Page 1

Digital Business System
Section 700
Feature
Operation
Version 7.0 Issued 8/1/95
Doc. Part No. 7A0605Z9DJ
Page 2

FCC Warning
Battery Recycling Statemen
t
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice and should not be
construed as a commitment by the Panasonic Communications & Systems Company (PCSC).
PCSC reserves the right, without notice, to make changes to equipment design as advances in
engineering and manufacturing methods warrant
.
The software and hardware described in this document may be used or copied only in accordance
with the terms of the license pertaining to said software or hardware
.
This document may be reproduced either electronically or in print as needed by certified dealers
and technicians of DBS products. However, the information contained in this document must not
be altered, copied, or changed in any way that misrepresents the installation, operation, or other
function or feature of the DBS product or Panasonic. Panasonic assumes no liability for any
alteration or misrepresentation of information contain herein
.Copyright 1995 by Panasonic Communications & Systems Compan
y
All rights reserved
.
Warning:
This service information is designed for experienced repair techn
i
-
cians only and is not designed for use by the general public. It does not contain
warnings or cautions to advise non-technical individuals of potential dangers in
attempting to service a product. Products powered by electricity should be se
r
-
viced or repaired only by experienced professional technicians. Any attempt to
service or repair the product or products dealt with in this service information
by anyone else could result in serious injury or death
.
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy, and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause interference to radio comm
u-nications. This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A
digital device pursuant to Part 15 of FCC Rules, which are designed to provide reasonable
protection against such interference when operated in a commercial environment. Operation
of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interference, in which case the user
at his own expense will be required to take necessary measures to correct the interference.
The following statement applies if you purchased backup batteries with your system
.
The product you have purchased contains rechargeable batteries. The batteries are recycl
a-ble. At the end of their useful life, under various state and local laws, it may be illegal to di
s-pose of these batteries into the municipal waste stream. Check with your local solid waste
officials for details on recycling options or proper disposal
.
Page 3
Contents
About This Manual
Chapter 1. List of Features
Chapter 2. System Features
Account Codes........................................................................................................................ 2-3
Non-Verified Account Codes ........................................................................................... 2-3
Verified Account Codes.................................................................................................... 2-4
Answer Supervision for Voice Mail ....................................................................................... 2-6
Auto Day Mode ...................................................................................................................... 2-7
Auto Day Mode ...................................................................................................................... 2-8
Auto Set Relocation................................................................................................................ 2-9
Background Music................................................................................................................ 2-11
Battery Backup ..................................................................................................................... 2-12
Call Forward ID Code for Voice Mail.................................................................................. 2-13
Caller ID ............................................................................................................................... 2-14
Caller ID Auto DISA ............................................................................................................ 2-15
Centrex/PBX Compatibility.................................................................................................. 2-16
Direct Inward Dialing (DID) ................................................................................................ 2-16
DID Night Ringing Assignment ..................................................................................... 2-17
DID Delayed Ringing ..................................................................................................... 2-18
DID/DNIS Flexible Ring Assignments ................................................................................ 2-18
DID/DNIS Text Name Assignment...................................................................................... 2-19
DID/DNIS to a Voice Mailbox............................................................................................. 2-20
Direct Inward System Access (DISA).................................................................................. 2-22
Direct Trunk Access ............................................................................................................. 2-24
Distinctive Ringing ............................................................................................................... 2-24
Door Box (Using Extension Adaptor) .................................................................................. 2-25
Door Box (Using Trunk Adaptor) ........................................................................................ 2-27
Sensor.............................................................................................................................. 2-28
DP/DTMF Stations ............................................................................................................... 2-29
DP to DTMF Signal Conversion .......................................................................................... 2-29
Hunting Priority for VAUs ................................................................................................... 2-30
Independent Timers .............................................................................................................. 2-32
Internal Hold Tone................................................................................................................ 2-32
Least Cost Routing (LCR) .................................................................................................... 2-33
Music-on-Hold...................................................................................................................... 2-34
Night Service ........................................................................................................................ 2-35
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95iii
Page 4
Contents Section 700 - Operation
Night Service ........................................................................................................................ 2-37
Off-Premises Extension ........................................................................................................ 2-39
Paging ................................................................................................................................... 2-39
Power Failure Transfer ......................................................................................................... 2-41
Remote Maintenance ............................................................................................................ 2-42
Remote Programming Mode........................................................................................... 2-42
Remote Programming Using PCAS or DBS Manager ................................................... 2-44
Station Class of Service ........................................................................................................ 2-45
Station Hunting..................................................................................................................... 2-46
Terminal and Circular Hunting ....................................................................................... 2-47
Terminal, Distributed and Longest Idle Hunting............................................................ 2-49
Station Message Detail Recording (SMDR) ......................................................................... 2-51
T1 Interface........................................................................................................................... 2-54
Telephony Services ............................................................................................................... 2-56
Toll Restriction ..................................................................................................................... 2-58
Trunk Groups........................................................................................................................ 2-61
Trunk Name Assignment...................................................................................................... 2-62
Trunk Queuing...................................................................................................................... 2-63
Universal Night Answer ....................................................................................................... 2-64
Voice Mail Ringing .............................................................................................................. 2-65
VAU...................................................................................................................................... 2-66
Recording and Playing Messages ................................................................................... 2-66
VAU Port Assignment.......................................................................................................... 2-67
Walking TRS Class of Service ............................................................................................. 2-69
Chapter 3. Attendant Features
Alternate Attendant................................................................................................................. 3-3
Attendant Assignment of Speed Dialing ................................................................................ 3-3
Attendant Busy Override ........................................................................................................ 3-4
Attendant Call Park................................................................................................................. 3-5
Attendant Control of Absence Messages,............................................................................... 3-7
Attendant-Controlled Text Assignment .................................................................................. 3-8
Attendant Feature Package ................................................................................................... 3-10
Attendant Groups.................................................................................................................. 3-11
Dial Tone Disable ................................................................................................................. 3-12
DSS/72.................................................................................................................................. 3-13
Headset Operation................................................................................................................. 3-17
Key Bank Hold ..................................................................................................................... 3-18
One-Touch VM Transfer ...................................................................................................... 3-18
Station Lockout Code Assignment ....................................................................................... 3-21
System Time and Date Control ............................................................................................. 3-22
Traffic Measurement............................................................................................................. 3-24
Walking COS Confirmation ................................................................................................. 3-25
iv DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 5

Section 700 - Operation Contents
Chapter 4. Key Telephone Features
Key Phone............................................................................................................................... 4-3
Absence Message.................................................................................................................... 4-3
Auto Redial............................................................................................................................. 4-6
Barge-In for Direct Lines ........................................................................................................ 4-6
Busy Override ......................................................................................................................... 4-7
Call Coverage Groups ............................................................................................................. 4-8
Call Duration Display ............................................................................................................. 4-9
Call Forwarding .................................................................................................................... 4-10
Call Hold ............................................................................................................................... 4-16
Exclusive Hold ................................................................................................................ 4-16
System Hold.................................................................................................................... 4-17
Call Park ............................................................................................................................... 4-20
Call Pickup ............................................................................................................................ 4-21
Group Call Pickup .......................................................................................................... 4-23
Call Transfer ......................................................................................................................... 4-24
Blind Transfer ................................................................................................................. 4-24
Screened Transfer ........................................................................................................... 4-26
Call Waiting .......................................................................................................................... 4-28
Call Waiting/OHVA Text Reply .......................................................................................... 4-31
Caller ID Call Log ................................................................................................................ 4-32
Camp-on................................................................................................................................ 4-36
CO Line Key Trunk Access .................................................................................................. 4-37
Conference Calls ................................................................................................................... 4-38
Delayed Ringing ................................................................................................................... 4-41
Dial “0” for Attendant........................................................................................................... 4-41
Dial Tone Disable ................................................................................................................. 4-43
Do-Not-Disturb (DND)......................................................................................................... 4-44
EM/24 Console ..................................................................................................................... 4-46
Flexible Function (FF) Keys ................................................................................................. 4-46
Handsfree Answerback ......................................................................................................... 4-53
Handsfree Operation............................................................................................................. 4-54
Headset Operation................................................................................................................. 4-54
Hot Dial Pad.......................................................................................................................... 4-55
Considerations ................................................................................................................ 4-55
Intercom Calling ................................................................................................................... 4-55
Last Number Redial.............................................................................................................. 4-58
Line Appearances ................................................................................................................. 4-59
DSS/BLF Appearances......................................................................................................... 4-60
Multi-CO (MCO) Appearances ...................................................................................... 4-62
Multi-Line (ML) Appearances ........................................................................................ 4-64
ML/MCO Separation ............................................................................................................ 4-65
Meet-Me Answer.................................................................................................................. 4-66
Message Waiting/Callback Request ..................................................................................... 4-67
Non-Appearing Outside Lines .............................................................................................. 4-69
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 v
Page 6

Contents Section 700 - Operation
Offhook Signaling................................................................................................................. 4-70
Offhook Voice Announce (OHVA) ...................................................................................... 4-71
One-Touch Keys ................................................................................................................... 4-73
One-Touch VM Access ........................................................................................................ 4-77
Onhook Dialing..................................................................................................................... 4-80
Pooled Trunk Access ............................................................................................................ 4-80
Prime Line Preference .......................................................................................................... 4-82
Private Line ........................................................................................................................... 4-83
Reminder Call ....................................................................................................................... 4-84
Ringing Line Preference ....................................................................................................... 4-86
Saved Number Redial........................................................................................................... 4-86
Speed Dialing........................................................................................................................ 4-87
System Speed Dial.......................................................................................................... 4-91
Speed Dial Linking ......................................................................................................... 4-93
Station Lockout..................................................................................................................... 4-95
Trunk-to-Trunk Transfer....................................................................................................... 4-96
Voice Mail Transfer Key ...................................................................................................... 4-97
Chapter 5. DSLT Features
DSLT ...................................................................................................................................... 5-3
Absence Message.................................................................................................................... 5-4
Auto Redial............................................................................................................................. 5-6
Busy Override ......................................................................................................................... 5-6
Call Forwarding ...................................................................................................................... 5-7
Call Hold ............................................................................................................................... 5-11
Call Park ............................................................................................................................... 5-12
Call Pickup ............................................................................................................................ 5-14
Direct Call Pickup........................................................................................................... 5-14
Group Call Pickup .......................................................................................................... 5-15
Call Transfer ......................................................................................................................... 5-16
Blind Transfer ................................................................................................................. 5-16
Screened Transfer ........................................................................................................... 5-17
Call Waiting .......................................................................................................................... 5-19
Camp-on................................................................................................................................ 5-21
Conference Calls ................................................................................................................... 5-22
Dial “0” for Attendant........................................................................................................... 5-23
Dial Tone Disable ................................................................................................................. 5-24
Direct Trunk Access ............................................................................................................. 5-24
Do-Not-Disturb (DND)......................................................................................................... 5-25
Intercom Calling ................................................................................................................... 5-26
Last Number Redial.............................................................................................................. 5-27
Meet-Me Answer.................................................................................................................. 5-28
Message Waiting/Callback Request ..................................................................................... 5-29
Off-Hook Voice Announce (OHVA).................................................................................... 5-30
vi DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 7

Section 700 - Operation Contents
Onhook Dialing..................................................................................................................... 5-32
Pooled Trunk Access ............................................................................................................ 5-32
Reminder Call ....................................................................................................................... 5-33
Saved Number Redial........................................................................................................... 5-34
Speed Dialing........................................................................................................................ 5-35
Personal Speed Dialing ................................................................................................... 5-35
Station Lockout..................................................................................................................... 5-37
System Speed Dial.......................................................................................................... 5-38
Chapter 6. SLT Features
Absence Message.................................................................................................................... 6-3
Busy Override ......................................................................................................................... 6-5
Call Forwarding ...................................................................................................................... 6-6
Call Hold ............................................................................................................................... 6-10
Call Park ............................................................................................................................... 6-11
Call Pickup ............................................................................................................................ 6-12
Direct Call Pickup........................................................................................................... 6-12
Group Call Pickup .......................................................................................................... 6-13
Call Transfer ......................................................................................................................... 6-14
Blind Transfer ................................................................................................................. 6-14
Screened Transfer ........................................................................................................... 6-15
Call Waiting .......................................................................................................................... 6-17
Camp-on................................................................................................................................ 6-19
Conference Calls ................................................................................................................... 6-20
Dial “0” for Attendant........................................................................................................... 6-21
Dial Tone Disable ................................................................................................................. 6-22
Direct Trunk Access ............................................................................................................. 6-23
Do-Not-Disturb (DND)......................................................................................................... 6-23
Intercom Calling ................................................................................................................... 6-25
Last Number Redial.............................................................................................................. 6-26
Meet-Me Answer.................................................................................................................. 6-27
Message Waiting/Callback Request ..................................................................................... 6-28
Off-Hook Voice Announce (OHVA).................................................................................... 6-29
Pooled Trunk Access ............................................................................................................ 6-30
Speed Dialing........................................................................................................................ 6-31
Personal Speed Dialing ................................................................................................... 6-31
Station Lockout..................................................................................................................... 6-33
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 vii
Page 8

Contents Section 700 - Operation
viii DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 9
Section 700 - Operation Introduction
About This Manual
Software Versions Covered by This Manual
This manual covers all versions of CPC-A, all versions of CPC-AII software
through Version 7.0 and CPC-B software through Version 7.0.
Differences in feature availability or operation are noted within each feature
description.
If you are using this manual for a single DBS system, make note of its
software version in the following table. This note may be referenced by
technicians or owners of the system.
Software version information for systems shipped with this
document
CPC Model: Software Version:
Organization
This manual contains detailed descriptions of DBS features. The feature
descriptions are organized according to the following categories:
Feature Categories Description
System Features System Features are either available on a
system-wide basis or aid in the overall
administration of the DBS.
Attendant Features Attendant Features assist the attendant in
serving as a central answering point. In addition,
attendant features also provide special
capabilities for monitoring and programming
extensions.
Key Telephone Features Key Telephone Features are available to DBS
key phones. DBS key phones are proprietary
digital sets that provide feature access through a
combination of feature keys and access codes.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 ix
Page 10
Introduction Section 700 - Operation
Purpose
Digital Single-Line
Telephone
(DSLT) Features
DSLT Features are available to Digital SingleLine Telephones. DSLTs provide digital audio
quality and limited feature key access in a
single-line set.
Single Line Telephone
Features
SLT Features are available to industry-standard
2500 sets. Since SLTs are not equipped with
feature keys, most features are accessed by
using the dialpad and/or the switchhook.
The purpose of this manual is to provide an overview of feature operation and
requirements. Where applicable, the following types of information are
provided for each feature.
Types of information Purpose
Description The Description section provides an overview
of how the feature works and, in some cases,
what it is typically used for.
Operation The Operation section includes step-by-step
instructions on how to use the feature.
Hardware Requirements
This section lists any special hardware that is
required to use the feature.
Related Programming The Related Programming section lists the pro-
gramming subsystems associated with the feature.
Considerations This section provides details on feature interac-
tions and limitations.
xDBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 11
Chapter 1. List of Features
The following tables list the features available with the DBS.
The following tables are included in this chapter:
TopicPage
System Features 1-3
Attendant Features 1-5
Extension Features 1-6
DBS-70-700 DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 1-1
Page 12

