Page 1

NFT 2100
Miniature High Speed CCD
Fixed Position Barcode Scanner
User’s Guide
Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01
Page 2

Contents
Section 1 Introduction and Getting Started 1
Product Overview 1
Quick Start-Up Procedure 1
Section 2 Technical Specifications 3
Physical Specifications 3
Symbologies Supported 3
Optical Specification 3
Pitch 4
Skew 4
Tilt (rotation) 5
Curvature 5
Electrical Specification 6
RS232 Communications Specifications 6
Connector Pin Outs 7
Environmental Specifications 7
Ordering Information 7
Section 3 Positioning the Scanner 8
Achieving Optimum Performance 8
Measuring Scanner Performance 10
Application Notes 10
Tips for Achieving High Throughput 10
Tips for Insuring Highest Data Integrity 10
Tips for Verifying the Presence of a Bar Code 11
Section 4 Configuring the Scanner 12
Configuring the Scanner 12
Programming Menus & Commands 12
Default Setting 12
Section 5 Application Engineering Support 13
Technical Assistance and Support 13
Common Causes of Poor Performance 13
Modified and/or Customized Scanners 13
Section 6 Scanner Labeling 14
Section 7 Scanner Servicing and Maintenance 14
Appendix A How to Program the Scanner 16
Appendix B Computer Programming Commands 18
Appendix C Bar Code Programming Commands 23
Appendix D Dimensional Drawings 64
Appendix E Optical Performance (Typical) 65
Appendix F Placement Drawings 66
Appendix G Placement Drawings for Test Tubes 67
Page 3

Organization of this Manual
This manual provides the necessary instructions for installing and using the Opticon NFT 2100 Fixed
Position Scanner. The manual is organized as follows:
Section 1 Introduction and Getting Started
Describes the general operation of the NFT 2100 scanner. Also provides a Quick StartUp Procedure that allows you to begin using the scanner immediately.
Section 2 Technical Specifications
Provides complete specifications, including mechanical details, optical performance,
RS232 communications and other technical data.
Section 3 Positioning the Scanner for Optimum Performance
Provides detailed instructions and tips for mounting and positioning the scanning to
obtain the best scanning performance. Application Notes describe guidelines for
maximizing specific characteristics.
Section 4 Configuring the Scanner
Describes how various parameters can be programmed to customize the scanner for
your specific application.
Section 5 Application Engineering Support
Discusses the most common questions and concerns when adapting the NFT 2100 and
scanner in your application.
Section 6 Scanner Compliance
Discusses the various labels on the product required by CE.
Section 7 Scanner Servicing and Maintenance
Discusses maintenance and cleaning procedures.
Appendix A How to Program the Scanner
Appendix B Computer Programming Commands
Appendix C Bar Code Programming Commands
Appendix D Dimensional Drawing
Appendix E Optical Performance
Page 4

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Section 1
Introduction and Getting Started
Product Overview
The NFT 2100 Fixed Position Scanner is a miniature, 200 scan per second, CCD barcode reader designed
to be easily incorporated into host equipment. The small physical size makes the scanner easy to
integrate into any hardware design. Durability and reliability are assured.
Advanced microprocessor technology coupled with Opticon’s proven decoding algorithms result in high
speed operation with superior accuracy. The scanner is fully programmable allowing the user to
customize parameters including changing communication settings, selecting symbologies, adding prefixes
and appending suffixes. Programmable settings can be downloaded from the host CPU or computer
directly to the scanner.
The scanner is encased in a compact, rugged, yet lightweight steel enclosure. The compact size permits
installation in the tightest areas allowing great flexibility in mounting and positioning the scanner for
optimum performance.
Quick Start-Up Procedure
This section is for those who wish to start using the scanner before reading the complete manual. In
only a few steps the scanner will be operable.
Turn off the power to your PC and connect the scanner to a RS232 communications port. Note: You
must provide +5 Volt DC power to the scanner. If you are using our standard LHA2107RR1S-054, you
can utilize power supply, P/N 32-00907-01, by plugging its connector directly into the power jack on the
DB9 connector. If the power supply is obtained from another source verify that it is identified with the
CE
mark. Turn on the power to the PC.
1) If you are operating in a Microsoft Windows 95/98/ 2000/ XP environment, you can set the
communication parameters using Hyper Terminal as follows:
♦ Open Hyper Terminal. This can be done from Start→Programs→Accessories/
Communications
♦ Select Hypertrm.exe to create a New Connection
♦ In the Connection Description dialog screen enter a name for the new file, like "Opticon". If
desired, select an Icon. Click OK
♦ In the
♦ In the
♦ The hyper-terminal folder you just created will open. From the File pull-down menu, select
Connect To (Phone Number)
the communication port, for example, “Direct to Com 1” Click OK
Com 1 Properties
Data bits = 8, Parity = None, Stop Character = 1, Handshaking = None, Click OK
Properties
then click on the
screen, enter the appropriate Port Settings: Bits per second = 9600,
dialog screen, in the box entitled:
Setting
Tab
Connect using
. select
♦ In the
Properties Settings
control key; then Select
default 500
dialog screen, Select
ANSI
for Emulation; the
Terminal keys
Back scroll
buffer line can remain at the
for the Function, arrow and
Page 1
Page 5

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
♦ Click on the ASCII Setup button. In the ASCII Setup Sending screen, select Line ends with
line feeds and Echo typed locally so that any keyboard commands you input will appear on
your screen. In the ASCII Setup Receiving screen, select Append line feeds to incoming line
ends and Wrap lines that exceed terminal width. Click OK. This returns you to the
Properties Setting. Click OK
2) Your PC and the scanner should now communicate. To verify that the scanner and the PC are
communicating properly, send the following command from your PC keyboard which will request
software settings to be displayed.
Send the command in four keystrokes: <Esc> Z3 <Enter>
Note
: Be sure to use capital letters, e.g. “Z3”, not “z3”.
A series of software setting should be displayed, indicating that good communications have
been established
3) A red LED light should be visible. If it is not visible, the scanner may be in a mode that requires
a “Trigger” Command from the PC to activate it. You can exit that mode by sending the
following command from your PC keyboard:
<Esc> S7 <Enter>
4) The “Trigger” mode will now be deactivated and the red LED light will be continuously
illuminated.
This Quick Start-Up procedure will get you started. However, to best understand the full capabilities of
this scanner, you should read the complete manual.
Page 2
Page 6

