Omron CP1L-L14D Series, CP1L-J14D Series, CP1L-L20D Series, CP1L-M30D Series, CP1L-M40D Series Getting Started Manual
...Page 1

CP1L CPU Unit
Cat. No. W07E-EN-02
CP1L-J14D@-@
CP1L-J20D@-@
CP1L-L10D@-@
CP1L-L14D@-@
CP1L-L20D@-@
CP1L-M30D@-@
CP1L-M40D@-@
CP1L-M60D@-@
GETTING STARTED GUIDE
Page 2
CP1L-J14D-
CP1L-J20D-
CP1L-L10D-
CP1L-L14D-
CP1L-L20D-
CP1L-M30D-
CP1L-M40D-
CP1L-M60D-
CP1L CPU Unit
Getting Started Guide
Page 3

Notice:
OMRON products are manufactured for use according to proper procedures by a qualified operator
and only for the purposes described in this manual.
The following conventions are used to indicate and classify precautions in this manual. Always heed
the information provided with them. Failure to heed precautions can result in injury to people or
damage to property.
DANGER Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or
serious injury. Additionally, there may be severe property damage.
WARNING Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or
serious injury. Additionally, there may be severe property damage.
Caution Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or
moderate injury, or property damage.
OMRON Product References
All OMRON products are capitalized in this manual. The word “Unit” is also capitalized when it refers to
an OMRON product, regardless of whether or not it appears in the proper name of the product.
The abbreviation “Ch,” which appears in some displays and on some OMRON products, often means
“word” and is abbreviated “Wd” in documentation in this sense.
The abbreviation “PLC” means Programmable Controller. “PC” is used, however, in some CX-Programmer displays to mean Programmable Controller.
Visual Aids
The following headings appear in the left column of the manual to help you locate different types of
information.
Trademarks
Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and other countries.
SYSMAC is a registered trademark of OMRON’s Programmable Controllers.
Other brand and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
© OMRON, 2007
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in
any form, or by any means, mechanical, electronic, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written
permission of OMRON.
No patent liability is assumed with respect to the use of the information contained herein. Moreover, because
OMRON is constantly striving to improve its high-quality products, the information contained in this manual is subject to change without notice. Every precaution has been taken in the preparation of this manual. Nevertheless,
OMRON assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions. Neither is any liability assumed for damages resulting
from the use of the information contained in this publication.
Note Indicates information of particular interest for efficient and convenient opera-
tion of the product.
1,2,3... 1. Indicates lists of one sort or another, such as procedures, checklists, etc.
2
Page 4
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PRECAUTIONS ............................................................... 9
1 Intended Audience.................................................................................................... 10
2 General Precautions................................................................................................. 10
3 Safety Precautions ................................................................................................... 10
4 Application Precautions ............................................................................................ 10
SECTION 1CP1L Overview ........................................... 11
1-1 CP1L Models ............................................................................................................ 12
1-2 Part Names and Functions ....................................................................................... 15
SECTION 2Designing Systems...................................... 19
2-1 Organization of this Manual...................................................................................... 20
2-2 About the Shutter Control System ............................................................................ 22
2-3 I/O Allocation for the Shutter Control System........................................................... 24
2-4 Example Ladder Program......................................................................................... 26
SECTION 3Mounting and Wiring ................................... 27
3-1 Installation Notes ...................................................................................................... 28
3-2 Mounting onto DIN Tracks ........................................................................................ 31
3-3 Wiring Devices.......................................................................................................... 32
3-4 Power Testing CP1L................................................................................................. 35
SECTION 4Creating Programs ...................................... 37
4-1 Preparing for Programming ...................................................................................... 38
4-2 Creating Ladder Programs ....................................................................................... 44
4-3 Using CX-Programmer ............................................................................................. 47
4-4 Using the Help .......................................................................................................... 50
4-5 Inputting Programs ................................................................................................... 53
4-6 Saving/Loading Programs ........................................................................................ 70
4-7 Editing Programs ...................................................................................................... 73
SECTION 5Transferring and Debugging Programs ....... 77
5-1 Going Online............................................................................................................. 78
5-2 Adjusting/Debugging Online ..................................................................................... 85
Appendix ........................................................................ 95
A-1 Channel/Relay Numbers .......................................................................................... 96
A-2 Instructions ............................................................................................................. 101
A-3 Inner Workings of CP1L ......................................................................................... 105
A-4 CP1L Programming Examples ............................................................................... 114
3
Page 5
About this Manual:
This manual describes installation and operation of the CP-series Programmable Controllers (PLCs)
and includes the sections described below. The CP Series provides advanced package-type PLCs
based on OMRON’s advanced control technologies and vast experience in automated control.
Please read this manual carefully and be sure you understand the information provided before
attempting to install or operate a CP-series PLC. Be sure to read the precautions provided in the following section.
This manual is intended for first-time users of the SYSMAC CP series. The basic use of the series is
explained based on SYSMAC CP1L.
Circuit configurations, wiring methods, and programs provided in this manual are given strictly as
examples. When constructing an actual system, check the specifications, performance, and safety of
each component by referring to the respective manuals.
Ladder programs in this manual are provided strictly as examples. When designing the actual circuits,
take adequate safety measures.
Precautions provide general precautions for using the Programmable Controller and related devices.
Section 1 introduces the types of CP1L, as well the part names.
Section 2 explains how to construct a CP1L system, using a shutter control system as an example.
Section 3 explains the how to install CP1L onto a DIN track, how to wire power supply and I/O lines,
and how to test operation.
Section 4 explains the basic functions of CX-Programmer creating the ladder program for the shutter
control system.
Section 5 describes how to transfer and debug programs.
The Appendices provide channel/relay numbers, instructions, inner workings of CP1L, and CP1L programming examples.
4
Page 6
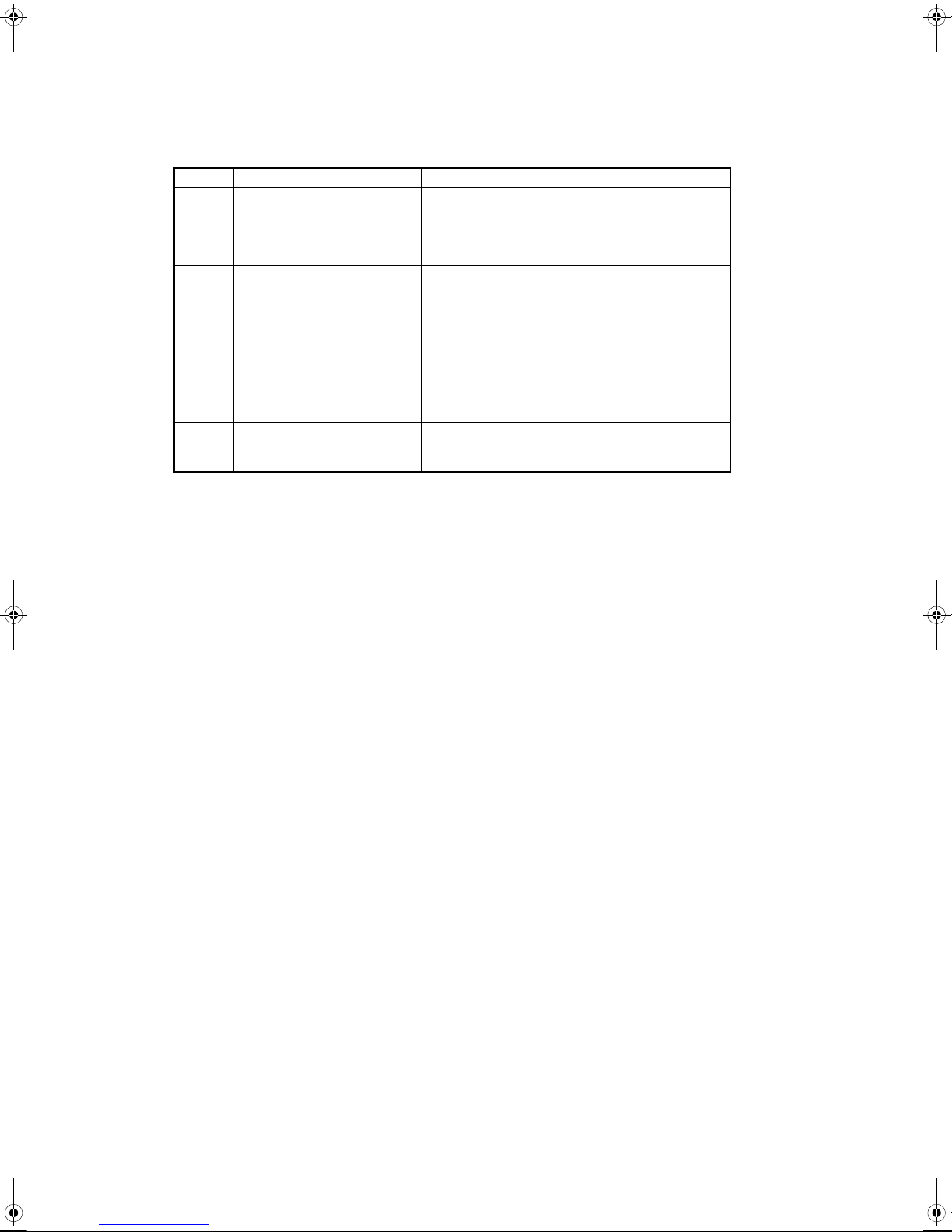
Related Manuals
The following manuals are used for the CP-series CPU Units. Refer to these manuals as required.
Cat. No. Manual name Description
W462 SYSMAC CP Series CP1L
CPU Unit User’s Manual
W451 SYSMAC CP Series
CP1H/CP1L CPU Unit Programming Manual
W446 SYSMAC CX-Programmer
Operation Manual
Explains the system configuration, installation, wiring, I/O allocation, pulse/counter functions, and
expansion unit connections in details. Also provides
information on errors, troubleshooting, maintenance, and inspection.
Provides the following information on the CP
Series:
• Programming instructions
• Programming methods
•Tasks
• File memory
• Functions
Use this manual together with the CP1H Program-
mable Controllers Operation Manual (W450).
Provides information on installing and operating the
CX-Programmer for all functions except for function
blocks.
5
Page 7
Read and Understand this Manual
Please read and understand this manual before using the product. Please consult your OMRON
representative if you have any questions or comments.
Warranty and Limitations of Liability
WARRANTY
OMRON's exclusive warranty is that the products are free from defects in
materials and workmanship for a period of one year (or other period if
specified) from date of sale by OMRON.
OMRON MAKES NO WARRANTY OR REPRESENTATION, EXPRESS
OR IMPLIED, REGARDING NON-INFRINGEMENT,
MERCHANTABILITY, OR FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE OF
THE PRODUCTS. ANY BUYER OR USER ACKNOWLEDGES THAT
THE BUYER OR USER ALONE HAS DETERMINED THAT THE
PRODUCTS WILL SUITABLY MEET THE REQUIREMENTS OF THEIR
INTENDED USE. OMRON DISCLAIMS ALL OTHER WARRANTIES,
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED.
LIMITATIONS OF LIABILITY
OMRON SHALL NOT BE RESPONSIBLE FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT, OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, LOSS OF PROFITS OR COMMERCIAL
LOSS IN ANY WAY CONNECTED WITH THE PRODUCTS, WHETHER
SUCH CLAIM IS BASED ON CONTRACT, WARRANTY, NEGLIGENCE,
OR STRICT LIABILITY.
In no event shall the responsibility of OMRON for any act exceed the
individual price of the product on which liability is asserted.
IN NO EVENT SHALL OMRON BE RESPONSIBLE FOR WARRANTY,
REPAIR, OR OTHER CLAIMS REGARDING THE PRODUCTS UNLESS
OMRON'S ANALYSIS CONFIRMS THAT THE PRODUCTS WERE
PROPERLY HANDLED, STORED, INSTALLED, AND MAINTAINED AND
NOT SUBJECT TO CONTAMINATION, ABUSE, MISUSE, OR
INAPPROPRIATE MODIFICATION OR REPAIR.
6
Page 8
Application Considerations
SUITABILITY FOR USE
OMRON shall not be responsible for conformity with any standards,
codes, or regulations that apply to the combination of products in the
customer's application or use of the products.
At the customer's request, OMRON will provide applicable third party
certification documents identifying ratings and limitations of use that apply
to the products. This information by itself is not sufficient for a complete
determination of the suitability of the products in combination with the end
product, machine, system, or other application or use.
The following are some examples of applications for which particular
attention must be given. This is not intended to be an exhaustive list of all
possible uses of the products, nor is it intended to imply that the uses
listed may be suitable for the products:
• Outdoor use, uses involving potential chemical contamination or
electrical interference, or conditions or uses not described in this
manual.
• Nuclear energy control systems, combustion systems, railroad systems,
aviation systems, medical equipment, amusement machines, vehicles,
safety equipment, and installations subject to separate industry or
government regulations.
• Systems, machines, and equipment that could present a risk to life or
property.
Please know and observe all prohibitions of use applicable to the
products.
NEVER USE THE PRODUCTS FOR AN APPLICATION INVOLVING
SERIOUS RISK TO LIFE OR PROPERTY WITHOUT ENSURING THAT
THE SYSTEM AS A WHOLE HAS BEEN DESIGNED TO ADDRESS THE
RISKS, AND THAT THE OMRON PRODUCTS ARE PROPERLY RATED
AND INSTALLED FOR THE INTENDED USE WITHIN THE OVERALL
EQUIPMENT OR SYSTEM.
PROGRAMMABLE PRODUCTS
OMRON shall not be responsible for the user's programming of a
programmable product, or any consequence thereof.
7
Page 9
Disclaimers
CHANGE IN SPECIFICATIONS
Product specifications and accessories may be changed at any time
based on improvements and other reasons.
It is our practice to change model numbers when published ratings or
features are changed, or when significant construction changes are made.
However, some specifications of the products may be changed without
any notice. When in doubt, special model numbers may be assigned to fix
or establish key specifications for your application on your request. Please
consult with your OMRON representative at any time to confirm actual
specifications of purchased products.
DIMENSIONS AND WEIGHTS
Dimensions and weights are nominal and are not to be used for
manufacturing purposes, even when tolerances are shown.
PERFORMANCE DATA
Performance data given in this manual is provided as a guide for the user
in determining suitability and does not constitute a warranty. It may
represent the result of OMRON's test conditions, and the users must
correlate it to actual application requirements. Actual performance is
subject to the OMRON Warranty and Limitations of Liability.
ERRORS AND OMISSIONS
The information in this manual has been carefully checked and is believed
to be accurate; however, no responsibility is assumed for clerical,
typographical, or proofreading errors, or omissions.
8
Page 10
PRECAUTIONS
This section provides general precautions for using the CP-series Programmable Controllers (PLCs)
and related devices.
The information contained in this section is important for the safe and reliable application of
Programmable Controllers. You must read this section and understand the information contained
before attempting to set up or operate a PLC system.
1 Intended Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2 General Precautions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3 Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4 Application Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
9
Page 11

Intended Audience
1 Intended Audience
This manual is intended for the following personnel, who must also have
knowledge of electrical systems (an electrical engineer or the equivalent).
• Personnel in charge of installing FA systems.
• Personnel in charge of designing FA systems.
• Personnel in charge of managing FA systems and facilities.
2 General Precautions
The user must operate the product according to the performance
specifications described in the operation manuals.
Before using the product under conditions which are not described in the
manual or applying the product to nuclear control systems, railroad systems,
aviation systems, vehicles, combustion systems, medical equipment,
amusement machines, safety equipment, and other systems, machines, and
equipment that may have a serious influence on lives and property if used
improperly, consult your OMRON representative.
Make sure that the ratings and performance characteristics of the product are
sufficient for the systems, machines, and equipment, and be sure to provide
the systems, machines, and equipment with double safety mechanisms.
This manual provides information for programming and operating the Unit. Be
sure to read this manual before attempting to use the Unit and keep this
manual close at hand for reference during operation.
WARNING It is extremely important that a PLC and all PLC Units be used for the
specified purpose and under the specified conditions, especially in
applications that can directly or indirectly affect human life. You must consult
with your OMRON representative before applying a PLC System to the
above-mentioned applications.
3 Safety Precautions
Caution When power is ON or has just been turned OFF, do not touch the power
supply, I/O terminals, or the surrounding areas. Doing so may result in burns.
After turning the power OFF, wait for the unit to cool down sufficiently before
touching it.
Caution Secure the AC power supply line to the terminal block with a 0.5N
torque. Loosening the screw may result in a fire or malfunction.
Caution Before starting online editing, confirm that the extension of cycle time will
have no adverse effects. Otherwise, input signals may not be read.
4 Application Precautions
Caution Confirm that the facility will not be affected by changing to MONITOR or RUN
mode.
·m of
10
Page 12

