OnLine Power Battery Backup System User Manual

d
-
r
ON LINE POWER
Me
Medical Grade Power Protection
Powe
User’s Manual - 10 kVA to 750 kVA
UPS Systems
On Line Power
www.onlinepower.com
800-227-8988
MED-POWER
OnLine Power
CAUTION !
Hazardous voltage exits inside the UPS (includes the connection
terminals). Cable connection and maintenance should be done by
professional or qualified personnel.
The UPS has its own internal power source (batteries). The output
terminals may be live even when the UPS is not connected to the
AC supply.
DC capacitors are employed in this unit. Hazardous voltage still
exists even when the unit is not energized. Do not touch any part
of the inside of the UPS.
WARNING !
Be sure to operate the UPS within the rated power level.
Prevent direct exposure to direct sunlight, rain or contaminating
environment.
Only qualified technicians should replace the batteries. Since
batteries have high short-circuit current capacity, mistakes in
connection or disconnection can cause severe burns or death to
servicing personnel.

R
MED-POWE
1. SYSTE M OVER VIEW ............................................................ 1-1
1.1. Constructio n of the UP S ........................................................................ 1-1
1.2. Features and A d vantages .......................................................................1-5
1.3. Rectifier ................................................................................................. 1-8
1.4. Inv erter ................................................................................................. 1-10
1.5. Static Switch ........................................................................................1-11
1.6. Main tenance B ypass Sw itch................................................................ 1-12
1.7. Dim e n s i o n & Drawings ......................................................................1-1 3
1.8. Fro nt Panel ........................................................................................... 1-18
Contents Page
OnLine Power
TECHNICAL SPECIFI CAT ION....................................................... 2-1
2.
2.2. 80KVA ~ 160KVA UPS 3–Phase Input / 3-Phase Output........................2-1
3.
INSTALLATION........................................................................................ 3-1
3.1. Site & Environ m ent Co n sid eration ....................................................... 3-1
3.2. Unpacking .............................................................................................. 3-4
3.3. Cable Selecti on ...................................................................................... 3-5
3.4. Terminal Connection .............................................................................3-8
4.
OPERATIONS............................................................................................ 4-1
4.1. Swi tch on Procedur e .............................................................................. 4-1
4.2. Shu tdown Procedure.............................................................................. 4-2
4.3. Fro m Inverter to Bypass Proced u re....................................................... 4-3
4.4. Fro m Bypass to Invert er Proced u re....................................................... 4-4
5.
LCD DI SP L AY....................................................................................... 5-1
5.1. Men u 0 – Main M e n u ............................................................................5-1
5.2. Men u 1 – Select Menu........................................................................... 5-2

R
MED-POWE
5.3. Menu 2 – Status / Warning Menu ............................................................5-3
5.4. Menu 3 – Real Time Data Menu..............................................................5-4
5.5. Menu 4 – Histor i cal Ev en t Menu.......................................................... 5-5
5.6. Men u 5 – Para meter Set ting Menu ....................................................... 5-6
5.7. Menu 6 – Recti fier Data Menu ............................................................. 5-7