Chapter 1. Features List Section 700 - Operation
1-2 DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 13
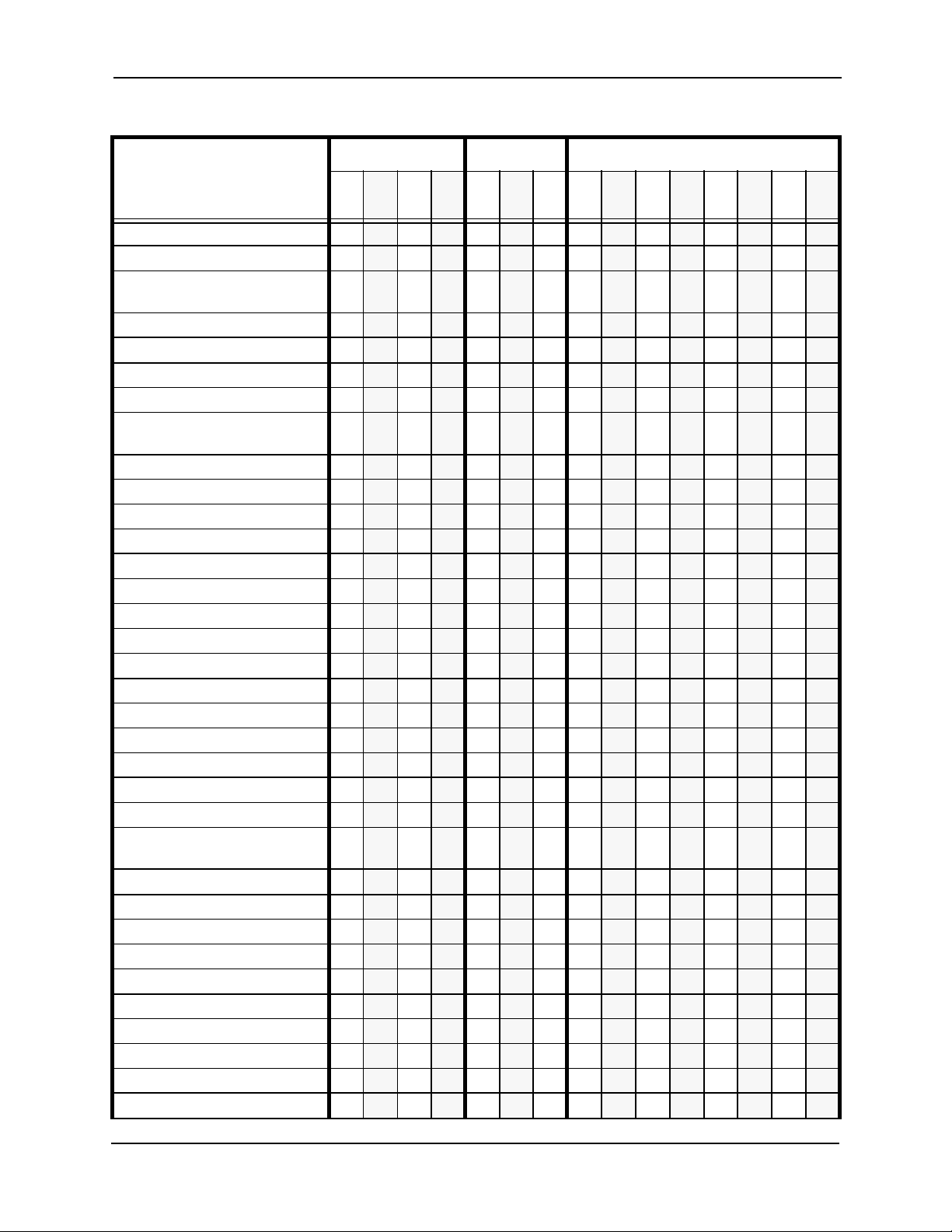
Section 700 - Operation Chapter 1. Features List
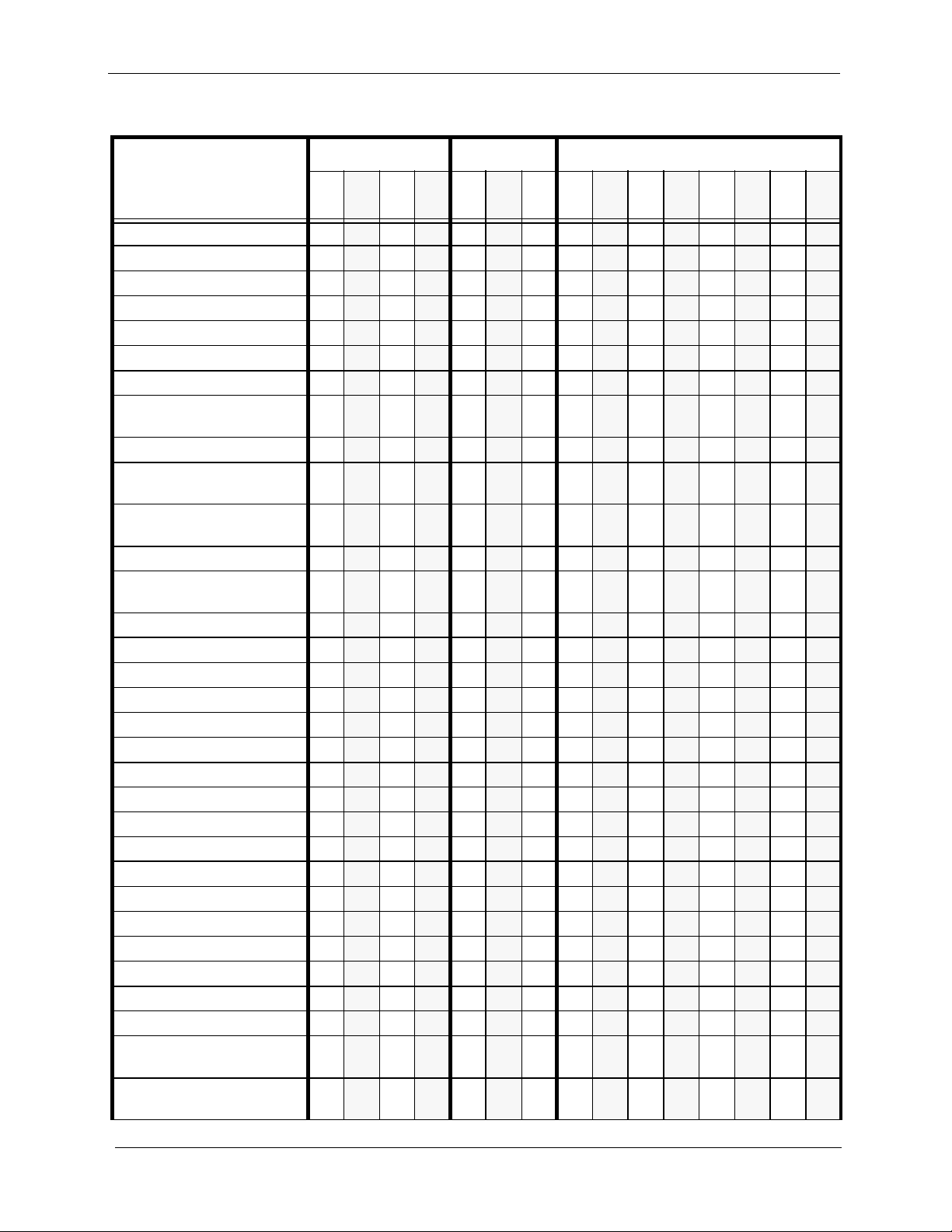
Table 1-1. System Features
Feature CPC-A CPC-AII CPC-B
3.03.13.23.
3
Account Codes: Non-verified x x x x x x x x x x x x
Account Codes: Verified x x x x x x x x x
Answer Supervision for Voice
Mail
Auto Day Mode x x x x x x x x
Auto Set Relocation x x x x x x x x x
Background Music x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Battery Backup x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Call Forward ID Code for
Voice Mail
Caller ID x x x x
Caller ID Auto DISA x x x x
Centrex/PBX Compatibility x x x x x x x x x x x x
DID (Direct Inward Dialing ) x x x x x x x
DID Night Ringing Assignment x x x x
DID Delayed Ringing x x x x
DID/DNIS Flex. Ring Assign. x x x x
DID/DNIS Text Name Assign. x x x x
DID/DNIS To a Voice Mailbox x x x
DISA x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Direct Trunk Access x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Distinctive Ringing x x x x x x x x x
Door Box (Extension Port) x x
Door Box (Trunk Port) x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
DP/DTMF Stations x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
DP to DTMF Signal
Conversion
Hunting Priority for VAUs x x x x x x x
Independent Timers x x x x x x x x x
Internal Hold Tone x x
Key Bank Hold x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Least Cost Routing x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Music-on-Hold x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Night Service x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Night Service (2 Modes) x x
Off-Premises Extension x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Paging x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
6.
6
x x x x x x x
1
7 1 2
3.
1
4 5 6
6.
1
7
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 1-3
Page 14
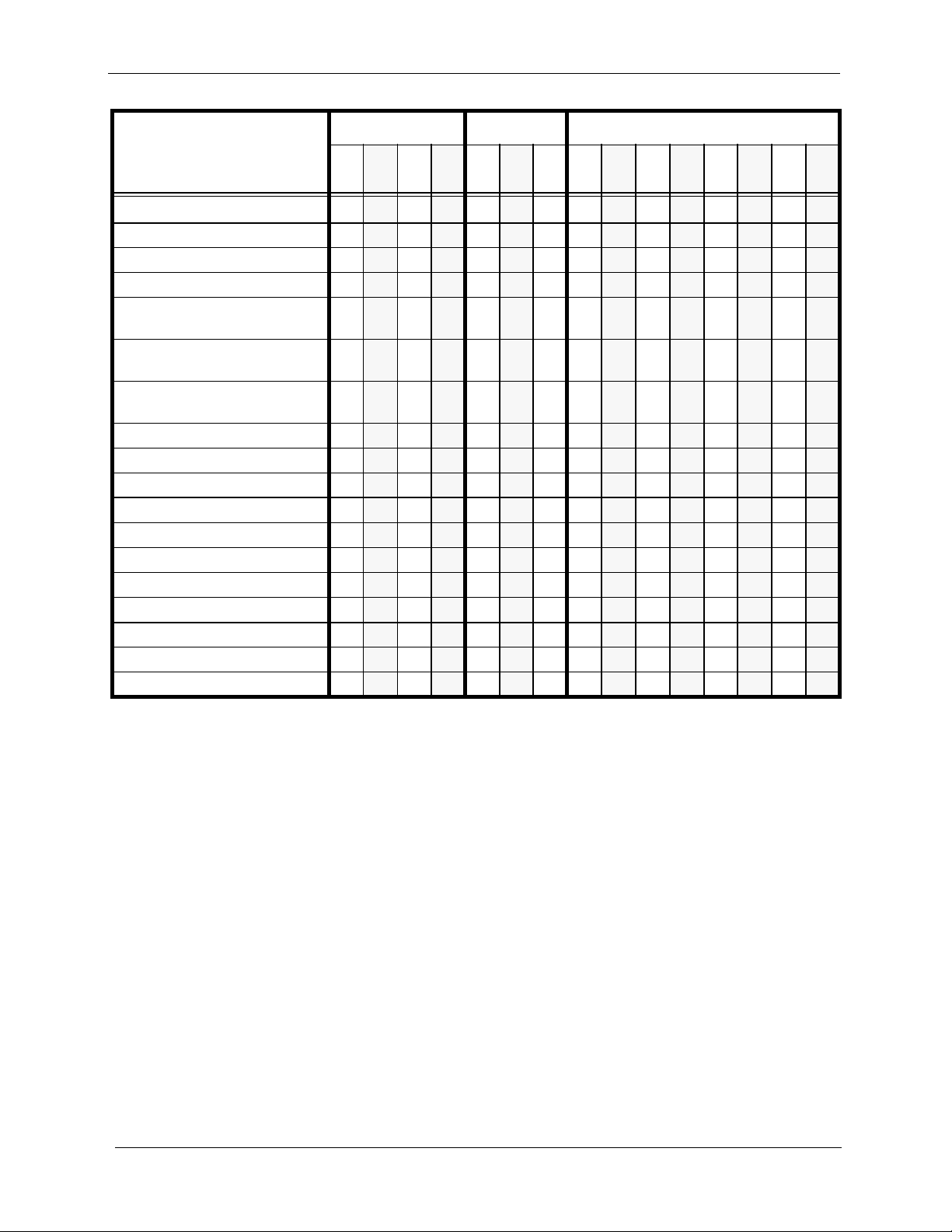
Chapter 1. Features List Section 700 - Operation
Feature CPC-A CPC-AII CPC-B
3.03.13.23.
3
Power Failure Transfer x x x x x x x x x
Remote Maintenance x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Sensor x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Station Class of Service x x x x x x x x x
Station Hunting: Terminal and
Circular
Station Hunting: Terminal,
Distributed, Longest Idle
Station Message Detail
Recording (SMDR)
T1 Interface x x x x x
Telephony Services x x
Toll Restriction x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Trunk Groups x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Trunk Name Assignment x x x x x x x x x x
Trunk Queuing x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Universal Night Answer x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Voice Mail Ringing x x x x x x x x x
VAU (Voice Announce Unit) x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
VAU Port Assignment x x x x x x x
Walking TRS Class of Service x x x x x x x x x
x x x x x
x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
6.
6
1
x x x
7 1 2
3.
4 5 6
1
x x x x x
x
x x x x x x
x
6.
1
7
1-4 DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 15
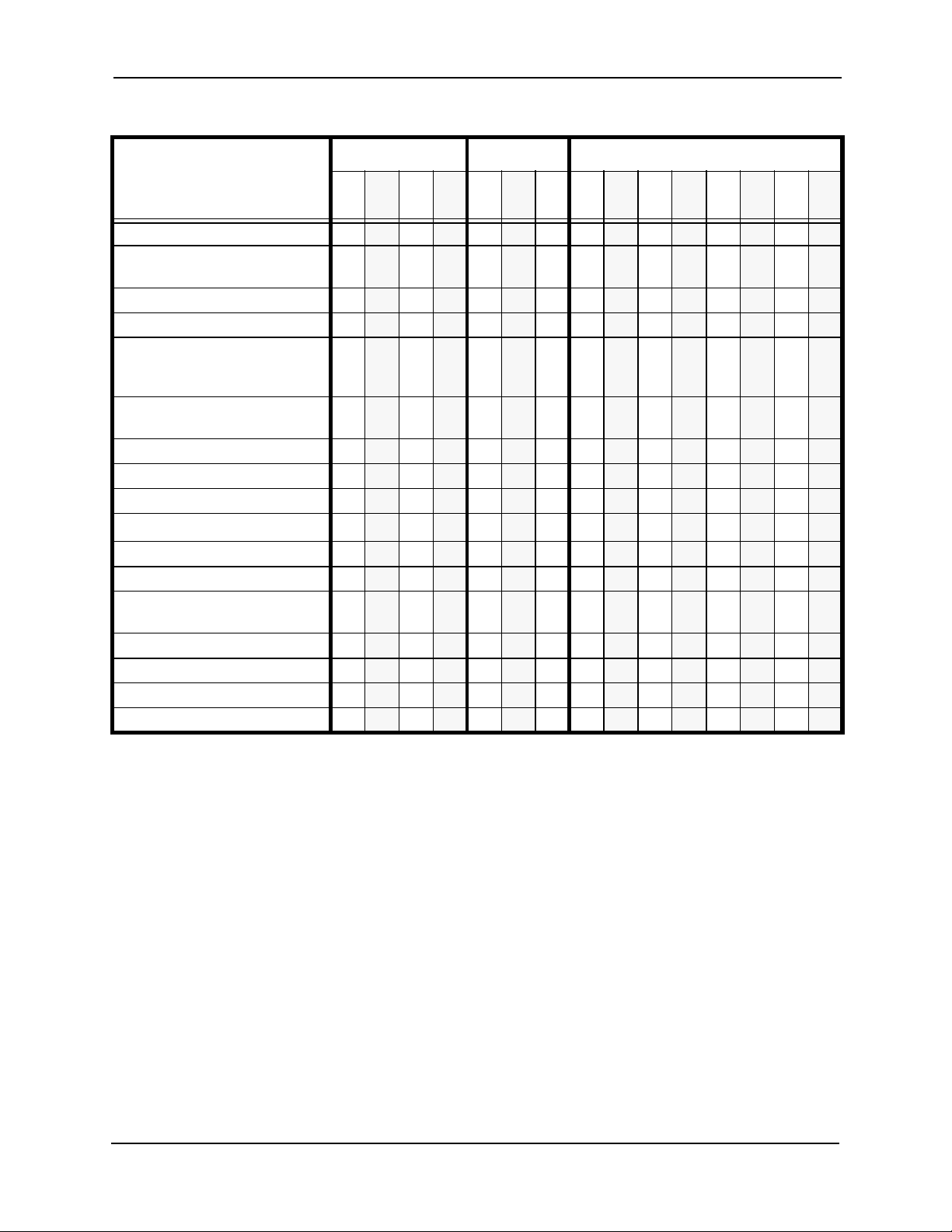
Section 700 - Operation Chapter 1. Features List
Table 1-2. Attendant Features
Feature CPC-A CPC-A II CPC-B
3.03.13.23.
3
Alternate Attendant x x x x x
Attendant Assignment of
Speed Dialing
Attendant Busy Override x x x x x x x x x x
Attendant Call Park x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Attendant Control of Absence
Messages, Call Forwarding,
and DND
Attendant-Controlled Text
Assignment
Attendant Feature Packag e x x x
Attendant Groups x x x x x x x x x x
Dial Tone Disable x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
DSS/72 x x x x x x x x
Headset Operation x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
One-Touch VM Transfer x x x x x x x
Station Lockout Code
Assignment
System Time and Date Control x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Traffic Measurement x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Voice Mail Transfer Key x x x x x x
Walking COS Confirmation x x x x x x x x x
x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
x x x x x x x x x
x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
6.
6
1
7 1 2
3.
4 5 6
1
x x x x x
x
x x x x x x
x
6.
1
7
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 1-5
Page 16
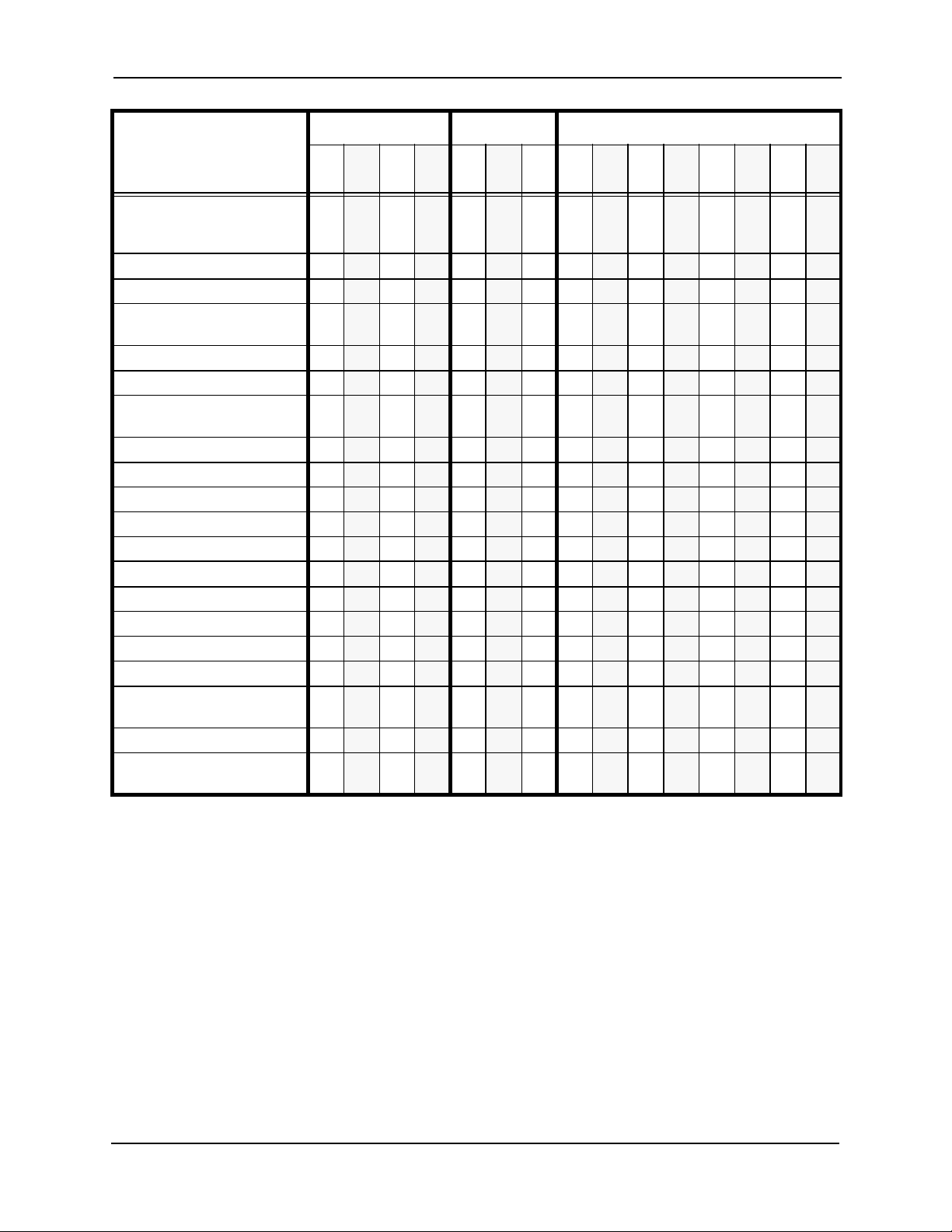
Chapter 1. Features List Section 700 - Operation
Table 1-3. Extension Features
Feature CPC-A CPC-A II CPC-B
3.03.13.23.
3
Absence Messag e x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Auto Redial x x
Barge-In for Direct Lines x x x x x x x
Busy Override x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Call Coverage Groups x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Call Duration Display x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Call Forwarding x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Call Hold: Exclusive and
System
Call Park x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Call Pickup: Direct and
Group
Call Transfer: Blind and
Screened
Call Waiting x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Call Waiting/OHVA Text
Reply
Caller ID Call Log x x x x
Camp-on x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
CO Line Key Trunk Access x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Conference Calls x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Delayed Ringing x x x x x x x x x x
Dial “0” for Attendant x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Direct Trunk Access x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Do-Not-Disturb (DND) x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
EM/24 Console x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Flexible Function (FF) Keys x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Handsfree Answerback x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Handsfree Operation x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Headset Operation x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Hot Dial Pad x x x x x x
Intercom Calling x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Last Number Redial x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Line Appearances x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
DSS/BLF Appearances:
Direct Line (DL)
DSS/BLF Appearances:
Multi-CO (MCO)
x x x x x x x x x
x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
x x x x x x x x
x x x x x x x x x x x x x
6.
6
x x x x x x x x
x x x x x x x x x x
1
7 1 2
3.
4 5 6
1
x x x x x
x
x x x x x x
x
6.
1
7
1-6 DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 17
Section 700 - Operation Chapter 1. Features List
Feature CPC-A CPC-A II CPC-B
3.03.13.23.
3
DSS/BLF Appearances:
Multi-Line (ML)
Appearances
ML/MCO Separation x x x x x x x x
Meet-Me Answer x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Message Waiting/Callback
Request
Non-appearing Outside Line x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Offhook Signaling x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Off-Hook Voice Announce
(OHVA)
One-Touch Keys x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
One-Touch VM Access x x x x x x x
Onhook Dialing x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Pooled Trunk Access x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Prime Line Preference x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Private Line x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Reminder Call x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Ringing Line Preference x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Saved Number Redial x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Speed Dial Linking x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Speed Dialing: System and
Personal
Station Lockout x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
Trunk-to-Trunk Transfer
(Unsupervised Conference)
x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
6.
6
x x x x x x x x x x
1
7 1 2
3.
1
4 5 6
6.
1
7
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 1-7
Page 18

