
Color TFT LCD Driver
MN838850
Source Driver for LCD Panel Drive
■ Overview
The MN838850 converts digital display data from a personal computer or an engineering workstation to analog signal
voltages to allow those signals to be displayed on a color TFT LCD panel.
■ Features
• Includes a built-in D/A converter and accepts 8-bit digital input data for 16.7-million color display.
• Output dynamic range: 14.6 V
• Supports both dot inversion drive and source inversion drive schemes.
• Number of drive outputs: 384
• Input data bus: acquires two pixels at the same time
• Supports control of data inversion at each clock cycle.
• Supports γ correction.
• Adopts a drive scheme that does not require precharging.
• Allows serial cascade connection.
• The clock is automatically stopped after the acquisition of a fixed amount of data.
• The shift register shift direction can be set to be either left-to-right or right-to-left.
• Digital circuit block features low-voltage operation:
2.7 to 3.6 V
• Maximum operating clock frequency:
50 MHz (3.1 to 3.6 V), 40 MHz (2.7 to 3.6 V)
(when AVDD = 15 V)
P-P
■ Applications
•
TFT LCD panels
1
MN838850 Color TFT LCD Driver
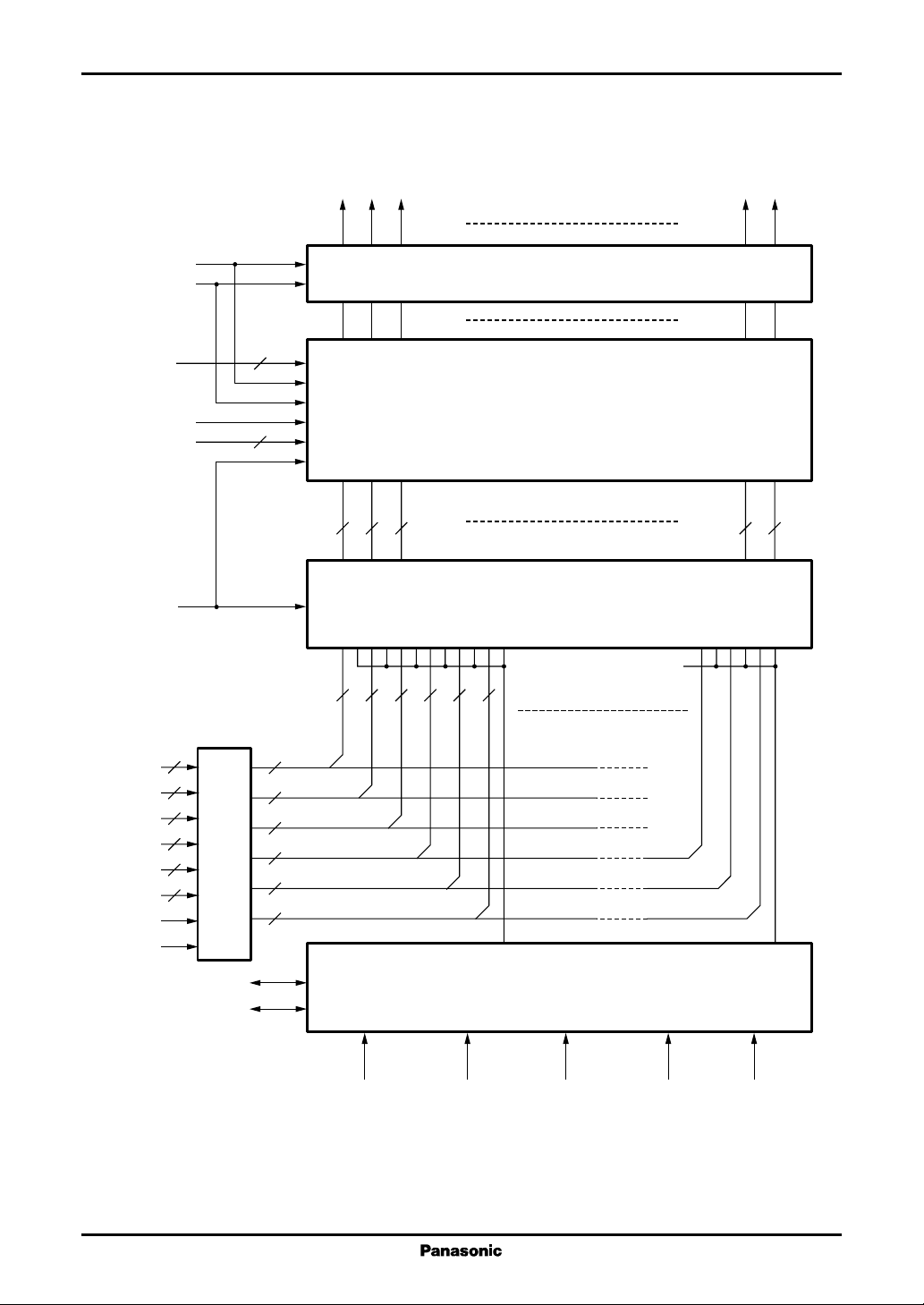
■ Block Diagram
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y383
Y384
VREF0 to 9
VOPU, VOPL
D00 to D07
D10 to D17
D20 to D27