SECTION 1
CP1L Overview
This section introduces the types of CP1L, as well the part names
used during operation.
1-1 CP1L Models ........................................................................ 12
1-2 Part Names and Functions ................................................... 15
Page 13
1
CP1L Overview
1
CP1L Overview
1-1 CP1L Models
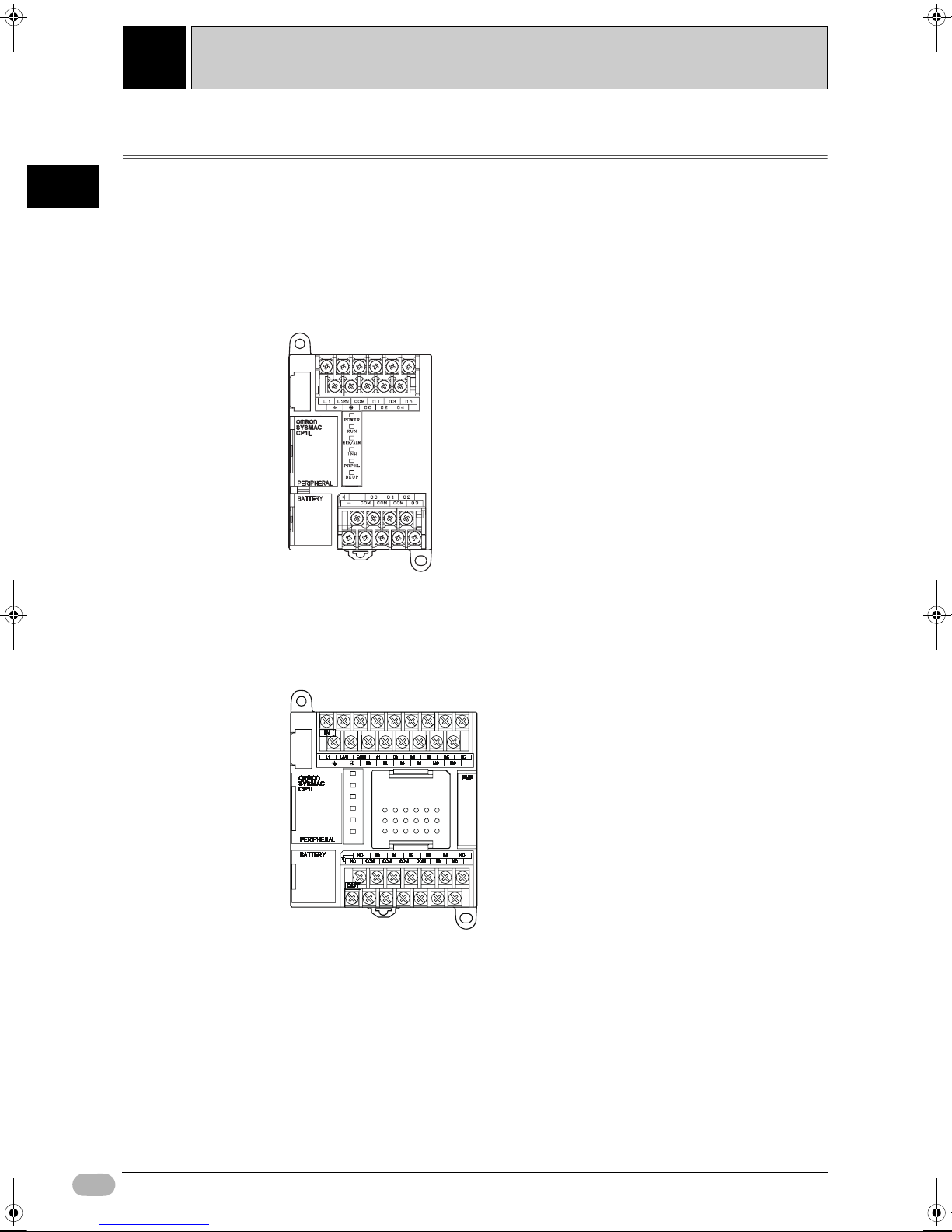
CP1L programmable controller is a PLC package type, available with 10, 14, 20, 30, 40, or 60 I/O points.
For application examples that use CP1L, refer to appendix A-4 CP1L Programming Examples.
10-point I/O Units (CP1L-L10D-)
• The CPU Unit has 6 inputs and 4 outputs built in.
• The PLC cannot use CP-series Expansion I/O Units to expand the maximum
total of I/O points.
14-point I/O Units (CP1L-L14D-/CP1L-J14D-)
• CPU unit has 8 input points and 6 output points.
• CP-series expansion I/O units can be used to add I/O points, up to a total of
54 I/O points.
12 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 14
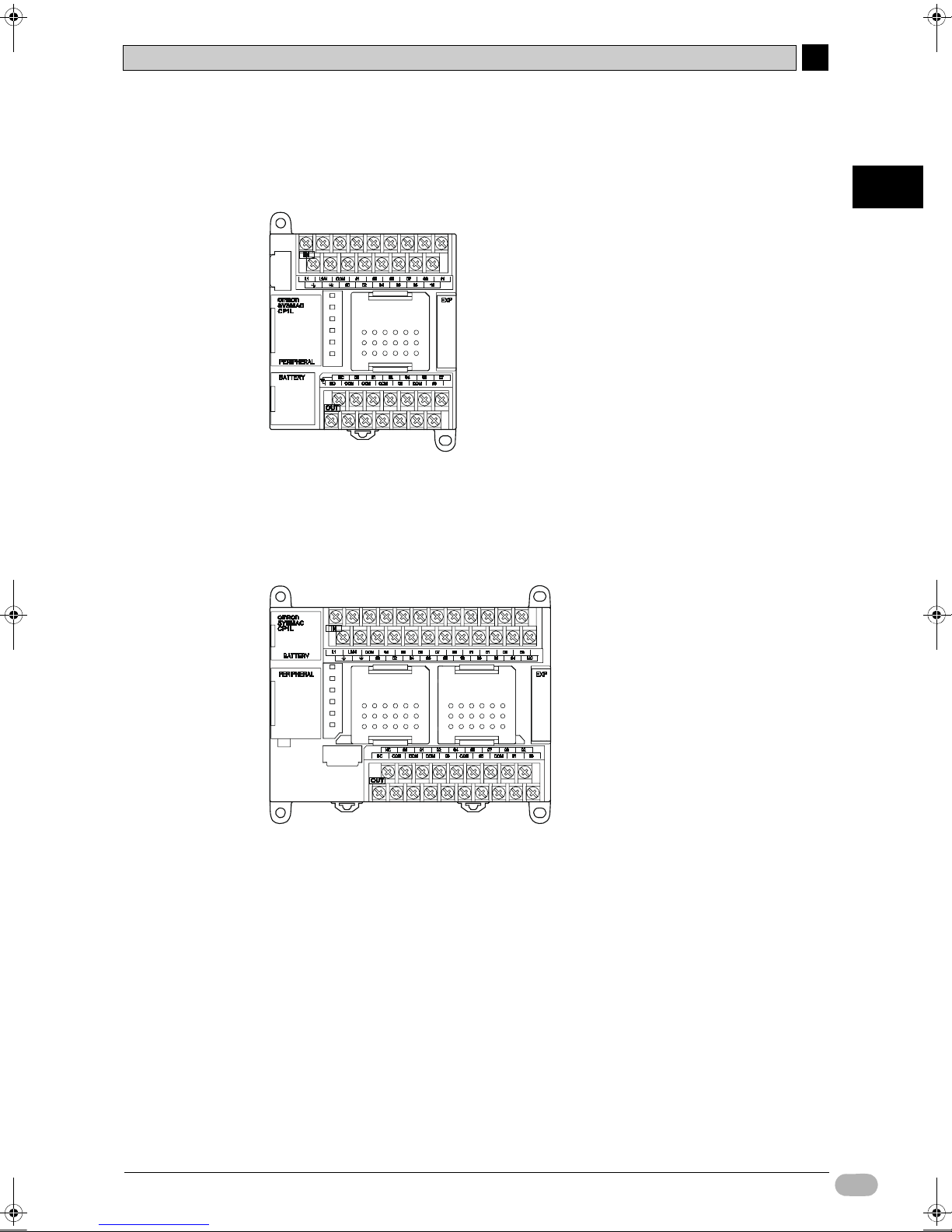
20-point I/O Units (CP1L-L20D-/CP1L-J20D-)
• CPU unit has 12 input points and 8 output points.
• CP-series expansion I/O units can be used to add I/O points, up to a total of 60 I/
O points.
30-point I/O Units (CP1L-M30D-)
• CPU unit has 18 input points and 12 output points.
• CP-series expansion I/O units can be used to add I/O points, up to a total of 150
I/O points .
1-1 CP1L Models
1
1
CP1L Overview
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 13
Page 15
1
CP1L Overview
1-1 CP1L Models
1
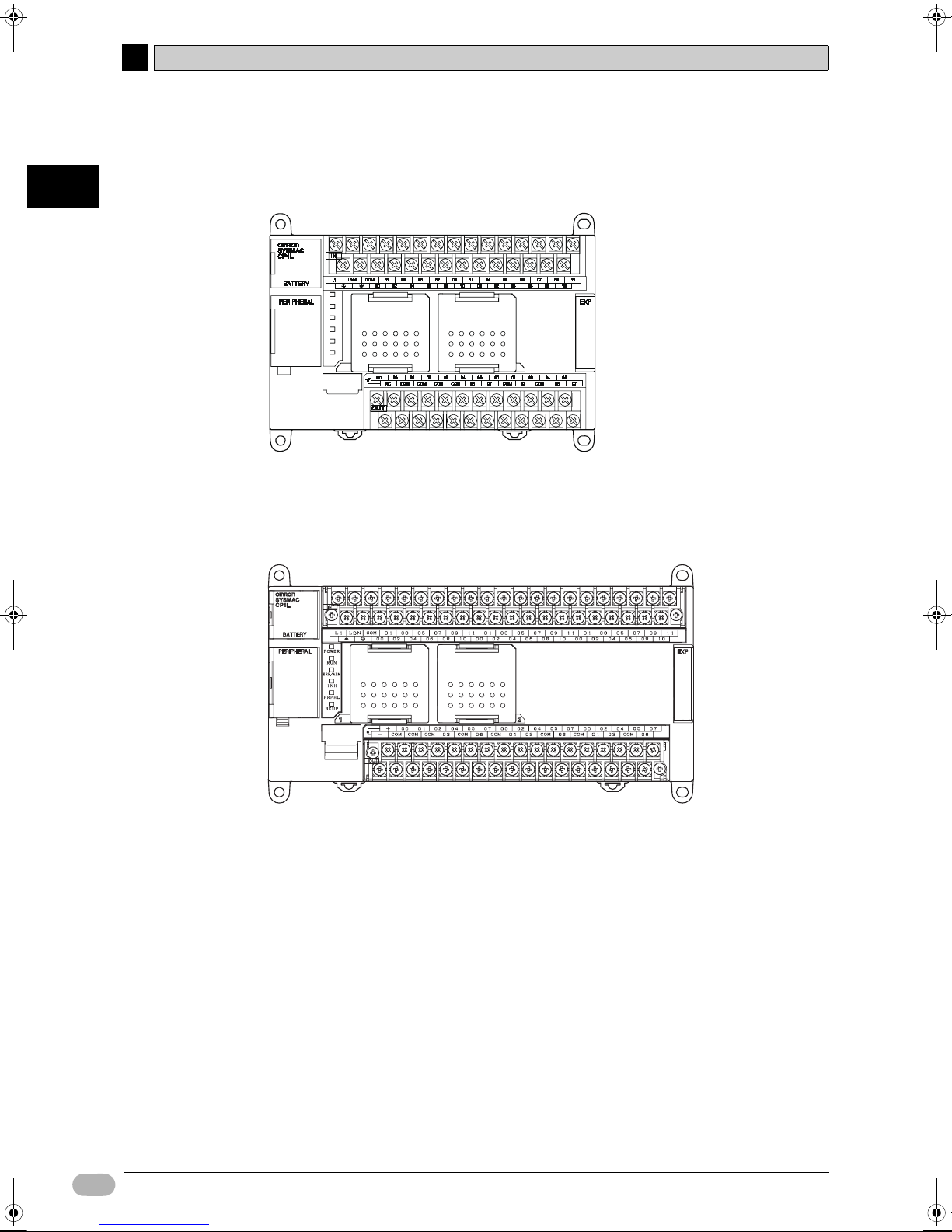
40-point I/O Units (CP1L-M40D-)
• CPU unit has 24 input points and 16 output points.
• CP-series expansion I/O units can be used to add I/O points, up to a total of 160
I/O points.
60-point I/O Units (CP1L-M60D-)
• CPU unit has 36 input points and 24 output points.
• CP-series expansion I/O units can be used to add I/O points, up to a total of 180
14 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 16
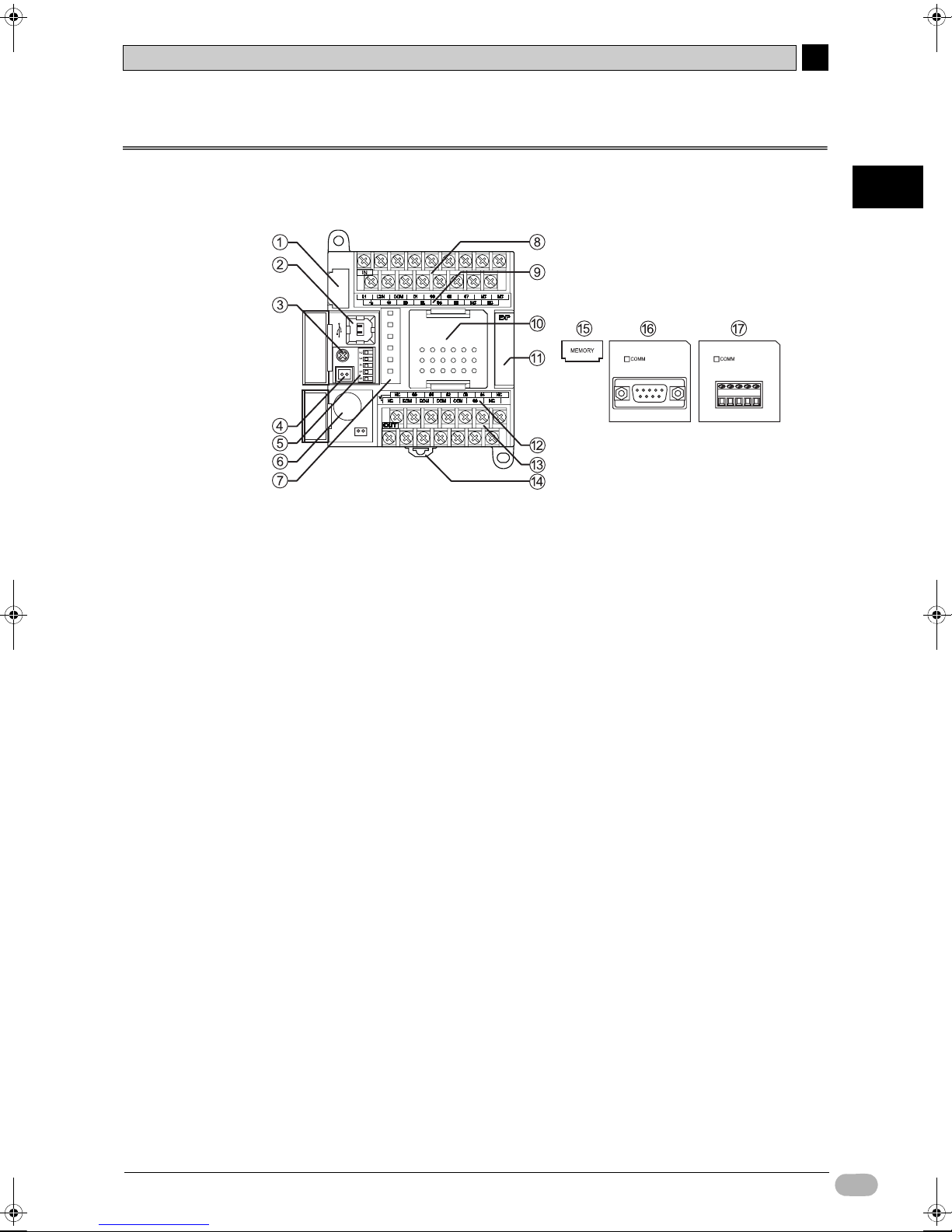
1-2 Part Names and Functions
1-2 Part Names and Functions
This section describes the part names and functions, using the 14-point I/O unit as an example.
14-point I/O Unit
1
1
CP1L Overview
(1) Memory cassette slot
Used to attach a memory cassette (15). Memory cassettes can be used to
store backups for CP1L programs, parameters, and data memory. They also
allow you to copy data to other CP1L units without using a programming tool
(software).
(2) Peripheral USB port
Used for connection to a computer. Computers can be used for programming
and monitoring.
(3) Analog adjuster
Rotate to adjust the value for auxiliary area A642CH to within the 0 to 255
range. Use to change timer and counter settings without using a programming
tool (software).
(4) External analog settings input connector
Takes an external input between 0 and 10V, and changes the value for
auxiliary area A643CH to a value between 0 and 256. This input is not
isolated.
(5) DIP switches
Used for settings such as write-permission on user memory, automatic
transfers from memory cassettes, and tool bus use.
For details, refer to 2-1 Part Names and Functions of CP Series CP1L CPU
Unit User's Manual (W462).
(6) Battery
Maintains the internal clock and RAM contents while the power supply is OFF.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 15
Page 17

