Page 1

Parallels® Plesk Panel
Page 2

Copyright Notice
Parallels IP Holdings GmbH
Vordergasse 59
CH-Schaffhausen
Switzerland
Phone: +41 526320 411
Fax: +41 52672 2010
Global Headquarters
500 SW 39th Street, Suite 200
Renton, WA 98057
USA
Phone: +1 (425) 282 6400
Fax: +1 (425) 282 6445
EMEA Sales Headquarters
Willy-Brandt-Platz 3
81829 Munich, DE
Phone: +49 (89) 450 80 86 0
Fax:+49 (89) 450 80 86 0
APAC Sales Headquarters
3 Anson Road, #36-01
Springleaf Tower, 079909
Singapore
Phone: +65 6645 32 90
Copyright © 1999-2012 Parallels IP Holdings GmbH. All rights reserved.
This product is protected by United States and international copyright laws. The product’s
underlying technology, patents, and trademarks are listed at http://www.parallels.com/trademarks.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows Server, Windows NT, Windows Vista, and MS-DOS are registered
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
All other marks and names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 3

Contents
Preface 6
Typographical Conventions ........................................................................................................... 6
Feedback ....................................................................................................................................... 7
About This Guide 8
Introduction to Panel 9
Installation and Upgrade Overview ............................................................................................. 11
Installing and Updating Third-Party Applications .............................................................. 12
Ports Used by Panel .................................................................................................................... 13
Licensing ..................................................................................................................................... 14
System Maintenance 15
Changing Your Server's Host Name ........................................................................................... 16
Changing IP Addresses ............................................................................................................... 17
Moving the Virtual Hosts Directory .............................................................................................. 18
Moving the Directory for Storing Panel Backups ......................................................................... 19
Moving the Directories for Storing Mail Data ............................................................................... 20
Switching Between MySQL and MSSQL Database Server Engines .......................................... 21
Using GUI to Switch Between Database Servers ............................................................. 22
Using Command-Line Interface to Switch Between Database Servers............................ 23
Programming Event Handlers to Execute Custom Scripts.......................................................... 26
Automating Administration Tasks with Command-Line Utilities .................................................. 27
Monitoring Status of System Services......................................................................................... 28
Managing Services from the Command Line and Viewing Service Logs ................................... 29
Predefining Values for Customizable PHP Parameters .............................................................. 34
Website Applications ................................................................................................................... 35
Multiple Web Apps in a Single Directory ........................................................................... 35
Hiding Commercial Apps ................................................................................................... 36
Spam Protection .......................................................................................................................... 37
Configuring SpamAssassin ............................................................................................... 38
Optimizing the Task Manager Performance ................................................................................ 39
Cloning Panel in Virtual Environment .......................................................................................... 41
Removing Panel .......................................................................................................................... 43
Third-Party Components 44
Web Deploy 2.0 ........................................................................................................................... 45
1. Install Web Deploy ........................................................................................................ 45
2. Improve the Security Level ............................................................................................ 46
3. Secure the Service with a Valid Certificate ................................................................... 46
4. Activate Web Deploy in Hosting Plans and Subscriptions ............................................ 46
Manual Installation of Web Deploy.................................................................................... 46
Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 48
Page 4
Preface 4
Backing Up Data .......................................................................................................................... 49
Backup Objects: Hierarchy and Volume ........................................................................... 50
Specifying Data for Backing Up ........................................................................................ 53
Defining Properties of Files That Compose Backup ......................................................... 60
Exporting Backup Files ..................................................................................................... 62
Defining How the Backup Process Is Performed .............................................................. 64
Backup Utility Commands and Options ............................................................................ 65
Restoring Data ............................................................................................................................. 69
Defining Objects for Restoration ....................................................................................... 69
Defining How the Restoration Process Is Performed........................................................ 76
Conflict Resolution Rules and Policies ............................................................................. 77
Restoration Utility Commands and Options ...................................................................... 98
Migrating Data ............................................................................................................................. 99
Changing Security Settings for File System Objects and Accounts 100
Panel's Security Policies ........................................................................................................... 101
Windows Accounts Used by Panel to Manage Windows Objects ............................................ 101
Default User Permissions for Disks................................................................................. 101
Windows Accounts Used by Panel to Manage Hosted Windows Objects ................................ 104
Administering Windows Objects Security on Panel-managed Server ...................................... 105
Initial Windows Security Configuration During Panel Installation or Hosting Account Creation
........................................................................................................................................ 106
Browsing Object Security Settings Through Panel GUI .................................................. 106
Customizing Object Security Settings in Panel ............................................................... 107
General Security Metadata Structure .............................................................................. 121
Restoring Disk User Permissions .............................................................................................. 125
Statistics and Logs 126
Calculating Statistics on Demand .............................................................................................. 127
Log Files and Log Rotation ....................................................................................................... 129
Customizing Panel Appearance and GUI Elements 130
Customizing Panel Appearance and Branding ......................................................................... 131
Hiding and Changing Panel GUI Elements ............................................................................... 132
Ways of Changing the Panel Functionality ..................................................................... 133
Changing the Panel Functionality ................................................................................... 137
Changing Web Presence Builder Functionality ............................................................... 172
Customizing Website Topics ..................................................................................................... 178
Adding Custom Website Topics ...................................................................................... 179
Rearranging and Removing Topics and Categories ....................................................... 186
Localization 188
Registering Additional Services with Panel Notifications 189
Preparing a Service for Registration ......................................................................................... 191
Registering the Service ............................................................................................................. 192
Code Samples ........................................................................................................................... 193
Implementation of Plan_Item_Interface .......................................................................... 194
Registration of an Additional Service .............................................................................. 198
Troubleshooting 199
Page 5

Preface 5
Repairing Panel Installation ....................................................................................................... 200
Detecting Newly Installed Components..................................................................................... 203
Restoring Mail Configuration ..................................................................................................... 204
Reducing Amounts of Notifications from Antivirus .................................................................... 205
Recovering Forgotten Password ............................................................................................... 205
Checking and Correcting Component and Folder Permissions ................................................ 206
Glossary 207
Page 6
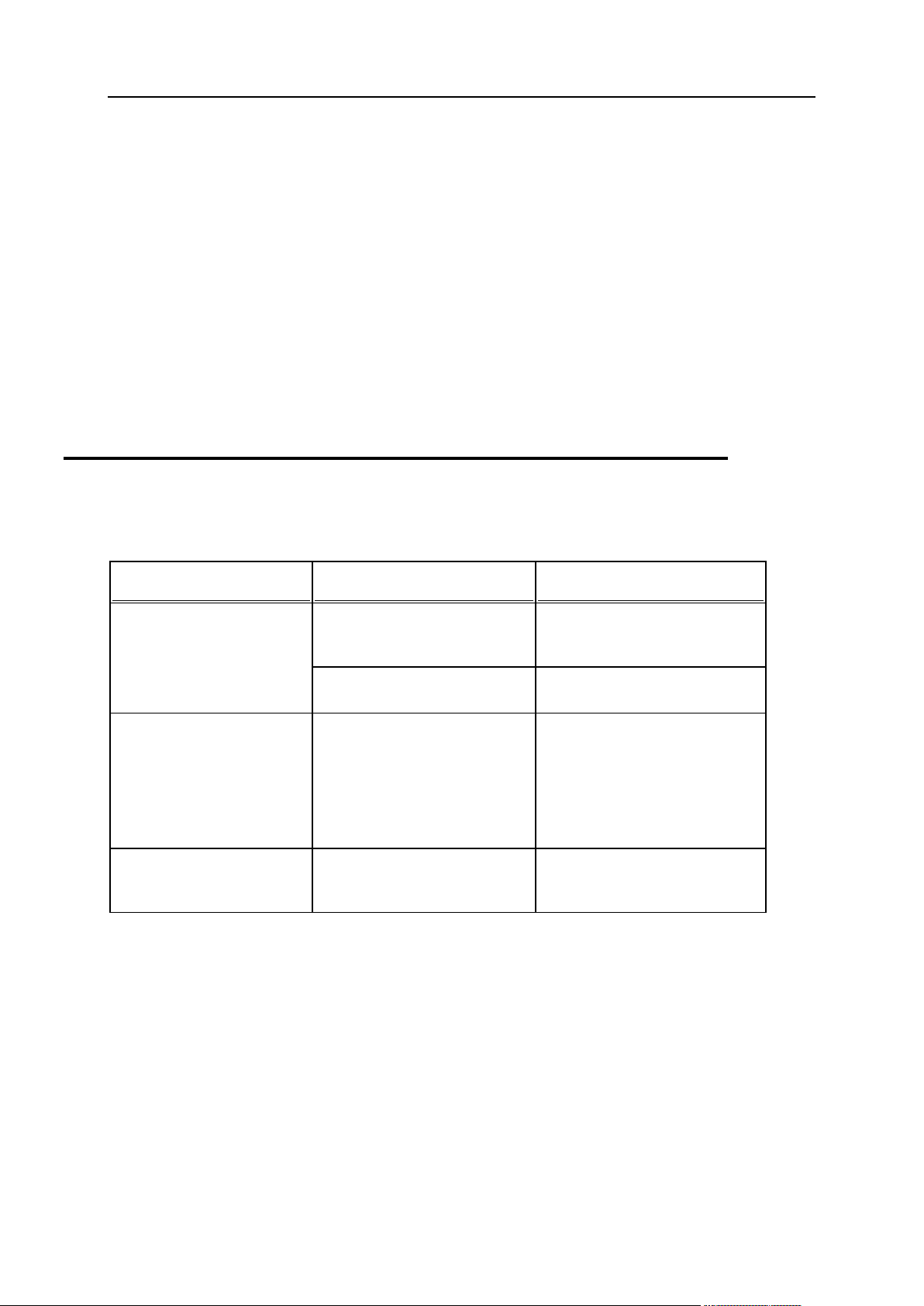
6 Preface
In this section:
Typographical Conventions ............................................................................... 6
Feedback .......................................................................................................... 7
Formatting convention
Type of Information
Example
Special Bold
Items you must select, such as
menu options, command
buttons, or items in a list.
Go to the QoS tab.
Titles of chapters, sections,
and subsections.
Read the Basic Administration
chapter.
Italics
Used to emphasize the
importance of a point, to
introduce a term or to
designate a command line
placeholder, which is to be
replaced with a real name or
value.
The system supports the so
called wildcard character
search.
Monospace
The names of style sheet
selectors, files and directories,
and CSS fragments.
The license file is called
license.key.
Preface
Typographical Conventions
The following kinds of formatting in the text identify special information.
Page 7
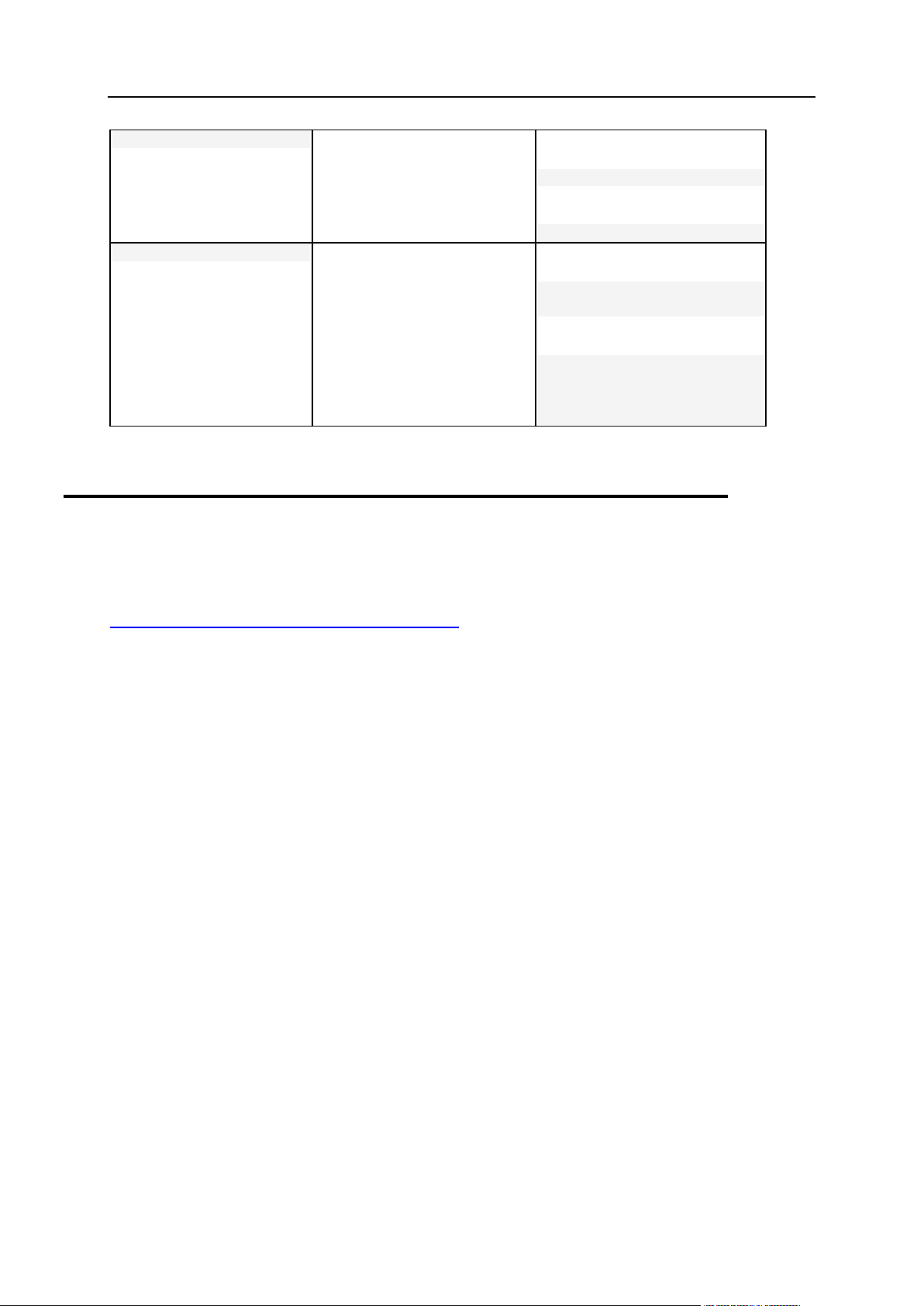
Preface 7
Preformatted Bold
What you type, contrasted with
on-screen computer output.
Unix/Linux:
# cd /root/rpms/php
Windows:
>cd %myfolder%
Preformatted
On-screen computer output in
your command-line sessions;
source code in XML, C++, or
other programming languages.
Unix/Linux:
# ls -al /files
total 14470
Windows:
>ping localhost
Reply from 127.0.0.1:
bytes=32 time<1ms
TTL=128
Feedback
If you have found an error in this guide, or if you have suggestions or ideas on how to
improve this guide, please send your feedback using the online form at
http://www.parallels.com/en/support/usersdoc/. Please include in your report the guide's title,
chapter and section titles, and the fragment of text in which you have found an error.
Page 8

Parallels Plesk Panel for Windows Advanced Administration Guide is a companion
C H A P T E R 1
About This Guide
guide for Parallels Panel Administrator's Guide. It is intended for server administrators
whose responsibilities include maintaining hosting servers and troubleshooting server
software problems.
The guide provides step-by-step instructions to perform server management tasks that
require use of Panel functionality other than the GUI and GUI-only tasks that
administrators may need to perform only in rare specific situations. Administrators can
use several additional tools that are supplied in the standard Parallels Plesk Panel
distribution package to add customized automation tasks, back up and restore data,
and repair Panel components and system settings. The tools include a number of
standalone Windows applications, command-line utilities, and the ability to integrate
custom scripting with Parallels Plesk Panel.
This guide consists of the following chapters:
Introduction to Panel. Describes the main components and services operated by
Panel, licensing terms, and the ways to install and update Panel components.
System Maintenance. Describes how to change server host name, IP addresses, and
locations of directories for storing virtual host files, backups, and mail content. This
chapter also introduces Panel's command-line tools, a mechanism for running
scripts on Panel events, and service monitor that allows monitoring and restarting
services without logging in to Panel.
Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data. Describes how to back up and restore Panel
data by means of the command-line utilities pleskbackup and pleskrestore,
and introduces the tools for migrating hosted data between servers.
Changing Security Settings for File System Objects and Accounts. Describes the process
of applying Parallels Plesk Panel security rules to file system objects and accounts.
Presents examples of commonly used security rules with explanations.
Customizing Panel Appearance and GUI Elements. Introduces Panel themes that can be
used to customize Panel appearance and branding and describes how to remove
specific elements of Panel GUI or change their behaviour.
Statistics and Logs. Describes how to run calculation of statistics on disk space and
traffic usage on demand and access web server logs.
Localization. Introduces the means to localize Panel GUI into languages for which
Parallels does not provide localization.
Troubleshooting. Describes how to troubleshoot malfunction of Panel services.
Glossary. Explains terms used in this guide.
Page 9

