Page 1

Cat.No. I62E-EN-01
L7Z
Quick Start Guide
Page 2

Page 3

L7Z Quick Start Guide
Table of Contents
Warnings..............................................................................1
Safety Precautions and Instructions ................................................................... 2
EMC Compatibility .............................................................................................. 3
Installation ...........................................................................5
Mechanical Installation ....................................................................................... 5
Electrical Connection .......................................................................................... 6
Keypad Operation ............................................................. 11
Digital Operator Display (optional) ................................................................... 11
Power Up and Basic Parameter Setup ............................12
Start Up Procedure ........................................................................................... 12
Before Power Up .............................................................................................. 13
Display after Power Up ..................................................................................... 13
Control Mode Selection .................................................................................... 13
Autotuning .........................................................................14
Autotuning Mode Selection .............................................................................. 14
Autotuning Alarms and Faults .......................................................................... 15
Autotuning Procedure with Induction Motors ................................................... 16
Autotuning Procedure for PM Motors ............................................................... 17
PM Motor Encoder Offset Tuning ..................................................................... 18
Ride Profile and Sequence Setup....................................19
Up and Down Commands and Speed Reference Selection ............................. 19
Speed Selection Sequence Using Digital Inputs .............................................. 19
Acceleration / Deceleration / Jerk Settings ....................................................... 22
Brake Sequence ............................................................................................... 22
Inertia Compensation (Feed Forward) ............................................................. 22
Troubleshooting ................................................................24
Fault and Alarm Detection ................................................................................ 24
Operator Programming Errors (OPE) ............................................................... 26
Auto-tuning Faults ........................................................................................... 27
Parameter Table ................................................................28
Page 4
Warnings
Cables must not be connected or disconnected, nor signal tests carried out, while the power is
switched on.
The Varispeed L7 DC bus capacitor remains charged even after the power has been switched off. To
avoid an electric shock hazard, disconnect the frequency inverter from the mains before carrying out
maintenance. Then wait for at least 5 minutes after all LEDs have gone out.
Do not perform a withstand voltage test on any part of the inverter. It contains semiconductors,
which are not designed for such high voltages.
Do not remove the digital operator while the mains supply is switched on. The printed circuit board
must also not be touched while the inverter is connected to the power.
Never connect general LC/RC interference suppression filters, capacitors or overvoltage protection devices to
the inverter input or output.
CAUTION
To avoid unnecessary over current faults, etc., being displayed, the signaling contacts of any contactor or switch fitted between inverter and motor must be integrated into the inverter control logic
(e.g. baseblock).
This is absolutely imperative!
This manual must be read thoroughly before connecting and operating the inverter. All safety precautions and instructions for use must be followed.
The inverter must be operated with the appropriate line filters, following the installation instructions
in this manual and with all covers closed and terminals covered.
Only then will adequate protection be provided. Please do not connect or operate any equipment
with visible damage or missing parts. The operating company is responsible for any injuries or
equipment damage resulting from failure to heed the warnings in this manual.
EN-1
Page 5

Safety Precautions and Instructions
1. General
Please read these safety precautions and instructions for use thoroughly before installing and operating this
inverter. Also read all of the warning signs on the inverter and ensure they are never damaged or removed.
Live and hot inverter components may be accessible during operation. Removal of housing components, the
digital operator or terminal covers runs the risk of serious injuries or damage in the event of incorrect installation or operation. The fact that frequency inverters control rotating mechanical machine components can give
rise to other dangers.
The instructions in this manual must be followed. Installation, operation and maintenance may only be carried
out by qualified personnel. For the purposes of the safety precautions, qualified personnel are defined as individuals who are familiar with the installation, starting, operation and maintenance of frequency inverters and
have the proper qualifications for this work. Safe operation of these units is only possible if they are used
properly for their intended purpose.
The DC bus capacitors can remain live for about 5 minutes after the inverter is disconnected from the power. It
is therefore necessary to wait for this time before opening its covers. All of the main circuit terminals may still
carry dangerous voltages.
Children and other unauthorized persons must not be allowed access to these inverters.
Keep these Safety Precautions and Instructions for Use readily accessible and supply them to all persons with
any form of access to the inverters.
2. Intended Use
Frequency inverters are intended for installation in electrical systems or machinery.
Their installation in machinery and systems must conform to the following product standards of the Low Voltage Directive:
EN 50178, 1997-10,Equipping of Power Systems with Electronic Devices
EN 60204-1, 1997-12Machine Safety and Equipping with Electrical Devices
Part 1: General Requirements (IEC 60204-1:1997)/
Please note: Includes Corrigendum of September 1998
EN 61010-1, A2, 1995Safety Requirements for Information Technology Equipment
(IEC 950, 1991 + A1, 1992 + A2, 1993 + A3, 1995 + A4, 1996, modified)
CE marking is carried out to EN 50178, using the line filters specified in this manual and following the appropriate installation instructions.
3. Transportation and storage
The instructions for transportation, storage and proper handling must be followed in accordance with the technical data.
4. Installation
Install and cool the inverters as specified in the documentation. The cooling air must flow in the specified
direction. The inverter may therefore only be operated in the specified position (e.g. upright). Maintain the
specified clearances. Protect the inverters against impermissible loads. Components must not be bent nor insulation clearances changed. To avoid damage being caused by static electricity, do not touch any electronic
components or contacts.
EN-2
Page 6