5.8. Men u 7 – Output Data Men u ................................................................ 5-8
5.9. Men u 8 – Other Data Me nu .................................................................. 5-8
5.10. Menu 9 – Reserve Data Menu .....................................................................5-9
5.11. Menu 10 – Boost Charge Setting Menu...................................................5-9
Contents Page
OnLine Power
5.12. Menu 11 – Data Time Setting Menu.........................................................5-11
5.13. Menu 12 – Other Setting Menu ............................................................. 5-12
6.
INTERFA CE CONN ECTI ONS ......................................................... 6-1
6.1. Dry Contacts ......................................................................................... 6-1
6.2. Ext e rnal Shutdown ................................................................................ 6-4
6.3. DB9 C o nnectio n .................................................................................... 6-4
OPTION S.............................................................................................7-1
7.
7.1. Batt e ry Cabine t...................................................................................... 7-1
7.2. Emergent St o p S witch........................................................................... 7-2
7.3. Remote Control Panel – UPSCAN ………………………………..7-2
7.4. Software for PC Monitoring – UPSCOM………………………….7-2
7.5. Auto Dialing Module – UPSCALL……………………
7.6. Battery Monitoring Module – DCMAN………
…
………………....7-3
…
……….. 7-3
8.
HELP……………………………………........................
...
..........
8-1
MED-POWER
1.
SYSTEM OVERVIEW
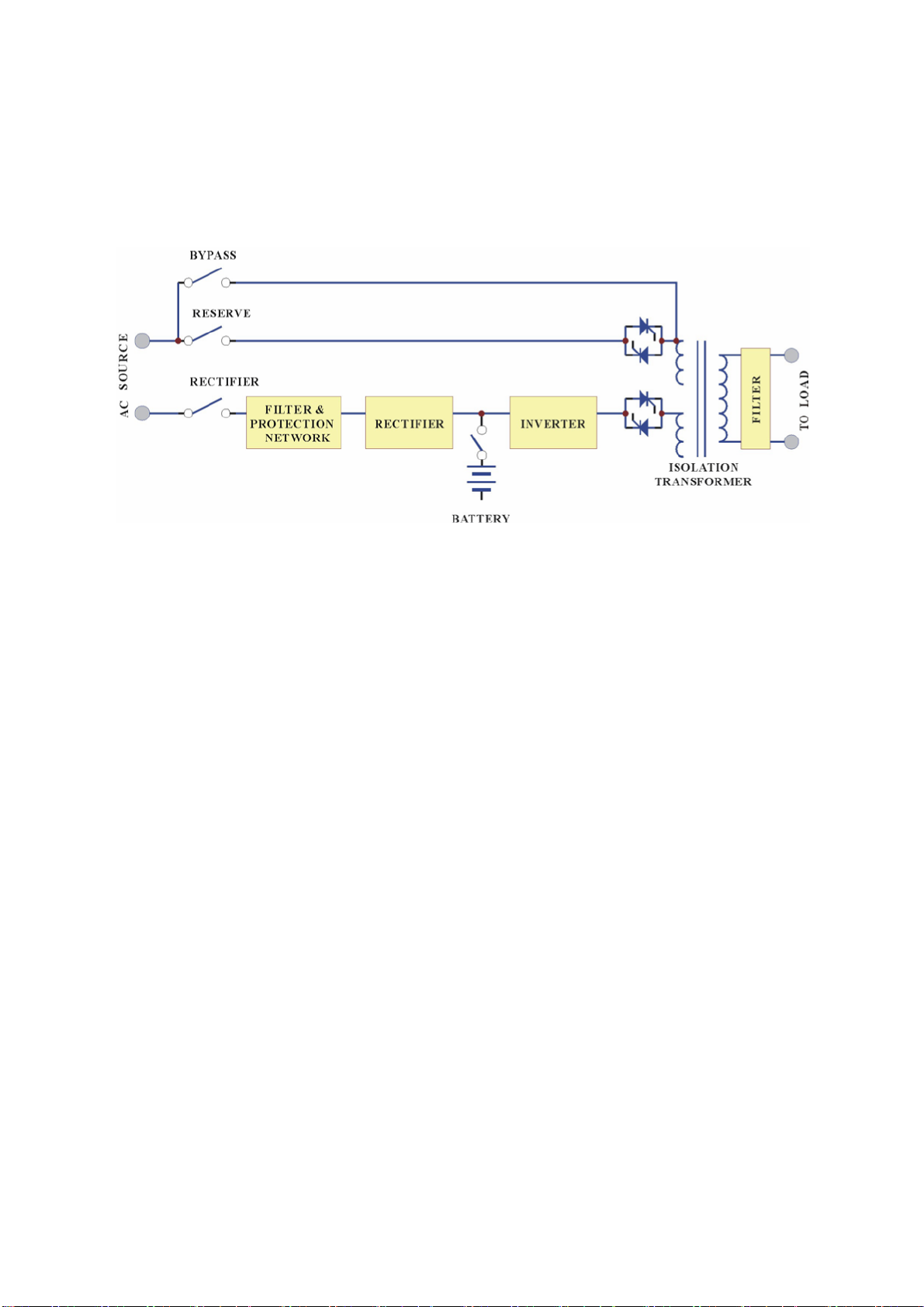
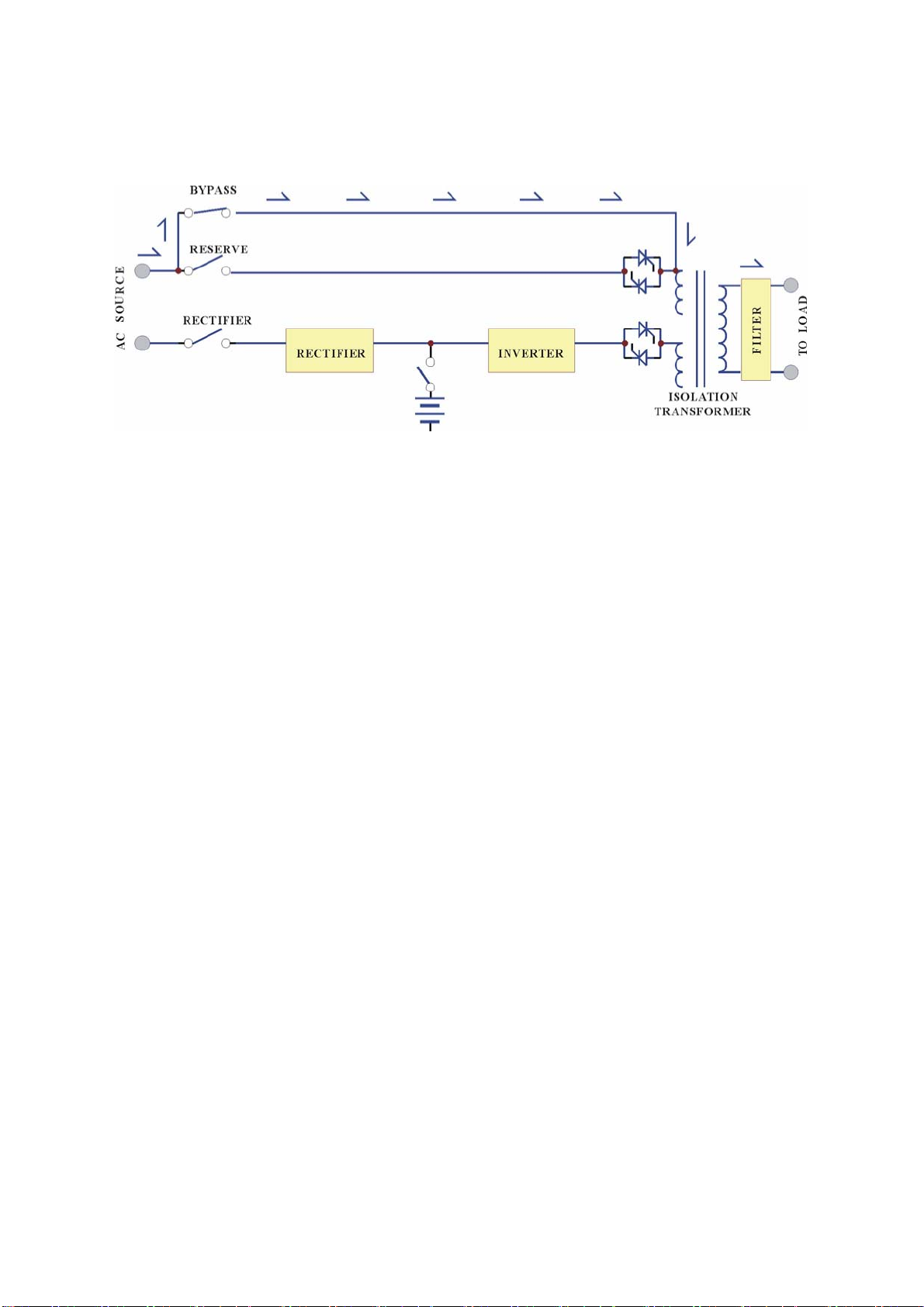
1.1. Construction of the OLP UPS General Topo logy:
OnLine Power
The UPS system is composed of input breakers, input filter, protection network,
rectifier, battery bank, inverter, static switch, bypass breaker, isolation transformer
and output filter. The basic topology is shown in the diagram above. Under normal
AC mode, energy from the AC source is converted to DC power and suppli ed to th e
inverter and charge the batteries to their full capacity all the time; keeping them
ready to support the output load in case of AC source failure.
Although the principle operation of a UPS seems simple and straightforward, the
requirement for a reliable medical grade UPS makes the design and manufacturing
one requiring advanced technology, intelligence and experience with imaging
modality power requirements. Many years have been spent in designing the most
rugged, medical grade and reliable UPS for the market, as well as simple and safe
for the user.
Choosing the best and most suitable UPS for a given application can be easy or
difficult, depending on the client’s knowledge of key parameters. The most obvious
specification, output power, depends on the size of the load during peak power
demands place on the UPS. An allowance for peak imaging power demand has
been added to the present load requirement to assure the imaging modality and the
UPS are compatible.
1-1
P
T
OL
Another important issue is reliability. The prime aim of a UPS is to protect the load.
Therefore, the UPS should be much more reliable than the AC source. An unreliable
UPS suffers the problem of frequent break downs, even more frequent than AC
failure. The cost of repair becomes more than the cost of the unit itself.
Generally, there are four different modes of operation, the NORMAL OPERATION
MODE, the BACK-UP (BATTERY) MODE, the RESERVE MODE and the
MAINTENANCE BYPASS MODE. These are explained below.
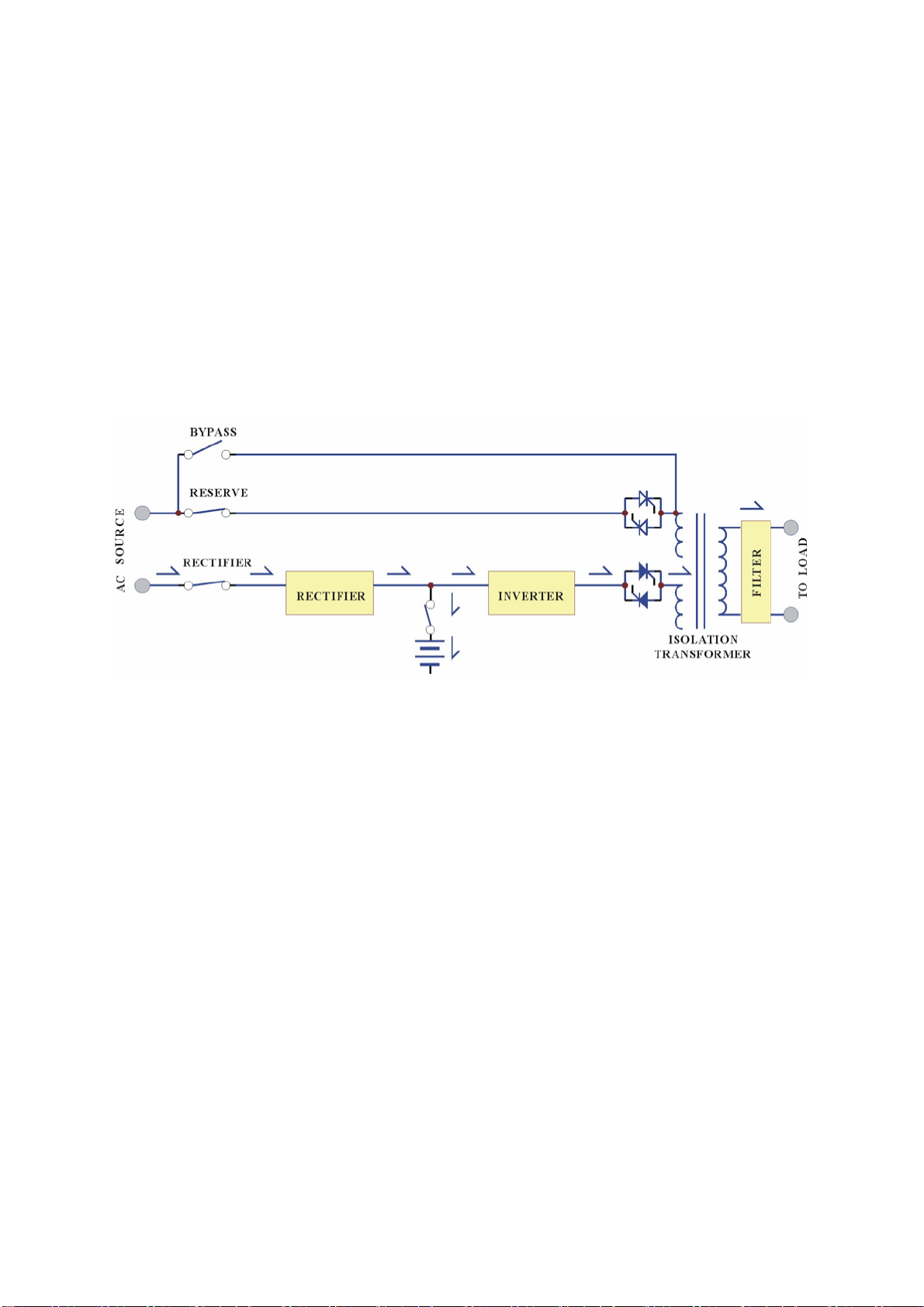
Normal Operation Mode:
hree Phase UPS Systems
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
The rectifier converts the AC input to DC power to supply the inverter and charge the
batteries at the same time. All the fluctuations, surges and spikes of the AC input are
removed during AC to DC conversion. Therefore, the DC supplied by the inverter is
clean and stable.