Parallels Plesk Panel consists of the following main components:
C H A P T E R 2
Introduction to Panel
Front-end GUI service. The GUI, served with the Internet Information Services (IIS)
server, is the main means of interaction with Panel.
Panel core. The core processes management requests from the Panel GUI,
command line interface, and API RPC. The core contains scripts, binary files and
other resources used to link Panel components with each other and with external
services.
Panel's main database called psa. The database stores information about Panel
objects, such as IP addresses, domains, user accounts, and many others. The
database is served by MySQL or the Microsoft SQL database engine.
Panel's configuration files.
Panel's log files.
Command-line utilities. Command-line interface allows integration of third-party
software with Panel, and provides the means to manage Panel through the server
console. For more information about the Panel command-line interface, refer to
Panel Command Line Reference.
API RPC. This interface is another way to integrate third-party software with Panel.
It allows to manage Panel objects from remote by sending specifically structured
XML packets and receiving responses from Panel. For more information on API
RPC, refer to Developer's Guide: Read Me First and API RPC Protocol Reference.
Services Managed by Panel
Panel uses standard packages for the following services:
IIS as a set of Internet services including HTTP, FTP, and others.
FTP servers - ServU, Gene-6, used as alternative FTP servers.
Mail servers - MailEnable, IceWarp (Merak), CommuniGate Pro, or
SmarterMail.
BIND or MS DNS - used as the domain name server.
MySQL used to store the Panel's database called psa that is used for administrative
purposes
MSSQL or MySQL - used as a database server by Panel users.
Tomcat - used as an infrastructure for servlet and JSP-based applications shipped
in the *.war format.
JDK (j2sdk) - used as a library for java applications.
SpamAssassin - used as protection against spam e-mail messages.
Parallels Premium Antivirus, Kaspersky Antivirus, or IceWarp
Antivirus - used as e-mail antivirus tools.
Page 10

10 Introduction to Panel
In this chapter:
Installation and Upgrade Overview .................................................................... 11
Ports Used by Panel .......................................................................................... 13
Licensing ........................................................................................................... 14
Files and Directories Used by Panel Installations
Parallels Plesk Panel and its components are installed by default in the directory
C:\Program Files\Parallels\Plesk\ on a physical server, or C:\Program
Files\Plesk\ in the Parallels Containers environment. The default installation
directory is referred to as %plesk_dir% in the following list. Some of the subdirectories
with corresponding components are listed below.
%plesk_dir%\admin\ - The core components used by Panel GUI.
%plesk_dir%\admin\plib\ - Panel's PHP files.
%plesk_dir%\admin\bin\ - Binary utilities.
%plesk_dir%\bin\ - Binary utilities.
%plesk_dir%\etc\ - Configuration files.
%plesk_dir%\MailServer\ - Mail servers.
%plesk_dir%\backup\ - Backup files.
%plesk_dir%\dns\ - BIND name server files.
%plesk_dir%\MySql\ - Panel's MySQL database server.
%plesk_dir%\Databases\ - Database servers for serving user data.
Page 11
Introduction to Panel 11
Installation and Upgrade Overview
In this section:
Installing and Updating Third-Party Applications ............................................... 12
The most common way of installing and upgrading Parallels Plesk Panel is to use the
Parallels Installer utility. This utility connects to the Parallels Updates server where the
Panel distribution packages are stored. It then retrieves, downloads, and installs Panel.
You can download the Parallels Installer utility from
http://www.parallels.com/eu/download/plesk/products/.
For detailed instructions on how to use Parallels Installer, refer to the Installation,
Upgrade, Migration, and Transfer Guide.
For information about installing third-party software services on Panel-managed
servers, refer to the section Installing and Updating Third-Party Applications (on page
12).
Installing Panel in Parallels Virtuozzo Containers Environment
If you operate in the Parallels Virtuozzo Containers (PVC) environment, you can use
application templates for installing Panel on containers.
When the application templates are installed on a PVC hardware node, they allow you
to easily deploy the application on as many containers as required, saving system
resources such as disk space.
You can obtain the Panel templates at
http://www.parallels.com/eu/download/plesk/products/ or download them using the
PVC command line utility call vzup2date -z (available on PVC 4 and above).
For more information on installing Panel on PVC, read the Installation, Upgrade, Migration,
and Transfer Guide, chapter (Advanced) Installation to Parallels Virtuozzo Containers.
Checking Potential Issues Before Upgrading to Panel 11
If you use Parallels Plesk Panel 9 or earlier and want to upgrade it to Panel 11, you
may encounter problems due to changes in the Panel business model. In particular, it
might be impossible to transfer some settings and business objects.
To efficiently anticipate or resolve the problems, we offer a tool called
plesk101_preupgrade_checker.php. This checks potential business logic issues
with upgrading to Panel 10 and later and gives recommendations that help you fix the
possible problems related to transition of Panel objects. You can download the tool and
find descriptions of the report messages at http://kb.parallels.com/9436.
Page 12
12 Introduction to Panel
Installing and Updating Third-Party Applications
To enable basic hosting services and functions on a Panel-managed server, Panel
distribution package includes several third-party software applications, that are installed
along with Parallels Plesk Panel. These applications are ultimately responsible for providing
various hosting services such as DNS, e-mail, FTP, and others.
All software components shipped with Panel can be installed and updated by means of
Parallels Installer. These components are listed at
http://download1.parallels.com/Plesk/PP11/11.0/release-notes/parallels-plesk-panel-11.0-forwindows-based-os.html#4.
You can also install and manage through Parallels Plesk Panel many other third-party
applications that are not included in the Parallels Plesk Panel distribution package. For the
complete list of third-party applications currently supported by Panel, refer to
http://download1.parallels.com/Plesk/PP11/11.0/release-notes/parallels-plesk-panel-11.0-forwindows-based-os.html#5.
Automatic Detection of Pre-installed Components
Supported third-party applications that have already been installed on a server prior to Panel
installation will be automatically detected during installation of Panel by Parallels Installer and
integrated as Panel components.
Manual Installation, Update, and Integration of Components Supported by Panel
If Panel is already installed and you want to install an application package or an update that
you obtained from a software vendor, you need to do the following:
1. Upload the package to the Panel-managed server and run the package installation
program or, when applicable, follow the vendor's installation instructions.
2. Complete the component installation or update by integrating the application with Panel:
a. Log in to Panel as administrator.
b. Go to Tools & Settings > Server Components. The list of the currently
registered Panel components is displayed.
c. Click Refresh under Tools. The list of registered Panel components is
refreshed. The integrated component entry appears in the list.
Alternately, you can use the following command line call to ensure detection of installed
components: "%plesk_bin%\defpackagemng.exe" --get --force
Note: For some newly installed applications, you might need to additionally configure the
application settings to ensure proper integration.
Installation of Software not Supported by Panel
You might want to install and use on the server other third-party applications not supported
by Panel. The applications will operate properly but will not be manageable through Panel.
Page 13

Introduction to Panel 13
In accordance with Panel security policies, Panel sets permissions for all its partitions to
Service name
Ports used by service
Administrative interface of Panel
TCP 8443, 8880
Samba (file sharing on Windows networks)
UDP 137, UDP 138, TCP 139, TCP
445
VPN service
UDP 1194
Web server and Panel Updater
TCP 80, TCP 443
FTP server
TCP 20, 21, 990
SSH (secure shell) server
TCP 22
SMTP (mail sending) server
TCP 25, TCP 465
POP3 (mail retrieval) server
TCP 110, TCP 995
IMAP (mail retrieval) server
TCP 143, TCP 993
Mail password change service
TCP 106
MySQL server
TCP 3306
MS SQL server
TCP 1433
Tomcat Java service
TCP 9080, 9008
Licensing Server connections
TCP 5224
Domain name server
UDP 53, TCP 53
Panel upgrades and updates
TCP 8447
restrict users' access to each other and to third-party applications which are unknown to
Panel. For this reason, to ensure proper operation of third-party applications not supported
by Panel, you need to set required permissions in Panel. For more information about Panel
security policies, see the chapter Changing Security Settings for File System Objects and
Accounts (on page 100).
To enable a third-party application not supported by Panel, allow the psacln and psaserv
groups the required access level to required directories of the application.
If you are installing any IIS extensions or COM components that need to be available on
customers' websites, we highly recommend that you install 32-bit versions of these
applications because websites that Panel creates are 32-bit.
Ports Used by Panel
On servers protected by a firewall, the following ports must not be blocked to ensure proper
operation of Panel and accessibility of Panel-managed services.
Page 14

14 Introduction to Panel
Licensing
After you install Parallels Plesk Panel, a trial license key for 14 days is installed by default.
To continue using Panel after the trial license key expires, you should obtain a lease license
key or purchase a permanent license key.
A leased license implies that you pay for a limited time during which you can use Panel, say,
for a couple of months. During the lease period, Panel will perform free monthly updates of
your license key. The lease license includes free upgrades to all new major versions of
Panel.
The permanent license implies that you buy a Panel license for a lifetime. A permanent
license is updated every three months for free. Upgrading a Panel installation with a
permanent license to the next major version requires a separate payment unless you use
Software Update Service (SUS). See http://www.parallels.com/support/sus/ for more
information on SUS.
Panel license keys have a grace period of 10 days right before the expiration date. During
the grace period, Panel automatically performs daily attempts to update the license key
automatically. If an automatic update fails, Panel notifies the administrator. If you do not
update a license key during the grace period, it expires and blocks Panel functions until you
install a valid license key.
Panel defines whether it needs to update the license key using the update-keys.php utility
located in the %plesk_dir%\admin\plib\DailyMaintainance\ directory, where
%plesk_dir% is an environment variable denoting the Panel installation directory. This utility
checks the license grace period and expiration date and tries to retrieve a new license key or
blocks Panel.
Panel runs the utility every day as a part of the daily maintenance script. If you want to check
for license updates, you can run the script manually by executing the command
"%plesk_bin%\php.exe" -d
auto_prepend_file="%plesk_dir%\admin\plib\DailyMaintainance\script.p
hp".
You can retrieve and manage license keys through the Panel GUI. The information about
current license key and controls for managing license keys are located in Server Administration
Panel > Tools & Settings > License Management.
Page 15

This chapter describes how to perform the following tasks:
In this chapter:
Changing Your Server's Host Name .................................................................. 16
Changing IP Addresses ..................................................................................... 17
Moving the Virtual Hosts Directory .................................................................... 18
Moving the Directory for Storing Panel Backups ................................................ 19
Moving the Directories for Storing Mail Data...................................................... 20
Switching Between MySQL and MSSQL Database Server Engines .................. 21
Programming Event Handlers to Execute Custom Scripts ................................. 26
Automating Administration Tasks with Command-Line Utilities.......................... 27
Monitoring Status of System Services ............................................................... 28
Managing Services from the Command Line and Viewing Service Logs ........... 28
Predefining Values for Customizable PHP Parameters ..................................... 34
Website Applications ......................................................................................... 35
Spam Protection ................................................................................................ 37
Optimizing the Task Manager Performance ...................................................... 39
Cloning Panel in Virtual Environment ................................................................ 41
Removing Panel ................................................................................................ 43
C H A P T E R 3
System Maintenance
Change server's host name.
Change server IP addresses. You may need to do this when, for instance, you are
moving your Panel server to a new datacenter, and need to reconfigure the Panel
installation to run on new IP addresses.
Move the directory where virtual hosts reside to another location on the same or
another partition. You might want to do this when disk space on the current partition
is running out.
Move the directory where Panel backup files are stored to another location on the
same or another partition. You might want to do this when, for instance, there is
insufficient disk space on the current partition to house new backup files, and you
want to move them all to a new, larger volume.
Move the directories that house mail content to another location on the same or
another partition. You might want to do this when there is insufficient amount of disk
space on the current partition to serve a larger amount of mailboxes, and you want
to move them all to a new larger volume.
Switch the database server engine used by Panel.
Stop, start, and restart Panel-managed services from command line, and access
their logs and configuration files.
Page 16

16 System Maintenance
Changing Your Server's Host Name
You specify your server's host name during your very first login to Panel. If you want to
change the host name later, you can do it through Panel.
Note: Specifying an invalid host name will result in unpredictable Panel behavior and server
malfunction. The host name must resolvable from the Panel-managed server, especially if
Customer and Business Manager is installed.
To change your server's host name:
1. Log in to Server Administration Panel.
2. Go to Tools & Settings > Server Settings.
3. Enter the new host name in the Full hostname field.
This should be a fully qualified host name, but without an ending dot (for example,
host.example.com).
4. Click OK.
Page 17

System Maintenance 17
Changing IP Addresses
You can switch from an existing IP address on your Panel-managed server to a newly
created IP address or to another existing address.
During life-time of a Panel installation, you may need to replace IP addresses used for
hosting with other IP addresses. Replacing all old IP addresses with new ones may be
necessary when moving a Panel server onto a new network. More often, you may need to
introduce more subtle changes in your server's IP address pool. For example, you may need
to free up one or more IP addresses currently used for hosting on the server. This will allow
you to use the addresses for other purposes or to eliminate them from the server's IP pool
altogether.
Every time you replace an IP address with a new one on a Parallels Plesk Panel server, you
need to reconfigure Panel and various services to use the new IP address instead of the
replaced one.
You can switch from one IP address to another and automatically reconfigure Panel and all
hosting services on the server to use the new address by using the Change Server IP
Addresses option in the Reconfigurator utility.
Note: By using this feature, you can only replace one IP address with another. You cannot
migrate a group of select domains from one or more IP addresses to a new IP address.
To change from one IP address on a Panel-managed server to another, follow
these steps:
1. Log in to the Panel-managed server as a user with administrator rights by
using Remote Desktop.
2. In the W indows Start menu, select All Programs > Parallels > Panel > PP
Reconfigurator. The Reconfigurator application window opens.
3. Select the Change server IP addresses option. The IP Addresses Reconfiguring
window opens.
4. Under Select the IP addresses to be changed, select the checkboxes corresponding
to the IP addresses that you want to change to other IP addresses.
To view the list of domains hosted on particular IP address, click the IP address entry to
highlight it. The list of hosted domains using the highlighted IP address is displayed in a
window to the right.
Page 18
18 System Maintenance
5. Map each selected to an IP address of your choice.
a. To map a selected address, click on the selected address entry. The
entry is highlighted.
b. Select the address to map to:
To map to an existing IP address, select Existing Address option and then select an
existing address entry. The entry information is displayed in the Mapping Information
column for the selected IP address entry under Select the IP addresses to be changed.
To map to a new IP address that will be created during mapping, select Create New
IP address option and then enter the IP address, network mask, and network
interface name. The entry information is displayed in the Mapping Information
column for the selected IP address entry under Select the IP addresses to be changed.
6. Click Next.
Panel installation is reconfigured to use the newly specified IP addresses in place of the
old ones. All relevant records in the Panel's database are updated, network adapters
settings are changed accordingly (the old IP addresses are removed), FTP and web
servers are reconfigured accordingly, DNS records are updated accordingly.
Note: If changing IP address fails during execution, all changes are rolled back. When
connected to the server through the Remote Desktop connection, a change of your server’s
IP address will terminate your session.
Moving the Virtual Hosts Directory
This option allows moving the directory where virtual hosts reside to another location on the
same or another partition. Use this feature when disk space is insufficient on the current
partition to house new virtual hosts, and you want to move them all to a new, larger volume.
To move the virtual hosts directory to a new location, follow these steps:
1. Log in to the Panel-managed server as a user with administrator rights by
using Remote Desktop.
2. In the W indows Start menu, select All Programs > Parallels > Panel > PP
Reconfigurator. The Reconfigurator application window opens.
3. Select the Change Virtual Hosts location option.
4. Specify the destination directory name. If the directory does n ot exist, it will
be created.
5. Click Next.
During this operation all Panel's services will be restarted.
Page 19

System Maintenance 19
Moving the Directory for Storing Panel Backups
By using Panel Reconfigurator utility, you can move the Panel backup files storage directory
to another location on the same or another partition. Use this option when disk space is
insufficient on the current partition to house new backup files, and you want to move them all
to a new, larger volume.
To change location of the backup files directory, follow these steps:
1. Log in to the Panel-managed server as a user with administrator rights by
using Remote Desktop.
2. In the W indows Start menu, select All Programs > Parallels > Panel > PP
Reconfigurator. The Reconfigurator application window opens.
3. Select the Change Plesk Backup Data location option.
4. Specify the destination directory name. If the directory does not exist, it will
be created.
5. Click Next. During this operation, all services will be restarted.
Page 20

