Page 1

INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Orion®
™
Atlas
#9874 Equatorial Reflector Telescope
10 EQ
Providing Exceptional Consumer Optical Products Since 1975
Customer Support (800)-676-1343
E-mail: support@telescope.com
Corporate Offices (831)-763-7000
89 Hangar Way, Watsonville, CA 95076
OrionTelescopes.com
IN 214 Rev. B 05/09
Page 2

Tube ring mounting plate
Tube ring mounting plate
lock‑knobs (2)
Declination setting circle
Declination lock lever
Counterweight shaft lock lever
Counterweight shaft
Counterweights
Finder scope
Finder scope bracket
Eyepiece
Focus knob
Tube rings
Right ascension
setting‑circle
Right ascension lock‑lever
Counterweight lock knobs
“Toe Saver”
Tripod leg
Leg lock lever
Mirror cell
Latitude scale
Latitude adjustment L‑bolts
Center support shaft
(not‑shown)
Hand controller
Tripod support tray
Figure 1a. The Atlas 10 EQ.
2
Page 3

Congratulations on your purchase of a quality Orion telescope. Your new Atlas 10 EQ is designed for
high‑resolution viewing of astronomical objects. With its precision optics, and its superb Atlas mount,
you’ll be able to locate and enjoy thousands of fascinating celestial denizens, including planets, Moon,
and a variety of galaxies, nebulas and star clusters. The built in dual internal DC stepper motor drives will
easily track these objects as they move through the night sky.
These instructions will help you set up and properly use your telescope. Please read them over thor‑
oughly before getting started.
Table of Contents
1. Unpacking........................ 3
2. Parts List......................... 3
3. Assembly ........................ 3
4. Balancing the Telescope............. 5
5. Using Your Telescope ............... 6
6. Setting Up and Using the
Equatorial Mount................... 7
7. Collimating ...................... 12
8. Astronomical Observing ............ 14
9. Astrophotography ................. 17
10. Care and Maintenance ............. 18
11. Specifications .................... 19
1. Unpacking
The entire telescope will arrive in three boxes, one contain‑
ing the tripod, one containing the equatorial mount, and the
third box containing the optical tube. Be careful unpacking the
boxes. We recommend keeping the boxes and original pack‑
aging. In the event that the telescope needs to be shipped to
another location, or returned to Orion for warranty repair, hav‑
ing the proper packaging will ensure that your telescope will
survive the journey intact.
Make sure all the parts in the Parts List are present. Be
sure to check each box carefully, as some parts are small.
If anything appears to be missing or broken, immediate‑
ly call Orion Customer Support (800‑676‑1343) or email
support@telescope.com for assistance.
2. Parts List
Box #1
1 Tripod
3 Counterweights
1 Tripod support tray
Box #2
1 Equatorial mount
1 Hand controller
1 Battery pack
1 Nylon hook‑and‑loop adhesive strip
Box #3
1 Optical tube
2 Tube rings
1 Tube ring mounting plate
1 25mm Sirius Plössl eyepiece
1 10mm Sirius Plössl eyepiece
1 9x50 Finder scope
1 Finder scope bracket with O‑ring
1 Collimation cap
1 Camera adapter
1 Dust cover
WARNING: Never look directly at the Sun
through your telescope or its finder scope—even
for an instant—without a professionally made
solar filter that completely covers the front of
the instrument, or permanent eye damage could
result. Young children should use this telescope
only with adult supervision.
3. Assembly
1. Stand the tripod legs upright and spread the legs out as
far as they will go. Make certain that the leg lock levers are
tightened. Assembly should take no more than 30 minutes.
Refer to Figure 1 during assembly. Assembling the tele‑
scope requires no tools other than the ones provided.
2. Place the base of the equatorial mount onto the tripod
head. Orient the equatorial mount so that the post on the
tripod head lines up with the azimuth adjustment knobs on
the equatorial mount (Figure 2). You may need to loosen
3
Page 4
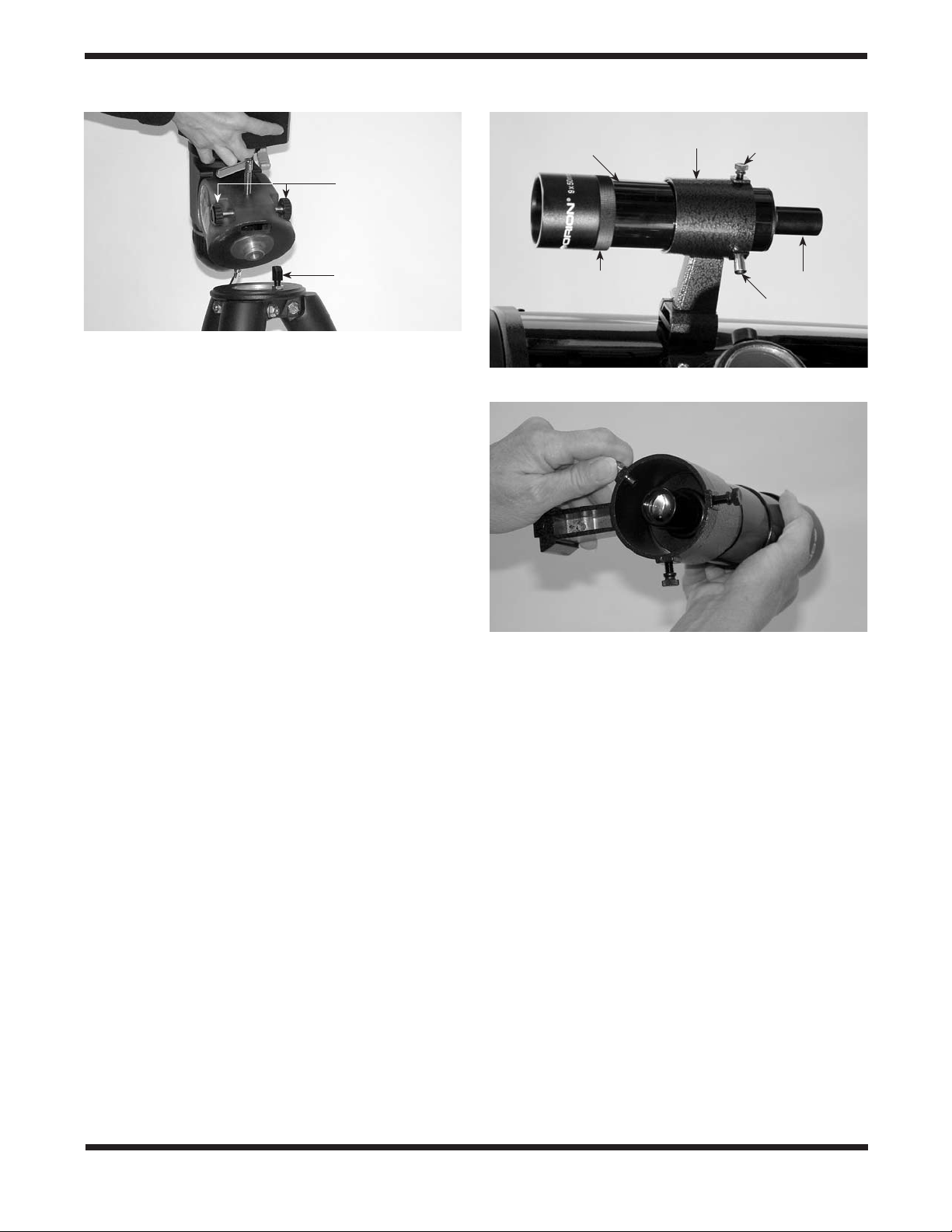
Azimuth
adjustment
knobs
Finder
scope
Finder scope
bracket
Nylon alignment
thumbscrew (2)
Post
Figure 2. Orient the equatorial head so that the post on the tripod
lines up with the azimuth adjustment knobs on the equatorial mount.
the azimuth adjustment knobs on the equatorial mount in
order to fit the mount onto the tripod head.
3. Thread the central support shaft into the equatorial mount
until tight. This will secure the equatorial mount to the tri‑
pod head.
4. Remove the knob and washer from the bottom of the cen‑
ter support shaft. Slide the tripod support tray up the bot‑
tom of the central support shaft until the three tray arms
are touching the legs of the tripod. The flat side of the sup‑
port tray should be facing up. Make sure the “V” of each
tray arm is against a tripod leg. Place the knob washer on
the center support shaft against the tray, and follow it by
threading the securing knob all the way up the center sup‑
port shaft until it is tight against the tray. The tripod support
tray provides additional stability for the tripod, and holds
up to five 1.25" eyepieces and two 2" eyepieces.
5. Loosen the counterweight shaft lock lever and let the
counterweight shaft extend into its downward position.
Retighten the lock lever.
6. Remove the knurled “toe saver” retaining screw on the
bottom of the counterweight shaft and slide all three coun‑
terweights onto the shaft. Make sure the counterweight
lock knobs are adequately loosened to allow the counter‑
weight shaft to pass through the hole. Position the coun‑
terweights about halfway up the shaft and tighten the lock
knobs. Replace the toe saver at the end of the bar. The toe
saver prevents the counterweights from falling on your foot
if the lock knobs happen to come loose.
7. Loosen and open the tube rings on the optical tube and
remove the optical tube from the tube rings. Attach the
tube rings to the mounting plate with the provided screws.
Loosen the two mounting plate securing knobs. Place the
mounting plate, with the tube rings attached, in the dove‑
tail slot on top of the equatorial mount. Position the mount‑
ing plate so that it is centered on the dovetail slot. Re‑tight‑
en the mounting plate securing knobs until the mounting
plate is secure.
8. Open the tube rings and lay the telescope optical tube in
the rings at about the midpoint of the tube’s length. Rotate
Focusing lock ring
Eyepiece
Tensioner
Figure 3a. The 9x50 finder scope and bracket.
Figure 3b. Pull back on the tensioner and slide the finder scope
into its bracket until the O‑ring is seated in the bracket ring.
the tube so that the focuser is at a convenient height for
viewing. Close the tube rings and tighten them.
9. Insert the plug on the end of the control cable from the
hand controller into its jack on the side of the equatorial
mount.
10. Insert eight D‑cell batteries into the battery pack. Orient
the batteries as indicated on the white plastic battery hold‑
er. Plug the battery cord into its jack on the mount.
11. Two strips of nylon adhesive (one strip of “hooks” and one
strip of “loops”) have been provided so you can create a
place to keep the hand controller out of the way when not in
use. Place the “hooks” strip of nylon adhesive on the back
of the hand controller and the “loops” strip on a tripod leg
or on the mount where it will be in a conveniently reached
spot. Simply hang the hand controller by the nylon adhe‑
sive when it is not in use. Make certain when you attach
the nylon adhesive to the mount that the hand controller’s
position will not interfere with the motion of the mount.
Installing the Finder Scope
To place the finder scope (Figure 3a) in the finder scope brack‑
et, unthread the two black nylon thumbscrews until the screw
ends are flush with the inside diameter of the bracket. Place
4
Page 5