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Section 2
Technical Specifications
Physical Specifications
Case Material Steel (Black)
Dimensions 2.16 x 1.85 x 0.78 in (WxDxH) (55 x 47 x 20 mm)
Weight 3.5 oz (100 grams) without cable
Cable Length 6.5 Feet (2000 mm)
Connector 9-pin, DB9F-SC connector with power Jack
Mounting 4 threaded (M-3) mounting holes, 2 on each side
Symbologies Supported
♦ Codabar (NW-7), Codabar ABC, & Codabar CX
♦ Code 39
♦ Code 93
♦ Code 128
♦ Industrial 2 of 5 / Interleaved 2 of 5 / Matrix 2 of 5
♦ MSI / Plessey, UK / Plessey
♦ WPC (UPC / EAN / JAN)
♦ IATA
♦ Telepen
♦ TriOptic
♦ SCode
Optical Specifications
Scan Rate 200 scans per second ±10%
Light source 660 nm, visible red LED
Light receiver CCD Linear image sensor with 2048 pixels
Focal Distance * 1.4" (35.4 mm)
Field size at focal distance. 3.1" (80 mm)
Narrow Bar Resolution 6 mil (0.15mm) at 0.9 PCS
Minimum PCS 0.45 (min. background reflectance of 70%)
Reading Distances NFT 2100. See Appendix E)
* measured from front edge of scanner.
Page 3
Page 7
Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
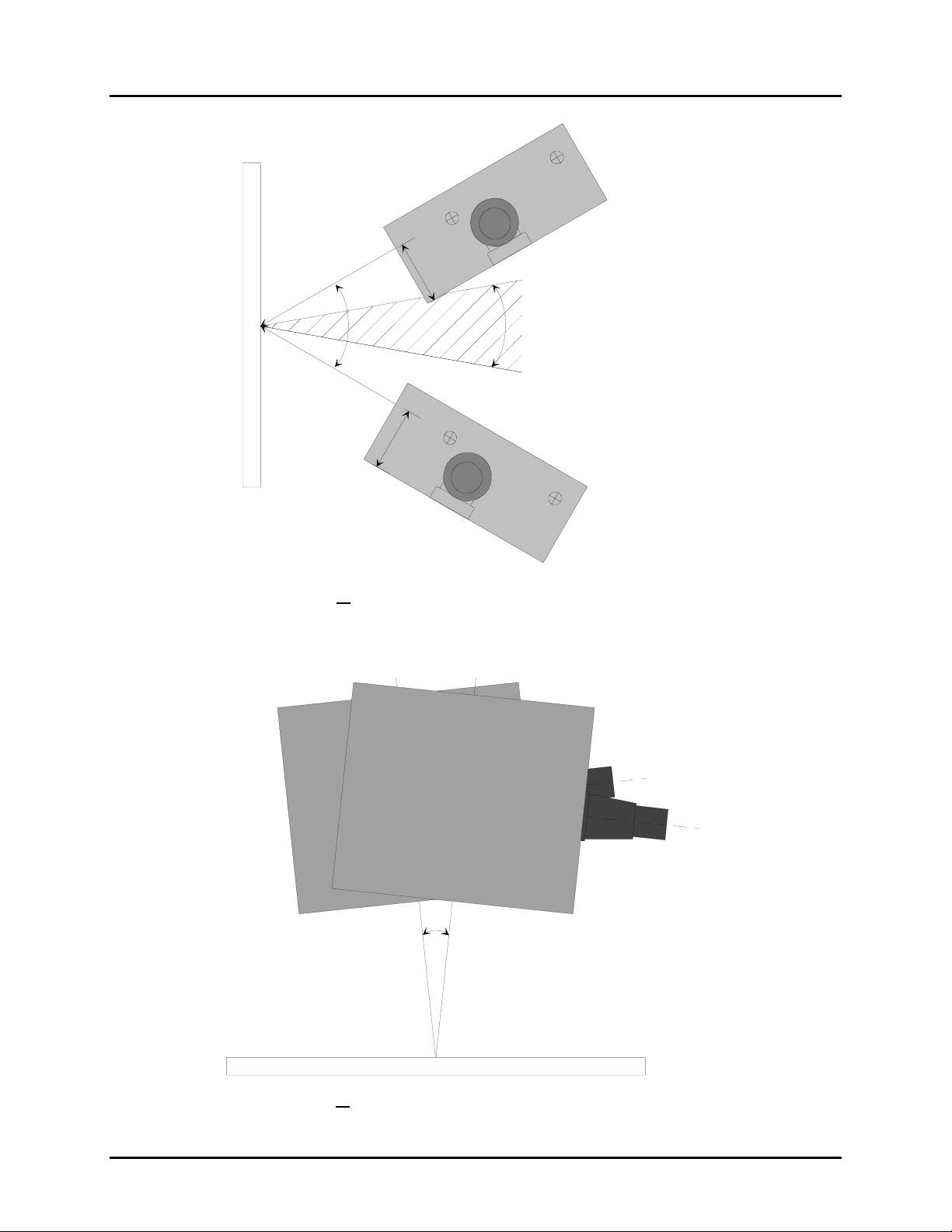
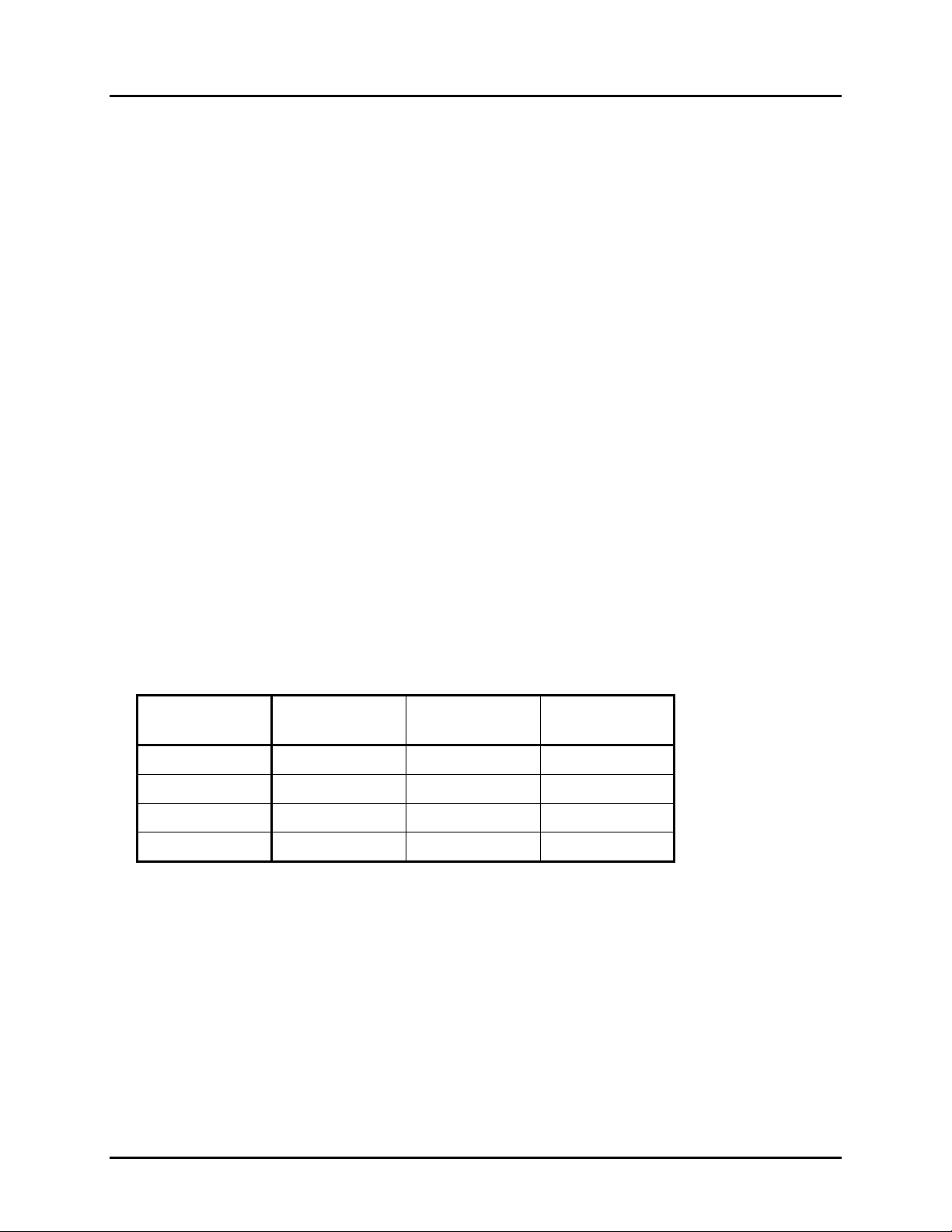
Skew
Specified operation (α) at + 30º or less. (Recommended at + or - 13º)
Avoid specular reflection in the dead zone (±10º).
±30º
α
1
4
.
5
Aviod this region
±10º
5
.
4
1
α
Pitch
β
Specified operation (β) at + 6º or less. (Recommended at 0º)
±6º
Page 4
Page 8
Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
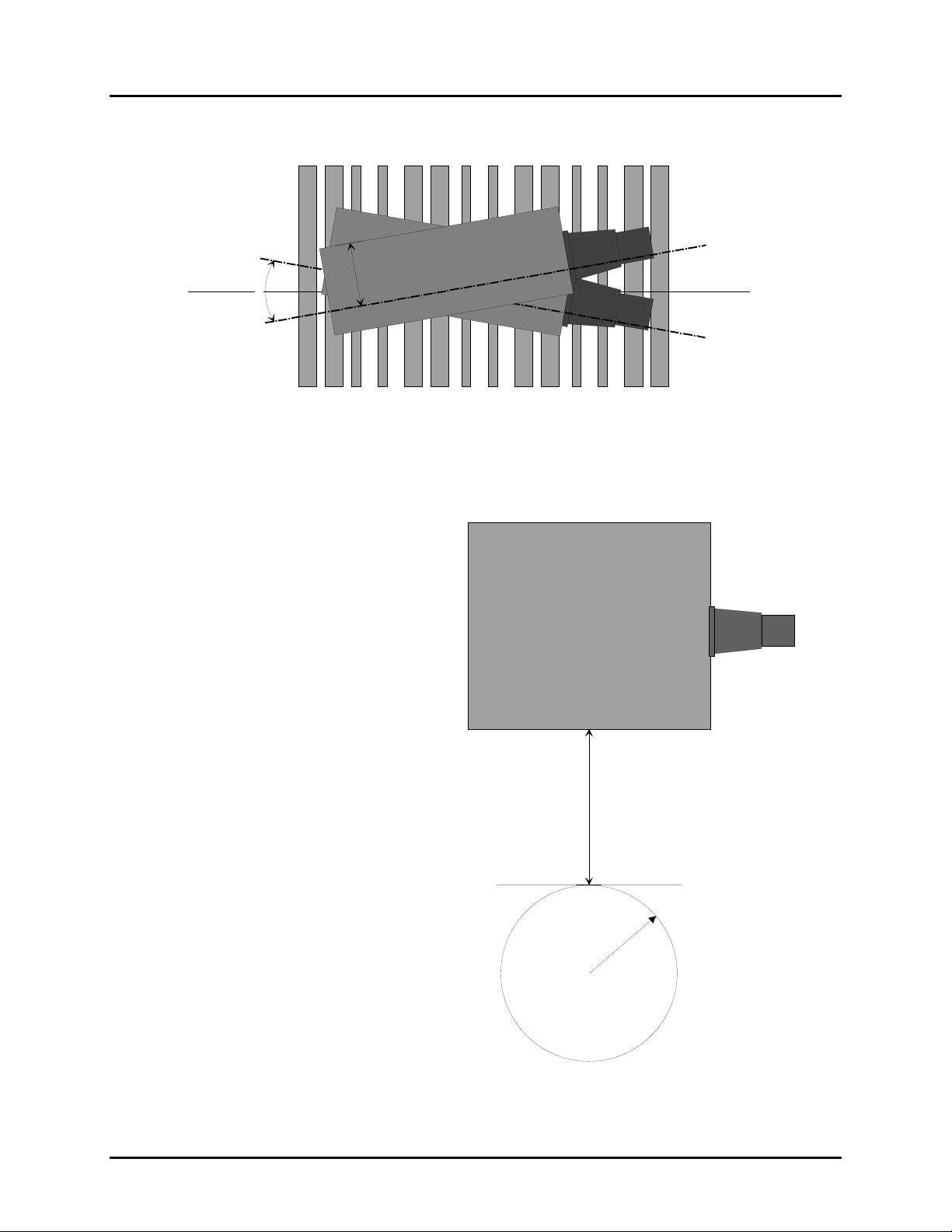
Tilt (Rotation)
φ
±10º
1
4
.5
Specified operation (θ) ±10º or less. (Barcode aspect ratio must allow the field of
view to cover all bars). (Recommended operation at 0º)
Curvature
EAN-8 / UPC-E: R = >20 mm (0.8”) or
EAN-13 / UPC-A: R => 30 mm (1.2”).
Where: PCS 0.9, h = 35.4 mm (1.4")
Skew=13°, Pitch=0°, Tilt=0°
35.4
R
Page 5
Page 9
Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Electrical Specifications
Operating Voltage +5VDC +
Current
Operating (LEDs are ON) 130mA (max)
Idle (LEDs are OFF) 45mA (max)
Pwr-On Surge 1000mA (max)
5%
RS232 Communications Specifications
RS232 Data Transmission Format
Parameter
Timing Asynchronous
No. of Start Bits 1 bit
No. of Stop Bits 1 bit 1 or 2 bits
No of Data Bits 8 bit 7 or 8 bits
Parity None Odd / Even / None
Baud Rate 9600 baud 150 to 38,400 baud
Handshaking None Hardware / Software/ None
RS232 Transmit / Receive Character Format
Default Optional Settings
Start
(First)
1 Bit LSB XXXXXX MSB 1 Bit 1 to 2 Bits
Data 7 to 8 Bits Parity
Stop
(Last)
RS232 Transmit Data Format, Output from Scanner
First to last Global Prefix Individual Prefix Barcode data Individual Suffix Global Suffix
Format
Default 0 0 1 to 44 CR 0
RS232 Receive Data Format, Command inputs to scanner.
RS232 Signal Level
0 to 8
characters
First to last
Format ESC or STX 1 or 2 characters CR or ETX
ESC Escape ASCII 27 (x1B)
CR Carriage Return ASCII 13 (x0D)
STX Start of Text ASCII 2 (x02)
ETX End of Text ASCII 3 (x03)
Signal Name In / Out Mark/Off Space/On
TXD Out -5 to -15 +5 to +15
RXD In -3 to -15 +3 to +15
0 to 4 characters
Prefix for all
commands
1 to 44
characters
Commands
0 to 4 characters
Suffix for all
Commands
0 to 8
characters
Page 6
Page 10
Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Connector Pin-outs
9 Pin D-Sub Female Connector (with power stereo jack)
Pin No. Signal Direction Power
Plug/Jack
1 Frame Ground Tip NC
2 TxD Output Center +5V
3 RxD Input Rear Signal Ground
4 NC
5 Signal Ground Pwr Return
6 NC
7 CTS Input
8 RTS Output
9 NC when plug is inserted
+5V when plug is removed
Pwr Input
Signal
Environmental Specifications
Temperature
Operating +32 to +113° F (0° to +45° C)
Storage
-14 to +140° F (-10° to +60° C)
Humidity (non-condensing)
Operating 20 to 80% RH
Storage
20 to 90% RH
Ambient Light Fluorescent or incandescent: 5,000 lx max
Anti Static 15KV (non-destructive)
Ordering Information
Part No. Description
LHA2107RR1S-054 Front View, 9 Pin D-Sub Female Connector (with power stereo jack)
(standard configuration, other configurations are available upon request)
LHA-2107R1-SK1 Developer’s Test and Evaluation Kit is available which contains all the items
needed to install and evaluate the scanner. The kit includes:
Scanner
5V Power Supply (32-00907-01)
User Manual
CD ROM (including manual, datasheet and supporting materials)
Regulatory
EMC EN55022, EN55024
FCC Class B
Page 7
Page 11
Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Section 3
Positioning the Scanner for Optimum Performance
Achieving Optimum Performance
Four items greatly impact performance:
1) Distance (from the scan window) to the bar code
2) Field of View
3) Specular Reflection
4) Quality of Bar Code Labels
1) Distance to the Bar Code and 'Depth of field'
The ideal location of the bar code relative to the scanner is at its focal distance, about 1.4" from the front
of the unit. A bar code located either too near or too far from the scanner will be out of focus for the
scanner camera causing the scanner to have difficulty decoding what appears to be fuzzy bars and
spaces.
Just as with any camera, the scanner has a working depth-of-field (DOF). It can read bar codes that are
not precisely at its focal distance - maybe a little closer, or a little farther away. The DOF varies based
on the density of the bar code, i.e., the thicker the bars and spaces the more DOF. Very high density bar
codes (which have very narrow bars) are readable over a much shorter DOF range than low density bar
codes with larger bars.
The following table shows the depth-of-field “specifications” (closest to farthest reading distances) for the
NFT 2100 scanner. The actual performance may differ slightly from unit to unit. Also, it is important to
note that this data was measured under ideal conditions using high quality bar code labels. In a “real
world” environment the conditions will not be as ideal. Therefore, the best practice is to position the
scanner at the center of the depth-of-field rather than at the extremes of its depth-of-field.
Depth-of Field NFT 2100 (Specification)*
Density
6 mil 0.9 1.6 0.7
10 mil 0.8 1.7 0.9
20 mil 0.8 2.0 1.2
40 mil 0.9 2.4 1.5
* measured from front edge of scanner
2) Reading width or Field of View of the scanner
The table below shows the field-of-view (FOV) at various distances from the window. The FOV is the
maximum width that the scanner is capable of reading. It is the distance from the left edge of the view
to the right edge. For the NFT 2100, the FOV will be 3.1" at its focal distance of 1.4". Any part of a bar
code label that is positioned outside of the FOV will make the label unreadable. Good design policy is to
position the barcode at the center of the FOV where the camera sees best.
Min. Distance
(inches)
Max Distance
(inches)
Range
(inches)
Remember
white space (quiet zone) on each end.
: The width of a bar code label includes not only the bars and spaces but also the required
Page 8
Page 12
Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Readable Width or Field of View for the NFT 2100
(Field-of-View Specification Based Upon 69º Degree Sweep)
Focal
Distance from Front
of Case
1.0"
Distance
1.4"
1.5 2.0" 2.5"
25.4mm 35.4mm 38.1mm 50.8mm 63.5mm
Field of View
2.6 3.1" 3.3 4.0 4.7
66mm 80mm 83mm 101mm 118mm
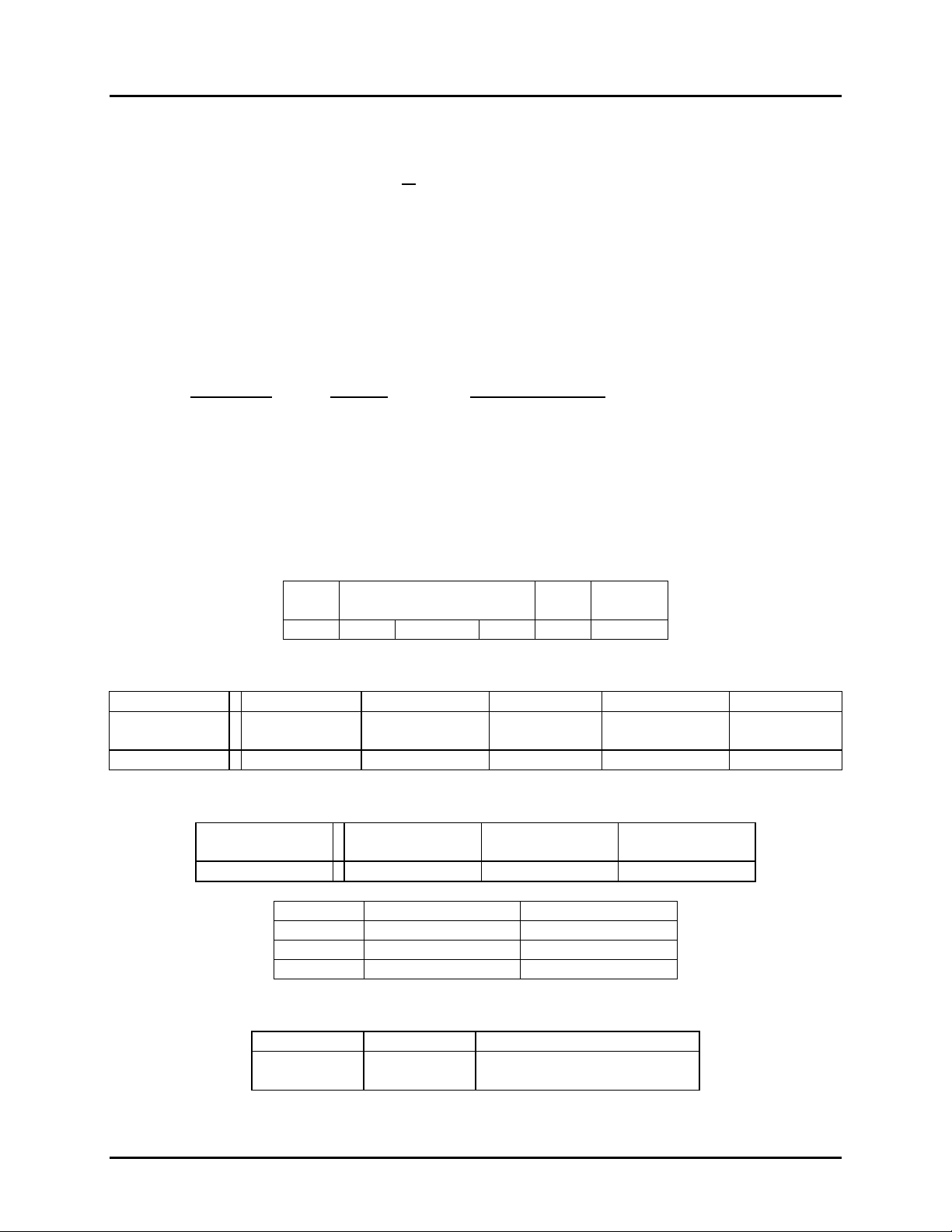
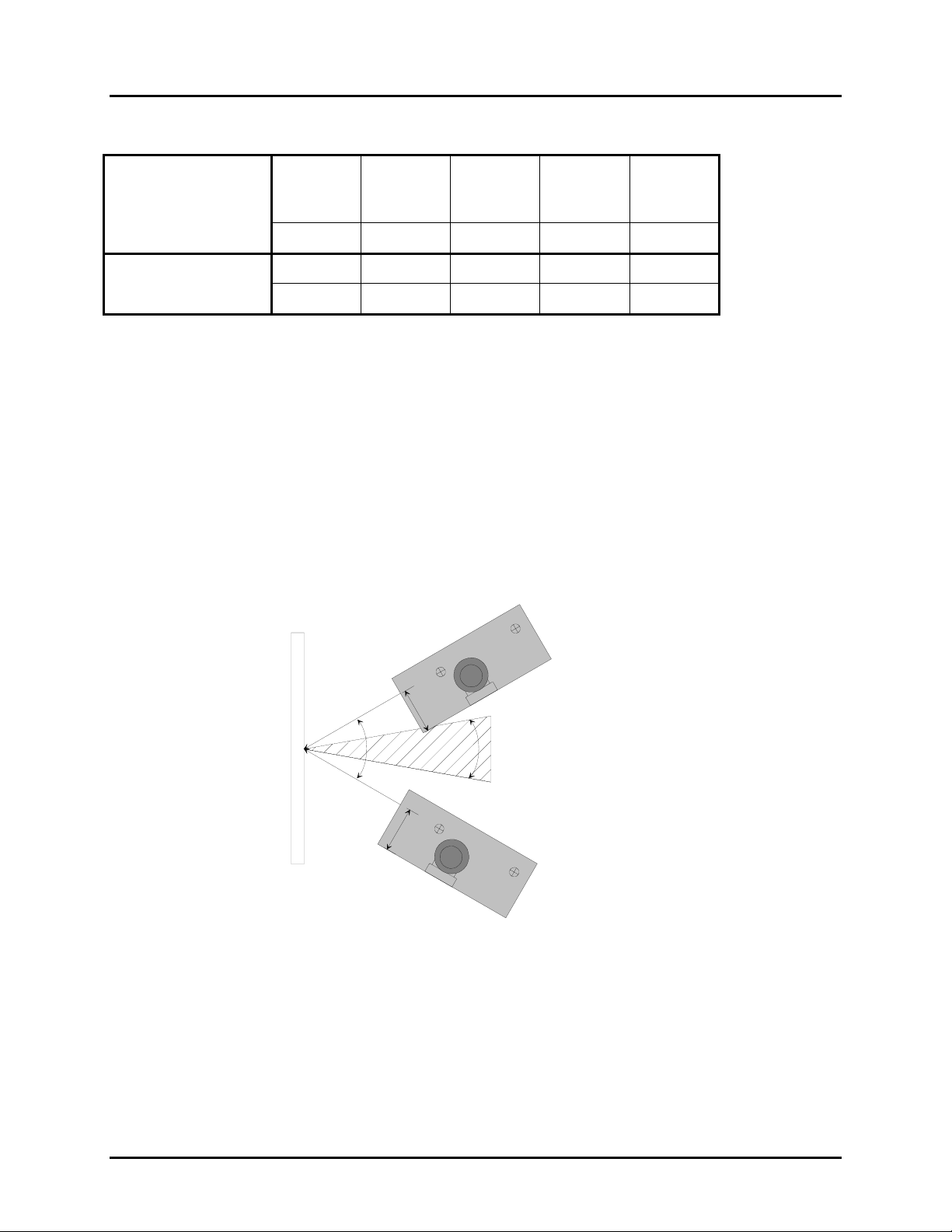
3) Avoiding Specular Reflection
Do not position the scanner at an angle that causes the LED light to be reflected directly back into the
scanner. This is called specular reflection. Too much reflected light can “blind” the scanner preventing a
good decode. For optimal performance we recommended pitching the scanner ±13º off the
perpendicular to the barcode label surface.
If the bar code label is located on a flat surface, specular reflectivity occurs in the region between ±10
degrees off perpendicular (See diagram). If the bar code label is located on a cylindrical surface, such as
a test tube, the angle of specular reflection is measured tangent to the curve. If the curved surface is
also moving, specular reflection may occur at some point along the movement. This is OK, as long as
there is sufficient regions on the test tube label where the label is out of the specular angle. The
following diagram indicates the region to avoid:
±30º
1
4
α
Aviod this region
5
4.
1
.
5
α
±10º
4) Quality Bar Code Labels
The quality of the bar code label can affect the scanning performance. Poor quality labels are more
difficult to decode and may result in non-reads or potential misreads. The bar code label should be
printed to specifications. This means that the bars are printed within spec, with the correct widths, no
ink spread, crisps edges and no voids. There should be a sufficient quiet zone on both end of the bar
code label. For best results, the paper or label stock should have a matte finish to diffuse light. The
print contrast signal (which is a comparison of the reflectance of the bars and the background stock)
should be as high as practical.
Page 9
Page 13

