Panasonic MN86063 Datasheet

For Communications Equipment
MN86063
High-Speed CODEC LSI for Facsimile Images
Overview
The MN86063 is a high-speed LSI codec for compressing
and decompressing facsimile images. Features include
real-time printing to laser printers, built-in line memory,
enlargement and reduction, and code conversion.
Features
Pixels per line:
between 16 and 4864 bits, in word (16-bit) increments.
Processing time per line:
Individual pixels are processed within two system
clock cycles. For a machine cycle of 10 MHz,
processing the worst-case pattern for a 4096-bit line
takes no more than 1 ms.
Time-shared, multiplex processing
Support for time-shared, multiplex processing allows
image I/O, enlargement/reduction processing, and
coding/decoding to proceed concurrently for a group
of lines. Image bus DMA transfers can also proceed
concurrently with command processing.
Multiple channels
If lines consist of 2432 bits or fewer, commands can
be processed simultaneously on two channels using
time-sharing. These commands may be issued
asynchronously.
Bus configuration
There are separate system and image buses. The latter
features two independent master DMA channels; the
former, four slave DMA channel pins.
Image data I/O
Image data I/O can use either the image or system bus.
Byte conversion
When the system bus is 16 bits wide, the chip can swap
the upper and lower bytes of image or coded data. It
can also swap the MSB and LSB.
Memory management
