Page 1

Parallels Remote
Application Server
Parallels Client for Linux User's Guide
v16.5
Page 2

Parallels International GmbH
Vordergasse 59
8200 Schaffhausen
Switzerland
Tel: + 41 52 672 20 30
www.parallels.com
Copyright © 1999-2018 Parallels International GmbH. All rights reserved.
This product is protected by United States and international copyright laws. The product’s underlying technology,
patents, and trademarks are listed at http://www.parallels.com/about/legal/.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows Server, Windows Vista are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Apple, Mac, the Mac logo, OS X, macOS, iPad, iPhone, iPod touch are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the US
and other countries.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
All other marks and names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 3

Contents
Getting Started .......................................................................................................... 5
System Requirements ..................................................................................................... 5
Installing Parallels Client for Linux ..................................................................................... 6
Configuring Parallels Client for Linux ................................................................................ 8
Checking for Updates...................................................................................................... 9
Using Parallels Client for Linux ............................................................................... 11
Adding a New Connection ............................................................................................. 11
Configuring a RAS Connection ...................................................................................... 13
Connection ............................................................................................................................ 14
Display .................................................................................................................................. 16
Printing .................................................................................................................................. 18
Local Resources .................................................................................................................... 20
Experience ............................................................................................................................ 23
Network ................................................................................................................................ 24
Authentication ....................................................................................................................... 24
Advanced Settings ................................................................................................................ 25
Configuring an RDP Connection .................................................................................... 26
Connection ............................................................................................................................ 27
Display .................................................................................................................................. 29
Local Resources .................................................................................................................... 31
Programs .............................................................................................................................. 34
Experience ............................................................................................................................ 34
Network ................................................................................................................................ 35
Authentication ....................................................................................................................... 35
Advanced Settings ................................................................................................................ 36
Configuring Global Options ............................................................................................ 38
Using a RAS Connection ............................................................................................... 40
Using an RDP Connection ............................................................................................. 41
Exporting and Importing Parallels Client Settings ............................................................ 41
Parallels Client Network Configuration File ...................................................................... 42
Format ................................................................................................................................... 42
Page 4

Contents
Parameters ............................................................................................................................ 42
Parallels Client Command Line Interface ........................................................................ 44
General Options .................................................................................................................... 44
RDP Options ......................................................................................................................... 45
Device Options ...................................................................................................................... 47
Other Options ........................................................................................................................ 48
Examples .............................................................................................................................. 48
Index ........................................................................................................................ 50
Page 5

C HAPTER 1
Getting Started
Parallels Client for Linux is an app that allows you to connect to Parallels Remote Application Server
(Parallels RAS) from a Linux computer.
In This Chapter
System Requirements ............................................................................................ 5
Installing Parallels Client for Linux ............................................................................ 6
Configuring Parallels Client for Linux ....................................................................... 8
Checking for Updates ............................................................................................. 9
System Requirements
Supported Linux distributions for 32-bit Parallels Client for Linux:
• Ubuntu 14.04 LTS (x86)
• Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (x86)
• Linux Mint 18 (x86)
• Linux Mint 18.2 (x86)
• Debian 8.7 (x86)
• Fedora 25 (x86)
• Fedora 26 (x86)
Supported Linus distributions for 64-bit Parallels Client for Linux:
• Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (x64)
• Linux Mint 18.2 (x64)
• Fedora 25 (x64)
• Fedora 26 (x64)
• CentOS7
Supported ARM distribution:
• Raspbian OS Stretch
Page 6

Getting Started
Installing Parallels Client for Linux
Your system administrator will send you an invitation email with the instructions on how to install
Parallels Client for Linux and configure a Parallels RAS connection in it. The invitation email will
contain the following information and action links:
• A message from your system administrator.
• A link to download Parallels Client for Linux.
• A link to automatically configure Parallels Client on your computer.
• Parallels RAS connection properties. You can use this information to manually create a Parallels
RAS connection. The automatic configuration via the link (see above) is the preferred and the
easiest method, but you can use this information to create a connection manually if needed.
To install Parallels Client for Linux using an invitation email:
1 Make sure you are logged into your computer as a user with administrative privileges.
2 In the invitation email, click the Linux thumbnail to download Parallels Client for Linux installer.
3 Download the installer and store it locally.
Installation Procedure — GUI
Installation via GUI is only valid on DEB and RPM versions:
• Install the package using the default package installer.
Installation Procedures — CLI
DEB Version
To install Parallels Client, switch to the root user and type the following at the command prompt:
dpkg -i parallelsclient.deb
If the installation fails because of missing dependencies, try installing these dependencies using the
following command:
apt-get -f install
Parallels Client for Linux binaries are now installed in the following directory:
/opt/2X/Client/bin
Run the following command to launch Parallels Client:
/opt/2X/Client/bin/2XClient
You can also run the following commands to obtain a list of all usage parameters for a Parallels
Client session:
cd /opt/2X/Client/bin
6
Page 7