Chapter 1. Features List Section 700 - Operation
1-8 DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 19
Chapter 2. System Features
This chapter contains detailed descriptions of DBS System Features. System
Features are either available on a system-wide basis or aid in the overall
administration of the DBS.
This chapter covers the following topics:
TopicPage
Account Codes 2-3
Answer Supervision for Voice Mail 2-6
Auto Day Mode 2-7
Auto Set Relocation 2-9
Background Music 2-11
Battery Backup 2-12
Call Forward ID Code for Voice Mail 2-13
Caller ID 2-14
Caller ID Auto DISA 2-15
Centrex/PBX Compatibility 2-16
Direct Inward Dialing (DID) 2-16
DID/DNIS Flexible Ring Assignments 2-18
DID/DNIS Text Name Assignment 2-19
DID/DNIS to a Voice Mailbox 2-20
Direct Inward System Access (DISA) 2-22
Direct Trunk Access 2-24
Distinctive Ringing 2-24
Door Box (Using Extension Adaptor) 2-25
Door Box (Using Trunk Adaptor) 2-27
DP/DTMF Stations 2-29
DP to DTMF Signal Conversion 2-29
Hunting Priority for VAUs 2-30
Independent Timers 2-32
Internal Hold Tone 2-32
Least Cost Routing (LCR) 2-33
Music-on-Hold 2-34
Night Service 2-35
Off-Premises Extension 2-39
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-1
Page 20

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
TopicPage
Paging 2-39
Power Failure Transfer 2-41
Remote Maintenance 2-42
Station Class of Service 2-45
Station Hunting 2-46
Station Message Detail Recording (SMDR) 2-51
T1 Interface 2-54
Telephony Services 2-56
Toll Restriction 2-58
Trunk Groups 2-61
Trunk Name Assignment 2-62
Trunk Queuing 2-63
Universal Night Answer 2-64
Voice Mail Ringing 2-65
VAU 2-66
VAU Port Assignment 2-67
Walking TRS Class of Service 2-69
Page 2-2DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 21

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Account Codes
You can assign account codes to clients to facilitate billing and to track call
dates and times, numbers called, and outside line numbers used. This
information is printed for each account on the SMDR record.
Non-Verified Account Codes
(CPC-A, CPC-AII, and CPC-B Versions prior to 3.1 and 6.0 and higher)
Description
In CPC-A and CPC-B Versions prior to 3.1, account codes are not verified.
With CPC-AII and with CPC-B Versions 6.0 and higher, account codes may
be verified or non-verified depending on system programming.
Non-verified account codes can be
extension programming.
With voluntary account codes, the user is not forced to enter an account code
before making a call. With forced account codes, the user must enter an
account code before accessing an outside line.
Non-verified account codes can be assigned to incoming and outgoing calls.
To assign an account code to an outgoing call, the user enters the account
code before making the call or during the call. To assign an account code to
an incoming call, the user enters the account code during the call.
To enter an Account Code before dialing:
1. Press the
• The phone issues intercom dial tone.
• The
2. Press the
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
AUTO
key.
LED lights.
key, then press “#.”
forced
or
voluntary
, depending on
• “Enter Account #” appears on the display.
• If you are using a Single Line Telephone (SLT) or Digital Single Line
Telephone (DSLT), dial “#7.”
3. Enter the Account Code (up to 10 digits).
4. Press “#.”
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-3
Page 22

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
“Entered Account #” appears on the display.
5. Press a vacant CO key or dial a trunk access code.
6. Dial the telephone number.
To enter an Account Code during an outside call:
1. Press the
2. Press “#.”
“Enter Account #” appears on the display.
3. Enter the Account Code (up to 10 digits).
The Account Code entered appears on the display.
4. Press “#.”
Hardware Requirements
• An SMDR printer or external call accounting system is required to collect
account code records.
Related Programming
• FF3 (Extension): Forced Account Codes
AUTO
key.
Considerations
• SLTs cannot assign account codes during a call.
Verified Account Codes
(CPC-AII and CPC-B, Version 3.1 or higher)
Description
Extensions with the Verified Account Codes feature
from making outside calls without the user first entering a valid Account
Code. After a valid Account Code is entered, the Toll Restriction Service
(TRS) type assigned to the code is substituted for the extension TRS type,
thus temporarily allowing calls based on the new TRS type.
Page 2-4DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
enabled
are restricted
Page 23

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Operation
Extensions with the Verified Account Codes feature
outside calls based on the TRS type assigned to the extension. If a user wishes
to place a call that would normally be restricted at the extension, the user can
enter a valid Verified Account Code to upgrade the TRS type assigned to the
extension.
1. Pick up the handset.
The phone issues intercom dial tone.
2. Dial “#11.”
3. Enter the four-digit Account Code.
4. Press “#.”
The phone issues intercom dial tone.
5. Press an available CO key or dial a trunk access code.
The phone issues outside dial tone.
disabled
can place
6. Dial the telephone number.
The Verified Account Code TRS type remains in effect until the call is
completed.
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Verified Forced Account Codes
• FF1 (System): Toll Restriction for Verified Forced Account Codes
• FF3 (Extension): Verified Forced Account Codes
• FF7 (TRS): Toll Restrictions
Hardware Requirements
• An SMDR printer or external call accounting system is required to collect
account code records.
Considerations
• Verified account codes are for outgoing calls only.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-5
Page 24

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
• The maximum number of verified account codes is 100.
• Each verified account code must consist of 4 digits.
• “0000” cannot be used for a verified account code.
• Verified account codes do not override station lockout.
• Verified account codes do not override Least Cost Routing (LCR) settings.
• With CPC-AII and CPC-B Version 3.1 to 5.04, non-verified account codes
can be used. However, they can only be used on a voluntary basis. Forced
non-verified
account codes are not available with CPC-B 3.1 to 5.04.
Answer Supervision for Voice Mail
(CPC-AII and CPC-B Version 5.0 or higher)
Description
Operation
This feature allows the DBS to send an answer signal to third-party voice
mail systems.
In previous releases, a third-party voice mail did not receive a signal to
indicate that a DBS extension had answered. To determine that the extension
had answered, the voice mail system had to wait until it stopped receiving
ringback tone. Waiting for the ringback to stop often delayed connection
times for calls from voice mail to extensions. Sending an answer signal
provides quicker response time between the DBS and the voice mail system.
The following programming can be performed from an attendant phone or
any other phone that has entered the programming access code.
To assign an answer signal code:
1. Press the
ON/OFF
key.
• The phone issues intercom dial tone.
• The
2. Press the
3. Dial “
Page 2-6DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
ON/OFF
PROG
#94
.”
LED lights.
key.
Page 25

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
4. Enter the Answer Signal Code (1 to 5 digits).
5. Press the
To view an answer signal code:
1. Press the
2. Press the
3. Dial “#94.”
Considerations
• The digits used for the answer signal code are determined by the
• If the called extension does not answer and is forwarded to voice mail, the
• During transmission of the answer signal code, other DTMF digits and
HOLD
ON/OFF
CONF
requirements of the voice mail system.
DBS sends a call forward ID code back to the voice mail system.
functions from the DBS extension are ignored.
key.
key.
key.
Auto Day Mode
(CPC-AII prior to 7.0 and CPC-B Version 4.0 to 6.11)
Description
Auto Day Mode allows the DBS to go into day mode automatically.
The DBS can also be programmed to go into night mode automatically (see
“Night Service,” page 2-35).
If only one of the auto modes is turned on, the
the auto mode. For instance, if night mode has been activated automatically,
the attendant must press the
If only one of the auto modes is turned on, the
to go into an auto mode before the scheduled time.
If both auto day and auto night modes are turned on, the attendant
key
cannot
be used.
NIGHT
NIGHT
key to go into day mode.
NIGHT
key is used to turn off
key can also be used
NIGHT
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-7
Page 26
Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Automatic Day Mode Start Time
• FF1 (System): Automatic Night Mode Start Time
Considerations
• If both auto modes are set, the starting times must differ by at least one
hour.
• When one auto mode is turned on, the mode cannot be reset by the
key until 3 minutes after the auto mode is activated. (When both auto
modes are set, the
• If a
NIGHT
NIGHT
key is not assigned, the access code #52 can be used instead.
key cannot be used.)
Auto Day Mode
(CPC-B Version 7.0 or higher and CPC-A II Version 7.0 and higher)
Description
Auto Day Mode allows the DBS to go into day mode automatically.
The DBS can also be programmed to go into night mode automatically (see
“Night Service,” page 2-37).
If only one of the auto modes is turned on, the
toggle key or the
mode. For instance, if
attendant must press the
to go into day mode. (Note: You must wait at least 3 minutes after the
automatic mode is activated before manually changing the mode. Otherwise
the system will immediately revert back to the automatic mode.)
DAY, NIGHT1
NIGHT1
DAY/NIGHT1/NIGHT2
mode has been activated automatically, the
, or
NIGHT2
DAY/NIGHT1/NIGHT2
NIGHT
is used to turn off the auto
toggle key or the
DAY
key
If only one of the auto modes is turned on, the
toggle key or the
an auto mode before the scheduled time. If auto day and both auto night
modes are turned on, the manual mode keys
DAY, NIGHT1
, or
NIGHT2
DAY/NIGHT1/NIGHT2
key can also be used to go into
can
be used.
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Auto Day Mode Start Timer
• FF1 (System): Auto Night1 Mode Start Timer
Page 2-8DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 27

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
• FF1 (System): Auto Night2 Mode Start Timer
Considerations
• If all auto modes are set, the starting times must differ by at least one hour.
• When one auto mode is turned on, the mode cannot be reset by the NIGHT
key until 3 minutes after the auto mode is activated. (When all auto modes
are set, the mode keys cannot be used.)
• If mode keys are not set, the access codes #520 (DAY/NIGHT1/NIGHT2
toggle), #521 (DAY), #522 (Night1) or #523 (Night2) can be used instead.
Auto Set Relocation
(CPC-AII and CPC-B Version 3.1 or higher)
Description
Operation
Auto Set Relocation can be used to relocate the program settings of one
extension to another extension.
Auto Set Relocation is commonly used when extension users want to trade
work areas. For example, if Extensions “A” and “B” are going to switch
office locations, Auto Set Relocation enables them to switch telephone
settings without re-programming.
Before a phone can be relocated, it must be assigned an Auto Set Relocation
code. See “Related Programming” for the program address used to set up the
Auto Set Relocation Code.
The following example illustrates how the program settings for extensions
200 and 300 could be switched.
To Transfer Extension Settings from 200 to 300:
1. At extension 300, pick up the handset.
2. Press “#10.”
3. Dial extension number 200.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-9
Page 28