D30 to D37
D40 to D47
D50 to D57
INV1
INV2
AVDD
AVSS
POL
A
8
8
8
8
8
8
Latch
10
2
Output Circuit
D/A Converter
8 8 88
8
Two-line 384 × 8-bit latch
8 8 8 8 8 8
8
8
8
8
8
8
PLSR
PRSL
DVDD
2
Shift Register
DVSS
RL
FY
TEST
Color TFT LCD Driver MN838850
■ Pin Arrangement
Y384
1 PRSL
2D57
3D56
4D55
5D54
6D53
7D52
8D51
9D50
10 D47
11 D46
12 D45
13 D44
14 D43
15 D42
16 D41
17 D40
18 D37
19 D36
20 D35
21 D34
22 D33
23 D32
24 D31
25 D30
26 DVDD
27 TEST
28 RL
29 VOPU
30 VREF9
31 VREF8
32 VREF7
33 VREF6
34 VREF5
35 A VDD
36 A VSS
37 VREF4
38 VREF3
39 VREF2
30 VREF1
41 VREF0
42 VOPL
43 DVSS
44 FY
45 A
46 POL
47 INV2
48 INV1
49 D27
50 D26
51 D25
52 D24
53 D23
54 D22
55 D21
56 D20
57 D17
58 D16
59 D15
60 D14
61 D13
62 D12
63 D11
64 D10
65 D07
66 D06
67 D05
68 D04
69 D03
70 D02
71 D01
72 D00
73 PLSR
Cu Foil Surface Top View
Y383
Y382
Y381
Y380
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
Y5
Y4
Y3
Y2
Y1
3
MN838850 Color TFT LCD Driver
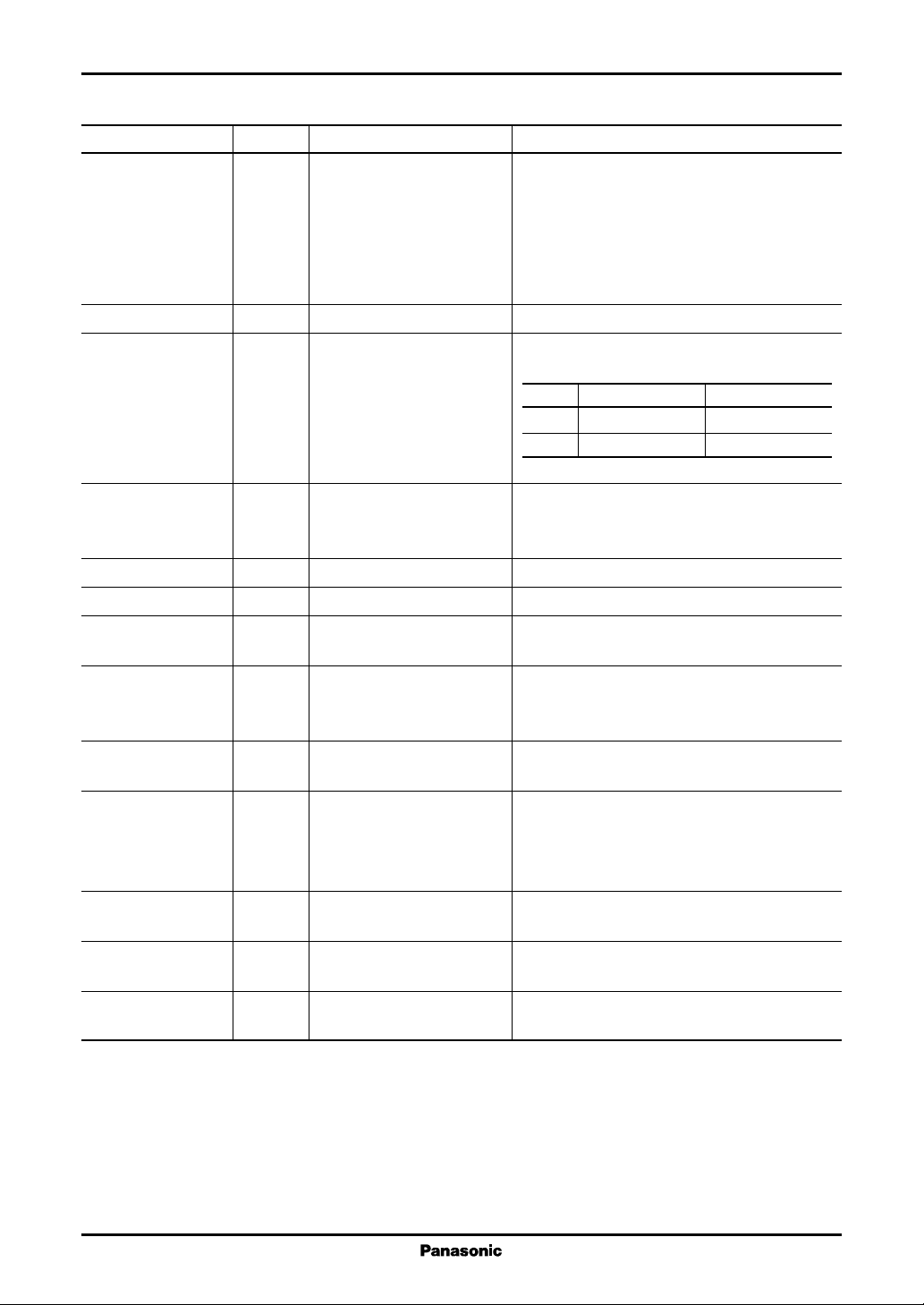
■ Pin Descriptions
Pin No. I/O Pin Name Description
D00 to D07 I Image data input Image data input pins.
D10 to D17 The R, G, and B image signals are input using
D20 to D27 these pins.
D30 to D37 D07, D17, D27, D37, D47, D57 : MSB
D40 to D47 D00, D10, D20, D30, D40, D50 : LSB
D50 to D57
Y1 to Y384 O Image signal output Analog image signal output pins.