Getting Started
/appserverclient -?
RPM Version
To install Parallels Client, switch to the root user and type the following command:
rpm –ivh 2XClient.i386.rpm
Parallels Client binaries are now installed in the following directory:
/opt/2X/Client/bin
Run the following command to launch Parallels Client:
/opt/2X/Client/bin/2XClient
You can also run the following commands to obtain a list of all usage parameters for a Parallels
Client session:
cd /opt/2X/Client/bin
/appserverclient -?
.TAR.BZ2 Version
To install Parallels Client, switch to the root user and then switch to the root directory:
cd /
To install, type the following command:
tar jxvf 2XClient.tar.bz2
Parallels Client binaries are now installed in the following directory:
/opt/2X/Client/bin
It is recommended that the post-install script is launched in order to register icons, mimetypes, URL
schema, and databases configurations. This script is located under: /opt/2X/Client/scripts/install.sh
Run the following command to launch Parallels Client:
/opt/2X/Client/bin/2XClient
You can also run the following commands to obtain a list of all usage parameters for a Parallels
Client session:
cd /opt/2X/Client/bin
/appserverclient -?
To unregister the components registered during installation, it is recommended to launch the
uninstall script located under: /opt/2X/Client/scripts/uninstall.sh
The SSO (Single Sign On) Module Installation Procedures
A separate package to install the SSO module is provided for each version of Linux (32-bit and 64bit versions):
• RASClient-sso_x86_64.deb
• RASClient-sso_x86_64.tar.bz2
7
Page 8
Getting Started
• RASClient-sso.x86_64.rpm
Debian SSO packages can be installed and removed using standard installers.
Tar SSO packages can be installed and uninstalled by running /opt/2X/Client/scripts/install_sso.sh
or /opt/2X/Client/scripts/uninstall_sso.sh respectively.
Rpm SSO packages need to be configured manually after the installation, as there is no tool
available to configure the module correctly. For manual configurations refer to README.SSO that is
being shipped inside the /opt/2X/Client/doc/ folder.
Known issues and limitations
In RPM environments (eg Fedora, OpenSUSE), where the pam-auth-update tool is not available,
the configuration of the pam module needs to be done manually. There are instructions in the
README.SSO file.
Configuring Parallels Client for Linux
Once Parallels Client for Linux is installed on your computer, you need to configure it, so you can
connect to Parallels RAS.
To configure Parallels Client:
1 In the invitation email that you received from your system administrator, find the Configure
section and click the Click Here to auto configure the downloaded client link and follow the
instructions.
2 Once the Parallels Client is configured, it will open and ask you to log into Parallels RAS.
8
Page 9
Getting Started
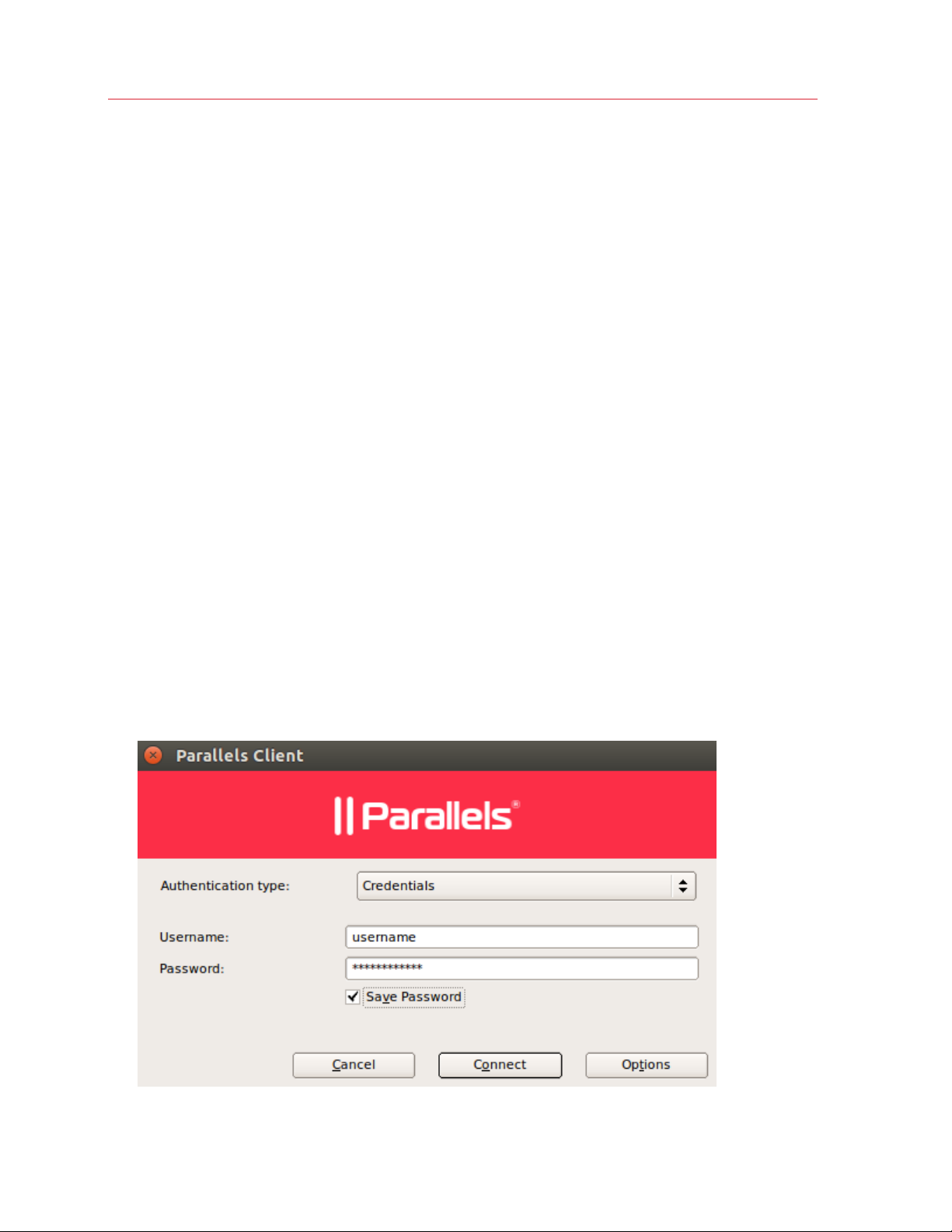
3 Select the Authentication type from the following:
• Credentials. Select this option to connect to Parallels RAS by supplying your credentials,
such as your domain user name and password.
• Smart card. Select this option to connect to Parallels RAS using a smart card.
• Single Sign-On. This option will be included in the list only if the Single Sign-On module is
installed during Parallels Client installation. Select this option to use local system credentials
to connect to the remote server
Note for Administrators: The allowed authentication type(s) must be specified in the RAS Console in
Connection / Authentication.
4 Depending on the authentication type selected, type your user name and password or insert a
smart card into a reader. If using a smart card, enter a PIN when prompted.
5 Click Connect. If the login is successful, the main Parallels Client window opens displaying the
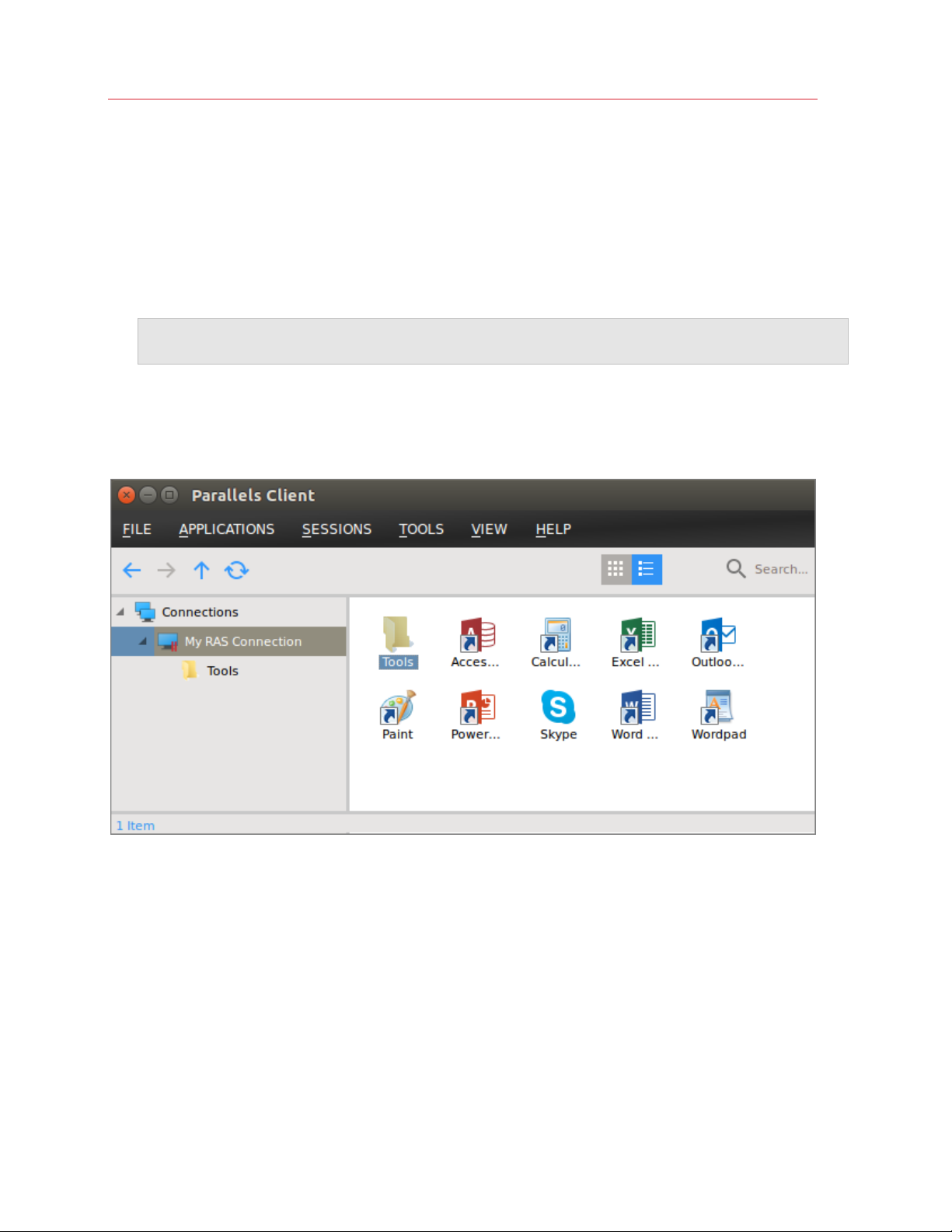
published resources that you can use.
To open a resource, navigate the published folder tree and double-click a desired resource to open
it.
Checking for Updates
To check for the latest available version of Parallels Client for Linux:
1 In the main Parallels Client for Linux window, click Tools > Options.
9
Page 10
Getting Started
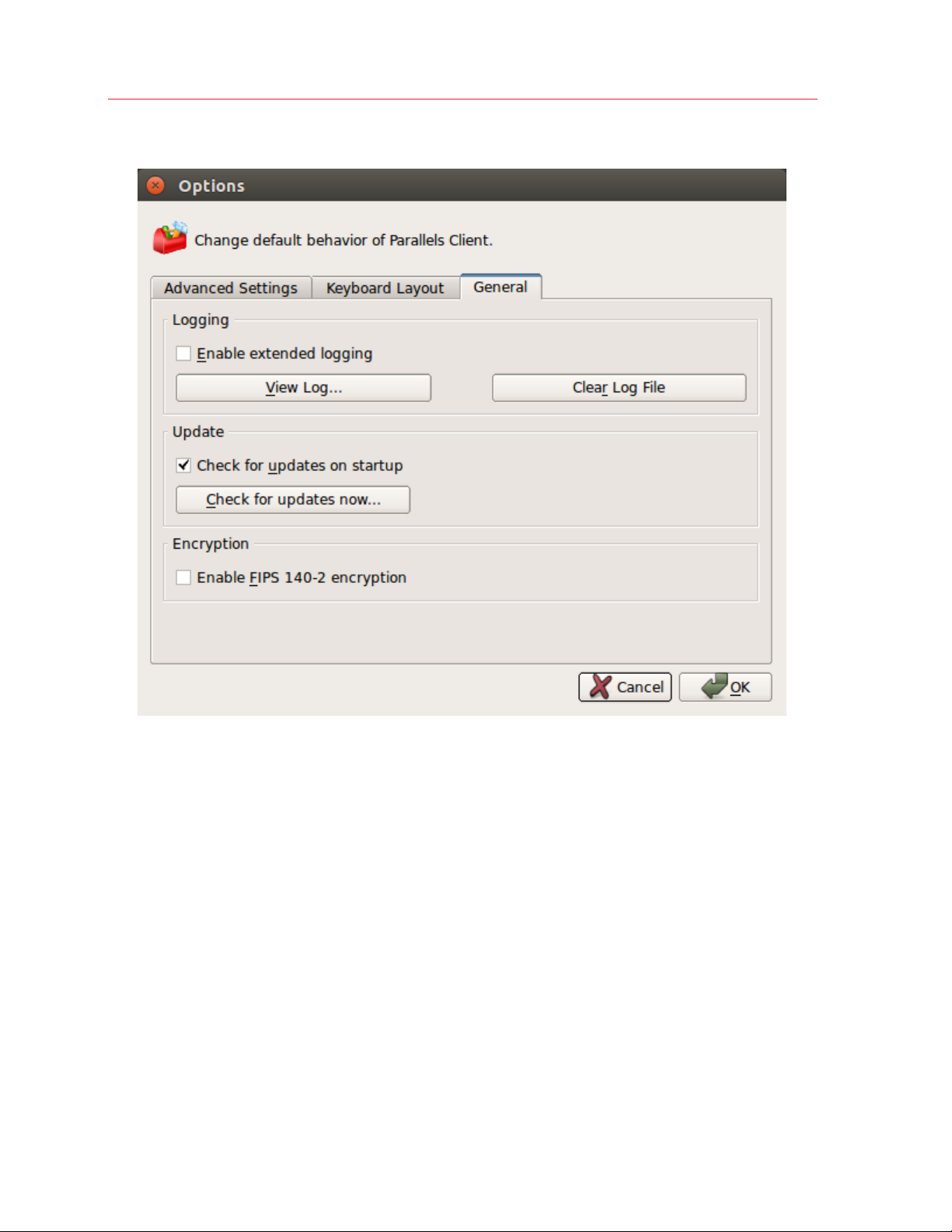
2 In the Options dialog, click the General tab.
3 Click the Check for updates now button to see if a newer version of Parallels Client for Linux is
available.
4 You can also select the Check for updates on startup option to check for Parallels Client
updates every time you open it.
5 Select the Enable FIPS 140-2 encryption option only if your IT administrator instructed you to
do so. If the option is selected, Parallels Client will use FIPS 140-2 encryption when connecting
to Parallels RAS. This is required when the encryption is enforced on the Parallels RAS side. If
the encryption is allowed (but not required), you can select or clear the option, depending on
your organization's policy.
The rest of the options are described in the Configuring Global Options section (p. 38).
10
Page 11