20 System Maintenance
Moving the Directories for Storing Mail Data
You can move the directories that store mail content to another location on the same or
another partition. Use this option when disk space is insufficient on the current partition to
serve larger data volume or amount of mailboxes and you want to move all mail content to a
new, larger volume.
To move the mail content directories to another location, follow these steps:
1. Log in to the Panel-managed server as a user with administrator rights by
using Remote Desktop.
2. In the W indows Start menu, select All Programs > Parallels > Panel > PP
Reconfigurator. The Reconfigurator application window opens.
3. Select the Change Plesk Mail Data location option.
4. Specify the destination directory name. If the directory does not exist, it will
be created.
5. Click Next. During this operation, Panel's services will be restarted.
Page 21

System Maintenance 21
Switching Between MySQL and MSSQL
In this section:
Using GUI to Switch Between Database Servers .............................................. 22
Using Command-Line Interface to Switch Between Database Servers .............. 23
Database Server Engines
Panel can use several different database engines to access the Panel's internal database. At
any time you can change the database location and select to use different database engine
to access the database. To switch from one database server to another, you need to migrate
the database to a new database server and configure Panel to connect to the server to
access the database. The following database servers are supported by Panel:
MySQL
Microsoft SQL
You can use the Switch Database Provider option in Reconfigurator to switch between database
servers to access Panel's internal database. Reconfigurator will migrate the Panel's internal
database to a new database server and configure Panel to access the database by means of
the new database server.
Two methods exist for switching between database servers: by using the Reconfigurator GUI
(on page 22) and by using the command-line interface (on page 23). This section describes
both of these methods.
Page 22

22 System Maintenance
Using GUI to Switch Between Database Servers
You can migrate Panel's internal database to a new database engine and configure Panel to
access the database at the database server.
To switch between database servers through Reconfigurator GUI, follow these
steps:
1. Log in to the Panel-managed server as a user with administrator rights by
using Remote Desktop.
2. In the W indows Start menu, select All Programs > Parallels > Panel > PP
Reconfigurator. The Reconfigurator application window opens.
3. Select the Switch DB provider option.
4. Enter the supported database server engine type in the Server type field.
5. Enter the server address (IP address or host name) and, if different from
default, port number in the corresponding fields.
(The field are available only if MySQL or MSSQL server type is entered.)
6. Enter the new server administrator's login and password.
Note: If you switch to MySQL database in Panel 8.2 or later, note the following:
* if MySQL database was not used as a Panel database provider before, MySQL
administrator's login is 'admin' and password is 'setup'.
* if MySQL database was already used as a Panel database provider in the past, you
should use MySQL administrator's login and password which were used before changing
of the Panel database provider from MySQL to another server type.
7. Under Create a new database to locate data in, enter information about the new
Panel's database that the data will be migrated to:
a. In the Database field, enter the new database name. For example:
plesk_new.
b. In the Database user name field, enter user name to be used by Panel to
access the migrated database.
c. In the Password and Confirm password fields, type the database user
password.
Warning! By changing the database user password, you also change the Panel
administrator's password for accessing Panel. The Panel administrator's password and
database user password are always the same (although usernames can be different).
Page 23

System Maintenance 23
To change MySQL database user password, follow these steps:
Option
Parameter
Description
Comment
--new-provider
MSSQL | MySQL
The new
database server
type.
1. Go to %Plesk_dir%\MySQL\Data.
2. Open the my.ini file and add to the [PleskSQLServer] section the
following line:
skip-grant-table
3. Go to Administrative Tools > Computer Management and start Panel's SQL server.
4. Issue the following in command line:
cd %Plesk_dir%\mysql\bin
mysql -P8306
mysql> use mysql
mysql> update user set password=password('<as your Panel admin
password>') where user="admin";
5. Go to %Plesk_dir%\MySQL\Data.
6. Erase from the [PleskSQLServer] section of the my.ini file the following
line:
skip-grant-table
7. Restart the Panel's SQL server.
Using Command-Line Interface to Switch Between Database Servers
You can migrate Panel's internal database to a new database server and configure Panel to
access the database at the database server.
The command for switching the Panel's database servers has the following syntax:
reconfigurator --switch-plesk-database --new-provider=<provider name> -host=<host name> --db=<database name> --login=<database user login> -password=<database user password> [--password=<port number>] [--adminlogin=<administrator login>] [--admin-password=<administrator password>]
See the following table for the command options descriptions.
Options
Page 24
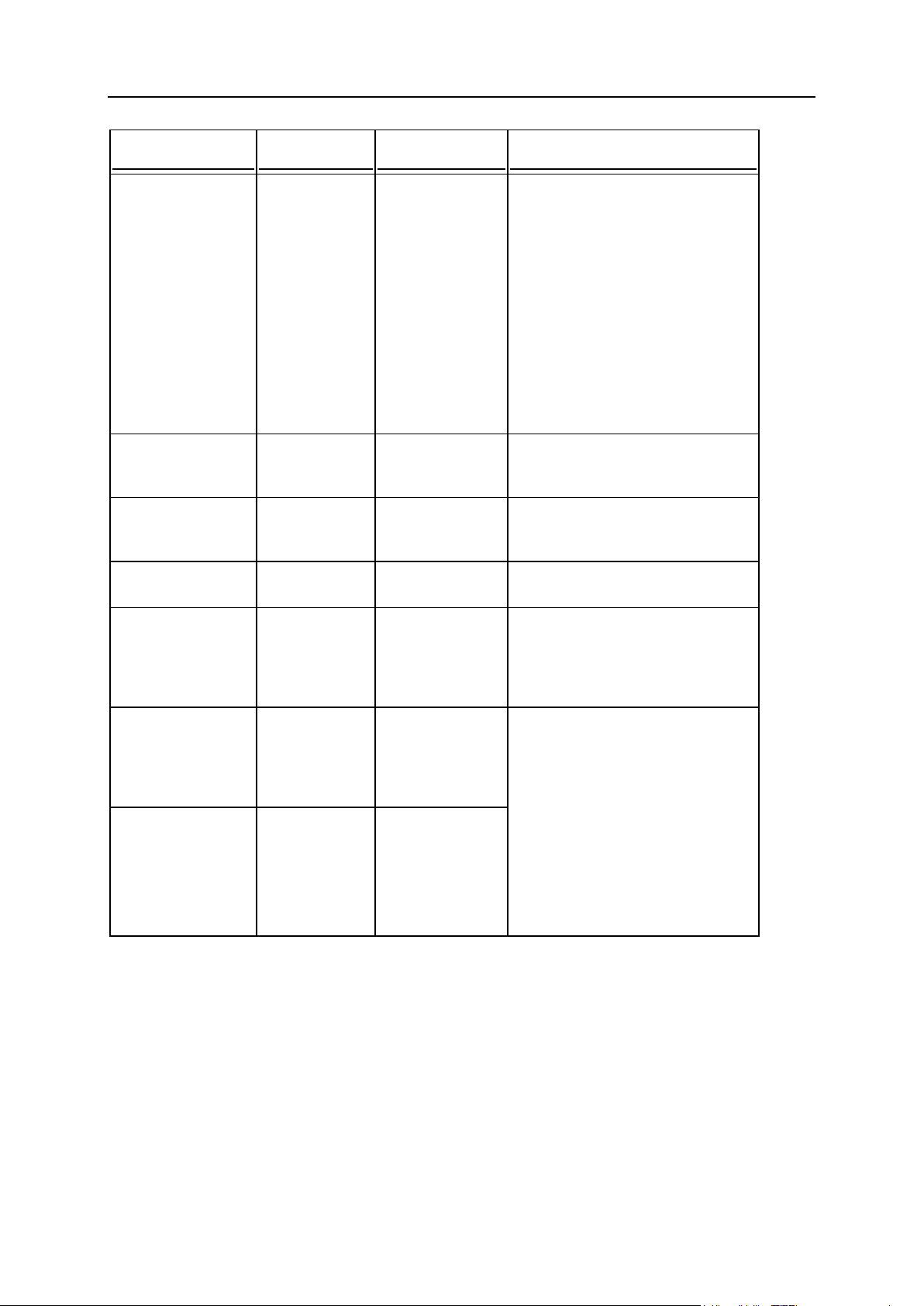
24 System Maintenance
Option
Parameter
Description
Comment
--db
<database
name>
Name of the
Panel's database
on the new
database server.
For MySQL and MSSQL
databases, you need to specify
only the database name on the
server. For example:
"--db=psa_new"
--host
<host name>
Database server
IP address or
host name.
--login
<user login
name>
Database user
name used by
Panel.
--password
<user
password>
Password used
by Panel.
--port
<port number>
New database
server port
number. This
parameter is
optional.
Define a port number if the new
database server uses a nondefault port number.
--admin-login
<administrator
login name>
Database server
administrator
login name. This
parameter is
optional.
Define the server administrator
credentials if you want a new
database user created with the
username and password specified
by the --login and --password
options. If the options are omitted
from the command, Panel will be
configured to use the database
user credentials specified by the -
-login and --password
options, no new user will be
created for the database.
--adminpassword
<administrator
password>
Database server
administrator
password. This
parameter is
optional.
Page 25

System Maintenance 25
To switch between database servers through command-line interface, follow
these steps:
1. Log in to the server as a user with administrator right s by using Remote
Desktop.
2. Start cmd.exe.
3. Change directory to the %plesk_dir%\admin\bin\ folder (where
%plesk_dir% is the system variable defining the folder where Panel is
installed).
4. Execute the server switch command.
For example, to migrate the Panel's internal database to a new location accessible at
c:\Program Files\Parallels\Plesk\admin\db\psa3.mdb, and instruct Panel
to use existing user credentials (login name dbadmin and password dbadminpass) to
access the database, use the following command:
reconfigurator --switch-plesk-database --host=localhost “--db=c:\Program
Files\Parallels\Plesk\admin\db\psa3.mdb” --login=dbadmin -password=dbadminpass
Warning! By changing the database user password, you also change the administrator's
password for accessing Panel. The administrator's password and database user password
are always the same (although user login names can be different).
Page 26
26 System Maintenance
Programming Event Handlers to Execute Custom Scripts
Parallels Plesk Panel provides a mechanism that allows administrators to track specific
Panel events and make Panel execute custom scripts when these events occur. The events
include operations that Panel users perform on accounts, subscriptions, websites, service
plans, and various Panel settings.
It works the following way: you create a script to be executed upon a certain Panel event,
and then set up an event handler in Server Administration Panel that triggers processing of
the event by the script. You can assign several handlers to a single event.
To learn how to track Panel events and set up execution of commands or custom scripts,
refer to Parallels Plesk Panel Administrator's Guide, chapter Event Tracking available at
http://download1.parallels.com/Plesk/PP11/11.0/Doc/en-US/online/plesk-administratorguide/59205.htm.
Page 27

System Maintenance 27
Automating Administration Tasks with Command-Line Utilities
Parallels Plesk Panel command-line utilities are designed to facilitate the processes of
creating various entities in Parallels Plesk Panel bypassing the Panel GUI. Command-line
utilities are executed via command prompt opened in the %plesk_dir%\admin\bin\
folder (where %plesk_dir% is a system variable containing the Panel installation directory).
You can see the list of available commands and options by running an utility with --help or
-h command. For more information about command line utilities usage refer to Parallels Plesk
Panel for Windows Command Line Interface Reference at
http://download1.parallels.com/Plesk/PP11/11.0/Doc/en-US/online/plesk-win-cli/.
Page 28
28 System Maintenance
Monitoring Status of System Services
You can monitor the status of your Panel-managed server without logging in to Panel. To do
this, you need to access your server over Remote Desktop.
A utility called Parallels Plesk Panel Services Monitor is loaded automatically every time
Panel starts. To manage the status of Panel's services, open the Parallels Plesk Panel
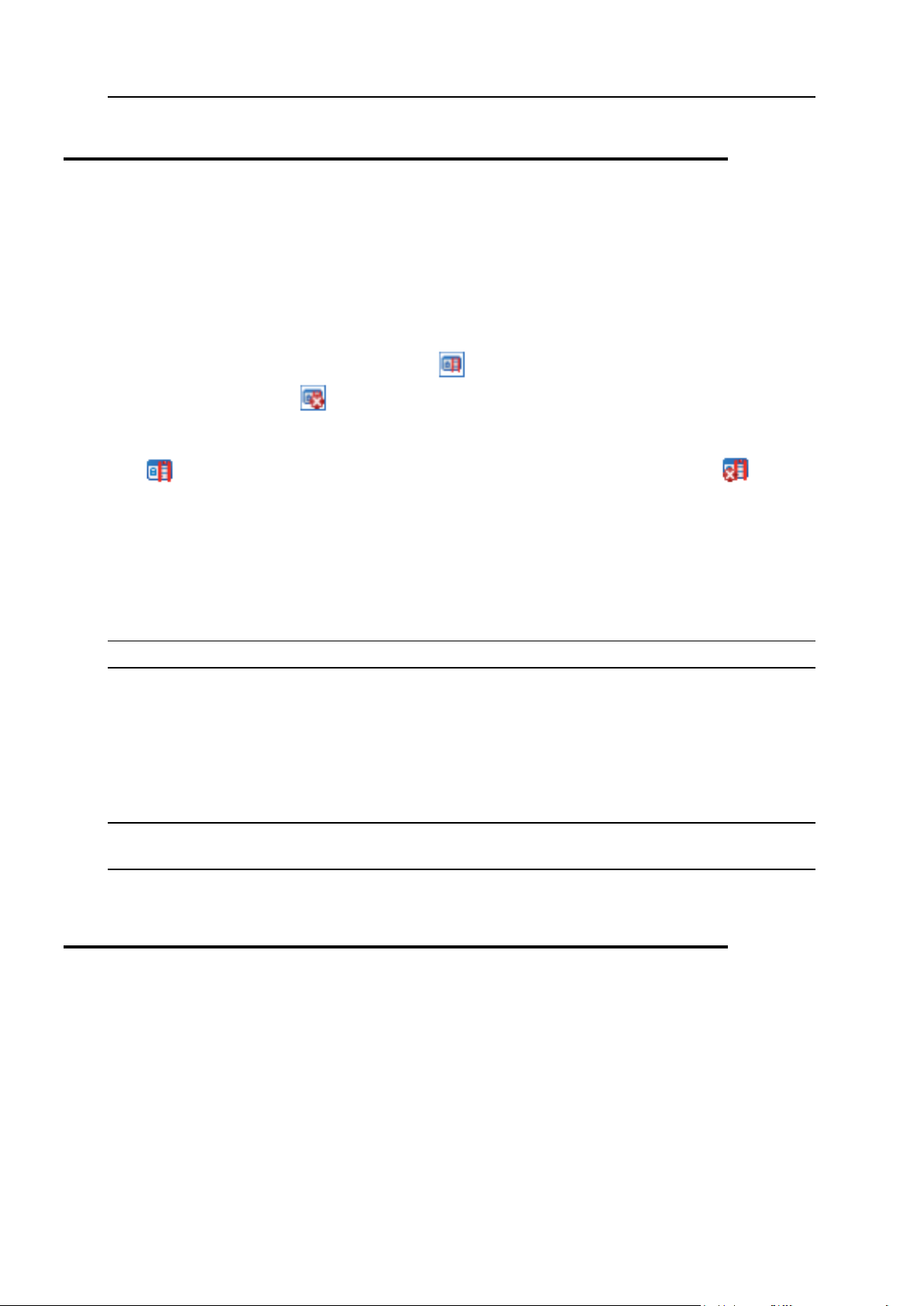
Services Monitor by double-clicking its icon in the taskbar. The look of the icon depends on
the state of crucial Panel services: the icon means that all Panel's services are
functioning, and the icon means that some services are stopped or not working correctly.
Once you open the Services Monitor, you can see the status of all vital Panel's services. The
icon indicates that a corresponding service is working correctly, and the icon
indicates that the corresponding service is stopped or is not working correctly.
To stop a service, select the corresponding checkbox and click Stop.
To restart a service, select the corresponding checkbox and click Restart.
To start a service, select the corresponding checkbox and click Start.
Note: You can use Select All and Clear All buttons to select or clear all available checkboxes.
To refresh the list of services and their respective statuses, click Refresh.
To remove all information about Panel sessions from Panel's database and disconnect all
users from Panel, click Delete Sessions. This is useful when you need to restart Panel, but
some users are still connected to it, and you want to avoid possible data loss or files
corruption.
Note: You can also start, stop, restart services and delete sessions by right-clicking the
Parallels Plesk Panel Services Monitor icon and selecting the required option from the menu.
To hide the Services Monitor back in the taskbar, click Hide.
Page 29
System Maintenance 29
Managing Services from the Command Line and Viewing Service Logs
This section describes how to stop, start, and restart services managed by Panel, and
access their logs and configuration files.
Parallels Plesk Panel web interface
To stop the service through command line:
net stop plesksrv
To start the service through command line:
net start plesksrv
net start poppassd
To restart the service through command line:
net stop plesksrv
net start plesksrv
net start poppassd
Panel's log file is located in:
%plesk_dir%\admin\logs\W3SVC<IIS site ID>\ex<date>.log
Panel's PHP configuration file is located in:
%plesk_dir%\admin\php.ini
Internet Information Services log file is accessible at:
IIS manager > Sites/Application Pools > PleskControlPanel
Web Presence Builder
%plesk_dir%\SiteBuilder\_logs Configuration files are accessible at:
IIS manager > Sites/Application Pools > sitebuilder(default) / SiteBuilderSitesWebAppPool
phpMyAdmin
Log files are located in:
%plesk_dir%\admin\logs\W3SVC<IIS site ID>\ex<date>.log
Configuration files are accessible at:
%plesk_dir%admin\htdocs\domains\databases\phpMyAdmin\config.inc.php
Page 30

