Panasonic X300 Service Manual
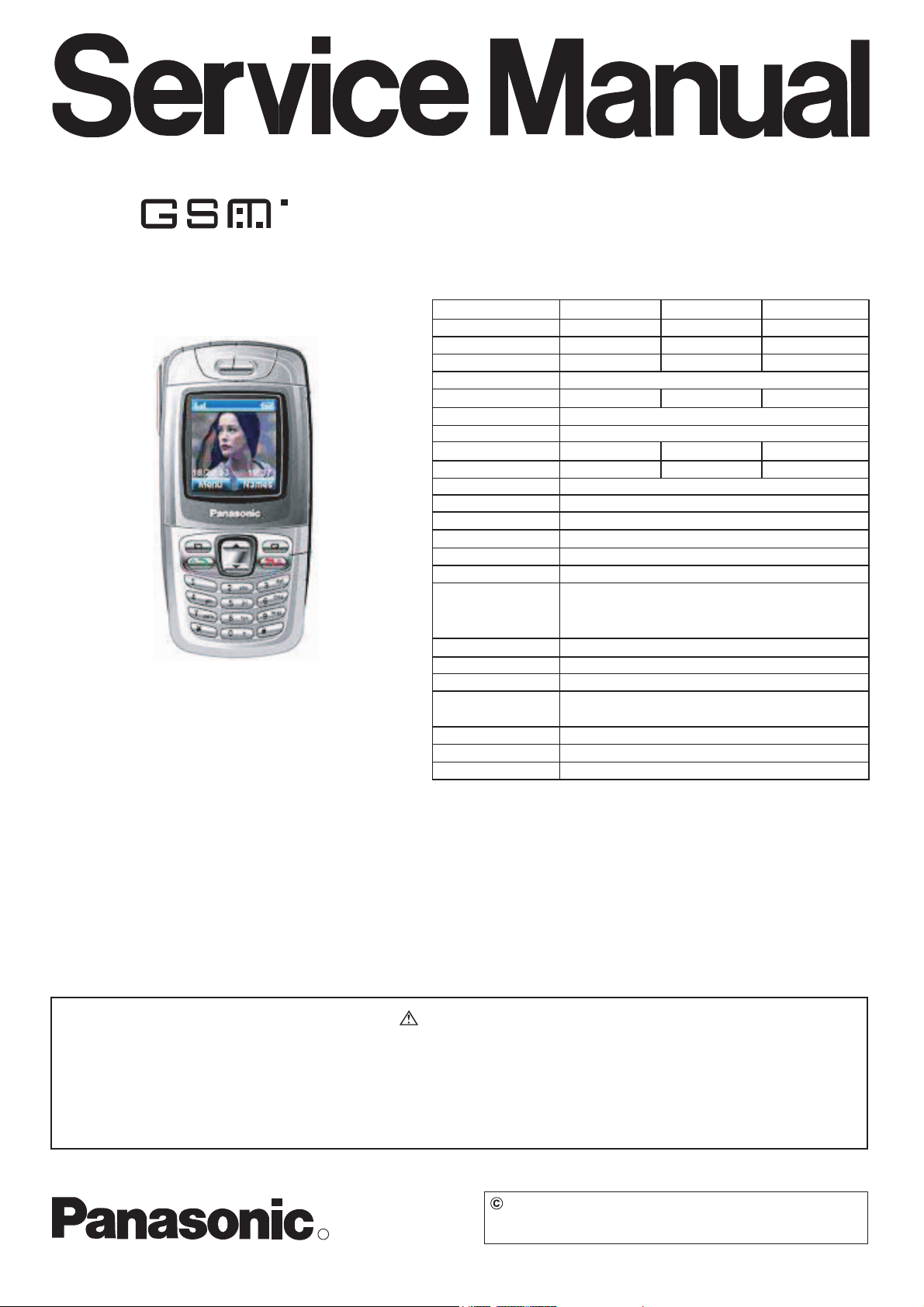
ORDER NO. OMTD0406xxC8
Personal Cellular Telephone
EB-X300
900 MHz 1800 MHz 1900 MHz
Tx Frequency Range: 880 - 915 MHz 1710 -1785 MHz 1850 -1910 MHz
Rx Frequency Range: 925 - 960 MHz 1805 -1880 MHz 1930 -1990 MHz
Tx / Rx separation 45 MHz 95 MHz 80 MHz
RF Channel Bandwidth 200 kHz
Number of RF channels 174 374 300
Speech coding Full rate / Enhanced Full rate
Operating temperature -10
Type Class 4 Handheld Class 1 Handheld Class 1 Handheld
RF Output Power 32 dBm maximum 29 dBm maximum 29 dBm maximum
Modulation GMSK
WAP / GPRS WAP 2.0 / GPRS class 8
Connection 8 ch / TDMA
Voice digitizing 13 kbps RPE-LTP / 13 kps ACLEP
Transmission speed 270.833 kbps
Signal Reception Direct conversion
Dimensions Height : 71.9 mm
(Excluding antenna)
Weight 80
Keys 17 Physical Keys, 2-Way Navigation key
SIM 3 V Plug-in type only
External DC Supply 3.8 V
Voltage
Battery Standard Li-Ion 780mAh
Standby Time 78.3 - 230 hrs (
Talk Time 1.6 - 8.0 hrs (
(
∗
) The network being used, SIM card usage, and the condition of the battery affect Battery life.
°
C to +55 °C
Width : 38.8 mm
Depth : 22.0 mm
g
(including battery)
∗
)
∗
)
WARNING
This service information is designed for experienced repair technicians only and is not designed for use by the general public.
It does not contain warnings or cautions to advise non-technical individuals of potential dangers in attempting to service a
product.
Products powered by electricity should be serviced or repaired only by experienced professional technicians. Any attempt to
service or repair the product or products dealt with in this service information by anyone else could result in serious injury or
death.
2004 Panasonic Mobile Communications Co., Ltd.
All rights reserved. Unauthorized copying and
R
distribution is a violation of law.

COMPANY LIABILITY
Every care has been taken to ensure that the contents of this manual give an accurate representation of the equipment.
However, Panasonic Mobile Communications Co., Ltd. accepts no responsibility for inaccuracies which may occur and reserves
the right to make changes to the specification or design without prior notice. The information contained in this manual and all
rights in any design disclosed therein, are and remain the exclusive property of Panasonic Mobile Communications Co., Ltd.
Other patents applying to material contained in this publication:
CP8 PATENTS
Comments or correspondence concerning this manual should be addressed to:
Panasonic Mobile Communications Co., Ltd.
600, Saedo-cho, Tsuzuki-ku, Yokohama, 224-8539, Japan
CONTENTS
1. INTRODUCTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
1.1. Purpose of the Manual. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
1.2. Structure of the Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
1.3. Servicing Responsibilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
2. GENERAL DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
2.1. General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
2.2. Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
2.3. Handportable Main Kits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
3. OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.1. General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.2. Liquid Crystal Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.3. Location of Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
3.4. Concept of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
3.5. Alpha Entry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
3.5.1. Character Set / Key Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
3.5.2. Editing Alpha Entry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
3.6. Menu Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
3.7. Incoming Call Line Identification (CLI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
3.8. Public Man Machine Interface (MMI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
3.8.1. General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
3.8.2. Reading the Phonebook Memory Location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
3.8.3. Presentation of IMEI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
3.8.4. Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
3.8.5. Call Hold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
3.8.6. Call Waiting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
3.8.7. Call Line Identification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
3.8.8. Telecommunication Services used for Public MMI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
3.8.9. Call Divert . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
3.8.10. Call Bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
3.9. Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
3.10. Important Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-10
3.11. Security Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-10
3.12. Glossary of Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
i

4. TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
4.1. Tx Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4.1.1. Frequency Error . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-1
4.1.2. Modulation Phase Error . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4.1.3. Output RF Spectrum due to Modulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4.1.4. Output RF Spectrum due to Switching Transients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4.1.5. Spurious Emissions at Antenna Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
4.1.6. Residual Peak Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-2
4.2. Rx Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
4.2.1. Sensitivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4-2
5. TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
5.1. RF Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
5.1.1. RF Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5-1
5.1.2. RF Function Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
5.1.3. Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
5.2. Baseband Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
5.2.1. Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
5.2.2. Digital Baseband Processor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
5.2.3. Keypad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-8
5.3.4. Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-8
5.3.5. CPU Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
5.3.6. LCD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
5.3.7. Real Tim Clock (RTC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
5.3. Audio System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-10
5.3.1. Voiceband Baseband Codec . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-10
5.3.2. Microphone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-11
5.3.3. Receiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-12
5.3.4. Loud Speaker . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-12
5.4. Power Management Subsystem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-13
5.4.1. Power Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-13
5.4.2. Regulator Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-13
5.4.3. Voltage Regulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-13
5.5. Battery Charging and Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-15
5.5.1. Charging Current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-15
5.5.2. Deeply Discharged Batteries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-15
5.6. Test Point . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-16
5.6.1. Test Point Layout. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-17
6. DISASSEMBLY / REASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
6.1. General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
6.1.1. Call Bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
6.2. Disassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
6.3. Reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-11
7. REPAIR PROCEDURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
7.1. Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
7.2. Lead Free (PbF) solder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
7.3. External Testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7-1
7.3.1. General Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
7.4. Test Equipment Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
7.4.1. Equipment Required . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
ii

8. SOFTWARE DOWNLOAD & ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-1
8.1. Service Software Upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8-1
8.2. MMI Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-3
8.3. Adjustment Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-4
8.3.1. Equipment Setting for TX/RX adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-4
8.3.2. Main Subjects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-4
8.3.3. Test Operation Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-5
8.3.4. Enter Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-5
8.3.5. TX Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-6
8.3.6. RX Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-9
8.3.7. Battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-11
9. REPLACEMENT PARTS LIST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-1
9.1. Exploded View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-1
9.2. Case and Cover Parts List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2
9.3. Main PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
10. BLOCK DIAGRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-1
10.1. Baseband . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-1
10.2. RF Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-2
11. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-1
11.1. Baseband . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-1
11.2. RF Band . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-2
11.3. Analogue Baseband and Power Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-3
11.4. LCD and Camera . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11-4
12. LAYOUT DIAGRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12-1
12.1. Main PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12-1
iii
1. INTRODUCTION
WARNING
The equipment described in this manual contains polarised capacitors utilising liquid electrolyte. These devices are entirely safe provided
that neither a short-circuit nor reverse polarity connection is made across the capacitor terminals. FAILURE TO OBSERVE THIS WARNING
COULD RESULT IN DAMAGE TO THE EQUIPMENT OR, AT WORST, POSSIBLE INJURY TO PERSONNEL RESULTING FROM
ELECTRIC SHOCK OR THE AFFECTED CAPACITOR EXPLODING. EXTREME CARE MUST BE EXERCISED AT ALL TIMES WHEN
HANDLING THESE DEVICES.
Caution
The equipment described in this manual contains electrostatic devices (ESDs). Damage can occur to these devices if the handling
procedures described in Section 4 are not adhered to.
Caution
This equipment may contain an internal battery in addition to the external battery packs. These batteries are recyclable and should be
disposed of in accordance with local legislation. They must not be incinerated, or disposed of as ordinary rubbish.
1.1. Purpose of the Manual
This Service Manual contains the information and procedures required for installing, operating and servicing the Panasonic
GSM Personal Cellular Mobile Telephone system operating on GSM Digital Cellular Networks.
1.2. Structure of the Manual
The manual is structured to provide service-engineering personnel with the following information and procedures:
1. General and technical information - provides a basic understanding of the equipment, kits and options, together with detailed
information for each of the major component parts.
2. Installation and operating information - provides instructions for unpacking, installing and operating the equipment.
3. Servicing information - provides complete instructions for the testing, disassembly, repair and reassembly of each major
component part. Step-by-step troubleshooting information is given to enable the isolation and identification of a malfunction,
and thus determine what corrective action should be taken. The test information enables verification of the integrity of the
equipment after any remedial action has been carried out.