C HAPTER 2
Using Parallels Client for Linux
Read this chapter to learn how to use Parallels Client for Linux.
In This Chapter
Adding a New Connection ...................................................................................... 11
Configuring a RAS Connection ............................................................................... 13
Configuring an RDP Connection ............................................................................. 26
Configuring Global Options ..................................................................................... 38
Using a RAS Connection ........................................................................................ 40
Using an RDP Connection ...................................................................................... 41
Exporting and Importing Parallels Client Settings ..................................................... 41
Parallels Client Network Configuration File ............................................................... 42
Parallels Client Command Line Interface ................................................................. 44
Adding a New Connection
Parallels Client allows you to have more than one connection, so you could easily connect to
different servers or using different connection properties, etc.
To manually add a connection:
1 From the main menu, click File > New Connection.
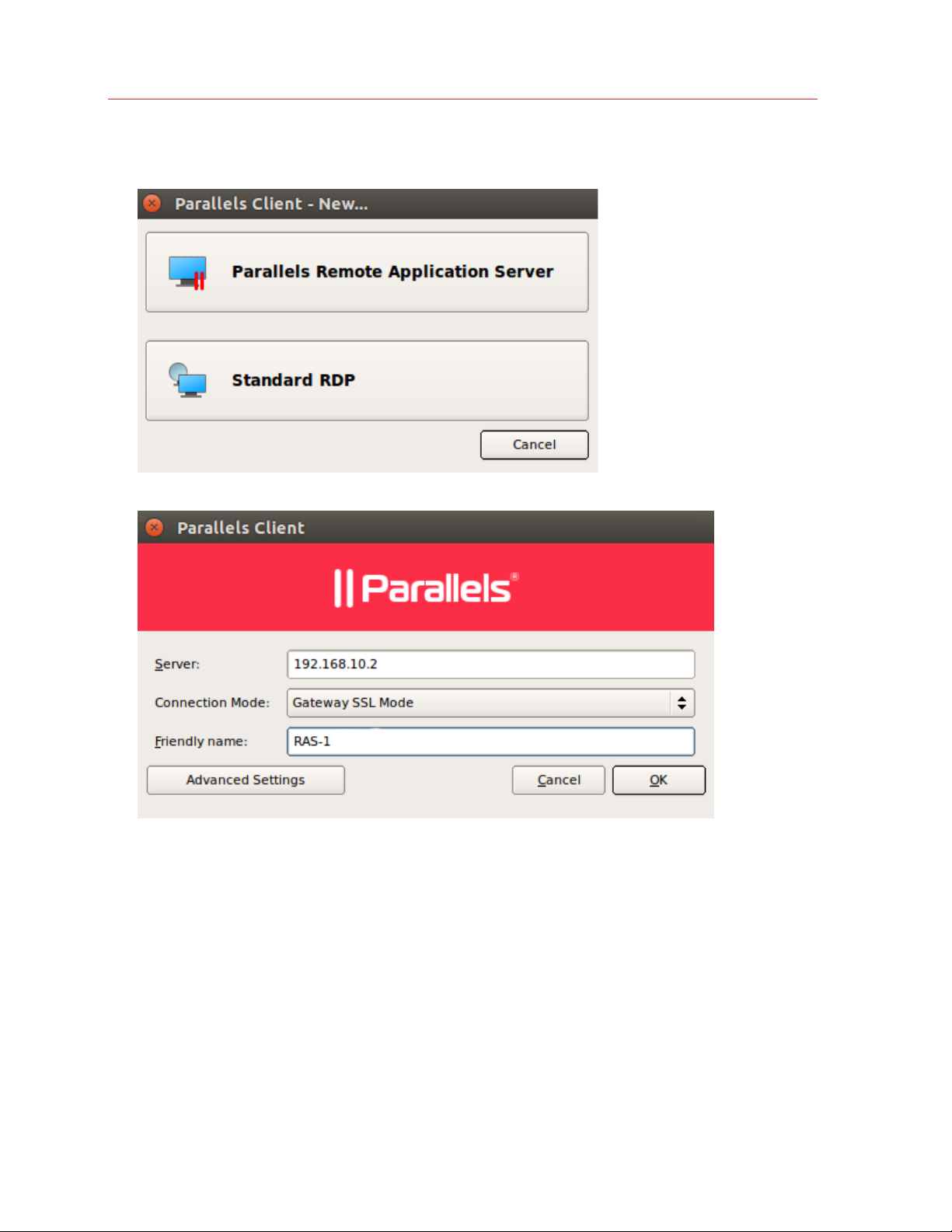
2 Select the type of connection to create:
• Parallels Remote Application Server allows you to use published applications,
documents, or desktops.
Page 12
Using Parallels Client for Linux
• Standard RDP allows you to connect to any remote computer that accepts standard
Remote Desktop connections.
3 On the next screen, enter the connection properties.
When creating a Parallels RAS connection, your system administrator should give you the
connection information that must be specified in this dialog. If you received an invitation email
from your administrator, you can find this information at the bottom of the message. The
information will look similar to the following:
To manually configure the Parallels RAS Connection, use the
following settings:
Server: 192.168.1.10
Port: 443
Connection Mode: Gateway Mode
When creating a Standard RDP connection, you need to know the IP address or hostname of
the remote computer you want to connect to.
12
Page 13

