Panasonic MN86157 Datasheet
For Communications Equipment
MN86157
Shading Correction LSI
Overview
The MN86157 contains a 7-bit A/D converter for use
in correcting, at the bit level, shading distortion for signals from image sensors, optics, and similar sources.
It uses external RAM to support adaptive correction
that responds to changes in distortion patterns. It also uses
ROM to provide fixed correction when a white reference
plane signal is not available.
The chip is also usable as a stand-alone A/D converter.
Features
Choice of correction range (50% or 75%) depending
on extent of shading distortion
Parallel A/D converter functions
Resolution: 7 bits
Non-linearity: ±1/2 LSB
Conversion speed: max. 5 MHz
Note: This is the guaranteed design value for the
chip used as a stand-alone A/D converter. The
guaranteed value at shipment is ±3 LSB
Ability to start and stop clock in the middle of a line
to support CdS contacting image sensors and other
devices with variable scanning rates
Overflow pin that simplifies task of adding auto
background control (ABC) circuit
Single 5 volt power supply
Guaranteed TTL levels for input
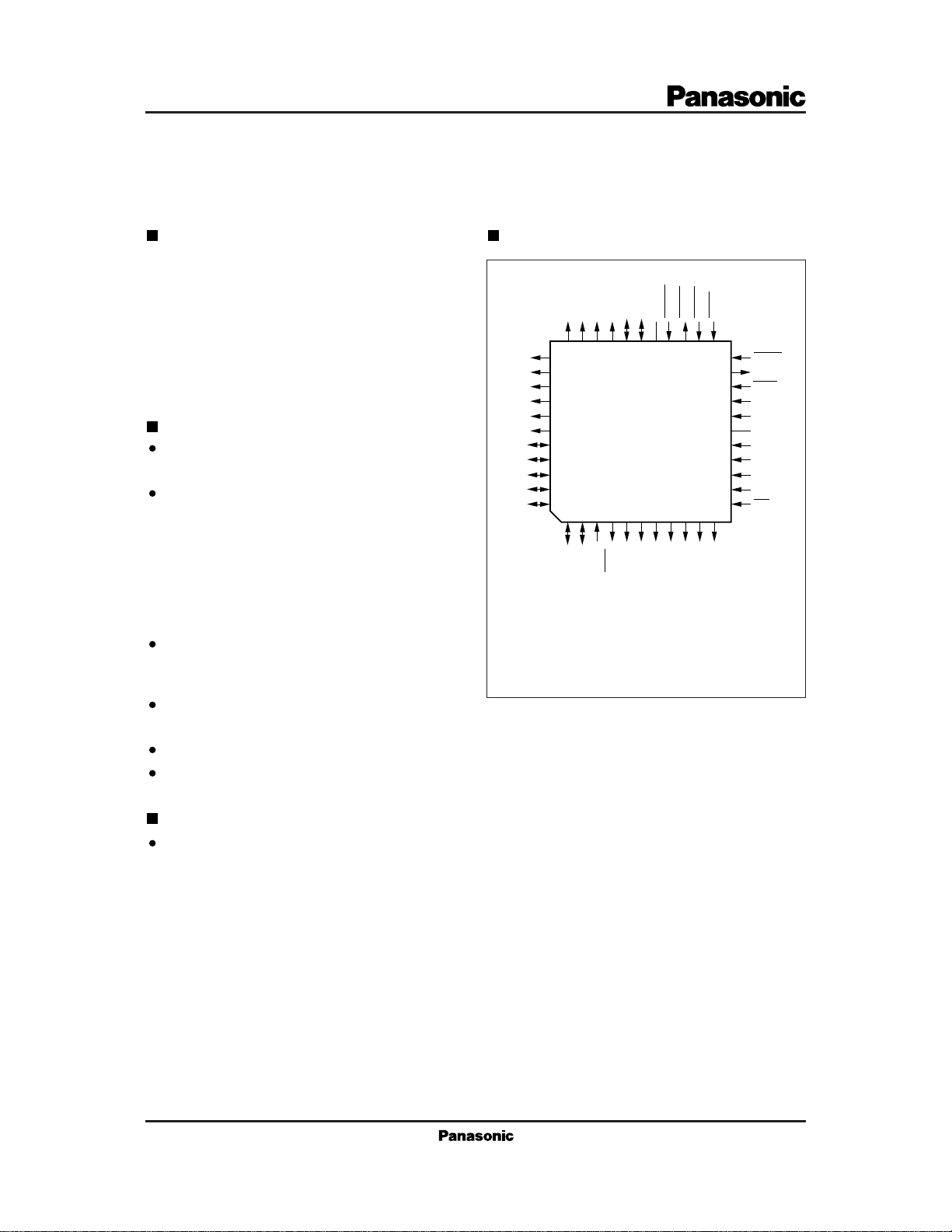
Pin Assignment
A6A7A8A9A10
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
3332313029282726252423
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
1234567891011
D5
D6
ROS
QFP044-P-1010
A11
N.C.