4. Illustrated parts list - provided to enable the identification of all equipment components, for the ordering of spare /
replacement parts.
1.3. Servicing Responsibilities
The procedures described in this manual must be performed by qualified service engineering personnel, at an authorised
service centre.
The service engineering personnel are responsible for fault diagnosis and repair of all equipment described in this manual.
– 1-1 –

2. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
2.1. General
This section provides a general description and kit composition details for the GSM Handportable Telephone System
and optional kits.
2.2. Features
The Panasonic Telephone Model EB-X300 is a high performance, small, light, handset for business and domestic use.
The following features are provided:
■ Dual Codec, which includes Full Rate and Enhanced Full Rate (EFR) Speech Codec.
■ Triple Band, E-GSM 900 and PCS 1800 /1900 operation.
■ Tegic T9 Text Entry.
■ Voice Ringer.
■ Desktop handsfree function comprising integral echo cancellation and noise suppression.
■ Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) Browser.
■ Backup Battery.
■ Downloadable polyphonic melody ring tones.
■ Clock, Calculator and Currency Converter.
2.3. Handportable Main Kit
Personal
Handsfree
Travel ChargerBattery
EB-X300
Data Cable
Figure 2.1: Handportable Main Unit Kit Contents
– 2-1 –

3. OP E R ATING INS TR UC TIONS
3.1. G eneral
This s ection provides a brief guide to the opera tion a nd facilities available on the telephone handset.
R efer to the O perating Ins tructions s upplied with the telephone for full operational information.
3.2. L iquid C rys tal Dis play
The telephone handset has a graphica l chip on glas s display. The following icons are a vailable:
S tatus Icons
F igu re 3.1: L iqu id C ry s tal Dis play
Icon Des cription
The received s igna l s trength indication Ð No C HP S ; : L ine1; : Line2
Indicated the ba ttery level / L ow B attery:
Dis played when the us er is regis tered to a non-home network-roaming
Dis played when call divert is enabled Ð No C PHS ; : Line1; : Line2; : Line1 &
Line2
Dis played when phone lock is enabled
Dis played when a n unrea d mes sage is s tore or lights when mes sage a rea is full
Voice ma il indica tor
Voice ma il icon
Indicated a larm is s et
Dis played when vibration a lert is enable
Dis played when all tones or ring volume is off
– 3-1 –

3.3. Location of Controls
Receiver
Display
Phone Jack & Charger Connection
The Phone Jack can be used as data transmission port to perform download and test tasks.
– 3-2 –

3.4. Concept of Operation
There is a close relationship between the Select keys, Navigation key and display.
Main Display
Right Hand SelectionLeft Hand Selection Area
Navigation Key
Send / answer Key
Navigation Key: moving up and down through the options in the display area. In idle mode, pressing to enter Own Menu.
Own Menu is a shortcut to access your favourite menus. You can set it in the Personalise.
Soft keys: Perform the functions indicated by text shown on the LCD screen. In idle, long press left soft key to enter Messages,
long press right soft key to enter Profile Mode List.
Numeric key pads: Long Press <+> to enter a "+" or "P". When you need to dial an extension number, dial the phone number
firstly then long press <+> to add a "P" and enter the extension number.
Send/Answer Key: Make a call or answer a call. In idle mode, check the last dialled list.
Soft Key
Power / End Key
Power/End Key: To end a call, return to idle mode, return to previous menu or reject an incoming call.
Long press it to switch the phone on/off.
<
∗> In idle, long press to activate Browser.
<#> In idle, long press to switch the Mute Mode on and off.
– 3-3 –
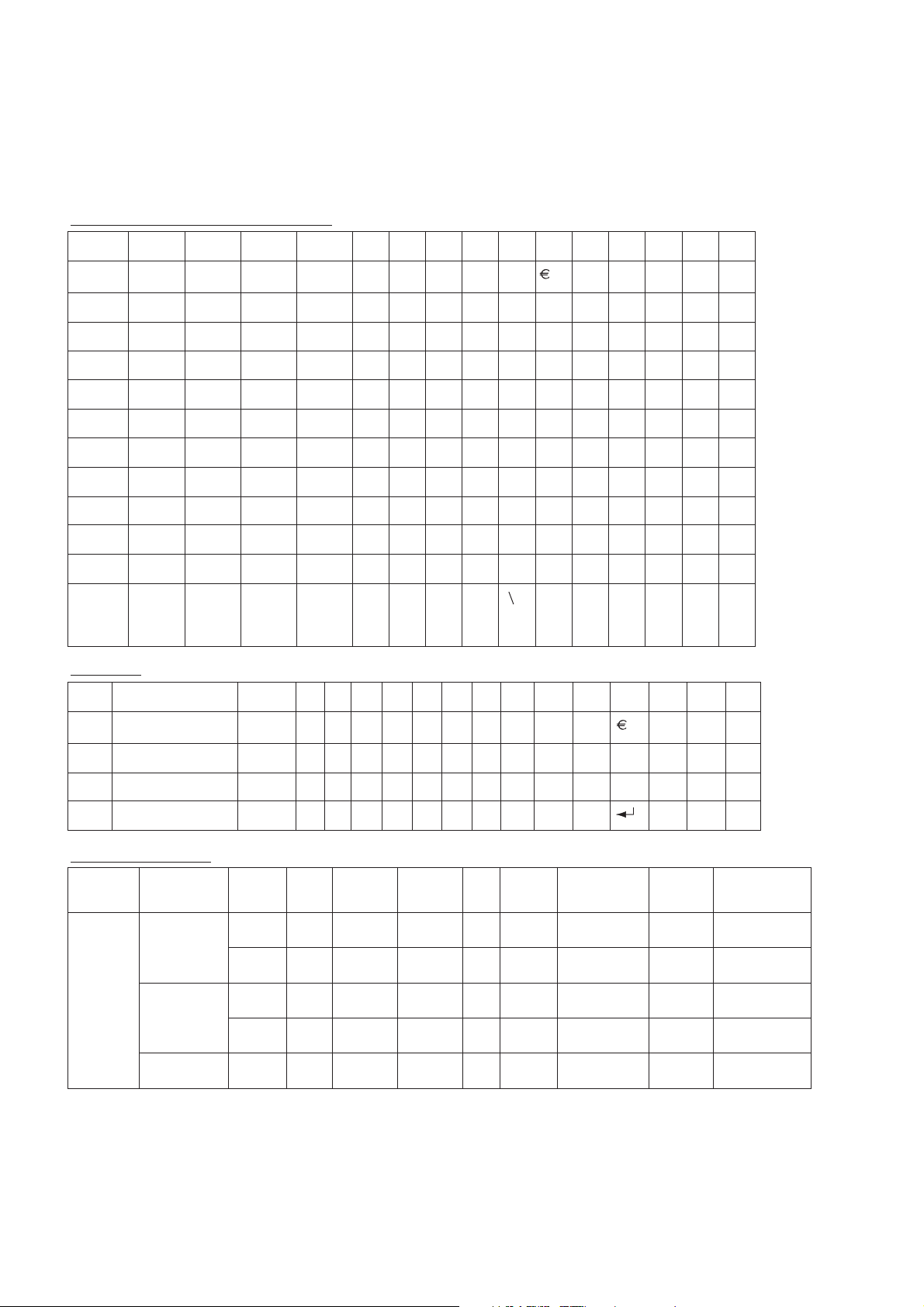
3.5. Alpha Entry
3.5.1. Character Set / Key Assignments
Alpha entry is used to enter alphanumeric characters in to the Phonebook, Short Message and Greeting Message areas.
Alphabetic, small / capital letter mode :
Key 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15.
11 / ( ) <=>%
22äà
a / A
d / D
33éè
4
g / G
j / J
55
66öñ
m / M
77ß
p / P
t / T
88üù
9z9æøå
w / W
∗∗ ΘΛΓ∆ ΞΠΣΦ
0 Space 0 . , ? ! + - : ¿ ¡ " ' ; _
#T9
on/off
mode
T9 mode :
Key 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16.
b / B
e / E
h / H
k / K
n / N
q / Q
u / U
x / X
Space # £ $ ¥ ¤ @
c / C
f / F
i / I
l /L
o / O
r / R s / S
v / V
y / Y
4ì
ç
ò
~
&
Ω
Ψ
§^I
1/()<>[]{%}~&
1
∗
∗ Γ∆ΘΛΞΠΣΦΨ Ω
0
Space .0?,!+-=:¿¡"';_
#
T9 on/off mode $£¥@¤Space # \ § ^ |
T9 Editor Sequence :
Key T9 Editor
Sequence
<Send>
• Key 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 long press provides corresponding numbers.
• All other keys are used for Tegic T9 intelligent text mapping.
• TC : Traditional Chinese; SC: Simplified Chinese; BPMF : Input method of Traditional Chinese
• The thirteenth character of Key 0 only exits in SMS editor.
• The Thai multitap only exists when Thai language exist and the mapping switch on it.
TC
SC
Thai
Tegic
mode
T9 on
T9 off
T9 on
T9 off Abc abc ABC 123 BPMF
T9 off Abc abc ABC 123 Thai
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
T9
AbcT9abc
T9
AbcT9abc
T9
AbcT9abc
T9
ABC
T9
ABC
T9
ABC
123 BPMF
123 BPMF
123 BPMF
StrokeTC
StrokeTC
StrokeTC
StrokeTC
7.
PinYin
PinYin
PinYin
PinYin
8.
StrokeSC
StrokeSC
Stroke_S
StrokeSC
– 3-4 –
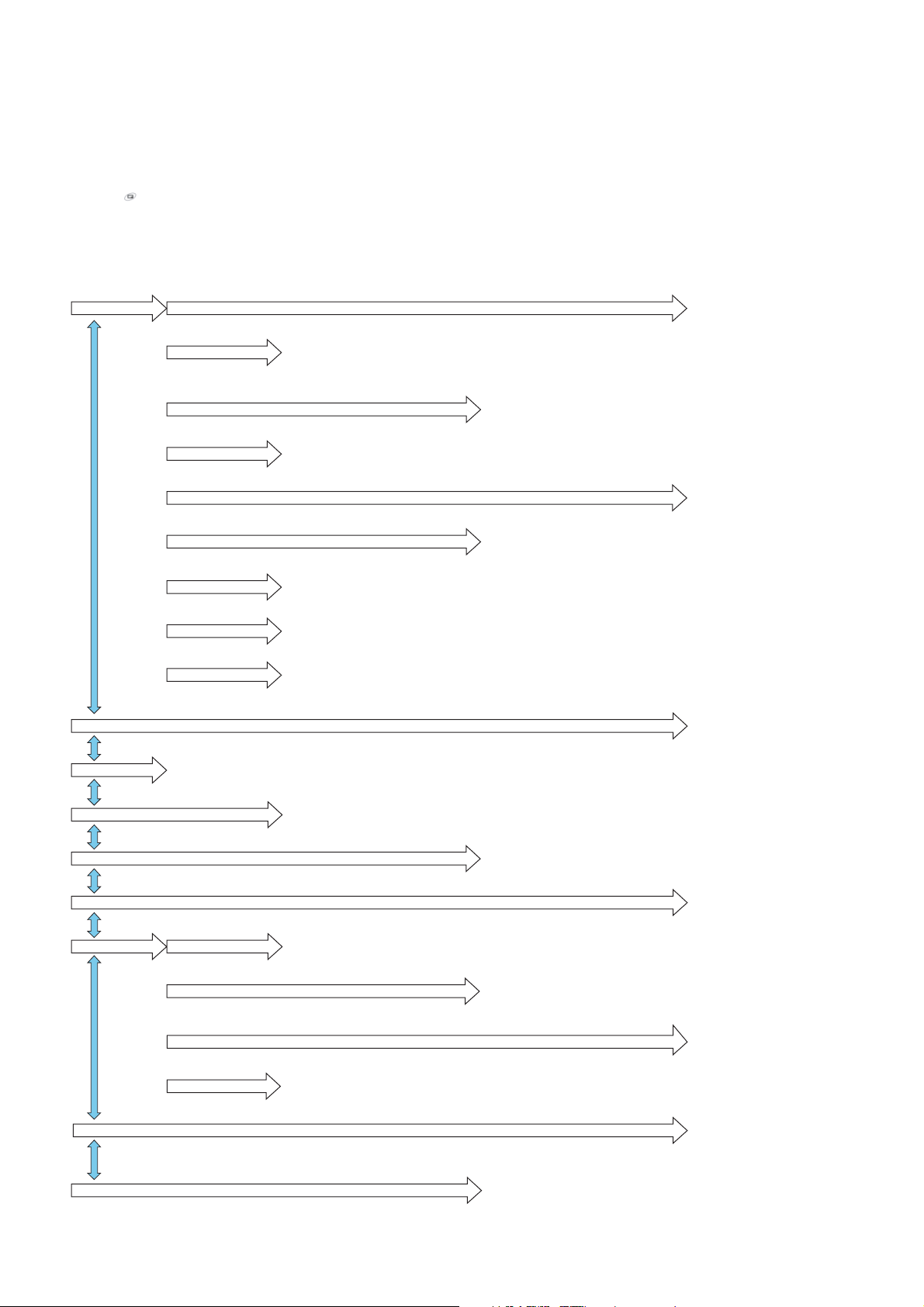
3.5.2. Editing Alpha Entry
Pressing will move the cursor up or down one line. Pressing will move the cursor left or right one character.