Using Parallels Client for Linux
4 In the Server field, enter the Parallels RAS IP address or hostname (this should be the server
where the RAS Secure Client Gateway resides). If creating a Standard RDP connection, specify
the remote computer IP address or hostname.
5 The Connection Mode drop-down list is enabled only when creating a Parallels RAS
connection. Select one of the following options:
• Gateway Mode. Parallels Client connects to the RAS Secure Client Gateway and the
session connection is tunneled through the first available connection. This mode is ideal for
servers that are only reachable via the gateway and do not require a high level of security.
• Direct Mode. Parallels Client first connects to the RAS Secure Client Gateway for the best
available terminal server and then connects directly to that server. This is best used when
the Parallels Client and the terminal server reside on the same network.
• Gateway SSL Mode. Same as the gateway mode above, but uses encryption to secure the
data.
• Direct SSL Mode. Same as the direct mode above, but uses encryption to secure the data.
6 In the Friendly name field, choose and type a friendly name for this connection.
7 The Advanced settings button opens the Connection Properties dialog where you can
specify additional connection properties. For more information, please see Configuring a RAS
Connection (p. 13) or Configuring an RDP Connection (p. 26).
8 Click OK to create a connection.
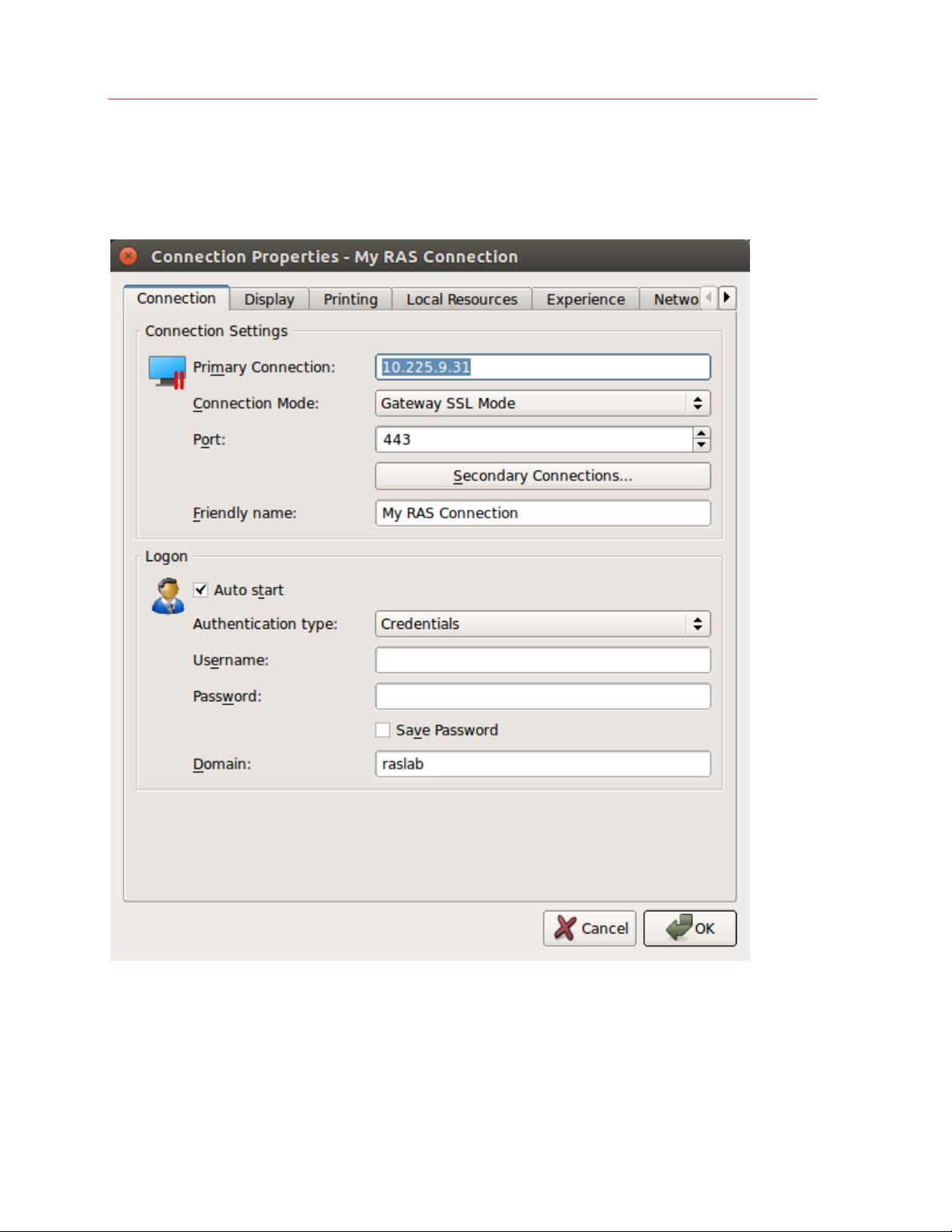
Configuring a RAS Connection
To modify the properties of an existing Parallels RAS connection, right-click it in the main Parallels
Client window and then click Connection Properties in the context menu. This will open the
Connection Properties dialog. Properties are grouped in the dialog by functionality using tab
pages. The following subsections describe each tab page in detail.
13
Page 14
Using Parallels Client for Linux
Connection
The Connection tab page allows you specify connection settings and logon information.
Configuring the Primary Connection
On the Connection tab page, you can define a primary connection and one or more secondary
connections.
14
Page 15

Using Parallels Client for Linux
The primary connection is what Parallels Client will use first to connect to the specified server. This
should be the server where the primary RAS Secure Client Gateway is running.
To specify the primary connection information:
1 In the Primary Connection field, specify the server name or IP address.
2 In the Connection Mode drop-down list, select one of the following options:
• Gateway Mode. Parallels Client connects to the RAS Secure Client Gateway and the
session connection is tunneled through the first available connection. This mode is ideal for
servers which are only reachable via the gateway and do not require a high level of security.
• Gateway SSL Mode. Same as the gateway mode above, but uses encryption to secure the
data.
• Direct Mode. Parallels Client first connects to the RAS Secure Client Gateway for the best
available terminal server and then connects directly to that particular server. This is best
used when the Parallels Client and the terminal server are on the same network.
• Direct SSL Mode. Same as the direct mode above, but uses encryption to secure the data.
3 In the Port field, specify the port on which the gateway listens for incoming connections. If the
default value (80) has been modified on the server side, you have to replace the default value
here as well. Ask your system administrator about the port number if you are having a problem
connecting to the server.
4 In the Friendly Name field, choose and type a name of your choice, so you could easily identify
the server in Parallels Client later.
Configuring a Secondary Connection
If the Parallels RAS farm that you are connecting to has more than one RAS Secure Client
Gateway, you can define a secondary connection, which will be used as a backup connection in
case the primary gateway connection fails.
To add a secondary connection:
1 Click the Secondary Connections button.
2 In the Secondary Connections dialog, click the Add button and specify a server name or IP
address. This should be a server hosting a secondary RAS Secure Client Gateway (the primary
gateway is used by the primary connection).
3 Select the connection mode and modify the port number if necessary. Click OK and then click
OK again to return to the Connection Properties dialog.
Configuring the Logon Information
In the Logon section, specify the following properties:
1 Select the Auto Logon option to enable Parallels Client to connect automatically (using this
connection) on startup.
15
Page 16

Using Parallels Client for Linux
2 In the Authentication type drop-down list, select the desired method of authentication:
• Credentials. Select this option and then enter the username, password, and domain
information. You will be authenticated on the remote server using the specified credentials.
• Smart Card. Select this option to authenticate using a smart card. When connecting to the
remote server, insert a smart card into the card reader and then enter a PIN when
prompted.
• Single Sign-On. This option will be included in the list only if the Single Sign-On module is
installed during Parallels Client installation. Select this option to use local system credentials
to connect to the remote server.
Note for Administrators: The allowed authentication type(s) must be specified in the RAS Console in
Connection / Authentication.
Display
The Display tab page allows you to configure display options.
16
Page 17