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Measuring Scanner Performance
A method for properly positioning the unit is to program the scanner for Trigger Disable (S7) and
Continuous Read (S2) modes. The scanner will now be always on and will continuously read the same
bar code. Since the buzzer sounds each time the bar code is read, the sound of the buzzer can be used
like a “Geiger counter”. As the position of the scanner changes the sound of the buzzer will change. The
buzzer sound will be loudest and most continuous at the best reading position.
Application Notes
Tips for Achieving High Throughput
In some applications your primary objective may be to achieve the highest possible throughput rate. The
following list identifies the parameters and scanner settings that can maximize scanning and decode
throughput speed. Note, by emphasizing maximum throughput, other areas of performance may be
affected. For example, the number of non-reads could increase.
If high throughput is critical, consider some or all of these settings:
♦ Operate in the Trigger Disabled mode. Operation of the trigger creates delay before decoding
begins, slowing down throughput rate.
♦ Only enable those symbologies that you will be decoding.
♦ Eliminate all suffixes and prefixes to reduce transmission time.
♦ Minimize the number of redundant reads required before transmitting data.
♦ Transmit the decoded data at the highest baud rate.
♦ Disable buzzer functions.
Tips for Insuring Highest Data Integrity
There are several parameters that can enhance your confidence that the correct bar code data is
transmitted. Note that by emphasizing the accuracy and security of the data other areas of the scanner
operation may be affected, for example, you may not achieve the highest throughput.
If accuracy and data integrity are critical, consider some or all of these settings:
♦ Program the scanner to require a high number of redundant decodes prior to transmitting. For
example, program the scanner to decode a bar code exactly the same way three consecutive times
before transmitting the data. Then decoding the bar code the same way 2 out of 3 times or any 3
out of 4 times is not sufficient. It must obtain three consecutive, identical decodes.
♦ Utilize a predetermined, fixed-length of bar code. Program the scanner to only decode a bar code
of that length. Bar codes of any other length will be ignored.
♦ The quality of the printed bar code must be excellent.
♦ Use a bar code symbology that contains an internal check digit and program the scanner to
calculate that check digit for validity prior to transmitting.
♦ Do not use a symbology with poor internal verification, or subject to partial decodes, such as 2 of 5
or MSI/Plessey.
♦ Only enable those symbologies that you will be decoding.
♦ Transmit data at low baud rates to minimize communication errors.
Page 10
Page 14
Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Tips for Verifying the Presence of a Bar Code
If the scanner is operated in the “trigger enabled” mode and the trigger is activated, one of three
conditions may occur:
A bar code is scanned and decoded.
A bar code is scanned but is not decoded
(e.g., print quality was poor)
No bar code is present No data is transmitted
In some applications, when no data is transmitted, it may be important to know why. Was there a bar
code present that could not be decoded, or was no bar code present at all?
This requirement is common in applications such as automated blood analysis equipment. Test tubes
containing blood samples from many different people are loaded into a rack for automatic analysis. The
bar code on each tube ties that sample and the results back to a specific individual. If no bar code data
is transmitted it is critical to understand the reason.
Your Opticon scanner, when operated in the Trigger Enabled mode, can be programmed to transmit an
error message indicating whether or not a bar code was present. See Section 33 of Appendix C of this
manual for details.
Decoded data is
transmitted
No data is transmitted
Page 11
Page 15
Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Section 4
Configuring the Scanner
Since the operation of the NFT 2100 scanners are microprocessor controlled, it is possible to modify or
program its operation to match your specific application. Changes in parameter settings can be
accomplished two ways.
The scanner can be programmed by sending software commands from the host PC to the scanner via
1.
the RS232 connection. Most commands will be immediately active, but are not stored into nonvolatile memory until the store command, Z2, is sent. A few commands, such as changing the
communication parameters will not be active until they are stored via the Z2 command.
The second method employs specially designed programming bar codes referred to as menu
2.
commands. Scanning these bar codes instructs the scanner to modify specific parameters. These
commands are stored into non-volatile memory as soon as the menu command mode is exited.
Once stored in non-volatile memory, these settings will remain even after powering the unit OFF and
ON.
Programming Menus & Commands
Appendix A contains full instructions on how to configure the scanner as well as a complete listing of the
computer commands and programming bar codes that are available to customize the scanner for your
application.
Default Settings
When you modify or change any parameters, the scanner can be programmed to retain the new
parameter in non-volatile memory, even if power is interrupted or terminated. If for any reason the
scanner is instructed to return all parameters to default settings (U2), it will return to the default settings
shown in the following table.
Default settings are indicated by a pointing hand symbol (
Parameter Factory Default Setting
9600 baud
8 data bits
RS 232 Communications
Trigger Function Disabled, (scanner is ON)
Read Mode Multiple Read Mode
No. of Redundant Decodes Read three times before transmitting
UPC-A (12 digits)
UPC-E (7 digits)
Code 39
Codabar
2 of 5 (Interleaved & Industrial) Do not calculate check digit
Min/Max length of bar code only Disabled
Buzzer Enabled
Positive bar codes only Enabled
Error indications Do not transmit error message
Suffix Carriage Return
1 stop bit
No parity
No handshaking
No leading zero transmitted (EAN 1
send check digit
No leading zero transmitted
Send check digit
Do not calculate check digit/Transmit check digit
Disable start/stop characters transmission (*.....*)
Disable start/stop characters transmission
Do not calculate check digit
) throughout the bar codes menus.
%
st
Position)
Page 12
Page 16