30 System Maintenance
ASP.Net Enterprise Manager
Configuration files are accessible at:
IIS manager > Sites > sqladmin(default)\mssql
myLittleAdmin 2000/2005
Configuration files are accessible at:
IIS manager > Sites > sqladmin(default)\myLittleAdmin
%plesk_vhosts%\sqladmin\myLittleAdmin\2005\config.xml
MailEnable
To stop the service through command line:
net stop meimaps && net stop melcs && net stop memtas && net stop mepops &&
net stop mepocs && net stop mesmtpcs
To start the service through command line:
net start meimaps && net start melcs && net start memtas && net start
mepops && net start mepocs && net start mesmtpcs
To restart the service through command line:
net stop meimaps && net stop melcs && net stop memtas && net stop mepops &&
net stop mepocs && net stop mesptpcs && net start meimaps && net start
melcs && net start memtas && net start mepops && net start mepocs && net
start mesmtpcs
Log files are located in:
%plesk_dir%Mail Servers\Mail Enable\Logging
Configuration files are accessible at:
%plesk_dir%\Mail Servers\Mail Enable\Bin\MailEnable.msc
DNS / Named / BIND
To stop the service through command line:
net stop named
To start the service through command line:
net start named
To restart the service through command line:
net stop named && net start named
Log files are accessible through Windows Event Viewer.
Configuration files are accessible at:
%plesk_dir%\dns
Page 31

System Maintenance 31
MySQL
To stop the service through command line:
net stop plesksqlserver
To start the service through command line:
net start plesksqlserver
To restart the service through command line:
net stop plesksqlserver && net start plesksqlserver
Log files are accessible through Windows Event Viewer.
Configuration file is accessible at:
%plesk_dir%MySQL\Data\my.ini
SpamAssassin
Log files are accessible through Windows Event Viewer.
Configuration files are accessible at:
%plesk_dir%\Additional\Perl\site\var\spamassassin\3.003001
Dr.Web Antivirus
To stop the service through command line:
net stop DrWebCom
To start the service through command line:
net start DrWebCom
To restart the service through command line:
net stop DrWebCom && net start DrWebCom
Log file is located in:
%plesk_dir%DrWeb\drcom.log
FTP service
To stop the service through command line:
net stop iisadmin
To start the service through command line:
net start iisadmin
To restart the service through command line:
net stop iisadmin && net start iisadmin
Log files are located in:
%plesk_vhosts%Servers\<ID>\logs
Page 32

32 System Maintenance
Configuration files are accessible at:
IIS Manager > FTP sites > <IP address>
Kaspersky Antivirus
To stop the service through command line:
net stop kavsvc
To start the service through command line:
net start kavsvc
To restart the service through command line:
net stop kavsvc && net start kavsvc
Log file is accessible through Windows Event Viewer.
Internet Information Services
To stop the service through command line:
net stop iisadmin
To start the service through command line:
net start iisadmin
To restart the service through command line:
net stop iisadmin && net start iisadmin
Web server log file is accessible through Windows Event Viewer.
Website logs are available at:
%plesk_vhosts%<domain>\statistics\logs\<SITE ID>
Configuration is available through IIS Manager.
AWStats
Configuration file is accessible at:
%plesk_vhosts%\<domain>\statistics\webstat\AWStats\cgibin\awstats.<domain>.conf
Webalizer
Configuration file is accessible at:
%plesk_dir%\Additional\Webalizer\conf\webalizer.conf
Page 33

System Maintenance 33
Plesk Backup Manager
Backup log files are located in:
%plesk_dir%\PMM\<session>\psadump.log
%plesk_dir%\PMM\<session>\migration.log
%plesk_dir%\PMM\logs\migration.log
%plesk_dir%\PMM\logs\pmmcli.log
Restoration log files are located in:
%plesk_dir%\PMM\rsessions\<session>\conflicts.log
%plesk_dir%\PMM\rsessions\<session>\migration.log
%plesk_dir%\PMM\logs\migration.log
%plesk_dir%\PMM\logs\pmmcli.log
Plesk Migration Manager
Log files are located in:
%plesk_dir%\PMM\msessions\<session>\migration.log
%plesk_dir%\PMM\rsessions\<session>\migration.log
%plesk_dir%\PMM\rsessions\<session>\conflicts.log
%plesk_dir%\PMM\logs\migration.log
%plesk_dir%\PMM\logs\pmmcli.log
%plesk_dir%\PMM\logs\migration_handler.log
Horde
Log file is located in:
%plesk_dir%\tmp\horde
Configuration files are accessible at:
Web interface - IIS manager > Sites > webmail (horde)
PHP settings - %plesk_vhosts%\webmail\horde\php.ini
Application settings - %plesk_vhosts%\webmail\horde\config\
Page 34

34 System Maintenance
Atmail
Error log is located in:
%plesk_dir%\tmp\atmail
Configuration files are accessible at:
Web interface - IIS manager > Sites > webmail (atmail)
Application settings - %plesk_vhosts%\webmail\atmail\libs\Atmail\config.php
Predefining Values for Customizable PHP Parameters
Panel allows to define custom PHP configuration for a certain service plan, add-on plan,
subscription, website, and even subdomain. For this purpose, the Panel GUI exposes 16
most often used PHP parameters that allow customization. The administrator or a customer
can set the value of each parameter either by selecting a value from a preset, typing a
custom value, or leaving the default value. In the latter case, Panel takes the parameter
value from the server-wide PHP configuration.
Using the %plesk_dir%\admin\conf\panel.ini file you can specify what PHP
parameters values will be available in the preset and toggle the visibility of the custom value
field.
Defining the Preset Values
To set the list of predefined values for a certain PHP parameter, add the line of the following
type to the [php] section of the panel.ini file:
settings.<parameter_group>.<parameter_name>.values[]=<value>
where
<parameter_group> - a group of a PHP parameter: performance for the
performance PHP settings and general if the parameter is placed in to the common
group. For more information about the groups of PHP parameters, read the
Administrator's Guide, Customizing PHP Configuration.
<parameter_name> - a name of a PHP parameter. Use the same syntax as in
php.ini.
<value> - a parameter's value added to the preset. Use the same syntax as in
php.ini.
Page 35

System Maintenance 35
Add such line for each value in the preset. For example, if you want Panel users to choose
the value of the memory_limit parameter between 8M and 16M, add the following lines to
panel.ini:
[php]
settings.performance.memory_limit.values[]=8M
settings.performance.memory_limit.values[]=16M
Hiding the Custom Value Fields
To hide the field that allows entering the custom value for a certain PHP parameter, add the
line of the following type to the [php] section of the panel.ini file:
settings.<parameter_group>.<parameter_name>.custom=false
where
<parameter_group> - a group of a PHP parameter: performance for the
performance PHP settings and general if the parameter is placed in to the common
group. For more information about the groups of PHP parameters, read the
Administrator's Guide,
<parameter_name> - a name of a PHP parameter. Use the same syntax as in
php.ini.
For example, if you do not want Panel users to set custom values to the memory_limit
parameter, add the following line to panel.ini:
[php]
settings.performance.memory_limit.custom=false
To switch the custom value field back on, replace false with true.
Website Applications
Multiple Web Apps in a Single Directory
Since Panel 10.4, when a site employs a number of various web apps, a site administrator
may apply the following site structure:
Install a number of apps to the same directory. More specifically, install one app into a
subdirectory of another.
Use the same document root for a subdomain and a web app.
For example, you can install an online store app to the httpdocs directory of your domain
(say, example.com), create a subdomain (say, support.example.com) in the
httpdocs/support, and install a help desk system there.
All earlier Panel versions (before 10.4) prohibited such scenarios as sometimes (in very rare
cases), the installation of two web apps into one directory could lead to the improper
functioning of one of them. If you want to return this restriction back, add the following lines
into %plesk_dir%\admin\conf\panel.ini:
Page 36

36 System Maintenance
[aps]
unsafePaths=false
Hiding Commercial Apps
You can hide commercial web applications by default, so that your customers are able to
install only free applications. To do this, add the following lines into panel.ini:
[aps]
commercialAppsEnabled = false
Page 37

System Maintenance 37
Spam Protection
SpamAssassin is a rule-based mail filter that identifies spam. It uses a wide range of
heuristic tests on mail headers and body text to identify spam.
SpamAssassin filtering is configured on two levels:
Server-level configuration is done by Panel administrator.
Mail directory-level configuration is done by users for specific mail directories.
At the server level, you (as a Panel administrator) can enable or disable any of these two
types of filters. Thus, there are four possible situations:
No filtering is applied:
both filters are disabled by the Parallels Plesk Panel administrator.
the personal filter is disabled at the mail directory level.
Filtering is applied at the server level only.
Filtering is applied at the mail box level only.
Filtering is applied at both levels.
When both filters are enabled for a specific mail name, a combined filter is created for the
corresponding mail directory. When processing messages, SpamAssassin calculates the
number of hits according to its internal rules. A message is considered to be spam if the
number of hits exceeds the established threshold, which is set to 7 by default. You can
change the threshold in Panel. White and Black lists can be considered special rules,
which assign constant hit rates to messages conforming to mail address patterns in these
lists:
If the message source address conforms to the Black list, the message gets +100 hits
by default.
If the message source address conforms to the White list, the message gets -100 hits by
default.
Sometimes, a message matches both Black and White lists. In that case, it has +100100=0 hits.
If the message destination address is included in the server-wide ignore list, then all
messages to this address will go directly to the addressed mail directory.
At the server level, you can configure SpamAssassin to mark messages with a special string
if they are recognized as containing spam. At the mailbox level, you can make
SpamAssassin delete or mark the message if it is considered as spam.
Starting from Panel 9.x, the maximum message size to filter is hardcoded in the spam
handler and set to 256KB. This value provides normal server loading. Since the
SpamAssassin service consists of perl modules, they may result in a heavy server load
when processing long messages.
You can obtain more information about SpamAssassin at spamassassin.apache.org
Page 38

38 System Maintenance
In this section:
Configuring SpamAssassin ............................................................................... 38
Configuring SpamAssassin
The SpamAssassin configuration is stored in the spamfilter and spamfilter_preferences
tables of the psa database. You can manage it with the
%plesk_dir%\admin\bin\spammng.exe utility. It displays help if started without any
options.
Server-wide SpamAssassin settings are stored in the following files:
The
%plesk_dir%\Additional\Perl\site\var\spamassassin\3.003001\updates
_spamassassin_org\*.cf files contain configuration details, e.g. White list and
Black list scores are assigned in the 50_scores.cf configuration file.
The
%plesk_dir%\Additional\Perl\site\etc\mail\spamassassin\local.cf
stores server-wide filter settings.
Personal user settings are stored in the file
%plesk_dir%\Additional\SpamAssassin\SpamFilterUserConfigsPath\<mailn
ame>\user_prefs.
For more information about the SpamAssassin configuration, refer to the respective
documentation at http://spamassassin.apache.org/doc/Mail_SpamAssassin_Conf.html.
To apply changes in the configuration files, you should restart SpamAssassin with the
following command:
for /F "usebackq tokens=5" %i in (`cmd /c "netstat -aon | findstr
0.0.0.0:8783"`) do taskkill /F /PID %i
Page 39

System Maintenance 39
Optimizing the Task Manager Performance
Parallels Customer and Business Manager automates certain hosting providers' tasks such
as creating Panel accounts and subscriptions, registering domain names, issuing invoices,
and so on. To do this, Business Manager uses its own task manager. This task manager
does the following:
Schedules and runs tasks.
Stores task details and execution statuses.
Suggests how to resolve possible task execution problems.
If you want to utilize your server resources better, consider optimizing task manager
performance in your environment by changing its settings defined in the
%plesk_dir%\billing\task-manager\config\config.ini configuration file. The
paragraphs of this section describe the ways to optimize certain aspects of the task
manager.
Reducing Disk Space Consumption
If you want the task manager to consume less disk space, you can reduce the size of its own
database. To do this, adjust the following settings that define how much information the task
manager stores in the database:
How long task manager stores information about processed tasks. The parameters that
set these intervals for completed, failed and canceled tasks are
completedTasksClearInterval, failedTasksClearInterval, and
canceledTasksClearInterval correspondingly.
By default, these intervals are equal to 1 year. If you want to change them, specify the
values in the ISO 8601 standard, for example, P1Y for the 1 year interval.
How much information about each task execution is stored. For troubleshooting
purposes, the task manager writes information about task executions to log files, one file
per each execution. The parameter that sets maximum number of stored log files for each
task is the maxTaskLogs. Its default value is 5. To make the logs consume less disk
space, specify a smaller value of this parameter.
Note: When you set the task removal intervals described above, remember that setting too
small values may make troubleshooting difficult since you may not have enough information
about recent task executions.
Increasing Task Manager Performance
When you run all scheduled tasks at once, task manager starts processing a certain number
of tasks simultaneously. After completing (or failing to complete) the task, the task manager
starts another task from the queue and so on. To make processing of multiple tasks faster,
increase the maximum number of tasks processed simultaneously. The parameter that sets
this number is runAllMaxInstances.
However, when you set a greater value for this parameter, remember that too big values
increase the system load and therefore may reduce the Panel performance or even block
customer access to the Control Panel.
Page 40

40 System Maintenance
Increasing Logs Detalization
To make the task manager produce more information that may help you in troubleshooting
issues, adjust the logging settings in the following ways:
Increase the number of execution logs for each task. To do this, edit the value of the
maxTaskLogs parameter. When you set a greater value, remember that this will increase
the disk space consumption.
Increase the verbosity of the logs. By default, the task manager writes only error
information to log files. To get more information on tasks execution, include tasks
execution messages into the logs by changing values of the parameters log.info and
log.sql to 1.
Important: Including debug information into the task manager logs will reduce its
performance; Therefore, we recommend that you include this information only when you
troubleshoot certain issues.
Page 41

System Maintenance 41
Cloning Panel in Virtual Environment
Why Do I Need Panel Cloning?
The popular and efficient way to start offering Panel services is to install Panel in a cloud and
then seamlessly scale your infrastructure and install more Panel instances as your business
grows. The challenge in this approach is that it is not possible just to copy the same Panel
again and again to different virtual machines because of the following:
Some clouds constantly change allocated IP addresses pools. If a Panel service was
bound to an IP address which was later removed from the system, the service will not be
operable.
Each Panel object, for example, a customer account, should have a unique identifier, so-
called GUID. This requirement is mandatory to avoid conflicts during migration from one
server to another or during recovery from a backup. If you simply keep copying Panel, all
the instances will share the same GUIDs.
The Panel cloning technology solves these and other scaling problems.
What Is Panel Cloning?
Panel cloning is the technology of copying the same Panel instance to different virtual
machines without compromising Panel operability. Two prevailing usage scenarios of the
cloning are:
Fast Panel setup. If you wish to create virtual machines (GoDaddy cloud, Amazon cloud,
KVM, Xen, and so on) with Panel on demand, the easiest way to streamline this process
is to create an image of a virtual machine with specifically prepared Panel and then
create new machines from this preset as many times as needed.
Full backup. Cloning is a recovery solution too because almost all Panel data remain in
cloned instances. Thus, you can first copy a prepared Panel to another virtual machine
and then start the machine if your original machine becomes inoperable.
The application scope of Panel cloning is wider: For example, you can clone Panel and then
safely test new features or configurations on it, but in this section, we will consider only the
given scenarios because others are their extensions or combinations.
Cloning and Panel Licensing
Before you start cloning Panel, please contact our sales representatives and provide the
range of IP addresses within which your Panel instances will be installed. Our licensing
system will activate Panel servers from this range only.
Page 42