PLSR I/O Start pulse input and output Internal shift register start pulse input and
PRSL output pins.
RL = "H" RL = "L"
PLSR Right shift input Left shift output
PRSL Right shift output Left shift input
RL I Shift direction selection Input signal that selects the shift direction.
signal input High: Right shift (Y1 to Y384)
Low: Left shift (Y384 to Y1)
FY I Clock input Data acquisition clock input pin.
A I Analog output control Controls the analog voltage output.
POL I Output polarity reversal Switches the reference voltage for odd and even
control input outputs.
INV1 I Data inversion control input Controls inversion of the input image signal.
INV2 INV1: Used for D2(7 : 0), D1(7 : 0), D0(7 : 0)
INV2: Used for D5(7 : 0), D4(7 : 0), D3(7 : 0)
VREF0 to 9 I γ correction voltage input Inputs the γ correction voltage used by the D/A
converter.
VOPU, VOPL I Analog reference voltage Provides the reference voltage that determines
the analog circuit operating point.
VOPU: Reference voltage for the high side output
VOPL: Reference voltage for the low side output
AVDD I Analog system power supply Provides the power for the analog circuits.
AVSS
DVDD I Digital system power supply Provides the power for the digital circuits.
DVSS
TEST I Test Used for device testing.
(Pull-down resistor: 100 kΩ) This pin must be left open during normal operation.
