Page 1

Parallels® Plesk Panel
Parallels Plesk Panel 9.5 Quick Start
Guide
Revision 1.2
Page 2

Copyright Notice
ISBN: N/A
Parallels
660 SW 39th Street
Suite 205
Renton, Washington 98057
USA
Phone: +1 (425) 282 6400
Fax: +1 (425) 282 6444
© Copyright 1999-2010,
Parallels, Inc.
All rights reserved
Distribution of this work or derivative of this work in any form is prohibited unless prior written
permission is obtained from the copyright holder.
Patented technology protected by U.S.Patents 7,328,225; 7,325,017; 7,293,033; 7,099,948;
7,076,633.
Patents pending in the U.S.
Product and service names mentioned herein are the trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 3

Contents
Preface 4
Typographical Conventions ........................................................................................................... 4
Feedback ....................................................................................................................................... 5
About This Guide 6
Becoming Familiar with Parallels Plesk Panel 7
Setting Up the Server 13
Simplifying Setup of User Accounts 34
Simplifying Setup of Domains and Web Sites 43
Creating User Accounts 48
Adding Reseller Accounts for Hosting Resellers ......................................................................... 49
Adding Client Accounts for End Users of Hosting Services ........................................................ 54
Hosting Web Sites 59
Setting Up a Hosting Account for a Web Site ............................................................................. 60
Allowing a Site Owner to Log In to Control Panel ............................................................. 66
Creating and Publishing a Site .................................................................................................... 68
Creating and Publishing Web Sites Using Sitebuilder ...................................................... 68
Publishing Sites Through FTP .......................................................................................... 69
Publishing Sites Through Parallels Plesk Panel File Manager ......................................... 69
Publishing Sites Through SSH Connection ...................................................................... 70
Publishing Sites with Microsoft FrontPage ........................................................................ 70
Publishing Sites with Adobe Dreamweaver ...................................................................... 74
Page 4
4 Preface
Preface
In this section:
Typographical Conventions ................................................................................. 4
Feedback ............................................................................................................. 5
Typographical Conventions
The following kinds of formatting in the text identify special information.
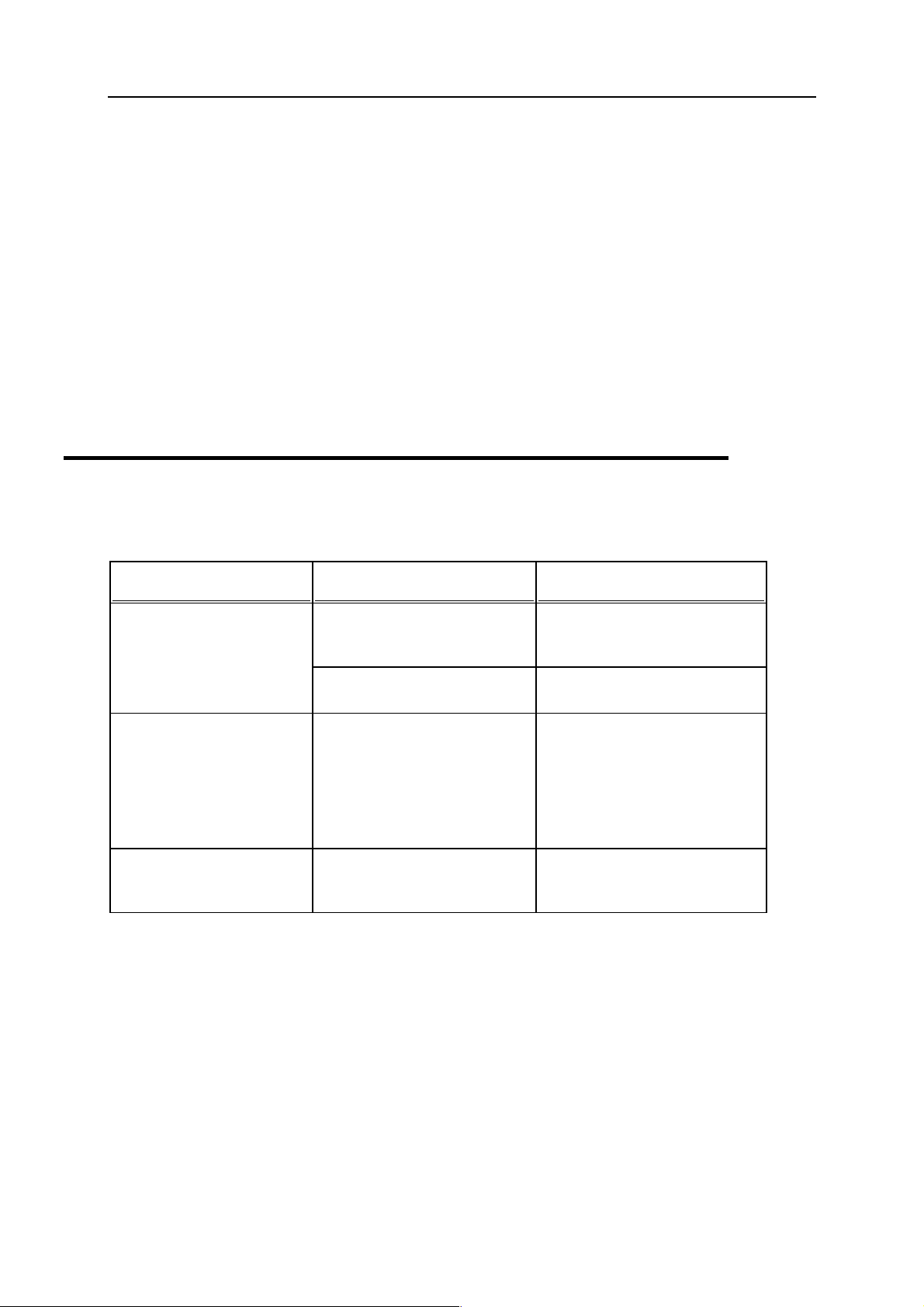
Formatting convention Type of Information Example
Special Bold
Italics
Monospace
Items you must select, such as
menu options, command
buttons, or items in a list.
Titles of chapters, sections,
and subsections.
Used to emphasize the
importance of a point, to
introduce a term or to
designate a command line
placeholder, which is to be
replaced with a real name or
value.
The names of style sheet
selectors, files and directories,
and CSS fragments.
Go to the QoS tab.
Read the Basic Administration
chapter.
The system supports the so
called wildcard character
search.
The license file is called
license.key.
Page 5
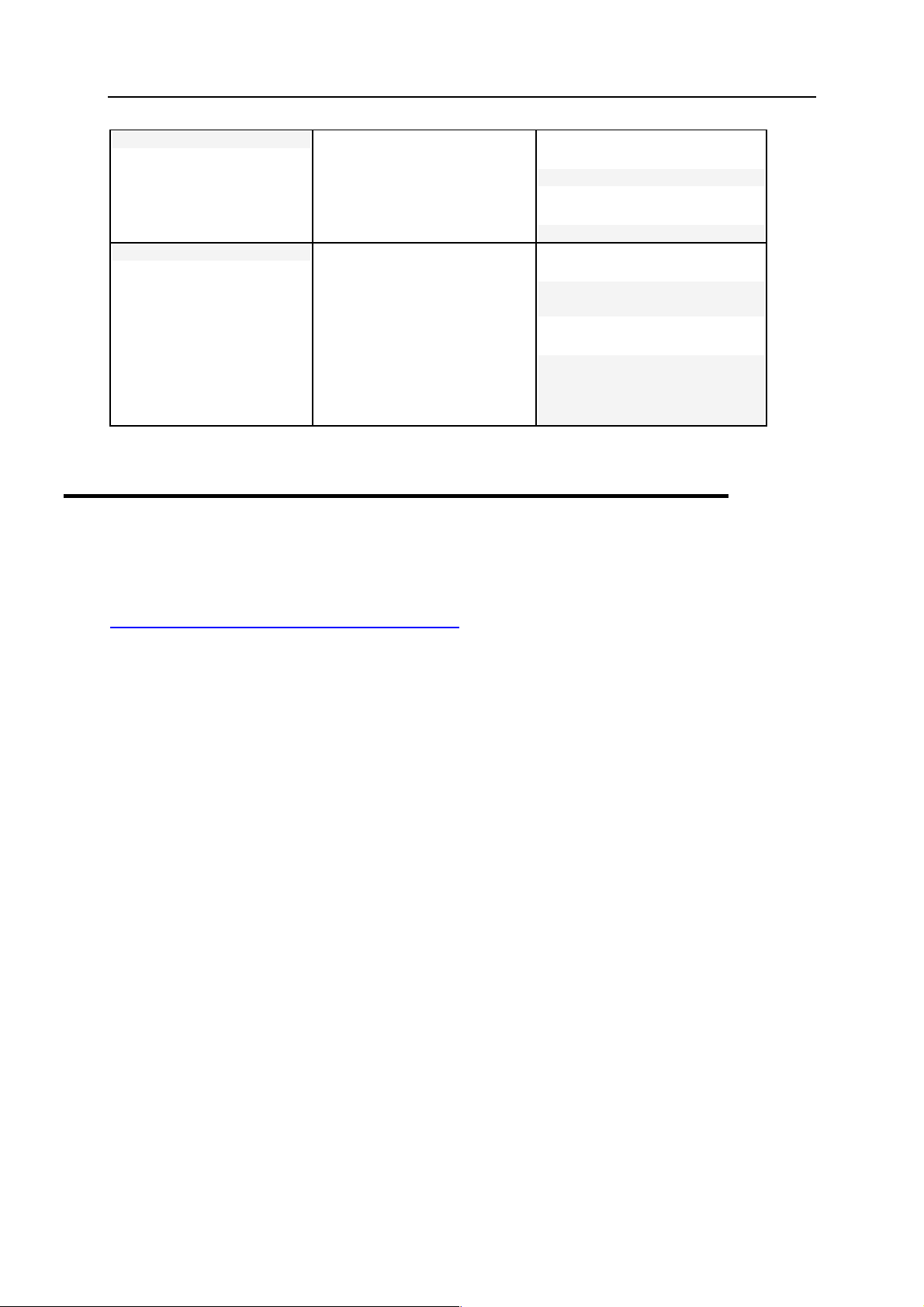
Preface 5
d
Preformatted Bol
What you type, contrasted with
on-screen computer output.
Unix/Linux:
# cd /root/rpms/php
Windows:
>cd %myfolder%
Preformatted
On-screen computer output in
your command-line sessions;
source code in XML, C++, or
other programming languages.
Unix/Linux:
# ls –al /files
total 14470
Windows:
>ping localhost
Reply from 127.0.0.1:
bytes=32 time<1ms
TTL=128
Feedback
If you have found an error in this guide, or if you have suggestions or ideas on how to
improve this guide, please send your feedback using the online form at
http://www.parallels.com/en/support/usersdoc/
chapter and section titles, and the fragment of text in which you have found an error.
. Please include in your report the guide's title,
Page 6
C HAPTER 1
About This Guide
This guide is intended to give administrators a practical introduction to Parallels Plesk
Panel™ by explaining how to perform basic administrative tasks and configure your
control panel for further use. It covers a straightforward Parallels Plesk Panel scenario
to help you start working with the control panel immediately after the installation.
For more information about Parallels Plesk Panel's functions, refer to Parallels Plesk
Panel Administrator's Guide at Parallels Web site available in HTML and printable PDF
formats: http://www.parallels.com/en/products/plesk/docs/
The Parallels Plesk Panel Administrator's Guide is also accessible from your control
panel as context-sensitive help: to open it, log in to control panel and click the Help
shortcut in the left navigation pane.
For information about installing Parallels Plesk Panel components, see the Parallels
Plesk Panel Installation Guide at Parallels Web site available in HTML and printable
PDF formats: http://www.parallels.com/en/products/plesk/docs/
For frequently asked questions related to Parallels Plesk Panel and other Parallels
products, visit the Parallels online knowledge base at http://kb.parallels.com
.
.
Page 7

C HAPTER 2
Becoming Familiar with Parallels Plesk Panel
Parallels Plesk Panel is a hosting automation solution that gives you full control over
the managed Web hosting servers and simplifies setup and management of user
accounts, Web sites, and e-mail accounts.
Parallels Plesk Panel effectively lowers the threshold for non-technical users to log in
and self administer their virtual host account on your Web server.
User accounts hierarchy of Parallels Plesk Panel is limited to five user levels:
Server administrator account.
Reseller accounts. These accounts are created for the customers who need to
resell hosting services and host their own Web sites.
Client accounts. These accounts are created for the customers who do not need to
resell hosting services, but need to host Web sites.
Domain administrator accounts. These accounts can be created to allow access to
the Parallels Plesk Panel for site administrators. One domain administrator account
per one site.
E-mail user accounts. These accounts can be created to allow access to the
Parallels Plesk Panel for e-mail users.
Parallels Plesk Panel also allows site owners to host personal Web pages or small
sites called Web users' personal pages. However, these accounts are considered sub
accounts and are not given access to the control panel.
¾ Now let's log in to the control panel and perform initial configuration
steps:
1. Log in to the Parallels Plesk Panel as administrator.
Open your Web browser, and in the address bar, type your server's IP address.
Parallels Plesk Panel requires that you access the control panel using a secure
SSL connection, so you need to use the https prefix and specify the port 8443 to
access the user interface. For example, https://192.168.10.10:8443, where
192.168.10.10 is your server's IP address.
Note: After you set up a host name for your server, you will be able to access your
Parallels Plesk Panel by host name instead of IP address.
Click through the SSL warning and type the user name "admin" and the default
password "setup" into the Username and Password boxes, respectively. If this is your
first login to the control panel, use the default password "setup". Click Log In.
Page 8
8 Becoming Familiar with Parallels Plesk Panel
2. Accept the license agreement. Note that if y ou run Parallels Plesk
Panel inside a Virtuozzo container, and the Offline management mode
is switched off in the Virtuozzo Power Panel, then this license
agreement is not shown.
Read the terms of the License Agreement and, if you agree to all the terms, select
the I agree to the terms of this license agreement and Do not show it again check boxes.
Click Accept.
3. Specify the following:
a Under Preferences, specify the full host name for your server. This is a three-part
name without WWW prefix, for example, host.example.com.
b Under Default IP Address, select the primary IP address that you would like to use
on your server.
c Under Shared IP Addresses, specify which of the available IP addresses should be
used for hosting Web sites. Select an IP address and click Shared >>.
You can skip this step and define the type of IP addresses later (Home > IP
Addresses).
d Under Administrator's Preferences, enter the new password and confirm it in the
New password and Confirm password boxes. The password can have up to 14
symbols. Note that the password is case sensitive.
4. Click OK.
5. Fill in administrator’s contact information.
6. Click OK.
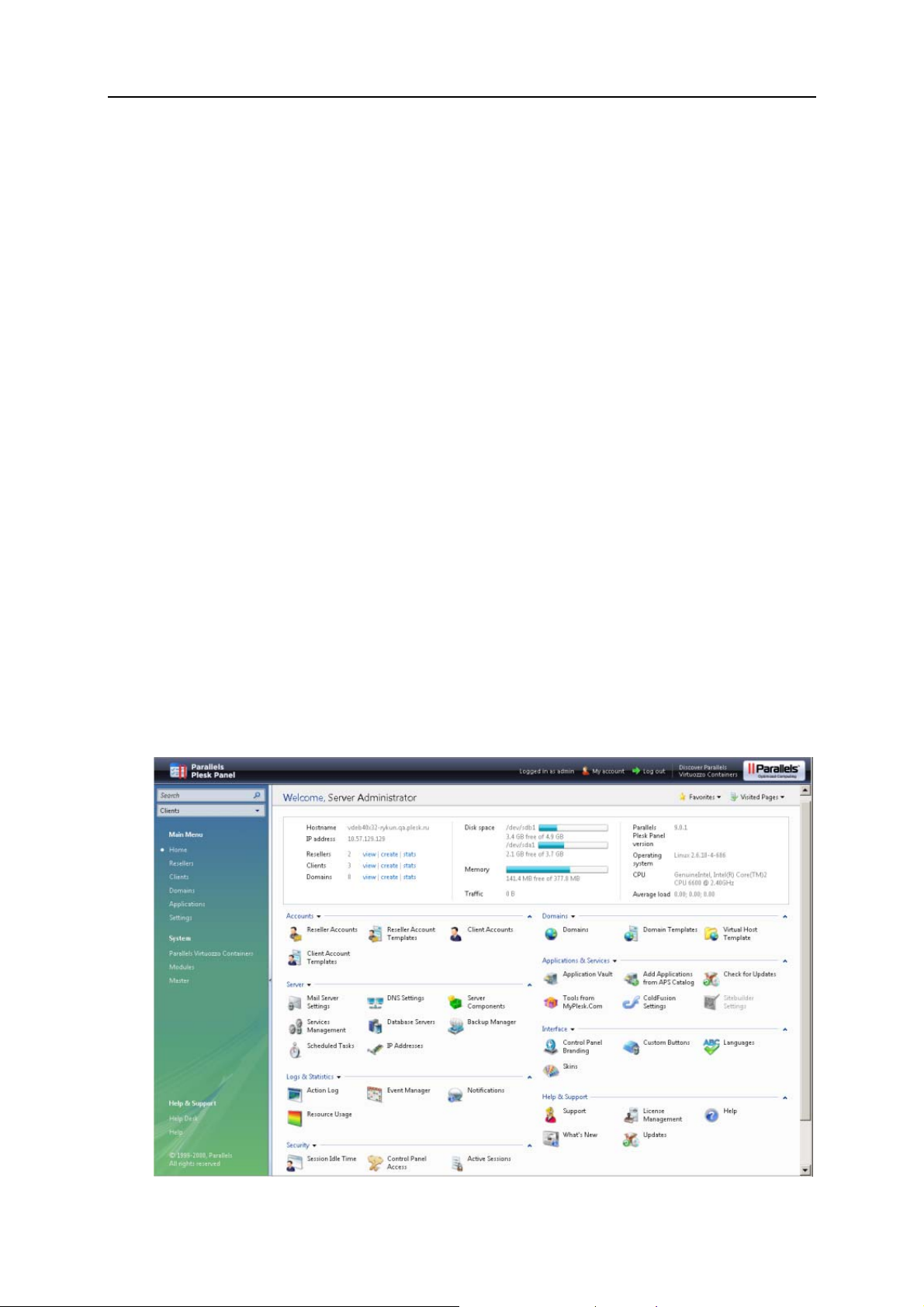
The control panel opens and you see the administrator's Home page. It provides
shortcuts to the most frequently performed operations.
Page 9