1
CP1L Overview
1-2 Part Names and Functions
1
(7) Operation indicators
(8) Power supply, ground, and input terminal block
(9) Input indicators
(10) Option board slot
(11) Expansion I/O unit connector
Indicates the operating status of CP1L. Indicated statuses include power
status, operating mode, errors, and peripheral USB communication status.
Used to connect the power supply line, ground line, and input lines.
Lit when the corresponding input terminal contact is ON.
Used to install an RS-232C option board (16) or an RS-422A/485 option
board (17).
14/20-point I/O units may have 1 serial communication option board installed.
30/40/60-point I/O units may have up to 2 serial communication option boards
installed.
Used to connect CP-series expansion I/O units and expansion units. 14/20point I/O units may have 1 expansion unit connected. 30/40/60-point I/O units
may have up to 3 expansion units connected.
(12) Output indicators
Lit when the corresponding output terminal contact is ON.
(13) External power supply and output terminal block
• External power supply terminal:
Units that use AC power supply have a 24VDC external power supply terminal
with a maximum capacity of 300mA.This can be used as a service power
supply for input devices.
• Output terminals: Used to connect output lines.
(14) DIN track mounting pin
Used for mounting unit to a DIN track.
(15) Memory cassette (optional)
Used to store data from the built-in flash memory. Insert into memory cassette
slot (1).
(16) RS-232C option board
Insert into option board slot (10).
(17) RS-422A/485 option board
Insert into option board slot (10).
16 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 18
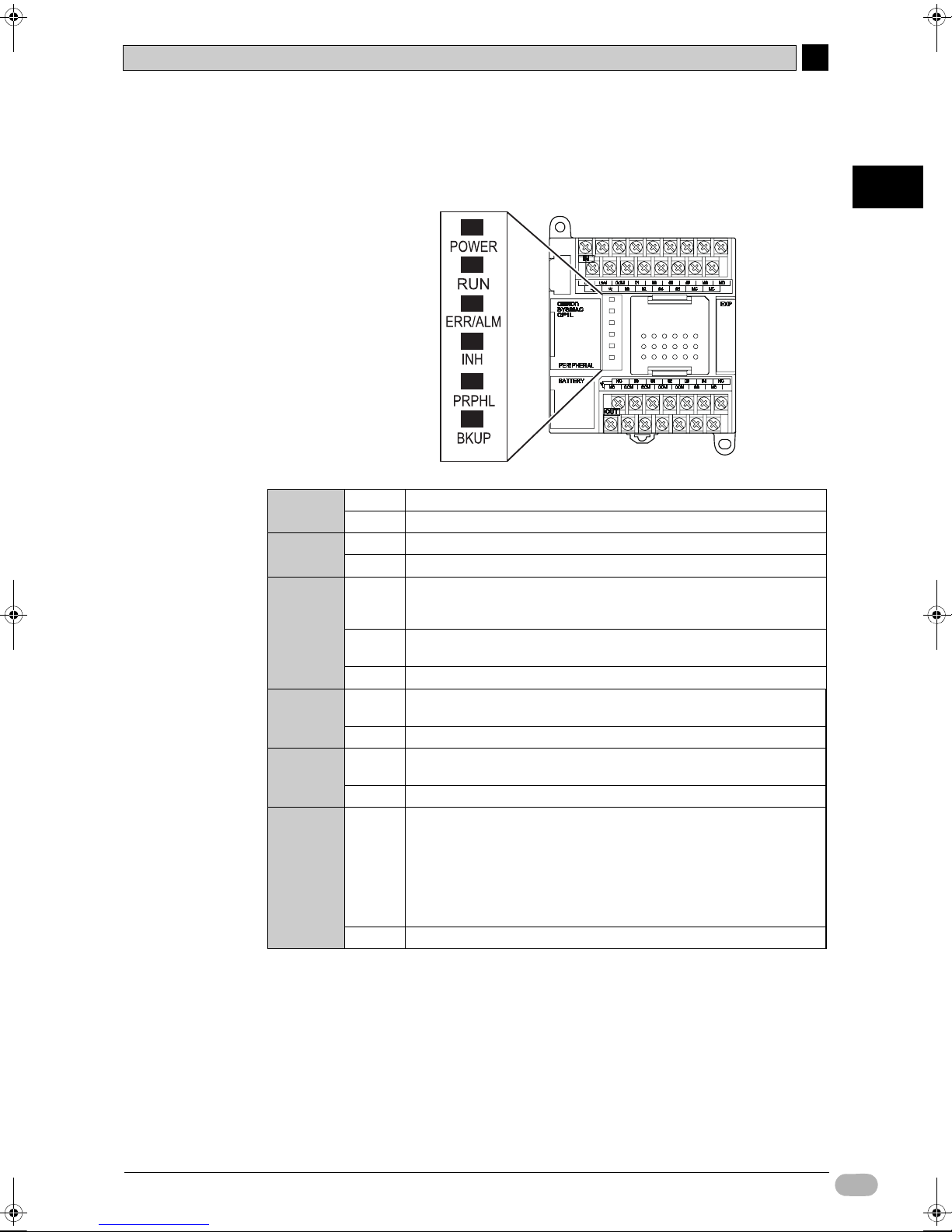
zIndicator Statuses
This section describes the operating statuses of CP1L as displayed by the
operation indicators.
1-2 Part Names and Functions
1
1
CP1L Overview
POWER
(Green)
RUN
(Green)
ERR/ALM
(Red)
INH
(Yellow)
PRPHL
(Yellow)
BKUP
(Yellow)
Lit Power is ON.
Not lit Power is OFF.
Lit CP1L is executing a program in either RUN or MONITOR mode.
Not lit Operation is stopped in PROGRAM mode, or stopped due to a fatal error.
Lit A fatal error (including FALS execution) or a hardware error (WDT error)
has occurred.
CP1L operation will stop, and all outputs will be turned OFF.
Blinking A non-fatal error (including FAL execution) has occurred.
CP1L operation will continue.
Not lit Operation normal.
Lit The output OFF bit (A500.15) has turned ON.
All outputs will be turned OFF.
Not lit Operation normal.
Blinking Communication (either sending or receiving) is active on the peripheral
USB port.
Not lit Any other state.
Lit • User program, parameter, or data memory is being written to or read
from the built-in flash memory (backup memory).
• User program, parameter, data memory, DM defaults, or comment
memory is being written to or read from the memory cassette.
• User programs, parameters, and data memory are being restored
following a PLC power-on.
Note: Do not turn the PLC power supply OFF while this indicator is lit.
Not lit Any other state.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 17
Page 19