4
Color TFT LCD Driver MN838850
■ Functional Description
•
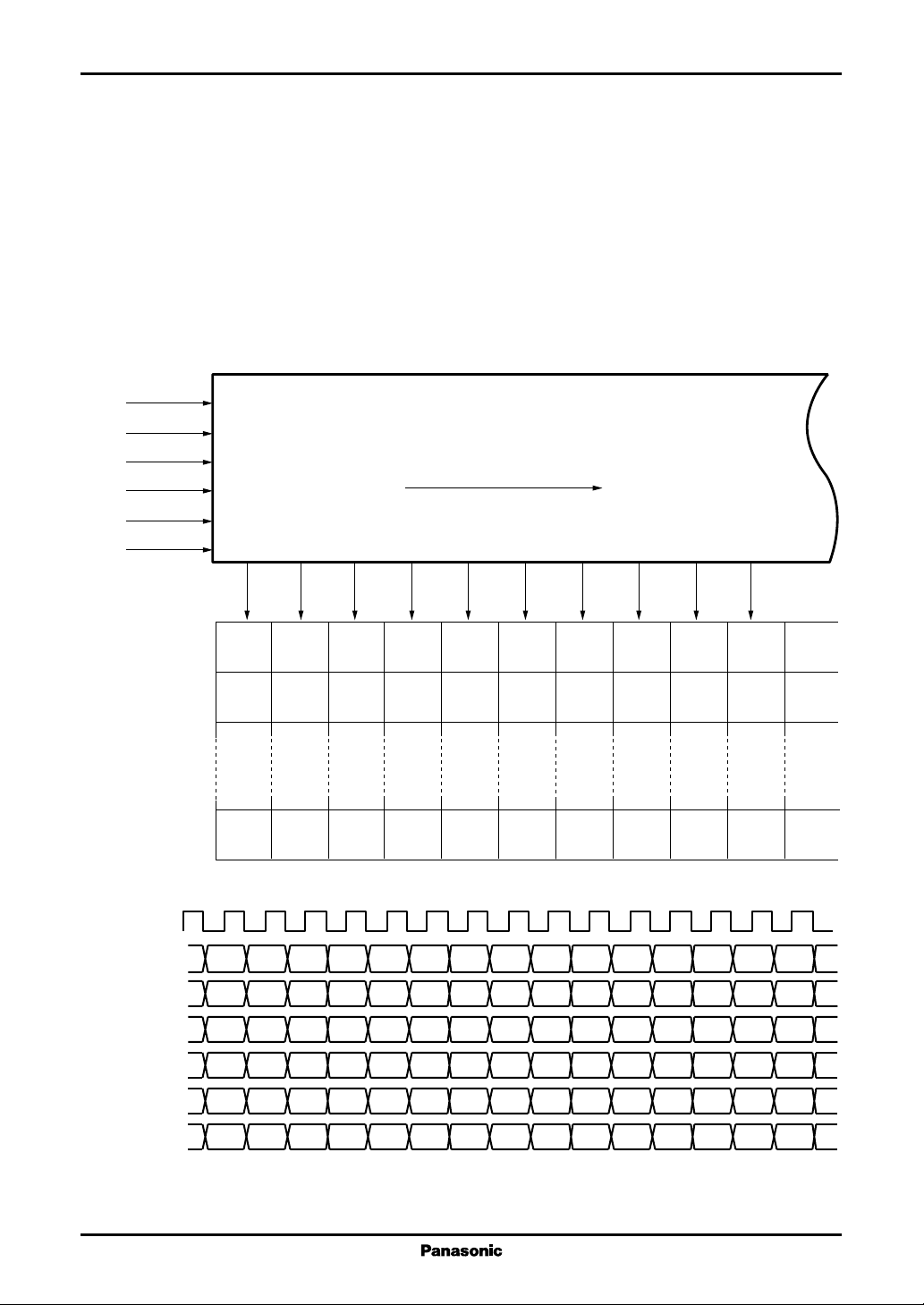
Relationship between the data input and the analog output pins
The input mode used by this IC is a two-pixel mode in which the data for two pixels is input in parallel from the D0(7:0),
D1(7:0), D2(7:0), D3(7:0), D4(7:0), and D5(7:0) input ports.
The correspondence between the data input ports and the output pins is as follows.