Becoming Familiar with Parallels Plesk Panel 9
The top banner area provides access to the following functions:
My account. This is where you can select a language and theme for your control
panel and change your contact information.
Switch user. This is where you can switch between user accounts. This shortcut is
shown only when single sign-on technology is enabled on the server.
Log out. This is where you close your session when you have finished working with
control panel.
The navigation pane on the left provides access to the following sets of functions:
Search area. Use it when you need to find user accounts and domains hosted on
your server.
Home. This is where you start working with the control panel. Most of the operations
you might need to perform are accessible from this area.
Resellers. This is where you perform operations on reseller accounts. Resellers can
use hosting services and resell the services to end users. Resellers cannot create
reseller accounts for other users. You can accomplish the following tasks from this
area of the control panel:
Create, modify, remove user accounts for resellers and their customers (referred
to as clients).
Create, modify, remove reseller account templates.
View traffic usage reports.
Clients. This is where you perform operations on user accounts. Clients are end
users of hosting services; they cannot resell hosting services. You can accomplish
the following tasks from this area of the control panel:
Create, modify, remove user accounts.
Create, modify, remove user account templates (referred to as client account
templates).
View traffic usage reports.
Domains. This is where you perform operations on Web sites. You can accomplish
the following tasks from this area of the control panel:
Add Web sites (set up DNS zones, configure Web hosting settings and resource
usage limits), modify Web hosting settings, remove Web sites.
Create, modify, remove Web site hosting templates (referred to as domain
templates).
Applications. This is where you select which applications will be available for
installation on users' sites.
Settings. This is where you configure and manage the server and program
components used by Parallels Plesk Panel.
Modules. This is where you manage the additional modules that extend Parallels
Plesk Panel capabilities, such as Firewall, Game Server, VPN, and others.
Master. This shortcut gives you access to centralized management of Parallels Plesk
Panel-enabled servers.
Page 10

10 Becoming Familiar with Parallels Plesk Panel
Global Account. This shortcut appears in your Parallels Plesk Panel when the single
sign-on capabilities are switched on on the hosting server. Single sign-on
technology allows you to log in to different Parallels products using a single global
login name and password. This shortcut is used for changing the global login
settings.
Help Desk. This is the help desk system integrated with your control panel. You can
use it to view and solve the problems reported to you by your customers.
Help. Provides context sensitive help with search function.
To see information about a tool or an item on the page, hover the cursor over an item,
without clicking it, and a small hover box appears with supplementary information
regarding the item being hovered over.
If you install the Sitebuilder component and configure it as described in the Parallels
Plesk Panel 9.5 Administrator's Guide, section Enabling Integration with Sitebuilder, the
following shortcuts are also shown in your control panel's navigation pane under the
Sitebuilder Administration group:
Desktop. This provides shortcuts to the task-oriented wizards. Here you can perform
any operations on your account and Web sites through the Sitebuilder system. For
more information, see
http://download1.parallels.com/SiteBuilder/4.5.0/doc/reseller/en_US/html/using_des
ktop_interface.htm.
Users. Here you can add and manage user accounts and service plans for your
customers. For more information, see
http://download1.parallels.com/SiteBuilder/4.5.0/doc/reseller/en_US/html/signing_u
p_customers.htm.
Sites. Here you can add and manage sites. For more information, see
http://download1.parallels.com/SiteBuilder/4.5.0/doc/reseller/en_US/html/managing
_sites.htm.
Server. Here you can view and manage the following system settings:
Trial Sites Settings. Here you can configure settings for trial sites created by your
prospective customers. For more information, see
http://download1.parallels.com/SiteBuilder/4.5.0/doc/reseller/en_US/html/setting
_up_sitebuilder_wizard_for_anonymous_visits.htm
Branding. Here you can configure the logo and title setting for your prospective
customers. For more information, see
http://download1.parallels.com/SiteBuilder/4.5.0/doc/reseller/en_US/html/setting
_up_logo_and_title_bar_text.htm
Notifications. Here you can configure settings for notifications sent by Sitebuilder
to your users. For more information, see
http://download1.parallels.com/SiteBuilder/4.5.0/doc/reseller/en_US/html/config
uring_email_message_sent_at_trial_site_publishing_attempt.htm.
Modules. Here you can view the list of available modules. For more information,
see
http://download1.parallels.com/SiteBuilder/4.5.0/doc/reseller/en_US/html/viewin
g_and_configuring_sitebuilder_wizard_presets_and_modules.htm.
Page 11
Becoming Familiar with Parallels Plesk Panel 11
Page Sets. Here you can view the list of available page sets. For more
information, see
http://download1.parallels.com/SiteBuilder/4.5.0/doc/reseller/en_US/html/viewin
g_and_configuring_sitebuilder_wizard_presets_and_modules.htm.
Site Families. Here you can view the list of available templates that combine
design templates and page sets. For more information, see
http://download1.parallels.com/SiteBuilder/4.5.0/doc/reseller/en_US/html/viewin
g_and_configuring_sitebuilder_wizard_presets_and_modules.htm.
The main working area on the right provides access to the tools available for the
current section of the control panel selected in the navigation pane. Additional
operations are accessible from drop-down menus that open when you click group titles.
To navigate through Parallels Plesk Panel, you can use a path bar: a chain of links that
appears in the right part of the screen, below the banner area.
To the right of the path bar, there are Favorites and Visited Pages menus. The Visited
Pages menu keeps the shortcuts to the recently visited control panel screens. These
shortcuts are added automatically. The Favorites menu keeps the shortcuts to the
screens that you manually add to favorites. For information about working with
shortcuts in the Favorites menu, see the Parallels Plesk Panel 9.5 Administrator's
Guide, section Customizing Your Home Page.
To return to a previous screen, use the shortcuts in the path bar, or the Up Level icon in
the upper-right corner of the screen.
When changing settings for a user account, domain name, or e-mail account, you can
quickly select another user account, domain name, or e-mail account whose settings
you also want to change. To do this, click a small arrow icon located to the right of the
user name, domain name, or e-mail address.
This will open a list of user accounts, domain names or e-mail addresses that you can
select.
Page 12

12 Becoming Familiar with Parallels Plesk Panel
To sort a list by a certain parameter in ascending or descending order, click on the
parameter's title in the column heading. The order of sorting will be indicated by a small
triangle displayed next to the parameter's title.
Now proceed to the following chapter and set up your server.
Page 13

C HAPTER 3
Setting Up the Server
¾ To set the global settings for a Linux-based hosting server:
1. On your Home page, open the Server group title menu, and select Server
Settings.
2. Specify the following:
Button label length. To prevent lengthy button captions in languages other than
English from overlapping in the control panel, you may want to specify a limit
here. Any button caption longer than the defined limit will be shortened and
ended with ellipsis (...).
Prevent users from working with the control panel until interface screens are completely
loaded. Leave this selected to avoid errors that might occur when users try to
interact with control panel before is it ready.
Administrator's interface language. Select the language for your control panel.
Administrator's interface skin. Select the skin (theme) for your control panel.
Home page preset. Once you customize the Home page and save the settings in a
template as described in Parallels Plesk Panel 9.5 Administrator's Guide,
section Customizing Your Home Page, you will be able to select your template
here. For now, leave the default value selected.
Allow multiple sessions under administrator's login. By default Parallels Plesk Panel
allows multiple simultaneous sessions for several users logged in to the control
panel using the same login and password combination. This can be useful when
delegating management functions to other users or in case if you accidentally
close your browser without logging out, thus becoming unable to log in again
until your session expires. You may want to switch off this capability if you do
not need it.
Full host name.
Apache restart interval. Any changes to hosting account settings made through
control panel take effect only when Web server is restarted. By default, Web
server is set to restart not more than once in every 15 minutes. This value is
optimal for most cases, and we recommend leaving this default setting. Note
that when there are no changes in hosting account settings, the Web server is
not forced to restart.
Web statistics and traffic usage statistics retention period. Specify how long the
statistics should be kept on the server.
Items that statistical utilities should count when calculating disk space and bandwidth
usage.
Page 14

14 Setting Up the Server
The option to forbid users from creating DNS subzones in other users' DNS superzones.
We recommend that you select this option, otherwise, users will be able to
create subdomains under domains belonging to other users, and set up Web
sites and e-mail accounts which could be used for spamming or even phishing
or identity theft.
3. Click OK.
¾ To set the global settings for a Windows-based hosting server:
1. On your Home page, open the Server group title menu, and select Server
Settings.
2. Specify the following:
Full host name.
Web statistics and traffic usage statistics retention period. Specify how long the
statistics should be kept on the server.
Items that statistical utilities should count when calculating disk space and bandwidth
usage.
The option to forbid users from creating DNS subzones in other users' DNS superzones.
We recommend that you select this option, otherwise, users will be able to
create subdomains under domains belonging to other users, and set up Web
sites and e-mail accounts which could be used for spamming or even phishing
or identity theft.
3. Click OK.
Now, let's set up the DNS service for serving your own domains. Setup of DNS zones
for newly added domains is automated: When you add a new domain name to control
panel, a zone file is automatically generated for it in accordance with the server-wide
DNS zone template and your server is instructed to act as a primary (master) DNS
server for the zone. If the DNS service on your Parallels Plesk Panel server will be
authoritative for Web sites that you host for your customers, and you do not want to set
up your own domain at this moment, skip this procedure and move on to the next
procedure for configuring the mail service. However, if you are going to set up in
Parallels Plesk Panel a domain name for hosting a Web site for your own organization
(let's call this domain "example.com"), follow these steps:
1. Register your domain name example.com with a domain name registrar
(domain name registration authority) of your choice. Provide the
registrar with the following information: nameservers ns1.example.com
and ns2 example.com, and two IP addresses assigned to your server
by your provider.
2. Log in to Parallels Plesk Panel, and click the Domains shortcut in the
navigation pane.
3. Click Create Domain.
Page 15

Setting Up the Server 15
4. In the Domain name field, leave the WWW box selected, and type your
domain name example.com. Having the www alias preceding a domain
name will allow users to get to the site no matter what they type in their
browsers: www.example.com and example.com will both point to the
same site.
5. From the Assign IP address menu, select the required IP address. You
should select a dedicated IP address (not shared among other sites),
or, in terms of Parallels Plesk Panel, exclusive IP address to be able to
install an authentic digital SSL certificate for securing customers'
communications to your hosting server.
6. In the Use domain template settings menu, leave the default domain value
selected. To facilitate setup of new Web sites, the control panel uses
settings inherited from domain templates. After your Web site is set up,
you can replace the default settings with other settings that suit your
needs better.
7. Under Switch on service, leave the Mail and DNS check boxes selected if
e-mail accounts and DNS zones will be served by the mail and DNS
services running on this server.
8. Under Hosting type, select the Web site hosting option to host the Web
site on this machine.
9. Specify the username and password that will be used for uploading site
content over FTP.
10. Click Next >>.
11. Specify the following settings:
SSL support. Secure Sockets Layer encryption is generally used for protecting
transfer of sensitive data during online transactions on e-commerce Web sites
that run on dedicated IP addresses. SSL certificates that participate in the
encryption process are usually applied to a single domain name on a single IP
address, therefore, each site that needs SSL protection must be hosted on a
dedicated IP address. An exception to this is subdomains, which you can
protect with a wildcard certificate. Installing an SSL certificate on a Web server
that hosts several Web sites with different domain names on a single IP address
(shared or name-based hosting) is technically possible, however, it is not
recommended: the encryption will be provided, but users will get warning
messages on attempt to connect to the secure site. To allow SSL encryption for
this Web site, select the SSL support check box.
Use a single directory for housing SSL and non-SSL content (available only for Linux
hosting). By default, when you publish a site through your FTP account, you
need to upload the Web content that should be accessible through secure
connections to the httpsdocs directory, and the content that should be
accessible via plain HTTP, to the httpdocs directory. For the convenience of
publishing all content through a single location – httpdocs directory on your
FTP account, select the Use a single directory for housing SSL and non-SSL content
check box.
Page 16
16 Setting Up the Server
FTP login and FTP password. Specify the username and password that will be
used for publishing the site to the server through FTP. Retype the password into
the Confirm Password box.
Hard disk quota (available only for Linux hosting). Specify the amount of disk
space in megabytes allocated to the Web space for this site. This is the socalled hard quota that will not allow writing more files to the Web space when
the limit is reached. At attempt to write files, an error message will show. Hard
quotas should be enabled in the server's operating system, so if you see the
"Hard disk quota is not supported" notice to the right of the Hard disk quota field,
but would like to use the hard quotas on your server, log in to the server shell
and run the quotaon -a command to enable the hard quotas.
Access to server over SSH (available only for Linux hosting) or Access to server over
Remote Desktop (available only for Windows hosting). This allows you to upload
securely Web content to the server through a Secure Socket Shell or Remote
Desktop connection, however, allowing access to the server also poses a
potential threat to the server security, so we recommend that you leave the
Forbidden option selected.
Support for hosting services and scripting languages. Specify which of the following
programming and scripting languages should be supported by the Web server:
Active Server Pages (ASP), ASP.NET (on Windows-based hosting), Server Side
Includes (SSI), PHP hypertext preprocessor (PHP), Common Gateway Interface
(CGI), Fast Common Gateway Interface (FastCGI), Perl, Python, ColdFusion,
and Miva scripting required for running Miva e-commerce solutions. By default,
PHP is configured to operate in safe mode with functional restrictions. To learn
more about PHP safe mode, refer to http://php.net/features.safe-mode
web applications may not work properly with safe mode enabled: If an
application on your site fails due to safe mode, switch the safe mode off by
clearing the PHP 'safe_mode' on check box in the hosting account properties
(Domains > domain name > Web Hosting Settings).
. Some
Web statistics. To allow the Web site owner to view the information on the
number of people visited his or her site and the pages of the site they viewed,
select the statistics program from the Web statistics menu, and select the
accessible via password protected directory /plesk-stat/webst at check box. This will
install the statistics software of your choice, which will generate reports and
place them into the password protected directory. The domain/web site owner
will then be able to access Web statistics at the URL: https://yourdomain.com/plesk-stat/webstat using his or her FTP account login and
password.
Note: When you switch from one statistics program to another, all reports
created by the previously used statistics program are deleted and new
reports are created in accordance with the information read from log files
kept on the server. This means that if you configured the system (at Domains
> domain name > Log Manager > Log Rotation) so as to keep log files only for the
last month, then Web statistics will be available only for the last month.
Custom error documents. When visitors coming to the site request pages that the
Web server cannot find, the Web server generates and displays a standard
HTML page with an error message. If you wish to create your own error pages
and use them on your Web server, select the Custom error documents check box.
Page 17

Setting Up the Server 17
Additional write/modify permissions (available only for Windows hosting). This
option is required if Web applications under a domain will be using a file-based
database (like Jet) located in the root of httpdocs or httpsdocs folders.
Please note that selecting this option might seriously compromise the Web site
security.
Use dedicated IIS application pool (available only for Windows hosting). This option
enables the use of dedicated IIS application pool for Web applications on a
domain. Using dedicated IIS application pool dramatically improves the stability
of domain Web applications due to worker process isolation mode. This mode
gives each Web site hosted on the server the possibility to allocate a separate
process pool for execution of its Web applications. This way, malfunction in one
application will not cause stopping of all the others. This is especially useful
when you are using shared hosting package.
12. Click Next >>.
13. Specify the following settings:
Overuse policy. Specify what should be done to the site when disk space and
traffic limits are exceeded: To block the site, select the Overuse is not allowed
option. To allow the site to operate, select the Overuse is allowed option. Leave
the check box Notify the domain owner about reaching the resource limit selected if
you want the control panel to notify you when the resource usage limit is
reached.
Disk space. Specify the total amount of disk space allocated to a hosting account
associated with the domain. This amount is measured in megabytes. It includes
disk space occupied by all files related to the domain/Web site: Web site
contents, databases, applications, mailboxes, log files and backup files.
Traffic. Specify the amount of data in megabytes that can be transferred from the
Web site during a month.
Subdomains. Specify the number of subdomains that can be hosted under this
domain.
Domain aliases. Specify the total number of additional alternative domain names
that can be used for this site.
Web users. Specify the number of personal Web pages that can be hosted for
other users under his or her domain. This service is mostly used in educational
institutions that host non-commercial personal pages of their students and staff.
These pages usually have web addresses like http://yourdomain.com/~username. If you wish to allow execution of scripts embedded in
personal Web pages, select also the Allow the web users scripting check box. For
more information, refer to Parallels Plesk Panel 9.5 Administrator's Guide,
section Hosting Personal Web Pages.
Microsoft FrontPage accounts (only for Windows hosting). Specify the maximum
number of additional Microsoft FrontPage accounts that can be created under
the domain.
FTP accounts (available only for Windows hosting). Specify the maximum number
of additional FTP accounts that can be created under the domain.
Mailboxes. Specify the number of mailboxes that can be hosted under this
domain.
Page 18

