Page 1

J1000 USER’S MANUAL
Manual No. SIEP-C71060633-01-OY
J1000
Compact General Purpose Inverter
Model: JZA
200 V Class Three-Phase Input 0.1 to 0.4 kW
200 V Class Single-Phase Input 0.1 to 1.5 kW
400 V Class Three-Phase Input 0.2 to 4.0 kW
USER’S MANUAL
Manual No.
SIEP-C71060633-01-OY
Page 2

Page 3
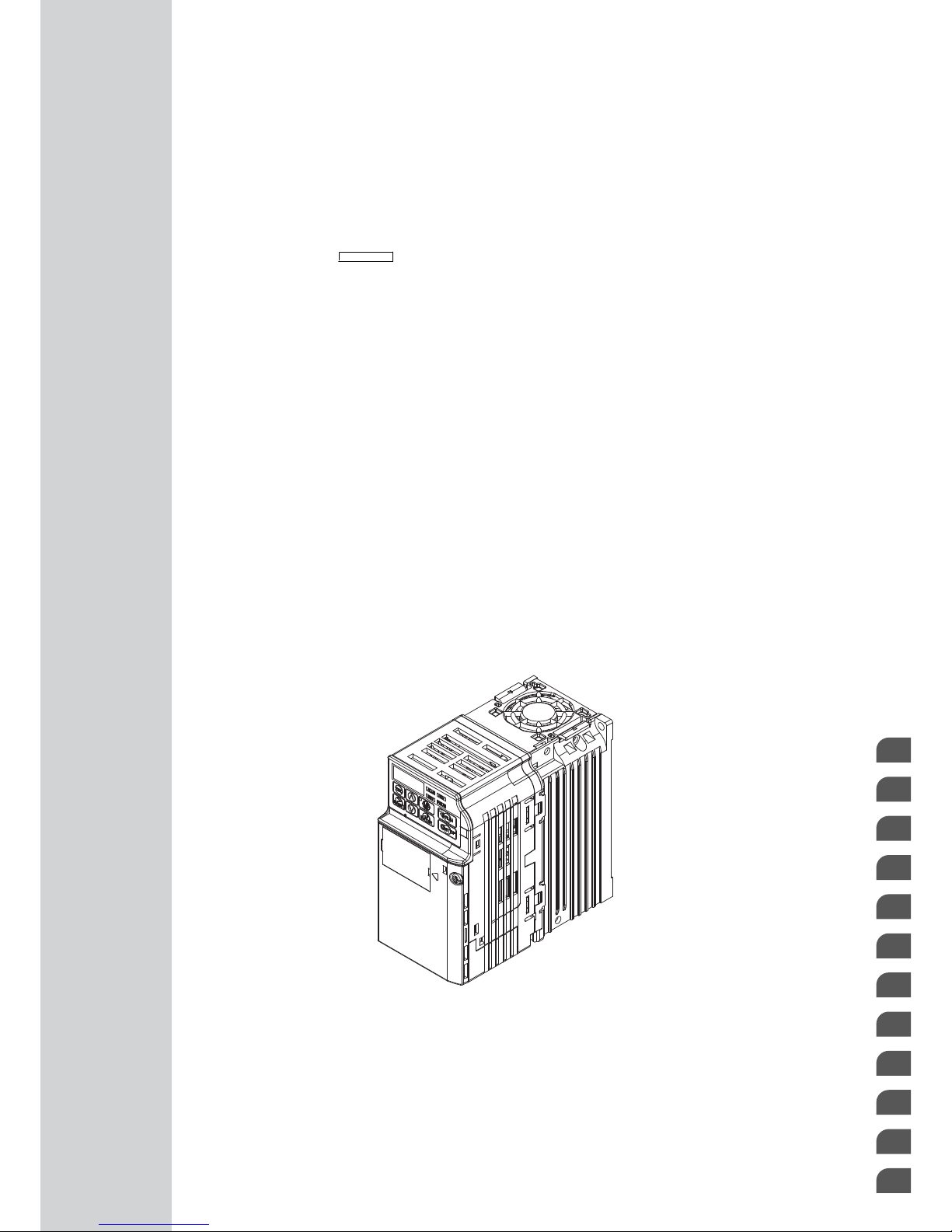
OYMC AC Drive – J1000
Compact V/f Control Drive
User Manual
Type: JZA
Model: 200 V Class, Single-Phase Input: 0.1 to 1.5 kW
200 V Class, Three-Phase Input: 0.1 to 4.0 kW
400 V Class, Three-Phase Input: 0.2 to 4.0 kW
To properly use the product, read this manual
thoroughly and retain for easy reference,
inspection, and maintenance. Ensure the end
user receives this manual.
MANUAL NO. SIEP C710606 33A
Receiving
1
Mechanical Installation
2
Electrical Installation
3
Start-Up Programming &
Operation
4
Parameter Details
5
Troubleshooting
6
Periodic Inspection &
Maintenance
7
Peripheral Devices &
Options
8
Specifications
A
Parameter List
B
MEMOBUS/Modbus
Communications
C
Standards Compliance
D
Page 4

This Page Intentionally Blank
2
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Copyright © 2008 OMRON YASKAWA MOTION CONTROL, B.V. All rights reserved.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted,
in any form or by any means, mechanical, electronic, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior
written permission of OYMC. No patent liability is assumed with respect to the use of the information contained
herein. Moreover, because OYMC is constantly striving to improve its high-quality products, the information
contained in this manual is subject to change without notice. Every precaution has been taken in the preparation
of this manual. OYMC assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions. Neither is any liability assumed for
damages resulting from the use of the information contained in this publication.
Page 5

Table of Contents
i. PREFACE & GENERAL SAFETY................................................................9
i.1 Preface .................................................................................................................. 10
Applicable Documentation..................................................................................................10
Symbols..............................................................................................................................10
Terms and Abbreviations ...................................................................................................10
i.2 General Safety ...................................................................................................... 11
Supplemental Safety Information .......................................................................................11
Safety Messages................................................................................................................11
Drive Label Warnings .........................................................................................................13
Warranty Information..........................................................................................................13
Quick Reference.................................................................................................................14
1. RECEIVING ................................................................................................15
1.1 Section Safety....................................................................................................... 16
1.2 Model Number and Nameplate Check ................................................................ 17
Nameplate ..........................................................................................................................17
1.3 Component Names............................................................................................... 19
IP20/Open-Chassis ............................................................................................................19
Front Views ........................................................................................................................21
2. MECHANICAL INSTALLATION................................................................. 23
2.1 Section Safety....................................................................................................... 24
2.2 Mechanical Installation ........................................................................................ 26
Installation Environment .....................................................................................................26
Installation Orientation and Spacing...................................................................................27
Exterior and Mounting Dimensions ....................................................................................27
3. ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION ..................................................................29
3.1 Section Safety....................................................................................................... 30
3.2 Standard Connection Diagram............................................................................ 32
3.3 Main Circuit Connection Diagram....................................................................... 34
Single-Phase 200 V Class (JZAB0P1 ~ B1P5) ..................................................................34
Three-Phase 200 V Class (JZA20P1 ~ 24P0); Three-Phase 400 V Class (JZA40P2 ~
44P0) ................................................................................................................................34
3.4 Terminal Block Configuration ............................................................................. 35
3.5 Protective Covers................................................................................................. 36
IP20/Open-Chassis Cover Removal and Installation .........................................................36
3.6 Main Circuit Wiring............................................................................................... 37
Main Circuit Terminal Functions.........................................................................................37
Wire Gauges and Tightening Torque .................................................................................37
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
3
Page 6

Main Circuit Terminal Power Supply and Motor Wiring................................................................ 38
3.7 Control Circuit Wiring ................................................................................................... 40
Control Circuit Terminal Block Functions ..................................................................................... 40
Terminal Configuration .................................................................................................................41
Wiring Procedure.......................................................................................................................... 42
3.8 I/O Connections............................................................................................................. 44
Sinking/Sourcing Mode Switch..................................................................................................... 44
3.9 Main Frequency Reference........................................................................................... 46
DIP Switch S1 Analog Input Signal Selection ..............................................................................46
3.10 Braking Resistor............................................................................................................ 47
Installation .................................................................................................................................... 47
3.11 Interlocking with Connected Machinery ..................................................................... 48
Drive Ready Signal....................................................................................................................... 48
3.12 Wiring Checklist ............................................................................................................ 49
4. START-UP PROGRAMMING & OPERATION ..................................................51
4.1 Section Safety................................................................................................................ 52
4.2 Using the Digital LED Operator.................................................................................... 54
Keys, Displays, and LEDs ............................................................................................................54
Digital Text Display....................................................................................................................... 55
LED Screen Displays ...................................................................................................................55
LO/RE LED and RUN LED Indications......................................................................................... 55
Menu Structure for Digital LED Operator .....................................................................................56
4.3 The Drive and Programming Modes............................................................................ 57
Navigating the Drive and Programming Modes............................................................................ 57
Changing Parameter Settings or Values ......................................................................................59
Verifying Parameter Changes: Verify Menu .................................................................................59
Switching Between LOCAL and REMOTE................................................................................... 60
Parameters Available in the Setup Group ....................................................................................60
4.4 Start-up Flowchart......................................................................................................... 62
Flowchart: Basic Start-up ............................................................................................................. 62
4.5 Powering Up the Drive .................................................................................................. 63
Powering Up the Drive and Operation Status Display.................................................................. 63
V/f Pattern Setting ........................................................................................................................ 63
4.6 No-Load Operation Test Run........................................................................................ 64
No-Load Operation Test Run ....................................................................................................... 64
4.7 Test Run with Load Connected.................................................................................... 65
Test Run with the Load Connected ..............................................................................................65
4.8 Verifying and Backing Up Parameter Settings ........................................................... 66
Parameter Access Level: A1-01................................................................................................... 66
Password Settings: A1-04, A1-05 ................................................................................................66
Copy Function (Optional) .............................................................................................................66
4.9 Test Run Checklist ........................................................................................................ 67
5. PARAMETER DETAILS .....................................................................................69
5.1 A: Initialization............................................................................................................... 70
A1: Initialization ............................................................................................................................ 70
5.2 b: Application................................................................................................................. 72
b1: Mode of Operation.................................................................................................................. 72
b2: DC Injection Braking............................................................................................................... 76
5.3 C: Tuning........................................................................................................................ 77
Table of Contents
4
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 7

C1: Acceleration and Deceleration Times ....................................................................................77
C2: S-Curve Characteristics......................................................................................................... 77
C3: Slip Compensation................................................................................................................. 78
C4: Torque Compensation ........................................................................................................... 78
C6: Carrier Frequency.................................................................................................................. 79
5.4 d: Reference Settings ................................................................................................... 82
d1: Frequency Reference.............................................................................................................82
d2: Frequency Upper/Lower Limits ..............................................................................................83
d3: Jump Frequency..................................................................................................................... 84
d4: Frequency Hold Function ....................................................................................................... 84
5.5 E: Motor Parameters ..................................................................................................... 86
E1: V/f Characteristics..................................................................................................................86
E2: Motor 1 Parameters ............................................................................................................... 88
5.6 H: Terminal Functions................................................................................................... 90
H1: Multi-Function Digital Inputs ..................................................................................................90
H2: Multi-Function Output ............................................................................................................95
H3: Analog Input Terminal A1 Settings ........................................................................................ 98
H4: Multi-Function Analog Output Terminal AM......................................................................... 101
H5: MEMOBUS/Modbus Serial Communication ........................................................................ 101
5.7 L: Protection Functions .............................................................................................. 102
L1: Motor Protection Functions ..................................................................................................102
L2: Momentary Power Loss Ride-Thru....................................................................................... 103
L3: Stall Prevention .................................................................................................................... 104
L4: Speed Agree ........................................................................................................................106
L5: Fault Restart.........................................................................................................................107
L6: Torque Detection..................................................................................................................108
L8: Hardware Protection............................................................................................................. 109
5.8 n: Special Adjustments............................................................................................... 111
n1: Hunting Prevention...............................................................................................................111
n3: Overexcitation Deceleration ................................................................................................. 111
5.9 o: Operator Related Settings...................................................................................... 112
o1: Display Settings and Selections ...........................................................................................112
o2: Operator Key Selections ......................................................................................................112
o3: Copy Function ...................................................................................................................... 113
o4: Maintenance Monitor Settings..............................................................................................114
5.10 U: Monitor Parameters................................................................................................ 116
U1: Operation Status Monitors ...................................................................................................116
U2: Fault History......................................................................................................................... 116
U4: Maintenance Monitors .........................................................................................................116
6. TROUBLESHOOTING......................................................................................117
6.1 Section Safety.............................................................................................................. 118
6.2 Motor Performance Fine Tuning ................................................................................ 120
Parameters for Tuning the Drive ................................................................................................ 120
Motor Hunting and Oscillation Control Parameters ....................................................................120
6.3 Drive Alarms, Faults, and Errors ............................................................................... 121
Types of Alarms, Faults, and Errors........................................................................................... 121
Alarm and Error Displays ...........................................................................................................121
6.4 Fault Detection ............................................................................................................ 123
Fault Displays, Causes and Possible Solutions ......................................................................... 123
6.5 Alarm Detection........................................................................................................... 129
Alarm Codes, Causes, and Possible Solutions ..........................................................................129
Table of Contents
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
5
Page 8

6.6 Operator Programming Errors ................................................................................... 132
oPE Codes, Causes, and Possible Solutions............................................................................. 132
6.7 Diagnosing and Resetting Faults............................................................................... 133
Fault Occurs Simultaneously with Power Loss ..........................................................................133
If the Drive Still has Power After a Fault Occurs ........................................................................ 133
Viewing Fault History Data After Fault .......................................................................................133
Fault Reset Methods .................................................................................................................. 133
6.8 Troubleshooting without Fault Display..................................................................... 134
Cannot Change Parameter Settings ..........................................................................................134
Motor Does Not Rotate Properly after Pressing RUN Button or after Entering External Run
Command .................................................................................................................................134
7. PERIODIC INSPECTION & MAINTENANCE ..................................................139
7.1 Section Safety.............................................................................................................. 140
7.2 Inspection .................................................................................................................... 142
Recommended Daily Inspection................................................................................................. 142
Recommended Periodic Inspection............................................................................................ 142
7.3 Periodic Maintenance ................................................................................................. 144
Replacement Parts.....................................................................................................................144
7.4 Drive Cooling Fans...................................................................................................... 145
Cooling Fan Replacement..........................................................................................................145
8. PERIPHERAL DEVICES & OPTIONS ............................................................147
8.1 Section Safety.............................................................................................................. 148
8.2 Drive Options and Peripheral Devices ...................................................................... 150
8.3 Connecting Peripheral Devices ................................................................................. 151
8.4 Installing Peripheral Devices ..................................................................................... 152
Installing a Molded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB) ..................................................................... 152
Installing a Leakage Breaker......................................................................................................152
Installing a Magnetic Contactor ..................................................................................................152
Connecting an AC or DC Reactor .............................................................................................. 153
Connecting a Surge Protector ....................................................................................................153
Connecting a Noise Filter ...........................................................................................................153
Installing Fuses on the Input Side .............................................................................................. 155
Installing a Motor Thermal Overload (oL) Relay on the Drive Output ........................................155
NEMA Type 1 Kit........................................................................................................................156
8.5 Communication Options............................................................................................. 159
A. SPECIFICATIONS ............................................................................................161
A.1 Heavy Duty and Normal Duty Ratings....................................................................... 162
A.2 Single/Three-Phase 200 V Class Drive ...................................................................... 163
A.3 Three-Phase 400 V Class Drives................................................................................ 164
A.4 Drive Specifications .................................................................................................... 165
A.5 Drive Watt Loss Data .................................................................................................. 167
A.6 Drive Derating Data ..................................................................................................... 168
Temperature Derating ................................................................................................................ 168
B. PARAMETER LIST...........................................................................................169
B.1 Parameter Groups ....................................................................................................... 170
B.2 Parameter Table .......................................................................................................... 171
A: Initialization Parameters......................................................................................................... 171
b: Application..............................................................................................................................171
Table of Contents
6
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 9

C: Tuning....................................................................................................................................172
d: References .............................................................................................................................173
E: Motor Parameters .................................................................................................................. 174
H Parameters: Multi-Function Terminals.................................................................................... 175
L: Protection Function ................................................................................................................177
n: Advanced Performance Set-Up.............................................................................................. 180
o: Operator Related Parameters ................................................................................................ 180
U: Monitors .................................................................................................................................181
B.3 Defaults by Drive Capacity (o2-04) and ND/HD (C6-01) ........................................... 183
C. MEMOBUS/MODBUS COMMUNICATIONS....................................................185
C.1 Section Safety.............................................................................................................. 186
C.2 MEMOBUS/Modbus Configuration ............................................................................ 187
C.3 Communication Specifications .................................................................................. 188
C.4 Connecting to a Network ............................................................................................ 189
Network Cable Connection......................................................................................................... 189
Wiring Diagram for Multiple Connection..................................................................................... 189
Network Termination .................................................................................................................. 190
C.5 MEMOBUS/Modbus Setup Parameters ..................................................................... 191
MEMOBUS/Modbus Serial Communication............................................................................... 191
C.6 Drive Operations by MEMOBUS/Modbus.................................................................. 193
Observing the Drive Operation...................................................................................................193
Controlling the Drive...................................................................................................................193
C.7 Communications Timing............................................................................................. 194
Command Messages from Master to Drive................................................................................ 194
Response Messages from Drive to Master ................................................................................ 194
C.8 Message Format .......................................................................................................... 195
Message Content ....................................................................................................................... 195
Slave Address ............................................................................................................................ 195
Function Code ............................................................................................................................195
Data............................................................................................................................................195
Error Check ................................................................................................................................ 195
C.9 Message Examples ..................................................................................................... 197
Reading Drive MEMOBUS/Modbus Register Contents .............................................................197
Loopback Test............................................................................................................................197
Writing to Multiple Registers....................................................................................................... 198
C.10 MEMOBUS/Modbus Data Table.................................................................................. 199
Command Data .......................................................................................................................... 199
Monitor Data...............................................................................................................................200
Broadcast Messages..................................................................................................................203
Fault History Contents................................................................................................................203
Alarm Register Contents ............................................................................................................ 204
C.11 Changing Drive Parameters ....................................................................................... 205
Drive Operations on Parameter Change ....................................................................................205
Issuing an Enter Command........................................................................................................205
C.12 Communication Errors ............................................................................................... 206
MEMOBUS/Modbus Error Codes............................................................................................... 206
Slave Not Responding................................................................................................................ 206
C.13 Self-Diagnostics .......................................................................................................... 207
D. STANDARDS COMPLIANCE ..........................................................................209
D.1 Section Safety.............................................................................................................. 210
Table of Contents
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
7
Page 10

D.2 European Standards ................................................................................................... 212
CE Low Voltage Directive Compliance....................................................................................... 212
EMC Guidelines Compliance .....................................................................................................212
D.3 UL Standards ............................................................................................................... 218
UL Standards Compliance .........................................................................................................218
Drive Motor Overload Protection ................................................................................................219
D.4 User Setting Table....................................................................................................... 221
INDEX ...............................................................................................................223
Table of Contents
8
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 11

Preface & General Safety
This section provides safety messages pertinent to this product, that, if not heeded, may result in
fatality, personal injury, or equipment damage. OYMC is not responsible for the consequences of
ignoring these instructions.
I.1 PREFACE..........................................................................................................10
I.2 GENERAL SAFETY..........................................................................................11
i
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
9
Page 12
i.1 Preface
OYMC distributes products used as components in a wide variety of industrial systems and equipment. The selection and
application of OYMC products remain the responsibility of the equipment manufacturer or end user. OYMC accepts no
responsibility for the way its products are incorporated into the final system design. Under no circumstances should any
OYMC product be incorporated into any product or design as the exclusive or sole safety control. Without exception, all
controls should be designed to detect faults dynamically and fail safely under all circumstances. All systems or equipment
designed to incorporate a product distributed by OYMC must be supplied to the end user with appropriate warnings and
instructions as to the safe use and operation of that part. Any warnings provided by OYMC must be promptly provided to
the end user. OYMC offers an express warranty only as to the quality of its products in conforming to standards and
specifications published in the OYMC manual. NO OTHER WARRANTY, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, IS OFFERED.
OYMC assumes no liability for any personal injury, property damage, losses, or claims arising from misapplication of its
products.
u
Applicable Documentation
The following manuals are available for J1000 series drives:
J1000 Series Compact V/f Control Drive Quick Start Guide
Read this manual first. This guide is packaged together with the product. It contains basic
information required to install and wire the drive. This guide provides basic programming and
simple setup and adjustment.
J1000 Series Compact V/f Control Drive User Manual
This manual describes installation, wiring, operation procedures, functions, troubleshooting,
maintenance, and inspections to perform before operation.
u
Symbols
Note: Indicates a supplement or precaution that does not cause drive damage.
TERMSTERMS
Indicates a term or definition used in this manual.
u
Terms and Abbreviations
TERMSTERMS
• Drive: OYMC J1000 Series Drive
• OYMC: Omron Yaskawa Motion Control B.V.
i.1 Preface
10
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 13
i.2 General Safety
u
Supplemental Safety Information
General Precautions
• The diagrams in this manual may be indicated without covers or safety shields to show details. Restore covers or shields before
operating the drive and run the drive according to the instructions described in this manual.
• Any illustrations, photographs, or examples used in this manual are provided as examples only and may not apply to all products
to which this manual is applicable.
• The products and specifications described in this manual or the content and presentation of the manual may be changed without
notice to improve the product and/or the manual.
• When ordering a new copy of the manual due to damage or loss, contact your OYMC representative or the nearest OYMC sales
office and provide the manual number shown on the front cover.
• If nameplate becomes worn or damaged, order a replacement from your OYMC representative or the nearest OYMC sales office.
WARNING
Read and understand this manual before installing, operating or servicing this drive. The drive must be installed according
to this manual and local codes.
The following conventions are used to indicate safety messages in this manual. Failure to heed these messages could
result in serious or possibly even fatal injury or damage to the products or to related equipment and systems.
DANGER
Indicates a hazardous situation, which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
WARNING
Indicates a hazardous situation, which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
WARNING! will also be indicated by a bold key word embedded in the text followed by an italicized safety message.
CAUTION
Indicates a hazardous situation, which, if not avoided, could result in minor or moderate injury.
CAUTION! will also be indicated by a bold key word embedded in the text followed by an italicized safety message.
NOTICE
Indicates a property damage message.
NOTICE: will also be indicated by a bold key word embedded in the text followed by an italicized safety message.
u
Safety Messages
DANGER
Heed the safety messages in this manual.
Failure to comply will result in death or serious injury.
The operating company is responsible for any injuries or equipment damage resulting from failure to heed the warnings
in this manual.
i.2 General Safety
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
11
Page 14
DANGER
Electrical Shock Hazard
Do not connect or disconnect wiring while the power is on.
Failure to comply will result in death or serious injury.
Before servicing, disconnect all power to the equipment. The internal capacitor remains charged even after the power
supply is turned off. The charge indicator LED will extinguish when the DC bus voltage is below 50 Vdc. To prevent
electric shock, wait at least one minute after all indicators are OFF and measure the DC bus voltage level to confirm safe
level.
WARNING
Sudden Movement Hazard
System may start unexpectedly upon application of power, resulting in death or serious injury.
Clear all personnel from the drive, motor and machine area before applying power. Secure covers, couplings, shaft keys
and machine loads before applying power to the drive.
Electrical Shock Hazard
Do not attempt to modify or alter the drive in any way not explained in this manual.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury.
OYMC is not responsible for any modification of the product made by the user. This product must not be modified.
Do not allow unqualified personnel to use equipment.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury.
Maintenance, inspection, and replacement of parts must be performed only by authorized personnel familiar with
installation, adjustment and maintenance of AC drives.
Do not remove covers or touch circuit boards while the power is on.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury.
Fire Hazard
Do not use an improper voltage source.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury by fire.
Verify that the rated voltage of the drive matches the voltage of the incoming power supply before applying power.
Crush Hazard
Do not use this drive in lifting applications without installing external safety circuitry to prevent accidental
dropping of the load.
The drive does not possess built-in load drop protection for lifting applications.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury from falling loads.
Install electrical and/or mechanical safety circuit mechanisms independent of drive circuitry.
CAUTION
Crush Hazard
Do not carry the drive by the front cover.
Failure to comply may result in minor or moderate injury from the main body of the drive falling.
i.2 General Safety
12
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 15
NOTICE
Observe proper electrostatic discharge procedures (ESD) when handling the drive and circuit boards.
Failure to comply may result in ESD damage to the drive circuitry.
Never connect or disconnect the motor from the drive while the drive is outputting voltage.
Improper equipment sequencing could result in damage to the drive.
Do not perform a withstand voltage test on any part of the drive.
Failure to comply could result in damage to the sensitive devices within the drive.
Do not operate damaged equipment.
Failure to comply could result in further damage to the equipment.
Do not connect or operate any equipment with visible damage or missing parts.
Install adequate branch circuit short circuit protection per applicable codes.
Failure to comply could result in damage to the drive.
The drive is suitable for circuits capable of delivering not more than 30,000 RMS symmetrical Amperes, 240 Vac
maximum (200 V Class) and 480 Vac maximum (400 V Class).
Do not expose the drive to halogen group disinfectants.
Failure to comply may cause damage to the electrical components in the drive.
Do not pack the drive in wooden materials that have been fumigated or sterilized.
Do not sterilize the entire package after the product is packed.
u
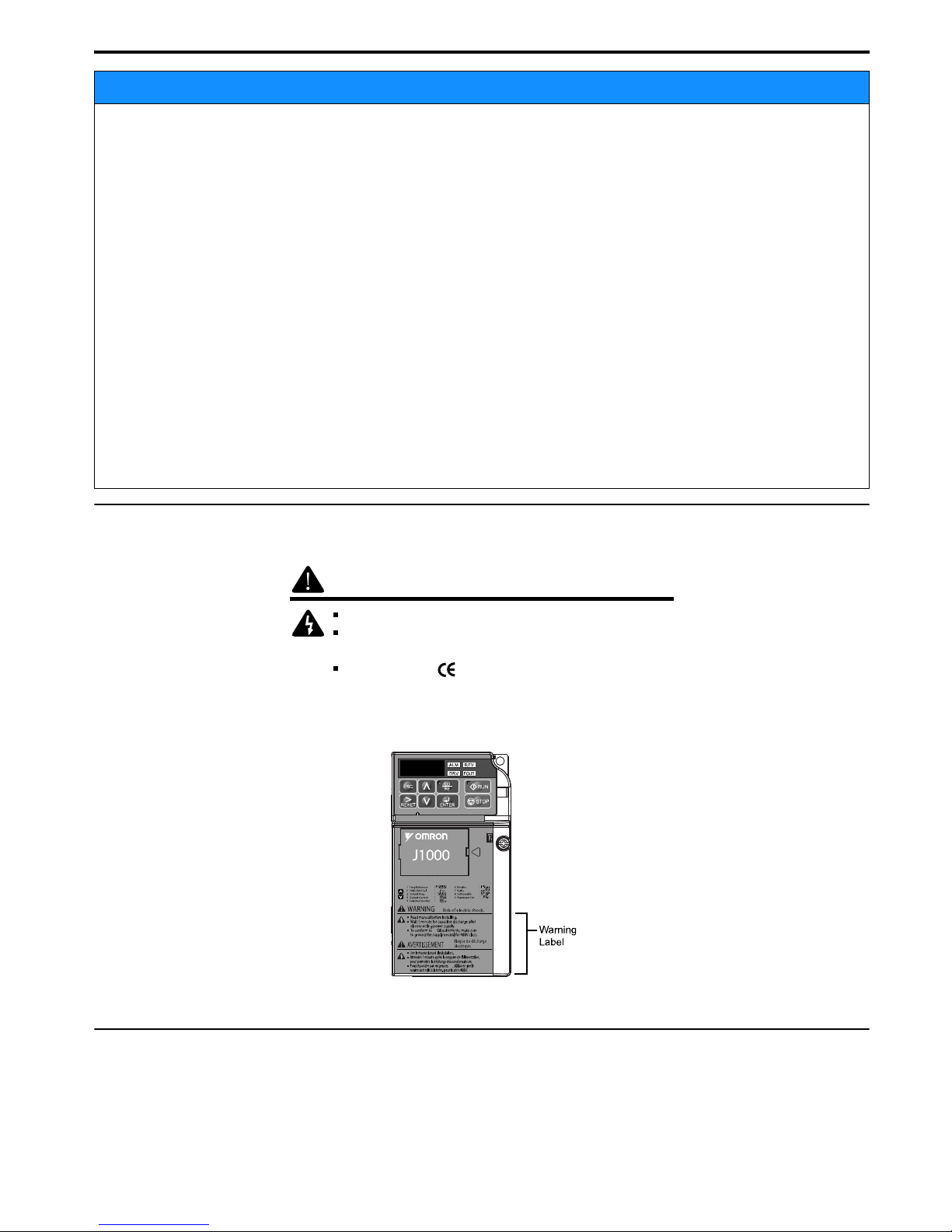
Drive Label Warnings
Always heed the warning information listed in Figure i.1 in the position shown in Figure i.2.
Risk of electric shock.
WARNING
Read manual before installing.
Wait 1 minute for capacitor discharge after
disconnecting power supply.
To conform to requirements, make sure
to ground the supply neutral for 400V class.
Figure i.1 Warning Information
Figure i.2 Warning Information Position
u
Warranty Information
n
Restrictions
The J1000 was not designed or manufactured for use in devices or systems that may directly affect or threaten human lives
or health.
i.2
General Safety
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
13
Page 16
Customers who intend to use the product described in this manual for devices or systems relating to transportation, health
care, space aviation, atomic power, electric power, or in underwater applications must first contact their OYMC
representatives or the nearest OYMC sales office.
This product has been manufactured under strict quality-control guidelines. However, if this product is to be installed in
any location where failure of this product could involve or result in a life-and-death situation or loss of human life or in a
facility where failure may cause a serious accident or physical injury, safety devices must be installed to minimize the
likelihood of any accident.
u
Quick Reference
Run a Motor of One-Frame Larger Capacity
When using this drive for variable torque loads such as fans and pumps, a motor one frame size larger can be used.
Know the Details of Safety Measures
The functions listed below affect the safe operation of the drive. Ensure that the settings fit the application requirements prior to operation.
Safe operations. Run by power on. Parameter setting b1-17.
LED operator stop key priority selection. Parameter o2-02.
Enter press required after changing the keypad frequency reference. Parameter o2-05.
Operation interlock when program mode is selected. Parameter b1-08.
Standards Compliance
Refer to European Standards on page 212 and Refer to UL Standards on page 218.
U
L
C
R
US
LISTED
i.2 General Safety
14
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 17