Y(6n−5) = D00 to D07 Y(6n−2) = D30 to D37
Y(6n−4) = D10 to D17 Y(6n−1) = D40 to D47
Y(6n−3) = D20 to D27 Y(6n) = D50 to D57 (n = 1, 2, ······, 64)
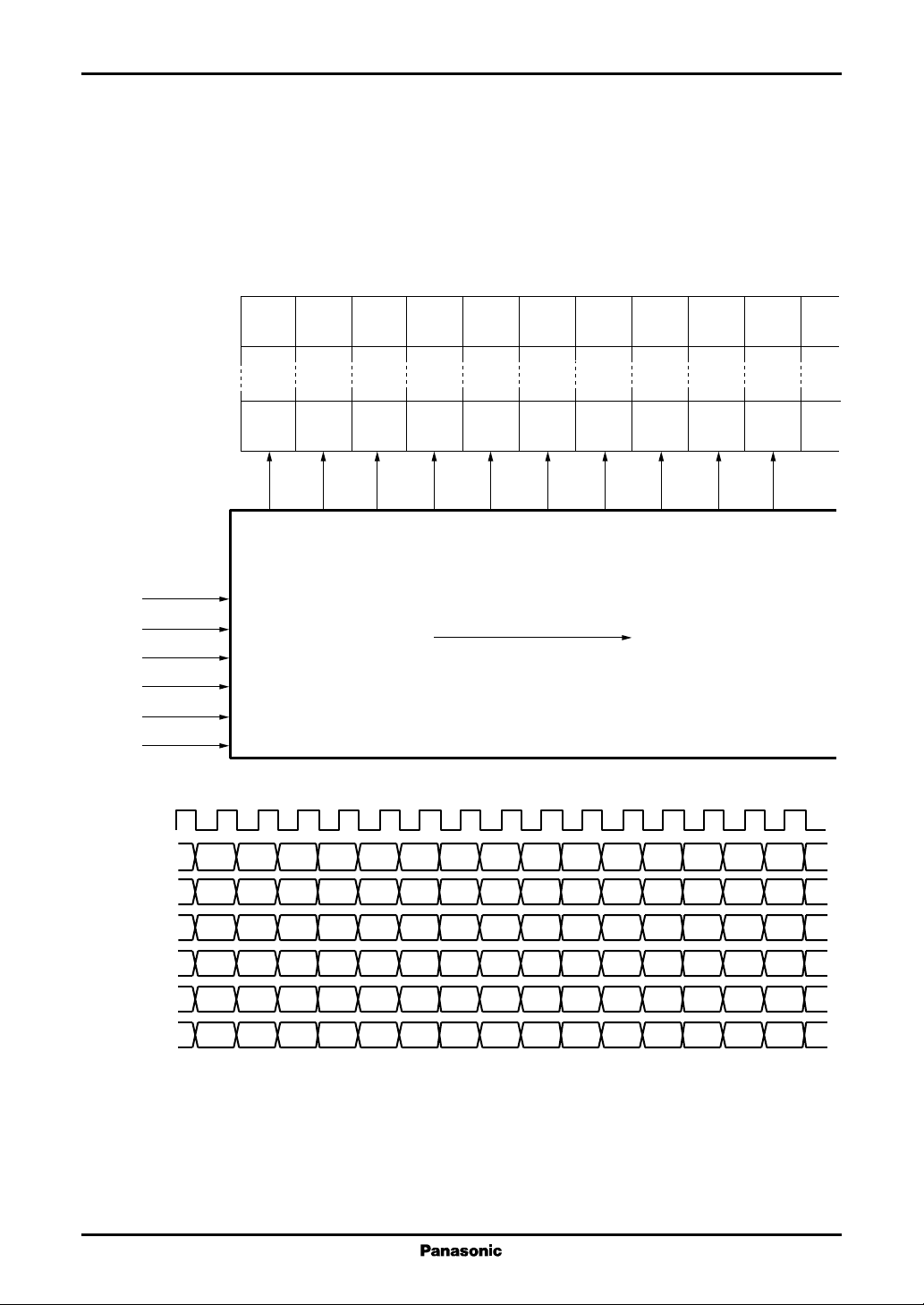
Figure 1 shows an example of color data and pin connections when RL is high.
This example shows the case where the pixels are in the order R, B, G starting at the left edge of the LCD panel.
D00 to D07
R2n-1
D10 to D17
B2n-1
G2n-1
R2n
B2n
G2n
(n=1..)