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
4. Enter the four-digit auto set relocation code assigned to extension 200.
5. Replace the handset.
• All programmed extension features and TRS settings from 200 are
transferred to 300.
• Extension 300 are placed out of service.
To Reactivate Extension 300:
1. Unplug the extension cable from 300.
2. Reconnect the cable.
Extension 300 assumes all extension features, TRS, and LCR settings that
were initially assigned to 200.
Related Programming
• FF3 (Extension): Auto Set Relocation Code
Considerations
• The following types of data can be transferred using this feature:
• Settings may not be transferred between extensions of different types. In
• Attendant 1 is excluded from this feature.
- TRS type settings
- Ring settings (trunk line, remote ringing, day/night, DID)
- FF key data
- Extension numbers and names
- System call forward settings
- All settings and data defined by programming.
other words, an SLT and a KTEL cannot exchange program settings.
Page 2-10DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 29

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Background Music
(All Versions)
Description
If your system is set up to provide Background Music, music can be played
from the speakers of idle telephones. If a call is made to an extension
receiving Background Music, the music stops and the phone rings.
Background Music is also interrupted when the phone goes offhook.
The system can also provide music-on-hold using the Background Music
source or a separate music source. If Music-on-Hold is provided, callers
automatically hear music when they are placed on hold. (See page 2-34 for
more information on Music-on-Hold.)
Operation
To turn Background Music on:
1. Press the
• The phone issues intercom dial tone.
• The
2. Dial “#53.”
“BGM ON” appears on the display.
3. Press the
The
To turn Background Music off:
1. Press the
• The phone issues intercom dial tone.
• The
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
key.
LED lights.
key.
LED goes off.
key.
LED lights.
2. Dial “#53.”
“BGM OFF” appears on the display.
3. Press the
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-11
ON/OFF
key.
Page 30
Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
• The
• The date and time appear on the display.
ON/OFF
Related Programming
• FF1 (System) Extension Class of Service Setting (CPC-AII and CPC-B 3.1
or higher)
• FF3 (Extension) Extension Class of Service Assignment (CPC-AII CPC-B
3.1 or higher)
Hardware Requirements
• The music source must be purchased separately. It is not provided with the
DBS.
• If a single music source is used for both Music-on-Hold and Background
Music, the music source connects to the CN5 on the DBS. If a separate
music source is used for background music, it connects directly to the SCC
card. See
set the option straps.
Installation (Section 300)
LED goes off.
for instructions. Be sure to corrrectly
• The input impedance for the music source is 10k ohms.
• The maximum input level is 10 dB.
Important:
Composers, Authors, and Publishers (ASCAP) or similar organizations to
transmit radio or recorded music through the Music-On-Hold feature.
Panasonic Communications & Systems Company, its distributors, and
affiliates assume no liability should users of Panasonic equipment fail to
obtain such a license.
A license may be required from the American Society of
Battery Backup
(All Versions)
Description
The DBS two 12-volt batteries for battery backup. (Some DBS 72 and 96
systems use four older-style 6-volt batteries.) The backup batteries are
connected in a series circuit, using cables provided with the DBS. With
maximum traffic, the backup batteries last up to 40 minutes for the DBS 40
and 72, and up to 30 minutes for the DBS 96. The backup batteries should be
replaced about every 3 years.
Page 2-12DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 31

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Call Forward ID Code for Voice Mail
(CPC-A Version 3.1, CPC-AII, and all CPC-B Versions)
Description
Call Forward ID Code for Voice Mail allows users to call forward to a thirdparty voice mail system. The ID Code sends the digits that are required by the
voice mail to identify the DBS extension and allow it to retrieve messages.
With CPC-A or CPC-B Version 1.0, you can only set the ID Code from the
phone to be forwarded. Beginning with CPC-B Version 2.0, ID Codes can be
set from any key phone; this is also true of CPC-AII.
Operation
To set a Call Forward ID Code for Voice Mail:
1. Press the
2. Press the
3. Press “*.”
4. If you are using CPC-AII or CPC-B Version 2.0 or later, enter the
extension number to be forwarded. If you are using CPC-A or CPC-B
Version 1.0, go to Step 5.
5. Enter up to 16 digits (0-9) for the mail box ID code. (Press the
key to insert a pause.)
6. Press the
To clear the ID Code:
1. Press the
2. Press the
3. Press “*.”
PROG
AUTO
HOLD
PROG
AUTO
key.
key.
key.
key.
key.
REDIAL
4. Enter the extension number.
5. Press the
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-13
HOLD
key.
Page 32

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
Considerations
• In CPC-A 3.1 and CPC-B Versions prior to 5.0, callers could hear the tones
as the ID code was transmitted to the voice mail system. Beginning with
CPC-A Version 3.3, CPC-AII and CPC-B Version 5.0, external callers do
not hear the tones.
• The Extension Copy program (FF9 2# 1-144# 1-144##) should
used to copy extension settings that include a Call Forward ID Code.
Copying extension settings in this manner allows the copy “destination” to
retrieve the messages of the copy “source.” For example, if you copy
extension settings from extension 200 to extension 300, extension 300 can
retrieve 200’s messages. Extension 300 can retrieve 200’s messages
because the Call Forward ID Code for 200 is also assigned to 300.
Caller ID
(CPC-A II Version 6.1 or higher and CPC-B Version 6.1 or higher)
Description
A properly equipped DBS supports Caller ID (CID), a service offered by the
network telephone service provider. The CO sends calling number
information to the DBS after the first ring. Users who have display telephones
can see CID information as incoming calls ring at their extension and can
have access to previous calls via the Caller ID Call Log feature. The CID
number is recorded in SMDR.
not
be
Related Programming
• FF1 (System Programming): Call Duration Display
• FF1 (System Programming): Call Duration Timer
• FF5 (Key Assignments): FF Key Assignments for Extensions
• FF2 (Trunk): Trunk Type
Hardware Requirements
• Loop-start trunk card (VB-43511A)
• Caller ID circuit card (VB-43511)
• MFR card (for Caller ID Auto DISA)
Page 2-14DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 33

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Considerations
• Caller ID service must be ordered from the local telephone operating
company or the interexchange carrier.
Caller ID Auto DISA
(CPC-A II Version 6.1 or higher and CPC-B Version 6.1 or higher)
Description
A DBS equipped for Caller ID (CID) can provide automatic DISA dial tone
based on Caller ID information. This allows up to 10 predetermined users to
access the DISA feature without requiring a trunk be left in the DISA mode.
When a CID call is sent to the DBS, the CID number is checked against the
table. If the number is found, the caller will automatically be connected to
DISA dial tone.
Related Programming
• FF1 (System Programming): Automatic DISA
Hardware Requirements
• Loop-start trunk card (VB-43511A)
• Caller ID circuit card (VB-43511)
• MFR card (Caller ID Auto DISA)
Considerations
• Caller ID feature must be enabled.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-15
Page 34

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
Centrex/PBX Compatibility
(CPC-A Version 3.2 or higher, CPC-AII, and CPC-B Version 2.1 or higher)
Description
Centrex/PBX Compatibility allows the DBS to be connected to centrex or
PBX lines.
The DBS supports up to 8 access codes for dialing centrex or a PBX. These
access codes allow the DBS SMDR output to exclude the number dialed to
reach a centrex or PBX line.
The DBS also supports transmission of a flash signal over the centrex or PBX
link.
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): PBX Access Code(s)
• FF2 (Trunks): Trunk Type
• FF8 (Least Cost Routing): LCR Add Tables
Considerations
• The LCR Add Table can be used to prefix digits for outgoing calls through
Centrex.
Direct Inward Dialing (DID)
(CPC-B Version 2.0 or higher)
Description
The Direct Inward Dialing (DID) feature allows an extension to have a
dedicated direct number. The dedicated number allows calls to be made
directly to the extension, without the caller going through the attendant.
Prior to CPC-B Version 3.1, only one DID number could be assigned to an
extension. Beginning with CPC-B Version 3.1, one DID number can be
assigned to several extensions, and one extension can have more than one
DID number; this is also true of CPC-AII.
If a DID number is assigned to more than one extension, incoming calls to the
DID number ring at all the assigned extensions simultaneously.
Page 2-16DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 35

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Multiple DID (CPC-B Version 3.1 or higher)
• FF3 (Extension): Inbound DID Dial Number (CPC-B Version 2.0 to 2.16)
• FF4 (Ring): DID, Delayed, Night , Delayed Night, Night 2, and Delayed
Night 2 Ring Assignments
Hardware Requirements
• Either the T-1 Card or DID trunk card is required. Each DID trunk card
provides 8 ports.
• The DID trunk card requires an external 48V power supply. See
Installation (Section 300)
for instructions.
Considerations
• The DID Trunk card supports 4-digit, dial-pulse DID.
• The T1 card supports 4-digit, dial-pulse or DTMF DID.
• DID numbers must be between 0000 and 9999.
• Beginning with CPC-B Version 3.1, a maximum of 500 DID/extension
settings is allowed.
DID Night Ringing Assignment
(CPC-B Version 5.0 or higher)
Description
For a description of this feature, see “DID/DNIS Flexible Ring Assignments”
on page 2-18.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-17
Page 36

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
DID Delayed Ringing
(CPC-B Version 5.0 or higher)
Description
For a description of this feature, see “DID/DNIS Flexible Ring Assignments”
on page 2-18.
DID/DNIS Flexible Ring Assignments
(CPC-B Version 5.0 or higher)
Description
DID/DNIS Flexible Ring Assignments allow night ringing and delayed
ringing for specific DID/DNIS numbers.
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Delayed Ring
• FF1 (System): Central Office Delayed Ring Timer
• FF1 (System): Inbound DID Dial Numbers
• FF1 (System): DNIS Number Setting
Considerations
• Timing for DID/DNIS delayed ringing is controlled by the Central Office
Delayed Ring Timer.
• The system uses a DID Numbers Table for DID assignment. The DID
Numbers Table allows up to 500 DID assignments. Each assignment
consists of the DID number and an associated extension.
• The system uses a separate DNIS Numbers Table for DNIS assignment.
The DNIS Numbers Table allows up to 500 DNIS assignments, with each
assignment consisting of the DNIS number and an associated extension.
• When multiple extensions are assigned delayed ringing for the same DID/
DNIS number, unanswered delay ringing forwards based on the extension
with the lowest port number.
For example, if port numbers 125 and 126 both have delayed ringing for the
Page 2-18DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 37

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
same DNIS number and both ports do not answer a delayed ringing call, the
call follows the call forwarding settings of port 125.
DID/DNIS Text Name Assignment
(CPC-B Version 5.0 or higher)
Description
DID/DNIS Text Name Assignment allows the assignment of text names to
specific DID/DNIS numbers. The text name can include up to six characters.
Text name assignments are especially useful when multiple DID or DNIS
lines terminate to the same extension or group. For example, a call center may
handle inquiries for three different companies. To easily identify which
customer is being called, individual DID or DNIS numbers can be assigned
for each customer, and then corresponding text names can be assigned to the
DID or DNIS trunks.
Up to 200 DID text names and 200 DNIS text names can be assigned.
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Inbound DID Dial Numbers
• FF1 (System): DNIS Number Setting
Considerations
• A DSS/72 is required to assign text names to DID/DNIS trunks.
• If text is assigned to a DID/DNIS number that rings at multiple extensions,
all of the extensions will receive the text display.
• The text display follows forwarded calls and transferred calls.
• If text is not assigned to a DID/DNIS line, the number will display.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-19
Page 38

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
DID/DNIS to a Voice Mailbox
(CPC-B Version 6.0 and higher)
Description
DID/DNIS to a voice mailbox allows DID/DNIS calls to be routed to a voice
mailbox that is not connected to a physical extension.
To implement this feature, the DID/DNIS trunks must be assigned to ring at
the voice mail system. Once voice mail answers, the DBS sends a DID/DNIS
Answer Code required by the voice mail system plus the final DID/DNIS
digits to the voice mail system. The DID/DNIS Answer Code signals the
voice mail system to open with a greeting and the DID/DNIS digits specify
the appropriate mailbox.
Operation
To assign a DID/DNIS Answer Code:
1. Pick up the receiver or press the ON/OFF key.
2. Press
3. Dial
4. Enter the DID/DNIS Answer code required by the voice mail system (1 to
5. Press
6. Press the
To display a DID/DNIS Answer Code:
1. Pick up the receiver or press the ON/OFF key.
2. Press
PROG
#95
6 digits).
HOLD
The
ON/OFF
CONF
.
.
.
ON/OFF
LED goes off.
.
key.
3. Dial
4. Press the
Page 2-20DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
The
#95
.
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
key.
LED goes off.
Page 39

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
To delete a DID/DNIS Answer Code:
1. Pick up the receiver or press the ON/OFF key.
2. Press
3. Dial
4. Press
5. Press the
The
PROG
#95
HOLD
ON/OFF
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Number of DID/DNIS Digits to Voice Mail
• FF1 (System): DID/DNIS Flexible Ringing Assignments
Considerations
DID/DNIS digit transmission.
that are assigned as voice mail.
Answer code entry.
attendant phone or a key phone that has entered the programming access
code.
.
.
.
ON/OFF
LED goes off.
The DID/DNIS Answer Code can be entered from an
key.
The DID/DNIS digits are only sent to ports
VM ports and hunt groups.
voice mail port or a voice mail hunt group.
Second hunt group.
transfers the call to a second hunt group, the DID/DNIS calls are not
transmitted to the second hunt group.
Third-party VM.
the feature is used with third-party voice mail systems, the voice mail can be
connected through analog extension ports or OPX ports.
Call forward ID.
Forward ID Code is transmitted to the voice mail. The DID/DNIS digits are
not.
DID/DNIS data transmission.
API link using the existing API key code packet.
If the DID/DNIS call rings into a hunt group that in turn
This feature can be used third-party voice mail systems. If
When DID/DNIS calls are forwarded to voice mail, the Call
The DID/DNIS digits can be sent to a specific
The DID/DNIS digits are transmitted over the
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-21
Page 40

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
Direct Inward System Access (DISA)
(All Versions)
Description
Direct Inward System Access (DISA) gives off-site users dial-in access to the
DBS. Users access DISA by dialing a 7-digit number assigned to a DISA
trunk.
For security reasons, one incoming DISA code and two outgoing DISA codes
can be assigned. If an incoming code is assigned, it must be entered as soon as
the DISA trunk answers. An outgoing code must be entered before the user
dials an outgoing call.
Operation
To make a DISA call to an extension:
1. Dial the DISA trunk number.
2. Once you hear DISA dial tone from the DBS, enter the 4-digit DISA code
(if an incoming DISA code is assigned). If the incoming DISA code is not
programmed, you can proceed to the next step.
3. Dial the extension number.
To make a DISA call to an outside number:
1. Dial the DISA trunk number.
2. Once you hear DISA dial tone from the DBS, enter the 4-digit DISA code
(if an incoming DISA code is assigned). If the incoming DISA code is not
programmed, you can proceed to the next step.
3. Dial #7 plus the 4-digit Outgoing DISA Code.
Two outgoing DISA codes are assigned. Either may be used after the #7.
4. Dial the trunk group number you want to use (81-86 or 9).
5. Dial the desired telephone number.
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Direct Inward System Access (DISA) ID Code
Page 2-22DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 41

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
• FF1 (System): DISA Outbound Call ID Code 1
• FF1 (System): DISA Outbound Call ID Code 2
• FF2 (Trunk): DISA Auto Answer
• FF2 (Trunk): DISA Start Time
• FF2 (Trunk): DISA End Time
To program an incoming code from an attendant phone:
In addition to the DISA ID Setting in FF1, the following procedure can be
used to program an incoming code.
1. Press the
• The phone issues intercom dial tone.
• The
2. Press the
3. Dial “#7.”
4. Enter the DISA code.
5. Press the
6. Press the
The
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
Hardware Requirements
• An MFR card is required for DISA. The MFR card is required to detect
DTMF tones entered via the DISA connection.
ON/OFF
LED lights.
CONF
HOLD
ON/OFF
key.
key.
LED goes off.
key.
key.
Considerations
• DISA can be used to access extensions as well as outside numbers.
• Once an incoming DISA code is entered, you cannot blank it out without
entering the programming mode.
• Busy override cannot be used for a DISA line.
• With CPC-A and CPC-B Versions 2.0 to 2.1, DISA calls cannot access
hunt groups.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-23
Page 42

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
Direct Trunk Access
(All Versions)
Description
Extensions can access a specific trunk for outgoing calls. Extensions can also
use Direct Trunk Access to test trunks or to access data trunks.
Operation
1. Press the
• The phone issues intercom dial tone.
• The
2. Dial “88,” then enter the desired line number (01-64).
• The phone issues outside dial tone.
• “CO TALK #XX” (where “XX” is the line number) appears on the
display.
3. Dial the telephone number.
The number appears on the display.
4. Complete the call and replace the handset.
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
key:
LED lights.
Distinctive Ringing
(CPC-AII and CPC-B Version 3.1 or higher)
Description
Distinctive trunk call ringing patterns can be set up for each extension using
the Distinctive Ringing feature. Distinctive Ringing allows users to determine
which extension is ringing when several telephones are in the same area. If no
distinctive ringing pattern is set, the extension rings based on the incoming
ring pattern assigned to the trunk.
Related Programming
• FF3 (Extension): Extension Ring Pattern
Page 2-24DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 43

