Page 1

Specifications
ORDER NO. ITD0107005C0
D10
Wide Plasma Display
TH-42PW4
TH-42PWD4
GP4D Chassis
Power Source:
Power Consumption: 395 W (US model)
Plasma Display panel: Drive method AC type
Contrast Ratio 3000:1
Brightness Capability (Panel only) 780 cd / m
Screen size: 920 mm (W)×518 mm (H)×1056 mm
Operating condition:
Temperature 34 °F - 104 °F (0 °C - 40 °C)
Humidity 20 % - 80 %
Applicable signals:
Color System NTSC, PAL, PAL60, SECAM, Modified NTSC
Scanning format 525i (480i), 625i (575i), 525p (480p), 625
PC signals VGA display
AC120V 50/60Hz (US model)
AC220-240V 50/60Hz (Except US model)
295W (Except US model)
1.2W (stand-by condition) (US model)
1.8W (stand-by condition)
(Except US model)
0.9W (Power off condition) (US model)
1.6W (Power off condition)
(Expct US model)
42-inch, 16:9 aspect ratio
2
(As a set) 400 cd / m
(diagonal)
No. of pixels
408,960 (852 (W)×480 (H)) [2,556×480 dots]
(575p), 750p (720p), 1125/60i, 50i, 24p, 24SF
(1080/60i, 50i, 24p, 24SF) ........SMPTE 274M
VGA
SVGA, SXGA, UXGA ...... (compressed)
Horizontal scanning frequency 15.5 - 110kHz
Vertical scanning frequency 48 - 120Hz
2
Connection terminals:
AV
Video in 1.0 Vp-p (75-ohm)
S-VIDEO IN
(MINI DIN 4PIN)
AUDIO IN
(RCA PIN JACK × 2)
COMPONENT/RGB
Y/G 1.0 Vp-p/composite (75-ohm)
PB/B 0.7 Vp-p (75-ohm)
PR/R 0.7 Vp-p (75-ohm)
HD 1.0 - 5.0 Vp-p (high impedance)
VD 1.0 - 5.0 Vp-p (high impedance)
AUDIO IN
(RCA PIN JACK×2)
PC
(HIGH-DENSITY
D-SUB15PIN)
AUDIO IN (M3.5 JACK) 0.5Vrms (high impedance)
SERIAL
EXTERNAL CONTROL
TERMINAL (D-SUB9PIN)
SPEAKERS (External
speakers)
Dimensions (W×H×D): 40.2” (1020 mm)24” (610mm) 3.5” (89 mm)
Weight (Mass) approx. 65.0 Ibs (29.0 kg) (main unit only)
Y: 1 Vp-p (75-ohm), C: 0.286 Vp-p
(75-ohm)
0.5 Vrms (high impedance)
0.7 Vp-p/non-composite (75-ohm)
0.5 Vrms (high impedance)
R,G,B/0.7 Vp-p (75-ohm)
HD, VD/1.0 - 5.0 Vp-p (high
impedance)
RS-232C COMPATIBLE
6Ω 8W×2 (10% THD)
approx. 74.3 Ibs (33.2kg) (with speakers)
© 2001 Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. All
rights reserved. Unauthorized copying and
distribution is a violation of law.
Page 2

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
CONTENTS
Page Page
1 Safety Precautions 4
1.1. General Guidelines
2 Prevention of Electro Static Discharge (ESD) to
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices
3 PCB Structure sheet of GP4D chassis
4 Service Hint
5 Location of Lead Wiring
6 Adjustment Procedure
6.1. +B Set-up
6.2. Driver Set-up
6.3. Initialization Pulse Adjust
6.4. P.C.B. (Printed Circuit Board) exchange
6.5. Adjustment Volume Location
6.6. Test Point Location
7 Serviceman mode
7.1. CAT (computer Aided Test) mode
7.2. IIC mode structure (following items value is sample data.)
8 Alignment
8.1. NTSC panel white balance
8.2. PAL/SECAM panel white balance
8.3. Pedestal setting
8.4. PC/RGB panel white balance
8.5. HD/ 525i /525p panel white balance
8.6. 625i panel balance
8.7. Sub brighness setting
9 Trouble shooting guide
9.1. Self Check
9.2. No Power (US model)
9.3. No Power (Except US)
9.4. No Picture
9.5. Local screen failure
9.6. D-Board
10 Option Setting
11 IC Block Diagram
12 Conductor Views
12.1. F-Board
12.2. P-Board (US model)
12.3. P1-Board (Except US)
12.4. P3, P5, P6, P7 and P8-Board (Except US)
12.5. HX-Board
12.6. H-Board (Option TY-42TM4H)
12.7. HY-Board (Option TY-42TM4Y)
12.8. HZ-Board (Option TY-42T\M4Z)
10
11
11
11
12
12
14
15
15
16
18
19
21
23
24
26
26
27
28
29
29
30
32
35
37
37
38
41
44
46
47
49
51
4
5
6
7
8
9
9
9
12.9. J-Board 53
12.10. D-Board
12.11. C1, C2, C3 and C4-Board
12.12. SC-Board
12.13. SU and SD-Board
12.14. SS, SS2 and SS3-Board
12.15. H3, S1 and V1-Board
13 Block and Schematic Diagrams
13.1. Schematic Diagram Notes
13.2. Main Block (US model) Diagrams
13.3. Main (Except US) Block Diagram
13.4. Power (US model) Block Diagram
13.5. P-Board (US model) Schematic Diagrams
13.6. Power (Except US) Block Diagram
13.7. P1-Board (Except US) Schematic Diagrams
13.8. F and P3-Board (Except US) Schematic Diagram
13.9. P5, P6, P7 and P8-Board (Except US) Schematic diagram
13.10. HX and H Block Diagram
13.11. HX-Board Schematic Diagrams
13.12. H-Board (Option TY-42TM4H) Schematic Diagram
13.13. HY and HZ Block Diagrams
13.14. HY-Board (1/2) (Option TY-42TM4Y) Schematic Diagrams
13.15. HY-Board (2/2) (Option TY-42TM4Y) Schematic Diagrams
13.16. HZ-Board (1/2) (Option TY-42TM4Z) Schematic Diagram
13.17. HZ-Board (2/2) (Option TY-42TM4Z) Schematic Diagram
13.18. J-Board Block Diagrams
13.19. J-Board (1/5) Schematic Diagrams
13.20. J-Board (2/5) Schematic Diagrams
13.21. J-Board (3/5) and H3-Board Schematic Diagrams
13.22. J-Board (4/5) Schematic Diagrams
13.23. J-Board (5/5) Schematic Diagrams
13.24. D-Block Diagrams
13.25. D-Board (1/14) Schematic Diagrams
13.26. D-Board (2/14) Schematic Diagrams
13.27. D-Board (3/14) Schematic Diagrams
13.28. D-Board (4/14) Schematic Diagrams
13.29. D-Board (5/14) Schematic Diagrams
13.30. D-Board (6/14) Schematic Diagrams
13.31. D-Board (7/14) Schematic Diagrams
55
58
60
63
65
68
69
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
2
Page 3

13.32. D-Board (8/14) Schematic Diagrams 101
13.33. D-Board (9/14) Schematic Diagrams
13.34. D-Board (10/14) Schematic Diagrams
13.35. D-Board (11/14) Schematic Diagrams
13.36. D-Board (12/14) Schematic Diagrams
13.37. D-Board (13/14) Schematic Diagrams
13.38. D-Board (14/14) Schematic Diagrams
13.39. C1-Board Schematic Diagrams
13.40. C2-Board Schematic Diagrams
13.41. C3-Board and V1-Board Schematic Diagrams
13.42. C4-Board Schematic Diagrams
13.43. SC-Board Block Diagrams
13.44. SC-Board (1/2) Schematic Diagrams
13.45. SC-Board (2/2) Schematic Diagrams
13.46. SU/SD Block Diagram
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
13.47. SU-Board Schematic Diagrams
13.48. SD-Board Schematic Diagrams
13.49. SS-Board Block Diagrams
13.50. SS, SS2, SS3 and S1-Board Schematic Diagrams
14 Parts Location
15 Mech anica l Replaceme nt Parts List
15.1. US model
15.2. Except US model
16 Repla ceme nt Parts List
16.1. Relpacement Parts List Notes
16.2. US model Electrical Replacement Parts List
16.3. Expect US model Electrical Replacement Parts List
16.4. Option (TY-42TM4H) Replacement Parts List
16.5. Option (TY-42TM4Y) Replacement Parts List
16.6. Option (TY-42TM4Z) Replacement Parts List
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
117
118
119
120
121
123
123
123
126
126
127
145
166
167
170
3
Page 4
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
1 Safety Precautions
1.1. General Guidelines
1. When servicing, observe the original lead dress. If a short circuit is found, replace all parts which have been overheated or
damaged by the short circuit.
2. After servicing, see to it that all the protective devices such as insulation barriers, insulation papers shields are properly
installed.
3. After servicing, make the following leakage current checks to prevent the customer from being exposed to shock hazards.
1.1.1. Leakage Current Cold Check
1. Unplug the AC cord and connect a jumper between the two
prongs on the plug.
2. Measure the resistance value, with an ohmmeter, between
the jumpered AC plug and each exposed metallic cabinet
part on the equipment such as screwheads, connectors,
control shafts, etc. When the exposed metallic part has a
return path to the chassis, the reading should be between
1MΩ and 5.2MΩ.
When the exposed metal does not have a return path to
the chassis, the reading must be
.
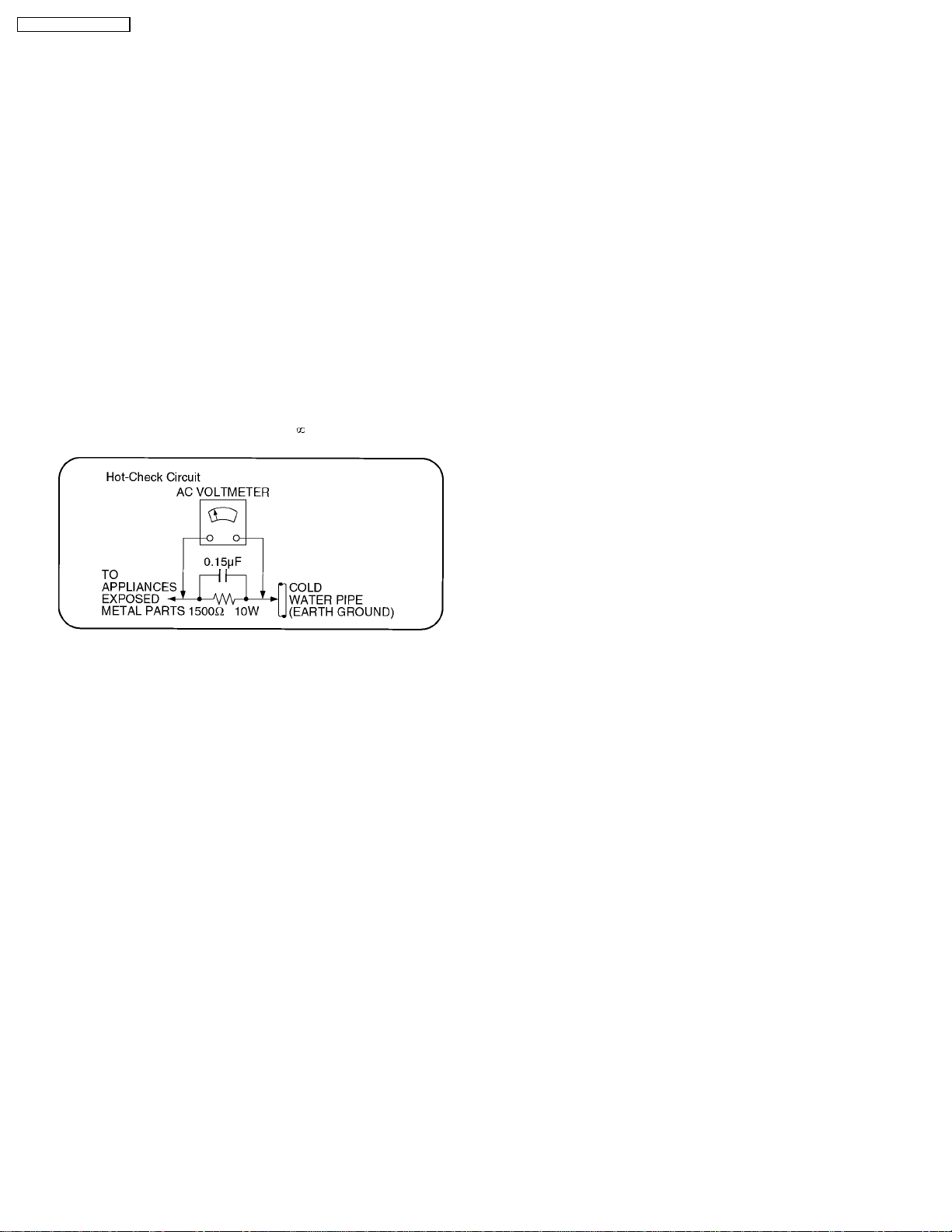
Figure 1
1.1.2. Leakage Current Hot Check (See
Figure 1.)
1. Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet. Do not use an
isolation transformer for this check.
2. Connect a 1.5kΩ, 10 watts resistor, in parallel with a 0.15µF
capacitors, between each exposed metallic part on the set
and a good earth ground such as a water pipe, as shown in
Figure 1.
3. Use an AC voltmeter, with 1000 ohms/volt or more
sensitivity, to measure the potential across the resistor.
4. Check each exposed metallic part, and measure the
voltage at each point.
5. Reverse the ACplugin the ACoutlet and repeat each of the
above measurements.
6. The potential at any point should not exceed 0.75 volts
RMS. A leakage current tester (Simpson Model 229 or
equivalent) may be used to make the hot checks, leakage
current must not exceed 1/2 milliamp. In case a
measurement is outside of the limits specified, there is a
possibility of a shock hazard, and the equipment should be
repaired and rechecked before it is returned to the
customer.
4
Page 5

