks, as shown in the following example:
PRL_HANDLE hHDD = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_UINT32 nCount;
// Get the number of disks available.
PrlVmCfg_GetHardDisksCount(hVmCfg, &nCount);
// Iterate through the list.
for (PRL_UINT32 i = 0; i < nCount; ++i)
{
// Obtain a handle to the hard disk object.
ret = PrlVmCfg_GetHardDisk(hVmCfg, i, &hHDD);
// The code selecting the desired HDD goes here...
// {
// Modify the disk size.
// The hard disk size is specified in megabytes.
ret = PrlVmDevHd_SetDiskSize(hHDD, 20000);
// }
}
Adding a new hard disk
In this example, we will add a hard disk to a virtual machine. The following options are
available:
You may create new or use an existing image file for your new disk.
Creating a dynamically expanding or a fixed-size disk. The expanding drive image will be
initially created with a size of zero. The space for it will be allocated dynamically on asneeded basis. The space for the fixed-size disk will be allocated fully at the time of creation.
Choosing the maximum disk size.
Creating a new image file
In the first example, we will create a new disk image and will add it to a virtual machine.
PRL_HANDLE hJobBeginEdit = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobCommit = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT nJobRetCode = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
// Timestamp the beginning of the configuration changes operation.
// The hVm specifies the virtual machine that we'll be editing.
//
hJobBeginEdit = PrlVm_BeginEdit(hVm);
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJobBeginEdit, 10000);
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJobBeginEdit, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n", prl_result_to_string(nJobRetCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJobBeginEdit);
return nJobRetCode;
}
// Create a new device handle.
// This will be our new virtual hard disk.
Page 91

Parallels C API by Example 91
PRL_HANDLE hHDD = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
ret = PrlVmCfg_CreateVmDev(
hVmCfg, // The target virtual machine.
PHT_VIRTUAL_DEV_HARD_DISK, // Device type.
&hHDD); // Device handle.
// Set disk type to "expanding".
ret = PrlVmDevHd_SetDiskType(hHDD, PHD_EXPANDING_HARD_DISK);
// Set max disk size, in megabytes.
ret = PrlVmDevHd_SetDiskSize(hHDD, 32000);
// This option determines whether the image file will be splitted
// into chunks or created as a single file.
ret = PrlVmDevHd_SetSplitted(hHDD, PRL_FALSE);
// Choose and set the name for the new image file.
// We must set both the "friendly" name and the "system" name.
// For a virtual device, use the name of the new image file in both
// functions. By default, the file will be
// created in the virtual machine directory. You may specify a
// full path if you want to place the file in a different
// directory.
//
ret = PrlVmDev_SetFriendlyName(hHDD, "harddisk4.hdd");
ret = PrlVmDev_SetSysName(hHDD, "harddisk4.hdd");
// Set the emulation type.
ret = PrlVmDev_SetEmulatedType(hHDD, PDT_USE_IMAGE_FILE);
// Enable the new disk on successful creation.
ret = PrlVmDev_SetEnabled(hHDD, PRL_TRUE);
// Create the new image file.
hJob = PrlVmDev_CreateImage(hHDD,
PRL_TRUE, // Do not overwrite if the file exists.
PRL_TRUE); // Use non-interactive mode.
// Commit the changes.
hJobCommit = PrlVm_Commit(hVm);
// Check the results of the commit operation.
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJobCommit, 10000);
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJobCommit, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Commit error: %s\n", prl_result_to_string(nJobRetCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJobCommit);
return nJobRetCode;
}
Using an existing image file
In the next example, we will use an existing image file to add a virtual hard disk to a virtual
machine. The procedure is similar to the one described above, except that you don't have to
specify the disk parameters and you don't have to create an image file.
// Timestamp the beginning of the configuration changes operation.
// The hVm specifies the virtual machine that we'll be editing.
//
hJobBeginEdit = PrlVm_BeginEdit(hVm);
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJobBeginEdit, 10000);
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJobBeginEdit, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n", prl_result_to_string(nJobRetCode));
Page 92