1-2
P
T
OL
Back-up Mode:
Since the batteries are connected directly to the DC link, when the AC fails, the
batteries change immediately from receiver to becoming the source, supplying
hree Phase UPS Systems
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
energy to the inverter instead of receiving energy from the rectifier. The output AC
is not interrupted; protecting the load connected to the output.
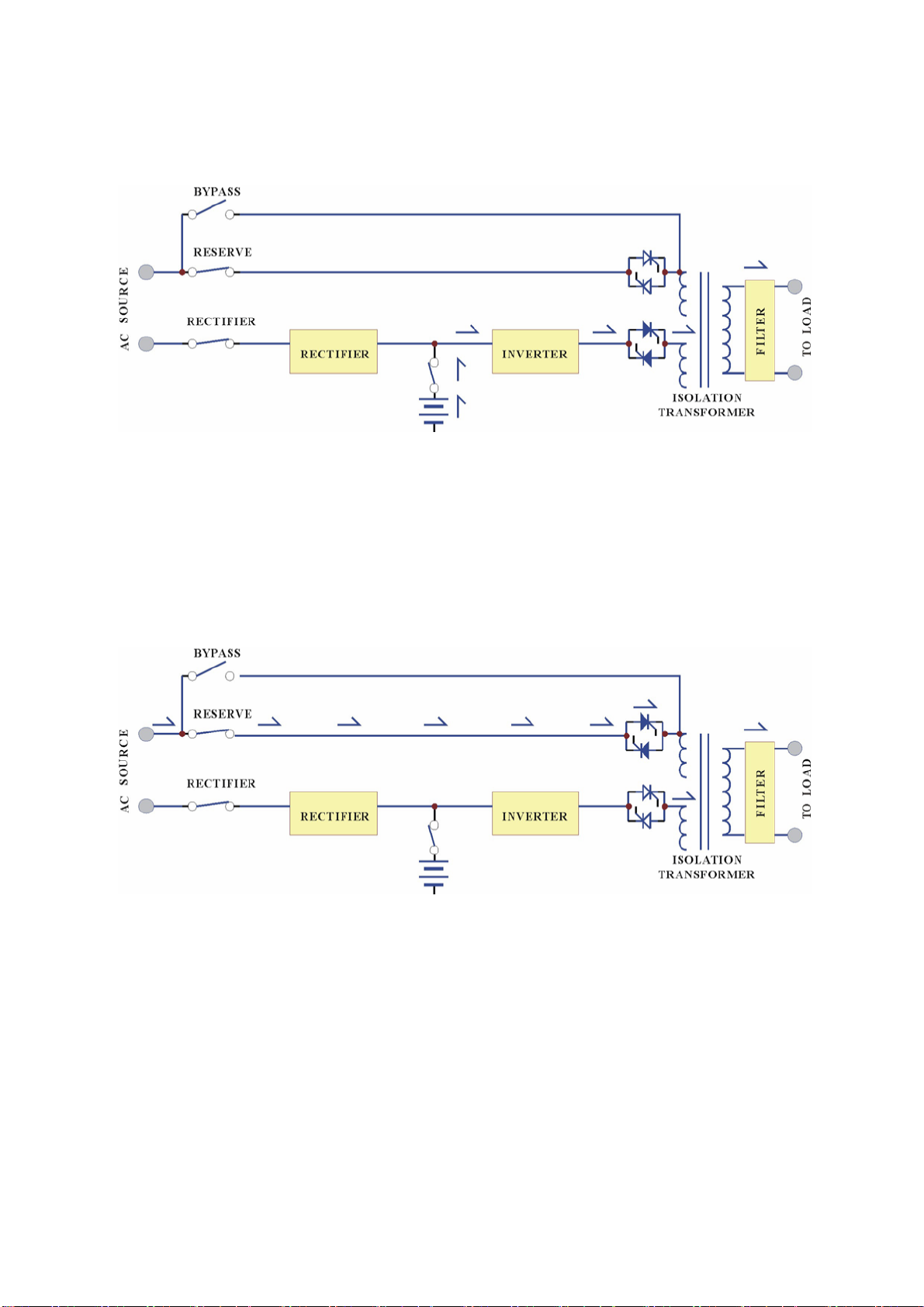
Reserve Mode:
When the inverter is in an abnormal condition, such as over temperature, short
circuit, abnormal output voltage or overloaded for a period exceeding the inverter’s
limit, the inverter will automatically shut down in order to protect itself from
damage. If the utility power is normal, the static switch will automatically tran sfer
the load to the reserve source without interruption of AC output.
1-3
P
T
OL
Maintenance Bypass Mode:
In case of UPS maintenance or during battery replacement, and where the load
cannot be interrupted, the user can invoke the static bypass, turn off the inverter,
hree Phase UPS Systems
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
close the bypass breaker and then open the rectifier and reserve breakers. The AC
output will not be interrupted during the manual bypass transfer procedure. The
maintenance bypass switch keeps continuously supplying power to the load.
Electricity will not exist in UPS power electronic circuitry except for the output
transformer, thus ensuring the safety of service personnel.
The UPS is designed to run 24 Hours a day in normal operation mode once it is
installed, except when the utility power fails, under overload conditions, or during
maintenance.
Normal operation with batteries connected provides clean, stable, regulated and
uninterrupted power to the load, free from any spikes and surges. The UPS is
regarded as a perfect AC power source, limited in back-up time, under mains failure,
only by the capacity of the batteries.
1-4

P
T
OL
1.2. Features and Advantages
hree Phase UPS Systems
Reliable input protection:
(a)
input branch to ensure power can continue through another branch in case of
breaker trip caused by an abnormal condition in either rectifier or load.
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
Circuit breakers are placed in each individual
(b) Input surge protection:
providing protection to both UPS and the load from any lightning surges, or
surges caused by neighboring large loads.
(c) EMI suppression:
limits. Very low noise is emitted, and no interference is back-feed to other
equipment connected to the same AC source.
Ruggedness:
(d)
DC link voltage. This is the most efficient method to charge the batteries. The
SCR used are inherently rugged. Additionally, a large inductor is added at the
input to avoid deforming the AC source waveform.
High frequency design:
(e)
IGBT, PWM methodology to convert the DC pow er to AC power. The n umber
of components is fewer, reliability is improved, and the size and weight of UPS
is reduced, performance is improved, and acoustic noise is minimized.
The rectifier employs phase control technology to regulate the
An EMI filter is added to meet the international EMC
An MOV (surge protector) is added at the input,
The inverter uses high frequency, high efficiency
True Galvanic isolation:
(f)
This solves the problem of poor input grounding, can allow a different ground
between input and output, can avoid the annoying problem of ground leakage
current, and can be tied to any potential provided on site. The AC output is
isolated under every mode of operation. Additionally, the load receives the
bonus of attenuation of common mode noise from the output isolation
transformer.
An isolation transformer is placed at the output.
1-5

P
T
OL
hree Phase UPS Systems
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
(g) Plug & Play Modular design:
modules plugged into slots in the UPS. These are easy to pull out, permitting
quick maintenance and easier trouble shooting.
(h)
Cold start function:
can be started with battery power only. This is possible because current limit
circuitry is added, preventing the problem of large inrush current blowing the
battery fuse and damaging the DC capacitors when batteries are connected to an
empty DC bus (before the DC bus is energized).
(i)
Multi-CPU design:
critical functions are designed with parallel redundancy to improve reliability. If
one CPU were to fail, the other CPUs keep the UPS operational, and the output
AC is not affected.
Protection against misuse:
(j)
power supply sensor, etc. any operational mistake made by the user causes no
the UPS can be started without an AC source, that is,
Several CPUs are employed in the control circuit and
The power circuit is separated into several
The UPS is designed with breaker on/off sensor,
harm to the UPS.
(k) Accepts wide input range:
voltage range, so that it can work effectively under an unstable AC source. All
of the input components used are specifically selected to handle extreme high
voltage and high current.