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
2 Prevention of Electro Static Discharge (ESD) to
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be damaged easily by static electricity. Such components commonly are called
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect transistors and
semiconductor "chip" components. The following techniques should be used to help reduce the incidence of component damage
caused by electro static discharge (ESD).
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or semiconductor-equipped assembly, drain off any ESD on your
body by touching a known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available discharging ESD wrist strap,
which should be removed for potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equipped with ES devices, place the assembly on aconductive surface such as alminum
foil, to prevent electrostatic charge buildup or exposure of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES devices.
4. Use only an anti-static solder removal device. Some solder removal devices not classified as "anti-static (ESD protected)" can
generate electrical charge sufficient to damage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective package until immediately before you are ready to install it. (Most
replacement ES devices are packaged with leads electrically shorted together by conductive foam, alminum foil or comparable
conductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the leads of a replacement ES device, touch the protective material
to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be installed.
Caution
Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.
8. Minimize bodily motions when handling unpackaged replacement ESdevices. (Otherwise hamless motion such as the brushing
together of your clothes fabric or the lifting of your foot from a carpeted floor can generate static electricity (ESD) sufficient to
damage an ES device).
5
Page 6
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
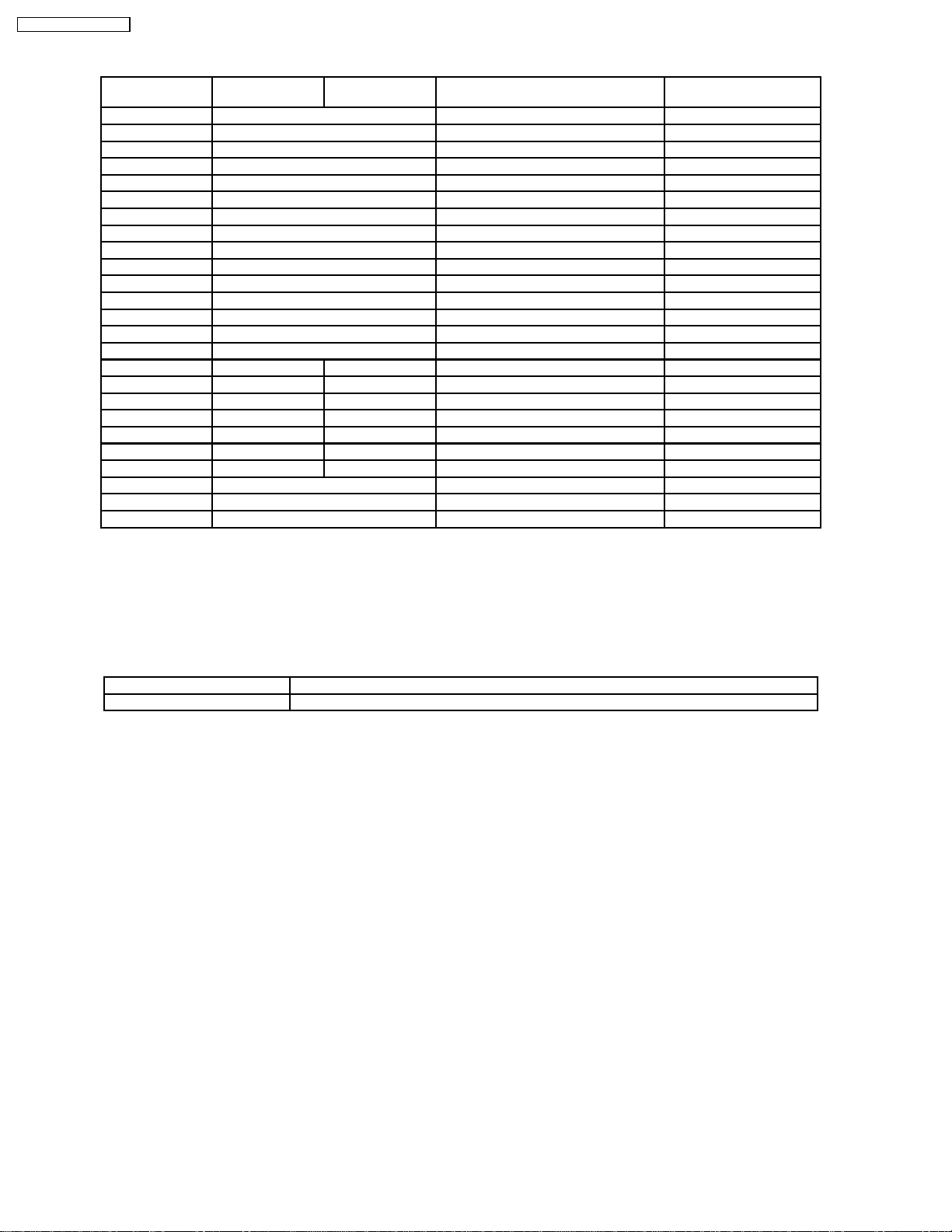
3 PCB Structure sheet of GP4D chassis
Board Name US model
Parts Number
D TZTNP01JCSE Digital process & control 1, 4
J TNPA2244 Separator / Audio Out 1
SS TNPA2262 Scan out 1
SC TNPA2261 Scan out 1
SU TNPA2259 Sustain connection (Upper) 1
SD TNPA2260 Sustain connection (Lower) 1
C1 TNPA2253 Data Drive (Upper Left)
C2 TNPA2254 Data Drive (Upper Right)
C3 TNPA2255 Data Drive (Lower Right)
C4 TNPA2256 Data Drive (Lower Left)
H3 TNPA2249 Speaker terminal
S1 TNPA2283 Power switch
SS2 TNPA2263 Sustain connection (Upper)
SS3 TNPA2264 Sustain connection (Lower)
V1 TNPA2282 Front SW. & Remote receiver
F TXN/F10JAS TXN/F1JASE Line filter
P TXN/P10JAS TXNP11JASE Power supply 1
P3 ---- TNPA1777 Drive voltage oscillator
P5 ---- TNPA1778 Primary oscillator
P6 ---- TNPA1779 PFC oscillator
P7 ---- TNPA1780 Drive voltage protection
P8 ---- TNPA1781 Process voltage protection
HX TZTNP020JAS PC_type_Input terminal
HY TNPA2245 BNC_type_Input terminal 2
HZ TNPA2248 RCA type_Input terminal 3
except US model
Parts Number
Function Remarks
Remarks
1. Recommend PCB´s for initial service for GP4D chassis.
2. For System model except UK, Europe
3. For Consumer model except UK, Europe
4. Parts number of System model is TZTNP01JASE
Note:
US model TH-42PW4UZ, TH-42PW D4UY
Except US model TH-42PW4AZ/B X/EX/HZ/RZ, TH-42PWD4AY/BX/EX/HY/RY
6
Page 7
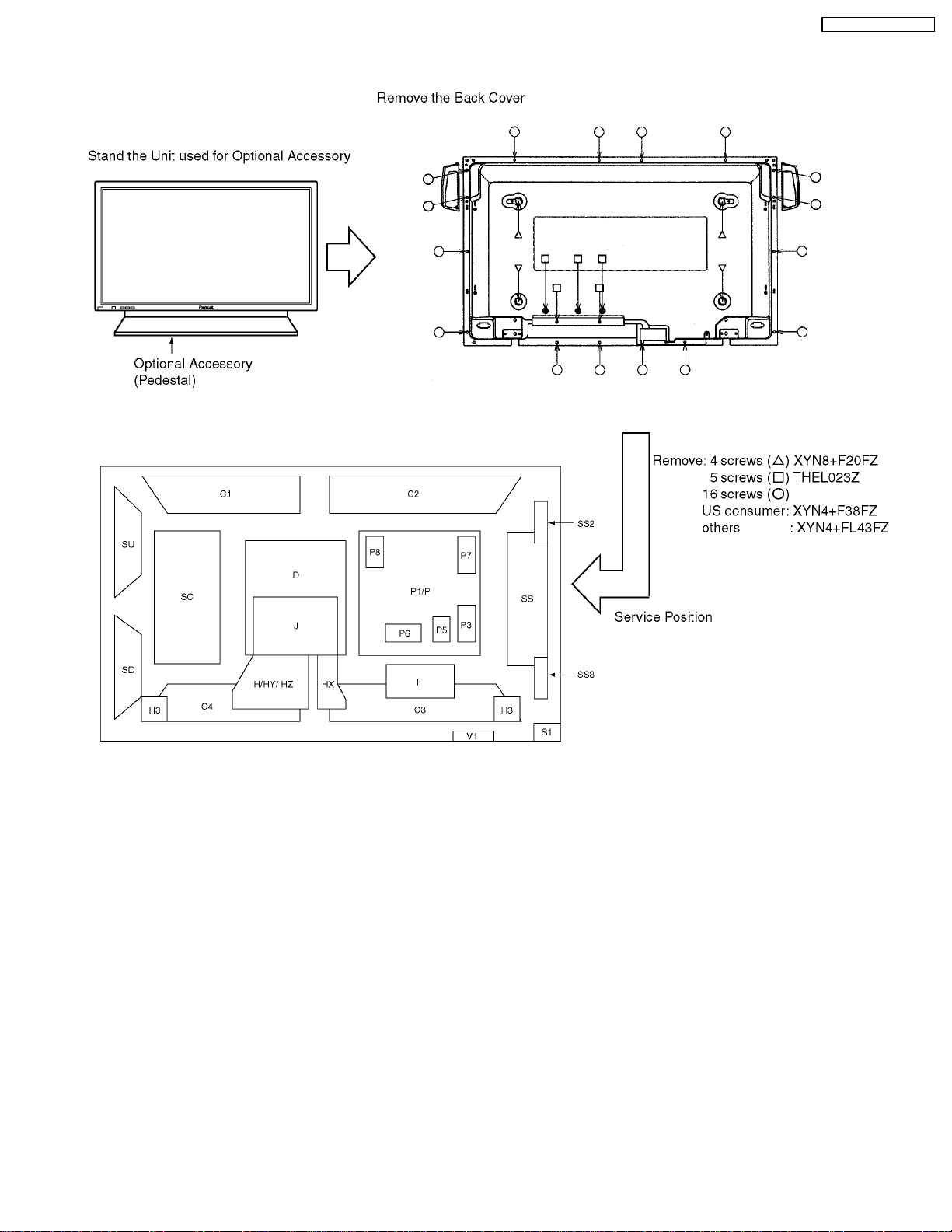
4 Service Hint
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
7
Page 8
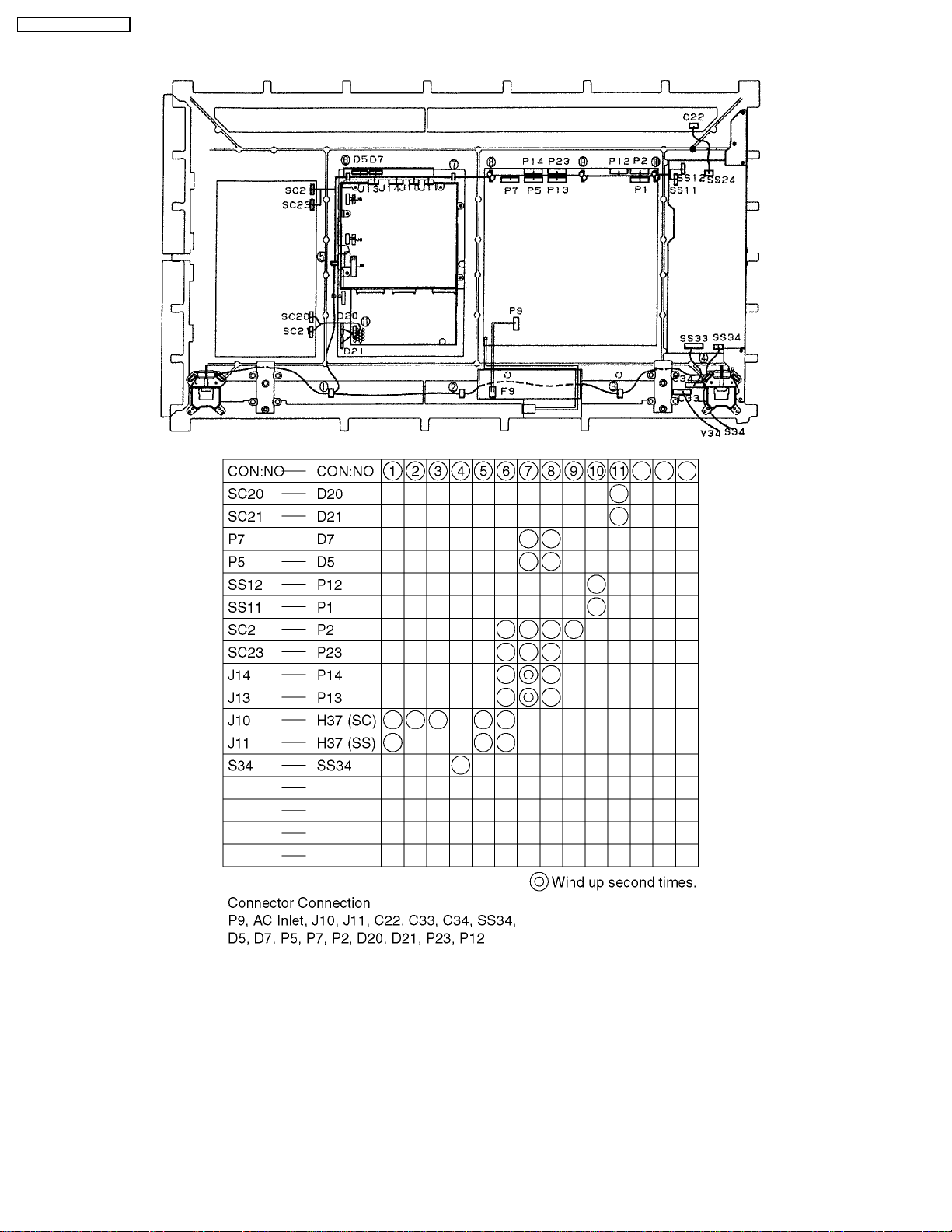
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
5 Location of Lead Wiring
8
Page 9
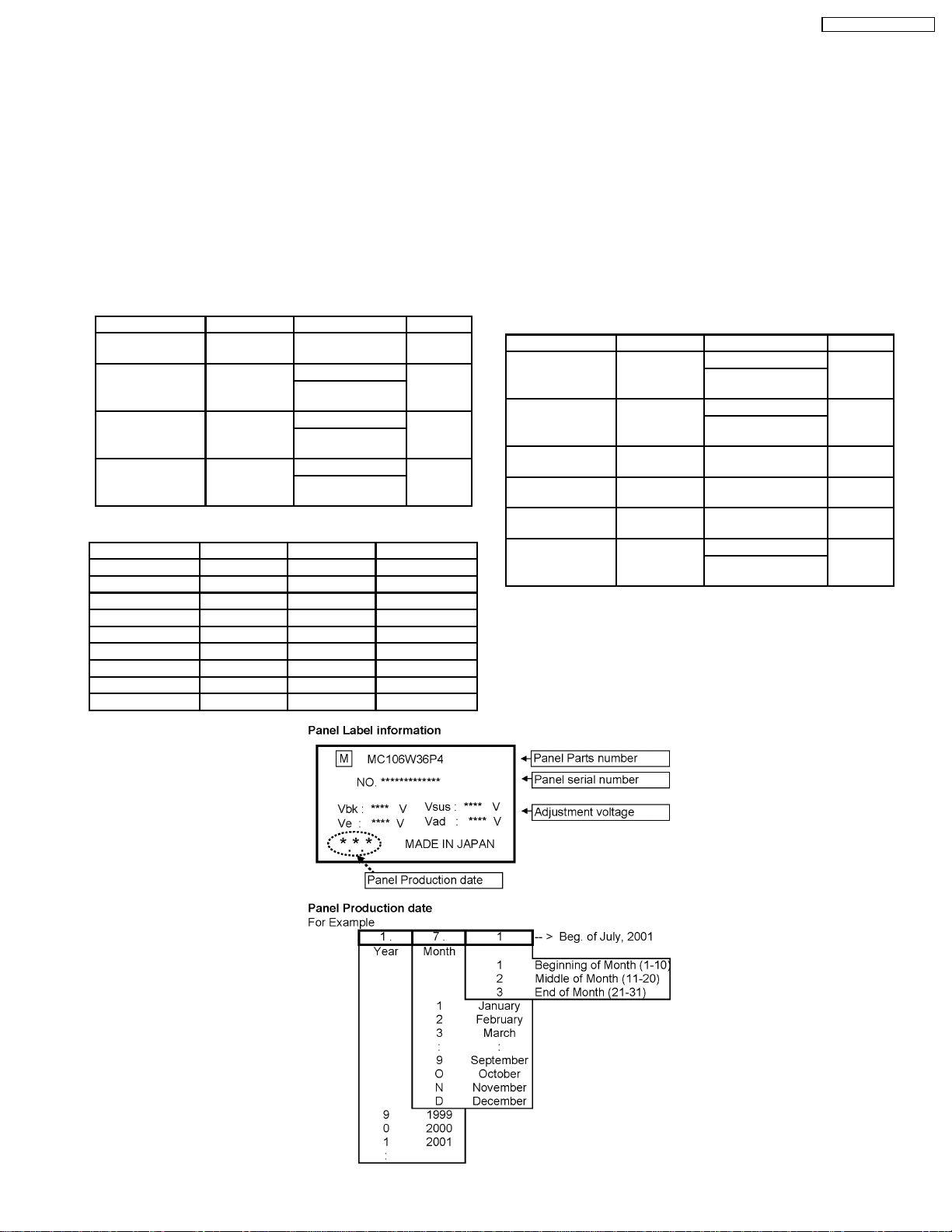
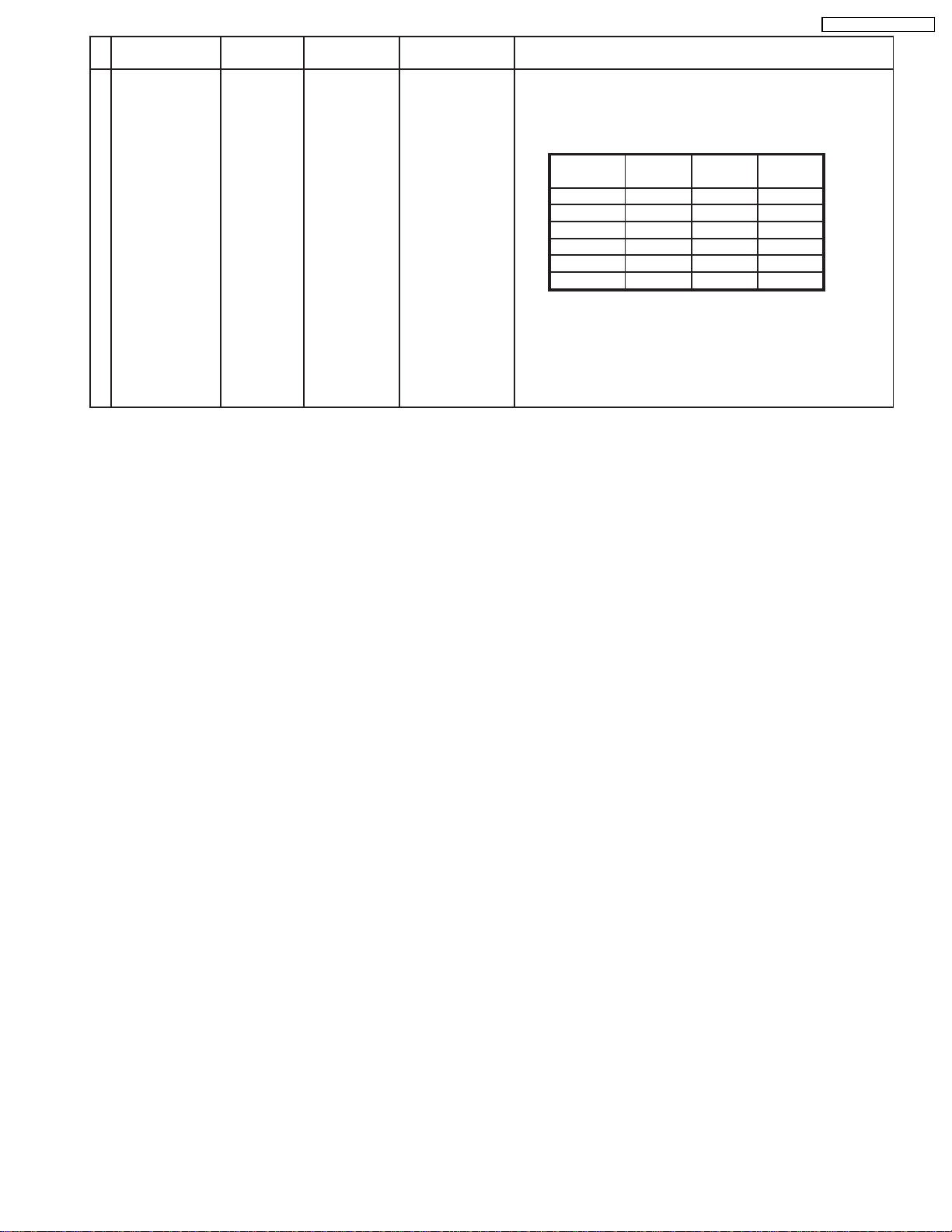
6 Adjustment Procedure
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
6.1. +B Set-up
6.1.1. Item / Preparation
1. Input a Grey scale signal.
2. Set the picture controls: Picture mode: Normal
White balance: Normal
6.1.2. Adjustments
Adjust and confirm indicated test point for the specified voltage.
Adjust
Test point Voltage Volume Name
P4 pin 1 (Hot) 400V ±1V R426 (P1)
Except US
P1 pin 3 170V ±1V R476 (P) US model Vsus
R625 (P3)
Expect US
P2 pin 3 160V ±1V R505 (P) US model Vbk
R498 (P1)
Except US
P12 pin 1 67V ±0.5V R473 (P) US model Vda
R519 (P1)
Except US
Confirm
Test point Voltage Volume Name
P23 pin 2 15V ±0.5V +15V
P5 pin 1 13.5V ±0.5V +13V
P13 pin 1 13.5V ±0.5V Audio 15V
P13 pin 3 -13.5V ±0.5V Audio -15V
P5 pin 5 5.1V ±0.3V 5V
P7 pin4 5V ±0.2V STB5V (1)
P14 pin 8 5.0V ±0.3V STB5V (2)
P10 pin 1 17.0V ±0.5V FAN +B
P10 pin 4 5.1V ±0.3V FAN 5V
PFC
6.2. Driver Set-up
6.2.1. Item / Preparation
1. Input an APL 100 % white signal.
2. Set the picture controls: Picture mode: Normal
White balance: Cool
Aspect: 16:9
6.2.2. Adjustments
Adjust driver section voltages referring the panel data on the
panel data label.
Test point Voltage Volume Name
TPVSUS
(SS-BOARD)
TPVBK
(SC-BOARD)
TPVE
(SS-BOARD)
TPVSET
(SC-BOARD)
TPVAD
(SC-BOARD)
TPVDA
(SC-BOARD)
*See the Panel label.
Vsus ±1V* R478 (P) US model Vsus
R625 (P3)
Except US
Vbk ±1V* R505 (P) US model Vbk
R498 (P1)
Except US
Ve ± 1V* R6774 (SS) Ve
218 V ±6V --- Vset
Vad ±1V* R6477 (SC) Vad
67V±1V R473 (P) US model Vda
R519 (P1)
Except US
9
Page 10
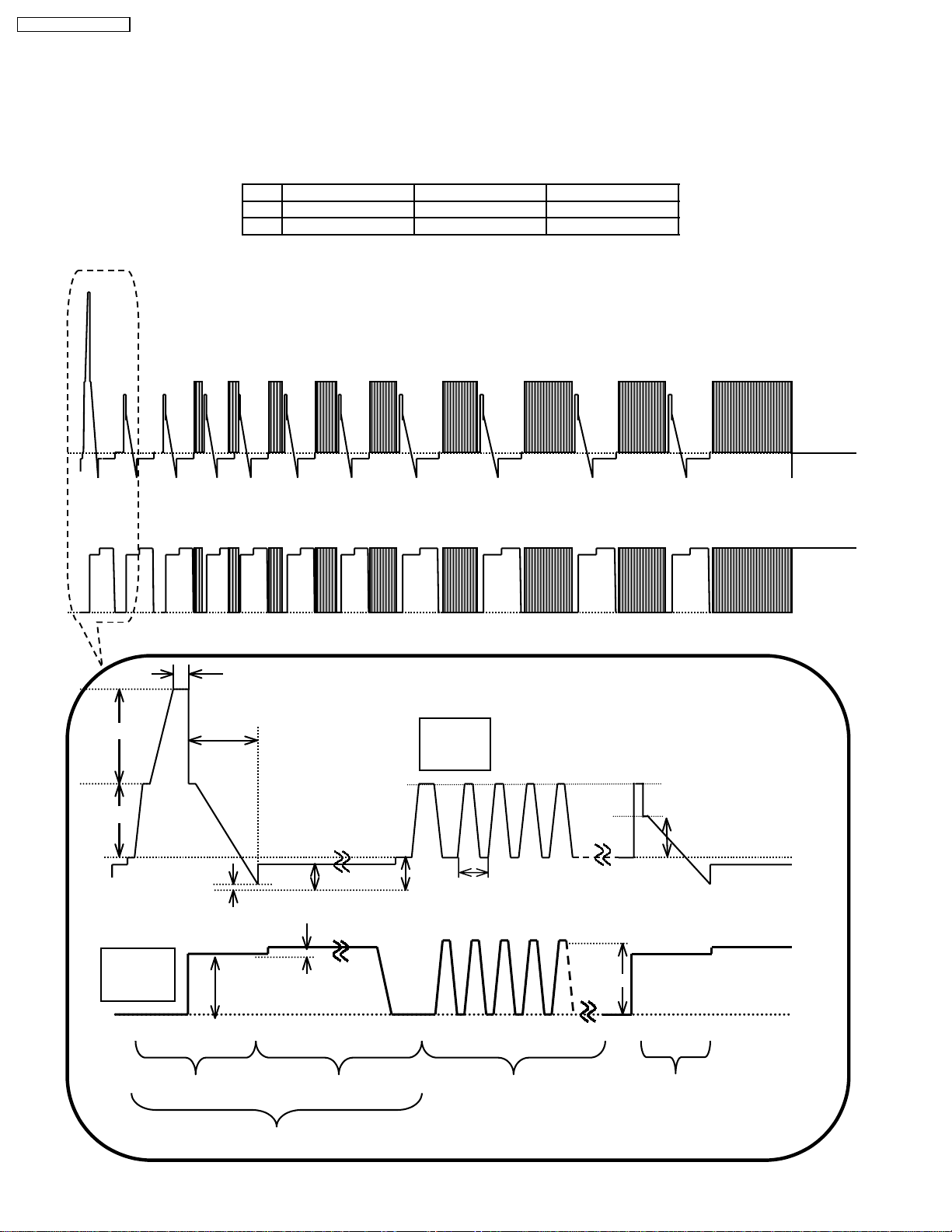
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
6.3. Initialization Pulse Adjust
1. Input a Cross hatch signal.
2. Set the picture controls: Picture mode: Normal
White balance: Cool
Adjust the indicated test point for the specified wave form.
Test point Volume Level
T1 TPSC1 (SC) R6523 (SC) 20 ± 15µ Sec
T2 TPSC1 (SC) R6557 (SC) 170 ± 20µ Sec
TPSC1 SCAN OUTPUT
TPSS1 SUSTAIN OUTPUT
T1 20±15µs
VSET
T2 170±20µs
Scan
TPSC1
VSUS VBK
VSCN VAD
VSET2
6µs
VSUS
Sustain
TPSS1
INITIALIZE SCAN PRE-INITIALIZE
VE
ADDRESS PERIOD
VE2
SUSTAIN
10
VSUS
Page 11
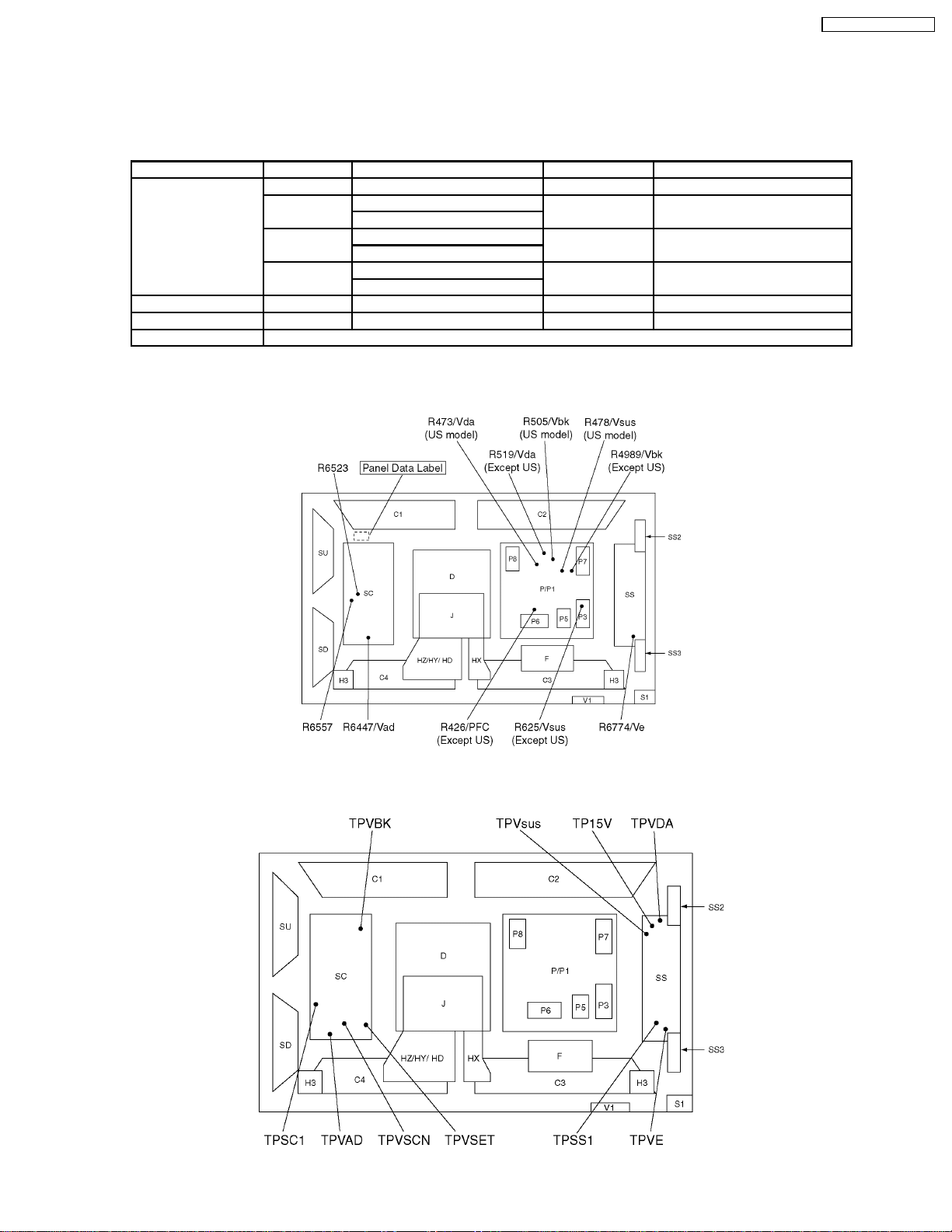
6.4. P.C.B. (Printed Circuit Board) exchange
6.4.1. Caution
1. To remove P.C.B. , wait 1 minute after power was off for discharge from electrolysis capacitors.
6.4.2. Quick adjustment after P.C.B. exchange
P.C.B. Item Volume Test point Level
P board PFC R426 (3) Except US P4 connector pin 1 400V ± 1 V
Vsus R478 (P) US model TPVsus (SS) 175V ± 1 V
R625 (P3) Except US
Vbk R505 (P) US model TPVBK (SC) 160V ± 5 V
R498 (P1) Except US
Vda R473 (P) US model TPVDA (SS) 67V ± 1 V
R519 (P1) Except US
SC board Vad R6477 TPVAD (SC) -90 ± 1 V
SS board Ve R6774 TPVE (SS) 150 ± 1 V
D board White balance, Pedestal and Sub brightness for NTSC, PAL, HD, PC and 625I signals.
6.5. Adjustment Volume Location
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
6.6. Test Point Location
11
Page 12
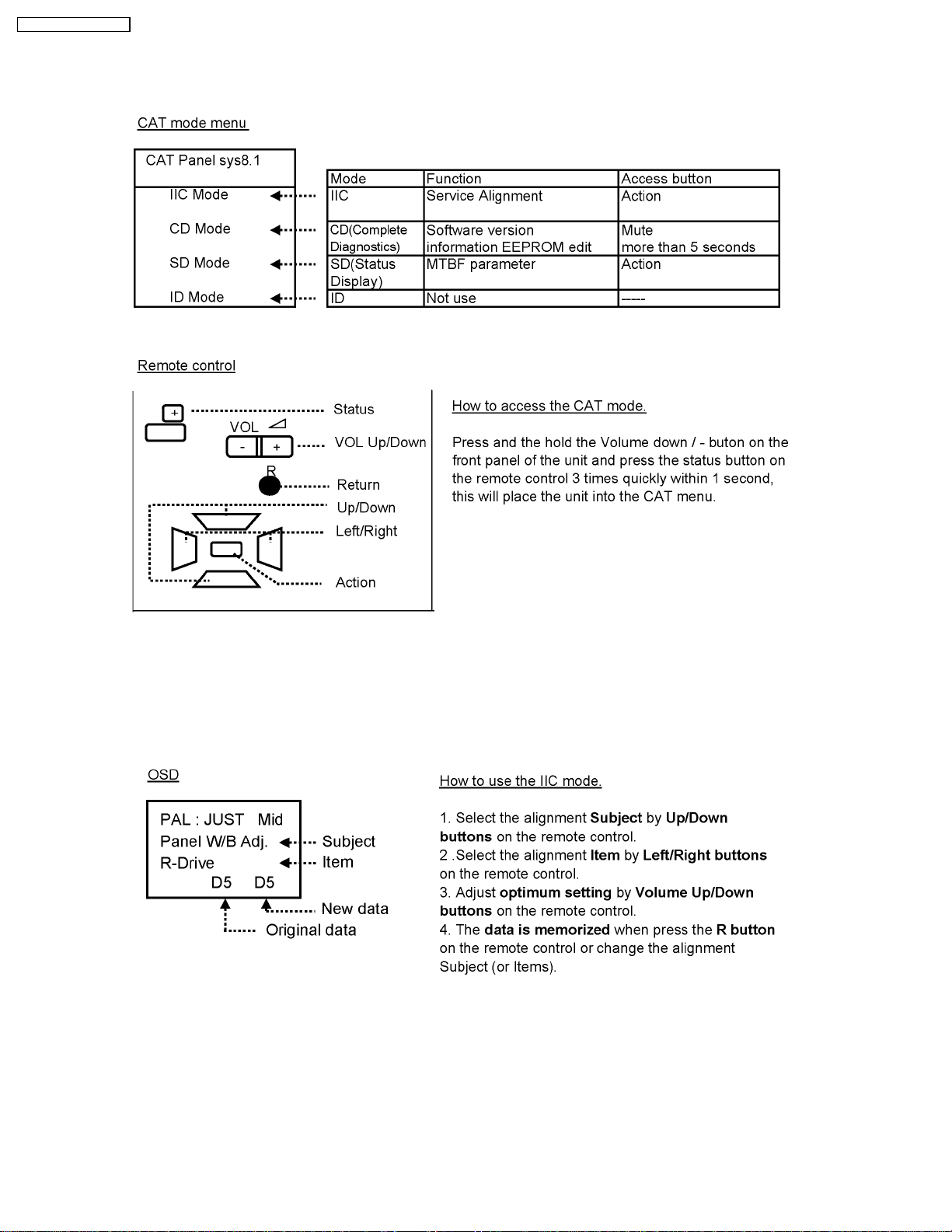
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
7 Serviceman mode
7.1. CAT (computer Aided Test) mode
To exit the CAT mode, access the ID mode and switch off the main power.
7.1.1. IIC mode
Select the IIC mode by Up/Down button on the remote control at the front page of CAT mode then press the Action button on
the remote control.
Subject and item are mentioned on page 14.
To exit the IIC mode, press the R button on the remote control.
12
Page 13
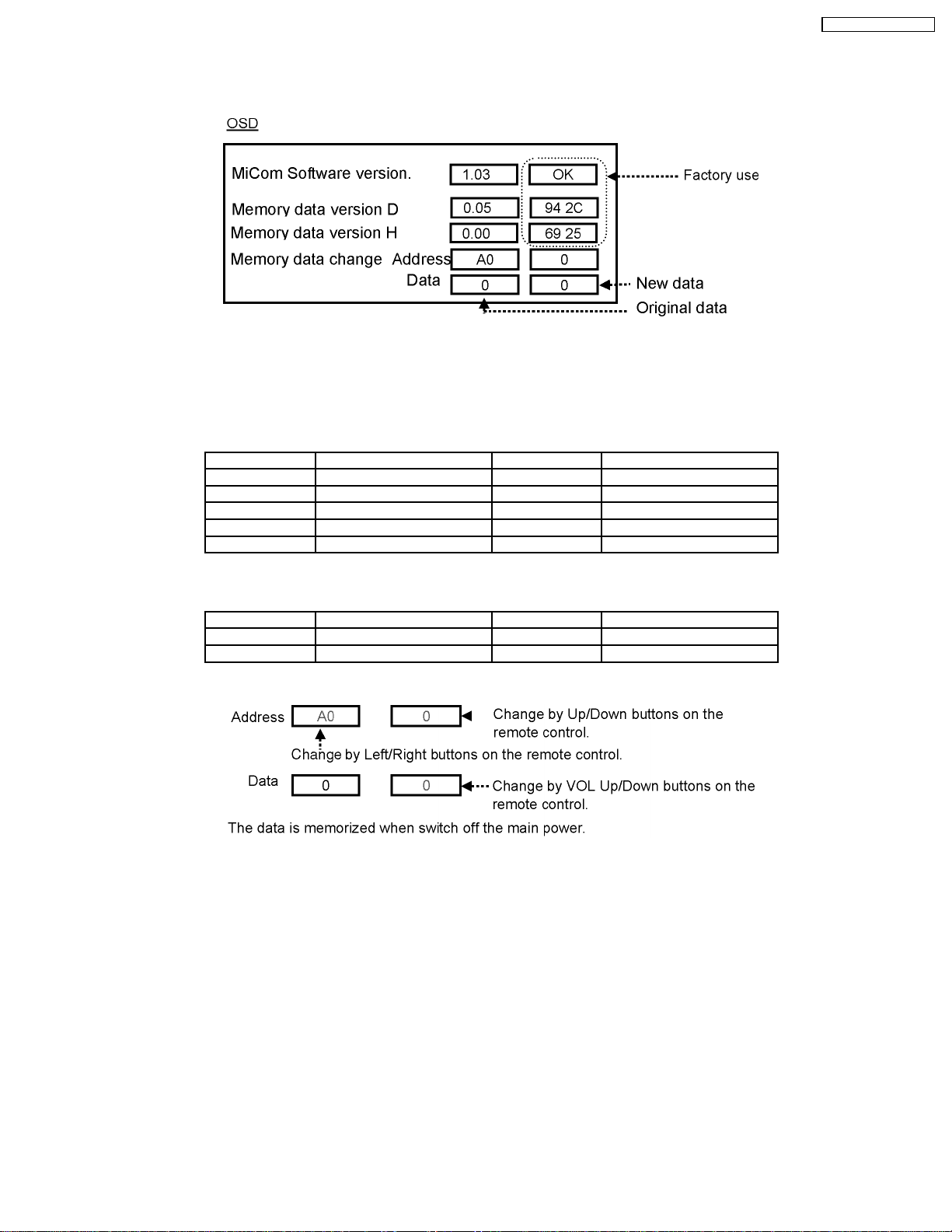
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
7.1.2. CD mode
Select the CD mode by Up/Down button on the remote control at the front page of CAT mode then press the Mute button on the
remote control more than 5 sec.
Micom software version ( IC9705 / TVRJ562), this version can be upgrade by
1. replace of new version IC
2. Loading the new version software from loader tool, TZSC07036.
Memory data version D (IC9706 /TVRJ601) in the D board
Version Model Type Destination
3.** PW4UZ Consumer USA
4.** PWD4UY System USA
5.** PW4BX,HZ, Consumer U.K.H.K.,
6.** PWD4AY,BX, EX, HY, RY System U.K. / Euro / Australia
7.** PW4AZ, EX, RZ Consumer Euro / Australia
Memory data version H (IC3699) in the H board
This version is difference depends on the H board type.
Version Type of H borad Version Type of H borad
1.** HY (BNC) 3.** HD (DVI)
2.** HZ (RCA) 4.** H (tuner)
Memory data change
To exit the CD mode, press the R button on the remote control.
13
Page 14
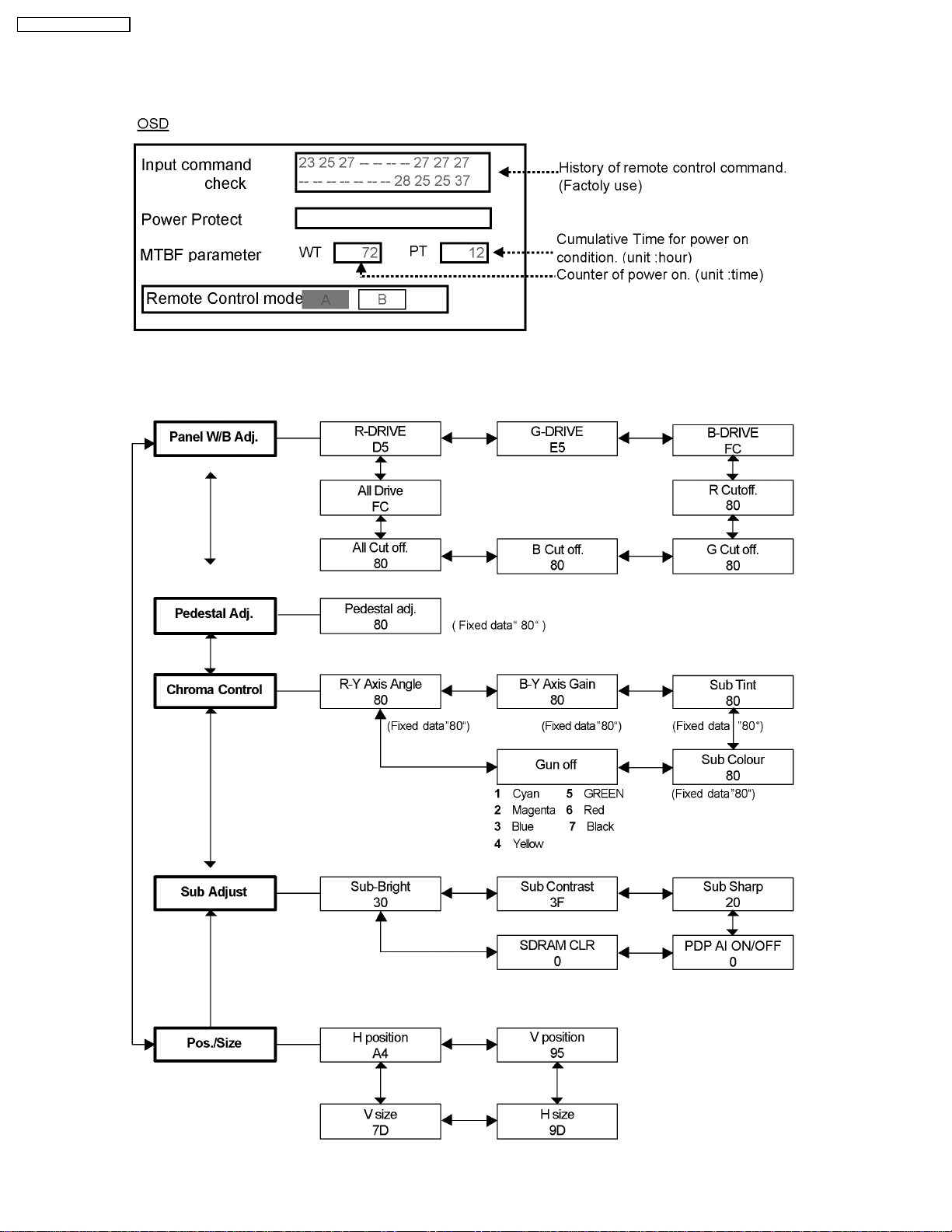
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
7.1.3. SD mode
Select the SD mode by Up/Down button on the remote control at the front page of CAT mode then press the Action button on the
remote control.
To exit the SD mode, press the R button on the remote control.
7.2. IIC mode structure (following items value is sample data.)
14
Page 15
8 Alignment
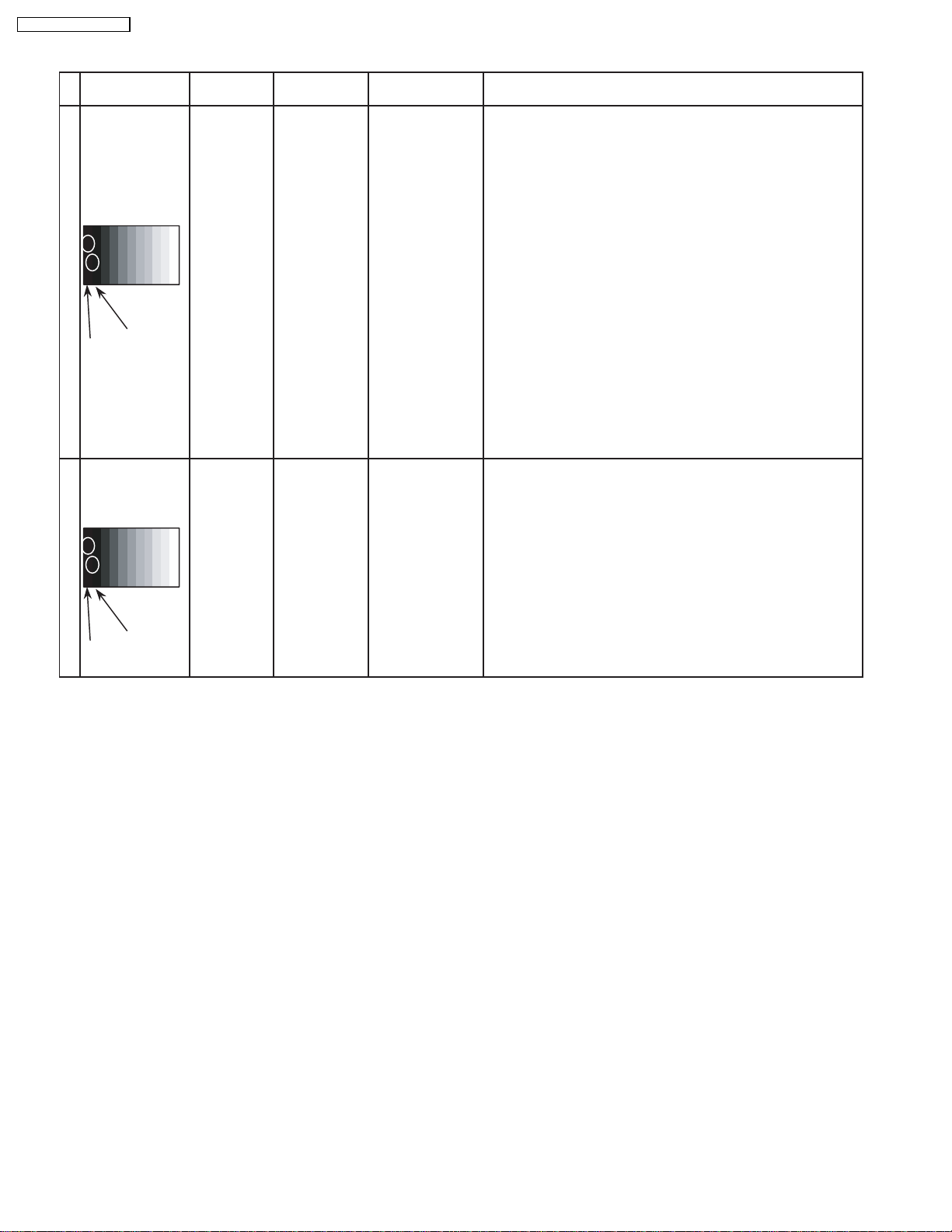
8.1. NTSC panel white balance
INPUT Alignment menu ProcedureEquipment Setting
1 NTSC Color Picture: 1) Find the nearest area to brightness of 10 cd/m2 as Low
Gray Scale Analyzer Normal Sub Adjust light by color sensor.
Pattern White balance: Sub Bright 2) Adjust Sub bright to set Low light level to 10 cd/m
Cool
Aspect: PANEL W/B
16:9 G cut off 3) Set G cut off to " 80 ".
PANEL W/B
B cut off 4) Adjust B and R cut off to set color temperature as
R cut off shown Fig.-01.
High light 75% Sub Adjust
Low light 15% Sub Bright 5) If Sub Bright is changed re-adjust it to set Low light
PANEL W/B
PANEL W/B
exactly.
2
to 10 cd/m
6)Find 75% of white area by color sensor.
G Drive 7) Set G Drive to " D8 ".
B Drive 8) Adjust B and R Drive to set color temperature
R Drive as shown Fig.-01.
.
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
2
9) Repeat item 4) to 7) to set both Low light and
high light.
PANEL W/B
R,G,B Drive 10) Increase same steps of R, G and B Drive to set
R,G,B Drive largest level of 3 color drive to "FC".
PANEL W/B
R,G,B cut off 11) Re-adjust Low light level again.
Color Temp. x y
Cool(Hi) 0.272 0.290
Normal(Mid) 0.288 0.296
Warm(Low) 0.313 0.329
Fig. -01
2 Picture: 1) Change white balance to "Normal".
Normal PANEL W/B
White balance: R,G,B cut off 2) Repeat procedure 3) to 11) of Cool mode.
Normal
PANEL W/B
Aspect: R,G,B Drive
16:9
3 Picture: 1) Change white balance to "Warm".
Normal PANEL W/B
White balance: R,G,B cut off 2) Repeat procedure 3) to 11) of Cool mode.
Warm
PANEL W/B
Aspect: R,G,B Drive
16:9
4 Picture: Picture Menu 1) Change color templature to "Cool".
Normal Sub Adjust
White balance: Sub Bright 2)Re-set Sub bright to "30"
Cool
Aspect:
16:9
Note:
OSD is the difference between US model and Except US model.
Picture:Normal (Except US)/Standard (US model)
White balance (Except US)/Color Temp (US model)
15
Page 16
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
8.2. PAL/SECAM panel white balance
INPUT Alignment menu ProcedureEquipment Setting
1 PAL Color Picture: 1) Find the nearest area to brightness of 10 cd/m2 as Low
Gray Scale Analyzer Normal Sub Adjust light by color sensor.
Pattern White balance: Sub Bright 2) Adjust Sub bright to set Low light level to 10 cd/m
Cool exactly.
Aspect: PANEL W/B
16:9 G cut off 3) Set G cut off to " 80 ".
PANEL W/B
High light 75% Sub Adjust
Low light 15% Sub Bright 5) If Sub Bright is changed re-adjust it to set Low light
PANEL W/B
PANEL W/B
PANEL W/B
PANEL W/B
B cut off 4) Adjust B and R cut off to set color temperature as
R cut off shown Fig.-02.
to 10 cd/m
2.
6)Find 75% of white area by color sensor.
G Drive 7) Set G Drive to " D8 ".
B Drive 8) Adjust B and R Drive to set color temperature
R Drive as shown Fig.-02.
9) Repeat procedure 4) to 7) to set both Low light and
high light.
R,G,B Drive 10) Increase same steps of R, G and B Drive to set
R,G,B Drive largest level of 3 color drive to "FC".
R,G,B cut off 11) Re-adjust Low light level again.
2
Color Temp. x y
Cool(Hi) 0.272 0.290
Normal(Mid) 0.288 0.296
Warm(Low) 0.313 0.329
Fig. -02
2 Picture: 1) Change white balance to "Normal".
Normal PANEL W/B
White balance: R,G,B cut off 2) Repeat procedure 3) to 11) of Cool mode.
Normal PANEL W/B
Aspect: R,G,B Drive
16:9
3 Picture: 1) Change white balance to "Warm".
Normal PANEL W/B
White balance: R,G,B cut off 2) Repeat procedure 3) to 11) of Cool mode.
Warm PANEL W/B
Aspect: R,G,B Drive
16:9
4 Picture: Picture Menu 1) Change color templature to "Cool".
Normal Sub Adjust
White balance: Sub Bright 2)Re-set Sub bright to "30"
Cool
Aspect:
16:9
16
Page 17
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
Alignment menu ProcedureEquipment Setting
5 Picture: 1) Write down each color temaparature of R,G,B drive and
Normal Cut off data as follows.
Aspect:
16:9
White
White balance:
Cool
Normal
Warm
Balance Cool Normal Warm
R Drive
G Drive
B Drive
R Cut off
G Cut off
B Cut off
SECAM signal 2) Input SECAM signal.
3) Copy PAL R,G,B drive and cut off data of each white
balance mode to SECAM position.
17
Page 18
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
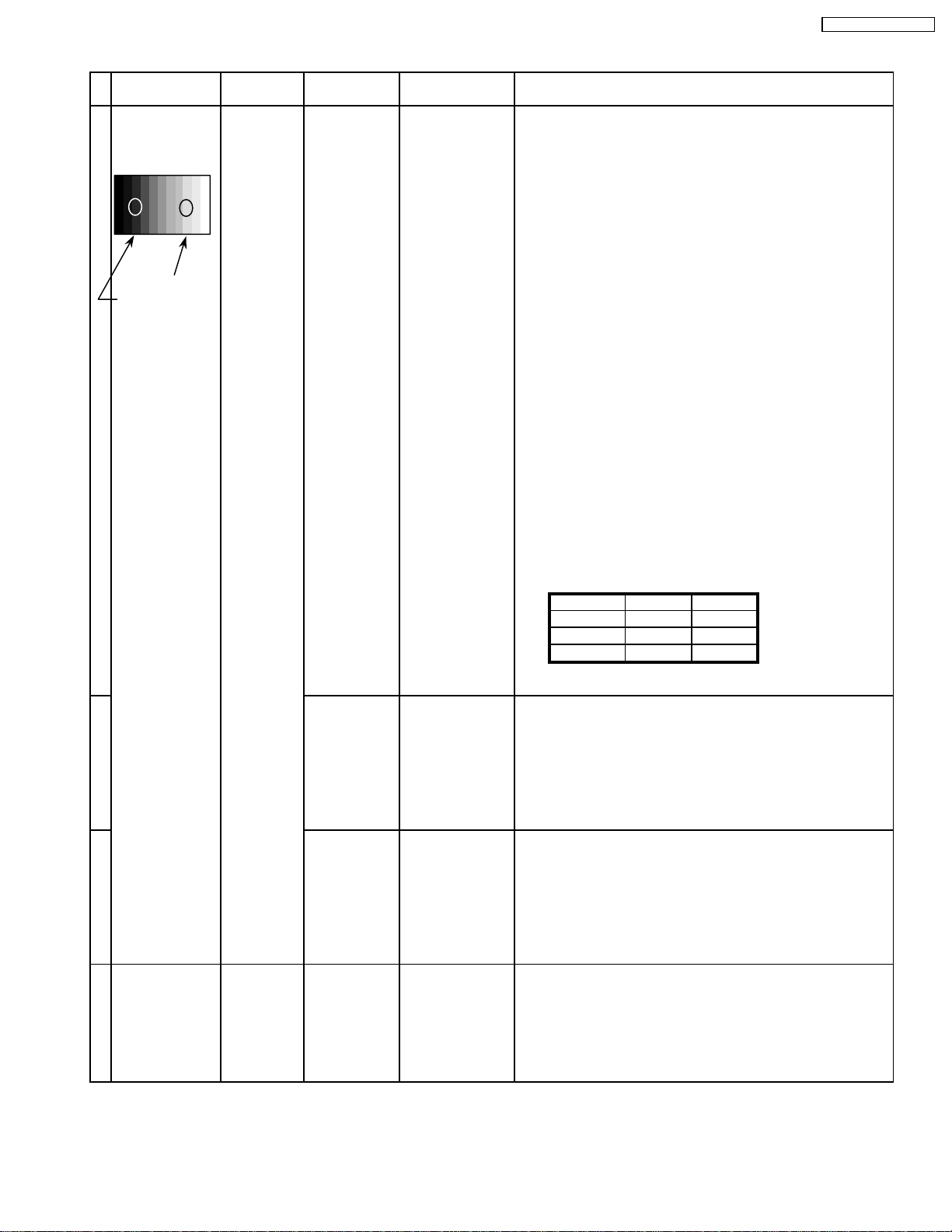
8.3. Pedestal setting
INPUT Alignment menu ProcedureEquipment Setting
1 Component Picture: PANEL W/B
(525i, 525p, 625i, Normal R cut off 1) Set R,G and B cut off to "