5. Electrical Connection
Carry out any work on live equipment in compliance with the national safety and accident prevention regulations. Carry out electrical installation in compliance with the relevant regulations. In particular, follow the
installation instructions ensuring electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), e.g. shielding, grounding, filter
arrangement and laying of cables. This also applies to equipment with the CE mark. It is the responsibility of
the manufacturer of the system or machine to ensure conformity with EMC limits.
Contact your supplier or Omron-Yaskawa Motion Control representative when using leakage current circuit
breaker in conjunction with frequency inverters.
In certain systems it may be necessary to use additional monitoring and safety devices in compliance with the
relevant safety and accident prevention regulations. The frequency inverter hardware must not be modified.
If Permanent Magnet Motors are used:
If a PM motor is turned by any external force, high voltage is generated in the windings.
• During wiring, maintenance or inspection make sure, that the motor is stopped and can not turn.
• If the inverter is turned off and the motor must be turned, make sure that motor and inverter output are
electrically disconnected.
6. Inverter Setup
This L7 inverter can drive induction motors as well as permanent magnet motors.
Always select the appropriate control mode:
• For induction motors use V/f, Open Loop Vector or Closed Loop Vector control (A1-01 = 0, 2 or 3).
• For permanent magnet motors use no other control mode than Closed Loop Vector for PM (A1-01 = 6).
A wrong control mode selection can damage the inverter and motor.
If a motor is exchanged or operated the first time, always set up the motor control relevant parameters using
the nameplate data or perform autotuning. Do not change the parameters recklessly. To ensure a safe operation
with PM motors always set the:
• correct motor data
• the PG open detection parameters
• the speed deviation detection parameters
• the over acceleration detection parameters
Wrong parameter settings can cause dangerous behavior or motor and inverter damage.
Refer to page 12, Start Up Procedure for details about the correct start up procedure.
7. Notes
The Varispeed L7 frequency inverters are certified to CE, UL, and c-UL.
EMC Compatibility
1. Introduction
This manual was compiled to help system manufacturers using Omron-Yaskawa Motion Control frequency
inverters to design and install electrical switch gear. It also describes the measures necessary to comply with
the EMC Directive. The manual's installation and wiring instructions must therefore be followed.
EN-3
Our products are tested by authorized bodies using the standards listed below.
Product standard: EN 61800-3:1996
EN 61800-3; A11:2000
Page 7
2. Measures to Ensure Conformity of Omron-Yaskawa Motion Control Frequency
Inverters to the EMC Directive
Omron-Yaskawa Motion Control frequency inverters do not necessarily have to be installed in a switch cabinet.
It is not possible to give detailed instructions for all of the possible types of installation. This manual therefore
has to be limited to general guidelines.
All electrical equipment produces radio and line-borne interference at various frequencies. The cables pass
this on to the environment like an aerial.
Connecting an item of electrical equipment (e.g. drive) to a supply without a line filter can therefore allow HF
or LF interference to get into the mains.
The basic countermeasures are isolation of the wiring of control and power components, proper grounding and
shielding of cables.
A large contact area is necessary for low-impedance grounding of HF interference. The use of grounding
straps instead of cables is therefore definitely advisable.
Moreover, cable shields must be connected with purpose-made ground clips.
3. Laying Cables
Measures Against Line-Borne Interference:
Line filter and frequency inverter must be mounted on the same metal plate. Mount the two components as
close to each other as possible, with cables kept as short as possible.
Use a power cable with well-grounded shield. Use a shielded motor cable not exceeding 20 meters in length.
Arrange all grounds so as to maximize the area of the end of the lead in contact with the ground terminal (e.g.
metal plate).
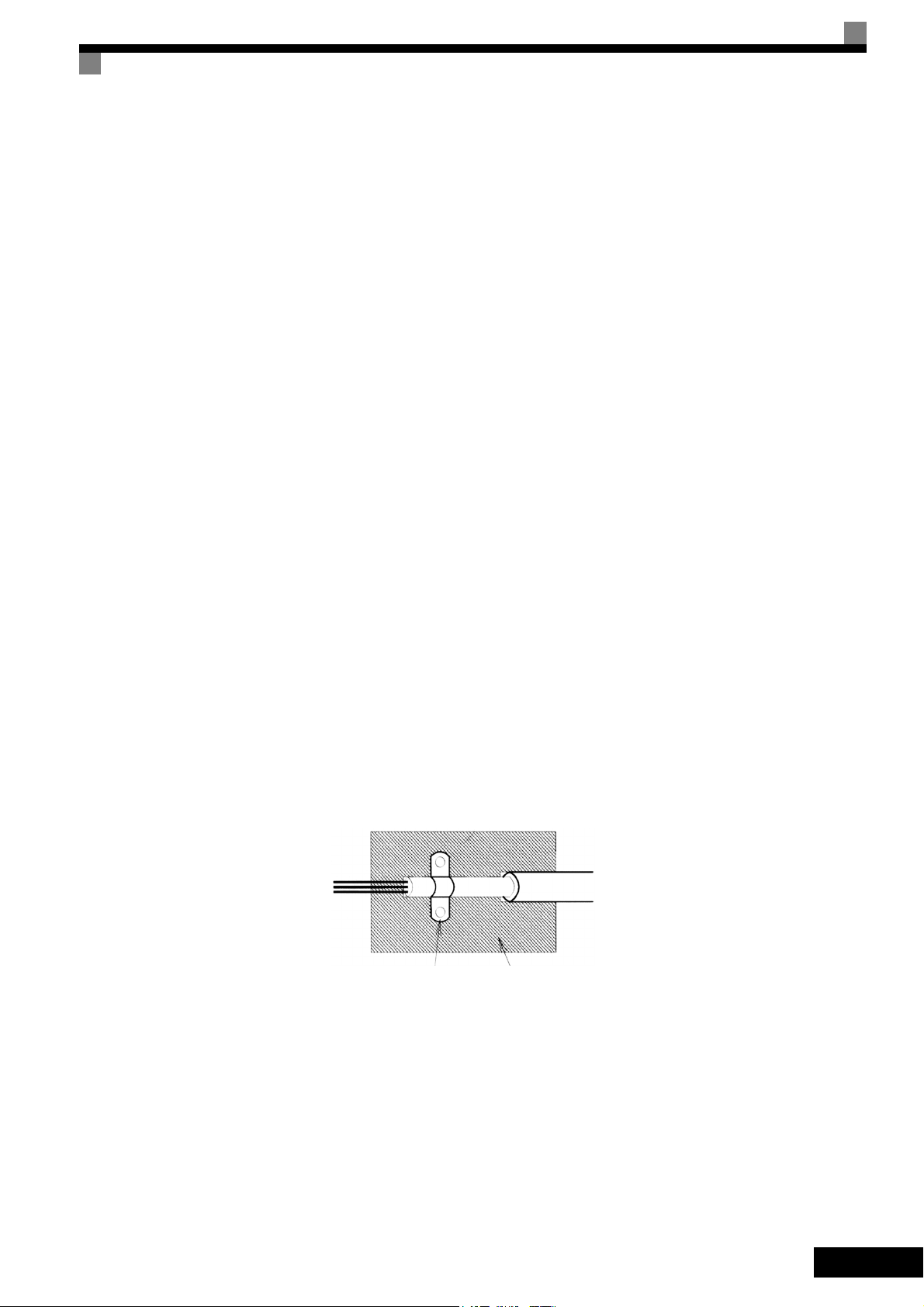
Shielded Cable:
• Use a cable with braided shield.
• Ground the maximum possible area of the shield. It is advisable to ground the shield by connecting the
cable to the ground plate with metal clips (see following figure).
Ground clip
The grounding surfaces must be highly conductive bare metal. Remove any coats of varnish and paint.
– Ground the cable shields at both ends.
– Ground the motor of the machine.
Ground plate
EN-4
Page 8
Installation
Mechanical Installation
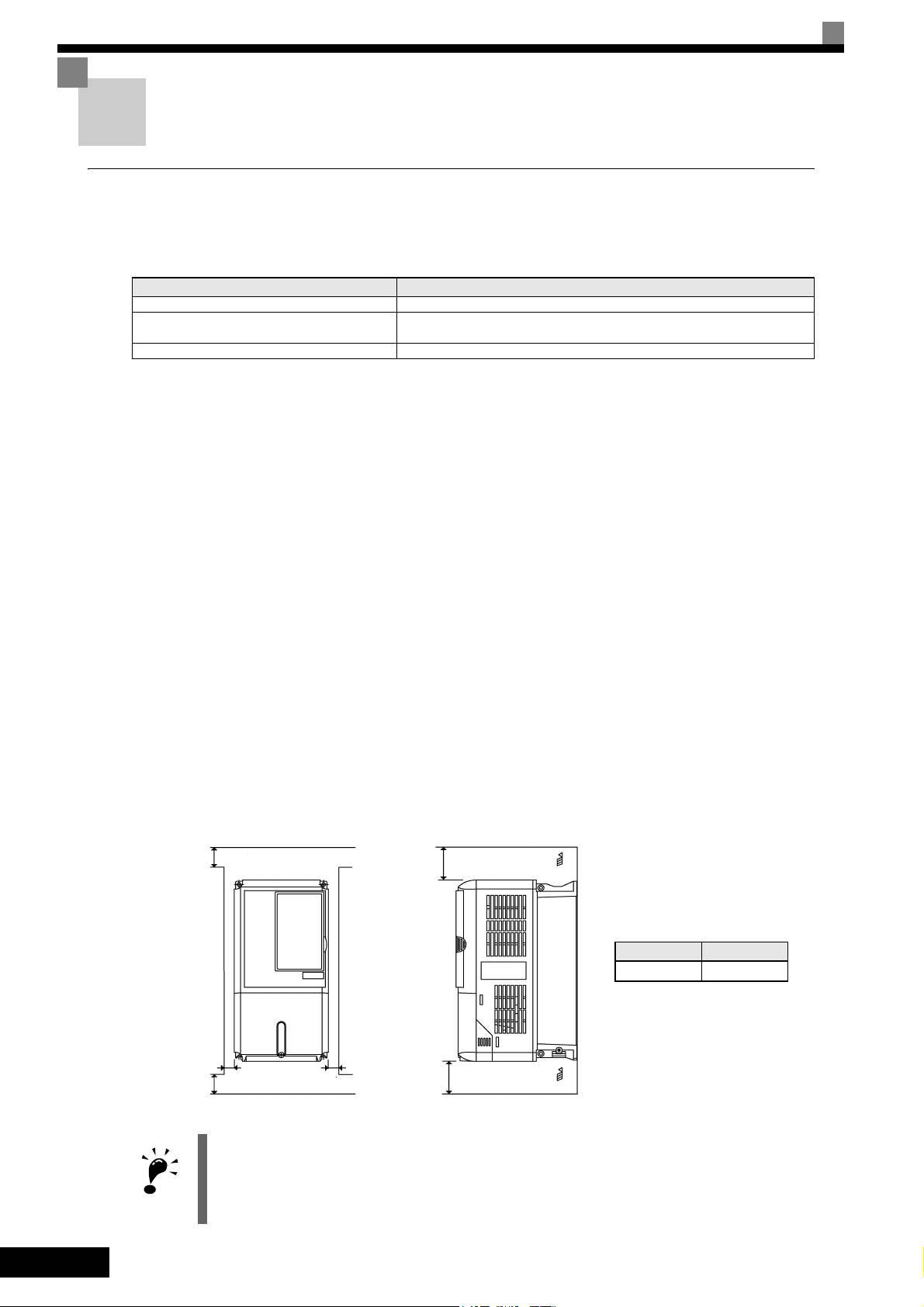
Unpacking the Inverter
Check the following items after unpacking the inverter.
Item Method
Has the correct model of Inverter been delivered? Check the model number on the nameplate on the side of the Inverter.
Is the Inverter damaged in any way?
Are any screws or other components loose? Use a screwdriver or other tools to check for tightness.
If you find any irregularities in the above items, contact the agency from which you purchased the Inverter or
your Omron-Yaskawa Motion Control representative immediately.
Checking the Installation Site
Before installing the inverter check the following:
• Make sure that the ambient temperature is not exceeded
• Install the Inverter in a clean location which is free from oil mist and dust. It can be installed in a totally
enclosed panel that is completely shielded from floating dust.
• When installing or operating the Inverter, always take special care so that metal powder, oil, water, or other
foreign matter does not get into the Inverter.
• Do not install the Inverter on combustible material, such as wood.
• Install the Inverter in a location free from radioactive materials and combustible materials.
• Install the Inverter in a location free from harmful gasses and liquids.
• Install the Inverter in a location without excessive oscillation.
• Install the Inverter in a location free from chlorides.
• Install the Inverter in a location free from direct sunlight.
Inspect the entire exterior of the Inverter to see if there are any scratches or other
damage resulting from shipping.
Installation Orientation
Install the Inverter vertically so as not to reduce the cooling effect. When installing the Inverter, always provide the following installation space to allow normal heat dissipation.
Air
A B
50 mm 120 mm
Air
50 mm min.
IMPORTANT
A
30 mm min.
30 mm min.
Horizontal Space
1. The same space is required horizontally and vertically for IP00, IP20 and NEMA 1 Inverters.
2. Always remove the top protection cover after installing an Inverter with an output of 18.5 kW or less in a
panel.
Always provide enough space for suspension eye bolts and the main circuit lines when installing an
Inverter with an output of 22 kW or more in a panel.
B
120 mm min.
Vertical Space
EN-5
Page 9