Receiving
This chapter describes the proper inspections to perform after receiving the drive and illustrates
the different enclosure types and components.
1.1 SECTION SAFETY............................................................................................16
1.2 MODEL NUMBER AND NAMEPLATE CHECK...............................................17
1.3 COMPONENT NAMES......................................................................................19
1
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
15
Page 18

1.1 Section Safety
CAUTION
Do not carry the drive by the front cover.
Failure to comply may cause the main body of the drive to fall, resulting in minor or moderate injury.
NOTICE
Observe proper electrostatic discharge procedures (ESD) when handling the drive and circuit boards.
Failure to comply may result in ESD damage to the drive circuitry.
A motor connected to a PWM drive may operate at a higher temperature than a utility-fed motor and the operating
speed range may reduce motor cooling capacity.
Ensure that the motor is suitable for drive duty and/or the motor service factor is adequate to accommodate the additional
heating with the intended operating conditions.
1.1 Section Safety
16
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 19
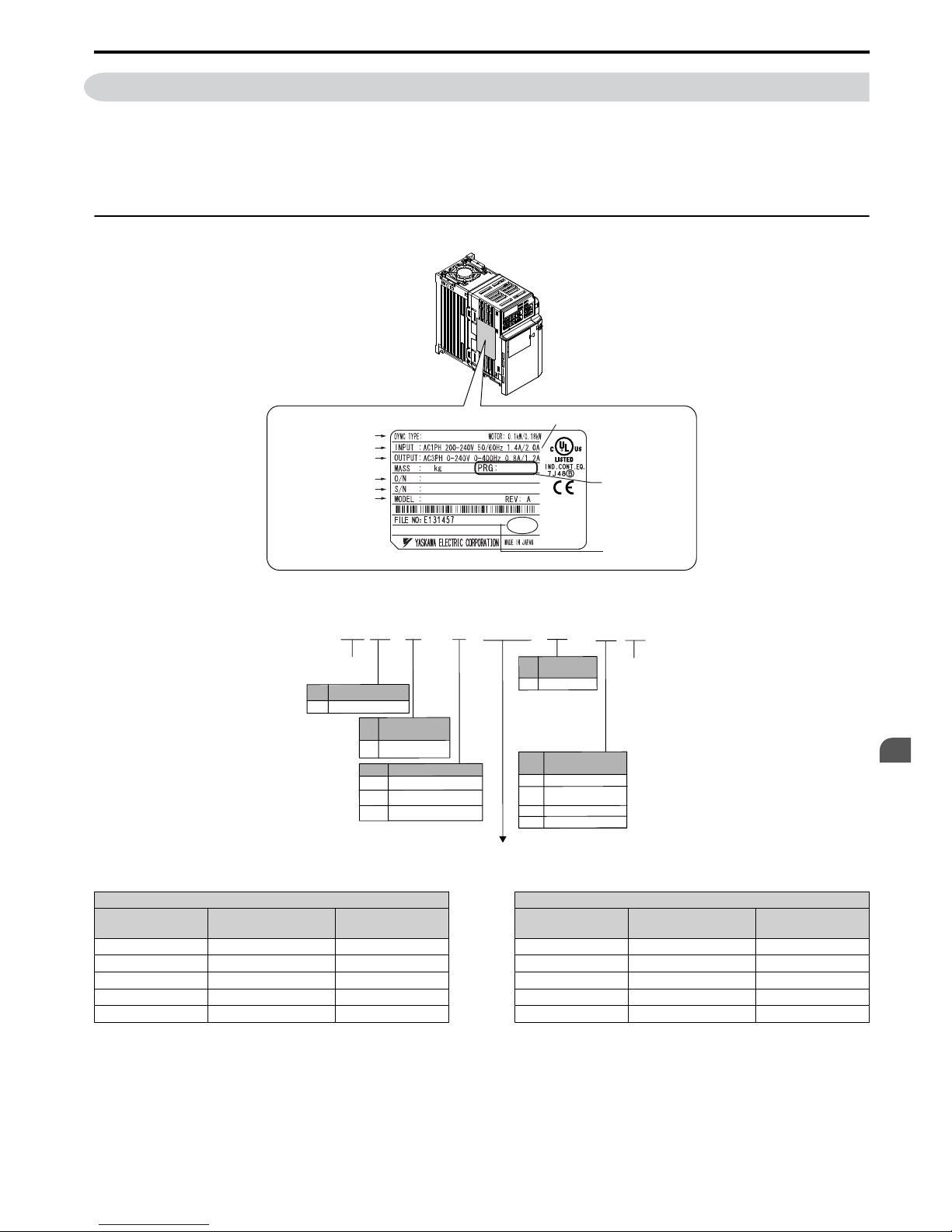
1.2 Model Number and Nameplate Check
Please perform the following tasks after receiving the drive:
• Inspect the drive for damage.
If the drive appears damaged upon receipt, contact the shipper immediately.
• Verify receipt of the correct model by checking the information on the nameplate.
• If you have received the wrong model or the drive does not function properly, contact your supplier.
u
Nameplate
PASS
RoHSRoHS
IP 20
JZAB0P1BAA
CIMR-JZBA0001BAA
0.6
5010
AC Drive Model
Input Specifications
Output Specifications
Lot Number
Serial Number
Yaskawa Ref. Number
Software Version
Heavy Duty Amps / Normal Duty Amps
Enclosure Type
Figure 1.1 Nameplate Information
J
Z
B
A
0P1
B
A
A
J1000
Series
No. Type
Z
European Standard
No.
Enclosure
Type
Design
Revision
Order
IP20
B
No. Voltage Class
B
1-phase, 200-240 Vac
No.
Customized
Specifications
A Standard model
3-phase, 200-240 Vac
3-phase, 380-480 Vac
2
4
No.
Environmental
Specification <1>
A
Humidity- and
dust-resistant
Standard
S
NMOil-resistant
Vibration-resistant
n
Single-Phase 200 V
Heavy Duty Normal Duty
No.
Max. Motor CapacitykWRated Output
Current A
No.
Max. Motor CapacitykWRated Output
Current A
B0P1 0.1 0.8 B0P1 0.2 1.2
B0P2 0.2 1.6 B0P2 0.4 1.9
B0P4 0.4 3.0 B0P4 0.75 3.3
B0P7 0.75 5.0 B0P7 1.1 6.0
B1P5 1.5 8.0 B1P5 2.2 9.6
1.2 Model Number and Nameplate Check
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
17
1
Receiving
Page 20
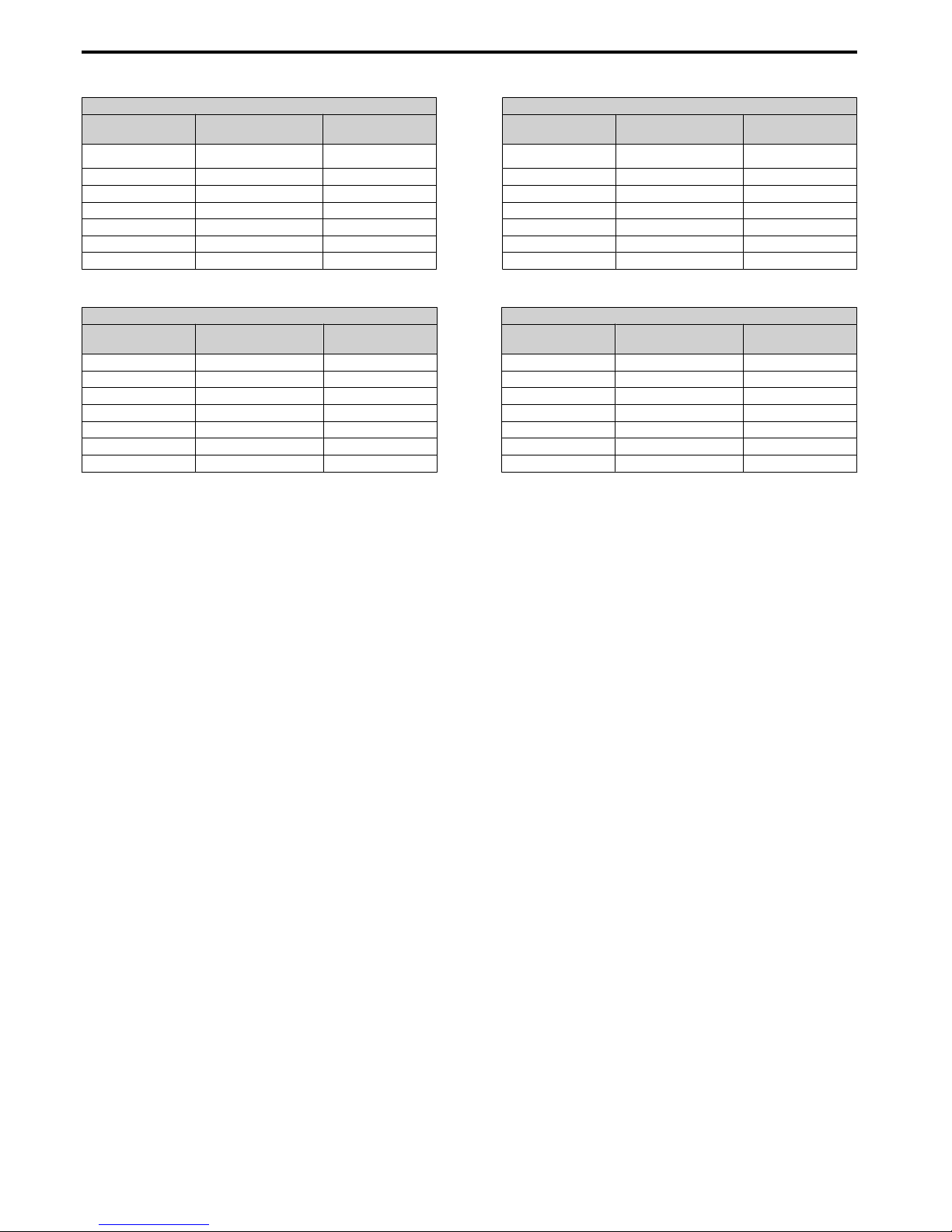
n
Three-Phase 200 V
Heavy Duty Normal Duty
No.
Max Motor CapacitykWRated Output
Current A
No.
Max. Motor CapacitykWRated Output
Current A
20P1 0.1 0.8 20P1 0.2 1.2
20P2 0.2 1.6 20P2 0.4 1.9
20P4 0.4 3.0 20P4 0.75 3.5
20P7 0.75 5.0 20P7 1.1 6.0
21P5 1.5 8.0 21P5 2.2 9.6
22P2 2.2 11.0 22P2 3.0 12.0
24P0 4.0 17.5 24P0 3.7 17.5
n
Three-Phase 400 V
Heavy Duty Normal Duty
No.
Max. Motor CapacitykWRated Output
Current A
No.
Max. Motor CapacitykWRated Output
Current A
40P2 0.2 1.2 40P2 0.4 1.2
40P4 0.4 1.8 40P4 0.75 2.1
40P7 0.75 3.4 40P7 1.5 4.1
41P5 1.5 4.8 41P5 2.2 5.4
42P2 2.2 5.5 42P2 3.0 6.9
43P0 3.0 7.2 43P0 4.0 8.8
44P0 4.0 9.2 44P0 5.5 11.1
<1> Drives with these specifications do not guarantee complete protection for the specified environmental condition.
1.2 Model Number and Nameplate Check
18
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 21
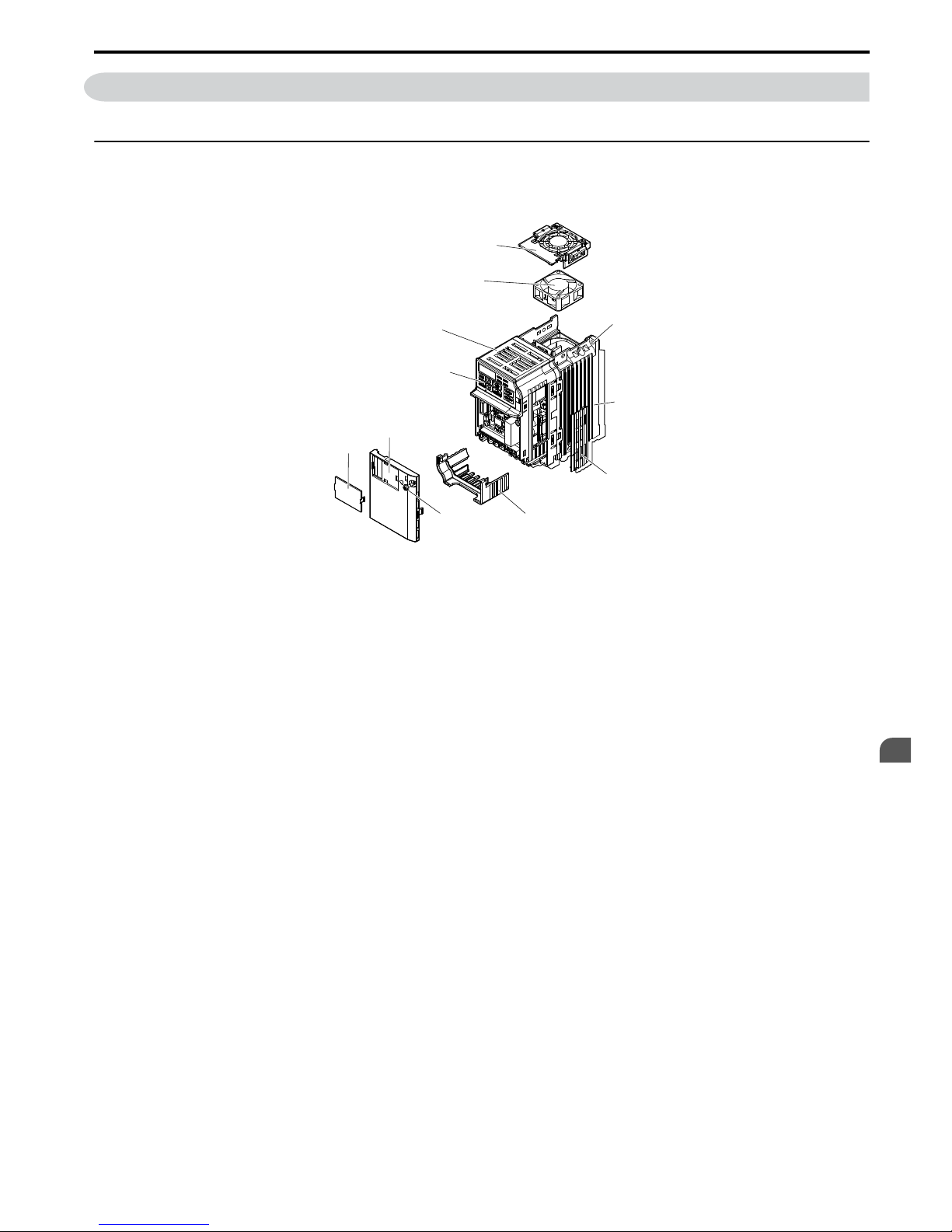
1.3 Component Names
This section illustrates the drive components as they are mentioned in this manual.
u
IP20/Open-Chassis
n
Single-Phase AC200 V JZAB0P1B ~ JZAB0P4B
Three-Phase AC200 V JZA20P1B ~ JZA20P7B
K
A
B
C
D
E
G
H
J
I
F
A –
Fan cover
<1>
B – Mounting hole
C – Heatsink
D – Cable cover
E – Terminal cover
F – Front cover screw
G – Option connector cover
H – Front cover
I – LED operator Refer to Using the Digital LED
Operator on page 54
J – Case
K –
Cooling fan
<1>
Figure 1.2 Exploded View of IP20/Open-Chassis Type Components Three-Phase AC200 V JZA20P7B
<1> The drives JZAB0P1B ~ JZAB0P4B and JZA20P1B ~ JZA20P4B do not have a cooling fan or a cooling fan cover.
1.3 Component Names
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
19
1
Receiving
Page 22
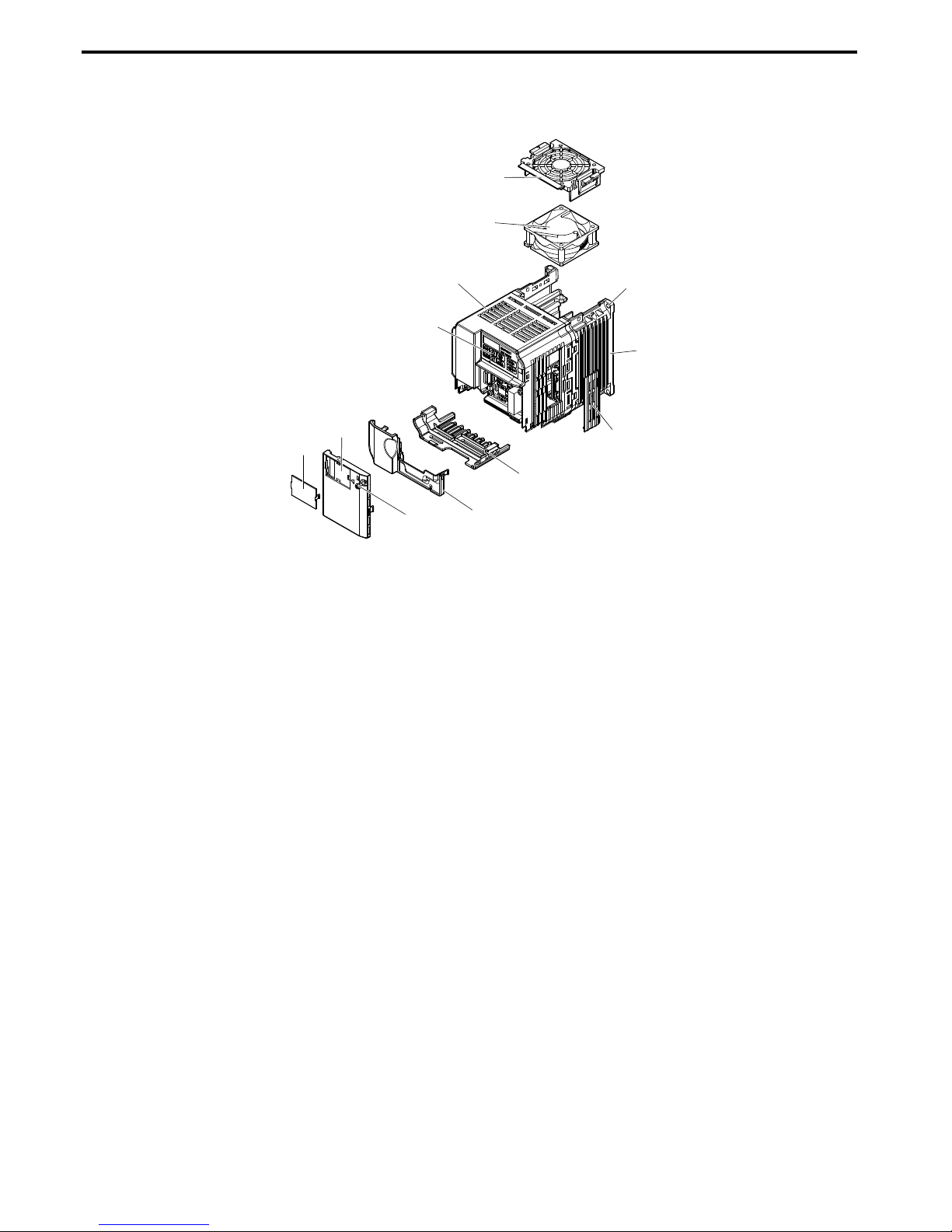
n
Single-Phase AC200 V JZAB0P7B ~ B1P5B
Three-Phase AC200 V JZA20P1B ~ 24P0B
Three-Phase AC400 V JZA40P2B ~ 44P0B
L
A
B
C
D
F
K
J
I
E
G
H
A – Mounting hole
B – Heatsink
C – Cable cover
D – Terminal cover
E – Bottom cover
F – Front cover screw
G – Option connector cover
H – Front cover
I – LED operator Refer to Using the Digital LED
Operator on page 54
J – Case
K –
Cooling fan
<1>
L –
Fan cover
<1>
Figure 1.3 Exploded view of IP20/Open-Chassis Type Components
Three-Phase AC200 V JZA22P2B
<1> The drives JZAB0P7B and 40P2B ~ 40P7B do not have a cooling fan or a cooling fan cover.
1.3 Component Names
20
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 23

u
Front Views
G
F
A
B
C
D
E
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
JZA20P7
JZA22P2
A – DIP switch S1 Refer to DIP Switch S1 Analog
Input Signal Selection on page 46
B – DIP switch S3 Refer to Sinking/Sourcing Mode
Switch on page 44
C – Control circuit terminal Refer to Control Circuit
Wiring on page 40
D – Main circuit terminal Refer to Wiring the Main
Circuit Terminal on page 39
E – Ground terminal
F – Terminal cover
G – Option unit connector Refer to Communication
Options on page 159
Figure 1.4 Front Views of Drives
1.3 Component Names
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
21
1
Receiving
Page 24