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Hardware Requirements
• SCC-B Version 1.2 or higher is required for this feature.
Considerations
• One of ten ringing patterns can be selected.
• The ringing patterns are different for key phones and SLT/OPX phones.
Door Box (Using Extension Adaptor)
(CPC-B Version 7.0 and higher and CPC-A II Version 7.0 and higher)
Description
Door boxes (also called door phones) and door openers work together. The
door box is an intercom that allows visitors to announce their presence from
the office door. The door opener enables a user to unlock the door using a
telephone. Door openers are not sold by Panasonic; they can be purchased
separately from an electronics dealer.
Operation
There are two types of door phone adaptors available for the DBS. The first
type (VB-43701) utilizes a trunk connection to connect to the door box. See
Door Box- (Using Trunk Adaptor
(VB-43711) utilizes a digital port extension to connect to the door box and
door opener and is described below.
To Open a Door When Talking to the Door Box:
1. Answer the Door Box.
2. While still connected to the call, dial:
#3 NNNN *
9999 by default)
3. The door will unlock. Listen for the person to enter the building before
hanging up.
To Open the Door When Not Talking to the Door Box:
(where NNNN is the Door Opener Access Code, if required -
) for more information. The second type
1. Press the
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-25
ON/OFF
key (or pick up the handset).
Page 44

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
2. While still connected to the call, dial:
#3 XXX NNNN *
NNNN is the Door Opener Access Code, if required - 9999 by default)
3. The door will unlock. Listen for the person to enter the building before
hanging up.
Related Programming
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): Ringing Assignments (all)
• FF1 (System Programming): Door Phone Assignments (all)
• FF1 (System Programming): Door Opener ID Requirement
Hardware Requirements
• The Door Box feature requires a Door Box Adaptor (VB-43711), Door
Box (Door Phone) (VA-43705), and door opener. The door opener can be
purchased from an electronics dealer.
• One Door Box can be connected to a Door Box Adaptor.
(where XXX is the Door Box extension number and
• Each Door Box Adaptor uses one digital extension port.
• Up to 4 Door Boxes may be connected.
Considerations
• The Door Box extension cannot take part in conference calls or be
• Door Box calls cannot be call forwarded or be hunting or coverage group
• The Door Opener can be set to open for 2 to 12 seconds.
overridden.
members.
Page 2-26DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 45

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Door Box (Using Trunk Adaptor)
(All Versions)
Description
Door Boxes (also called door phones) and door openers work together. The
door box is an intercom that allows visitors to announce their presence from
the office door. The door opener enables a user to unlock the door using a
telephone. Door openers are not sold by Panasonic; they can be purchased
separately from an electronics dealer.
There are two types of door box adaptors available for the DBS. The first type
(VB-43701) utilizes a trunk connection to connect to the door box and is
described below. The second type (VB-43711) utilizes a digital port extension
to connect to the door phone and door opener. See “Door Box (Using
Extension Adaptor)” on page 2-25 for more information.
Operation
1. Answer the door box. (Door Box calls ring in on a dedicated FF key.)
2. Press “3” while connected to the door box extension.
The door opens automatically.
Related Programming
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): Ringing Assignments (all)
• FF2 (Trunk Programming): DTMF/Pulse Dialing for Trunks
Hardware Requirements
• The Door Box requires a Door Box Adaptor (VB-43701), Door Box (VA-
43705), and door opener. The door opener can be purchased from an
electronics dealer.
• Up to two Door boxes can be connected to a Door Box Adaptor and utilize
the same trunk.
• The Door Box extension cannot take part in conference calls.
• The Door Opener can be set to open for 15 seconds, 30 seconds, or one
minute.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-27
Page 46

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
• While the Door Opener is functioning, a call from another Door Box on the
same door box adaptor cannot be answered.
Considerations
• The trunk connected to the Door Box Adaptor must be set to dial pulse.
Sensor
(All Versions)
Description
The sensor is a device that detects when a circuit is opened or closed. Sensors
can be used to detect events such as the opening of windows or doors. When
the sensor is tripped, a tone sounds at a designated extension. Sensors are not
sold by Panasonic; they can be purchased separately from an electronics
dealer.
Hardware Requirements
The sensor is attached to the Door Box Adaptor (VB-43701).
Trunk lines connected to the Door Box Adaptor signal the designated
extension when the sensor is tripped.
Related Programming
• FF2 (Trunks): DTMF/Pulse Dialing for Trunks
• FF4 (Ring Assignments): CO Day Ring Assignments
• FF4 (Ring Assignments): CO Night Ring Assignments
Considerations
• The trunk connected to the sensor must be a dial-pulse trunk.
Page 2-28DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 47

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
DP/DTMF Stations
(All Versions)
Description
The DBS allows both dial pulse and DTMF extension types.
Related Programming
• FF2 (Trunk): DTMF/Pulse Dialing for Trunks
Considerations
• DP to DTMF Signal Conversion allows DTMF extensions to use either
dial pulse or DTMF trunks.
DP to DTMF Signal Conversion
(All Versions)
Description
This feature allows an extension user to switch from DP to DTMF signaling
when using a DP trunk.
For instance, if a user dials into a voice mail system using a DP trunk, the user
can switch to DTMF signaling to communicate with the voice mail system.
DTMF tones can be sent either during the call or while the call is being
dialed.
Operation
To switch from dial pulse to DTMF dialing, press “*” or “#.”
Related Programming
• FF2 (Trunk): DTMF/Pulse Dialing for Trunks
Considerations
• DTMF dialing remains in effect for the duration of the call. Pulse dialing is
restored when the handset is replaced.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-29
Page 48

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
• Once DTMF dialing is invoked, the user cannot switch back to pulse
dialing without disconnecting the call.
• Changing from dial pulse to DTMF is possible even if the “*” or “#” key is
programmed for speed dialing.
Hunting Priority for VAUs
(CPC-AII and CPC-B Version 5.0 or higher)
Description
This feature allows hunting priority to be assigned to calls that overflow from
the hunt group to the VAU. If the caller hears the VAU message and then
decides to dial back into the hunt group, he or she is placed before other calls
that have just entered the hunt group queue. For an illustration of the flow of
calls, see Figure 2-1 on page 2-31.
To further improve VAU operation, DID, DISA, and transferred calls are now
routed to the first VAU message. (In previous releases, these calls were routed
to the second VAU message.)
In addition, a digital port can now be assigned as a VAU through system
programming. In previous releases, VAUs were assigned as standard digital
ports. Using the standard digital port assignment required the installer to
make the following program changes:
• The CO Offhook Signal option had to be set to “on” (FF3 1-144# 7#).
• The Call Waiting Notification Tone/OHVA option had to be set to “off”
(FF3 1-144# 8#).
• Auto Pickup had to be set to “on” (FF3 1-144# 12#).
• All FF keys for the extension port had to be cleared.
The VAU assignment now eliminates the need to make these program
changes. Once a port is assigned as a VAU, the system treats that port as if
these changes have been made.
Note:
settings have been made, it does not actually change the settings. If the port is
later assigned as a standard digital port, the original program settings will still
be in effect.
Though the VAU assignment treats the VAU port as if the program
Page 2-30DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 49

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Figure 2-1. VAU hunting priority
CO
Direct
Trunk Call
to the Hunt Group
Pilot Number
Calls that transfer
back into the hunt group
are placed at the top
of the queue.
Hunt
Group
Queue
Hunt Group
Related Programming
• FF3 (Extension): VAU Port Assignment
• FF3 (Extension): VAU Hunting Priority
Considerations
• The following call types are routed to the first VAU message:
- Trunk calls (including DID and DNIS calls)
- Transferred trunk calls
- Intercom calls
- Transferred intercom calls.
VAU
All recalls are routed to the second VAU message.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-31
Page 50

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
Independent Timers
(CPC-AII and CPC-B, Version 3.1 or higher)
Description
Beginning with CPC-B Version 3.1, the DBS provides separate timers for
Call Forwarding-No Answer, CO Delayed Ring, Extension Delayed Ring,
and Hunt Group--No Answer.
The Call Forwarding-No Answer timer determines how long a call will ring
an extension before forwarding.
The CO Delayed Ring and Extension Delayed Ring timers determine how
long a call will ring an extension before ringing other extensions assigned to
delayed ringing.
The Hunt Group-No Answer timer determines how long a call will ring an
idle member of a hunt group before hunting to the next idle group member.
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Call Forward--No Answer Timer
• FF1 (System): Central Office Delayed Ring Timer
• FF1 (System): Extension Delayed Ring Timer
• FF1 (System): Hunt Group No Answer Timer
Internal Hold Tone
(CPC-AII Version 7.0 and higher and CPC-B Version 7.0 and higher)
Description
If a music-on-hold sound source is unavailable, a periodic hold tone
generated in the DBS can be provided to caller.
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Internal Hold Tone
Page 2-32DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 51

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Least Cost Routing (LCR)
(All Versions)
Description
Least cost routing (LCR) automatically selects the least expensive route
available for toll calls.
LCR is accessed by dialing “9” before placing a call.
Related Programming
Primary Program Areas:
• FF1 (System): Least Cost Routing (LCR) Access
• FF3 (Extension): Forced Least Cost Routing
• FF8 (LCR): Time Priority Tables
• FF8 (LCR): LCR Trunk Group Tables
• FF8 (LCR): Least Cost Routing Area Codes
• FF8 (LCR): Special LCR Area Codes
• FF8 (LCR): Least Cost Routing (LCR) Office Codes
• FF8 (LCR): Special LCR Office Codes Tables
Other Program Areas:
• FF8 (LCR): LCR Add Tables
• FF8 (LCR): LCR Delete Tables
Considerations
• If LCR is enabled, ML and MCO keys can be assigned for trunk group 89.
However, the FF keys will not light.
• If the LCR feature is deactivated, Pooled Trunk Access is selected
automatically.
• Your system can be programmed to use the LCR feature for
calls.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-33
all
outgoing
Page 52

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
Music-on-Hold
(All Versions)
Description
The DBS can provide Music-on-Hold to parties on hold on a CO line. The
Music-on-Hold feature can also be used to play announcements or
advertisements if desired.
The system can provide Music-on-Hold using the background music source
or a separate music source. See “Background Music” on page 2-11 for more
information.
Beginning with CPC-AII Version 7.0 and CPC-B Version 7.0, if no music-onhold sound source is available, an internally generated periodic hold tone can
be supplied to calls on hold. See“Internal Hold Tone” on page 2-32 for more
information.
Hardware Requirements
• The music source must be purchased separately. It is not provided with the
DBS.
• If a single music source is used for both Music-on-Hold and background
music, the music source connects to the CN5 on the DBS. If a separate
music source is used for background music, it is connected directly to the
SCC card. See
option straps are correctly set.
• The input impedance for the music source is 10k ohms.
• The maximum input level is 10 dB.
Important:
Composers, Authors, and Publishers (ASCAP) or similar organizations to
transmit radio or recorded music through the Music-On-Hold feature.
Panasonic Communications & Systems Company, its distributors, and
affiliates assume no liability should users of Panasonic equipment fail to
obtain such a license.
Installation (Section 300)
A license may be required from the American Society of
for instructions. Make sure the
Page 2-34DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 53

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Night Service
(CPC-AII prior to Version 7.0 and CPC-B Prior to Version 7.0)
Description
The Attendant can switch the system between Day and Night Modes for
answering outside calls. It is also possible to program the system to
automatically switch between night and day modes. (CPC-AII or CPC-B
Version 4.0 or higher is required for automatic day mode settings.)
While in Night Mode (generally used at night or any time when your office is
closed), incoming calls can ring at selected extensions (a night watchman’s
extension, for example), an extension connected to an answering machine, or
to a Universal Night Answer point. Universal Night Answer (UNA) is used to
allow calls to be picked up from any extension.
See page 2-64 for information on setting a UNA point.
See “Auto Day Mode” (page 2-6) for information on a CPC-B Version 4.0
enhancement (also available in CPC-AII) that allows automatic switching
between day and night modes.
Operation
To switch to Night Mode:
1. Press the
• The phone issues intercom dial tone.
• The
2. Dial “#52.”
3. Press the
• The
• “NIGHT MODE” appears on the display.
To switch to Day Mode:
1. Press the
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
key.
LED lights.
key.
LED goes off.
key.
• The phone issues intercom dial tone.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-35
Page 54

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
• The
2. Dial “#52.”
3. Press the
• The
• “DAY MODE” appears on the display.
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Ring Patterns for UNA Terminals (M, C, & B)
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): CO Day Ring Assignment
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): CO Night Ring Assignment
Hardware Requirements
• Calls during Night Mode are often directed to external paging speakers or
to an external ringing device, such as a night bell. External paging and
ringing devices are not provided with the DBS; they must be purchased
separately.
LED lights.
ON/OFF
LED goes off.
key.
Considerations
• If “#52” is assigned to an FF key on an attendant phone, the attendant can
• If there are two Attendant Phones and both DSS consoles have a
• If the system is programmed to switch between night and day modes
switch between Day and Night Modes simply by pressing the key. The FF
key lights red when the system is in night mode.
NIGHT
key (programmed on a FF key), both
when Night Mode is activated.
automatically, you
cannot
switch between modes by using “#52.”
NIGHT
indicators will light red
Page 2-36DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 55

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Night Service
(CPC-AII Version 7.0 and higher and CPC-B Version 7.0 and higher)
Description
The Attendant can switch the system between Day and two Night Modes for
answering outside calls. It is also possible to program the system to
automatically switch between night and day modes.
While in a Night Mode (generally used at night or any time when your office
is closed), incoming calls can ring at selected extensions (a night watchman’s
extension, for example), an extension connected to an answering machine, or
to a Universal Night Answer point. Universal Night Answer (UNA) is used to
allow calls to be picked up from any extension.
See page 2-64 for information on setting a UNA point.
See “Auto Day Mode” (page 2-8) for information that allows automatic
switching between day and night modes.
Operation
To switch to a Night Mode:
1. Press the
• The phone issues intercom dial tone.
• The
2. Dial “
can be used to toggle between Day, Night1 and Night2 modes.)
3. Press the
• The
• “NIGHT MODE” or “NIGHT2 MODE” appears on the display.
To switch to Day Mode:
1. Press the
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
#522
” for Night1 mode or “
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
key.
LED lights.
key.
LED goes off.
key.
#523
” for Night 2 mode. (Note:
#520
• The phone issues intercom dial tone.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-37
Page 56

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
• The
2. Dial “
3. Press the
• The
• “DAY MODE” appears on the display.
ON/OFF
#521
ON/OFF
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Ring Patterns for UNA Terminals (M, C, & B)
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): CO Day Ring Assignments
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): CO Night Ring Assignments
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): CO Night2 Ring Assignments
Hardware Requirements
LED lights.
.” (Note: #520 can be used to toggle between modes.)
ON/OFF
key.
LED goes off.
• Calls during a Night Mode are often indicated by external paging speakers
Considerations
• Day, Night and Night 2 modes can be assigned to FF keys on an attendant
• If the same mode key is assigned on different attendant positions, each key
• If the system is programmed to switch between night and day modes
or an external ringing device, such as a night bell. External paging and
ringing devices are not provided with the DBS; they must be purchased
separately.
phone. The attendant can switch between Day, Night and Night 2 modes
simply by pressing the appropriate key. The FF key lights red when the
system is in the assigned mode. Alternatively a DAY/NIGHT1/NIGHT2
toggle mode key can be assigned. Pressing the key toggles between modes.
When in Day mode, the FF key LED is not lit. When in NIGHT1 mode, the
LED lights red. When in NIGHT2 mode, the LED lights green.
indicates the current mode. For instance, if a
two attendants, both light when in
automatically, you
“#520/#521/#522/#523.” (This is different than earlier versions of
software.)
can manually switch
NIGHT1
NIGHT1
mode.
between modes by using the
key is assigned for
Page 2-38DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 57

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Off-Premises Extension
(All Versions)
Description
SLTs that are located in remote locations can be connected to the DBS
through the Off-Premises Extension (OPX) Adaptor.
Off-premise phones can be connected through a direct line to the DBS or
through the central office, depending on how far they are from the main
cabinet. For specifications, see
Operation
Feature operation for OPX extensions is the same as for local SLTs connected
to the DBS.
Installation (Section 300).
Related Programming
• FF3 (Extension): Terminal Type
Hardware Requirements
• One OPX Adaptor (VB-43702) is required for each OPX extension.
• When OPX extensions are connected through the central office, an
external ringer supply may be required. If required, the ringing supply is
connected to the OPX Adaptor.
Considerations
• Up to 8 OPX extensions can be connected to a system.
• The DBS side of the OPX Adaptor is connected to a
Paging
(All Versions)
digital
extension port.
Description
Internal paging is accomplished through the speakers of your system’s key
phones. The Paging feature allows you to contact someone temporarily away
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-39
Page 58