Electrical Connection
Installation of Inverters and EMC filters
PEL1L2
L3
Ground Bonds
Remove any paint!
For an EMC rules compliant installation consider the following
points:
• Use a line filter.
• Use shielded motor cables.
• Mount the inverter and filter on a grounded conductive plate.
• Remove any paint or dirt before mounting the parts in order to
reach the lowest possible grounding impedance.
Wiring Main Circuit Inputs
PE
Line
Filter
Load
Cable Length
as short as possible
Grounded
Metal Plate
GND
Ground Bonds
Remove any paint!
Inverter
L2
U
L1
L3
V
M
~3
W
GND
Screened
Motor cable
Consider the following precautions for the main circuit power supply input.
• If a moulded case circuit breaker is used for the power supply connection (R/L1, S/L2, and T/L3), ensure
that the circuit breaker is suitable for the Inverter.
• If an earth leakage breaker is used, it should be able to detect all kinds of current should be used in order to
ensure a safe earth leakage current detection
• A magnetic contactor or other switching device can be used at the inverter input. The inverter should not
be powered up more than once per hour.
• The input phases (R/S/T) can be connected in any sequence.
• If the Inverter is connected to a large-capacity power transformer (600 kW or more) or a phase advancing
capacitor is switched nearby, an excessive peak current could flow through the input power circuit, causing
an inverter damage. As a countermeasure install an optional AC Reactor at the inverter input or a DC reactor at the DC reactor connection terminals.
• Use a surge absorber or diode for inductive loads near the Inverter. Inductive loads include magnetic con-
tactors, electromagnetic relays, solenoid valves, solenoids, and magnetic brakes.
Wiring the Output Side of the Main Circuit
The following precautions should be considered for the output circuit wiring.
• Never connect any power source to the inverter output terminals. Otherwise the inverter can be damaged.
• Never short or ground the output terminals. Otherwise the inverter can be damaged.
• Do not use phase correction capacitors. Otherwise the inverter and capacitors can be damaged.
• Check the control sequence to make sure, that the magnetic contactor (MC) between the Inverter and
motor is not turned ON or OFF during inverter operation. If the MC is turned ON during the Inverter is
operation, a large inrush current will be created and the inverter’s over current protection may operate.
Ground Connection
The following precautions should be considered for the ground connection.
• Do not share the ground wire with other devices, such as welding machines or power tools.
• Always use a ground wire, that complies with technical standards on electrical equipment and minimize
the length of the ground wire.
EN-6
Page 10
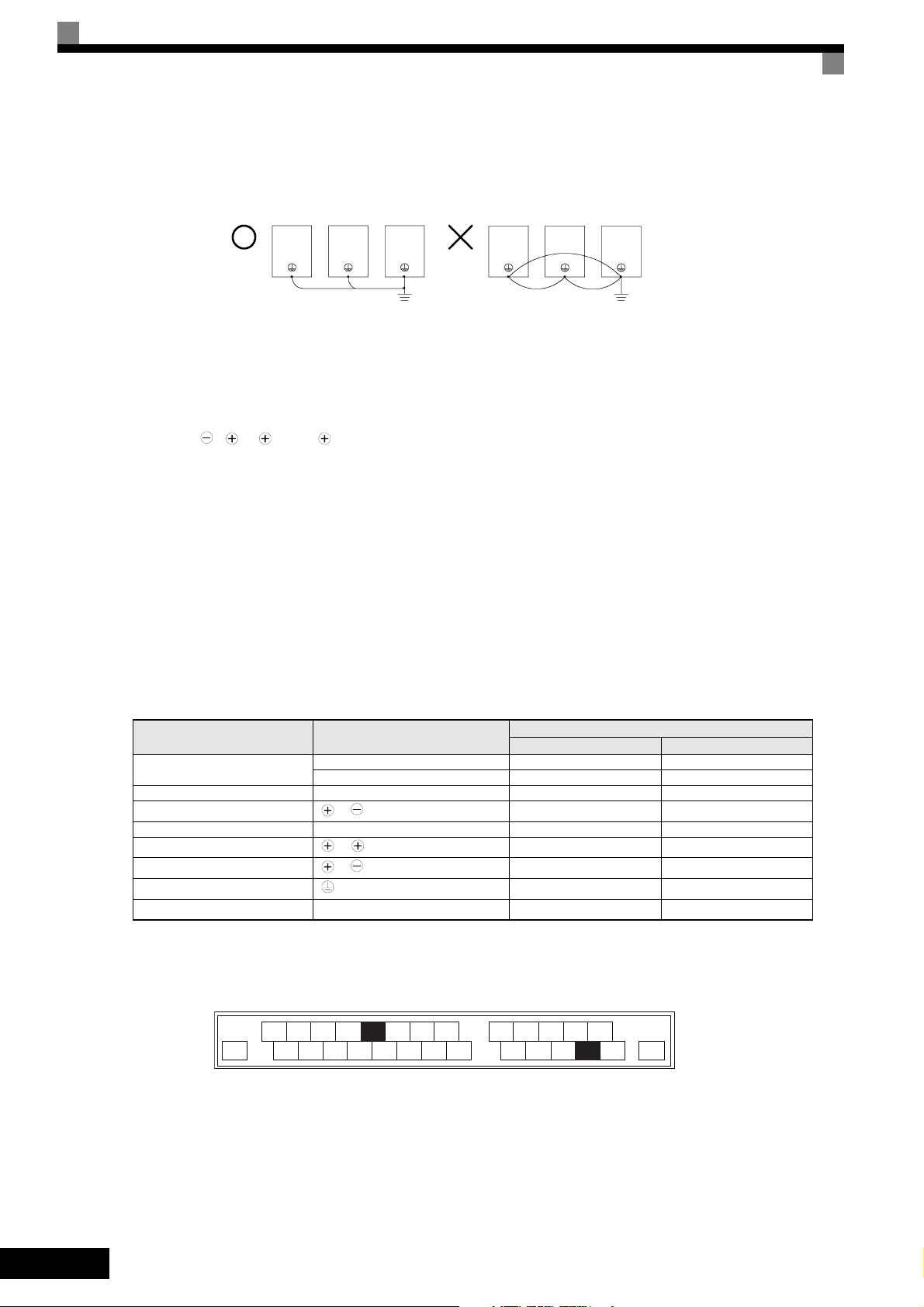
Leakage current is caused by the Inverter. Therefore, if the distance between the ground electrode and the
ground terminal is too long, potential on the ground terminal of the Inverter will become unstable.
• When more than one Inverter is used, do not to loop the ground wire.
OK
NO
Fig 1 Ground Wiring
Control Circuit Wiring Precautions
Consider the following precautions for wiring the control circuits.
• Separate control circuit wiring from main circuit wiring (terminals R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, B1, B2, U/T1, V/T2,
W/T3, , 1, 2, and 3, PO, NO) and other high-power lines.
• Separate wiring for control circuit terminals MA, MB, MC, M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, and M6 (contact out-
puts) from wiring to other control circuit terminals.
• If an optional external power supply is used, it should be a UL Listed Class 2 power supply.
• Use twisted-pair or shielded twisted-pair cables for control circuits to prevent operating faults.
• Ground the cable shields with the maximum contact area of the shield and ground.
• Cable shields have to be grounded on both cable ends.
Main Circuit Terminals
Main circuit terminal functions are summarized according to terminal symbols in Table 1. Wire the terminals
correctly for the desired purposes.
Table 1 Main Circuit Terminal Functions (200 V Class and 400 V Class)
Purpose Terminal Symbol
Main circuit power input
Inverter outputs U/T1, V/T2, W/T3 23P7 to 2055 43P7 to 4055
DC bus terminals
Braking Resistor Unit connection B1, B2 23P7 to 2018 43P7 to 4018
DC reactor connection
Braking Unit connection
Ground 23P7 to 2055 43P7 to 4055
Control Power Supply PO, NO 23P7 to 2055 43P7 to 4055
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3 23P7 to 2055 43P7 to 4055
R1/L11, S1/L21, T1/L31 2022 to 2055 4022 to 4055
1,
1, 2
3,
Model: CIMR-L7Z
200 V Class 400 V Class
23P7 to 2055 43P7 to 4055
23P7 to 2018 43P7 to 4018
2022 to 2055 4022 to 4055
EN-7
Control Circuit Terminals
Fig 2 shows the control terminal arrangement. The functions of the control circuit terminals are shown in
Table 2. Use the appropriate terminals for the correct purposes.
E(G)
SC SC SC
S1
S2
BB
S3 S4
Fig 2 Control terminal arrangement
+V
A1 AC
S5 S6 S7 BB1
M5
M6
M3
MA MB MC
M4
M1
M2
E(G)
Page 11
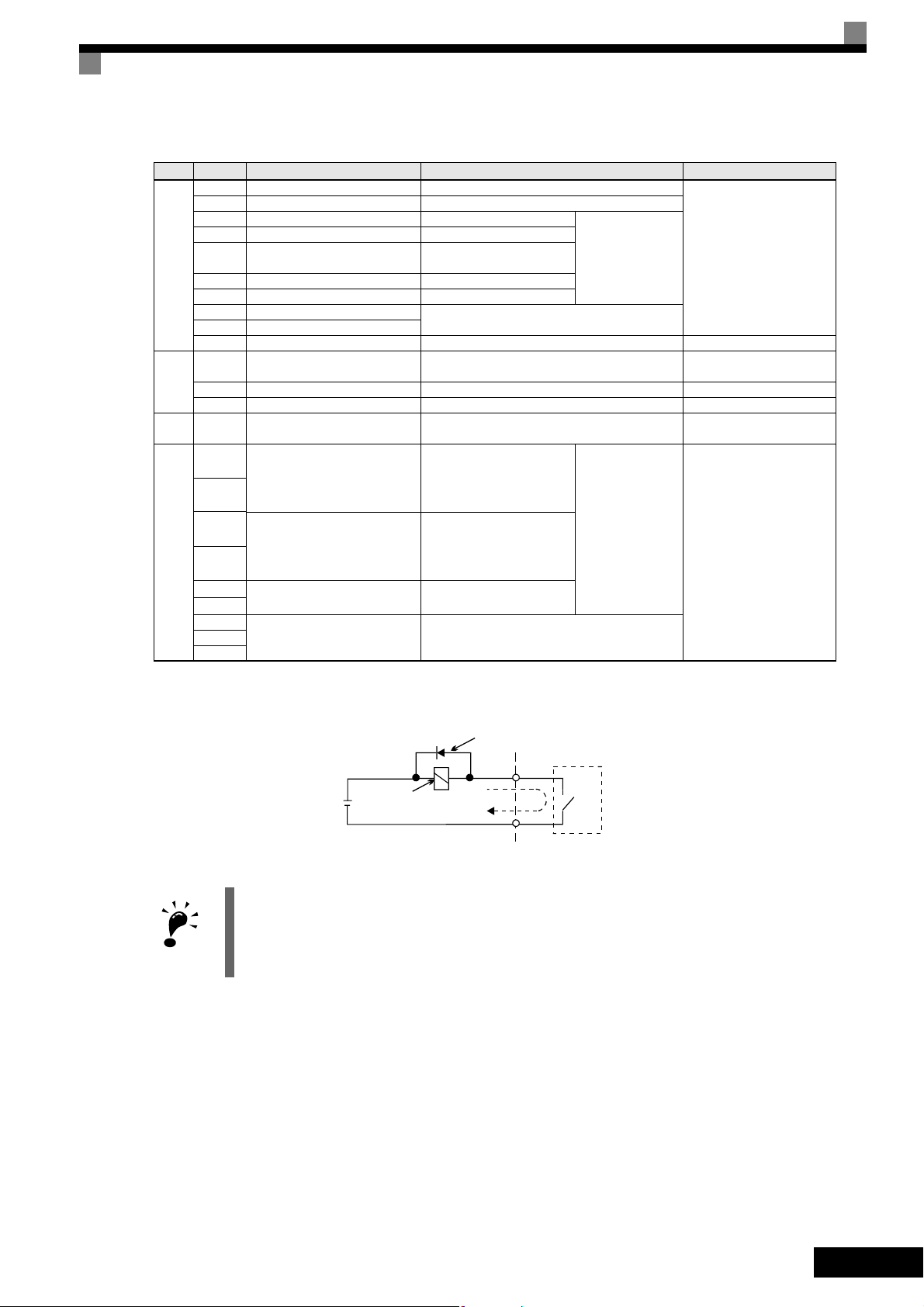
Table 2 Control Circuit Terminals with default settings
Type No. Signal Name Function Signal Level
S1 Forward run/stop command Forward run when ON; stopped when OFF.
S2 Reverse run/stop command Reverse run when ON; stopped when OFF.
S3 Nominal speed Nominal speed when ON.
Dig-
input
signals
S4 Inspection Run Inspection RUN when ON.
S5 Intermediate speed
ital
Intermediate speed when
ON.
S6 Leveling speed Leveling speed when ON.
S7 Not used –
BB Hardware baseblock Both inputs must be enabled to enable the inverter
outputBB1 Hardware baseblock 1
SC Digital input common – –
Ana-
input
signals
Dig-
output
signals
+V
log
15 V power supply
A1 Frequency reference 0 to +10 V/100% 0 to +10 V(20 kΩ)
AC Analog reference neutral – –
Shield wire, optional ground line
E(G)
connection point
M1
Brake command
(1NO contact)
M2
M3
ital
*1. Do not use this power supply for supplying any external equipment.
*2. When driving a reactive load, such as a relay coil with DC power supply, always insert a flywheel diode as shown in Fig 3.
Contactor Control
(1NO contact)
M4
M5
Inverter Ready
(1NO contact)
M6
MA
Fault output signal (SPDT)
MB
(1 Change over contact)
MC
*1
15 V power supply for analog references
––
Brake command when ON.
Contactor Control when ON
Inverter Ready when ON.
Fault when CLOSED across MA and MC
Fault when OPEN across MB and MC
Functions are
selected by setting
H1-01 to H1-05.
Multi-function contact outputs
24 VDC, 8 mA
Photo-coupler
15 V
(Max. current: 20 mA)
Relay contacts
Contact capacity:
1 A max. at 250 VAC
1 A max. at 30 VDC
*2
Flywheel diode
The rating of the flywheel diode must
External power: 30
VDC max.
Coil
1 A max.
be at least as high as the circuit voltage.
Fig 3 Flywheel Diode Connection
1. In Fig 4 the wiring of the digital inputs S1 to S7 and BB, BB1 is shown for the connection of contacts or NPN
transistors (0V common and sinking mode). This is the default setting.
For the connection of PNP transistors or for using a 24V external power supply, refer to Ta ble 3.
IMPORTANT
2. A DC reactor is an option only for Inverters of 18.5 kW or less. Remove the short circuit bar when connecting a
DC reactor.
Sinking/Sourcing Mode (NPN/PNP Selection)
The input terminal logic can be switched over between sinking mode (0-V common, NPN) and sourcing mode
(+24V common, PNP) by using the jumper CN5. An external power supply is also supported, providing more
freedom in signal input methods.
EN-8
Page 12