Parallels C API by Example 92
PrlHandle_Free(hJobBeginEdit);
return nJobRetCode;
}
// Create a device handle.
PRL_HANDLE hHDD = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
ret = PrlVmCfg_CreateVmDev(
hVmCfg, // Target virtual machine.
PHT_VIRTUAL_DEV_HARD_DISK, // Device type.
&hHDD); // Device handle.
// In this example, these two functions are used
// to specify the name of the existing image file.
// By default, it will look for the file in the
// virtual machine directory. If the file is located
// anywhere else, you must specify the full path here.
//
ret = PrlVmDev_SetFriendlyName(hHDD, "harddisk4.hdd");
ret = PrlVmDev_SetSysName(hHDD, "harddisk4.hdd");
// Set the emulation type.
ret = PrlVmDev_SetEmulatedType(hHDD, PDT_USE_IMAGE_FILE);
// Enable the drive on completion.
ret = PrlVmDev_SetEnabled(hHDD, PRL_TRUE);
// Commit the changes.
hJobCommit = PrlVm_Commit(hVm);
If the commit operation is successful, a hard disk will be added to the virtual machine and will
appear in the list of the available devices.
Network Adapters
When adding a network adapter to a virtual machine, you first have to choose a networking
mode for it. The following options are available:
Host-only networking. A virtual machine can communicate with the host and other virtual
machines, but not with external networks.
Shared networking. Uses the NAT feature. A virtual machine shares the IP address with the
host.
Bridged networking. A virtual adapter in the VM is bound to a network adapter on the host.
The virtual machine appears as a standalone computer on the network.
Page 93

Parallels C API by Example 93
Host-only and Shared Networking
The following sample function illustrates how to add virtual network adapters using the hostonly and shared networking (both types are created similarly). The steps are:
1 Call the PrlVm_BeginEdit function to mark the beginning of the virtual machine
editing operation. This step is required when modifying any of the virtual machine
configuration parameters.
2 Obtain a handle of type PHT_VM_CONFIGURATION containing the virtual machine
configuration information.
3 Create a new virtual device handle of type PHT_VIRTUAL_DEV_NET_ADAPTER (virtual
network adapter) using the PrlVmCfg_CreateVmDev function.
4 Set the desired device emulation type (host or shared) using the
PrlVmDev_SetEmulatedType function. Virtual network adapter emulation types are
defined in the PRL_VM_DEV_EMULATION_TYPE enumeration.
5 The MAC address for the adapter will be generated automatically. If needed, you can set the
address manually using the PrlVmDevNet_SetMacAddress function.
6 Call the PrlVm_Commit function to finalize the changes.
PRL_RESULT AddNetAdapterHostOrShared(PRL_HANDLE hVm)
{
PRL_HANDLE hJobBeginEdit = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobCommit = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hVmCfg = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT nJobRetCode = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_UINT32 ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Timestamp the beginning of the configuration changes operation.
// The hVm parameter specifies the target virtual machine.
hJobBeginEdit = PrlVm_BeginEdit(hVm);
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJobBeginEdit, 10000);
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJobBeginEdit, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n", prl_result_to_string(nJobRetCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJobBeginEdit);
return nJobRetCode;
}
// Obtain a handle of type PHT_VM_CONFIGURATION containing
// the virtual machine configuration information.
ret = PrlVm_GetConfig(hVm, &hVmCfg);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error.
}
// Create a virtual network adapter device handle.
PRL_HANDLE hNet = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
ret = PrlVmCfg_CreateVmDev(
hVmCfg, // The virtual machine configuration handle.
PDE_GENERIC_NETWORK_ADAPTER, // Device type.
&hNet); // Device handle.
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error.
}
// For host-only networking, set the device emulation type
Page 94

Parallels C API by Example 94
// to PDT_USE_HOST_ONLY_NETWORK, which is an enumerator from the
// PRL_VM_DEV_EMULATION_TYPE enumeration.
// For shared networking, set the device emulation type
// to PDT_USE_SHARED_NETWORK, which is also an enumerator from
// the same enumeration.
// Un-comment one of the following lines (and comment out the other)
// to set the the desired emulation type.
PRL_VM_DEV_EMULATION_TYPE pdtType = PDT_USE_HOST_ONLY_NETWORK;
//PRL_VM_DEV_EMULATION_TYPE pdtType = PDT_USE_SHARED_NETWORK;
ret = PrlVmDev_SetEmulatedType(hNet, pdtType);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error.
}
// By default, a new device is created disabled.
// You can set the "connected" and "enabled" properties
// as desired.
PrlVmDev_SetConnected(hNet, PRL_TRUE);
PrlVmDev_SetEnabled(hNet, PRL_TRUE);
// Commit the changes.
hJobCommit = PrlVm_Commit(hVm);
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJobBeginEdit, 10000);
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJobBeginEdit, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
// Handle the error.
}
// Release all handles.
PrlHandle_Free(hNet);
PrlHandle_Free(hVmCfg);
PrlHandle_Free(hJobBeginEdit);
PrlHandle_Free(hJobCommit);
return PRL_ERR_SUCCESS;
}
Page 95