1.3 Component Names
This Page Intentionally Blank
22
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 25

Mechanical Installation
This chapter explains how to properly mount and install the drive.
2.1 SECTION SAFETY............................................................................................24
2.2 MECHANICAL INSTALLATION.......................................................................26
2
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
23
Page 26

2.1 Section Safety
WARNING
Fire Hazard
Provide sufficient cooling when installing the drive inside an enclosed panel or cabinet.
Failure to comply could result in overheating and fire.
When multiple drives are placed inside the same enclosure panel, install proper cooling to ensure air entering the enclosure
does not exceed 40 °C.
CAUTION
Crush Hazard
Do not carry the drive by the front cover.
Failure to comply may result in minor or moderate injury from the main body of the drive falling.
NOTICE
Observe proper electrostatic discharge (ESD) procedures when handling the drive.
Failure to comply could result in ESD damage to the drive circuitry.
It may be difficult to perform maintenance on the cooling fans of drives installed in a vertical row inside an
enclosure.
Ensure adequate spacing at the top of the drive to perform cooling fan replacement when required.
Operating the motor in the low-speed range diminishes the cooling effects, increases motor temperature, and may
lead to motor damage by overheating.
Reduce the motor torque in the low-speed range whenever using a standard blower cooled motor. If 100% torque is
required continuously at low speed, consider using a special drive or vector motor. Select a motor that is compatible with
the required load torque and operating speed range.
Do not operate motors above the maximum rated RPM.
Failure to comply may lead to bearing or other mechanical motor failures.
The speed range for continuous operation differs according to the lubrication method and motor manufacturer.
If the motor is to be operated at a speed higher than the rated speed, consult with the manufacturer.
Continuously operating an oil-lubricated motor in the low-speed range may result in burning.
2.1 Section Safety
24
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 27

NOTICE
When the input voltage is 440 V or higher or the wiring distance is greater than 100 meters, pay special attention
to the motor insulation voltage or use a drive-rated motor.
Failure to comply could lead to motor winding failure.
Motor vibration may increase when operating a machine in variable-speed mode, if that machine previously
operated at a constant speed.
Install vibration-proof rubber on the motor base or use the frequency jump function to skip a frequency resonating the
machine.
The motor may require more acceleration torque with drive operation than with a commercial power supply.
Set a proper V/f pattern by checking the load torque characteristics of the machine to be used with the motor.
The rated input current of submersible motors is higher than the rated input current of standard motors.
Select an appropriate drive according to its rated output current. When the distance between the motor and drive is long,
use a cable thick enough to connect the motor to the drive to prevent motor torque reduction.
When using an explosion-proof motor, it must be subject to an explosion-proof test in conjunction with the drive.
This is also applicable when an existing explosion-proof motor is to be operated with the drive. Since the drive itself is
not explosion-proof, always install it in a safe place.
Do not use a drive for a single-phase motor.
Replace the motor with a three-phase motor.
If an oil-lubricated gearbox or speed reducer is used in the power transmission mechanism, oil lubrication will be
affected when the motor operates only in the low speed range.
The power transmission mechanism will make noise and experience problems with service life and durability if the motor
is operated at a speed higher than the rated speed.
2.1 Section Safety
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
25
2
Mechanical Installation
Page 28

2.2 Mechanical Installation
This section outlines specifications, procedures, and environment for proper mechanical installation of the drive.
u
Installation Environment
To help prolong the optimum performance life of the drive, install the drive in the proper environment. The table below
provides a description of the appropriate environment for the drive.
Table 2.1 Installation Environment
Environment Conditions
Installation Area Indoors
Ambient Temperature
-10 °C to +50 °C (IP20/Open-Chassis)
Drive reliability improves in environments without wide temperature fluctuations.
When using an enclosure panel, install a cooling fan or air conditioner in the area to ensure that the air temperature
inside the enclosure does not exceed the specified levels.
Do not allow ice to develop on the drive.
Humidity 95% RH or less and free of condensation
Storage Temperature -20 °C to +60 °C
Surrounding Area
Install the drive in an area free from:
• oil mist and dust
• metal shavings, oil, water or other foreign materials
• radioactive materials
• combustible materials (e.g., wood)
• harmful gases and liquids
• excessive vibration
• chlorides
• direct sunlight
Altitude 1000 m or lower
Vibration
10 to 20 Hz at 9.8 m/s
2
20 to 55 Hz at 5.9 m/s
2
Orientation Install the drive vertically to maintain maximum cooling effects.
NOTICE: Prevent foreign matter such as metal shavings or wire clippings from falling into the drive during installation and project
construction. Failure to comply could result in damage to the drive. Place a temporary cover over the top of the drive during installation.
Remove the temporary cover before startup, as the cover will reduce ventilation and cause the drive to overheat.
2.2 Mechanical Installation
26
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 29
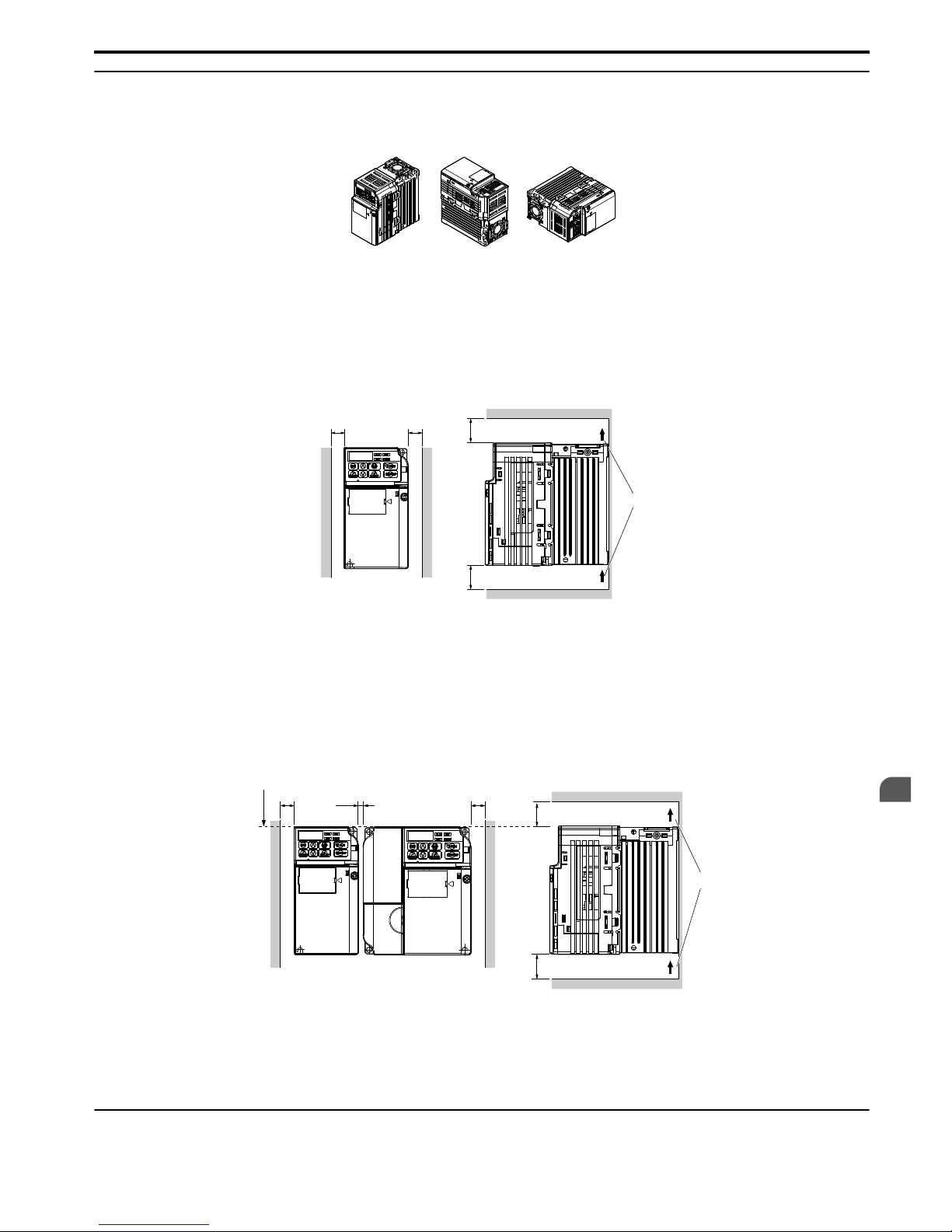
u
Installation Orientation and Spacing
Install the drive upright as illustrated in Figure 2.1 to maintain proper cooling.
A
B
B
A – Correct B – Incorrect
Figure 2.1 Correct Installation Orientation
n
Single Drive Installation
Figure 2.2 explains the required installation spacing to maintain sufficient space for airflow and wiring. Install the heatsink
against a closed surface to avoid diverting cooling air around the heatsink.
A
A
C
C
B
Side Clearance
Top/Bottom Clearance
A – 30 mm minimum
B – Airflow direction
C – 100 mm minimum
Figure 2.2 Correct Installation Spacing
n
Multiple Drive Installation
When installing multiple drives into the same enclosure panel, mount the drives according to Figure 2.2. When mounting
drives with a minimum side-by-side clearance of 2 mm according to Figure 2.3, derating must be considered and parameter
L8-35 must be set. Refer to Parameter List on page 169.
2 mm
D
C
C
B
B
A
A – Line up the tops of the drives.
B – 30 mm minimum
C – 100 mm minimum
D – Airflow direction
Figure 2.3 Space Between Drives (Side-by-Side Mounting)
Note: When installing drives of different heights in the same enclosure panel, the tops of the drives should line up. Leave space between the top
and bottom of stacked drives for cooling fan replacement if required. Using this method, it is possible to replace the cooling fans later.
u
Exterior and Mounting Dimensions
Refer to NEMA Type 1 Kit on page 156 for exterior and mounting dimensions for NEMA Type 1.
2.2
Mechanical Installation
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
27
2
Mechanical Installation
Page 30

n
IP20/Open-Chassis Drives
Table 2.2 IP20/Open-Chassis (without an EMC filter)
t1
D1
D
W
H1H2
H
2-M4
W1
D2
Voltage Class
Drive Model
JZA
Dimensions (mm)
W H D W1 H1 H2 D1 D2 t1 Weight (kg)
Single-Phase
200 V Class
B0P1B 68 128 76 56 118 5 6.5 67.5 3 0.6
B0P2B 68 128 76 56 118 5 6.5 67.5 3 0.6
B0P4B 68 128 118 56 118 5 38.5 109.5 5 1.0
Three-Phase
200 V Class
20P1B 68 128 76 56 118 5 6.5 67.5 3 0.6
20P2B 68 128 76 56 118 5 6.5 67.5 3 0.6
20P4B 68 128 108 56 118 5 38.5 99.5 5 0.9
20P7B 68 128 128 56 118 5 58.5 119.5 5 1.1
Table 2.3 IP20/Open-Chassis (without an EMC filter)
t1
D
D1
4-M4
H
W1
W
H2 H1
D2
Voltage Class
Drive Model
JZA
Dimensions (mm)
W H D W1 H1 H2 D1 D2 t1 Weight (kg)
Single-Phase
200 V Class
B0P7B 108 128 137.5 96 118 5 58 129 5 1.7
B1P5B 108 128 154 96 118 5 58 145.5 5 1.8
Three-Phase
200 V Class
21P5B 108 128 129 96 118 5 58 120.5 5 1.7
22P2B 108 128 137.5 96 118 5 58 129 5 1.7
24P0B 140 128 143 128 118 5 65 134.5 5 2.4
Three-Phase
400 V Class
40P2B 108 128 81 96 118 5 10 72.5 5 1.0
40P4B 108 128 99 96 118 5 28 90.5 5 1.2
40P7B 108 128 137.5 96 118 5 58 129 5 1.7
41P5B 108 128 154 96 118 5 58 145.5 5 1.7
42P2B 108 128 154 96 118 5 58 145.5 5 1.7
43P0B 108 128 154 96 118 5 58 145.5 5 1.7
44P0B 140 128 143 128 118 5 65 134.5 5 2.4
2.2 Mechanical Installation
28
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 31

Electrical Installation
This chapter explains proper procedures for wiring the control circuit terminals, motor and power
supply.
3.1 SECTION SAFETY............................................................................................30
3.2 STANDARD CONNECTION DIAGRAM...........................................................32
3.3 MAIN CIRCUIT CONNECTION DIAGRAM.......................................................34
3.4 TERMINAL BLOCK CONFIGURATION...........................................................35
3.5 PROTECTIVE COVERS....................................................................................36
3.6 MAIN CIRCUIT WIRING....................................................................................37
3.7 CONTROL CIRCUIT WIRING...........................................................................40
3.8 I/O CONNECTIONS...........................................................................................44
3.9 MAIN FREQUENCY REFERENCE...................................................................46
3.10 BRAKING RESISTOR.......................................................................................47
3.11 INTERLOCKING WITH CONNECTED MACHINERY.......................................48
3.12 WIRING CHECKLIST........................................................................................49
3
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
29
Page 32

3.1 Section Safety
DANGER
Electrical Shock Hazard
Do not connect or disconnect wiring while the power is on.
Failure to comply will result in death or serious injury.
WARNING
Electrical Shock Hazard
Do not operate equipment with covers removed.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury.
The diagrams in this section may show drives without covers or safety shields to show details. Be sure to reinstall covers
or shields before operating the drives and run the drives according to the instructions described in this manual.
Always ground the motor-side grounding terminal.
Improper equipment grounding could result in death or serious injury by contacting the motor case.
Do not perform work on the drive while wearing loose clothing, jewelry or without eye protection.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury.
Remove all metal objects such as watches and rings, secure loose clothing, and wear eye protection before beginning
work on the drive.
Do not remove covers or touch circuit boards while the power is on.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury.
Do not allow unqualified personnel to perform work on the drive.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury.
Installation, maintenance, inspection, and servicing must be performed only by authorized personnel familiar with
installation, adjustment, and maintenance of AC drives.
Do not touch any terminals before the capacitors have fully discharged.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury.
Before wiring terminals, disconnect all power to the equipment. The internal capacitor remains charged even after the
power supply is turned off. The charge indicator LED will extinguish when the DC bus voltage is below 50 Vdc. To
prevent electric shock, wait at least one minute after all indicators are off and measure the DC bus voltage level to confirm
safe level.
Fire Hazard
Tighten all terminal screws to the specified tightening torque.
Loose electrical connections could result in death or serious injury by fire due to overheating of electrical connections.
Do not use improper combustible materials.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury by fire.
Attach the drive to metal or other noncombustible material.
Do not use an improper voltage source.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury by fire.
Verify that the rated voltage of the drive matches the voltage of the incoming power supply before applying power.
3.1 Section Safety
30
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 33

NOTICE
Observe proper electrostatic discharge procedures (ESD) when handling the drive and circuit boards.
Failure to comply may result in ESD damage to the drive circuitry.
Never connect or disconnect the motor from the drive while the drive is outputting voltage.
Improper equipment sequencing could result in damage to the drive.
Do not use unshielded cable for control wiring.
Failure to comply may cause electrical interference resulting in poor system performance. Use shielded, twisted-pair
wires and ground the shield to the ground terminal of the drive.
Check all the wiring to ensure that all connections are correct after installing the drive and connecting any other
devices.
Failure to comply could result in damage to the drive.
Do not modify the drive circuitry.
Failure to comply could result in damage to the drive and will void warranty.
OYMC is not responsible for any modification of the product made by the user. This product must not be modified.
3.1 Section Safety
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
31
3
Electrical Installation
Page 34

3.2 Standard Connection Diagram
Connect the drive and peripheral devices as shown in Figure 3.1. It is possible to run the drive via the digital operator
without connecting digital I/O wiring. This section does not discuss drive operation; Refer to Start-Up Programming &
Operation on page 51 for instructions on operating the drive.
NOTICE: Inadequate branch short circuit protection could result in damage to the drive. Install adequate branch circuit short circuit
protection per applicable codes. The drive is suitable for circuits capable of delivering not more than 30,000 RMS symmetrical amperes,
240 Vac maximum (200 V Class) and 480 Vac maximum (400 V Class).
NOTICE: When the input voltage is 440 V or higher or the wiring distance is greater than 100 meters, pay special attention to the motor
insulation voltage or use a drive duty motor. Failure to comply could lead to motor insulation breakdown.
NOTICE: Do not connect AC control circuit ground to drive enclosure. Improper drive grounding can cause control circuit malfunction.
NOTICE: The minimum load for the multi-function relay output MA-MB-MC is 10 mA.
SA
Motor
Cooling fan
Forward run/stop
Reverse run/stop
External fault
Fault reset
0 to +10 Vdc
(2 mA)
DIP
switch S3
DC reactor
(option)
Digital inputs
(default setting)
Fault
J1000
Shield ground
terminal
Thermal relay
(option)
Braking resistor
(option)
Main circuit
Control circuit
Thermal relay for
motor cooling fan
Fault relay
1 MCCB
MC
2 MCCB
r1
s1
t1
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
<3>
<1>
<2>
-
B1+1+2 B2
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
MC
THRX
TRX
MC
TRX
MC MA
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3
24 V
MA
MB
MC
I V
+
24 V 8 mA
M
M
r1
s1
t1
FU
FV
FW
U
V
W
SC
AM
AC
+
-
AM
+V
A1
AC
2 k
Ground
10 or less (400 V class)
100 or less (200 V class)
Setting power supply
+10.5 max. 20 mA
For single phase 200 V
power supply, use
R/L1 and S/L2.
Analog monitor
output
Digital output
250 Vac, 10 mA to 1 A
30 Vdc, 10 mA to 1 A
(default setting)
Main speed
frequency
reference.
Multi-function
programmable
Multi-step
speed 1
main/aux switch
2 MCCB
THRX
OFF
ON
MC
SA
SA
Three phase
power supply
200 to 240 V
Jumper
DIP switch S1
Sink
Source
Terminals +1, +2, , B1, and B2
are for connecting options.
Never connect power supply
lines to these terminals.
_
Monitor
output
Option unit
connector
main circuit terminal
shielded line
twisted-pair shielded line
control terminal
<4>
<5>
<6>
<7>
0 to +10 V (20 k )
(0)4 to 20 mA (250 )
Figure 3.1 Drive Standard Connection Diagram (200 V Class Example)
<1> Remove the jumper when installing an optional DC reactor.
<2> The MC on the input side of the main circuit should open when the thermal relay is triggered.
<3> Self-cooled motors do not require separate cooling fan motor wiring.
<4> Connected using sequence input signal (S1 to S5) from NPN transistor; Default: sink mode (0 V com).
<5> Use only a +24 V internal power supply in sinking mode; the source mode requires an external power supply Refer
to I/O Connections on page 44.
<6> Minimum load: 5 Vdc, 10 mA (reference value).
3.2
Standard Connection Diagram
32
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 35

<7> Monitor outputs work with devices such as analog frequency meters, ammeters, voltmeters and wattmeters; they
are not intended for use as a feedback-type of signal.
WARNING! Sudden Movement Hazard. Do not close the wiring for the control circuit unless the multifunction input terminal parameter
is properly set (S5 for 3-Wire; H1-05 = “0”). Improper sequencing of run/stop circuitry could result in death or serious injury from moving
equipment.
WARNING! Sudden Movement Hazard. Ensure start/stop and safety circuits are wired properly and in the correct state before energizing
the drive. Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury from moving equipment. When programmed for 3-Wire control, a
momentary closure on terminal S1 may cause the drive to start.
WARNING! When 3-Wire sequence is used, set the drive to 3-Wire sequence before wiring the control terminals and ensure parameter
b1-17 is set to 0 (drive does not accept a run command at power up (default). If the drive is wired for 3-Wire sequence but set up for 2Wire sequence (default) and if parameter b1-17 is set to 1 (drive accepts a Run command at power up), the motor will rotate in reverse
direction at power up of the drive and may cause injury.
Figure 3.2 illustrates an example of a 3-Wire sequence.
Drive
Sequence input common
Run relay (N.O.)
Stop relay (N.C.)
Run command (run on momentary close)
Stop command (stop on momentary open)
Foward/reverse command
(multi-function input: H1-05 = 0)
S1
S2
S5
SC
Figure 3.2 3-Wire Sequence
3.2 Standard Connection Diagram
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
33
3
Electrical Installation
Page 36

3.3 Main Circuit Connection Diagram
Refer to diagrams in this section for the Main Circuit wiring connections. Connections may vary based on drive capacity.
The main circuit DC power supply powers the control circuit.
NOTICE: Do not use the negative DC bus terminal “-” as a ground terminal. This terminal is at high voltage DC potential. Improper
wiring connections could result in damage to the drive.
u
Single-Phase 200 V Class (JZAB0P1 ~ B1P5)
Drive
Jumper
Single-phase
200 Vac
Motor
DC reactor
(option)
Braking Resistor
Unit (option)
R/L1
S/L2
+1
+2
–
B1 B2
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3
Figure 3.3 Connecting Single-Phase Main Circuit Terminals
NOTICE: Do not connect T/L3 terminal when using single-phase power supply input. Incorrect wiring may damage the drive.
u
Three-Phase 200 V Class (JZA20P1 ~ 24P0); Three-Phase 400 V Class (JZA40P2 ~
44P0)
—
Drive
Motor
Three phase 200 Vac
(400 Vac)
Braking
Resistor Unit
(option)
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3
B1 B2
Jumper
DC reactor
(option)
+1
+2
Figure 3.4 Connecting Three-Phase Main Circuit Terminals
3.3 Main Circuit Connection Diagram
34
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 37

3.4 Terminal Block Configuration
The figures in this section provide illustrations of the main circuit terminal block configurations of the different drive sizes.
Models:
Models:
JZAB0P1, B0P2, B0P4
JZA20P1, 20P2, 20P4, 20P7
JZAB0P7, B1P5
JZA21P5, 22P2, 24P0
JZA40P2, 40P4, 40P7, 41P5
JZA42P2, 43P0, 44P0
Figure 3.5
Main Circuit Terminal Block Configurations
3.4 Terminal Block Configuration
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
35
3
Electrical Installation
Page 38

3.5 Protective Covers
Follow the procedure below to remove the protective covers before wiring the drive and to reattach the covers after wiring
is complete.
u
IP20/Open-Chassis Cover Removal and Installation
n
Removing the Protective Covers
1.
Loosen the screw that locks the front cover in place to remove.
Figure 3.6 Remove the Front Cover on an IP20/Open-Chassis Drive
2.
Apply pressure to the tabs on each side of the terminal cover. Pull the terminal cover away from the drive while
pushing in on the tabs to pull the cover free.
Figure 3.7 Remove the Terminal Cover on an IP20/Open-Chassis Drive
n
Reattaching the Protective Covers
Properly connect all wiring and route power wiring away from control signal wiring. Reattach all protective covers when
wiring is complete. Apply only a small amount of pressure to lock the cover back into place.
Figure 3.8 Reattach the Protective Covers on an IP20/Open-Chassis Drive
3.5 Protective Covers
36
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 39