Table 3 Sinking/Sourcing Mode and Input Signals
S1
S2
SC
IP24V
(+24V)
CN5
A1 A3
B1
B3B2
A2
S1
S2
SC
IP24V
(+24V)
CN5
A1 A3
B1
B3B2
A2
24 VDC
+
S1
S2
SC
IP24V
(+24V)
CN5
A1 A3
B1
B3B2
A2
24 VDC
-
Internal Power Supply – Sinking Mode (NPN)
Internal Power Supply – Sourcing Mode (PNP)
S1
S2
B1
SC
A1 A3
A2
B3B2
CN5
IP24V
(+24V)
External Power Supply – Sinking Mode (NPN)
External Power Supply – Sourcing Mode (PNP)
EN-9
Page 13

Wiring the Inverter
3-phase power
380 to 480V
50/60Hz
Multi function
Inputs
(Factory setting)
Magnetic
Contactor
L1
L2
L3
PE
Forward run/stop
Reverse run/stop
Nominal Speed
Inspection Run
Intermediate Speed
Leveling Speed
Not used
Hardware Baseblock (note 3)
Line
Filter
DC reactor to improve input
power factor (optional)
Link
(+1) (+2)
L1(R)
L2(S)
L3(T)
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
S6
S7
BB
BB1
SC
(-)
+24V, 8mA
IP24V (24V)
Braking Resistor
unit (optional)
B1
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3
TA 1
PG-X2
(Optional)
TA 3
TA 2
B2
A Pulse
B Pulse
Z Pulse
Pulse Monitor Output
RS-422
(100m or less)
Motor
IM/PM
P
P
PG
Voltage adjustment
Analog input
(Speed reference)
2kOhm
Optional control power
supply input for Rescue
Operation
Note:
1
. Main circuit terminals are indicatied with double circles and
control circuit terminals are indicatied with a single circles
2. The CN5 factory setting is NPN
3. To enable the inverter both inputs, BB and BB1 must be closed. If
only one of the inputs is closed, “BB” will be displayed in the
operator panel and the inverter will not start.
2kOhm
0 to 10 V
P
Input option cards
to terminal B1
to terminal -
CN5(NPN setting)
E(G)
+V
Analog input power
supply +15V, 20mA
A1
Master speed
reference 0 to 10V
AC
0 V
2CN
P0
Control Power
Supply Input
N0
Shielded
wires
Fig 4 Wiring Diagram
MA
MB
MC
M1
M2
M3
M4
M5
M6
3CN
Twisted-pair
wires
Fault contact output
250VAC, max. 1A
30VDC, max. 1A
Brake Command
(Factory setting)
Contactor Control
(Factory setting)
Inverter Ready
(Factory setting)
Output option
cards
Multi-function
contact output
250VAC, max. 1A
30VDC, max. 1A
EN-10
Page 14

Keypad Operation
Digital Operator Display (optional)
The key names and functions of the Digital Operator are described below
Drive Status Indicators
FWD: Lights up when a forward run command is input.
REV: Lights up when a reverse run command is input.
SEQ: Lights up when any other run command source
REF: Lights up when any other frequency reference
ALARM:Lights up when an error or alarm has
Data Display
Displays monitor data, parameter numbers and parameter settings.
Mode Display (displayed at the upper left of data display)
DRIVE: Lights up in Drive Mode.
QUICK: Lights up in Quick Programming Mode.
ADV: Lights up in Advanced Programming Mode.
VERIFY: Lights up in Verify Mode.
A. TUNE: Lights up in Autotuning Mode.
Keys
Execute operations such as setting parameters, monitoring, jogging, and autotuning.
than the digital operator is selected
source than the digital operator is selected
occurred.
Digital Operator Keys
Key Name Function
LOCAL/REMOTE Key
MENU Key Selects menu items (modes).
ESC Key Returns to the status before the DATA/ENTER key was pressed.
JOG Key
FWD/REV Key
Shift/RESET Key
Increment Key
Decrement Key
DATA/ENTER Key Enters menus and parameters, and set validates parameter changes.
Switches between operation via the Digital Operator (LOCAL) and the settings in
b1-01 and b1-02 (REMOTE).
This key can be enabled or disabled by setting parameter o2-01.
Starts jog operation when the inverter is operated by the Digital Operator and d1-18
is set to 0.
Selects the rotation direction of the motor when the Inverter is operated by the Digital Operator.
Sets the active digit when programming parameters.
Also acts as the Reset key when a fault has occurred.
Selects menu items, sets parameter numbers, and increments set values.
Used to move to the next item or data.
Selects menu items, sets parameter numbers, and decrements set values.
Used to move to the previous item or data.
EN-11
RUN Key Starts the Inverter operation when the Inverter is controlled by the Digital Operator.
STOP Key
Note: Except in diagrams, Keys are referred to the key names listed in the above table.
Stops Inverter operation.
This key can be enabled or disabled using parameter o2-02 when operating from a
source different than the operator.
Page 15

Power Up and Basic Parameter Setup
Start Up Procedure
START
Mechanical installation
Main and control circuit wiring
Check the encoder power supply selection
Select the control mode in parameter A1-02
Perform motor data / encoder offset auto tuning
* V/f control
* Open Loop Vector Control
* Closed Loop Vector Control
* Closed Loop Vector Control for PM
Speed reference
source
Set up the analog/digital I/O’s in the H1-xx,
H2-xx and H3-xx parameters
* (Closed Loop only)
Switch on the power supply
page 16, Autotuning Procedure with Induction Motors
page 17, Autotuning Procedure for PM Motors
Digital operator (b1-02 = 0)
Analog Input
Select the control sequence in
paramerter d1-18
Set up the digital I/O’s in the H1-xx
and H2-xx parameters
* Acceleration / Deceleration times (C1-xx)
Set up the
* S-Curves (Jerk) (C2-x)
Make test runs
Fine Tuning
* Brake sequence tuning
* Special functions setup
FINISH
Fig 5 Basic Start Up Sequence
* Preset speed values (d1-xx)
Set up the
* Acceleration / Deceleration times (C1-xx)
* S-Curves (Jerk) (C2-xx)
EN-12
Page 16

Before Power Up
The following points should be checked carefully before the power is switched on.
• Check if the power supply meets the inverter specification.
• Check if the power supply cables are tightly connected to the right terminals (L1, L2, L3).
• Check if the motor cables are tightly connected to the right terminals on the inverter side (U, V, W) as well
as on the motor side.
• Check if the braking unit / braking resistor is connected correctly.
• Check if the Inverter control circuit terminal and the control device are wired correctly.
• Set all Inverter control circuit terminals to OFF.
• When a PG card is used, check if it is wired correctly.
Display after Power Up
After normal power up without any problems the operator display shows the following messages
-DRIVE-
Display for normal operation The Baseblock message blinks.
Base Block
Rdy
BB
When a fault occurs or an alarm is active, a fault or alarm message will appear. In this case, refer to page 28,
Factory settings are in bold..
Display for fault operation
-DRIVE-
UV
Main Power Loss
A fault or alarm message is shown on the
display.
The example shows a low voltage alarm.
Control Mode Selection
As the first thing after power up one of the four control modes must be selected depending on the machine
type. The Closed Loop Vector modes require PG feedback cards. Table 4 shows the required / possible PG
cards for each mode.
Table 4 Control Mode Selection
Machine Type Control Mode
Induction motor without encoder
Induction motor with incremental encoder Closed Loop Vector Control 3 PG-B2 / PG-X2
Permanent magnet motor with Hiperface
encoder
Yaskawa IPM motor with incremental encoder
y
or EnDat 2.1
Closed Loop Vector Control for
Closed Loop Vector Control for
V/f control 0 -
Open Loop Vector Control 2 -
PM motors
PM motors
A1-02 setting PG Card
6PG-F2
6 PG-X2
EN-13
CAUTION
• For Permanent Magnet motors do not use any other control mode than Closed Loop Vector for PM
(A1-02 = 6). Using any other control mode can cause damage to the equipment or can cause dangerous
behavior.
Page 17

Autotuning
The motor data autotuning function sets the V/f pattern parameters (E1-), motor data parameters
(E2-, E5-) and the encoder data (F1-01) automatically. The steps which have to be performed during
the autotuning depend on the tuning mode selection.
Autotuning Mode Selection
The autotuning mode has to be selected according to selected control mode and the mechanical system (motor
no load rotation possible or not). Table 5 shows the selectable tuning mode for each control mode.
Table 5 Motor Data Autotuning Modes
Tuning
Autotuning Mode Function
Standard tuning with rotating motor Tunes all motor parameters. 0 No Yes Yes Yes
IM tuning with not rotating motor Tunes the basic motor parameters. 1 No Yes Yes No
IM Line-to-line resistance tuning
Encoder offset tuning
Tunes the line-to-line resistance
only
Tunes the offset between the
encoder and magnetic zero position.
Mode
Selection
(T1-01)
2YesYesYesNo
4NoNoNoYes
V/f
Control Mode
Open
Loop
Vector
Closed
Vector
Loop
Closed
Loop
Vector
(PM)
Autotuning Modes
Autotuning with Rotating Motor (T1-01 = 0)
This autotuning mode can be used in any Vector control mode. After the motor nameplate data have been
input, the inverter will operate the motor for approximately 1~2 minutes and set the required motor parameters
automatically.
Use this tuning mode only, if the motor can rotate freely which means that the ropes must be removed
and the brake must be open. The gearbox can remain connected to the motor.
IMPORTANT
Autotuning with Not Rotating Motor (T1-01 = 1)
This autotuning mode can be used for Open Loop and Closed Loop Vector control for IM only. The inverter
supplies power to the motor for approximately 1 minute and some of the motor parameters are set automatically while the motor does not turn. The motor no-load current and the rated slip value will automatically be
fine tuned during the first time operation.
Verify the rated slip value (E2-02) and the no-load current (E2-03) after the first run with nominal speed.
Autotuning for Line-to-Line Resistance (T1-01 = 2)
Non-rotating autotuning for line-to-line resistance can be used in V/f control, Open Loop Vector control and
Closed loop Vector control. The Inverter supplies power to the motor for approximately 20 seconds to measure
the motor line-to-line resistance and cable resistance. The motor does not turn during this tuning procedure.
Encoder Offset Tuning (T1-01=4)
This tuning mode is available in Closed Loop Vector control for PM motors only. It automatically sets the offset between the magnetic pole and the encoder zero position. It can be used to retune the offset after an
encoder change without changing the motor data settings.
EN-14
Page 18