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
from an extension, give instructions to an entire group, or communicate with
several people at once. If an external paging system is connected to your
system, pages can also be sent through its speakers.
Beginning with CPC-B Version 3.1, the Paging feature can also be
programmed to time out after sixty seconds. When a page call times out, a
busy tone is sent to the extension that initiated the page.
Operation
To use the Paging feature:
1. Pick up the handset.
2. Press “#,” then enter the number of the desired Paging Group (00-07).
The
EXT
LED lights.
3. Make your announcement.
4. Replace the handset.
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Page Duration (CPC AII and CPC-B Version 3.1 or higher)
• FF1 (System): External Page Interface Control for Paging Groups
• FF3 (Extension): Extension Page Group
Hardware Requirements
• External relays and an amplifier are required for external paging.
Considerations
• If an external paging system has been connected to Paging Groups 00-07,
pages can be made through the external speakers. Voice Paging can also be
heard over the extensions in groups 00-07.
• An extension can belong to more than one paging group.
• A maximum of eight Paging Groups can be assigned to a system.
• Only one page may be performed at a time with one exception. Pages to
group 00 always take priority. If you page group 00 while another
extension is paging group 01-07, the other page terminates. The other
pager receives busy and “Page Overridden” displays on the telephone.
Page 2-40DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 59

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
• Paging cannot be heard at busy extensions or at extensions for which the
Do Not Disturb, Call Forwarding, or Absence Message feature is activated.
• You can answer Paging from an idle extension by dialing the Meet-Me
Answer code (“77”) during a page or if in a call, placing the call on hold
and dialing “77.”
Power Failure Transfer
(All Versions)
Description
This feature provides telephone service to a limited number of SLTs during a
power failure. The SLTs are connected to the CO via a Power Failure Unit
(PFU).
In the event of a power failure, the power failure extensions have dial tone
directly from the CO; system features and restrictions do not apply.
Hardware Requirements
• Power Failure Unit (VA-43703)
• An SLT that will be connected to the PFU.
Considerations
• Up to four SLTs can be connected to one Power Failure Unit.
• If a call is in progress through the PFU when the power is restored, the call
will be disconnected.
• For added protection against power outages, backup batteries can be
installed in the DBS. Backup batteries provide full telephone service and
system features to all DBS extensions for a limited amount of time.
With maximum traffic, the backup batteries last up to 40 minutes for the
DBS 40 and 72, and up to 30 minutes for the DBS 96.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-41
Page 60

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
Remote Maintenance
(All Versions)
Description
The DBS can be programmed from a remote terminal or from a remote PC.
Remote programming can be accomplished using the Remote Programming
Mode or by using Panasonic’s PCAS (Personal Computer Administration
System) or DBS Manager software.
Remote Programming Mode
(All Versions)
Description
Remote Programming Mode uses a “dumb” terminal or a PC to access the
DBS. This method of remote maintenance is less sophisticated and more
difficult than using PCAS or DBS Manager.
Operation
You can enter the Remote Programming Mode through any of these three
methods:
• By using a local PC and communications package to connect directly to
the DBS serial port
• By dialing into the system through a direct DISA trunk
• By dialing into the system through a regular CO trunk, then requesting the
operator to enter the Remote Programming ID Code.
Terminal Programming Through a Direct Connection
When programming from a terminal connected to the RS-232C (SMDR) port,
perform the following steps:
1. Make certain the cables are configured and connected as outlined in
Section 300.
2. Make certain the DBS is in the SMDR mode by entering the following
code from the attendant port:
ON/OFF
#93
3. Enter your terminal communications program and make sure your PC’s
data communications settings match those of the DBS.
Page 2-42DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 61

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
4. From your terminal communications program, type the following
command:
#99xxxx
(where xxxx = the site’s password)
5. After the DBS responds, type P and then press Enter.
Follow the directions on the screen to access the desired program. (See
“Terminal Programming Commands.”)
Terminal Programming Through DISA
Note:
The DBS must be equipped with an MFR card and a RAI card to allow
terminal programming using this method.
When programming through a DISA trunk, perform the following steps:
1. Dial into the DBS through a DISA trunk.
2. Once you are connected, type
#69999
from your terminal communications
program.
3. After the DBS responds with REMT>, type P and then press Enter.
Follow the directions on the screen to access the desired program. (See
“Terminal Programming Commands.”)
Terminal Programming Through a CO Trunk and Operator Transfer
Note:
The DBS must be equipped with an MFR card and a RAI card to allow
terminal programming using this method.
When programming through a normal trunk, perform the following steps:
1. Dial into the DBS through a normal trunk.
2. Ask the operator to place you on hold and dial
#69999
to transfer you into
remote programming.
3. After the DBS responds with REMT>, type P and then press Enter.
Follow the directions on the screen to access the desired program. (See
“Terminal Programming Commands.”)
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-43
Page 62

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
Terminal Programming Commands
Use the following commands to navigate terminal programming:
Command Description
~01 Access System parameters
~02 Access Trunk parameters
~03 Access Extension parameters
~04 Access Ring assignments
~05 Access FF-key assignments
~06 Access Name assignments
~07 Access Toll Restriction data
~08 Access Least Cost Routing data
~09 Access Copy mode
~10 Access Speed Dial data
~B Back to previous address
~b Back to previous port
~F Forward to next address
~f Forward to next port
~R Return to provide mode
Ctrl-Z Quit
Remote Programming Using PCAS or DBS Manager
(CPC-A 3.1 and higher, CPC-A II, and CPC-B 1.0 and higher)
Description
PCAS provides a menu-driven interface for remote maintenance. For
complete details about using PCAS, see the
Very similar to PCAS but more enhanced is the Windows-based program
DBS Manager. For complete details of using DBS Manager, see the
Manager User’s Guide
.
The primary function of these programs is to allow you to set up and maintain
DBS settings using a PC. Their communications capabilities allow you to
maintain the DBS settings while you are on-site with the DBS, or while you
are off-site at a remote location.
These programs enable you to perform tasks such as:
• Setting up communications information
PCAS User’s Guide
.
DBS
Page 2-44DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 63

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
• Connecting your PC with a customer’s DBS
• Maintaining DBS parameters
• Backing up and restoring customer databases.
Station Class of Service
(CPC-AII and CPC-B Version 3.1 or higher)
Description
Station Class of Service provides a way to restrict access to certain extension
features. Station Class of Service 0 provides access to all features. By default,
all extensions are assigned to this class of service. Classes of Service 1-8 can
be modified to allow and restrict access to specific features. The following
table shows the features that can be enabled/disabled for station classes of
service.
Table 2-1. Station Classes of Service
Class of Service Features
Number Feature
1 Dial Tone On/Off (#50)
2 Head/Handset Exchange (#51)
3 BGM On/Off (#53)
4 Absence Message Set/Reset (71)
5 Call Forward Set/Reset (72)
6 Do Not Disturb (73)
7 Station Lockout (74)
8 Park Hold (75)
9 Park Pick Up (76)
10 Meet Me Answer (77)
11 UNA Pickup (78)
12 Direct Pickup (79)
13 Group Pickup (70)
14 Tone/Voice Mode (1)
15 Message Waiting Set (2)
16 Busy Override (4)
17 Call Waiting (3)
18 Offhook Voice Announce (5)
19 Central Office Call Queuing (2)
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-45
Page 64

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
20 SLT Transfer (8)
21 Call Forwarding--Outside (720, 721, 722, 724) (
higher)
Call Forwarding--External (723) ( CPC-A and CPC-AII/CPC-B Versions prior to 7.0)
Note:
Call forwarding -- External (723) only allows external call forwarding for internal
calls.
CPC AII and
CPC-B Version 7.0 or
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Extension Class Of Service Setting
• FF3 (Extension): Extension Class of Service Assignment
Considerations
• Some features that are in use at the time they are disabled from the Class of
Service cannot be cancelled. For instance, if background music is turned
on at a phone at the time background music is disabled from the class of
service, the background music at the phone cannot be turned off. Make
certain that features are not in use when removed from a class of service.
(If a feature is accidentially left active, simply reenable the feature in the
class of service and turn off the feature.)
Station Hunting
(All Versions)
Station hunting allows calls to be automatically transferred among a
preselected group of phones.
When a call terminates to a busy extension in a hunt group, the call
automatically transfers to another extension in the group. If the second
extension is busy, the call automatically transfers to another member of the
group.
Several methods of station hunting are available. The CPC version
determines which methods are available.
Page 2-46DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 65

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Terminal and Circular Hunting
(CPC-A; CPC-B Versions Prior to 2.0)
Description
CPC-A and CPC-B Versions prior to 2.0 provide terminal and circular hunt
groups.
Terminal Hunt Groups
With terminal hunt groups, a call must ring at the first extension in the group
in order for hunting to be invoked.
If the first extension of the hunt group is busy, the call automatically transfers
to the next extension in the group. If that extension is busy, the call continues
to hunt through the group. The order in which the call hunts is determined by
how the group is programmed. Up to eight extensions can be placed in the
group, and calls will always hunt from member 1, to member 2, to member 3,
and so on.
If desired, another hunt group can be designated to receive calls should all the
members of the original group be busy or not answer.
A pilot number must be designated as the first extension in a terminal hunt
group. A pilot number is a fictitious extension number that, when dialed,
starts the hunting process through the group. In CPC-A and CPC-B Versions
prior to 2.0, a pilot number can be provided by adding a resistor to an analog
port. See “Hardware Requirements” for details.
Circular Hunt Groups
With circular hunting, hunting is initiated by calling any extension in the
group. If the called extension is busy, the call will hunt through the next
members of the group until the end of the hunt group is reached. If the call
reaches the end of the group without reaching an idle extension, it will
transfer back to the first member of the group until one full circle is
completed.
If desired, another hunt group can be designated to receive calls should all the
members of the original group be busy.
Related Programming
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): Hunt Group Member Table
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Group): Call Next Hunt Group
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-47
Page 66

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): Terminal/Circular Hunt Groups
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): Ringing Assignments (all)
Hardware Requirements
• A pilot number can be provided by installing a 2 watt 450 Ohm resistor on
the analog port that will be dialed to initiate station hunting. The resistor is
placed across the tip and ring of the designated analog port.
The resistor will “busy” the port. When the busy pilot number is called, the
call will hunt through the other extensions in the group.
Considerations
• Eight Station Hunt Groups can be programmed; a single Hunt Group can
contain up to eight extensions, including the pilot extension.
• If all extensions in a group are busy and an alternate group has not been
designated, CO calls will queue, and intercom calls will receive busy tone.
• If the first extension within a hunt group activates an absence message, call
forwarding, or DND, the hunt feature will not work.
• If an extension other than the first extension activates an absence message,
call forwarding, or DND, the hunt feature will skip that extension, and
proceed to the next extension within the group.
• The amount of time a call rings at a hunt group member before transferring
to another hunt group member is determined by the Call Forward--No
Answer Timer.
• An SLT hunt group member that places a call on hold and then replaces the
handset will not receive additional hunt group calls until the held call is
released.
• An extension that is a member of a hunt group cannot be a member of
another hunt group or a member of call coverage group.
• The offhook signaling option should be removed from members in a hunt
group.
Page 2-48DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 67

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Terminal, Distributed and Longest Idle Hunting
(CPC-AII and CPC-B Version 2.0 or higher)
Beginning with CPC-B Version 2.0, three types of hunt groups are available:
Terminal, Distributed, and Longest Idle. In addition, CPC-AII and CPC-B
Version 2.0 and higher also provide a software-defined pilot extension
number. The software-defined pilot number eliminates the need for the 2 W
450 Ohm resistor required for a pilot number in CPC-A and CPC-B Versions
prior to 2.0.
CPC-AII and CPC-B Versions 2.0 or higher also allow calls from busy hunt
groups to overflow to a transfer extension. The transfer extension can be the
pilot of another hunt group, the pilot (0) of the attendant group, or a single
extension number.
Terminal Hunt Groups
When the Terminal method is selected, a call to the pilot number will
repeatedly search hunt group members until the Transfer Timer expires. If
none of the members is free when the timer expires, the call is transferred to
the transfer extension.
Distributed Hunt Groups
When the Distributed method is selected, calls are distributed through the
pilot number based on which extension in the group received a call in the last
search. The incoming call begins its search at the next available extension in
the group and then repeatedly searches the group, in sequence, until the
Transfer Timer expires. If none of the members is free when the timer expires,
the call is transferred to the transfer extension.
Longest Idle Hunt Groups
With Longest Idle hunting, a call to the pilot number rings the extension in
the group that has been available the longest.
As with the other two methods, the search then continues through the Hunt
Group until the Transfer Timer expires. If a member does not become
available before the timer expires, the call is transferred to the transfer
extension.
An extension is not considered idle if it rings.
Related Programming
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): Hunt Group Search Method
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): Pilot Extension Number
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-49
Page 68

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): Hunt Group Transfer Timer
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): Hunt Group Extension Number
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): Transfer Extension Number
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): CO Delayed Day Ring Assignments for
Hunt Group Pilot Numbers
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): CO Delayed Night Ring Assignments for
Hunt Group Pilot Numbers
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): Central Office Day Ring Assignment for
Hunt Group Pilot Numbers
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): Central Office Night Ring Assignment
for Hunt Group Pilot Numbers
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): Ringing Assignments (all)
• FF1 (System): Hunt Group No Answer Timer (CPC-AII and CPC-B
Version 3.1 or higher)
Considerations
• Eight Station Hunt Groups can be programmed. A single Hunt Group can
• The transfer destination of any Hunt Group can be set to the pilot number
• A Transfer Timer adjusts the transfer time between hunt groups. The
• Central office trunks can be set to terminate to different hunt group pilot
• With CPC-AII and beginning with CPC-B 3.1, the Hunt Group No Answer
contain up to sixteen extensions (CPC-AII and CPC-B Version 6.0 or
higher) or eight extensions (CPC-B Version 2.0 to 5.04) plus a pilot
extension number.
of the next group, the pilot number (0) of the Attendant Group, the pilot
number of the same group, or a real extension. The transfer destination
cannot be voice mail.
transfer time can be set from 0 to 32 seconds. If the timer is set to 0
seconds, CO calls will be queued at the hunt group until a member is
available. Intercom calls will also queue.
numbers during day and night mode operation.
Timer determines how long a hunt group member rings before the call is
transferred to the next hunt group member. In previous releases, this time
was determined by the Call Forwarding--No Answer Timer.
• With CPC-AII and beginning with CPC-B Version 4.0, a call arriving at
the the pilot number of a hunt group will hunt to a member that has call
Page 2-50DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 69

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
forwarding set, unless call forwarding is set to an outside number. In
previous versions, hunting would skip an extension with call forwarding
set. The following call types will hunt to a member that has call forwarding
set:
- Intercom calls
- Transferred intercom calls
- Incoming CO calls (including DID calls)
- Transferred CO calls
- DISA calls
Station Message Detail Recording (SMDR)
(All Versions)
Description
Station Message Detail Recording (SMDR) provides detailed call records of
outgoing calls. SMDR records can be output to a printer or an external call
accounting system.
Figure 2-2 shows the SMDR format for CPC-AII and CPC-B Version 3.1 or
higher. Figure 2-3 shows the SMDR format for CPC-A and CPC-B Versions
prior to 3.1.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-51
Page 70

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
Figure 2-2. SMDR Format for CPC-AII and CPC-B Version 3.1 or higher
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
012345678901234567890123456789012345678901234567890123456789012345678901234567
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
T MM/DD HH:MM:SS HH:MM.SS NNN DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDDD AAAAAAAAAA VVVVV NN
1=Call type
S=Inbound DISA
s=Outbound DISA
I=Incoming
O=Outgoing
T=Transfer (See Note 1.)
N=DNIS
D=DID
2=Date
MM=month
DD=day
3=Call start time
HH=hours
MM=minutes
SS=seconds
4=Call duration
HH=hours
MM=minutes
SS=seconds
Notes:
1. Transferred calls include direct and group call pickups and conference calls.
If a station call is transferred to an outside number, an SMDR record is
also created for the station that is transferred.
2. The * symbol appears as a greater-than sign (>) on the SMDR printout; the # symbol
appears as a less-than sign (<). Centrex and PBX codes, as well as LCR access codes, do
not appear as dialed digits. If the Caller ID Feature is installed and enabled,
“Private” appears with calls that have restricted Caller ID display and “Out of Area”
with long distance calls that do not provide Caller ID information.
5=Extension number
10-69, 100-699=extensions
CO number=DISA
6=Dialed digits or Caller ID
DD=digits 0-9 or symbols * or
(See Note 2.)
7=Account code
A=0-9999999999
8=Verified account code or walking
COS code
V0000-V9999=verified account codes
W0000-W9999=walking COS codes
9=Trunk Number
NN=number (01-64)
#
Page 2-52DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 71