720i or 1080i) White balance: G cut off
Gray Scale Aspect:
Pattern 16:9
Black 2 %
Black 0 % at black 2% area and no emission at black 0% area.
Cool B cut off
Chroma Control:
Gun off
RGB Sub Adjust:
G Sub Bright
Chroma Control:
Gun off
RGB Sub Adjust:
B Sub Bright
Chroma Control:
Gun off
RGB Sub Adjust:
R Sub Bright
** Adjust at the dark room.
80 ".
2) Set Gun off to "
3) Adjust G Sub bright to start some of green pixels emission
at black 2% area and no emission at black 0% area.
4) Set Gun off to "
5) Adjust B Sub bright to start some of blue pixels emission
6) Set Gun off to "
7) Adjust R Sub bright to start some of red pixels emission
at black 2% area and no emission at black 0% area.
5". (Only green pixels can emit.)
3". (Only blue pixels can emit.)
6". (Only red pixels can emit.)
2 RGB(PC) Picture: 1) Change input to RGB signal.
Gray Scale Normal PANEL W/B
Pattern White balance: R,G,B cut off 2) Repeat procedure 1) to 7) of Component input signal.
Cool PANEL W/B
Aspect: R,G,B Drive
16:9
Black 2 %
Black 0 %
18
Page 19
8.4. PC/RGB panel white balance
INPUT Alignment menu ProcedureEquipment Setting
1 PC Color Picture: 1) Find the nearest area to brightness of 10 cd/m2 as Low
Gray Scale Analyzer Normal Sub Adjust light by color sensor.
Pattern White balance: Sub Bright 2) Adjust Sub bright to set Low light level to 10 cd/m
Cool exactly.
Aspect: PANEL W/B
16:9 G cut off 3) Set G cut off to " 80 ".
PANEL W/B
B cut off 4) Adjust B and R cut off to set color temperature as
R cut off shown Fig.-03.
High light 75% Sub Adjust
Low light 15% Sub Bright 5) If Sub Bright is changed re-adjust it to set Low light
to 10 cd/m
6)Find 75% of white area by color sensor.
PANEL W/B
G Drive 7) Set G Drive to " D8 ".
PANEL W/B
B Drive 8) Adjust B and R Drive to set color temperature
R Drive as shown Fig.-03.
9) Repeat item 4) to 7) to set both Low light and
high light.
PANEL W/B
R,G,B Drive 10) Increase same steps of R, G and B Drive to set
R,G,B Drive largest level of 3 color drive to "FC".
PANEL W/B
R,G,B cut off 11) Re-adjust Low light level again.
2
.
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
2
Color Temp. x y
Cool(Hi) 0.272 0.290
Normal(Mid) 0.288 0.296
Warm(Low) 0.313 0.329
Fig. -03
2 Picture: 1) Change white balance to "Normal".
Normal PANEL W/B
White balance: R,G,B cut off 2) Repeat procedure 3) to 11) of Cool mode.
Normal PANEL W/B
Aspect: R,G,B Drive
16:9
3 Picture: 1) Change white balance to "Warm".
Normal PANEL W/B
White balance: R,G,B cut off 2) Repeat procedure 3) to 11) of Cool mode.
Warm PANEL W/B
Aspect: R,G,B Drive
16:9
4 Picture: Picture Menu 1) Change color templature to "Cool".
Normal Sub Adjust
White balance: Sub Bright 2)Re-set Sub bright to "30"
Cool
Aspect:
16:9
19
Page 20
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
5 Picture: 1) Write down each color temaparature of R,G,B drive and
RGB
Gray Scale
Pattern
High light 75%
Low light 15% 3) Copy PC R,G,B drive and cut off data of each white
6 Picture: 1) Write down each color temaparature of R,G,B drive and
INPUT Alignment menu ProcedureEquipment Setting
Normal Cut off data as follows.
Aspect:
White balance:
Normal G Drive
Normal Cut off data as follows.
Aspect:
16:9
White
Balance Cool Normal Warm
Cool R Drive
Warm B Drive
R Cut off
G Cut off
B Cut off
2) Input RGB signal.
balance mode to RGB position.
16:9
White
DVI
Gray Scale
Pattern
White balance:
Cool R Drive
Normal G Drive
Warm B Drive
Balance Cool Normal Warm
R Cut off
G Cut off
B Cut off
2) Input DVI signal.
High light 75%
Low light 15% 3) Copy PC R,G,B drive and cut off data of each white
balance mode to DVI position.
20
Page 21
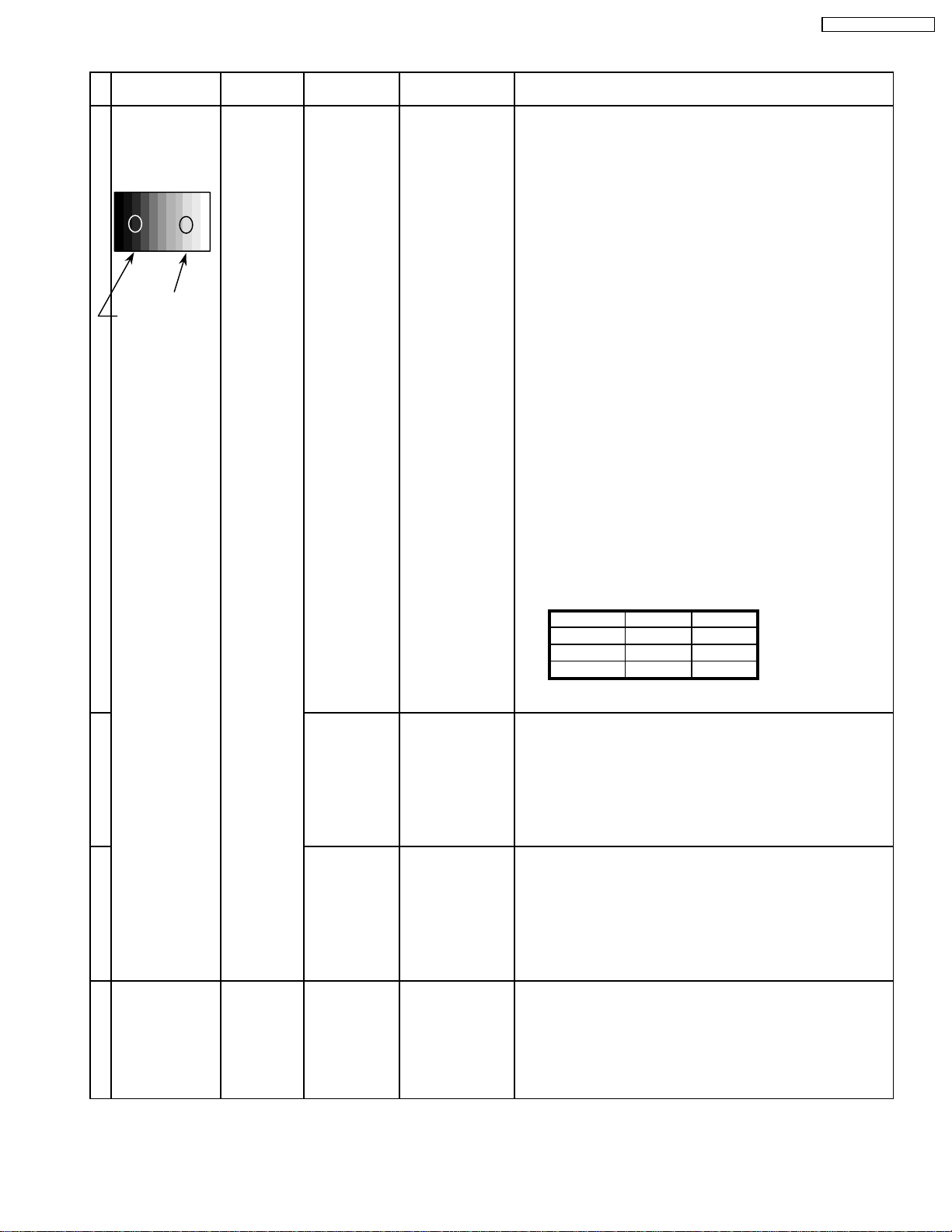
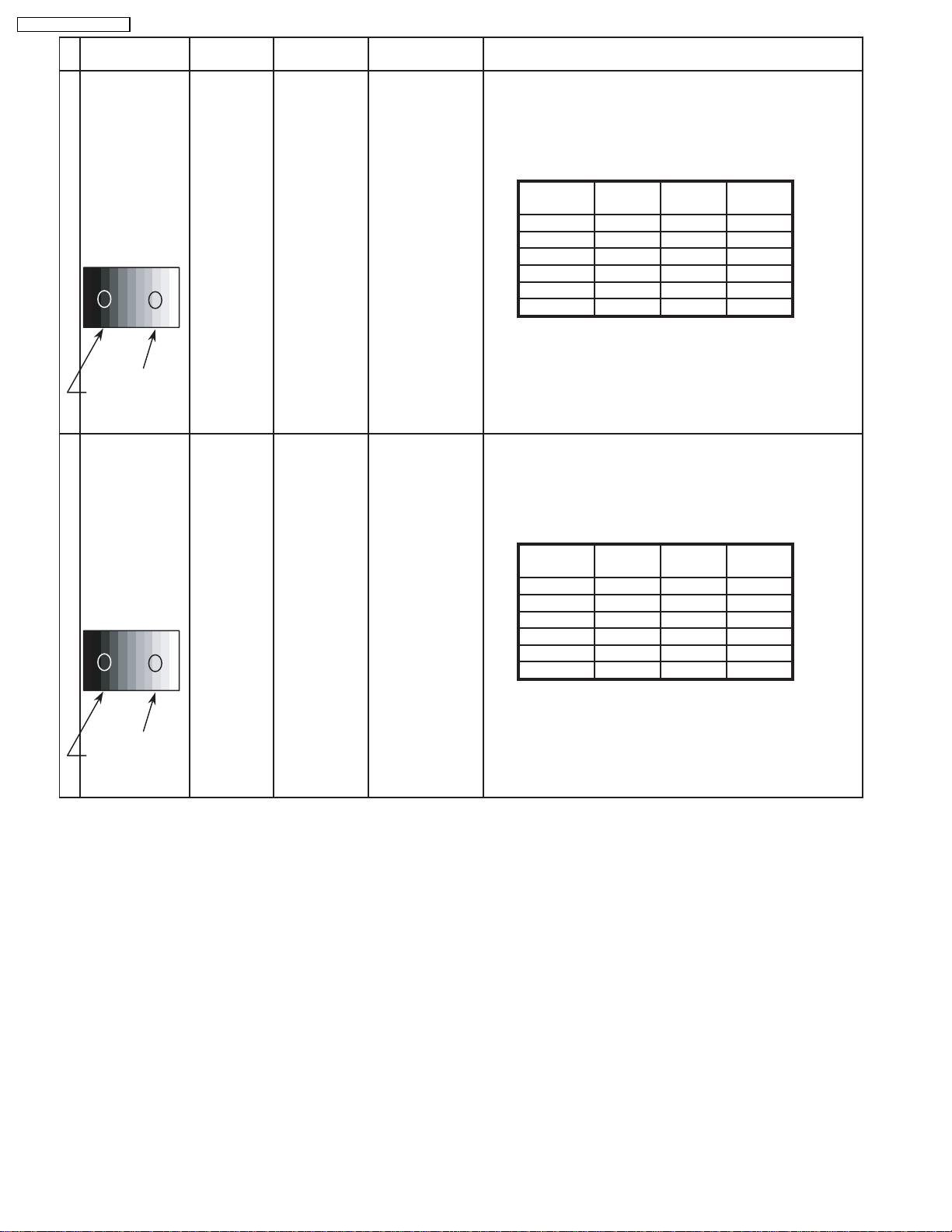
8.5. HD/ 525i /525p panel white balance
INPUT Alignment menu ProcedureEquipment Setting
1HD(720i or 1080i) Color Picture: 1) Find the nearest area to brightness of 10 cd/m2 as Low
Gray Scale Analyzer Normal Sub Adjust light by color sensor.
Pattern White balance: Sub Bright 2) Adjust Sub bright to set Low light level to 10 cd/m
Cool
exactly.
Aspect: PANEL W/B
16:9 G cut off 3) Set G cut off to " 80 ".
PANEL W/B
B cut off 4) Adjust B and R cut off to set color temperature as
R cut off shown Fig.-04.
High light 75% Sub Adjust
Low light 15% Sub Bright 5) If Sub Bright is changed re-adjust it to set Low light
2
to 10 cd/m
.
6)Find 75% of white area by color sensor.
PANEL W/B
G Drive 7) Set G Drive to " D8 ".
PANEL W/B
B Drive 8) Adjust B and R Drive to set color temperature
R Drive as shown Fig.-04.
2
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
9) Repeat item 4) to 7) to set both Low light and
high light.
PANEL W/B
R,G,B Drive 10) Increase same steps of R, G and B Drive to set
R,G,B Drive largest level of 3 color drive to "FC".
PANEL W/B
R,G,B cut off 11) Re-adjust Low light level again.
Color Temp. x y
Cool(Hi) 0.272 0.290
Normal(Mid) 0.288 0.296
Warm(Low) 0.313 0.329
Fig. -04
2 Picture: 1) Change white balance to "Normal".
Normal PANEL W/B
White balance: R,G,B cut off 2) Repeat procedure 3) to 11) of Cool mode.
Normal
PANEL W/B
Aspect: R,G,B Drive
16:9
3 Picture: 1) Change white balance to "Warm".
Normal PANEL W/B
White balance: R,G,B cut off 2) Repeat procedure 3) to 11) of Cool mode.
Warm
PANEL W/B
Aspect: R,G,B Drive
16:9
4 Picture: Picture Menu 1) Change color templature to "Cool".
Normal Sub Adjust
White balance: Sub Bright 2)Re-set Sub bright to "30"
Cool
Aspect:
16:9
21
Page 22
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
5 Picture: 1) Write down each color temaparature of R,G,B drive and
RGB
Gray Scale
Pattern
High light 75%
Low light 15% 3) Copy HD drive and cut off data of each white
INPUT Alignment menu ProcedureEquipment Setting
Normal Cut off data as follows.
Aspect:
White balance:
Normal
16:9
Cool
Warm
White
Balance Cool Normal Warm
R Drive
G Drive
B Drive
R Cut off
G Cut off
B Cut off
2)Change input signal to 525i and 525p.
balance mode to each signals position.
22
Page 23
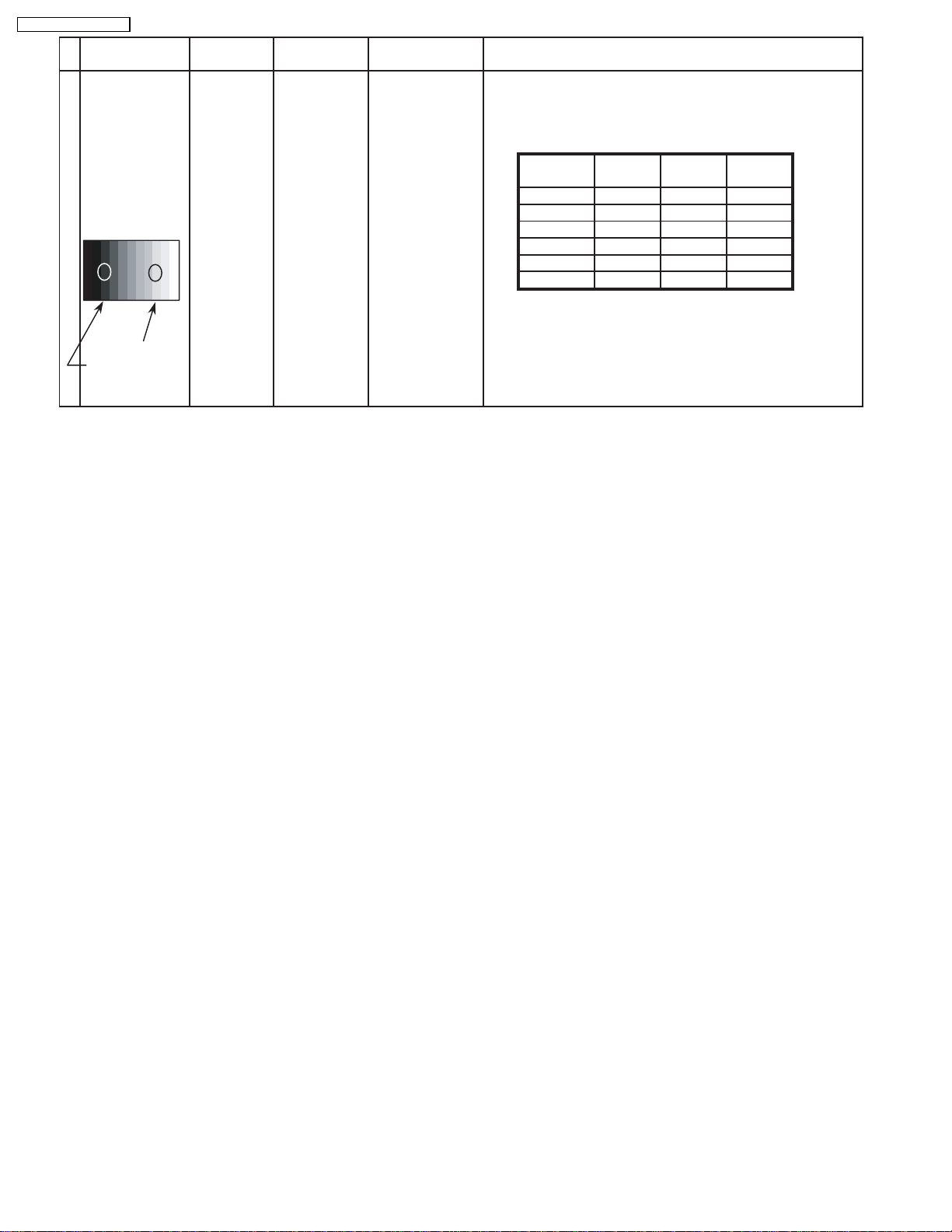
8.6. 625i panel balance
INPUT Alignment menu ProcedureEquipment Setting
1 625i Color Picture: 1) Find the nearest area to brightness of 10 cd/m2 as Low
Gray Scale Analyzer Normal Sub Adjust light by color sensor.
Pattern White balance: Sub Bright 2) Adjust Sub bright to set Low light level to 10 cd/m
Cool exactly.
Aspect: PANEL W/B
16:9 G cut off 3) Set G cut off to " 80 ".
PANEL W/B
B cut off 4) Adjust B and R cut off to set color temperature as
R cut off shown Fig.-05.
High light 75% Sub Adjust
Low light 15% Sub Bright 5) If Sub Bright is changed re-adjust it to set Low light
to 10 cd/m
2
.
6)Find 75% of white area by color sensor.
PANEL W/B
G Drive 7) Set G Drive to " D8 ".
PANEL W/B
B Drive 8) Adjust B and R Drive to set color temperature
R Drive as shown Fig.-05.
9) Repeat item 4) to 7) to set both Low light and
high light.
PANEL W/B
R,G,B Drive 10) Increase same steps of R, G and B Drive to set
R,G,B Drive largest level of 3 color drive to "FC".
PANEL W/B
R,G,B cut off 11) Re-adjust Low light level again.
2
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
Color Temp. x y
Cool(Hi) 0.272 0.290
Normal(Mid) 0.288 0.296
Warm(Low) 0.313 0.329
Fig. -05
2 Picture: 1) Change white balance to "Normal".
Normal PANEL W/B
White balance: R,G,B cut off 2) Repeat procedure 3) to 11) of Cool mode.
Normal PANEL W/B
Aspect: R,G,B Drive
16:9
3 Picture: 1) Change white balance to "Warm".
Normal PANEL W/B
White balance: R,G,B cut off 2) Repeat procedure 3) to 11) of Cool mode.
Warm PANEL W/B
Aspect: R,G,B Drive
16:9
4 Picture: Picture Menu 1) Change color templature to "Cool".
Normal Sub Adjust
White balance: Sub Bright 2)Re-set Sub bright to "30"
Cool
Aspect:
16:9
23
Page 24
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
8.7. Sub brighness setting
INPUT Alignment menu ProcedureEquipment Setting
1 NTSC Picture: PANEL W/B
Gray Scale Normal All cut off 1) Set white balance to
Pattern Aspect:
** Adjust at the dark room.
Cool
.
16:9 2) Adjust All cut off to start some pixels emission
at black 2% area and no emission at black 0% area.
3) Write down all cut off data.
4) Set white balance to
Black 2 %
Black 0 % 5) Adjust All cut off to set same data of Cool mode.
6) Set white balance to
7) Adjust All cut off to set same data of Cool mode.
** Adjust at the dark room.
2 PAL Picture: PANEL W/B
Gray Scale Normal All cut off 1) Set white balance to
Pattern Aspect:
16:9 2) Adjust All cut off to start some pixels emission
at black 2% area and no emission at black 0% area.
3) Write down all cut off data.
4) Set white balance to
Black 2 %
Black 0 % 5) Adjust All cut off to set same data of Cool mode.
6) Set white balance to
7) Adjust All cut off to set same data of Cool mode.
SECAM 8) Change to SECAM signal.
Gray Scale
Pattern 9) Copy PAL All cut off data to SECAM mode.
Nornal
warm
Cool
Nornal
warm
.
.
.
.
.
** Adjust at the dark room.
3 PC Picture: PANEL W/B
Gray Scale Normal All cut off 1) Set white balance to
Pattern Aspect:
16:9 2) Adjust All cut off to start some pixels emission
at black 2% area and no emission at black 0% area.
3) Write down all cut off data.
4) Set white balance to
Black 2 %
Black 0 % 5) Adjust All cut off to set same data of Cool mode.
6) Set white balance to
7) Adjust All cut off to set same data of Cool mode.
RGB
Gray Scale
Pattern
DVI
Gray Scale
Pattern
8) Change to RGB input signal.
9) Copy PC All cut off data to RGB mode.
10) Change to DVI input signal.
11) Copy PC All cut off data to DVI mode.
Cool
Nornal
warm
.
.
.
24
Page 25
Alignment menu ProcedureINPUT Equipment Setting
** Adjust at the dark room.
4 525i Picture: PANEL W/B
Gray Scale Normal All cut off 1) Set white balance to
Pattern Aspect:
16:9 2) Adjust All cut off to start some pixels emission
at black 2% area and no emission at black 0% area.
3) Write down all cut off data.
Cool
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
.
4) Set white balance to
Nornal
.
Black 2 %
Black 0 % 5) Adjust All cut off to set same data of Cool mode.
6) Set white balance to
warm
.
7) Adjust All cut off to set same data of Cool mode.
525p 8) Change to 525p signal.
Gray Scale
Pattern 9) Copy 525i All cut off data to 525p mode.
HD
(720i or 1080i) 8) Change to HD signal.
Gray Scale
Pattern 9) Copy 525i All cut off data to HD mode.
** Adjust at the dark room.
5 625i Picture: PANEL W/B
Cool
Gray Scale Normal All cut off 1) Set white balance to
.
Pattern Aspect:
16:9 2) Adjust All cut off to start some pixels emission
at black 2% area and no emission at black 0% area.
3) Write down all cut off data.
4) Set white balance to
Nornal
.
Black 2 %
Black 0 % 5) Adjust All cut off to set same data of Cool mode.
6) Set white balance to
warm
.
7) Adjust All cut off to set same data of Cool mode.
25
Page 26
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
9 Trouble shooting guide
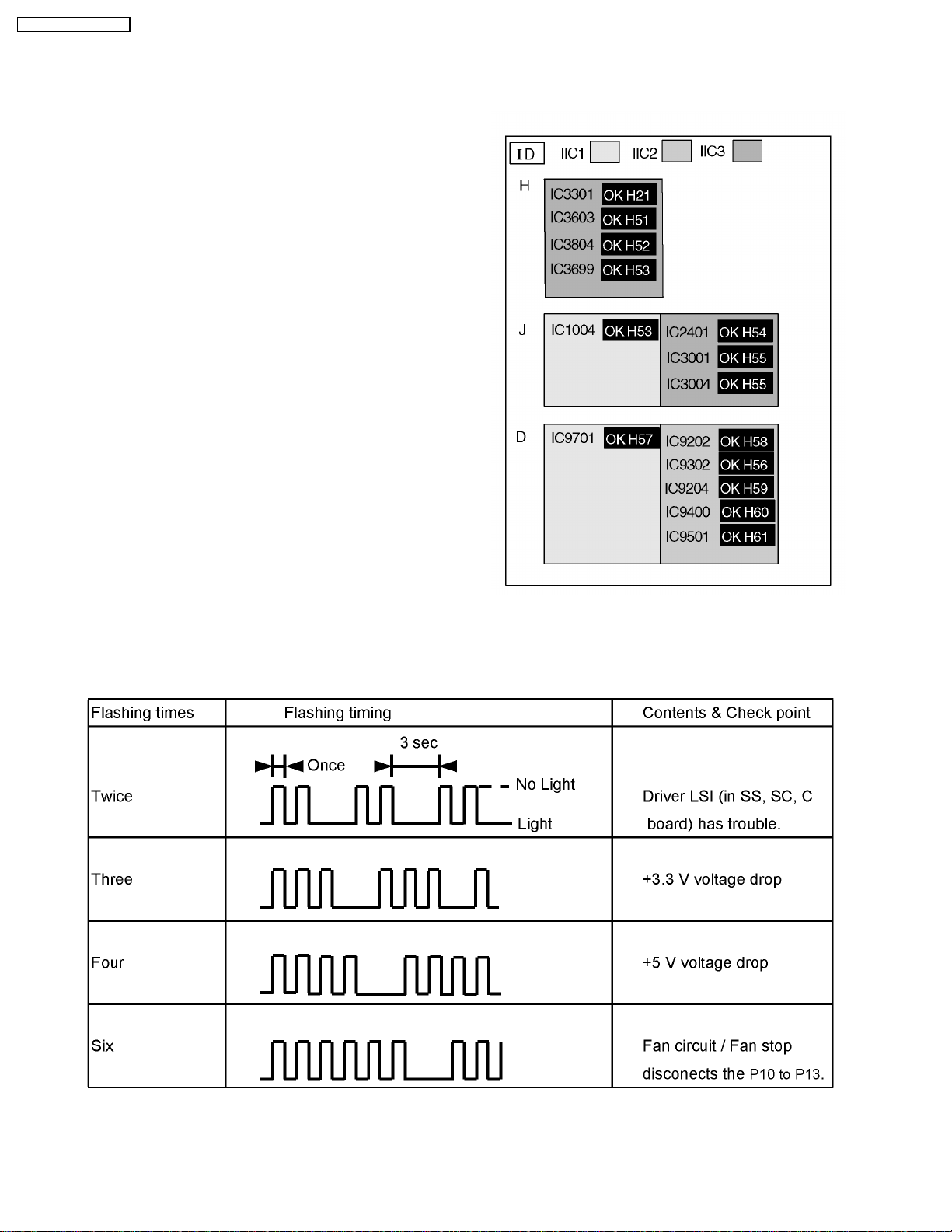
9.1. Self Check
9.1.1. Display Indication
1. Self-check is used to automatically check the bus line
controlled circuit of the Plasma display.
2. To get into the Self-check mode press the volume down
button on the customer controls at the front of the set, at the
same time pressing the OFF-TIMER button on the remote
control, and the screen will show :-
If the CCU ports have been checked and found to be incorrect
Or not located then " - - " will appear in place of " OK "
Note:
In case of disconnected of H/HY/HZ “IC3699 - -” is
displayed.
9.1.2. Power LED Flashing timing chart
When an abnormality has occurred the unit, the protection circuit operates and cuts the power supply. At this time, the defective
part can be identified by the number of flashes of the Power LED at the front of the unit.
Above Fan function is operated during the fan is set.
26
Page 27
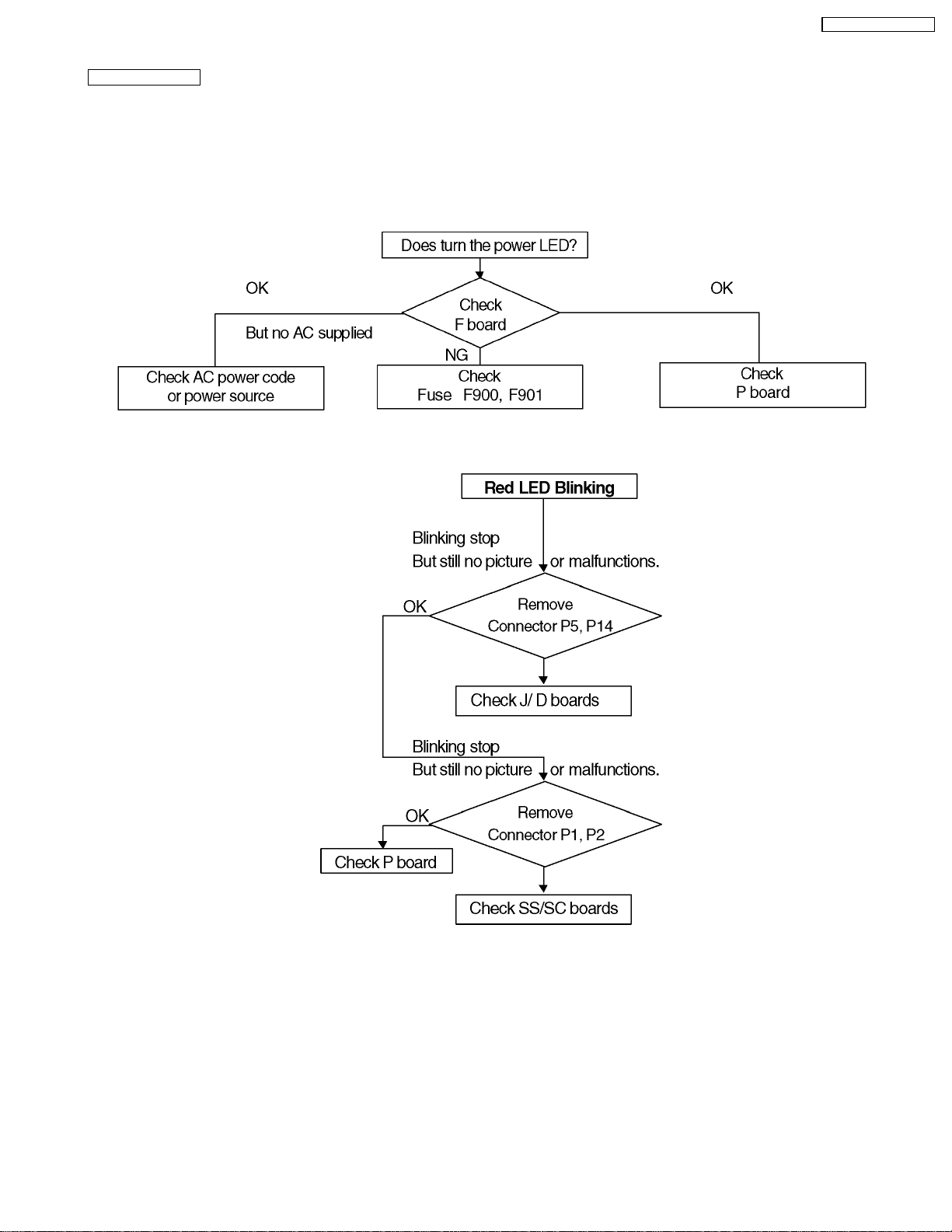
9.2. No Power (US model)
First check point
There are following 3 states of No Power indication by power LED.
1. No lit
2. Green is lit then turns red blinking a few seconds later.
3. Only red is lit.
1. No lit
2. Red LED Blinking
When one or some of supply voltages from power supply circuit are declined red LED will be blinking as power
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
27
Page 28
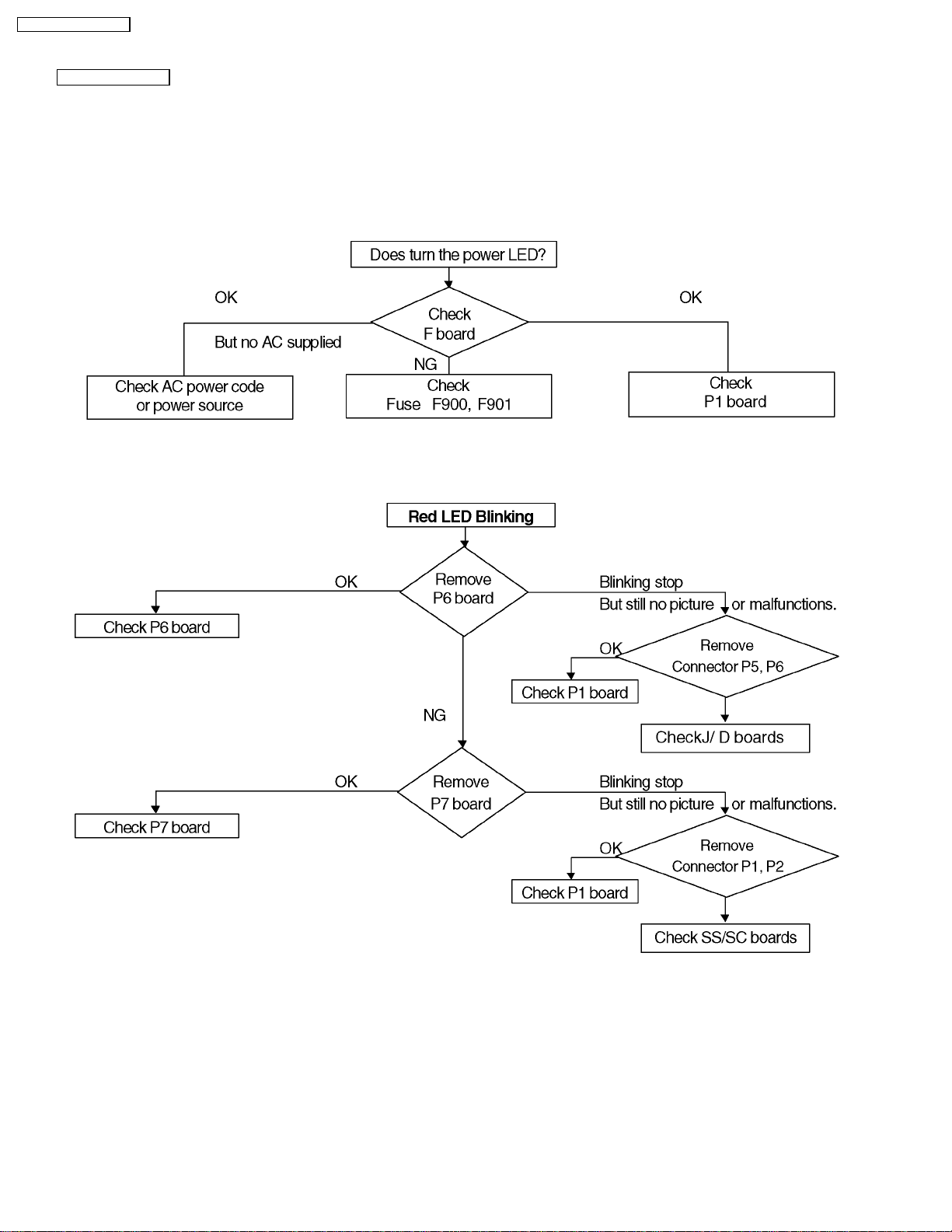
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
9.3. No Power (Except US)
First check point
There are following 3 states of No Power indication by power LED.
1. No lit
2. Green is lit then turns red blinking a few seconds later.
3. Only red is lit.
1. No lit
2. Red LED Blinking
When one or some of supply voltages from power supply circuit are declined red LED will be blinking as power
28
Page 29
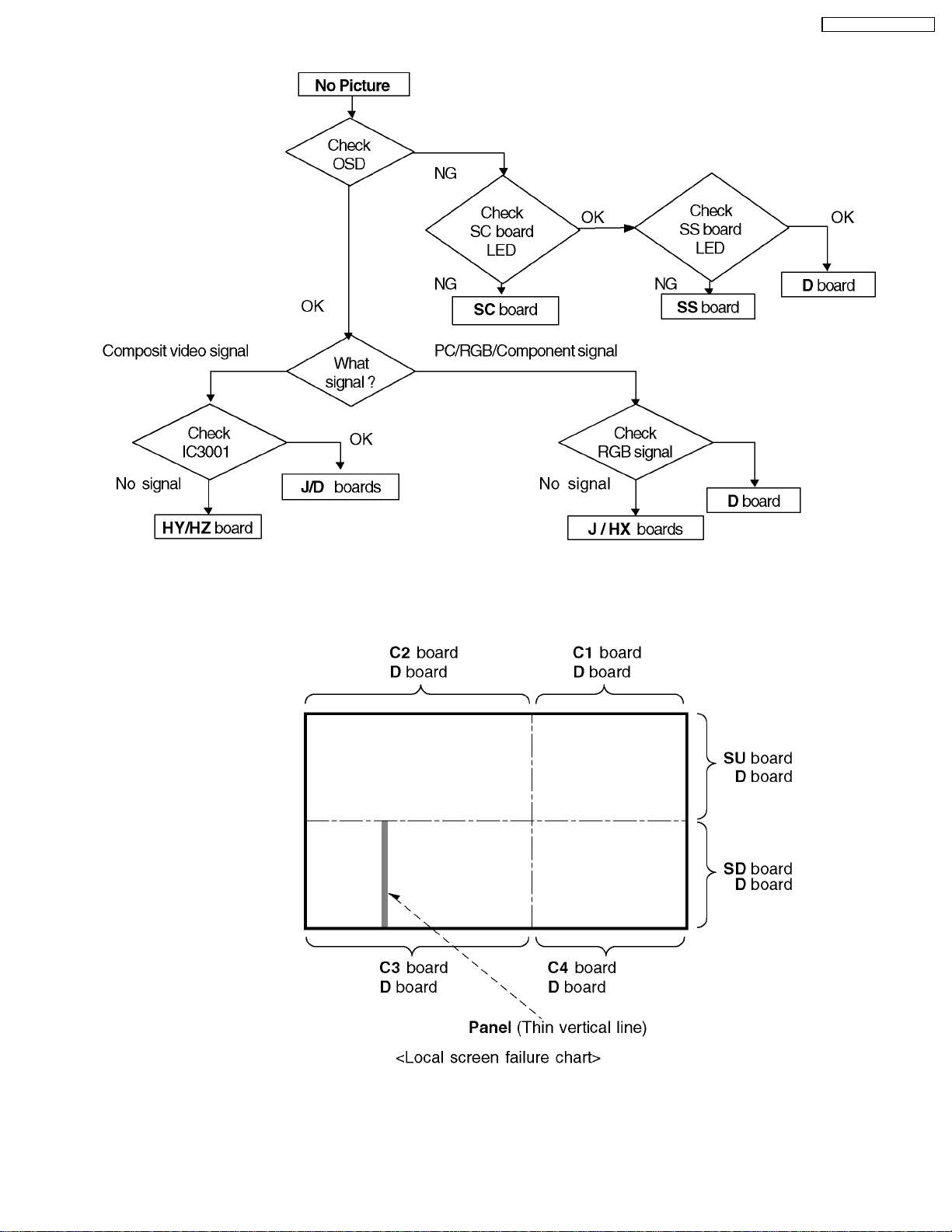
9.4. No Picture
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
9.5. Local screen failure
Plasma display may have local area failure on the screen. Fig - 1 is the possible defect P.C.B. for each local area.
Fig - 1
29
Page 30