1
CP1L Overview
1-2 Part Names and Functions
1
18 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 20

SECTION 2
Designing Systems
This section explains how to construct a CP1L system, using a
shutter control system as an example.
All subsequent sections are written based on the sample program
used in this section.
2-1 Organization of this Manual .................................................. 20
2-2 About the Shutter Control System ........................................ 22
2-2-1 Operation........................................................................ 22
2-2-2 System Components ...................................................... 23
2-3 I/O Allocation for the Shutter Control System ....................... 24
2-4 Example Ladder Program..................................................... 26
Page 21
2
Designing Systems
2-1 Organization of this Manual
Sections 2 through 5 of this manual explain the construction process of a CP1L system, from design to
operation, using a shutter control system as an example. Section contents are as follows:
2
Designing Systems
Section 2: Workflow from design to operation, shutter control system
specifications, components, and I/O allocation.
Section 3: CP1L installation, component wiring, and power testing.
Section 4: Connecting CP1L to a computer, and creating ladder programs.
Section 5: Setting PLC clock and PLC operation mode, transferring data from
computer to CP1L, operation, adjustment, and debugging.
Note Circuit configurations, wiring methods, and programs provided in this manual
are given strictly as examples. When constructing an actual system, check the
specifications, performance, and safety of each component by referring to the
respective manuals.
20 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 22
2-1 Organization of this Manual
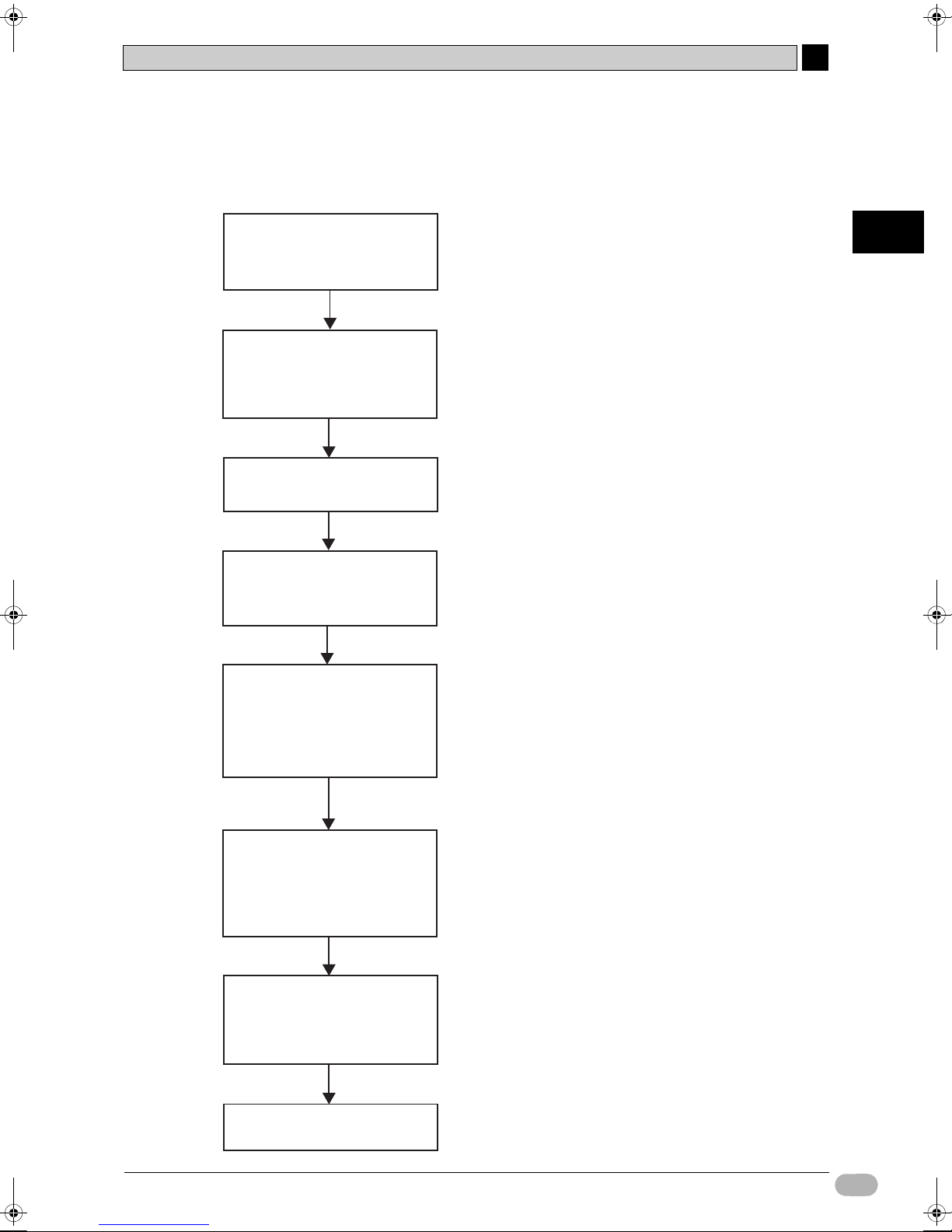
zWorkflow from Design to Operation
The workflow for constructing a CP1L shutter control system is shown below. For details, refer
to the respective sections of the manual.
2
I/O allocation
· Allocate relay numbers
to sensors and switches
Preparing the equipment
· Equipment preparation
· Wire power supply and ground
· Wire I/O devices
Supplying power to CP1L
· Test PLC operation
Preparing to write program
· Install USB driver onto computer
· Connecting CP1L to a computer
Writing programs
· Enter ladder programs
in CX-Programmer
· Compile
· Save
· Edit
Refer to 2-3 I/O Allocation for the Shutter Control
System.
Refer to 3-2 Mounting onto DIN Tracks and 3-3
Wiring Devices.
Refer to 3-4 Power Testing CP1L.
Refer to 4-1 Preparing for Programming.
Refer to 4-2 Creating a Ladder Program, 4-3 Using
CX-Programmer, 4-5 Inputting Programs, 4-6 Saving/
Loading Programs, and 4-7 Editing Programs.
2
Designing Systems
Going online with CP1L
and the computer
· Set the CP1L clock
· Switch to PROGRAM mode.
· Transfer the program
Online debugging
· Monitor power
· Force-set/force-reset commands
· Online Editing
Production run
Refer to 5-1 Going Online.
Refer to 5-2 Adjusting/Debugging Online.
Refer to 5-1 Going Online.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 21
Page 23
2
Designing Systems
2-2 About the Shutter Control System
2
2-2 About the Shutter Control System
This section defines the operation and components of a shutter control system.
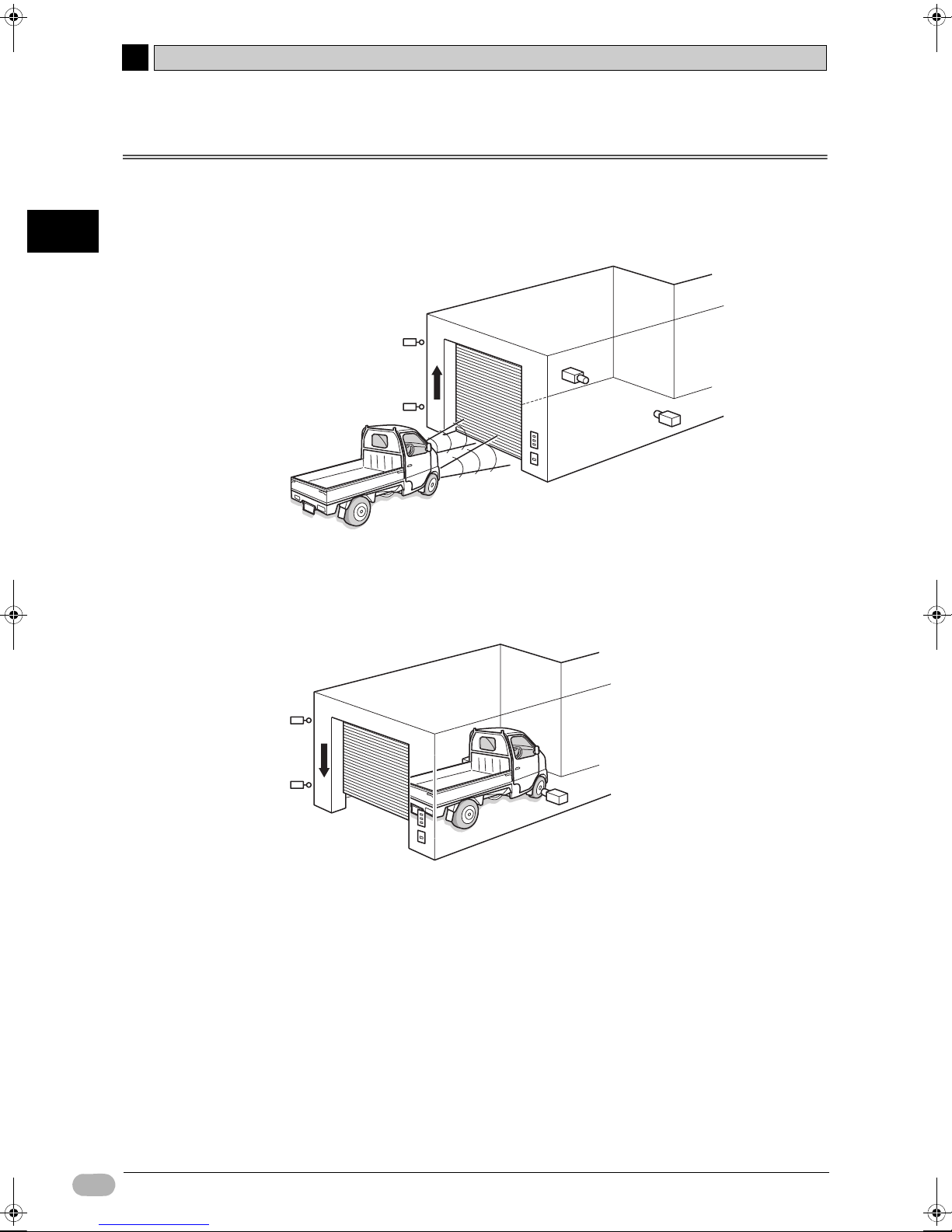
2-2-1 Operation
This section defines the operation of a shutter control system.
A car approaches the shutter.
• When a sensor detects 3 headlight flashes within 5 seconds, the shutter
opens.
• The shutter can also be opened, closed, and stopped with buttons.
• When a sensor detects full car entrance into the garage, the shutter closes.
• When pulling the car out of the garage, use the buttons to operate the shutter.
22 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 24
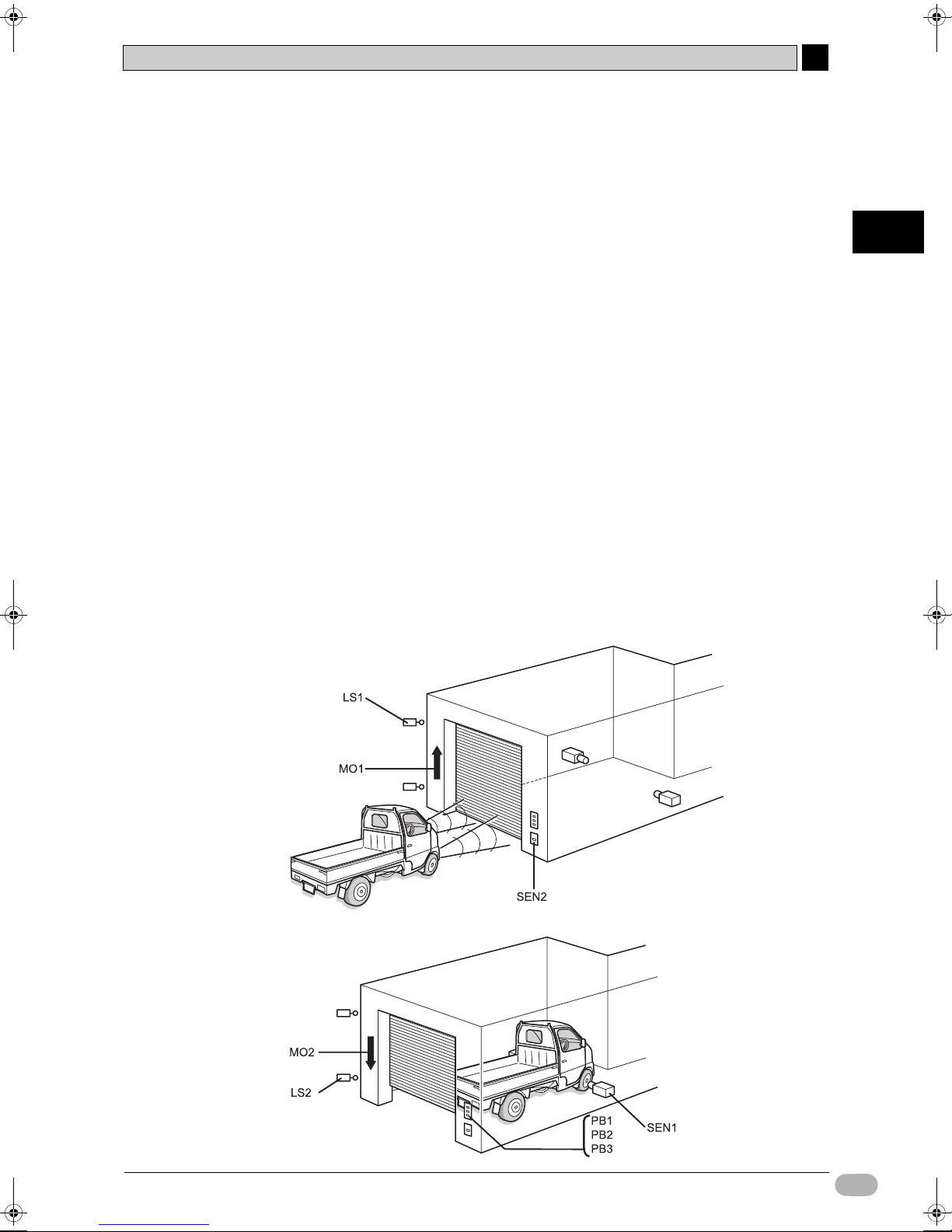
2-2-2 System Components
This section defines components to be used in the shutter control system. The
following components are to be used.
zPLC
• CP1L (14-point I/O unit with AC power supply)
2-2 About the Shutter Control System
2
2
zEquipment and Software for Programming
• CX-Programmer
•Computer
• USB cable (A-B)
zInputs
• Shutter OPEN button : PB1
• Shutter STOP button : PB2
• Shutter CLOSE button : PB3
• Car detection sensor : SEN1
• Headlight detection sensor : SEN2
• Limit switch, turned ON when shutter is fully open : LS1
• Limit switch, turned ON when shutter is fully closed : LS2
zOutputs
• Contact for activating the shutter escalation motor : MO1
• Contact for activating the shutter de-escalation motor : MO2
Designing Systems
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 23
Page 25
2
Designing Systems
2-3 I/O Allocation for the Shutter Control System
2
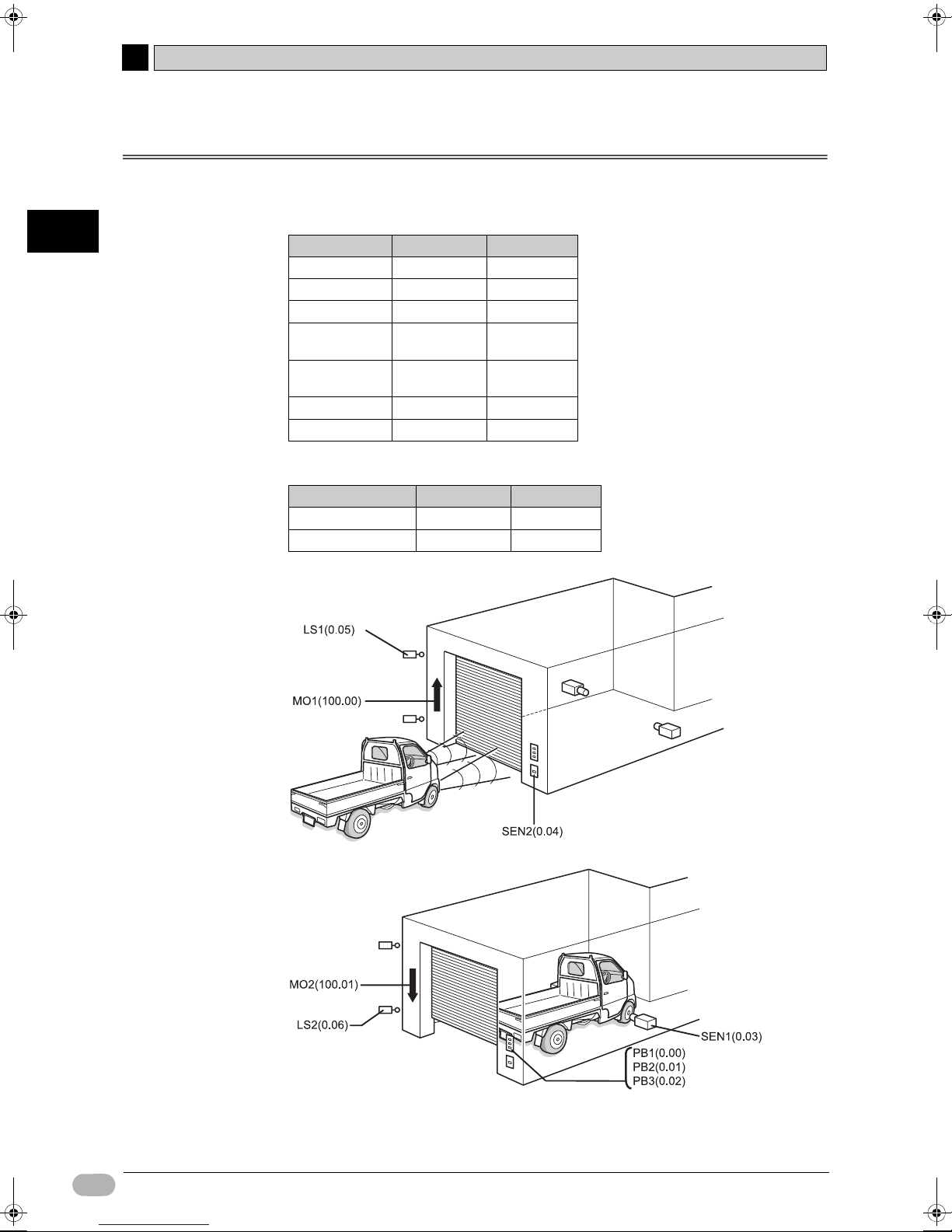
2-3 I/O Allocation for the Shutter Control System
I/O relays on CP1L are allocated to contacts as defined by following.
zInputs
Device Contact Address
OPEN button PB1 0.00
STOP button PB2 0.01
CLOSE button PB3 0.02
Car detection
sensor
Light detection
sensor
Upper limit LS LS1 0.05
Lower limit LS LS2 0.06
zOutputs
Device Contact Address
Escalation motor MO1 100.00
De-escalation motor MO2 100.01
SEN1 0.03
SEN2 0.04
24 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 26
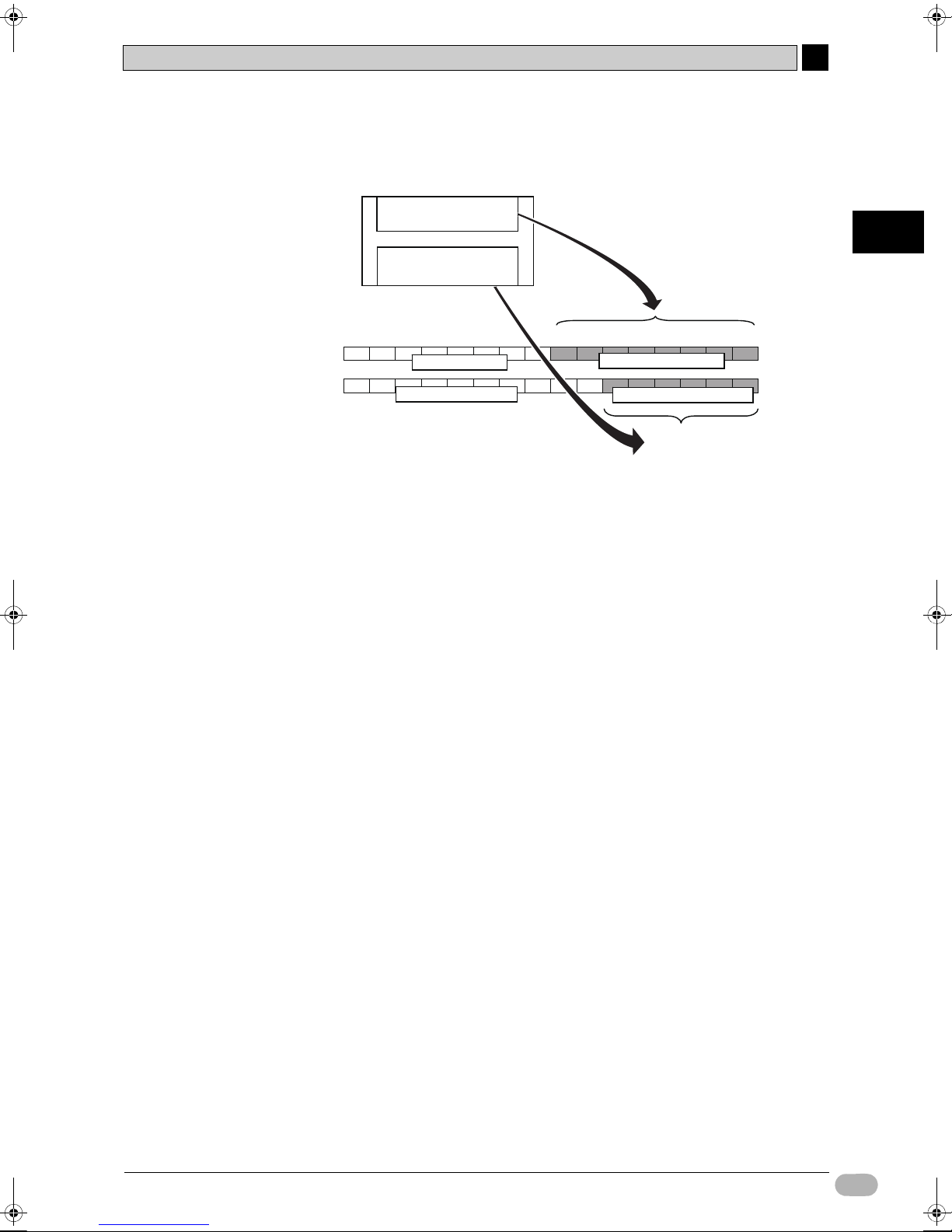
2-3 I/O Allocation for the Shutter Control System
Used as work area
zI/O Allocation on CP1L with 14-point I/O
8 inputs
2
Input Area
Output Area
100 CH
15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
0 CH
0 CH (0.00~0.07)
100 CH (100.00~100.05)
6 outputs
Not available
Allocate
Allocate
Input area : 8 inputs
Output area : 6 outputs
On 14-point I/O units, 8 inputs, from 0.00 to 0.07 (bits 00 to 07 on 0CH), are
allocated to the input terminal block.
Also, 6 output relays, from 100.00 to 100.05 (bits 00 to 05 on 100CH), are
allocated to the output terminal block.
Unused upper bits on the input channel (bits 08 to 15) cannot be used as a work
area. Unused upper bits on the output channel (bits 06 to 15) , however, can be
used.
2
Designing Systems
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 25
Page 27
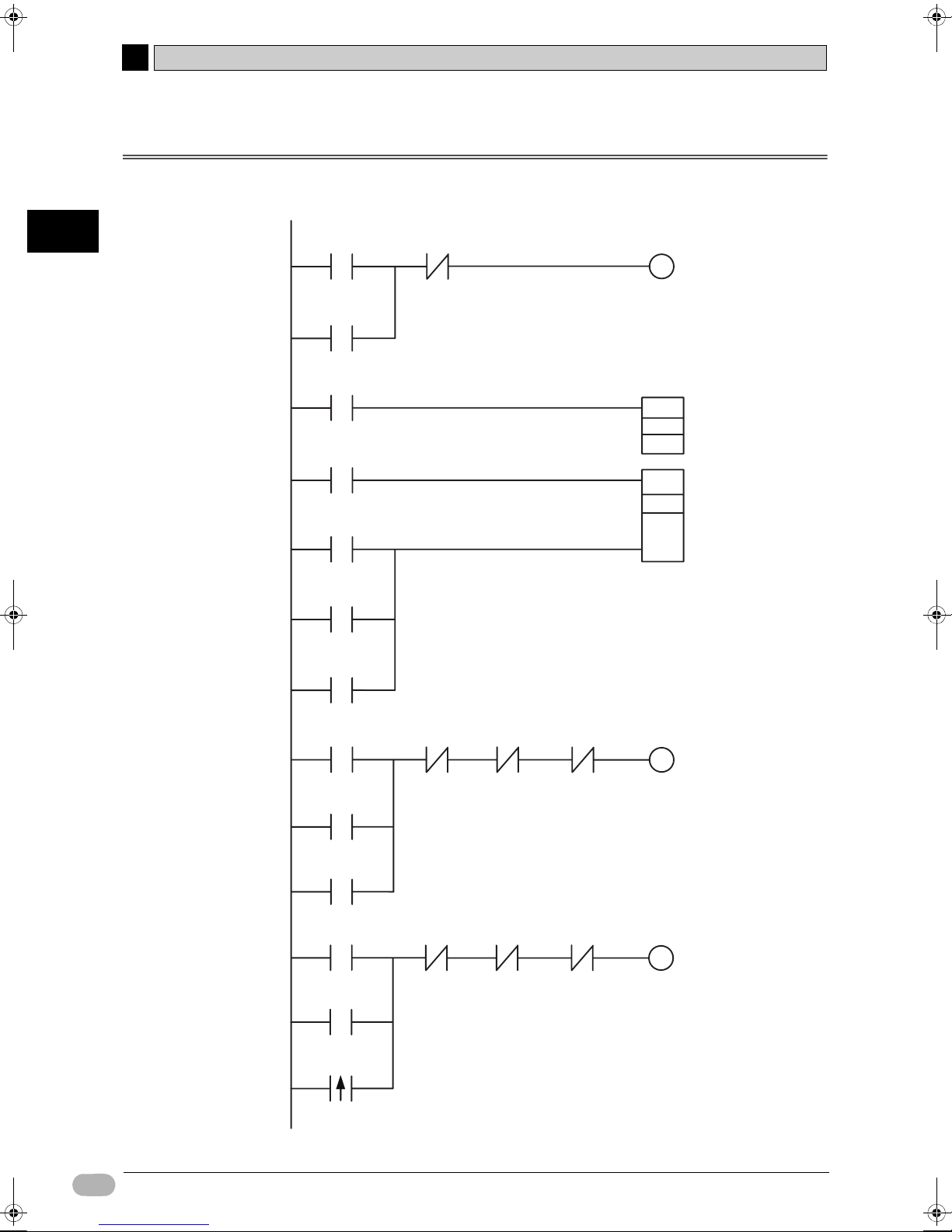
2-4 Example Ladder Program
2
2-4 Example Ladder Program
An example ladder program for the shutter control system is shown below. Program creation is explained
in SECTION 4.
2
Designing Systems
0.04
Light detection
sensor
W0.00
Work area
W0.00
Work area
0.04
Light detection sensor
T0000
Timer
C0000
Counter
A200.11
T0000
Timer
W0.00
Work area
TIM
0000
#50
CNT
0000
#3
Timer
Counter
P_First_Cycle First cycle flag
C0000
Counter
0.00
OPEN button
100.00
Escalation
motor
0.02
CLOSE button
100.01
De-escalation
motor
0.03
Car detection sensor
0.01
STOP button
0.01
STOP button
0.05
Upper
limit LS
0.06
Lower
limit LS
100.01
De-escalation
motor
100.00
Escalation
motor
100.00
Escalation
motor
100.01
De-escalation
motor
26 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 28