1.25" eyepiece
adapter
2" eyepiece adapter
Focus lock
thumbscrew
Focus
knobs
Collimation
screw pair
(3)
Figure 4. The 2" focuser of the Atlas 10 EQ.
the O‑ring that comes on the base of the bracket over the body
of the finder scope until it seats into the slot on the middle of
the finder scope. Slide the eyepiece end (narrow end) of the
finder scope into the end of the bracket’s cylinder opposite
the alignment screws while pulling the chrome, spring‑loaded
tensioner on the bracket with your fingers (Figure 3b). Push
the finder scope through the bracket until the O‑ring seats
just inside the front opening of the bracket cylinder. Release
the tensioner and tighten the two black nylon thumbscrews
a couple of turns each to secure the finder scope in place.
Insert the base of the finder scope bracket into the dovetail
holder on the top of the focuser. Lock the bracket into position
by tightening the knurled thumbscrew on the dovetail holder.
Inserting the Eyepiece
Loosen the thumbscrew on the 1.25" adapter (Figure 4) and
remove the small dust cap. Insert the 25mm eyepiece into the
focuser and secure it with the thumbscrew.
Your Atlas 10 EQ is now fully assembled and should resemble
Figure 1.
Note about the Atlas 10 EQ Mount Weight
The Atlas 10 EQ mount is very heavy. Alone it weighs 54 lbs.
With the optical tube and counterweights it weighs over 120
lbs. Keep this in mind when moving the telescope even small
distances, and use assistance when needed. It is best to
remove the optical tube and counterweights when moving the
mount, or adjusting the length of the tripod legs.
4. Balancing the Telescope
To ensure smooth movement of the telescope on both axes
of the equatorial mount, it is imperative that the optical tube
is properly balanced. We will first balance the telescope with
respect to the right ascension (R.A.) axis, then the declination
(Dec.) axis.
1. Keeping one hand on the telescope optical tube, loosen
the R.A. lock lever. Make sure the Dec. lock lever is locked,
for now. The telescope should now be able to rotate freely
a. b.
c. d.
Figure 5a-d. Proper operation of the equatorial mount requires
that the telescope tube be balanced on the R.A. and Dec. axes. (a)
With the R.A. lock lever released, slide the counterweights down
the counterweight shaft until they just counterbalance the telescope
tube. (b) When you let go with both hands, the tube should not drift
up or down (c) with the Dec. lock lever released, loosen the tube ring
lock clamps a few turns and slide the telescope forward or back in
the tube rings. (d) When the tube is balanced about the Dec. axis, it
will not move when you let go.
about the right ascension axis. Rotate it until the counter‑
weight shaft is parallel to the ground (i.e., horizontal).
2. Now loosen the counterweight lock knobs and slide the
weights along the shaft until they exactly counterbalance
the telescope (Figure 5a). That’s the point at which the
shaft remains horizontal even when you let go with both
hands (Figure 5b).
3. Retighten the counterweight lock knobs. The telescope is
now balanced on the right ascension axis.
4. To balance the telescope on the declination axis, first
tighten the R.A. lock lever, with the counterweight shaft
still in the horizontal position.
5. With one hand on the telescope optical tube, loosen the
Dec. lock lever. The telescope should now be able to rotate
freely about the declination axis.
6. Loosen the knurled ring clamps on the tube rings a few
turns, until you can slide the telescope tube forward and
back inside the rings (this can be aided by using a slight
twisting motion on the optical tube while you push or pull
on it) (Figure 5c).
7. Position the telescope in the tube rings so it remains hori‑
zontal when you carefully let go with both hands. This is
the balance point for the optical tube with respect to the
Dec. axis (Figure 5d).
8. Retighten the knurled rings clamps.
The telescope is now balanced on both axes. When you loos‑
en the lock lever on one or both axes and manually point the
telescope, it should move without resistance and should not
drift from where you point it.
5
Page 6

Naked‑eye view
View through finder scope and telescope
Figure 6. The view through a standard finder scope and reflector
telescope is rotated 180°. This is true for the Atlas 10 EQ and its
finder scope as well.
5. Using Your Telescope
Focusing the Telescope
With the 25mm eyepiece inserted in the focuser, loosen the
R.A. and Dec.lock levers and move the telescope so the front
(open) end is pointing in the general direction of an object at
least 1/4‑mile away. Now, with your fingers, slowly rotate one
of the focusing knobs until the object comes into sharp focus.
Go a little bit beyond sharp focus until the image just starts to
blur again, then reverse the rotation of the knob, just to make
sure you’ve hit the exact focus point.
NOTE: The image in the telescope will appear rotated
180° (upside down and reversed left-to-right). This is normal for astronomical scopes. The finder scope view will
also be rotated 180° (see Figure 6).
tion and the 50 indicates a 50mm diameter front lens. The
finder scope makes it easier to locate the object you want
to observe in the telescope, because the finder scope has a
much wider field‑of‑view.
The Atlas 10 EQ’s finder scope uses a spring‑loaded bracket
that makes alignment of the finderscope very easy. As you
turn either of the thumbscrews, the spring in the bracket’s ten‑
sioner moves in and out to keep the finder scope secure in
the bracket.
The finder scope must be aligned accurately with the tele‑
scope for proper use. To align it, first aim the main telescope
in the general direction of an object at least a 1/4 mile away—
the top of a telephone pole, a chimney, etc. Loosen the R.A.
and Dec. lock levers and move the telescope until it is pointing
toward the desired object. Then sight along the tube to pre‑
cisely aim the telescope. Turn the focus knob until the object
is properly focused. Retighten the lock levers.
Now look in the finder scope. Is the object visible? Ideally it
will be somewhere in the field of view. If not, some coarse
adjustment to the finder scope bracket’s alignment thumb‑
screws will be needed until the object comes into the finder
scope’s field of view.
With the image in the finder scope’s field of view, you now
need to fine‑adjust the alignment thumbscrews to center the
object on the intersection of the crosshairs. Adjust the aim of
the finder scope by turning the thumbscrews, one at a time,
until the object is centered.
The finder scope alignment needs to be checked before
every observing session. This can easily be done at night,
before viewing through the telescope. Choose any bright star
or planet, center the object in telescope eyepiece, and then
adjust the finder scope bracket’s alignment thumbscrews until
the star or planet is centered on the finder’s crosshairs.
If you have trouble focusing, rotate the focusing knob so the
drawtube is in as far as it will go. Now look through the eyepiece
while slowly rotating the focusing knob in the opposite direction.
You should soon see the point at which focus is reached.
The black nylon thumbscrew on the top of the body of the
focuser (see Figure 4) will lock the focuser drawtube in place
once the telescope is properly focused. Before focusing,
remember to first loosen this thumbscrew.
Viewing with Eyeglasses
If you wear eyeglasses, you may able to keep them on while
you observe, if the eyepiece has enough “eye relief” to allow
you to see the whole field of view. You can try this by looking
through the eyepiece first with your glasses on, and then with
them off, and see if the glasses restrict the view to only a
portion of the full field. If they do, you can easily observe with
your glasses off by just re‑focusing the telescope the needed
amount. If you suffer from severe astigmatism, however, you
may find images noticeably sharper with your glasses on.
Aligning the Finder Scope
The Atlas 10 EQ Deluxe comes with a 9x50 achromatic finder
scope (Figure 3a). The number 9 means six‑times magnifica‑
6
Focusing the finder scope
If, when you look through the finder scope, the images appear
somewhat out of focus, you will need to refocus the finder
scope for your eyes. Loosen the lock ring located behind the
objective lens cell on the body of the finder scope (see Figure
3a). Back the lock ring off by a few turns, for now. Refocus
the finder scope on a distant object by threading the objec‑
tive lens cell in or out of the finderscope body. Precise focus‑
ing will be achieved by focusing the finder scope on a bright
star. Once the image appears sharp, retighten the locking ring
behind the objective lens cell. The finder scope’s focus should
not need to be adjusted again.
Magnification & Eyepieces
Magnification, or power, is determined by the focal length of
the telescope and the focal length of the eyepiece. Therefore,
by using eyepieces of different focal lengths, the resultant
magnification can be varied.
Magnification is calculated as follows:
Telescope Focal Length (mm)
Eyepiece Focal Length (mm)
= Magnification
Page 7