The chip includes pointer management for the image
buffer connected to the image bus.
Machine cycle
The limit is 10 MHz. This means that the maximum
input clock is twice this, or 20 MHz.
Function
Message coding:
MH, MR, MMR, and MG3. The chip also supports
data transfers on the image and system buses and DMA
transfers on the image bus alone.
Coding conversion
The chip converts between all supported message
coding systems: MH, MR, MMR, and MG3.
Enlargement/reduction
These may be added to coding, decoding, code
conversion, and data transfer operations.
(1) In the primary scan direction, the chip uses
multiplication on the change point address. The
scaling factor can be anywhere between approximately
0.1% and 200% in increments of approximately
0.1%. Integral multiplication is also available
beyond this
(2) In the subscanning direction, the chip uses
decimation and replication. The scaling factor can
be anywhere between approximately 0.0015% and
200% in increments of approximately 0.0015%.
Integral multiplication is also available from 2 to
65,535.
White masks for both edges
These may be added to coding, decoding, code
conversion, and data transfer operations. They change
all pixels within the margins, specified in bit
increments, to white.
Decoding error processing
The chip offers a choice of replacing with the previous
line or a white line.
Applications
Facsimile equipment
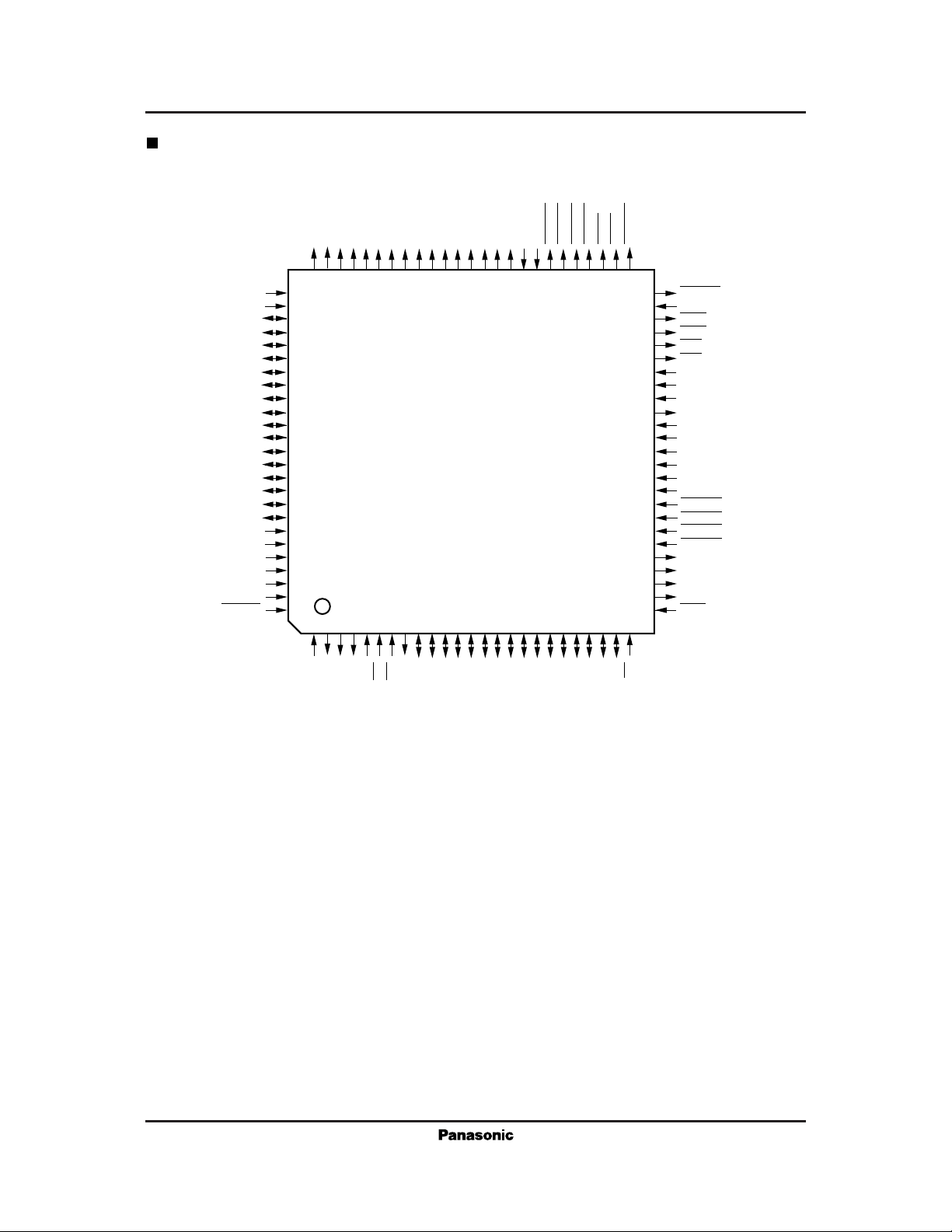
MN86063 For Communications Equipment
Pin Assignment
V
SS3
V
DD3
ID15
