Page 1
Section 7
25mm min.
25mm min.
Chemical Resistance
IDタ グ取 り 付け時の注意事項
V680-D1KP52MT
Differences in Surrounding Metals (Reference)
Communications distances are affected by the type of metal in back of or surrounding the Tag, as
shown in the following table.
鉄 SUS 黄銅 アルミ ニウム
形V680-D1KP52MT 100% 85~90% 80~85% 80~85%
注. 周囲/背面金属が鉄の場合を100% と し て います。
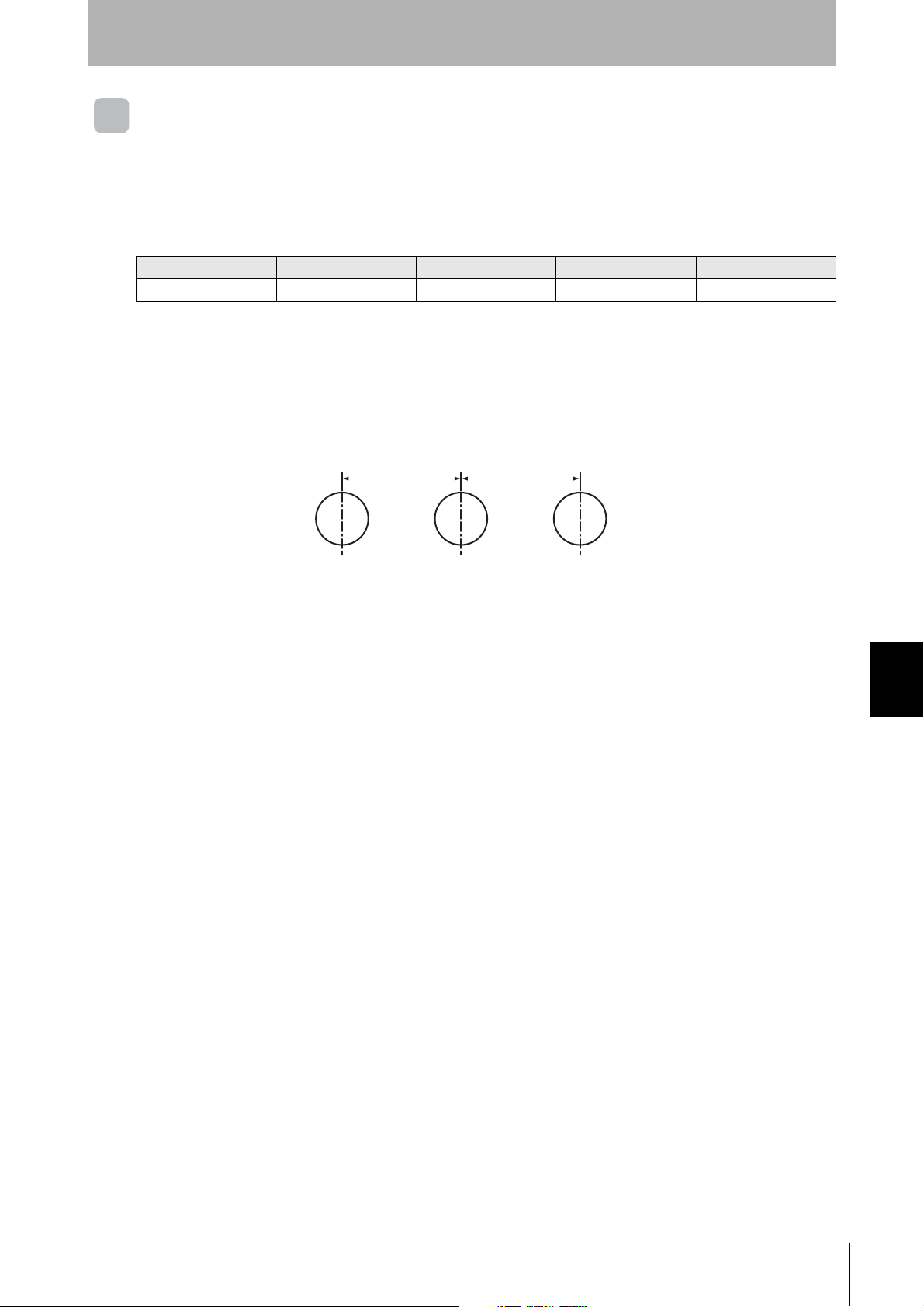
Mutual Interference with Tags (Reference)
Provide the mounting distances indicated below to prevent malfunctions due to mutual interference
when using more than one Tag.