DB5
DB4
MOE
OVF/DB6
(TOP VIEW)
MODE
ENBO
DB3
DB2
CKSH
ENBI
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
DB1
DB0
SHST
R/W
INHI
V
SS
V
DD
N.C.
VREFL
VIN
VREFH
V
DD
OE
Applications
Facsimile equipment
MN86157 For Communications Equipment
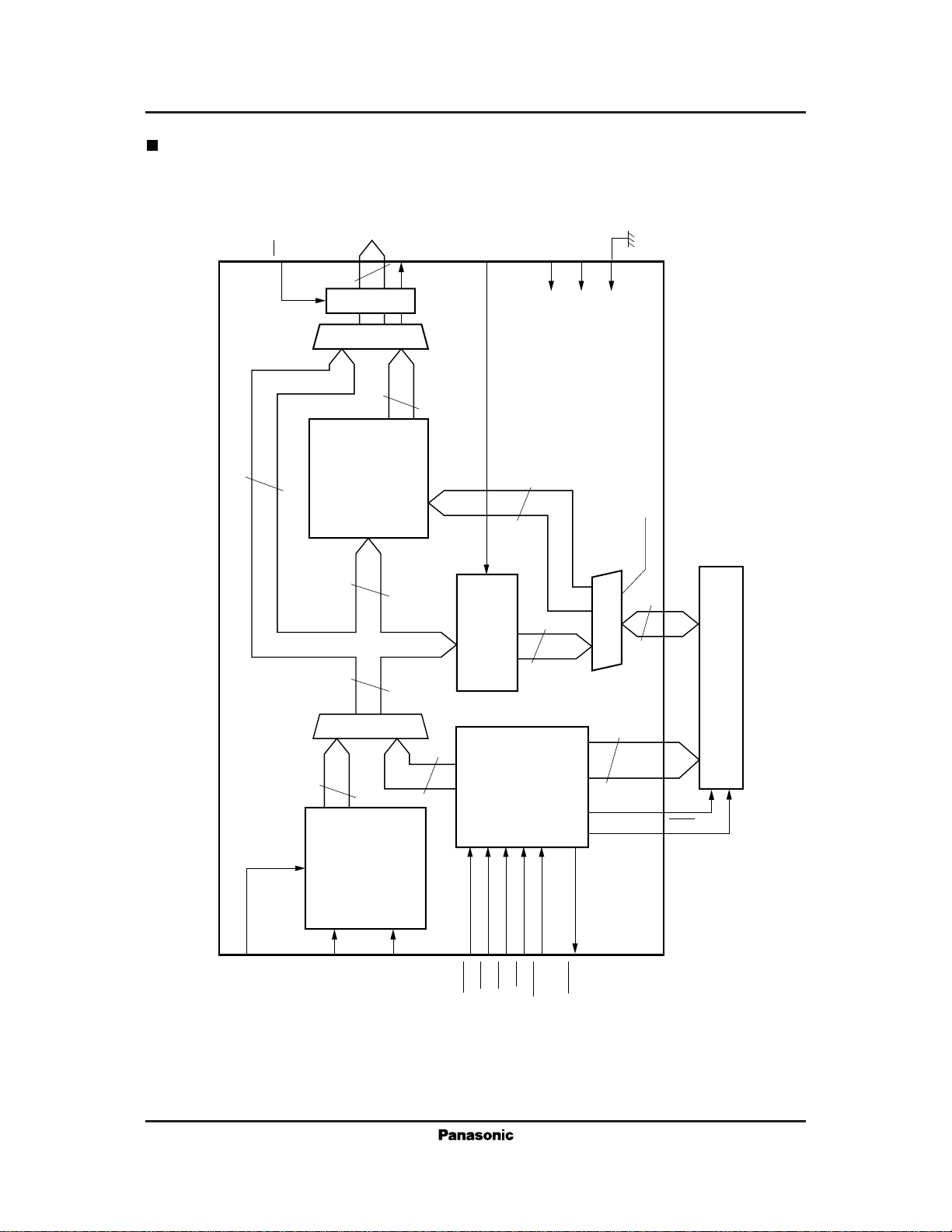
Block Diagram
DB0 to 5
OE
12
7
6
Selector
7
Multiplier
7
7
SHADING CORRECTOR LSI
Selector
OVF/DB6
5
ROS
3
Distortion-
Coefficient
ROM
DDVDD
V
13
18
7
7
SS
V
19
Selector
D0 to 6
7
RAM or ROM
A0 to 11
VR
7
VREFH
ADC
VREFL
7
Controller
2423222026
INHI
ENBI
SHST
CKSH
MODE
25
ENBO
12
21
R/W
4
MOE

For Communications Equipment MN86157
MN86157 Block Configuration
The MN86157 consists of four basic blocks: (1) A/D
converter, (2) distortion coefficient mapping ROM, (3)
multiplier, and (4) controller.
The following are brief descriptions of each block.
(1) A/D converter
This uses comparison with the reference voltages
to convert the scanner's image data signal from
the VIN pin to a 7-bit digital output.
(2) Distortion coefficient mapping ROM
This constitutes a look-up table for converting the
A/D converter output to a final value for storage
in the external RAM.
(3) Multiplier
This provides high-speed parallel multiplication
of 7 × 7 bits data.
(4) Controller
This controls operation of the shading correction
circuits, the A/D converter, and interface to
external ROM or RAM.
Operation
Shading correction (MODE pin at "H" level)