(l)
Operating environment:
safety margin to accommodate extreme environments, such as temperature,
humidity, altitude, shock or contamination.
Intelligent charger:
(m)
batteries every time the batteries are depleted to a voltage level equal to 2V/Cell.
Thus, the batteries can be restored to full capacity as soon as possible and made
ready for the next back-up requirement. In order to keep the batteries in the
best condition, the UPS will boost charge the batteries for several hours
(selectable) automatically every month. To avoid over charging the batteries,
boost charge will stop when the ambient temperature is over 35
The UPS automatically recharges (boost charge) the
The UPS is designed to accept a wide input
Each component of the UPS is chosen with a large
o
C (95oF).
1-6

P
T
OL
hree Phase UPS Systems
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
(n) Intelligent battery test:
by battery discharge or by the monthly boost charge cycle). This is done without
interrupting the operation of the rectifier, preventing the risk of output AC
failure in case of a bad battery. The user is infor med of the battery condition, so
that action can be taken before the full capacity of the batteries is needed.
Selectable charging power:
(o)
(Lo/Me/Hi) according to A/H rating of the batteries, and can charge up
ba tt ery ba nks providing more than 8Hrs back-up time without adding an extra
charger.
(p)
light load, so that the life expectancy of the fans is extended beyond the normal.
(q)
redundancy for supplying power to the static switch; assuring there will be AC
output regardless of any internal failure.
Long life fans: The f
Redundant power supply:
The batteries are tested after every boost (initiated
The charging power is selectable
ans used to cool the UPS are designed to slow down under
A supplemental power supply is added to provide
(r)
Variety of Communication ports:
communication interface as well as output ports of RS-232, RS-485 and dry
contacts, there are several options available. These options include remote
control panel, 3 phases software for PC monitoring, auto dialing module, battery
monitoring module, 3 phases SNMP card, and emergency power off (EPO) switch.
Please refer to the chapter 7 option details
.
With built-in intelligent
1-7
T
R
R
OLP
hree Phase UPS Systems
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
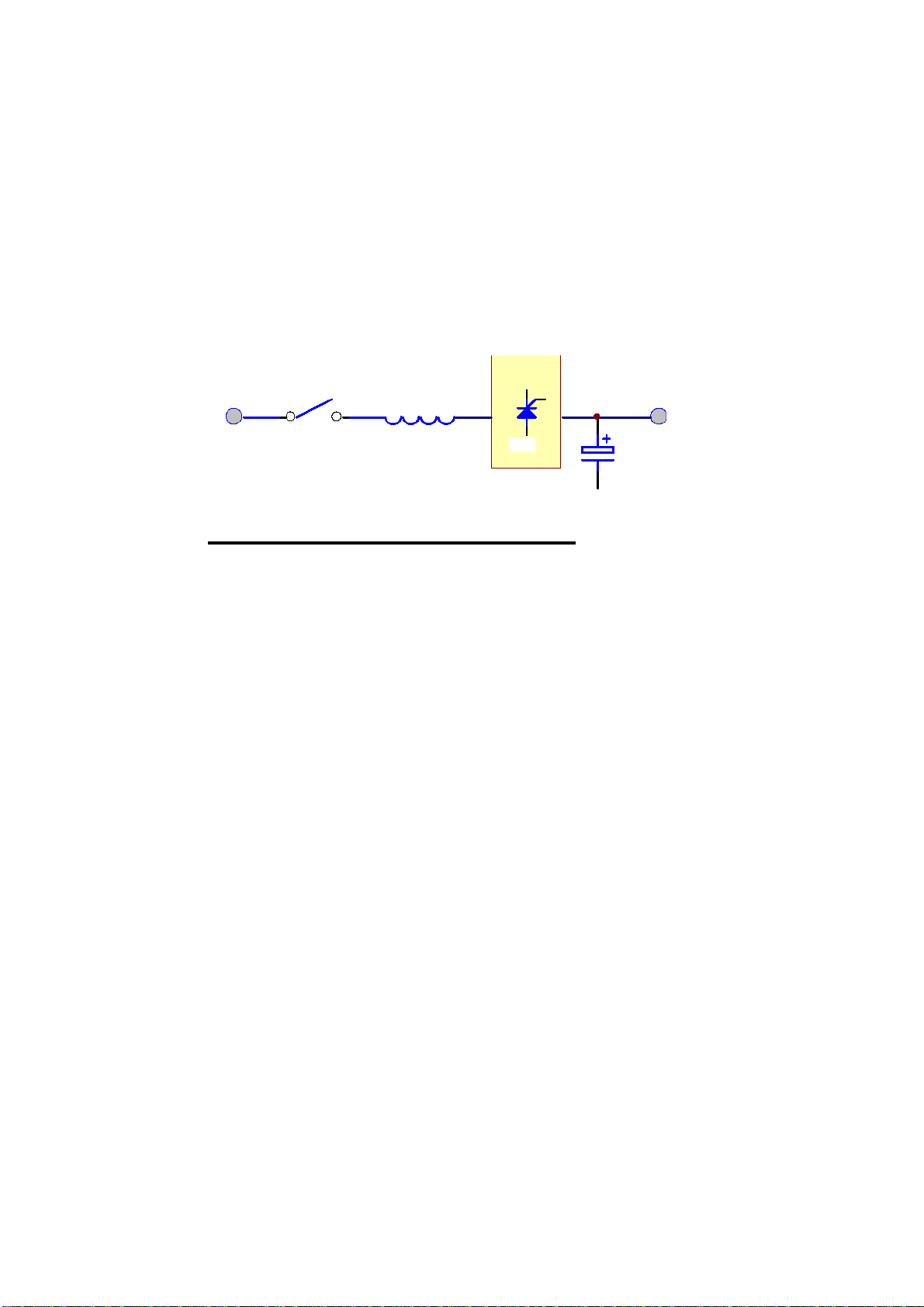
1.3. Rectifier
The main function of a rectifier is to convert the AC input to DC power and supply it
to the inverter. The inverter then converts the DC power to AC p ower for the load.
The UPS also uses the DC power to charge the batteries as well; a very efficient
AC
INPUT
RECTIFIER
BREAKERINDUCTO
DC
OUTPUT
SC
CAPACITOR
method of charging.
6 PULSE FULL CONTROL RECTIFIER
The 10KVA to 60KVA UPS use 6-pulse fully controlled rectification. An inductor is
added before the rectifier to improve the power factor, smooth the current waveform
and eliminate the harmonic current. The control circuit regulates the DC bus within
1%. Soft walk-in circuitry (approximately 20sec.) and current limit circuitry is
used to prevent over current or instantaneous surge current.
Extra under-voltage and over-voltage protections are added to improve reliability and
to shutdown the rectifier in case of abnormal conditions. The DC bus is adjustable to
fit different types of batteries. The power component used in the rectifier is specially
selected to handle extreme high voltage and high current. The rectifier is designed to
operate under a wide range of AC input. The UPS will operate from 384 to 552
VAC and under poor power conditions found in some areas.