General Precautions:
1. Use rotating autotuning whenever high precision is required or for a motor that is not connected to a load.
2. Use not rotating autotuning whenever the load cannot be disconnected from the motor (e.g. the ropes can’t be
IMPORTANT
removed).
3. Make sure, that the mechanical brake is not open for not rotating autotuning.
4. During autotuning the motor contactors have to be closed.
5. For autotuning the BB and BB1 signals must be ON (Inverter must not be in base block condition).
6. Confirm, that the motor is mechanically fixed and can not move.
7. Power is supplied during auto tuning, even though the motor does not turn. Do not touch the motor until autotuning has been completed.
8. Remove the feather key from the motor shaft before performing a tuning with rotating motor with a stand alone
motor (no traction sheave or gear mounted).
9. To cancel autotuning, press the STOP key on the Digital Operator.
Precautions for rotating and encoder offset autotuning:
1. The load should be disconnected which means, that the ropes have to be removed and the brake must be open.
2. If the load can’t be removed, the tuning can be done with a balanced car. The tuning result accuracy will be
lower which can result in a performance loss.
3. Make sure that the brake is open during autotuning.
4. During autotuning the motor can be started and stopped repeatedly. When the tuning is finished, “END” will be
displayed in the operator panel. Do not touch the motor until this display is shown and the motor has completely
stopped.
Autotuning Alarms and Faults
Data Input Errors
The inverter will show a “Data Invalid” message and will not perform autotuning if:
• the motor speed, rated frequency and pole pair number do not correspond.
Base Frequency 60⋅
Motor Speed
---------------------------------------------------
<
2 Motor pole⋅
• the rated current does not correspond to the rated power value
The inverter calculates the motor power using the input current value and data from the internal motor data
table. The calculated value must be between 50% and 150% of the input value for the rated power.
Other Alarms and Faults During Autotuning
For an overview of possible autotuning alarms or faults and corrective actions refer to page 27, Auto-tuning
Faults.
EN-15
Page 19

Autotuning Procedure with Induction Motors
Fig 6 shows the autotuning procedure for an induction motor with or without encoder in V/f-, Open loop vec-
tor and Closed loop vector control.
START
Set the Base Block Inputs BB and
BB1
No
V/f Control ?
(A1-02 = 0)
(A1-02 = 2/3)
Yes
Enter auto tuning mode and
set parameter T1-01 = 2
Set:
T1-02 - Motor rated power
T1-04 - Motor rated current
Press the UP button until
“Tuning Ready” display appears
Can the motor
rotate freely ?
No
Enter auto tuning mode and
set parameter T1-01 = 1
T1-02 - Motor rated power
T1-03 - Motor rated voltage
T1-04 - Motor rated current
T1-05 - Rated motor frequency
T1-06 - Motor pole number
T1-07 - Motor rated speed
T1-08 - PG pulse number*
“Tuning Ready” display appears
Set:
(*CLV only)
Press the UP button until
Yes
(ropes removed?)
“Tuning Ready” display appears
Enter auto tuning mode and
set parameter T1-01 = 0
T1-02 - Motor rated power
T1-03 - Motor rated voltage
T1-04 - Motor rated current
T1-05 - Rated motor frequency
T1-06 - Motor pole number
T1-07 - Motor rated speed
T1-08 - PG pulse number*
Set:
(*CLV only)
Press the UP button until
Open the brake
Refer to
page 27, Auto-tuning Faults
and eliminate the fault source
Close the motor contactor(s)
Press the RUN button
Tuning
No
(Fault code is
displayed)
Open the contactors, open the base
block inputs and close the brake if auto
tuning with rotating motor was performed
successful ?
(” Tuning successful”
Yes
is displayed)
FINISH
Fig 6 Autotuning for Induction Motors
EN-16
Page 20

Autotuning Procedure for PM Motors
Fig 7 shows the autotuning procedure for permanent magnet motors. Before tuning make sure that the control
mode is set to PM Closed Loop Vector (A1-02 = 6).
START
* Remove the ropes so that the motor can rotate freely
* Set the Base Block inputs BB and BB1
Switch ON the power supply if it is OFF
Does a OPE06 fault
occur?
No
Does a CPF24 fault
occur?
No
Does a OPE02 fault
occur?
No
S3-13 - Tr acti on sheave diam eter
S3-14 - Ropi ng
turn the motor slowly in Forward direction*
Set mechanical constants:
Open the brake, close the motor contactor,
Does PGO (no
encoder feedback)
occur?
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
S3-15 - Gear r atio
1
and check monitor U1-05.
Yes
Check parameter
* F1-01
* n8-35
* Check parameter n8-35
* If EnDat / Hiperface is used
- check the encoder power supply
- check the CLOCK and DATA signal wiring
* Switch off the power supply.
* Check if the correct PG constant (F1-01) and
absolute encoder resolution (F1-21) has been set.
* Refer to:
page 26, Operator Programming Errors (OPE)
Switch off the power supply
and check if the right PG card
is correctley installed
and eliminate the fault source
* C heck the w ir ing
* C heck/r eadjust the encoder
power supply
EN-17
U1-05 value positive
T1- 01 = 0 - R otational Tuning
T2-01 - Motor rated power
T2- 02 - Mot or base fr equency
T2-03 - Motor rated voltage
Pres s the UP but ton until the “T uning Ready” displ ay appears
Cl ose the mot or cont actor( s) and pr ess the R UN butt on
(”Tuning successful” is displayed)
Set the autot uning par ameter s:
Wait until tuning is finsihed
Tuning successful?
Yes
Open the cont actors , open the basebloc k
inputs and close t he brake
Fig 7 Autotuning for Permanent Magnet Motors
Is the sign of the
(not -)?
Yes
FINISH
No
T2-04 - Motor rated current
T2- 05 - Mot or pole num ber
T2-09 - Encoder resolution
T2- 10 - Mot or vol tage constant
No
(Fault code is displayed)
* 1. Forward direction means:
* C heck the enc oder wi ring
* C hange param eter F 1-05
Refer to
page 27, Auto-tuning Faults
and eli mi nate the faul t sourc e
The direction the motor turns with an UP command at terminal S1 (i.e.
with a clockwise rotating 3 phase supply and U-U, V-V, W-W wiring
between inverter and motor). Usually the direction is clockwise seen
from the motor shaft (traction sheave) side.
Refer to the motor instruction manual or consult the manufacturer for
details about the rotation direction.
Page 21

PM Motor Encoder Offset Tuning
Fig 8 shows the autotuning procedure for an encoder offset tuning. The procedure should be performed if the
encoder has been changed or has not been aligned correctly. Before tuning make sure that PM losed loop vector control is selected (A1-02 = 6) and that the E1- and E5- parameters are set up correctly.
START
Is it possible to remove
the ropes ?
Yes
Remove the ropes.
Set the Base Block inputs BB and BB1
Switch ON the power supply if it is OFF
Does a OPE06 fault
occur?
No
Does a CPF24 fault
occur?
No
Does a OPE02 fault
occur?
No
Open the brake, close the motor contactor,
turn the motor slowly in Forward direction*
monitor U1-05.
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
1
and check
Balance the car so that it does not move
with open brakes.
Note: The tuning accuracy will be lower
in this tuning mode
Check parameter
* F1-01
* n8-35
* Check parameter n8-35
* If EnDat / Hiperface is used
- check the encoder power supply
- check the CLOCK and DATA signal wiring
* Switch off the power supply.
* Check if the correct PG constant (F1-01) and
absolute encoder resolution (F1-21) has been set.
* Refer to:
page 26, Operator Programming Errors (OPE)
and eliminate the fault source
Switch off the power supply
and check if PG card is
correctly installed
Press the UP button until the “Tuning
(”Tuning successful”
display is shown)
Yes
Does PGO (no
encoder feedback)
occur?
No
Is the sign of the
U1-05 value positive
(not -)?
Yes
T1-01 = 4 - Encoder Offset Tuning
Close the motor contactor(s) and
Wait until the tuning is finished.
Open the contactors, open the base
block inputs and close the brake
Set:
Ready” display appears.
press the RUN key.
Tuning successful?
FINISH
Fig 8 Encoder Offset Autotuning
Yes
No
No
(Fault code is
displayed)
* C heck the wi ri ng
* Chec k/readj ust the encoder
power supply
* Chec k the encoder wir ing
* C hange parameter F1- 05
Refer to
page 27, Auto-tuning Faults
and eliminate the fault source.
* 1. Forward direction means:
The direction the motor turns with an UP command at terminal S1 (i.e.
with a clockwise rotating 3 phase supply and U-U, V-V, W-W wiring
between inverter and motor). Usually the direction is clockwise seen
from the motor shaft (traction sheave) side.
Refer to the motor instruction manual or consult the manufacturer for
details about the rotation direction.
EN-18
Page 22

Ride Profile and Sequence Setup
Up and Down Commands and Speed Reference Selection
Up / Down Command Source Selection
The input source for the Up and Down signal can be selected in parameter b1-02. The factory setting is Up/
Down command by the terminals S1/S2 (b1-02 = 1).
Travel start in Up or Down direction
To start in the elevator in Up or Down direction the following conditions have to be fulfilled:
• At least one speed reference must be selected if digital inputs are used for speed reference selection.
• The hardware base block signal (Terminal BB and BB1) must be set (not base block condition).
• The Up/Down signal must be set to start in the corresponding direction.
Travel stop
The inverter can be stopped as follows:
• The direction command (UP or Down) signal is removed.
• The speed reference selection signal is removed if digital inputs are used for speed reference selection.
• If d1-18 is set to 3 and all speed inputs are removed
Speed Reference Source Selection
The speed reference source can be selected using parameter b1-01. The factory setting is the digital operator
(b1-01 = 0), i.e. the speeds can be selected using digital inputs.
Speed Selection Sequence Using Digital Inputs
If the digital inputs are used for speed selection, the speed selection method and the speed priority depends on
the setting of parameter d1-18 (Speed priority selection).
Multi-Step Speed Operation 1/2 (Binary Input) (d1-18=0/3)
If d1-18 = 0
8 preset speed steps (defined in the parameters d1-01 to d1-08) can be selected using 3 binary coded digital
inputs. The Up/Down command starts the inverter. It stops when the Up/Down command is removed.
If d1-18 = 3
7 preset speed steps (defined in the parameters d1-02 to d1-08) can be selected using 3 binary coded digital
inputs. The Up/Down command starts the inverter. It is stopped when the Up/Down command is removed or
when no speed is selected (all D/Is off).
Multi-function Digital Input Settings (H1-01 to H1-05) (Example)
EN-19
Terminal
S4 H1-02 3 Multi-step speed command 1
S5 H1-03 4 Multi-step speed command 2
S6 H1-04 5 Multi-step speed command 3
Parameter
Number
Set Value Details
Page 23