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Section 5
Application Engineering Support
Technical Assistance and Support
Opticon is eager to help you integrate the NFT 2100 scanner into your application. Our technical support
staff is available to answer any questions or work with you to adapt the scanner to your specific
situation. We are happy to answer your questions, assist in configuring and positioning the scanner for
optimum operation, and help resolve any problems you encounter. Call us at 1 (800) 636-0090, and ask
for technical support.
Common Causes of Poor Performance
The most common reasons for poor scanning performance are listed below:
♦ Bar codes are not positioned at the focal distance of the scanner.
♦ Specular reflection is impacting the scanner. Change the angle/position of the scanner or the bar
code.
♦ Poor quality of printed bar codes. Bar codes are out of specification.
♦ The paper on which the bar code is printed is highly reflective or has a glossy finish causing light to
be reflected into the scanner.
♦ The paper background is not white, but some color like dark blue, causing poor contrast.
♦ The distance from the scanner to the bar code is not suitable for the density of the bar code. Or the
density of the bar code is beyond the scanners capability. If the red illuminating light of the scanner
is not on, the scanner may be in the “Trigger Enable” mode expecting a trigger signal.
♦ If the com port setting is set to Handshaking, the scanner will not transmit until the CTS signal (RTS
from Host) is activated.
Modified and/or Customized Scanners
Opticon will work with you to modify or customize scanners to match your requirements. Scanners can
be modified in terms of connector type, pin-outs, cable length, default settings, custom software and
many other areas.
Opticon will modify scanners in our factory and ship you scanners that match your specific requirements.
By incorporating your modifications directly into production scanners, you receive scanners tailored for
your need. They can be used immediately without the need for further modification or rework.
Page 13
Page 17
Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Section 6
Scanner Labeling
IEC 825-1 Class 1 LED Devices
The NFT 2100 has been examined and found to be a CE Class 1 LED Device according to the relevant
requirements of IEC 825-1 and corresponding EN 60825-1 (1993-11) including amendment 1 (1997-09)
and amendment 2 (2001-01).
The NFT 2100 scanner uses low-power visible LEDs. As with any very bright light source, such as a
flashlight, you should avoid staring into the light. Momentary exposure to an IEC 825-1 Class 1 LED is
not known to be harmful.
A manufacturer’s label, as shown below, indicating the manufacturer, product model, ordering number,
serial number, CE mark and place of manufacture is affixed to each scanner.
OPTICON
NFT-2100-I-RS232C
xxxxxx
******
Ordering Number
Serial Number
MADE IN JAPAN
Section 7
Scanner Servicing and Maintenance
The NFT 2100 scanner contains no user adjustable or serviceable parts in the interior of the scanner. All
product service must be performed by the Opticon Service Department in Orangeburg, NY. Opening the
scanner will void the warranty.
The NFT 2100 is warranted for 7 year including parts and workmanship. If you need warranty or out-ofwarranty repair, first
call 1-800-636-0090 to obtain a Returned Material Authorization (RMA)
number. You will be provided a number and shipping instructions.
There is no scheduled maintenance required for the NFT 2100. The scanner can be cleaned using a
water dampened, lint free or lens cloth. Be careful to avoid excessive moisture that would penetrate the
housing or obscure the window. While use of cleaning fluids other than water are not recommended, a
neutral detergent or ethanol would be preferred if necessary. Do not use bleach at full or diluted
strength as damage to the painted case and/or window may result.
Page 14
Page 18

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Appendices
Appendix A How to Program the Scanner
Appendix B Computer Programming Commands
Appendix C Bar Code Programming Commands
Appendix D Dimensional Drawing
Appendix E Optical Performance (typical)
Page 15
Page 19

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Appendix A
Programming the Scanner
Two different methods can be used to program parameters to configure the scanner:
a. Programming via Computer Commands
b. Programming via special Bar Codes from a menu page
Most parameters can be programmed using either of these two methods. However, there are certain
parameters that are only programmable via the bar code menu.
a. Programming via Computer Commands
Parameters can be programmed by sending software commands or keyboard strokes from the host
computer to the scanner in the following format:
<ESC> Computer Command <CR>
Note:
Only upper case letters are recognized, e.g., “AB” not” ab”
Each command normally consists of two characters
Downloading of software commands cannot be “grouped” together. Each command
must be preceded by <ESC> or <STX> and followed by a <CR> or <ETX>
Parameters programmed by downloaded commands can be stored permanently by transmitting a
“<ESC> Z2 <CR>” command. It is not necessary to send a “Z2” command after each parameter that is
changed. One Z2 command will save all changes.
Appendix B lists all of the Computer Commands. In Appendix C, Bar Code Programming Menus, the lefthand column in all menus contains the Computer Command associated with that bar code.
b. Programming via Bar Codes
Use the following steps to program parameters via the bar code menus:
1.
Scan the “Start/End” bar code. This instructs the scanner to enter the Programming Mode.
While in this mode the scanner will beep intermittently.
Scan the bar code(s) associated with the desired parameter(s). The scanner will beep when the
2.
bar code is read. Note: because of the close proximity of bar codes on the page, it is important
to aim carefully to ensure that only the desired bar code is scanned.
Scan the “Start/End” bar code. This instructs the scanner to exit the Programming Mode.
3.
All the parameters that were scanned are retained in non-volatile memory and are stored permanently
(even if the scanners is powered down) or until they are changed again.
Page 16
Page 20