When the cursor is moved over a character and another key pressed will insert the new character.
Pressing will delete the character to the left of the character.
3.6. Menu Structure
My Phone
Contacts
Game
Browser
My Media
Sounds
Display
Language
Alerts
Profiles
Auto answer On/Off
Any key answer On/Off
Auto key lock On/Off
Shortcuts
Defaults
Puddieland
Quadball
Exode
Volume
Ringtones
Keytone
Warning tone
Warning Shutter sound
Shutter sound
T9 Input
Display Ianguages
Start browser
Bookmarks
Settings
Push setting
Connectivity
Wallpaper
Greeting
Animation
Contrast
Brightness
Colour themes
Hide network name
Normal
Quiet
Outdoors
Headset
Meeting
Customer
My Pictures
My Sounds
My Videos
User1
User2
User3
User4
Memory status
Ring only
None
Ring & Vibrate
Vibrate only
Ring once
Browse
Greate
Groups
SDN
Memory status
My Numbers
Hotkey dial
My Contacts
Camera
Messages
Phone Menu
Records
Applications
Call Service
Call Diverts
Security
Network
Tome/Charge
Call waiting
Withhold ID
Caller's ID
Charge setting
Auto net work
New network
Network list
Band Select
– 3-5 –
Video
Camera
All voice calls
Not reachable
Noe reply
Busy
Status check
Calendar
Scheduler
Notes
Clock
Calculator
Currency
Melody Composer
Create
Inbox
Outbox
User Messages
Memory Status
Settings
Connectivity
Cell Broadcast
Call bar
Code
Fixed dial
SIM lock
Last dialled
Answered
Unanswered
Delete records

3.7. Incoming Call Line Identification (CLI)
When a call is received the last eight digits of the CLI information is matched with the phonebook.
Therefore an incoming call could be matched to the wrong phonebook entry.
3.8. Public Man Machine Interface (MMI)
3.8.1. General
It is possible to operate all GSM telephones in the same way using the Public MMI. The following operations will work with all
GSM telephones. However, this information is restricted to those operations supported by the telephone.
The * and # in the following procedures should be replaced by and respectively. Also <SND> and <END> should be
replaced with and keys.
3.8.2. Reading the Phonebook Memory Location
# <MEMORY LOCATION>
Leading zeros can be left out of the location number, e.g. 007 can be 7.
3.8.3. Presentation of IMEI
* # 0 6 #
3.8.4. Security
Change PIN * * 0 4 * <OLD PIN> * <NEW PIN> * <NEW PIN> #
Change PIN2 * * 0 4 2 * <OLD PIN2> * <NEW PIN2> * <NEW PIN2> #
Unblock PIN * * 0 5 * <PIN UNBLOCKING KEY> * <NEW PIN> * <NEW PIN> #
Unblock PIN2 * * 0 5 * <PIN2 UNBLOCKING KEY> * <NEW PIN2> * <NEW PIN2> #
3.8.5. Call Hold
Place a Call on Hold 2 <SND>
Recall a Held Call 2 <SND>
Make a Second Call <TELEPHONE NUMBER>?<SND>
Swap between two Held Calls 2 <SND>
End Held Call 0 <SND>
End Active Call 1 <SND>
Reject Incoming Call 0 <SND>
3.8.6. Call Waiting
Enable Call Waiting *43 * <SND>
Disable Call Waiting #43 * <SND>
Call Waiting Status * # 4 3 * # <SND>
– 3-6 –

3.8.7. Call Line Identification
Feature Service Code
Calling Line Identification Presentation (CLIP) 30
Calling Line Identification Restriction (CLIR) 31
Connected Line Presentation (CLOP) 76
Connected Line Restriction (CLOR) 77
Enable * <SERVICE CODE> * # (SND>
Disable # <SERVICE CODE> * # (SND>
Temporary Suppress Identification # 31 # <TELEPHONE NUMBER> <SND>
Temporary Display Identification * 31 # <TELEPHONE NUMBER> <SND>
3.8.8. Telecommunication Services used for Public MMI
Teleservice
Service MMI Service Code
All teleservices 10
Telephony 11
All data teleservices 12
Facsimile services 13
Short Message Service (SMS) 16
All teleservices except SMS 19
Voice group service 17
Bearer Service
Service MMI Service Code
All bearer services 20
All asynchronous services 21
All synchronous services 22
All data synchronous services 24
All data asynchronous services 25
All dedicated packet access 26
All dedicated PAD access 27
– 3-7 –
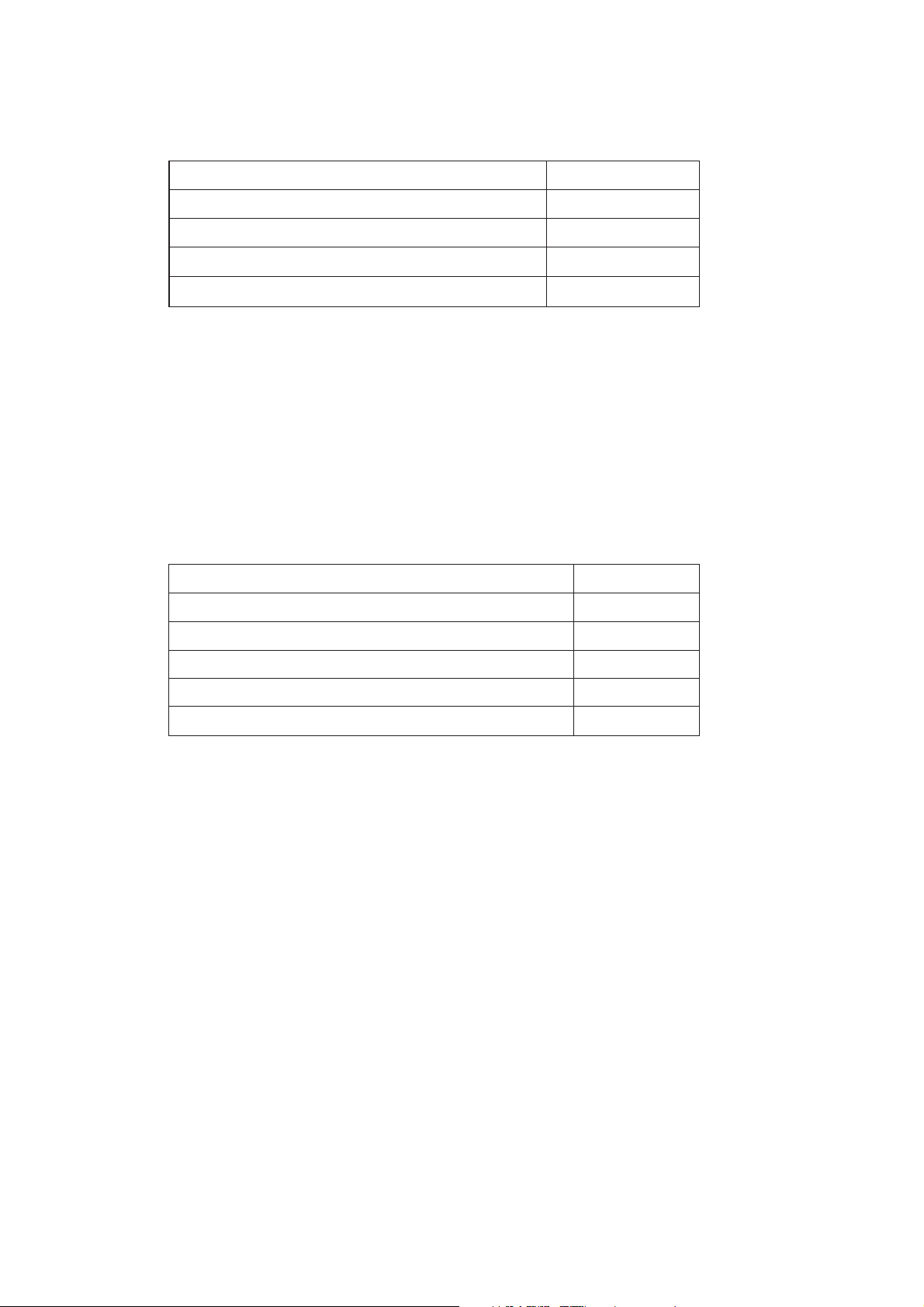
3.8.9. Call Divert
Call Divert Type Service Code
Divert all calls 21
Divert all calls if busy 67
Divert all calls if no reply 61
Divert if not reachable 62
Set Call Bar * * <SERVICE CODE> * <FORWARD TELEPHONE NUMBER> *
(Except "No Reply") <TELECOMMUNICATION SERVICE> # <SND>
Set "No Reply" Call Bar * * <SERVICE CODE> * <FORWARD TELEPHONE NUMBER> *
<TELECOM' SERVICE> * <TIME TO RING (sec)>#<SND>
Clear # # <SERVICE CODE> * <TELECOMMUNICATION SERVICE> * # <SND>
Status * * # <SERVICE CODE> * <TELECOMMUNICATION SERVICE> * # <SND>
Clear all Call Diverts # # 002 #
3.8.10. Call Bar
Call Bar Type Service Code
All outgoing calls 33
Outgoing International calls 331
Outgoing International calls except those to the PLMN 332
All incoming calls 35
Incoming international calls when roaming 351
Set * <PASSWORD> * <TELECOMMUNICATION SERVICE> # <SND>
Clear # <TELECOMMUNICATION SERVICE> # <SND>
Status # <TELECOMMUNICATION SERVICE> # <SND>
Clear all Call Bar Type # 330 * <PASSWORD> # <SND>
Change Call Bar Password * * 03 * * <OLD PASSWORD> * <NEW PASSWORD> * <NEW PASSWORD # <SND>
– 3-8 –
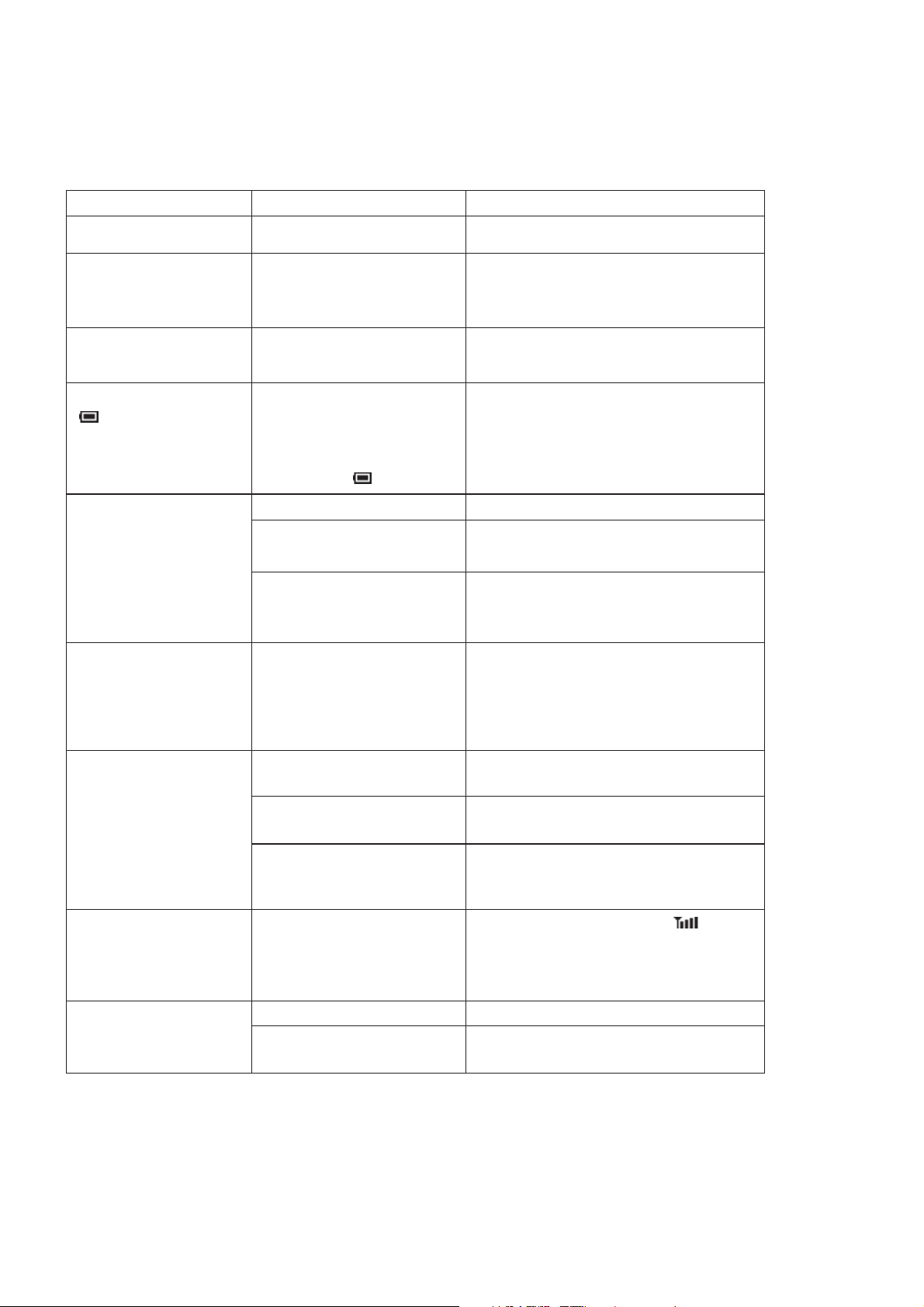
3.9. Troubleshooting
The user is given the following information and advised to contact the dealer if the problems persist:
Problem Cause Remedy
Telephone will not switch on Ensure batteries are fully charged.