Dec. lock lever
Right
Ascension
(R.A.) axis
Declination (Dec.) axis
Dec. setting circle
R.A.
setting‑circle
Front opening
Azimuth adjustment knobs (2)
Figure 7.
The Atlas 10 EQ has a focal length of 1200mm, which when
used with the supplied 25mm eyepiece yields a magnification
of:
1200mm
25mm
The magnification provided by the 10mm eyepiece is:
1200mm
10mm
The maximum attainable magnification for a telescope is
directly related to how much light it can gather. The larger the
aperture, the more magnification is possible. In general a fig‑
ure of 60x per inch of aperture is the maximum attainable
for most telescopes. Your Atlas 10 EQ has an aperture of 10
inches, so the maximum magnification would be about 600x.
This level of magnification assumes you have ideal conditions
for viewing.
Keep in mind that as you increase magnification, the bright‑
ness of the object viewed will decrease; this is an inherent
principle of the laws of physics and cannot be avoided. If
magnification is doubled, an image appears four times dim‑
mer. If magnification is tripled, image brightness is reduced
by a factor of nine!
Always start with your lowest power eyepiece and work your
way up. Start by centering the object being viewed in the 25mm
eyepiece. Then you may want to increase the magnification
to get a closer view. If the object is off‑center (i.e., it is near
the edge of the field of view) you will lose it when you increase
magnification since the field of view will be narrower with the
higher‑powered eyepiece. To change eyepieces, first loosen
the securing thumbscrew on the focuser’s 1.25" adapter. Then
carefully lift the eyepiece out of the holder. Do not tug or pull the
eyepiece to the sides, as this will knock the telescope off its tar‑
get. Replace the eyepiece with the new one by sliding it gently
= 48x
= 120x
R.A. lock lever
Polar axis
finder‑scope
Latitude scale
Latitude
adjustment
L‑bolts
The Atlas EQ Mount.
into the holder. Re‑tighten the thumbscrew, and refocus for your
new magnification.
Using 2" eyepieces
The Atlas 10 EQ’s focuser is capable of accepting optional 2"
eyepieces. To use 2" eyepieces you must remove the 1.25"
adapter from the focuser by loosening the two thumbscrews
that hold it in place (Figure 4). Once this adapter is removed,
insert a 2" eyepiece into the focuser and use the same thumb‑
screws to secure the larger eyepiece. 2" eyepieces typically
provide a wider field of view than 1.25" eyepieces.
6. Setting Up and Using the
Equatorial Mount
When you look at the night sky, you no doubt have noticed that
the stars appear to move slowly from east to west over time.
That apparent motion is caused by the Earth’s rotation (from
west to east). An equatorial mount (Figure 7) is designed to
compensate for that motion, allowing you to easily “track” the
movement of astronomical objects, thereby keeping them
from drifting out of your telescope’s field of view while you’re
observing.
This is accomplished by slowly rotating the telescope on its
right ascension (R.A.) axis, using the built in motor drive. But
first the R.A. axis of the mount must be aligned with the Earth’s
rotational (polar) axis—a process called polar alignment.
Polar Alignment
For Northern Hemisphere observers, approximate polar align‑
ment is achieved by pointing the mount’s right ascension axis
at the North Star, or Polaris. It lies within 1° of the north celes‑
tial pole (NCP), which is an extension of the Earth’s rotational
7
Page 8

Little Dipper
(in Ursa Minor)
Eyepiece
focus ring
Alignment
setscrew (3)
Focus
lock ring
Objective
lens
Big Dipper
(in Ursa Major)
Pointer
Stars
N.C.P.
Polaris
Cassiopeia
Figure 8. To find Polaris in the night sky, look north and find the
Big Dipper. Extend an imaginary line from the two “Pointer Stars”
in the bowl of the Big Dipper. Go about five times the distance
between those stars and you'll reach Polaris, which lies within 1° of
the north celestial pole (NCP).
axis out into space. Stars in the Northern Hemisphere appear
to revolve around the NCP.
To find Polaris in the sky, look north and locate the pattern
of the Big Dipper (Figure 8). The two stars at the end of the
“bowl” of the Big Dipper point right to Polaris.
Observers in the Southern Hemisphere aren’t so fortunate to
have a bright star so near the south celestial pole (SCP). The
star Sigma Octantis lies about 1° from the SCP, but it is barely
visible with the naked eye (magnitude 5.5).
For general visual observation, an approximate polar align‑
ment is sufficient.
1. Level the equatorial mount by adjusting the length of the
three tripod legs. For your safety, remove the optical tube
and counterweights when doing this.
2. There are two altitude adjusting L‑bolts (see Figure 7);
loosen one while tightening the other. By doing this you
will adjust the latitude of the mount. Continue adjusting the
mount until the pointer on the latitude scale is set at the
latitude of your observing site. If you don’t know your lati‑
tude, consult a geographical atlas to find it. For example,
if your latitude is 35° North, set the pointer to 35. The lati‑
tude setting should not have to be adjusted again unless
you move to a different viewing location some distance
awa y.
3. Loosen the Dec. lock lever and rotate the telescope’s opti‑
cal tube until it is parallel with the right ascension axis, as
it is in Figure 7.
4. Move the tripod so the telescope tube and right ascen‑
sion axis point roughly at Polaris. If you cannot see Polaris
directly from your observing site, consult a compass and
rotate the tripod so the telescope points north.
The equatorial mount is now polar aligned for casual observ‑
ing. More precise polar alignment is recommended for astro‑
photography. For this we recommend using the optional polar
axis finder scope
From this point on in your observing session, you should not
make any further adjustments to the latitude of the mount,
Figure 9. The optional polar axis finder scope.
nor should you move the tripod. Doing so will undo the polar
alignment. The telescope should be moved only about its R.A.
and Dec. axes.
Using the Polar Axis Finder Scope
The Atlas EQ mount comes with a polar axis finder scope
(Figure 9) housed inside the right ascension axis of the
mount. When properly aligned and used, it makes accurate
polar alignment quick and easy to do.
Alignment of the Polar Axis Finder Scope
1. Loosen the Dec. lock lever and rotate the optical tube on
the declination axis so that the tube is at a 90° to the right
ascension axis (Figure 10). Tighten the Dec. lock lever.
2. Look through the polar finder at a distant object (during
the day) and center it on the crosshairs. You may need to
adjust the latitude adjustment L‑bolts and the tripod posi‑
tion to do this.
3. Rotate the mount 180° about the R.A. axis. It may be con‑
venient to remove the counterweights and optical tube
first.
4. Look through the polar finder again. Is the object being
viewed still centered on the crosshairs? If it is, then no
further adjustment is necessary. If not, then look through
the polar finder while rotating the mount about the R.A.
axis. You will notice that the object you have previously
centered moves in a circular path. Use the three alignment
setscrews on the polar axis finder (Figure 9) to redirect the
crosshairs of the polar finder to the apparent center of this
circular path. Repeat this procedure until the position that
the crosshairs point to does not rotate off‑center when the
mount is rotated in R.A.
The polar axis finder scope is now ready to be used. When
not in use, replace the plastic protective cover to prevent the
polar finder from getting bumped.
Using the Polar Axis Finder Scope
The reticle of the polar axis finder scope for the Atlas has a
tiny star map printed on it that makes precise polar alignment
8
Page 9