18 Setting Up the Server
Mailbox quota. Specify the amount of disk space in kilobytes that is allocated for
storing e-mail messages and autoresponder attachment files to each mailbox
under this domain.
Mail redirects. Specify the number of mail forwarders that can be used in a
domain.
Mail groups. Specify the number of simple mailing lists that can be set up in a
domain.
Autoresponders. Specify the number of automatic responses that can be set up in
a domain.
Mailing lists. Specify the number of mailing lists that can run in a domain.
Databases. Specify the number of databases that can be hosted under this
domain.
Databases quota (only for Windows hosting). Specify the maximum disk space
amount in megabytes that MySQL and Microsoft SQL Server databases
respectively can occupy under the domain.
ODBC connections (available only for Windows hosting). Specify the total number
of ODBC connections that can be used under the domain.
ColdFusion DSN connections (available only for Windows hosting). Specify the total
number of ColdFusion DSN connections that can be used under the domain.
Java applications. Specify the maximum number of Java applications or applets
that the domain owner can install under a domain.
Shared SSL links (available only for Windows hosting). Specify the total number of
shared SSL links that can be used under the domain.
Expiration date. Specify the term for the Web site hosting account. At the end of
the term, the domain (Web site) will be suspended, its Web, FTP and mail
services will no longer be accessible to the Internet users, and domain owner
will not be able to log in to the control panel. Hosting accounts cannot be
automatically renewed, therefore, in order to bring the hosted domain name
(and Web site) back to operation, you will need to manually renew the hosting
account: click the Domains shortcut in the navigation pane, click the domain
name your need, click the Resource Usage icon, specify another expiration date,
click OK, then click the Unsuspend icon (Domains > domain name > Unsuspend).
14. Click Finish. You are taken to the domain management screen.
15. Correct the information in the DNS zone of your domain:
a In the Web Site group, click DNS Settings.
b Locate the records example.com NS ns.example.com and ns.example.com A <IP
address>, select the respective check boxes and click Remove. Now the default
records are removed, and you can specify the name servers that you have
registered with your registrar.
c Click Add Record. In the Record type menu, select the NS value, leave the Enter
domain name box blank, and in the Enter nameserver box, type ns1.example.com,
then click OK.
d Click Add Record. In the Record type menu, select the NS value, leave the Enter
domain name box blank, and in the Enter nameserver box, type ns2.example.com,
then click OK.
Page 19

Setting Up the Server 19
e Click Add Record. In the Record type menu, select the A value, in the Enter domain
name box, type the ns1 value, and in the Enter IP address box, type the first IP
address of your server that you registered with a registrar, then click OK.
f Click Add Record. In the Record type menu, select the A value, in the Enter domain
name box, type the ns1 value, and in the Enter IP address box, type the second IP
address of your server that you registered with a registrar, then click OK.
16. Specify the correct name servers in the server-wide DNS template:
a Click the Home shortcut in the navigation pane and then click DNS Settings. A list
of record templates opens.
b Locate the records <domain> NS ns.<domain> and ns.<domain> A <IP>, select the
respective check boxes and click Remove. Now the default records are removed,
and you can specify the name servers that you have registered with your
registrar.
c Click Add DNS Record. In the Record type menu, select the NS value, leave the
Enter domain name box blank, and in the Enter nameserver box, type
ns1.example.com, then click OK.
Click Add DNS Record. In the Record type menu, select the NS value, leave the
Enter domain name box blank, and in the Enter nameserver box, type
ns2.example.com, then click OK.
Now the server-wide DNS settings are set up properly, your domain example.com is
hosted on the server, and you can publish the site content. For instructions on
publishing a Web site, refer to the Publishing a Site section of this guide.
Now, let's set up the mail service. Your control panel works in cooperation with mail
server software, which provides mail services for your domains. After installation the
mail server is configured automatically and is ready to serve, however, we recommend
that you review the default settings to ensure that they satisfy your needs:
1. Click the Ho me shortcut in the navigation pane and then click Mail Server
Settings. The server-wide mail preferences screen will open on the
Preferences tab.
2. If you wish to limit the size of an e-mail message that can be sent
through your server, type the desired value in kilobytes into the
Maximum message size box, otherwise, leave this field blank.
3. If you wish to protect your users from dictionary attacks by not allowing
them to use simple passwords, select the Check the passwords for
mailboxes in the dictionary option.
A dictionary attack is when someone tries to find out a valid user name and
password by running a program that tries different combinations of dictionary words
in different languages. Dictionary attacks can be successful because many users
choose their passwords carelessly.
Note for Windows hosting users: To make this function work properly on
Windows platforms, make sure that the Password must meet complexity requirements
option is switched on in your server's Local Security Policy settings (the option is
located in Start > Administrative Tools > Local Security Policy > Account Policies >
Password policy).
Page 20
20 Setting Up the Server
4. To protect your server against unauthorized mail relaying or injection of
unsolicited bulk mail, select the Enable message submission check box to
allow your customers to send e-mail messages through the port 587.
Also notify your customers that they need to specify in their e-mail programs'
settings the port 587 for outgoing SMTP connections, and be sure to allow
connections to this port in your firewall settings.
5. Select the mail relay mode.
With closed relay the mail server will accept only e-mail addressed to the users who
have mailboxes on this server. Your customers will not be able to send any mail
through your outgoing SMTP server, therefore, we do not recommend closing mail
relay.
With relay after authorization, only your customers will be able to receive and send
e-mail through your mail server. We recommend that you leave the authorization is
required option selected, and specify allowed authentication methods:
POP3 authorization. With POP3 authorization, once a user has successfully
authenticated to the POP server, he or she is permitted to receive and send email through the mail server for the next 20 minutes (default value). You can
adjust this interval by specifying another value in the lock time box.
SMTP authorization. With SMTP authorization, your mail server requires
authorization if the e-mail message must be sent to an external address.
Note for Windows hosting users: If you do not wish to use relay restrictions
for networks that you trust, specify the network IP and mask in the Use no
relay restrictions for the following networks: field (e.g., 123.123.123.123/16) and
click the
corresponding to the network you wish to remove.
The relay hosts on the networks in the list are considered not to be potentially
operated by spammers, open relays, or open proxies. A trusted host could
conceivably relay spam, but will not originate it, and will not forge header
data. DNS blacklist checks will never query for hosts on these networks.
There is also an option to allow open relay without authorization, which, by default,
is hidden from the user interface. Opening mail relay without authorization is not
recommended because it allows spammers to send unsolicited mail through your
server. If you want to set the open relay, log in to the server's file system, locate the
file root.controls.lock in your Parallels Plesk Panel installation directory
(PRODUCT_ROOT_D/var/root.controls.lock on Unix and
PRODUCT_DATA_D/var/root.controls.lock on Windows platforms) and
remove the line /server/mail.php3:relay_open from this file. The open relay
option will show in your control panel.
icon. To remove a network from the list, click the icon
6. If you are setting up a Linux-based server, select antivirus and webmail
program components that should be available to the users. If you are
setting up a Windows-based server, you can select webmail and
antivirus later: click Settings in the navigation pane, and then click Select
Webmail and Select Antivirus.
7. Select the mail account name format (available only on Linux hosting).
Page 21

Setting Up the Server 21
Selecting the Use of short and full names is allowed option will allow users to log in to
their mail accounts by specifying only the left part of e-mail address before the @
sign (for example, username), or by specifying the full e-mail address (for example,
username@your-domain.com).
To avoid possible authorization problems for e-mail users who reside in different
domains but have identical user names and passwords, we recommend that you
choose the Only use of full mail account names is allowed option.
Once you have set your mail server to support only full mail account names, you
will not be able to switch back to supporting short account names until you make
sure there are no encrypted passwords for mailboxes and user accounts with
coinciding user names and passwords residing in different domains.
8. Click OK to submit any changes.
Set up spam filters. Parallels Plesk Panel supports anti-spam systems, such as
SpamAssassin spam filter, and protection systems based on DomainKeys, DNS
blackhole lists, Sender Policy Framework (SPF), and greylisting. This guide covers the
setup of SpamAssassin spam filter. For instruction on using DomainKeys, DNS
blackhole lists, Sender Policy Framework, and greylisting, refer to Parallels Plesk Panel
9.5 Administrator's Guide, section Setting Up Spam Protection.
¾ To set up spam filtering with SpamAssassin:
1. On your Home page, open the Server group title menu, and select Spam
Filter Settings.
2. To allow server-wide filtering based on the settings you define, select
the Switch on server-wide SpamAssassin spam filtering check box.
3. To let your users set their own spam filtering pref erences on a per-
mailbox basis, select the Apply individual settings to spam filtering check
box.
4. If you wish to adjust the amount of system resources the spam filter
should use (available only for Linux hosting), type the desired value
from 1 to 5 into the Maximum number of worker spamd processes to run (1-5)
box (1 is the lowest load, and 5 is the highest). We recommend that you
use the default value.
5. If you wish to adjust the spam filter's sensitivity, type the desired value
in the The score that a message must receive to qualify as spam box.
6. SpamAssassin performs a number of different tests on contents and
subject line of each message. As a result, each message scores a
number of points. The higher the number, the more likely a message is
spam. For example, a message containing the text string “BUY VIAGRA
AT LOW PRICE!!!” in Subject line and message body scores 8.3 points.
By default, the filter sensitivity is set so that all messages that score 7
or more points are classified as spam.
When your users receive lots of spam messages with the current setting, to
make filter more sensitive, try setting a lesser value in the The score that a
message must receive to qualify as spam box; for example, 6.
Page 22

22 Setting Up the Server
When your users are missing e-mails because your spam filter thinks they are
junk, try reducing filter sensitivity by setting a higher value in the The score that a
message must receive to qualify as spam box.
7. To reduce the load on your Windows server, you can select the Do not
filter if mail size exceeds specified size check box and specify the maximum
size of the message that the spam filter will test. Recommended mail
size limit is 150 - 250 Kbytes, which is usual for mail messages in
HTML format with images. The size of the mail is considered critical for
filter and server overload when it exceeds 500 Kbytes, which is usual
for mail messages containing attachments.
8. To make sure that the spam filter on your Windows server is not leaving
some e-mail messages unchecked (this can happen if the amount of
incoming mail is very large), limit the number of e-mail messages that
can be checked simultaneously in the Number of threads that spam filter
can create field.
9. Specify how to mark messages recognized as spam.
10. At the server level, you cannot set the server-wide spam filter to
automatically delete spam: you can do it only on a per-mailbox basis.
So, for the server-wide policy, you can choose only marking messages
as spam: “X-Spam-Flag: YES” and “X-Spam-Status: Yes” headers are
added to the message source by default, and if you want, the spam
filter will additionally include a specific text string to the beginning of
Subject line. To include a desired combination of symbols or words to
the message subject, type it into the Add the following text to the beginning
of subject of each message recognized as spam box. If you do not want the
spam filter to modify message subject, leave this box blank. If you want
to include into the subject line the number of points that messages
score, type _SCORE_ in this box.
11. If you use Parallels Plesk Panel for Windows, define the language
characteristics of mail that should always pass the filter by specifying
trusted languages and locales.
Select the required items from the boxes under Trusted languages and Trusted
locales and click Add >>.
Letters written in the specified languages and with the defined character sets
will not be marked as spam.
12. If you do not want your users to receive e-mail from specific domains or
individual senders, click the Black List tab, and then add the respective
entries to the spam filter’s black list:
Page 23

Setting Up the Server 23
To add entries to the black list, click Add Addresses. If you have a list of entries
stored in a file, click Browse to specify it, and then click OK. Otherwise, select the
From List option, and type the e-mail addresses into the E-mail addresses box.
Place each address in one row, or separate addresses with a coma, a colon, or
a white space. You can use an asterisk (*) as a substitute for a number of
letters, and question mark (?) as a substitute for a single letter. For example:
address@spammers.net, user?@spammers.net, *@spammers.net. Specifying
*@spammers.net will block the entire mail domain spammers.net. To save the
entries you added, click OK, then confirm adding, and click OK again.
To remove entries from the black list, under the Black List tab, select the entries
and click Remove. Confirm removal and click OK.
13. If you want to be sure that you and your users will not miss e-mail from
specific senders, click the White List tab, and then add e-mail addresses
or entire domains to the spam filter’s white list:
To add entries to the white list, click Add Addresses. If you have a list of entries
stored in a file, click Browse to specify it, and then click OK. Otherwise, select the
From List option, and type the e-mail addresses into the E-mail addresses box.
Place each address in one row, or separate addresses with a coma, a colon, or
a white space. You can use an asterisk (*) as a substitute for a number of
letters, and question mark (?) as a substitute for a single letter. For example:
address@mycompany.com, user?@mycompany.com, *@mycompany.com.
Specifying *@mycompany.com will add to the white list all e-mail addresses that
are under the mycompany.com mail domain. To save the entries you added,
click OK, then confirm adding, and click OK again.
To remove entries from the white list, under the White List tab, select the entries
and click Remove. Confirm removal and click OK.
14. Once finished with setting up the spam filter, click OK.
Now all the incoming mail will be filtered on the server side. By default, spam filter does
not delete spam mail, it only adds the "X-Spam-Flag: YES" and "X-Spam-Status: Yes"
headers to the message, and "*****SPAM*****" text string to the beginning of Subject
line of each message recognized as spam.
If you have enabled the Apply individual settings to spam filtering option, then your users
will be able to set their spam filters so as to automatically delete junk mail. They will
also be able to set up their personal black and white lists of correspondents that will
override the server settings, and teach the spam filter on a per-mailbox basis.
Now let's set up antivirus for protecting your customers' mailboxes from viruses.
¾ To set up antivirus on a Windows-based hosting server:
1. Click the Settings shortcut in the navigation pane, and then click Select
Antivirus.
2. Select the antivirus program that you want to use and click OK.
3. Click Up Level, and then click Virus Protection Settings.
4. From the Server-wide settings menu, select the desired scanning mode.
Page 24

24 Setting Up the Server
5. To allow users to adjust scanning settings for incoming and outgoing
mail, select the respective check boxes.
6. Click OK.
The antivirus is now switched on. It will scan mail and delete all infected messages.
¾ To set up antivirus on a Linux-based hosting server:
1. Go to Home > Updates.
2. Click your Parallels Plesk Panel version.
3. In the list of components, select either Parallels Premium Antivirus or
Kaspersky Antivirus.
4. Click Install.
After the installation is completed, obtain and install a license key for the selected
antivirus program, as described in the following steps.
5. Go to Home > License Management.
6. Click Order Control Panel Add-ons. The Parallels online store page listing
available add-ons opens in a new browser window.
7. On this page, select the check box next to Parallels Premium Antivirus or
Kaspersky Antivirus and click ADD TO MY BASKET.
8. Because Parallels Plesk Panel add-ons are added to the license keys
that already exist, you will need to specify the number of your license
key to which you add this feature and click Submit.
9. In the next steps, indicate the cu rrency, number of keys, provide
contact details, billing address, and payment method, and submit the
form. You will be notified by e-mail when your order is processed.
10. When you receive the e-mail notice, return to the License Management
screen (Home > License Management) and click Retrieve Keys to retrieve
the ordered license key. Parallels Plesk Panel License Manager will
retrieve the upgraded license key from the Parallels licensing server
and install it to your control panel.
11. Go to Settings > Virus Protection Settings.
12. Under Antivirus preferences, select the antivirus you need and click OK.
If you installed Parallels Premium Antivirus, you can switch on antivirus protection only
on a per-mailbox basis, and only after you have set up mailboxes.
For instructions on setting up anti-virus protection for a mailbox, refer to Parallels Plesk
Panel 9.5 Administrator's Guide, section Protecting Mailboxes from Viruses.
Page 25

Setting Up the Server 25
If you installed Kaspersky Antivirus, click the Modules shortcut in the navigation pane,
click Kaspersky Antivirus, and then click the Server-wide scanning settings tab. If you need
further instructions on using Kaspersky antivirus, see Kaspersky Antivirus Module
Administrator's Guide at http://www.parallels.com/en/products/plesk/docs/
Now let's set up e-mail notification. When new user accounts or domains are created in
the system, or when disk space and bandwidth allotments are overused, the control
panel notifies you and the appropriate users by e-mail. With the default settings,
however, domain and web site owners are not notified. We recommend that you enable
resource overage notification for domain and Web site owners because they need to
know what happens to their domains and Web sites.
The control panel can notify the appropriate users when:
New user accounts are created.
New domains are added.
Hosting accounts are expired (expiration date is defined for user accounts and Web
sites separately).
Resource usage limits are exceeded.
There are new requests for assistance (trouble tickets) from your customers in Help
Desk.
The requests are fulfilled and the trouble tickets are closed in Help Desk.
New comments are posted to the existing trouble tickets.
The closed trouble tickets are reopened because the customer has encountered
the same problem again.
.
¾ To view or modify the notification system settings:
1. Go to Home > Notifications.
2. By selecting the check boxes in the Notifications table, specify the types
of control panel users or external e-mail users who should receive
notices on events.
We recommend that you also select all check boxes in the domain administrator
column in order to let your resellers' customers know what happens to their Web
sites.
3. To view or edit the default notice text, click the respective icon in the
Text column.
In notices you can use tags that will be replaced with actual data (see the table
below).
4. Specify when to send the user account and domain (Web site) hosting
account expiration notices. By default, such notices are sent 10 days in
advance. Click OK.
The following table lists the tags (variables) that you can use in notification messages.
Page 26