1-8
P
T
R
R
OL
hree Phase UPS Systems
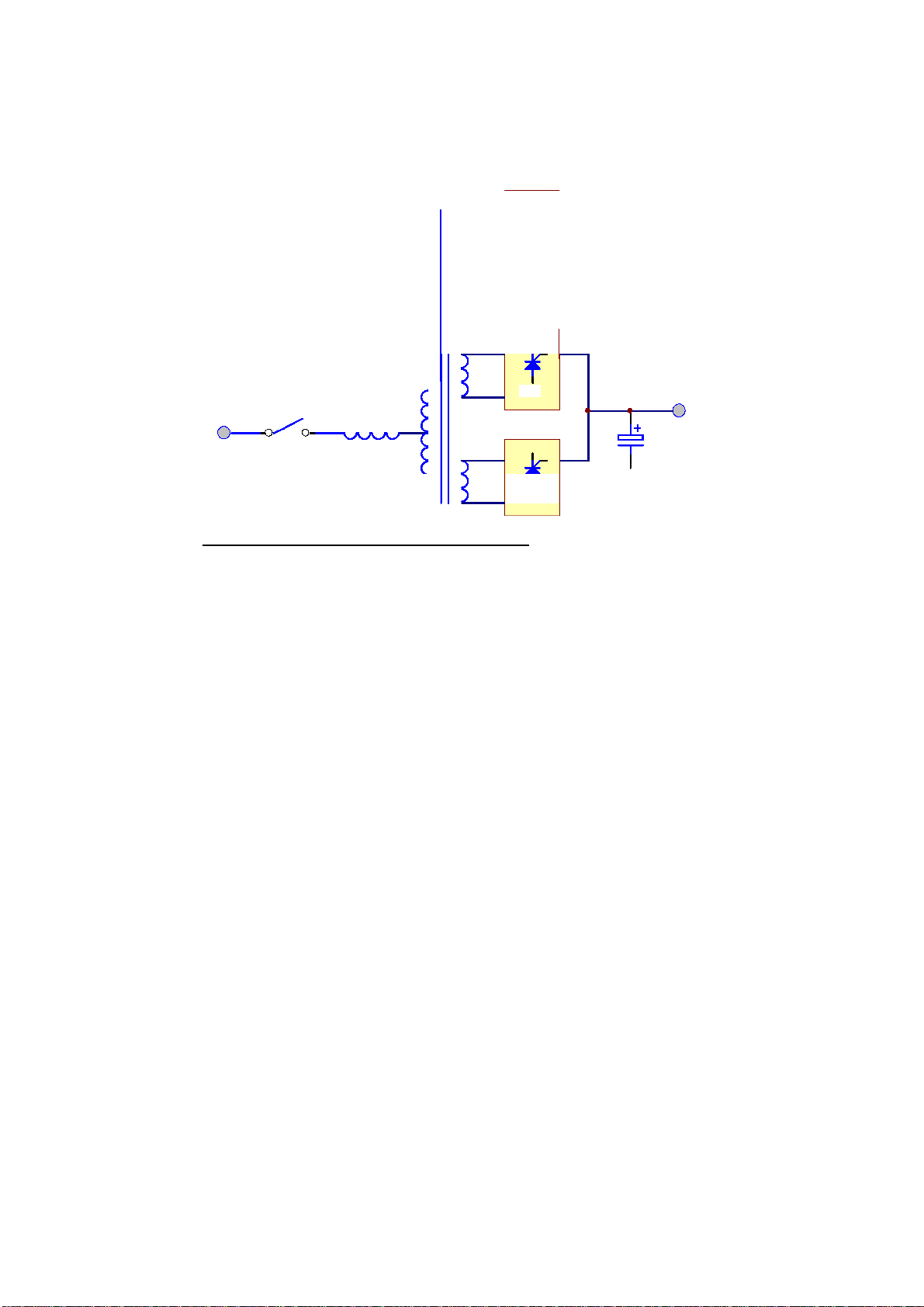
PHASE SHIFT
TRANSFORMER
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
AC
INPUT
12 PULSE FULL CONTROL RECTIFIER
RECTIFIER
BREAKERINDUCTO
SC
SCR
DC
OUTPUT
CAPACITOR
In order to further improve the power factor and reduce harmonic cu rrent drawn by
the rectifier, UPS systems rated 80KVA and above use the 12-pulse full controlled
rectifier. The total current harmonic current is reduced and power factor improved to
over 0.8. A phase shift transformer is added to achieve this performance. An input
inductor is retained also to obtain the best result. The use of 12 pulse rectification
distributes the rectification work load over more devices and increases the reliability of
the overall system. There is no need to increase the input breaker and cable sizes, since
input power and harmonic current drawn is minimized, fulfilling the international
energy saving requirements.
1-9
P
T
CAC
C
-
OL
hree Phase UPS Systems
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
DC+
D
A
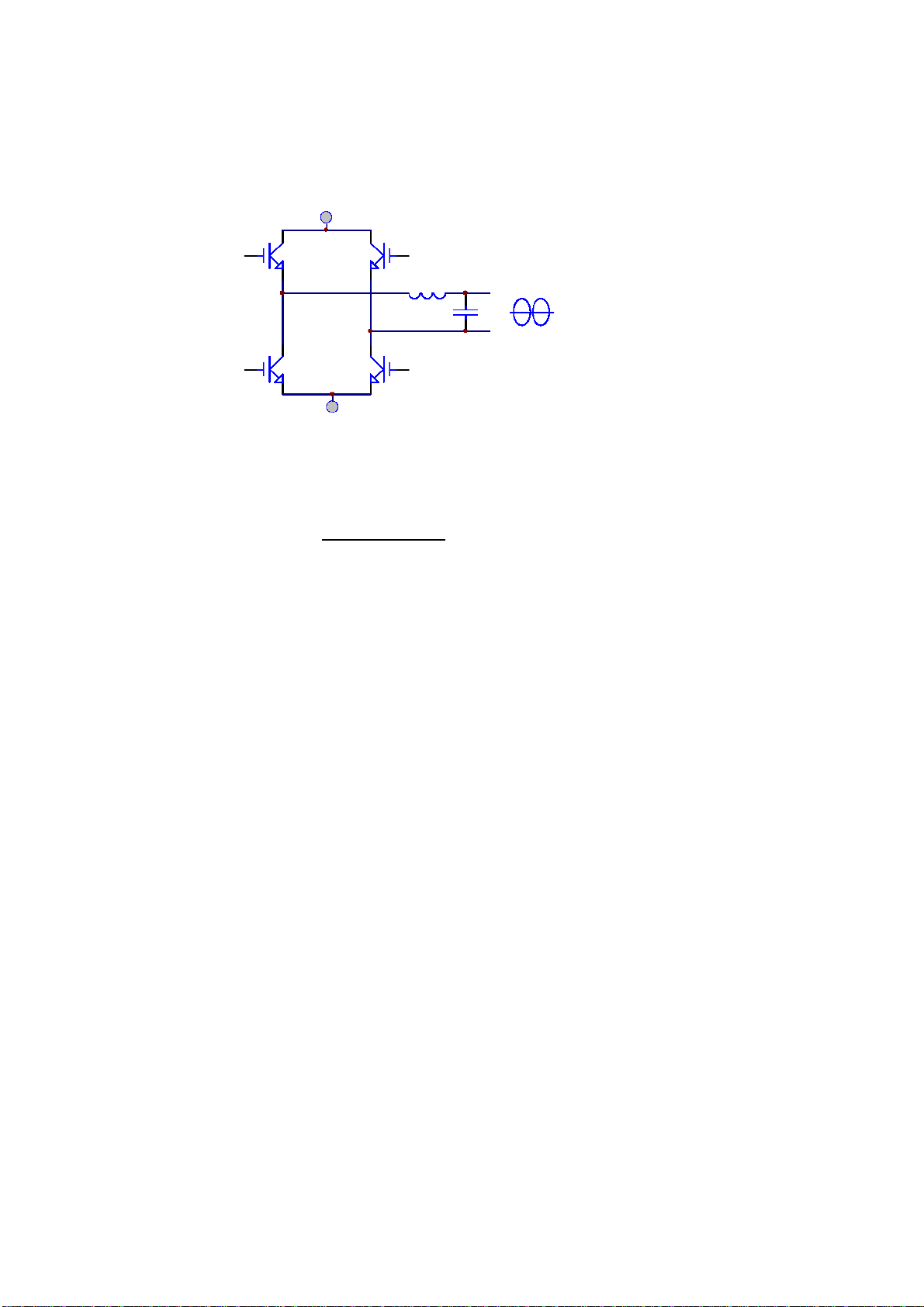
1.4. Inverter
IGBT INVERTER
The inverter is composed of IGBT, inductor, capacitor, snubber, control circuitry and
protection circuitry. The inverter converts the DC power from the DC link to AC
power to supply the output load. The UPS uses IGBT technology which switches at
frequencies beyond the audible range, therefore ensuring quiet operation.
The UPS uses voltage regulation circuitry to limit the voltage variation within 1%.
Custom compensation circuitry, for the dynamic loads and medical imaging power
signature is added to decrease the ge ner ation of output distortion. Every component is
oversized to accept the wide DC input range (from 285 to 420VDC); providing the
power and support to kee p the ou tput wa veform si nusoidal throughout the range.
With the aid of the dynamic feedback loop the inverter maintains a sine waveform
throughout high current demands and imaging procedures.
An independent inverter and feedback control is used for each phase. The
independent control assures the voltage is unaffected when load is added to the
adjacent phase; producing excellent line to line voltage regulation under 100%
unbalanced load.
The IGBT is always operated in its optimal condition to obtain best efficiency thus
minimizing the overall cost of operation.
1-10
P
T
OL
hree Phase UPS Systems
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
Usually, the most frequent failures of the UPS occur at the inverter. Therefore, the
UPS has redundant protection circuitry to protect the inverter. A strong snubber is added
to suppress the spikes and noise, oversized high quality components are used
throughout, semi-conductor fuses are provided, and ventilation is maximized. The
result of this design is a more rugged, reliable and high efficient inverter. At the same
time, the inverter can sustain overload and high peak current drawn by the load.