3.6 Main Circuit Wiring
This section describes the functions, specifications, and procedures required to safely and properly wire the main circuit
of the drive.
NOTICE: Do not solder the ends of wire connections to the drive. Soldered wiring connections can loosen over time. Improper wiring
practices could result in drive malfunction due to loose terminal connections.
u
Main Circuit Terminal Functions
Table 3.1 Main Circuit Terminal Functions
Terminal Type Function Reference
R/L1
Main circuit power
supply input
Connects line power to the drive.
Drives with single-phase 200 V input power use terminals R/L1 and S/L2 only (T/
L3 must not be used).
34S/L2
T/L3
U/T1
Drive output Connects to the motor. 38V/T2
W/T3
B1
Braking resistor Available for connecting a braking resistor or the braking resistor unit option. 47
B2
+1
DC reactor connection
These terminals are shorted at shipment. Remove the shorting bar between +1 and
+2 when connecting a DC reactor to this terminal.
153
+2
+1
DC power supply input For connecting a DC power supply. –
–
(2 terminals)
Ground
Grounding Terminal
For 200 V class: 100 Ω or less
For 400 V class: 10 Ω or less
38
u
Wire Gauges and Tightening Torque
Select the appropriate wires and crimp terminals from Table 3.2 through Table 3.4.
Note: 1. Wire gauge recommendations based on drive continuous current ratings using 75 °C 600 Vac vinyl-sheathed wire assuming ambient
temperature within 30 °C and wiring distance less than 100 m.
2. Terminals +1, +2, –, B1 and B2 are for connecting optional devices such as a DC reactor or braking resistor. Do not connect other
non-specified devices to these terminals.
• Consider the amount of voltage drop when selecting wire gauges. Increase the wire gauge when the voltage drop is
greater than 2% of motor rated voltage. Ensure the wire gauge is suitable for the terminal block. Use the following
formula to calculate the amount of voltage drop:
•
Line drop voltage (V) = 3 x wire resistance (Ω/km) x wire length (m) x current (A) x 10
-3
• Refer to instruction manual TOBPC72060000 for braking unit or braking resistor unit wire gauges.
• Refer to UL Standards Compliance on page 218 for information on UL compliance.
n
Single-Phase 200 V Class
Table 3.2 Wire Gauge and Torque Specifications
Model
JZA
Terminal Screw Size
Tightening
Torque
N•m (lb.in.)
Applicable
Gauge
mm2 (AWG)
Recommended
Gauge
mm2 (AWG)
B0P1
B0P2
B0P4
R/L1, S/L2, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3, –, +1, +2,
B1, B2,
M3.5
0.8 to 1.0
(7.1 to 8.9)
0.75 to 2.5
(18 to 14)
2.5
(14)
B0P7
R/L1, S/L2, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3, –, +1, +2,
B1, B2,
M4
1.2 to 1.5
(10.6 to 13.3)
2.5 to 6
(14 to 10)
2.5
(14)
B1P5
R/L1, S/L2, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3,
M4
1.2 to 1.5
(10.6 to 13.3)
2.5 to 6.0
(14 to 10)
4
(12)
–, +1, +2, B1, B2 M4
1.2 to 1.5
(10.6 to 13.3)
2.5 to 6.0
(14 to 10)
6
(10)
n
Three-Phase 200 V Class
Table 3.3 Wire Gauge and Torque Specifications
Model
JZA
Terminal
Screw
Size
Tightening
Torque
N•m (lb.in.)
Applicable
Gauge
mm2 (AWG)
Recommended
Gauge
mm2 (AWG)
20P1
20P2
20P4
20P7
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3, –, +1,
+2, B1, B2,
M3.5
0.8 to 1.0
(7.1 to 8.9)
0.75 to 2.5
(18 to 14)
2.5
(14)
3.6 Main Circuit Wiring
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
37
3
Electrical Installation
Page 40

Model
JZA
Terminal
Screw
Size
Tightening
Torque
N•m (lb.in.)
Applicable
Gauge
mm2 (AWG)
Recommended
Gauge
mm2 (AWG)
21P5
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3, –, +1,
+2, B1, B2
M4
1.2 to 1.5
(10.6 to 13.3)
2.5 to 6
(14 to 10)
2.5
(14)
M4
1.2 to 1.5
(10.6 to 13.3)
2.5 to 6
(14 to 10)
4
(12)
22P2
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3, –, +1,
+2, B1, B2,
M4
1.2 to 1.5
(10.6 to 13.3)
2.5 to 6
(14 to 10)
4
(12)
24P0
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3, –, +1,
+2, B1, B2,
M4
1.2 to 1.5
(10.6 to 13.3)
2.5 to 6
(14 to 10)
6
(10)
n
Three-Phase 400 V Class
Table 3.4 Wire Gauge and Torque Specifications
Model
JZA
Terminal
Screw
Size
Tightening Torque
N•m (lb.in.)
Applicable Gauge
mm2 (AWG)
Recommended
Gauge
mm2 (AWG)
40P2
40P4
40P7
41P5
42P2
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3, –, +1,
+2, B1, B2,
M4
1.2 to 1.5
(10.6 to 13.3)
2.5 to 6.0
(14 to 10)
2.5
(14)
43P0
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3, –, +1,
+2, B1, B2
M4
1.2 to 1.5
(10.6 to 13.3)
2.5 to 6
(14 to 10)
2.5
(14)
M4
1.2 to 1.5
(10.6 to 13.3)
2.5 to 6
(14 to 10)
4
(12)
44P0
R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3, –, +1,
+2, B1, B2
M4
1.2 to 1.5
(10.6 to 13.3)
2.5 to 6
(14 to 10)
2.5
(14)
M4
1.2 to 1.5
(10.6 to 13.3)
2.5 to 6
(14 to 10)
4
(12)
u
Main Circuit Terminal Power Supply and Motor Wiring
This section outlines the various steps, precautions, and checkpoints for wiring the main circuit terminals and motor
terminals.
NOTICE: When connecting the motor to the drive output terminals U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3, the phase order for the drive and motor should
match. Failure to comply with proper wiring practices may cause the motor to run in reverse if the phase order is backward.
NOTICE: Do not connect phase-advancing capacitors or LC/RC noise filters to the output circuits. Improper application of noise filters
could result in damage to the drive.
NOTICE: Do not connect the AC power line to the output motor terminals of the drive. Failure to comply could result in death or serious
injury by fire as a result of drive damage from line voltage application to output terminals.
n
Cable Length Between Drive and Motor
When the cable length between the drive and the motor is too long (especially at low frequency output), note that the cable
voltage drop may cause reduced motor torque. Drive output current will increase as the leakage current from the cable
increases. An increase in leakage current may trigger an overcurrent situation and weaken the accuracy of the current
detection.
Adjust the drive carrier frequency according to the following table. If the motor wiring distance exceeds 100 m because
of the system configuration, reduce the ground currents.
Refer to Table 3.5 to set the carrier frequency to an appropriate level.
Table 3.5 Cable Length Between Drive and Motor
Cable Length 50 m or less 100 m or less Greater than 100 m
Carrier Frequency 15 kHz or less 5 kHz or less 2 kHz or less
Note: When setting carrier frequency, calculate the cable length as the total distance of wiring to all connected motors when running multiple
motors from a single drive.
n
Ground Wiring
Follow the precautions to wire the ground for one drive or a series of drives.
WARNING! Electrical Shock Hazard. Always use a ground wire that complies with technical standards on electrical equipment and
minimize the length of the ground wire. Improper equipment grounding may cause dangerous electrical potentials on equipment chassis,
which could result in death or serious injury.
WARNING! Electrical Shock Hazard. Be sure to ground the drive ground terminal. (200 V Class: Ground to 100 Ω or less, 400 V Class:
Ground to 10 Ω or less). Improper equipment grounding could result in death or serious injury by contacting ungrounded electrical
equipment.
NOTICE: Do not share the ground wire with other devices such as welding machines or large-current electrical equipment. Improper
equipment grounding could result in drive or equipment malfunction due to electrical interference.
3.6
Main Circuit Wiring
38
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 41

NOTICE: When using more than one drive, ground multiple drives according to instructions. Improper equipment grounding could result
in abnormal operation of drive or equipment.
Refer to Figure 3.9 when using multiple drives. Do not loop the ground wire.
A
B
A – Correct B – Incorrect
Figure 3.9 Multiple Drive Wiring
n
Wiring the Main Circuit Terminal
WARNING! Electrical Shock Hazard. Shut off the power supply to the drive before wiring the main circuit terminals. Failure to comply
may result in death or serious injury.
Note: A cover placed over the DC Bus and braking circuit terminals prior to shipment helps prevent miswiring. Cut away covers as needed for
terminals with a needle-nose pliers.
A
A – Protective Cover to Prevent Miswiring
Main Circuit Connection Diagram
Refer to section 3.3 Main Circuit Connection Diagram on page 34 for drive main power circuit connections.
WARNING! Fire Hazard. The braking resistor connection terminals are B1 and B2. Do not connect braking resistors to any other
terminals. Improper wiring connections could cause the braking resistor to overheat and cause death or serious injury by fire. Failure
to comply may result in damage to the braking circuit or drive.
3.6 Main Circuit Wiring
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
39
3
Electrical Installation
Page 42

3.7 Control Circuit Wiring
NOTICE: Do not solder the ends of wire connections to the drive. Soldered wire connections can loosen over time. Improper wiring
practices could result in drive malfunction due to loose terminal connections.
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
24 V
I V
+
24 V 8 mA
SC
AM
AC
+
-
AM
+V
A1
AC
2 k
MA
MB
MC
Forward run/stop
Reverse run/stop
External fault
Fault reset
Digital inputs
(default setting)
J1000
Control circuit
Multi-step
speed 1
main/aux switch
DIP switch S1
Option unit
connector
<1>
DIP
switch S3
Shield ground
terminal
0 to +10 V (20 k )
(0)4 to 20 mA (250 )
Setting power supply
+10.5 max. 20 mA
Digital output
250 Vac, 10 mA to 1 A
30 Vdc, 10 mA to 1 A
(default setting)
Main speed
frequency
reference.
Multi-function
programmable
Sink
Source
<2>
<3>
0 to +10 Vdc
(2 mA)
Analog monitor
output
Monitor
output
main circuit terminal
shielded line
twisted-pair shielded line
control terminal
Figure 3.10 Control Circuit Connection Diagram
<1> Connected using sequence input signal (S1 to S5) from NPN transistor; Default: sink mode (0 V com)
<2> Use only the +24 V internal power supply in sinking mode; the source mode requires an external power supply. Refer
to I/O Connections on page 44.
<3> Minimum load: 5 Vdc, 10 mA (reference value).
u
Control Circuit Terminal Block Functions
Drive parameters determine which functions apply to the multi-function digital inputs (S1 to S5), multi-function digital
outputs (MA, MB, MC), and multi-function analog output (AM). The default is called out next to each terminal in Figure
3.10.
WARNING! Sudden Movement Hazard. Always check the operation and wiring of control circuits after being wired. Operating a drive
with untested control circuits could result in death or serious injury.
WARNING! Confirm the drive I/O signals and external sequence before starting test run. Failure to comply may result in death or serious
injury.
n
Input Terminals
Table 3.6 Control Circuit Input Terminals
Type No. Terminal Name (Function) Function (Signal Level) Default Setting
Multi-Function
Digital Inputs
S1
Multi-function input 1 (Closed: Forward run, Open:
Stop)
24 Vdc, 8 mA
Note: Drive preset to sinking mode. When using source mode, set
DIP switch S3 to allow for a 24 Vdc (±10%) external power supply.
Refer to Sinking/Sourcing Mode Switch on page 44.
S2
Multi-function input 2 (Closed: Reverse run, Open:
Stop)
S3 Multi-function input 3 (External fault (N.O.)
S4 Multi-function input 4 (Fault reset)
S5 Multi-function input 5 (Multi-step speed reference 1)
SC Multi-function input common (Control common) Sequence common
3.7 Control Circuit Wiring
40
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 43

Type No. Terminal Name (Function) Function (Signal Level) Default Setting
Main
Frequency
Reference
Input
A1 Frequency reference
Input voltage or input current (Selected by DIP switch S1 and
H3-01) 0 to +10 Vdc (20 kΩ),
Resolution: 1/1000
4 to 20 mA (250 Ω) or 0 to 20 mA (250 Ω),
Resolution: 1/500
+V Analog input power supply +10.5 Vdc (max allowable current 20 mA)
AC Frequency reference common 0 Vdc
n
Output Terminals
Table 3.7 Control Circuit Output Terminals
Type No. Terminal Name (Function) Function (Signal Level) Default Setting
Multi-Function Digital
Output
MA N.O. output (fault)
Digital output
30 Vdc, 10 mA to 1 A; 250 Vac, 10 mA to 1 A
Minimum load: 5 Vdc, 10 mA (reference value)
MB N.C. output (fault)
MC Digital output common
Monitor Output
AM Analog monitor output 0 to 10 Vdc (2 mA or less) Resolution: 1/256
AC Monitor common 0 V
u
Terminal Configuration
S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 SC A1 +V AC AM AC
MCMBMA
Figure 3.11 Control Circuit Terminal
n
Wire Size and Torque Specifications
Select appropriate wire type and size from Table 3.8. For simpler and more reliable wiring, crimp ferrules to the wire ends.
Refer to Table 3.9 for ferrule terminal types and sizes.
Table 3.8 Wire Size and Torque Specifications (Same for All Models)
Terminal
Screw
Size
Tightening
Torque
N•m
Tightening
Torque
(in-lbs)
Bare Wire Terminal Ferrule-Type Terminal
Applicable wire
size
mm2 (AWG)
Recomm.
mm
2
(AWG)
Applicable
wire size
mm
2
(AWG)
Recomm.
mm2 (AWG)
Wire Type
MA, MB, MC M3 0.5 to 0.6 4.4 to 5.3
Stranded: 0.25 to
1.5
(24 to 16)
Single: 0.25 to 1.5
(24 to 16)
0.75 (18)
0.25 to 1.0
(24 to 17)
0.5 (20)
Shielded
line, etc.
S1-S5, SC, +V,
A1, AC, AM
M2 0.22 to 0.25 1.9 to 2.2
Stranded: 0.25 to
1.0
(24 to 18)
Single: 0.25 to 1.5
(24 to 16)
0.75 (18)
0.25 to 0.5
(24 to 20)
0.5 (20)
n
Ferrule-Type Wire Terminations
Crimp a ferrule to signal wiring to improve wiring simplicity and reliability. Use CRIMPFOX ZA-3, a crimping tool
manufactured by PHOENIX CONTACT.
3.7
Control Circuit Wiring
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
41
3
Electrical Installation
Page 44

d1
d2
6 mm
L
Figure 3.12 Ferrule Dimensions
Table 3.9 Ferrule Terminal Types and Sizes
Size mm2 (AWG)
Type L (mm) d1 (mm) d2 (mm) Manufacturer
0.25 (24) AI 0.25-6YE 10.5 0.8 2.0
PHOENIX CONTACT
0.34 (22) AI 0.34-6TQ 10.5 0.8 2.0
0.5 (20) AI 0.5-6WH 12 1.1 2.5
0.75 (18) AI 0.75-6GY 12 1.3 2.8
1.0 AI 1-6RD 12 1.5 3.0
u
Wiring Procedure
This section describes the proper procedures and preparations for wiring the control terminals.
WARNING! Electrical Shock Hazard. Do not remove covers or touch the circuit boards while the power is on. Failure to comply could
result in death or serious injury.
NOTICE: Separate control circuit wiring from main circuit wiring (terminals R/L1, S/L2, T/L3, B1, B2, U/T1, V/T2, W/T3, -, +1, +2) and
other high-power lines. Improper wiring practices could result in drive malfunction due to electrical interference.
NOTICE: Separate wiring for digital output terminals MA, MB and MC from wiring to other control circuit lines. Improper wiring practices
could result in drive or equipment malfunction or nuisance trips.
NOTICE: Use a class 2 power supply (UL standard) when connecting to the control terminals. Improper application of peripheral devices
could result in drive performance degradation due to improper power supply.
NOTICE: Insulate shields with tape or shrink tubing to prevent contact with other signal lines and equipment. Improper wiring practices
could result in drive or equipment malfunction due to short circuit.
NOTICE: Connect the shield of shielded cable to the appropriate ground terminal. Improper equipment grounding could result in drive
or equipment malfunction or nuisance trips.
Wire the control terminals using Figure 3.13 as a guide. Prepare the ends of the control circuit wiring as shown in Figure
3.14. Refer to Wire Size and Torque Specifications on page 41.
NOTICE: Do not tighten screws beyond the specified tightening torque. Failure to comply may damage the terminal.
NOTICE: Use shielded twisted-pair cables as indicated to prevent operating faults. Improper wiring practices could result in drive or
equipment malfunction due to electrical interference.
Connect control wires as shown in the following figure:
S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 SC A1 +V AC AM AC
A
D
C
E
B
Preparing wire
terminal ends
A – Control terminal block
B – Avoid fraying wire strands when stripping
insulation from wire. Strip length 5.5 mm.
C – Single wire or stranded wire
D – Loosen screw to insert wire.
E – Blade depth of 0.4 mm or less
Blade width of 2.5 mm or less
Figure 3.13 Terminal Board Wiring Guide
3.7 Control Circuit Wiring
42
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 45

A
F
C
D
E
B
A – Drive side
B – Connect shield to ground terminal of drive.
C – Insulation
D – Control device side
E – Shield sheath (Insulate with tape)
F – Shield
Figure 3.14 Preparing the Ends of Shielded Cables
When setting the frequency by analog reference from an external potentiometer, use shielded twisted-pair wires and ground
the shield of twisted-pair wires to the ground terminal of the drive.
NOTICE: The analog signal lines between the drive and the operator station or peripheral equipment should not exceed 50 meters
when using an analog signal from a remote source to supply the frequency reference. Failure to comply could result in poor system
performance.
+V
A1
AC
A
B
C
D
A – Drive
B – Ground terminal (shield connection)
C – (+V) Frequency setting power source +10.5 Vdc
maximum 20 mA
D – (A1) Main speed frequency reference 0 to +10
Vdc (20 kΩ)
or
4 to 20 mA (250 Ω)/
0 to 20 mA (250 Ω)
Figure 3.15
Wiring the Frequency Reference to the Control Circuit Terminals (External Reference)
3.7 Control Circuit Wiring
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
43
3
Electrical Installation
Page 46

3.8 I/O Connections
u
Sinking/Sourcing Mode Switch
Set the DIP switch S3 on the front of the drive to switch the digital input terminal logic between sinking mode and sourcing
mode; the drive is preset to sinking mode.
Table 3.10 Sinking/Sourcing Mode Setting
Set Value Details
SINK Sinking Mode (0 V common): default setting
SOURCE Sourcing Mode (+24 V common)
SINK
SOURCE
DIP Switch S3
Figure 3.16 DIP Switch S3
n
Transistor Input Signal Using 0 V Common/Sink Mode
When controlling the digital inputs by NPN transistors (0 V common/sinking mode), set the DIP switch S3 to SINK and
use the internal 24 V power supply.
S1
SINK
SOURCE
S2
S3
S3
+24 V
S4
S5
SC
SINK
SOURCE
FWD Run/Stop
REV Run/Stop
External Fault N.O.
Fault Reset
Multi-step Speed 1
Shielded Cable
Multi-funciton input
Figure 3.17 Sinking Mode: Sequence from NPN Transistor (0 V Common)
n
Transistor Input Signal Using +24 V Common/Source Mode
When controlling digital inputs by PNP transistors (+24 V common/sourcing mode), set the DIP switch S3 to SOURCE
and use an external 24 V power supply.
3.8
I/O Connections
44
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 47

S1
+24V
S2
S3
+24V
S4
S5
SC
S3
SINK
SOURCE
SINK
SOURCE
External
power supply
FWD Run/Stop
REV Run/Stop
External Fault N.O.
Fault reset
Multi-step speed 1
Shielded cable
Figure 3.18 Source Mode: Sequence from PNP Transistor (+24 V Common)
3.8 I/O Connections
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
45
3
Electrical Installation
Page 48

3.9 Main Frequency Reference
u
DIP Switch S1 Analog Input Signal Selection
The main frequency reference can either be a voltage or current signal input at terminal A1.
When using input A1 as a voltage input, set DIP switch S1 to “V” (right position, default setting) and program parameter
H3-01 to “0” (0 to +10 Vdc with lower limit) or “1” (0 to +10 Vdc without lower limit).
To use current input at terminal A1, set the DIP switch S1 to "I" and set parameter H3-01 = “2” or “3” (4-20 mA or 0-20
mA).
Table 3.11 Frequency Reference Configurations
Voltage Input Current Input
+10.5 V
20 mA current
Main speed frequency
reference (voltage input)
Frequency reference
common
Drive
+V
A1
AC
0 to 10 V
+10.5 V
20 mA current
Main speed
frequency reference
(current input)
Frequency
reference
common
+V
A1
AC
Drive
4 to 20 mA input
or
0 to 20 mA input
I V
DIP Switch S1
Figure 3.19 DIP Switch S1
Table 3.12 DIP Switch S1 Settings
Setting Value Description
V ( right position) Voltage input (0 to 10 V): default setting
I ( left position) Current input (4 to 20 mA or 0 to 20 mA)
Table 3.13 Parameter H3-01 Details
No. Parameter Name Description
Setting
Range
Default
Setting
MEMOBUS
Register
H3-01
Frequency ref. (voltage/
current)
terminal A1 signal level
selection
Selects the signal level for terminal A1.
0: 0 to +10 V, unipolar input (negative frequency
reference values are zeroed)
1: 0 to +10 V, bipolar input (negative frequency reference
changes the direction)
2: 4 to 20 mA
3: 0 to 20 mA
0 to 3 0 0
3.9 Main Frequency Reference
46
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 49

3.10 Braking Resistor
Dynamic braking (DB) helps bring the motor to a smooth and rapid stop when working with high inertia loads. As the
drive lowers the frequency of a motor with high inertia connected, regeneration occurs. This can cause an overvoltage
situation when the regenerative energy flows back into the DC bus capacitors. A braking resistor prevents these overvoltage
faults.
NOTICE: Do not allow unqualified personnel to use the product. Failure to comply could result in damage to the drive or braking circuit.
Carefully review the braking resistor instruction manual when connecting a braking option to the drive.
Note: The braking circuit must be sized properly in order to dissipate the power required to decelerate the load in the desired time. Ensure that
the braking circuit can dissipate the energy for the set deceleration time prior to running the drive.
NOTICE: Use a thermal overload relay or an over-temperature contact to interrupt input power to the drive in the event the braking
resistor overheats. In the event of a possible thermal overload, the relay will trigger the input contactor and prevent the braking resistor
from burning up.
u
Installation
WARNING! Fire Hazard. The braking resistor connection terminals are B1 and B2. Do not connect a braking resistor directly to any
other terminals. Improper wiring connections could result in death or serious injury by fire. Failure to comply may result in damage to
the braking circuit or drive.
NOTICE: Connect braking resistors to the drive as shown in the I/O wiring examples. Improperly wiring braking circuits could result in
damage to the drive or equipment.
n
Installation Procedure
1.
Disconnect all electrical power to the drive and wait at least one minute before servicing the drive and any
connected components.
2.
Remove drive front cover.
3.
Use a voltmeter to verify that voltage is disconnected from incoming power terminals and that the DC bus no
longer holds a charge.
Power
supply
Thermal
relay
Motor
Drive
Braking resistor
Thermal relay switch for
external braking resistor
Fault contact
MC
SA
SA
SA
MCONMCOFFTHRX
THRX
TRX
MC
TRX
MA MC
R/L1
B1 B2
S/L2
T/L3
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3
MCCB
Figure 3.20 Connecting a Braking Resistor
4.
Follow manufacturer instructions to connect the resistor unit to the drive using proper wire gauge according to
local electrical codes.
Power leads for the remote mount resistors generate high levels of electrical noise; group these signal leads
separately.
5.
Mount the resistor unit on a noncombustible surface. Maintain minimum side and top clearances according to
resistor manufacturer instructions.
WARNING! Fire Hazard. Do not use improper combustible materials. Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury
by fire. Attach the drive or braking resistors to metal or other noncombustible material.
6.
Reinstall drive covers and resistor covers, if provided.
7.
Set parameter L3-04 = “0” to disable stall prevention during deceleration.
Set parameter L8-01 to “1” to enable overheat protection when using a heatsink-mounted braking resistor option.
Set L8-01 = “0” for other braking resistor types.
Table 3.14 Braking Resistor Settings
Parameter Settings
L8-01: Internal Dynamic Braking Resistor Protection Selection
0: Disabled. The drive will not provide overheat protection.
Supply separate means of overheat protection.
1: Enabled. Braking Resistor is protected from overheat.
L3-04: Stall Prevention During Deceleration 0: Stall prevention disabled.
8.
Operate the system and verify the required deceleration rate is obtained during dynamic braking or stopping.
3.10
Braking Resistor
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
47
3
Electrical Installation
Page 50

3.11 Interlocking with Connected Machinery
For safety reasons, applications that may be affected by the operation status of the drive should be set up so that operation
can only occur when the drive is ready to operate. A "Drive ready" and "Fault" signal should be assigned to the multifunction outputs to guarantee interlock with application.
u
Drive Ready Signal
The "Drive ready" signal is output to one of the multi-function terminals after the drive has booted up and there is no fault
present. It indicates that the drive is ready for operation.
• The power is off.
• A fault situation is present.
• There is a problem with the drive internal power supply.
• Parameter settings restrict a Run command from being entered.
• An overvoltage or undervoltage situation is present so that when the Run command is given a fault is immediately
triggered.
• The drive is in the programming mode and parameter settings restrict a Run command from being entered in the
programming mode.
3.11 Interlocking with Connected Machinery
48
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 51