Using Parallels Client for Linux
• Color Depth. Specify the desired color depth.
• Size. This option is available for standard RDP connections only.
• Graphics Acceleration. Choose the graphics encoding. The more advanced the acceleration,
the better will be the quality of the graphics. Please keep in mind that higher quality
accelerations require more processing power and faster network.
Note: The acceleration setting does not affect connections with color depth less than 32 bit.
• None. No graphics acceleration.
• Basic. Basic acceleration.
• RemoteFX. More powerful graphics acceleration using the RemoteFX codec.
• RemoteFX Adaptive. Best graphics acceleration using RemoteFX Adaptive and H.264
codecs.
Note: If you select RemoteFX or RemoteFX Adaptive, the color depth is forced to 32 bit.
• Published Applications - Use primary monitor only. If selected, only the primary monitor
connected to your Mac will be used to display remote applications.
• Desktop Options - Span desktops across all monitors. If selected, remote desktops will be
spanned across all connected monitors.
17
Page 18

Using Parallels Client for Linux
Printing
The Printing tab page allows you to configure printing options.
In the Technology drop-down list, select the technology to use when redirecting printers to a
remote computer:
• None. No printer redirection will be configured.
• RAS Universal Printing technology. Select this option to use RAS Universal
Printing technology.
18
Page 19

Using Parallels Client for Linux
• Microsoft Basic Printing Redirection technology. Select this option to use Microsoft Basic
printing technology.
• RAS Universal Printing and Microsoft Basic redirection technologies. Select this option to
use both Parallels RAS and Microsoft technologies.
RAS Universal Printing Technology
If you selected RAS Universal Printing technology, you need to select printers to redirect in the
Redirect Printers drop-down list:
• All. All printers on the client side will be redirected.
• Default only. Only the Windows default printer will be redirected.
• Specific only. Select the printers to redirect in the provided list. The list becomes enabled for
selection only if you select this option.
Microsoft Basic Printing Redirection Technology
If you selected Microsoft Basic Printing Redirection technology, you can modify printer
properties by selecting a printer in the list and then clicking the Edit button. In the dialog that
opens, specify a desired printer manufacturer and model number.
Default printer settings
To configure default printer settings, click the Change Default Printer settings button.
The default printer list shows the available printers that are ready to be redirected by the client to
the remote computer. The list also includes the printing technology that the available printers will
use. The technology reflects the setting selected, as described in the Technology section (above).
For example, if the technology was set to RAS Universal Printing technology, only the printers
using RAS Universal Printing will be listed.
To disable the default printer, select <none>. To redirect the default local printer on the client side
to the remote computer, select <defaultlocalprinter>. When <custom> is selected, you can
specify a custom printer which might be installed on the remote computer. The first printer that
matches the printer name inserted in the custom text box, will be set as the default printer on the
remote computer.
Select Match exact printer name to match the name exactly as inserted in the custom text box.
Please note that the remote printer name may be different than the original printer name. Also note
that local printers may not be redirected due to server settings or policies.
You can specify the time a printer will be forced as default. If the default printer is changed during
this time after the connection is established, the printer is reset as default.
19
Page 20

Using Parallels Client for Linux
Select the Update the remote default printer if the local default printer is changed option to
change the remote default printer automatically when the local default printer is changed. Please
note that the new printer must have been previously redirected.
Local Resources
Use the Local Resources tab page to configure how local resources are handled by the remote
desktop.used in a remote session.
20
Page 21

Using Parallels Client for Linux
Remote Audio and Recording
Use the Remote audio playback drop-down list to select one of the following remote audio
playback options:
• Bring to this computer. Audio from the remote computer will play on your local computer.
• Do not play. Audio from the remote computer will not play on your local computer and will be
muted on the remote computer as well.
• Leave at remote computer. Audio will not play on your local computer but will play normally
on the remote computer.
Use the Remote audio recording drop-down box to select one of the following:
• Record from this computer. Audio from this computer will be recorded using a remote
application.
• Do not record. Do not recored audio.
Keyboard
Select how you want to apply key combinations (e.g. Alt+Tab) that you press on the keyboard:
• On the local computer. Key combinations will be applied to Windows running on the local
computer.
• On the remote computer. Key combinations will be applied to Windows running on the
remote computer.
• In full screen mode only. Key combinations will be applied to the remote computer only when
in the full-screen mode.
Local Devices and Resources
Choose local disk drives, devices, and other resources that you want to redirect to a remote
computer. Redirecting a resource makes it available for use in a remote session. For example, a
redirected local disk drive will be available in a remote application, so you can read from and write
to it.
The following options are available:
• Clipboard. Select this option to enable the local clipboard in a remote session.
• Disk drives. Select this option and then click Configure Drives. See the Configure Drives
subsection below for details.
21
Page 22

Using Parallels Client for Linux
• Devices. Select this option and then click Configure Devices. Devices that are currently
connected to your local computer will appear in the list. This includes supported Plug and Play
devices, media players based on the Media Transfer Protocol (MTP), and digital cameras based
on the Picture Transfer Protocol (PTP). If a device is connected to your computer, but does not
appear in the list, it means it is not a supported Plug and Play device. Please note that disk
drives and smart cards are excluded from this list (you redirect them using dedicated Disk
drives and Smart cards options). The Show previously connected devices option displays
devices that are not currently connected but were connected previously.
Note: Please note device redirection is an experimental feature in Parallels Client for Linux and as such
may have certain issues. Depending on a specific PTP/MTP device used, some operations can make
the device stop responding to PTP/MTP requests. For example, if you start a copy operation to or from
a device and then cancel it, the device may stop responding to all other requests. As a workaround, if
you experience such an issue with your device, disconnect it from your Linux computer and then
reconnect it.
• Printers. Select this option to redirect printers.
• Serial ports. Select this option to redirect serial ports.
• Smart cards. Select this option to redirect smart cards.
Configure Drives
The Configure Drives button opens a dialog where you can map local Linux directories as disk
drives and then use them in remote applications during a remote session.
To map a directory, click the Add button and specify the following:
22
Page 23

Using Parallels Client for Linux
• Share Point: Type the drive name as you want it to appear during a remote session (e.g. sd2).
Please note that share names must be unique, use Latin characters only, and cannot be longer
than seven characters.
• Mount Point: Type a local Linux directory you would like to map (e.g. /home).
Click OK to save the new drive information. The new drive will appear in the Configure Drives
dialog. To edit an existing drive, click Edit. To delete a drive, click Delete.
You can enable or disable disk drives by selecting or clearing a corresponding checkbox. To enable
all drive, select the Use all disk drives available option.
Experience
The Experience tab page allows you to tweak the connection speed to optimize the performance
of the connection with the remote server.
23
Page 24

Using Parallels Client for Linux
In the drop-down list, select your connection speed:
• If not sure, select the Detect connection quality automatically option. Please note that if you
select this option, all other options will be disabled and will be configured automatically based
on the actual connection speed when Parallels Client is connected to Parallels RAS.
• If you select a specific speed (e.g. LAN 10 Mbps or higher), select the desired user experience
options. If you are connecting to a remote computer on a local network that runs at 100 Mbps
or higher, it is usually safe to have all of the experience options turned on. Otherwise, select
only the options that you require.
Network
Use the Network tab page to configure a proxy server if you use one to connect to the remote
computer.
To configure a proxy server, select the Use proxy server option and then select the protocol from
the following list:
• SOCKS4. Enable this option to transparently use the service of a network firewall.
• SOCKS4A. Enable this option to allow a client that cannot connect to resolve the destination
host’s name to specify it.
• SOCKS5. Enable this option to be able to connect using authentication.
• HTTP 1.1. Enable this option to connect using the standard HTTP 1.1 protocol connections.
Specify the proxy host domain name or IP address and the port number.
For SOCKS5 and HTTP 1.1 protocols, select Proxy requires authentication and enter user
credentials.
Authentication
Use the Authentication tab page to specify what happens if server authentication fails.
In the If authentication fails drop-down list, select one of the following options:
• Connect. The user can ignore the certificate of the server and still connect.
• Warn. The user is alerted about the certificate and still has the ability to choose whether to
connect or not.
• Do not connect. The user is not allowed to connect.
24
Page 25