Power switch Rate switch
Indicator light
Reverse
switches
Figure 10. The optical tube must be at a 90° angle to the R.A.
axis in order to view through the polar axis finder.
quick and easy. To align the mount using the polar axis finder
scope, follow these instructions:
1. Approximately polar‑align the mount as outlined in the pre‑
vious alignment procedure.
2. Loosen the Dec. lock lever and rotate the optical tube on
the declination axis so that the tube is at a 90° to the right
ascension axis (Figure 10). Tighten the Dec. lock lever.
3. Remove the cap on the front opening of the equatorial
mount (Figure 7). Focus the polar finder by rotating the
eyepiece. Now, sight Polaris in the polar axis finder scope.
If you have followed the approximate polar alignment pro‑
cedure accurately, Polaris will probably be within the field
of view. If not, move the tripod left‑to‑right, and adjust the
latitude up‑and down until Polaris is somewhere within the
field of view of the polar axis finder scope.
4. Flip the power switch on the hand controller (Figure 11)
to the N or S position. With the power on, you can now
use the illuminator on the polar axis reticle. Look through
the polar axis finder and adjust the illuminator by turning
the small dial on the mount (located above the power and
hand controller jacks) counter‑clockwise to make it bright‑
er, and clockwise to make it dimmer. Use the dimmest
possible setting that allows you to see the reticle without
difficulty. Note the constellation Cassiopeia and the Big
Dipper in the reticle. They do not appear in scale, but they
indicate the general positions of Cassiopeia and the Big
Dipper relative to the north celestial pole (which is indi‑
cated by the cross at the center of the reticle). Rotate the
reticle so the constellations depicted match their current
orientation in they sky when viewed with the naked eye.
To do this, release the R.A. lock lever and rotate the main
telescope around the R.A. axis until the reticle is oriented
with sky. You may need to remove the tube from the mount
to prevent it from bumping into the mount. Once the reticle
is correctly oriented, use the right ascension lock lever to
secure the mount’s position.
5. Now use the azimuth adjustment knobs (Figure 2) and
the latitude adjustment L‑bolts (Figure 7) on the mount
to position the star Polaris inside the tiny circle marked
R.A.
pushbuttons
Dec.
pushbuttons
Figure 11. The Atlas EQ Mount hand controller.
“Polaris” on the finder’s reticle. You must first loosen the
knob underneath the equatorial mount on the center sup‑
port shaft to use the azimuth adjustment knobs. Once
Polaris is properly positioned within the reticle, you are
precisely polar aligned.
If you do not have a clear view of Polaris from your observing
site, you will not be able to use the polar axis finder to pre‑
cisely polar align the telescope.
From this point on in your observing session, you should not
make any fur ther adjustments in the azimuth or the latitude
of the mount, nor should you move the tripod. Doing so will
undo the polar alignment. The telescope should be moved
only about its right ascension and declination axes.
Additional Note Regarding Focusing the Polar
Axis Finder Scope
The polar axis finder scope is normally focused by simply
rotating the eyepiece focus ring. However, if after adjusting
the focus ring you find that the image of the reticle is sharp,
but the stars are out of focus, then you must adjust the focus
of the polar axis finder’s objective lens. To do this, first remove
the polar axis finder from the mount. Look through the polar
axis finder at a star (at night) or distant object at least 1/4 mile
away (during daylight). Use the eyepiece focus ring to bring
the reticle into sharp focus. Now, loosen the focus lock ring
(Figure 9) and thread the entire objective end of the finder
inwards or outwards until images appear sharp. Re‑tighten
the focus lock ring. Once the polar axis finder’s objective lens
is focused, it should not need to be adjusted again.
Operation of the Atlas Mount Motor Drives
The Atlas EQ mount comes with dual built‑in motor drives.
These motor drives will be used to “track” objects in the night
sky, as well as to make small adjustments when aiming the
telescope. The motors are controlled from the hand controller
(Figure 11). To start the drives, flip the power switch on the
hand controller to “N” if you live in the northern hemisphere,
or “S” if you live in the southern hemisphere. When you flip
9
Page 10

the power switch, the power indicator light on the mount will
glow red and the power indicator light on the hand controller
will glow green. Your mount will now be moving at the sidereal
rate, which is the same rate as the sky’s apparent motion. If
the mount is properly polar aligned, it is now “tracking” the
motion of astronomical objects as the Earth rotates.
To move your telescope to a new object, loosen both the
R.A. and Dec. lock levers and move the telescope until it is
pointed in the general direction of the object you wish to view.
Retighten the R.A and Dec. lock levers. To center the object
in the eyepiece’s field of view, you will usually need to use the
hand controller.
There are four pushbuttons on the hand controller. If no but‑
tons are pushed, the R.A. motor will turn the R.A. axis at side‑
real rate to track the motion of the night sky. The left and right
buttons move the mount about its R.A. axis, and the up and
down buttons move the mount about its Dec. axis. The rate of
speed is determined by the rate switch at the top right of the
hand controller. If the switch is at the 2x position, the mount
will move at two times sidereal rate when the right hand but‑
ton is pushed, which will cause objects to viewed in the eye‑
piece to move slowly eastward. If the left button is pushed,
the drive will stop turning, which will cause objects in the eye‑
piece to move slowly westward. The top and bottom bottoms
will cause the telescope to move north and south in declina‑
tion at the 2x speed. Similarly, if the switch is at the 8x or
16x position, the mount will move eight times or sixteen times
sidereal rate when a button is pushed.
The 2x sidereal rate is the best setting for making guiding
corrections during long‑exposure astrophotography. The 8x
and 16x rates are best for centering an object within the tele‑
scope’s eyepiece.
Whenever any of the four buttons on the hand controller are
pressed, the LED in the center of the controller will shine red;
when the button is released, the LED will be green. Also, when
the LED starts to blink at a constant rate, its time to change
the batteries in the battery pack.
Using the R.A. and Dec. Reversal Switches
On the side of the hand controller, there are two reversal
switches, one for the R.A. axis, and one for the Dec. axis. When
these switches are flipped to the “REV” setting, the function of
the pushbuttons on the hand controller will be reversed. The
reversal switches allow you to orient the pushbuttons to the
direction of the apparent movement of a guide star in a guide
scope for astrophotography.
Understanding the Setting Circles
The setting circles on an equatorial mount (Figure 12) enable
you to locate celestial objects by their “celestial coordinates”.
Every object resides in a specific location on the “celestial
sphere”. That location is denoted by two numbers: its right
ascension (R.A.) and declination (Dec.). In the same way,
every location on Earth can be described by its longitude and
latitude. Right ascension is similar to longitude on Earth, and
declination is similar to latitude. The R.A. and Dec. values for
Dec. setting circle
Dec. setting circle
thumbscrew (2)
Dec. indicator arrow
R.A. setting circle
R.A. indicator arrow
R.A. setting circle
thumbscrew (2)
Figure 12. The R.A. and Dec. setting circles.
celestial objects can be found in any star atlas or star cata‑
log.
The R.A. setting circle is scaled in hours, from 1 through 24,
with small marks in between representing 10‑minute incre‑
ments (there are 60 minutes in 1 hour of right ascension).
The lower set of numbers apply to viewing in the Northern
Hemisphere, while the numbers above them apply to viewing
in the Southern Hemisphere.
The Dec. setting circle is scaled in degrees, with each mark
representing 2° increments. Values of declination coordinates
range from +90° to ‑90°. The 0° mark indicates the celestial
equator. When the telescope is pointed north of the celestial
equator, values of the declination setting circle are positive;
when the telescope is pointed south of the celestial equator,
values of the declination setting circle are negative.
So, the coordinates for the Orion Nebula listed in a star atlas
will look like this:
R.A. 5h 35.4m Dec. – 5° 27'
That’s 5 hours and 35.4 minutes in right ascension, and –5
degrees and 27 arc‑minutes in declination (there are 60 arc‑
minutes in 1 degree of declination).
Before you can use the setting circles to locate objects, the
mount must be accurately polar aligned, and the setting cir‑
cles must be calibrated.
Calibrating the Declination Setting Circle
1. Loosen the Dec. lock lever and position the telescope as
accurately as possible in declination so it is parallel to the
R.A. axis as shown in Figure 7. Re‑tighten the lock lever.
2. Loosen one of the thumbscrews on the Dec. setting circle,
this will allow the setting circle to rotate freely. Rotate the
10
Page 11