Additionally, a longer MTBF is achieved.
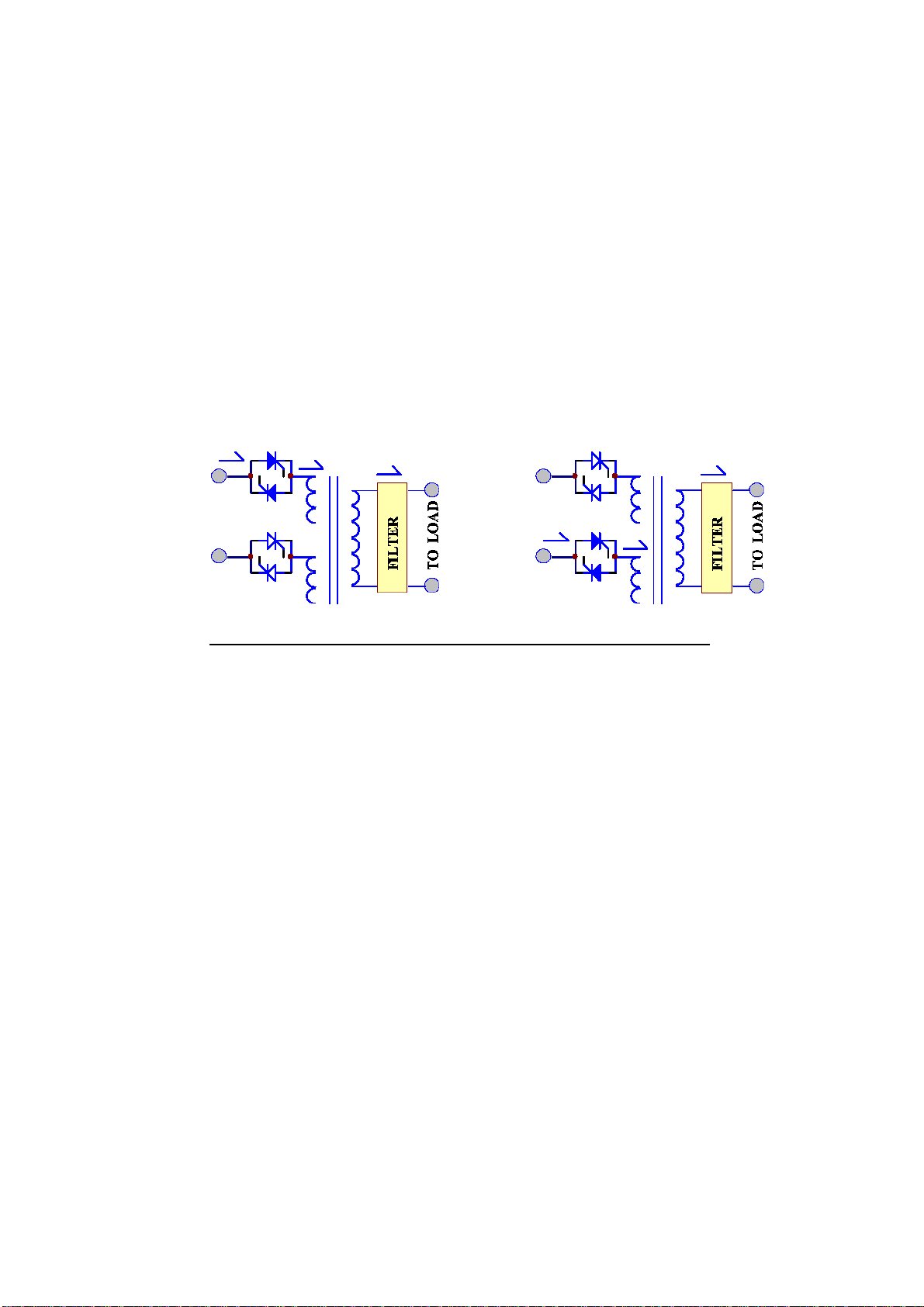
1.5. Static Switch
RESERVE
INVERTER
RESERVE
INVERTER
RESERVE MODE INVERTER MODE
The static switch is composed of two pairs of SCR's, connected back-to-back. The
switch transfers the load from reserve to inverter or from inverter to reserve without
losing power at the output. It is a very important portion of a UPS.
Custom detection and logic circuitry is incorporated to achieve a zero dead time
transfer of the static switch module. If the output exceeds the inverter rating, the
static switch will be invoked to protect the inverter providing that the input voltage
and frequency are within safe limits for the load. If the output is short circuited, the
UPS will shut down to protect the inverter and the reserve power ci rcuit r y.
Following any transfer, the CPU performs a check for validation of successful
transfer.
1-11

T
OLP
1.6. Maintenance Bypass Switch
Unlike other UPS, the maintenance bypass switch is already installed inside the UPS
for convenience. It should be open under normal operation, and only closed during