Parallels C API by Example 95
Bridged Networking
Compared to host-only and shared network adapters, adding an adapter using bridged
networking involves additional steps. In a bridged networking mode, you are binding the virtual
adapter inside a virtual machine to an adapter on the host machine. Therefore, you first have to
retrieve the list of adapters from the host and select the one you would like to use. The complete
procedure of creating an adapter using bridged networking is as follows:
1 Obtain a list of network adapters installed on the host. This steps is preformed using the
PrlSrvCfg_GetNetAdaptersCount, PrlSrvCfg_GetNetAdapter, and
PrlSrvCfgDev_GetName functions.
2 Begin the virtual machine editing operation and create a new network adapter handle as
described in the Host-only and Shared Networking section (p. 93).
3 Bind the new virtual network adapter to the desired host machine adapter using the
PrlVmDevNet_SetBoundAdapterName function.
4 Finalize the changes by calling the PrlVm_Commit function.
You can also bind a virtual network adapter to the default adapter on the host machine. In this
case, you don't have to obtain the list of adapters from the host, so you can skip step 1 (above).
In step 3, instead of setting the adapter name, set its index as -1 using the
PrlVmDevNet_SetBoundAdapterIndex function.
The following are two sample functions that show the implementation of the steps described
above. The two functions are similar except that the first one shows how to bind a virtual
network adapter to a specific adapter on the host, whereas the second function shows how to
bind the virtual adapter to the default host network adapter.
Example 1:
The function accepts a server handle and a virtual machine handle. The server handle will be
used to obtain the list of network adapters from the host.
PRL_RESULT AddNetAdapterBridged(PRL_HANDLE hServer, PRL_HANDLE hVm)
{
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobResult = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobBeginEdit = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobCommit = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hVmCfg = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT nJobRetCode = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_UINT32 ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Obtain a list of the network adapters installed on
// the host.
// First, obtain a handle containing the
// host configuration info.
hJob = PrlSrv_GetSrvConfig(hServer);
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 10000);
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
// Handle the error.
}
// Get job results.
ret = PrlJob_GetResult(hJob, &hJobResult);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
Page 96

Parallels C API by Example 96
{
// Handle the error.
}
// server config handle.
PRL_HANDLE hSrvCfg = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
// counter.
PRL_UINT32 nCount = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
// Now obtain the actual handle containing the
// host configuration info.
PrlResult_GetParam(hJobResult, &hSrvCfg);
// Get the number of the available adapters from the
// host configuration object.
PrlSrvCfg_GetNetAdaptersCount(hSrvCfg, &nCount);
// Net adapter handle.
PRL_HANDLE hHostNetAdapter = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_CHAR chHostAdapterName[1024];
// Iterate through the list of the adapters.
for (PRL_UINT32 i = 0; i < nCount; ++i)
{
PrlSrvCfg_GetNetAdapter(hSrvCfg, i, &hHostNetAdapter);
// Get adapter name.
PRL_CHAR chName[1024];
PRL_UINT32 nBufSize = sizeof(chName);
ret = PrlSrvCfgDev_GetName(hHostNetAdapter, chName, &nBufSize);
// Normally, you would iterate through the entire list
// and select an adapter to bind the virtual network adapter to.
// For simplicity, we will simply pick the first one and use it.
strcpy(chHostAdapterName, chName);
break;
}
// Now that we have the name of the host network adapter,
// we can add a new virtual network adapter to the virtual machine.
// Timestamp the beginning of the configuration changes operation.
// The hVm parameter specifies the target virtual machine.
hJobBeginEdit = PrlVm_BeginEdit(hVm);
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJobBeginEdit, 10000);
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJobBeginEdit, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n", prl_result_to_string(nJobRetCode));
PrlHandle_Free(hJobBeginEdit);
return nJobRetCode;
}
// Obtain a handle of type PHT_VM_CONFIGURATION containing
// the virtual machine configuration information.
ret = PrlVm_GetConfig(hVm, &hVmCfg);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error.
}
// Create a virtual network adapter device handle.
PRL_HANDLE hNet = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
ret = PrlVmCfg_CreateVmDev(
hVmCfg, // The virtual machine configuration handle.
Page 97