a. b. c. d.
Figure 13a-d. These illustrations show the telescope pointed in the four cardinal directions. (a) north, (b) south, (c) east, (d) west. Note
that the tripod and mount have not been moved; only the telescope has been moved on the its R.A. and Dec. axes.
Dec. setting circle until the pointer reads exactly 90°. Re‑
tighten the setting circle thumbscrew.
Calibrating the Right Ascension Setting Circle
1. Identify a bright star in the sky near the celestial equa‑
tor (declination = 0°) and look up its coordinates in a star
atlas.
2. Loosen the R.A. and Dec. lock levers on the equatorial
mount, so the telescope optical tube can move freely.
3. Point the telescope at the bright star whose coordinates
you know. Lock the R.A. and Dec. lock levers. Center the
star in the telescope’s field of view with the hand control‑
ler.
4. Loosen one of the R.A. setting circle thumbscrews (see
Figure 12) this will allow the setting circle to rotate freely.
Rotate the setting circle until the R.A. pointer arrow indi‑
cates the R.A. coordinate listed in the star atlas for the
object. Re‑tighten the setting circle thumbscrew.
Finding Objects With the Setting Circles
Now that both setting circles are calibrated, look up in a star
atlas the coordinates of an object you wish to view.
1. Loosen the Dec. lock lever and rotate the telescope until
the declination value from the star atlas matches the read‑
ing on the Dec. setting circle. Remember that values of the
Dec. setting circle are positive when the telescope is point‑
ing north of the celestial equator (Dec. = 0°), and negative
when the telescope is pointing south of the celestial equa‑
tor. Retighten the lock lever.
2. Loosen the R.A. lock lever and rotate the telescope until
the right ascension value from the star atlas matches the
reading on the R.A. setting circle. Remember to use the
lower set of numbers on the R.A. setting circle. Retighten
the lock lever.
Most setting circles are not accurate enough to put an object
dead‑center in the telescope’s eyepiece, but they should
place the object somewhere within the field of view of the find‑
er scope, assuming the equatorial mount is accurately polar
aligned. Use the hand controller to center the object in the
finder scope, and it should appear in the telescope’s field of
view.
The setting circles should be re‑calibrated every time you wish
to locate a new object. Do so by calibrating the setting circles
for the centered object before moving on to the next one.
Confused About Pointing the Telescope?
Beginners occasionally experience some confusion about
how to point the telescope overhead or in other directions. In
Figure 1 the telescope is pointed north as it would be during
polar alignment. The counterweight shaft is oriented down‑
ward. But it will not look like that when the telescope is pointed
in other directions. Let’s say you want to view an object that is
directly overhead, at the zenith. How do you do it?
DO NOT make any adjustment to the latitude adjustment L‑
bolts. That will spoil the mount’s polar alignment. Remember,
once the mount is polar aligned, the telescope should be
moved only on the R.A. and Dec. axes. To point the scope
overhead, first loosen the R.A. lock lever and rotate the tele‑
scope on the right ascension axis until the counterweight
shaft is horizontal (parallel to the ground). Then loosen the
Dec. lock lever and rotate the telescope until it is pointing
straight overhead. The counterweight shaft is still horizontal.
Then retighten both lock levers.
What if you need to aim the telescope directly north, but at
an object that is nearer to the horizon than Polaris? You can’t
do it with the counterweights down as pictured in Figure 1.
Again, you have to rotate the scope in right ascension so that
the counterweight shaft is positioned horizontally. Then rotate
the scope in declination so it points to where you want it near
the horizon.
To point the telescope directly south, the counterweight shaft
should again be horizontal. Then you simply rotate the scope
on the declination axis until it points in the south direction.
To point the telescope to the east or west, or in other direc‑
tions, you rotate the telescope on its right ascension and dec‑
lination axes. Depending on the altitude of the object you want
to observe, the counterweight shaft will be oriented some‑
where between vertical and horizontal.
Figure 13 illustrates how the telescope will look when pointed
at the four cardinal directions: north, south, east and west.
The key things to remember when pointing the telescope are
that a) you only move it in right ascension and declination, not
in azimuth or latitude (altitude), and b) the counterweight and
11
Page 12

shaft will not always appear as it does in Figure 1. In fact it
almost never will!
7. Collimating
(Aligning The Mirrors)
Collimating is the process of adjusting the mirrors so they are
aligned with one another. Your telescope’s optics were aligned
at the factory, and should not need much adjustment unless
the telescope is handled roughly. Accurate mirror alignment is
important to ensure the peak performance of your telescope,
so it should be checked regularly. Collimating is relatively
easy to do and can be done in daylight.
To check collimation, remove the eyepiece and look down the
focuser drawtube. You should see the secondary mirror cen‑
tered in the drawtube, as well as the reflection of the primary
mirror centered in the secondary mirror, and the reflection of
the secondary mirror (and your eye) centered in the reflection
of the primary mirror, as in Figure 14a. If anything is off‑cen‑
ter, as in Figure 14b, proceed with the following collimating
procedure.
Note About the 2" Focuser
The Atlas 10 EQ’s 2" focuser can be collimated by 3 pairs
of push‑pull screws located on the ring at the base of the
focuser (Figure 4). The focuser was collimated at the factory
and should never need to be adjusted. Focuser collimating
is only required under very rare circumstances but has been
made available for this telescope should such a need arise.
a.
b.
c.
The Collimation Cap and Mirror Center Mark
Your Atlas 10 EQ comes with a collimation cap. This is a sim‑
ple cap that fits on the focuser drawtube like a dust cap, but
has a hole in the center and a silver bottom. This helps center
your eye so that collimating is easy to perform. Figures 14b
through 14e assume you have the collimation cap in place.
In addition to the collimation cap, the primary mirror is marked
with a circle at its exact center. This “center mark” allows you
to achieve a precise collimation of the primary mirror; you
don’t have to guess where the center of the mirror is. You
simply adjust the mirror position (described below) until the
reflection of the hole in the collimation cap is centered in the
ring. The center mark is also required for best results when
using other collimating devices, such as Orion’s LaserMate
Laser Collimator, obviating the need to remove the primary
mirror and mark it yourself.
Note: The center ring sticker need not ever be removed
from the primary mirror. Because it lies directly in the
shadow of the secondary mirror, its presence in no way
adversely affects the optical performance of the telescope or the image quality. That might seem counterintuitive, but its true!
Aligning the Secondary Mirror
With the collimation cap in place, look through the hole in the
cap at the secondary (diagonal) mirror. Ignore the reflections
d.
Figure 14. Collimating the optics. (a) When the mirrors are
properly aligned, the view down the focuser drawtube should look
like this (b) With the collimation cap in place, if the optics are out
of alignment, the view might look something like this. (c) Here, the
secondary mirror is centered under the focuser, but it needs to be
adjusted (tilted) so that the entire primary mirror is visible. (d) The
secondary mirror is correctly aligned, but the primary mirror still needs
adjustment. When the primary mirror is correctly aligned, the “dot” will
be centered, as in (e).
for the time being. The secondary mirror itself should be cen‑
tered in the focuser drawtube, in the direction parallel to the
length of the telescope. If it isn’t, as in Figure 14b, it must be
adjusted. This adjustment will rarely, if ever need to be done.
It helps to adjust the secondary mirror in a brightly lit room
with the telescope pointed towards a bright surface, such as
white paper or wall. Also placing a piece of white paper in
the telescope tube opposite the focuser (in other words, on
the other side of the secondary mirror) will also be helpful in
collimating the secondary mirror. Using a 2mm hex wrench,
e.
12
Page 13

15. 16.
Figure 15. To center the secondary mirror under the focuser,
hold the secondary mirror holder in place with your fingers while
adjusting the center screw with a Phillips screwdriver. Do not touch
the mirror’s surface!
Figure 16. Adjust the tilt of the secondary mirror by loosening or
tightening the three alignment screws with a 2mm Allen wrench.
loosen the three small alignment set screws in the center hub
of the 4‑vaned spider several turns. Now keep the mirror’s
holder stationary (be careful not to touch the surface of the
mirrors), while turning the center screw with a Phillips head
screwdriver (See Figure 15). Turning the screw clockwise will
move the secondary mirror toward the front opening of the
optical tube, while turning the screw counter‑clockwise will
move the secondary mirror toward the primary mirror.
Note: When making these adjustments, be careful not to
stress the spider vanes or they may bend.
Figure 17. The three thumb screws that lock the primary mirror in
place must first be loosened before any adjustments can be made.
When the secondary mirror is centered in the focuser draw‑
tube, rotate the secondary mirror holder until the reflection of
the primary mirror is as centered in the secondary mirror as
possible. It may not be perfectly centered, but that is OK. Now
tighten the three small alignment screws equally to secure the
secondary mirror in that position. This adjustment will rarely, if
ever need to be done.
If the entire primary mirror reflection is not visible in the sec‑
ondary mirror, as in Figure 14c; you will need to adjust the tilt
of the secondary mirror. This is done by alternately loosen‑
ing one of the three alignment set screws while tightening the
other two, as depicted in Figure 16. The goal is to center the
primary mirror reflection in the secondary mirror, as in Figure
14d. Don’t worry that the reflection of the secondary mirror
(the smallest circle, with the collimation cap “dot” in the cen‑
ter) is off‑center. You will fix that in the next step.
Adjusting the Primary Mirror
The final adjustment is made to the primary mirror. It will need
adjustment if, as in Figure 14d, the secondary mirror is cen‑
tered under the focuser and the reflection of the primary mir‑
ror is centered in the secondary mirror, but the small reflec‑
tion of the secondary mirror (with the “dot” of the collimation
cap) is off‑center.
The tilt of the primary mirror is adjusted with three spring‑
loaded collimation thumbscrews on the back end of the opti‑
cal tube (bottom of the primary mirror cell); these are the
Figure 18. The tilt of the primary mirror is adjusted by turning
one or more of the three spring‑loaded collimation thumb screws.
larger thumbscrews. The other three smaller thumbscrews
lock the mirror’s position in place; these thumbscrews must
be loosened before any collimation adjustments can be made
to the primary mirror.
To start, turn the smaller thumbscrews that lock the primary
mirror in place a few turns each. (Figure 17) Use a screw‑
driver in the slots, if necessary.
Now, try tightening or loosening one of the larger collima‑
tion thumbscrews with your fingers (Figure 18). Look into the
focuser and see if the secondary mirror reflection has moved
closer to the center of the primary. You can tell this easily with
the collimation cap and mirror center mark by simply watch‑
ing to see if the “dot” of the collimation cap is moving closer
or further away from the “ring” on the center of the primary
mirror mark. When you have the dot centered as much as
is possible in the ring, your primary mirror is collimated. The
view through the collimation cap should resemble Figure 15e.
Re‑tighten the locking thumbscrews.
A simple star test will tell you whether the optics are accu‑
rately collimated.
13
Page 14