Using Parallels Client for Linux
Advanced Settings
The Advanced Settings tab page allows you to customize the default behavior or Parallels Client.
You can specify the following properties:
• Create shortcuts configured on server. For each published application, the administrator can
configure shortcuts that can be created on the client's desktop and the Start menu. Select this
option to create the shortcuts, or clear the option if you don't want to create them.
• Redirect URLs to this computer. Enable this option to use the local web browser when
opening 'http:" links.
• Redirect Mail to this computer. Enable this option to use the local mail client when opening
‘mailto:’ links.
• Enable Compression. Enables compression to have a more efficient connection.
• Connect to console. This option is disabled for Parallels RAS connections.
25
Page 26

Using Parallels Client for Linux
• Use Pre Windows 2000 login format. If this option is selected, it allows you to use legacy
(pre-Windows 2000) login format.
• Network Level Authentication. Check this option to enable network level authentication,
which will require the client to authenticate before connecting to the server.
The Override computer name field specifies the name that your computer will use during a remote
desktop session. If set, this will override the default computer name. Any filtering set by the
administrator on the server side will make use of this name.
Configuring an RDP Connection
To modify the properties of an existing standard RDP connection, right-click it in the main Parallels
Client window and then click Connection Properties in the context menu. This will open the
Connection Properties dialog. Properties are grouped in the dialog by functionality using tab
pages. The following subsections describe each tab page in detail.
26
Page 27

Using Parallels Client for Linux
Connection
The Connection tab page allows you specify connection settings and logon information.
27
Page 28

Using Parallels Client for Linux
In the Connection Settings section, specify the following properties:
1 In the Primary Connection field, specify the remote computer hostname or IP address.
2 The Port field contains the TCP port 3389 by default, which is the standard port for RDP
connections. You can modify it if the port number was changed on the remote computer.
3 In the Friendly Name field, choose and type a name of your choice, so you could easily identify
the server in Parallels Client later.
In the Logon section, specify the following properties:
1 Select the Auto Logon option to enable Parallels Client to connect automatically (using this
connection) on startup.
2 In the Authentication type drop-down list, select the desired method of authentication:
• Credentials. Select this option and then enter the username, password, and domain
information. You will be authenticated on the remote server using the specified credentials.
• Smart Card. Select this option to authenticate using a smart card. When connecting to the
remote server, insert a smart card into the card reader and then enter a PIN when
prompted.
• Single Sign-On. This option will be included in the list only if the Single Sign-On module is
installed during Parallels Client installation. Select this option to use local system credentials
to connect to the remote server.
Note for Administrators: The allowed authentication type(s) must be specified in the RAS Console in
Connection / Authentication.
28
Page 29

Display
The Display tab page allows you to configure display options.
Using Parallels Client for Linux
• Color Depth. Choose the color quality.
• Size. Choose the size of a remote desktop as it will appear on your screen.
• Graphics Acceleration. Choose the graphics acceleration type. The more advanced the
acceleration, the better will be the quality of the graphics. Please keep in mind that higher
quality accelerations require more processing power and faster network.
Note: The acceleration setting does not affect connections with color depth less than 32 bit.
• None. No graphics acceleration.
• Basic. Basic acceleration.
• RemoteFX. More powerful graphics acceleration using the RemoteFX codec.
29
Page 30

Using Parallels Client for Linux
• RemoteFX Adaptive. Best graphics acceleration using RemoteFX Adaptive and H.264
codecs.
Note: If you select RemoteFX or RemoteFX Adaptive, the color depth is forced to 32 bit.
• Use all monitors for Desktop session (if applicable). If you have more than one monitor
connected to a remote computer, the RDP session will display both of them. The screen size
must be set to Full Screen. The Span desktop across all monitors option must be disabled.
• Published Applications - Use primary monitor only. Not used (disabled for RDP
connections)
• Desktop Options - Span desktops across all monitors. If selected, a remote desktop will be
spanned across all connected monitors.
30
Page 31

Using Parallels Client for Linux
Local Resources
Use the Local Resources tab page to configure how local resources are used in a remote session.
Remote Audio and Recording
Use the Remote audio playback drop-down list to select one of the following remote audio
playback options:
31
Page 32

Using Parallels Client for Linux
• Bring to this computer. Audio from the remote computer will play on your local computer.
• Do not play. Audio from the remote computer will not play on your local computer and will be
muted on the remote computer as well.
• Leave at remote computer. Audio will not play on your local computer but will play normally
on the remote computer.
Use the Remote audio recording drop-down box to select one of the following:
• Record from this computer. Audio from this computer will be recorded using a remote
application.
• Do not record. Do not recored audio.
Keyboard
Select how you want to apply key combinations (e.g. Alt+Tab) that you press on the keyboard:
• On the local computer. Key combinations will be applied to Windows running on the local
computer.
• On the remote computer. Key combinations will be applied to Windows running on the
remote computer.
• In full screen mode only. Key combinations will be applied to the remote computer only when
in the full-screen mode.
Local Devices and Resources
Choose local disk drives, devices, and other resources that you want to redirect to a remote
computer. Redirecting a resource makes it available for use in a remote session. For example, a
redirected local disk drive will be available in a remote application, so you can read from and write
to it.
The following options are available:
• Clipboard. Select this option to enable the local clipboard in a remote session.
• Disk drives. Select this option and then click Configure Drives. See the Configure Drives
subsection below for details.
• Devices. Select this option and then click Configure Devices. Devices that are currently
connected to your local computer will appear in the list. This includes supported Plug and Play
devices, media players based on the Media Transfer Protocol (MTP), and digital cameras based
on the Picture Transfer Protocol (PTP). If a device is connected to your computer but does not
appear in the list, it means it is not a supported Plug and Play device. Please note that disk
drives, printers, and smart cards are excluded from this list (you redirect them using dedicated
Disk drives, Printers, and Smart cards options). The Show previously connected devices
option displays devices that are not currently connected but were connected previously.
32
Page 33

Using Parallels Client for Linux
Note: Please note that device redirection is an experimental feature in Parallels Client for Linux and as
such may have certain issues. Depending on a specific PTP/MTP device used, some operations can
make the device stop responding to PTP/MTP requests. For example, if you start a copy operation to or
from a device and then cancel it, the device may stop responding to all other requests. As a
workaround, if you experience such an issue with your device, disconnect it from your Linux computer
and then reconnect it.
• Printers. Select this option to redirect printers.
• Serial ports. Select this option to redirect serial ports.
• Smart cards. Select this option to redirect smart cards.
Configure Drives
The Configure Drives button opens a dialog where you can map local Linux directories as disk
drives and then use them during a remote session.
To map a directory, click the Add button and specify the following:
• Share Point: Type the drive name as you want it to appear during a remote session (e.g. sd2).
Please note that share names must be unique, use Latin characters only, and cannot be longer
than seven characters.
• Mount Point: Type a local Linux directory you would like to map (e.g. /home).
Click OK to save the new drive information. The new drive will appear in the Configure Drives
dialog. To edit an existing drive, click Edit. To delete a drive, click Delete.
33
Page 34

Using Parallels Client for Linux
You can enable or disable disk drives by selecting or clearing a corresponding checkbox. To enable
all drive, select the Use all disk drives available option.
Programs
The Programs tab page allows you to specify a program that will be started automatically on the
remote computer when you establish a connection with it. Select the Start the following program
on connection option and then specify the Program path and file name and Start in the
following folder options.
Experience
The Experience tab page allows you to tweak the connection speed to optimize the performance
of the connection with the remote server.
34
Page 35

Using Parallels Client for Linux
In the drop-down list, select your connection speed:
• If not sure, select the Detect connection quality automatically option. Please note that if you
select this option, all other options will be disabled and will be configured automatically based
on the actual connection speed when Parallels Client is connected to Parallels RAS.
• If you select a specific speed (e.g. LAN 10 Mbps or higher), select the desired user experience
options. If you are connecting to a remote computer on a local network that runs at 100 Mbps
or higher, it is usually safe to have all of the experience options turned on. Otherwise, select
only the options that you require.
Network
Use the Network tab page to configure a proxy server if you have to use one to connect to the
remote computer.
To configure a proxy server, select the Use proxy server option and then select the protocol from
the following list:
• SOCKS4. Enable this option to transparently use the service of a network firewall.
• SOCKS4A. Enable this option to allow a client that cannot connect to resolve the destination
host’s name to specify it.
• SOCKS5. Enable this option to be able to connect using authentication.
• HTTP 1.1. Enable this option to connect using the standard HTTP 1.1 protocol connections.
Specify the proxy host domain name or IP address and the port number.
For SOCKS5 and HTTP 1.1 protocols, select Proxy requires authentication and enter user
credentials.
Authentication
Use the Authentication tab page to specify what happens if server authentication fails.
In the If authentication fails drop-down list, select one of the following options:
• Connect. The user can ignore the certificate of the server and still connect.
• Warn. The user is alerted about the certificate and still has the ability to choose whether to
connect or not.
• Do not connect. The user is not allowed to connect.
35
Page 36