Section 7 Reference Data
RFID System
User's Manual
149
Page 2
Section 7
ID Tag
3.5mm min.
Metal
Embedded
ID Tag
Metal
Surface-mounted
金属
IDタ グ
xx
• V680-HS52 &V680-D1KP66MT
10 20 30 40 50 (mm)
0
50
70
Distance to metal (x)
60
40
30
20
10
90
(%)
100
80
The communications distance without
metal is 100%
• V680-HS63 &V680-D1KP66MT
10 20 30 40 50 (mm)
0
50
70
Distance to metal (x)
60
40
30
20
10
90
(%)
100
80
The communications distance without
metal is 100%
• V680-HS65 &V680-D1KP66MT
10 20 30 40 50 (mm)
0
50
70
Distance to metal (x)
60
40
30
20
10
90
(%)
100
80
The communications distance without
metal is 100%
60
100mm min.
100mm min.
Chemical Resistance
V680-D1KP66MT
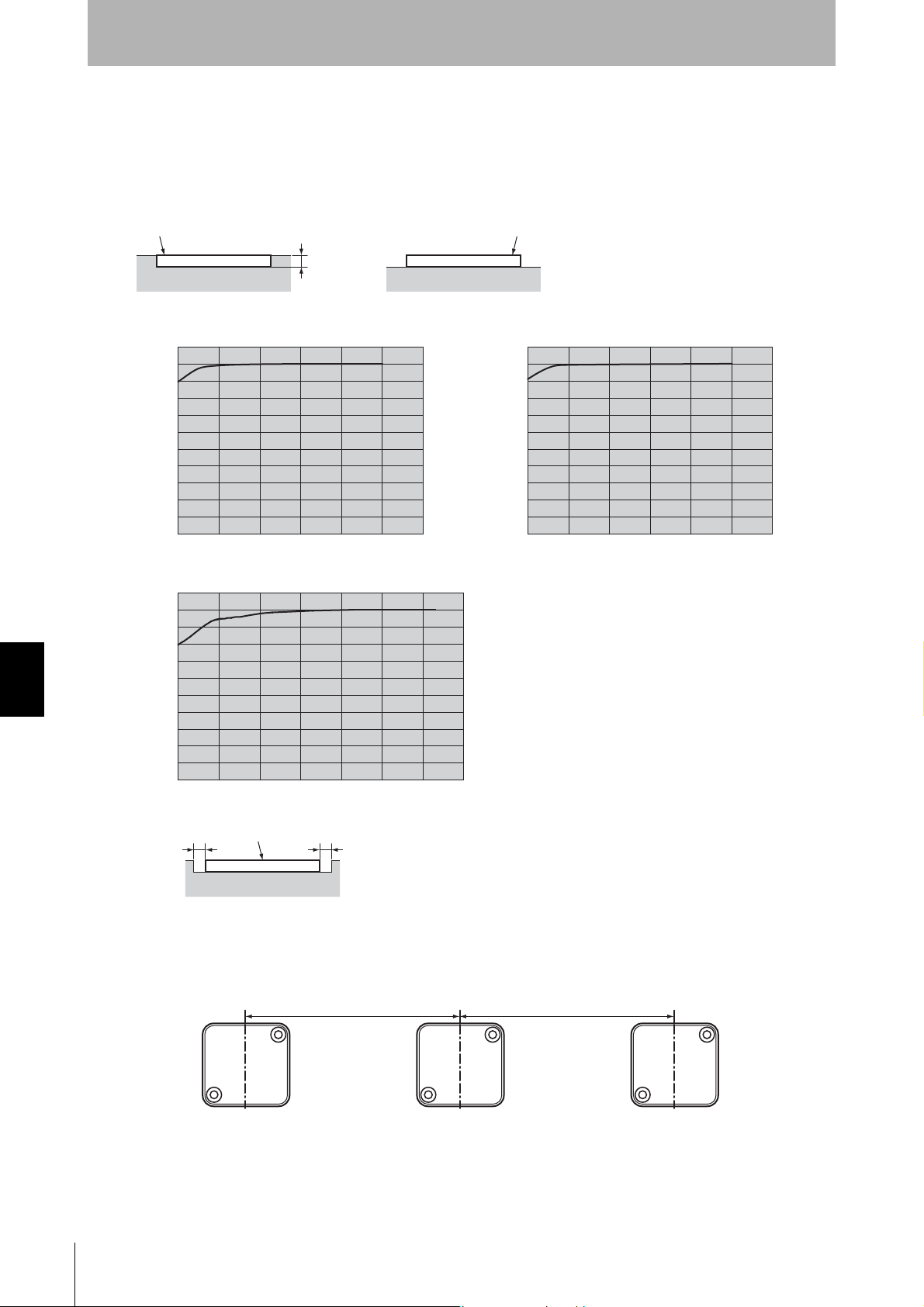
Effect of Metal behind Tags (Reference)
The V680-D1KP66MT can be surface-mounted or it can be embedded in metal. If it is embedded in
metal, the height of the metal casing must not exceed that of the Tag.