Figure 19. A star test will determine if a telescope’s optics are
properly collimated. An unfocused view of a bright star through the
eyepiece should appear as illustrated on right if optics are perfectly
collimated. If circle is unsymmetrical, as in illustration on left, scope
needs collimation.
Figure 20. Megrez connects the Big Dipper’s handle to it’s
“pan”. It is a good guide to how conditions are. If you can not see
Megrez (a 3.4 mag star) then conditions are poor.
Star-Testing the Telescope
When it is dark, point the telescope at a bright star and accu‑
rately center it in the eyepiece’s field‑of‑view. Slowly defocus
the image with the focusing knob. If the telescope is correct‑
ly collimated, the expanding disk should be a perfect circle
(Figure 19). If the image is unsymmetrical, the scope is out
of collimation. The dark shadow cast by the secondary mirror
should appear in the very center of the out‑of‑focus circle, like
the hole in a doughnut. If the “hole” appears off‑center, the
telescope is out of collimation.
If you try the star test and the bright star you have selected
is not accurately centered in the eyepiece, then the optics
will always appear out of collimation, even though they may
be perfectly aligned. It is critical to keep the star centered,
so over time you will need to make slight corrections to the
telescope’s position in order to account for the sky’s apparent
motion.
8. Astronomical Observing
For many users, the Atlas 10 EQ telescope will be a major
leap into the world of amateur astronomy. This section is
intended to get you ready for your voyages through the night
sky.
Observing Tips
A. Site Selection
Pick a location away from street lights and bright yard light‑
ing. Avoid viewing over rooftops and chimneys, as they often
have warm air currents rising from them, which distort the
image seen in the eyepiece. Similarly, you should not observe
through an open window from indoors. Better yet, choose
a site out‑of‑town, away from any “light pollution”. You’ll be
stunned at how many more stars you’ll see! Most importantly,
make sure that any chosen site has a clear view of a large
portion of the sky.
B. Seeing and Transparency
Atmospheric conditions play a huge part in quality of view‑
ing. In conditions of good “seeing”, star twinkling is minimal
and objects appear steady in the eyepiece. Seeing is best
overhead, worst at the horizon. Also, seeing generally gets
better after midnight, when much of the heat absorbed by the
Earth during the day has radiated off into space. Typically,
seeing conditions will be better at sites that have an altitude
over about 3000 feet. Altitude helps because it decreases
the amount of distortion causing atmosphere you are looking
through.
A good way to judge if the seeing is good or not is to look at
bright stars about 40° above the horizon. If the stars appear to
“twinkle”, the atmosphere is significantly distorting the incom‑
ing light, and views at high magnifications will not appear
sharp. If the stars appear steady and do not twinkle, seeing
conditions are probably good and higher magnifications will
be possible. Also, seeing conditions are typically poor during
the day. This is because the heat from the Sun warms the air
and causes turbulence.
Good “transparency” is especially important for observ‑
ing faint objects. It simply means the air is free of moisture,
smoke, and dust. All tend to scatter light, which reduces an
object’s brightness.
One good way to tell if conditions are good is by how many
stars you can see with your naked eye. If you cannot see
stars of magnitude 3.5 or dimmer then conditions are poor.
Magnitude is a measure of how bright a star is, the brighter a
star is, the lower its magnitude will be. A good star to remem‑
ber for this is Megrez (mag. 3.4), which is the star in the “Big
Dipper” connecting the handle to the “dipper”. If you cannot
see Megrez, then you have fog, haze, clouds, smog, light pol‑
lution or other conditions that are hindering your viewing (See
Figure 20).
C. Cooling the Telescope
All optical instruments need time to reach “thermal equilib‑
rium” to achieve maximum stability of the lenses and mirrors,
which is essential for peak performance. When moved from a
warm indoor location outside to cooler air (or vice‑versa), a
telescope needs time to cool to the outdoor temperature. The
bigger the instrument and the larger the temperature change,
the more time will be needed. The Atlas 10 mirror is made
of Pyrex, which is a low‑expansion material used for supe‑
rior thermal stability. The use of Pyrex reduces the amount of
14
Page 15

cool‑down time required for the Atlas 10, however, some cool‑
ing time will still be required for optimal viewing.
Allow at least 30 minutes for your Atlas 10 EQ to equilibrate.
If the scope has more than a 40° temperature adjustment,
allow an hour or more. In the winter, storing the telescope
outdoors in a shed or garage greatly reduces the amount of
time needed for the optics to stabilize. It also is a good idea to
keep the scope covered until the Sun sets so the tube does
not heat greatly above the temperature of the outside air.
Youc an attach a small fan to the Atlas 10 EQ to make cooling
the tube faster. On the bottom of the mirror cell there are four
holes (M4x.7 thread) where a fan can be mounted.
D. Let Your Eyes Dark-Adapt
Do not expect to go from a lighted house into the darkness
of the outdoors at night and immediately see faint nebulas,
galaxies, and star clusters—or even very many stars, for that
matter. Your eyes take about 30 minutes to reach perhaps
80% of their full dark‑adapted sensitivity. Many observers
notice improvements after several hours of total darkness. As
your eyes become dark‑adapted, more stars will glimmer into
view and you will be able to see fainter details in objects you
view in your telescope. Exposing your eyes to very bright day‑
light for extended periods of time can adversely affect your
night vision for days. So give yourself at least a little while to
get used to the dark before you begin observing.
To see what you are doing in the darkness, use a red‑filtered
flashlight rather than a white light. Red light does not spoil
your eyes’ dark adaptation like white light does. A flashlight
with a red LED light is ideal, or you can cover the front of a
regular incandescent flashlight with red cellophane or paper.
Beware, too, that nearby porch and streetlights and automo‑
bile headlights will spoil your night vision.
Eyepiece Selection
By using eyepieces of varying focal lengths, it is possible to
attain many magnifications with the Atlas 10 EQ. The tele‑
scope comes with two high‑quality Sirius Plössl eyepieces:
a 25mm, which gives a magnification of 48x, and a 10mm,
which gives a magnification of 120x. Other eyepieces can be
used to achieve higher or lower powers. It is quite common for
an observer to own five or more eyepieces to access a wide
range of magnifications. This allows the observer to choose
the best eyepiece to use depending on the object being
viewed. At least to begin with, the two supplied eyepieces will
suffice nicely.
Whatever you choose to view, always start by inserting your
lowest power (longest focal length) eyepiece to locate and
center the object. Low magnification yields a wide field of
view, which shows a larger area of sky in the eyepiece. This
makes acquiring and centering an object much easier. If you
try to find and center objects with high power (narrow field of
view), it’s like trying to find a needle in a haystack!
Once you’ve centered the object in the eyepiece, you can
switch to higher magnification (shorter focal length eyepiece),
if you wish. This is especially recommended for small and
bright objects, like planets and double stars. The Moon also
takes higher magnifications well.
Deep‑sky objects, however, typically look better at medium
or low magnifications. This is because many of them are
quite faint, yet have some extent (apparent width). Deep‑sky
objects will often disappear at higher magnifications, since
greater magnification inherently yields dimmer images. This
is not the case for all deep‑sky objects, however. Many galax‑
ies are quite small, yet are somewhat bright, so higher power
may show more detail.
The best rule of thumb with eyepiece selection is to start with
a low power, wide field, and then work your way up in magnifi‑
cation. If the object looks better, try an even higher magnifica‑
tion. If the object looks worse, then back off the magnification
a little by using a lower power eyepiece.
What to Expect
So what will you see with your telescope? You should be able
to see bands on Jupiter, the rings of Saturn, craters on the
moon, the waxing and waning of Venus, and thousands of
deep sky objects. Do not expect to see as much color as you
in NASA photos, since those are taken with long‑exposure
cameras and have “false color” added. Our eyes are not sen‑
sitive enough to see color in deep‑sky objects except in a few
of the brightest ones.
Remember that you are seeing these objects using your own
telescope with your own eyes! The object you see in your
eyepiece is in real‑time, and not some conveniently provided
image from an expensive space probe. Each session with
your telescope will be a learning experience. Each time you
work with your telescope it will get easier to use, and stellar
objects will become easier to find. Take it from us, there is big
difference between looking at a well‑made full‑color NASA
image of a deep‑sky object in a lit room during the daytime,
and seeing that same object in your telescope at night. One
can merely be a pretty image someone gave to you. The other
is an experience you will never forget!
A. The Moon
With is rocky and cratered surface, the moon is one of the
most interesting and easy subjects for your scope. The best
time to view it is during its partial phases when shadows fall
on the craters and canyon walls to give its features definition.
While the full moon may look like a tempting target, it is actu‑
ally the worst time for viewing! The light of a full moon is too
bright and lacks any decent surface definition.
Use an optional Moon filter to dim the Moon when it is very
bright. It simply threads onto the bottom of the eyepiece from
the focuser (you must first remove the eyepiece from the
focuser to attach the filter). You’ll find the Moon filter improves
viewing comfort, and helps bring out the subtle features if the
lunar surface.
B. The Sun
You can change your nighttime telescope into a daytime Sun
viewer by installing an optional full‑aperture solar filter over
the front opening of a Atlas 10 EQ. The primary attraction is
sunspots, which change shape, appearance, and location
15
Page 16