26 Setting Up the Server
Event type Tags that can be used in notices The data that tags denote
Creation of a
user account
<client_contact_name>
<reseller_contact_name>
<user_contact_name>
<client_login>
<reseller_login>
<user_login>
<password>
<client_company_name>
<reseller_company_name>
<user_company_name>
<client_cr_date>
user's first and last name
user name for authorization
in the control panel
user's password for
authorization in the control
panel
company name
user account creation date
<reseller_cr_date>
<user_cr_date>
<client_phone>
<reseller_phone>
<user_phone>
<client_fax>
<reseller_fax>
<user_fax>
<client_country>
<reseller_country>
<user_country>
phone number
fax number
country
Page 27

Setting Up the Server 27
<client_state_province>
<reseller_state_province>
<user_state_province>
<client_city>
<reseller_city>
<user_city>
<client_postal_ZIP_code>
<reseller_postal_ZIP_code
>
<user_postal_ZIP_code>
<client_address>
state or province
city
postal or ZIP code
address
Expiration of a
user account
<reseller_address>
<user_address>
<client_id>
<reseller_id>
<user_id>
<hostname>
<client_login>
<reseller_login>
<user_login>
<client_contact_name>
<reseller_contact_name>
<user_contact_name>
unique identifier assigned
by the system
host name for access to
control panel
user name for authorization
in the control panel
user's first and last name
Page 28

28 Setting Up the Server
Addition of a
new domain
name to the
server
<client_expiration_date>
<reseller_expiration_date>
<user_expiration_date>
<domain_name>
<client_login>
<reseller_login>
<user_login>
<client_contact_name>
<reseller_contact_name>
<user_contact_name>
<dom_id>
<ip>
user account expiration
date
domain name
user name for authorization
in the control panel
user's first and last name
unique identifier assigned
by the system
IP address the domain is
hosted on
Domain (Web
site) hosting
account
expiration
Resource
overage
<domain_name>
<client_login>
<reseller_login>
<user_login>
<client_contact_name>
<reseller_contact_name>
<user_contact_name>
<dom_id>
<domain_expiration_date>
<domain_name>
<client_login>
<reseller_login>
domain name
user name for authorization
in the control panel
user's first and last name
unique identifier assigned
by the system
domain hosting account
expiration date
domain name
user name for authorization
in the control panel
<user_login>
Page 29

Setting Up the Server 29
<client_contact_name>
<reseller_contact_name>
<user_contact_name>
<disk_usage>
<disk_space_limit>
<resource_table>
<traffic>
<traffic_limit>
user's first and last name
information about disk
space usage
information about the
amount of disk space
allocated to the account
information about all
resource limits that were or
will soon be reached
information about
bandwidth usage
information about the
bandwidth amount allotted
to the account
Help Desk
events
<ticket_id>
<reporter>
<server>
<ticket_comment>
trouble ticket identification
number automatically
assigned by the system
returns user name for
requests submitted by
resellers or multi-domain
customers, a domain name
for requests submitted by
domain owner, and e-mail
address if the request was
submitted by e-mail.
host name
the contents of a ticket, or a
comment posted
Page 30

30 Setting Up the Server
Now let's obtain and install an authentic digital SSL certificate to secure connections to
your control panel.
For security reasons, you can access your control panel only through a secure
connection provided by Secure Sockets Layer-enabled hypertext transfer protocol. All
data you exchange with the Parallels Plesk Panel-managed server are encrypted, thus
preventing interception of sensitive information. The SSL certificate used in the data
encryption process is automatically generated and installed on the server during
installation of the control panel. This is the so-called self-signed certificate: it is not
signed by a recognized certification authority (CA), therefore, upon attempt to connect
to your control panel, you and your customers will see warning messages in Web
browsers.
To gain customer confidence, you should purchase an SSL certificate from a reputable
certification authority, and install it to the control panel.
You can either:
use the facilities for purchasing SSL certificates from Comodo, GeoTrust, Inc. or
GoDaddy provided by your control panel,
OR
create a certificate signing request (CSR) from the control panel and submit it to the
certification authority of your choice, which will create an SSL certificate for you.
Note: If you are going to use the control panel's facilities for purchasing a certificate
through MyPlesk.com online store, you should not use command line tools for
creating the certificate signing request.
¾ To purchase an SSL certificate from Comodo, GeoTrust, Inc. or GoDaddy
through MyPleskCom online store and secure your control panel:
1. On your Home page, open the Security group title menu, and select SSL
Certificates. A list of SSL certificates that you have in your repository will
be displayed.
2. Click Add SSL Certificate.
3. Specify the certif icate properties:
Certificate name. This will help you identify this certificate in the repository.
Encryption level. Choose the encryption level of your SSL certificate. We
recommend that you choose a value more than 1024 bit.
Specify your location and organization name. The values you enter should not
exceed the length of 64 symbols.
Specify the host name for which you wish to purchase an SSL certificate. For
example: your-domain.com
Enter your e-mail address.
4. Make sure that all the provided information is correct and accurate, as it
will be used to generate your private key.
Page 31

Setting Up the Server 31
5. Click Buy SSL Certificate.
Your private key and certificate signing request will be generated. Do not delete
them. MyPlesk.com login page will open in a new browser window.
6. Register or log in to an existing MyPlesk.com account and you will be
taken step by step through the certificate purchase procedure.
7. Choose the type of certificate that you wish to purchase.
8. Click Proceed to Buy and order the certificate. In the Approver E-Mail
drop-down box, please select the correct Approver e-mail.
The approver e-mail is an e-mail address that can confirm that certificate for
specific domain name was requested by an authorized person.
9. Once your certificate request is processed, you will be sent a
confirmation e-mail. After you confirm, the certificate will be sent to your
e-mail.
10. When you receive your SSL certificate, save it on your local machine or
network.
11. Return to the SSL Certificates repository (Home > Security group title
menu > SSL Certificates).
12. Click Browse in the middle of the page and navigate to the location of
the saved certificate. Select it, and then click Send File. This will upload
the certificate to the repository.
13. Select the check box corresponding to the certificate you just added,
and click Secure control panel.
Now you can register the server at MyPlesk.com. My.Plesk.com (MPC) is the Parallels
commerce center that you can customize for your clients. Your registration is free with
your Parallels Plesk Panel 9.5 license. Click the Home shortcut in the navigation pane,
open the Applications & Services menu, select the Register Your Server option, and follow
the directions on MPC. The system creates an administrator's account in the
commerce portal for your server. Customize the account to offer any of the services or
applications you like. When your customers log in to the system, they become part of
your server's account. As your customers become familiar with the portal they can use
it to register domains, purchase SSL certificates, and purchase a pre-selected list of
applications available for the Parallels Plesk Panel system and their domains. Every
time they use the portal for their accounts you enjoy the revenue without the tax or
accounting responsibilities. My.Plesk.com gives you a management portal to view your
sales and the system accounts and instantly get an update on what your customers are
purchasing as well as the amount of revenue you will receive at the end of each month.
No headaches, no minimum purchases, no partnership fees, just additional revenue for
you to enjoy from your customizable portal.
Now let's set up Help Desk. Help Desk is a convenient way for your customers to reach
you when they need your assistance. After you set it up and switch on, the Help Desk
becomes accessible to all users who were granted access to control panel, including
your resellers, clients, domain owners, and e-mail users. Additionally, you can allow
submission of problem reports by e-mail.
Page 32

32 Setting Up the Server
Your Help Desk shows all reports posted by your resellers and their customers. Your
reseller's Help Desk shows only reports posted by himself or herself and his or her
customers. A client's Help Desk shows only reports posted by himself or herself and
domain administrator's of his or her sites, if domain administration privileges were
granted to the client's users. The domain owner's Help Desk shows only reports posted
by himself or herself and by e-mail users under his or her domain.
¾ To configure Help Desk and allow your customers post problem reports
through the control panel:
1. Go to Help Desk > General Settings.
2. Select the Allow customers to submit tickets check box.
3. Select the trouble ticket queue, priority and category that will be offered
to your customers as the default choice.
When users post a new ticket, they can specify the order in which they would prefer
their problems to be resolved (queue), the priority of their requests (priority), and
the category to which the problem is related (category). The queue, priority and
category are abstract entities: they have no effect on the system, but they can help
you decide what problems to resolve in the first place. There are three predefined
queues and priority levels and nine predefined categories including Database, DNS,
FTP, General, Hosting, Mail, Mailing Lists, Web Applications, and Tomcat Java. You can
remove these items and add your own.
4. Click Switch On in the Tools group, then click OK.
¾ If you wish to allow users to submit problem reports by e-mail:
1. Create a POP3 mailbox with an e-mail address like helpdesk@your-
domain.com or anything you like.
2. Configure the help desk to periodically retrieve problem reports from
that mailbox and post them to your Help Desk.
3. Inform your customers of the Help Desk's e-mail address.
¾ To allow users to submit problem reports to Help Desk by e-mail:
1. Go to Help Desk > Mail Gate Settings.
2. Specify the following settings:
Notification sender's name, and Notification sender's return address. Once a report has
been retrieved by e-mail and posted to the Help Desk, the Help Desk sends a
notice to the report sender. This allows the report sender to subsequently add
comments to the report by replying to the message. Therefore, we recommend
that you specify your Help Desk's e-mail address in the Notification sender's return
address box, and type a phrase like "<company name> Help Desk" into the
Notification sender's name box. Be sure to specify your organization name in place
of <company name> and omit the quotation marks.
POP3 server: POP3 server the mail should be fetched from.
Page 33

Setting Up the Server 33
POP3 login: user name for authentication to the mail server.
New POP3 password: password that will be used for authentication to the mail
server and retrieving problem reports from the mailbox.
Confirm POP3 password: retype password for confirmation.
Query mail once in: specify how often Help Desk should check for new reports.
Ticket subject must start with: specify the combination of symbols the subject line
of e-mail messages (problem reports) must start with. This can help filter out
spam. All e-mail messages that do not have the specified combination of
symbols in the subject line will be deleted.
3. Click Switch On in the Tools group and click OK.
Now your server is set up and you can do the following:
Prepare user account templates (referred to as reseller account templates and
client account templates in Parallels Plesk Panel) to simplify setup of new user
accounts. (on page 34)
Prepare Web site hosting account templates (referred to as domain templates in
Parallels Plesk Panel) to simplify set up of new Web sites. (on page 43)
Create new user accounts for your customers or resellers. (see page 48)
Host Web sites. (see page 59)
Page 34

C HAPTER 4
Simplifying Setup of User Accounts
Before you start signing up new users for your services, you should create account
configuration presets, referred to as reseller account templates and client account
templates. They will simplify setting up user accounts for new customers. The
templates cover all resource usage allotments, permissions and limits that you can
define for a user account. There are predefined reseller account and client account
templates: You can modify them as required and use them, or you can create your own
templates. The default templates cannot be removed.
¾ To create a reseller account template:
1. Go to Resellers > Reseller Account Templates > Create Reseller Account Template.
2. Specify the following settings:
Template name. Specify a name for this template. During setup of a new reseller
account, you will be prompted to select the required template by its name.
Therefore, we recommend that you choose a meaningful name that
corresponds to one of your hosting plans or describes the amount of allotted
resources. For example, Reseller account, 50 GB disk space, 100 domains.
Access to control panel. Select this to allow the reseller to access the control panel
for managing his or her account, users accounts, and sites.
Client account creation. Select this to allow the reseller to create user accounts.
Domain creation and Physical hosting management. Select these two options to allow
the reseller to set up hosting accounts for new sites, modify hosting account
features and switch on or off support for programming and scripting languages.
Hosting performance settings management. Specify whether the reseller will be able
to limit bandwidth usage and number of connections to his or her Web sites.
PHP safe mode management (available only for Linux hosting). Specify whether the
reseller will be able to switch the PHP safe mode off for his or her sites. By
default, PHP is configured to operate in safe mode with functional restrictions.
To learn more about PHP safe mode, refer to http://php.net/features.safe-
mode. Some Web applications may not work properly with safe mode enabled:
If an application on a site fails due to safe mode, switch the safe mode off by
clearing the PHP 'safe_mode' on check box in the hosting account properties
(Domains > domain name > Web Hosting Settings).
Management of access to the server over SSH or Remote Desktop connection. Specify
whether the reseller will be able to access the server shell through Secure Shell
or Remote Desktop protocols.
Hard disk quota assignment. Specify whether the reseller will be able to assign
hard quotas on disk space for his or her own Web sites and for Web sites of his
or her customers.
Page 35

Simplifying Setup of User Accounts 35
Subdomains management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to set up
additional sites under his or her domains and allow his or her customers to do
so.
Domain aliases management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to set up
additional alternative domain names for his or her Web sites and allow his or her
users to do so.
Log rotation management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to adjust the
cleanup and recycling of processed log files for his or her sites.
Anonymous FTP management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to have an
FTP directory where all users could download and upload files without the need
to enter login and password. A web site should reside on a dedicated IP
address in order to use anonymous FTP service.
FTP accounts management (only for Windows hosting). Specify whether the reseller
will be able to manage additional FTP accounts for Web sites.
Task scheduling. Specify whether the reseller will be able to schedule tasks in the
system. Scheduled tasks can be used for running scripts or utilities on schedule.
Domain limits adjustment. Specify whether the reseller will be able to adjust
resource allotments for his or her Web sites. You must select this option,
otherwise the reseller will not be able to set up new user accounts and Web
sites.
DNS zone management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to manage the
DNS zones of his or her domains.
Java applications management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to install
Java applications and applets on Web sites through the control panel.
Mailing lists management. Specify whether the customer will be able to use mailing
lists provided by the GNU Mailman software.
Spam filter management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to use
SpamAssassin spam filter and customize filtering settings.
Antivirus management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to use server-side
antivirus protection for filtering incoming and outgoing mail.
Backup and restore functions. Specify whether the reseller will be able to use the
control panel's facilities to back up and restore his or her sites. To allow storing
backup files on the server, select the local repository check box. To allow the
customer to use an arbitrary FTP server for storing backups, select the remote
(FTP) repository check box.
Ability to use remote XML interface. Specify whether the reseller will be able to
remotely manage his or her Web sites through custom applications. The XML
interface can be used for developing custom applications integrated with Web
sites, which could be used, for instance, for automating setup of hosting
accounts and provisioning of services for customers purchasing hosting
services from a site. To learn more about using Parallels Plesk Panel's XML
interface (also referred to as Parallels Plesk Panel API RPC), refer to the API
RPC documentation available at
http://www.parallels.com/ptn/documentation/ppp/
.
Ability to use Sitebuilder. Specify whether the reseller will be able to use
Sitebuilder for creating and editing his or her Web sites.
Page 36

36 Simplifying Setup of User Accounts
IIS application pool management (available only for Windows hosting). Specify
whether the reseller will be able to manage his or her IIS application pool.
Web statistics management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to manage
Web statistics for his or her Web sites.
Additional write/modify permissions management (available only for Windows
hosting). Specify whether the reseller will be able to manage additional
write/modify permissions for their domains. These permissions are required if
customer's Web applications are using a file-based database (like Jet) located in
the root of httpdocs or httpsdocs folders. Please note that selecting this
option might seriously compromise the Web site security.
Shared SSL management (available only for Windows hosting). Specify whether the
reseller will be able to manage shared SSL for his or her Web sites.
Home page management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to customize his
or her Home page.
Ability to select a database server. Specify whether the reseller will be able to select
a database server of each type for creating his or her databases, not only use
the default database server.
Overuse and overselling. Specify whether the reseller will be able to sell more
resources to the customers than his or her hosting plan actually provides.
Overselling is a marketing strategy based on the following scheme: a reseller,
who was allotted, for example, ten gigabytes of disk space, allocates five
gigabytes of disk space to each of his or her customers, assuming that none of
them will actually use all of their allocated disk space. When the amount of disk
space used by reseller’s customers exceeds reseller’s disk space allotment (ten
gigabytes in our example), two things can happen depending on the overuse
policy selected for this reseller account. If overuse is allowed for this reseller,
then the reseller will have to pay overage charges and upgrade his or her
hosting account to accommodate the increased needs of his or her customers. If
overuse is not allowed for this reseller, all Web sites and user accounts of this
reseller's customers will be suspended which can lead to customer
dissatisfaction and complaints since customers did not actually exceed their
own limits. Due to this, it is not generally recommended to allow overselling for
reseller accounts. If you want to allow overselling for a reseller account, it is
recommended to also allow overuse for this account.
Maximum number of domains. Specify the total number of domain names (Web
sites) that the reseller will be able to host on the server. This includes Web sites
hosted on this server, and domain forwarders that point to Web sites hosted on
other servers. Domain aliases (additional domain names for a site hosted on
this server) and subdomains are counted separately and are not limited by this
resource type.
Maximum number of subdomains. Specify the total number of subdomains that the
reseller will be able to host.
Maximum number of domain aliases. Specify the total number of additional
alternative domain names that the reseller will be able to use for his or her Web
sites.
Disk space. Specify the total amount of disk space in megabytes that is allocated
to the reseller. It includes disk space occupied by all files related to user
accounts and sites: Web site contents, databases, applications, mailboxes, log
files and backup files.
Page 37