42 System Maintenance
Preparing a Panel Instance for Cloning
If you want to use Panel cloning, you should start with preparing your Panel instance. The
following preparatory steps help you reset all environment- and initialization-specific settings
(like the IP addresses pool) to prevent copying of unique information to other virtual
machines. Omit steps 2 and 3 if your scenario is full backup.
1. (Fast setup, full backup) Instruct Panel to reconfigure its IP pool after restart. After
running the following command, a Panel instance will discover actual IP addresses and
reconfigure its IP pool each time you restart the corresponding virtual machine.
# %plesk_cli%\ipmanage --auto-remap-ip-addresses true
Note: This step is not mandatory if a virtual machine to which you want to copy Panel
uses a static IP address. Moreover, omitting this option will make Panel start faster
because Panel will not reconfigure its IP pool on each startup. However, we highly
recommend to complete this step if you deploy Panel to a cloud.
2. (Fast setup only, optional) Initialize the instance programmatically or from the Panel GUI.
Specify the administrator's information, locale, and other initialization settings using the
init_conf command-line utility or the Panel GUI. Read more about the initialization in
the Installing Panel > Post-Installation Setup section of the Installation, Upgrade, Migration, and
Transfer Guide.
3. (Fast setup only) Prepare Panel for cloning by resetting some of its data (for example, the
administrator's password, see the full list below) and remove the license key on the next
start. Note that this utility does not perform cloning, it only modifies Panel settings.
# %plesk_cli%\cloning --update -prepare-public-image true -resetlicense true
When preparing a Panel instance for cloning, avoid restarting Plesk Management
Service and shutting down the virtual machine on which the instance is installed.
How to Clone Panel
We assume that you have a virtual machine with Panel and you wish to clone this machine.
The cloning procedure consists of three steps:
1. Prepare the Panel instance for cloning using the instructions we provided earlier.
2. If your software for managing virtual machines supports creating copies of virtual
machines, which is normally true, stop (shut down) the virtual machine and create the
image copy. Otherwise, if images copying is unavailable, you should use a special
shutdown call that resets some instance data and then copy the machine by available
means. The shutdown is performed by the following command from the command prompt
(Cmd.exe):
sysprep /oobe /generalize /shutdown
Once you have the virtual machine image, use it as a preset for new virtual machines or as a
Panel snapshot.
Page 43

System Maintenance 43
What Data Are Reset by the cloning Utility?
The following list contains the items that are reset by the cloning utility:
The IP pool
Panel GUIDs
Passwords for all IIS users (Anonymous and Application pool users for the Panel website
and all sites created by Panel: Horde, Atmail, and all customer sites)
The administrator's password
(Optionally) The license key
The rest of the data, including the default SSL certificate, remain intact.
Removing Panel
You can remove Panel as any other program in Windows by using Control Panel > Uninstall a
Program. For the complete instruction on how to remove programs in Microsoft Windows,
read this article: http://windows.microsoft.com/en-US/windows-vista/Uninstall-or-change-a-
program.
Page 44

This chapter explains how to install and configure third-party components on the Panel-
In this chapter:
Web Deploy 2.0 ................................................................................................. 45
C H A P T E R 4
Third-Party Components
managed server.
Page 45

Third-Party Components 45
Web Deploy 2.0
Web Deploy (Web Deployment Tool) is a Microsoft's tool that significantly simplifies
migration, management, and deployment of IIS web servers, web applications, and websites.
Here are two reasons to have Web Deploy on your server:
Simple applications publishing. Web developers who write code in Visual Studio® (IDE)
and WebMatrix® (development tool) can use Web Deploy to publish their applications to
a production server. If you would like to give your customers this time-saving and easy-touse publication method, install Web Deploy on your server.
Note: You should not install Visual Studio® and WebMatrix® on Panel servers. This
software is installed by customers themselves on their PCs.
New market for your hosting plans. WebMatrix® helps its users find a suitable hosting
plan in Microsoft Web Hosting Gallery, a catalog where hosting providers advertise
hosting offers. If you want your hosting plans to be present in the gallery, one of the
requirements is to have Web Deploy.
1. Install Web Deploy
There are two ways of installing Web Deploy - as a Panel component, the recommended
way, or manual installation. The first way assumes that you install Web Deploy as any other
Panel component, from Tools & Settings > Updates and Upgrades > Add / Remove Components. If
you use Panel 10.4 and earlier versions, the component installation is unavailable, so you
should perform manual installation. For the installation instructions, see the Manual Installation
of Web Deploy section below.
Note: Microsoft Windows Powershell is required for proper installation of Web Deploy.
Ensure that it is installed on server. (It should be available automatically in Windows 2008
R2). Learn how to install the component at http://www.microsoft.com/powershell.
After the successful installation, you are able to check that Web Deploy is discovered by
Panel. To do this, log in as the Panel administrator and go to Tools & Settings > Server
Components. The new component, Web Publishing, will appear in the list. Additionally, the
ability to use web publishing will be added to all existing subscriptions, to the Hosting
Parameters tab, and set as not provided by default.
If your customers use MySQL databases for their applications, you should additionally install
the MySQL Connector/Net component from Microsoft Web Platform Installer.
Page 46

46 Third-Party Components
2. Improve the Security Level
During the installation, Web Deploy adds a number of delegation rules to IIS that allow nonadministrators to perform operations on databases and files on their IIS sites. Panel
automatically adds an exception from one of the rules, namely, from appPoolPipeline. This
exception prevents Panel from changing the .NET version of application pools in IIS. But for
this automatic amendment, the version change will lead to malfunctioning of .NET
applications that are not compatible with the updated version. Say, if the version has
changed from 2.0 to 3.5, some apps that required 2.0 will not run.
In addition to this rule change, we recommend that you set IIS to run applications of each
subscription in a separate pool. This setting will guarantee that other pools will continue to
operate even if a certain app damages a pool on a certain subscription. You can specify to
use separate pools in plan settings, the Performance tab > Dedicated IIS application pool.
3. Secure the Service with a Valid Certificate
During its installation, Web Deploy installs (as needed) and activates IIS Manager service
that secures connections to Web Deploy. We highly recommend that you provide IIS
Manager with a valid SSL certificate to let your customers verify your server's identity before
transferring their data to your server. Learn how to do it in
http://learn.iis.net/page.aspx/144/how-to-set-up-ssl-on-iis-7/. If you choose not to do it, your
customers will fail to publish their sites if they specify to use a secure connection in
publication settings of Visual Studio® or WebMatrix®.
4. Activate Web Deploy in Hosting Plans and Subscriptions
Now when you have successfully installed and configured Web Deploy, activate this feature
in Hosting Parameters of hosting plans and existing unsynced subscriptions as needed.
Manual Installation of Web Deploy
To successfully install Web Deploy, you should meet the following requirements:
The target operating system must be Windows Server 2008 or later.
The server must have Windows PowerShell installed. Windows Server 2008 does not
have this component by default (though 2008 R2 has it). Learn how to install the
component at http://www.microsoft.com/powershell.
The server must have the Management Service role service (Server Manager > Web
Server > Add Role Services, under Management Tools).
The installation procedure is straightforward: In Microsoft Web Platform Installer, find the
Web Deployment Tool product and add it to the server. For more information about the
installer, see http://www.microsoft.com/web/downloads/platform.aspx.
Page 47

Third-Party Components 47
Alternatively, you can download the Web Deploy binary and run it as administrator. The
download link is available at http://www.iis.net/download/WebDeploy.
Note: You should select either the complete installation or select the custom installation and
specify the Configure for Non-Administrator Deployments option.
Page 48

This chapter describes how to back up and restore data by means of the command-line
In this chapter:
Backing Up Data ............................................................................................... 49
Restoring Data .................................................................................................. 69
Migrating Data ................................................................................................... 99
C H A P T E R 5
Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
utilities pleskbackup and pleskrestore, and introduces the tools for migrating
hosted data between servers.
Backing up by means of the pleskbackup utility is done by issuing a command that
specifies the objects to be backed up. The utility creates a backup archive containing
settings and content. You can then perform a full or a selective restoration of data, and
specify how to resolve possible conflicts that might occur.
Page 49

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 49
Backing Up Data
In this section:
Backup Objects: Hierarchy and Volume ............................................................ 50
Specifying Data for Backing Up ......................................................................... 53
Defining Properties of Files That Compose Backup........................................... 60
Exporting Backup Files ...................................................................................... 62
Defining How the Backup Process Is Performed ............................................... 64
Backup Utility Commands and Options ............................................................. 65
To perform backup of Panel hosting data, you need to execute the pleskbackup
utility command composed so that it does the following:
1. Defines the data that need to be backed up.
2. Defines the way of how the backup process will be performed.
3. Defines properties of the files that will be contained in backup.
4. Defines options for exporting backup as a single file.
Note: Only the first component is obligatory, others are optional.
The following sections explain each component meaning and implementation in detail.
The pleskbackup utility is located in %plesk_dir%\bin\
where %plesk_dir% is an environment variable for Panel installation directory. By
default, it is "C:\Program Files\Parallels\Plesk"
To see a complete list of the pleskbackup commands and options, refer to the
section Backup Utility Commands and Options (on page 65).
If the command execution succeeds, backup is created in the default server backups
location or exported to a file in case exporting options were specified. For details on
exporting options, refer to the section Exporting Backup Files (on page 62). If the
command execution fails, backup is not created.
You can perform advanced configuration of the backup operation through the file
%plesk_dir%/admin/share/pmmcli/pmmcli-rc. For more details, refer to the
section Defining How the Backup Process Is Performed (on page 64).
Page 50

50 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
Backup Objects: Hierarchy and Volume
Panel provides opportunities for backing up and restoring nearly all hosting data, which
includes its major objects: administrator account, settings for Panel-managed services,
reseller accounts, customer accounts, subscriptions, websites, databases and mail
accounts. These backup objects are organized into a hierarchy where parent object is
always an owner of its children. The hierarchy comprises of four levels: server,
resellers, customers and subscriptions. The levels are such that a higher level includes
objects on the lower levels but a lower level is completely separated from the higher
objects.
Page 51

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 51
You can create either a full or a partial backup. A full backup is the highest-level
Backup Object
Type
Configuration
Content
server
This backup level includes the following:
Administrator's information.
Web Presence Builder settings.
SSO settings.
IP addresses.
Database server settings.
DNS settings.
Mail server settings.
Antivirus and spam protection settings.
SSL certificates.
Reseller plans, hosting plans, and add-on
plans.
Information about administrator's subscriptions,
reseller accounts, customer accounts and
websites.
Information about user roles.
Information about auxiliary users who can
access Control Panel.
Information about mail accounts and individual
settings for protection from spam and viruses .
Site isolation settings.
Settings for notification on system events.
License keys for Panel,
virtual host templates,
website content, error
documents, log files, and
content of mailboxes.
backup, it includes all data related to a Panel installation. A partial backup includes only
backup objects you need, of any of the levels. For information on available options
when creating a partial backup, refer to the section Defining Data for Backup (on page
53).
Restoring a backup, in turn, can also be either full or partial. Full restoration recovers
all data contained in a backup, and partial recovers a part. For information on available
options when restoring data from backup, refer to the Defining Objects for Restoration (on
page 69) section.
Each backup object includes the following:
Configuration defines properties of the backup object and its descendants.
Content contains binary data related only to the backup object (website content and
content of mailboxes).
This table shows what data (configuration and content) are related to each backup
object.
Page 52

52 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
Backup Object
Type
Configuration
Content
reseller
This backup level includes the following:
Reseller information.
Reseller's hosting plans.
Resource allotments and permissions for
operations in Panel.
Allocated IP addresses.
Information about customer accounts,
subscriptions, and websites with DNS settings.
Information about user roles.
Information about auxiliary users who can
access Control Panel.
Information about mail accounts and individual
settings for protection from spam and viruses.
Website content, error
documents, log files,
content of mailboxes.
customer
This backup level includes the following:
Customer information.
Hosting plans to which the customer is
subscribed.
Resource allotments and permissions for
operations in Control Panel.
IP addresses used by customer's
subscriptions.
Information about websites with DNS settings.
Information about user roles.
Information about auxiliary users who can
access Control Panel.
Information about mail accounts and individual
settings for protection from spam and viruses.
Website content, error
documents, log files,
content of mailboxes.
subscription
This backup level includes the following:
Information about a subscription, its owner and
associated hosting plan.
IP addresses allocated to the subscription.
Resource allotments and permissions for
operations in Control Panel.
Information about websites with DNS settings.
Information about mail accounts and individual
settings for protection from spam and viruses.
Website content, error
documents, log files,
content of mailboxes.
Page 53

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 53
Specifying Data for Backing Up
(All)
Only web hosting
settings
option: --onlyhosting
Only mail
option: --only-mail
(All)
Only
configuration
option: -c
(All)
Only
configuration
option: -c
(All)
Only
configuration
option: -c
Server
command:
--server
(All)
Excluding resellers
options:
--excludereseller or
--excludereseller-file
Excluding customers
options:
--exclude-client
or
--excludeclient-file
Excluding
subscriptions
options:
--exclude-domain
or
--excludedomain-file
Defining data that should be backed up includes the following:
1. Defining backup level and, unless it is the server level, optionally, selecting which
resellers, customers, or subscriptions should be backed up.
2. (optional) Defining which resellers, customers, or subscriptions should be excluded
from the backup.
3. (optional) Restricting backup to either only mail or only web hosting settings, and
only to configuration.
4. (optional) Defining that log files are excluded from backup.
Generally speaking, the data that can be backed up with one call of the pleskbackup
utility are represented by any single cell of the following table.
Page 54

54 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
All or selected
resellers
command:
-resellersname
or
-resellersid
(All) / (All selected)
Example 1
Excluding resellers
options:
--excludereseller or
--excludereseller-file
Example 1*
Excluding customers
options:
--exclude-client
or
--excludeclient-file
Excluding
subscriptions
options:
--exclude-domain
or
--excludedomain-file
All or selected
customers
command:
--clientsname
or
--clientsid
(All) / (All selected)
Excluding customers
options:
--exclude-client
or
--excludeclient-file
Excluding
subscriptions
options:
--exclude-domain
or
--excludedomain-file
Page 55

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 55
All or selected
subscriptions
command:
--domainsname
or
-domainsid
(All) / (All selected)
Example
2
Excluding
subscriptions
options:
--exclude-domain
or
--excludedomain-file
Page 56

56 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
Example 1: With one call of pleskbackup, you can back up hosting data for several
resellers (row 5 or 6 in the table, depending on what is more convenient: to list resellers
that should be included or those excluded) and restricting the backup data to
configuration of web hosting on sites owned by the resellers or their customers (column
4 in the table).
To back up website hosting configuration of resellers with usernames reseller1 and
reseller2, issue the following command:
pleskbackup --resellers-name "reseller1 reseller2" --only-hosting -c
Example 2: With one call of pleskbackup, you can back up mail configuration and
content of mail accounts (column 5) for all subscriptions existing on the server (row 12).
To back up mail accounts with messages for all subscriptions:
pleskbackup --domains-name --only-mail
The rest of this section explains each option in detail and provides examples of
commands.
Defining backup level and selecting objects
To define backup level and select backup objects, the commands of pleskbackup
utility are used.
If performing a selective backup, resellers, customers or subscriptions selected for the
backup should be specified by their identifiers which are either usernames or IDs. The
specification can be done in one of the following two ways:
Command line specification. The backup command takes objects identifiers as
arguments separated with spaces.
File specification. The backup command takes the --from-file option which
specifies the file where the identifiers of objects are listed. The file must be in plain
text format, and object identifiers are separated by line breaks (i.e., one identifier
per line).
Note: If a command contains both specifications, file specification is used and the
command line specification is ignored.
To back up all data related to Panel installation:
pleskbackup --server
To back up all resellers, customers, or subscriptions:
pleskbackup --<resellers|clients|domains>-<name|id>
For example, to back up all customer accounts:
pleskbackup clients-name
or
pleskbackup clients-id
Page 57

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 57
To back up several resellers, customers, or subscriptions defined in the
command line:
pleskbackup --<resellers|clients|domains>-<name|id> [
<identifier1> [
<identifier2> ... [<identifier n>]]
For example, to back up three resellers defined in the command line:
pleskbackup --resellers-name "johndoe janedoe josephine"
To back up several resellers, customers, or subscriptions listed in a
file: pleskbackup --<resellers|clients|domains>-<name|id> --fromfile=<file>
For example,
pleskbackup --resellers-name --from-file="E:\backup lists\j.txt"
Defining which objects should be excluded
Objects that should be excluded from backup are specified by their usernames
(reseller, customer accounts) or domain names (subscriptions). The specification can
be done as follows:
Command line specification. The backup command takes objects identifiers as
values of the --exclude-<reseller|client|domain> option separated by
commas.
File specification. The backup command takes the objects identifiers from the file
specified by the --exclude-<reseller|client|domain>-file option. The
file must be in plain text format, and object identifiers are separated by line breaks
(that is, one identifier per line).
Note: It is acceptable to use both specifications in one command. In such case, all
specified objects are excluded from backup.
To back up all reseller accounts except for several selected resellers:
pleskbackup --resellers-name --excludereseller=<login1>,<login2>[,<login n>]
or
pleskbackup --resellers-name --exclude-reseller-file=<file>
For example,
pleskbackup --resellers-name --exclude-reseller=johndoe,janedoe
or
pleskbackup --resellers-name --exclude-reseller-file="E:\backup
lists\j.txt"
Page 58