daily. Sunspots are directly related to magnetic activity in the
Sun. Many observers like to make drawings of sunspots to
monitor how the Sun is changing from day to day.
Important Note: Do not look at the Sun with any optical
instrument without a professionally made solar filter, or
permanent eye damage could result. Also, be sure to
cover the finder scope, or better yet, remove it altogether.
C. The Planets
The planets don’t stay put like the stars, so to find them you
should refer to Sky Calendar at our website telescope.com,
or to charts published monthly in Astronomy, Sky & Tele-
scope, or other astronomy magazines. Venus, Mars, Jupiter,
and Saturn are the brightest objects in the sky after the Sun
and the Moon. Your Atlas 10 EQ is capable of showing you
these planets in some detail. Other planets may be visible but
will likely appear starlike. Because planets are quite small in
apparent size, optional higher power eyepieces are recom‑
mended and often needed for detailed observations. Not all
the planets are generally visible at any one time.
JUPITER The largest planet, Jupiter, is a great subject for
observation. You can see the disk of the giant planet and
watch the ever‑changing positions of its four largest moons—
Io, Callisto, Europa, and Ganymede. Higher power eyepieces
should bring out the cloud bands on the planet’s disk.
SATURN The ringed planet is a breathtaking sight when it is
well positioned. The tilt angle of the rings varies over a peri‑
od of many years; sometimes they are seen edge‑on, while
at other times they are broadside and look like giant “ears”
on each side of Saturn’s disk. A steady atmosphere (good
seeing) is necessary for a good view. You will probably see a
bright “star” close by, which is Saturn’s brightest moon, Titan.
VENUS At its brightest, Venus is the most luminous object in
the sky, excluding the Sun and the Moon. It is so bright that
sometimes it is visible to the naked eye during full daylight!
Ironically, Venus appears as a thin crescent, not a full disk,
when at its peak brightness. Because it is so close to the Sun,
it never wanders too far from the morning or evening horizon.
No surface markings can be seen on Venus, which is always
shrouded in dense clouds.
MARS The Red Planet makes its closest approach to Earth
every two years. During close approaches you’ll see a red
disk, and may be able to see the polar ice cap. To see surface
detail on Mars, you will need a high power eyepiece and very
steady air!
D. The Stars
Stars will appear like twinkling points of light. Even powerful
telescopes cannot magnify stars to appear as more than a
point of light! You can, however, enjoy the different colors of
the stars and locate many pretty double and multiple stars.
The famous “Double‑Double” in the constellation Lyra and the
gorgeous two‑color double star Albireo in Cygnus are favor‑
ites. Defocusing a star slightly can help bring out its color.
E. Deep-Sky Objects
Under dark skies, you can observe a wealth of fascinating
deep‑sky objects, including gaseous nebulas, open and glob‑
Figure 21. Starhopping is a good way to locate hard‑to‑find
objects. Refer to a star chart to map a route to the object that uses
bright stars as guideposts. Center the first star you’ve chosen
in the finder scope and telescope eyepiece (1). Now move the
scope carefully in the direction of the next bright star (2), until it
is centered. Repeat (3 and 4). The last hop (5) should place the
desired object in the eyepiece.
ular star clusters, and a variety of different types of galaxies.
Most deep‑sky objects are very faint, so it is impor tant that
you find an observing site well away from light pollution. Take
plenty of time to let your eyes adjust to the darkness. Do not
expect these subjects to appear like the photographs you see
in books and magazines; many will look like dim gray smudg‑
es. But as you become more experienced and your observing
skills get sharper, you will be able to ferret out more and more
subtle details and structure.
How to Find Deep-sky Objects: Starhopping
Starhopping, as it is called by astronomers, is perhaps the
simplest way to hunt down objects to view in the night sky. It
entails first pointing the telescope at a star close to the object
you wish to observe, and then progressing to other stars
closer and closer to the object until it is in the field of view
of the eyepiece. It is a very intuitive technique that has been
employed for hundreds of years by professional and amateur
astronomers alike. Keep in mind, as with any new task, that
starhopping may seem challenging at first, but will become
easier over time and with practice.
To starhop, only a minimal amount of additional equipment
is necessary. A star chart or atlas that shows stars to at least
magnitude 5 is required. Select one that shows the positions
of many deep‑sky objects, so you will have a lot of options to
choose from. If you do not know the positions of the constel‑
lations in the night sky, you will need to get a planisphere to
identify them.
16
Page 17

Figure 22a. First remove both the 1.25"
and 2" adapters as shown.
Figure 22b. Thread the camera adapter
into the focuser drawtube.
Figure 22c. The SkyView Pro 8 EQ with
35mm SLR camera attached.
Start by choosing bright objects to view. The brightness of
an object is measured by its visual magnitude; the brighter
an object, the lower its magnitude. Choose an object with a
visual magnitude of 9 or lower. Many beginners start with the
Messier objects, which represent some of the best and bright‑
est deep‑sky objects, first catalogued about 200 years ago by
the French astronomer Charles Messier.
Determine in which constellation the object lies. Now, find the
constellation in the sky. If you do not recognize the constella‑
tions on sight, consult a planisphere. The planisphere gives
an all‑sky view and shows which constellations are visible on
a given night at a given time.
Now, look at your star chart and find the brightest star in the
constellation that is near the object you are trying to find.
Using the finder scope, point the telescope at this star and
center it on the crosshairs. Next, look again at the star chart
and find another suitably bright star near the bright star cur‑
rently centered in the finder. Keep in mind that the field of
view of the finder scope is approximately 5°, so you should
choose another star that is no more that 5° from the first star,
if possible. Move the telescope slightly, until the telescope is
centered on the new star.
Continue using stars as guideposts in this way until you are
at the approximate position of the object you are trying to find
(Figure 21). Look in the telescope’s eyepiece, and the object
should be somewhere within the field of view. If it’s not, sweep
the telescope carefully around the immediate vicinity until the
object is found.
If you have trouble finding the object, start the starhop again
from the brightest star near the object you wish to view. This
time, be sure the stars indicated on the star chart are in fact
the stars you are centering in the eyepiece. Remember, the
finder scope (and main telescope eyepiece, for that matter)
gives an inverted image, so you must keep this in mind when
starhopping from star to star.
9. Astrophotography
When coupled to a 35mm single‑lens reflex camera, the Atlas
10 EQ becomes a telephoto lens. To attach a camera, you
need only a T‑ring for your specific camera model and the
included camera adapter. First you must attach the includ‑
ed camera adapter to the Atlas 10 EQ’s focuser. To do this,
remove the 1.25" and 2" eyepiece adapters from the focuser
drawtube (Figure 22a). Then screw the camera adapter into
the focuser drawtube (Figure 22b). Now attach the T‑Ring to
your camera and thread it onto the camera adapter (Figure
22c).
Use the camera’s viewfinder to frame the picture. Use the
telescope’s focuser to focus the image. You may want to con‑
sider using a remote shutter release instead of the shutter
release on the camera; touching the camera can vibrate the
system and blur the resulting photographic image on the film.
Use the focus lock knob on the focuser to fix the focus when
the image is sharp.
Several different types of astrophotography can be success‑
fully attempted with the Atlas 10 EQ.
Moon Photography
This is perhaps the simplest form of astrophotography. Point
the telescope toward the Moon, and center it within the cam‑
era’s viewfinder. Focus the image with the telescope’s focuser.
Try several exposure times, all less than 1 second, depending
on the phase of the moon and the ISO (film speed) of the film
being used. A remote shutter release is recommended, as
touching the camera’s shutter release can vibrate the camera
enough to ruin the exposure.
Planetary Photography
Once basic Moon photography has been mastered, it’s time to
get images of the planets. This type of astrophotography also
works to get highly magnified shots of the Moon. In addition
to the T‑ring, you will need a Universal 1.25" Camera Adapter.
The equatorial mount must be accurately polar aligned, too.
As before, connect the T‑ring to your camera. Before connect‑
ing the universal camera adapter to the T‑ring, an eyepiece
must be inserted and locked into the body of the universal
camera adapter. Start by using a medium‑low power eye‑
piece (about 25mm); you can increase the magnification later
with a high‑power eyepiece. Then connect the entire camera
adapter, with eyepiece inside, to the T‑Ring. Insert the whole
system into the focuser’s 1.25" adapter and secure firmly with
the thumbscrew.
Aim the telescope at the planet (or Moon) you wish to shoot.
The image will be highly magnified, so you may need to use
17
Page 18