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
When the scanner is in the Programming Mode, you can change more than one parameter at a time.
However, this may become confusing. Until you become proficient at programming you may prefer to
change only a few parameters at one time. We recommend that you keep a record of the changes you
have made to the scanner. Note, while you are in the programming mode the scanner will not read
regular bar codes.
What if you make a mistake?
Don’t worry. If you are programming the scanner but are unsure of which parameters have been
changed, scan the
settings that were installed in the factory at the time the product was manufactured. Scanning this bar
code erases any changes you have made, including any changes that were made during previous
programming.
Reset All Defaults U2 Command
This command will return all settings to the defaults that were installed in the factory
Reset All Defaults bar code. This bar code returns the scanner to the default
Page 17
Page 21
Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Appendix B
Computer Programming Commands
All commands listed below must be preceded by an 'ESC' (x1B) or 'STX' (x02) character and be followed
by a 'Carriage Return' (x0D) or 'ETX' (x03) character. Shaded areas indicate factory default settings.
Enable Disable Global Defaults
U2 Enable Factory Default Settings
Z1 Transmit software version
Z2 Save all values set by command
Z3
Display software setting flags,
prefix/suffix, & min/max lengths.
Only Add Symbology Selection
A0
B0 Disable all symbologies
J0 Enable all UPC and EAN plus add-ons
A2 B2 Code 39
A3 B3 Codabar (NW-7)
A4 B4 IATA
A5 B5 Code 93
A6 B6 Code 128 (Inc. EAN-128)
A7 B7 MSI/Plessey
A1 B1 UK/Plessey
A9 B9
J1 R1 UPC (A/E)
J2 R2 UPC (A/E)+2
J3 R3 UPC (A/E)+5
J4 R4 EAN (13/8)
J5 R5 EAN (13/8) +2
J6 R6 EAN (13/8) +5
J7 R7 2 or 5 Industrial
J8 R8 2 or 5 Interleaved
JD JZ
RA R9
Enable all symbologies
Telepen
TriOptic
SCode
Enable Disable Options for UPC-A and UPC-E
E2 UPC-A as EAN13 (13 Digits)
Transmit leading zero & CD
E3 UPC-A (12 Digits) No leading zero
but transmit CD
E4 UPC-A as EAN13 (12 Digits)
Transmit leading zero but No CD
E5 UPC-A (11 Digits) No leading zero
& no CD transmitted
E6 UPC-E (8 Digits)Transmit leading
zero & CD
E7 UPC-E (7 Digits) No leading zero
but transmit CD
E8 UPC-E (7 Digits) Transmit leading
zero but no CD
E9 UPC-E (6 Digits) No leading zero
& no CD transmitted
6P 6Q Transmit UPC-E as UPC-A
Enable Disable Options for EAN-8 & EAN-13
6K 6J EAN-13 Transmit CD
6I 6H EAN-8 Transmit CD
IA IB Enable ISBN translation
HO HN Enable ISSN translation
Enable Disable Options for Code 39
8E
8D
C0 C1 Enable Check Digit calculation
D9 D8* Enable Check Digit Transmission
D0 D1
-Y
Enable read of 1 or more
character lengths
Enable read of 3 or more
character lengths
Enable start/stop characters
transmission (*…..*)
Enables primary decode
algorithms for Code 39, I & D 2 of
Page 18
Page 22
Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
5, IATA, & Codabar
-Z
Enable Disable Options for Code 39 (cont.)
.S
Alternate decode algorithm no.1
for Code 39
Alternate decode algorithm no.2
for Code 39
Enable Disable Options for IT Pharmaceutical
D6 D5 IT Pharmaceutical only
D7 D5 IT Pharmaceutical if possible
DB DA Transmit Leading A
Enable Disable Options for Codabar (NW-7)
HC Enable 1 character read minimum
HB Enable 3 character read minimum
HF Enable 5 character read minimum
F0
F1
F2 Tr ansmit start/stop as abcd/tn*e
F3
F4 T ransmit start/stop as abcd/abcd
H8 H9 Transmit check digit
H6 H7 Calculate check digit
H4 HA Enable ABC Codabar
H5 HA Enable Cx Codabar
H3 HA
HH HI Intercharacter gap check
-Y -X Primary/Alternative Algorithm
Do not transmit start/stop
characters
Transmit start/stop as
ABCD/TN*E
Transmit start/stop as
ABCD/ABCD
Enable Normal ABC & Cx
Codabar
Enable Disable Options for I 2 of 5 / SCode
G1 G0 Calculate check digit
E0 E1 Transmit check digit
GE Enable 1 character minimum
GF Enable 3 characters minimum
GI Enable 5 characters minimum
GG GH Transmit S-Code as I 2 of 5
-Y -X Primary/Alternative Algorithm
Enable Disable Options for IATA
4H Do not calculate check digit
4J
4I Calculate CD (Form + Serial)
4K Calculate check digit (all data)
4L 4M Transmit check digit
-Y -X Primary/Alternative Algorithm
Calculate CD (CPN + Form +
Serial)
Enable Disable
JF OF EAN-128 Only
MO MP Concatenation
Options Code 128/EAN 128
Enable Disable
Options for Code 93
+V +W Concatenation
Setting the Number of Digits
H1
HK
HL
HM
H0
length setting all symbologies
Length setting on selected symbologies
Minimum length setting on selected
symbologies
Maximum length setting on selected
symbologies
Disable length setting on all symbologies
Prefix Suffix
RY RZ All codes
N1 N6 UPC-A
M0 O0 UPC-A +2 or +5
N2 N7 UPC-E
M1 O1 UPC-E +2 or +5
N3 N8 EAN13
M2 O2 EAN-13 +2 or +5
N4 N9 EAN-8
M3 O3 EAN-8 +2or +5
M4 O4 Code 39
Select Symbology for
prefix/Suffix
Page 19
Page 23

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Prefix Suffix
M5 O5 Codabar (NW-7)
M6 O6 Industrial 2 of 5
Select Symbology for
prefix/Suffix
Prefix Suffix
M7 O7 Interleaved 2 of 5
M8 O8 Code 93
M9 O9 Code 128
I8 I9 IATA
N0 N5 MSI/Plessey
MB OB SCode
L8 L9 Telepen
MZ PS Preamble/Postamble
Select Symbology for
prefix/Suffix (cont.)
Direct Input Alpha/Numeric Characters
Cmd Char. Cmd Char. Cmd Char.
Q0 0 0A A $A a
thru thru thru thru thru thru
Q9 9 0Z Z $Z z
Direct Input ASCII Control Characters
Cmd. Char. Cmd. Char. Cmd Char.
9G null 1K VT 1V SYN
1A SOH 1L FF 1W ETB
1B STX 1M CR 1X CAN
1C ETX 1N SO 1Y EM
1D EOT 1O SI 1Z SUB
1E ENQ 1P DLE 9A ESC
1F ACK 1Q DC1 9B FS
1G BEL 1R DC2 9C GS
1H BS 1S DC3 9D RS
1I HT 1T DC4 9E US
1J LF 1U NAK 9F DEL
Direct Input Miscellaneous Characters
Cmd. Char. Cmd. Char. Cmd Char.
Direct Input Miscellaneous Characters
5A
<SPAC
E)
5M , 7A [
5B ! 5N - 7B \
5C “ 5O . 7C ]
5D # 5P / 7D ^
5E $ 6A : 7E _
5G & 6B ; 7F ‘
5H ` 6C < 9T {
5I ( 6D = 9U |
5J ) 6E > 9V }
5K * 6F ? 9W ~
5L + 6G @
Communication Parameters
K0 150 baud
K1 300 baud
K2 600 baud
K3 1,200 baud
K4 2,400 baud
K5 4,800 baud
K6 9,600 baud
K7 19,200 baud
K8 38,400 baud
L0 7 Data Bits
L1 8 Data Bits
L2 Parity = None
L3 Parity = Even
L4 Parity = Odd
L5 1 Stop bit
L6 2 Stop bits
Communication Handshaking
I0 Unlimited wait for CTS from terminal
I1 100 mS wait for CTS from terminal
I2 200 ms wait for CTS from terminal
I3 400 mS wait for CTS from terminal
P0 No Handshaking
Page 20
Page 24

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Communication Handshaking
P1 Busy/Ready
P2 Modem
P3 ACK/NAK (1 sec timeout with error buzzer)
ACK/NAK no response (100 ms timeout,
P4
terminates with good read buzzer)
ZG XON/OFF
Communication Delays
KA No intercharacter delay
KB 20 ms intercharacter delay
KC 50 ms intercharacter delay
KD 100 ms intercharacter delay
Buzzer Operation
T0 Volume = Maximum
T1 Volume = Upper mid-range
T2 Volume = Lower mid-range
T3 Volume = Minimum
W0 Disable Buzzer
W1 Enable buzzer at 3kHz
W2 Enable buzzer at 3kHz with 2.5kHz interval
W3 Enable buzzer at 3kHz with 4kHz interval
W4 Buzzer duration 0.10 sec
W5 Buzzer duration 0.20 sec
W6 Buzzer duration 0.40 sec
W7 Buzzer duration 0.05 sec
W8 Enable buzzer
Setting the Trigger Functions
S7 Disable the trigger function (LED On)
Enable the trigger function (LED OFF until the
S8
trigger is activated )
Z Activate the trigger; turns the LEDs ON
Y Terminate the trigger.
S1 Multiple Read Mode
S2 Continuous Read Mode
Scanner Timeout (Trigger Mode)
Y1 1 second after triggering
Y2 2 second after triggering
Y3 3 second after triggering
Y4 4 second after triggering
Y5 5 seconds after triggering
Y6 6 second after triggering
Y7 7 seconds after triggering
Y8 8 seconds after triggering
Y9 9 seconds after triggering
YL Read time x 10
Scan time follows Hardware trigger active
Y0
YM
time. Can be terminated by sending the Y
command
Stays ON indefinitely after triggering. Must be
terminated by sending the Y commands.
EAN/UPC Add On Wait Times
XA Add-on Wait Time - Disable
XB Add-on Wait Time – 250 msec
XC Add-on Wait Time – 500 msec
XD Add-on Wait Time – 750 msec
S1 Multiple read reset time for same
labels
AH Multiple Read Reset Time – 50 msec
AI Multiple Read Reset Time – 100 msec
AJ Multiple Read Reset Time – 200 msec
AK Multiple Read Reset Time – 300 msec
AL Multiple Read Reset Time – 400 msec
AM Multiple Read Reset Time – 500 msec
AN Multiple Read Reset Time – 600 msec
AG Multiple Read Reset Time - Indefinite
Selecting the Read Mode
Single Read Mode (Trigger must be Enabled,
S0
S8)
Quiet Zone Options
YN No margin check
Page 21
Page 25

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
YO Margin check 1/7 nominal
YP Margin check 2/7 nominal
YQ Margin check 3/7 nominal
YR Margin check 4/7 nominal
YS Margin check 5/7 nominal
YT Margin check 6/7 nominal
YU Margin check normal
Redundant Decoding
X2 Read bar code 3 times before transmitting
X3 Read bar code 4 times before transmitting
Xmit Error (Trigger Enabled Mode only)
TH User defined error message for no label
TI User defined error message for no decode
TG Clear error messages for no label, no decode
T4 Disable good read LED (GRL)
T5 GRL ON for 0.20 seconds after decode
T6 GRL ON for 0.40 seconds after decode
T7 GRL ON for 0.80 seconds after decode
ACK/NAK response to Host transmissions
WD No response to command
WC
Response to command – OK=ACK,
ERROR=NAK
Good Read LED Operation
Page 22
Page 26