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
9.6. D-Board
9.6.1. OUTLINE
D board is consists of Analogue and Digital signal process, Discharge control and Micro control block.
D-board is operated by supply voltages of 3.3V, 5V, 13,5V and Standby 5V , RGB analogue (0.7Vp-p) and Sync. Signal.
D-board output parallel data video signal with control signal for the data driver circuit, Discharge control signal for Scan and Sustain
drive circuits and Micro control signals.
9.6.2. MAIN IC OPERATION
IC9007 ~ 9009 A/D Converter
RGB analogue signals are converted to 8 bits digital signal.
IC9204 FORMAT CONVERTER (LSI33)
Number of Horizontal line of input signals are converted to 480 lines.
This IC uses two clock lines, one is 15M 55MHz for input signal (ICK) and other one is 25M to 40MHz for out put signal. (OCK)
IC9400 PLASMA AI (LSI27)
At first input 8 bit signal data is memorized into two field memory (IC9402, IC9403), Plasma AI analyze APL level and
distribution of dark and bright components.
Plasma AI re-arrange 8 bit signal data to 12 bit signal data.
This IC also insert OSD (On-Screen Display signal) from Micro.
IC9501 SUB FIELD PROCESSOR
R,G and B 12 bit signal data is layout to fit with each electrodes of panel.
One field signal data is separated to upper 240 lines and lower 240 lines.
Both upper and lower signals are again separated odd and even number line and output.
9.6.3. DIAGNOSTIC
(1) General
Depend on the phenomenon possible defective section from Signal processing, Discharge control or Micro control section on
D-board can be diagnosed as follows.
1. Signal Processing section
a. No picture but panel has discharge.
b. Missing R, G or B signal
c. Dark Picture.
d. No OSD signal.
e. Vertical band noise appeared.
f. No picture or distortion on 1/4 area on the screen.
2. Micro control section
a. Does not turn on power.
b. No panel discharge.
3. Discharge control section
a. No discharge but Micro control is operated.
b. Dark picture
30
Page 31