SECTION 3
Mounting and Wiring
This section explains how to install CP1L onto a DIN track, how to
wire power supply and I/O lines, and how to test operation.
3-1 Installation Notes .................................................................. 28
3-2 Mounting onto DIN Tracks .................................................... 31
3-3 Wiring Devices...................................................................... 32
3-3-1 Connecting Power Supply and Ground Lines ................ 32
3-3-2 Connecting I/O Lines ...................................................... 33
3-4 Power Testing CP1L ............................................................. 35
Page 29
3
Mounting and Wiring
3
Mounting and Wiring
3-1 Installation Notes
For improved reliability and maximized functionality, take the following factors into consideration when
installing a CP1L system.
Installation Location
Do not install in the following locations:
• Locations subject to ambient temperature lower than 0°
°C.
55
• Locations subject to dramatic temperature changes, causing possible
condensation.
• Locations subject to relative humidity lower than 10%RH or higher than
90%RH.
• Locations subject to corrosive or flammable gases.
• Locations subject to excessive dust, salt, or metal powder.
• Locations subject to shock or vibration.
• Locations exposed to direct sunlight.
• Locations subject to water, oil, or chemical reagent splashes.
C or higher than
Shield the system sufficiently when installing in the following locations:
• Locations subject to static electricity and other forms of noise.
• Locations subject to strong electromagnetic fields.
• Locations subject to possible radioactive exposure.
• Locations in close proximity to close to power lines.
Installation into Cabinets and Control Panels
When installing CP1L into a cabinet or control panel, ensure adequate
environment resistance, as well as sufficient accessibility for operation and
maintenance.
zTemperature Control
The ambient operating temperature for CP1L is 0 to 55°C. The following
precautions apply.
• Provide adequate space for air flow.
• Do not install above equipment, which generates significant heat (i.e. heaters,
transformers, high-capacity resistors).
• If the ambient temperature is to exceed 55
conditioner.
°C, install a cooling fan or air
28 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 30
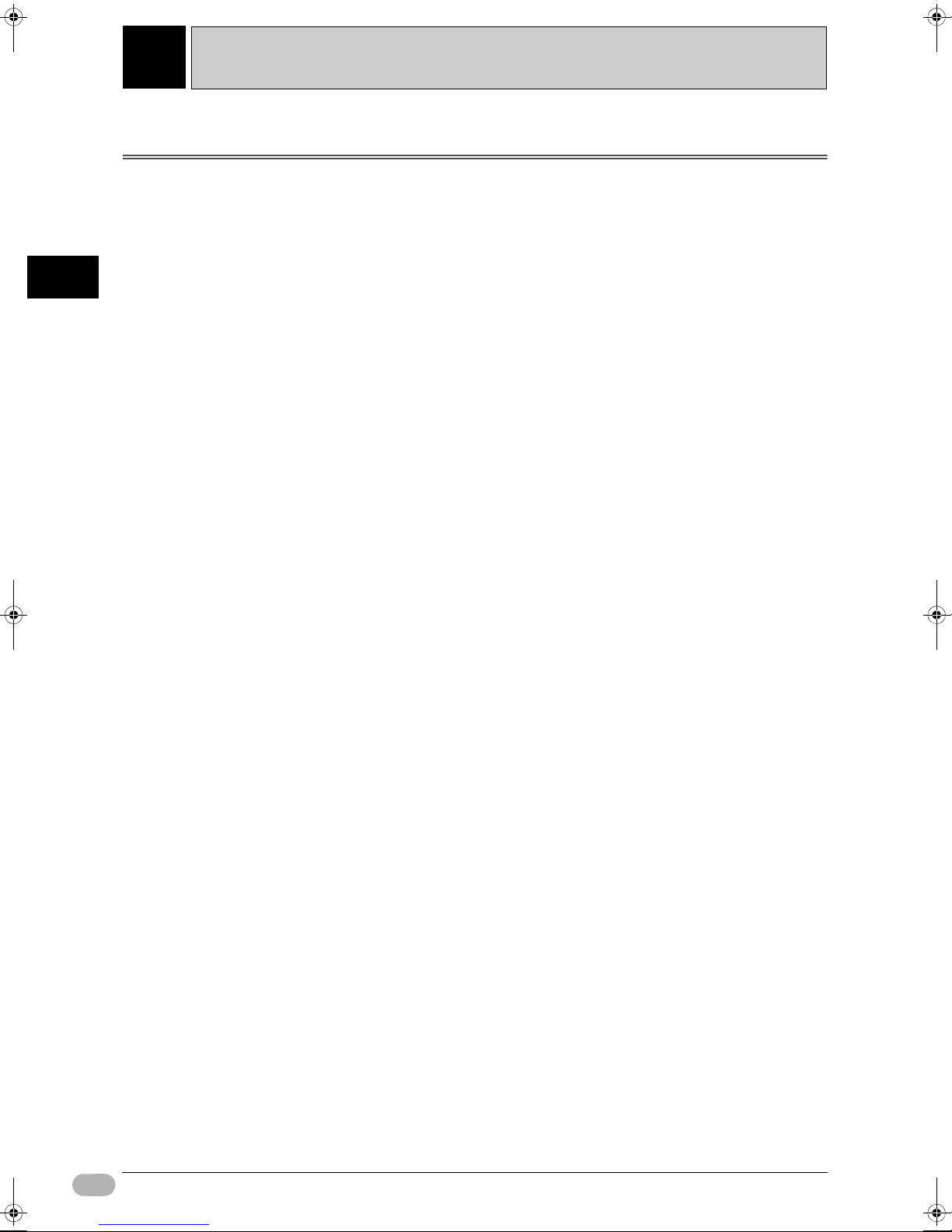
(1) Control panel
(2) Fan
(3) Louver
zAccessibility for Operation and Maintenance
• For safety during operation and maintenance, separate the unit as far as
possible from high-voltage equipment and power machinery.
• For ease of operation, mount the unit onto the control panel at a height of
1,000 to 1,600mm.
3-1 Installation Notes
3
3
Mounting and Wiring
Caution When power is ON or has just been turned OFF, do not touch the power supply,
I/O terminals, or the surrounding areas. Doing so may result in burns.
After turning the power OFF, wait for the unit to cool down sufficiently before
touching it.
zImproving Noise Resistance
• Avoid installing into a cabinet, which also has high-voltage equipment
installed.
• Secure at a distance of 200mm or more from power lines.
Power Line
200mm min.
CP1L
• Properly ground the mounting plate between the unit and the mounting
surface.
200mm min.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 29
Page 31

3
Mounting and Wiring
3-1 Installation Notes
3
zMounting
For heat dissipation, mount CP1L in the orientation shown below.
External Dimensions
DIN Track
Model W1 W2
CP1L-L10D- 66 56
CP1L-L14D- 86 76
CP1L-L20D- 86 76
CP1L-L30D- 130 120
CP1L-L40D- 150 140
CP1L-M60D- 195 185
Secure the DIN track onto the control panel, using at least 3 screws.
• Use M4 screws at intervals of 210mm (6 holes) or less. Screw torque is
·m.
1.2N
For details on installing CP1L, refer to SECTION 3 Installation and Wiring of CP
Series CP1L CPU Unit User’s Manual (W462).
30 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 32

3-2 Mounting onto DIN Tracks
This section explains how to mount CP1L onto a DIN track.
1. Pull out the DIN track mounting pin (1).
2. Hook the rear panel of CP1L onto the DIN track (1), as shown.
3-2 Mounting onto DIN Tracks
3
3
Mounting and Wiring
3. Push in the DIN track mounting pin (1) to secure CP1L.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 31
Page 33

3
Mounting and Wiring
3-3 Wiring Devices
3
3-3 Wiring Devices
This section explains how to wire CP1L (14-point I/O unit with AC power supply).
Protective Label
Wire scraps may be scattered during wiring. To prevent them from entering the
unit, leave the protective label (adhered on the top surface of the unit) on until
wiring is done.
When wiring is complete, remove the label to ensure proper heat dissipation.
3-3-1 Connecting Power Supply and Ground Lines
This section explains how to wire the power and ground lines.
Units with AC Power Supply
Power and ground terminals (A) are located near the top of CP1L.
Terminal block layout at (A)
4
1
2
(1) Power supply terminal
Supply 100 to 240VAC voltage at 50/60Hz.
The acceptable supply voltage range is 85 to 264VAC.
• Use separate circuits for the power supply circuit and the motor circuit, in
order to prevent voltage drops due to starting currents and inrush currents
from other equipment.
• Use a twisted-pair of power supply cables to prevent noise from the power
supply line. Adding a 1:1 isolating transformer will further reduce electrical
noise.
3
NC
NC
NC
NC
6.2mm max.
32 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 34

3-3 Wiring Devices
• In consideration of voltage drops and allowable current, use the thickest
electrical wire possible.
(2) LG
LG is a functional ground terminal (noise-filtered neutral terminal). To
resolve errors and electrical shocks caused by noise, short the LG and GR
terminals for a class D grounding (ground resistance of 100 or less).
3
(3) GR
GR is a protective ground terminal. To prevent electrical shocks, use a
dedicated ground line (2mm
resistance of 100 or less).
• To prevent electrical shocks and noise, always ground the terminal with
class D grounding (ground resistance of 100 or less).
• If the power supply has a grounded phase, connect the grounded phase to
the L2/N terminal.
• Do not share the ground line with other equipment, or connect it to building
structure beams. The results may be unfavorable.
(4) Recommended crimp terminal
When wiring the AC power supply, use ring-type crimp terminals to prevent
unintended disconnection.
WARNING Secure the AC power supply line to the terminal block with 0.5N·m of torque.
Loosening the screw may result in a fire or malfunction.
3-3-2 Connecting I/O Lines
14-point I/O Units
CP1L has input terminals located at the top, and output terminals located at the
bottom.
2
or thicker) for a class D grounding (ground
3
Mounting and Wiring
(1) Input terminal
(2) Output terminal
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 33
Page 35

3
Mounting and Wiring
3-3 Wiring Devices
3
zWiring Inputs
zWiring Outputs
1. Wire the inputs as shown, while referring to 2-3 I/O Allocation for the
Shutter Control System.
1. Wire the outputs as shown, while referring to 2-3 I/O Allocation for the
Shutter Control System.
For details on wiring, refer to 3-5-4 I/O Wiring for CPU Units with 14 I/O Points
of CP Series CP1L CPU Unit User’s Manual (W462).
34 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 36

3-4 Power Testing CP1L
After wiring CP1L, perform a power test.
Turning Power ON
Supply power to CP1L, and then check the status with the indicators.
3-4 Power Testing CP1L
3
1. Turn the power OFF for all components (escalation motor,
de-escalation motor, etc.).
2. Turn the power ON for CP1L.
3. Wait 2 seconds for the CP1L to initialize.
4. Check the indicators on CP1L. If [POWER] and [RUN] are lit, CP1L is
operating normally.
Note When CP1L is turned ON, it will go into RUN mode automatically.
3
Mounting and Wiring
5. Turn the power OFF for CP1L.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 35
Page 37

3
3-4 Power Testing CP1L
3
Note Battery
• Using a battery
The battery maintains the internal clock and retained regions of I/O memory
while the power supply is OFF.
If no battery is installed, or if the installed battery is running low, the internal
clock will stop, and data in the retained regions of I/O memory will be lost.
Data such as user programs and PLC system settings are not lost even when
the power is OFF and no battery is installed.
Mounting and Wiring
For details on replacing the battery, refer to 10-2 Replacing User-servicable
Parts of CP Series CP1L CPU Unit User’s Manual (W462).
• Battery-free operation
If there is no need to reference the PLC clock and RAM data, CP1L can be
used without a battery (battery-free operation).
For details, refer to 6-5 Battery-free Operation of CP Series CP1L CPU Unit
User’s Manual (W462).
36 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 38

SECTION 4
Creating Programs
In this section, the steps for creating ladder programs essential to
CP1L operation will be shown, using CX-Programmer. In creating
the ladder program for the shutter control system, the basic
functions of CX-Programmer will be explained.
4-1 Preparing for Programming................................................... 38
4-1-1 What is CX-Programmer? .............................................. 38
4-1-2 Connecting to a Computer
and Installing the USB Driver ......................................... 39
4-2 Creating Ladder Programs ................................................... 44
4-2-1 Operation........................................................................ 44
4-2-2 Ladder Program.............................................................. 46
4-3 Using CX-Programmer.......................................................... 47
4-3-1 Starting CX-Programmer ................................................ 47
4-3-2 Operation Screens.......................................................... 48
4-4 Using the Help ...................................................................... 50
4-5 Inputting Programs ............................................................... 53
4-5-1 Creating New Projects.................................................... 53
4-5-2 Inputting Contacts........................................................... 56
4-5-3 Inputting Output Coils ..................................................... 59
4-5-4 Inputting Timers.............................................................. 61
4-5-5 Inputting Counters .......................................................... 63
4-5-6 Inputting Auxiliary Areas................................................. 66
4-5-7 Inputting Differentiated Up Contacts............................... 68
4-5-8 END Instruction .............................................................. 69
4-6 Saving/Loading Programs .................................................... 70
4-6-1 Compiling Programs ....................................................... 70
4-6-2 Saving Programs ............................................................ 71
4-6-3 Loading Programs .......................................................... 72
4-7 Editing Programs .................................................................. 73
4-7-1 Editing I/O Comments .................................................... 73
4-7-2 Inputting Rung Comments.............................................. 74
4-7-3 Editing Rungs ................................................................. 75
Page 39

4
Creating Programs
4
Creating Programs
4-1 Preparing for Programming
This section explains the necessary preparations, such as connecting CP1L to a computer and installing
the USB driver, in order to begin creating ladder programs.
4-1-1 What is CX-Programmer?
CX-Programmer is a programming tool (software) for creating the ladder
programs that are to be executed by CP1L.
In addition to programming functions, it also offers other useful functions for CP1L
setup and operation, such as debugging programs, address and values display,
PLC setup and monitoring; and remote programming and monitoring via the
network.
CX-Programmer can be run on computers running Windows 98 SE, Me, NT 4.0
(SP6a), 2000 (SP3 or later), or XP.
For details on installing CX-Programmer, refer to 1-1 Installation of CX-
Programmer of CX-Programmer Introduction Guide (R132).
For details on using CX-Programmer, refer to CX-Programmer Operation Manual
(W446).
38 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 40

4-1 Preparing for Programming
4-1-2 Connecting to a Computer and Installing the USB Driver
To use CX-Programmer, you must connect CP1L to a computer, which has CXProgrammer installed. This section explains how to connect CP1L to a computer.
The computer to be connected to must have CX-Programmer Ver.7.1 or later
installed.
You will also need a USB cable to connect CP1L to the computer.
Furthermore, a USB driver must be installed for CP1L to be recognized by the
computer.
4
zItems Required for Connection
Operating system Windows 98, Me, 2000, or XP
Software CX-One (i.e. CX-Programmer)
USB driver Included with software
USB cable USB 1.1 (or 2.0) cable (A-B), 5m or shorter
zRestrictions on USB Connections
Due to limitations of the USB specifications, the following restrictions apply when
connecting CP1L to a computer.
• Only 1 CP1L can be connected to a computer at any given time. You cannot
connect multiple CP1Ls simultaneously.
• Do not disconnect the USB cable while the system is online. Before
disconnecting the USB cable, switch the application to offline status. If the USB
cable is disconnected while online, the following will occur:
[Windows 2000, XP]
Simply reconnecting the USB cable will not restore CX-Programmer to online
status. First switch CX-Programmer to offline status, reconnect the USB cable,
and then switch CX-Programmer back to online status.
[Windows 98, Me]
If the USB cable is disconnected while the system is online, a blue error
screen may be displayed. In this case, you will need to reboot the computer.
4
Creating Programs
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 39
Page 41

4
Creating Programs
4-1 Preparing for Programming
4
Connecting to a Computer and Installing the USB Driver
This section explains how to connect CP1L to a computer running Windows XP.
For details on connecting CP1L to a computer running Windows 2000, refer to
1-3-1 Connecting with a Commercially Available USB Cable of CP Series CP1L
CPU Unit User’s Manual (W462).
1. Turn the power ON for CP1L and the computer.
2. Using a USB cable (2), connect the peripheral USB port (3) on CP1L to a
USB port on the computer
(1).
When the computer detects CP1L, the following message will be displayed.
The Found New Hardware Wizard dialog box will be displayed. This screen will be
used to install the USB driver.
Note The programming console is not available for CP1L.
3. On the Found New Hardware Wizard dialog box, select [No, not this time],
and click [Next].
Depending on computer environment, the Found New Hardware Wizard dialog box
may not be displayed. If it is not displayed, proceed to step 4.
40 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 42

4-1 Preparing for Programming
4
4. Select [Install from a list of specific location (Advanced)], and click [Next].
5. Confirm that [Include this location in the search] is checked, and that
[C:\Program Files\OMRON\CX-Server\USB\Win2000_XP\Inf] is displayed
in the location field. Click [Next].
Driver installation will begin.
When the installation is complete, a dialog box will be displayed, confirming that
installation is complete.
4
Creating Programs
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 41
Page 43
4
Creating Programs
4-1 Preparing for Programming
4
If the Hardware Installation dialog box is displayed, click [Continue Anyway].
6. Click [Finish].
USB driver installation is now complete.
p
42 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 44
Confirming Installation
Confirm that the driver has been installed properly.
1. On the desktop, select [Start], and then right-click [My Computer].
A context menu will be displayed.
2. Select [Properties].
The System Properties dialog box will be displayed.
4-1 Preparing for Programming
4
3. Select the Hardware tab, and click [Device Manager].
The Device Manager dialog box will be displayed.
4. Double-click [Universal Serial Bus controllers].
5. Confirm that [OMRON SYSMAC PLC Device] is displayed.
If so, the USB driver has been installed successfully.
4
Creating Programs
6. Close the Device Manager dialog box, and then the System Properties
dialog box.
If [OMRON SYSMAC PLC Device] is not displayed, reinstall the USB driver.
For details on reinstalling the USB driver, refer to 1-3-1 Connecting with a
Commercially Available USB Cable of CP Series CP1L CPU Unit User’s
Manual (W462).
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 43
Page 45

4-2 Creating Ladder Programs
4
4-2 Creating Ladder Programs
A ladder program can now be created for the example introduced in SECTION 2 System Design. First,
however, the functions of the ladder program will be described.
4-2-1 Operation
The ladder program to be created will open and close a garage shutter.
For details on the example application, refer to 2-2-1 Operation.
4
Creating Programs
zEntering the Garage
2
2
1
3
The component functions and operations will be defined in detail below.
(1) Push-buttons:
• The shutter can be opened, closed, and stopped with buttons.
• The OPEN and CLOSE buttons will continue operating the shutter even when
they are not held down. A self-maintaining bit is used to achieve this.
(2) Limit switches:
• When the shutter is fully opened or fully closed, it will be stopped by a limit
switch.
• When the shutter is opening, the de-escalation motor will be interlocked to
prevent damage.
(3) Light detection sensor:
• A light detection sensor detects light from headlights pointed at the garage.
When 3 headlight flashes are detected by a counter instruction, the shutter
escalation motor is activated.
• After the first headlight flash, a timer is activated by a timer instruction. After 5
seconds, a reset command is given to the counter instruction.
• The present value of the counter instruction is retained even when CP1L is
powered OFF. To prevent malfunction, a reset command is given to the
counter instruction when CP1L is powered ON.
44 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 46

zAfter Entering the Garage / Exiting the Garage
(1) Car detection sensor:
• A car detection sensor will detect full car entrance into the garage, and activate
the shutter de-escalation motor.
(2) Push-buttons:
• When pulling the car out of the garage, use the buttons to operate the shutter.
• When pulling the car out of the garage, a differentiated up contact should be
used as the car detection sensor, so that the shutter does not close
immediately upon fully opening.
4-2 Creating Ladder Programs
4
4
Creating Programs
A ladder program will be set forth hereafter based on the description above.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 45
Page 47