• Fixed distortion coefficients (external memory
is ROM)
This configuration provides 6-bit corrected data
using fixed distortion coefficients stored in an
external ROM and thus invariant.
• Adaptive distortion coefficients (external
memory is RAM)
This configuration provides 6-bit corrected data
using distortion coefficients, stored in external
RAM, that the chip constantly updates using
white reference plane line training.
• Pixels per line
The chip supports line lengths up to 4096 pixels
with a built-in 12-bit address counter supporting
interfaces to two 2
equivalent of a 2732 ROM (2
• Input clock
The chip uses an input clock signal with a
frequency twice that of the image clock.
• Selecting correction range
The ROS pin provides a choice of two correction
ranges and consequently correction precisions.
11
× 8-bit RAM chips or the
12
× 8 bits).
ROS
Correction Correction
Range Precision
H 50% ±1.5%
L 75% ±3.0%
• Correction start/stop function
Pulling the INHI pin to "L" level in the middle
of a line suspends correction and maintains the
output data at its current value. Returning the
pin to "H" level restarts correction.
• Auto clamp and overflow functions for output
data
If the image input signal level exceeds the white
reference plane level, the chip clamps the output
data at the full-scale value (3F
) and drives the
H
overflow pin (OVF) at "H" level.
 Loading...
Loading...