(2) First Check Point
Confirm that follow signals are input to D board.
Power Supply
Connector Pin Function Connector Pin Function
D5
1 13.5 V DC
3 5.0 V DC 2 3.3 V DC
- - 3 3.3 V DC
Input Signal
Connector Function Pin Function
D8-12 Analogue Green signal
D8-13 Analogue Blue signal 29 VD (Vertical Drive pulse)
D8-14 Analogue Red signal 34 CLP (Clamp pulse)
(3) Trouble shooting
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
1 STB 5 V DC
D6
37 HD (Horizontal Drive pulse)
D9
31
Page 32

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
10 Option Setting
How to access the Option menu
32
Page 33

(Not available for TH-42PW4 series models)
System route models TH-42PWD4 series have special function and operation setting facility called
Option Menu. This Option Menu is useful for special function required customers. This should be set
at the installation stage. The end user could not set or change these because of hidden On screen menu.
Option menus
default
setting
Contents
Wobbling Off
Screen image shift OFF.
Turns off the screen shift function that prevents after-images from
appearing on the screen.
Off-timer function Enable
Off-timer operation invalidation.
The off-timer function is made invalid.
On Screen display On
On-screen display OFF.
Turns off the on-screen display that indicates power on, input modes
and when no signal is received.
Initial Input Off
Startup input setting.
Sets the input mode when the power is turned on (VIDEO,
COMPONENT, VIDEO/RGB, PC). Input mode switching is possible
after the power is turned on.
Initial VOL. level Off
Startup volume setting.
Sets the volume level when the power is turned on. Volume can be
adjusted after the power is turned on.
Maximum VOL. Level Off
Maximum volume setting Fix input mode.
Sets the maximum volume level. Volume cannot exceed this limit.
INPUT lock Off
Input mode cannot be switch.
Fixes the input mode to (VIDEO, COMPONENT, VIDEO/RGB, PC) and
input mode cannot be switched.
Button lock Off
Front operation button invalidation.
Front operation buttons are made invalid. Several combinations of
button invalidation are possible ; just the selection keys (VOL. keys, just
the INPUT key, or both VOL. keys and INPUT key.).
Studio W/B Off
Set the screen color temperature to 3,200 kelvin.
(use when the contents displayed on the screen needs to be firmed for
use in news programs or other purposes.) This is valid when the setting
is turned ON and the WHITE BALANCE in the PICTURE menu is set to
WARM.
Remocon User Level Off
Remocon key invalidation.
Off : Valid key is all key of remocon.
User1 : Valid key are only Stand-by (ON/OFF), Input, Status, Surround,
Sound mute On/Off, and volume adjustment.
User2 : Valid key is only Stand-by (ON/OFF).
Note of Remocon User Level:
All key of remote control is valid in the service mode (CAT-mode) regardless of the setting of Remocon
User Level. To change the option setting when the Remocon User Level is set in the User1 or User2,
access the service mode (CAT-mode) first, then display the option menu the same method.
Hidden Option Menu for TH-42PWD4 series
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
33
Page 34

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
34
Page 35

11 IC Block Diagr am
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
35
Page 36

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
INPUTA
A
36
Page 37

12 Conductor View s
12.1. F-Board
6
5
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
F
4
F-BOARD
TXN/F10JAS (US model)
TXN/F1JASE (Except US)
3
2
1
ABCDEFGH I
37
Page 38

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
12.2. P-Board (US model)
6
5
P-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
TXN/P10JAS
4
3
2
1
ABCDEFGH I
38
Page 39

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
P
Parts Location
IC
IC401 F-1
IC403 D-5
IC426 E-3
IC427 E-2
IC461 C-2
IC462 C-3
IC464 C-2
IC465 C-3
IC468 B-5
IC470 B-4
IC471 C-6
IC472 B-2
IC473 C-5
IC474 C-3
P-BOARD (FOIL SIDE)
TRANSISTOR TP
Q461 C-3
Q463 C-3
Q464 C-2
Q465 C-2
Q467 C-3
Q469 C-6
Q480 B-2
Q481 B-3
Q483 B-6
Q485 C-6
Q500 C-6
Q515 C-5
Q516 C-5
TPP1 D-4
Parts Location
P-BOARD (COMPONENT SIDE)
IC
IC401 C-1
IC403 D-5
IC426 C-3
IC427 C-2
IC461 E-2
IC462 E-3
IC464 E-2
IC465 E-3
IC468 F-5
IC470 F-5
IC471 E-6
IC472 F-2
IC473 E-5
IC474 F-3
TRANSISTOR
Q461 E-3
Q463 E-3
Q464 E-2
Q465 E-2
Q467 E-3
Q469 E-6
Q480 F-2
Q481 F-2
Q483 F-6
Q485 E-6
Q500 F-6
Q515 E-5
Q516 E-5
39
Page 40

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
6
5
P-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE) US Model
TXN/P10JAS
4
3
2
1
ABCDEFGH I
40
Page 41

12.3. P1-Board (Except US)
P1-BOARD (FOIL SIDE)
TXNP11JASE
6
5
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
4
3
2
1
ABCDEFGH I
41
Page 42

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
P1
Parts Location
IC
IC401 F-3
IC402 F-3
IC403 D-5
IC406 D-2
IC407 C-5
IC409 C-3
IC410 C-5
IC411 C-5
IC412 B-3
IC464 D-1
P-BOARD (FOIL SIDE)
TRANSISTOR
Q401 F-4
Q402 E-3
Q404 F-3
Q405 F-2
Q406 F-2
Q407 F-1
Q408 F-1
Q409 E-2
Q410 E-3
Q412 C-6
Q413 B-5
Q414 C-6
Q415 C-6
Q416 E-3
Q417 E-3
Q418 B-5
Q419 B-4
Q420 B-3
Q421 B-5
Q422 F-4
Q423 B-5
Q464 C-1
Q465 D-1
Parts Location
P-BOARD (COMPONENT SIDE)
IC
IC401 B-3
IC402 B-3
IC403 E-5
IC406 E-2
IC407 E-5
IC409 F-3
IC410 F-5
IC411 F-5
IC412 F-3
IC464 E-1
TRANSISTOR
Q401 B-3
Q402 C-4
Q404 B-3
Q405 B-2
Q406 B-2
Q407 B-1
Q408 B-1
Q409 C-2
Q410 D-3
Q413 F-5
Q414 E-6
Q415 E-6
Q416 C-3
Q417 C-3
Q418 F-5
Q419 F-4
Q420 F-3
Q421 F-5
Q422 B-3
Q423 F-5
Q464 E-1
Q465 D-1
42
Page 43

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
P1-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE) Except US
TXNP11JASE
6
5
4
3
2
1
ABCDEFGH I
43
Page 44

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
12.4. P3, P5, P6, P7 and P8-Board (Except US)
P5-BOARD (FOIL SIDE)
TNPA1778
6
5
P7-BOARD (FOIL SIDE)
TNPA1780
4
P6-BOARD (FOIL SIDE)
TNPA1779
P8-BOARD (FOIL SIDE)
TNPA1781
P8 P7
P6
P5 P3
3
P3-BOARD (FOIL SIDE)
TNPA1777
2
1
ABCDEFGH I
44
Page 45

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
P6-BOARD (COMPONENT SIDE)
TNPA1779
P5-BOARD (COMPONENT SIDE)
TNPA1778
P8 P7
6
5
P6
P5 P3
P8-BOARD (COMPONENT SIDE)
TNPA1781
P7-BOARD (COMPONENT SIDE)
TNPA1780
4
3
P3-BOARD (COMPONENT SIDE)
TNPA1777
2
1
ABCDEFGH I
45
Page 46

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
12.5. HX-Board
6
HX-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
TZTNP020JAS
HX-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE)
TZTNP020JAS
5
HX
4
Parts Location
HX-BOARD
IC
3
IC3502 F-2
IC3515 E-2
TRANSISTOR
Q3507 F-3
Q3508 F-3
Q3509 F-3
Q3513 E-4
Q3514 E-4
Q3515 F-4
Q3516 F-4
Q3531 E-3
Q3532 F-3
2
1
ABCDEFGH I
46
Page 47

12.6. H-Board (Option TY-42TM4H)
6
H-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
TXN/H10JKS
5
A24
A25 A1
B24
B25
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
A2
A20
A1
A19
B2
B20
B1
H1
B19
H2
A2
B2
B1
IC3699
8
54
1
4
H
TNPA2247
SEE REVERSE FOR ORDER NO.
2H
3
2
JK3311
1
10
19 26
9
18
1
ABCDEFGH I
47
Page 48

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
6
5
H-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE)
TXN/H10JKS
H2
JS28
JS29
JS30
IC3699
C3506
R3522
R3521
H1
4
H
TNPA2247
2H
L3460
R3482
Q3451
R3467
R3476
R3465
R3475
C3468
Q3458
R3497
R3492
R3469
L3458
C3463
R3466
R3496
C3457
R3491
R3470
C3465
R3471
C3458
Q3457
D3452
R3479
Q3454
D3451
R3483
C3466
R3484
C3464
R3480
Q3455
L3459
R3472
R3473
C3459
R3459
L3455
R3460
R3474
Q3452
R3478
L3456
R3488
R3461
R3481
L3457
R3486
C3461
R3485
C3451
C3460
C3452
Q3456
R3453
R3451
IC3451
R3489 R3490
R3494
C3462
R3493
C3453
R3452
R3454
R3495
Q3459
R3498 R3499
C3454
Parts Location
H-BOARD (COMPONENT SIDE)
IC
IC3451 B-2
IC3699 D-2
TRANSISTOR
Q3451 A-2
Q3452 B-3
Q3453 A-2
Q3454 B-2
Q3455 B-2
Q3456 B-3
Q3457 B-2
Q3458 A-2
Q3459 B-3
3
C3467
R3487
Q3453
R3468
R3477
R3462
R3463
R3464
C3455
R3455
L3451
R3456
L3452
R3457
L3453
C3456
R3458
L3454
2
JK3311
1
ABCDEFGH I
48
Page 49

12.7. HY-Board (Option TY-42TM4Y)
6
HY-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
TNPA2245
5
4
5
JS32
JS31
41
IC699
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
A2
A24
A25
B24
B25
H1
R516
R522
R521
R517
R866
R519
R520
R518
C705
C709
8
C506
C706
C896
C707
C702
C704
R841
C854
Q816
C895
R883
C888
R888
C869
R887
C862
C867
C863
R847
R843
JS15
R872
R880
R882
C876
R878
C889
Q814
R851
R881
R842
JS14
JS16
R860
R861
C891
R852
C899
R870
Q817
A20
A1
A19
B2
B20
B1
B19
JS30
JS29
R537
R550
R534
R509
JS19
JS13
C885
C877
R853
C874
C882
C884
C897
R864
R865
R848
R874
R877
R503
R869
R875
R873
R846
C729
C878
C880
C881
H2
JS28
R536
R549
R514
R508
R868
R879
R886
JS36
JS35
R535
R548
R507
R513
R506
R502
JS23
R876
R885
A2
A1
B2
B1
C507
R511
R505
R504
R532R533
JS21
R501
JS22
JS24
JS20
HY
CR NO.
R301
C843
JS8
HY
3
R307
R303
R814
Q808
C807
R809
R810
R805
R804
Q804
R310
C302
R319
C301
R304
JK303
R819
R807
C819
R817
R821
R822
R322
R384
R381 R382
C356
R359
R352
LR
C824
C840
C841
R831
R830
C839
R829
Q810
R832
R833
R823
R824
Q809
R825
R827
R383
R380
C355
R358
R351
GAP11
3
R340
Q306
R337
R346
2
R330
R331
JK300
R
R336
R347
C306
R328
R327
C307
R329
L
R306
R308
R345
R348
R342
R344
R343
R341
R326
R321
R315
R305
R350
R309
JK301
Y
Q302
C309
R324
R320
R312
R317
R313
R314
R349
C
R302
TNPA2245
SEE REVERSEFOR ORDERNO.
JK302
R828
C825
R826
JS9
C828
R834
C832
C822
R378
R366
R379
R361
R367
C352
R357
GAP10
R836
C826
C820
R816
R806
R389
R393
C351
JK304
C842
JS10
R813
R812
L807
C805
R808
C801
R803
R394
R390
R356
R392
R391
R360
C359
R355
GAP9
L805
Parts Location
HY-BOARD (FOIL SIDE)
IC
IC3699 C-4 Q3302 B-2
R385
C360
C357
R368
R365
C358
C354
R354
C353
R353
GAP7
GAP8
TRANSISTOR
Q3306 B-2
Q3804 C-2
Q3808 D-2
Q3809 D-2
Q3810 D-2
Q3814 D-4
Q3816 D-4
Q3817 D-3
1
ABCDEFGH I
49
Page 50

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
6
5
HY-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE)
TNPA2245
C513
Q510
R552
R538
TPHY1
Q501
C502
Q507
4
L817
L815
C701
3
L805
JS4
JS1
Q351
2
C363
L359
R373
R363
R364
R377
R362
C362
H2
R551
TPHR1
TPHB1
R539
Q502
C503
Q813
L818
C898
C700
L830
C723
C726
C844
C812
C803
C814
C813
L804
Q357
Q356
R386
R374
R388
L354
L353
R540
Q508
Q503
C504
Q815
L819
R856
R884
R890
R889
TPHV1
TPHH1
IC303
JS18
L820L821
L809
JS7
C815
L803
C802
L806
R811
Q801
R387
D352
L355
JK304
L501
R892
Q509
Q308
R891
R858
R854
R867
Q812
C887
R855
C365
R845
R844
C864
C855
IC809
C852
R835
D801
C808
IC802
Q805
Q803
L801
R801
Q358
C806
C804
Q359
L356
C512
C717
C718
R894
L814
C892
C893
R849
R857
C879
C883
R859
R850
C870
IC804
C833
C836
R818
C818
L808
JS3
C838
C835
IC801
C817
Q352
Q353
D351
L357
H1
C511
L825
C712C713
JS17
C875
L813
R863
C872
R871
R862
C868
C830
C834
C837
C821
C823
C816
C361
R371
R375
C364
L358
C510
C509
L822
C711
L824
C710
C716
C714
C728
C727
C890
C871
C873
L812
C886
C865
C866
C861
C853
C851
C850
C846
C831
C847
X801
R820
Q354
JS2
R372
L351
GAP5
JS12
C810
Q807
C809
R815
Q806
Q355
C313
R370
R376
R369
L307
L352
GAP6
C505
L823
C501
IC501
R895
C715
R541
L816
C894
C703
IC805
JK303
IC803
JS6
JS5
LC805
L802
R311
R316
C708
C860
TNPA2245
IC806
L811
C849
R840
C845
R838
C859
JS11
R802
Q802
Q301
L301
GAP1
C314
L829
IC699
C856
R837
CR NO.
H0
L826
L827
L828
HY
C857
C858
C848
R839
L810
C829
Parts Location
HY-BOARD (COMPONENT SIDE)
R396
C811
HY
3
C303
L302
JK302
GAP2
Q307
C304
L303
IC302
R893
Q309
R395
R335
R334
C312
R323
C305
Q303
R325
Q304
R318
GAP12
JK301
IC301
C310
L306
C311
Q305
R332
R338
R339
R333
GAP3
L305
GAP4
JK300
L304
IC
IC3301 E-2
IC3302 E-3
IC3303 B-4
IC3501 D-4
IC3699 D-4
IC3801 B-2
IC3802 B-3
IC3803 D-2
IC3804 C-4
IC3805 C-4
IC3806 C-4
IC3809 B-3
TRANSISTOR
Q3301 D-1
Q3303 E-2
Q3304 E-2
Q3305 F-2
Q3307 E-2
Q3308 B-4
Q3309 E-2
Q3351 A-2
Q3352 C-2
Q3353 B-2
Q3354 C-2
Q3355 C-2
Q3356 A-2
Q3357 B-2
Q3358 B-2
Q3369 B-2
Q3501 A-4
Q3502 A-4
Q3503 B-4
Q3507 A-4
Q3508 B-4
Q3509 B-4
Q3510 A-5
Q3801 B-2
Q3802 C-2
Q3803 B-2
Q3805 B-3
Q3806 C-2
Q3807 C-2
Q3812 B-4
Q3813 B-4
Q3815 B-4
TP
TPHB B-5
TPHH B-4
TPHR B-5
TPHV B-4
TPHY A-4
1
ABCDEFGH I
50
Page 51