Extremely short battery life
for a new battery pack
Short battery life for an
old battery pack
The battery level indicator
does not light when
charging
Calls cannot be made
Calls cannot be made from
Fixed Dial Store
The network in use and the
condition of the battery pack can
affect battery life.
The battery pack was worn out. Replace with a new one.
If a battery is deeply discharged
it will take a short time before
there is sufficient power in the
telephone to light the battery
level indicator .
The telephone is locked. Unlock the telephone.
Outgoing calls are barred. Disable the outgoing call barring
The telephone is not registered
to a network.
Avoid areas of poor reception. Ensure
batteries fully charged.
Leave to charge for several minutes in
temperatures between +5 °C and +35 °C
(Phone Option: Security: Call bar).
Move to a coverage area and operate the
telephone after it has registered with a
network.
Check that SIM supports Fixed Dial
Check if the Fixed Dial is switched on
(Phone Operation: Security: Fixed Dial).
Check the telephone number is stored in the
Fixed Dial.
Calls cannot be received
Emergency calls cannot be
made
be recalled
The telephone is not switched
on.
Incoming calls are barred. Disable the incoming call barring (Phone
The telephone is not
registered to a network.
User's phone is not in a GSM
coverage area.
The telephone is locked. Unlock the telephone.Telephone numbers Cannot
Fixed Dial is switched on Switched off Fixed Dial
Switch the telephone on.
Option: Security: Call Bar).
Move to a coverage area and operate the
telephone after it has registered with a
network.
Check that the antenna symbol is
displayed. Move to a coverage area and
operate the telephone when the antenna
symbol is displayed.
(Phone Option: Security: Fixed Dial).
– 3-9 –
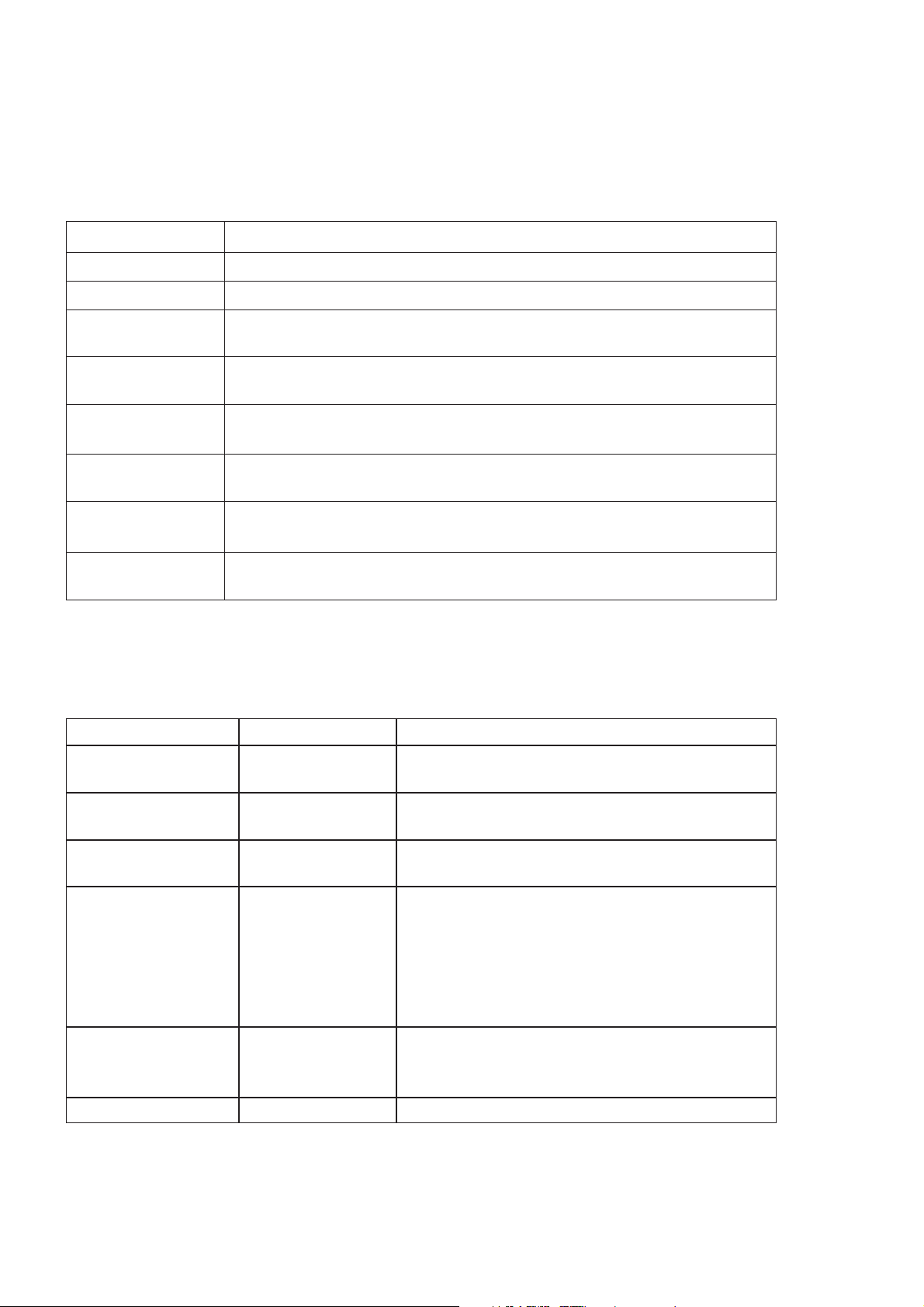
3.10. Important Error Messages
The following table is a list of error messages that may occur during use of the telephone, with a description and suggested
course of action:
Error Message Explanation / Remedy
Area not Allowed Roaming in the selected area is not allowed.
Network not allowed Roaming with the selected network is not allowed.
Security Failure The network has detected authentication failure because the SIM is not registered with
that network. Contact the Service Provider.
SIM Blocked The SIM is blocked because the wrong PUK has been entered 10 times.
Contact the Service Provider.
SIM Error The telephone has detected a problem with the SIM. Switch the telephone off and then
back on. If the message does not disappear, contact the Service Provider.
Message Rejected
Store Full
PIN2 Invalidated The PIN2 is blocked permanently because the wrong PUK2 has been entered 10
Warning Store Full
Continue?
A message has been received but the message store is full. To receive messages,
delete some of the currently stored messages.
times. Services controlled by PIN2 cannot be used. Contact the Service Provider.
The message area is full. New messages cannot be stored unit some of the currently
stored messages are deleted.
3.11. Security Codes
Code Type Number or Digits Description
Personal Identification
Number (PIN)
PIN2 4 to 8 Controls memory security. Supplied by the service provider.
PIN/PIN2 Unblocking
Key
(PUK/PUK2) 8 Used to unblock PIN and PIN2. A PIN or PIN2 will become
4 to 8 Controls SIM security. Supplied by the service provider.
Supplied by the service provider.
blocked if the wrong PIN or PIN2 is entered three times.
When the blocked PIN or PIN2 is unblocked, a new PIN or
PIN2 must be entered.
If the wrong PUK or PUK2 is entered 10 times, the cursor
SIM will be unusable.
Password 4 Controls the call bar function. If the wrong password is
entered three times, this service will be revoked.
Supplied by the service provider.
Phone Lock Code 4 to 8 Controls telephone security.