the finder scope to center it within the camera’s viewfinder.
Turn the motor drive on. Adjust the telescope’s focuser so
that the image appears sharp in the camera’s viewfinder. The
camera’s shutter is now ready to be opened. A remote shut‑
ter release must be used or the image will be blurred beyond
recognition. Try exposure times between 1 and 10 seconds,
depending upon the brightness of the planet to be photo‑
graphed and the ISO of the film being used.
“Piggyback Photography”
The Moon and planets are interesting targets for the bud‑
ding astrophotographer, but what next? Literally thousands
of deep‑sky objects can be captured on film with a type of
astrophotography called “piggybacking”. The basic idea is
that the camera with its own camera lens attached rides on
top of the main telescope. The telescope and camera both
move with the rotation of the Earth when the mount is polar
aligned and the motor drive is engaged. This allows for a long
exposure through the camera without having the object or
background stars blurred. An illuminated reticle eyepiece will
also be needed. The T‑ring and camera adapter are not need‑
ed, since the camera is exposing through its own lens. Any
camera lens with a focal length between 35mm and 400mm
is appropriate.
On the top of one of the tube rings is a piggyback camera
adapter. This is the black knob with the threaded shaft pro‑
truding through it. The tube ring with the piggyback adapter
should be closest to the open end of the telescope tube.
Remove the tube rings from the equatorial mount and swap
their position if necessary. Now, connect the camera to the
piggyback adapter. There should be a 1/4"‑20 mounting hole
in the bottom of the camera’s body. Thread the protruding
shaft of the piggyback adapter into the 1/4"‑20 mounting hole
in the camera a few turns. Position the camera so it is paral‑
lel with the telescope tube and turn the knurled black knob of
the piggyback adapter counter‑clockwise until the camera is
locked into position.
Aim the telescope at a deep‑sky object. It should be a fairly
large deep‑sky object, as the camera lens will likely have a
wide field of view. Check to make sure that the object is also
centered in the camera’s viewfinder. Turn the motor drive on.
Now, look into the telescope’s eyepiece and center the bright‑
est star within the field of view. Remove the eyepiece and
insert the illuminated reticle eyepiece into the focuser draw‑
tube. Turn the eyepiece’s illuminator on (dimly!). Recenter the
bright star (guide star) on the crosshairs of the reticle eye‑
piece. Check again to make sure that the object to be pho‑
tographed is still centered within the camera’s field of view.
If it is not, recenter it by repositioning the camera on the pig‑
gyback adapter, or by moving the main telescope. If you move
the main telescope, then you will need to recenter another
guide star on the illuminated eyepiece’s crosshairs. Once the
object is centered in the camera and a guide star is centered
in the reticle eyepiece, you’re ready to shoot.
Deep‑sky objects are quite faint, and typically require expo‑
sures on the order of 10 minutes. To hold the camera’s shut‑
ter open this long, you will need a lock shutter release cable.
Set the camera’s shutter to the “B” (bulb) setting. Depress the
locking shutter release cable and lock it. You are now expos‑
ing your first deep‑sky object.
While exposing through the camera lens, you will need to
monitor the accuracy of the mount’s tracking by looking
through the illuminated reticle eyepiece in the main telescope.
If the guide star drifts from its initial position, then use the
hand controller (at the 2x rate) to “move” the guide star back
to the center of the crosshairs. Any drifting along the Dec. axis
is a result of improper polar alignment, so if the guide star
drifts greatly in declination, the mount may need to be polar
aligned more accurately.
When the exposure is complete, unlock the shutter release
cable and close the camera’s shutter.
Astrophotography can be enjoyable and rewarding, as well
as frustrating and time‑consuming. Start slowly and consult
outside resources, such as books and magazines, for more
details about astrophotography. Remember ... have fun!
10. Care and Maintenance
If you give your telescope reasonable care, it will last a life‑
time. Store it in a clean, dry, dust‑free place, safe from rapid
changes in temperature and humidity. Do not store the tele‑
scope outdoors, although storage in a garage or shed is OK.
Small components like eyepieces and other accessories
should be kept in a protective box or storage case. Keep the
dust cover on the front of the telescope when not in use.
Your Atlas 10 EQ requires very little mechanical maintenance.
The optical tube is steel and has a smooth painted finish that
is fairly scratch‑resistant. If a scratch does appear on the
tube, it will not harm the telescope. Smudges on the tube can
be wiped off with a soft cloth and a household cleaner such
as Windex or Formula 409.
Cleaning Lenses
Any quality optical lens cleaning tissue and optical lens clean‑
ing fluid specifically designed for multi‑coated optics can be
used to clean the exposed lenses of your eyepieces or find‑
er scope. Never use regular glass cleaner or cleaning fluid
designed for eyeglasses. Before cleaning with fluid and tissue,
however, blow any loose particles off the lens with a blower
bulb or compressed air. Then apply some cleaning fluid to a
tissue, never directly on the optics. Wipe the lens gently in
a circular motion, then remove any excess fluid with a fresh
lens tissue. Oily fingerprints and smudges may be removed
using this method. Use caution; rubbing too hard may scratch
the lens. On larger lenses, clean only a small area at a time,
using a fresh lens tissue on each area. Never reuse tissues.
Cleaning Mirrors
You should not have to clean the telescope’s mirrors very
often; normally once every year or so. Covering the telescope
with the dust cover when it is not in use will prevent dust from
accumulating on the mirrors. Improper cleaning can scratch
mirror coatings, so the fewer times you have to clean the mir‑
rors, the better. Small specks of dust or flecks of paint have
virtually no effect on the visual performance of the telescope.
18
Page 19

The large primary mirror and the elliptical secondary mirror of
your telescope are front‑surface aluminized and over‑coated
with hard silicon dioxide, which prevents the aluminum from
oxidizing. These coatings normally last through many years of
use before requiring re‑coating (which is easily done).
To clean the secondary mirror, first remove it from the tele‑
scope. Do this by holding the secondary mirror holder station‑
ary while turning the center Phillips‑head screw. Be careful,
there is a spring between the secondary mirror holder and the
Philips‑head screw; be sure that it will not fall into the optical
tube and hit the primary mirror. Handle the mirror by its hold‑
er; do not touch the mirror surface. Then follow the same pro‑
cedure described below for cleaning the primary mirror. You
do not need to remove the secondary mirror from its holder
when cleaning.
To clean the primary mirror, carefully remove the mirror cell
from the telescope. To do this means you must remove the six
screws on the side of the tube near the primary mirror. You do
not need to remove the collimation screws on the bottom of
the mirror cell. Remove the mirror cell from the tube. You will
notice the primary mirror is held down with four clips held by
two screws each. Loosen the screws and remove the clips.
You may now remove the mirror from the mirror cell. Do not
touch the surface of the mirror with your fingers. Lift the mirror
carefully by the edges. Set the mirror on a clean soft towel.
Fill a clean sink free of abrasive cleanser, with room‑tempera‑
ture water, a few drops of liquid dishwashing detergent, and
if possible, a capful of rubbing alcohol. Submerge the mirror
(aluminized face up) in the water and let it soak for a few min‑
utes (or hours if it’s a very dirty mirror). Wipe the mirror under
water with clean cotton balls, using extremely light pressure
and stroking in straight line across the mirror. Use one ball
for each wipe across the mirror. Then rinse the mirror under
a stream of lukewarm water. Any particles on the surface can
be swabbed gently with a series of cotton balls, each used
just one time. Dry the mirror in a stream of air (a “blower bulb”
works great), or remove any stray drops of water with the
corner of a paper towel. Water will run off a clean surface.
Cover the mirror surface with Kleenex, and leave the mirror
in a warm area until it is completely dry before reassembling
the telescope.
11. Specifications
Primary mirror diameter: 254mm
Primary mirror coating: Aluminized, SiO
Primary mirror material: Pyrex
®
Focal length: 1200mm
Focal ratio: f/4.7
Secondary mirror axis: 64mm
Secondary mirror holder: Four‑vaned spider
Eyepiece: 25mm and 10mm Sirius Plössls, fully coated,
1.25"
Magnification: 48x (with 25mm) and 120x (10mm)
Finder scope: 9x50 achromatic, 5° field of view
Focuser: Rack and pinion, push‑pull tilt adjustment for
collimating, accepts 2" and 1.25" eyepieces
Camera adapter: couples 35mm SLR camera T‑Ring to
focuser
Mount: Atlas, German equatorial
Tripod: Steel
Tripod support tray: Aluminum, provides additional stability,
holds five 1.25" eyepeices and two 2" eyepieces
Weight: 54 lbs.
Counterweights: Quantity 3, 11 lbs. each
Setting circles: R.A. scaled in 10 min. increments, Dec.
scaled in 2° increments for N or S hemisphere
Polar axis latitude adjustment: 10° to 65°
Polar axis finder scope: Included
Motor drives: Dual‑axis, internally housed
Power requirements: 12V DC, tip positive
Battery type: Eight D‑cells
Operation: Northern or Southern hemisphere
Guiding rates: Sidereal ±100% sidereal
Centering rates: ±8x sidereal, ±16x sidereal
overcoat
2
19
Page 20

20
One-Year Limited Warranty
This Orion Atlas 10 EQ is warranted against defects in materials or workmanship for a period of one year from the date of
purchase. This warranty is for the benefit of the original retail purchaser only. During this warranty period Orion Telescopes &
Binoculars will repair or replace, at Orion’s option, any warranted instrument that proves to be defective, provided it is returned
postage paid to: Orion Warranty Repair, 89 Hangar Way, Watsonville, CA 95076. If the product is not registered, proof of pur‑
chase (such as a copy of the original invoice) is required.
This warranty does not apply if, in Orion’s judgment, the instrument has been abused, mishandled, or modified, nor does it
apply to normal wear and tear. This warranty gives you specific legal rights, and you may also have other rights, which vary
from state to state. For further warranty service information, contact: Customer Service Department, Orion Telescopes &
Binoculars, 89 Hangar Way, Watsonville, CA 95076; (800) 676‑1343.
Orion Telescopes & Binoculars
89 Hangar Way, Watsonville, CA 95076
Customer Support Help Line (800) 676-1343 • Day or Evening
 Loading...
Loading...