4-2 Creating Ladder Programs
4
4-2-2 Ladder Program
The ladder program for the example application is shown below.
4
Creating Programs
0.04
Light detection
sensor *1
W0.00
Work area *2
W0.00
Work area
0.04
Light detection sensor
T0000
Timer
C0000
Counter
A200.11
T0000
Timer *3
W0.00
Work area *4
*1 Refer to Inputting Contacts of 4-5-2 Inputting Contacts.
*2 Refer to Inputting OR Circuits of 4-5-2 Inputting Contacts.
*3 Refer to Inputting Closed Contacts of 4-5-2 Inputting Contacts.
*4 Refer to 4-5-3 Inputting Output Coils.
TIM
0000
Timer *5
#50
CNT
Counter *6
0000
#3
*5 Refer to 4-5-4 Inputting Timers.
*6 Refer to 4-5-5 Inputting Counters..
*7 Refer to 4-5-6 Inputting Auxiliary Areas.
P_First_Cycle First cycle flag *7
C0000
Counter
0.00
OPEN button
100.00
Escalation
motor
0.02
CLOSE button
100.01
De-escalation
motor
0.03
Car detection sensor *8
0.01
STOP button
0.01
STOP button
0.05
Upper
limit LS
0.06
Lower
limit LS
100.01
De-escalation
motor
100.00
Escalation
motor
*8 Refer to 4-5-7 Inputting Differentiated Up Contacts.
100.00
Escalation
motor
100.01
De-escalation
motor
Creating the program in CX-Programmer will be explained in the next section.
46 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 48

4-3 Using CX-Programmer
This section explains CX-Programmer start-up and operation screens..
4-3-1 Starting CX-Programmer
1. On the desktop, select [Start] - [All Programs] - [OMRON] - [CX-One] - [CX-
Programmer] - [CX-Programmer].
CX-Programmer will start.
The title screen will be displayed, followed by the main window.
4-3 Using CX-Programmer
4
4
Creating Programs
Note For details on installing CX-Programmer, refer to Chapter 1 Overview and
Installation of CX-One of CX-One Introduction Guide (R145).
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 47
Page 49

4
Creating Programs
4-3 Using CX-Programmer
4
4-3-2 Operation Screens
This section explains the functions available on the CX-Programmer main window.
For details on using CX-Programmer, refer to CX-Programmer Operation Manual
(W446).
zMain Window
1
2
3
4
5
6
9
7
8
10
(1) Title bar
Displays the data file name, created in CX-Programmer.
(2) Main menu
Used to select CX-Programmer functions.
(3) Toolbars
Displays icons for frequently used functions. Place the mouse cursor over an
icon to display the corresponding function name.
Select View - Toolbars from the main menu to show/hide toolbars. Drag the
toolbars to change their position.
(4) Project tree / (6) Project workspace
Used to manage programs and settings. Drag & drop items to copy the data.
Select [View] - [Windows] - [Workspace] from the main menu to show/hide the
workspace.
(5) Section
Programs can be split into and managed as multiple parts.
(7) Diagram workspace
Used to create and edit ladder programs.
(8) I/O comment bar
Displays the name, address/value, and I/O comment for the variable selected
by the mouse cursor.
48 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 50

4-3 Using CX-Programmer
(9) Output window
Select [View] - [Windows] - [Output] from the main menu to show/hide the
output window. Displays the following information:
Compile:
Displays program check results.
Find Report:
Displays search results for contacts, instructions, and coils.
Transfer:
Displays errors which occurred while loading a project file.
4
(10) Status bar
Displays information such as PLC name, offline/online status, and active cell
position.
If an online connection error or other errors occur and are recorded by the
error log while online, a blinking red error message will be displayed. Select
[View] - [Windows] - [Status Bar] from the main menu to show/hide the status
bar.
zDiagram Workspace
(1) Rung number
(2) Program address
4
Creating Programs
(3) Rung header
If a rung is incomplete, a red line will be displayed to the right of its rung
header.
(4) Bus bar
zInformation Window
Displays basic shortcut keys used in CX-Programmer.
Select [View] - [Windows] - [Information Window] from the main menu to show/hide
the information window.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 49
Page 51

4
Creating Programs
4-4 Using the Help
4
4-4 Using the Help
CX-Programmer Help provides information on the CX-Programmer screens, and explains all operations
including basic functions, program creation, and monitoring. Instructions, as well as formats and operand
functions, are also explained.
Referencing CX-Programmer Help
1. While using CX-Programmer, press the [F1] key.
The help window will be displayed.
CX-Programmer Help can also be displayed in several other ways.
zFrom the Desktop Menu
1. On the desktop, select [Start] - [All Programs] - [OMRON] - [CX-One] - [CX-
Programmer] - [CX-Programmer Help].
CX-Programmer Help will be displayed.
50 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 52

zFrom CX-Programmer
1. Select [Help] - [Help Contents] from the main menu.
CX-Programmer Help will be displayed.
Referencing PLC Instruction Sets
For details on instructions used in ladder programs, refer to PLC Instruction Sets.
4-4 Using the Help
4
4
Creating Programs
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 51
Page 53

4
Creating Programs
4-4 Using the Help
4
zFrom CX-Programmer
1. Select [Help] - [Instruction Reference] - [CS/CJ-Series and CP-Series]
from the main menu.
CP-Series PLC Instruction Sets will be displayed.
zWhile Creating Ladder Programs
1. While creating a ladder program instruction, click [Instruction Help] on
the New Instruction dialog box.
CP-Series PLC Instruction Sets will be displayed.
Note When selecting a special instruction, Instruction Help will be displayed.
52 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 54

4-5 Inputting Programs
4-5 Inputting Programs
Using the commands available in CX-Programmer, create a program for the example application.
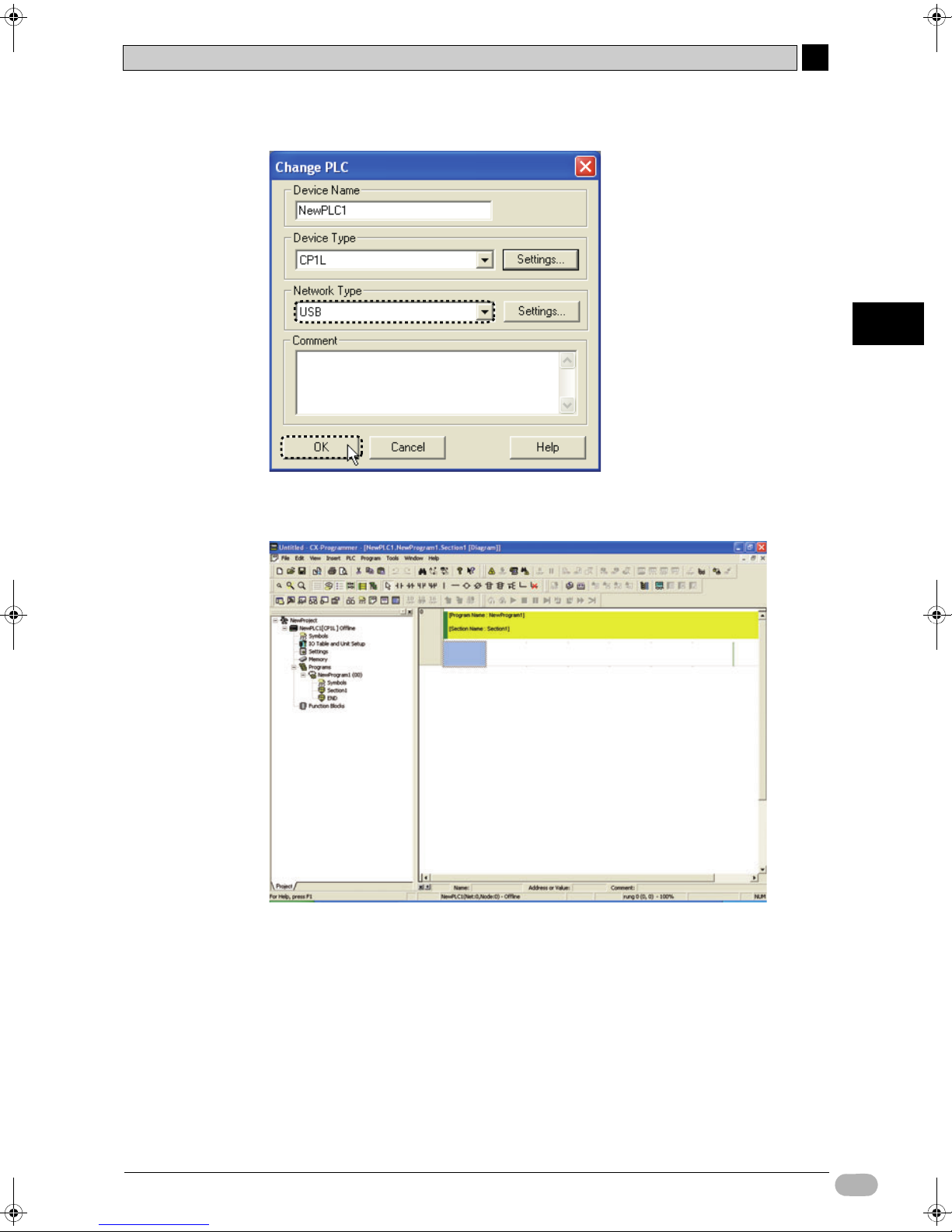
4-5-1 Creating New Projects
When using CX-Programmer for the first time, you will need to create a new
project. When creating a new project, you must set the target device type and CPU
type for the program and data being created.
4
1. Select [File] - [New] from the main menu.
The Change PLC dialog box will be displayed.
2. Select [CP1L] from the Device Type drop-down list.
4
Creating Programs
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 53
Page 55

4
Creating Programs
4-5 Inputting Programs
4
3. Click [Settings].
The Device Type Settings dialog box will be displayed.
4. Select the CPU from the CPU Type drop-down list. Click [OK].
The Device Type Settings dialog box will be closed.
54 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 56
4-5 Inputting Programs
5. Confirm that [USB] is displayed for Network Type. Click [OK].
The Change PLC dialog box will be closed. Main window for the new project will be
displayed.
4
4
Creating Programs
If [USB] is not displayed for Network Type, refer to 4-1-2 Connecting to a Computer
and Installing the USB Driver and confirm that the USB driver has been installed
properly.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 55
Page 57

4
Creating Programs
4-5 Inputting Programs
4
4-5-2 Inputting Contacts
Input a contact. For details on ladder programs, refer to 4-2-2 Ladder Program.
Inputting Contacts
1. Press the [C] key.
The New Contact dialog box will be displayed.
2. Input address "4". Press the [Enter] key.
"4" is entered. The Edit Comment dialog box will be displayed.
3. Input "Light detection sensor" as the I/O comment. Press the [Enter] key.
A contact representing input from the light detection sensor will be displayed on the
ladder program.
Next, input an OR circuit.
56 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 58

Inputting OR Circuits
1. Place the cursor on the program. Press the [Enter] key.
A space for inserting an OR circuit will be created.
2. Press the [W] key.
The New Contact OR dialog box will be displayed.
4-5 Inputting Programs
4
4
Creating Programs
3. Input address "W0". Press the [Enter] key.
"W0" is entered. The Edit Comment dialog box will be displayed.
4. Input "Work Area" as the I/O comment. Press the [Enter] key.
An OR circuit representing the work area contact will be displayed.
Next, input a closed contact.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 57
Page 59

4
Creating Programs
4-5 Inputting Programs
4
Inputting Closed Contacts
1. Press the up arrow key.
The cursor is moved upward.
2. With the cursor in the up position, press the [/] key.
The New Closed Contact dialog box will be displayed.
3. Input address "T0". Press the [Enter] key.
"T0" is entered. The Edit Comment dialog box will be displayed.
4. Input "Timer" as the I/O comment. Press the [Enter] key.
An AND circuit representing the timer closed contact will be displayed.
Next, input a work area output.
58 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 60
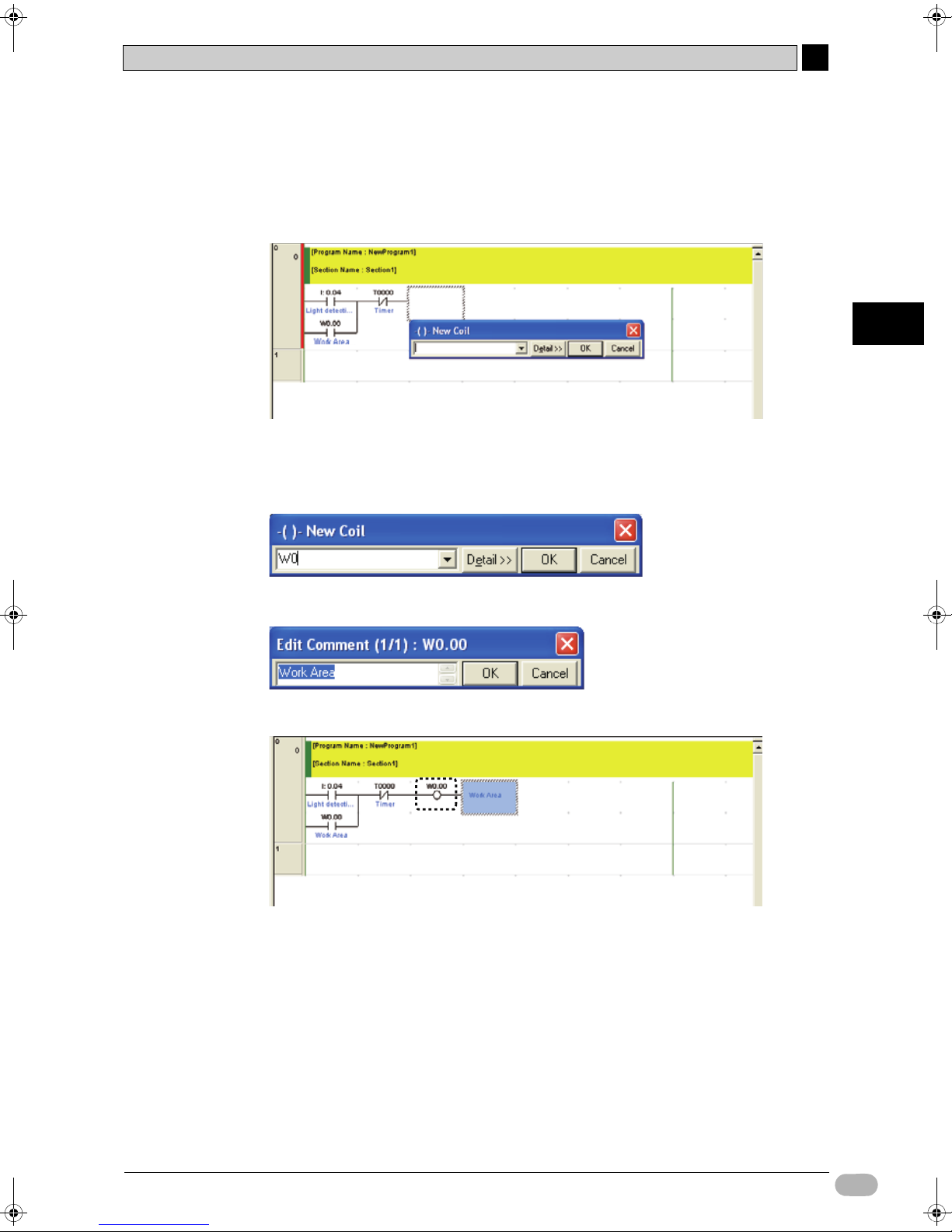
4-5-3 Inputting Output Coils
Input an output coil for the work area.
1. Press the [O] key.
The New Coil dialog box will be displayed.
2. Input address "W0". Press the [Enter] key.
"W0" is entered. The Edit Comment dialog box is displayed with the I/O comment
already entered.
4-5 Inputting Programs
4
4
Creating Programs
3. Press the [Enter] key.
An output coil for the work area will be displayed on the ladder program.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 59
Page 61

4
Creating Programs
4-5 Inputting Programs
4
4. Press the down arrow key 2 times.
Note Duplicated Coils
When the cursor is positioned on the next rung, the current rung input is complete.
Next, input a timer instruction.
Do not duplicate coils.
If the same address is specified for multiple outputs, only the rung closer to the
END instruction will be valid.
This is because programs are executed sequentially from top to bottom. Invalid
rungs caused by duplicated coils will be detected by CX-Programmer as an error.
E.g. A program with duplicated coils
The error may be resolved by modifying the program as shown below.
60 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 62

4-5-4 Inputting Timers
1. Press the [C] key. Input contact "W000". Then, press the [Enter] key
while the Edit Comment dialog box is up.
For details on inputting a contact, refer to 4-5-2 Inputting Contacts.
2. Press the [I] key.
The New Instruction dialog box will be displayed.
4-5 Inputting Programs
4
4
Creating Programs
3. Input timer instruction "TIM 0 #50". Press the [Enter] key.
"TIM 0 #50" is entered. The Edit Comment dialog box is displayed with the I/O
comment already entered.
"TIM 0 #50" indicates a 5.0 second delay timer, with a timer completion flag of
T0000.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 61
Page 63

4
Creating Programs
4-5 Inputting Programs
4
4. Press the [Enter] key.
A timer instruction will be displayed on the ladder program.
5. Press the down arrow key 3 times.
When the cursor is positioned on the next rung, timer instruction input is complete.
Next, input a counter instruction.
62 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 64

4-5-5 Inputting Counters
1. Press the [C] key. Input contact "004". Then, press the [Enter] key while
the Edit Comment dialog box is up.
For details on inputting a contact, refer to 4-5-2 Inputting Contacts.
2. Press the [I] key.
The New Instruction dialog box will be displayed.
4-5 Inputting Programs
4
4
Creating Programs
3. Input counter instruction "CNT 0 #3". Press the [Enter] key.
"CNT 0 #3" is entered. The Edit Comment dialog box is displayed with the I/O
comment already entered.
"CNT 0 #3" indicates a decrementing counter starting at count 3, with a counter
completion flag of C0000.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 63
Page 65

4
Creating Programs
4-5 Inputting Programs
4
4. Input "Counter" as the I/O comment. Press the [Enter] key.
A counter instruction will be displayed on the ladder program.
Next, input a reset input for the counter instruction.
The timer contact (TIM 0000) will be used as the reset input.
5. Place the cursor below the contact created in step 1.
64 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 66