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Appendix C:
Bar Code Programming Menus & Commands - Index
1. Global Default & Scanner Configurations.......................................24
2. Symbology Selection..............................................................25-26
3. Add/Activate Specific Bar Code Symbologies............................ 27-28
4. Delete/Deactivate Bar Code Symbologies......................................28
5. Options for UPC..........................................................................29
6. Options for EAN-8 & EAN-13........................................................30
7. Options for Code-39 & IT Pharmaceutical)............................... 31-32
8. Options for Codabar (NW-7)................................................... 32-33
9. Options for 2 of 5 (Including SCode)............................................35
10. Options for IATA.......................................................................36
11. Options for Code-128 & EAN-128................................................37
12. Options for Code-93...................................................................37
13. Setting the Number of Digits.......................................................38
14. Creating a Prefix and/or Suffix............................................... 39-40
15. Setting Prefixes (Identifying the Symbology)........................... 41-42
16. Setting Suffixes (Identifying the Symbology)........................... 42-44
17. Direct Input of Numeric Characters .............................................45
18. Direct Input of Alpha Characters .................................................46
19. Direct Input of Alpha Characters (Lower Case)…………………………….47
20. Direct Input of Control Characters.......................................... 48-49
21. Direct Input Characters Miscellaneous .................................... 50-51
22. Communication Parameters................................................... 52-53
23. Handshaking ........................................................................53-54
24. Buzzer Operation.......................................................................55
25. Setting the Trigger Functions......................................................56
26. Selecting the Read Mode.......................................................56-57
27. Add-on Wait Mode.....................................................................58
28. Scanner Timeout (Trigger Enabled Mode only).............................59
29. Multiple Read Reset Time...........................................................60
30. Quiet Zone Options....................................................................61
31. Redundant Decoding..................................................................62
32. Transmitting Error Indications (Trigger Enabled only) ...................62
33. Programming No Read Error Messages........................................63
34. Good Read LED Operation..........................................................63
Page 23
Page 27

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
1. Global Default & Scanner Configurations
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
U2
Z1
Z2*
Z3
Note: Where computer commands appear in parenthesis, bar code commands must be used to start and
end manual programming of the scanner.
START/END Programming Menu
Transmit software version
Save all values set by com port
(not lost upon power off)
Display software settings,
prefix/suffix, & min/max lengths
Function
/Description
Return all parameters to
Default settings
commands
Bar Code
Command
[[
V3
[2
[3
[!
%
Note: Scanner default settings are indicated by a pointing hand (
follow.
* Use Z2 (Save all values set by command) after sending com port commands to store settings in nonvolatile memory prior to power off.
%) symbol throughout the menus to
Page 24
Page 28

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
2. Symbology Selection
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
A0
J0
A2
A3
A4
A5
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
Enable all bar code
symbologies
Enable all UPC and EAN
Only Code-39
Only Codabar (NW-7)
Only IATA
Only Code-93
Bar Code
Command
[[
B1
K1
B3
B!
B5
B6
A6
A7
A1
A9
J1
J2
J3
Only Code-128 (Inc. EAN-128)
Only MSI/Plessey
Only UK/Plessey
Only Telepen
Only UPC (A/E)
Only UPC (A/E)+2
Only UPC (A/E)+5
B7
B8
B2
B:
K2
K3
K!
CONTINUED ON NEXT PAGE…
Page 25
Page 29

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
2. Symbology Selection (continued)
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
J4
J5
J6
J7
J8
JD
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
Only EAN (13/8)
Only EAN (13/8) +2
Only EAN (13/8) +5
Only Industrial 2 of 5
Only Interleaved 2 of 5
TriOptic
Bar Code
Command
[[
K5
K6
K7
K8
K9
KE
RA
SCode
SB
Page 26
Page 30

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
3. Add/Activate Specific Bar Code Symbologies
Computer
Command
Function
/Description
Bar Code
Command
(ZZ)
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
B7
B1
START/END
Programming Menu
Enable Code 39
Enable Codabar (NW-7)
Enable IATA
Enable Code 93
Enable Code 128
Enable MSI/Plessey
Enable UK/Plessey
[[
C3
C!
C5
C6
C7
C8
C2
%
%
%
%
%
%
%
B9
R1
R2
R3
R4
R5
Enable Telepen
Enable UPC (A/E)
Enable UPC (A/E) +2
Enable UPC (A/E) +5
Enable EAN (13/8)
Enable EAN (13/8) +2
C:
S2
S3
S!
S5
S6
CONTINUED ON NEXT PAGE…
%
%
%
Page 27
Page 31

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
3. Add/Activate Specific Bar Code Symbologies (continued)
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
R6
R7
R8
JZ
R9
START/END Programming Menu
Enable Interleaved 2 of 5
Function
/Description
Enable EAN (13/8) +5
Enable Industrial 2 of 5
TriOptic
SCode
Bar Code
Command
[[
S7
S8
S9
K[
S:
%
%
%
%
4. Delete/Deactivate Bar Code Symbologies
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
BO
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
Disable all symbologies
Bar Code
Command
[[
C1
Page 28
Page 32

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
5. Options for UPC
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
E2
E3
E4
E5
E6
E7
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
Translate UPC-A to EAN-13
(13 Digits) Add leading zero &
Transmit check digit
UPC-A (12 Digits)
Do not add leading zero;
Transmit check digit
Translates UPC-A to EAN-13
(12 Digits) Add leading zero;
Do not transmit check digit
UPC-A (11 Digits)
Do not add leading zero;
Do not transmit check digit
UPC-E (8 Digits), Transmit first
character & check digit
UPC-E (7 Digits) Do not transmit
first character, do transmit check
digit
Bar Code
Command
[[
F3
F!
F5
F6
F7
F8
%
%
UPC-E (7 Digits)
E8
E9
6Q
6P
Do transmit first character, do
not transmit check digit
UPC-A (6 Digits)
Do not transmit first character
nor check digit
Do not expand UPC-E to UPC-A
Expand UPC-E to UPC-A
F9
F:
7R
7Q
%
Page 29
Page 33

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
6. Options for EAN-8 & EAN-13
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
6J
6K
6H
6I
IB
IA
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
EAN-13 Do not transmit CD
EAN-13 Transmit CD
EAN-8 Do not transmit CD
EAN-8 Transmit CD
Disable ISBN translation
Enable ISBN translation
Bar Code
Command
[[
7K
7L
7I
7J
JC
JB
%
%
%
HN
HO
Disable ISSN translation
Enable ISSN translation
IO
IP
%
Page 30
Page 34

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
7. Options for Code 39 and IT Pharmaceutical
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
8E
8D
C1
C0
D9
D8
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
Enable 1 character (3 characters
including start/stop characters)
Enable 3 characters
Disable check digit calculation
Enable check digit calculation
Transmit check digit
Do not transmit check digit
Bar Code
Command
[[
9F
9E
D2
D1
E:
E9
%
%
%
D1
D0
-Y
-Z
.S
Do not transmit start/stop
characters (*……*)
Transmit start/stop characters
(*……*)
Enables primary decode
algorithms for Code 39, I & D 2
of 5, IATA, & Codabar
Alternate decode algorithm no.1
for Code 39
Alternate decode algorithm no.2
for Code 39
E2
E1
.Z
.[
/T
CONTINUED ON NEXT PAGE
%
%
Page 31
Page 35

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
7. Options for Code 39 and IT Pharmaceutical (continued)
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
D5
D6
D7
DB
DA
8. Options for Codabar (NW-7)
/Description
Programming Menu
Disable IT Pharmaceutical &
enable code 39
Enable IT Pharmaceutical &
disable code 39
Enable IT Pharmaceutical if
IT Pharmaceutical, enable
transmit of leading A
IT Pharmaceutical, disable
transmit of leading A
Function
START/END
possible
Bar Code
Command
[[
E6
E7
E8
EC
EB
%
%
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
HC
HB
HF
F0
F1
F2
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
Enable 1 character (3 characters
including start/stop characters)
Enable 3 characters
Enable 5 characters
Do not transmit
start/stop characters
Transmit start/stop
characters as ABCD/TN*E
Transmit start/stop
characters as abcd/tn*e
Bar Code
Command
[[
ID
IC
IG
G1
G2
G3
%
%
F3
Transmit start/stop
characters as ABCD/ABCD
G!
Page 32
Page 36

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
T
Scanner
8. Options for Codabar (NW-7) (continued)
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
F4
HJ
H8
H9
H7
H6
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
Transmit start/stop
characters as abcd/abcd
ransmit start/stop as
DC1, DC2, DC3, DC4
Transmit check digit
Do not transmit check digit
Do not calculate check digit
Calculate check digit (MOD 16)
Bar Code
Command
[[
G5
IK
I9
I:
I8
I7
%
%
H4
H5
H3
HA
HI
HH
-Y
-X
Enable ABC Codabar
Enable CX Codabar
Enable normal, ABC & CX
Codabar
Disable ABC & Cx Codabar
Disable Inter-character Gap
Check
Enable Inter-character Gap
Check
Enables primary decode
algorithms for Code 39, I & D 2
of 5, IATA, & Codabar
Alternate decode algorithm for
Codabar
I5
I6
I!
IB
IJ
II
.Z
.[
%
%
%
Page 33
Page 37

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Codabar (NW-7) Format
Start
Character
1 to 42
data digits
Check
digit
Stop
Character
A . . . . . . . . T
a . . . . . . . . t
A . . . . . . . . A
a . . . . . . . . a
• Codabar (NW-7) has four different start/stop character schemes as shown above. The check digit is
optional and, if present, would be the last character before the stop character.
• If the scanner is programmed to calculate the check digit and the bar code is not printed with a
check digit, the bar code will not be read.
Page 34
Page 38

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
9. Options for Interleaved & Industrial 2 of 5
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
G0
G1
E0
E1
GE
GF
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
Do not calculate check digit
Calculate check digit
Do not transmit Check digit
Transmit check digit
Enable 1 character minimum
Enable 3 character minimum
Bar Code
Command
[[
H1
H2
F1
F2
HF
HG
%
%
GI
GG
GH
-Y
-X
2 of 5 Format (Standard (Industrial) and Interleaved)
Opticon strongly recommends that the “Setting the Number of Digits” featured in Section 13 be employed
whenever 2 of 5 bar codes are used.
Enable 5 character minimum
Enable transmit SCode as
Interleaved 2 of 5
Disable transmit SCode as
Interleaved 2 of 5
Enables primary decode
algorithms for Code 39, I & D 2
of 5, IATA, & Codabar.
Alternate algorithm for I 2 of 5,
D 2 of 5 & IATA
1 to 44 data digits CD
numeric only (0 to 9) Check Digit
HJ
HH
HI
.Z
.Y
%
%
%
Page 35
Page 39

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
10. Options for IATA
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
4H
4J
4I
4K
4L
4M
-Y
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
Do not calculate check digit
Calculate check digit
(CPN + Form + Serial)
Calculate check digit
(Form + Serial)
Calculate check digit
(All data)
Transmit check digit
Do not transmit check digit
Enables primary decode
algorithms for Code 39, I & D 2
of 5, IATA, & Codabar.
Bar Code
Command
[[
5I
5K
5J
5L
5M
5N
.Z
%
%
%
-X
The IATA code is a variable length symbology with an optional check digit and non-printable start/stop
characters. The following characters are supported: Digits 0 up to 9.
The checksum is calculated as modulo seven of the data string. IATA is an acronym for International Air
Transport Association.
Meaning of Acronym Coupon
Number of digits (15 total) 1 3 2 8 1
♦ Enable check digit check
♦
Selection of the check digit calculation
♦
Disable transmission of the check digit
Check digit calculation: If the check digit calculation is required, then the appropriate calculation method
must be selected.
Alternate algorithm for I 2 of 5,
D 2 of 5, IATA & Codabar
String format CPN AC FC SN CD
.Y
Airline
Code
Form
Code
Serial
Number
Check
Digit
Page 36
Page 40