D20 to D27
D30 to D37
D40 to D47
D50 to D57
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y4
MN838850
Y5
Y6
Y7
Y8
Y9
Y10
············
FY
D0(7 : 0)
D1(7 : 0)
D2(7 : 0)
D3(7 : 0)
D4(7 : 0)
D5(7 : 0)
R1 B1 R2 B2 G2 R3 B3 G3 R4
R1 B1 R2 B2 G2
R1 B1
G1
G1
G1 R2 B2 G2
R3 B3 G3 R4
R3 B3 G3 R4
LCD Panel
R1
R3
R5
R7
R9
R11
R13
R15
R17
R19
R21
R23
R25
B1
B3
B5
B7
B9
B11
B13
B15
B17
B19
B21
B23
B25
G1
G3
G5
G7
G9
G11
G13
G15
G17
G19
G21
G23
G25
R2
R4
R6
R8
R10
R12
R14
R16
R18
R20
R22
R24
R26
B2
B4
B6
B8
B10
B12
B14
B16
B18
B20
B22
B24
B26
G2
G4
G6
G8
G10
G12
G14
G16
G18
G20
G22
G24
G26
···
···
···
R27
B27
G27
R28
B28
G28
Figure 1 Relationship between Input and Output Pins (When RL is high and the shift direction is Y1 to Y384)
5
MN838850 Color TFT LCD Driver
■ Functional Description (continued)
•
Relationship between the data input and the analog output pins (continued)
The following presents the case with the same LCD panel color arrangement as figure 1 but with RL low.
In figure 2, R1 corresponds to Y384, B1 to Y383, and G1 to Y382. Note that the relationship between the color data
and the data ports here differs from that in figure 1.
LCD Panel
R2n-1
B2n-1
G2n-1
R2n
B2n
G2n
(n=1..)
FY
D50 to D57
D40 to D47
D30 to D37
D20 to D27
D10 to D17
D00 to D07
R1 B1 R2 B2 G2
R1 B1G1G1 R2 B2 G2
Y384
Y383
Y382
Y381
Y380
MN838850
R3 B3 G3 R4
R3 B3 G3 R4
Y379
Y378
Y377
Y376
Y377
···
···
·········
G2
G4
G6
G8
G10
G12
G14
G16
G18
G20
G22
G24
B24
R24
G23
B23
R23
G26
B26
R26
G25
B25
R25
D0(7 : 0)
B2
B4
B6
B8
B10
B12
B14
B16
B18
B20
R20
G19
B19