3.12 Wiring Checklist
No. Item Page
Drive, peripherals, option cards
1 Check drive model number to ensure receipt of correct model. 17
2 Check for correct braking resistors, DC reactors, noise filters, and other peripheral devices. 47
Installation area and physical setup
3 Ensure area surrounding the drive complies with specifications. 26
Power supply voltage, output voltage
4 The voltage from the power supply should fall within the input voltage specification range of the drive. 86
5 The voltage rating for the motor should match the drive output specifications. 17
Main circuit wiring
6 Confirm proper branch circuit protection exists per National and Local codes. 32
7 Properly wire the power supply to drive terminals R/L1, S/L2 and T/L3. 34
8
Properly wire the drive and motor together.
The motor lines and drive output terminals R/T1, V/T2 and W/T3 should match in order to produce the desired
phase order. If the phase order is incorrect, the drive will rotate in the opposite direction.
38
9 Use 600 Vac vinyl-sheathed wire for the power supply and motor lines. 37
10
Use the correct wire gauges for the main circuit. Refer to Wire Gauge and Torque Specifications on page 37,
Table 3.3, or Table 3.4.
37
• When using comparatively long motor cable, calculate the amount of voltage drop.
3 x voltage resistance (Ω/km) x cable length (m) x motor rated current (A) x 10
-3
Motor rated voltage (V) x 0.02 ≥
37
• If the cable between the drive and motor exceeds 50 m, adjust the carrier frequency (C6-02) accordingly. 38
11 Properly ground the drive. Review page 38. 38
12
Tightly fasten all terminal screws (control circuit terminals, grounding terminals).
Refer to Wire Gauge and Torque Specifications on page 37, Table 3.3, or Table 3.4.
37
13
Set up overload protection circuits when running multiple motors from a single drive.
M1
OL1
OL2
OLn
MC1
MC2
MCn
M2
Mn
Drive
MC1 - MCn
OL 1 - OLn
... magnetic contactor
... thermal relay
Power supply
Note: Close MC1 through MCn before operating the drive.
-
14
If using a braking resistor or dynamic braking resistor unit, install a magnetic contactor. Properly install the
resistor, and ensure that overload protection shuts off the power supply.
47
15 Verify phase advancing capacitors are NOT installed on the output side of the drive. -
Control circuit wiring
16 Use twisted-pair cables for all drive control circuit wiring. 40
17 Ground the shields of shielded wiring to the GND terminal. 42
18
If using a 3-Wire sequence, properly set parameters for multi-function contact input terminals S1 through S5,
and properly wire control circuits.
33
19
Check for any other wiring mistakes.
Only use a multimeter to check wiring.
-
20
Properly fasten the control circuit terminal screws in the drive.
Refer to Wire Gauge and Torque Specifications on page 37, Table 3.3, or Table 3.4.
37
21 Pick up all wire clippings. -
22 Ensure that no frayed wires on the terminal block are touching other terminals or connections. -
23 Properly separate control circuit wiring and main circuit wiring. -
24 Analog signal line wiring should not exceed 50 m. -
3.12 Wiring Checklist
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
49
3
Electrical Installation
Page 52

3.12 Wiring Checklist
This Page Intentionally Blank
50
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 53

Start-Up Programming & Operation
This chapter explains the functions of the LED operator and how to program the drive for initial
operation.
4.1 SECTION SAFETY............................................................................................52
4.2 USING THE DIGITAL LED OPERATOR..........................................................54
4.3 THE DRIVE AND PROGRAMMING MODES....................................................57
4.4 START-UP FLOWCHART.................................................................................62
4.5 POWERING UP THE DRIVE.............................................................................63
4.6 NO-LOAD OPERATION TEST RUN.................................................................64
4.7 TEST RUN WITH LOAD CONNECTED............................................................65
4.8 VERIFYING AND BACKING UP PARAMETER SETTINGS............................66
4.9 TEST RUN CHECKLIST...................................................................................67
4
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
51
Page 54

4.1 Section Safety
DANGER
Electrical Shock Hazard
Do not connect or disconnect wiring while the power is on.
Failure to comply will result in death or serious injury.
WARNING
Electrical Shock Hazard
Do not operate equipment with covers removed.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury.
The diagrams in this section may include drives without covers or safety shields to illustrate details. Be sure to reinstall
covers or shields before operating the drives and run the drives according to the instructions described in this manual.
Always ground the motor-side grounding terminal.
Improper equipment grounding could result in death or serious injury by contacting the motor case.
Do not touch any terminals before the capacitors have fully discharged.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury.
Before wiring terminals, disconnect all power to the equipment. The internal capacitor remains charged even after the
power supply is turned off. The charge indicator LED will extinguish when the DC bus voltage is below 50 Vdc. To
prevent electric shock, wait at least one minute after all indicators are off and measure the DC bus voltage level to confirm
safe level.
Do not allow unqualified personnel to perform work on the drive.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury.
Installation, maintenance, inspection, and servicing must be performed only by authorized personnel familiar with
installation, adjustment and maintenance of AC drives.
Do not perform work on the drive while wearing loose clothing, jewelry or without eye protection.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury.
Remove all metal objects such as watches and rings, secure loose clothing, and wear eye protection before beginning
work on the drive.
Do not remove covers or touch circuit boards while the power is on.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury.
Fire Hazard
Tighten all terminal screws to the specified tightening torque.
Loose electrical connections could result in death or serious injury by fire due to overheating of electrical connections.
Do not use an improper voltage source.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury by fire.
Verify that the rated voltage of the drive matches the voltage of the incoming power supply before applying power.
Do not use improper combustible materials.
Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury by fire.
Attach the drive to metal or other noncombustible material.
4.1 Section Safety
52
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 55

NOTICE
Observe proper electrostatic discharge procedures (ESD) when handling the drive and circuit boards.
Failure to comply may result in ESD damage to the drive circuitry.
Never connect or disconnect the motor from the drive while the drive is outputting voltage.
Improper equipment sequencing could result in damage to the drive.
Do not use unshielded cable for control wiring.
Failure to comply may cause electrical interference resulting in poor system performance. Use shielded twisted-pair wires
and ground the shield to the ground terminal of the drive.
Do not allow unqualified personnel to use the product.
Failure to comply could result in damage to the drive or braking circuit.
Carefully review instruction manual TOBPC72060000 when connecting a braking option to the drive.
Do not modify the drive circuitry.
Failure to comply could result in damage to the drive and will void warranty.
OYMC is not responsible for any modification of the product made by the user. This product must not be modified.
Check all the wiring to ensure that all connections are correct after installing the drive and connecting any other
devices.
Failure to comply could result in damage to the drive.
4.1 Section Safety
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
53
4
Start-Up Programming
& Operation
Page 56

4.2 Using the Digital LED Operator
Use the LED operator to enter run and stop commands, display data, edit parameters, as well as display fault and alarm
information.
u
Keys, Displays, and LEDs
P
9
5
1
2
3
6
7
8
10
STOP
11
14
12
13
15
4
J1000
STOP
据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据
据据据据据据据据据据据5据据据据据据据据据据据据
据据据据据据据
400V
据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据
据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据
据据据据据据据据据据据据据据据
据据据
Read manual before installing.
Wait 5 minutes for capacitor discharge after
disconnecting power supply.
To conform to requirements, make sure
to ground the supply neutral for 400V class.
Risk of electric shock.
WARNING
1
据据据据据
2
据据据据据据
3
据据据据据
4
据据据据
5
据据据据
:
:
:
:
:
:
:
:
:
6
据据据
7
据据据据据
8
据据据据据据
9
据据据据据据据
Table 4.1 Keys and Displays on the LED Operator
No. Display Name Function
1 Data Display Area Displays the frequency reference, parameter number, etc.
2 ESC Key Returns to the previous menu.
3 RESET Key
Moves the cursor to the right.
Resets the drive to clear a fault situation.
4 RUN Key Starts the drive.
5 Up Arrow Key Scrolls up to select parameter numbers, setting values, etc.
6 Down Arrow Key Scrolls down to select parameter numbers, setting values, etc.
7
STOP
STOP Key
Stops the drive.
Note: Stop priority circuit. A fast-stop is available by pressing the STOP key when
the drive detects a danger even if the drive is running by a signal from the multifunction contact input terminal (REMOTE is set). To avoid stoppage by using the
STOP key, set o2-02 (STOP Key Function Selection) to 0 (Disabled).
8 ENTER Key
Selects all modes, parameters, settings, etc.
Selects a menu item to move from one display screen to the next.
9 LO/RE Selection Key
Switches drive control between the operator (LOCAL) and the control circuit
terminals (REMOTE).
Note: LOCAL/REMOTE key effective during stop in drive mode.
10 RUN Light Lit while the drive is operating the motor.
11 LO/RE Light Lit while the operator (LOCAL) is selected to run the drive.
4.2 Using the Digital LED Operator
54
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 57

No. Display Name Function
12 ALM LED Light
Refer to LED Screen Displays on page 55.
13 REV LED Light
14 DRV LED Light
15 FOUT LED Light
u
Digital Text Display
Text appears on the LED Operator as shown below. This section explains the meaning of text as it appears on the display
screen.
Lit Flashing
Table 4.2 Digital Text Display
Text LED Text LED Text LED Text LED
0 9 I R
1 A J S
2 B K T
3 C L U
4 D M
<1>
V
5 E N W
<1>
6 F O X none
7 G P Y
8 H Q Z none
<1> Displayed in two digits.
u
LED Screen Displays
Display Lit Flashing Off
When the drive detects an alarm or error
• When an alarm occurs
• oPE detected
Normal state (no fault or alarm)
Motor is rotating in reverse — Motor is rotating forward
Drive Mode — Programming Mode
Displays output frequency (Hz) — —
As illustrated in
this manual
u
LO/RE LED and RUN LED Indications
LED Lit Flashing
Flashing Quickly
<1>
Off
When run command is
selected from LED operator
(LOCAL)
— —
Run command is selected from
device other than LED operator
(REMOTE)
During run
• During deceleration to stop
• When a run command is input
and frequency reference is 0
• During deceleration at a faststop.
• During stop by interlock
operation.
During stop
As shown
<1> Refer to Figure 4.1 for the difference between “flashing” and “flashing quickly”.
4.2
Using the Digital LED Operator
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
55
4
Start-Up Programming
& Operation
Page 58

Flashing
ON ON
ON
ON ON
ON
1 s
Flashing
quickly
Figure 4.1 RUN LED Status and Meaning
/
Drive output frequency
during stop
Frequency setting
OFF
ON
Flashing
OFF
OFF
RUN LED
RUN
0 Hz
6 Hz
RUN
STOP
STOP
Figure 4.2 RUN LED and Drive Operation
u
Menu Structure for Digital LED Operator
XXXX
XX
XX
XX
XX
XX
XX
XX
XX
XX
XX
XX
XX
XX
XX
:
:
:
:
Turn the power on
Forward Selection
Reverse Selection
Output Frequency
Output Current
Output Voltage
Monitor Display
Note: “XX” characters are shown in this manual.
The drive will display the actual setting values.
<1>
Verify Menu
Set Up Mode
Parameter Setting Mode
Description of Key Operations
PROGRAMMING MODE
DRIVE MODE
Figure 4.3 Digital LED Operator Screen Structure
<1> Reverse can only be selected when LOCAL is set.
4.2
Using the Digital LED Operator
56
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 59

4.3 The Drive and Programming Modes
The drive functions are divided into two main groups accessible via the Digital LED Operator:
Drive Mode: The Drive mode allows motor operation and parameter monitoring. Parameter settings cannot be changed
when accessing functions in the Drive Mode (Table 4.3).
Programming Mode: The Programming Mode allows access to setup/adjust, verify parameters. The drive prohibits
changes in motor operation such as start/stop when the Digital LED Operator is accessing a function in the Programming
Mode.
Table 4.3 illustrates the different functions visible as the “Up arrow” is scrolled immediately after powering up the drive.
Note: When b1-08 (Run Command Selection while in Programming Mode) is set to 1 (enabled), the drive can run even if the mode is switched
to the programming mode. When setting b1-08 to 0 (disabled), the mode cannot be switched to the programming mode while the drive is
running.
Table 4.3 Summary of Modes
Mode Group Description Key Press LED Digital Operator Display
Drive Mode Functions
(Motor operation and monitoring)
Frequency Reference Display (Initial
power-up state)
Forward/Reverse
Output Frequency Display
Output Current Display
Output Voltage Reference
Monitor Display
Programming Mode Functions
(Changing parameters)
Verify Function
Setup Group Parameters
All Parameters
u
Navigating the Drive and Programming Modes
The drive is set to operate in Drive Mode when it is first powered up. Switch between display screens by using the
and keys.
Power Up
Frequency Reference
STOP
Default Setting
This display screen allows the user to monitor and set the frequency reference while the
drive is running. Refer to The Drive and Programming Modes on page 57.
Note: The user can select items to display when the drive is first powered up by setting
parameter o1-02.
Drive Mode
Forward/Reverse
: Motor rotates forward.
: Motor rotates in reverse.
Note: For applications that should not run in reverse (fans, pumps, etc.), set parameter
b1-04 = “1” to prohibit the motor from rotating in reverse. This sequence also puts the
drive in LOCAL mode.
The LED is lit when
LOCAL is selected
Switching to reverse:
Output Frequency Display
Monitors the frequency output by the drive.
Output Current Display
Monitors the output current of the drive.
4.3 The Drive and Programming Modes
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
57
4
Start-Up Programming
& Operation
Page 60

Drive Mode
Output Voltage Reference
Monitors the output voltage of the drive.
Monitor Display
Monitor parameters (U parameters) are displayed.
Programming
Mode
Verify Function
Lists all parameters that have been edited or changed from default settings. Refer to
Verifying Parameter Changes: Verify Menu on page 59.
Setup
A select list of parameters necessary to get the drive operational quickly. Refer to
The Setup Group within the Programming Mode on page 59.
Parameter Setting
Allows the user to access and edit all parameter settings. Refer to Parameter List
on page 169.
Drive Mode
Frequency Reference
Returns to the frequency reference display screen.
n
Drive Mode Details
The following actions are possible in the Drive Mode:
• Run and stop the drive.
• Monitor the operation status of the drive (frequency reference, output frequency, output current, output voltage, etc.).
• View information on an alarm.
Note: Select "Drive Mode" when running. The mode can be switched to any mode (program mode, etc.) other than drive mode while the drive
is stopped. However, the drive cannot be operated in other modes. Return the mode to "Drive Mode" after completing periodic inspection.
Figure 4.4 illustrates changing the default frequency reference of F 0.00 (0 Hz) to F 6.00 (6 Hz) while in Drive Mode.
This example assumes the drive is set to LOCAL.
STOP
Frequency reference
display at power up
Press to select LOCAL
Press until the frequency
reference becomes 6 Hz
Press to select the
digit to the right
Figure 4.4 Setting the Frequency Reference while in Drive Mode
Note: The drive will not accept a frequency reference set value unless the ENTER key is pressed after the frequency reference is entered. This
feature prevents accidental setting of the frequency reference. By setting o2-05 (Frequency Reference Setting Method Selection) to 1
(Enabled), the drive will accept the frequency reference while it is being adjusted on the digital operator.
n
Programming Mode Details
The following actions are possible in the programming mode:
• Verify Function: Verify parameter setting changes from original default values.
• Setup Group: Access a list of commonly used parameters to simplify setup.
• Parameter Setting Mode: Access and edit all parameter settings.
4.3
The Drive and Programming Modes
58
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 61

The Setup Group within the Programming Mode
In Setup Group, the user can access the minimum group of parameters required to operate the application.
Note: Setup Group parameters are listed in Table 4.4.
Figure 4.5 illustrates the keys to press to enter the Setup Group.
In this example, the source of the frequency reference is changed from the control circuit terminals to the LED Operator
(i.e., b1-01 is changed from 1 to 0).
STOP
(2x)
<1> Move to the right to change parameter settings. Scroll
down to view and check settings in the Setup Mode.
<2> To return to the Top Menu, press .
To view or edit
other parameters, press and .
Control Circuit
Terminal
Select digit
to edit
Parameter Display
LED Operator
Frequency reference
appears when powered up
Parameter Display
Press until
appears
<1>
<2>
Figure 4.5 Setup Group Example
u
Changing Parameter Settings or Values
This example explains changing C1-01 (Acceleration Time 1) from 10.0 seconds (default) to 20.0 seconds.
Step Display/Result
1. Turn on the power to the drive. The initial display appears.
2.
Press the key until the Setup Mode Screen appears.
3.
Press the key to view the parameter setting display.
4.
Scroll through parameters by pressing the key until C1-01 appears.
5.
Press to view the current setting value (10.0). (Number farthest to the left flashes)
6.
Press until the desired number is selected. (“1” flashes)
7.
Press the key and enter 0020.0.
8.
Press and the drive will confirm the change.
9. The display automatically returns to the screen shown in Step 4.
10.
Press the key until back at the initial display.
u
Verifying Parameter Changes: Verify Menu
The Verify Menu lists edited parameters from the Programming Mode. The Verify Menu helps determine which settings
have been changed, and is particularly useful when replacing a drive. If no settings have been changed the Verify Menu
will read . The Verify menu also allows users to access and re-edit edited parameters.
Note: The Verify Menu will not display parameters from the A1 group even if those parameters have been changed from default settings.
4.3
The Drive and Programming Modes
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
59
4
Start-Up Programming
& Operation
Page 62

The following example is a continuation of the steps beginning on page 59. Here, parameter C1-01 is accessed using the
Verify Menu and is changed again to 20.0 s.
To check the list of edited parameters:
Step Display/Result
1. Turn on the power to the drive. The initial display appears.
2.
Press until the display shows the “Verify” representation.
3.
Press to enter the list of parameters that have been edited from their original
default settings.
Scroll through the list by pressing the key.
4.
Press the key until C1-01 appears.
5.
Press the key to access the setting value. (number farthest to the left flashes)
u
Switching Between LOCAL and REMOTE
Entering the run command using the LED operator is referred to as LOCAL, while entering the run command from an
external device via the control circuit terminals or network option unit is referred to as REMOTE.
WARNING! Sudden Movement Hazard. The drive may start unexpectedly if the Run command is already applied when switching from
LOCAL mode to REMOTE mode when b1-07 = 1, resulting in death or serious injury. Be sure all personnel are clear of rotating machinery
and electrical connections prior to switching between LOCAL mode and REMOTE mode.
There are two ways to switch between LOCAL and REMOTE.
Note: 1. After selecting LOCAL, the LO/RE light will remain lit.
2. The drive will not allow the user to switch between LOCAL and REMOTE during run.
n
Using the LO/RE Key on the LED Operator
Step Display/Result
1. Turn on the power to the drive. The initial display appears.
2.
Press . The LO/RE light will light up. The drive is now in Local.
To set the drive for REMOTE operation, press the
key again.
STOP
n
Using Input Terminals S1 through S5 to Switch between LO/RE
Switch between LOCAL and REMOTE using one of the digital input terminals S1 through S5 (set the corresponding
parameter H1-01 through H1-05 to “1”).
Follow the example below to set the digital input terminals.
Note: 1. For a list of digital input selections, Refer to Parameter List on page 169.
2. Setting a multi-function input terminal to a value of 1 disables the LO/RE key on the LED operator.
u
Parameters Available in the Setup Group
n
Setup Mode (STUP)
Parameters used for this drive are classified into A to U. To simplify the drive setup, frequently used parameters are selected
and input into Setup Mode.
1.
To set a parameter, the Setup Mode must be displayed first. Press the Up/Down key until
is displayed.
2.
Select the parameter and change the setting. Table 4.4 lists parameters available in the Setup group. If the desired
parameter cannot be set in the Setup mode, use the Parameter Setting mode.
Table 4.4 Setup Group Parameters
Parameter Name
b1-01 Frequency Reference Selection
b1-02 Run Command Selection
b1-03 Stop Method Selection
C1-01 Acceleration Time 1
C1-02 Deceleration Time 1
Parameter Name
C6-01 Duty Selection
C6-02 Carrier Frequency Selection
d1-01 Frequency Reference 1
d1-02 Frequency Reference 2
d1-03 Frequency Reference 3
4.3 The Drive and Programming Modes
60
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 63

Parameter Name
d1-04 Frequency Reference 4
d1-17 Jog Frequency Reference
E1-01 Input Voltage Reference
E1-04 Maximum Output Frequency
E1-05 Maximum Voltage
E1-06 Base Frequency
Parameter Name
E1-09 Minimum Output Frequency
E2-01 Motor Rated Current
H4-02 Terminal AM Gain Setting
L1-01 Motor Protection Function Selection
L3-04 Stall Prevention Selection during Deceleration
4.3 The Drive and Programming Modes
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
61
4
Start-Up Programming
& Operation
Page 64

4.4 Start-up Flowchart
This section summarizes the basic steps required to start the drive. The flowchart is intended as a quick reference to help
familiarize the user with start-up procedures.
u
Flowchart: Basic Start-up
Figure 4.6 describes basic start-up sequence for the drive and motor system. This sequence varies slightly depending on
application. Use drive default parameter settings in simple applications that do not require high precision.
Install and wire the drive as explained in Chapters 1, 2 and 3
Run the motor without load; check the rotation direction and operation.
Verify external signal commands to the drive work as desired.
Couple the load or machine to the motor. Run the machine and check for desired operation.
Fine tune parameters. Adjust application settings if necessary.
Check the machine operation and verify parameter settings.
Drive is ready to run the application.
START
Apply main power on to the drive.
Adhere to safety messages concerning application of power.
Set the basic parameters:
* b1-01/02 for frequency reference and run command source selection
* H1-, H2-01, H3-, H4-, H5- for I/O terminal setting
* d1- for multi-speed references if used
* C1- and C2- for accel./decel. and S-curve time settings
* C6-01 for heavy/normal duty mode selection
* L3-04 if braking options are used
* E1-, V/f Characteristics
* E2-, Motor 1 parameters
Figure 4.6 Basic Start-Up
4.4 Start-up Flowchart
62
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 65

4.5 Powering Up the Drive
u
Powering Up the Drive and Operation Status Display
n
Powering Up the Drive
Review the following checklist before turning the power on.
Item to Check Description
Power supply voltage
Ensure the power supply voltage is correct:
200 V class: single-phase 200 to 240 Vac 50/60 Hz
200 V class: 3-phase 200 to 240 Vac 50/60 Hz
400 V class: 3-phase 380 to 480 Vac 50/60 Hz
Properly wire the power supply input terminals (R/L1, S/L2, T/L3).
(for single-phase 200 V class models, wire only R/L1 and S/L2)
Check for proper grounding of drive and motor.
Drive output terminals
and motor terminals
Properly wire drive output terminals U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3 with motor terminals U, V, and W.
Control circuit terminals Check control circuit terminal connections.
Drive control terminal status Open all control circuit terminals (off).
Status of the load
and connected machinery
Uncouple the motor from the load.
n
Status Display
When the power supply to the drive is turned on, the LED operator lights will appear as follows:
No. Name Description
Normal
Operation
The data display area displays the frequency reference. is lit.
Fault
Main circuit low voltage (ex)
Data displayed varies by the type of fault. Refer to Fault Displays, Causes and Possible
Solutions on page 123 for more information and possible solution. and are lit.
u
V/f Pattern Setting
Setting the V/f pattern according to the application. Refer to E: Motor Parameters on page 86 for details on setting the
V/f pattern.
n
Notes when Setting the V/f Pattern
Set the maximum output frequency to match the motor characteristics.
If the V/f pattern voltage is increased motor torque may also increase. However, if the V/f voltage is set too high these
problems may occur:
• Excessive motor current.
• Motor overheat or vibration.
4.5 Powering Up the Drive
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
63
4
Start-Up Programming
& Operation
Page 66

4.6 No-Load Operation Test Run
u
No-Load Operation Test Run
This section explains how to operate the drive with the motor uncoupled from the load during a test run.
n
Before Starting the Motor
Check the following items before operation:
• Ensure the area around the motor is safe.
• Ensure external emergency stop circuitry is working properly and other safety precautions have been taken.
n
During Operation
Check the following items during operation:
• The motor should rotate smoothly (i.e., no abnormal noise or oscillation).
• The motor should accelerate and decelerate smoothly.
n
No-Load Operation Instructions
The following example illustrates a test run procedure using the digital operator.
Note: Before starting the motor, set the frequency reference d1-01 to 6 Hz.
Step Display/Result
1. Turn on the power to the drive. The initial display appears.
2.
Press the key to select LOCAL. The LO/RE LED will turn on.
STOP
3.
Press to give the drive a Run command. RUN will light and the motor will rotate
at 6 Hz.
STOP
Off On
4. Ensure the motor is rotating in the correct direction and no faults or alarms occur.
Motor
Forward
5.
If there is no error in step 4, press to increase the frequency reference. Increase
the frequency in 10 Hz increments verifying smooth operation results at all speeds. For
each frequency, monitor the drive output current (U1-03) through the LED operator to
confirm the current is well below the motor rated current. Example: 6 Hz → 50 Hz.
6.
The drive should operate normally. Press
STOP
to stop the motor. RUN flashes until
the motor comes to a complete stop.
STOP
Flashing Off
4.6 No-Load Operation Test Run
64
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 67

4.7 Test Run with Load Connected
u
Test Run with the Load Connected
After performing a no-load test run connect the motor and proceed to run the motor and load together.
n
Notes on Connected Machinery
• Clear the area around the motor.
• The motor should come to a complete stop without problems.
• Connect the machinery.
• Fasten all installation screws properly. Check that the motor and connected machinery are held in place.
• Confirm that the Fast-stop circuit or mechanical safety measures operate correctly.
• Be ready to press the STOP button in case of emergency.
n
Checklist Before Operation
• The motor should rotate in the proper direction.
• The motor should accelerate and decelerate smoothly.
n
Operating the Motor under Loaded Conditions
Test run the application similarly to the no-load test procedure when connecting the machinery to the motor.
• Check monitor parameter U1-03 to ensure there is no overcurrent.
• If the application permits running the load in the reverse direction, try changing motor direction and the frequency
reference while watching for abnormal motor oscillation or vibration.
• Correct any problems that occurs with hunting, oscillation, or other control-related issues.
4.7 Test Run with Load Connected
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
65
4
Start-Up Programming
& Operation
Page 68