Simplifying Setup of User Accounts 37
Maximum amount of traffic. Specify the total amount of data in megabytes that can
be transferred from the reseller's Web sites during a month.
Maximum number of Web users. Specify the total number of personal Web pages
that the reseller can host for other users under his or her domains. This service
is mostly used in educational institutions that host non-commercial personal
pages of their students and staff. These pages usually have Web addresses like
http://your-domain.com/~username.
Maximum number of databases. Specify the total number of databases that the
reseller can host on the server.
Maximum number of mailboxes. Specify the total number of mailboxes that the
reseller can host on the server.
Mailbox quota. Specify the amount of disk space in kilobytes that is allocated for
storing e-mail messages and autoresponder attachment files to each mailbox in
a domain.
Maximum number of mail forwarders. Specify the total number of mail forwarders
that the reseller can set up.
Maximum number of mail autoresponders. Specify the total number of automatic
responses that the reseller can set up.
Maximum number of mail groups. Specify the total number of mail groups that the
reseller can set up.
Maximum number of mailing lists. Specify the total number of mailing lists that the
reseller can host on the server.
Maximum number of Java applications. Specify the total number of Java applications
or applets that can be hosted on the server.
MySQL databases quota and Microsoft SQL databases quota (available only for
Windows hosting). Specify the maximum disk space amount in megabytes that
MySQL and Microsoft SQL Server databases respectively can occupy under
domains belonging to the reseller.
Maximum number of MySQL databases and Maximum number of Microsoft SQL server
databases (available only for Windows hosting). Specify the maximum number of
MySQL and Microsoft SQL Server databases respectively that the reseller can
create under his or her domains.
Maximum number of additional Microsoft FrontPage accounts (available only for
Windows hosting). Specify the maximum number of additional Microsoft
FrontPage accounts that the reseller can create under his or her domains.
Maximum number of additional FTP accounts (available only for Windows hosting).
Specify the maximum number of additional FTP accounts that the reseller can
create on his or her domains.
Maximum number of IIS application pools (available only for Windows hosting).
Specify the total number of dedicated IIS application pools that the reseller can
allocate between his or her domains.
Maximum number of shared SSL links (available only for Windows hosting). Specify
the total number of shared SSL links that the reseller can use on his or her
domains.
Page 38

38 Simplifying Setup of User Accounts
Maximum number of ODBC connections (available only for Windows hosting).
Specify the total number of ODBC connections that the reseller can use on his
or her domains.
Maximum number of ColdFusion DSN connections (available only for Windows
hosting). Specify the total number of ColdFusion DSN connections that the
reseller can use on his or her domains.
Expiration date. Specify the term for a hosting account. At the end of the term, all
reseller's sites and sites of the reseller's customers will be suspended, their
Web, FTP and mail services will no longer be accessible to the Internet users,
and the users will not be able to log in to the control panel. Accounts cannot be
automatically renewed, therefore, in order to bring the hosted domain names
(Web sites) back to operation, you will need to manually renew the user
account: go to Resellers > reseller's name > Resource Usage, specify another term,
click OK, then click the Unsuspend.
IP address allocation. Specify the shared IP addresses that you wish to allocate to
the reseller. If you wish to automatically provision dedicated IP addresses,
select the Allocate exclusive IP addresses to reseller check box and specify the
number of IP addresses that should be taken from your IP range and assigned
to the reseller.
Creation of a user account in Sitebuilder. To allow the reseller to create and manage
Web sites using Sitebuilder, select the Create a corresponding user account in
Sitebuilder check box.
3. Click OK to complete creation of a template.
During setup of a new reseller account, you will select the required template and
the account will be created and allocated the resources you defined.
¾ To create a client account template:
1. Go to Clients > Client Account Templates > Create Client Account Template.
2. Specify the following settings:
Template name. Specify a name for this template. During setup of a new user
account, you will be prompted to select the required template by its name.
Therefore, we recommend that you choose a meaningful name that
corresponds to one of your hosting plans or describes the amount of allotted
resources. For example, Shared hosting user account, 5GB disk space, 10 domains.
Access to control panel. Specify whether the customer will be able to access the
control panel for managing his or her account and sites.
Domain creation. Specify whether the customer will be able to set up hosting
accounts for new sites.
Physical hosting management. Specify whether the customer will be able to set up
hosting accounts, modify hosting account features and switch on or off support
for programming and scripting languages.
Hosting performance management. Specify whether the customer will be able to
limit bandwidth usage and number of connections to his or her Web sites.
Page 39

Simplifying Setup of User Accounts 39
PHP safe mode management. Specify whether the customer will be able to switch
the PHP safe mode off for his or her sites. By default, PHP is configured to
operate in safe mode with functional restrictions. To learn more about PHP safe
mode, refer to http://php.net/features.safe-mode
. Some web applications may
not work properly with safe mode enabled: If an application on a site fails due to
safe mode, switch the safe mode off by clearing the PHP 'safe_mode' on check
box in the hosting account properties (Domains > domain name > Web Hosting
Settings).
Management of access to the server over SSH or Remote Desktop connection. Specify
whether the customer will be able to access the server shell through Secure
Shell or Remote Desktop protocols.
Hard disk quota assignment. Specify whether the customer will be able to assign
hard quotas on disk space for his or her own web sites and for web sites of his
or her customers.
Subdomains management. Specify whether the customer will be able to set up
additional sites under his or her domains and allow his or her customers to do
so.
Domain aliases management. Specify whether the customer will be able to set up
additional alternative domain names for his or her web sites and allow his or her
users to do so.
Log rotation management. Specify whether the customer will be able to adjust the
cleanup and recycling of processed log files for his or her sites.
Anonymous FTP management. Specify whether the customer will be able to have
an FTP directory where all users could download and upload files without the
need to enter login and password. A web site should reside on a dedicated IP
address in order to use anonymous FTP service.
FTP accounts management (this option is available only for hosting accounts based
on Microsoft Windows platforms). Specify whether the customer will be able to
create and manage additional FTP accounts.
Task scheduling. Specify whether the customer will be able to schedule tasks in
the system. Scheduled tasks can be used for running scripts or utilities on
schedule.
Domain limits adjustment. Specify whether the customer will be able to adjust
resource allotments for his or her account. This option must be selected if the
customer should be able to set up new Web sites.
DNS zone management. Specify whether the customer will be able to manage the
DNS zones of his or her domains.
Java applications management. Specify whether the customer will be able to install
Java applications and applets on web sites through the control panel.
Mailing lists management. Specify whether the customer will be able to use mailing
lists provided by the GNU Mailman software.
Spam filter management. Specify whether the customer will be able to use
SpamAssassin spam filter and customize filtering settings.
Antivirus management. Specify whether the customer will be able to use server-
side antivirus protection for filtering incoming and outgoing mail.
Page 40

40 Simplifying Setup of User Accounts
Backup and restore functions. Specify whether the customer will be able to use the
control panel's facilities to back up and restore his or her sites. To allow storing
backup files on the server, select the local repository check box. To allow the
customer to use an arbitrary FTP server for storing backups, select the remote
(FTP) repository check box.
Ability to select a database server. Specify whether the customer will be able to
select a database server of each type for creating his or her databases, not only
use the default database server.
Ability to use remote XML interface. Specify whether the customer will be able to
remotely manage his or her Web sites through custom applications. The XML
interface can be used for developing custom applications integrated with Web
sites, which could be used, for instance, for automating setup of hosting
accounts and provisioning of services for customers purchasing hosting
services from a site. To learn more about using Parallels Plesk Panel's XML
interface (also referred to as Parallels Plesk Panel API RPC), refer to the API
RPC documentation available at
http://www.parallels.com/ptn/documentation/ppp/
Ability to use Sitebuilder. Specify whether the customer will be able to use
Sitebuilder for creating and editing his or her Web sites.
.
IIS application pool management (available only for Windows hosting). Specify
whether the customer will be able to manage his or her IIS application pool.
Web statistics management. Specify whether the customer will be able to manage
Web statistics for his or her Web sites.
Additional write/modify permissions management (available only for Windows
hosting). Specify whether the customer will be able to manage additional
write/modify permissions for their domains. These permissions are required if
customer's Web applications are using a file-based database (like Jet) located in
the root of httpdocs or httpsdocs folders. Please note that selecting this
option might seriously compromise the Web site security.
Shared SSL management (available only for Windows hosting). Specify whether the
customer will be able to manage shared SSL for their domains.
Home page management. Specify whether the customer will be able to customize
his or her Home page.
Maximum number of domains. Specify the total number of domain names (Web
sites) your customer will be able to host on the server. This includes Web sites
hosted on this server, and domain forwarders that point to Web sites hosted on
other servers. Domain aliases (additional domain names for a site hosted on
this server) and subdomains are counted separately and are not limited by this
resource type.
Maximum number of subdomains. Specify the total number of subdomains that the
customer will be able to host.
Maximum number of domain aliases. Specify the total number of additional
alternative domain names that the customer will be able to use for his or her
Web sites.
Disk space. Specify the total amount of disk space in megabytes that is allocated
to the customer. It includes disk space occupied by all files related to user's
domains (Web sites): Web site contents, databases, applications, mailboxes,
log files and backup files.
Page 41

Simplifying Setup of User Accounts 41
Maximum amount of traffic. Specify the amount of data in megabytes that can be
transferred from the customer's Web sites during a month.
Maximum number of Web users. Specify the total number of personal Web pages
that your customer can host for other users under his or her domains. This
service is mostly used in educational institutions that host non-commercial
personal pages of their students and staff. These pages usually have Web
addresses like http://your-domain.com/~username.
Maximum number of databases. Specify the total number of databases that the
customer can host on the server.
Maximum number of mailboxes. Specify the total number of mailboxes that the
customer can host on the server.
Mailbox quota. Specify the amount of disk space in kilobytes that is allocated for
storing e-mail messages and autoresponder attachment files to each mailbox in
a domain.
Maximum number of mail forwarders. Specify the total number of mail forwarders
that the customer can set up.
Maximum number of mail autoresponders. Specify the total number of automatic
responses that the customer can set up.
Maximum number of mail groups. Specify the total number of mail groups that the
customer can set up.
Maximum number of mailing lists. Specify the total number of mailing lists that you
customer can host on the server. To provide users with mailing lists, you should
install the GNU Mailman software.
Maximum number of Java applications. Specify the total number of Java applications
or applets that can be hosted on the server.
MySQL databases quota and Microsoft SQL databases quota. Specify the maximum
disk space amount in megabytes that MySQL and Microsoft SQL Server
databases respectively can occupy on a domains belonging to the customer.
Maximum number of MySQL databases and Maximum number of Microsoft SQL server
databases. Specify the maximum number of MySQL and Microsoft SQL Server
databases respectively that the customer can create on his or her domains.
Maximum number of additional Microsoft FrontPage accounts. Specify the maximum
number of additional Microsoft FrontPage accounts that the customer can
create on his or her domains.
Maximum number of additional FTP accounts. Specify the maximum number of
additional FTP accounts that the customer can create on his or her domains.
Maximum number of IIS application pools (available only for Windows hosting).
Specify the total number of dedicated IIS application pools that the customer
can allocate between his or her domains.
Maximum number of shared SSL links (available only for Windows hosting). Specify
the total number of shared SSL links that the customer can use on his or her
domains.
Maximum number of ODBC connections (available only for Windows hosting).
Specify the total number of ODBC connections that the customer can use on his
or her domains.
Page 42

42 Simplifying Setup of User Accounts
Maximum number of ColdFusion DSN connections (available only for Windows
hosting). Specify the total number of ColdFusion DSN connections that the
customer can use on his or her domains.
Expiration date. Specify the term for a hosting account. At the end of the term, all
customer's domains (Web sites) will be suspended, their Web, FTP and mail
services will no longer be accessible to the Internet users, and the user will not
be able to log in to the control panel. Accounts cannot be automatically
renewed, therefore, in order to bring the hosted domain names (Web sites) back
to operation, you will need to manually renew the user account: Click the Clients
shortcut in the navigation pane, click the client name you need, click the
Resource Usage icon, specify another term, click OK, then click the Unsuspend
shortcut.
IP address allocation. Specify the shared IP addresses that you wish to allocate to
the customer. If you wish to automatically provision dedicated IP addresses,
select the Allocate exclusive IP addresses to client check box and specify the
number of IP addresses that should be taken from your IP range and assigned
to the customer.
Creation of a user account in Sitebuilder. To allow the customer to create and
manage Web sites using Sitebuilder, select the Create a corresponding user
account in Sitebuilder check box.
3. Click OK to complete creation of a template.
During setup of a new user account, you will select the required template and the
account will be created and allocated the resources you defined.
Page 43

C HAPTER 5
Simplifying Setup of Domains and Web Sites
Before you start hosting Web sites, you should create hosting configuration presets,
referred to as domain templates. The templates cover all resource usage allotments,
permissions and resource limits that you can define for a hosting account, plus mail
bounce and Web statistics retention settings. There is a predefined domain template
available from the control panel: You can modify it as required and use it, or you can
create your own templates. The default template cannot be removed.
¾ To create a domain template:
1. Go to Domains > Domain Templates > Create Domain Template.
2. Specify the following settings:
Template name. Specify a name for this template. During setup of a new hosting
account, you will be prompted to select the required template by its name.
Therefore, we recommend that you choose a meaningful name that
corresponds to one of your hosting plans or describes the amount of allotted
resources. For example, Mail hosting, 5GB disk space, 500 mailboxes.
Availability to other users. If you want your customers to be able to use this
template, select the check box Make this template available to other users (sub-
logins).
Mail to nonexistent users. Specify the domain-wide mail bounce options: When
somebody sends an e-mail message to an e-mail address that does not exist
under your domain, the mail server on your domain accepts mails, processes it,
and when it finds out that there is no such a recipient under your domain, it
returns the mail back to sender with the “this address no longer accepts mail”
notice. You can choose to:
change the default notice if you do not like it (leave the Reject with message
option selected and type another message into the input box),
forward undelivered mail to another e-mail address (select the Forward to
address option and specify the e-mail address you need), or
reject mail without accepting it (select the Reject option). This setting can
decrease mail server load caused by a large amount of spam, which is often
directed at randomly generated user names. However, for spammers this
can somewhat speed up scanning of your mail server for valid e-mail
addresses.
forward to external mail server (available only for Windows hosting). With
this setting, all mail addressed to nonexistent users will be forwarded to the
specified external mail server.
Page 44

44 Simplifying Setup of Domains and Web Sites
Webmail. Specify whether the users of mailboxes in this domain should be able
to read their mail through a browser based webmail application, and select the
application that should be used.
Overuse policy. Specify what should be done to the site when disk space and
traffic limits are exceeded: To block the site, select the Overuse is not allowed
option. To allow the site to operate, select the Overuse is allowed option. Leave
the check box Notify the domain owner about reaching the resource limit selected if
you want the control panel to notify you when the resource usage limit is
reached.
Subdomains. Specify the number of subdomains that can be hosted under this
domain.
Domain aliases. Specify the total number of additional alternative domain names
that can be used for this site.
Disk space. Specify the total amount of disk space allocated to a hosting account
associated with the domain. This amount is measured in megabytes. It includes
disk space occupied by all files related to the domain/Web site: Web site
contents, databases, applications, mailboxes, log files and backup files.
Traffic. Specify the amount of data in megabytes that can be transferred from the
Web site during a month.
Web users. Specify the number of personal Web pages that can be hosted for
other users under his or her domain. This service is mostly used in educational
institutions that host non-commercial personal pages of their students and staff.
These pages usually have web addresses like http://yourdomain.com/~username. If you wish to allow execution of scripts embedded in
personal Web pages, select also the Allow the web users scripting check box. For
more information, refer to Parallels Plesk Panel 9.5 Administrator's Guide,
section Hosting Personal Web Pages.
MySQL Databases. Specify the number of databases that can be hosted under this
domain.
Mailboxes. Specify the number of mailboxes that can be hosted under this
domain.
Mailbox quota. Specify the amount of disk space in kilobytes that is allocated for
storing e-mail messages and autoresponder attachment files to each mailbox
under this domain.
Mail redirects. Specify the number of mail forwarders that can be used in a
domain.
Mail groups. Specify the number of simple mailing lists that can be set up in a
domain.
Autoresponders. Specify the number of automatic responses that can be set up in
a domain.
Mailing lists. Specify the number of mailing lists that can run in a domain.
Java applications. Specify the maximum number of Java applications or applets
that the domain owner can install under a domain.
Databases quota (only for Windows hosting). Specify the maximum disk space
amount in megabytes that MySQL and Microsoft SQL Server databases
respectively can occupy under the domain.
Page 45