ID14
ID13
ID12
ID11
ID10
ID9
ID8
ID7
ID6
ID5
ID4
ID3
ID2
ID1
ID0
V
SS4
V
DD4
TEST3
TEST2
TEST1
TEST0
RESET
IA0
IA1
IA2
IA3
IA4
IA5
IA6
IA7
IA8
IA9
IA10
IA11
IA12
75747372717069686766656463626160595857565554535251
76
IA13
IA14
IA15
DD2VSS2
V
DACK1
DACK0
DSTR0
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
123456789
INTR1
INTR2
RD
HEX
INTR0
2SYSCLK
101112131415161718192021222324
WR
D15
D14
D13
D9D8D7D6D5D4D3D2D1D0CS
D12
D11
D10
SYSCLK
DSTR1
IMLE
IMUE
DCMP0
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
DCMP1
IREADY
IOW
IMW
IOR
IMR
DREQ0
DREQ1
IHACK
IHREQ
V
DD1
V
SS1
A0
A1
A2
A3
ACKD1
ACKD0
ACKC1
ACKC0
REQD1
REQD0
REQC1
REQC0
UBE
QFP100-P-1818
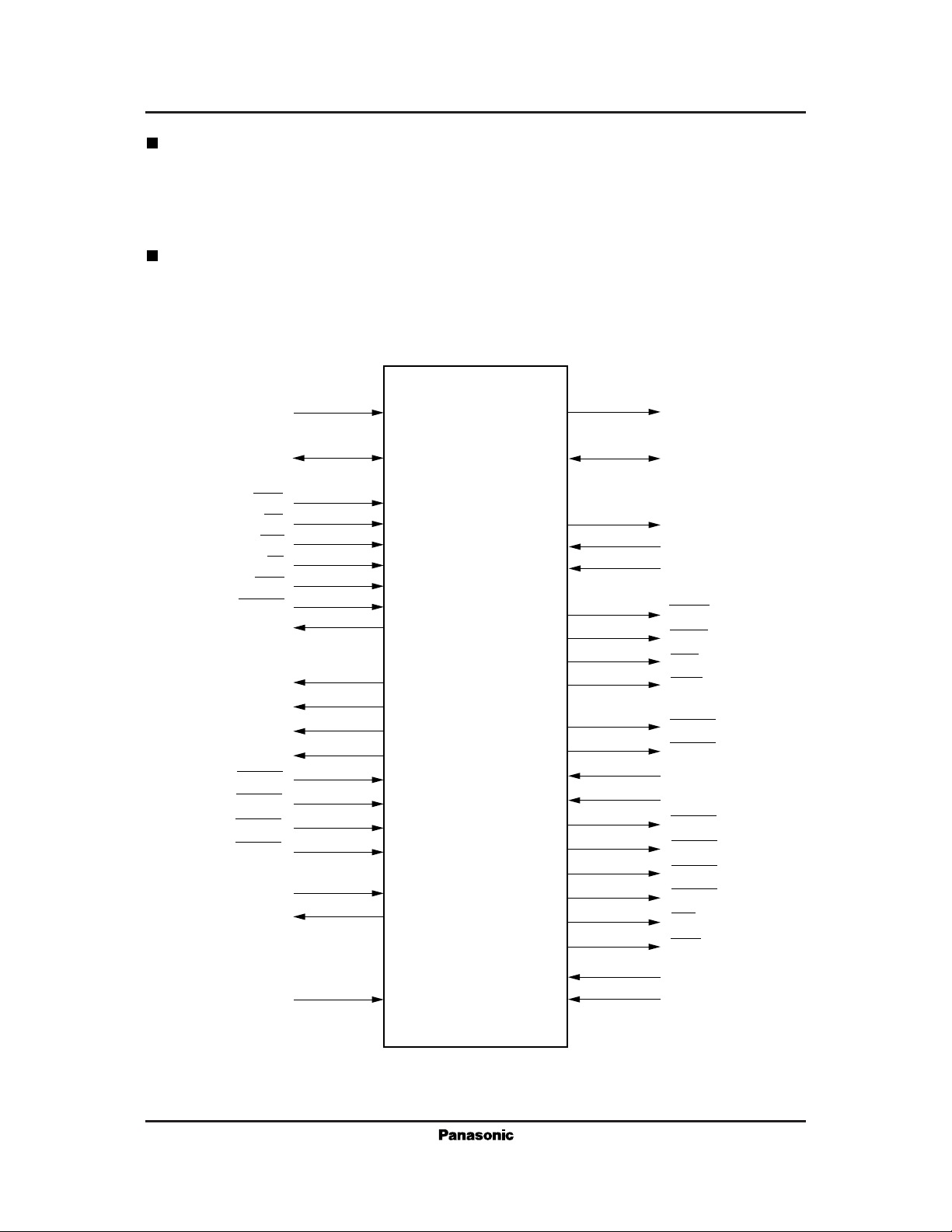
For Communications Equipment MN86063
Pin Configuration
The MN86063 features two buses: the system bus, which is primarily used for transferring coded data to and from
a microprocessor and other components and the image bus, which is used for transferring image data to or from a
scanner, printer, or the like.
Pin Function Chart
The chip has a total of 100 pins: 39 for the system bus, 49 for the image bus, and 12 for testing, power supply, and
other purposes.
System bus pins
A0 to A3
D0 to D15
UBE
RD
WR
CS
HEX
RESET
INTR0 to 2
REQC0
REQC1
REQD0
REQD1
ACKC0
ACKC1
ACKD0
ACKD1
2SYSCLK
SYSCLK
MN8606X
Image bus pins
IA0 to 15
ID0 to 15
IHREQ
IHACK
IREADY
IMUE
IMLE
IMR
IMW
DSTR0
DSTR1
DREQ0
DREQ1
DACK0
DACK1
DCMP0
DCMP1
IOR
IOW
TEST0 to 3
VDD0 to 3
VSS0 to 3
 Loading...
Loading...