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
11. Options for Code-128 / EAN-128
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
OF
JF
MP
MO
12. Options for Code-93
Computer
Command
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
Disable EAN-128 only
Enable EAN-128 only
Disable concatenation
Enable concatenation
Function
/Description
Bar Code
Command
[[
PG
KG
NQ
NP
Bar Code
Command
%
%
(ZZ)
+W
+V
START/END
Programming Menu
Disable concatenation
Enable concatenation
[[
,X
,W
%
Page 37
Page 41

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
13. Setting the Character length that is allowed to be read.
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
H0
H1
HK
HL
HM
To avoid truncation errors, the scanner can be programmed to only decode bar codes of one specific
length, i.e., containing a specific number of digits. It is also possible to program the scanner to only
decode bar codes of either of two specific lengths.
Disable length setting on all
Enable length setting on all
Enable length setting for selected
Enable minimum length for
Enable maximum length for
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
symbologies
symbologies
codes
selected codes
Selected codes
Bar Code
Command
[[
I1
I2
IL
IM
IN
%
To set one or two lengths for all
symbologies:
Scan “START” to enter the
1.
programming mode.
Scan “Enable length setting (H1)
2.
for all symbologies”.
Scan a sample bar code of
3.
the desired length.
Repeat Step #3, re-scanning
4.
the sample bar code length or a
different bar code length to get 2
lengths.
Scan “END” to exit the
5.
programming mode
“Setting the Number of Digits” can only be applied to Code 39, NW-7, 2 of 5, and MSI/Plessey. WPC,
Code 93, IATA, and Code 128 are not affected.
Setting Minimum/Maximum Length
This option modifies the default minimum length table. To use this option, perform the following steps:
Scan “START” to enter the programming mode
1.
Scan “Enable minimum length for selected codes” (HL)
2.
Scan bar codes of the
3.
required type and length
To set one or two lengths for selected
symbologies:
Scan “START” to enter
1.
the programming mode
Scan “Enable length setting (HK)
2.
for selected symbologies”.
Scan a sample bar code of
3.
the desired length #1
Repeat Step #3, re-scanning
4.
the sample bar code length or a
different bar code length to get 2
lengths.
Scan “END” to exit the
5.
programming mode
.
Scan “END” to end the programming sequence.
4.
Page 38
Page 42

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
For example, if a Code 39 label containing 2 characters were scanned in Step 3 then only Code 39 labels
would be checked for a minimum length of 2 characters. If a second label had been read in Step 3
(immediately following the first), then that particular symbology would have been set to its associated
minimum character length.
In a similar manner, the maximum length for selected codes can be established by using the “Enable
maximum length for selected codes” (HM) command.
14. Creating a Prefix and/or Suffix
Computer
Command
Function
/Description
Bar Code
Command
(ZZ)
Z3
The Z3 command can be used to instruct the scanner to provide a list of its current software settings
including prefixes and suffixes.
The scanner can be programmed to transmit a prefix and/or suffix with the decoded data. A Prefix (or a
Suffix) is composed of up to 4 characters. The following steps are used to establish a Prefix that will be
Example
Suffix to UPC-A bar code data:
Scan “START/END Programming Mode”
1.
Scan N1, representing a Prefix for UPC-A
2.
Scan 0A, representing the alpha character “A”
3.
Scan N6, representing a Suffix for UPC-A
4.
Scan 0B, representing the alpha character “B”
5.
Scan “START/END Programming Mode”
6.
transmitted with the bar code data:
Prefix/Suffix value and length
: To add the alpha character “A” as a Prefix and “B” as a
START/END
Programming Menu
Display Settings including
(expressed in hexidecimal
format)
[[
[!
Scan Start
1.
2.
Scan the bar code representing the symbology to which you wish to add a Prefix/Suffix
3.
Scan the character(s) that will comprise the Prefix/Suffix. Up to four numeric, alpha or control
character(s) may be used. Scanning no characters will delete the Prefix/Suffix
Scan “STOP” to exit the Programming Mode.
4.
In addition, the scanner can be programmed to transmit a preamble and/or postamble with the decoded
data. A Preamble and/or postamble can be composed of up to 8 characters each and will apply to all
symbologies. The following steps are used to establish a Preamble and/or postamble that will be
transmitted with the bar code data:
Scan Start
1.
2.
Scan the MZ for preamble or PS for Postamble
3.
Scan the character(s) that will comprise the Preamble/Postamble. Up to eight characters may be
used. Scanning no characters will delete the Preamble/Postamble.
Scan “STOP” to exit the Programming Mode.
4.
Page 39
Page 43

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Example
Suffix to UPC-A bar code data:
: To add the alpha character “A” as a Prefix and “B” as a
Scan “START/END Programming Mode”
7.
Scan N1, representing a Prefix for UPC-A
8.
Scan 0A, representing the alpha character “A”
9.
Scan N6, representing a Suffix for UPC-A
10.
Scan 0B, representing the alpha character “B”
11.
Scan “START/END Programming Mode”
12.
Page 40
Page 44

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
15. Setting Prefixes (Identifying the Symbology)
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
RY
N1
M0
N2
M1
N3
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
All codes
UPC-A
UPC-A +2 or +5
UPC-E
UPC-E +2 or +5
EAN-13
Bar Code
Command
[[
SZ
O2
N1
O3
N2
O!
M2
N4
M3
M4
M5
M6
EAN –13 +2 or +5
EAN-8
EAN-8 +2 or +5
Code 39
Codabar (NW-7)
Industrial 2 of 5
N3
O5
N!
N5
N6
N7
CONTINUED ON NEXT PAGE...
Page 41
Page 45

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
15. Setting Prefixes (Identifying the Symbology) (continued)
Computer
Command
Function
/Description
Bar Code
Command
(ZZ)
M7
M8
M9
I8
N0
MB
L8
START/END
Programming Menu
Interleaved 2 of 5
Code 93
Code 128
IATA
MSI/Plessey
SCode
Telepen
[[
N8
N9
N:
J9
O1
NC
M9
MZ
Preamble (all codes)
N[
Page 42
Page 46

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
16. Setting Suffixes (Identifying the Symbology)
Computer
Command
Function
/Description
Bar Code
Command
(ZZ)
RZ
N6
O0
N7
O1
N8
O2
START/END
Programming Menu
All Codes
UPC-A
UPC-A +2 or +5
UPC-E
UPC-E +2 or +5
EAN-13
EAN–13 +2 or +5
[[
S[
O7
P1
O8
P2
O9
P3
N9
O3
O4
O5
O6
CONTINUED ON NEXT PAGE...
EAN-8
EAN-8 +2 or +5
Code 39
Codabar (NW-7)
Industrial 2 of 5
O:
P!
P5
P6
P7
Page 43
Page 47

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
16. Setting Suffixes (Identifying the Symbology) (continued)
Computer
Command
Function
/Description
Bar Code
Command
(ZZ)
O7
O8
O9
I9
N5
OB
L9
START/END
Programming Menu
Interleaved 2 of 5
Code 93
Code 128
IATA
MSI/Plessey
SCode
Telepen
[[
P8
P9
P:
J:
O6
PC
M:
PS
Postamble (All Codes)
QT
Page 44
Page 48

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
17. Direct Input of Numeric Characters
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
Q0
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
Q5
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
0
1
2
3
4
5
Bar Code
Command
[[
R1
R2
R3
R!
R5
R6
Q6
Q7
Q8
Q9
6
R7
7
R8
8
R9
9
R:
Page 45
Page 49

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
18. Direct Input of Alpha Characters
START/END
(ZZ)
Program
Menu
[[
0N N
1O
0A A
0B B
0C C
0D D
0E E
0F F
0G G
0H H
1B
1C
1D
1E
1F
1G
1H
1I
0O O
0P P
0Q Q
0R R
0S S
0T T
0U U
0V V
1P
1Q
1R
1S
1T
1U
1V
1W
0I I
0J J
0K K
0L L
0M M
1J
1K
1L
1M
1N
0W W
0X X
0Y Y
0Z Z
(ZZ)
START/END
Program
Menu
1X
1Y
1Z
1[
[[
Page 46
Page 50

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
19. Direct Input of Alpha Characters (Lower Case)
START/END
(ZZ)
Program
Menu
[[
$N n
%O
$A a
$B b
$C c
$D d
$E e
$F f
$G g
$H h
%B
%C
%D
%E
%F
%G
%H
%I
$O o
$P p
$Q q
$R r
$S s
$T t
$U u
$V v
%P
%Q
%R
%S
%T
%U
%V
%W
$I i
$J j
$K k
$L l
$M m
%J
%K
%L
%M
%N
$W w
$X x
$Y y
$Z z
(ZZ)
START/END
Program
Menu
%X
%Y
%Z
%[
[[
Page 47
Page 51

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
20. Direct Input of Control Characters
(ZZ)
9G
1A
1B
1C
1D
1E
START/END
Program
Menu
^@
(null)
^A
(SCH)
^B
(STX)
^C
(ETX)
^D
(EOT)
^E
(ENQ
)
[[
:H
2B
2C
2D
2E
2F
1M
1N
1O
1P
1Q
1R
1S
^M
(CR)
^N
(SO)
^O
(SI)
^P
(DLE)
^Q
(DC1)
^R
(DC2)
^S
(DC3)
2N
2O
2P
2Q
2R
2S
2T
1F
1G
1H
1I
1J
1K
1L
^F
(ACK)
^G
(BEL)
^H
(BS)
^I
(HT)
^J
(LF)
^K
(VT)
^L
(FF)
2G
2H
2I
2J
2K
2L
2M
START/END
1T
1U
1V
1W
1X
1Y
Program
Menu
^T
(DC4)
^U
(NAK)
^V
(SYN)
^W
(ETB)
^X
(CAN)
^Y
(EM)
(ZZ)
2U
2V
2W
2X
2Y
2Z
[[
Page 48
Page 52

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
20. Direct Input of Control Characters (Continued)
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
1Z ^Z (SUB)
9A ^[ (ESC)
9B ^\ (FS)
9C ^] (GS)
9D ^^ (RS)
9E ^_ (US)
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
Bar Code
Command
[[
2[
:B
:C
:D
:E
:F
9F
DEL
(ASCII 127) :G
Page 49
Page 53

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
21. Direct Input Characters Misc.
START/END
(ZZ)
5A
Program
Menu
(SPACE)
[[
6B
5N -
5O .
6O
6P
5B !
5C “
5D #
5E $
5F %
5G &
5H `
5I (
6C
6D
6E
6F
6G
6H
6I
6J
5P /
6A :
6B ;
6C <
6D =
6E >
6F ?
6G @
6Q
7B
7C
7D
7E
7F
7G
7H
5J )
5K *
5L +
5M ,
6K
6L
6M
6N
7A [
7B \
7C ]
START/END
Program
Menu
(ZZ)
8B
8C
8D
[[
CONTINUED ON NEXT PAGE...
Page 50
Page 54

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
21. Direct Input Characters Misc. (Continued)
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
7D ^
7E _
7F ‘
9T {
9U |
9V }
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
Bar Code
Command
[[
8E
8F
8G
:U
:V
:W
9W ~
:X
Page 51
Page 55