Section 7 Reference Data
Mutual Interference with Tags (Reference)
Provide the mounting distances indicated below to prevent malfunctions due to mutual interference
when using more than one Tag.
150
RFID System
User's Manual
Page 3
Section 7
25mm min.
25mm min.
Chemical Resistance
V680-D2KF52M
Differences in Surrounding Metals (Reference)
Communications distances are affected by the type of metal in back of or surrounding the Tag, as
shown in the following table.
Steel SUS Brass Aluminum
V680-D2KF52M 100% 80% to 85% 80% to 85% 75% to 80%
The values for steel are set to 100%
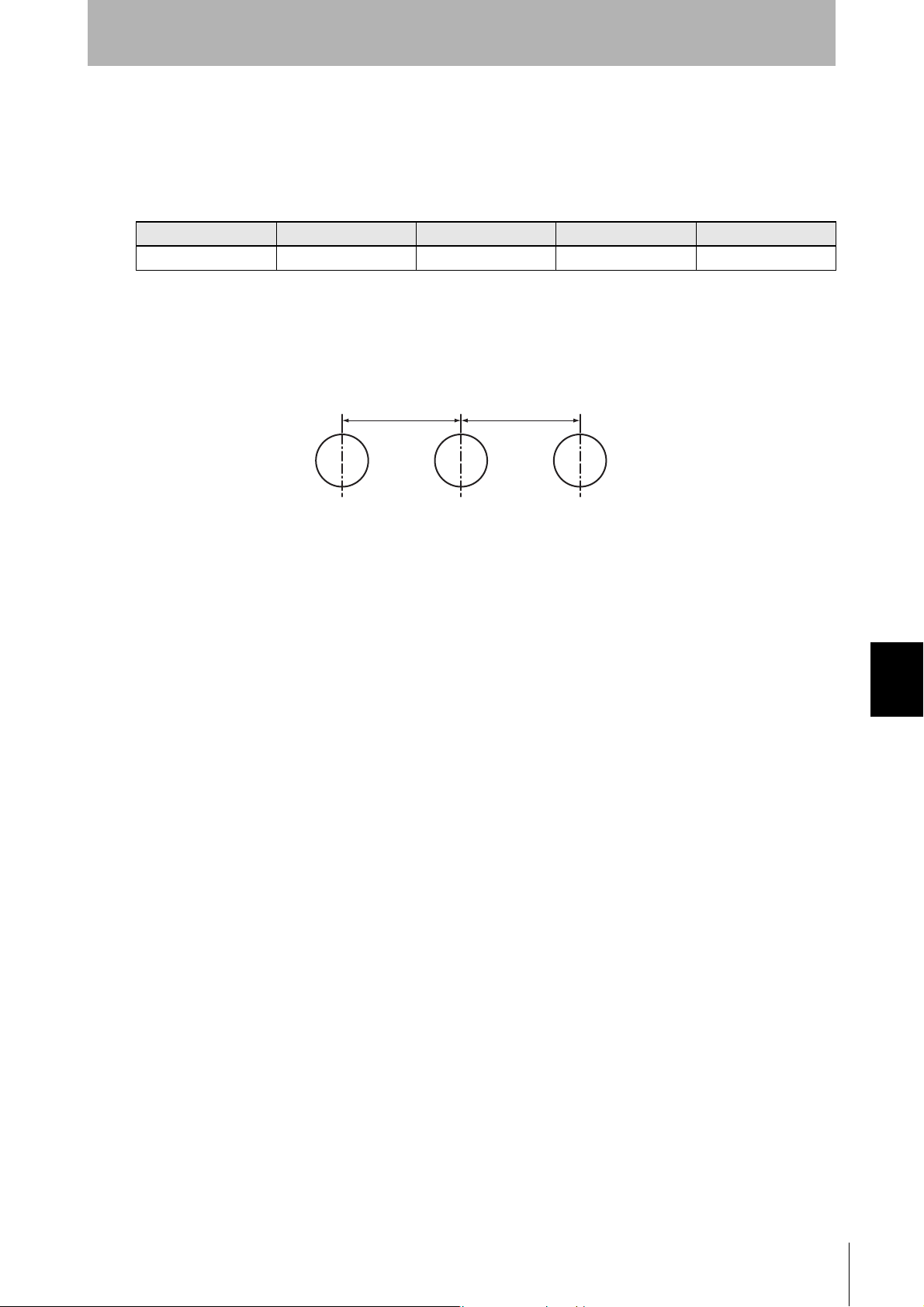
Mutual Interference with Tags (Reference)
Provide the mounting distances indicated below to prevent malfunctions due to mutual interference
when using more than one Tag.
Section 7 Reference Data
RFID System
User's Manual
151
Page 4
Section 7
ID Tag
4.5mm min.
Metal
Embedded