12.8. HZ-Board (Option TY-42T\M4Z)
6
HZ-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
TNPA2248
5
A24
A25
B24
B25
R516
R522
R521
R517
R519
5
JS32
JS31
41
R520
IC699
4
R518
C705
C709
8
C506
C706
C896
C707
C702
C704
C862
R841
C854
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
A2
A20
A1
A19
B2
B20
B1
B19
H1
JS15
R866
C895
R883
C888
C869
R887
C863
R843
R872
Q816
R880
R882
C876
R878
C889
Q814
R888
R851
C867
R881
R847
R842
JS14
JS13
JS16
C885
R860
R861
C877
C891
R852
C899
R870
R853
C874
R864
Q817
R865
JS30
JS28
JS29
R537
R550
R534
R869
R846
C729
C897
C878
C880
C881
C882
C884
R848
R874
R877
R549
R509
R514
R508
JS19
R503
R879
R886
R875
R873
JS36
JS35
H2
R536
R533
R868
R535
R548
R507
R513
R506
R502
JS23
R876
R885
A2
A1
B2
B1
C507
R511
R505
R504
R532
JS21
R501
JS22
JS24
JS20
1
HZ
HZ
3
CR NO.
R340
R337
Q306
R345
R348
2
R346
C306
R328
R330
C307
R327
R331
R329
JK305
R306
R
R336
R347
R342
C309
R344
R343
R341
R326
R321
R315
R314
R308
B
C843
JS8
R814
Q808
3
R810
Q302
R324
R320
R307
R312
R317
R313
R301
GR
R303
R305
R309
R350
JK301
Y
C807
R809
R805
R804
Q804
R310
R319
C302
C301
R304
R349
C
R819
R807
C819
R817
R821
R822
R322
R384
R381 R382
C356
R359
R352
R
C824
C840
C841
R831
R833
R823
R830
R829
R824
C839
Q810
Q809
R825
R827
R383
R380
C355
R358
R351
L
R828
R826
C825
JS9
C828
R834
R832
C832
C822
R378
R366
R379
R361
R367
C352
R357
JK308
GAP11
R
GAP10
R836
C826
C820
R816
R806
R389
C351
L
C842
JS10
R813
R812
L807
C805
R808
C801
R803
R393
R394
R390
R360
R391
C359
R356
R355
GAP9
R
L805
R392
R385
R368
GAP8
R365
C358
C354
R354
C353
R353
GAP7
C360
C357
JK306JK307
SEE REVERSEFOR ORDERNO.
TNPA2248
Parts Location
HZ-BOARD (FOIL SIDE)
IC
IC3699 B-4 Q3302 B-2
GRB
TRANSISTOR
Q3306 A-2
Q3804 B-2
Q3808 C-3
Q3809 C-2
Q3810 C-2
Q3814 C-4
Q3816 C-4
Q3817 C-3
1
ABCDEFGH I
51
Page 52

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
6
5
HZ-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE)
TNPA2248
C513
R552
R538
TPHY1
Q501
C502
4
TNPA2248
L817
Q507
Q502
C503
L815
C701
C700
C723
HZ
3
2
C363
C362
L359
C844
L805
C814
JS4
JS1
Q356
Q351
R362
R373
R363
R364
R377
L353
JK306
TPHR1
TPHB1
Q813
L818
C898
L830
C726
C812
C803
C813
L804
Q357
R386
R374
R388
L354
R540
R539
Q508
Q503
C504
Q815
L819
Q812
R889
R856
R890
R884
TPHV1
TPHH1
JS18
L820L821
L809
JS7
C815
Q805
L803
C802
L806
R811
Q801
R387
D352
L355
L501
R892
Q509
Q308
R891
R858
R867
R854
C887
R855
C365
R845
IC303
R844
C864
C855
IC809
C852
R835
D801
C808
IC802
Q803
L801
R801
Q358
C806
C804
Q359
L356
JK308
C512
C718
C717
R894
L814
C892
C893
R849
R857
C879
C883
R859
R850
C870
IC804
C833
C838
C836
R818
C818
C835
IC801
L808
C817
JS3
Q352
Q353
D351
L357
H2
R551
Q510
L813
R863
R862
C868
C834
C837
C821
C823
C361
L358
H1
C511
L825
C712C713
JS17
C875
C872
R871
C830
C816
R371
R375
C364
GAP5 GAP6
C510
C509
L822
C711
L824
C710
C716
C714
C728
C890
C727
C871
C873
L812
C886
C865
C866
C861
C853
C851
C850
C846
C831
C847
X801
R820
Q354
JS2
R372
L351
JS12
C810
Q807
C809
R815
Q806
Q355
C313
R370
R376
R369
L307
L352
JK307
C505
L823
C501
IC501
R895
C715
R541
L816
C894
C703
IC805
C708
IC803
L811
IC806
C849
R840
C845
R838
IC699
H0
L826
L827
L828
L829
C856
R837
C857
C858
C848
R839
L810
C829
Parts Location
HZ
HZ-BOARD (COMPONENT SIDE)
IC
C859
JS11
LC805
JS5
CR1NO.
L802
R802
Q802
Q301
R316
R311
L301
C314
GAP1
L302
JK301
C860
JS6
3
C303
GAP2
C811
R396
IC302
R893
Q309
R335
Q307
C304
L303
R395
R334
C312
R323
C305
Q303
R318
GAP12
JK305
L306
C310
C311
Q305
R332
IC301
Q304
R339
R338
R325
L304
R333
GAP4
GAP3
L305
IC3301 E-2
IC3301 E-2
IC3302 D-2
IC3303 B-4
IC3501 D-4
IC3699 D-4
IC3801 B-2
IC3802 B-3
IC3803 D-3
IC3804 C-4
IC3805 C-4
IC3806 C-4
IC3809 B-3
TRANSISTOR
Q3301 D-2
Q3303 D-2
Q3304 E-2
Q3305 E-2
Q3307 D-2
Q3308 B-4
Q3309 D-2
Q3351 A-2
Q3352 C-2
Q3353 B-2
Q3354 C-2
Q3355 C-2
Q3356 A-2
Q3357 B-2
Q3358 B-2
Q3359 B-2
Q3501 A-4
Q3502 A-4
Q3503 B-4
Q3507 A-4
Q3508 B-4
Q3509 B-4
Q3510 B-5
Q3801 B-2
Q3802 C-2
Q3803 B-2
Q3805 B-3
Q3806 C-2
Q3807 C-2
Q3812 B-4
Q3813 B-4
Q3815 B-4
TP
TPHB1 B-5
TPHH1 B-4
TPHR1 B-5
TPHV1 B-4
TPHY1 A-4
1
ABCDEFGH I
52
Page 53

12.9. J-Board
J-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
TNPA2244
6
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
J4
1
6
J6
1
A25
B25
A24
B24
R3046
R3045
6
D3001
C3028
C961
5
C3030
C2342
R2301
C2437
R2452
C2317
R2304
C2333
R2327
C2332
C2313
C2325
C2324
C2346
C2452
R2453
C2434
R2307
R2431
R2308
C2329
JS2301
R2347
R2346
C2319
C2343
R2434
C2438
C2315
C2461
C2436
D2309
C2426
R2456
Q2306
L2302
C2321
R2447
R2318
R2317
R2348
C2347
20
1
D2305
JS2303
R2441
C2327
C2432
C2463
R2305
IC2302
R2476
JS2302
R2449
R2448
R2333
11 10
L2303
R3048 R3049R3050
R3016
R1018
C3046
C3048
C3009
R3019
R3069
R1017
R3058
R3072
R3064
R3020
Q3007
R3021
R3004
R1062
R1016
R3031
R1055
R1015
R3051 R3052R3053
C3043
C3044
R1053
Q3001
R3063
R3027
R3030
R1054
R1014
R3054
C3004
C3008
R8023
R8024
C8016
C8018
C8021
R3028
R3029
R3024
R3025
R3026
R1006
R1048
R1049
R1050
R1012
R1013
R1010
R1011
14
R1008
11
10
JS8019
R8007
R8001
Q1001
R8034
R8026
J3002
R8021
R8022
R8031
R1044
R1043
R1034
R1032
R1030
R1024
R1020
JS8023
R8032
Q8030
R8030
R8028
R8029
R8010
C8014
C8012
C8013
R8006
R8005
R2482
C2480
C2442
R2481
R3032R3033
R1070
Q1005
Q1003
R1065
R1067
R1063
R2484
R2457
R3034 R3035
R8033
R8027
R1068
C1006
C2314
R2467
R2468
R8013
C8015
C2453
C8020
R2336
7
C2350
C2339
R8025
R2324
R2331
R2329
C2336
1
C2433
32
Q2302
11 10
L2304
C2312
C2431
C2429
TNPA2244
JS8022
JS8021
C8022
R8011
R8015
R8018
IC8001
20
R2466
R2463
R2460
1
R8008
C8007
R8002
R8003
R8004
C2484
C3050
C1005
R1019
Q1004
C1014
R1069
R1066
R1064
C1013
Q1002
J3001
1
J1
B2A1A2
B1
4
A20
A19
C3020
B20
B19
JS3006
JS3005
JS3004
R3013
C3017
R3012
C3016
R3011
C3019
C3015
R3056
R3066
R3067
C3018
Q3003
R3073
Q3009
C3045
C3047
C3014
Q3005
R3070
R3074
Q3011
C3013
R3105
R3104
R3103
J2
R3095
R3096
R3097
3
B2
A2
A1
B1
A20
B20
A19
B19
R3023
R1072
R3022
C1010
C1009
R3018
R3017
R1059
J99
2
R1047
18
J3
B2A1A2
B1
R1033
R1027
R1021
R1041
R1039
R1060
R1061
R1056
R1035
R1029
R1023
R1045
R1042
R1037
R1025
R1031
R1057
SEE REVERSE FOR ORDERNO.
D2306
C2337
16 17
IC2401
D2308
R2477
C2330
C2316
C2458
R2321
R2335
R2330
C2460
Q2301
C2349
C2338
R2319
R954
C2340
C2462
C2464
C2331
R2326
R951
C2318
C2323
C2322
C2344
C2320
L953
C960
R960
R961
R955
D951
Q951
R953
C954
C3035
C2341
C2328
R2322 R2323
1
J
R956
L2301
R959
R958
R957
1
J13
C955
C957
7
C951
C952
D952
L951
C953
110
J
J14
R3043
R3042
J11
C3033
C2345
20
1
C2326
IC2301
J10
1413
Parts Location
IC
IC2301 E-2
IC2302 E-2
IC2401 E-3
IC8001 D-4
J-BOARD (FOIL SIDE)
TRANSISTOR
Q951 E-4
Q1001 C-2
Q1002 C-2
Q1003 C-2
Q1004 C-2
Q1005 C-2
Q2301 E-3
Q2302 D-3
Q2306 D-3
Q3001 C-5
Q3003 B-5
Q3005 C-5
Q3007 C-4
Q3009 B-2
Q3011 C-4
1
ABCDEFGH I
53
Page 54

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
6
J-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE)
TNPA2244
J4
R3010
R3007
C3025
R3009
R3061
R3076
R1003
R1001
R1004
R3057
R3068
IC3009
C3042
R3094
R3093
R3092
R3087
IC3008
C3049
R3047
C3019
Q3086
R3014
R3015
C3034
L3001
R3088
R3106
R3108
R3107
JS3003
JS3002
JS3001
J2J3
Q3085
J1
D3002
R3109
Parts Location
IC
IC951 B-4
IC1001 D-2
IC1002 E-1
IC1003 E-3
IC1004 D-1
IC2301 B-2
IC2302 C-2
IC2304 C-4
IC2401 C-3
IC3001 E-3
IC3002 E-3
IC3003 D-3
IC3004 D-2
IC3006 C-5
IC3007 B-3
IC3008 E-1
IC3009 E-2
IC8001 D-4
IC8002 D-4
IC8003 D-5
J
J-BOARD (COMPONENT SIDE)
TRANSISTOR TP
Q2303 C-3
Q2304 C-3
Q2305 C-3
Q2406 C-4
Q2408 D-3
Q2410 D-3
Q3002 E-5
Q3004 E-5
Q3006 E-5
Q3008 E-4
Q3010 E-4
Q3012 E-4
Q3085 E-2
Q3086 E-5
Q8021 D-3
TP3085 D-4
TP3086 D-5
TP3087 D-4
TP3088 D-4
TP3089 D-4
TP3110 B-5
TP3111 B-3
TP3112 B-3
TP3113 B-3
J6
R3038
IC8002
IC8001
C1006
R3037
R8020
J3001
L1001
C8010
Q8021
D1001
L2401
C2455
R8019
C8004
L3007
R3036
R8014
L8001
C1011
R2483
R2480
R8012
X1001
J8
R8036
IC8003
R8035
TP3087
C8023
R8017
C8002
R1046
R1040
R1038
R1036
R2438
R8016
C8019
C8017
D8001
C8003
R2464
Q2410
Q2408
C1012
IC1004
L8002L8003
D8002
C8008
C8005
C3023
IC3004
R1071
C1015
L3003
C1001
R1052
R1009
TP3089
C3001
R8009
C8011
C8009
C8006
R3001
C8001 C2435
C3024
R1005
R1007
IC1001
R1051
R1028
R1026
R1022
C1016
J3002
C2450
C2429
C2437
C2390C2391
C2314
R2343
R2344
L2304
C2325
R2325
R2410
D2315
R2461
C3029
IC3006
L2306
R2473
IC2304
C2335
C2456
R2470
R2471
R2462
R2472
C2465
C2440
C2441
R3039
C961
C2344
R3043
TP3110
L953
D2306
C960
C959
C956
C958
IC951
R952
C3031
C3038
C2427
C2430
R2450
C2422
C2466
C2467
C3032
IC2401
IC3007
C2474
C2417
Q2305
R2408
TP3112
R2341
R2342
R2320
R2328
D2314
C2347
C2323
C2334
IC2301
C2388
C2389
C2316
L2303
D2301
D2302D2303 D2304
R2445
C2457
C2348
R2439
R2332
IC2302
D2305
L2305
C2313
R2440
C2419
R2442
Q2406
C2423
C2438
C2451
L2302
R2334
R2469
C2459
R2345
Q2303
Q2304
R2310
C2346
C2317
1
C2454
R2306
R2309
D2307
J
5
J13J14
4
L951
3
J10 J11
R959
R958
R957
L952
D953
C951
C3039
C3036
TP3113
R3042
C3037
TP3111
C2345
2
L2301
TNPA2244
C3005
C3006
C3007
C3002
R3002
C1007
R3040 R3041
TP3086
TP3088
TP3085
C3003
R3003
IC3003
R3005
C1004
Q3008
R3101
C3021
X1002
R1058
IC1002
R3091
R3098
Q3002
L3004
L3002
J9
R3060
R3090
R3006
R3055
R3065
R3075
R3102
R3089
C3022
Q3012
C1008
IC3001
Q3006
R3099
L3005
R3062
R3008
R3059
R3071
R3077
C1002
C1003
Q3010
IC1003
C3011
C3010
J99
C3012
Q3004
R3100
L3006
IC3002
R1002
L1002
1
ABCDEFGH I
54
Page 55

12.10. D-Board
D-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
TZTNP01JCSE (PW4 SERIES)
TZTNP01JASE (PW4D SERIES)
6
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
C936
Q801
LC007
LC008
R009
R006
R022
3
R017
4
R016
5
LC004
4
3
R620
R621
R623
R624
R622
C012
R036
R037
R035
R059
Q009
Q010
R101
IC006
R100
16
C031
C030
R045
1
C047
R028
R124
R027
R051
Q001
Q002
R092R093
16
C023
C022
R039
1
C041
R120
R032R033
R031
R055
Q005
Q006
R097
R096
C016
16
C027
C026
R042
1
IC005
C061
R179
C001
C005
R004
R181
R183
R180
R182
R185
R547
R612
R613
C567
C568
2
R011
R010
IC001
R008
IC000
R007
R015
R013
3
1
1
5
5
4
4
R137
R020
R018
R136
R014
C011
R012
C013
Q011
R099
C017
R046
R029
Q003
C018
R040
C032
C015
R609
C563
R562
R546
R544
R542
R540
R538
R536
R533
R531
R528
C113
9
C029
C097
1
R047
8
R125
C057
C048
10 11
IC019
R144
1
C095
IC004
9
R091
R041
C021
C111
8
R122
C055
10
C104
C045
IC020
1
C096
Q007
R095
9
C112
C025
C053
8
10
R043
R044
L014
C035
C068
C042
C044
R005
R550
C564
C538
C527
LC013
IC002
3
1
5
R138
C033
IC021
C100
R172
L006
L005
96
97
128
C531
L015
R205
C034
C019
L013
C036
R196
20
R142
11
C098
20
C099
C541
1
C535
R107
R106
C082
C107
R193
R154
R190
C110
C103
R194
R191
20
C105
R152
R188
C108
C101
R195
R192
C106
R153
R189
D717
R116
C109
11
R049
C102
R050
C091
C092
65
32
IC508
R201
R200
R204
C308
R307
C315
C077
C071
Q703
R788
C539
64
33
C528
R309
C317
C322
C327
C333
C306
C335
C305
C334
R410
R409
C402
C401
C400
C410
R602
C532
C937
C809
C808
C807
C811
C812
C806
R315
R316
C309
R347
R348
R310
C307
Q701
C336
C422
R403
C411
C407
IC503
50
51
R521
80
81
LC803
R808
C810
C813
C814
C815
C816
C314
C310
C311
C319
R267
R313
C331
R314
R319
R351
C337
R318
C404
R404
C403
C409
31
C421
C412
C408
C515
31
30
R601
1
100
C511
R810
R809
R286
R273
C804
R279
C802
LC801
R278
LC802
80
81
R226
C232
R308
100
R219
R263
R342
R268
C229
R350
R264
R334
R333
R222
C227
81
R225
R224
R223
R257
C224
100
30
50
51
C417
IC502
C507
50
51
R522
R603
C508
80
81
R272
R212
R298
R259
R285
R118
IC209
C250
1
C251
C240
R249
C241
C205
80
1
IC201
1
100
31
C420
81
80
IC403
C505
C514
31
R530
30
R604
1
100
C509
C512
R169
D201
C239
R260
51
50
C235
R231
C259
R229
C231
31
50
30
51
C204
51
50
80
81
C223
C201
C214
31
30
30
50
51
IC402
C572
C504
IC506
C524
50
51
R607
80
81
C522
C513
D200
R235
R234
R230
R233
R232
R228
C230
31
C213
C200
C203
C210
1
100
81
80
R647
C558
L507
R512
R511
31
30
51
C506
R605
R608
C510
1
80
100
C255
R261
R240
R250
R246
C243
R258
C249
R262
R270
R251
R242
C254
R255
C258
C244
R247
R294
R295
C287
R292
30
IC217
10
1
100
IC200
IC704
R787
11
R218
R217
C218
C415
C413
R416
R423
R649
C560
R648
R650
C559
C562
45
1
8
IC516
50
81
IC213
C256
R269
C253
R253
R256
R399
R281
C248
R291
C271
R216
X500
C260
R300
Q201
R299
D012
Q202
C291
IC214
C257
R714
C292
R716
C261
R715
R398
R397
D202
C272
1
20
C290
R642
R644
C500
31
100
C525
R171
R167
C702
R773
IC703
C734
R320
R772
R771
R730
R729
C706
R727
C707
R725
C708
C709
R724
R708
R780
C749
R749
R713
R778
R712
R187
R711
R754
R710
C710
R709
C705
R781
C736
R784
R785
IC705
R876
R882
R851
R865
C921
C900
R639
R979
R885
C905
R895
R906
R908
C927
C906
R916
R918
R919
R914
R949
C910
C902
30
R606
1
C519
C517
IC507
R178
C050
D016
D015
R731
R733
R734
C735
R748
R777
44
122
R776
C904
R643
R855
R864
R881
C926
IC902
L901
C912
C911
C914
R853
R859
C908
C928
32
33
C536
64
65 96
C533
C529
C740
D013
C742
R783
R755
C716
C711
C714
R735
R736
C715
R742
R775
R870
14
C929
R951
R792
R750
C717
C719
R741
R744
R743
Q013
C052
R779
IC509
Q702
C051
R176
R186
D703
R774
D706
R973
R977
C901
C922
R880
R875
R868
R852
R883
C920
R905
R871
78
1
R896
4
3
R948
1
C932
C933
X900
C913
R940
R924
C909
R925
R926
C540
1
C534
TNPA2243 D
SEE REVERSE FOR ORDER NO.
12 3
1
10 11
IC904
R758
R759
R756
C726
C725
R751
R793
R757
C727
R765
R767
R766
R764
C730
R770
R763
R769
R768
21
C738
R761
C737
23
40
R879
C903
R877
R890
R892
R891
C924
R854
8
R966
R947
IC907
5
1
C925
R917
5
4
IC906
C930
R645
R646
C907
R920
128
C537
97
1
20
C916
R907
10
R745
R746
R747
C720
C724
C722
C739
R782
C741
20
IC702
D702
C732
C733
1
C748
R705
R869
R862
R874
C934
C935
R886
R888
R902
C743
R967
R969
R915
C526
C530
C919
20
11
R616
C565
C543
C744
R619
R630
R561
R545
R543
R541
R539
R537
R535
R534
R532
R529
CR NO.9
C915
IC903
R636
R637
R618
R617
C566
R631
R628
R629
R627
R596
R599
R626
1
94V-0
L902
R614
1
ABCDEFGH I
55
Page 56

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
D
Parts Location
IC
IC9000 C-5
IC9001 C-5
IC9002 C-5
IC9004 C-4
IC9005 B-3
IC9019 C-4
IC9020 C-4
IC9021 C-5
IC9200 F-4
IC9201 E-4
IC9209 E-5
IC9213 F-5
IC9214 F-5
IC9217 F-5
IC9402 E-3
IC9403 E-3
IC9502 E-2
IC9503 D-2
IC9506 E-2
IC9507 F-2
IC9508 C-1
IC9509 G-2
IC9516 F-2
IC9702 G-4
IC9703 G-5
IC9704 F-4
IC9705 G-4
IC9902 G-3
IC9903 G-5
IC9904 G-5
IC9907 G-3
D-BOARD (FOIL SIDE)
TRANSISTOR
Q9001 B-4
Q9002 B-4
Q9003 C-4
Q9005 B-4
Q9006 B-4
Q9007 C-4
Q9009 B-5
Q9010 B-5
Q9011 C-5
Q9013 G-4
Q9201 F-5
Q9202 F-5
Q9701 D-4
Q9702 G-4
Q9703 D-4
Q9801 E-6
Parts Location
D-BOARD (COMPONENT SIDE)
IC
IC9003 H-3
IC9007 G-4
IC9008 G-4
IC9009 G-5
IC9010 H-3
IC9012 H-3
IC9013 G-4
IC9013 G-4
IC9014 D-3
IC9018 G-3
IC9202 G-5
IC9204 E-4
IC9206 E-5
IC9207 E-5
IC9211 D-5
IC9212 D-5
IC9215 D-4
IC9216 E-5
IC9223 D-4
IC9302 F-5
IC9400 F-3
IC9401 G-3
IC9404 F-3
IC9501 E-1
IC9510 H-3
IC9511 B-3
IC9513 C-1
IC9515 B-3
IC9600 D-3
IC9614 G-2
IC9701 C-4
IC9706 C-5
IC9707 C-4
IC9801 F-5
IC9802 F-5
IC9803 F-5
IC9804 F-6
IC9812 G-2
IC9900 C-2
IC9901 D-2
IC9905 B-3
TRANSISTOR
Q9200 D-4
Q9700 D-5
Q9704 G-4
Q9705 C-3
Q9706 B-3
TP
TP40 G-5
TPD1 F-4
TPD2 F-5
TPD3 F-4
TPD4 F-4
TPD5 E-3
TPD6 E-3
TPD7 C-5
TPD10 G-5
TPD11 G-4
TPD12 G-4
56
Page 57

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
D-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE)
TZTNP01JCSE (PW4 SERIES)
TZTNP01JASE (PW4D SERIES)
6
R811
D9
C918
D2
5
4
D43
3
C545
C544
2
D35
D20D21
R159
R126
R161
R162
R163
R164
R960
R166
R131
R173
R140
R141
R132
C049
R128
R127
R134
C712
LC502
R980
R959
R955
C917
R594
R592
C570
C569
LC500
R961
R968
R972
TPD7
R133
C703
C704
C731
X701
C729
IC905
R549
R548
R551
R553
R615
R556
Q706
C746
R794
R760
R589
R591
C557
R704
Q705
R887
IC511
R786
R962
IC515
R965
R567
R569
R571
R573
R575
R577
R579
R581
R583
R585
R587
R706
R707
R721
C750
R790
R791
R752
D720
R753
C728
C713
R762
IC707
R963
R964
R938
R974
R873
R872
C551
C555
R170
LC012
IC706
D018
D022
R737
R738
R739
R740
R722
C723
R703
R702
C745
C721
IC701
R978
C549
C718
C747
R701
C701
R850
R976
R641
R208
IC900
R928
IC513
R945
R933
R937
C550
D4
R244
R160
R165
R177
C262
D023
Q700
R700
D700
R718
R717
R728
R726
R720
R732
D705
R944
R946
C503
IC211
C245
C263
C246
R719
C278
R288
R289
C279
R290
C274
C225
C215
R248
Q200
C219
C923
R889
R903
R904
R950
R953
R954
IC901
C523
C502
C285
R238
R227
R241
R239
C286
C211
C212
R254
C280
C273
IC223
R215
IC014
R282
C266
IC500
C501
R265
IC212
C216C217
R293
C277
C276
C275
R287
L206
C265
C561
IC207
R243
IC215
R266
R209
C206
C226
C202
C233
C237
R283
R651
R519
R523
R520
R175
R174
R245
IC216
C234
R210
C222
C221
C220
C418
C571
R508
R507
R252
C281
R296
C238
R211
R268
R267
C207
C416
C414
R417
TPD6
R424
TPD5
R506
IC501
R274
R280
R284
IC206
R909
R236
C236
IC204
C801
R237
C242
R297
X200
R276
C264
C803
R213
R271
TPD2
TPD1
R221
R220
TPD3
C419
R517
R518
D8
R807
R806
R805
R804
R275
C805
TPD4
IC400
R412
R411
R513
R514
IC804
C819
R803
IC803
R801
R802
IC801
R400
IC404
C423
C818
IC202
C817
IC802
R206
R202
R203
R207
IC302
R332
C516
C084
C078
C079
C072 C073
R341
R789
R331
Q704
C074
R407
R405
R406
R408
IC018
R505
C405
C406
C518
C553
TP40
C208
L201
C083
R112
R277
R113
C080
IC009
C081
R110
R111
C075
IC008
C076
C069
R109
IC007
C093
R146
C094
C067
R114
R115
IC401
IC512
C554
D6
C003
D035
C010
C007
R019
R023
C039
R026
R105
TPD10
R108
C070
IC013
R145
C117
C548
TPD11
R103
R073
R088
C119
R065
R104
C118
R156
R080
R157
R158
R069
TPD12
R084
C063
C046
R610
R611
C552
D3
C006
C009
C008
R024
R025
C038
C037
LC025
R064
R087
R053
LC017
R079
R057
R068
LC021
R123
R083
C043
R168
L008
IC012
C014
IC510
C556
C542
R568
IC514
R570
R572
R574
R576
R578
R580
R582
R584
R586
R588
C002
R021
LC024
R086
R063
R052
R061
R072
LC016
R067
R078
R056
LC020
R121
R082
IC003
C058
R590
R552
R554
R555
LC014
LC015
R598
LC019
LC006
C059
LC501
DMM1
D5
R060
R071
LC023
D7
DMM2
C060
D13
IC010
R593
R595
R597
C546
C547
D23
CR NO.9
TNPA2243
1
D
1
ABCDEFGH I
57
Page 58