Simplifying Setup of Domains and Web Sites 45
Microsoft FrontPage accounts (only for Windows hosting). Specify the maximum
number of additional Microsoft FrontPage accounts that can be created under
the domain.
FTP accounts (available only for Windows hosting). Specify the maximum number
of additional FTP accounts that can be created under the domain.
Microsoft SQL Server databases (available only for Windows hosting). Specify the
number of databases that can be hosted under this domain.
ODBC connections (available only for Windows hosting). Specify the total number
of ODBC connections that can be used under the domain.
ColdFusion DSN connections (available only for Windows hosting). Specify the total
number of ColdFusion DSN connections that can be used under the domain.
Shared SSL links (available only for Windows hosting). Specify the total number of
shared SSL links that can be used under the domain.
Expiration date. Specify the term for the Web site hosting account. At the end of
the term, the domain (Web site) will be suspended, its Web, FTP and mail
services will no longer be accessible to the Internet users, and domain owner
will not be able to log in to the control panel. Hosting accounts cannot be
automatically renewed, therefore, in order to bring the hosted domain name
(and Web site) back to operation, you will need to manually renew the hosting
account: click the Domains shortcut in the navigation pane, click the domain
name your need, click the Resource Usage icon, specify another expiration date,
click OK, then click the Unsuspend icon (Domains > domain name > Unsuspend).
Log rotation. All connections to the Web server and requests for files that were
not found on the server are registered in log files. These log files are analyzed
by the statistical utilities running on the server, which then present graphical
reports on demand. If you need to view the contents of these raw log files for
debugging purposes, go to Domains > domain name > Log Manager, and then click
the log file name you need. To prevent these log files from growing too large,
you should enable automatic cleanup and recycling of log files:
select the Switch on log rotation check box,
specify when to recycle log files,
specify how many instances of each log file processed by Parallels Plesk
Panel's statistical utilities to store on the server,
specify whether they should be compressed,
specify whether they should be sent to an e-mail address after processing.
Web and traffic statistics retention. Specify the number of months during which the
Web and bandwidth usage statistics should be kept on the server.
DNS. Specify whether the DNS server on your Web host should act as a master
(primary) or slave (secondary) name server for the domain name zone. A
primary name server stores locally the zone file it serves, while a secondary
server only retrieves a copy of this file from the primary. You would normally
leave the Master option selected.
Physical hosting account. If you are going to host not only domain names (DNS
zone settings), but also Web sites, select the Physical hosting check box and
specify the hosting features:
Page 46

46 Simplifying Setup of Domains and Web Sites
Hard disk quota. In addition to the soft quota, you can specify the so-called
hard quota that will not allow writing more files to the web space when the
limit is reached. At attempt to write files, users will get "Out of disk space"
error.
SSL support. Secure Sockets Layer encryption is generally used for protecting
transfer of sensitive data during online transactions on e-commerce Web
sites that run on dedicated IP addresses. SSL certificates that participate in
the encryption process are usually applied to a single domain name on a
single IP address, therefore, each site that needs SSL protection must be
hosted on a dedicated IP address. An exception to this is subdomains, which
you can protect with a wildcard certificate. Installing an SSL certificate on a
Web server that hosts several web sites with different domain names on a
single IP address (shared or name-based hosting) is technically possible,
however, it is not recommended: the encryption will be provided, but users
will get warning messages on attempt to connect to the secure site. To allow
SSL encryption for Web sites, select the SSL support check box.
Create and publish Web site using Sitebuilder. This will enable the site owner to
create and manage a Web site using Sitebuilder.
Use a single directory for housing SSL and non-SSL content (available only for
Linux hosting). By default, when users publish their sites through their FTP
accounts, they need to upload the Web content that should be accessible via
secure connections to the httpsdocs directory, and the content that should
be accessible via plain HTTP, to the httpdocs directory. For the convenience
of publishing all content through a single location – httpdocs directory, select
the Use a single directory for housing SSL and non-SSL content check
box.Microsoft FrontPage support. Microsoft FrontPage is a popular Web site
authoring tool. To enable users to publish and modify their sites through
Microsoft FrontPage, select the Microsoft FrontPage support and FrontPage over
SSL support check boxes and set the Remote Microsoft FrontPage authoring
option to allowed.
Support for hosting services and scripting languages. Specify which of the
following programming and scripting languages should be interpreted,
executed or otherwise processed by the Web server: Active Server Pages
(ASP), ASP.NET (on Windows-based hosting), Server Side Includes (SSI),
PHP hypertext preprocessor (PHP), Common Gateway Interface (CGI), Fast
Common Gateway Interface (FastCGI), Perl, Python, ColdFusion, and Miva
scripting required for running Miva e-commerce solutions.
Web statistics. To allow domain (Web site) owner to view the information on
the number of people visited his or her site and the pages of the site they
viewed, select the statistical package you need from the Web statistics menu,
and select the accessible via password protected directory /plesk-stat/webstat
check box. This will install the statistical software of your choice, which will
generate reports and place them into the password-protected directory. The
domain/web site owner will then be able to access Web statistics at the URL:
https://your-domain.com/plesk-stat/webstat using his or her FTP account
login and password.
Custom error documents. When visitors coming to your site request pages that
the web server cannot find, the web server generates and displays a
standard HTML page with an error message. If you wish to create your own
error pages and use them on your server or allow your customers to do that,
select the Custom error documents check box.
Page 47

Simplifying Setup of Domains and Web Sites 47
Access to the server over SSH or Remote Desktop with FTP user's cr edentials. This
allows a site owner to upload securely Web content to the server through a
Secure Socket Shell or Remote Desktop connection, however, allowing
access to the server also poses a potential threat to the server security, so
we recommend that you leave the Forbidden option selected.
Additional write/modify permissions (available only for Windows hosting). This
option is required if customer's web applications are using a file-based
database (like Jet) located in the root of httpdocs or httpsdocs folders.
Please note that selecting this option might seriously compromise the Web
site security.
Use dedicated IIS application pool (available only for Windows hosting). This
option enables the use of dedicated IIS application pool for Web applications
on a domain. Using dedicated IIS application pool dramatically improves the
stability of domain Web applications due to worker process isolation mode.
This mode gives each Web site hosted on the server the possibility to
allocate a separate process pool for execution of its Web applications. This
way, malfunction in one application will not cause stopping of all the others.
This is especially useful when you are using shared hosting package.
Maximum CPU use (available only for Windows hosting). To limit the amount of
CPU resources that domain's IIS application pool can use, clear the Unlimited
check box and type in the number (in percents).
Performance. To avoid excessive usage of bandwidth, which can lead to
resources overage, you can set various performance limitations for a domain.
Maximum bandwidth usage. To limit the maximum speed (measured in kilobytes
per second) that a domain can share between all its connections, clear the
Unlimited check box and type in a number in kilobytes.
Connections limiting. To limit the maximum number of simultaneous
connections to a domain, clear the Unlimited check box and type in a number.
3. Click OK to complete creation of a template.
During setup of a hosting account for a new domain (Web site), you will select the
required template and the hosting account will be created and allocated the
resources and hosting services you defined.
Page 48

C HAPTER 6
Creating User Accounts
This chapter focuses on creating reseller accounts that you will create for resellers, and
client accounts that you will create for end users of Web hosting services.
If you need to create a domain administrator's account, see Parallels Plesk Panel 9.5
Administrator's Guide, section Setting Up Hosting Account for a Web Site.
If you need to create an e-mail user account, see Parallels Plesk Panel 9.5
Administrator's Guide, section Creating Mailboxes.
In this chapter:
Adding Reseller Accounts for Hosting Resellers ................................................. 49
Adding Client Accounts for End Users of Hosting Services ................................ 54
Page 49

Creating User Accounts 49
Adding Reseller Accounts for Hosting Resellers
¾ To accommodate a new reseller:
1. Go to Home > Accounts group title menu > Create Reseller Account.
2. Specify the contact and billing information. Contact name, login name
and password are mandatory fields.
3. If you have predefined user account templates, you can select the
template you need from the Select template menu.
4. If the Sitebuilder Web site creation and management service is installed
on the server, leave the Create a corresponding user account in Sitebuilder
check box selected.
5. Click Next >>.
6. Specify the following settings:
Overuse and overselling. Specify whether the reseller will be able to sell more
resources to the customers than his or her hosting plan actually provides.
Overselling is a marketing strategy based on the following scheme: a reseller,
who was allotted, for example, ten gigabytes of disk space, allocates five
gigabytes of disk space to each of his or her customers, assuming that none of
them will actually use all of their allocated disk space. When the amount of disk
space used by reseller’s customers exceeds reseller’s disk space allotment (ten
gigabytes in our example), two things can happen depending on the overuse
policy selected for this reseller account. If overuse is allowed for this reseller,
then the reseller will have to pay overage charges and upgrade his or her
hosting account to accommodate the increased needs of his or her customers. If
overuse is not allowed for this reseller, all Web sites and user accounts of this
reseller's customers will be suspended which can lead to customer
dissatisfaction and complaints since customers did not actually exceed their
own limits. Due to this, it is not generally recommended to allow overselling for
reseller accounts. If you want to allow overselling for a reseller account, it is
recommended to also allow overuse for this account.
Maximum number of clients. Specify the total number of user accounts that the
reseller can create for his or her customers.
Maximum number of domains. Specify the total number of domain names (Web
sites) that the reseller will be able to host on the server. This includes Web sites
hosted on this server, and domain forwarders that point to Web sites hosted on
other servers. Domain aliases (additional domain names for a site hosted on
this server) and subdomains are counted separately and are not limited by this
resource type.
Maximum number of subdomains. Specify the total number of subdomains that the
reseller will be able to host.
Page 50

50 Creating User Accounts
Maximum number of domain aliases. Specify the total number of additional
alternative domain names that the reseller will be able to use for his or her Web
sites.
Maximum number of Web users. Specify the total number of personal Web pages
that the reseller can host for other users under his or her domains. This service
is mostly used in educational institutions that host non-commercial personal
pages of their students and staff. These pages usually have Web addresses like
http://your-domain.com/~username. See the Hosting Personal Web Pages
section for details.
Maximum number of additional Microsoft FrontPage accounts (available only for
Windows hosting). Specify the maximum number of additional Microsoft
FrontPage accounts that the reseller can create under his or her domains.
Maximum number of additional FTP accounts (available only for Windows hosting).
Specify the maximum number of additional FTP accounts that the reseller can
create on his or her domains.
Disk space. Specify the total amount of disk space in megabytes that is allocated
to the reseller. It includes disk space occupied by all files related to user
accounts and sites: Web site contents, databases, applications, mailboxes, log
files and backup files.
Maximum amount of traffic. Specify the total amount of data in megabytes that can
be transferred from the reseller's Web sites during a month.
MySQL databases quota and Microsoft SQL databases quota (available only for
Windows hosting). Specify the maximum disk space amount in megabytes that
MySQL and Microsoft SQL Server databases respectively can occupy under
domains belonging to the reseller.
Maximum number of MySQL databases and Maximum number of Microsoft SQL server
databases (available only for Windows hosting). Specify the maximum number of
MySQL and Microsoft SQL Server databases respectively that the reseller can
create under his or her domains.
Maximum number of ODBC connections (available only for Windows hosting).
Specify the total number of ODBC connections that the reseller can use on his
or her domains.
Maximum number of ColdFusion DSN connections (available only for Windows
hosting). Specify the total number of ColdFusion DSN connections that the
reseller can use on his or her domains.
Maximum number of mailboxes. Specify the total number of mailboxes that the
reseller can host on the server.
Mailbox quota. Specify the amount of disk space in kilobytes that is allocated for
storing e-mail messages and autoresponder attachment files to each mailbox in
a domain.
Maximum number of mail forwarders. Specify the total number of mail forwarders
that the reseller can set up.
Maximum number of mail autoresponders. Specify the total number of automatic
responses that the reseller can set up.
Maximum number of mail groups. Specify the total number of mail groups that the
reseller can set up.
Page 51

Creating User Accounts 51
Maximum number of mailing lists. Specify the total number of mailing lists that the
reseller can host on the server.
Maximum number of Java applications. Specify the total number of Java applications
or applets that can be hosted on the server.
Maximum number of IIS application pools (available only for Windows hosting).
Specify the total number of dedicated IIS application pools that the reseller can
allocate between his or her domains.
Maximum number of shared SSL links (available only for Windows hosting). Specify
the total number of shared SSL links that the reseller can use on his or her
domains.
Expiration date. Specify the term for a hosting account. At the end of the term, all
reseller's sites and sites of the reseller's customers will be suspended, their
Web, FTP and mail services will no longer be accessible to the Internet users,
and the users will not be able to log in to the control panel. Accounts cannot be
automatically renewed, therefore, in order to bring the hosted domain names
(Web sites) back to operation, you will need to manually renew the user
account: go to Resellers > reseller's name > Resource Usage, specify another term,
click OK, then click Unsuspend.
7. Click Next >>.
8. Grant the required permissions to the reseller:
Access to control panel. Select this to allow the reseller to access the control panel
for managing his or her account, users accounts, and sites.
Client account creation. Select this to allow the reseller to create user accounts.
Domain creation and Physical hosting management. Select these two options to allow
the reseller to set up hosting accounts for new sites, modify hosting account
features and switch on or off support for programming and scripting languages.
Hosting performance management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to limit
bandwidth usage and number of connections to his or her Web sites.
PHP safe mode management (available only for Linux hosting). Specify whether the
reseller will be able to switch the PHP safe mode off for his or her sites. By
default, PHP is configured to operate in safe mode with functional restrictions.
To learn more about PHP safe mode, refer to http://php.net/features.safe-
mode. Some Web applications may not work properly with safe mode enabled:
If an application on a site fails due to safe mode, switch the safe mode off by
clearing the PHP 'safe_mode' on check box in the hosting account properties
(Domains > domain name > Web Hosting Settings).
Management of access to the server over SSH or Remote Desktop connection. Specify
whether the reseller will be able to access the server shell through Secure Shell
or Remote Desktop protocols.
Hard disk quota assignment. Specify whether the reseller will be able to assign
hard quotas on disk space for his or her own Web sites and for Web sites of his
or her customers.
Subdomains management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to set up
additional sites under his or her domains and allow his or her customers to do
so.
Page 52

52 Creating User Accounts
Domain aliases management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to set up
additional alternative domain names for his or her Web sites and allow his or her
users to do so.
Log rotation management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to adjust the
cleanup and recycling of processed log files for his or her sites.
Anonymous FTP management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to have an
FTP directory where all users could download and upload files without the need
to enter login and password. A web site should reside on a dedicated IP
address in order to use anonymous FTP service.
FTP accounts management (only for Windows hosting). Specify whether the reseller
will be able to manage additional FTP accounts for Web sites.
Task scheduling. Specify whether the reseller will be able to schedule tasks in the
system. Scheduled tasks can be used for running scripts or utilities on schedule.
Domain limits adjustment. Specify whether the reseller will be able to adjust
resource allotments for his or her customers and Web sites. This option must be
selected if the reseller should be able to set up new user accounts and Web
sites.
DNS zone management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to manage the
DNS zones of his or her domains.
Java applications management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to install
Java applications and applets on Web sites through the control panel.
Mailing lists management. Specify whether the customer will be able to use mailing
lists provided by the GNU Mailman software.
Spam filter management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to use
SpamAssassin spam filter and customize filtering settings.
Antivirus management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to use server-side
antivirus protection for filtering incoming and outgoing mail.
Backup and restore functions. Specify whether the reseller will be able to use the
control panel's facilities to back up and restore his or her sites. To allow storing
backup files on the server, select the local repository check box. To allow the
customer to use an arbitrary FTP server for storing backups, select the remote
(FTP) repository check box.
Ability to use remote XML interface. Specify whether the reseller will be able to
remotely manage his or her Web sites through custom applications. The XML
interface can be used for developing custom applications integrated with Web
sites, which could be used, for instance, for automating setup of hosting
accounts and provisioning of services for customers purchasing hosting
services from a site. To learn more about using Parallels Plesk Panel's XML
interface (also referred to as Parallels Plesk Panel API RPC), refer to the API
RPC documentation available at
http://www.parallels.com/ptn/documentation/ppp/
.
Ability to use Sitebuilder. Specify whether the reseller will be able to use
Sitebuilder for creating and editing his or her Web sites.
IIS application pool management (available only for Windows hosting). Specify
whether the reseller will be able to manage his or her IIS application pool.
Page 53

Creating User Accounts 53
Web statistics management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to manage
Web statistics for his or her Web sites.
Additional write/modify permissions management (available only for Windows
hosting). Specify whether the reseller will be able to manage additional
write/modify permissions for their domains. These permissions are required if
customer's Web applications are using a file-based database (like Jet) located in
the root of httpdocs or httpsdocs folders. Please note that selecting this
option might seriously compromise the Web site security.
Shared SSL management (available only for Windows hosting). Specify whether the
reseller will be able to manage shared SSL for his or her Web sites.
Home page management. Specify whether the reseller will be able to customize his
or her Home page.
Ability to select a database server. Specify whether the reseller will be able to select
a database server of each type for creating his or her databases, not only use
the default database server.
9. Click Next >>.
10. Allocate IP addresses to the user: select IP addresses and click Add >>.
11. Click Finish.
You can now send the URL to control panel and login credentials to the reseller.
Page 54