58 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
To back up a selected reseller without several subscriptions belonging to
him or her, or his or her customers:
pleskbackup --resellers-name <username> --excludedomain=<name1>,<name2>,<name n>
or
pleskbackup --resellers-name <username> --exclude-domain-file=<file>
For example,
pleskbackup --resellers-name johndoe --excludedomain=example.com,example.net,example.org
or
pleskbackup --resellers-name johndoe --exclude-domain-file="D:\backuplists\excl-example-domains.txt"
Restricting backup to only mail or only physical hosting, and to only
configuration
The amount of backup data can be further narrowed to backing up either mail or
physical hosting content and configuration by using the --only-mail or --only-
hosting options, respectively.
Specifying the --only-hosting option results in backing up only website-specific
data which includes the following, for each domain with physical hosting:
website content (including protected directories, web users, MIME types)
web hosting configuration (including settings of anonymous FTP, log rotation,
hotlink protection, shared SSL, web users)
installed site applications
databases
subdomains
Specifying the --only-mail option results in backing up only mail-specific data which
includes the following:
if used for the partial backup, for each domain included in backup:
configuration of per-subscription mail settings
mail accounts
mailing lists
if used for the full backup, in addition to previous:
RBL protection settings
ACL white and black list configurations
The amount of backup data can also be narrowed in another way: by specifying that
only configurations of the selected objects should be backed up. The specification is
done by using the --only-configuration option.
Such backups are useful when the objects content is backed up by a third-party
system.
Page 59

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 59
To back up mail configuration on subscriptions belonging to a
customer: pleskbackup --clients-<name|id> <name|id> --only-mail -configuration
For example,
pleskbackup --clients-id 42 --only-mail --configuration
To back up websites content and hosting configuration on subscriptions
belonging to all resellers:
pleskbackup --resellers-id --only-hosting
Excluding log files from back up
In case Panel's log files related to the hosted objects are not required to be backed up,
they can be excluded from the backup by using the --skip-logs option.
To back up the Panel configuration without log files:
pleskbackup --server -c --skip-logs
Page 60

60 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
Defining Properties of Files That Compose Backup
Defining properties of the files that will be contained in backup includes the following:
1. Defining that archives with backup object contents should not be compressed.
2. Defining that a prefix should be added to names of the backup files.
3. Defining that backup files should be split into parts of the specified size.
Defining that archives with backup object contents should not be compressed
By default, Panel saves backed up content to compressed .zip archives to save disk
space when the backup is stored. However, restoring backups that contain
compressed archives requires almost two times more disk space than restoring those
with uncompressed files. If you want to create your backups without compression, use
the -z option in your backup command.
Defining that a prefix should be added to names of the backup files
In order to better distinguish files that were created during one backup session from
another, pleskbackup adds a prefix to backup file name. By default, it is backup, so
every backup file name looks like backup_<file-name>.<ext>. The prefix in
names of the files that compose a particular backup can be customized by using the -prefix option. The option's value will be added as a prefix to names of files of the
created backup.
For example, to create a backup of the server mail configuration so that all files in
backup have prefix mail-friday:
pleskbackup --server --only-mail --configuration --prefix="friday"
Defining that backup files should be split into parts of the specified size
The pleskbackup utility is capable of splitting backup files into parts of a particular
size, which is vitally useful in cases when the file size is critical. Such cases can be, for
example, the following:
if backups are burnt to DVDs, file size should not exceed approximately 4 Gbytes
if backups are stored on the FAT32 file system, file size should not exceed
approximately 4 Gbytes
if backups are stored on FTP, FTP server may have its own restrictions on the size
of a single file transferred to the server
To make pleskbackup split the backup files to parts of a particular size, use the -s|--
split option and specify the required size as the option value. For details on the
format of size specification, refer to the section Backup Utility Commands and Options (on
page 65). The default value used by pleskbackup if no custom size is specified is 2
Gbytes. The utility numbers file parts created as a result of split by adding numerical
suffixes to the file names starting from .1.
Page 61

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 61
For example, to back up a subscription and split backup files into parts of no more than
700 Mbytes:
pleskbackup --domains-name example.com --only-hosting --split=700M
Page 62

62 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
Exporting Backup Files
By default, pleskbackup stores backups in Panel's backup repository located on the
server in %plesk_dir%\Backup\.
Panel is capable of exporting the created backup as a single .zip file in one of the
following ways:
to stdout
to local file system
to FTP server
To export backup as a single file, use the --output-file option. Particular export
mode requires specific option values.
Important: After a backup is exported, pleskbackup removes it from the Panel's
backup repository.
The exported file can also be created not compressed and/or split in parts of a
particular size, just as the files composing backup in repository (details (on page 60)).
Exporting to stdout
To export a backup as file to stdout, use the --output-file option with the
stdout value.
For example, to create backup of a subscription with ID 1 and export it to stdout:
pleskbackup --domains-id 1 --output-file stdout
Exporting to local file system
To export a backup as a file to local file system, use the --output-file option with a
<full-path-to-file>\<file-name> value.
For example, to create backup of a subscription with ID 1 and export it to the file
domain1.zip located at c:\tmp folder:
pleskbackup --domains-id 1 --output-file="c:\tmp\domain1.zip"
Exporting to FTP server
To export a backup as a file to an FTP server, use either of the following options:
--output-file=ftp://<login>:<password>@<server>/<filepath>
--output-file=ftp://<server>/<filepath> --ftp-login=<ftp
login> --ftp-password=<ftp password>
You may want to use passive mode FTP connection in case a firewall prevents the
export. For this, use the --ftp-passive-mode option.
Page 63

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 63
For example, to create backup of a subscription with ID 1 and export it to FTP server
example.com to the storage/backups/ directory, using johndoe as login and jjFh6gsm as
password:
pleskbackup --domains-id 1 --outputfile=ftp://johndoe:jjFh6gsm@example.com/storage/backups
or
pleskbackup --domains-id 1 --outputfile=ftp://example.com/storage/backups --ftp-login=johndoe --ftppassword=jjFh6gsm
Page 64

64 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
Defining How the Backup Process Is Performed
You can specify the following options for the backup operation:
1. Do not perform the backup if your server does not have specified free disk space.
2. Do not perform the backup if your server does not have enough free disk space to
store the backup content.
3. Temporarily suspend websites during backup.
4. Configure the backup utility to include more details in backup reports.
Specifying disk space requirements for the backup
You can prevent the start of the backup operation if your server has not enough disk
space to complete it. To set the free disk space requirements, change the parameters
in the file %plesk_dir%/admin/share/pmmcli/pmmcli-rc.
There are two ways to prevent the start of the backup operation:
Specify minimal free disk space on your server.
If the server does not have the specified disk space, Panel will not start the backup
operation. Set the minimal free disk space in MB by changing the value of the
FREE_DISK_SPACE parameter. Say, to prevent the backup if free disk space on
the server is less than 100 MB, edit the line in the following way:
FREE_DISK_SPACE 100
Restrict the backup if your server does not have enough free disk space to store
the backup content. If this option is turned on, Panel calculates the future backup
size and compares it with the free disk space on the server. If there is not enough
disk space, Panel will not start the backup operation. Note that this option can
significantly increase the backup time.
To turn this option on, set the CHECK_BACKUP_DISK_SPACE to 1. To turn this
option off, set the parameter to 0. Say:
CHECK_BACKUP_DISK_SPACE 0
Suspending websites
If your backup will include websites, we recommend that you suspend them during the
backup process by using the --suspend option of the backup utility. This will help you
avoid possible errors that may be caused by changes done to the site configuration or
content during the backup.
The suspension is made up to be as short as possible: each site is suspended only for
the time it is being backed up: The site is started automatically as soon as its data are
processed.
Page 65

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 65
Defining level of backup verbosity
Command
Argument
Description
--server
Backs up all data related to the Panel installation.
-resellersname
[<username-1>
<username-2> <...>
<username-n>]
Backs up all data for the resellers specified by
usernames.
Usernames should be separated by spaces and enclosed
in quotes.
Can be used with the --from-file option. In such
case, resellers specified in the file are backed up and
resellers specified as command arguments are ignored.
If no usernames are specified and the -f option is not
used, all resellers are backed up.
Verbose mode of backup process is defined by the -v option:
1. No -v option used. The minimum level, only general errors are displayed, like, for
example, syntax errors (no or wrong command specified, invalid input parameters),
runtime errors and unhandled exceptions, low disk space for backup, and so on.
2. The -v option used. Sets up the maximum verbosity level: additionally includes
debugging information and response/request messages to the internal backup
utility.
Note: pleskbackup outputs information on its execution to stdout only. If you want
to have the backup log saved, redirect the utility output to a file with standard command
line means.
To run a task on creating a complete server backup with maximum level of
verbosity:
pleskbackup --server -v
Backup Utility Commands and Options
Location
%plesk_dir%\bin\pleskbackup
where %plesk_dir% is an environment variable for Panel installation
directory. By default, it is "C:\Program Files\Parallels\Plesk".
Usage
pleskbackup <command> [<arguments>] [<options>]
Commands
Page 66

66 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
Command
Argument
Description
-resellersid
[<ID1> <ID2> <...>
<IDn>]
Backs up all data for the resellers specified by IDs.
IDs should be separated by spaces and enclosed in
quotes.
Can be used with the --from-file option. In such
case, resellers specified in the file are backed up and
resellers specified as command arguments are ignored.
If no IDs are specified and the -f option is not used, all
resellers are backed up.
--clientsname
[<username-1>
<username-2> <...>
<username-n>]
Backs up all data for the customers specified by
usernames.
Usernames should be separated by spaces and enclosed
in quotes.
Can be used with the --from-file option. In such
case, customers specified in the file are backed up and
customers specified as command arguments are ignored.
If no usernames are specified and the -f option is not
used, all customer accounts are backed up.
--clientsid
[<ID1> <ID2> <...>
<IDn>]
Backs up all data for the customers specified by IDs.
IDs should be separated by spaces and enclosed in
quotation marks.
Can be used with the --from-file option. In such
case, customers specified in the file are backed up and
customers specified as command arguments are ignored.
If no IDs are specified and the -f option is not used, all
customer accounts are backed up.
--domainsname
[<name-1> <name-2>
<...> <name-n>]
Backs up all data for the subscriptions specified by
domain names.
Names should be separated by spaces and enclosed in
quotation marks.
Can be used with the --from-file option. In such a
case, subscriptions specified in the file are backed up
and subscriptions specified as command arguments are
ignored.
If no names are specified and the -f option is not used,
all subscriptions are backed up.
--domainsid
[<ID1> <ID2> <...>
<IDn>]
Backs up all data for the subscriptions specified by IDs.
IDs should be separated by spaces and enclosed in
quotation marks.
Can be used with the --from-file option. In such
case, subscriptions specified in the file are backed up
and subscriptions specified as command arguments are
ignored.
If no IDs are specified and the -f option is not used, all
subscriptions are backed up.
--help
Displays help on the utility usage.
Page 67

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 67
Option
Description
--excludereseller[=<username1>,<usernam
e2>,...]
Skips resellers with the specified usernames during
backup.
--exclude-resellerfile[=<file>]
Skips resellers listed in the specified file during backup.
--excludeclient=[<username1>,<username2
>,...]
Skips customer accounts with the specified usernames
during backup.
--exclude-client-file=<file>
Skips customer accounts listed in the specified file during
backup.
--excludedomain[=<name1>,<name2>,...]
Skips subscriptions with the specified names during
backup.
--exclude-domain-file=<file>
Skips subscriptions listed in the specified file during
backup.
Option
Description
-v|--verbose
Shows more information about the backup process.
-c|--configuration
Backs up only configurations of Panel objects, excluding their
content.
-s|-split[=<integer>[K|M|
G]]
Splits the backup files into parts of the specified size. The parts are
numbered by appending numerical suffixes starting with .1.
Size is specified in Kbytes, Mbytes or Gbytes. If none is defined, then
interpreted as being in bytes.
If no argument is specified, the default value of 2 Gbytes is used.
-z|--no-gzip
Sets that objects content is archived without compressing.
--only-mail
Backs up only mail configuration and content.
When used with the resellers|clients|domains-login|id
commands, backs up configuration of domain-level mail system, and
content and configuration of mail accounts.
When used with the server command, backs up also server-wide
mail configuration.
Cannot be used together with the --only-hosting option.
--only-hosting
Backs up only web hosting configuration and website content,
including site applications, databases and subdomains.
Cannot be used together with the --only-mail option.
--suspend
Suspends sites during backup operation.
Exclude Options
General Options
Page 68

68 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
Option
Description
-f| --from-file=<file>
Backs up resellers|customers|subscriptions listed in the specified file,
ignoring those specified in the command line as arguments.
The file should be in plain text format and should contain a list of
resellers|customers|subscriptions, one per line.
Used only with the resellers-name, resellers-id, clients-
name, clients-id, domains-name, domains-id commands.
Depending on the command, resellers|customers|subscriptions are
listed in the file by either usernames or IDs.
--skip-logs
Sets that log files are not saved to backup.
--prefix=<string>
Adds specified prefix to the backup file names.
Used to customize backup file name which is created with the backup
prefix by default.
Option
Description
--ftplogin=<ftp_username>
Specifies FTP account username that will be used for uploading
backup file to the FTP server.
--ftppassword=<ftp_password
>
Specifies password that will be used for uploading backup file to the
FTP server.
--ftp-passive-mode
Specifies that the passive mode for FTP connection should be
used.
Option
Description
--output-file
Exports backup as a single file to stdout and removes
backup from Panel's repository.
--outputfile=<fullpath/filename>
Exports backup as a single file with the specified name to
a local file system and removes backup from Panel's
repository.
--outputfile=<ftp://[<username>[:<pass
word>]@]<server>/<filepath>>
Exports backup as a single file to the specified FTP
server and removes backup from Panel's repository.
The FTP_PASSWORD environment variable can be used
for setting password.
The --ftp-login and --ftp-password FTP options
can be used for setting username and password.
FTP Options
Output File Option
Page 69

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 69
Restoring Data
In this section:
Defining Objects for Restoration ........................................................................ 69
Defining How the Restoration Process Is Performed ......................................... 76
Conflict Resolution Rules and Policies .............................................................. 77
Restoration Utility Commands and Options ....................................................... 98
Restoration levels specified with the -level option
Server
Resellers
Customers
Subscriptions
Selected
with the
-filter
option
Selected
with the filter option
Selected
with the filter option
To perform restoration of Panel hosting data, you should execute the pleskrestore
utility command composed so that it does the following:
1. Defines the Panel objects to be restored.
2. Defines how the restore process will be performed.
3. Defines conflict resolution rules and policies.
The following sections explains each component in detail.
The pleskrestore utility is located in %plesk_dir%\bin\
where %plesk_dir% is an environment variable for the Panel installation directory. By
default, it is "C:\Program Files\Parallels\Plesk\".
To see a list of the pleskrestore commands and options, refer to the section
Restoration Utility Commands and Options (on page 98).
Defining Objects for Restoration
Defining objects for restoration includes the following:
1. Specifying a source backup file.
2. Defining the level of restored objects.
3. Applying filter on the specified level.
Generally speaking, the data that can be restored with one call of the pleskrestore
utility are represented by any cell of the following table.
Page 70

70 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
Backup
file
<server>.xml |
zip
Full
restoratio
n
All reseller
accounts
Selected
reseller
account
s
All customer
accounts
belonging to
administrator
Selected
customer
accounts
belonging
to
administrat
or
All
subscriptio
ns
belonging
to
administrat
or
Selected
subscriptio
ns
belonging
to
administrat
or
<reseller>.xml |
zip
Full
restoration
of a reseller
account
All customer
accounts
belonging to
reseller
Selected
customer
accounts
belonging
to reseller
All
subscriptio
ns
belonging
to reseller
Selected
subscriptio
ns
belonging
to reseller
<customer>.xml
| zip
Full
restoration of
a customer
account
All
subscriptio
ns
belonging
to customer
Selected
subscriptio
ns
belonging
to customer
<subscription>.x
ml | zip
Full
restoration
of a
subscriptio
n
Page 71

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 71
Specifying a source backup file
The source backup file defined for restoration can be of one of the following types:
<info>.xml - backup metadata file, in case of restoring from backup located in
Panel's repository.
<backup>.<zip> - archived backup file, in case of restoring from an exported
backup.
For example, to restore the whole server backup, you choose a <backup
repository root>\<server>.xml file, or an exported server backup file. To
restore a customer account belonging to a reseller, you choose a <backup
repository root>\resellers\<reseller ID>\clients\<customer
ID>\<customer>.xml file.
Defining level of restored objects
Defining level of restored objects allows you to narrow the amount of restored data
according to your needs. For example, you may want to restore only subscriptions
which belong to a customer or a reseller, skipping all other data not related to
subscriptions.
To define the level of restored objects, use the -level option with appropriate value.
The option is required, so in cases when you do not need any narrowing but just
restoring all data from a backup, define the level equal to the level of file.
To restore entire server:
pleskrestore --restore <backup repository root>\<server>.xml -level
server
Note: When the whole server backup is restored, license keys are not restored by
default. To restore license keys along with other server content, use the -license
option in your restore command.
To restore entire server with license keys:
pleskrestore --restore <backup repository root>\<server>.xml -level
server -license
To restore all subscriptions and sites belonging to a reseller:
pleskrestore --restore <backup repository root>\resellers\<reseller
ID>\<reseller>.xml -level domains
To restore all reseller accounts:
pleskrestore --restore <backup repository root>\<server>.xml -level
resellers
Page 72