maintenance.
To properly use the maintenance bypass breaker, switch off the inverter first. The
static switch will automatically transfer the load to reserve without de ad time. Then
one can close the maintenance bypass breaker, followed by opening the reserve
breaker so that the load gets power from the output without interruption.
hree Phase UPS Systems
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
Technical Note:
maintained during the both the static bypass mode and the maintenance mode. All
power is routed through the power transformer for filtering and voltage conversion.
SAFETY NOTE:
For the sake of safety of maintenance personnel, all power supplies inside the UPS
must be disconnected from their associated power source before touching any parts
inside the UPS. Thus, the maintenance bypass switch is a necessity to maintain AC
power at the output and yet keep maintenance personnel safe at the same time.
If the bypass breaker is closed under normal operation, the inverter will stop and the
load will be automatically transferred to reserve to prevent the inverter connecting
directly to the AC source. Of course, the inverter cannot be energized as long as the
maintenance bypass breaker is closed.
Voltage Conversion from the UPS input to the UPS output will be
1-12
OLP
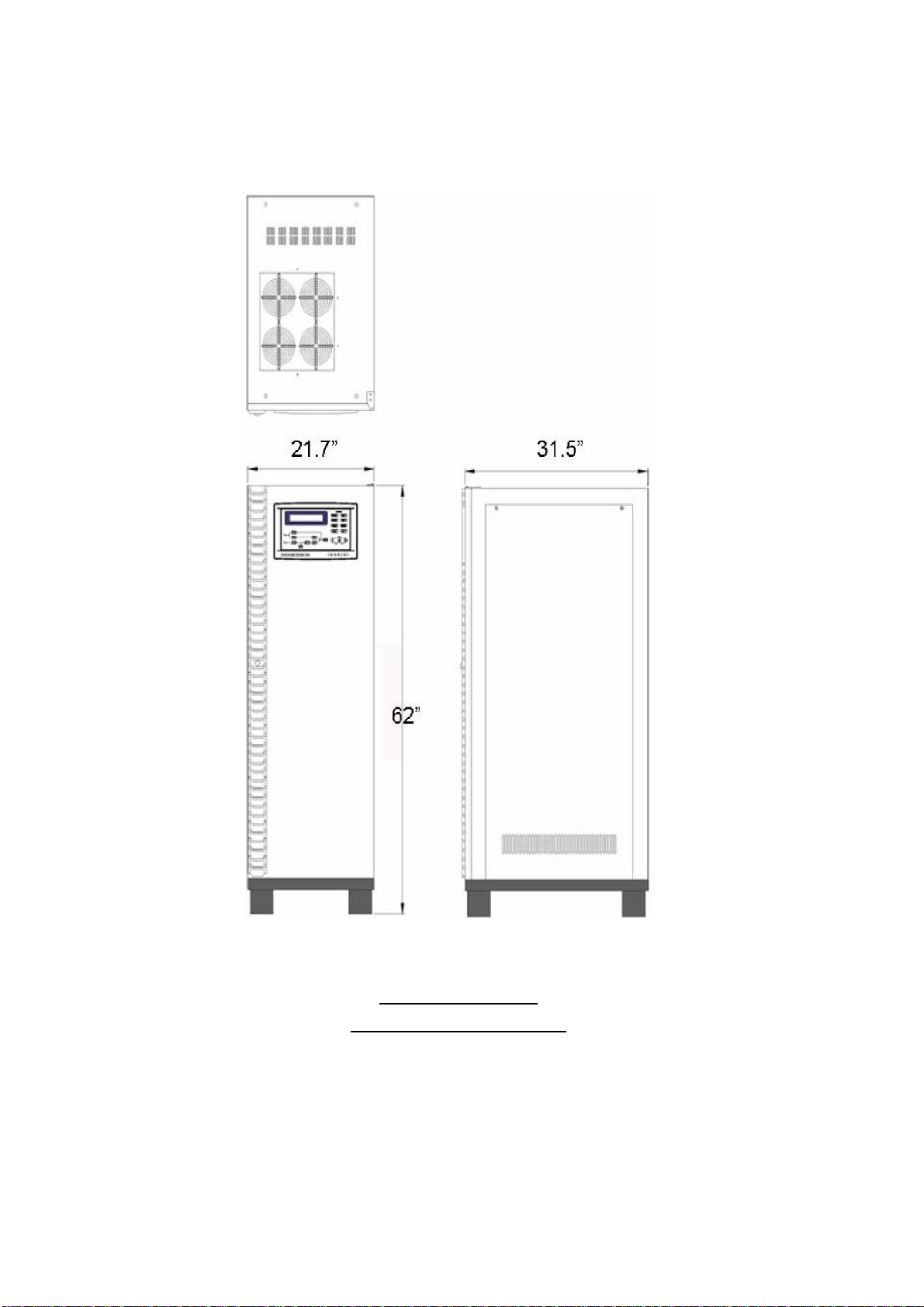
1.7. Dimension & Drawings
Three Phase UPS Systems
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
10KVA - 60KVA
OUTLINE DRAWING
1-13
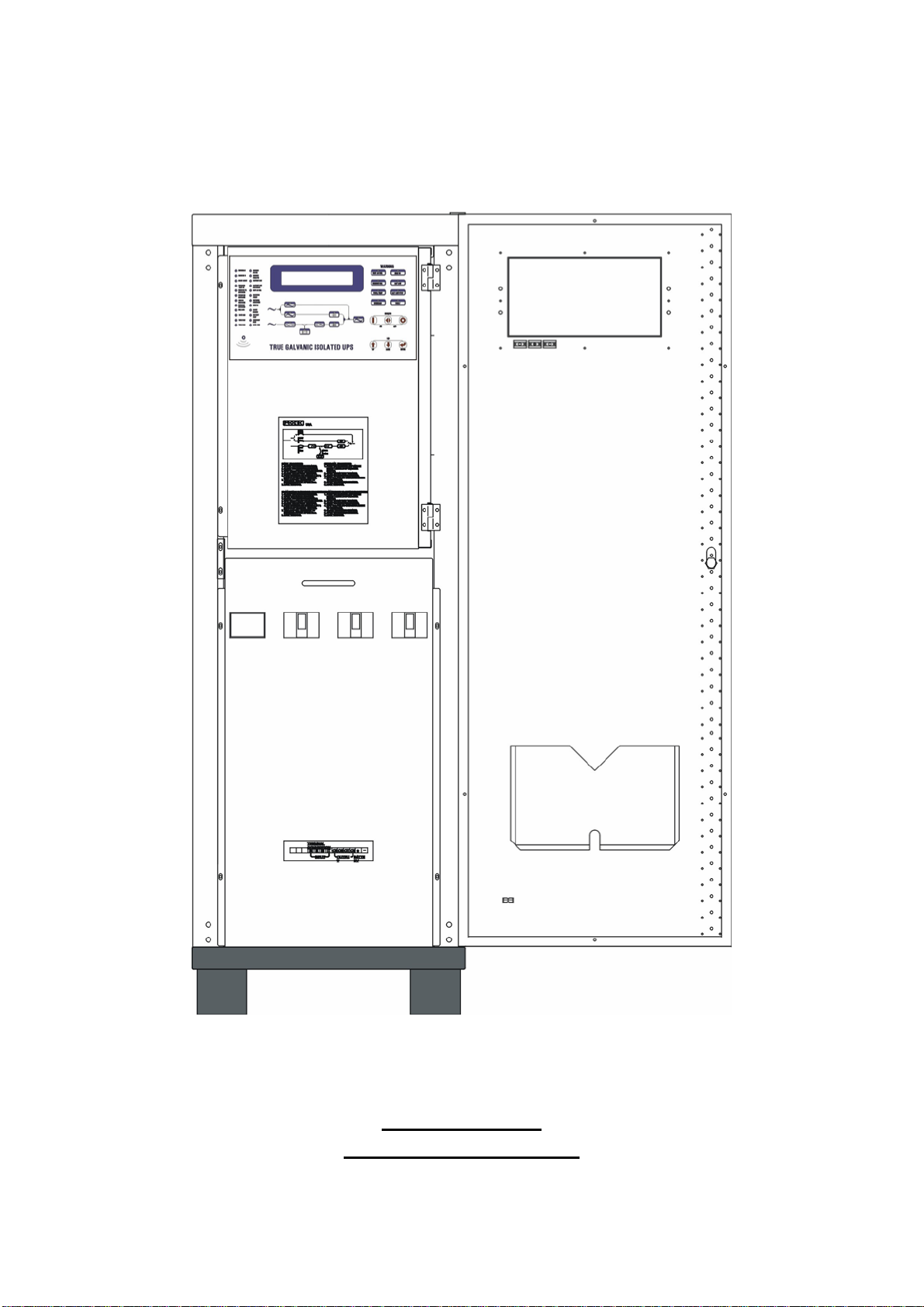
OLP
T
hree Phase UPS Systems
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
10KVA - 60KVA
INTERIOR DRAWING
1-14
OLP
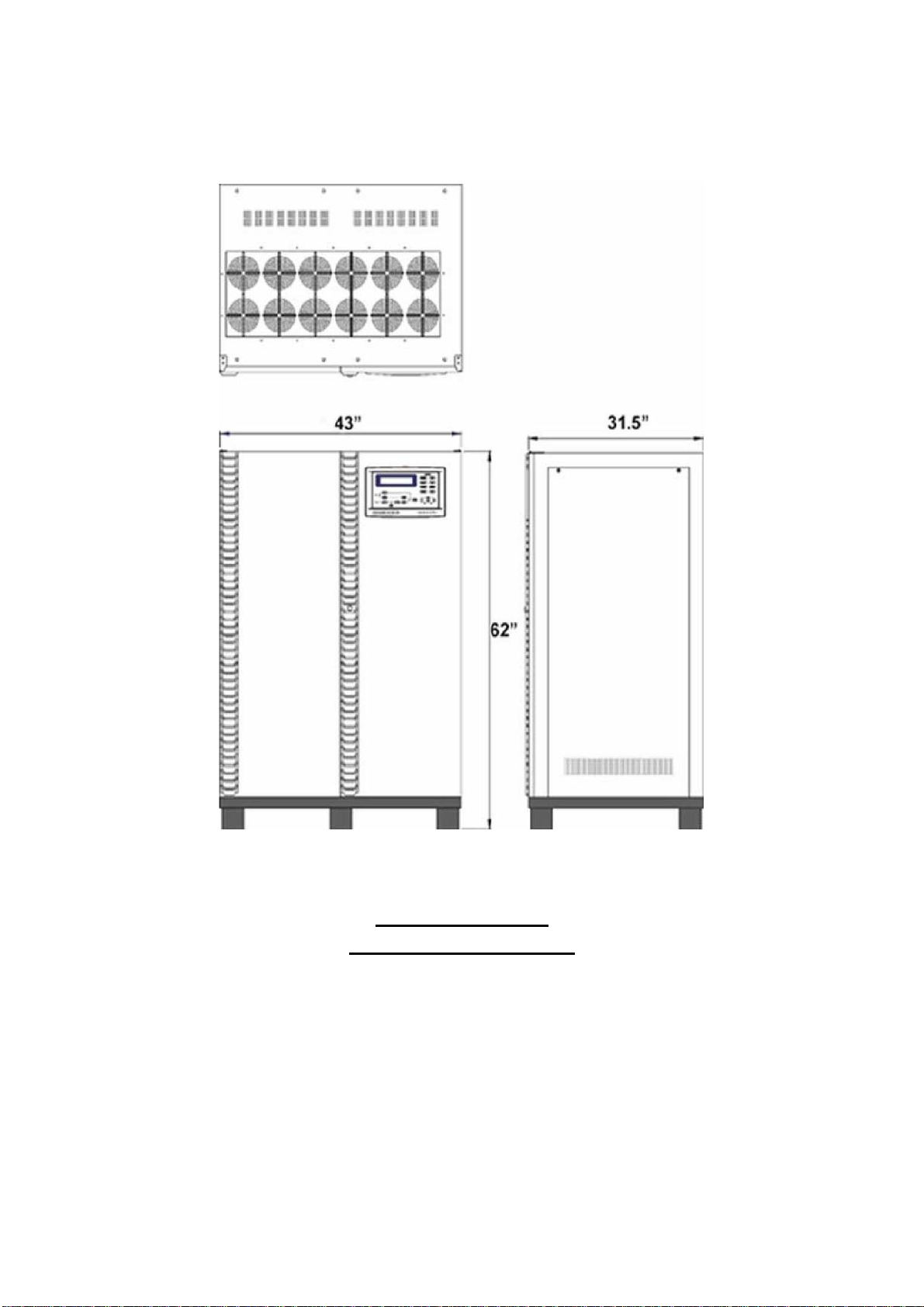
Three Phase UPS Systems
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
80KVA - 160KVA
OUTLINE DRAWING
1-15
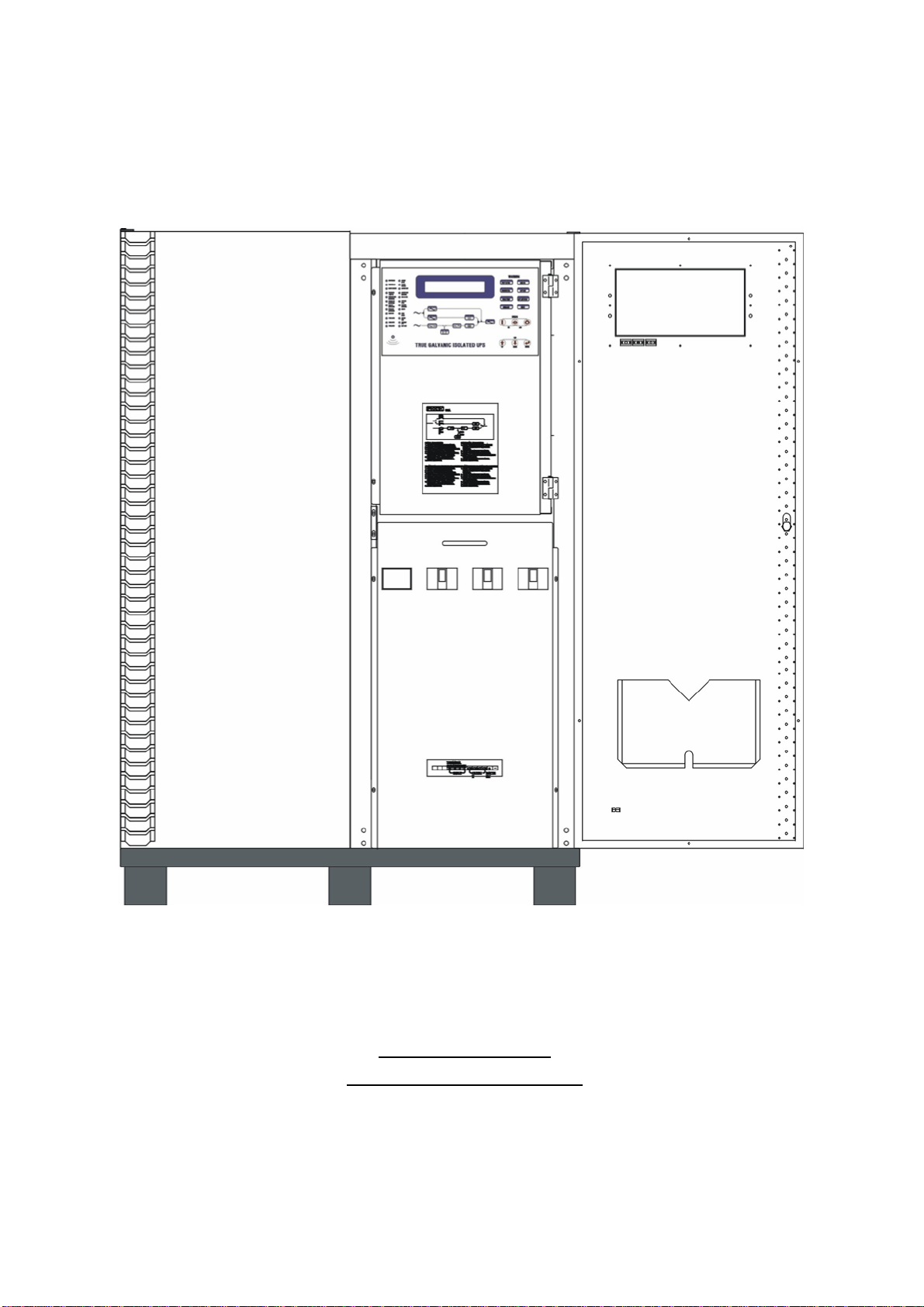
T
OLP
hree Phase UPS Systems
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
80KVA - 160KVA
INTERIOR DRAWING
1-16

P
T
OL
INTER-PCB DIAGRAM
hree Phase UPS Systems
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
1-17
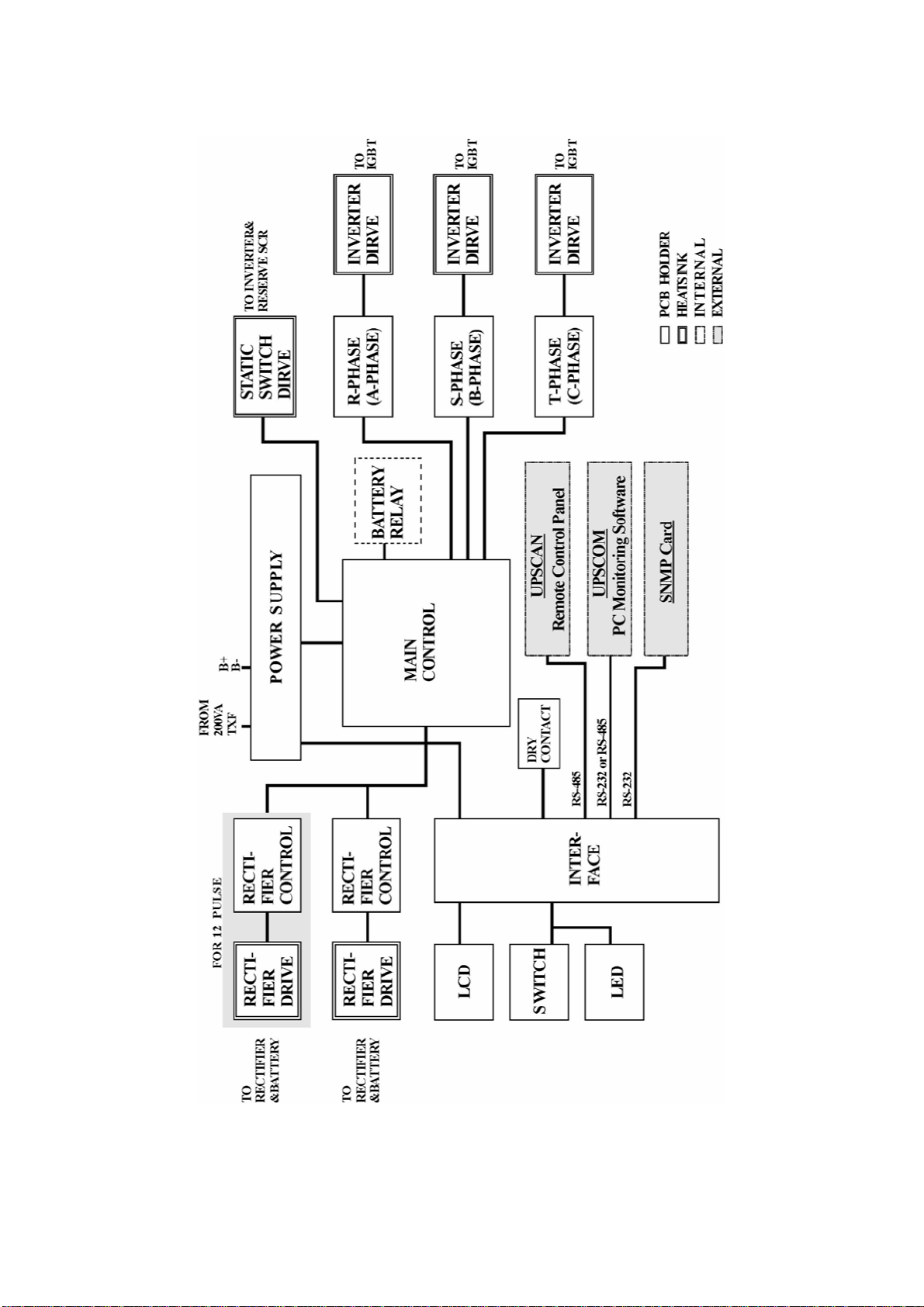
P
T
OL
hree Phase UPS Systems
1. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
1-18
 Loading...
Loading...