4-5 Inputting Programs
6. Input contact "T0000".
7. Press the down arrow key 2 times.
When the cursor is positioned on the next rung, counter instruction input is
complete.
4
4
Creating Programs
Next, input an auxiliary area.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 65
Page 67

4
Creating Programs
4-5 Inputting Programs
4
4-5-6 Inputting Auxiliary Areas
Auxiliary area is a relay with a specific purpose.
The first cycle flag will be ON for only 1 cycle after the PLC has been powered ON.
Here, it will be used to reset the counter when CP1L is powered ON.
1. Press the [W] key. Input an OR circuit contact "C0000". Then, press the
[Enter] key while the Edit Comment dialog box is up.
For details on inputting a contact, refer to 4-5-2 Inputting Contacts.
2. Press the [Enter] key.
A space for inserting an OR circuit will be created.
66 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 68

3. Press the left arrow key.
4. Press the [W] key.
The New Contact OR dialog box will be displayed.
5. Input address "A20011". Press the [Enter] key.
4-5 Inputting Programs
4
A first cycle flag will be displayed on the ladder program.
4
Creating Programs
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 67
Page 69

4
Creating Programs
4-5 Inputting Programs
4
4-5-7 Inputting Differentiated Up Contacts
1. While referring to 4-2-2 Ladder Programs, enter a ladder program,
extending to de-escalation motor contact,
2. Press the [Enter] key.
A space for inserting an OR circuit will be created.
3. Press the [W] key.
The New Contact OR dialog box will be displayed.
"10001".
4. Input address "3". Press the [Enter] key.
The Edit Comment dialog box will be displayed.
5. Input "Car detection sensor" as the I/O comment. Press the [Enter] key.
A contact representing input from the car detection sensor will be displayed as an
OR circuit.
6. Double-click contact "003".
The Edit Contact dialog box will be displayed.
68 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 70

7. Click [Detail].
8. Select [Up] for Differentiation. Click [OK].
4-5 Inputting Programs
4
4
Creating Programs
An upward arrow representing a differentiated up condition will be displayed on the
contact.
4-5-8 END Instruction
Ladder programs must be terminated with an END instruction.
When a new program is created in CX-Programmer, a section inclusive of an END
instruction will be inserted automatically. Hence, there is no need to input an END
instruction manually.
To confirm the ladder program containing only the END instruction, double-click the
[END] section.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 69
Page 71

4
Creating Programs
4-6 Saving/Loading Programs
4
4-6 Saving/Loading Programs
Created ladder programs must be saved. This section explains how to check, save, and load ladder
programs.
4-6-1 Compiling Programs
By compiling, you can check for errors in the program.
1.
Select [PLC] - [Compile All PLC Programs] from the main menu.
The compilation is started.
When the compilation is complete, program check results will be displayed in the
output window.
2. If an error has been detected, double-click the error message in the
output window.
The cursor is moved to where the error was detected. Correct the error.
70 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 72

4-6-2 Saving Programs
Save the created ladder program. Programs are saved in groups for each project.
1. Select [File] - [Save As] from the main menu.
The Save CX-Programmer File dialog box will be displayed.
2. Specify the save location, and input a file name. Click [Save].
The CX-Programmer project file will be saved.
4-6 Saving/Loading Programs
4
4
Creating Programs
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 71
Page 73

4
Creating Programs
4-6 Saving/Loading Programs
4
4-6-3 Loading Programs
Load a saved ladder program into CX-Programmer. Programs are loaded in groups
for each project.
1. Select [File] - [Open] from the main menu.
The Open CX-Programmer Project dialog box will be displayed.
2. Specify the save location and file. Click [Open].
The CX-Programmer project file will be opened, and the saved programs will be
displayed.
72 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 74

4-7 Editing Programs
4
4-7 Editing Programs
Created ladder programs can be edited in CX-Programmer. I/O comments and rung comments can also
be added or edited.
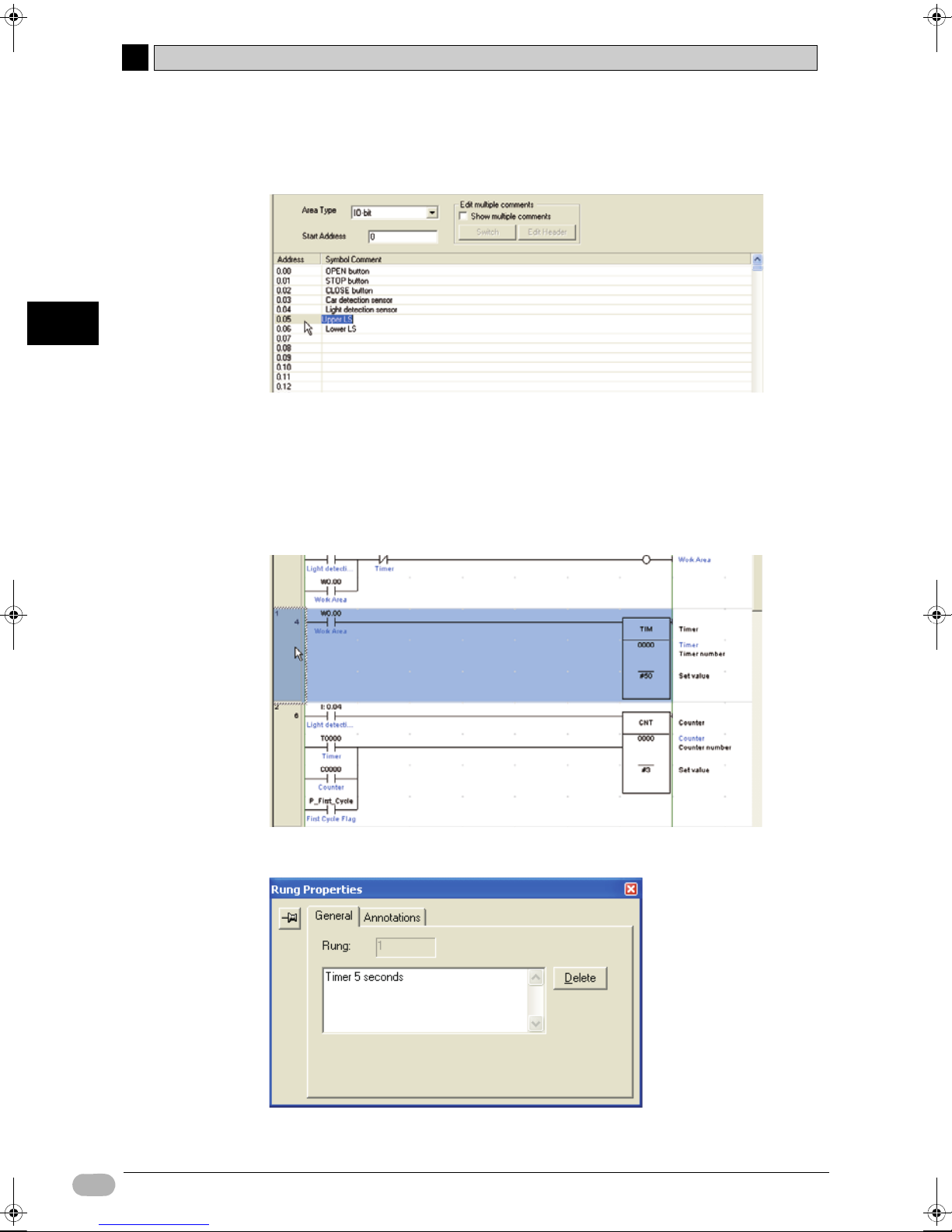
4-7-1 Editing I/O Comments
I/O comments can be added and edited via a list of addresses.
1. Select [Edit] - [I/O Comment] from the main menu.
4
Creating Programs
The I/O comment window will be displayed.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 73
Page 75
4
Creating Programs
4-7 Editing Programs
4
2. Double-click the address for which you wish to input or edit the I/O
comment.
The I/O comment field will become editable. Input or edit the I/O comment.
4-7-2 Inputting Rung Comments
Comments can be added to each rung of a ladder program.
1. Double-click the rung header for the rung you wish to add a comment to.
The Rung Properties dialog box will be displayed.
2. On the General tab, input the comment into the comment field.
74 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 76
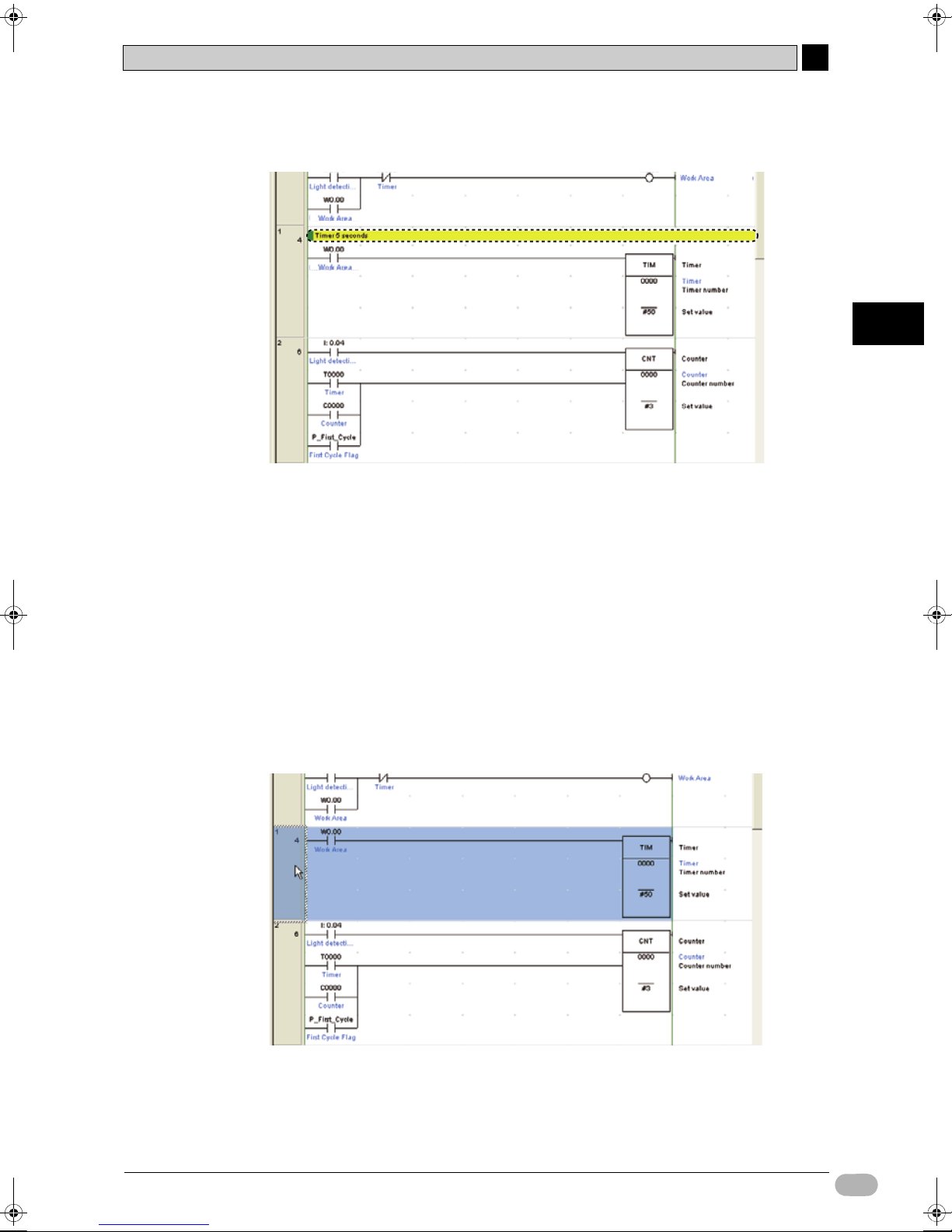
3. Close the Rung Properties dialog box.
The entered rung comment will be displayed on the ladder program.
4-7 Editing Programs
4
4
Creating Programs
4-7-3 Editing Rungs
Created ladder programs can be edited.
Deleting
zContacts/Instructions
1. Place the cursor on a contact or on an instruction. Press the [Delete] key.
The selected contact or instruction will be deleted.
zRungs
1. Click a rung header.
The whole rung will be selected.
2. Press the [Delete] key.
The selected rung will be deleted.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 75
Page 77

4
Creating Programs
4-7 Editing Programs
4
Creating Vertical/Horizontal Lines
Vertical and horizontal connection lines can be created.
Vertical lines are created as follows:
1. Position the cursor at the starting point of the vertical line.
2. Hold down the [Ctrl] key, and press the up/down arrow key.
Horizontal lines can be created in the same manner.
(1) Starting point
(2) Cursor
• Creating a line from right to left:
Hold down the [Ctrl] key and press the left arrow key.
• Creating a line from left to right:
Hold down the [Ctrl] key and press the right arrow key.
• Creating a line from bottom to top:
Hold down the [Ctrl] key and press the up arrow key.
• Creating a line from top to bottom:
Hold down the [Ctrl] key and press the down arrow key.
Note Repeating the process over an existing connection line will delete it.
Copying/Pasting Contacts/Instructions/Rungs
zContacts/Instructions
1. Place the cursor on a contact or an instruction.
2. Hold down the [Ctrl] key and press the [C] key.
The selected contact or instruction will be copied to the clipboard.
3. Move the cursor to where you wish to paste. Hold down the [Ctrl] key and
press the [V] key.
The contact or instruction on the clipboard will be pasted.
zRungs
1. Click the rung header of the rung you wish to copy.
The whole rung will be selected.
2. Hold down the [Ctrl] key and press the [C] key.
The selected rung will be copied to the clipboard.
3. Move the cursor to the rung where you wish to paste. Hold down the [Ctrl]
key and press the [V] key.
The rung on the clipboard will be pasted.
76 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 78

SECTION 5
Transferring and Debugging
Programs
To transfer data from a computer to CP1L, the computer and CP1L
must first be online.
Monitoring and debugging programs executed on CP1L are also
performed with the computer and CP1L online.
5-1 Going Online......................................................................... 78
5-1-1 Setting the CP1L Clock .................................................. 79
5-1-2 Changing the Operating Mode ....................................... 80
5-1-3 Transferring Programs.................................................... 82
5-1-4 Executing Operations ..................................................... 84
5-2 Adjusting/Debugging Online ................................................. 85
5-2-1 Monitoring....................................................................... 85
5-2-2 Force-Setting/Force-Resetting ....................................... 88
5-2-3 Changing Timer Settings ................................................ 90
5-2-4 Searching ....................................................................... 90
5-2-5 Online Editing ................................................................. 93
5-2-6 Confirming Cycle Time ................................................... 94
Page 79

5
Transferring and Debugging Programs
5
Transferring and Debugging Programs
5-1 Going Online
To configure CP1L settings, transfer programs, or execute programs, the computer and CP1L must first
be online.
1. In CX-Programmer, open the program to be transferred.
2. Select [PLC] - [Work Online] from the main menu.
A dialog box will be displayed to confirm going online.
3. Click [Yes].
The dialog box will be closed.
When the system goes online, the ladder section window will turn light grey.
Online status is one in which the computer and CP1L are connected. To
execute a program created with CX-Programmer on CP1L, the program will
need to be transferred. For details on transferring programs, refer to 5-1-3
Transferring Programs.
78 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 80

5-1 Going Online
5
Note
If the system fails to go online, check the PLC type setting and communication
settings.
To check the settings, double-click [NewPLC1[CP1L]Offline] in the project tree. For
details on the settings, refer to 4-5-1 Creating New Projects.
5-1-1 Setting the CP1L Clock
The CP1L clock should be set to match your time zone. Use CX-Programmer to
set the time. If the time on CP1L is not set properly, the error log will not be
displayed correctly.
1. In CX-Programmer, open an existing project.
For details on opening a project, refer to 4-6-3 Loading Programs.
2. Double-click [PLC Clock].
The PLC Clock dialog box will be displayed.
5
5
Transferring and Debugging Programs
3. Select [Options] - [Set PLC Clock] from the menu.
The Set PLC Clock dialog box will be displayed.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 79
Page 81

5-1 Going Online
5
4. Set the date and time. Click OK.
The Set PLC Clock dialog box will be closed.
5
Transferring and Debugging Programs
5. Select [File] - [Exit] from the menu.
The clock on CP1L is now set.
5-1-2 Changing the Operating Mode
Change to PROGRAM mode.
The procedure for changing to the PROGRAM operation mode is as follows.
1. Select [PLC] - [Operating Mode] - [Program] from the main menu.
A dialog box will be displayed to confirm the operating mode change.
80 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 82

5-1 Going Online
2. Click [Yes].
The operating mode will be changed.
o
The operating mode will be displayed on the title bar and on the project tree.
5
5
5
Transferring and Debugging Programs
CP1L Operating Mode
CP1L has 3 operating modes: PROGRAM, MONITOR, and RUN. Change the
operating mode to reflect the operation to be performed. The operation mode
affects the whole user program, and is common to all tasks.
• PROGRAM mode:
In this state, the program is stopped. This mode is used to prepare for program
execution by performing initial settings such as PLC setup, transferring the
program, checking the program, and force-setting/force-resetting.
• MONITOR mode:
In this state, the program is executed. You can perform online editing, force-set/
force-reset, and change I/O memory values. This mode is also used for making
adjustments during test runs.
• RUN mode:
In this state, the program is executed. Use this mode for production runs.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 81
Page 83