ID Tag
Metal
Surface-mounted
• V680-HS52 &V680-D2KF67M
10 20 30 40 50 (mm)
0
50
70
Distance to metal (x)
60
40
30
20
10
90
(%)
100
80
The communications distance without
metal is 100%
• V680-HS63 & V680-D2KF67M
10 20 30 40 50 (mm)
0
50
70
Distance to metal (x)
60
40
30
20
10
90
(%)
100
80
The communications distance without
metal is 100%
• V680-HS65 & V680-D2KF67M
10 20 30 40 50 (mm)
0
50
70
Distance to metal (x)
60
40
30
20
10
90
(%)
100
80
The communications distance without
metal is 100%
ID Tag
X
X
120mm min.
120mm min.
Chemical Resistance
V680-D2KF67M
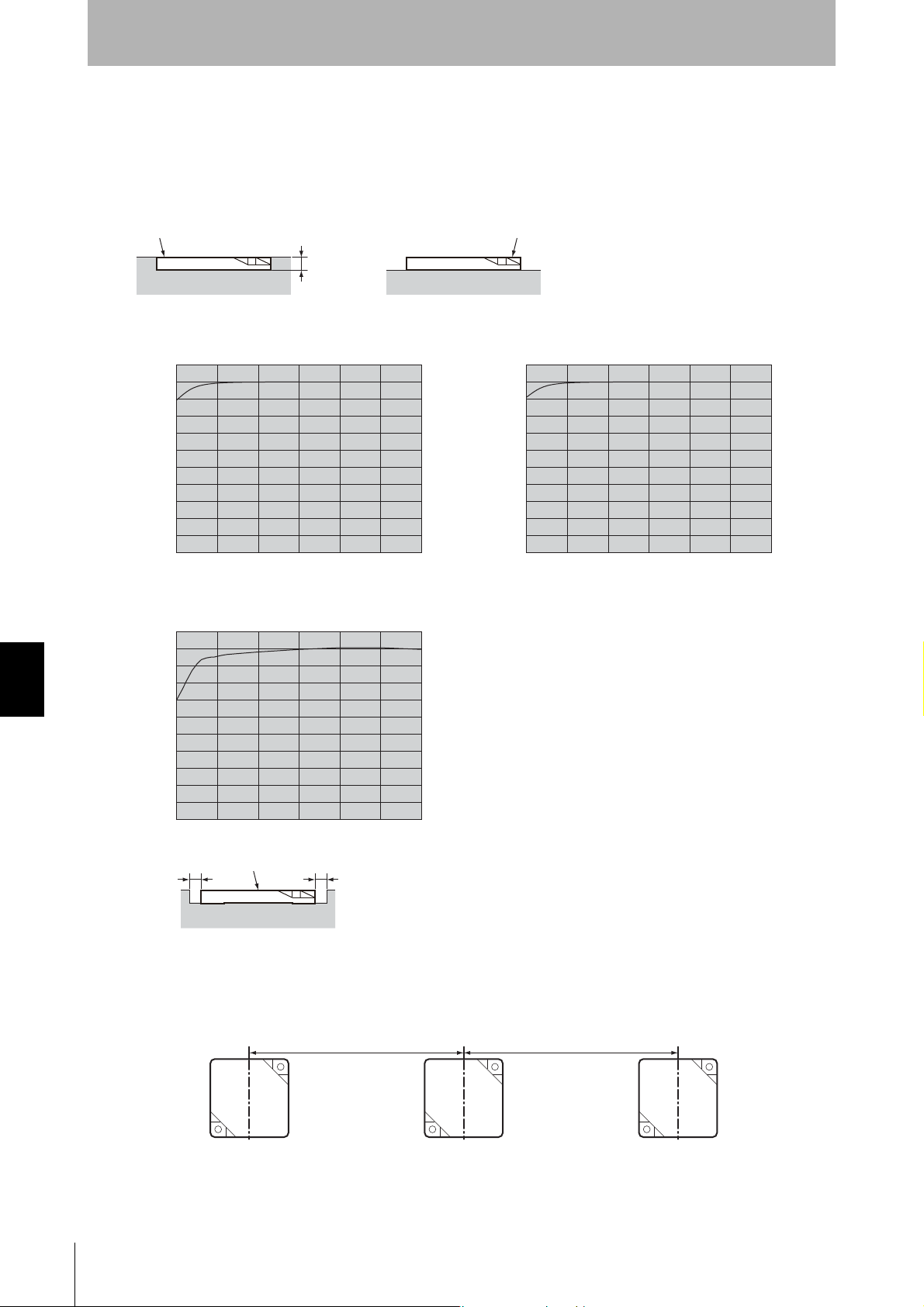
Effect of Surrounding Metals (Reference)
The V680-D2KF67M can be surface-mounted or it can be embedded in metal. If it is embedded in
metal, the height of the metal casing must not exceed that of the Tag.
Section 7 Reference Data
152
Mutual Interference with Tag (Reference)