72 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
Applying filter on the specified level
In this section:
Backup File Structure ........................................................................................ 72
<info>.xml
Metadata files of full and server-level
backups, one per backup, describe
configuration and content.
To perform a more selective restore, use a filter (the -filter option) which selects for
restoring particular objects of the specified level (resellers, customers, subscriptions).
The objects are specified by their names, which are domain names for subscriptions,
and usernames for resellers and customers. The specification can be done as follows:
Command line specification. The restore command takes objects identifiers as
values of the -filter option defined in the following string:
list:<item1>,<item2>,...,<itemN>.
File specification. The restore command takes the objects identifiers from the file
specified as argument of the -filter option. The file must be in plain text format,
and object identifiers are separated by line breaks (that is, one identifier per line).
To restore two resellers from a server backup:
pleskrestore --restore <backup repository root>\<server>.xml -level
resellers -filter list:JohnDoe,JaneDoe
or
pleskrestore --restore <upload directory>\<server backup name>.zip level resellers -filter list:JohnDoe,JaneDoe
To restore two subscriptions owned by server administrator:
pleskrestore --restore <backup repository root>\<server>.xml -level
domains -filter list:example.com,sample.org
To restore several subscriptions of a customer defined in a file:
pleskrestore --restore <backup repository
root>\resellers\SandyLee\clients\JaneDow\<customer>.xml -level domains
-filter <path to the file>\restore-subscriptions.txt
Backup File Structure
By default, all backups are created in a backup repository located on the Panelmanaged server: in %plesk_dir%\Backup\ folder, where %plesk_dir% is
environment variable specifying directory where Panel is installed (if installed to default
locations, it is "C:\Program Files\Parallels\Plesk\")
The repository is structured as follows, starting with the content of repository root folder
(we omit auxiliary files and folders which are irrelevant for backing up and restoring
Panel data using pleskbackup and pleskrestore utilities).
Page 73

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 73
<content>.<zip>
Archives with content related to
server configuration and Panel
settings.
clients\
Directory containing the following
backup data:
customer accounts belonging to
the server administrator
objects related to those accounts
Organization of the directory is the
same as that of
<repository>\resellers\<rese
ller ID>\clients\.
domains\
Directory containing the following
backup data:
subscriptions belonging to the
server administrator
objects related to administrator's
subscriptions
Organization of the directory is the
same as that of
<repository>\resellers\<rese
ller ID>\clients\<client
ID>\domains.
<subscription name 1>.tld
Directory containing data related to all
sites hosted under a subscription.
<subscription name 2>.tld
Directory containing data related to all
sites hosted under a subscription.
resellers\
Directory containing the following
backup data:
reseller accounts
objects owned by the resellers
<reseller ID>\
Directories containing backup data of
particular resellers, one reseller per
directory, and the objects owned by
them.
The reseller ID stands for the reseller
username.
<info>.xml
Metadata files of the reseller backups,
one file per backup, describe
configuration and content of the
reseller and the objects they own.
<content>.<zip>
Archives with the content.
Page 74

74 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
domains\
Directory containing the following
backup data:
subscriptions owned by the
reseller
objects owned by the
subscriptions
Organization of the directory is the
same as that of
<repository>\resellers\<rese
ller ID>\clients\<client
ID>\domains\.
clients\
Directory containing the following
backup data:
customer accounts owned by the
reseller
objects owned by the customers
<customer's username>\
Directories containing backup data of
particular customers, one customer
per directory, and the objects owned
by them.
<info>.xml
Metadata files of the customer
backups, one file per backup,
describe configuration and content of
the customer account and the objects
it owns.
<content>.<zip>
Archives with the customer content.
domains\
Directory containing the following
backup data:
subscriptions owned by the
customer
objects owned by the
subscriptions
<subscription
name 1>.tld
Directory containing data related to all
sites hosted under a subscription.
<info>.x
ml
Metadata files of the domain backups,
one file per backup, describe
configuration and content of the
backed up webspace.
<content>
ZIP archives containing data related
to the hosted websites and mail
accounts.
Page 75

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 75
Files of each backup are placed in the repository folders according to the described
structure.
If a partial backup is created, its files will be places according to the place the backup
objects have in the hierarchy. For example, if backing up domain example.com owned
by reseller JaneDoe, its files will be located in the <repository root
directory>\resellers\JaneDoe\domains\example.com\ folder. If backing up
reseller JohnDoe who owns the subscription joe.info and has one customer Client1
who owns the subscription sample.org, the backup files will be located in the following
folders:
1. <repository root directory>\resellers\JohnDoe\
2. <repository root
directory>\resellers\JohnDoe\domains\joe.info\
3. <repository root
directory>\resellers\JohnDoe\clients\Client1\
4. <repository root
directory>\resellers\JohnDoe\clients\Client1\domains\sample.o
rg\
To distinguish files belonging to different backups of the same object, specific prefix
and suffix are added to the file names:
the backup is added by default, and, if you like, you can change it to your own on a
per-backup basis
suffix designating the backup creation date is always added to each backup file, the
date format is <yymmddhhmm>. For example, files of backup created on 6 April
2011, 8:58 PM will have suffix 1104062058.
Panel is capable of exporting backup as a single .zip file. Each archive has the same
structure as the repository, the only difference is that there is only one <info>.xml
file on each level.
In case a partial backup is exported, the resulting file structure is reduced from the top
so that the highest level corresponds to the level of the highest backup object. For
example, if a backup of a single customer (called, for example, SandyLee) is exported,
the resulting file will have the following structure:
zip {
<sandy lee info>.xml
<content>.zip
domains\
subscription1\
...
subscription_N\
...
}
Page 76

76 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
Defining How the Restoration Process Is Performed
When restoring data, you can also do the following:
1. Temporarily suspend websites during restoration.
2. Configure the restoration utility to include more details in backup reports.
Suspending websites
If you are going to restore websites, we recommend that you suspend them during the
restoration by using the -suspend option. This will help you avoid possible errors in
the restored sites that may be caused by changes done to the site configuration or
content during the restoration.
The suspension is made up to be as short as possible: each site is suspended only for
the time it is being restored: The site is started automatically as soon as the data are
processed.
Defining level of restore verbosity
pleskrestore works in one of the following verbosity modes:
1. Non-verbose mode. Default mode. The minimum level, only general errors are
displayed, like, for example, syntax errors (no or wrong command specified, invalid
input parameters), runtime errors and unhandled exceptions, and so on.
2. Verbose mode. Restore runs with verbosity level which additionally includes
deployer errors, information about conflicts (read about restore conflicts in the
section Conflict Resolution Rules and Policies (on page 77)), and so on. Enabled by
adding the -verbose option to the pleskrestore command.
Page 77

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 77
Conflict Resolution Rules and Policies
Conflict is a situation when settings in a backup and settings in a destination Panel are
such that restoring backup objects leads to an error or unpredictable Panel behavior.
Types of Conflicts
The restoration process can encounter several types of conflicts, which are the
following:
Timing conflicts. An object being restored might exist in the system and its last
modification date might be more recent than the date of backup. Or an object could
be deleted from the system later than the backup was created.
Resource usage conflicts. There are two groups of resource usage conflicts:
Common resource usage conflict: The total amount of measurable resources
after restoration might appear to be over the limits for this particular user (e.g.,
disk space limit).
Unique resource usage conflict: An object being restored requires a unique
resource which is already used by another object in the system or does not exist
(e.g., domain).
Configuration conflicts. It might happen that configuration being restored is not
enabled on the destination server. Two types of cases can happen here:
Configuration options are not enabled for the domain.
Required configuration options are not available (e.g., site applications are not
available for the customer, database server is not configured on the host, IP
address is not allocated to the reseller, etc.)
Conflict Resolutions
The following types of conflicts resolutions are possible:
Overwrite. Means that all objects will be restored from the backup files regardless
of their current presence in the system. Overwrite works as follows:
If an object/setting from backup does not exist in Panel, it is created.
If an object/setting from backup exists in Panel, it replaces the existing.
If an object/setting exists in Panel but is missed in a backup, the existing
remains.
Proceed with current. Means that objects which currently present in the system
won’t be affected by the restoration process. The restoration process will move to
the objects belonging to that one, not touching the object itself.
Do not restore. Means that the objects which currently present in the system or
were deleted after the backup won’t be restored together with the lower level
objects belonging to it.
Automatic. Means that configuration option that should be enabled for domain is
enabled automatically.
Page 78

78 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
Overuse. Means that objects are restored with the resources overuse. Can be
applied only to objects that belong to a reseller who works in the oversell mode.
Rename. Means that unique resources for the restored domain are reassigned with
the specified, existing in the system (mapping).
Conflict Resolution Policies and Rules
Depending on the scope of a conflict resolution, we distinguish conflict resolution rules
and policies:
Rule defines the way of how a specific single conflict should be resolved.
Policy defines the way of how all conflicts of a particular type should be resolved.
Conflicts Resolving Mechanism: Default Policies, Custom Policies, and Rules
The restoration utility brings a set of default, hard-coded conflict resolution policies,
which are as follows:
for timing conflicts - Overwrite
for common resource usage conflicts - Overuse
for unique resource usage conflicts - Do not restore
for configuration conflicts - Automatic
The default policies are always applied during restoration and cannot be changed or
overridden.
Applying default policies may resolve not all the conflicts occurred. In such cases,
those who perform restore should additionally define custom rules and/or policies that
resolve the remaining conflicts. Custom rules and policies are defined in an XML format
as described in the section Resolutions Description Format (on page 81).
Simplified presentation of the conflicts resolving during restore is as follows:
1. Administrator runs pleskrestore with specific parameters.
2. pleskrestore detects the conflicts occurred and resolves them with the default
policies.
3. pleskrestore checks if any conflicts remain unresolved.
In case all conflicts are resolved, the restoration continues.
4. pleskrestore stops the restoration and, if run in debug or verbose mode,
returns detailed description (in XML format) of each remaining conflict.
5. Basing on the returned description of the conflicts, administrator creates a file that
defines a resolution for each conflict (with rules) and/or in bulk (with custom
policies).
6. Administrator runs the pleskrestore utility with the --conflicts-resolution
option and the file created at the previous step as its argument.
7. pleskrestore detects the conflicts occurred and resolves them with the default
policies.
Page 79

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 79
8. pleskrestore processes the remaining conflicts:
In this section:
Custom Conflict Resolutions ............................................................................. 79
In this section:
Conflict Description Messages .......................................................................... 79
Resolutions Description Format ......................................................................... 81
Samples of Policy Description ........................................................................... 89
Samples of Conflict Resolution With Rules ........................................................ 89
Value of message element
Message displayed in Panel GUI
backup__restore__object_vhost
Virtual host
backup__restore__object_plesk_admi
n
server administrator
backup__restore__conflict_object_n
ame
<object name>
backup__restore__conflict_object_c
omplex_name
<object name> of <group name>
a pleskrestore applies resolution rules from the file.
b pleskrestore applies resolution policies from the file to the rest of the
conflicts.
9. pleskrestore checks if any conflicts remain unresolved.
In case all conflicts are resolved, the restoration continues.
In case any conflicts remain unresolved, pleskrestore stops the restoration
and, if run in debug or verbose mode, returns detailed description (in XML
format) of each remaining conflict.
To have such dump restored, admin should add resolution rules for each
remaining conflict to the conflict resolution file and repeat the restoration task.
Custom Conflict Resolutions
This section describes how to implement custom conflict resolutions during restore.
Conflict Description Messages
Conflict descriptions returned by pleskrestore utility contain message elements
included for the GUI generation purposes. Despite of the self-explaining character of
XML conflict descriptions, values of the message elements may be confusing, so this
section describes the meanings of these messages as they are displayed in Panel GUI.
Page 80

80 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
Value of message element
Message displayed in Panel GUI
backup__restore__conflict_object_m
ailname
<mail name>@<domain name>
backup__restore__object_ftpuser
FTP account
backup__restore__object_frontpageu
ser
Frontpage account
backup__restore__object_webuser
web user
backup__restore__object_domain
subscription name or domain name
backup__restore__object_subdomain
subdomain
backup__restore__object_domainalia
s
domain alias
backup__restore__object_client
customer
backup__restore__object_reseller
reseller
backup__restore__object_autorespon
der
auto-reply
backup__restore__object_mailalias
mail alias
backup__restore__object_database
database
backup__restore__object_mailname
mail account
backup__restore__conflict_timing_r
eason_owner_absent
Cannot restore object: object owner is not specified
backup__restore__conflict_timing_r
eason_wrong_owner
Cannot restore object: object owner does not exist in
Panel
backup__restore__conflict_timing_r
eason_object_already_exists
Cannot restore <object name>: <object name> <object
type> already exists in Panel
backup__restore__conflict_configur
ation_reason_ip
Cannot restore object: required IP address <IP> not
found in owner's IP pool
backup__restore__conflict_configur
ation_reason_db
Cannot restore database: required database server
<host> is not registered in Panel
backup__restore__conflict_configur
ation_reason_site_app
Cannot restore web application: required web
application <application name> not found in owner's
web application pool
backup__restore__conflict_unique_r
eason_name_already_used
Cannot restore <object>: name <unique resource
name> is already used in Panel by another <object>
backup__restore__conflict_resource
_usage_reason
Cannot restore object: resource limit <limit name> will
be exceeded (required: <value>, available: <value>)
Page 81

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 81
Resolutions Description Format
In this section:
Policies .............................................................................................................. 81
Rules ................................................................................................................. 84
Policies
The file should be structured as follows.
Page 82

82 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
conflict-resolution-rules
Required, document root element.
policy
Required, contains the policies descriptions. Children, if present, must be placed in
the order shown on the scheme.
timing
Optional, contains description of policy on resolving timing conflicts. See the
structure below.
Must be present in the document if a timing policy should be used during the
restore.
May not be present in the document if no policy required for timing conflicts.
resource-usage
Optional, contains description of policy on resolving resource usage conflicts.
See the structure below.
Must be present in the document if a resource usage policy should be used
during the restore.
May not be present in the document if no policy required for resource usage
conflicts.
configuration
Optional, contains description of policy on resolving configuration conflicts. See
the structure below.
Must be present in the document if a configuration policy should be used during
the restore.
May not be present in the document if no policy required for configuration
conflicts.
rule
Optional, contains the rule descriptions. For details on the node structure, refer to
the Resolutions Description Format: Rules section.
The policy elements have the same structure:
resolution
Required, contains a definition of conflict resolution. Structured as follows:
Page 83

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 83
The resolution element must not be empty, it is required that it contains one, and
only one of its children elements:
do-not-restore
Sets the Do Not Restore resolution, empty value.
proceed-with-current
Sets the Proceed With Current resolution, empty value.
automatic
Sets the Automatic resolution, empty value.
overuse
Sets the Overuse resolution, empty value.
overwrite
Sets the Overwrite resolution, empty value.
rename
Sets the Rename resolution, empty value.
new-name
Required, makes sense only if defined for configuration conflicts. Specifies a
name of new configuration that should be assigned to all conflict objects. The
value must be a string.
Page 84

84 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
Rules
The file should be structured as follows.
Page 85

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 85
conflict-resolution-rules
Required, document root element.
policy
Required, contains the policies descriptions. For details on the node format,
refer to the section Resolutions Description Format: Policies (on page 81).
The element content must reflect the conditions under which the conflicts were
detected.
rule
Optional, contains a rule description.
Must be present in the document when defining conflict resolution rules. Should
be present as many times as the number of unresolved conflicts.
At least one of the attributes (conflict-id, conflict-guid) MUST be
present.
conflict-id
Optional, defines ID of the conflict being resolved. Value is integer.
The ID should be obtained from the conflict description returned by
pleskrestore (the "/conflicts-description/conflict[@id]"
attribute value)
conflict-guid
Optional, defines global ID of the conflict being resolved. Value is string.
The GUID should be obtained from the conflict description returned by
pleskrestore (the "/conflicts-description/conflict[@guid]"
attribute value).
If omitted, the conflict for resolution is identified by ID.
dump-objects
Optional, holds a collection of descriptions of backup objects involved into
the conflict and taking the same conflict resolution
Must be present in the document in case when different objects involved in
the same conflict should be resolved in different ways.
May not be present in the document in case when all objects involved in the
conflict should be resolved the same way.
See the structure below.
resolution
Required, contains definition of resolution for the conflict, see the structure
below.
dump-objects structure:
Page 86