Speed Selection Table
The following table shows the combinations of the digital input and the according speed.
If b1-02 is set to “1”, frequency reference 1 is input as analog reference at terminal A1.
Multi-step
Speed
Speed Com-
mand 1
1 OFF OFF OFF Frequency reference 1 d1-01 Stop
2 ON OFF OFF Frequency reference 2 d1-02 Frequency reference 2 d1-02
3 OFF ON OFF Frequency reference 3 d1-03 Frequency reference 3 d1-03
4 ON ON OFF Frequency reference 4 d1-04 Frequency reference 4 d1-04
5 OFF OFF ON Frequency reference 5 d1-05 Frequency reference 5 d1-05
6 ON OFF ON Frequency reference 6 d1-06 Frequency reference 6 d1-06
7 OFF ON ON Frequency reference 7 d1-07 Frequency reference 7 d1-07
8 ON ON ON Frequency reference 8 d1-08 Frequency reference 8 d1-08
Multi-step
Speed Com-
mand 2
Multi-step
Speed Com-
mand 3
Selected Frequency
d1-18 = 0 d1-18 = 3
Separate Speed Selection Inputs, High Speed Has Priority (d1-18=1)
With this setting 6 different speeds (defined in the parameters d1-09 to d1-17) can be set and selected using
four digital inputs.
Digital Input Factory Settings
Terminal
S3 H1-01 80 Nominal speed selection (d1-09)
S4 H1-02 84 Inspection speed selection (d1-14)
S5 H1-03 81 Intermediate speed selection (d1-10)
S6 H1-04 83 Leveling speed selection (d1-17)
Parameter
Number
Set Value Details
Higher Speed has Priority and a Leveling Speed Input is Selected (H1-=83)
If d1-18 is set to 1 and one multi-function digital input is set to leveling speed selection (H1-=83), the
inverter decelerates to the leveling speed (d1-17) when the selected speed signal is removed. Inspection Speed
can not be selected as travel speed. The higher speed has priority over the leveling speed, i.e. as long as a
higher speed is selected, the leveling signal is disregarded (see the fig. below)
The inverter stops when the leveling signal or the Up/Down signal is removed.
DC Injection/
zero servo
No effect
Input is set
Speed
Hardware BB
Up/Donw
Leveling speed
Selected speed
DC Injection/
zero servo
Higher Speed Priority is Selected and a Leveling Speed Input is Not Selected (H1-K83)
When the leveling speed command is not selected for any digital input, the inverter decelerates to the leveling
speed (d1-17) when the selected speed signal is removed. Inspection Speed can not be selected as travel speed
To select the leveling speed as travel speed the frequency reference loss detection must be disabled (S3-09=0).
The inverter stops when the direction signal Up/Down is removed.
EN-20
Page 24

When no speed selection input is set the leveling speed is taken as the speed reference.
Speed
Hardware BB
Up/Down
Selected speed
DC Injection/
zero servo
DC Injection/
zero servo
The inverter stops when the direction signal (UP or DOWN signal) is removed.
With this configuration the drive stops with a “FRL” (frequency reference loss fault) when no speed
reference input is selected during the start.
IMPORTANT
To disable the FRL detection, set parameter S3-09 to “0”.
Separate Speed Selection Inputs, Leveling Speed Has Priority (d1-18=2)
The related parameters and the digital input pre-settings are the same as for the High Speed Priority setting
(d1-18=1).
Leveling Speed has Priority and a Leveling Speed Input is Selected (H1-=83)
If d1-18 is set to “2” and one multi-function digital input is set to leveling speed (H1-=83) the inverter
decelerates to the leveling speed (d1-17) when the leveling speed selection input is activated. The leveling signal has priority over the selected speed, i.e. the selected speed is disregarded. The selected travel speed must
be different from inspection speed.
The inverter stops when the leveling speed command is removed.
Speed
Hardware BB
Up/Down
Leveling speed
Selected speed
DC Injection/
zero servo
DC Injection/
zero servo
Leveling speed has priority
Leveling Speed Priority is Selected and a Nominal Speed Input is Not Selected (H1-K80))
If d1-18 is set to “2” and no digital input is set to nominal speed selection, the speed reference with speed
selection input set is nominal speed (d1-09). When the leveling speed signal is set, the inverter starts to decelerate to the leveling speed. The leveling speed signal has priority over all other speed signals, i.e. the intermediate speed 1 and 2 and the revelling signals are disregarded when leveling speed is selected.
The inverter can be stopped by removing the leveling speed signal or the Up/Down command.
CAUTION: This sequence can be risky if e.g. the speed selection doesn’t work for any reason (broken wire
etc.).
Speed
Hardware BB
Up/Down
Leveling speed
DC Injection/
zero servo
DC Injection/
zero servo
EN-21
Page 25

Acceleration / Deceleration / Jerk Settings
The acceleration time indicates the time to increase the speed from 0% to 100% of the maximum speed set in
E1-04. The deceleration time indicates the time to decrease the speed from 100% to 0% of E1-04.
The standard acceleration/deceleration times are set in the parameters C1-01/02, the jerk settings (S-curve) are
set in the C2- parameters as shown in Fig 9.
C2-02
Accel Time
C2-01
C1-01
Fig 9 Acceleration / Deceleration and Jerk (S-curve) settings
Brake Sequence
The figure below shows the standard brake sequence.
S1-04
Zero servo/
S1-16
DC Injection
at start
RUN delay time
Speed
S1-06
Delay time
Brake open
RUN
Inverter Hardware BB D/I
Brake Open Command
Decel Time
C1-02
Selected Speed
C2-03
C2-04
C2-05
Leveling Speed
Leveling Speed
S1-07
Brake close
delay time
S1-05
Zero servo/
DC inhection
at stop
S1-19
Contactor open delay
Fig 10 Timing chart of Brake sequence without torque compensation at start
Inertia Compensation (Feed Forward)
Feed Forward Control is used to eliminate the speed overshoot or undershoot by compensating inertia effects.
It can be enabled by setting parameter n5-01 to 1. After that the motor acceleration time n5-05 must be tuned.
Motor Acceleration Time Auto Tuning (n5-05)
Before the n5-02 auto tuning is performed, the motor data autotuning and the general setup should have been
finished. Do the tuning with the factory settings for the n5- parameters.
Use the following procedure:
1. Set n5-05 to “1” to enable the auto tuning and go back to the speed reference display.
2. Set the base block input.
3. Enable the inspection speed input. “FFCAL” will blink in the display to signalize that the calculation is
active.
4. Set an UP command. The inverter will accelerate the motor up to the nominal speed. Release the UP command a few seconds after the top speed has been reached.
EN-22
Page 26

5. When the motor has stopped, apply a DOWN command. The inverter will accelerate the motor in the
opposite direction to the nominal speed. Release the DOWN command a few seconds after the nominal
speed has been reached.
To abort the tuning set parameter n5-05 to “0”.
1. The order of giving the UP or DOWN command has no influence.
2. n5-01 should not be changed from the factory value for the tuning.
3. After the run in both directions is finished, parameter n5-05 is automatically set back to “0”.
IMPORTANT
4. The autotuning will be performed only if the inspection speed input is set.
5. Do not change the mechanical constants (load, inertia) between the runs.
Feed Forward Compensation P-Gain Setup
• Increase the gain to improve the responsiveness to the speed reference.
• Decrease the gain if vibrations or oscillations occur.
EN-23
Page 27

Troubleshooting
Fault and Alarm Detection
Faults and Alarms are functions that indicate unusual inverter / application conditions.
An alarm does not necessarily switch of the inverter but a message is displayed on the keypad and an alarm
output is generated at the multi-function outputs (H2-01 to H2-03) if programmed. An alarm automatically
disappears if the alarm condition is not present anymore.
A fault switches the inverter off immediately, a message is displayed on the keypad and the fault output is
switched. The fault must be reset manually after the cause has been removed.
The following tables shows a list of faults and alarms with their corrective actions.
Display
BUS
Option Com Err
(flashing)
CF
Out of Control
CPF00
CPF01
COM-
ERR(OP&INV)
CPF02 - CPF 04
CPF24
Option Comm Err
DEV
Speed Deviation
DV3
DV4
DV6
Over Accelera-
tion
EF0
Opt External Flt
EF
Ext Fault S
EF
External Fault
(flashing)
Ext Run Active
Cannot Reset
Displayed as
Alarm Fault
Meaning Corrective Actions
Option Communications Alarm
After initial communication was established, the connection was lost.
A torque limit was reached continuously for 3 seconds or longer during a deceleration stop in Open
Loop Vector control.
• Digital Operator/LED Monitor Communication
Fault 1 / 2
• Communication fault between Operator and
inverter
• CPU External RAM Fault
• Baseblock circuit error
•EEPROM error
• CPU Internal A/D Converter Fault
Hiperface serial communication error
Detected when no data were received from the
encoder for 200 msec
F1-04 = 0, 1 or 2 and A1-02 = 3 or 6
The speed deviation is higher than the F1-10 value
for the time F1-11 or longer.
F1-04 = 3 and A1-02 = 3 or 6
The speed deviation is higher than the F1-10 value
for the time F1-11 or longer.
Wrong rotation direction
Detected when the speed deviation is higher than
30% and the torque reference and acceleration have
opposite signs.
Wrong rotation direction
Detected when F1-19 is not 0, the speed reference
and motor speed have opposite signs and the detection threshold set in F1-19 is exceeded.
An over acceleration of the car was detected
(A1-02 = 6 only)
External fault input from Communications Option
Card
External fault at terminal S ( stands for terminals
S3 to S7)
Forward/Reverse Run Commands Input Together
Both the forward and the reverse run commands are
input simultaneously for 500ms or more. This alarm
stops the motor.
Fault reset was tried during run.
Check the connections and all user-side software configurations.
Check the motor parameters.
• Disconnect the Digital Operator/LED Monitor and
then connect it again.
• Replace the Inverter.
• Cycle the Inverter power supply.
• Replace the Inverter.
• Perform an initialization to factory defaults.
• Cycle the Inverter power supply.
• Replace the Inverter.
Check the encoder connection or replace the encoder
if necessary
• Reduce the load.
• Lengthen the acceleration time and deceleration
time.
• Check the mechanical system.
• Check the settings of F1-10 and F1-11.
• Check the sequence and if the brake is opened when
the inverter starts to increase the speed.
•Check the PG wiring
• Correct the wiring
• Verify the PG direction and execute an encoder offset auto tuning
• Reduce the load and check the brake
• Verify the PG direction and execute an encoder offset auto tuning
• Reduce the load and check the brake
• Reduce the load
• Check the PG direction, check F1-22 and perform
an encoder offset tuning.
• Verify the settings of S3-13, S3-14 and S3-15.
• Adjust the acceleration and deceleration times.
• Check for an external fault condition.
• Verify the parameters.
• Verify communication signals
Eliminate the cause of the external fault condition.
Check external sequence logic, so that only one input
is received at a time.
• Remove the direction signal and retry a fault reset.
• If a PLC handles the fault reset, check the sequence.
EN-24
Page 28