R19
B22
R22
G21
B21
R21
D1(7 : 0)
R2
R4
R6
R8
R10
R12
R14
R16
G15
B15
R15
R18
G17
B17
R17
D2(7 : 0)
G1
G3
G5
G7
G9
G11
B11
R11
G13
B13
R13
D3(7 : 0)
B1
B3
B5
B7
R7
B9
R9
D4(7 : 0)
R1
R3
D5(7 : 0)
Figure 2 Relationship between Input and Output Pins (When RL is low and the shift direction is Y384 to Y1)
6
R5
G28
B28
R28
G27
B27
R27
Color TFT LCD Driver MN838850
■ Functional Description (continued)
•
Dot inversion drive
Since dot inversion drive is used, the analog output voltages with respect to the opposite electrode voltage differ in polarity
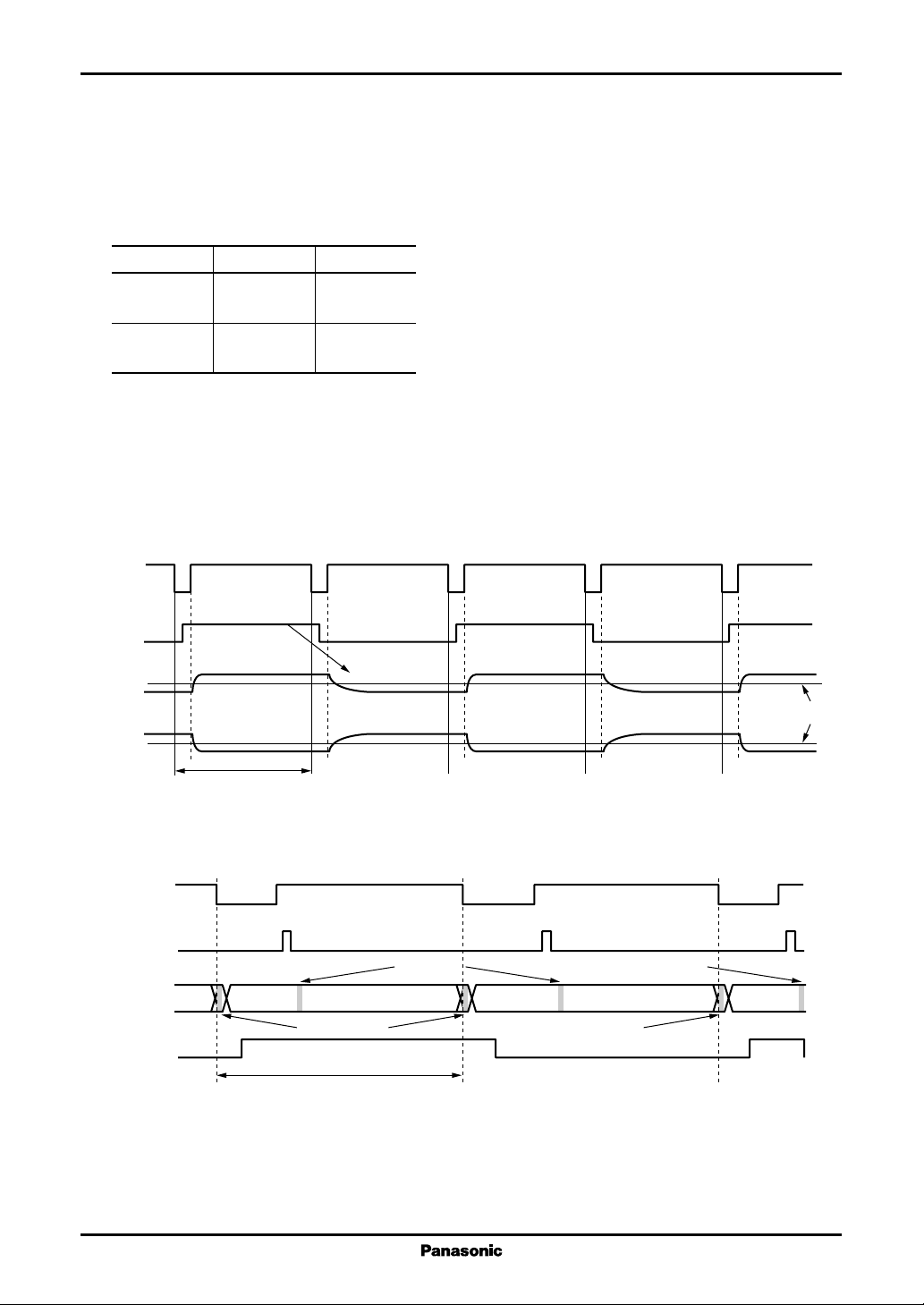
for each of the odd and even numbered output pins. This output voltage polarity is controlled by POL. The table below
lists the correspondence between the POL polarity setting, the analog output polarity and the VREF used.
POL Y2n-1 Y2n
"L"
"H"
The POL switching timing is presented below.
POL should be switched during the period when A is low, after the last data has been input, and before the next start
signal has been input. The POL signal level is acquired by the device internally on the falling edge of the A signal. The
output polarity is determined by the acquired signal level.
A
Positive polarity Negative polarity
VREF9 to 5 VREF4 to 0
Negative polarity Positive polarity
VREF4 to 0 VREF9 to 5
POL
Y
2n-1
Y
2n
(n=1 to 192)
A
Start Signal
Dxx
POL
One horizontal period
One horizontal period
Negative
polarity
Positive
polarity
Positive
polarity
Negative
polarity
POL Switching Timing
First data First data
Last data
Details of the POL Switching Timing