54 Creating User Accounts
Adding Client Accounts for End Users of Hosting Services
¾ To accommodate a new Web hosting service customer:
1. To sign up your own customer, go to Home > Accounts group title menu >
Create Client Account. To sign up a reseller's customer, go to Resellers >
reseller's name > Clients group title menu > Create Client Account.
2. Specify the contact and billing information. Contact name, login name
and password are mandatory fields.
3. If you have predefined user account templates, you can select the
template you need from the Select template menu.
4. If the Sitebuilder Web site creation and management service is installed
on the server, leave the Create a corresponding user account in Sitebuilder
check box selected.
5. Click Next >>.
6. Specify the following settings:
Overuse policy. Specify what should be done when disk space and monthly
bandwidth (traffic) allotments are exceeded. We recommend setting this option
to Overuse is allowed. Otherwise, the user account and user's sites will be blocked
when the resource limits are exceeded.
Maximum number of domains. Specify the total number of domain names (Web
sites) your customer will be able to host on the server. This includes Web sites
hosted on this server, and domain forwarders that point to Web sites hosted on
other servers. Domain aliases (additional domain names for a site hosted on
this server) and subdomains are counted separately and are not limited by this
resource type.
Maximum number of subdomains. Specify the total number of subdomains that the
customer will be able to host.
Maximum number of domain aliases. Specify the total number of additional
alternative domain names that the customer will be able to use for his or her
Web sites.
Maximum number of Web users. Specify the total number of personal Web pages
that your customer can host for other users under his or her domains. This
service is mostly used in educational institutions that host non-commercial
personal pages of their students and staff. These pages usually have web
addresses like http://your-domain.com/~username. See the Hosting Personal
Web Pages section for details.
Maximum number of additional Microsoft FrontPage accounts (available only for
Windows hosting). Specify the maximum number of additional Microsoft
FrontPage accounts that the customer can create on his or her domains.
Page 55

Creating User Accounts 55
Maximum number of additional FTP accounts (available only for Windows hosting).
Specify the maximum number of additional FTP accounts that the customer can
create on his or her domains.
Disk space. Specify the total amount of disk space in megabytes that is allocated
to the customer. It includes disk space occupied by all files related to user's
domains (Web sites): Web site contents, databases, applications, mailboxes,
log files and backup files.
Maximum amount of traffic. Specify the amount of data in megabytes that can be
transferred from the customer's Web sites during a month.
Maximum number of MySQL databases and Maximum number of Microsoft SQL server
databases. Specify the maximum number of MySQL and Microsoft SQL Server
databases respectively that the customer can host under his or her domains.
MySQL databases quota and Microsoft SQL databases quota. Specify the maximum
disk space amount in megabytes that MySQL and Microsoft SQL Server
databases respectively can occupy on a domains belonging to the customer.
Maximum number of ODBC connections (available only for Windows hosting).
Specify the total number of ODBC connections that the customer can use on his
or her domains.
Maximum number of ColdFusion DSN connections (available only for Windows
hosting). Specify the total number of ColdFusion DSN connections that the
customer can use on his or her domains.
Maximum number of mailboxes. Specify the total number of mailboxes that the
customer can host on the server.
Mailbox quota. Specify the amount of disk space in kilobytes that is allocated for
storing e-mail messages and autoresponder attachment files to each mailbox in
a domain.
Maximum number of mail forwarders. Specify the total number of mail forwarders to
a single recipient that the customer can set up.
Maximum number of mail groups. Specify the total number of mail forwarders to
multiple recipients that the customer can set up.
Maximum number of mail autoresponders. Specify the total number of automatic
responses that the customer can set up.
Maximum number of mailing lists. Specify the total number of mailing lists that you
customer can host on the server.
Maximum number of Java applications. Specify the total number of Java applications
or applets that can be hosted on the server.
Maximum number of IIS application pools (available only for Windows hosting).
Specify the total number of dedicated IIS application pools that the customer
can allocate among his or her domains.
Maximum number of shared SSL links (available only for Windows hosting). Specify
the total number of shared SSL links that the customer can use on his or her
domains.
Page 56

56 Creating User Accounts
Expiration date. Specify the term for the hosting account. At the end of the term,
all domains (Web sites) of the user will be suspended, their Web, FTP and mail
services will no longer be accessible to the Internet users, and the user will not
be able to log in to the control panel. Accounts cannot be automatically
renewed, therefore, in order to bring the hosted domain names (Web sites) back
to operation, you will need to manually renew the user account: go to Clients >
client name > Resource Usage, specify another term, click OK, then click the
Unsuspend shortcut.
7. Click Next >>.
8. Grant the required permissions to the customer (if you created this user
account without using an account template):
Access to control panel. Specify whether the customer will be able to access the
control panel for managing his or her account and sites.
Domain creation. Specify whether the customer will be able to set up hosting
accounts for new sites.
Physical hosting management. Specify whether the customer will be able to set up
hosting accounts, modify hosting account features and switch on or off support
for programming and scripting languages.
Hosting performance management. Specify whether the customer will be able to
limit bandwidth usage and number of connections to his or her Web sites.
PHP safe mode management (available only for Linux hosting). Specify whether the
customer will be able to switch the PHP safe mode off for his or her sites. By
default, PHP is configured to operate in safe mode with functional restrictions.
To learn more about PHP safe mode, refer to http://php.net/features.safe-
mode. Some web applications may not work properly with safe mode enabled: If
an application on a site fails due to safe mode, switch the safe mode off by
clearing the PHP 'safe_mode' on check box in the hosting account properties
(Domains > domain name > Web Hosting Settings).
Management of access to the server over SSH or Remote Desktop. Specify whether the
customer will be able to access the server shell through Secure Shell (for Linux
hosting) or Remote Desktop (for Windows hosting) protocols.
Hard disk quota assignment. Specify whether the customer will be able to assign
hard quotas on disk space for his or her Web sites.
Subdomains management. Specify whether the customer will be able to set up
additional sites under his or her domains.
Domain aliases management. Specify whether the customer will be able to set up
additional alternative domain names for his or her Web sites.
Log rotation management. Specify whether the customer will be able to adjust the
cleanup and recycling of processed log files for his or her sites.
Anonymous FTP management. Specify whether the customer will be able to have
an FTP directory where all users could download and upload files without the
need to enter login and password. A Web site should reside on a dedicated IP
address in order to use anonymous FTP service.
FTP accounts management (available only for Windows hosting). Specify whether
the customer will be able to create and manage additional FTP accounts.
Page 57

Creating User Accounts 57
Task scheduling. Specify whether the customer will be able to schedule tasks in
the system. Scheduled tasks can be used for running scripts or utilities on
schedule.
Domain limits adjustment. Specify whether the customer will be able to change
resource allotments for his or her own account. This option must be selected if
the customer should be able to set up new Web sites.
DNS zone management. Specify whether the customer will be able to manage the
DNS zones of his or her domains.
Java applications management. Specify whether the customer will be able to install
Java applications and applets on web sites through the control panel.
Mailing lists management. Specify whether the customer will be able to use mailing
lists.
Spam filter management. Specify whether the customer will be able to use spam
filter provided by the SpamAssassin software.
Antivirus management. Specify whether the customer will be able to use server-
side antivirus protection for filtering incoming and outgoing mail.
Data backup and restore functions. Specify whether the customer will be able to use
the control panel's facilities to back up and restore his or her sites. For Linux
hosting accounts, you also need to select the following check boxes: To allow
storing backup files on the server, select the local repository check box, to allow
the customer to use an arbitrary FTP server for storing backups, select the
remote (FTP) repository check box.
Ability to use remote XML interface. Specify whether the customer will be able to
remotely manage his or her Web sites through custom applications. The XML
interface can be used for developing custom applications integrated with Web
sites, which could be used, for instance, for automating setup of hosting
accounts and provisioning of services for customers purchasing hosting
services from a site. To learn more about using Parallels Plesk Panel's XML
interface (also referred to as Parallels Plesk Panel API RPC), refer to the API
RPC documentation available at
http://www.parallels.com/ptn/documentation/ppp/
.
Ability to use Sitebuilder. Specify whether the customer will be able to use
Sitebuilder for creating and editing his or her Web site.
IIS Application Pool Management (available only for Windows hosting). Specify
whether the customer will be able to manage his or her IIS application pool.
Web statistics management. Specify whether the customer will be able to manage
Web statistics for his or her domains.
Additional write/modify permissions management (available only for Windows
hosting). Specify whether the customer will be able to manage additional
write/modify permissions for his or her domains. These permissions are required
if customer's Web applications are using a file-based database (like Jet) located
in the root of httpdocs or httpsdocs folders. Please note that selecting this
option might seriously compromise the Web site security.
Shared SSL management (available only for Windows hosting). Specify whether the
customer will be able to manage shared SSL for his or her domains.
Home page management. Specify whether the customer will be able to customize
his or her Home page.
Page 58

58 Creating User Accounts
Ability to select a database server. Specify whether the customer will be able to
select a database server of each type for creating his or her databases, not only
use the default database server.
9. Click Next >>.
10. Allocate IP addresses to the user: select IP addresses and click Add >>.
11. Click Finish.
You can now send the URL to control panel and login credentials to your customer.
Page 59

C HAPTER 7
Hosting Web Sites
This chapter explains how to:
Create a hosting account for publishing a site.
Specify the amount of disk space and monthly bandwidth a site can consume.
Delegate privileges to manage a site through Parallels Plesk Panel to another user,
if that user does not have access to a client level account.
Publish a site to the server.
In this chapter:
Setting Up a Hosting Account for a Web Site ...................................................... 60
Creating and Publishing a Site ............................................................................ 68
Page 60

60 Hosting Web Sites
Setting Up a Hosting Account for a Web Site
¾ To host a Web site on the server:
1. Go to Home > Domains group title menu > Create Domain.
2. Select the user account to which the site will belong (click an option
button to the left of the user name).
3. Click Next >>.
4. In the Domain name field, leave the WWW box selected, and type your
domain name example.com. Having the www alias preceding a domain
name will allow users to get to the site no matter what they type in their
browsers: www.example.com and example.com will both point to the
same site.
5. From the Assign IP address menu, select the required IP address. You
should select a dedicated IP address (not shared among other sites),
or, in terms of Parallels Plesk Panel, exclusive IP address to be able to
install an authentic digital SSL certificate for securing customers'
communications to your hosting server.
6. In the Use domain template settings menu, select the template you created,
or leave the default domain value selected if you did not create custom
templates. To facilitate setup of new Web sites, the control panel uses
settings inherited from domain templates. After your Web site is set up,
you can replace the default settings with other settings.
7. Under Switch on service, leave the Mail and DNS check boxes selected if e-
mail accounts and DNS zones will be served by the mail and DNS
services running on this server.
8. Under Hosting type, select the Web site hosting option to host the Web site
on this machine.
Upon completion of this procedure, your control panel will set up the domain name
server on this machine to serve the new domain name and prepare the Web server
to serve the new Web site: a new zone file with appropriate resource records will be
added to the Domain Name Server's configuration files, a Web space will be
created inside the Web server's directory, and necessary user accounts will be
created on the server.
Page 61

Hosting Web Sites 61
Note: If the site is hosted on another machine, and you wish to set up your control
panel's DNS server only to serve the DNS zone for that site, select either Frame
forwarding or Standard forwarding option. With standard forwarding, a user is
redirected to the site and the actual site's URL is shown in the user's browser, so
the user always knows that he or she is redirected to another URL. With frame
forwarding, a user is redirected to the site without knowing that the site actually
resides at another location. For example: your customer has a free personal web
site with his or her Internet Service Provider or a free Web host, and the Web site
address is http://www.geocities.com/~myhomepage. The customer purchased a
second level domain name www.myname.com and wants you to provide domain
forwarding to his Web site. In this case you would normally choose the Frame
forwarding service. For more information, refer to the Parallels Plesk Panel 9.5
Administrator's Guide, section Serving Domain Names for Sites Hosted on Other
Servers (Domain Forwarding).
9. Type in the username and passwor d that will be used for uploading
Web site content over FTP and Microsoft FrontPage.
10. Select the Configure advanced Web hosting settings check box and click Next
>>.
11. Specify the following settings:
SSL support. Secure Sockets Layer encryption is generally used for protecting
transfer of sensitive data during online transactions on e-commerce Web sites
that run on dedicated IP addresses. SSL certificates that participate in the
encryption process are usually applied to a single domain name on a single IP
address, therefore, each site that needs SSL protection must be hosted on a
dedicated IP address. An exception to this is subdomains, which you can
protect with a wildcard certificate. Installing an SSL certificate on a Web server
that hosts several Web sites with different domain names on a single IP address
(shared or name-based hosting) is technically possible, however, it is not
recommended: the encryption will be provided, but users will get warning
messages on attempt to connect to the secure site. To allow SSL encryption for
Web sites, select the SSL support check box.
Use a single directory for housing SSL and non-SSL content (available only for Linux
hosting). By default, when users publish their sites through their FTP accounts,
they need to upload the web content that should be accessible via secure
connections to the httpsdocs directory, and the content that should be
accessible via plain HTTP, to the httpdocs directory. For the convenience of
publishing all content through a single location – httpdocs directory, select the
Use a single directory for housing SSL and non-SSL content check box.
Hard disk quota (available only for Linux hosting). Specify the amount of disk
space in megabytes allocated to the Web space for this site. This is the socalled hard quota that will not allow writing more files to the Web space when
the limit is reached. At attempt to write files, users will get the "Out of disk
space" error. Hard quotas should be enabled in the server's operating system,
so if you see the "Hard disk quota is not supported" notice to the right of the Hard
disk quota field, but would like to use the hard quotas, log in to the server shell
and run the command quotaon -a.
Page 62

62 Hosting Web Sites
Access to the server over SSH or Remote Desktop with FTP user's cr edentials. This
allows a site owner to upload securely Web content to the server through a
Secure Socket Shell or Remote Desktop connection, however, allowing access
to the server also poses a potential threat to the server security, so we
recommend that you set this option to Forbidden.
Create and publish Web site using Sitebuilder. This allows a site owner to create and
manage his or her Web site using the Sitebuilder program installed on your
server.
Microsoft FrontPage support. Microsoft FrontPage is a popular Web site authoring
tool. To enable users to publish and modify their sites through Microsoft
FrontPage, select the options Microsoft FrontPage support, Microsoft FrontPage over
SSL support, and Remote FrontPage authoring allowed.
Support for hosting services and scripting languages. Specify which of the following
programming and scripting languages should be supported by the Web server:
Active Server Pages (ASP), ASP.NET (on Windows-based hosting), Server Side
Includes (SSI), PHP hypertext preprocessor (PHP), Common Gateway Interface
(CGI), Fast Common Gateway Interface (FastCGI), Perl, Python, ColdFusion,
and Miva scripting required for running Miva e-commerce solutions. By default,
PHP is configured to operate in safe mode with functional restrictions. To learn
more about PHP safe mode, refer to http://php.net/features.safe-mode
web applications may not work properly with safe mode enabled: If an
application on your site fails due to safe mode, switch the safe mode off by
clearing the PHP 'safe_mode' on check box in the hosting account properties
(Domains > domain name > Web Hosting Settings).
. Some
Web statistics. To allow the Web site owner to view the information on the
number of people visited his or her site and the pages of the site they viewed,
select the statistics program from the Web statistics menu, and select the
accessible via password protected directory /plesk-stat/webst at check box. This will
install the statistics software of your choice, which will generate reports and
place them into the password protected directory. The domain/web site owner
will then be able to access Web statistics at the URL: https://yourdomain.com/plesk-stat/webstat using his or her FTP account login and
password.
Note: When you switch from one statistics program to another, all reports
created by the previously used statistics program are deleted and new
reports are created in accordance with the information read from log files
kept on the server. This means that if you configured the system (at Domains
> domain name > Log Manager > Log Rotation) so as to keep log files only for the
last month, then Web statistics will be available only for the last month.
Custom error documents. When visitors coming to a site request pages that the
Web server cannot find, the Web server generates and displays a standard
HTML page with an error message. If you wish to create your own error pages
and use them on your Web server or allow your customers to do that, select the
Custom error documents check box.
Additional write/modify permissions (available only for Windows hosting). This
option is required if Web applications under a domain will be using a file-based
database (like Jet) located in the root of httpdocs or httpsdocs folders.
Please note that selecting this option might seriously compromise the Web site
security.
Page 63

Hosting Web Sites 63
Use dedicated IIS application pool (available only for Windows hosting). This option
enables the use of dedicated IIS application pool for Web applications on a
domain. Using dedicated IIS application pool dramatically improves the stability
of domain Web applications due to worker process isolation mode. This mode
gives each Web site hosted on the server the possibility to allocate a separate
process pool for execution of its Web applications. This way, malfunction in one
application will not cause stopping of all the others. This is especially useful
when you are using shared hosting package.
12. Click Next >>.
13. Specify the following settings:
Overuse policy. Specify what should be done to the site when disk space and
traffic limits are exceeded: To block the site, select the Overuse is not allowed
option. To allow the site to operate, select the Overuse is allowed option.
Maximum number of subdomains. Specify the number of subdomains that can be
hosted under this domain.
Maximum number of domain aliases. Specify the total number of additional
alternative domain names that the site owner will be able to use for his or her
Web site.
Disk space. Specify the total amount of disk space allocated to a hosting account
associated with the domain. This amount is measured in megabytes. It includes
disk space occupied by all files related to the domain/Web site: Web site
contents, databases, applications, mailboxes, log files and backup files.
Maximum amount of traffic. Specify the amount of data in megabytes that can be
transferred from the Web site during a month.
Maximum number of Web users. Specify the number of personal Web pages that
the domain owner can host for other users under his or her domain. This service
is mostly used in educational institutions that host non-commercial personal
pages of their students and staff. These pages usually have web addresses like
http://your-domain.com/~username. If you wish to allow execution of scripts
embedded in personal Web pages, select also the Allow the web users scripting
check box. See the Hosting Personal Web Pages section for details.
Maximum number of MySQL databases. Specify the number of databases that can
be hosted in a domain.
Maximum number of mailboxes. Specify the number of mailboxes that can be
hosted in a domain.
Mailbox quota. Specify the amount of disk space in kilobytes that is allocated for
storing e-mail messages and autoresponder attachment files to each mailbox in
a domain.
Maximum number of mail forwarders. Specify the number of mail forwarders that
can be used in a domain.
Maximum number of mail autoresponders. Specify the number of automatic
responses that can be set up in a domain.
Page 64