4.8 Verifying and Backing Up Parameter Settings
Check changes to parameter settings using the Verify function. Refer to Verifying Parameter Changes: Verify Menu on
page 59.
Save the verified parameter settings. Change the access level or set a password to the drive to prevent accidental
modification of parameter settings.
u
Parameter Access Level: A1-01
Setting the Access Level for “Operation only” (A1-01 = 0) allows the user to access parameters A1- and U-
only. Other parameters are not displayed.
No.
Parameter
Name
Description
Setting
Range
Default
A1-01
Access Level
Selection
Selects which parameters are accessible via the digital operator.
0: Operation only ( A1-01 and A1-04 can be set and monitored. U parameters can be
monitored)
2: Advanced Access Level (All parameters can be set and monitored)
0,2 2
u
Password Settings: A1-04, A1-05
The user can set a password to the drive to restrict access. The password is selected via parameter A1-05. The selected
password must be entered in parameter A1-04 to unlock parameter access (i.e., parameter setting A1-04 must match the
value programmed into A1-05). The following parameters cannot be viewed or edited until the value programmed into
A1-04 correctly matches the value as programmed in parameter A1-05: A1-01 and A1-03.
Note:
Parameter A1-05 is hidden from view. To display A1-05, access parameter A1-04 and simultaneously depress the
key and the
key.
u
Copy Function (Optional)
Parameter settings can be copied to another drive to simplify parameter restoration or multiple drive setup. The drive
supports the following options:
n
USB/Copy Unit
The copy unit is an external option connected to the drive to copy parameter settings to another drive. It includes a USB
adapter to connect the drive to a PC.
n
CX-Drive
CX-Drive is a PC software tool for parameter management, monitoring, and diagnosis. CX-Drive can load, store, and copy
drive parameter settings. For details, refer to Help in the CX-Drive software.
4.8 Verifying and Backing Up Parameter Settings
66
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 69

4.9 Test Run Checklist
Review the checklist before performing a test run. Check each item that applies.
No. Checklist Page
1 Thoroughly read the manual before performing a test run. —
2 Turn the power on. 63
3 Set the voltage for the power supply to E1-01. 86
Check the items that correspond to the control mode being used.
WARNING! Ensure start/stop and safety circuits are wired properly and in the correct state before energizing the drive. Failure to comply
could result in death or serious injury from moving equipment. When programmed for 3-Wire control, a momentary closure on terminal
S1 may cause the drive to start.
No.
Checklist Page
4 The should illuminate after giving a run command. —
5
To give a run command and frequency reference from the LED Digital Operator, press to set to LOCAL.
The LO/RE key lights while LOCAL is displayed.
60
6
If the motor rotates in the opposite direction during the test run, switch two of the drive output terminals (U/
T1, V/T2, W/T3).
63
7 Select the correct duty rating (C6-01) for the application. —
8
Set the correct values for the motor rated current (E2-01) and the motor protection selection (L1-01) to ensure
motor thermal protection.
—
9
If the run command and frequency reference are provided via the control circuit terminals, set the drive for
REMOTE and be sure the LO/RE light is out.
60
10
If the control circuit terminals should supply the frequency reference, select the correct voltage input signal
level (0 to 10 V) or the correct current input signal level (4 to 20 mA or 0 to 20 mA).
60
11 Set the proper voltage to terminal A1. (0 to 10 V). 72
12 When current input is used, switch the drive built-in DIP switch S1 from the V-side (OFF) to I-side (ON). —
13
Set the minimum and maximum frequency references to the desired values. Make the following adjustments
if the drive does not operate as expected:
Gain adjustment: Set the maximum voltage/current signal and adjust the analog input gain (H3-03) until the
frequency reference value reaches the desired value.
Bias adjustment: Set the minimum voltage/current signal and adjust the analog input bias (H3-04) until the
frequency reference value reaches the desired minimum value.
—
4.9 Test Run Checklist
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
67
4
Start-Up Programming
& Operation
Page 70

4.9 Test Run Checklist
This Page Intentionally Blank
68
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 71

Parameter Details
5.1 A: INITIALIZATION...........................................................................................70
5.2 B: APPLICATION..............................................................................................72
5.3 C: TUNING........................................................................................................77
5.4 D: REFERENCE SETTINGS.............................................................................82
5.5 E: MOTOR PARAMETERS...............................................................................86
5.6 H: TERMINAL FUNCTIONS..............................................................................90
5.7 L: PROTECTION FUNCTIONS.......................................................................102
5.8 N: SPECIAL ADJUSTMENTS.........................................................................111
5.9 O: OPERATOR RELATED SETTINGS...........................................................112
5.10 U: MONITOR PARAMETERS.........................................................................116
5
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
69
Page 72

5.1 A: Initialization
The initialization group contains parameters associated with initial setup of the drive. Parameters involving the display
language, access levels, initialization, and password are located in this group.
u
A1: Initialization
n
A1-01: Parameter Access Level
Allows or restricts access to drive parameters.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
A1-01 Access Level Selection 0, 2 2
Setting 0: Operation Only
Access is restricted to parameters A1-01, A1-04, and all U monitor parameters.
Setting 2: Advanced Access Level (A) and Setup Access Level (S)
All parameters can be viewed and edited.
Notes on Parameter Access
• If the drive parameters are password protected by A1-04 and A1-05, parameters A1-01 and A1-03 cannot be modified.
• If parameters are changed via serial communication the parameters can not be changed from the digital operator until
an Enter command is received from the serial communication.
n
A1-03: Initialization
Resets parameter settings back to their original default values. After the initialization the parameter automatically returns
to 0.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
A1-03 Initialize Parameters 0, 2220, 3330 0
Setting 0: No Initialize
No initialization.
Setting 2220: 2-Wire Initialization
Resets all parameters back to their original default settings with digital inputs S1 and S2 configured as forward run and
reverse run, respectively.
Setting 3330: 3-Wire Initialization
The drive parameters are returned to factory default values with digital inputs S1, S2, and S5 configured as run, stop, and
forward/reverse respectively.
Notes on Parameter Initialization
The parameters shown in Table 5.1 will not be reset when the drive is initialized by setting A1-03 = 2220 or 3330.
Table 5.1 Parameters not Changed by Drive Initialization
No. Parameter Name
C6-01 Duty Selection
E1-03 V/f Pattern Selection
o2-04 Drive/kVA Selection
L8-35 Installation Selection
n
A1-04, A1-05: Password and Password Setting
A1-04 is for entering the password when the drive is locked. A1-05 is a hidden parameter used to set the password.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
A1-04 Password
0 to 9999 0
A1-05 Password Setting
How to use the Password
The user can set a password for the drive to restrict access. The password is set to A1-05 and must be entered to A1-04 to
unlock parameter access. Until the correct password is entered, the following parameters cannot be viewed or edited: A1-01
and A1-03.
The instructions below demonstrate how to set a new password. Here, the password set is “1234”. An explanation follows
on how to enter the password to unlock the parameters.
5.1
A: Initialization
70
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 73

Table 5.2 Setting the Password for Parameter Lock
Step Display/Result
1. Turn on the power to the drive. The initial display appears.
2.
Scroll to the Parameter Setup display and press .
3.
Scroll to the right by pressing .
4.
Select the flashing digits by pressing .
5.
Select A1-04 by pressing .
6.
Press the key while holding down at the same time. A1-05 will appear.
Note: A1-05 is normally hidden, but can be displayed by following the directions listed
here.
“05” flashes
7.
Press the key.
8.
Use , and to enter the password.
9.
Press to save what was entered.
10. The display automatically returns to the display shown in step 5.
Table 5.3 Check to see if A1-01 is locked (continuing from step 10 above)
Step Display/Result
1.
Press to display A1-01.
“01” flashes
2.
Press to display the value set to A1-01.
3.
Press and , making sure that the setting values cannot be changed.
4.
Press to return to the first display.
Table 5.4 Enter the Password to Unlock Parameters (continuing from step 4 above)
Step Display/Result
1.
Press to enter the parameter setup display.
2.
Press to select the flashing digits as shown.
“01” flashes
3.
Press to scroll to A1-04.
4. Enter the password “1234”.
5.
Press to save the new password.
6. Drive returns to the parameter display.
7.
Press and scroll to A1-01.
8.
Press to display the value set to A1-01. If the first "0" blinks, parameter settings
are unlocked.
9.
Use and to change the value if desired. This is not typical.
10.
Press to save the setting, or to return to the previous display without saving
changes.
11. The display automatically returns to the parameter display.
Note: Parameter settings can be edited after entering the correct password. Performing a 2-Wire or 3-Wire initialization resets the password to
“0000”. Reenter the password to parameter A1-05 after drive initialization.
5.1
A: Initialization
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
71
5
Parameter Details
Page 74

5.2 b: Application
Application parameters configure the source of the frequency reference, the Run command, DC Injection Braking, and
other application-related settings.
u
b1: Mode of Operation
n
b1-01: Frequency Reference Selection
Use parameter b1-01 to select the frequency reference source for the REMOTE mode.
Note: 1. If a Run command is input to the drive but the frequency reference entered is 0 or below the minimum frequency, the RUN indicator
LED on the digital operator will light and the STOP indicator will flash.
2. Press the LO/RE key to set the drive to LOCAL and use the operator keypad to enter the frequency reference.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
b1-01 Frequency Reference Selection 0 to 3 1
Setting 0: Operator Keypad
Using this setting, the frequency reference can be input by:
•
Switching between the multi-speed references in the d1- parameters.
• Entering the frequency reference on the operator keypad.
Setting 1: Terminals (Analog Input Terminals)
Using this setting, an analog frequency reference can be entered from terminal A1 using a 0 to 10 Vdc or a 0/4 to 20 mA
signal.
Note: The input signal type must be set up by setting DIP switch S1 and adjusting parameter H3-01. Refer to H3-01: Terminal A1 Signal Level
Selection on page 98.
Using a 0 to 10 Vdc Voltage Input Signal:
Use a circuit such as the one shown in Figure 5.1 or an external 0 to 10 Vdc voltage source like a PLC analog output and
set the input level selection for A1 in parameter H3-01 as desired. Refer to H3-01: Terminal A1 Signal Level Selection
on page 98 .
Figure 5.1 Setting the Frequency Reference by Voltage Input
Using a 0/4 to 20 mA Current Input Signal:
Connect input A1 to an external current source such as the one shown in Figure 5.2. Make sure that switch S1 is set to
“I” and set the appropriate signal level by entering 2 (4 to 20 mA) or 3 (0 to 20 mA) into parameter H3-01.
5.2
b: Application
72
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 75

Figure 5.2 Setting the Frequency Reference by Current Input
Setting 2: MEMOBUS/Modbus Communications
Using this setting, the frequency reference can be entered via RS-422/485 serial communications using the MEMOBUS/
Modbus protocol by using an optional SI-485/J Interface for MEMOBUS communication. Refer to Peripheral Devices
& Options on page 147. For details about the MEMOBUS/Modbus protocol, Refer to MEMOBUS/Modbus
Communications on page 185.
Note: If the frequency reference source is set for MEMOBUS/Modbus but a communication interface option is not installed, an oPE05
Programming Error will be displayed on the digital operator and the RUN command will not be accepted.
Setting 3: Potentiometer Option
Using this setting, the frequency reference can be set by a potentiometer mounted at the drive using an AI-V3/J
Potentiometer option unit. Refer to Peripheral Devices & Options on page 147 and the option unit documentation.
Note: If the frequency reference source is set for the potentiometer option (b1-01 = 3) but an option board is not installed, an oPE05 Programming
Error will be displayed on the digital operator and the RUN command will not be accepted.
n
b1-02: Run Command Selection
Parameter b1-02 determines the Run and Stop command source in the REMOTE mode.
WARNING! Sudden Movement Hazard. Clear personnel, secure equipment, and check sequence and safety circuitry before starting
the drive. Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury from moving equipment.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
b1-02 Run Command Selection 0 to 2 1
Setting 0: Operator
Using this setting, the RUN and STOP keys on the operator keypad will start and stop the motor. The LED in the LO/RE
key will be on to indicate that the Run command is assigned to the operator. The example below shows how the drive can
be operated if b1-02 is set to 0.
Step Display/Result
1. Turn on the power to the drive. The initial display appears.
2. Set the frequency reference to F6.00 (6 Hz).
3.
Press the key to start the motor. The RUN indicator LED will light and the motor
will begin rotating at 6 Hz.
STOP
off on
4.
Press the key to stop the motor. The RUN light will flash until the motor comes
to a complete stop.
flashing
off
Setting 1: Control Circuit Terminal
This setting requires that the Run and Stop commands are entered from the digital input terminals. The following sequences
can be used:
5.2
b: Application
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
73
5
Parameter Details
Page 76

• 2-Wire sequence:
Two inputs (FWD/Stop-REV/Stop). Initializing the drive by setting A1-01 = 2220, presets the terminals S1 and S2 to
these functions. This is the default setting of the drive. Refer to Setting 40/41: Forward Run/Reverse Run Command
for 2-Wire Sequence on page 94.
• 3-Wire sequence:
Inputs S1, S2, S5 (Start-Stop-FWD/REV). Initialize the drive by setting A1-01 = 3330 presets the terminals S1, S2 and
S5 to these functions. Refer to Setting 0: 3-Wire Sequence on page 90.
Setting 2: MEMOBUS/Modbus Communications
Using this setting, the Run command can be entered via RS-422/485 serial communications using the MEMOBUS/Modbus
protocol and the optional SI-485/J Interface for MEMOBUS/Modbus communication. Refer to Peripheral Devices &
Options on page 147. For details about the MEMOBUS/Modbus protocol, Refer to MEMOBUS/Modbus
Communications on page 185.
n
b1-03: Stopping Method Selection
Select how the drive stops the motor when a Stop command is entered or when the Run command is removed.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
b1-03 Stopping Method Selection 0, 1 0
Setting 0: Ramp to Stop
When a Stop command is issued or the Run command is removed, the drive will decelerate the motor to stop. The
deceleration rate is determined by the active deceleration time. The default deceleration time is set to parameter C1-02.
DC Injection braking can be applied at the end of the ramp in order to completely stop high inertia loads. Refer to b2:
DC Injection Braking on page 76 for details.
Run Command
Decelerates according to the
specified deceleration time
Minimum Output Freq.
(E1-09)
DC Injection
Current (b2-02)
DC Braking
T
ime at Stop (b2-04)
Decel Time
(C1-02, etc.)
Output Frequency
DC Injection Braking
ON OFF
Figure 5.3 Ramp to Stop
Setting 1: Coast to Stop
When a Stop command is issued or the Run command is removed, the drive will shut off its output and the motor will
coast (uncontrolled deceleration) to stop where the stopping time is determined by the inertia and the friction in the driven
system.
Drive output frequency is shut off
Run
Command
Output
Frequency
Motor rpm
ON OFF
Figure 5.4 Coast to Stop
Note: After a stop is initiated, any subsequent Run command that is entered will be ignored for a certain time. Do not attempt to start the motor
again until it has come to a complete stop. To start the motor before it has stopped completely, use DC Injection at start (Refer to b2-03:
DC Injection Braking Time at Start on page 76).
5.2
b: Application
74
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 77

n
b1-04: Reverse Operation Selection
For some applications, reverse motor rotation is not appropriate and may even cause problems (e.g., air handling units,
pumps, etc.). Setting parameter b1-04 to 1 instructs the drive to ignore any Reverse run commands.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
b1-04 Reverse Operation Selection 0 or 1 0
Setting 0: Reverse Operation Enabled
Possible to operate the motor in both forward and reverse directions.
Setting 1: Reverse Operation Disabled
Drive disregards a Reverse run command or a negative frequency reference.
n
b1-07: LOCAL/REMOTE Run Selection
The drive has the following three separate control sources that can be switched using digital inputs or the LO/RE key on
the digital operator (for details Refer to Setting 1: LOCAL/REMOTE Selection on page 91 and Refer to Setting 2:
Serial Communication Reference Selection on page 91):
• LOCAL - The digital operator is used to set the reference and the Run command.
• REMOTE - The settings of b1-01 and b1-02 determine where the frequency reference and Run command are input from.
• Serial Communications by MEMOBUS/Modbus.
When switching from LOCAL to REMOTE, or to serial communication , the Run command may already be present at
the location the source was switched to. Parameter b1-07 can be used to determine how the Run command is treated in
this case.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
b1-07 LOCAL/REMOTE Run Selection 0 or 1 0
Setting 0: Run Command Must Be Cycled
If the Run command is issued differently in the old and new control source (e.g. old - terminals, new - serial
communications) and it is active at the new source when switching takes place, the drive will either not start or it will stop
if it was running before. The Run command has to be cycled to start from the new control source.
Setting 1: Continue Running
If the Run command is active at the new control source, the drive starts or continues running. There is no need to cycle
the Run command.
WARNING! The drive may start unexpectedly if switching control sources when b1-07 = 1. Clear all personnel away from rotating
machinery and electrical connections prior to switching control sources. Failure to comply may cause death or serious injury.
n
b1-08: Run Command Selection while in Programming Mode
As a safety precaution, the drive will not normally respond to a Run input when the digital operator is being used to adjust
parameters in the Programming Mode (Verify Menu, Setup Mode, Parameter Settings Mode). If required by the application
b1-08 can be used to changed this functionality.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
b1-08 Run Command Selection while in Programming Mode 0 to 2 0
Setting 0: Disabled
A Run command is not accepted while the digital operator is in Programming Mode.
Setting 1: Enabled
A Run command is accepted in any digital operator mode.
Setting 2: Prohibit Programming During Run
It is not possible to enter the Programming Mode as long as the drive output is active.
n
b1-14: Phase Order Selection
Sets the phase order for drive output terminals U/T1, V/T2, and W/T3.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
b1-14 Phase Order Selection 0 or 1 0
Setting 0: Standard Phase Order
Setting 1: Switched Phase Order
5.2
b: Application
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
75
5
Parameter Details
Page 78
n
b1-17: Run Command at Power Up
This parameter is used to determine whether an external Run command that is active during power up of the drive will
start the drive or not.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
b1-17 Run Command at Power Up 0 or 1 0
Setting 0: Run Command at Power Up is not Issued
The Run command has to be cycled to start the drive.
Note: For safety reasons, the drive is initially set up not to accept a Run command at power up (b1-17 = "0"). If a Run command is issued at
power up, the RUN indicator LED will flash quickly. Change parameter b1-17 to 1 if a Run command active at power up shall be accepted
by the drive.
Setting 1: Run Command and Power Up is Issued
An external Run command active during power up is issued and the drive starts to operate the motor as soon as it gets
ready for operation (i.e. once the internal start up process is complete).
WARNING! Sudden Movement Hazard. If b1-17 is set to 1 and an external Run command is active during power up, the motor will
begin rotating as soon as the power is switched on. Proper precautions must be taken to ensure that the area around the motor is safe
prior to powering up the drive. Failure to comply may cause serious injury.
u
b2: DC Injection Braking
These parameters determine how the DC Injection Braking feature operates. Parameters involving the starting frequency,
current level, braking time are located here.
n
b2-02: DC Injection Braking Current
Sets the DC Injection Braking current as a percentage of the drive rated current. If set to larger than 50%, the carrier
frequency is automatically reduced to 1 kHz.
No. Name Setting Range Default
b2-02 DC Injection Braking Current 0 to 75% 50%
The level of DC Injection Braking current affects the strength of the magnetic field attempting to lock the motor shaft.
Increasing the current level will increase the amount of heat generated by the motor windings. This parameter should only
be increased to the level necessary to hold the motor shaft.
n
b2-03: DC Injection Braking Time at Start
Sets the time of DC Injection Braking at start. It can be used to stop a coasting motor before restarting it or to apply a
braking torque at start. Disabled when set to 0.00 s.
No. Name Setting Range Default
b2-03 DC Injection Braking Time at Start 0.00 to 10.00 s 0.00 s
Note: Before starting an uncontrolled rotating motor (e.g. a fan motor driven by windmill effect), use DC Injection to stop the motor before
starting it. Otherwise motor stalling and other faults can occur.
n
b2-04: DC Injection Braking Time at Stop
When the output frequency falls below the minimum output frequency setting E1-09, the drive applies DC injection for
the time set in b2-04. Used to completely stop a motor with high inertia load after ramp down. Increase the setting if the
motor tends to coast by inertia after a stop.
No. Name Setting Range Default
b2-04 DC Injection Braking Time at Stop 0.00 to 10.00 s 0.50 s
5.2 b: Application
76
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 79

5.3 C: Tuning
C parameters are used to set the acceleration and deceleration characteristics, as well as S-curves. Other parameters in this
group cover settings for slip compensation, torque compensation, and carrier frequency.
u
C1: Acceleration and Deceleration Times
n
C1-01 to C1-04: Accel/Decel Times 1 and 2
Two sets of acceleration and deceleration times can be set in the drive. They can be selected by a digital input. Acceleration
time parameters always set the time to accelerate from 0 to the maximum output frequency (E1-04). Deceleration time
parameters always set the time to decelerate from maximum output frequency to 0. C1-01 and C1-02 are the default active
accel/decel settings.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
C1-01 Acceleration Time 1
0.0 to 6000.0 s 10.0 s
C1-02 Deceleration Time 1
C1-03 Acceleration Time 2
C1-04 Deceleration Time 2
Switching Acceleration Times by Digital Input
Accel/decel times 1 are active by default if no input is set. The accel/decel time 2 can be activated by a digital input (H1= 7) as explained in Table 5.5.
Table 5.5 Accel/Decel Time Selection by Digital Input
Accel/Decel Time Sel. H1- = 7
Active Times
Acceleration Deceleration
0 C1-01 C1-02
1 C1-03 C1-04
Figure 5.5 shows an operation example for changing accel/decel. times. The example below requires that the stopping
method be set for "Ramp to Stop" (b1-03 = 0).
Output
frequency
Accel Time 1
(C1-01)
Decel Time 1
(C1-02)
Accel Time 2
(C1-03)
Decel Time 2
(C1-04)
Decel Time 1
(C1-02)
FWD (REV)
Run command
ON
OFF
ON
ON
Accel/Decel Time Selection
(Digital Input H1-0x = “7”)
Figure 5.5 Timing Diagram of Accel/Decel Time Change
n
C1-09: Fast-stop Time
Parameter C1-09 will set a special deceleration that is used when certain faults occur or that can be operated by closing a
digital input configured as H1- = 15 (N.O. input) or H1- = 17 (N.C. input). The input does not have to be closed
continuously, even a momentary closure will trigger the Fast-stop operation.
Unlike standard deceleration, once the Fast-stop operation is initiated, the drive cannot be restarted until the deceleration
is complete, the Fast-stop input is cleared, and the Run command is cycled.
A digital output programmed for “During Fast-stop” (H2-01/02/03 = 4C) will be closed as long as Fast-stop is active.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
C1-09 Fast-stop Time 0.0 to 6000.0 s 10.0 s
NOTICE: Rapid deceleration can trigger an overvoltage fault. When faulted, the drive output shuts off, and the motor coasts. To avoid
this uncontrolled motor state and to ensure that the motor stops quickly and safely, set an appropriate Fast-stop time to C1-09.
u
C2: S-Curve Characteristics
Use S-curve characteristics to smooth acceleration and deceleration and to minimize abrupt shock to the load.
5.3
C: Tuning
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
77
5
Parameter Details
Page 80

n
C2-01 to C2-04: S-Curve Characteristics
C2-01 through C2-04 set separate S-curves for each section of the acceleration or deceleration.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
C2-01 S-Curve Characteristic at Accel Start
0.00 to 10.00 s
0.20 s
C2-02 S-Curve Characteristic at Accel End 0.20 s
C2-03 S-Curve Characteristic at Decel Start 0.20 s
C2-04 S-Curve Characteristic at Decel End 0.00 s
Figure 5.6 explains how S-curves are applied.
C2-02
C2-01
C2-03
C2-04
C2-02
C2-01
C2-03
C2-04
FWD run
REV run
Output
frequency
Figure 5.6 S-Curve Timing Diagram - FWD/REV Operation
Setting the S-curve will increase the acceleration and deceleration times.
Actual accel time = accel time setting + (C2-01 + C2-02)/2
Actual decel time = decel time setting + (C2-03 + C2-04)/2
u
C3: Slip Compensation
The Slip Compensation function prevents motor speed loss due to an increase in load.
Note: Before making changes to the Slip Compensation parameters, make sure the motor parameters and V/f pattern are set properly.
n
C3-01: Slip Compensation Gain
This parameter sets the gain for the motor slip compensation function. Although this parameter rarely needs to be changed,
adjustments might be needed under the following situations:
• If the speed at constant frequency reference is lower than the frequency reference, increase C3-01.
• If the speed at constant frequency reference is higher than the frequency reference, decrease C3-01.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
C3-01 Slip Compensation Gain 0.0 to 2.5 0.0
n
C3-02: Slip Compensation Primary Delay Time
Adjusts the filter on the output of the slip compensation function. Although this parameter rarely needs to be changed,
adjustments might be needed under the following situations:
• Decrease the setting when the slip compensation response is too slow.
• Increase this setting when the speed is not stable.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
C3-02 Slip Compensation Primary Delay Time 0 to 10000 ms 2000 ms
u
C4: Torque Compensation
The torque compensation function compensates for insufficient torque production at start-up or when a load is applied.
Note: Before making changes to the torque compensation gain make sure the motor parameters and V/f pattern are set properly.
n
C4-01: Torque Compensation Gain
Sets the gain for the torque compensation function.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
C4-01 Torque Compensation Gain 0.00 to 2.50 1.00
5.3 C: Tuning
78
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 81