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
22. Communication Parameters
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
K0
K1
K2
K3
K4
K5
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
150 baud
300 Baud
600 Baud
1,200 Baud
2,400 Baud
4,800 Baud
Bar Code
Command
[[
L1
L2
L3
L!
L5
L6
K6
K7
L0
L1
L2
L3
L4
9,600 Baud
19,200 Baud
7 Data Bits
8 Data bits
Parity = None
Parity = Even
Parity = Odd
L7
L8
M1
M2
M3
M!
M5
CONTINUED ON NEXT PAGE
%
%
%
Page 52
Page 56

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
22. Communication Parameters. (Continued)
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
L5
L6
23 Communication Handshaking.
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
I0
Unlimited wait for CTS from
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
1 Stop Bit
2 Stop Bits
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
terminal
Bar Code
Command
[[
M6
M7
Bar Code
Command
[[
J1
%
%
I1
I2
I3
P0
P1
P2
P3
ZG
100 mS wait for CTS from
terminal
200 mS wait for CTS from
terminal
400 mS for CTS from terminal
No Handshaking
or ACK/NAK
Busy/Ready
Modem
ACK/NAK
XON/XOFF
J2
J3
J!
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q!
[H
%
CONTINUED ON NEXT PAGE...
Page 53
Page 57

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
23. Communication Delays
ACK/NAK no response (100 ms
P4
timeout, terminates with good
read buzzer)
Q5
KA
KB
KC
KD
No intercharacter delay
20 ms intercharacter delay
50 ms intercharacter delay
100 ms intercharacter delay
LB
LC
LD
LE
%
Page 54
Page 58

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
24. Buzzer Operation
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
T0
T1
T2
T3
W0
W8
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
Volume = Maximum
Volume = Upper Mid-range
Volume = Lower Mid-range
Volume = Minimum
Disable buzzer
Enable buzzer
Bar Code
Command
[[
U1
U2
U3
U!
X1
X9
%
%
W1
W2
W3
W4
W5
W6
W7
Set buzzer at 3kHz
Set buzzer at 3kHz
with 2.5kHz interval
Set buzzer at 3kHz
with 4kHz interval
Buzzer duration 0.10 sec
Buzzer duration 0.20 sec
Buzzer duration 0.40 sec
Buzzer duration 0.05 sec
X2
X3
X!
X5
X6
X7
X8
%
%
Page 55
Page 59

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
25. Setting the Trigger Functions
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
S7
S8
Z
Y
The Trigger function is not enabled in the default setting. This means that the LEDs are “ON” and ready
to scan until the trigger mode is set by the S8 command.
Once in the trigger mode, the host can trigger the unit by sending a <ESC> Z <CR> command. (See
Scanner Timeout to establish the length of time the scanning light remains ON after the trigger is
activated.) A hardware trigger can also be used to turn the scanner ON.
Disable the trigger function
/LEDs are ON continuously
Enable the trigger function /LEDs
are OFF until trigger is activated
Activate the trigger; turns the
Terminates the trigger 'on time'
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
or “pulled”
scanner ON.
Bar Code
Command
[[
T8
T9
Use as
Com Port Command
Use as
Com Port Command
%
26. Selecting the Read Mode
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
S0
S1
S2
The operation of the scanner in the various read modes is described in the table below. The “Continuous
Read” mode is helpful in positioning the scanner for optimum reading. In “Continuous Read,” the
scanner’s buzzer functions like a Geiger counter, sounding the most active at the position achieving the
greatest number of good reads.
(Trigger enabled mode only)
Multiple Read Mode. (will read
Continuous Read Mode. (will
read the same label over and
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
Single Read Mode
more then 1 label)
over)
Bar Code
Command
[[
T1
T2
T3
%
Page 56
Page 60

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Mode Trigger Function Enabled (S8)
After receiving a trigger pulse,
scanner will read multiple, different
bar codes in succession until it times
Multiple
Read
(S1)
Continuous
Read
(S2)
Single
Read
(S0)
out. (Each read will reset the
scanner’s time out)
Scanner may not read the same bar
code twice if they are consecutive.
(See Sect. 32)
Scanner will read the same bar code
continuously after receiving a trigger
pulse until the label is removed. The
LEDs then time out.
Scanner will read only one bar code
after receiving a trigger pulse. The
scanner time out is terminated on a
good read.
Trigger Function Disabled (S7)
Scanner will read different bar codes
in succession if they are presented to
the read window.
Scanner may not read the same bar
code twice if they are consecutive.
(See Sect. 32)
Scanner will read the same bar code
continuously.
Same as Multiple Read mode, above.
Page 57
Page 61

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
27. Add-on Wait Mode (Applies to UPC/EAN only)
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
XA
XB
XC
XD
These commands are used when UPC/EAN when add-on is enabled. The reader searches within the
selected time for a valid add-on code. If a valid add-on code is found, the reader transmits the data
immediately. If nothing is found behind the code, the reader will transmit the data without the add-on.
Disable Add-on wait mode
Enable Add-on wait mode of
Enable Add-on wait mode of
Enable Add-on wait mode of
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
0.25 seconds
0.50 seconds
0.75 seconds
Bar Code
Command
[[
YB
YC
YD
YE
%
Page 58
Page 62

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
28. Scanner Timeout (Trigger Enabled Mode only)
These commands, which are only applicable in the Trigger Enabled mode, establish the time-out period
after the trigger pulse is received. In Single Read Mode, the time out is terminated upon a good read.
In Multiple Read and Continuous Read Modes the time out period is restarted after any good read.
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y4
Y5
Y6
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
1 Second after triggering
2 Seconds after triggering
3 Seconds after triggering
4 Seconds after triggering
5 Seconds after triggering
6 Seconds after triggering
Bar Code
Command
[[
Z2
Z3
Z!
Z5
Z6
Z7
%
Y7
Y8
Y9
YL
Y0
YM
7 Seconds after triggering
8 Seconds after triggering
9 Seconds after triggering
Read time x 10
On time follows the Hardware
trigger active time. Can be
terminated by sending the Y
command
Stays ON indefinitely after
triggering. Must be terminated
by sending the Y commands.
Z8
Z9
Z:
ZM
Z1
ZN
Page 59
Page 63

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
29. Multiple Read Reset Time
This option is used in conjunction with the multiple read mode. The selected time sets the period the
scanners should be pointed away from a label before that same label can be decoded again. Indefinitely
means that the next bar code must always be different during the time the scanner is triggered.
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
AH
AI
AJ
AK
AL
AM
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
Set at 50 msec
Set at 100 msec
Set at 200 msec
Set at 300 msec
Set at 400 msec
Set at 500 msec
Bar Code
Command
[[
BI
BJ
BK
BL
BM
BN
%
AN
AG
Set at 600 msec
Set indefinitely
BO
BH
Page 60
Page 64

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
30. Quiet Zone Options
With this option the scanner can decode bar codes that have smaller quiet zone margins than specified
for the symbology. Be careful when using this option as its use may increase the possibility of partial and
ghost reads. Do not use smaller margin checks than necessary. If possible, replace the bar codes labels
with others that have the correct quite zone margins.
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
YN
YO
YP
YQ
YR
YS
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
No margin check
Margin check 1/7 nominal
Margin check 2/7 nominal
Margin check 3/7 nominal
Margin check 4/7 nominal
Margin check 5/7 nominal
Bar Code
Command
[[
ZO
ZP
ZQ
ZR
ZS
ZT
YT
YU
Margin check 6/7 nominal
Margin check normal
ZU
ZV
%
Page 61
Page 65

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
31. Redundant Decoding
The Number of Redundant Decodes determines how many times the scanner must decode a bar code
and obtain the same value before it will transmit the data. For example, if the redundancy is set at three
times, the scanner will not transmit data until it has completed three consecutive, identical “good reads”.
In the case of a poor label which generates an intermediate “no decode” within a sequence of four scans
where three of the four have resulted in “good reads”, the scanner will transmit the data after the fourth
scan. In other words, a “no decode” does not restart the sequence.
Computer
Command
Function
/Description
Bar Code
Command
(ZZ)
X2
X3
32. Transmitting Error Indications
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
START/END
Programming Menu
Read bar code three times
Read bar code four times
Function
/Description
START/END
Programming Menu
[[
Y3
Y!
Bar Code
Command
[[
%
WD
WC
Disable ACK/NAK response to
sent command
Enable OK=ACK, ERROR=NAK,
response to sent command
XE
XD
%
Page 62
Page 66

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
33. No read error messages.
The scanner can be programmed to transmit an error message when no barcode is read. The unit must
be in trigger mode, then, the error message will be sent at the end of a trigger time out. 2 types of
messages can be sent. The first type will indicate that no label was present or that nothing was in front
of the scanner. The second type will indicated that a barcode was present but could not be decoded.
To program an error message, scan the appropriate command below then scan up to 4 direct input
characters. To remove the error message, scan the appropriate command below but do not scan any
direct input characters.
33. Programming No read Error Messages
Computer
Command
Function
/Description
Bar Code
Command
(ZZ)
TH
TI
34. Good Read LED Operation
Computer
Command
(ZZ)
T4
T5
Programming Menu
Program Error message for No
Program Error message for label
present but not decodable.
Programming Menu
disabled after decode
Good read LED ON after
decode for .20 seconds
START/END
label present.
Function
/Description
START/END
Good read LED
[[
UI
UJ
Bar Code
Command
[[
U5
U6
%
T6
T7
Good read LED ON after
decode for .40 seconds
Good read LED ON after
decode for .80 seconds
U7
U8
Page 63
Page 67

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Appendix D:
Dimensional Drawing (All dimensions in millimeters [inches])
Page 64
Page 68

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Appendix E:
NFT 2100 – Optical Performance
NFT 2100 Depth of Field Table
(Grade A Labels)
Density
6 mil 0.9 1.6 0.7
10 mil 0.8 1.7 0.9
20 mil 0.8 2.0 1.2
40 mil 0.9 2.4 1.5
Min. Distance
(inches)
Max Distance
(inches)
Range
(inches)
NFT 2100 Depth of Field Chart
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
Focal Distance 1.4" (35.4 mm)
6 Mil
10 Mil
20 Mil
40 Mil
Distance from front of scanner case (inches)
NFT 2100 Field of View Table
Focal
Distance from Front
of Case
1.0"
25.4mm 35.4mm 38.1mm 50.8mm 63.5mm
Distance
1.4"
1.5 2.0" 2.5"
Field of View
2.6 3.1" 3.3 4.0 4.7
66mm 80mm 83mm 101mm 118mm
Page 65
Page 69

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Appendix F:
Placement Drawing (All dimensions in millimeters [inches])
This Drawing shows one possible placement of the scanner relative to the target label. Other
orientations are possible depending on barcode density and barcode length. Please use the optical
information provided in appendix E as guidance.
Page 66
Page 70

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Appendix G:
Placement Drawing for test tubes (All dimensions in millimeters [inches])
This Drawing shows one possible placement of the scanner relative to the target label. Other
orientations are possible depending on barcode density and barcode length. Please use the optical
information provided in appendix E as guidance.
Page 67
Page 71

Manual No. 25-ULNFT2100-01; Mar, 2005 NFT 2100 CCD Fixed Mount Barcode
Scanner
Notes
Page 68
 Loading...
Loading...