64 Hosting Web Sites
Maximum number of mailing lists. Specify the number of mailing lists that the
domain owner can run in a domain. The mailing lists are served by the GNU
Mailman software, which may or may not be installed on the server. If it is not
installed and your customers would like to use it, you may want to to install it. To
allow the use of mailing lists, you should also put a check mark into the Mailing
lists check box under the Preferences group.
Maximum number of Java applications. Specify the maximum number of Java
applications or applets that the domain owner can install under a domain.
MySQL databases quota and Microsoft SQL databases quota. Specify the maximum
disk space amount in megabytes that MySQL and Microsoft SQL Server
databases respectively can occupy under a domain.
Maximum number of additional Microsoft FrontPage accounts (only for Windows
hosting). Specify the maximum number of additional Microsoft FrontPage
accounts that can be created under a domain.
Maximum number of MySQL databases and Maximum number of Microsoft SQL server
databases. Specify the maximum number of MySQL and Microsoft SQL Server
databases that can be hosted under a domain.
Maximum number of additional FTP accounts (available only for Windows hosting).
Specify the maximum number of additional FTP accounts that can be created
under a domain.
Maximum number of shared SSL links (available only for Windows hosting). Specify
the total number of shared SSL links that can be used under a domain.
Maximum number of ODBC connections (available only for Windows hosting).
Specify the total number of ODBC connections that can be used under a
domain.
Maximum number of ColdFusion DSN connections (available only for Windows
hosting). Specify the total number of ColdFusion DSN connections that can be
used under a domain.
Expiration date. Specify the term for a hosting account. At the end of the term, the
domain (Web site) will be suspended, its Web, FTP and mail services will no
longer be accessible to the Internet users, and domain owner will not be able to
log in to the control panel. Hosting accounts cannot be automatically renewed,
therefore, in order to bring the hosted domain name/web site back to operation,
you will need to manually renew the hosting account: click the Domains shortcut
in the navigation pane, click the domain name your need, click the Resource
Usage icon, specify another term, click OK, then click the Unsuspend icon (Domains
> domain name > Unsuspend).
14. Click Finish.
Now your server is ready to accommodate the new Web site, and the site owner can
publish the site to the server. For instructions on publishing a Web site, refer to the
Publishing a Site (see page 68) section of this guide.
Note: If you transferred this domain name from another Web host, you will need to
update the host DNS address with the domain name registrar so as to point to your
name servers: log in to your registrar's web site, locate the forms used to manage the
domain host pointers, and replace the current DNS host settings with your name
servers' host names. The information on new name servers will spread across the DNS
system within 48 hours.
Page 65

Hosting Web Sites 65
If you have registered several domain names that you would like to point to a site
hosted on this server, you should set up domain aliases. For more information, refer to
the Parallels Plesk Panel 9.5 Administrator's Guide, section Setting Up Additional
Domain Names for a Site (Domain Aliases).
If you need to host several domains on your machine that will point to a site hosted on
another server, you should set up domain forwarding. For more information, refer to
the Parallels Plesk Panel 9.5 Administrator's Guide, section Serving Domain Names for
Sites Hosted on Other Servers (Domain Forwarding).
In this section:
Allowing a Site Owner to Log In to Control Panel ............................................... 66
Page 66

66 Hosting Web Sites
Allowing a Site Owner to Log In to Control Panel
If you have set up a Web site for a user, whom you did not grant access to the client
level account, you can create a domain owner's account to allow the site owner to log
in to control panel for managing his or her own Web site.
¾ To allow the site owner to log in to control panel for managing his or her
Web site:
1. Go to Domains > domain name > Domain Administrator Access.
2. Select the Allow domain administrator's access check box.
3. Type the password for access to the site owner's control panel.
For security reasons, the password should be more than 8 symbols, and it should
comprise a combination of letters, numbers, and punctuation; dictionary words and
proper names should be avoided.
4. Specify the settings related to the appearance of user's control panel, if
desired: interface language, theme (skin), the limit on number of
characters that can appear on custom buttons placed into the control
panel by the site owner.
5. Leave the Allow multiple sessions check box selected to allow the site
owner to have several simultaneous sessions in the control panel.
6. Leave the Prevent users from working with the control panel until interface screens
are completely loaded check box selected.
This will forbid users from submitting data or performing operations until the control
panel is ready to accept them.
7. Specify the operations that the site owner will be able to perform in his
or her control panel:
Physical hosting management. Allow or disallow full control of the hosting account
and Web space.
Hosting performance settings management. Specify whether the user will be able to
limit bandwidth usage and number of connections to his or her Web site.
PHP safe mode management (available only for Linux hosting). Specify whether the
user will be able to switch the PHP safe mode off for the site. By default, PHP is
configured to operate in safe mode with functional restrictions. To learn more
about PHP safe mode, refer to http://php.net/features.safe-mode
applications may not work properly with safe mode enabled: If an application on
a site fails due to safe mode, switch the safe mode off by clearing the PHP
'safe_mode' on check box in the hosting account properties (Domains > domain
name > Web Hosting Settings).
. Some Web
Management of access to the server over SSH or Remote Desktop. Specify whether the
user will be able to access the server shell through Secure Shell (for Linux
hosting) or Remote Desktop (for Windows hosting) protocols.
Page 67

Hosting Web Sites 67
Hard disk quota assignment. Specify whether the user will be able to assign hard
quota on disk space for this Web site.
Subdomains management. Specify whether the user will be able to set up
additional sites under this domain.
Domain aliases management. Specify whether the user will be able to set up
additional alternative domain names for this site.
Log rotation management. Specify whether the user will be able to adjust the
cleanup and recycling of processed log files for this sites.
Anonymous FTP management. Specify whether the user will be able to have an
FTP directory where all other users could download and upload files without the
need to enter login and password. A Web site should reside on a dedicated IP
address in order to use anonymous FTP service.
FTP accounts management (available only for Windows hosting). Specify whether
the user will be able to create and manage additional FTP accounts.
Task scheduling. Specify whether the user will be able to schedule tasks in the
system. Scheduled tasks can be used for running scripts or utilities on schedule.
DNS zone management. Specify whether the user will be able to manage the DNS
zone of this site.
Java applications management. Specify whether the user will be able to install Java
applications and applets on the site.
Mailing lists management. Specify whether the user will be able to use mailing lists.
Spam filter management. Specify whether the user will be able to use spam filter.
Antivirus management. Specify whether the user will be able to use server-side
antivirus protection for filtering incoming and outgoing mail.
Data backup and restore functions. Specify whether the user will be able to use the
control panel's facilities to back up and restore the site.
Ability to use Sitebuilder. Specify whether the user will be able to use Sitebuilder
for creating and editing his or her Web site.
IIS application pool management (available only for Windows hosting). Specify
whether the user will be able to manage his or her IIS application pool.
Web statistics management. Specify whether the user will be able to manage Web
statistics for this site.
Additional write/modify permissions management (available only for Windows
hosting). Specify whether the user will be able to manage additional write/modify
permissions for this site. These permissions are required if user's Web
applications are using a file-based database (like Jet) located in the root of
httpdocs or httpsdocs folders. Please note that selecting this option might
seriously compromise the Web site security.
Home page management. Specify whether the customer will be able to customize
his or her Home page.
8. Specify the site owner's contact information.
9. Click OK.
Page 68

68 Hosting Web Sites
Now you can send the control panel's URL, login and password to the site owner. The
URL is https://user's_domain_name:8443, where user's_domain_name is the domain
name without the www alias. The login name that the site owner should specify in order
to log in to the control panel is his or her domain name, for example, your-domain.com.
Creating and Publishing a Site
If you installed Sitebuilder and a license key for it on the server, you can create and
publish Web sites using Sitebuilder. Or you can create your site content (Web pages,
scripts and graphic files that compose your site) on your home or office computer and
then publish it to the server in any of the following ways:
Through FTP connection (most common and easiest way)
Through control panel's file manager
Through Secure Shell connection (only for users of Linux and FreeBSD operating
systems)
Through Adobe Dreamweaver or Microsoft FrontPage software (only for users of
Microsoft Windows operating systems)
FTP is one of the most common and easiest ways to upload files.
In this section:
Creating and Publishing Web Sites Using Sitebuilder ........................................ 68
Publishing Sites Through FTP ............................................................................ 69
Publishing Sites Through Parallels Plesk Panel File Manager ........................... 69
Publishing Sites Through SSH Connection ......................................................... 70
Publishing Sites with Microsoft FrontPage .......................................................... 70
Publishing Sites with Adobe Dreamweaver ........................................................ 74
Creating and Publishing Web Sites Using Sitebuilder
¾ To start creating a Web site using Sitebuilder:
1. Go to Domains > domain name > Edit in Sitebuilder. The Sitebuilder wizard
opens.
2. Select the Create your site option and click Next at the bottom of the
screen.
For further instructions on creating or editing your site, refer to the online Sitebuilder
Wizard user's guide at
http://download1.parallels.com/SiteBuilder/4.5.0/doc/user/en_US/html/index.htm
.
Page 69

Hosting Web Sites 69
Publishing Sites Through FTP
¾ To publish a site through FTP:
1. Connect to the server with an FTP client program, using FTP account
credentials that you specified during setup of hosting account or
obtained from your provider. The FTP address should be ftp://yourdomain-name.com, where your-domain-name.com is your site's Internet
address.
Enable the passive mode if you are behind a firewall.
2. Upload files and directories that should be accessible through HTTP
protocol to the httpdocs directory, and files/directories that should be
transferred securely over SSL protocol to the httpsdocs directory.
3. Place your CGI scripts into the cgi-bin directory.
4. Close your FTP session.
Publishing Sites Through Parallels Plesk Panel File Manager
¾ To upload files through Parallels Plesk Panel File Manager:
1. Log in to Parallels Plesk Panel.
2. Go to Domains > domain name > File Manager.
3. Create and upload files and directories.
Place the files and directories that should be accessible via HTTP protocol to the
httpdocs directory, and files/directories that should be transferred securely over
SSL protocol to the httpsdocs directory. Place your CGI scripts into the cgi-bin
directory.
To create a new directory within your current location, click the Add New Directory
button.
To create new files in the required directory, click Add New File, in the File creation
section specify the file name, select the Use html template check box, if you want
file manager to insert some basic html tags to the new file, and click OK. A page
will open allowing you to enter the content or html-formatted source of a new
file. After you are done, click OK.
To upload a file from the local machine, click Add New File, specify the path to its
location in the File source box (or use the Browse button to locate the file), and
click OK.
Page 70

70 Hosting Web Sites
To modify permissions for a file or directory, in the Permissions column, click the
respective hyperlink representing the set of permissions. Modify the permissions
as desired and click OK.
To edit the source code of a file, click
To edit the Web page in the built-in visual editor (available only to users of
Microsoft Internet Explorer), click
Panel opens internal WYSIWYG editor by default. If you want to edit the source
code of the HTML file, click HTML. To return back to WYSIWYG mode, click
Design.
To view the file, click
To rename a file or directory, click
To copy or move a file or directory to another location, select the required file or
directory using the appropriate check box, and click Copy/Move. Specify the
destination for the file or directory to be copied or renamed to, then click Copy to
copy, or Move to move it.
To update the file or directory creation date, click Change Timestamp. The time
stamp will be updated with the current local time.
To remove a file or directory, select the corresponding check box, and click
Remove. Confirm removal and click OK.
.
.
. When editing an HTML file, Parallels Plesk
. Type in a new name and click OK.
Publishing Sites Through SSH Connection
If your are using a Linux or FreeBSD operating system on your local computer and
have access to server shell, use the ‘scp’ command to copy files and directories to the
server: scp your_file_name login@remoteserver.com:path to copy files,
and scp –r your_directory_name login@remoteserver.com:path to copy
entire directories.
After publishing, you will be able to work with files and directories on your account
using SSH terminal Web application integrated in your Parallels Plesk Panel (Domains >
domain name > SSH Terminal).
Publishing Sites with Microsoft FrontPage
Microsoft FrontPage deals with two kinds of Web sites: disk-based and server-based.
In short, a disk-based site is a FrontPage Web site you create on your local hard disk
and then later publish to a Web server. A server-based site is one you create and work
with directly on a Web server, without the extra step of publishing. This section
provides you with instructions on publishing only disk-based web sites.
You can publish disk-based web sites either through FTP or HTTP. If your server is
running FrontPage Server Extensions, you would publish your site to an HTTP location.
For example: http://your-domain.com/MyWebSite. If your server supports FTP, you
would publish to an FTP location. For example: ftp://ftp.your-domain.com/myFolder.
After publishing, you can manage your site through FrontPage Server Extensions.
Page 71

Hosting Web Sites 71
¾ To access FrontPage Server Extensions management interface:
1. Log in to Parallels Plesk Panel.
2. Click the Domains shortcut in the navigation pane.
3. Click the required domain name in the list.
4. To manage a site, which is not protected by SSL, open the Web Site
group title menu, and click Frontpage Webadmin. To manage an SSLenabled site, open the Web Site group title menu, and click Frontpage SSL
Webadmin.
5. Type your FrontPage administrator ’s login name and password, and
click OK.
For instructions on using FrontPage server extensions, see online help (Frontpage
Webadmin > Help) or visit Microsoft Web site.
In this section:
Publishing from Microsoft FrontPage through FTP ............................................. 72
Publishing from Microsoft FrontPage through HTTP .......................................... 73
Page 72

72 Hosting Web Sites
Publishing from Microsoft FrontPage through FTP
¾ To publish files through FTP:
1. Open your FrontPage program.
2. Open a FrontPage Web site: open File menu and select the Open Site
item.
3. Go to Remote Web site view: click the Web Site tab, and then the Remote Web
Site button at the bottom of the window.
4. Set up your Remote Web Site Properties:
Click the Remote Web Site Properties button in the upper-right corner of the
window.
Select FTP as the remote Web server.
In the Remote Web site location box, type your host name (e.g., ftp://ftp.your-
domain.com)
In the FTP directory box, type your FTP directory if your hosting company
provided one. Leave it blank if they did not specify one.
Select the Use Passive FTP check box if your computer or network is protected by
a firewall.
5. Click OK to connect to the remote site.
The Remote Web site view will show files that you have in your local and remote
sites.
6. Click the Publish Web site button in the lower-right corner of the window.
Page 73

Hosting Web Sites 73
Publishing from Microsoft FrontPage through HTTP
¾ To publish files through HTTP on a server that supports FrontPage Server
Extensions:
1. Open your FrontPage program.
2. Open a FrontPage Web site: open File menu and select the Open Site
item.
3. Go to Remote Web site view: click the Web Site tab, and then the Remote Web
Site button at the bottom of the window.
4. Click the Remote Web Site Properties button in the upper-right corner of the
window.
5. On the Remote Web Site tab, under Remote Web server type, click FrontPage or
SharePoint Services.
6. In the Remote Web site location box, type the Internet address, including
the protocol, of the remote Web site that you want to publish folders
and files to — for example, http://www.your-domain.com — or click
Browse to locate the site.
7. Do any of the following:
To use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) for establishing a secure communications
channel to prevent the interception of critical information, click Encryption
connection required (SSL). To use SSL connections on your Web server, the
server must be configured with a security certificate from a recognized certificate
authority. If the server does not support SSL, clear this check box. Otherwise,
you will not be able to publish folders and files to the remote Web site.
To remove specific types of code from Web pages as they are being published,
on the Optimize HTML tab, select the options you want.
To change the default options for publishing, on the Publishing tab, select the
options you want.
8. Click OK to connect to the remote site.
The Remote Web site view will show files that you have in your local and remote sites.
9. Click the Publish Web site button in the lower-right corner of the window.
Page 74

74 Hosting Web Sites
Publishing Sites with Adobe Dreamweaver
Before publishing a site from Dreamweaver, you need to define the site properties, that
is, you need to tell Dreamweaver where your site files are located on your computer,
and to specify the server to which you want to publish the site.
¾ To define a site in Dreamweaver:
1. From the Site menu, choose New Site. The Site Definition screen opens.
2. Click the Advanced tab.
3. In the Local Info category, specify the following:
Site name. This will show in Web browser’s title bar.
Local root folder. This is the folder on your computer where all of your site files
are stored. For example c:\My Site
Default images folder. Specify the folder where your site’s graphic files are stored.
For example c:\My Site\images
HTTP address. Specify your domain name. For example, http://your-
domain.com
4. From the Category menu, select the Remote Info item.
5. From the Access menu, select the FTP option. Most likely, your server
supports publishing through FTP (File Transfer Protocol, commonly
used for transferring files over the Internet).
6. Specify the following settings:
FTP host. Type your FTP host name without the ftp:// prefix. For example,
your-domain.com.
Host directory. Specify the directory on the server where your site will reside. In
most cases, this is httpdocs.
Login and password. Specify the login name and password for access to the FTP
account.
Use passive FTP. Select this option only if your computer is behind a firewall.
7. To ensure that you specified the correct login and password, and that
Dreamweaver can connect to the server, click the Test button.
8. To save the settings, click OK.
¾ To publish your site:
1. Open your site in Dreamweaver.
2. From the Site menu, select the Put option (or press Ctrl+Shift+U
simultaneously).
 Loading...
Loading...