Display
FF_CAL
FRL
Ref Missing
GF
Ground Fault
LF
Output Phase
Loss
OC
Over Current
OH
Heatsink Over-
temp
OH1
Heatsink Max
Tem p
OL1
Motor Overload
OL2
Inv Overload
OS
Motor Over speed
Det
OV
DC Bus Overvolt
PF
Input Phase Loss
PGO
PG Open
(PG Disconnec-
tion)
Displayed as
Alarm Fault
(only in
stop
condi-
tion)
Meaning Corrective Actions
Feed forward motor acceleration time active
No speed was selected before the inverter start. Check the speed selection/start sequence.
The ground current at the Inverter output exceeded
50% of the Inverter rated output current and L8-09=1
(Enabled).
An open-phase occurred at the Inverter output.
The fault is detected when the output current falls
below 5% of the inverter rated current and L8-07=1
The Inverter’s output current exceeded the over cur-
rent detection level.
L8-03 = 0,1 or 2 and the temperature of the Inverter's
cooling fin exceeded the L8-02 value.
Inverter's Cooling Fan Stopped
L8-03 = 3 and the temperature of the Inverter's cooling fin exceeded the L8-02 value.
The temperature of the Inverter’s heatsink exceeded
105 °C.
Inverter’s Cooling Fan Stopped
Detected when L1-01 is set to 1,2 or 3 and the
Inverter’s output current exceeded the motor overload curve.
The overload curve is adjustable using parameter E2-
01 (Motor Rated Current), L1-01 (Motor Protection
Selection) and L2-02 (Motor Protection Time Constant)
The Inverter output current exceeded the Inverter’s
overload capability.
F1-03 = 0, 1 or 2 and A1-02 is set to 3 or 6.
The motor speed feedback (U1-05) exceeded the F1-
08 value for the time F1-09.or longer.
F1-03 = 3 and A1-02 is set to 3 or 6.
The motor speed feedback (U1-05) exceeded the F108 value for the time F1-09.or longer.
The DC bus voltage has exceeded the overvoltage
detection level.
Default detection levels are:
200 V class: 410 VDC
400 V class: 820 VDC
Too big DC bus voltage ripple.
Only detected when L8-05=1 (enabled)
F1-02 = 0, 1 or 2 and A1-02 = 3 or 6
No PG (encoder) pulses are received for the time F1-
14 or longer.
F1-02 = 3 and A1-02 = 3 or 6.
No PG (encoder) pulses are received for the time F114 or longer.
• Perform the complete tuning procedure
• Abort the tuning by setting
n5-05 = 0.
• Remove the motor and run the Inverter without the
motor.
• Check the motor for a phase to ground short.
• Check the output current with a clampmeter to verify the DCCT reading.
• Check the control sequence for wrong motor contactor signals.
• Reset the fault after correcting its cause.
• Check the motor and Inverter capacity.
• Remove the motor and run the Inverter without the
motor.
• Check the motor for a phase-to-phase short.
• Verify the accel/decel times
•(C1-).
• Check the Inverter for a phase-to-phase short at the
output.
• Check for dirt build-up on the fans or heatsink.
• Reduce the ambient temperature around the drive.
• Replace the cooling fan(s).
• Check for dirt build-up on the fans or heatsink.
• Reduce the ambient temperature around the drive.
• Replace the cooling fan(s).
• Recheck the cycle time and the size of the load as
well as the accel/decel times
•(C1-).
• Check the V/f characteristics (E1-).
• Check the setting of Motor Rated Current Setting
(E2-01).
• Recheck the cycle time and the size of the load as
well as the accel/decel times
•(C1-).
• Check the V/f characteristics (E1-).
• Check the setting of Motor Rated Current Setting
(E2-01).
• Adjust the ASR settings in the C5 parameter group.
• Check the reference circuit and reference gain.
• Check the settings in F1-08 and F1-09.
• Increase the deceleration time (C1-02/04/06/08) or
connect a braking option.
• Check the power supply and decrease the voltage to
meet the inverter’s specifications.
• Check the braking chopper / resistor.
• Tighten the input terminal screws
• Check the power supply voltage
• Fix the broken/disconnected wiring.
• Fix the wiring.
• Supply power to the PG
•properly.
• Check the sequence and if the brake is opened when
the inverter starts to increase the speed.
EN-25
Page 29

Display
PUF
DC Bus Fuse
Open
RR
DynBrk Transistr
SE1
Sequence Error 1
SE2
Sequence Error 2
SE3
Sequence Error 3
SVE
Zero Servo Fault
UV1
DC Bus Under-
volt
UV2
CTL PS Under-
volt
Displayed as
Alarm Fault
(only in
condi-
tion)
stop
Meaning Corrective Actions
The fuse in the main circuit is blown.
War ni ng:
Never run the Inverter after replacing the DC bus
fuse without checking for shorted components.
The built-in dynamic braking transistor failed.
No output contactor response S1-16 or longer. Check the output contactor.
The output current at start was below 25% of no-load
current.
The output current during run was below 25% of noload current.
The motor position moved during Zero Servo Operation.
The DC bus voltage is below the under voltage
Detection Level
(L2-05). The default settings are:
200V class: 190 VDC
400 V class: 380 VDC
Main Circuit MC Operation Failure
No MC response during Inverter operation.
Control Power Supply Undervoltage
Undervoltage of the control circuit while the Inverter
was running.
• Check the motor and the motor cables for short circuits or insulation failures (phase-to-phase).
• Replace the inverter after correcting the fault.
• Cycle power to the Inverter.
• Replace the Inverter.
Check the output contactor.
Check the output contactor.
• Increase the torque limit.
• Decrease the load torque.
• Check for signal noise.
• Check the input voltage.
• Check the wiring of the input terminals.
• Check the input voltage and the wiring of the input
terminals.
• Extend the settings in
• C1-01/03/05/07
Replace the Inverter.
• Remove all connection to the control terminals and
cycle the power to the Inverter.
• Replace the Inverter.
Operator Programming Errors (OPE)
An Operator Programming Error (OPE) occurs when two or more parameter related to each other are set inappropriate or an individual parameter setting is incorrect. The Inverter does not operate until the parameter setting is set correctly; however, no other alarm or fault outputs will occur. If an OPE occurs, change the related
parameter by checking the cause shown in the table below. When an OPE error is displayed, press the ENTER
key to see U1-34 (OPE Detected). This monitor displays the parameter that is causing the OPE error.
Display Meaning Corrective Actions
OPE01
kVA Selection
OPE02 Limit
OPE03
Ter mi nal
OPE05
Sequence Select
OPE06
PG Opt Missing
OPE08
Constant Selection
OPE10
V/f Ptrn Setting
Inverter kVA Setting Error Enter the correct kVA setting in o2-04.
Parameter Setting out of Range
Hiperface selected (n8-35=4) and:
• F1-01 is different from 512 or 1024
• F1-21 is set to 2
EnDat selected (n8-35=5) and:
• F1-01 is different from 512 or 2048
• F1-21 is set to 0 or 1
Multi-function Input Selection Error (H1-01 to H1-05):
• Functions were selected duplicative.
• External Baseblock NO (8) and External Baseblock NC
(9) were selected at the same time.
The Emergency Stop Command NO (15) and NC(17) are
set simultaneously.
RUN/Reference Command Selection Error
The Reference Source Selection b1-01 and/or the RUN
Source Selection parameter b1-02 are set to 3 (option
board) but no option board is installed.
Control method selection error /
PG-card missing
Function Selection Error Verify the control method and the function.
V/f Parameter Setting Error
Verify the parameter settings.
Verify the parameter settings in H1-
• Verify that the board is installed. Remove the power supply
and re-install the option board again
• Recheck the setting of b1-01 and b1-02.
Verify the control method selection in parameter A1-02 and/or
the installation of the PG option board.
Check parameters (E1-). A frequency/voltage value may
be set higher than the maximum frequency/voltage.
EN-26
Page 30

Auto-tuning Faults
Auto-tuning faults are shown below. When the following faults are detected, the fault is displayed on the dig-
ital operator and the motor coasts to stop. No fault or alarm outputs will be operated.
Display Meaning Corrective Actions
Acceleration error (detected during rotating autotuning
Accelerate
End - 1
V/f Over Setting
End - 2
Saturation
End - 3
Rated FLA Alm
Fault Motor data fault
I-det. Circuit
KE_ERR
(PM motor only)
LD_ERR
(PM motor only)
Leakage Induc-
tance Fault
Minor Fault
Motor Speed
No-Load Current No-Load Current Fault • Check the input data.
Resistance Line-to-Line Resistance Fault
Rated slip Rated Slip Fault
RS_ERR
(PM motor only)
STOP key STOP key input -
Z_SRCH_ERR
(PM motor only)
only)
The motor did not accelerate in the specified time.
V/f Settings Alarm
Displayed after auto-tuning is complete
The torque reference exceeded 100% and the no-load current exceeded 70% during auto-tuning.
Motor Core Saturation Fault
Displayed after auto-tuning is complete.
Detected only for rotating autotuning
Rated Current Setting Alarm
Displayed after auto-tuning is complete
During auto-tuning, the measured value of motor rated
current (E2-01) was higher than the set value.
Current detection error
The current exceeded the motor rated current or any output phase is open
Voltage constant error Check the motor wiring
Inductance error Check the motor wiring
The leakage inductance measurement caused an error.
The leakage inductance tuning current was too high or too
low (Closed Loop Vector for PM only)
Any of the above listed alarms occured during autotuning
or the inverter was in Base Block condition when the tuning was started.
Motor Speed Fault
Detected only for rotating autotuning
The torque reference exceeded 100% during acceleration.
Detected only when A1-02 is set to 2 (Open Loop Vector
control).
Line-to-line resistance error
All encoders:
The motor speed exceeded 20 rpm at the auto tuning start.
The magnetic pole position tuning could not be performed
in the specified time.
Encoder with Z-pulse:
The difference between two measurements of the magnet
pole position was higher than 3°.
Serial encoders:
The difference between two measurements of the magnet
pole position was higher than 5° or an encoder serial communication error has occurred during the tuning.
• Increase C1-01 (Acceleration Time 1).
• Increase L7-01 and L7-02 (Torque Limits) if they are low.
• Remove the ropes and repeat the tuning.
• Check and correct the motor settings
• If the motor and the machine are connected, disconnect the
motor from the machine.
• Check the input data.
• Check the motor wiring.
• If the motor and the machine are connected, disconnect the
motor from the machine.
Check the motor rated current value.
• Check the input data.
• The motor and inverter capacity do not fit. Check the Inverter
and motor capacity.
• Check the motor rated current and no-load current.
Check wiring of the Inverter and the mounting.
• Check the motor wiring.
• Check the motor rated current input value
• Reduce or increase the current level for leakage inductance
tuning by changing parameter n8-46.
• Leave the tuning menu, check the alarm content and remove
the cause as described in the alarm list above.
• Check the input data.
• Make sure that the inverter is not in Base Block condition
during the tuning.
• If the motor is connected to the machine, disconnect it.
• Increase C1-01 (Acceleration Time 1).
• Check the input data (particularly the number of PG pulses
and the number of motor poles).
• Perform not rotating auto tuning
• Check the motor wiring.
• If the motor is connected to the machine, disconnect it.
• If the setting of T1-03 is higher than the Inverter input power
supply voltage (E1-01), change the input data.
• Check the motor wiring
• Check the motor input data
• Remove the ropes and repeat the tuning
• Check the encoder rotation direction and if necessary change
F1-05.
• Check the encoder wiring (order, shield etc.)
• Check the encoder power supply.
Replace the encoder.
EN-27
Page 31