Parallels C API by Example 97
PDE_GENERIC_NETWORK_ADAPTER, // Device type.
&hNet); // Device handle.
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error.
}
// Set the virtual network adapter emulation type (networking type).
// Bridged networking is set using the PDT_USE_BRIDGE_ETHERNET enumerator
// from the PRL_VM_DEV_EMULATION_TYPE enumeration.
ret = PrlVmDev_SetEmulatedType(hNet, PDT_USE_BRIDGE_ETHERNET);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error.
}
// Set the host adapter to which this adapter should be bound.
PrlVmDevNet_SetBoundAdapterName(hNet, chHostAdapterName);
// By default, a new device is created disabled.
// You can set the "connected" and "enabled" properties
// as desired.
PrlVmDev_SetConnected(hNet, PRL_TRUE);
PrlVmDev_SetEnabled(hNet, PRL_TRUE);
// Commit the changes.
hJobCommit = PrlVm_Commit(hVm);
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJobBeginEdit, 10000);
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJobBeginEdit, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
// Handle the error.
}
// Release all handles.
PrlHandle_Free(hNet);
PrlHandle_Free(hVmCfg);
PrlHandle_Free(hJobBeginEdit);
PrlHandle_Free(hJobCommit);
return PRL_ERR_SUCCESS;
}
Example 2:
This function shows how to add a virtual network adapter to a virtual machine and how to bind
it to the default adapter on the host.
PRL_RESULT AddNetAdapterBridgedDefault(PRL_HANDLE hVm)
{
PRL_HANDLE hJobBeginEdit = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hJobCommit = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hVmCfg = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_RESULT nJobRetCode = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_UINT32 ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Timestamp the beginning of the configuration changes operation.
// The hVm parameter specifies the target virtual machine.
hJobBeginEdit = PrlVm_BeginEdit(hVm);
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJobBeginEdit, 10000);
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJobBeginEdit, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s\n", prl_result_to_string(nJobRetCode));
Page 98

Parallels C API by Example 98
PrlHandle_Free(hJobBeginEdit);
return nJobRetCode;
}
// Obtain a handle of type PHT_VM_CONFIGURATION containing
// the virtual machine configuration information.
ret = PrlVm_GetConfig(hVm, &hVmCfg);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error.
}
// Create a virtual network adapter device handle.
PRL_HANDLE hNet = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
ret = PrlVmCfg_CreateVmDev(
hVmCfg, // The virtual machine configuration handle.
PDE_GENERIC_NETWORK_ADAPTER, // Device type.
&hNet); // Device handle.
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error.
}
// Set the virtual network adapter emulation type (networking type).
// Bridged networking is set using the PDT_USE_BRIDGE_ETHERNET enumerator
// from the PRL_VM_DEV_EMULATION_TYPE enumeration.
ret = PrlVmDev_SetEmulatedType(hNet, PDT_USE_BRIDGE_ETHERNET );
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error.
}
// Set the host adapter index to -1. This will
// bind the virtual adapter to the default adapter on the
// host.
PrlVmDevNet_SetBoundAdapterIndex(hNet, -1);
// By default, a new device is created disabled.
// You can set the "connected" and "enabled" properties
// as desired.
PrlVmDev_SetConnected(hNet, PRL_TRUE);
PrlVmDev_SetEnabled(hNet, PRL_TRUE);
// Commit the changes.
hJobCommit = PrlVm_Commit(hVm);
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJobBeginEdit, 10000);
PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJobBeginEdit, &nJobRetCode);
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobRetCode))
{
// Handle the error.
}
// Release all handles.
PrlHandle_Free(hNet);
PrlHandle_Free(hVmCfg);
PrlHandle_Free(hJobBeginEdit);
PrlHandle_Free(hJobCommit);
return PRL_ERR_SUCCESS;
}
Page 99