Last data
Negative
polarity
Positive
polarity
Opposite electrode
voltages
7
MN838850 Color TFT LCD Driver
■ Functional Description (continued)
•
Dot inversion drive (continued)
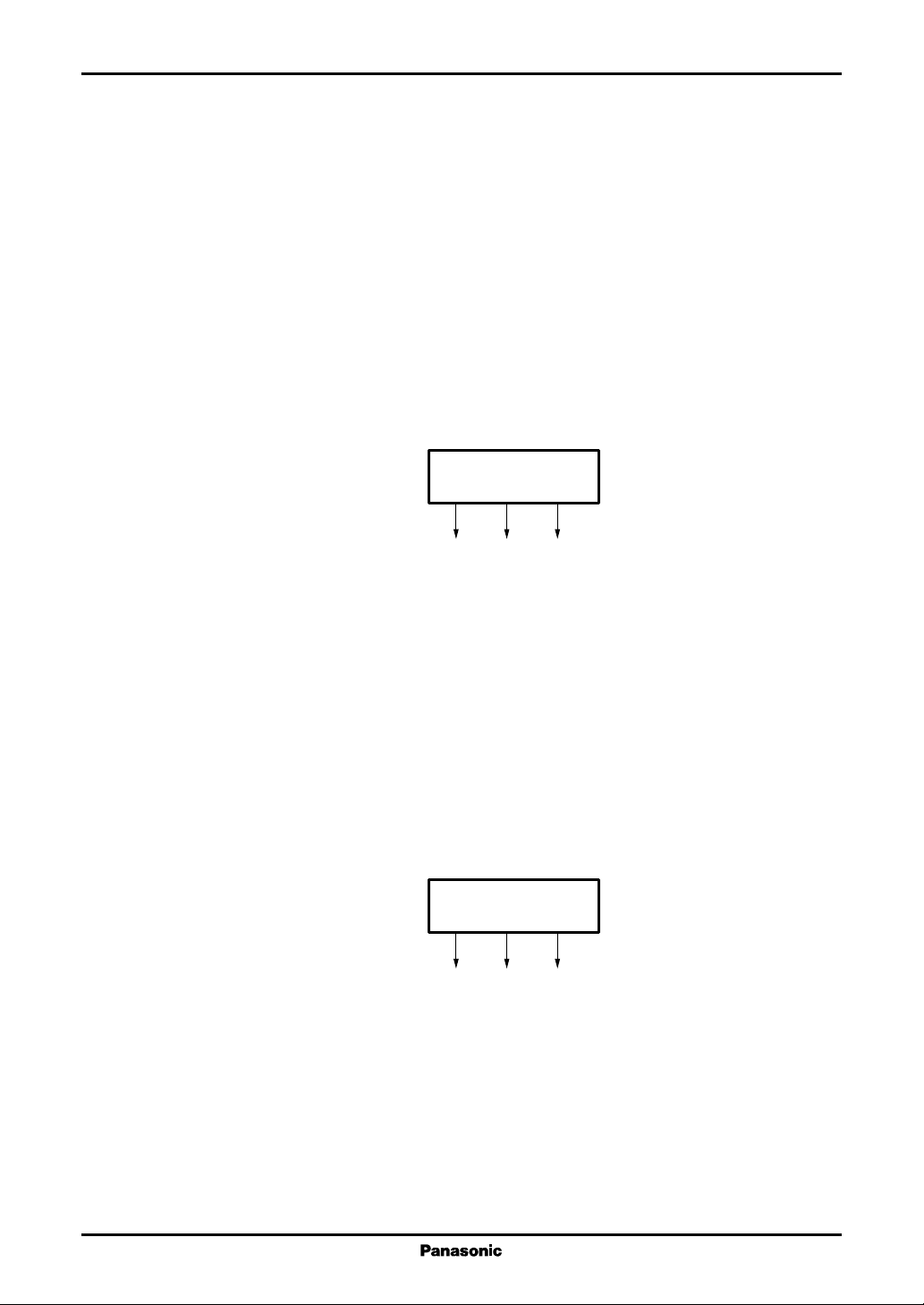
Next we describe dot inversion drive operation.
The symbol "+" here means a voltage that is positive with respect to the voltage on the opposite electrode, and "−" means
a voltage that is negative with respect to the voltage on the opposite electrode.
The figure below shows the dot inversion drive operation.
Since POL is low in the first line of the first field, Y1 will be + and Y2 will be −, that is, odd-numbered output pins
will have positive polarity and even-numbered output pins will have negative polarity.
Since POL is switched to high for the second line, odd-numbered output pins will have negative polarity and evennumbered output pins will have positive polarity.
Thereafter, the polarity of the output voltages is determined by the POL polarity.
In the second field, the POL polarity will be the opposite of what it was for the first field, so the output voltage polarities
will be reversed.
Y1
Y2
Y3
Field 1 Line 1 +−+ "L"
Line 2 −+− "H"
Line 3 +−+ "L"
Line 4 −+− "H"
·
·
·
·
·
·
Field 2 Line 1 −+− "H"
Line 2 +−+ "L"
Line 3 −+− "H"
POL
Note that if POL is inverted not every line, but only every field, the output polarities will be as shown below.
Y1
Y2
Y3
Field 1 Line 1 +−+ "L"
Line 2 +−+ "L"
Line 3 +−+ "L"
·
·
·
·
·
·
Field 2 Line 1 −+− "H"
Line 2 −+− "H"
Line 3 −+− "H"
8
POL
 Loading...
Loading...