Using Parallels Client for Linux
Advanced Settings
The Advanced Settings tab page allows you to customize the default behavior or Parallels Client.
You can specify the following properties:
• Create shortcuts configured on server. For each published application, the administrator can
configure shortcuts that can be created on the client's desktop and the Start menu. Select this
option to create the shortcuts, or clear the option if you don't want to create them.
• Redirect URLs to this computer. Enable this option to use the local web browser when
opening 'http:" links.
• Redirect Mail to this computer. Enable this option to use the local mail client when opening
‘mailto:’ links.
• Enable Compression. Enables compression to have a more efficient connection.
36
Page 37

Using Parallels Client for Linux
• Connect to console. This option is used for administration of a Remote Desktop Session Host
server. It acts as if a standard Remote Desktop connection is initiated from the command line
with the /admin option.
• Use Pre Windows 2000 login format. If this option is selected, it allows you to use legacy
(pre-Windows 2000) login format.
• Network Level Authentication. Check this option to enable network level authentication,
which will require the client to authenticate before connecting to the server.
The Override computer name field specifies the name that your computer will use during a remote
desktop session. If set, this will override the default computer name. Any filtering set by the
administrator on the server side will make use of this name.
37
Page 38

Using Parallels Client for Linux
Configuring Global Options
To configure Parallels Client for Linux global options, click Tools > Options on the main toolbar.
Advanced Settings
The Advanced Settings tab page allows you to configure advanced options:
• Language. Allows you to select the graphical user interface language.
• Always on top. With this option enabled, other applications will no longer mask the launcher.
38
Page 39

Using Parallels Client for Linux
• Do not warn if server certificate is not verified. When connected over SSL, and the
certificate is not verified, a warning message will be displayed. You can disable this warning
message by enabling this option.
• Show folders page. Enabling this option will show the available folders while showing the
hierarchy of the application groups as configured on the server.
• Swap mouse buttons. Swap mouse left and right buttons.
• Minimize to tray on close or escape. Enable this feature to place the Parallels Client into the
System Tray when you click on the Close button or hit escape.
Keyboard Layout
The Keyboard Layout tab page allows you to select a keyboard layout to use in the graphical user
interface. Select System Default to use the default layout or select User defined and then select a
keyboard from the list.
General
39
Page 40

Using Parallels Client for Linux
The General tab page allows you to configure general options:
• Logging. The Enable extended logging option enables or disables logging. Click the View
Log button to view the log. Click the Clear Log File button to remove the information from the
file. A log file contains information about standard Parallels Client actions, including establishing
a connection, connection retries, starting of applications, and some others.
• Check for updates on startup. This option is available only with administrative rights. If this
option is selected, Parallels Client will check for available Parallels Client updates on startup.
You can also click the Check for updates now button to check for updates at any time.
• Enable FIPS 140-2 encryption. Select this option if your IT administrator instructed you to do
so. If the option is selected, Parallels Client will use FIPS 140-2 encryption when connecting to
Parallels RAS.
Note: At the time of this writing, FIPS 140-2 encryption works on a 32-bit version (Linux x86) of
Parallels Client for Linux only.
Using a RAS Connection
To connect to Parallels RAS, double-click a connection in the Connections list (or right-click >
Connect).
You can have multiple active connections at the same time (both Parallels RAS and standard RDP).
To switch between active connections in Parallels Client, click a connection in the left pane or click
the corresponding tab page in the right pane.
Right-click an active connection to perform the following actions:
• Connect. This menu item is disabled for an active connection.
• Refresh. Use this option to refresh the session and the the published resources view in the
right pane. If there were changes on the Parallels RAS side, they will be reflected in the Parallels
Client.
• Connection Properties. Display the connection properties dialog where you can view (but not
modify) the connection properties. To modify the connection properties, you must disconnect it
first.
• Change Domain Password. Allows you to change the current user's domain password.
Displays the Parallels Client Logon dialog where you need to specify the existing password.
Then displays the Change Domain Password dialog allowing you to specify a new password.
The password must meet the requirements set by your system administrator. The requirements
are displayed in the dialog, and the password that you enter is validated against these
requirements. To proceed with changing your password, all of the requirements must be met.
• Create Shortcuts for All Visible Applications. Creates shortcuts on the local desktop for all
applications that are displayed in the published resources pane in the main Parallels Client
window.
40
Page 41

Using Parallels Client for Linux
• Delete Shortcuts from Desktop. Deletes shortcuts from the local desktop that were previously
created by clicking the Create Shortcuts for all visible Applications menu item.
• Disconnect. Disconnects the selected connection.
• Log Off. Logs off Parallels Client from the session.
• Delete. Deletes a connection. A confirmation dialog is displayed before the connection is
deleted.
Using an RDP Connection
To connect to a remote computer, double-click an RDP connection (or right-click > Connect).
You can have multiple active connections at the same time (both standard RDP and RAS). To
switch between active connections in Parallels Client, click a connection in the left pane or click the
corresponding tab page in the right pane.
Right-click an active RDP connection to perform the following actions:
• Connect. This menu item is disabled for an active connection.
• Connection Properties. Display the connection properties dialog where you can view (but not
modify) the connection properties. To modify the connection properties, you must disconnect it
first.
• Create Shortcut. Creates a shortcut for this connection on the local desktop.
• Delete Shortcut from Desktop. Deletes the shortcut from the local desktop that was
previously created by clicking the Create Shortcut menu item.
• Disconnect. Disconnects the connection.
• Delete. Deletes a connection. A confirmation dialog is displayed before the connection is
deleted.
Exporting and Importing Parallels Client Settings
You can export current Parallels Client settings to a file to have a backup or to import the settings
into Parallels Client installed on a different computer. The following settings are exported:
• All existing connections including all individual connection properties.
• Parallels Client preferences (global options).
To export the current Parallels Client settings to a file, click File on the main toolbar and then click
Export Settings. In the dialog that opens, specify a file name and destination folder. Click Save to
export the settings. The file is saved with the ".2xc" extension.
41
Page 42

Using Parallels Client for Linux
To import the settings, click File > Import Settings. In the dialog that opens, select the ".2xc" file
and click Open. Please note that the imported settings override the current Parallels Client settings.
Parallels Client Network Configuration File
Parallels Client for Linux network settings can be specified using the configuration file, which can be
found at the following location:
~/.config/2X/Client/parallelssettings
The settings are user specific. If a Linux machine is used by multiple users, each user needs to
modify his/her own file.
Format
The settings can be specified using the following format:
[SETTING]=[VALUE]
Example:
NETWORK_CHECK_INTERVAL=10000
Parameters
This section describes parameters that can be used in the parallelssettings configuration
file.
NETWORK_CHECK_INTERVAL
Specifies the network downtime limit. All connections are disconnected if the network is offline for
the specified time period.
Value: Time in milliseconds
Default: 10000 milliseconds (10 seconds)
Example:
Set the time limit to 20 seconds.
NETWORK_CHECK_INTERVAL=20000
42
Page 43

Using Parallels Client for Linux
KA_ENABLE
Enable or disable the network keep-alive option. Sends network probes to detect if the network
connection is alive.
Value: 1 (Enabled) or 0 (Disabled)
Default: 1 (Enabled)
Example:
Disable network probing:
KA_ENABLE=0
KA_MAXIDLE
Specifies the idle time before the keep-alive network probing is initiated. Depends on the
KA_ENABLE option being enabled.
Value: Time in seconds.
Default: 5 seconds
Example:
Set the idle time to 10 seconds:
KA_MAXIDLE=10
KA_COUNT
Specifies the number of keep-alive probes to send before closing the connection. Depends on the
KA_ENABLE option being enabled.
Value: An integer greater than 0.
Default: 3
Example:
Set the number of probes to 6:
KA_COUNT=6
43
Page 44