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
12.11. C1, C2, C3 and C4-Board
C1-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
6
TNPA2253
TNPA2253
SEE REVERSEFOR ORDERNO.
C1
1
123
C1 C2
5
C4-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
TNPA2256
23
TNPA2256 1
SEE REVERSE FOR ORDER NO.
C4
1
4
C4 C3
C3-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
TNPA2255
3
2
C2-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
123
TNPA2255 1
SEE REVERSE FOR ORDER NO.
C3
TNPA2254
231
SEE REVERSE FOR ORDER NO.
C2
1
1TNPA2254
ABCDEFGH I
58
Page 59

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
C1-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE)
6
TNPA2253
CA1
R7102
C7110
R7103
R7107
R7131
R7132
L7102
C7122
C7121
C7126
C7125
L7103
CA2
R7104
R7108
TNPA2253
C7111
R7111
R7112
R7113
1
FAN1
C1
C11
R7122
R7121
L7104
C7124
C7123
FAN2
R7123
D7101
R7105
R7109
CA3
R7133
R7101
C7117
IC7102
L7101
C7112
C7115
C7116
C13
IC7101
R7134
D7102
C14
C1 C2
5
C4-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE)
TNPA2256
C7421
C7422
R7405
R7403
CB1
R7409
L7402
C7410
4
CB2
R7406
C7411
R7410
L7403
C7424
C7423
C4MM1
TNPA2256
C4
1
C7426
C7425
L7404
R7411
R7407
C43
CB3
C7412
C7414
IC7401
C7415
L7401
R7412
C7417
R7423
R7422
R7421
IC7402
C42
C4 C3
C3-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE)
TNPA2255
R7306
R7309
R7315
R7316
L7303
C7325
R7313
R7314
C7326
Q7301 Q7302
C7316
TNPA2255 1
3
C35
C32
2
C2-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE)
IC7301
C7314
IC7302
R7318
C7315
R7319
R7320
C7313
C3
CB4
C7321
R7312
C7322
R7311
L7306
C3MM1
C7309
CB5
R7305
L7302
C7323
C7324
R7308
C7310
C3MM2
CB6
R7317
C7317
C34
C33
L7305
L7304
C7327
R7310
R7307
C7328
C7311
R7303
CB7
TNPA2254
IC7202
C7212
R7211
R7212
C24
C7214
IC7201
CA4
R7213
C7215
C23
R7210
L7206
C7221
C7222
R7209
C7209
CA5
R7203
R7206
C7224
FAN3
D7201
R7233
L7202
TNPA2254 1
C2
C7223
R7231
R7232
C7210
CA6
R7204
R7207
1
L7203
C7226
C7225
R7241
FAN4
R7242
R7243
R7201
C7216
L7201
C7227
C7228
C7211
R7205
R7208
L7204
C22
CA7
R7202
ABCDEFGH I
59
Page 60

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
12.12. SC-Board
SC-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
TNPA2261
6
K
TP57
L6644
Q6621
DG
B
C
E
D6622
S
L6645
TP56
Q6550
AA
S
TP55
A
DG
K
L6632
L6633
Q6622
TP35
C6598
D6628
TP46
TP47
75V
20V
75V
20V
TP26
C6476
E
E
C6492
TP49
TP50
C6461
D6469
TP51
TP48
A2
A1
B2
B1
C6655
D6474
BASE
+B
COLL
EE
T6471
D6454
C6475
BASE
+B
COLL
EE
T6451
B
C
E
TP12
TP13
TP16
TP27
TP17
C6455
R6495
TP24
TP25
TP19
TP21
TP23
TP18
TP22
TP59
TP61
D6629
L6634
A
C6627
C6626
C6625
C6624
C6513
L6623
K
TP63
K
L6472
L6635
A
TP62
D6621
C6640
L6622
L6621
C6629
C6628
TP60
C6601C6602C6603C6604
C6605
D6620
L6620
AAKAA
D6583
R6499
D6467
C6550
R6498
TP20
B
C
E
A20
B20
R6465
C6456
C6459
C6457
A19
B19
R6477
Q6453
Q6491 Q6492
B
C
E
TP10
TP14
TP15
TP11
TP54
D6573
K
AA
L6630
L6631
S
DG
A20
K
B20
B19
1
SC
D6627
AA
L6629
DG
Q6623
SC42 SC43 SC44
A19 A1
D6626
K
AA
L6627
L6628
S
A
Q6624
3
6
K
L6626
DG
2
D6625
A2
B2
B1
1
45
Q6604Q6605Q6606
DG
S
D6624
L6624
L6625
S
DG
Q6625
L6642
A20
C6522
S
L6643
A19
B20
B19
C6526
DG
L6640
R6557
R6523
S
L6641
A2
B2
DG
L6638
L6639
R6513
B1
Q6601Q6602Q6603
DG
S
L6636
L6637
AAKA
A
A
K
S
DG
Q6626
TP28TP29TP30TP31TP32TP33TP34
A
A
K
S
A
A
K
D6631D6632D6633
D6630
C6623
C6622
C6621
C6630
A
A
K
C6641
TP41
TP42
TP44
TP43
B20
B19
TP45
A2
SC41
A1
B2
B1
TP58
R6550
TP40
A20
A19 A1
5
C6651
Q6671
R6671
E
4
B
C
Q6607
S
S
Q6608
DG
TNPA2261
SEE REVERSE FOR ORDERNO.
DG
S
DG
3
C6608
L6604
L6611
L6612
TP8
TP6
TP9
3
L6606
1
TP36
TP37
L6613
L6614
L6605
TP7
1
SC23
L6615
L6616
2
TP5
L6601
TP4
L6602
TP1
TP2
6
SC2
1
ABCDEFGH I
60
Page 61

SC
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
Parts Location
TRANSISTOR
Q6453 H-3
Q6491 H-2
Q6492 H-2
Q6550 C-5
Q6601 F-2
Q6602 F-2
Q6603 E-3
Q6604 E-3
Q6605 C-3
Q6606 C-3
Q6607 B-3
Q6608 B-3
Q6621 C-2
Q6622 D-2
Q6623 D-2
Q6624 E-2
Q6625 E-2
Q6626 E-2
Q6671 B-4
SC-BOARD (FOIL SIDE)
TP
TP1 B-2
TP2 B-1
TP4 B-2
TP5 B-2
TP6 B-2
TP7 B-2
TP8 C-2
TP9 C-1
TP10 H-1
TP11 H-1
TP12 H-2
TP13 H-2
TP14 H-1
TP15 H-1
TP16 H-1
TP17 H-1
TP18 H-1
TP19 H-1
TP20 H-1
TP21 H-1
TP22 H-1
TP23 H-1
TP24 H-2
TP25 H-2
TP26 H-1
TP27 H-1
TP28 E-1
TP29 E-1
TP30 E-1
TP31 E-1
TP32 D-1
TP33 D-1
TP34 D-1
TP35 D-1
TP36 B-2
TP37 B-1
TP40 B-6
TP41 B-6
TP42 B-6
TP43 B-5
TP44 B-5
TP45 B-5
TP46 H-6
TP47 H-6
TP48 H-5
TP49 H-5
TP50 H-5
TP51 H-6
TP54 D-6
TP55 C-6
TP56 C-6
TP57 C-6
TP58 C-6
TP59 G-6
TP60 G-5
TP61 G-6
TP62 G-5
TP63 G-6
Parts Location
IC
IC6451 B-3
IC6452 C-2
IC6453 B-5
IC6464 B-5
IC6471 B-4
IC6472 C-3
IC6491 B-2
IC6501 B-5
IC6502 B-5
IC6511 C-5
IC6521 E-4
IC6541 E-5
IC6542 B-5
IC6581 C-2
IC6601 F-3
IC6602 F-2
IC6603 I-5
IC6605 B-2
IC6606 B-2
TRANSISTOR
Q6451 B-2
Q6452 B-3
Q6453 B-3
Q6454 B-3
Q6471 B-4
Q6472 B-4
Q6474 B-4
Q6476 B-5
Q6491 B-2
Q6511 C-6
SC-BOARD (COMPONENT SIDE)
Q6512 C-5
Q6520 E-4
Q6521 E-5
Q6522 E-4
Q6523 F-4
Q6524 F-4
Q6525 F-4
Q6526 G-4
Q6527 G-4
Q6528 G-4
Q6529 H-4
Q6530 E-4
Q6541 E-5
Q6542 E-5
Q6543 F-5
Q6544 F-5
Q6545 F-5
Q6546 G-5
Q6547 G-5
Q6548 G-5
Q6549 H-5
Q6550 G-5
Q6551 E-5
Q6552 D-5
Q6553 C-5
Q6555 C-5
Q6556 C-5
Q6581 C-2
Q6601 D-3
Q6602 D-3
Q6603 E-3
Q6604 E-3
Q6605 G-3
Q6606 H-3
Q6607 H-3
Q6608 H-3
Q6611 F-3
Q6612 F-3
Q6613 G-3
Q6614 F-3
Q6621 G-2
Q6622 G-2
Q6623 F-2
Q6624 F-2
Q6625 E-2
Q6626 E-2
Q6627 G-2
Q6628 G-2
Q6629 F-2
Q6630 F-2
Q6641 H-5
Q6642 H-4
Q6645 H-5
Q6646 H-5
Q6650 C-4
Q6671 I-4
TP
TPSC D-6
TPVAD C-5
TPVBK H-2
TPVSCN C-3
61
Page 62

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
6
SC-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE)
TNPA2261
R514
D511 D512
C512
D509
C581
5
4
3
2
IC502
C580
IC501
R505
C505
D505
R575
C575
Q472
R475
R474
R473
D472
C474
C472
Q471
C475
Q452
D452
R454
R453
C454
C451
Q451
C455
R495
C546
R690
R691
R486
R488
R506
R508
C506
C508
D506
D508
D501
R576
R578
C576
C578
D502
R572
C572
C655
D470
R484
C473
D475
D473
C471
R472
R471
D471
D455
C453
R455
R452
IC451
D453
C452
R451
D451
R595
IC491
R596
R496
Q492
IC606
C462
IC454
C509
R509
Q476
R501
C501
D461
R571
C571
R502
C502
R500
Q474
D469
D474
D454
R490
R497
R494
R679
R694
R695
R696
R699
R681
R680
R693
IC542
C463
R487
R485
R466
IC453
D551
C461
C504
Q477
D503
R570
D478
R573
C476
IC471
R598
R479
T471
R480
Q454
R456
R460
C492
R594
R492
R678
R697
R698
R493
C647
R692
Q553
C545
D550
R503
R561
R565
R566
R504
D552
D504
R574
D529
D530
C574
C550
R478
R597
D460
R467
R468
R477
R470
D466
R465
R476
D476
L471
R461
R458
L451
T451
D457
R491
C494
IC605
D467
C456
TPVSCN
IC472
Q453
R462
R457
R482
D456
R459
L452
Q491
R483
R463
R481
C459
IC452
C457
TPVSET
D468
D492
R498
R583
R584
C493
C585
D582
C584
IC581
R591
R587R589
R685
R683
R684
R688
R689
R511
R512
R518
C511
D513
R516
R517
IC511
D514
R515
R564
Q556
C601 C602 C603
C649
R469
C648
D465
Q650
C605
R630
R631
D620
D491
L620
R499
R489
R582
R586
D585
D586
D583
Q581
D584
R590
R686
R682
R687
Q511
R519
R520
Q512
R563
Q555
L472
TPVAD
R633
R634
R632
D621
C661
C660
L622
L621
C490
C491
C640
C629
C628
R513
TPSC1
C513
D549
R540
Q552
R560
R635
Q601
D607
R611
L623
L635
L637
L634
D629
C627
C641
C626
C625
C624
Q602
C611
R612
R613
R623
L639
L636
D630
C623
C622
C621
C630
SC43SC44
C543 C544
R559
R614
L638
R558
R557
D546
D547
D548
C604
C612 C613
R615
D608
L641
D631
Q626
R568
C542
D541
Q551
R556
C540
D544
R567
D545
R555
C525
R528
R525
C524
R524
D524
R523
D522
Q520
C526
Q603
R616
D609
L640
D632
D635
IC541
D526
R527
R526
D525
C521
R522
D521
R521
R539
C522
D495
R617
L642
L643
D633
R655
D636
Q541
R541
D542
C541
Q521
R592
D572
R593
IC521
D527
R538
R529
R530
Q530
TNPA2261
Q604
R618
R656
R652
C614 C615
D610
D624
L624
C638
R651
R649
Q625
Q542
Q522
R657
R650
SC42
R542
R543
Q543
Q523
R531
R544
Q544
Q524
R532
1SC
C484
C481
C483
C482
IC601
C631
R624
Q611
Q612
D625
L625
L626
Q629
Q630
R647
R648
R658
Q624
C633
D615
L618
R627
D626
L627
L628
R660
D647
R659
C636
C635
L629
IC602
Q623
D573
R551
Q550
D543
D570
Q545
Q525
R533
C598
R554
R545
Q546
R534
R569
R546
Q547
Q526
Q527
R535
R552R553
R550
R547
R548
Q548
Q528
R536
Q549
Q529
R537
6
C632
R626
Q614
R628
D627
L630
L647
C634
Q613
D628
L631
L632
D640
Q628
R654
R645
R646
Q622
Q605
D611
R619
D622
L633
L645
L644
R644
R643
Q627
R641
R642
R653
Q606
C616
R620
R621
R625
D612
D613
L611
R638
R639
R636
L612
R637
Q621
SC41
Q645
R549
Q641
D641
R661
R665
R662
D642
Q642
Q607
C617
D614
C487
C618
R622
L613
L614
C608
TPVBK
L605
L604
C607
SC23
R605
C644
Q646
D645
R671
Q608
C485
C486
C488
L606
L602
SC2
R607
R606
R667
R668
C646
C645
D646
R666
IC603
L648
C651
R674
D672
D673
L615
L616
R675
R676
D671
R672
R673
Q671
L601
1
ABCDEFGH I
62
Page 63

12.13. SU and SD-Board
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
6
5
SU
SD
SU-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
TNPA2259
TNPA2259
SEE REVERSE FOR ORDER NO.
4
SU41
SU42
SU
1
213
3
SD-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
TNPA2260
213
2
1
ABCDEFGH I
TNPA2260
SEE REVERSE FOR ORDER NO.
SD
SD44
1
SD43
63
Page 64

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
6
SU
SD
5
SU-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE)
TNPA2259
C6418
C6419
SU1 SU2 SU3
IC6401
R6423
D6405
R6422
R6410R6411
C6417
D6403
Q6401
4
D6402
R6401
C6411
C6413
C6401
R6421
R6414
IC6402
R6420
D6408
R6412
C6412
R6402
TPSU2
D6401
C6402
TNPA2259
ORDER NO.
C6414
SU41
SU
1
R6403
TPSU1
C6415
C6403
IC6403
IC6404
R6404
C6404
R6413
C6416
SU42
3
SD-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE)
TNPA2260
C6428
C6425
C6407
D6406
C6429
R6430
R6408
C6408
IC6408
C6426
C6422
D6409
SD1 SD2 SD3
IC6405
TPSD2
2
IC6406
TNPA2260
TPSD1
IC6407
ORDER NO.
SD43
C6423
C6405
C6421
D6407
R6405
R6429
C6424
R6406
C6406
R6426
SD 1
SD44
R6425
R6407
R6427R6428
1
ABCDEFGH I
64
Page 65

12.14. SS, SS2 and SS3-Board
SS-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
6
TNPA2262
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
SS41A
C6708
Q6752
B
C
E
L6750
1
SS44A
Q6753
B
C
E
R6778
13
R6777
S
DG
S
Q6707Q6708
DG
13
Q6751
C
E
B
1
SS49
5
7
SS44
2
6
SS34
1
3
R6774
SS43
1
S
1
SS43A
Q6706
DG
Q6705
S
DG
13
13
Q6704
DG
S
TNPA2262
D6756
4
11
SS33
TP23
TP22
TP19
3
TP18
1
C6756
TP16
TP15
TP21
TP20
TP17
TP13TP14
C6754
C6748
C6747
D6765
C6729
C6730
L6713
L6716
C6766
C6725
C6726
C6727
C6728
L6712
L6715
C6765
L6711
L6714
C6721
C6722
C6723
C6724
SEEREVERSEFORORDERNO.
A
L6744
L6745
DG
TP30TP31
D6724
K
A
A
L6725
L6724
S
D6722
K
A
Q6721
D6725
K
L6727
S
DG
Q6722
TP28TP29
D6726 D6727 D6728
K
AA
AA
L6728
L6729
L6726
S
DG
Q6723
SS42A
1
K
L6731
1
L6730
1
SS42
S
SS
AA
L6733
DG
Q6724
Q6703
DG
K
L6732
S
D6729
AA
L6734
A
S
K
DG
Q6725
TP27
13
13
Q6702
DG
123
456
L6735
L6736
A
A
D6730
S
TP26
L6702
TP2
1
C6705
C6706
C6704
TP10
TP6
L6701
TP4
1
1
Q6701
DG
S
A
L6722
L6741
A
K
D6720D6721
A
A
L6720
L6721
L6743
L6742
A
A
D6733
K
C6753
K
A
L6723
L6737
L6738
L6739
L6740
A
D6731
K
DG
Q6726
TP25
A
A
S
TP24
A
D6732
K
K
SS41
13
TP11
TP12
TP9
TP5
L6705
TP8
TP3
L6703
1
TP1
7
C6703
C6701C6702
SS11
SS22
TP7
SS48
L6704
5
13
3
1
6
2
SS12
71
1
C6707
2
SS3-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
TNPA2264
SS46
1
TNPA2264
SEE REVERSE FOR ORDERNO.
13
SS3
1
SS40
1
2
6
7
SS2-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
TNPA2263
TNPA2263
SEE REVERSE FOR ORDERNO.
7
1
SS47
6
2
1
1SS2
SS45
13
1
ABCDEFGH I
65
Page 66

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
SS2
SS
SS3
Parts Location
TRANSISTOR
Q6701 G-5
Q6702 F-5
Q6703 F-5
Q6704 F-5
Q6705 D-5
Q6706 D-5
Q6707 C-5
Q6708 C-5
Q6721 D-3
Q6722 E-3
Q6723 E-3
Q6724 F-3
Q6725 F-3
Q6726 G-3
Q6751 B-5
Q6752 B-5
Q6753 B-5
SS-BOARD (FOIL SIDE)
TP
TP1 H-3
TP2 H-3
TP3 H-3
TP4 H-3
TP5 H-3
TP6 H-3
TP7 I-3
TP8 H-3
TP9 H-4
TP10 H-4
TP11 I-4
TP12 I-4
TP13 B-2
TP14 B-2
TP15 B-2
TP16 B-2
TP17 B-2
TP18 B-2
TP19 B-2
TP20 B-2
TP22 B-2
TP23 B-2
TP24 G-3
TP25 G-3
TP26 F-3
TP27 F-3
TP28 E-3
TP29 E-3
TP30 E-3
TP31 D-3
Parts Location
IC
IC6704 H-3
IC6705 H-3
IC6706 H-4
IC6755 H-3
SS-BOARD (COMPONENT SIDE)
TRANSISTOR
Q6701 C-5
Q6702 D-5
Q6703 D-5
Q6704 D-5
Q6705 F-5
Q6706 F-5
Q6707 G-5
Q6708 H-5
Q6713 F-5
Q6714 F-5
Q6721 F-3
Q6722 E-3
Q6723 E-3
Q6724 D-3
Q6725 D-3
Q6726 C-3
Q6729 D-3
Q6730 D-4
Q6741 H-5
Q6742 H-4
Q6743 H-4
Q6745 H-3
Q6746 H-3
Q6751 H-5
Q6752 H-2
Q6753 H-5
Q6756 H-3
TP
TPSS H-4
TPV15 B-3
TPVDA B-3
TPVE H-5
TPVSUS B-3
66
Page 67

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
SS-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE)
6
TNPA2262
DIP
SS41
SS41A
SS42
SS42A
SS43A
SS43
C6705
5
SS48
C6706
C6707
SS22
C6703
C6704
D6720
L6720
R6730
L6721
R6731
R6732
C6760
C6761
R6733
L6722
D6721
R6735
R6734
Q6701
C6711
C6771
D6707
R6711
R6712
TNPA2262 SS
L6723
R6723
Q6702
R6713
R6714
D6708
C6772
C6712
R6715
R6716
D6709
D6728
Q6704
C6773
Q6703
C6713
R6717
R6718
Q6712
D6710
Q6711
R6724
L6718
D6715
1
D6727
D6726
4
R6701
L6705
C6701
C6702
L6701
L6743
L6742
D6733
L6741
L6740
D6732
TPVDA
L6704
L6703
3
SS12
C6755
SS11
TPV15
L6702
TPVSUS
C6753
L6739
Q6726
L6738
D6731
D6735
D6736
L6737
R6755
L6736
D6730
R6751
R6752
L6735
Q6725
L6734
D6729
C6738
R6749
R6750
R6756
Q6724
L6732
R6757
L6733
R6747
R6748
Q6729
L6730
Q6730
L6731
R6758
C6735
D6741
IC6702
L6728
C6736
Q6723
L6729
L6726
R6759
C6774
C6734
C6714
R6745
Q6722
C6733
D6725
R6760
R6754
R6753
C6731
IC6701
R6761
L6727
Q6728
R6746
R6727
Q6727
C6740
D6724
L6724
R6743
C6776
C6732
R6728
L6725
R6744
R6741
R6726
Q6714
R6742
D6740
L6745
Q6713
D6722
R6736
L6747
R6737
Q6721
Q6705
L6744
C6775
R6738
L6711
R6739
C6715
R6719
Q6706
D6711
C6721
C6722
C6723
C6724
C6716
Q6707
L6712
R6720
D6712
D6713
L6715 L6716
L6714
C6765
C6725
L6713
C6726
C6727
C6728
C6717
R6721
D6714
R6722
C6766
SS44A
R6725
C6718
C6729
C6730
C6777
C6747
C6778
R6784
C6750
Q6708
TPSS1
D6756
D6765
D6767
IC6705
R6820
R6777
R6821
D6766
R6819
R6824
R6823
R6818
R6778
D6763
R6825
D6751
Q6746
D6750
R6764
Q6741
Q6756
R6826
C6748
D6764
Q6742
R6786
Q6751
SS44
R6765
TPVE
D6753
C6751
R6785
C6708
Q6753
C6741
R6767
R6780
Q6745
R6768
IC6706
IC6704
L6750
C6746
R6790
Q6755
C6754
R6779
Q6752
R6766
Q6743
D6752
R6772
R6770
R6769
R6783
C6745
D6755
D6760
R6806
D6761
R6781
R6771
Q6744
R6787
R6788
C6756
R6775
R6809
R6808
C6744
R6805
R6807
R6791
SS33
SS49
D6754
C6743
R6773
IC6711
IC6703
R6811
R6804
R6803
R6774
R6810
R6812
R6801
R6802
R6776
R6762
R6763
SS34
2
SS2-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE)
TNPA2263
SS45
TNPA2263
SS2
1
SS47
SS3-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE)
TNPA2264
TNPA2264
SS40
SS46
SS31
1
ABCDEFGH I
67
Page 68

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
12.15. H3, S1 and V1-Board
6
H3-BOARD
TNPA2249
5
4
V1-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
S1-BOARD(FOIL SIDE)
TNPA2283
S1-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE)
TNPA2283
H3 V1 H3 S1
TNPA2282
3
V1-BOARD(COMPONENT SIDE)
2
1
ABCDEFGH I
TNPA2282
68
Page 69

13 Block and Sche matic Diagrams
13.1. Schematic Diagram Notes
Important Safety Notice
Components identified by mark have special characteristics important for safety.
When replacing any of these components, use only manufacture's specified parts.
Notes:
1. Resistor
All resistors are cabon 1/4W resistor, unless marked as follows:
Unit of resistance is OHM [W] (K=1,000, M=1,000,000).
: Nonflammable : Metal Oxide
: Solid : Metal Film
: Wire Wound : Fuse:
2. Capacitor
All capacitors are ceramic 50V capacitor, unless marked as follows:
Unit of capacitance is mF, unless otherwise noted.
: Temperature Compensation : Electrolytic
: Polyester : Bipolar
M
m T
: Metalized Polyester : Dipped Tantalum
: Polypropylene : Z-Type
3. Coil
Unit of inductance is mF, unless otherwise noted.
4. Test Point
: Test Point position
5. Earth Symbol
: Chassis Earth (Cold) : Line Earth (Hot)
6. Voltage Measurement
Voltage is measured by a DC voltmeter.
Conditions of the measurement are the following:
Power Source ................................................... AC 120V, 50/60Hz
Receiving Signal ............................................... Colour Bar signal (RF)
All customer's controls ...................................... Maximum positions
7. Number in red circle indicates waveform nember.
(See waveform pattern table.)
8. When arrow mark ( ) is found, connection is easily found from the direction of arrow
NP
+
-
Z
(US model)/AC220-240V,
50/60Hz (Except US)
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
Remarks:
1. The Power Circuit contains a circuit area which uses a separate power supply to isolate the
earth connection.
The circuit is defined by HOT and COLD indications in the schematic diagram. Take the
follwing precautions.
All circuits, except the Power Circuit, are cold.
Precautions
a. Do not touch the hot part or the hot and cold parts at the same time or you may
be shocked.
b. Do not short- circuit the hot and cold circuits or a fuse may blow and parts may
break.
c. Do not connect an instrument, such as an oscilloscope, to the hot and cold
circuits simultaneously or a fuse may blow.
Connect the earth of instruments to the earth connection of the circuit being
measured.
d. Make sure to disconnect the power plug before removing the chassis.
2. Following diodes are interchangeable.
MA150- MA162 (Replacement part)
9. Indicates the major signal flow. : Video Audio
10. This schematic diagram is the latest at the time of printing and subject to change without
notice.
69
Page 70