– 3-10 –
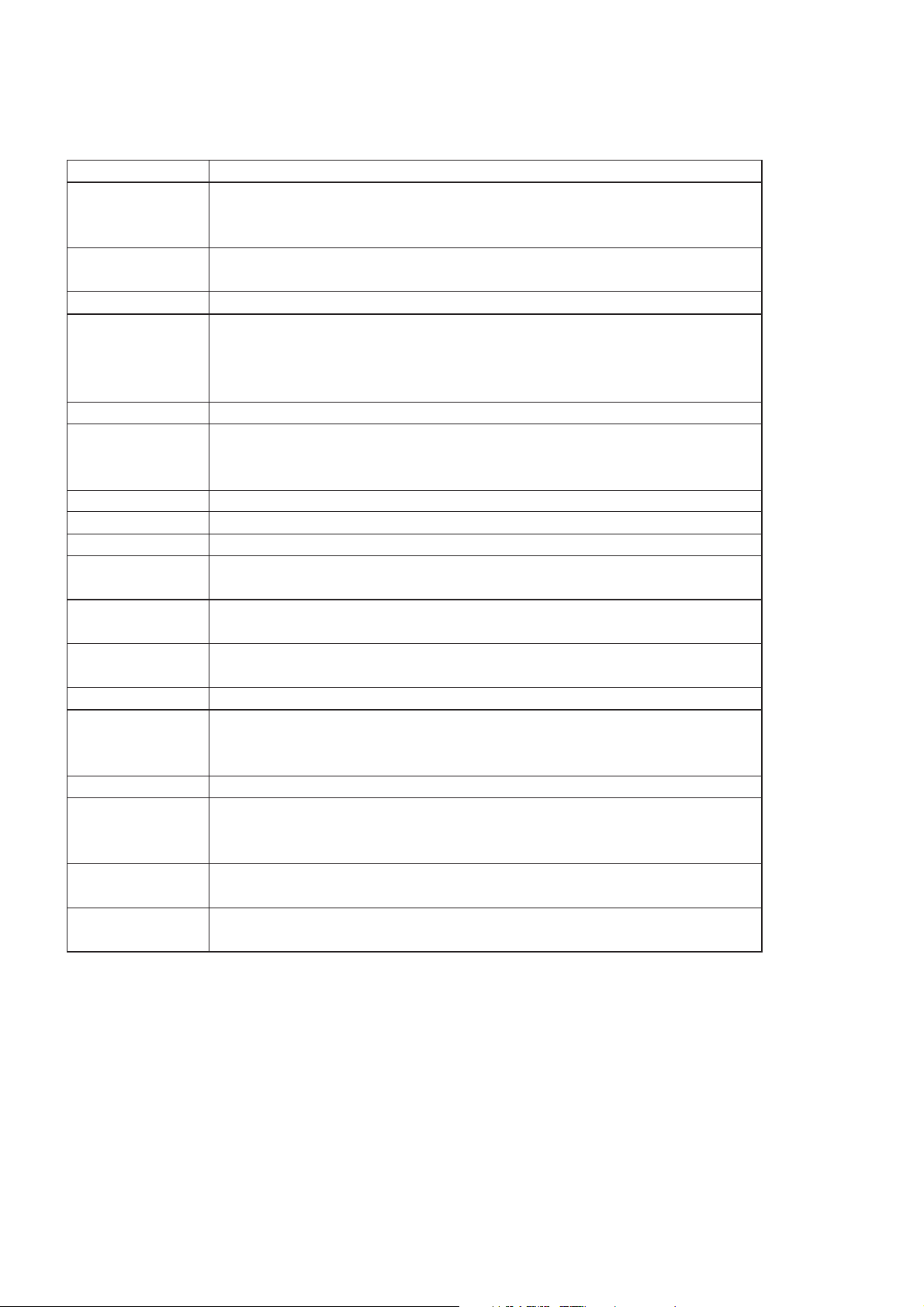
3.12. Glossary of Terms
Term Definition
DTMF Dual Tone Multiple Frequency tones. The numeric keys 0 to 9, and * and # will generate
different DTMF tones when pressed during conversation. These are used to access
voice mail, paging and Home banking services.
GSM Global System for Mobile communications. The name given to the advanced digital
technology that the telephone uses.
Home network The GSM network on which subscription details are held.
Hot Key Dial Hot Key Dial allows quick access to numbers stored in the Phonebook of Service Dial
Number list. The source of the Hot Key Dial may be defined by the user or
preprogrammed by the Service Provide. It is most likely to be preprogrammed to the
Service Dial Numbers by the Service Provider.
Phone Lock code Used for security of the telephone.
Message Centre Where messages are sent before they are forwarded on to their destination. The
Message Centre telephone number may be programmed into the SIM or supplied by
the service provider.
Network operator The organisation responsible for operating a GSM network.
Password Used for the control of the call bar function. Supplied by the service provider.
PIN Personal Identification Number used for SIM security. Supplied by the service provider.
PIN2 Personal Identification Number used for the control of Fixed Dial Memory and call
charge metering. Supplied by the service provider.
PUK / PUK2 PIN/PIN2 Unblocking Key. Used to unblock the PIN/PIN2. Supplied by the service
provider.
Registration The act of locking on to a GSM network. This is usually performed automatically by the
telephone.
Roaming The ability to use the telephone on networks other than the Home network.
Service Dial Service Dial Numbers are predefined numbers that allow the user to access a set of
Numbers special services provided by the Service Provider. For example billing information or
access to Voice Mail.
Service provider The organisation responsible for providing access to the GSM network.
SIM Subscriber Identification Module. A small smart-card which stores unique subscriber
and user-entered information such as Phone Book, Fixed Dial Memory and short
messages. Supplied by the service provider.
Supplementary Network-controlled GSM functions supported by the telephone. Supplementary services
Service may only be available on a subscription basis.
Wild numbers Spaces in a stored telephone number. When the telephone number is recalled pressing
a numeric key will fill in a space. This can be used to restrict dialling to a specific area.
– 3-11 –
4. TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
4.1. Tx Characteristics
All data is applicable to E-GSM 900 and GSM 1800 except where stated.
4.1.1. Frequency Error
±0.1 ppm max., relative to base station frequency.
4.1.2. Modulation Phase Error
RMS: Equal to or less than 5 °
Peak: Equal to or less than 20 °
4.1.3. Output RF Spectrum due to Modulation
Offset from Centre Frequency (kHz)
±100 +0.5
±200 –30
±250 –33
±400 –60
±600 to 1800 –60
4.1.4. Output RF Spectrum due to Switching Transients
Offset from Centre Frequency (kHz)
±400 –19 –22 –22
±600 –21 –24 –24
±1200 –21 –24 –24
±1800 –24 –27 –27
Measurement conditions for output RF spectrum measurements:
Frequency Span 0 Hz
Measurement Bandwidth: 30 kHz
Video Bandwidth: 30 kHz (modulation)
100 kHz (switching)
Average (Modulation) Over 200 burst
Peak Hold (Switching) Over 10 burst
Maximum Level Relative to Carrier (dB)
Maximum Level (dBm)
E-GSM 900 GSM 1800
GSM 1900
– 4-1 –

4.1.5. Spurious Emissions at Antenna Connector
Frequency Range
100 kHz to 50 MHz – 10 kHz 30 kHz –36 –36
50 MHz to 500 MHz – 100 kHz 300 kHz –36 –36
500 MHz to 1 GHz 0 to 1 MHz 100 kHz 300KHz – 36 –36
1 GHz to 12.75 GHz
Excl. relevant TX band :
E-GSM : 880 MHz to 915 MHz
DCS : 1710 MHz to 1785 MHz
-and the Rx bands
925 MHz - 960 MHz
1805 MHz - 1880 MHz
Relevant TX band:
E-GSM : 880 MHz to 915 MHz
DCS :1710 MHz to 1785 MHz
Frequency
offset
0 to 10 MHz
> 10 MHz
> 30 MHz
(offset from edge
of relevant Tx band)
1.8 MHz to 6.0 MHz
> 6.0 MHz
Filter
Bandwidth
100 kHz
300 kHz
3 MHz
30 kHz
100 kHz
Approx
Video B/W
300 kHz
1 MHz
3 MHz
100 kHz
300 kHz
E-GSM 900 GSM1800/1900
–30
–30
–30
–36
–36
4.1.6. Residual Peak Power
Equal to or less than 70 dBc (BW = 300 kHz).
4.2. Rx Characteristics
Limits (dBm)
–30 (1.0 GHz - 1.710 GHz)
–36 (1.710 GHz - 1.785GHz)
–30 (1.785 GHz - 12.75GHz)
–36
–36
4.2.1. Sensitivity
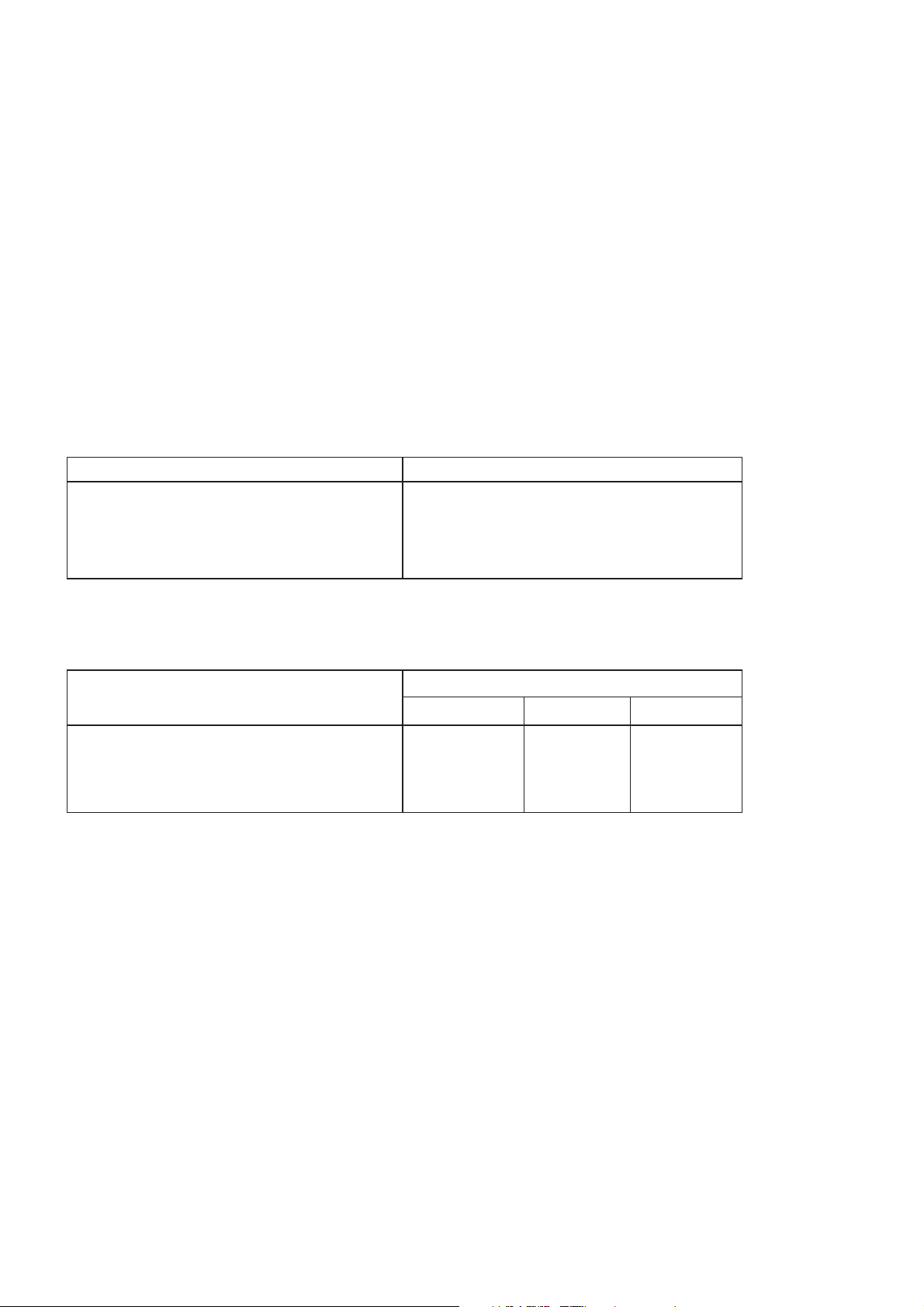
E-GSM 900 Full Rate Speech
The reference sensitivity performance in terms of frame erasure, bit error, or residual bit error rates (whichever is appropriate) is
specified in the following table, according to the propagation conditions.
The reference sensitivity level is < -102 dBm.
NOTE: 1 < α < 1.6. The value of α can be different for each channel condition but must remain the
same for FER and class 1b RBER measurements for the same channel condition.