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Figure 2-3. SMDR Format for CPC-A and CPC-B Versions Prior to 3.1
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
01234567890123456789012345678901234567890123456789012345678901234567890
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
MM DD HH:MM H:MM.X C NN DDDDD-DDD-DDD-DDDD NNN AAAAAAAAAA
1=Date
MM=month
DD=day
2=Call start time
HH=hour
MM=minute
3=Call duration
H=hour (0-9)
MM=minutes
X=1/10th of a minute (0-9)
4=Call condition
I=incoming
i=DISA incoming
O=DISA outgoing
D=Call longer than 10 hours
5=Trunk number
NN=number (01-64)
6=Dialed digits
DD=digits 0-9 or symbols * or
(See the Note following item 8.)
7=Extension number or DISA number
10-73, 100-699=extensions
#01-#64=DISA numbers
8=Account code
A=digits 0-9 or symbols * or #
Note: The * symbol appears as a
greater-than sign (>) on the SMDR
printout; the # symbol appears as a
less-than sign (<).
#
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Parity Check
• FF1 (System): Odd/Even Parity
• FF1 (System): Baud Rate
• FF1 (System): Stop Bit Length
• FF1 (System): Data Length
• FF1 (System): Serial Port Flow Control (X On/ X Off)
• FF1 (System): SMDR Display Start Timer for CO Calls
• FF1 (System): SMDR Printing Mode 1: Outbound and Inbound
• FF1 (System): SMDR Printing Mode 2: Long Distance and Local Calls
• FF1 (System): SMDR Printing Mode 3: Header Title
• FF3 (Extension) Station Message Detail Recorder (SMDR) Report
Hardware Requirements
• A printer or external call accounting system is required to receive SMDR
data.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-53
Page 72

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
T1 Interface
(CPC-B Version 4.0 or higher)
Description
The T1 Interface is a digital trunk card that provides twenty-four 64 kbps
channels, for a total transmission rate of 1.544 Mbps. T1 lines can be leased
from local exchange carriers and long-distance carriers.
The DBS T1 Interface supports the following options:
SF or ESF Framing Formats
Either super frame (SF) or extended super frame (ESF) formats can be used
with the DBS T1.
The superframe consists of 12 frames, with each frame including 193 bits.
Each frame is separated by a framing bit.
An extended super frame consists of 24 frames, double the length of the super
frame (SF) format. ESF also supports monitoring and maintenance
capabilities that are not available with the SF format.
Flexible Trunk Signaling Modes
The T1 Interface provides the following trunk signaling modes. The
signaling modes can be assigned on a per-channel basis:
• Loop start
• Ground start
• E&M.
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): T1 Settings (all)
• FF2 (Trunks): Trunk Type
• FF2 (Trunks): Trunk Port Class
• FF3 (Extension): Station Port Class
Hardware Requirements
• The following hardware is required to install a T1 in a single cabinet:
Page 2-54DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 73

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
- 1 T1 Trunk Card (VB-43561
- 1 T1 MDF Card (VB-43562)
- 1 Sync Card (VB-43563).
In addition, one T1 Cable (VB-43564) is required to install a T1 in a double
cabinet if the T1 card is located in the slave cabinet.
To install two T1s in a double cabinet, you must have 2 T1 Trunk Cards and
2 T1 MDF Cards.
• The installer must provide a Channel Service Unit (CSU) that complies
with FCC Part 15 and Part 68. The CSU is installed between the DBS and
the public network. The CSU provides alarm, diagnostic, and monitoring
functions, as well as network protection.
Considerations
•
Fractional T1
Fractional T1 allows you to use only a portion of the 24 channels provided
on the T1 card.
can be used when fewer than 24 T1 trunks are needed.
• Though each T1 Interface provides 24 trunk channels, T1 trunks do not
increase the overall trunk capacity of the DBS. Each T1 channel subtracts
from the total number of analog trunks that can be installed. Furthermore,
the number of analog trunks that can be used may be decremented in
quantities of 1 or 8.
For instance, if you are installing a T1 in a DBS 96 and you only want to
use 12 T1 channels, the logical number of analog trunks that would be
available is 20 (32 - 12 = 20).
With CPC-B 5.00 and later, the number of analog trunks available are
decremented in quantities of 1. With CPC-B earlier than 5.00, the number
of analog trunks must be decremented in quantities of 8; the actual number
of analog trunks that can be used is 16:
(32 total trunks - 16 (two 8-trunk increments) = 16.)
• The current version of the T1 supports voice communications only. Data
can be transmitted only if it reaches the T1 in analog form. Examples of
analog data that can be transmitted over the T1 include fax transmissions
and PC files that have been converted into analog form using a modem.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-55
Page 74

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
(CPC-AII Version 7.1 and higher and CPC-B Version7.1 and higher
)
Descriptio
n
Computer Telephony Integration (CTI) provides communication and
coordination of operation between computers and the telephone system. One
of the most significant emerging standards in CTI is the Telephony Services
Application Programming Interface from Novell®
.
Telephony Services is basically a third party call controller. Applications
designed for Telephony Services act on behalf of a group of users. With its
group orientation, Telephony Services provides easy operation, distribution
and transfer of calls and reporting of call handling among other features
.
The DBS talks with the Telephony Server using a serial link from a specially
designed Panasonic API Card. There is no physical link between the
telephones and the networked computers. However, a logical link is
established on the Tserver to relate a telephone to a networked computer
.
New applications are currently being developed that will work with DBS
Telephony Services. The possibilities for applications are unlimited. For
example
:- inbound callers may be routed to the most appropriate customer
representative based on the caller’s phone number. As the call is
answered, the representative’s computer screen automatically
displays the customer’s information.
- a computer-based phone directory may be used to not only look
up a phone number but also initiate a call. A corresponding
called party database may be automatically accessed when the
call is initiated
.- the vast array of PBX features may be more easily utilized using
computer screen icons and prompting instead of complicated
telephone feature access codes and procedure
s
In addition to general Telephony Services applications, since the DBS
Telephony Services meets a published standard, customized applications may
be developed to meet specific needs.
For more information on DBS Telephony Services, see the
“
in the DBS Section 520. Each
application used in conjunction with Telephony Services provides its own
user documentation
.
Telephony Services
Services Installation and Feature Description”
Page 2-5 6 DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
DBS Telephony
Page 75

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Connections
.
Telephony
Outside CO
Trunk Lines
DBS
Novell
Server
Serial
Communication
Line
API Port
TRK1 TRK2 TRK3 EC1 EC2 EC3 EC4 EC5 EC6 EC7 EC8 EC/TRK SCC CPC AUX1 AUX2
Novell Network
...
Logical
...
Telephone Extensions
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): API Port Type
• FF1 (System): API Baud Rate
Hardware Requirements
• VB-43941 Telephony Services Kit. This kit includes a Panasonic API
Card, the API Serial Connector (two ports) and one 3 1/2” floppy disk
containing the Telephony Services DBS Driver “Panadrvr.”
• A Novell 3.12 (or later), 486 (or greater) server with at least 8 megabytes
of RAM and equipped with an available serial port of at least 9600 baud
capacity (16550 UART required).
• One customized serial cable (provided). The RS232 limits should not be
exceeded (50 feet).
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-57
Page 76

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
Toll Restriction
(All Versions)
Description
Access levels, including the prohibition of long distance calls or after-hours
calls, can be assigned to specific extensions or CO lines using the Toll
Restriction feature. This minimizes non-business related calls and reduces
phone bills by only allowing long distance calls over designated lines.
The following access levels are available:
Table 2-2. Toll Restriction Types
Toll Restriction
Type
0 Restriction of outbound dialing. (911 Calls allowed with CPC-AII/CPC-B
1 Full restriction of outbound dialing (911 Calls allowed with CPC-AII/
2 Local calls allowed
Characteristics
Version 6.0 only.)
Inbound ringing trunks can be answered by or transferred to Type 0 exten-
sions.
Intercom calls are allowed.
Group Call Pickup (intercom calls only)
CPC-B Version 6.0 only)
Inbound trunk calls to all phones can be answered and/or transferred.
Intercom calls are allowed.
Group call pickup is allowed.
1-800 calls allowed
Inbound trunk calls can be answered and transferred from a Type 2 phone.
Full restriction of international calls.
Full restriction of operator calls (old numbering plan)
Selectable restriction of operator calls (new NANP) - see Notes.
Selectable restriction of Speed dial numbers.
Selectable restriction of N11 codes (see Notes for 911).
Restriction of up to 10 three-digit office codes (new NANP).
Restriction of up to 50 seven-digit numbers.
Inter-digit timing is set to 6 seconds.
Page 2-58DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 77

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
3 Full restriction of operator calls (old dialing plan).
Selectable restriction of operator calls (new NANP).
Selectable restriction of international calls (defaulted to full restriction -
ssee Notes)
Selectable restriction of N11 codes (211-911) (see Notes for 911).
Selectable restriction of Speed dial numbers.
Restriction of up to 50 seven-digit numbers.
Trunk calls can be answered and transferred.
Defaulted to full restriction of area-code dialing (see Notes).
Defaulted to full restriction of office-code dialing (see Notes).
Inter-digit timing is set to 6 seconds.
4 Identical to Type 3, except that office-code dialing is allowed by default;
type 4 also allows Operator Calls (old dialing plan) (See Notes).
5 Programmable TRS Type; defaulted to no restrictions (see Notes).
6 Programmable TRS Type; defaulted to no restrictions (see Notes).
7 No restriction of outbound dialing.
Notes:
For TRS types 3-6 and the old numbering plan, operator calls are allowed if FF7 1# 1# is set to
“on.” The office code tables are used to restrict all 0 plus dialing; the next two digits will also
be analyzed.
For TRS types 2 to 6 and the new NANP (CPC-AII/CPC-B Version 6.0 and later), operator
access is determined by an extension-based operator access switch. TRS Types 0 and 1 are fully
restricted and TRS Type 7 is not restricted.
For TRS types 2 to 6 beginning with CPC-AII/CPC-B Version 6.0, 911 is always allowed.
For TRS types 3-6, area code and office code restrictions can be changed using “Area Code
Table For TRS Types 3-6‚” “Office Code Table For TRS Types 3-6‚” “Special Area Code Table
For TRS Types 3-6‚” and “Special Office Code Table For TRS Types 3-6‚”explained in Chapter 8 of
Programming (Section 400)
.
For TRS types 3-6, area and office code restrictions can be further managed using “Special
Area Code Table For TRS Types 3-6” and “Special Office Code Table For TRS Types 3-6”
found in Chapter 8 of
Programming (Section 400)
. Four area codes can be associated with special area code tables 1-4 (one area code per table). Within each of these tables, the entire range
of valid office codes can be individually allowed or restricted. Thus, the Special Area and
Office Codes work together to provide specific toll restrictions.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-59
Page 78

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
The following calling restrictions are also available:
• Station Lockout Key Code Restriction
A key code must be entered before calling out when the Station Lockout
feature is activated.
• Account Code Restriction
An Account Code must be entered before calling out.
• Forced LCR Restriction
The LCR feature controls outside calls.
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Override Toll Restrictions with SSD Numbers
• FF3 (Extension) Extension Lockout Code
• FF7 (Toll Restriction): Toll Restriction Settings (all)
• FF8 (LCR): Least Cost Routing
Considerations
• The dialing restrictions included in this feature help prevent unauthorized
outgoing calls. It is possible, however, to program your system to allow
System Speed Dialing to override Toll Restrictions.
Page 2-60DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 79

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Trunk Groups
(All Versions)
Description
Trunks can be placed in trunk groups. When a trunk group is accessed, the
DBS automatically selects an open trunk from the group.
Operation
To access a trunk group, do one of the following:
• Dial a trunk group access code before dialing the telephone number. Trunk
group access codes are 9, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, and 86.
• Press an FF key that is assigned as a pooled trunk key.
Related Programming
• FF2 (Trunks): Pooled Trunk Access for Group “9”
• FF2 (Trunks): Pooled Trunk Access for Groups “81-86”
Considerations
• Trunks can appear in more than one trunk group.
• If Least Cost Routing is enabled, the trunk group “9” automatically
accesses the LCR features.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-61
Page 80

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
Trunk Name Assignment
(CPC-AII and CPC-B Version 2.0 or higher)
Description
You can display a name, number, or message of up to six characters on the
LCD in place of your CO trunk line number. The name will appear when a
CO call is ringing or connected.
For example, you can assign specific CO lines to different individuals or
departments. Then, when an extension rings, the individual’s name or the
department’s name will appear on the display, immediately identifying the
person for whom the call is intended.
While you are speaking on the extension, “CO TALK
on the LCD. (
While the extension is ringing, “INCOMING
the extension is ringing and you are speaking on the extension at the same
time, “INCOMING
Related Programming
• FF6 (Name and Message): Trunk Name Assignment
Considerations
• Trunk names can be assigned with a DSS.
• If a text name is assigned to a CO trunk, the trunk number does not appear
on the display.
XXXXXX
XXXXXX
XXXXXX
represents the six characters of the Trunk Name.)
XXXXXX
” will appear on the second line of the display.
” will appear. While
” will appear
Page 2-62DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 81

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Trunk Queuing
(All Versions)
Description
If all outside lines in a Trunk Group are busy, the system can call you when a
line becomes free. Simply pick up the handset and dial the telephone number
when the Trunk Callback alert tone rings.
Operation
To set Trunk Queuing:
1. Press the
2. Press the CO line key or dial a trunk access code.
The phone issues busy tone.
3. Press “2.”
“In CO Queuing” appears on the display.
4. Press the
5. Wait for the Trunk Callback alert tone.
To respond to the Trunk Callback alert tone:
Pick up the handset.
• The outside line is automatically accessed.
• The phone issues dial tone.
• “CO TALK #XX” (where “XX” is the line number) appears on the display.
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
key.
key.
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Extension Class of Service Setting
• FF3 (Extension): Extension Class of Service Assignment
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-63
Page 82

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
Considerations
• Response to the Trunk Callback alert tone must be within sixteen seconds
or Trunk Queuing will be canceled.
• If a call arrives from an outside line while the Trunk Queuing feature is
activated, Trunk Queuing will be suspended for the duration of the
incoming call.
• If you are engaged in another call on a different line for more than twenty
minutes after the desired outside line becomes available, that outside line’s
assignment to you will be canceled.
• The Trunk Queuing feature may also be used if you hear a busy tone when
trying to make a call using the Pooled Trunk Access feature.
• Trunk Queuing can be used by all telephone types including SLTs and
DSLTs.
Universal Night Answer
(All Versions)
Description
During night mode, Universal Night Answer (UNA) sends incoming calls to
an external ringer, such as a night bell.
As an alternative to using a night bell, UNA can also be configured to ring
external paging speakers.
Universal Night Answer calls can be picked up from any extension, provided
the extension’s Class of Service allows UNA answer.
Operation
To answer a UNA call:
1. Pick up the handset.
The phone issues intercom dial tone.
2. Dial “78.”
“CO TALK #XX” appears on the display (where “XX” = the trunk
number).
Page 2-64DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 83

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Extension Class of Service Setting
• FF1 (System): Ring Patterns for UNA Terminals (M, C, & B)
• FF3 (Extension): Extension Class of Service Assignment
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): CO Day Ring Assignment
• FF4 (Ringing and Hunt Groups): CO Night Ring Assignment
Hardware Requirements
• An external ringing device is not provided with the DBS. It can be
purchased separately from an electronics dealer.
• External paging speakers are not provided with the DBS; they must be
purchased separately.
Considerations
• With CPC-A and CPC-AII, extension port 73 is used to assign ringing to
an external page/UNA interface.
• With CPC-B, extension port 145 is used to assign ringing to an external
page/UNA interface.
Voice Mail Ringing
(CPC-AII and CPC-B Version 3.1 or higher)
Description
The Voice Mail Ringing feature allows calls from a DBS Automated
Attendant or from an ACD port to ring an extension with the same ring tone
as a CO trunk. The ring pattern is selected in the Extension Distinctive
Ringing program. If a distinctive ringing pattern is not specified, the ringing
pattern will be two seconds on/two seconds off.
Related Programming
• FF3 (Extension): Extension Ring Pattern
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-65
Page 84