Using Parallels Client for Linux
KA_INTERVAL
Specifies the idle time between sending keep-alive network probes. Depends on the KA_ENABLE
option being enabled.
Value: Time in seconds.
Default: 2 seconds
Example:
Set the idle time to 4 seconds:
KA_INTERVAL=4
USER_TIMEOUT
Specifies the time period during which the transmitted data may remain unacknowledged before
the connection is closed. This option is only supported on Linux kernel v2.6.37 and later.
Value: Time in milliseconds
Default: 9000 milliseconds (9 seconds)
Example:
Set the time period to 10 seconds.
USER_TIMEOUT=10000
Parallels Client Command Line Interface
Usage
/opt/2X/Client/bin/appserverclient -s Server -u User [options]
General Options
General options:
-m: operating mode
2G for Parallels RAS gateway access client(default)
44
Page 45

Using Parallels Client for Linux
2D for Parallels RAS direct access client
AL for Parallels RAS application list
MS for Microsoft Terminal Server client
MF for Microsoft Terminal Server fullscreen client
MX for Microsoft Terminal Server fullscreen client, that spans over all monitors
-s: server[:port] (default port is 80 for 2G and 2D modes and 3389 for MS and MF modes)
-s: ssl://server[:port] secure access client (TLS/SSL)
-b: altserver[:port] (default port is 80 for 2G and 2D modes and 3389 for MS and MF modes)
-u: user name. It can include domain: -u user@host.domain or -u user@ntdomain
-p: password.
-d: domain.
-a: application to start.
-f: working folder.
-i: 2xa shortcut file.
2xa shortcut files available through Parallels RAS web interface, and include published
application settings.
-o: full path to application listing output file
-x: proxy, can be:
socks4://[username@]proxy[:port]
socks4a://[username@]proxy[:port]
socks5://[username[:password]@]proxy[:port]
http://[username[:password]@]proxy[:port]
RDP Options
RDP options:
-H: client hostname.
-T: window title for desktop connection.
-w: override desktop width. It should be used with -h parameter.
45
Page 46

Using Parallels Client for Linux
-h: override desktop height. It should be used with -w parameter.
-g, -geometry {width}x{height}[{+-}{xoff}[{+-}{yoff}]]:
standard application geometry, should be used with -m MS parameter only.
-c: connection color depth in bits (default: 24 bits).
-1: force seamless application placement on primary monitor only.
-X: embed into another window with a given id, should be used with -m MS parameter only.
-K: keep window manager key bindings.
-e: RDP experience one or more ORed value(s) from:
0x7F to disable everything
0x01 to disable wallpapers
0x02 to disable full window drag
0x04 to disable menu animations
0x08 to disable theming
0x20 to disable cursor shadow
0x40 to disable cursor blinking
0x80 to enable font smoothing
0x00 to disable nothing (default)
-z: RDP compression
0x00 to disable nothing (default)
0x01 to disable compression
0x02 to limit to RDP4 compression
0x03 to limit to RDP5 compression
-t: maximum network timeout in seconds (default: 5 seconds)
-l: locale identifier in HEX format (default: 0x0409 - English (United States))
--admin or -q: connect to administer server
46
Page 47

Using Parallels Client for Linux
Device Options
Device options:
-P: redirect printer(s) (this flag can be repeated), can be
"printcap" to use printers from '/etc/printcap'
use this option if printcap was configured to contain driver name as printer comment:
lp0|drivername:rm=clientname:rp=lp0:
"printername" to use default printer driver
"printername=drivername" to specify driver name
-S: redirect sound, can be
"off" to disable sound (default)
"local"= quality to bring it to the client with:
"normal" for normal quality
"good" for good quality (default)
"verygood" for very good quality
"remote" to leave it on the server
-D: redirect drive(s) (this flag can be repeated), can be
"remotename=localpath"
-O [option]: redirect serial ports (this flag can be repeated with option)
"off" to disable port redirection (default)
"auto" for COM1=/dev/ttyS0, COM2=/dev/ttyS1, LPT1=/dev/lp0
or option to override local device path: COM1=/dev/debugtty
-C: redirect smart card reader; pcscd smart card manager should be installed in order to use this
feature.
-U [options]: redirect URI. options are comma separated list of:
"off" disable URI redirection (default).
"url" redirect URL (http: and https:).
"mailto" redirect Mail (mailto:).
Use "url,mailto" to redirect both URL and Mail.
-k [command]: execute special command in active session, where command is one of:
47
Page 48

Using Parallels Client for Linux
"logoff" gracefully log off a published application session.
"disconnect" gracefully disconnect a session.
Other Options
Other options:
-v: print version info
--help or -?: to get help information
Examples
The following examples illustrate the use of the Parallels Client for Linux command-line interface:
appserverclient -s<Server IP> -a<"Application Name"> -u<User Name>
appserverclient -s192.168.0.1 -a"Internet Explorer" -uAdministrator
In this case you are requested to logon before the application is loaded.
appserverclient -s<Server IP> -a<"Application Name"> -u<User Name> -p<Password>
appserverclient -s192.168.0.1 -a"Media Player" -uAdministrator –ppassword
In this case, the logon screen is bypassed if the password is correct.
Note: The application name is case sensitive and must be enclosed in quotes. Examples: "Notepad",
"Internet Explorer", "Media Player".
Table of Available Locale Identifiers
Identifier Name
0x0401 Arabic (Saudi Arabia)
0x0403 Catalan (Spain)
0x0404 Chinese (Taiwan)
0x0804 Chinese (People's Republic of China)
0x0405 Czech (Czech Republic)
0x0406 Danish (Denmark)
0x0407 German (Germany)
48
Page 49

0x0807 German (Swiss)
0x0408 Greek (Greece)
0x0409 English (United States)
0x0809 English (Great Britain)
0x0C0A Spanish - Modern Sort (Spain)
0x0425 Estonian (Estonia)
0x040B Finnish (Finland)
0x040C French (France)
0x080C French (Belgium)
0x0C0C French (Canada)
0x100C French (Swiss)
0x040D Hebrew (Israel)
0x040E Hungarian (Hungary)
0x0410 Italian (Italy)
0x0411 Japanese (Japan)
0x0412 Korean (Korea)
0x0427 Lithuanian (Latvia)
0x0426 Latvian (Latvia)
0x0413 Dutch (Netherlands)
0x0813 Dutch (Belgium)
0x0414 Norwegian (Norway)
0x0415 Polish (Poland)
0x0416 Portuguese (Brazil)
0x0816 Portuguese (Portugal)
0x0418 Romanian (Romania)
0x0419 Russian (Russia)
0x041A Croatian (Croatia)
0x041B Slovak (Slovakia)
0x041D Swedish (Sweden)
0x041E Thai (Thailand)
0x041F Turkish (Turkey)
0x0424 Slovenian (Slovenia)
0x042A Vietnamese (Vietnam)
0x042D Basque (Spain)
0x040F Icelandic (Iceland)
Using Parallels Client for Linux
49
Page 50

Index
Index
A
Adding a New Connection - 11
Advanced Settings - 25, 36
Authentication - 24, 35
C
Checking for Updates - 9
Configuring a RAS Connection - 13
Configuring an RDP Connection - 26
Configuring Global Options - 38
Configuring Parallels Client for Linux - 8
Connection - 14, 27
D
Device Options - 47
Display - 16, 29
E
Examples - 48
Experience - 23, 34
Exporting and Importing Parallels Client
Settings - 41
F
Format - 42
G
General Options - 44
Getting Started - 5
I
L
Local Resources - 20, 31
N
Network - 24, 35
NETWORK_CHECK_INTERVAL - 42
O
Other Options - 48
P
Parallels Client Command Line Interface - 44
Parallels Client Network Configuration File -
42
Parameters - 42
Printing - 18
Programs - 34
R
RDP Options - 45
S
System Requirements - 5
U
USER_TIMEOUT - 44
Using a RAS Connection - 40
Using an RDP Connection - 41
Using Parallels Client for Linux - 11
Installing Parallels Client for Linux - 6
K
KA_COUNT - 43
KA_ENABLE - 43
KA_INTERVAL - 44
KA_MAXIDLE - 43
 Loading...
Loading...