86 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
node
Required, contains a description of backup object involved in the conflict.
The element contents must be taken from the conflict description returned by
pleskrestore (the "/conflicts-description/conflict/conflictingobjects/node" element).
Structured as follows:
Page 87

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 87
name
Required, specifies the object type, value must be a string.
context
Optional, holds a collection of data specifying the object position in backup.
path
Required if the context element is present in the document, specifies the
location of object definition in the backup metadata. Value must be a string
conforming to the XPath notation.
attributes
Required, holds a collection of the object properties.
attribute
Required, specifies a particular property of the object (e.g., login, ID, GUID,
etc.), empty value.
name
Required, specifies the property name, value must be a string.
value
Required, specifies the property value, value must be a string.
resolution structure:
Page 88

88 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
The resolution element must not be empty, it is required that it contains one, and
only one of its children elements:
do-not-restore
Sets the Do Not Restore resolution for the conflict, empty value.
proceed-with-current
Sets the Proceed With Current resolution for the conflict, empty value.
automatic
Sets the Automatic resolution for the conflict, empty value.
overuse
Sets the Overuse resolution for the conflict, empty value.
overwrite
Sets the Overwrite resolution for the conflict, empty value.
rename
Sets the Rename resolution for the conflict, empty value.
new-name
Required, specifies a name of unique resource that should be assigned to the
conflicting objects, value must be a string.
Makes sense only for unique resource usage conflicts (mapping of IP, database
server, object owner).
Page 89

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 89
Samples of Policy Description
In this section:
Sample 1: Configuration Conflict with Missing IP Address ................................. 90
Sample 2: Configuration Conflict With Missing Database Server ....................... 93
The default conflict resolution policies are described in the following XML:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<conflict-resolution-rules>
<policy>
<timing>
<resolution>
<proceed-with-current />
</resolution>
</timing>
<resource-usage>
<resolution>
<do-not-restore />
</resolution>
</resource-usage>
<configuration>
<resolution>
<automatic />
</resolution>
</configuration>
</policy>
</conflict-resolution-rules>
The following conflict resolution file resolves all configuration conflicts with database
mapping. This can be done in case all configuration conflicts beyond default policies
appear because a database server defined in the backup is missed on the target Panel
installation.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<conflict-resolution-rules>
<policy>
<configuration>
<resolution>
<rename new-name="host:192.0.2.12:port:3306"/>
</resolution>
</configuration>
</policy>
</conflict-resolution-rules>
Samples of Conflict Resolution With Rules
This reference section contains format specification of conflict resolution rules
description, and several examples of conflicts that may appear and their possible
resolutions.
Page 90

90 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
Sample 1: Configuration Conflict with Missing IP Address
Backup
Destination Panel
Subscription example.com owned by the reseller
with ID 30 has web hosting configured on shared
IP address 192.0.2.200.
Reseller with ID 30 does not have
shared IP address 192.0.2.200 in
his or her IP pool.
In this section:
Conflicts Description .......................................................................................... 91
Conflicts Resolution ........................................................................................... 92
This sample represents descriptions of a conflict which appeared unresolved upon
using default policies, and its resolution.
The conflict appears because of the following mismatch in backup data and destination
Panel configuration:
The conflict is resolved with IP mapping suggesting that the restored subscription will
be hosted on shared IP 192.0.2.34 which is in the owner's IP pool.
Note that the conflict resolution XML contains no conflict resolution policies.
Page 91

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 91
Conflicts Description
<conflicts-description>
<conflict id="0">
<type>
<configuration>
<reason-description>
<required-resource-description>
<ip type="shared" value="192.0.2.200"></ip>
</required-resource-description>
<plesk-object-identifier>
<!-- beginning of definition of Panel object that conflicts
with an object in the backup -->
<!-- In resource usage conflicts, the plesk-objectidentifier element specifies Panel object which is an owner of the
conflicting resource. In this example, the conflicting resource is IP,
and its owner is a described reseller with ID 30. -->
<type>reseller</type>
<database-id>30</database-id>
<guid>93dbe1b1-cff5-430f-8466-5b810099772f</guid>
</plesk-object-identifier>
<!-- end of definition of Panel object that conflicts with
an object in the backup -->
</reason-description>
<resolve-options>
<option name="do-not-restore"></option>
<option name="rename"></option>
<option name="automatic"></option>
</resolve-options>
<!-- resolve-options element lists all resolutions that are
possible for this particular conflict. When composing the conflict
resolution rule, you should choose one of these resolutions. -->
</configuration>
</type>
<conflicting-objects>
<!-- beginning of definition of backup objects that conflict with
destination Panel objects. Here, it is a domain example.com -->
<node children-processing-type="" name="domain">
<attributes>
<attribute name="id" value="25"></attribute>
<attribute name="guid" value="0822c175-a10d-459e-bd3ae5cbc497e1f0"></attribute>
<attribute name="owner-guid" value="93dbe1b1-cff5-430f-84665b810099772f"></attribute>
<attribute name="name" value="example.com"></attribute>
</attributes>
</node>
</conflicting-objects>
<!-- end of definition of backup objects that conflict with
destination Panel objects -->
<overview>
<!-- beginning of more detailed conflict overview. Here, the
conflict appears because the required IP 192.0.2.200 is not in the
owner's IP pool -->
<object>
<message>backup__restore__conflict_object_name</message>
<name>example.com</name>
<type>domain</type>
Page 92

92 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
<reasons>
<reason>
<message>backup__restore__conflict_configuration_reason_ip</message>
<param name="ip-address" value="192.0.2.200"></param>
<param name="ip-type" value="shared"></param>
<param name="type" value="reseller"></param>
</reason>
</reasons>
</object>
</overview>
<!-- end of detailed conflict overview -->
</conflict>
</conflicts-description>
Conflicts Resolution
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<resolve-conflicts-task-description>
<conflict-resolution-rules>
<policy />
<rule conflict-id="0">
<dump-objects>
<node name="domain">
<attributes>
<attribute name="id" value="25"></attribute>
<attribute name="guid" value="0822c175-a10d-459e-bd3ae5cbc497e1f0"></attribute>
<attribute name="owner-guid" value="93dbe1b1-cff5-430f-84665b810099772f"></attribute>
<attribute name="name" value="example.com"></attribute>
</attributes>
</node>
</dump-objects>
<resolution>
<!-- beginning of the conflict resolution definition: IP
mapping: upon restore, the conflicting domain example.com should have
hosting configured on IP 192.0.2.34 -->
<rename new-name="ip-type:shared:ip-address:192.0.2.34"/>
</resolution>
<!-- end of the conflict resolution definition -->
</rule>
</conflict-resolution-rules>
</resolve-conflicts-task-description>
Page 93

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 93
Sample 2: Configuration Conflict With Missing Database Server
Backup
Destination Panel
Domain sample.net has database
mysql_db2_7469 on the MySQL database server
with host name 192.0.2.15 listening on port 3306.
No MySQL servers configured on
host 192.0.2.15.
Domain 69.sample.net has database
mysql_db1_6319 on the MySQL database server
with host name 192.0.2.15 listening on port 3306.
In this section:
Conflicts Description .......................................................................................... 94
Conflicts Resolution ........................................................................................... 97
This sample represents description and resolution of configuration conflicts which
appeared unresolved due to the lack of the required database server on the destination
server.
The conflicts appear because of the following mismatches in backup data and
destination Panel configuration.
These conflicts are resolved with database mapping (Rename resolution) suggesting
that the first databases will be restored on the MySQL server with host name
192.0.2.12, and the second to the local MySQL database server.
Page 94

94 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
Conflicts Description
<conflicts-description>
<conflict id="0">
<type>
<configuration>
<reason-description>
<required-resource-description>
<db-server host="192.0.2.15" type="mysql"
port="3306"></db-server>
</required-resource-description>
<plesk-object-identifier>
<!-- beginning of definition of Panel object that conflicts
with an object in the backup. In resource usage conflicts it is owner
of the conflicting resource. Here, it is Panel administrator who is
the owner of all database servers -->
<type>admin</type>
<database-id>1</database-id>
<guid>00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000</guid>
</plesk-object-identifier>
<!-- end of definition of Panel object that conflicts with
an object in the backup -->
</reason-description>
<resolve-options>
<option name="do-not-restore"></option>
<option name="rename"></option>
<option name="automatic"></option>
</resolve-options>
</configuration>
</type>
<conflicting-objects>
<!-- beginning of definition of backup objects that conflict with
destination Panel objects. Here, it is database mysql_db2_7469 -->
<node children-processing-type="" name="database">
<attributes>
<attribute name="guid" value="86124f4a-5935-48c4-80df6d3e9c645378_db_20"></attribute>
<attribute name="owner-guid" value="86124f4a-5935-48c4-80df6d3e9c645378"></attribute>
<attribute name="name" value="mysql_db2_7469"></attribute>
</attributes>
</node>
</conflicting-objects>
<!-- end of definition of backup objects that conflict with
destination Panel objects -->
<overview>
<!-- beginning of detailed overview of the conflict. This conflict
appears because database mysql_db2_7469 requires MySQL database server
with host name 192.0.2.15 listening on port 3306, which is not
configured on the destination Panel. -->
<object>
<message>backup__restore__conflict_object_complex_name</message>
<name>mysql_db2_7469</name>
<type>database</type>
<owner-name>sample.net</owner-name>
<reasons>
<reason>
Page 95

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 95
<message>backup__restore__conflict_configuration_reason_db</message>
<param name="db-type" value="mysql"></param>
<param name="db-host" value="192.0.2.15"></param>
<param name="db-port" value="3306"></param>
<param name="type" value="admin"></param>
<param name="name"
value="backup__restore__object_plesk_admin"></param>
</reason>
</reasons>
</object>
</overview>
<!-- end of detailed overview of the conflict -->
</conflict>
<!-- =============== begin new conflict description ===============
-->
<conflict id="1">
<type>
<configuration>
<reason-description>
<required-resource-description>
<db-server host="192.0.2.15" type="mysql" port="3306">
</db-server>
</required-resource-description>
<plesk-object-identifier>
<!-- beginning of definition of Panel object that conflicts
with an object in the backup. In resource usage conflicts it is the
owner of the conflicting resource. Here, it is Panel administrator who
is the owner of all database servers -->
<type>admin</type>
<database-id>1</database-id>
<guid>00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000</guid>
</plesk-object-identifier>
<!-- end of definition of Panel object that conflicts with
an object in the backup -->
</reason-description>
<resolve-options>
<option name="do-not-restore"></option>
<option name="rename"></option>
<option name="automatic"></option>
</resolve-options>
</configuration>
</type>
<conflicting-objects>
<!-- beginning of definition of backup objects that conflict with
destination Panel objects. Here, it is database mysql_db1_6319 -->
<node children-processing-type="" name="database">
<attributes>
<attribute name="guid" value="e1fbb4b2-538b-4542-922056808741a3d3_db_19"></attribute>
<attribute name="owner-guid" value="e1fbb4b2-538b-4542-922056808741a3d3"></attribute>
<attribute name="name" value="mysql_db1_6319"></attribute>
</attributes>
</node>
</conflicting-objects>
<!-- end of definition of backup objects that conflict with
destination Panel objects -->
<overview>
Page 96

96 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
<!-- beginning of detailed overview of the conflict. This conflict
appears because database mysql_db1_6319 requires MySQL database server
with host name 192.0.2.15 listening on port 3306, which is not
configured on the destination Panel server. -->
<object>
<message>backup__restore__conflict_object_complex_name</message>
<name>mysql_db1_6319</name>
<type>database</type>
<owner-name>69.sample.net</owner-name>
<reasons>
<reason>
<message>backup__restore__conflict_configuration_reason_db</message>
<param name="db-type" value="mysql"></param>
<param name="db-host" value="192.0.2.15"></param>
<param name="db-port" value="3306"></param>
<param name="type" value="admin"></param>
<param name="name"
value="backup__restore__object_plesk_admin"></param>
</reason>
</reasons>
</object>
</overview>
<!-- end of detailed overview of the conflict -->
</conflict>
</conflicts-description>
Page 97

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 97
Conflicts Resolution
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<resolve-conflicts-task-description>
<conflict-resolution-rules>
<policy />
<rule conflict-id="0">
<!-- beginning of the first conflict resolution rule: restore the
database described in the node element on local MySQL server
listening on the port 3306 -->
<dump-objects>
<node name="database">
<attributes>
<attribute name="name" value="mysql_db2_7469"/>
</attributes>
</node>
</dump-objects>
<resolution>
<rename new-name="host:192.0.2.12:port:3306"/>
</resolution>
</rule>
<!-- end of the first conflict resolution rule -->
<rule conflict-id="1">
<!-- beginning of the second conflict resolution rule: restore the
database described in the node element on local MySQL server
listening on the port 3306 -->
<dump-objects>
<node name="database">
<attributes>
<attribute name="name" value="mysql_db1_6319"/>
</attributes>
</node>
</dump-objects>
<resolution>
<rename new-name="host:localhost:port:3306"/>
</resolution>
</rule>
<!-- end of the second conflict resolution rule -->
</conflict-resolution-rules>
</resolve-conflicts-task-description>
Page 98

98 Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data
Restoration Utility Commands and Options
Command
Argument
Description
--restore
<backup_file>
Restores data from the specified backup.
Requires the -level option.
--checkbackup
<backup_file>
Checks integrity of the specified backup file, which is:
backup digital sign match
backup file format
content files integrity
-i|--info
<backup_file>
Shows the backup file description.
-h|--help
Displays help on the utility usage.
Option
Argument
Description
-level
clients|resellers
|domains|server
Specifies restoring level.
Required with the --restore command.
-filter
<file>|<list:<ite
m1_name>[,<item2_
name>[,...]]>
Specifies list of subscription, customer or reseller names
for restoring. The object names are listed either in a
specified file, one per line, or as the option argument,
separated by commas.
-license
Restores Panel license key from the backup.
-verbose
Enables verbose restore mode.
-debug
Enables debugging restore mode.
-conflictsresolution
<file>
Specifies file that describes conflict resolution policies
and rules.
-suspend
Suspends the sites being restored.
Location
%plesk_dir%\bin\pleskrestore
where %plesk_dir% is an environment variable for Panel installation
directory. By default, it is "C:\Program Files\Parallels\Plesk\".
Usage
pleskrestore <command> [<arguments>] [<options>]
Commands
Options
Page 99

Backing Up, Restoring, and Migrating Data 99
Migrating Data
You can migrate data to Parallels Plesk Panel 11.0.0 from other servers managed by
Panel 10 or earlier by using the Panel's Migration Manager function. This function is
available in Server Administration Panel > Tools & Settings > Migration Manager if the
corresponding component is installed on the server. This component is not included in
typical installations.
For detailed information about migrating data to Panel-managed servers, refer to
Parallels Plesk Panel Installation, Upgrade, and Migration Guide at
http://download1.parallels.com/Plesk/PP11/11.0/Doc/en-US/online/plesk-installationupgrade-migration-guide/.
Page 100

Panel has a built-in mechanism for customizing security settings for Windows objects
In this chapter:
Panel's Security Policies ................................................................................... 101
Windows Accounts Used by Panel to Manage Windows Objects ...................... 101
Windows Accounts Used by Panel to Manage Hosted Windows Objects .......... 104
Administering Windows Objects Security on Panel-managed Server ................ 105
Restoring Disk User Permissions ...................................................................... 125
C H A P T E R 6
Changing Security Settings for File System Objects and Accounts
on the server disks. You can specify security rules and then have Panel automatically
apply the rules to Windows object security settings. The security files are easily
accessible, and once you understand the logic of their use, you will be able to
customize security settings on any folder or file found on a Panel-managed server.
Incorrect security settings on Windows objects found on Panel-managed servers may
result in a number of server problems including but not limited to unavailability of site
applications and services. We recommend that you become acquainted with this
section before attempting to modify security settings on folders and files found on
Panel-managed server.
Panel creates different Windows user accounts to manage servers and to serve
Internet requests by IIS. Panel has to assign the user accounts necessary permissions
to access and manage Windows objects on managed servers. When assigning user
account permissions, Panel exercises two different security policies towards Windows
objects - Disk security and Hosting security. Security settings for all Windows objects
on a Panel-managed server are initially configured according to the policies during
Panel installation. Compliance with the policies ensures maximum security without
compromising server performance. The Windows objects security settings can be
further customized. To manage object security settings, Panel uses a flexible system
based on Panel's own security metadata files and the DACL inheritance mechanisms
implemented in Windows. Security settings can be customized by using the security
metadata files and command-line utilities that are distributed with Parallels Plesk Panel.
Warning: Before making any changes to the security metadata, make a backup copy
of the metadata file that you want to modify. For information why backing up security
metadata files before modifying them is a good idea, see the sections Customizing Disk
Security (on page 110) and Customizing Hosting Security (on page 111).
 Loading...
Loading...