Channels Propagation Conditions
TU high
TCH/FS FER
Class lb (RBER)
Class ll (RBER)
Test Limit
error rate
%
6.742*α
0.42/α
8.33
Minimum
No of
samples
8,900
1,000,000
120,000
Propagation Conditions
RA
Test Limit
error rate
7.5 24,000 9.333 60,000
%
Minimum
No of
samples
Propagation Conditions
HT
Test Limit
error rate
%
Minimum
No of
samples
Static Conditions
Test Limit
error rate
%
0.122*α
0.41/α
2.439
Minimum
No of
samples
164,000
20,000,000
8,200
– 4-2 –
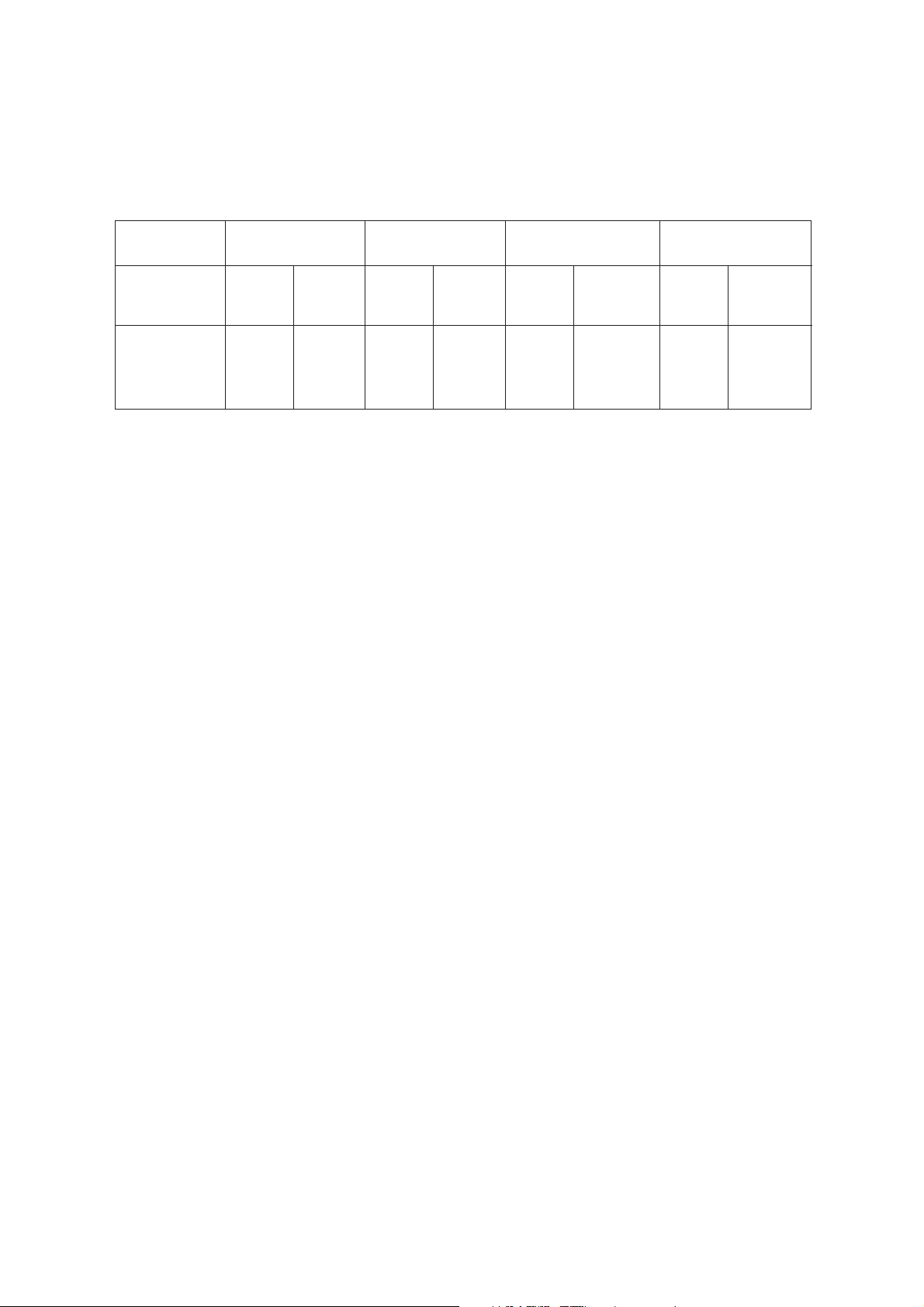
GSM 1800/1900 Full Rate Speech
The reference sensitivity performance in terms of frame erasure, bit error, or residual bit error rates (whichever is appropriate)
is specified in the following table, according to the propagation conditions.
Channels Propagation Conditions
TU high
Test Limit
error rate
TCH/FS FER
Class lb (RBER)
Class ll (RBER)
The reference sensitivity level is < -102 dBm.
NOTE: 1 < α < 1.6. The value of α can be different for each channel condition but must remain the same for FER and class 1b
RBER measurements for the same channel condition.
4.478*α
0.32/α
8.333
%
Minimum
No of
samples
13400
1,500,000
60,000
Propagation Conditions RAPropagation Conditions
HT
Test Limit
error rate
7.5 24,000 9.333 30,000
%
Minimum
No of
samples
Test Limit
error rate
%
Minimum
No of
samples
Static Conditions
Test Limit
error rate
%
0.122*α
0.41/α
2.439
Minimum
No of
samples
164,000
20,000,000
8,200
– 4-3 –
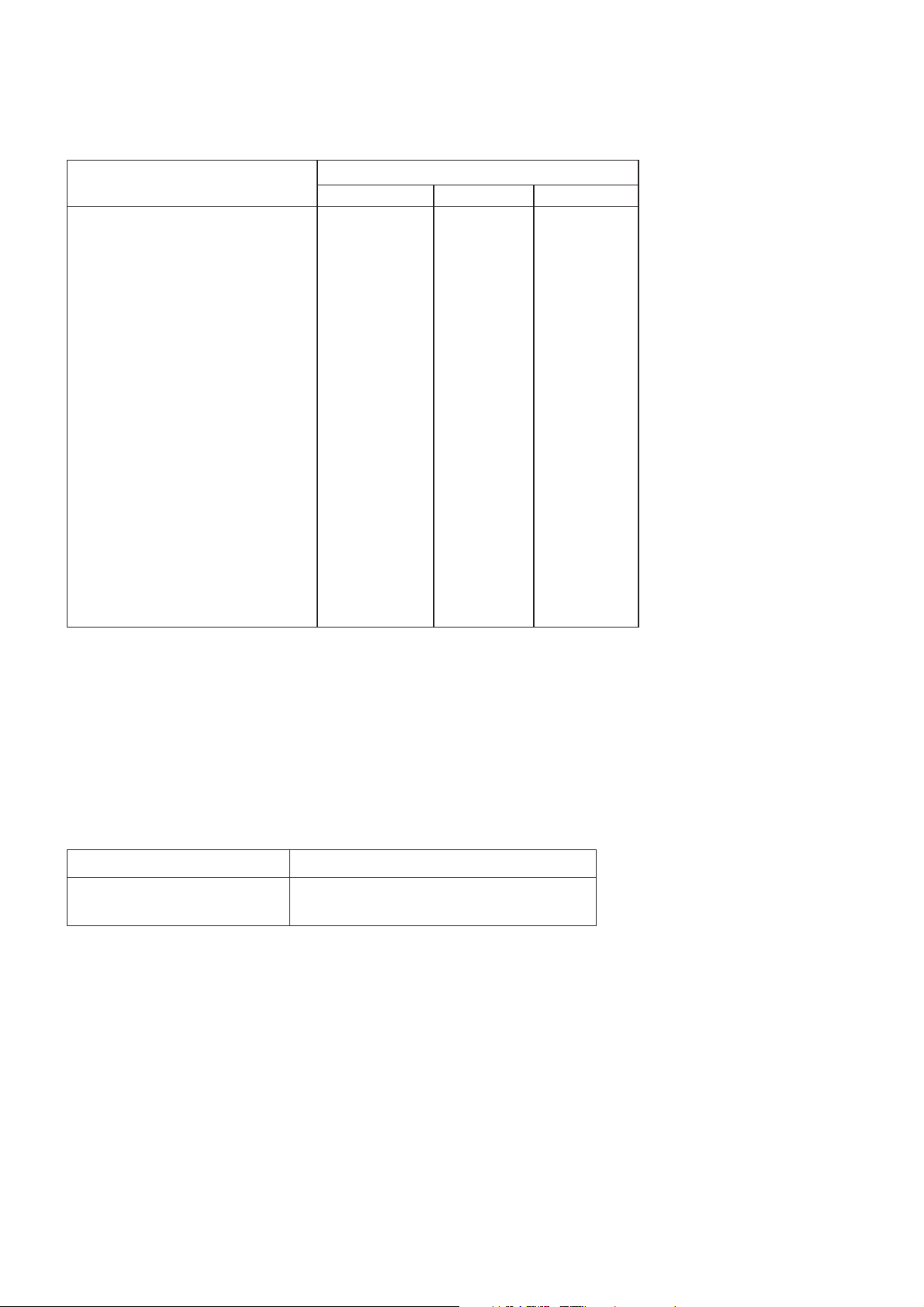
Blocking:
Frequency
±
600 kHz to FR ± 800 kHz
FR
FR ± 800 kHz to FR ± 1.6 MHz
FR ± 1.6 MHz to FR ± 3 MHz
915 MHz to FR - 3 MHz
FR ± 3 MHz to FR 980 MHz
FR ± 600 kHz to FR ± 800 kHz
1,785 MHz to FR - 3 MHz
835 MHz to < 915 MHz
> 980 MHz to 1,000 MHz
100 KHz to < 835 MHz
> 1000 MHz to 12.75 GHz
100 kHz to 1,705 MHz
> 1,705 MHz to < 1,785 MHz
> 1,920 MHz to 1,980 MHz
> 1,980 MHz to 12.75 GHz
Small MS level in dBµVemf( )
E-GSM 900 GSM 1800
70
70
80
90
90
–
–
113
113
90
90
–
–
–
–
70
70
80
–
–
87
87
–
–
–
–
113
101
101
90
GSM 1900
70
70
80
–
–
87
87
–
–
–
–
113
101
101
90
Measurement Conditions:
Wanted carrier is 3 dB above reference sensitivity.
Interferer is CW.
Spurious response exceptions:
Six exceptions are permitted IN band 915 MHz - 980 MHz.
24 exceptions are permitted OUTSIDE band 915 MHz - 980 MHz.
Intermodulation Characteristics
Interferer Level ( f1 & f2) dBm Interferer Frequencies ( f1 & f2 )
–49 Wanted frequency= 2f1 - f2, and [ f1 - f2] = 800 kHz
– 4-4 –
5. TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
5.1. RF Overview
5.1.1. Introduction
■ General Specifications
The telephone is a Tri-Band product.