Parameter Table
Note: Factory settings are in bold.
Param.
Num.
Name Description
Initialize Data
Language
selection for
Digital Opera-
A1-00
tor display
(JVOP-160-OY
only)
Parameter
A1-01
access level
Control method
A1-02
selection
A1-03 Initialize
0:English
1:Japanese
2:German
3:French
4:Italian
5:Spanish
6: Portuguese
0:Monitoring only (Monitoring drive
mode and setting A1-01 and A1-04.)
1:Used to select user parameters (Only
parameters set in A2-01 to A2-32 can
be read and set.)
2:Advanced
(Parameters can be read and set in both,
quick programming mode (Q) and
advanced programming mode (A).)
0:V/f control
2: Open loop vector
3:Closed Loop Vector
6:Closed Loop Vector for PM motors
0: No initializing
1110:Initializes to user parameters
2220:.Initializes to the factory setting
Sequence / Reference Source
b1-01
b1-02
Reference
source selection
RUN command source
selection
0:Digital Operator
1:Control circuit terminal (analog input)
3:Option Card
0:Digital Operator
1:Control circuit terminal (digital
multi function inputs)
3:Option Card
Acceleration / Deceleration Settings
Accel./Decel.
C1-
C2-
time 1
S-curve characteristic
Refer to page 1-22
Set the S-curve times at speed changes to
reduce the jerk. Refer to page 1-22
Slip Compensation
• Increase the value if slip compensation
C3-01
C3-02
Slip compensation gain
Slip compensation delay time
value is too low
• Decrease the value if slip is overcompensated
• Reduce the value if the slip compensation responsiveness is low.
• When speed is not stable, increase the
setting.
Automatic Speed Regulator (ASR)
ASR propor-
C5-01
tional (P) gain 1
ASR integral (I)
C5-02
time 1
ASR propor-
C5-03
tional (P) gain 2
ASR integral (I)
C5-04
time 2
C5-06 ASR delay time Sets the ASR output delay time.
ASR switching
C5-07
frequency
Set the proportional gain 1 and the integral time 1 of the speed control loop
(ASR) for the frequency C5-07.
Set the proportional gain 2 and the integral time 2 of the speed control loop
(ASR) for the minimum frequency.
The setting is active only for acceleration.
Sets the frequency for switching between
Proportion Gain 1, 2,3 and Integral Time
1, 2, 3.
Param.
Num.
C5-09
C5-10
Name Description
ASR proportional (P) gain 3
ASR integral (I)
time 3
Set the proportional gain 3 and the integral time 3 of the speed control loop
(ASR) for the minimum frequency.
The settings is active for deceleration
only.
Carrier Frequency Setup
C6-02
C6-11
Carrier frequency selection 1
Carrier frequency selection 2
Selects the carrier frequency for Induction motor control modes.
Selects the carrier frequency for PM
motor control modes
Speed Settings
d1-01
Multi speed ref.
to
1 to 8
d1-08
d1-09 Nominal speed
d1-10 Interm. speed 1
d1-11 Interm. speed 2
d1-12 Interm. speed 3
d1-13 Relevel. speed
d1-14 Inspect. speed
d1-17 Leveling Speed
Speed priority
d1-18
selection
Refer to page 19, Speed Selection
Sequence Using Digital Inputs
0:Use Multi-Speed ref. (d1-01 to d1-08)
1:High Speed reference has priority.
2:Leveling speed reference has priority.
3:Use multi-speed reference
With no speed selected, the up/ down
signal is switched off
Refer to page 1-19
V/f Pattern Settings
E1-01
E1-04
E1-05
E1-06
E1-08
E1-10
E1-13
Input voltage
setting
Max. output
frequency
(FMAX)
Max. output
voltage
(VMAX)
Base frequency
(FA)
Mid. output frequency voltage
(VB)
Min. output frequency voltage
(VMIN)
Base voltage
(VBASE)
This setting is used as a reference value
for protection functions.
Output Voltage (V)
To set V/f characteristics in a straight
line, set the same values for E1-07 and
E1-09. In this case, the setting for E1-08
will be disregarded.
Always ensure that the four frequencies
are set in the following manner:
E1-04 (FMAX) ≥ E1-06 (FA) > E1-07
(FB) ≥ E1-09 (FMIN)
Frequency (Hz)
EN-28
Page 32

Param.
Num.
Name Description
Motor Data Settings
E2-01 Rated current
E2-02 Rated slip
E2-03 No-load current
E2-04 Pole number
Line-to-line
E2-05
resistance
Leak induct-
E2-06
ance
E5-02 Rated power
E5-03 Rated current
E5-04 Pole number
Line-to-line
E5-05
resistance
E5-06 d-Inductance
E5-07 q- Inductance
Motor voltage
E5-09
constant
Motor Data for induction motors
Motor Data for PM motors
Encoder Feedback Settings
F1-01 PG constant
PG rotation
F1-05
direction
Absolute
encoder resolu-
F1-21
tion (Hiperface
or EnDat)
Magnet posi-
F1-22
tion offset
Sets the number of PG pulses per revolution
0:Phase A leads with forward run com-
mand. (Phase B leads with reverse
run command; Counter Clockwise
rotation)
1:Phase B leads with forward run com-
mand. (Phase A leads with reverse run
command; Clockwise rotation)
0:16384
1:32768
2:8192
(if EnDat is selected (n8-35=5), F1-21 is
fixed to 2)
Sets the Offset between the rotor magnet
and encoder zero position.
Digital I/O Settings
Terminal S3 to
H1-01
to
H1-05
H2-01
to
H2-03
S7 function
selection
Terminal M1M2 / M3-M4 /
M5-M6 function selection
Refer to the end of this list for a list of
selections
Refer to the end of this list for a list of
selections
Motor Protection
0: Disabled
1:General-purpose motor protection
(fan cooled motor)
2: Inverter motor protection (externally
cooled motor)
3: Vector motor protection
When the Inverter power supply is
turned off, the thermal value is reset, so
even if this parameter is set to 1, protection may not be effective.
5:Permanent magnet constant torque
motor protection
L1-01
Motor protection selection
Feed Forward Compensation
n5-01
n5-02
Feed forward
control sel.
Motor acceleration time
0:Disabled
1: Enabled
Param.
Num.
n5-03
n5-05
Name Description
Feed forward
proportional
gain
Motor acceleration time tuning
Speed reference response will increase as
the setting of n5-03 is increased.
0:Disabled
1:Enabled
Brake Sequence
Zero Speed
S1-01
level at stop
DC injection
S1-02
braking current
at start
DC injection
S1-03
braking current
at stop
DC inj. braking/
S1-04
Zero speed time
at start
DC inj. braking/
S1-05
Zero speed time
at stop
Brake release
S1-06
delay time
Brake close
S1-07
delay time
S1-20 Zero-servo gain
Sets the brake close command speed level
at stop.
Sets as a percentage of the Inverter rated
current.
Refer to page 22, Brake Sequence.
Zero servo position loop gain for closed
loop vector control.
Speed Reference Slip Compensation
S2-01
S2-02
S2-03
Motor rated
speed
Slip compensation gain in
motoring mode
Slip compensation gain in
regenerative
mode
Sets the motor rated speed.
Sets the slip compensation gain in motoring mode. Can be set for leveling accuracy improvement.
Sets the slip compensation gain in regenerative mode.
It can be used to improve the
leveling accuracy.
Special Functions Setup
Short-floor
S3-01
function selection
Nominal/Lev-
S3-04
eling speed
detection level
Output phase
S3-08
order
Traction sheave
S3-13
diameter
S3-14 Roping Ratio
S3-15 Gear Ratio Sets the mechanical gear ratio.
Enables or disables the short floor operation function
0:disabled
1:enabled (Standard)
2:enabled (Advanced)
Nominal/Leveling speed detection level
when multispeed inputs are used. (d118=0/3)
0:Output phase order is U-V-W
1:Output phase order is U-W-V
Sets the diameter of the traction sheave
for m/s display units.
1:1:1
2:1:2
Monitor Data
U1-01 Frequency reference in Hz / rpm
U1-02 Output frequency in Hz / rpm
U1-03 Output current in A
U1-05 Motor speed in Hz / rpm
U1-06 Output voltage in VAC
U1-07 DC bus voltage in VDC
EN-29
Page 33

Param.
Num.
Name Description
U1-08 Output power in kW
U1-09 Torque reference in % of the motor rated torque
Shows input ON/OFF status.
1: FWD command
(S1) is ON
1: REV command
(S2) is ON
1: Multi input 1
(S3) is ON
1: Multi input 2
(S4) is ON
1: Multi input 3
(S5) is ON
1: Multi input 4
(S6) is ON
1: Multi input 5
(S7) is ON
U1-10
Input terminal
status
Shows output ON/OFF status.
1: Multi-function
contact output 1
(M1-M2) is ON
1: Multi-function
contact output 2
U1-11
Output terminal status
(M3-M4) is ON
1: Multi-function
contact output 3
(M5-M6) is ON
Not used
(Always 0).
1: Error output
(MA/MB-MC) is
ON
Inverter operating status.
Run
1: Zero speed
1: Reverse
U1-12
Operation status
1: Reset signal
input
1: Speed agree
1: Inverter ready
1: Minor fault
1: Major fault
U1-13 Cumulative operation time
U1-20 Frequency reference after soft-starter
U1-34 OPE fault parameter
U1-51 Max Current during acceleration
U1-52 Max Current during deceleration
U1-53 Max Current during Top speed
U1-54 Max Current during leveling speed
U1-55 Number of travels
Fault Trace Data
U2-01 Current fault
U2-02 Last fault
U2-03 Reference frequency at fault
U2-04 Output frequency at fault
U2-05 Output current at fault
U2-06 Motor speed at fault
U2-07 Output voltage reference at fault
U2-08 DC bus voltage at fault
U2-09 Output power at fault
U2-10 Torque reference at fault
U2-11 Input terminal status at fault
U2-12 Output terminal status at fault
Param.
Num.
Name Description
U2-13 Operation status at fault
U2-14 Cumulative operation time at fault
Fault History Data
U3-01
to
Last fault to Fourth last fault
U3-04
U3-05
to
Cumulative operation time at fault 1 to 4
U3-08
U3-09
to
Fifth last to tenth last fault
U3-14
U3-15
to
Accumulated time of fifth to tenth fault
U3-20
* The following errors are not recorded in the error log:
CPF00, 01, 02, 03, UV1, and UV2.
Digital Input Function Selections
3 Multi-step speed reference 1
4 Multi-step speed reference 2
Jog frequency command (higher priority than multi-step
6
speed reference)
F Not used (Set when a terminal is not used)
14 Fault reset (Reset when turned ON)
External fault; Input mode: NO contact/NC contact, Detec-
20 to
2F
tion mode: Normal/during operation
80 Nominal Speed Selection (d1-09)
81 Intermediate Speed Selection (d1-10)
82 Releveling Speed Selection (d1-13)
83 Leveling Speed Selection (d1-17)
84 Inspection Run Selection (d1-14)
Digital Output Function Selections
During run 1 (ON: run command is ON or voltage is being
0
output)
Inverter operation ready; READY: After initialization or no
6
faults
8 During baseblock (NO contact, ON: during baseblock)
Car stuck/undertorque detection 1 NO (NO contact, ON:
B
Overtorque/undertorque detection)
F Not used. (Set when the terminal is not used.)
10 Minor fault (ON: Alarm displayed)
Car stuck/undertorque detection 1 NC (NC Contact, OFF:
17
Torque detection)
1A During reverse run (ON: During reverse run)
40 Brake Release Command
41 Output Contactor Close Command
EN-30
Page 34

EN-31
 Loading...
Loading...