5
Transferring and Debugging Programs
5-1 Going Online
5
The following table lists the status and available operations for each mode.
Operating Mode PROGRAM RUN MONITOR
Program status Stopped Running Running
I/O refreshing Execute Execute Execute
External I/O status OFF Depends on
I/O memory Non-holding memory Cleared
Holding memory Held
Operations from
CX-Programmer
I/O memory monitoring OK OK OK
Program monitoring OK OK OK
Program
transfer
Compiling OK X X
PLC setup OK X X
Changing program OK X OK
Force-setting/Force-resetting OK X OK
Changing timer/counter SV OK X OK
Changing timer/counter PV OK X OK
Changing I/O memory PV OK X OK
From PLC OK OK OK
To PLC OK X X
program
Depends on
program
Depends on
program
Depends on
program
5-1-3 Transferring Programs
A program created with CX-Programmer can be transferred to CP1L.
1. Select [PLC] - [Transfer] - [To PLC] from the main menu.
The Download Options dialog box will be displayed.
82 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 84
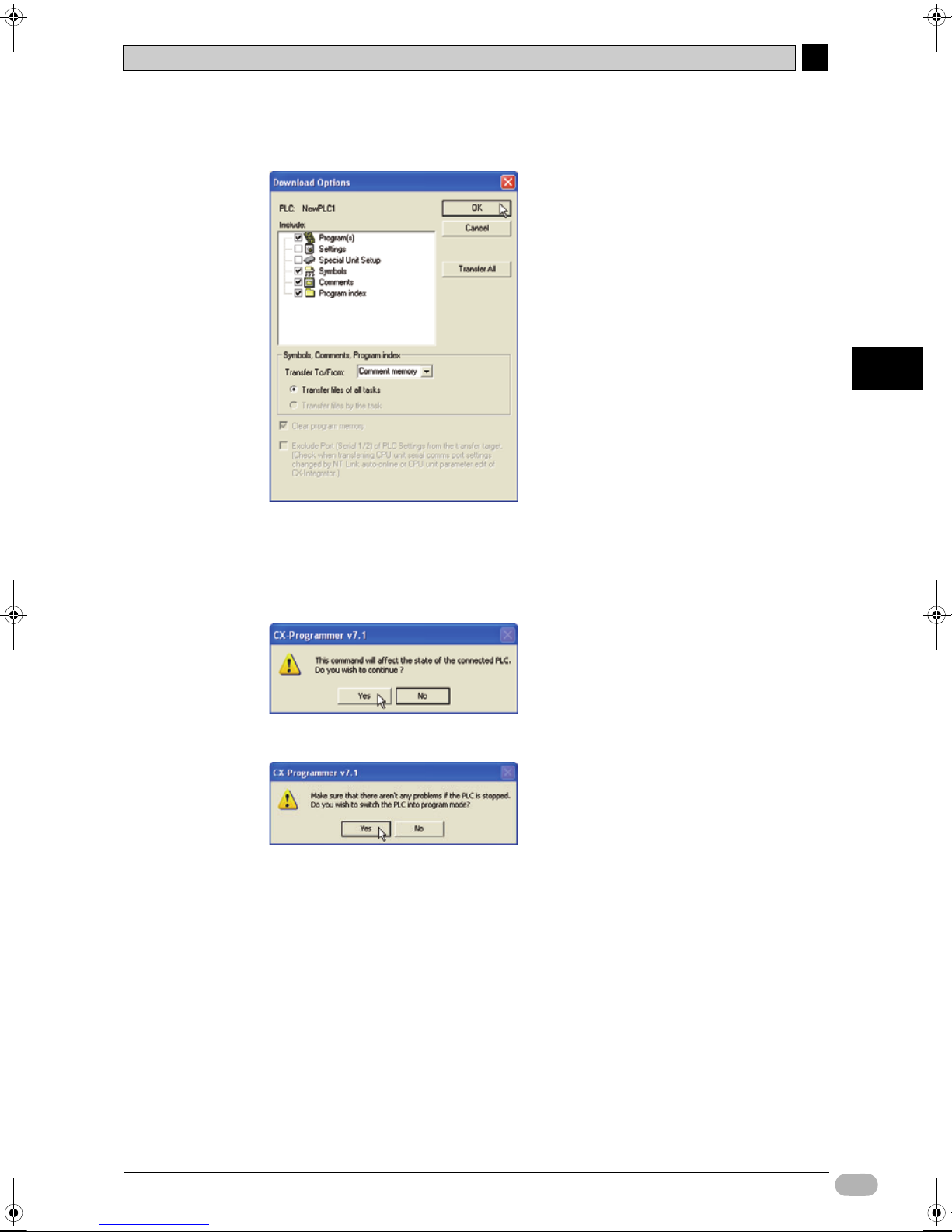
2. Click [OK].
A dialog box will be displayed to confirm the transfer.
5-1 Going Online
5
5
5
Transferring and Debugging Programs
Note
For details on the transfer options, refer to SECTION 9 Transferring/Monitoring/
Debugging Programs of CX-Programmer Operation Manual (W446).
3. Click [Yes].
If the following dialog box is displayed, click [Yes].
The transfer will begin. The Download dialog box will be displayed.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 83
Page 85

5
Transferring and Debugging Programs
5-1 Going Online
5
4. Click [OK].
Transferring of the program is now complete.
5-1-4 Executing Operations
To perform a production run, change to the RUN operating mode. The procedure
for changing to RUN mode is described below.
To perform a trial run for adjustments and debugging, change to MONITOR mode.
Caution Confirm that the facility will not be affected by changing to MONITOR or RUN
mode.
1. Select [PLC] - [Operating Mode] - [Run] from the main menu.
A dialog box will be displayed to confirm the operating mode change.
2. Click [Yes].
The system will change to RUN mode and begin operating.
84 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 86

5-2 Adjusting/Debugging Online
5-2 Adjusting/Debugging Online
This section explains functions used for debugging and for adjustments during test runs.
5-2-1 Monitoring
Displaying Conduction Status
The conduction status of the program rungs will be displayed. This will allow you to
confirm program execution.
1. Change CP1L to the MONITOR operating mode.
2. Select [PLC] - [Monitor] - [Monitoring] from the main menu.
5
5
5
Transferring and Debugging Programs
The conduction status is displayed on the program.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 85
Page 87

5
5-2 Adjusting/Debugging Online
5
Displaying Conduction Status at Multiple Sections
The diagram workspace can be split. Multiple sections of the program can be
viewed simultaneously.
1
Transferring and Debugging Programs
1
(1) Window divider
Drag the window divider to split the diagram workspace. The workspace can be
split in up to 4 sections.
86 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 88

Monitoring Specific Addresses
I/O values can be monitored by specifying their address.
1. Select [PLC] - [Monitor] - [Monitoring] from the main menu.
2.
Select [View] - [Windows] - [Watch] from the main menu.
3. Input an address.
The I/O value will be displayed. For Boolean values, "0" indicates OFF.
5-2 Adjusting/Debugging Online
5
5
5
Note • Input the address as the channel followed by a period and the bit. For example,
"0 CH 04 bit" should be input as "0.04".
• You can input addresses by dragging & dropping items from the diagram
workspace to the watch window. Select the rung header to input all addresses
included in the rung.
Transferring and Debugging Programs
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 87
Page 89

5
Transferring and Debugging Programs
5-2 Adjusting/Debugging Online
5
5-2-2 Force-Setting/Force-Resetting
CX-Programmer can control inputs, independent of inputs from I/O devices. Use
this function to force input conditions and output conditions during test runs.
Note Before force-setting/force-resetting/releasing or setting/resetting, confirm that the
facility will not be affected.
The force-setting procedure is as follows.
1. Change CP1L to the MONITOR or PROGRAM operating mode.
2. Place the cursor on the contact to force-set.
88 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 90

5-2 Adjusting/Debugging Online
3. Select [PLC] - [Force] - [On] from the main menu.
Force-set will be set. The contact will be marked with the force-set symbol.
5
5
5
Transferring and Debugging Programs
Note
• Select [On] to force the contact ON, and [Off] to force the contact OFF.
• To undo the force-set/force-reset, select [Cancel].
• The following areas can be force-set/force-reset:
CIO area (I/O area, data link area, CPU bus unit area, special I/O area, and work
area), work area (WR), timer completion flag, holding area (HR), counter
completion flag
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 89
Page 91

5
Transferring and Debugging Programs
5-2 Adjusting/Debugging Online
5
5-2-3 Changing Timer Settings
Timer settings can be changed to better suit operating conditions.
1. Change CP1L to the MONITOR or PROGRAM operating mode.
2. Double-click the timer setting to be changed.
The Set Timer/Counter Value dialog box will be displayed.
3. Input the new value. Click [OK].
The timer setting will be updated.
5-2-4 Searching
Address Reference Tool
The address reference tool displays which instructions are using the address being
pointed to with the cursor. It also allows jumping to another instruction with the
same address.
The address reference tool will display the following items:
• Address at the cursor position
• Variables (local, global)
• Program name, section name
• Program address (step)
• Instruction using the address
90 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 92

5-2 Adjusting/Debugging Online
1. Select [View] - [Windows] - [Address Reference Tool] from the main
menu.
The address reference tool will be displayed.
5
5
5
Transferring and Debugging Programs
2. Input the address to search for. Click [Find].
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 91
Page 93

5
Transferring and Debugging Programs
5-2 Adjusting/Debugging Online
5
A list of used addresses will be displayed. Click an address to display the program
being used.
Ladder Backtracking
This function is used to backtrack the ladder, to determine why a contact does not
turn ON, for example.
1. Place the cursor on the contact being investigated.
2. Press the [Space] key.
The cursor will be moved to the source output for the contact.
92 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 94

5-2-5 Online Editing
The CP1L program can be edited online.
Caution Before starting online editing, confirm that the extension of cycle time will have no
adverse effects.
Otherwise, input signals may not be read.
Note • Note that if CP1L is running in MONITOR mode, changing the program via
editing online may cause the cycle time to become longer and/or failure to read
input signals.
• When making large changes, when moving or copying rungs, or when inserting
or deleting block programs, edit offline, then transfer the program.
1. Change CP1L to the MONITOR or PROGRAM operating mode.
2. Click the rung header of the rung you wish to edit.
3. Select [Program] - [Online Edit] - [Begin] from the main menu.
The grey shading in the diagram workspace will disappear, and the program
becomes editable.
5-2 Adjusting/Debugging Online
5
5
5
Transferring and Debugging Programs
4. Edit the program.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 93
Page 95

5
Transferring and Debugging Programs
5-2 Adjusting/Debugging Online
5
5. Select [Program] - [Online Edit] - [Send Changes] from the main menu.
The edited rungs will be transferred to CP1L.
5-2-6 Confirming Cycle Time
1. Change CP1L to the MONITOR or RUN operating mode.
2. Click the diagram workspace.
Cycle time will be displayed on the status bar.
Note For details on cycle time, refer to A-3-2 CPU Unit Behavior.
94 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 96

Appendix
This section briefly explains channel and relay numbers,
instructions, and the inner workings of CP1L. This section also
provides examples of applications utilizing CP1L functions such as
pulse functions, communication functions, and special instructions.
A-1 Channel/Relay Numbers....................................................... 96
A-2 Instructions ......................................................................... 101
A-2-1 Using Instructions ......................................................... 101
A-2-2 Basic I/O Processing Instructions................................. 102
A-3 Inner Workings of CP1L...................................................... 105
A-3-1 Inner Structure of CPU Units ........................................ 105
A-3-2 CPU Unit Behavior ....................................................... 107
A-4 CP1L Programming Examples............................................ 114
A-4-1 Using Adjusters to Set Timers .......................................114
A-4-2 Capturing Short Signals.................................................117
A-4-3 Using Interrupt Inputs to Accelerate Processes ........... 121
A-4-4 Using Calendar Timers................................................. 127
A-4-5 Using Rotary Encoders to Measure Positions.............. 132
A-4-6 Using Servo Drivers for Positioning.............................. 137
A-4-7 Using Inverters for Speed Control (1)........................... 143
A-4-8 Using Inverters for Speed Control (2)........................... 150
A-4-9 Exchanging Data between CP1Ls................................ 160
Page 97

A
Appendix
Appendix
A-1 Channel/Relay Numbers
In CP1L, channel (CH) numbers and relay numbers are specified as described below.
Each channel consists of 16 bits.
Hence, relay numbers are expressed as [channel number] + [bit number (00 to
15)].
Relay numbers are used to handle contacts. Channel numbers are mainly used
as operands for special instructions when processing data by the channel.
Note In CX-Programmer (abbreviated as CX-P below), upper bits of channel
numbers and relay numbers are not displayed if their value is 0. For example,
0000CH will be displayed as 0.
Relay numbers are displayed as a channel number followed by a period and a
bit number. The bit number ranges in value from 00 to 15.
Area Channel Relay
In CX-P In CX-P
I/O area 00 to 199 0 to 199 00000 to 19915 0.00 to 199.15
1:1 link area 3000 to 3063 CH 3000 to 3063 300000 to 306300 3000.00 to
CIO
area
Work area W000 to W511 CH W000 to W511 W00000 to
Holding area H000 to H511 CH H000 to H511 H00000 to H51115 H0.00 to H511.15
Auxiliary area A000 to A959 CH A000 to A959 A00000 to A95915 A0.00 to A959.15
DM area D00000 to D32767* D0 to D32767* - -
Timer T000 to T511 T0 to T511 T000 to T511 T0000 to T0511
Counter C000 to C511 C000 to C511 C000 to C511 C0000 to C0511
Serial PLC link area 3100 to 3189 CH 3100 to 3189 310000 to 318915 3100.00 to
Work area 3800 to 6143 CH 3800 to 6143 380000 to 614300 3800.00 to
W51115
3063.00
3189.15
6143.00
W0.00 to W511.15
*For 14/20-point I/O units: D0 to D9999, D32000 to D32767.
Note The work words in CIO Area may be assigned to new functions in future
versions of the CPU Units. Be sure to use the work words in W000 to W511CH
first.
96 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 98

zChannel Data Notation
Channel data is represented by 4 hexadecimal digits, derived from 16 binary digits,
representing the ON/OFF state of the 16 bits.
In other words, for each 4 bits, the sum of ON bits are calculated and expressed as
a single digit.
A-1 Channel/Relay Numbers
MSB
(Most Significant Bit)
Bit 15141312111009 080706050403020100
Bit value
Content
(1=ON,
0=OFF)
Digit value 0 F 7 C
3222120232221202322212023222120
2
00001 1 1 101111100
The above channel will be expressed as "0F7C (Hex)".
zConstants Notation
Constants used in CP1L instructions are represented as follows.
Notation Content/Purpose
#0000 to 9999 (BCD) Timer/counter values, BCD arithmetic instruction, etc.
#0000 to FFFF (Hex) Comparison data for comparison instructions, transfer data,
&0 to 65535 Unsigned decimal notation
BIN arithmetic instructions, etc.
(Available in certain special instructions only. Can be loaded
into CX-Programmer by converting to and from hex digits.)
zInstruction Execution Conditions
There are 2 types of instructions: cyclic instructions, and differentiated instructions.
• Cyclic Instructions
The instruction is executed on each cycle, for as long as the execution condition
is ON.
Example
(Least Significant Bit)
LSB
A
Appendix
W00000
• Differentiated Instructions
The instruction is executed only once (i.e. on 1 cycle only) when the execution
condition turns ON.
The instruction name is prefixed with an "@".
Example
W00001
Some instructions cannot be specified as a differentiated instruction (with the "@"
prefix). If such is the case, use the UP(521)/DOWN(522) or
DIFU(013)(differentiated UP)/DIFD(014)(differentiated DOWN) instructions.
MOV (021)
H010
D00010
@MOV (021)
H020
D00020
On each cycle for which work area W00000 is
ON, data in holding area H010CH is transferred
to DM D00010.
When work area W00001 switches from OFF to
ON, data in holding area H020CH is transferred
to DM D00020.
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 97
Page 99

A
Appendix
A-1 Channel/Relay Numbers
zCondition Flags
Condition flags are used to reflect the processing results during or after the
execution of instructions. Whether a flag is used or not will depend on the
instruction. These flags are used in ladder programs as contacts.
Name Label In CX-P Function
Error flag ER P_ER • Turns ON when an instruction handling BCD
Access error flag AER P_AER Turns ON when unauthorized access is
Carry flag CY P_CY • Turns ON when the number of digits is
Equals flag
Unequal flag
Greater than flag
Greater than or
equals flag
Less than flag
Less than or
equals flag
Negative flag
Overflow flag OF P_OF Turns ON when the calculation result overflows.
Underflow flag UF P_UF Turns ON when the calculation result
Always ON flag ON P_ON Remains ON at all times. Used as an execution
Always OFF flag OFF P_OFF Remains OFF at all times.
data attempts to execute using non-BCD data.
• Turns ON when an operand value specified by
the instruction is invalid (e.g. a value outside
the work area).
attempted on an area that is not meant to be
accessed.
increased or decreased as a result of
executing an arithmetical instruction.
• Data shift instructions and some arithmetical
instructions may handle the carry as part of
their processing.
=
< >
>
>=
<
<=
N P_N Turns ON when the MSB becomes 1 as a result
P_EQ • Turns ON when data comparison returns an
"equal".
• Turns ON when data becomes 0 as a result of
calculations or transfers.
P_NE Turns ON when data comparison returns an
"unequal".
P_GT Turns ON when data comparison returns
"data1>data2".
P_GE Turns ON when data comparison returns
"data1>=data2".
P_LT Turns ON when data comparison returns
"data1<data2".
P_LE Turns ON when data comparison returns
"data1=<data2".
of calculations.
underflows.
condition for instructions that cannot be
connected directly to the bus bar.
98 SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide
Page 100

zClock Pulses
Clock pulses are contacts that turn ON/OFF at a fixed time interval.
A-1 Channel/Relay Numbers
Name Label In CX-P Function
0.02s clock pulse 0.02s P_0.02s
0.1s clock pulse 0.1s P_0.1s
0.2s clock pulse 0.2s P_0.2s
0.02s
0.01s 0.01s
0.05s 0.05s
0.1s
0.2s
0.1s 0.1s
1.0s clock pulse 1s P_1s
1min clock pulse 1min P_1min
1.0s
0.5s 0.5s
1min
30s 30s
Note To enter a clock pulse or condition flag into CX-Programmer, first enter a contact,
then press the [P] key to select from the drop-down list.
A
Appendix
SYSMAC CP1L Getting Started Guide 99
 Loading...
Loading...