The transmit and receive bands for the mobile are given in the table below:
Tx Rx
E-GSM 900 880 MHz - 915 MHz 925 MHz - 960 MHz
GSM 1800 1,710 MHz - 1,785 MHz 1,805 MHz - 1,880 MHz
PCS 1900 1,850 MHz - 1,910 MHz 1,930 MHz - 1,990 MHz
Other salient technical features are as follows:
E-GSM 900 GSM 1800 PCS 1900
RX Bandwidth 35 MHz 75 MHz 60 MHz
TX Bandwidth 35 MHz 75 MHz 60 MHz
Number of Channels 174 374 299
AFRCN (Channel Numbers) 0 - 124 512 - 885 512 - 810
975 - 1023
1st TX Channel 880.2 MHz 1,710.2 MHz 1,850.2 MHz
(Ch 975) (Ch 512) (Ch 512)
Last TX Channel 914.8 MHz 1,784.8 MHz 1,909.8 MHz
(Ch 124) (Ch 885) (Ch 810)
1st RX Channel 925.2 MHz 1,805.2 MHz 1,930.2 MHz
(Ch 975) (Ch 885) (Ch 512)
Last RX Channel 959.8 MHz 1,879.8 MHz 1,989.8 MHz
(Ch 124) (Ch 885) (Ch 810)
Maximum TX Power 33.0 dBm 30.0 dBm 30.0 dBm
(Class 4)(PL 5) (Class 1)(PL 0) (Class 1)(PL 0)
Minimum TX Power 5.0 dBm 0.0 dBm 0.0 dBm
(PL 19) (PL 15) (PL 15)
– 5-1 –
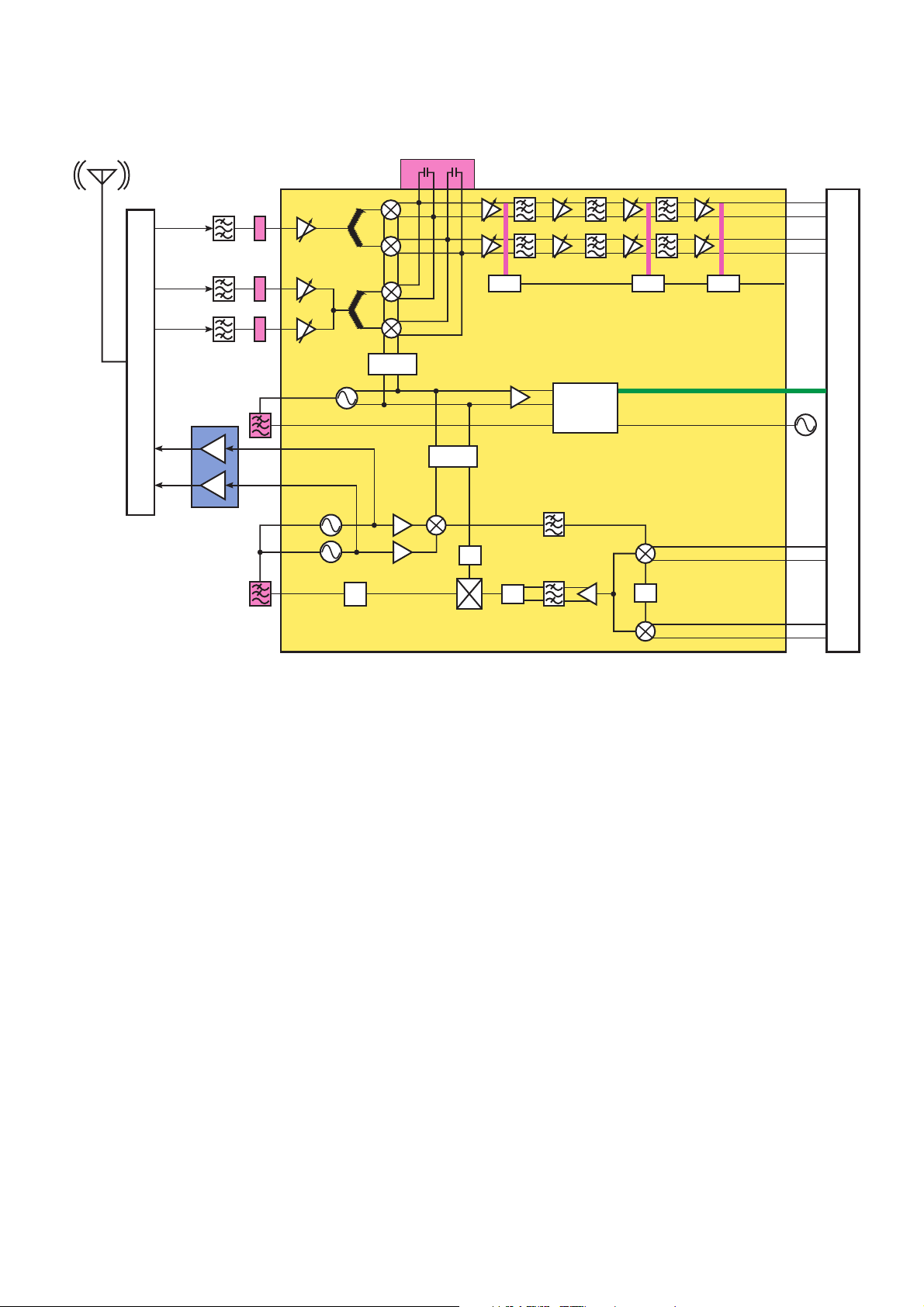
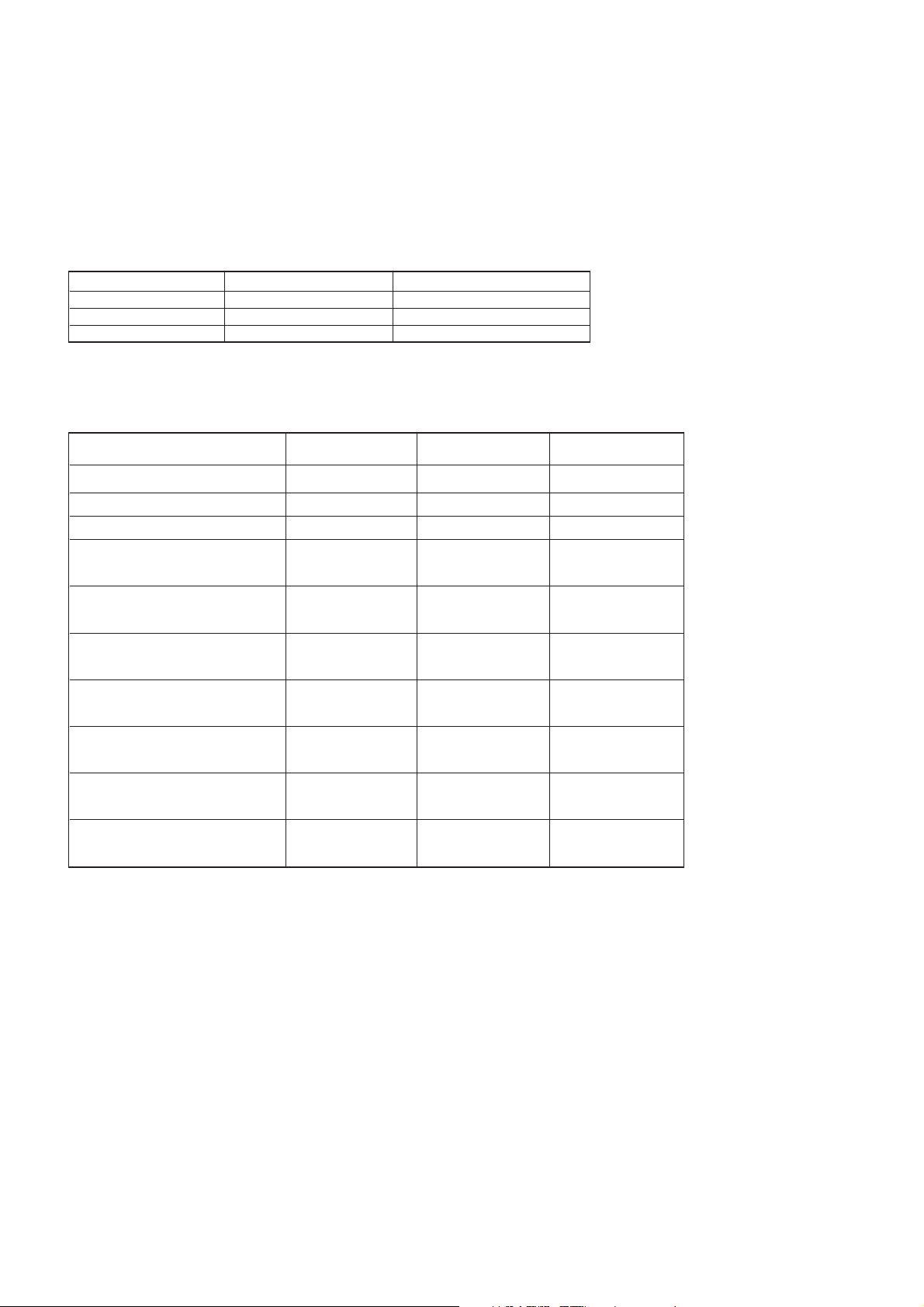
5.1.2. RF Function Block
GSM
DCS
PCS
ANTENNA SWITCH
GSM
DCS
PCS
PA
PA
U1101
LNA900IN
LNA1800IN
LNA1900IN
UVTUNE
VCPO
TXVCO
TLCPO
CP
LOG EN
LOG EN
DIV
DC O/C
DIV
Σ∆
FRAC-N PLL
Σ
DC O/C DC O/C
DATA, CLKL
90
RXI+
RXI–
RQI+
RQI–
T/H
FREF
TXI+
TXI–
TQI+
TQI–
26 MHz
VCTCXO
BASEBAND
U1201
RF Transceiver with Power Ramping Controller, Integrated Crystal Oscillator for Multi-Band GSM, GPRS and EDGE Applications
Figure 5.1. : RF Function Block Diagram
– 5-2 –
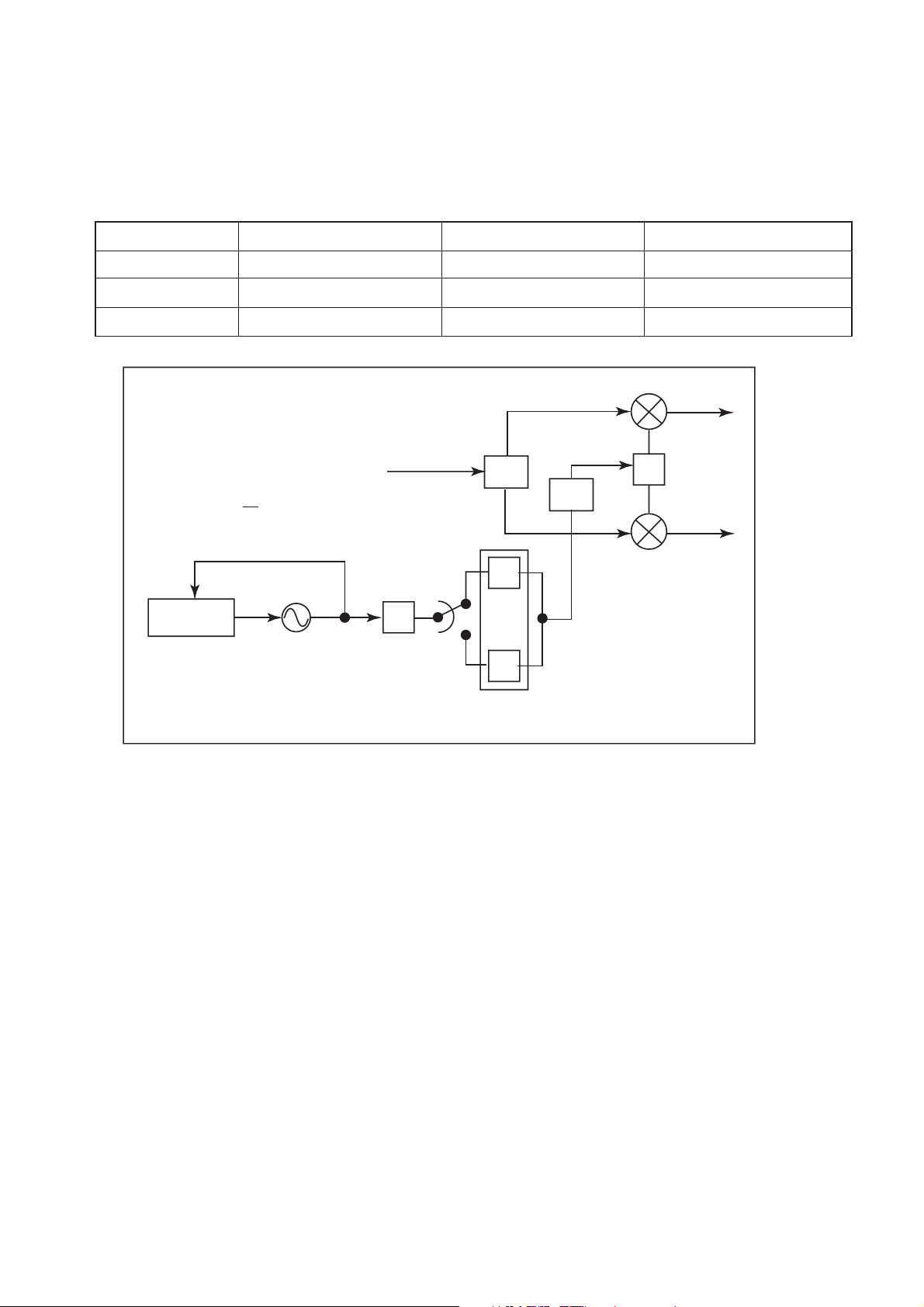
5.1.3. Functional Description
■ Frequency Plan
The frequency plan is shown below:
TX FrequencyTX Frequency Plan TX IF TX RF LO
E-GSM 900 880.2 MHz - 914.8 MHz 88.46 MHz - 114.35 MHz 1,459.59 MHz -1,543.725 MHz
GSM 1800 1,710.2 MHz - 1,784.8 MHz 90.316 MHz - 1,04.776 MHz 1,354.737 MHz - 1,414.482 MHz
PCS 1900 1,850.2 MHz - 1,909.8 MHz 97.379 MHz - 1,12.341 MHz 1,460.684 MHz - 1,516.606 MHz
RX I
RX RF from
LNA
FVCO = FRX
Where k is 1 for low band and 2 for high band.