The drive calculates the motor primary voltage loss using the output current and the terminal resistance value (E2-05) and
then adjusts the output voltage to compensate insufficient torque at start or when load is applied. The effect of this voltage
compensation can be increased or decreased using parameter C4-01.
Adjustment
Although this parameter rarely needs to be adjusted, small changes in increments of 0.05 may help in the following
situations:
• Increase this setting when using a long motor cable.
• Decrease this setting when motor oscillation occurs.
Adjust C4-01 so that the output current does not exceed the drive rated current.
u
C6: Carrier Frequency
n
C6-01: Drive Duty Mode Selection
The drive has two different duty modes from which to select based on the load characteristics. The drive rated current,
overload capacity , and carrier frequency will change depending upon the duty mode selection. Use parameter C6-01 (Duty
Cycle) to select Heavy Duty (HD) or Normal Duty (ND) for the application. The default setting is ND. Refer to
Specifications on page 161 for details about the rated current.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
C6-01 Duty Mode Selection 0 or 1 0
Table 5.6 Differences between Heavy and Normal Duty
Mode Heavy Duty Rating (HD) Normal Duty Rating (ND)
C6-01 0 1
Characteristics
100 %
100 %
0 Motor Speed
Rated Load
Overload
150 %
Motor Speed
0
100 %
100 %
120 %
Rated Load
Overload
Application
Use Heavy Duty Rating for applications requiring a high
overload tolerance with constant load torque. Such
applications include extruders and conveyors.
Use Normal Duty Rating for applications in which the torque
requirements drop along with the speed. Examples include
fans or pumps where a high overload tolerance is not
required.
Over load capability (oL2) 150% of drive rated Heavy Duty current for 60 s 120% of drive rated Normal Duty current for 60 s
L3-02 Stall Prevention
during Acceleration
150% 120%
L3-06 Stall Prevention
during Run
150% 120%
Default Carrier Frequency 8/10 kHz 2 kHz Swing PWM
Note:
By changing the Duty Mode the drive maximum applicable motor power changes and the E2-parameters are automatically set to
appropriate values.
n
C6-02: Carrier Frequency Selection
Parameter C6-02 sets the switching frequency of the drive’s output transistors. It can be changed in order to reduce audible
noise and also reduce leakage current.
Note: The drive rated current is reduced when the carrier frequency is set higher than the default value. Refer to Rated Current Depending on
Carrier Frequency on page 80.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
C6-02 Carrier Frequency Selection 1 to 7, F
Determined by o2-04.
Reset when C6-01 is changed.
Settings:
C6-02 Carrier Frequency C6-02 Carrier Frequency
1 2.0 kHz 5 12.5 kHz
2 5.0 kHz 6 15.0 kHz
3 8.0 kHz 7 Swing PWM
4 10.0 kHz F User defined (C6-03 to C6-05)
Note: Swing PWM uses 2.0 kHz carrier frequency as a base but by applying special PWM patterns the audible noise of the motor is kept low.
Guidelines for Carrier Frequency Parameter Setup
5.3
C: Tuning
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
79
5
Parameter Details
Page 82

Symptom Remedy
Speed and torque are unstable at low speeds.
Lower the carrier frequency.
Noise from the drive is affecting peripheral devices.
Excessive leakage current from the drive.
Wiring between the drive and motor is too long.
<1>
Audible motor noise is too loud.
Increase the carrier frequency or use Swing PWM.
<2>
<1> The carrier frequency may need to be lowered if the motor cable is too long. Refer to the table below.
<2> In Normal Duty default setting is 7 (Swing PWM), equivalent to setting 2 kHz. Increasing the carrier frequency is fine when using the drive
is set for Normal Duty, but remember that the drive rated current falls when the carrier frequency is increased.
Wiring Distance Up to 50 m Up to 100 m Greater than 100 m
C6-02 (Carrier Frequency Selection) 1 to F (15 kHz) 1, 2 (5 kHz), 7 1 (2 kHz), 7
n
C6-03/C6-04/C6-05: Carrier Frequency Upper Limit/Lower Limit/Proportional Gain
Use these parameters to set a user defined or a variable carrier frequency. To set the upper and lower limits, first set C6-02
to “F”.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
C6-03 Carrier Frequency Upper Limit 1.0 to 15.0 kHz
<1>
C6-04 Carrier Frequency Lower Limit 1.0 to 15.0 kHz
C6-05 Carrier Frequency Proportional Gain 0 to 99
<1> The default value is determined by the drive capacity (o2-04), and is reinitialized when the value set to C6-01 is changed.
Setting a Fixed User Defined Carrier Frequency
A carrier frequency between the fixed selectable values can be entered in parameter C6-03 when C6-02 is set to “F”.
Parameter C6-04 must also be adjusted to the same value as C6-03.
Setting a Variable Carrier Frequency
The carrier frequency can be set up to change linearly with the output frequency. In this case the upper and lower limits
for the carrier frequency and the carrier frequency proportional gain (C6-03, C6-04, C6-05) have to be set as shown in
Figure 5.7.
C6-03
C6-04
E1-04
x C6-05 x K*
Output Frequency
Output
Frequency
Max Output Frequency
Carrier Frequency
Figure 5.7 Carrier Frequency Changes Relative to Output Frequency
K is a coefficient determined by the value of C6-03:
• 10.0 kHz > C6-03 ≥ to 5.0 kHz: K = 2
• 5.0 kHz > C6-03: K = 1
• C6-03 ≥ 10.0 kHz: K = 3
Note: 1. A carrier frequency error (oPE11) will occur when the carrier frequency proportional gain is greater than 6 while C6-03 is less than
C6-04.
2. When C6-05 is set lower than 7, C6-04 is disabled and the carrier frequency will be fixed to the value set in C6-03.
n
Rated Current Depending on Carrier Frequency
The tables below show the drive output current depending on the carrier frequency settings. The 2 kHz value is equal to
the Normal Duty rated current, the 8/10 kHz value is equal to the Heavy Duty rated current. The carrier frequency
determines the output current linearly. Use the data below to calculate output current values for carrier frequencies not
listed in the tables.
Note: In Heavy Duty mode the maximum rated output current is equal to the 8/10 kHz value, even if the carrier frequency is reduced.
Table 5.7 Drives with Heavy Duty Default Carrier Frequency of 10 kHz
200 V Single Phase Units 200 V Three Phase Units
Model JZA
Rated Current [A]
Model JZA
Rated Current [A]
2 kHz 10 kHz 15 kHz 2 kHz 10 kHz 15 kHz
B0P1 1.2 0.8 0.6 20P1 1.2 0.8 0.6
B0P2 1.9 1.6 1.3 20P2 1.9 1.6 1.3
B0P4 3.5 3.0 2.4 20P4 3.5 3.0 2.4
5.3 C: Tuning
80
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 83

200 V Single Phase Units 200 V Three Phase Units
Model JZA
Rated Current [A]
Model JZA
Rated Current [A]
2 kHz 10 kHz 15 kHz 2 kHz 10 kHz 15 kHz
B0P7 6.0 5.0 4.0 20P7 6.0 5.0 4.0
Table 5.8 Drives with Heavy Duty Default Carrier Frequency of 8 kHz
200 V Single Phase Units 200 V Three Phase Units 400 V Three Phase Units
Model
JZA
Rated Current [A]
Model
JZA
Rated Current [A]
Model
JZA
Rated Current [A]
2 kHz 8 kHz 15 kHz 2 kHz 8 kHz 15 kHz 2 kHz 8 kHz 15 kHz
B1P5 9.6 8.0 6.4 — — — — 40P2 1.2 1.2 0.7
— — — — 21P5 9.6 8.0 6.4 40P4 2.1 1.8 1.1
— — — — 22P2 12.0 11.0 8.8 40P7 4.1 3.4 2.0
— — — — — — — — 41P5 5.4 4.8 2.9
— — — — 24P0 19.6 17.5 14.0 42P2 6.9 5.5 3.3
— — — — — — — — 43P0 8.8 7.2 4.3
— — — —
— — — —
44P0 11.1 9.2 5.5
5.3 C: Tuning
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
81
5
Parameter Details
Page 84

5.4 d: Reference Settings
The drive offers various ways of entering the frequency reference. The figure below gives an overview of the reference
input, selections, and priorities.
MS 2
MS 3
MS 4
MS 7
MS 8
Jog
d1-03
d1-04
d1-07
d1-08
d1-17
d1-02
REMOTE
LOCAL
MS 1
0
1
ComRef
=3
=2
=1
=0
0
1
Digital Input
H1- = 2
MEMOBUS comm.
d1-01
(Freq.Ref 1)
b1-01
(Freq. Reference Source 1)
Option Card
Digital Input (H1-)
Jog Reference (=6)
Frequency
Reference
2 through 8
Jog Frequency
Multi-Step Speed
Terminal A1
Frequency
Reference
Figure 5.8 Frequency Reference Setting Hierarchy
u
d1: Frequency Reference
n
d1-01 to d1-08, d1-17: Frequency Reference 1 to 8 and Jog Reference
Up to 9 preset references (including Jog reference) can be programmed in the drive. The references can be switched during
Run by digital inputs. The acceleration/deceleration to the new reference is performed using the active acceleration/
deceleration time.
The Jog frequency must be selected by a separate digital input and has priority over the references 1 to 8.
Multi-speed reference 1 can be provided by analog input A1.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
d1-01 to d1-08 Frequency Reference 1 to 8
0.00 to 400.00 Hz
<1>
0.00 Hz
d1-17 Jog Frequency Reference
0.00 to 400.00 Hz
<1>
6.00 Hz
<1> The upper limit is determined by the maximum output frequency (E1-04) and upper limit for the frequency reference (d2-01).
Multi-Step Speed Selection
Depending on how many speeds are used, some digital inputs have to be programmed for Multi-Step Speed Selection 1,
2, 3 and 4 (H1- = 3, 4, 5). For the Jog reference a digital input must be set to H1- = 6.
Notes on using analog inputs as multi-speed 1 and 2:
• If the frequency reference source is assigned to analog input A1 (b1-01 = 1), then this input will be used for Frequency
Reference 1 instead of d1-01. If the reference source is assigned to the digital operator (b1-01 = 0), then d1-01 will be
used as Frequency Reference 1.
The different speed references can be selected as shown in Table 5.9. Figure 5.9 illustrates the multi-step speed selection.
Table 5.9 Multi-Step Speed Reference and Terminal Switch Combinations
Reference
Multi-Step
Speed
H1- = 3
Multi-Step
Speed 2
H1- = 4
Multi-Step
Speed 3
H1- = 5
Jog Reference
H1- = 6
Frequency Reference 1 (d1-01/A1) OFF OFF OFF OFF
Frequency Reference 2 (d1-02) ON OFF OFF OFF
Frequency Reference 3 (d1-03) OFF ON OFF OFF
Frequency Reference 4 (d1-04) ON ON OFF OFF
Frequency Reference 5 (d1-05) OFF OFF ON OFF
Frequency Reference 6 (d1-06) ON OFF ON OFF
Frequency Reference 7 (d1-07) OFF ON ON OFF
5.4 d: Reference Settings
82
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 85

Reference
Multi-Step
Speed
H1- = 3
Multi-Step
Speed 2
H1- = 4
Multi-Step
Speed 3
H1- = 5
Jog Reference
H1- = 6
Frequency Reference 8 (d1-08) ON ON ON OFF
Jog Frequency Reference (d1-17)
<1>
− − − ON
<1> The Jog frequency overrides the frequency reference being used.
d1-04
d1-01
d1-02
d1-03
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
d1-05
d1-06
d1-07
d1-08
d1-17
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
Frequency
reference
Time
Multi-step Speed Ref. 1
Multi-step Speed Ref. 2
Multi-step Speed Ref. 3
Jog Reference
FWD (REV) Run/Stop
(A1)
Figure 5.9 Preset Reference Timing Diagram
u
d2: Frequency Upper/Lower Limits
By entering upper or lower frequency limits, the drive programmer can prevent operation of the drive above or below
levels that may cause resonance and or equipment damage.
n
d2-01: Frequency Reference Upper Limit
Sets the maximum frequency reference as a percentage of the maximum output frequency. This limit applies to all frequency
references.
Even if the frequency reference is set to a higher value, the drive internal frequency reference will not exceed this value.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
d2-01 Frequency Reference Upper Limit 0.0 to 110.0% 100.0%
n
d2-02: Frequency Reference Lower Limit
Sets the minimum frequency reference as a percentage of the maximum output frequency. This limit applies to all frequency
references.
If a lower reference than this value is input, the drive will run at the d2-02 level. If the drive is started with a lower reference
than d2-02, it will accelerate up to d2-02.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
d2-02 Frequency Reference Lower Limit 0.0 to 110.0% 0.0%
Internal frequency
reference
d2-01
Operating
range
Frequency Reference Upper Limit
Set frequency reference
Frequency Reference Lower Limit
d2-02
Figure 5.10 Frequency Reference: Upper and Lower Limits
5.4 d: Reference Settings
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
83
5
Parameter Details
Page 86

u
d3: Jump Frequency
n
d3-01, d3-02, d3-04 : Jump Frequencies 1, 2, and Jump Frequency Width
In order to avoid continuous operation at a speed that causes resonance in driven machinery, the drive can be programmed
with three separate Jump frequencies that will not allow continued operation within specific frequency ranges. If the speed
reference falls within a Jump frequency dead band, the drive will clamp the frequency reference just below the dead band
and only accelerate past it when the frequency reference rises above the upper end of the dead band.
Setting parameters d3-01 and d3-02 to 0.0 Hz disables the Jump frequency function.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
d3-01 Jump Frequency 1 0.0 to 400.0 Hz 0.0 Hz
d3-02 Jump Frequency 2 0.0 to 400.0 Hz 0.0 Hz
d3-04 Jump Frequency Width 0.0 to 20.0 Hz 1.0 Hz
Figure 5.11 shows the relationship between the Jump frequency and the output frequency.
Output
frequency
Frequency
reference
decreases
Frequency
reference
increases
Frequency
reference
Jump Frequency 1
d3-01
Jump Frequency 2
d3-02
Jump
Frequency
Width
d3-04
Jump
Frequency
Width
d3-04
Figure 5.11 Jump Frequency Operation
Note: 1. The drive will use the active accel/decel time to pass through the specified dead band range but will not allow continuous operation
in that range.
2.
When using more than one Jump frequency, make sure that d3-01 ≥ d3-02.
u
d4: Frequency Hold Function
n
d4-01: Frequency Reference Hold Function Selection
This parameter is effective when either of the digital input functions listed below is used.
•
Accel/decel ramp hold function (H1-= A)
•
Up/Down function (H1- = 10 and 11, sets the frequency reference by digital inputs)
Parameter d4-01 determines whether the frequency reference value is saved when the Run command is cleared or the
power supply is shut down.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
d4-01 Frequency Reference Hold Function Selection 0 or 1 0
The operation depends on with what function parameter d4-01 is used.
Setting 0: Disabled
• Acceleration Hold
The hold value will be reset to 0 Hz when the Run command is canceled or the drive power is switched off. The active
frequency reference will be the value the drive uses when it restarts.
• Up/Down
5.4
d: Reference Settings
84
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 87

The frequency reference value will be reset to 0 Hz when the Run command is canceled or the drive power is switched
off. The drive will start from 0 Hz when restarted.
Setting 1: Enabled
• Acceleration Hold
The last hold value will be saved when the Run command or the drive power is switched off. The drive will use the value
that was saved as the frequency reference when it restarts. The accel/decel hold input must be enabled the entire time or
else the hold value will be cleared.
Power supply
Forward Run / Stop
Hold Accel/Decel
Frequency reference
Output frequency
d4-01 = 1
d4-01 = 0
Hold Hold
OFF
OFFOFF
OFF OFF
ON
ON ON
ON ON
ON
Figure 5.12 Frequency Reference Hold with Accel/Decel Hold Function
• Up/Down
The frequency reference value will be saved when the Run command or the drive power is switched off. The drive will
use the frequency reference that was saved when it restarts.
Clearing the Value that was Saved
Depending on which function is used, the frequency reference value that was saved can be cleared by:
• Releasing the acceleration hold input.
• Setting an Up or Down command while no Run command is active.
5.4 d: Reference Settings
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
85
5
Parameter Details
Page 88

5.5 E: Motor Parameters
E parameters cover V/f pattern and motor data settings.
u
E1: V/f Characteristics
n
E1-01: Input Voltage Setting
Set the input voltage parameter to the nominal voltage of the AC power supply. This parameter adjusts the levels of some
protective features of the drive (overvoltage, Stall Prevention, etc.).
NOTICE: Set parameter E1-01 to match the input voltage of the drive. Drive input voltage (not motor voltage) must be set in E1-01 for
the protective features of the drive to function properly. Failure to comply could result in improper drive operation.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
E1-01
<1>
Input Voltage Setting 155 to 255 V 200 V
<1> The setting range and default value shown here are for 200 V class drives. Double this for 400 V class units.
E1-01 Related Values
The input voltage setting determines the over-/undervoltage detection level and the operation levels of the braking
transistor.
Voltage Setting Value of E1-01
(Approximate Values)
ov Detection Level BTR Operation Level Uv Detection Level
200 V Class all settings 410 V 394 V
190 V
(single-phase = 160 V)
400 V Class
setting ≥ 400 V
820 V 788 V 380 V
setting < 400 V 740 V 708 V 350 V
Note: The braking transistor operation levels are valid for the drive internal braking transistor. If an external CDBR braking chopper is used,
refer to the instruction manual of that unit.
n
V/f Pattern Settings
The drive utilizes a set V/f pattern to determine the appropriate output voltage level for each relative to the frequency
reference.
V/f Pattern Setup for V/f Control
1.
Set the input voltage for the drive. Refer to E1-01: Input Voltage Setting on page 174.
2.
Set the V/f pattern. Refer to V/f Pattern Settings E1-04 to E1-10 on page 174.
n
V/f Pattern Setting Examples
This section provides examples of how to set a V/f pattern using E1-04 to E1-10.
Setting V/f Pattern
Table 5.10 V/f Pattern Examples
Example Specification Characteristic Application
0 50 Hz (default setting)
Constant torque
For general purpose applications. Torque remains
constant regardless of changes to speed.
1 60 Hz
2 60 Hz (with 50 Hz base)
3 72 Hz (with 60 Hz base)
4 50 Hz, Heavy Duty 2
Derated torque
For fans, pumps, and other applications that require torque
derating relative to the load.
5 50 Hz, Heavy Duty 1
6 50 Hz, Heavy Duty 1
7 50 Hz, Heavy Duty 2
8 50 Hz, mid starting torque
High starting torque
Select high starting torque when:
• Wiring between the drive an motor exceeds 150 m
• A large amount of starting torque is required
• An AC reactor is installed
9 50 Hz, high starting torque
10 60 Hz, mid starting torque
11 60 Hz, high starting torque
12 90 Hz (with 60 Hz base)
Constant output
When operating at greater than 60 Hz the output voltage
will be constant.
13 120 Hz (with 60 Hz base)
14 180 Hz (with 60 Hz base)
The following tables show details onV/f patterns.
The following graphs are for 200 V class drives. Double the values when using a 400 V class drive.
5.5
E: Motor Parameters
86
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 89

V/f Pattern Examples
Table 5.11 Constant Torque Characteristics, Examples 0 to 3
Example 0
50 Hz
(default)
Example 1 60 Hz Example 2 60 Hz Example 3 72 Hz
0
12
200
1.3 2.5 50
16
Voltage (V)
Frequency (Hz)
0
12
16
200
1.5 3 60
Voltage (V)
Frequency (Hz)
0
12
16
200
1.5 3 6050
Voltage (V)
Frequency (Hz)
0
12
16
200
1.5 3 7260
Voltage (V)
Frequency (Hz)
Table 5.12 Derated Torque Characteristics, Examples 4 to 7
Example 4 50 Hz Example 5 50 Hz Example 6 60 Hz Example 7 60 Hz
0
8
200
1.3 25 50
35
Voltage (V)
Frequency (Hz)
0
9
200
1.3 25 50
50
Voltage (V)
Frequency (Hz)
0
8
200
1.5 30 60
35
Voltage (V)
Frequency (Hz)
0
9
200
1.5 30 60
50
Voltage (V)
Frequency (Hz)
Table 5.13 High Starting Torque, Examples 8 to 11
Example 8 50 Hz Example 9 50 Hz Example 10 60 Hz Example 11 60 Hz
0
12
200
1.3 2.5 50
19
Voltage (V)
Frequency (Hz)
0
13
200
1.3 2.5 50
24
Voltage (V)
Frequency (Hz)
0
12
200
1.5 3 60
19
Voltage (V)
Frequency (Hz)
0
15
200
1.5 3 60
24
Voltage (V)
Frequency (Hz)
Table 5.14 Rated Output Operation, Examples 12 to 14
Example 12 90 Hz Example 13 120 Hz Example 14 180 Hz
0
12
16
200
1.5 3 9060
Voltage (V)
Frequency (Hz)
0
12
16
200
1.5 3 12060
Voltage (V)
Frequency (Hz)
0
12
16
200
1.5 3 18060
Voltage (V)
Frequency (Hz)
5.5 E: Motor Parameters
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
87
5
Parameter Details
Page 90

n
V/f Pattern Settings E1-04 to E1-10
Set up the V/f pattern as shown in Figure 5.13.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
E1-04 Maximum Output Frequency 40.0 to 400.0 Hz 50 Hz
E1-05 Maximum Voltage
0.0 to 255.0 V
<1>
200 V
E1-06 Base Frequency 0.0 to 400.0 Hz 50 Hz
E1-07 Middle Output Frequency 0.0 to 400.0 Hz 2.5 Hz
E1-08 Middle Output Frequency Voltage
0.0 to 255.0 V
<1>
16.0 V
E1-09 Minimum Output Frequency 0.0 to 400.0 Hz 1.3 Hz
E1-10 Minimum Output Frequency Voltage
0.0 to 255.0 V
<1>
12.0 V
<1> Values shown here are for 200 V class drives. Double values when using a 400 V class unit.
E1-05
E1-08
E1-10
E1-09 E1-07 E1-06 E1-04
Output Voltage (V)
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 5.13 V/f Pattern
Note: 1. The following condition must be true when setting up the V/f pattern: E1-09 ≤ E1-07 ≤ E1-06 ≤ E1-04
2. To make the V/f pattern a straight line set E1-09 = E1-07. In this case the E1-08 setting is disregarded.
3. E1-03 is unaffected when the drive is initialized using parameter A1-03, but the settings for E1-04 through E1-10 are returned to their
default values.
u
E2: Motor 1 Parameters
These parameters contain the most important motor data needed for optimal motor control.
n
E2-01: Motor Rated Current
Set E2-01 to the full load amps (FLA) stamped on the motor nameplate.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
E2-01 Motor Rated Current
10% to 200% of the drive
rated current.
(unit: 0.01 A)
Depending on
o2-04
n
E2-02: Motor Rated Slip
Sets the motor rated slip in Hz.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
E2-02 Motor Rated Slip 0.00 to 20.00 Hz
Depending on
o2-04
Calculate the motor rated slip using the information written on the motor nameplate and the formula below:
E2-02 = f - (n x p)/120
(f: rated frequency (Hz), n: rated motor speed (r/min), p: number of motor poles)
n
E2-03: Motor No-Load Current
Set E2-03 to the motor no-load current at rated voltage and rated frequency. Contact the motor manufacturer for information
about the no-load current.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
E2-03 Motor No-Load Current
0 to [E2-01]
(unit: 0.01 A)
Depending on
o2-04
n
E2-05: Motor Line-to-Line Resistance
Sets the line-to-line resistance of the motor stator winding. Remember this value must be entered as line-line and not lineneutral.
5.5
E: Motor Parameters
88
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 91