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
13.2. Main Block (US model) Diagrams
OUT LINE
SU
SD
FF
64
FF
64
FF
64
FF
48
FF
64
FF
64
FF
64
FF
48
SC
SS.R. SS.R. SS.R. SS.R. SS.R. SS.R.
C2
C24
SUB-FIELD
SUB MPU
J3
H3
PC
C23
D23
D35
RS232C
HX
P
D5
D7
J13
J14
13.5V
P5
5V
SOS
STV 5V
P7
ON/OFF
+15V
-15V
P13
5V
13.5V
15V
P14
5V
STB7V
STB5V
REMOTE
RECEIVE
V
VSUS, Vbk
DRIVE
VOLTAGE
GENERATOR
ON/OFF
SWITCH CIRCUIT
POWER
LED
V34
C1
SC2
CONTROL
PULSE
SUSTAIN
PULSE
SCAN
PULSES
VOLTAGE
GENERATOR
FLOATING
GROUND
SC23
C14
C13
D13
D
SC21
D21
SC20
D20
J
J11
J10
HZ
/HY
DISCHARGE
CONTROL
MAIN MPU
D9
J9
AUDIO
AMP
AUDIO SW
BUFFER
AV RGB
AUDIO IN
I/P CONV.
RGB PROCESSOR
DVI
J2
H2
VIDEO/YUV
CONVERTE
BUFFER
V/Y
SW
AV /
S-VIDEO
PLASMA AI
D8
J8
YUV/RGB SW
BUFFER
RGB/
COMPONENT
FORMAT
CONV.
INFO.
ROM
HD/VD
Vda
PROCESSOR
D43
SYNC. SW
SYNC.
SEPARATOR
P23
15V
PROTECTOR
PRIMARY
P9
INPUT - +
SS.R.
P2
VSUS
Vbk
Vda, +15V, -15V
-15V, 13.5V, 5V
PROCESS
VOLTAGE
GENERATOR
STAND BY
STB7V
STB5V
VSUS
C22
Vda
SS33
SS2
SS48
ADDRESS
VOLTAGE
(VE)
SUSTAIN
PULSE
SS49
SS34
SS
P1
SS1
P12
SS12
S
S34
POWER
SWITCH
H3
+
R
-
SPEAKER
TERMINAL
C4
SS.R.
C43
SS.R. SS.R. SS.R. SS.R. SS.R. SS.R.
C49
C35
C48
C38
C41
C31
Vda
C39
C34
C3
70
F
AC120V
C33
F9
LINE
FILTER
F1
H3
from J10
+
L
-
SPEAKER
TERMINAL
Page 71

P7
P3
P5
P8
P6
FLOATING
GROUND
INPUT - +
SS.R.
C13
D13
SS.R. SS.R. SS.R. SS.R. SS.R. SS.R.
SC
SC2
PLASMA AI
MAIN MPU
I/P CONV.
RGB PROCESSOR
FORMAT
CONV.
D
D43
D35
FF
64
SU
FF
48
FF
64
FF
64
VIDEO/YUV
CONVERTE
DIGITAL
RGB
INTERFACE
SYNC. SW
J
V/Y
SW
AUDIO SW
HX
C23
P
SS.R.
V
S
POWER
SWITCH
PC
RGB/
COMPONENT
AV /
S-VIDEO
AV RGB
AUDIO IN
REMOTE
RECEIVE
POWER
LED
SS2
SS1
ADDRESS
VOLTAGE
(VE)
SUSTAIN
PULSE
ERASE
PULSE
SS48
SS49
SS33
C22
LINE
FILTER
F1
F9
F
SS
SS.R. SS.R.
SS.R. SS.R. SS.R. SS.R.
C49
C4
C3
C39
C34
C33
C41
V34
L
SPEAKER
TERMINAL
-
+
R
SPEAKER
TERMINAL
-
+
J10
J11
CONTROL
PULSE
SD
FF
48
FF
64
FF
64
FF
64
C1
C48
C38
C43
C31
C2
C14
C24
Vda
Vda
Vda
from J10
DISCHARGE
CONTROL
SC20
SC21
D21
D20
SUSTAIN
PULSE
SCAN
PULSES
C35
AC220 -
240V
H3H3
HZ
/HY
RS232C
BUFFER
BUFFER
BUFFER
INFO.
ROM
HD/VD
J2
H3
J3
H2
J8
AUDIO
AMP
D8
J9
D9
SUB MPU
SYNC.
SEPARATOR
YUV/RGB SW
VOLTAGE
GENERATOR
SUB-FIELD
PROCESSOR
STB7V
STB5V
SOS
STV 5V
ON/OFF
J13
+15V
-15V
5V
J14
13.5V
15V
5V
STB7V
STB5V
13.5V
5V
VSUS
VSUS
Vbk
SC23
15V
D5
D7
OUT LINE
D23
SUSTAIN
VOLTAGE
PROTECTOR
SUSTAIN
VOLTAGE
CONTROL
15V
Vda
PROCESS
VOLTAGE
PROTECTOR
POWER
FACTOR
CONTROL
STAND BY
P1
P5
P7
PROCESS
VOLTAGE
CONTROL
P22
PRIMARY
CIRCUIT
P19
P9
P18
P15P16
P21
PROCESS
VOLTAGE
RECTIFIER
P2
P23
P13
P14
SS12
SS34
S34
SUSTAIN
VOLTAGE
RECTIFIER
P12
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
13.3. Main (Except US) Block Diagram
71
Page 72

1
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
13.4. Power (US model) Block Diagram
AC IN
F1 1 5
F900
F901
LINE
FILTER
F9 5 1
P9 5 1
RL403
RL401
P
LINE
FILTER
LINE
FILTER
LINE
FILTER
D401
D426
D419
P1
T401
5
IC401
(DRIVE VOLTAGE OSCILLATOR)
4
DRV.REG
OSC
OSC
T403
5
7
3
1
8.3V
DRIVE
+
-
IC426
DRV.REG
8.3V
DRIVE
+
-
+
-
+
+
+
IC427
3
+
11
12
14
15
AVR
2
2
5
1
1
2
5
IC471
AVR
+
-
+
-
1
IC473
1
3
AVR
3
START
O.V.P
LATCH
18V
(PROCESS VOLTAGE OSCILLATOR)
O.V.P
LATCH
IC426
D435
3
OSC
2
REG
T.S.D
4
START
REG
T.S.D
15V
1
17V
+
-
R426
+
-
+
IC403
6
8
9
3
1
1
2
3
4
8
9
6
7
D434
STB5V
2
STB5V
2
4
Q515 Q516
K
A
D409
18
17
16
13
12
15
14
11
10
IC462
R
12
13
14
15
18
19
K
A
+
-
+
-
+
-
Q461
(70V)
+
R
+
-
+
-
+
Q463 Q467
Vda
+
-
VCC
for
IC474
IC472
-
+15V
-15V
IC468
1
IC470
1
-
VSUS
IC472
AVR
3
AVR
3
Q485
(190V)
Q462
Q465
IC464
K
A
vsus
7
+
+
1
2
POWER STOP SOS
5V
2
13.5V
2
IC465
K
A
R
Q469
15V
4
R
IC474
VSUS
9
+
14
OVP
(170V)
Vbk
Vda
34
+
2
+
-
Vbk
11
+
13
Q483
Q481
Q500
C460
TO SS1
2
3
VSUS
P2
TO SC2
1
VSUS
2
3
Vbk
P13
TO J13
1
+15V
3
-15V
5V
6
P23
TO SC23
1
UN 15V
2
P10
TO FAN
1
UN 15V
3
FAN SOS
5
5V
P5
TO D5
3
5V
1
13.5V
P14
TO J14
13.5V
1
STB7V
3
4
5V
6
15V
8
9
P7
1
2
4
5
6
7
8
P12
1
2
4
5
for J
STB5V
MICRO ON/OFF
TO D
RUSH ON/OFF
TV ON/OFF
STB5V
KILL SOS
FAN SOS
PS SOS
ALL OFF
Vda
UN 15V
POWER SW
for D
72
Page 73

13.5. P-Board (US model) Schematic Diagrams
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
73
Page 74

DRIVE VOLTAGE PROTECTOR
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
13.6. Power (Except US) Block Diagram
PROCESS VOLTAGE PROTECTOR
P3
D604
Q601
P16 SOS IN VCC
1
IC603
VSUS 15V VSUS 5V
D606
Q600
8 VDA Vbk SOS 15Vs
IC601 -15Vs P2 To SC2
IC600 3
AC IN
AC INLET 1 1
5
2
OSC
4
OVP 15V 11 1
7
TO FAN
F1 3
15
Q604
2
9
6
Q602
7
Q603
2
4
P15 Vbk 2
Q407
IC401
3
AVR
1
18V 12
6 1
Q405
Q406
Q408
IC602 4
F901 F900 13
Q417
LINE D446 VDA
Q416
3
IC402
AVR
1
T401
FILTER
START +
STOP
F RL402 D403 -
1 5 F9 P9 POWER FACTOR CONTROL TO SC23
3 L401 D412 D445 15V 1
RL401 3
1 -
FULL
WAVE
RECTIFIER
Q402
Q410
Q404
Q422/Q401
STOP STOP
118
IC735 IC650 D443 -
6
10
IC737
IC736
Q730
5
8
9
Q650
Q651
STOP
Q412
Q414
Q415
T402 5V
IC403
3
2
P19 4 11 9 5 1 P18
1
D419
D440 D439 D434 OSC.
7
PFC
+ +
3
- 110V PROTECTION
1
IC407
AVR
5
230V P6
PFC : Power Factor Control
STB 7V
STB 5V
MAIN POWER SWITCH ON/OFF -
Q750
IC750
COMPARATOR
D751
Q775
Q776
IC775
COMPARATOR
P7 P8
8 54321 7 4321 6
P21
P22
13.5V
Vbk
Q465
VSUS
Q464
T400 P1 To SS1
+
IC464
2
VSUS
P10
UN 15V
FAN SOS
5V
P5
TO D5
3
Q419
1
5V
13.5V
Q420
IC412
P23
IC409
1 2
+
AVR
D441 +15V To J13
+
+
For AUDIO 6
P13
1
3
15V
+15V
-15V
5V
-15V
P14
P5
D435
D436
D442
K
A
IC411
1 2
+
AVR
13.5V
Q421
R
Q423
4
IC410
1
AVR
Q413
SOS
Q413
2
TO J14
4
5V
3
STB7V
1
13.5V
6
8
STB5V
9
S.MPU
P7
ON/OF
TO D7
2
TV ON/OFF
STB5V
5
KILL SOS
6
FAN SOS
7
PS SOS
8
ALL OFF
P12
TO SS12
1
+
Vda
2
15V
4
5
POWER SW
74
Page 75

13.7. P1-Board (Except US) Schematic Diagrams
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
75
Page 76

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
13.8. F and P3-Board (Except US) Schematic Diagram
76
Page 77

13.9. P5, P6, P7 and P8-Board (Except US) Schematic diagram
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
77
Page 78

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
13.10. HX and H Block Diagram
PC AUDIO IN
R IN
L IN
PC IN
R IN
G IN
B I N
SCL
SDA
1
2
3
13
14
12
15
HX
IC3509
DDC
EEPROM
PC Terminal Board
Q3531
Q3532
Q3507
Q3508
Q3509
Q3513 / Q3514
Q3515 / Q3516
7
6
5
VCLK
HX1
B
20
18
16
12
14
A
19
20
4
5
R OUT
L OUT
R OUT
G OUT
B OUT
HD OUT
VD OUT
SCL
SDA
TUNER IN
R IN
L IN
G IN
B I N
R IN
HD IN
VD IN
TXD
RXD
21
19
Tuner Terminal Board
H
7
8
1
2
3
4
5
Q3451
Q3453
Q3459
Q3456
Q3452
Q3454 / Q3455
Q3457 / Q3458
IC3451
13
14
12
11
H2
B
11
13
19
17
15
9
15
14
A
R OUT
L OUT
G OUT
B OUT
R OUT
7
HD OUT
VD OUT
RXD-XC
TXD-XC
RS-232C
TXD
RXD
12V
DTR
IC3515
3
2
6
4
13
14
12
11
7
8
10
9
10
9
8
7
6
12V
RXD-XC
TXD-XC
DCE-XC
DTE-XC
CABLE
DET.
REMOTE OUT
POWER
STATUS
25
24
6
10
CABLE
DET.
12
REMOTE
POWER
11
TERMINAL
BOARD
INFORMATION
IC3699
6
EEPROM
5
19
20
STATUS
SCL
SDA
This board is for TH-42PW4U only.
78
Page 79

13.11. HX-Board Schematic Diagrams
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
79
Page 80

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
13.12. H-Board (Option TY-42TM4H) Schematic Diagram
TXN/H10JKS
80
Page 81

13.13. HY and HZ Block Diagrams
(
)
HY (for TH-42PWD4 series)
for TH-42PW4 series
HZ
S-DET.
C
Y
Q3302
IC3301
6
7
5
S SELECT
AV
S-VIDEO
IN
VIDEO
IN
VIDEO
OUT
# 42PWD4
only
R IN
AUDIO IN
L IN
1
3
4
Q3307
Q3505
Q3504
IC3302
+
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
H1
B
A
IC3803 for NTSC 3D COMB FILTER
16M SDRAM
2 ~ 12, 39 ~ 49 15 ~ 32
IC3804 GC1
Q3809
Q3810
SDA
SCL
C
62
Y
84
83
89
90
94
VCO
96
Q3301
1
Q3306
Q3802
Q3804
Q3801/Q3803/Q3805
Q3806/Q3807
LPF
Q3808
100 ~ 119
Memory Controllor
DIGITAL
COMB
FILTER
A/D
COLOUR
SYSTEM
SEPARATOR
PLL
120 ~ 138
3D
DET.
SYNC. DET.
SYNC.
Q3817
Y
Pb
Pr
OUT
PLL
184 161
SYNC. PULSE
GENERATOR
H(15K~ 45K)
H
PICTURE
IMPROVER
D/A
V(50~120)
8
Y
20
Pb
200
Pr
195
7
156
H OUT FREE RUN
L: FREE RUN
H:LOCK
Q3812
Q3813
Q3815
SYNC, BUFFER
6
4
Q3501/Q3507
Q3502/Q3508
Q3503/Q3509
IC3809
5V
3.3V
STB5V
H2
B
1
3
5
14
16
6
19V
5
9
13
A
6
8
2
TO J1
TO J2
Y
Pb
Pr
HD
VD
S2 DET.
AUDIO L
AV
R IN
AUDIO IN
L IN
COMPONENT/RGB IN
Pb/B
Y/G
Pr/R
HD
VD
Q3351
Q3356
Q3357
Q3352
Q3353
Q3358
Q3359
Q3505
Q3504
IC3501
12
DAC - IIC
EXPANDER
9
4
14
15
SCL
SDA
TERMINAL
BOARD
INFORMATION
IC3699
EEPROM
4
AUDIO R
19
20
AUDIO L
AUDIO R
B / Pb
G / Y
R / Pr
HD
VD
SCL3
SDA3
RGB/
COMPONENT
1
13
17
19
15
7
9
6
5
81
Page 82

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
13.14. HY-Board (1/2) (Option TY-42TM4Y) Schematic Diagrams
82
Page 83

13.15. HY-Board (2/2) (Option TY-42TM4Y) Schematic Diagrams
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
83
Page 84

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
13.16. HZ-Board (1/2) (Option TY-42TM4Z) Schematic Diagram
84
Page 85

13.17. HZ-Board (2/2) (Option TY-42TM4Z) Schematic Diagram
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
85
Page 86

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
13.18. J-Board Block Diagrams
AV
RGB/
COMP.
AV
AV
RGB/
COMP.
RGB/
COMP.
PC
FROM H1
DVI IN
FROM H2
G / Y
B / Pb
R / Pr
S2 DET.
AUDIO L
AUDIO R
AUDIO L
AUDIO R
SCL3
SDA3
FROM H3
RXD-XC
TXD-XC
DCE-XC
DTE-XC
SDA
SCL
Y
Pb
Pr
HD
VD
HD
VD
R
R
G
B
HD
VD
B
10
24
B
1
3
5
19
17
15
6
1
13
7
9
AB
L
20
18
16
12
14
9
8
7
6
5
4
J1
A
J2
A
6
8
2
4
19
20
J3
19
2
TO IC1002
J
RGB/COMP.
IIC VOLTAGE CONVERT
5V - 3.3V
Q3085
Q3082 / Q3081
Q3083 / Q3080
AV
PC
DVI
SDA2
SCL2
Y
Pb
Pr
G / Y
B / Pb
R / Pr
G
R
59
61
15
B
17
IC3001
INPUT SELECT
6
5
7
9
1
J8
1
10
Q3007/Q3008
Q3001/Q3002
Q3011/Q3012
4
Q3005/Q3006
Q3009/Q3010
46
Q3003/Q3004
44
27
26
26
SCL3
SDA3
S2 DET.
For IC3003 AUDIO SELECT
AV
RGB/COMP.
PC
For IC3002 SYNC. SELECT
AV
RGB/COMP.
PC
12
13
14
A/DAC2 B/DAC3
H
L
H H
A/DAC0 B/DAC1
H
L
H H
TO D8
G / Y
B / Pb
R / Pr
IC2302
IC3003
PC
|
Q8021
REMOTE
14
15
AUDIO SELECT
5
14
2
15
4
11
AB
DAC2 DAC3
SYNC. ON G
IC3002
SYNC. SELECT
14
5
15
2
11
4
AB
DAC0 DAC1
IC1001
6
OUT
SCL3
SDA3
L
R
910
HD
VD
910
STB 5
1
3
2
1
RS-232C
Q3086
Q3086
from
SCL1
SDA1
IC2401
AUDIO AMP
32
1
29
Q2406
27
SCL3 SDA3
SYNC. SEPALATOR
4
SYNC.
SEPALATOR
6
8
IC1002
38
31
32
47
52
51
31
45
IC1004
1
2
3
4
IC8001
POWER
STATUS
CABLE
DET
RXD-XC
TXD-XC
DCE-XC
DTE-XC
TIMER
CLOCK
20
12
1615
HD-
15
VD
13
CLP
17
SUB MPU
8
7
6
5
10
13
1
9
IIC CONT.
REMOTE IN
AV
RGB/COMP.
AV
RGB/
COMP.
PC
For
TUNER
L
H
L
H
DAC 3
DAC 2
DAC 1
DAC0
IC3004
4
5
DAC
6
7
IIC
IC8002
INVERTOR
SCL1
SDA1
RESET
IIC INT.
LED G
ALL OFF
+
C1006
-
Q2301 1
Q2303
Q2304
53
54
53
54
28LED R
29
40
33
17
MUTE
11
12
2
8
IC1003
619
STB 5V
7
L
4
12
IC2301
R
12
IC8003
17
2
15
4
1
STB 5
18
16
J10
TO SPEAKER
1
J11
4
3
5
7
TO SPEAKER
1Q2302
J9
NHS
33
NHD
37
NVS
38
NVD
29
NHCLP
34
IIC 5V
25
SCL1
SDA1
26
22
SCL2
SDA2
21
17
SCL3
SDA3
18
IIC CONT.
30
IIC INT.
14
3
LED R
LED G
2
REMOTE IN
6
5
ALL OFF
86
Page 87

13.19. J-Board (1/5) Schematic Diagrams
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
87
Page 88

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
13.20. J-Board (2/5) Schematic Diagrams
88
Page 89

13.21. J-Board (3/5) and H3-Board Schematic Diagrams
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
89
Page 90

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
13.22. J-Board (4/5) Schematic Diagrams
90
Page 91

13.23. J-Board (5/5) Schematic Diagrams
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
91
Page 92

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
13.24. D-Block Diagrams
D
D8
FROM J8
1
DVI
IN
10
IC9000
12
G/Y
3
8MHz / 525P
15MHz / XGA
25MHz / HD,UXGA
IC9001
13
B/Pb
R/Pr
TO J9
SCL1
SDA1
SCL2
SDA2
SCL3
SDA3
IIC CONT.
IIC INT.
REMOTE
ALL OFF
LED R
LED G
NHD
NVD
NHCLP
NHS
NVS
14
D9
25
26
22
21
17
18
30
14
6
5
3
2
37
29
34
33
38
3
IC9001
3
IC9202
IC9801
9 ~ 20
Q9001
1 15MHz
Q9002
Q9003
Q9005
1 15MHz
Q9006
Q9007
Q9009
1 15MHz
Q9010
Q9011
IIC
Q9700
LED R
29
D43
LED G
30
TO D43
4
Q9200
3
5
27 ~ 55
8MHz
25MHz
LC9015
LC9016
LC9017
8MHz
25MHz
LC9019
LC9020
LC9021
8MHz
25MHz
LC9023
LC9024
LC9025
IC9803
IC9004
BAND SW
1
8
10169
IC9005
BAND SW
1
8
10169
IC9006
BAND SW
16
1
8
10
D4
REMOTE IN
IC9223
1 2
5 6
9 8
13 12
11 10
3 4
LATCH
2 ~ 7
19~12
CONTRAST
5
5
5
9
IIC
SCL1
SDA1
SCL2
SDA2 IC9200 IC9201 IC9209 To SC Board
SCL3 IC9705 FIELD MEMORY
SDA3
HD
VD
CLP
HS
VS
HDP
2~7
IC9019
8
6
IC9020
6
IC9020
6
IC9701
97
98
89
90
70
71
75
76
110
66
B/Pb
MAIN MPU
DVI G
IC9802
19~12
2~7
19
G/Y
14
17
19
14
17
19
R/Pr
14
17
IC9215
PLLM 50MHz
IC9211
PLL2 50MHz
IC9212
PLL1 95MHz
DVI B
DVI R
19~12
IC980
DIGITAL RGB PROCESSOR
BRIGHTNESS
IC9008 SUB-FIELD PROCESSOR
CLAMP
A/D
A/D
7
IC9007
7
IC9009
7
IC9702
67
68
69
98
11~2011~20
A/D
A/D
11~20
IC9216
BUFFER
IC9207
BUFFER
IC9206
BUFFER
1 Mbit VRAM
8M FLASH
MEMORY
NO SYNC.
G/Y
19 ~26
B/Pb
11~18
R/Pr
3~10
FAN SOS
IC9302
~62
289
~296
720
625
55
16M
SDRAM
CTI / COLOUR
CONTRAST
W/B-g
102
113
~9594~87
~10
244
233
~252
~242
YUV OUT
480
SDRAM
D13
TO C13
9
FAN SOS
RGB-YUV
CONVERTER
34
~4144~51
271
281
~278
~288
YUV IN
IC9204 FORMAT CONVERTER
(LINE DOWN CONVERTER)
1080
16M
SDRAM
D7
TO P7
1
RUSH ON/OFF
TV ON/OFF
2
KILL SOS
5
6
POWER STOP SOS
7
ALL OFF
8
123~116
135~128
113~106
254
~262
16M
IC9402
PLASMA AI CONTROL IC9503 FIELD MEMORY
8M FLASH MEMORY
IC9400
24~1716 ~ 9
PLASMA AI
QUAGI 9bit
PROCESSOR
QUAGI PAL 100Hz
18 ~ 1
16M SDRAM
FIELD
MEMORY
IC9402 IC9403 DB
IC9900 DF
DISCHARGE
CONTROL
SYNC . IN
HDVDCLPHS
22
14 15 43 41 42 16
VS
HDP
16M SDRAM
MEMORY
FIELD
BUFFER
BUFFER
UF
171~156191~172
211~192
IC9904
IC9903
IC9905
BUFFER
28 ~ 39
14 ~ 252 ~ 13
IC9507
16M SDRAM
IC9501
SUB-FIELD
PROCESSOR
UF1UF2
UB1DB1
UB2
DF1DF2
DB2
LSI28
16M SDRAM
FIELD
MEMORY
D20
D21
CLK D1 D2 D3
D13
To C13 To C23
IC9510
CLOCK
BUFFER
IC9502 FIELD MEMORY
UB
16M SDRAM
IC9506
16M SDRAM
FIELD
MEMORY
IC9511
CLOCK
BUFFER
S/CONVERTER
UPPER LEFT
IC9508 IC9512
IC9509 IC9513
S/P CONVERTER
LOWER LEFT
D4 D5 D6 D7 CLK
S/CONVERTER
UPPER RIGHT
IC9514
CLOCK
BUFFER
IC9515
CLOCK
BUFFER
S/P CONVERTER
LOWER RIGHT
D23
92
SC PULSE CLK D1 D2 D3
D43
To C43 To C35
D4 D5 D6 D7 CLK
D35
Page 93

13.25. D-Board (1/14) Schematic Diagrams
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
93
Page 94

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
13.26. D-Board (2/14) Schematic Diagrams
94
Page 95

13.27. D-Board (3/14) Schematic Diagrams
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
95
Page 96

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
13.28. D-Board (4/14) Schematic Diagrams
96
Page 97

13.29. D-Board (5/14) Schematic Diagrams
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
97
Page 98

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
13.30. D-Board (6/14) Schematic Diagrams
98
Page 99

13.31. D-Board (7/14) Schematic Diagrams
TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
99
Page 100

TH-42PW4 / TH-42PWD4
D-Board Schematic Diagram is Continued
100
 Loading...
Loading...