Fractional-N
PLL
3
2k
FVCO
UHF VCO
Figure 5.2. Receiver Block Frequency Plan
FRX
/3
k = Frequency multiplier
90°
x 1
x 2
90°
x 2
RX Q
■ General
RF circuit design is built based on the direction conversion transceiver IC integrated by SAW filters (U1201), power amplifier with
control circuit, and Transmitter/receiver switch.
RF LO always requires external frequency sources with VCTCXO. The LO is frequency is adjusted periodically to synchronise
with the network cell frequency.
■ Antenna
EB-X300 uses a Helical-type monopole antenna which is optimised for operation on GSM, DCS and PCS bands.
– 5-3 –
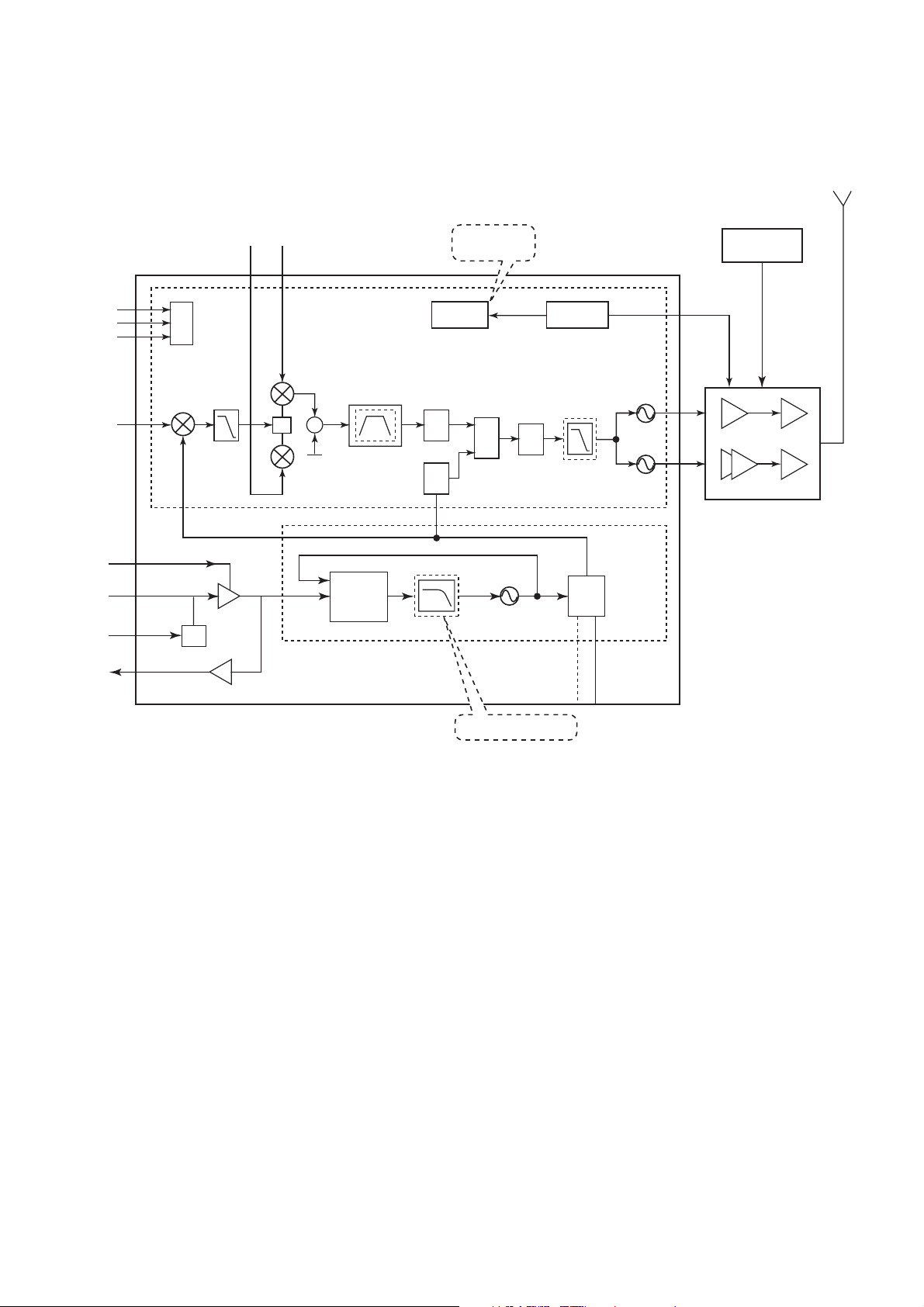
■ Transceiver - - Transmitter
Antenna
3-wire bus
TX IN
TX IN I/Q
UHF synthesiser
PA gain
controller
PFD
PAVAPC
TXVCO
Base-band
Band Select
PA
section
VAPC
900
1800/1900
UHF synthesiser
Figure 5.3. Transmitter block diagram
TX path is a translation loop architecture consisting of an IQ modulator, integrated high power VCO, offset mixer, programmable
divider, PFD, charge pump, and power amplifier with its control circuit.
The device consists of an In-phase and Quadrature (I/Q) modulator within a frequency translation loop designed to perform
frequency up-conversion with high output spectral purity.
The clock source is 26 MHz VCTCXO external instead of XTAL function block active.
The VCTCXO provides an external clock source which is more stable over extreme temperature conditions than an internal clock.
It has a power saving function in standby mode.
– 5-4 –
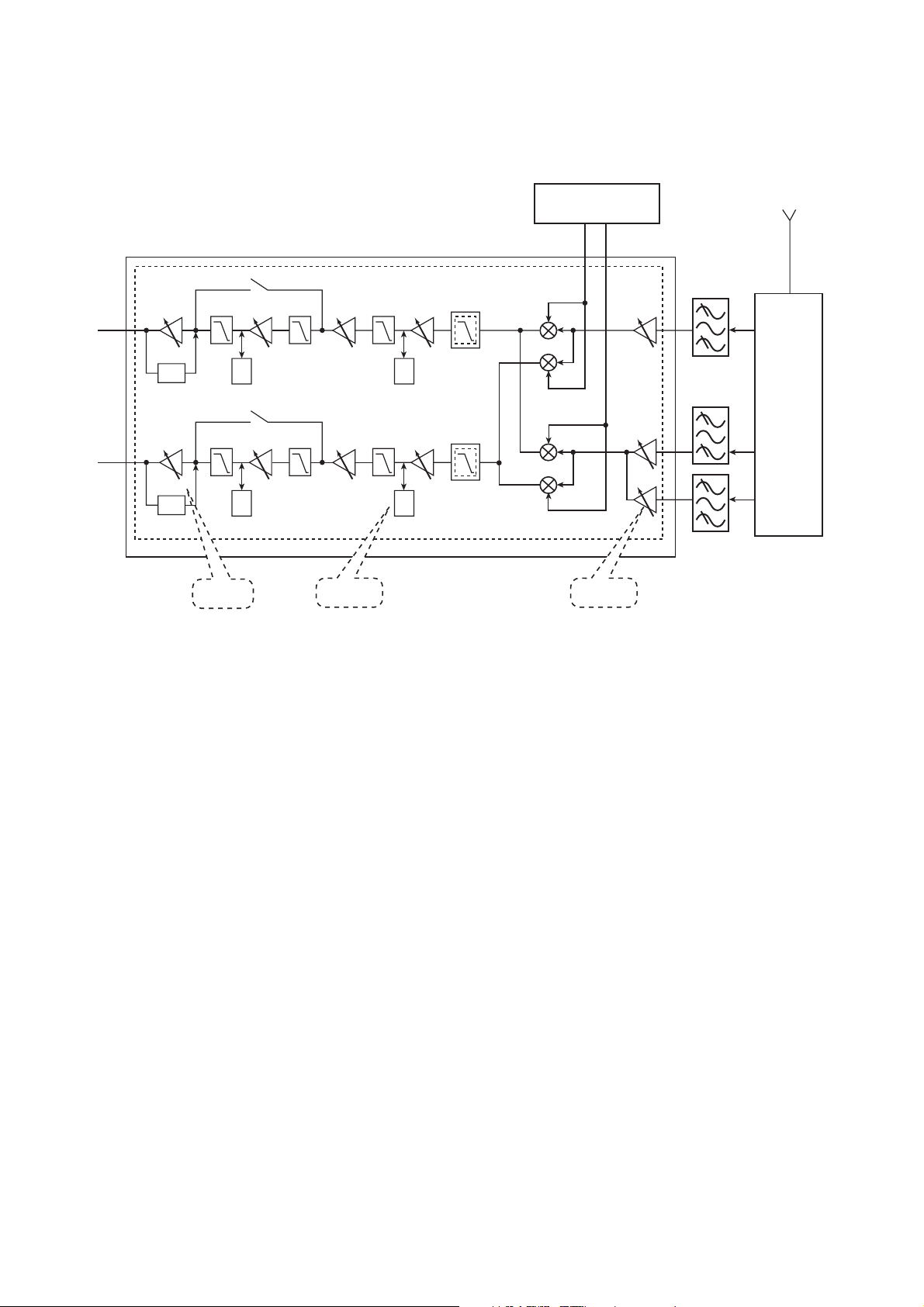
■ Transceiver - - Receiver
RXIN
RXIP
RX LO
source from chip
Antenna
RF SAW
FILTER
900
T/R
Switch
&
Diplexer
RXQN
RXQP
VGA
The transceiver uses a direct conversion receiver which eliminates the requirement for Intermediate Frequency (IF) stages.
The transceiver chip includes three LNAs for each band, a quadrature demodulator, baseband amplifier circuit with I/Q outputs
and three stages of DC-offset correction.
The DCOC correction loop ensures DC-offsets, generated in the U1201, do not overload baseband chain.
The receiver can be calibrated to optimise IP2 performance, which ensures limited baseband interfering signal amplitude.
The U1201 also features an integrated, fully programmable, sigma-delta fraction-N synthesiser suitable for GPRS multi-slot
operation.
DCOC LNA
Figure 5.4. Receiver block diagram
1800
1900
– 5-5 –
 Loading...
Loading...