No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
E2-05 Motor Line-to-Line Resistance 0.000 to 65.000 Ω
Depending on
o2-04
Note: The setting range becomes 0.00 to 130.00 when using JZAB0P2, JZA20P2, JZA40P2 and smaller.
Contact the motor manufacturer to find out the line-to-line resistance or measure it manually. When using the manufacturer
Motor Test Report, calculate E2-05 by the formulas below.
• E-type insulation: Multiply 0.92 times the resistance value (Ω) listed on the Test Report at 75 °C
• B-type insulation: Multiply 0.92 times the resistance value (Ω) listed on the Test Report at 75 °C.
• F-type insulation: Multiply 0.87 times the resistance value (Ω) listed on the Test Report at 115 °C.
5.5 E: Motor Parameters
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
89
5
Parameter Details
Page 92
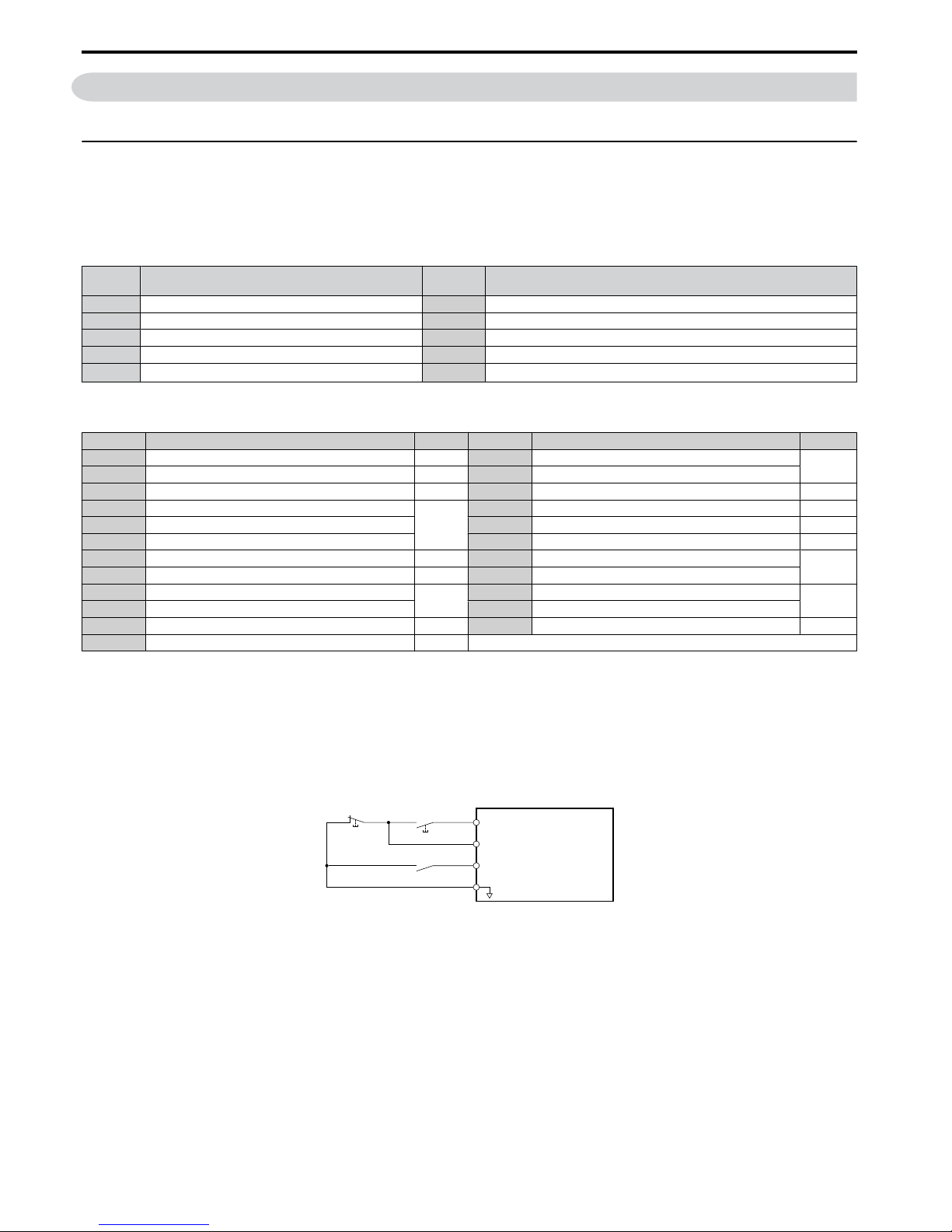
5.6 H: Terminal Functions
H parameters are used to assign functions to the external terminals.
u
H1: Multi-Function Digital Inputs
n
H1-01 to H1-05: Functions for Terminals S1 to S5
These parameters assign functions to the multi-function digital inputs. The settings 0 to 67 determine function for each
terminal and are explained below.
Note: If not using an input terminal or if using the through-mode, set that terminal to “F”.
No. Parameter Name
Setting
Range
Default
H1-01 Digital Input S1 Function Selection 1 to 9F 40: Forward Run Command (2-wire sequence)
H1-02 Digital Input S2 Function Selection 1 to 9F 41: Reverse Run Command (2-wire sequence)
H1-03 Digital Input S3 Function Selection 0 to 9F 24: External Fault
H1-04 Digital Input S4 Function Selection 0 to 9F 14: Fault Reset
H1-05 Digital Input S5 Function Selection 0 to 9F
3 (0)
<1>
: Multi-Step Speed Reference 1
<1> Number appearing in parenthesis is the default value after performing a 3-Wire initialization.
Table 5.15 Digital Multi-Function Input Settings
Setting Function Page Setting Function Page
0 3-Wire Sequence 90 10 Up Command
92
1 LOCAL/REMOTE Selection 91 11 Down Command
2 Serial Communication Reference Selection 91 14 Fault Reset 93
3 Multi-Step Speed Reference 1
91
15 Fast-Stop (N.O.) 93
4 Multi-Step Speed Reference 2 17 Fast-stop (N.C.) 93
5 Multi-Step Speed Reference 3 20 to 2F External Fault 94
6 Jog Reference Selection 91 40 Forward Run/Stop (2-wire sequence)
94
7 Accel/Decel Time 1 91 41 Reverse Run/Stop (2-wire sequence)
8 Baseblock Command (N.O.)
91
61 External Speed Search Command 1
94
9 Baseblock Command (N.C.) 62 External Speed Search Command 2
A Accel/Decel Ramp Hold 92 67 Communications Test Mode 95
F Not used/Through Mode 92
Setting 0: 3-Wire Sequence
When one of the digital inputs is programmed for 3-Wire control, that input becomes a forward/reverse directional input,
S1 becomes the Run command input, and S2 becomes the Stop command input.
The drive will start the motor when the Run input S1 is closed for longer than 50 ms. The drive will stop the operation
when the Stop input S2 is released for a brief moment. Whenever the input programmed for 3-Wire sequence is open, the
drive will be set for forward direction. If the input is closed, the drive is set for reverse direction.
Note: When 3-Wire sequence is selected the Run and Stop command must be input at S1 and S2.
S1
S2
S5
SC
Run Command (Runs when Closed)
DRIVE
Stop Switch
(N.C.)
Run Switch
(N.O.)
Stop Command (Stops when Open)
FWD/REV (Multi-Function Input)
(H1-05 = 0)
Sequence Input Common
Figure 5.14 3-Wire Sequence Wiring Diagram
5.6 H: Terminal Functions
90
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 93

50 ms min.
Run command
OFF (stopped)
Can be either ON or OFF
OFF (forward)
Motor speed
Forward/reverse
command
Stop command
Stop Reverse Stop Foward
TIME
Forward
ON (reverse)
Figure 5.15 3-Wire Sequence
Note: 1. The Run and Stop command must be open/closed for a short moment only to start and stop the drive.
2. If the Run command is active at power up and b1-17 = 0 (Run command at power up not accepted), the Run LED will flash to indicate
that protective functions are operating. If required by the application, set b1-17 to “1” to have the Run command issued automatically
as soon as the drive is powered up.
WARNING! Sudden Movement Hazard. The drive may start unexpectedly in reverse direction after power up if it is wired for 3-Wire
sequence but set up for 2-Wire sequence (default). When using 3-Wire sequence first set the drive properly (H1-
= 0) and then
connect the control wires. Make sure b1-17 is set to “0” (drive does not accept Run command active at power up). When initializing the
drive use 3-Wire initialization. Failure to comply could result in death or serious injury from moving equipment.
Setting 1: LOCAL/REMOTE Selection
This setting allows the input terminal to determine if the drive will run in LOCAL mode or REMOTE mode.
Status Description
Closed LOCAL: Frequency reference and Run command are input from the digital operator.
Open REMOTE: Frequency reference and Run command are input from the selected external reference. (b1–01/b1–02)
Note: 1. If one of the multi-function input terminals is set to for LOCAL/REMOTE, then the LO/RE key on the operator will be disabled.
2. When the drive is set to LOCAL, the LO/RE LED will light.
3. The default setting of the drive is not to allow switching between LOCAL and REMOTE during run. to Refer to b1-07: LOCAL/
REMOTE Run Selection on page 75 if this feature is required by the application.
Setting 2: Serial Communication Reference Selection
This function can be used to switch the Run command and frequency reference source from the current selection (LOCAL
or b1-01/02) to Serial Communication.
Status Description
Open LOCAL or the source defined by parameters b1-01/02
Closed Run command and frequency reference are set by Serial Communications via MEMOBUS/Modbus
Note: The default setting of the drive is not to allow switching reference sources during run. Refer to b1-07: LOCAL/REMOTE Run
Selection on page 75 if this feature is required by the application.
Setting 3 to 5: Multi-Step Speed Reference 1 to 3
Used to switch Multi-Step Speed frequency references d1-01 to d1-08 by digital inputs. Refer to d1-01 to d1-08, d1-17:
Frequency Reference 1 to 8 and Jog Reference on page 82 for details.
Setting 6: Jog Frequency Reference Selection
Used to select the Jog frequency set in parameter d1-17 as active frequency reference. Refer to d1-01 to d1-08, d1-17:
Frequency Reference 1 to 8 and Jog Reference on page 82 for details.
Setting 7: Accel/Decel Time Selection 1
Used to switch between accel/decel times 1 and 2. Refer to C1-01 to C1-04: Accel/Decel Times 1 and 2 on page 77 for
details.
Setting 8/9: External Baseblock (N.O.) and External Baseblock (N.C.)
Setting 8 or 9 assign the Baseblock command to digital input terminals. When the drive receives a Baseblock command,
the output transistor stop switching and the motor coasts to stop. During this time, the alarm “bb” will flash on the LED
operator to indicate baseblock. For more information on alarms, Refer to Alarm Detection on page 129. When baseblock
ends and a Run command is active, the drive performs Speed Search to get the motor running again.
Operation
Inputs
Setting 8 (N.O.) Setting 9 (N.C.)
Normal operation Open Closed
5.6 H: Terminal Functions
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
91
5
Parameter Details
Page 94

Operation
Inputs
Setting 8 (N.O.) Setting 9 (N.C.)
Baseblock (Interrupt output) Closed Open
NOTICE: If using baseblock in hoist applications, make sure the brake closes when the drive output is cut off by a Baseblock input.
Failure to do so will result in the motor suddenly coasting when the Baseblock command is entered, causing the load to slip.
Begin Speed Search from the
previous frequency reference
Run command
Baseblock input
Frequency
reference
Output frequency
OFF ON
Output off, motor coasts
ON
Baseblock
release
Figure 5.16 Baseblock Operation During Run
Setting A: Accel/Decel Ramp Hold
When the digital input programmed for the Accel/Decel Ramp Hold function closes, the drive will lock ("hold") the output
frequency. All acceleration or deceleration will cease, and the drive will hold the current speed. Acceleration or deceleration
will resume once the input is opened again.
If the Accel/Decel Ramp Hold function is enabled (d4-01 = 1), the drive will save the output frequency to memory whenever
the Ramp Hold input is closed. When the drive is restarted after stop or after power supply interruption, the output frequency
that was saved will become the frequency reference (provided that the Accel/Decel Ramp Hold input is still closed). Refer
to d4-01: Frequency Reference Hold Function Selection on page 84 for details.
Setting F: Not Used/Through Mode
Any digital input that is not used should be set to F. When set to “F”, an input does not trigger any function in the drive.
Setting F, however, still allows the input status to be read out by a PLC via an optional MEMOBUS/Modbus
communications interface . This way external sensors can be connected to unused drive digital inputs, thus reducing the
need for separate PLC I/O units.
Setting 10/11: Up/Down Command
Using the Up/Down function allows the frequency reference to be set by two push buttons. One digital input must be
programmed as the Up input (H1-= 10) to increase the frequency reference, the other one must be programmed as the
Down input (H1-= 11) to decrease the frequency reference.
The Up/Down function has priority over the frequency references digital operator and analog inputs (b1-01 = 0, 1). If the
Up/Down function is used, then references provided by these sources will be disregarded.
The inputs operate as shown in the table below.
Status
Description
Up (10) Down (11)
Open Open Hold current frequency reference
Closed Open Increase frequency reference
Open Closed Decrease frequency reference
Closed Closed Hold current frequency reference
Note: 1. An oPE03 alarm will occur when only one of the functions Up/Down is programmed for a digital input.
2. An oPE03 alarm will occur if the Up/Down function is assigned to the terminals while another input is programmed for the Accel/
Decel Ramp Hold function. For more information on alarms, Refer to Drive Alarms, Faults, and Errors on page 121.
3. The Up/Down function can only be used for external reference 1. Consider this when using Up/Down and the external reference
switching function (H1- = 2).
Using the Up/Down Function with Frequency Reference Hold (d4-01)
• When the frequency reference hold function is disabled (d4-01 = 0), the Up/Down frequency reference will be reset to
0 when the Run command is cleared or the power is cycled.
• When d4-01 = 1, the drive will save the frequency reference set by the Up/Down function. When the Run command or
the power is cycled, the drive will restart with the reference value that was saved. The value that was saved can be reset
by closing either the Up or Down input without having a Run command active. Refer to d4-01: Frequency Reference
Hold Function Selection on page 84.
5.6
H: Terminal Functions
92
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 95

Using the Up/Down Function with Frequency Reference Limits
The upper frequency reference limit is determined by parameter d2-01.
The value for the lower frequency reference limit can be set by an analog input or parameter d2-02. When a Run command
is applied, the lower limits work as follows:
• If the lower limit is set by parameter d2-02 only, the drive will accelerate to this limit as soon as a Run command is
entered.
• If the lower limit is determined by an analog input only, the drive will accelerate to the limit as long as the Run command
and an Up or Down command are active. It will not start running if only the Run command is on.
• If the lower limit is set by both an analog input and d2-02, and the analog limit is higher than the d2-02 value, the drive
will accelerate to the d2-02 value when a Run command is input. Once the d2-02 value is reached, it will continue
acceleration to the analog limit only if an Up or Down command is set.
Figure 5.17 shows an Up/Down function example with a lower frequency reference limit set by d2-02 and the frequency
reference hold function enabled/disabled.
Accelerates to
lower limit
Output frequency
upper limit
Lower limit
FWD run/stop
Up command
Down command
Power supply
Same
frequency
d4-01 = 1
d4-01 = 0
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
Frequency
reference
reset
Figure 5.17 Up/Down Command Operation
Setting 14: Fault Reset
Whenever the drive detects a fault condition, the fault output contact will close and the drive’s output will shut off. The
motor then coasts to stop (specific stopping methods can be selected for some faults such as L1-04 for motor overheat).
Once the Run command is removed, the fault can be cleared by either the RESET key on the digital operator or by closing
a digital input configured as a Fault Reset (H1- = 14).
Note: Fault Reset commands are ignored as long as the Run command is present. To reset a fault, first remove the Run command.
Setting 15/17: Fast-stop (N.O./N.C.)
The Fast-stop function operates much like an emergency stop input to the drive. If a Fast-stop command is input while the
drive is running, the drive will decelerate to a stop by the deceleration time set to C1-09 (Refer to C1-09: Fast-stop
Time on page 77). The drive can only be restarted after is has come to a complete stop, the Fast-stop input is off, and the
Run command has been switched off.
•
To trigger the Fast-stop function with a N.O. switch, set H1- = 15
•
To trigger the Fast-stop function with a N.C. switch, set H1- = 17
Figure 5.18 shows an operation example of Fast-stop.
Run/Stop
TIME
Fast-Stop
H1- = 17
Decelerates at C1-09
ON ON
ONON
Output Frequency
Figure 5.18
Fast-stop Sequence
5.6 H: Terminal Functions
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
93
5
Parameter Details
Page 96

NOTICE: Rapid deceleration can trigger an overvoltage fault. When faulted, the drive output shuts off, and the motor coasts. To avoid
this uncontrolled motor state and to ensure that the motor stops quickly and safely, set an appropriate Fast-stop time to C1-09.
Setting 20 to 2F: External Fault
By using the External Fault function, the drive can be stopped when problems occur with external devices.
To use the external fault function, set one of the multi-function digital inputs to any value between 20 to 2F. The operator
will display EF where is the number of the terminal (terminal S) to which the external fault signal is assigned.
For example, if an external fault signal is input to terminal S3, “EF3” will be displayed.
Select the value to be set in H1- from a combination of any of the following three conditions:
• Signal input level from peripheral devices (N.O./N.C.)
• External fault detection method
• Operation after external fault detection
The following table shows the relationship between the conditions and the value set to H1-:
Setting
Terminal Status
<1>
Detection Method
<2>
Stopping Method
N.O. N.C.
Always
Detected
Detected
during Run
only
Ramp to Stop
(fault)
Coast to Stop
(fault)
Fast-stop
(fault)
Alarm Only
(continue
running)
20 O O O
21 O O O
22 O O O
23 O O O
24 O O O
25 O O O
26 O O O
27 O O O
28 O O O
29 O O O
2A O O O
2B O O O
2C O O O
2D O O O
2E O O O
2F O O O
<1> Determine the terminal status for each fault, i.e., whether the terminal is normally open or normally closed.
<2> Determine whether detection for each fault should be enabled only during run or always detected.
Setting 40/41: Forward Run/Reverse Run Command for 2-Wire Sequence
Sets the drive for 2-Wire sequence.
When the input set to 40 is closed, the drive operates in the forward direction. When the input set for 41 is closed, the drive
will operate in reverse. Closing both inputs at the same time will result in an external fault.
Note: These functions are assigned to the terminals S1 and S2 when the drive is initialized for 2-Wire sequence.
S1
S2
SC
Drive
Forward Run
Reverse Run
Digital Input Common
Figure 5.19 Example Wiring Diagram for 2-Wire Sequence
Setting 61/62: Speed Search 1/2
These input functions can be used to enable Speed Search. When the Speed Search 1 input (H1- = 61) is enabled the
drive will search the motor speed starting from the maximum output frequency. With Speed Search 2 input (H1- =
62) enabled the Speed Search will be performed starting from the frequency reference.
Note: Operator error oPE03 will result if both Speed Search 1 and Speed Search 2 are set to the input terminals at the same time.
5.6
H: Terminal Functions
94
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 97

Setting 67: Communication Test Mode
If a RS-422/485 communications options is attached to the drive, this function can be used to perform a self-diagnosis of
the communication interface. The drive transmits data and then confirms the communications are received normally. Refer
to Self-Diagnostics on page 207 for details on how to use this function.
u
H2: Multi-Function Output
n
H2-01: Terminal MA/MB/MC Function Selection
The drive has a multi-function output terminal. Set parameter H2-01 between 0 and 13D to assign functions to this terminal.
Default values are listed in the following table.
No. Parameter Name Setting Range Default
H2-01 Terminal MA, MB and MC Function Selection (relay) 0 to 13D E: Fault
Note: If not using an input terminal or if using it in the through-mode, be sure to set that terminal to “F”.
Table 5.16 Multi-Function Output Terminal Settings
Setting Function Page Setting Function Page
0 During Run 95 E Fault 97
1 Zero Speed 95 F Not used/Through Mode 97
2 Speed Agree 96 10 Alarm 97
4 Frequency Detection 1 96 17 Torque Detection 1 (N.C.) 97
5 Frequency Detection 2 96 1A During Reverse Operation 98
6 Drive Ready 97 1E Restart Enabled 98
7 DC Bus Undervoltage 97 3C LOCAL/REMOTE Status 98
8 During Baseblock (N.O.) 97 3D During Speed Search 98
B Torque Detection 1 (N.O.) 97 100 to 13D
H2 Parameter Functions Reversed Output
Switching of 0 to 92
98
Setting 0: During Run
Output closes when the drive is outputting a voltage.
Status Description
Open Drive is stopped.
Closed A Run command is input or the drive is during deceleration or during DC injection.
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
ONOFF
Run command
Baseblock
command
Output
frequency
During Run
Figure 5.20 During Run Time Chart
Setting 1: Zero Speed
Terminal closes whenever the output frequency falls below the minimum output frequency set to E1-09.
Status Description
Open Output frequency is above the minimum output frequency set to E1-09
Closed Output frequency is less than the minimum output frequency set to E1-09
OFF
Output frequency
or
motor speed
Zero Speed
ON
E1-09 (Max. Output Frequency)
Figure 5.21 Zero-Speed Time Chart
5.6 H: Terminal Functions
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
95
5
Parameter Details
Page 98

Setting 2: Speed Agree (f
ref/fout
Agree )
Closes whenever the actual output frequency is within the current frequency reference regardless of the direction, plus or
minus 2 Hz.
Status Description
Open Output frequency does not match the frequency reference while the drive is running.
Closed Output frequency is within the range of frequency reference ± 2 Hz.
Note: Detection works in both directions, forward and reverse.
2 Hz
2 Hz
Frequency
reference
Output
frequency
Speed agree
ON
OFF
Figure 5.22 Speed Agree Time Chart
Refer to L4-01: Speed Agreement Detection Level on page 106 for details on setting the detection width.
Setting 4: Frequency Detection 1
Output is closed as long as the output frequency is below the detection level set in L4-01 plus 2 Hz. It closes when the
output frequency falls below L4-01.
Status Description
Open Output frequency exceeded L4-01 + 2 Hz.
Closed Output frequency is below L4-01 or has not exceeded L4-01 + 2 Hz.
Note: The detection works in both forward and reverse. The value of L4-01 will be used as the detection level for both directions.
Output
frequency
2 Hz
Frequency
detection 1
ON
OFF
2 Hz
L4-01
L4-01
Figure 5.23 Frequency Detection 1 Time Chart
Refer to L4-01: Speed Agreement Detection Level on page 106 for details on setting the detection width.
Setting 5: Frequency Detection 2
Output closes whenever the output frequency is equal to or above the detection level set in L4-01. The output opens when
the output frequency falls below L4-01 minus 2 Hz.
Status Description
Open Output frequency is below L4-01 minus 2 Hz or has not exceeded L4-01.
Closed Output frequency exceeded L4-01.
Note: The detection works in both forward and reverse. The value of L4-01 will be used as the detection level for both directions.
5.6
H: Terminal Functions
96
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
Page 99

Output
frequency
2 Hz
Frequency
Detection 2
ON
OFF
2 Hz
L4-01
L4-01
Figure 5.24 Frequency Detection 2 Time Chart
Refer to L4-01: Speed Agreement Detection Level on page 106 for details on setting the detection width.
Setting 6: Drive Ready
Output closes whenever the drive is ready to operate the motor.
Status Description
Open During power up, initialization, fault or in Programming Mode (while b1-08 = 0 or 2).
Closed Drive is ready for operation.
Refer to b1-08: Run Command Selection while in Programming Mode on page 75 for details on the setting of b1-08.
Setting 7: DC Bus Undervoltage
Output closes whenever the DC bus voltage or control circuit power supply drops below the trip level. The undervoltage
trip level depends on the setting of parameter E1-01. Refer to E1-01 for details. A fault in the DC bus charge circuit will
also cause the DC Bus Undervoltage output to close.
Status Description
Open DC bus voltage is above the undervoltage level.
Closed DC bus voltage has fallen below the undervoltage level.
Setting 8: During Baseblock (N.O.)
Output closes to indicate that the drive is in a baseblock state. While Baseblock is executed, output transistors are not
switched and no voltage will be output.
Status Description
Open Drive is not in a baseblock state.
Closed Baseblock is being executed.
Settings B and 17: Torque Detection (N.O./N.C.)
These digital output functions can be used to signal an overtorque situation to an external device.
Set up the torque detection and select the output function from the table below. Refer to L6: Torque Detection on page
108 for details.
Setting Status Description
B Closed
Torque Detection (N.O.):
Output current/torque exceeds the torque value set in parameter L6-02 for longer than the time specified in
parameter L6-03.
17 Open
Torque Detection (N.C.):
Output current/torque exceeds the torque value set in parameter L6-02 for longer than the time specified in
parameter L6-03.
Setting E: Fault
The Fault configured digital output will close whenever the drive experiences a fault (this excludes faults CPF00 and
CPF01).
Setting F: Not Used
Use this setting when the terminal is not used or when using the terminal as a throughput.
When set to “F”, the output is not set by any drive function but it can be switched by a PLC via MEMOBUS/Modbus
communications interface (through mode).
Setting 10: Minor Fault
Output closes when a minor fault condition is present.
5.6
H: Terminal Functions
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
97
5
Parameter Details
Page 100

Setting 1A: During Reverse
The During Reverse digital output will close whenever the drive is turning the motor in the reverse direction.
Status Description
Open Motor is driven in the forward direction or stopped.
Closed Motor is driven in reverse.
Output frequency
time
FWD Run command
REV Run command
During Reverse
OFF
ON
Figure 5.25 Reverse Direction Output Example Time Chart
Setting 1E: Restart Enabled
The Restart Enabled output will be closed once the fault restart function becomes active and will remain closed until a
successful restart is accomplished or the number of Auto Restart attempts as specified by L5-01 is reached. Refer to L5:
Fault Restart on page 107 for details on automatic fault restart.
Setting 3C: LOCAL/REMOTE Status
Output terminal closes while the drive is set for LOCAL and opens when in REMOTE.
Status Description
Open
REMOTE: The selected external reference (b1-01/02 or MEMOBUS/Modbus) is used as frequency reference and Run command
source
Closed LOCAL: The digital operator is used as frequency reference and Run command source
Setting 3D: During Speed Search
Output terminal closes while Speed Search is being performed.
Setting 100 to 13D: Reverse Switching for Functions 0 to 3D
These settings reverse the switching status of the specified function. Set as 1, where the last two digits specify the
setting number of the function to be reversed.
Examples:
• To reverse the output for “8: During Baseblock”, set “108”.
• To reverse the output for “3C: Run command” set “13C”.
u
H3: Analog Input Terminal A1 Settings
These parameters adjust the signal level and characteristics of the analog frequency reference input A1.
n
H3-01: Terminal A1 Signal Level Selection
Selects the input signal level for analog input A1.
No. Name Setting Range Default
H3-01 Terminal A1 Signal Level Selection 0 to 3 0
Setting 0: 0 to 10 Vdc with Limit
The input level is 0 to 10 Vdc. Negative input values will be limited to 0.
Example: Terminal A1 is set to supply the frequency reference, and the bias (H3-04) is set to -100%. The frequency
reference can be set from 0 to 100% with an analog input of 5 to 10 V. The frequency reference will be zero when the
analog input is between 0 and 5 V.
5.6
H: Terminal Functions
98
SIEP C710606 33A OYMC AC Drive – J1000 User Manual
 Loading...
Loading...