Chapter 2. System Features Section 700 - Operation
VAU
(All Versions)
Description
The Voice Announce Unit (VAU) is a digital answering device that can be
connected to the DBS. It provides for the recording and playback of up to two
voice messages, along with the ability to transfer incoming calls.
When a call reaches the VAU, it plays a prerecorded voice message. The
caller is then allowed to dial a number or is automatically transferred to a
predetermined extension.
The VAU is often used to back up operators or hunt groups. Callers
overflowing from either of these positions hear a message and can then dial a
number or wait to be transferred back to the operator or hunt group.
The VAU can be used to provide a variety of other services to callers, such as
a menu of dialing options or transfer to an answering machine.
Recording and Playing Messages
You can record the VAU messages from either an extension or a trunk.
Notes:
• You must use a DTMF telephone to record and play VAU messages.
• To change existing messages, record over them.
To record and play messages, complete the following steps.
1. Do one of the following:
If . . . Then . . .
You are recording or playing from an extension
You are recording or playing from a trunk
Take your phone off hook.
Dial the VAU extension number. (If the inter-
com is set for Voice, dial 1 to change from
Voice to Tone.)
Dial the phone number of the VAU, or call in
and have the operator transfer you to the VAU
extension.
Page 2-66DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 85

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
2. After the VAU answers, do one of the following:
If . . . Then . . .
You want to record the
first message
You want to record the
second message
You want to play the first
message
You want to play the
second message
Notes:
• You can enter the *97 codes again to replay messages without ending
your call.
• You can only record one message at a time. To record another message,
you must end your call and redial the VAU.
3. When the operation is complete, put the phone on hook.
Dial
* 98 1
Wait for a beep. After the beep, record the
message.
Dial
* 98 2
Wait for a beep. After the beep, record the
message.
Dial
* 97 1
The VAU plays the message.
Dial
* 97 2
The VAU plays the message.
Considerations
• For more information on the VAU and its operation, see Section 770,
“Voice Announce Unit User Guide.”
VAU Port Assignment
(CPC-AII and CPC-B Version 5.0 or higher, CPC-A Version 3.3 and higher)
Operation
A digital port can now be assigned as a VAU through system programming.
In previous releases, VAUs were assigned as standard digital ports. Using the
standard digital port assignment required the installer to make the following
program changes:
•The CO Offhook Signal option had to be set to “off” (FF3 1-144# 7#).
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-67
Page 86

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
•The Call Waiting/OHVA option had to be set to “off.” (FF3 1-144# 8#).
•Auto Pickup had to be set to “on” (FF3 1-144# 12#).
•All FF keys for the extension port had to be cleared.
The VAU assignment now eliminates the need to make these program
changes. Once a port is assigned as a VAU, the system treats that port as if
these changes have been made.
Note:
Though the VAU assignment treats the VAU port as if the program
settings have been made, it does not actually change the settings. If the port is
later assigned as a standard digital port, the original program settings will still
be in effect.
To further improve VAU operation, the following call types are now routed to
the first VAU message:
•DID calls
•DNIS calls
•DISA calls
•Transferred trunk calls
•Transferred intercom calls.
In previous releases, only intercom and CO trunk calls were routed to the first
VAU message.
All recalls are routed to the second message.
Programming
• FF3 (Extension): VAU Port Assignment
• FF3 (Extension): VAU Hunting Priority
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-68
Page 87

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
Walking TRS Class of Service
(CPC-AII and CPC-B Version 3.1 or higher)
Description
Walking TRS Class of Service allows an extension user to “carry” his or her
toll restrictions to another phone.
Before the Walking TRS Class of Service feature can be used, a Walking
Class of Service code must be entered at your extension before using dialing
privileges at another extension.
Operation
To enter a Walking Class of Service code:
1. Pick up the handset.
The phone issues intercom dial tone.
2. Dial “#12.”
3. Enter the four-digit Walking Class of Service code (0001-9999).
4. Press “#.”
5. Replace the handset.
To use a Walking Class of Service code:
1. Pick up the handset of an extension other than your own.
The phone issues intercom dial tone.
2. Dial “#13.”
3. Enter
4. Enter your Walking Class of Service code.
5. Press “#.”
your
extension number.
6. Enter a trunk access code (88XX, 9, 81-86).
The phone issues outside dial tone.
7. Dial the telephone number.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-69
Page 88

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 2. System Features
The Walking Class of Service remains in effect until you replace the
handset.
To clear a Walking Class of Service code:
1. Pick up the handset.
The phone issues intercom dial tone.
2. Dial “#12.”
3. Enter the original Walking Class of Service code.
4. Press “#.”
5. Replace the handset.
To confirm a Walking Class of Service code (Attendant Phone only):
1. Pick up the handset.
2. Press the
3. Dial “#12.”
4. Enter the extension number.
Considerations
• Walking Class of Service can be used by KTELs, DSLTs, and SLTs.
• The same Walking Class of Service code can be used on more than one
• If an extension is locked out, the Walking Class of Service feature will
The phone issues intercom dial tone.
CONF
key.
The Walking Class of Service code for that extension appears on the
display.
extension.
override the lockout.
• LCR and TRS dialing privileges follow the Walking Class of Service.
• Before entering a new walking COS code, you must first clear the existing
code.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 Page 2-70
Page 89

Chapter 3. Attendant Features
This chapter describes features that are available to an attendant phone.
In addition to functioning as a central answering point, an attendant phone
also has special capabilities for monitoring and programming other phones.
This chapter covers the following topics:
TopicPage
Alternate Attendant 3-3
Attendant Assignment of Speed Dialing 3-3
Attendant Busy Override 3-4
Attendant Call Park 3-5
Attendant Control of Absence Messages, 3-7
Attendant-Controlled Text Assignment 3-8
Attendant Feature Package 3-10
Attendant Groups 3-11
Dial Tone Disable 3-12
DSS/72 3-13
Headset Operation 3-17
Key Bank Hold 3-18
One-Touch VM Transfer 3-18
Station Lockout Code Assignment 3-21
System Time and Date Control 3-22
Traffic Measurement 3-24
Walking COS Confirmation 3-25
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/953-1
Page 90

3-2 DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 91

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 3. Attendant Features
Alternate Attendant
(CPC-A and CPC-B Versions Prior to 2.0)
Description
The alternate attendant receives intercom calls directed to the primary
attendant if the primary attendant is busy or out of service.
In addition to receiving overflow intercom calls, the alternate attendant has
full access to attendant features.
With CPC-B 2.0 and above, the “Alternate Attendant” program is replaced by
the Second, Third, and Fourth Attendant Positions.
Considerations
Alternate Attendant Extension Number.
extension number 11 or 101. By default, extension 11 or 101 is assigned to
port 2. To assign another port as an alternate attendant, you must assign
extension number 11 or 101 to that port.
The alternate attendant is always
Attendant Assignment of Speed Dialing
(All Versions)
Description
The attendant can assign system speed dialing numbers. System speed dialing
numbers are shared by all DBS extensions.
Operation
1. Press the
• The phone issues intercom dial tone.
ON/OFF
key.
• The
2. Press the
“F” appears on the display.
3. Press
“FA” appears on the display.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 3-3
ON/OFF
PROG
AUTO
.
LED lights.
key.
Page 92

Chapter 3. Attendant Features Section 700 - Operation
4. Enter the Speed Dial code (00-89 or 000-199).
“Enter SSD XX” appears on the display (where “XX” is the System
Speed Dial code).
5. To select pooled trunk access, press
6. Dial the telephone number to be stored.
7. Press the
8. Repeat steps 2 to 7 to store additional numbers.
Considerations
• Storing a new number erases any previously stored data.
• To delete a System Speed Dial number, perform the programming steps,
CONF
the pooled trunk number (9, 1-6).
For each pause required, press
when
REDIAL
P
appears.)
The number appears on the display.
“SSD XX” (where “XX” is the Speed Dial code) and the stored telephone
number appear on the display.
but do not enter a number before pressing
is pressed . If the Speed Dial number is later displayed, a
HOLD
key.
REDIAL
followed by the last digit of
. (An R appears on the display
HOLD
.
• Names for System Speed Dialing can also be stored using a DSS console
connected to the attendant phone.
Attendant Busy Override
(CPC-AII and CPC-B Version 2.0 or higher)
Description
The Attendant Busy Override feature allows the attendant to break in on an
Intercom Call or a CO Call that is already in progress.
Attendant Busy Override can break into any extension, even if the extension
has “Busy Overridden” turned off. (The extension feature “Busy Override”
cannot break into an extension that has “Busy Overridden” turned off.)
System programming determines whether the override is preceded by an alert
tone. By default, Attendant Override does not sound an alert tone.
3-4 DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 93

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 3. Attendant Features
Operation
To override a busy extension:
Press “4.”
“CONF XXX YYY” (where “XXX” and “YYY” are the extension numbers)
appears on the display.
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Attendant Override
• FF1 (System): Alert Tone for Busy Override & OHVA
Considerations
• Replace the handset to exit the three-party conference call.
• The alert tone can be turned on or off through system programming.
Attendant Call Park
(All Versions)
Description
Using the Attendant Call Park feature, the Attendant may park an outside call
until the called party can be found. The attendant can then use the Paging
feature to inform the called party of the call’s Park Number. The parked call
can then be retrieved from any extension by dialing the Park Number.
The attendant phone is equipped with ten outside line Park Numbers (00-09).
Programming a Call Park key into an FF key on a telephone or a DSS console
makes one-touch Call Park possible.
Operation
To park an outside call:
1. Press the
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 3-5
HOLD
key.
Page 94

Chapter 3. Attendant Features Section 700 - Operation
• The outside call is placed on hold.
• “CO HOLD #XX” (where “XX” is the trunk number) appears on the
display.
2. Dial “75.”
“PARK HOLD” appears on the display.
3. Enter desired Park Number (00-09).
“PARK HOLD 01” appears on the display if you selected Park Number
01.
To retrieve a call parked by the attendant (after receiving the Park
Number from the Attendant):
1. Pick up the handset.
The phone issues intercom dial toned.
2. Dial “76.”
3. Enter the Park Number assigned to the call.
“PARK PICK XX” (where “XX” is the park number) appears, and then
“CO TALK #XX” (where “XX” is the trunk number of the call) appears.
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Attendant Park Hold Recall Timer
Considerations
• With CPC-A and CPC-B Versions prior to 3.1, an FF key assigned to Call
Park does not indicate when a call is parked. Beginning with CPC-B
Version 3.1, the FF key lights red to indicate a call is parked.
• If a parked call is not answered before the Attendant Park Hold Recall
Timer expires, the parked call recalls to the attendant.
• Intercom calls cannot be parked.
3-6 DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 95

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 3. Attendant Features
Attendant Control of Absence Messages,
Call Forwarding, and DND
(All Versions)
Description
An attendant phone can cancel the Absence Message, Call Forwarding, and
Do-Not-Disturb (DND) features activated on any extension.
Operation
To cancel an Absence Message, Call Forwarding, or DND:
1. Press the
2. Press the
3. Dial the extension number.
4. Press “*.”
5. Press the
Considerations
• On DSS consoles equipped with DSS keys, the indicator for an extension
ON/OFF
• The phone issues intercom dial tone.
• The
The
that has Absence Message, Call Forwarding, or DND activated lights
green. This indicator goes off when the feature is canceled. The indicator
does not light for Permanent Call Forwarding.
ON/OFF
CONF
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
key.
LED lights.
key.
key.
LED goes off.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 3-7
Page 96

Chapter 3. Attendant Features Section 700 - Operation
Attendant-Controlled Text Assignment
(All Versions)
Description
The attendant can assign text to extensions, system speed dial numbers, and
Call Waiting/OHVA text replies without using a DSS/72 or entering the
programming mode.
Text is assigned through the dial pad on the attendant phone.
Operation
To assign names to extensions:
1. Pick up the receiver or press the
2. Press
3. Dial #2.
4. Enter the extension’s port number. (This must be entered as a 3-digit
5. Press
6. Use the dialpad sequences shown in Table 3-1 on page 3-10 to enter
7. To store your entry, press
To assign names to System Speed Dial numbers:
PROG
number if CPC-B is used or a 2-digit number if CPC-A or CPC-AII is
used. If necessary add leading zeros.)
AUTO
letters and/or numbers.
Press
FLASH
Press
CONF
.
to backspace and erase the existing name.
after each letter or number.
to switch between numbers and letters.
HOLD.
ON/OFF
key.
1. Pick up the receiver or press the
2. Press
3. Dial #1
4. Press
5. Dial the desired of system speed dial number (00-89).
3-8 DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
PROG
AUTO
.
.
ON/OFF
key.
Page 97

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 3. Attendant Features
6. Press
AUTO
to backspace and erase the existing name.
7. Use the dialpad sequences shown in Table 3-1 on page 3-10 to enter
letters and/or numbers.
Press
FLASH
Press
CONF
8. To store your entry, press
Note:
The name does not change on the extension until the extension goes off
after each letter or number.
to switch between numbers and letters.
HOLD.
hook.
To assign text to Call Waiting/OHVA Text Replies (CPC-AII and CPCB Version 4.0 or higher):
1. Pick up the handset or press
2. Press
PROG
.
ON/OFF
.
3. Dial #5
4. Dial 1-5, depending on which text message you want to change.
5. Press
AUTO
to backspace and erase the existing name.
6. Use the dialpad sequences shown in Table 3-1 on page 3-10 to enter
letters and/or numbers.
Press
FLASH
Press
CONF
7. To store your entry, press
after each letter.
to switch between numbers and letters.
HOLD.
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 3-9
Page 98

Chapter 3. Attendant Features Section 700 - Operation
Table 3-1. Key sequences for text assignment.
Key Number of Key Presses
Once Twice Three
times
1 Space Q Z Space q z
2 A B C a b c
3 D E F d e f
4 G H I g h i
5 J K L j k l
6 M N O m n o
7 P R S p r s
8 T U V t u v
9 W X Y w x y
0 . : . : . :
* * - ? * - ?
# # / ! # / !
Four
times
Five
times
Six
times
Attendant Feature Package
(CPC-B Version 2.0 - 4.0)
Description
The Attendant Feature Package (AFP) software affects the attendant’s DSS
console.
Note:
The Attendant Feature Package was discontinued in CPC-B Version
5.0.
When the AFP is installed, the DSS console provides the following preconfigured features:
• Z 0-7 (Paging Zones)
• P 0-9 (Park keys)
•
NIGHT
•
BUSY
key
key
3-10 DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
Page 99

Section 700 - Operation Chapter 3. Attendant Features
•
WAIT
•
OHVA
•
EXT
•
SSD
•
STATE
•
RESET
•
ALM
•
MSG
•
CNCT
•
CNCL
• Configuration of line/loop keys on large display as multiline
key
key
key
key
key
key
key
key
(connect) key
(Cancel) key
• Ability to assign line/loop keys to FF keys
• 26 search keys for extensions
• 2 arrow keys.
Attendant Groups
(CPC-AII and CPC-B Version 2.0 or higher)
Description
The DBS can accommodate up to four attendant positions. The first attendant
is fixed at port 1, extension 100. The other Attendants can be set to any port
or extension. When there is more than one attendant in a system, you can
create an Attendant Group with a pilot number of 0.
When all Multi-Line keys on the first attendant phone are busy, internal calls
are forwarded to the second, third, and fourth attendant phones, in that order.
Related Programming
• FF1 (System): Second Attendant Position
• FF1 (System): Third Attendant Position
DBS-70-700DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 3-11
Page 100

Chapter 3. Attendant Features Section 700 - Operation
• FF1 (System): Fourth Attendant Position
• FF1 (System): Attendant Transfer Extension
Considerations
• If all ML keys on all attendants are busy, internal calls are transferred to a
preset destination, which must be a real extension number. The forwarding
destination cannot be the pilot number of a hunt group.
• The third and fourth attendants cannot have a DSS/72.
• Prior to CPC-B Version 2.0, the DBS supported a maximum of two
attendant positions.
• In previous software releases, if a user dialed “0” for the attendant group
but the first attendant had call forwarding activated, the call would skip to
the next attendant in the group. For example, if the first attendant activated
call forwarding--busy/no answer, the dial “0” call would skip to the second
attendant. If all attendants in the group activated call forwarding, dial “0”
calls did not reach the group.
Beginning with CPC-B Version 5.0, dial “0” calls ring the first attendant,
even if the first attendant has call forwarding activated. However, if a call is
unanswered, it does not skip to the next attendant. The call continues to
ring the first attendant until the caller hangs up.
• DSLTs and SLTs cannot be used for attendant positions.
• Ringing assignments will be required for all attendants other than
Attendant Position 1 (Port 1) and Attendant Postion 2 (when assigned to
port 2).
Dial Tone Disable
(All Versions)
Description
The intercom dial tone can be turned off at an attendant phone. Dial tone is
turned off when a headset is used.
3-12 DBS Manual - Issued 8/1/95 DBS-70-700
 Loading...
Loading...