Parallels C API by Example 99
Managing User Access Rights
This topic applies to Parallels Server only,
User authorization (determining user access rights) is performed using OS-level file access
permissions. Essentially, a virtual machine is a set of files that a user can read, write, and
execute. When determining access rights of a user for a particular virtual machine, Parallels
Service looks at the rights the user has on the virtual machine files and uses this information to
allow or deny privileges. The Parallels Server Administration Guide has a section that describes
the Parallels Server tasks in relation to the file access rights. Using this information, you can
determine the tasks that a user is allowed to perform based on the file access rights the user has.
The same goal can also be accomplished programmatically through Parallels C API.
The Parallels C API contains a PHT_ACCESS_RIGHTS object that is used to manage user
access rights. A handle to it is obtained using the PrlVmCfg_GetAccessRights or the
PrlVmInfo_GetAccessRights function. The difference between the two function is that
PrlVmInfo_GetAccessRights takes an additional step: obtaining a handle of type
PHT_VM_INFO which will also contain the virtual machine state information. If user access
rights is all you need, you can use the PrlVmCfg_GetAccessRights function.
The PHT_ACCESS_RIGHTS object provides an easy way of determining access rights for the
currently logged in user with the PrlAcl_IsAllowed function. The function allows to
specify one of the available virtual machine tasks (defined in the
PRL_ALLOWED_VM_COMMAND enumeration) and returns a boolean value indicating whether
the user is allowed to perform the task or not. The security is enforced on the server side, so if a
user tries to perform a tasks that he/she is not authorized to perform, the access will be denied.
You can still use the functionality described here to determine user access rights in advance and
use it in accordance with your client application logic.
An administrator of the host has full access rights to all virtual machines. A non-administrative
user has full rights to the machines created by him/her and no rights to any other virtual
machines by default (these machines will not even be included in the result set when the user
requests a list of virtual machines from the host). The host administrator can grant virtual
machine access privileges to other users when needed. Currently, the privileges can be granted
to all existing users only. It is not possible to set access rights for an individual user through the
API. The PrlAcl_SetAccessForOthers function is used to set access rights. The
function takes the PHT_ACCESS_RIGHTS object identifying the virtual machine and one of
the enumerators from the PRL_VM_ACCESS_FOR_OTHERS enumerations identifying the
access level, which includes view, view and run, full access, and no access. Once again, the
function sets access rights for all existing users (the users currently present in the Parallels
Service user registry (p. 45)). To determine the current access level for other users on a
particular virtual machine, use the PrlAcl_GetAccessForOthers function. For the
complete set of user access management functions, see the PHT_ACCESS_RIGHTS object
description in the Parallels C API Reference guide.
The following sample function demonstrates how to set virtual machine access rights and how
to determine access rights on the specified virtual machine for the currently logged in user. The
function accepts a virtual machine handle and operates on the referenced virtual machine.
PRL_RESULT AccessRightsSample(PRL_HANDLE hVm)
{
PRL_HANDLE hJob = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
PRL_HANDLE hAccessRights = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
Page 100

Parallels C API by Example 100
PRL_RESULT ret = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
PRL_RESULT nJobReturnCode = PRL_ERR_UNINITIALIZED;
// Obtain a PHT_VM_CONFIGURATION handle.
PRL_HANDLE hVmCfg = PRL_INVALID_HANDLE;
ret = PrlVm_GetConfig(hVm, &hVmCfg);
// Obtain the access rights handle (this will be a
// handle of type PHT_ACCESS_RIGHTS).
ret = PrlVmCfg_GetAccessRights(hVmCfg, &hAccessRights);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hVmCfg);
return -1;
}
PrlHandle_Free(hVmCfg);
// Get the VM owner name from the access rights handle.
PRL_CHAR sBuf[1024];
PRL_UINT32 nBufSize = sizeof(sBuf);
ret = PrlAcl_GetOwnerName(hAccessRights, sBuf, &nBufSize);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
PrlHandle_Free(hAccessRights);
return -1;
}
printf("Owner: %s\n", sBuf);
// Change the virtual machine access rights for other users
// to PAO_VM_SHARED_ON_VIEW_AND_RUN, which means that the
// users will be able to see the machine in the list and to
// run it. When this operation completes, we will use
// PrlAcl_IsAllowed function to determine whether the user
// is allowed to perform a particular task on the virtual
// machine.
PRL_VM_ACCESS_FOR_OTHERS access = PAO_VM_SHARED_ON_VIEW_AND_RUN;
ret = PrlAcl_SetAccessForOthers(hAccessRights, access);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Commit the changes.
hJob = PrlVm_UpdateSecurity(hVm, hAccessRights);
ret = PrlJob_Wait(hJob, 1000);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Analyze the result of PrlVm_UpdateSecurity.
ret = PrlJob_GetRetCode(hJob, &nJobReturnCode);
PrlHandle_Free(hJob);
if (PRL_FAILED(ret))
{
// Handle the error...
return -1;
}
// Check the job return code.
if (PRL_FAILED(nJobReturnCode))
{
// Handle the error...
 Loading...
Loading...