To prevent malfunctioning due to mutual interference when using more than one Tag,
leave sufficient space between them as shown in the following diagram.
RFID System
User's Manual
Page 5
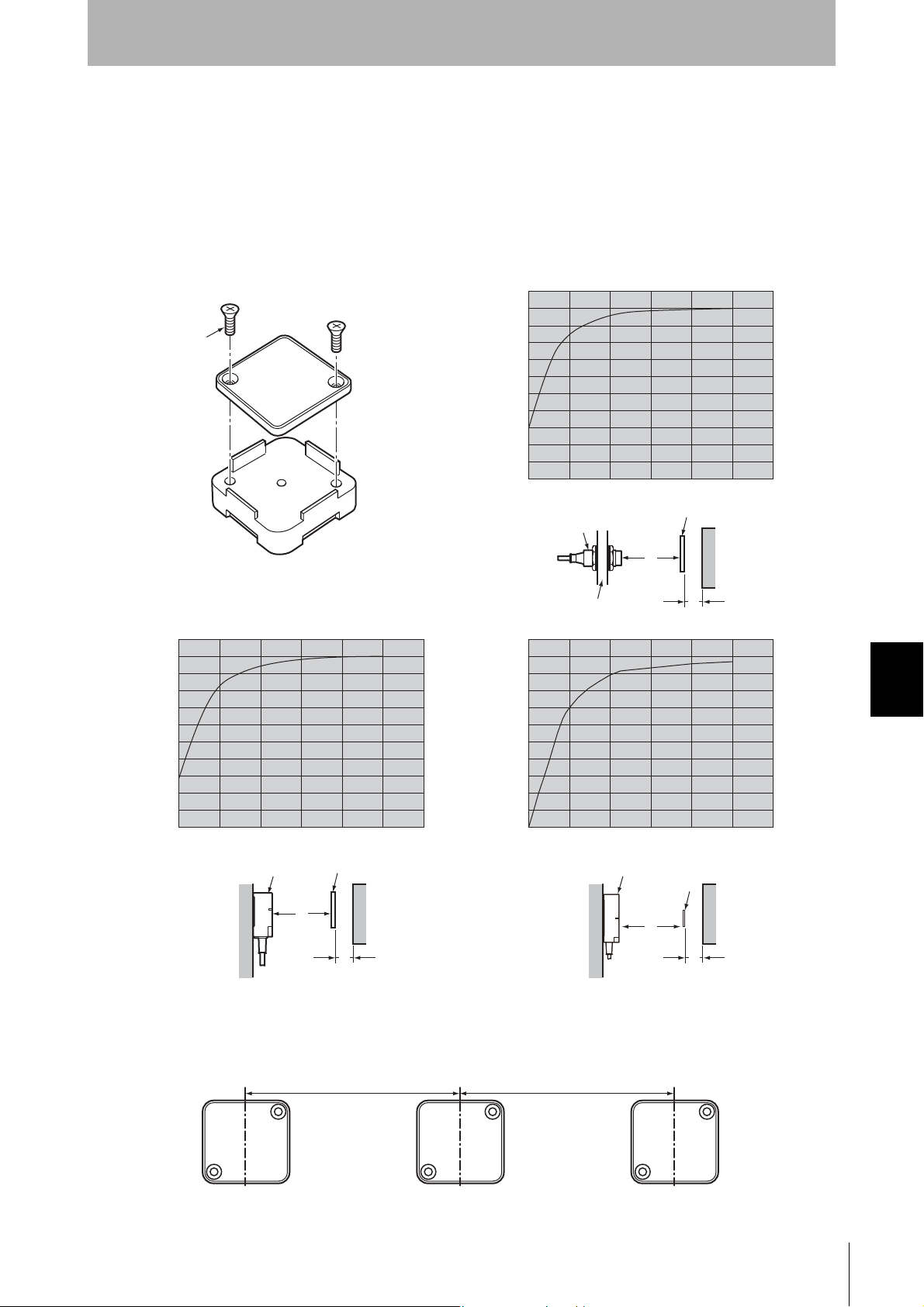
Section 7
M3 countersunk screw
V600-A86 Attachment Installation
Install so that the mounting holes are aligned.
• V680-HS52 &V680-D1KP66T
10 20 30 40 50 (mm)
0
50
70
Distance to metal (x)
60
40
30
20
10
90
(%)
100
80
The communications distance without
metal is 100%
ID Tag
Metal on back
Antenna
Communications
distance
Y
X
Metal
• V680-HS63 &V680-D1KP66T
10 20 30 40 50 (mm)
0
50
70
Distance to metal (x)
60
40
30
20
10
90
(%)
100
80
The communications distance without
metal is 100%
• V680-HS65 &V680-D1KP66T
10 20 30 40 50 (mm)
0
50
70
Distance to metal (x)
60
40
30
20
10
90
(%)
100
80
The communications distance without
metal is 100%
Antenna
ID Tag
Metal on back
Metal
Y
X
Communications
distance
Antenna
ID Tag
Metal on back
Metal
Y
X
Communications
distance
100mm min.
100mm min.
Chemical Resistance
V680-D1KP66T
Effect of Metal behind Tags (Reference)
The V680-D1KP66T communications distance is reduced if there is any met al material behind the Tag.
If the Tag is to be mounted to metal, then either use a V600-A86 Attachment (sold sep ar ately) or insert
a non-metal spacer (such as plastic or resin). The relationship between the distance from the Tag to
the metal surface and the communications dista nce is shown below.
The Attachment is 10 mm thick, and more than one Attachment can be stacked.
Mutual Interference with Tag (Reference)
To prevent malfunctioning due to mutual interference when using more than one Tag, leave sufficient
space between them as shown in the following diagram.
RFID System
User's Manual
Section 7 Reference Data
153
Page 6
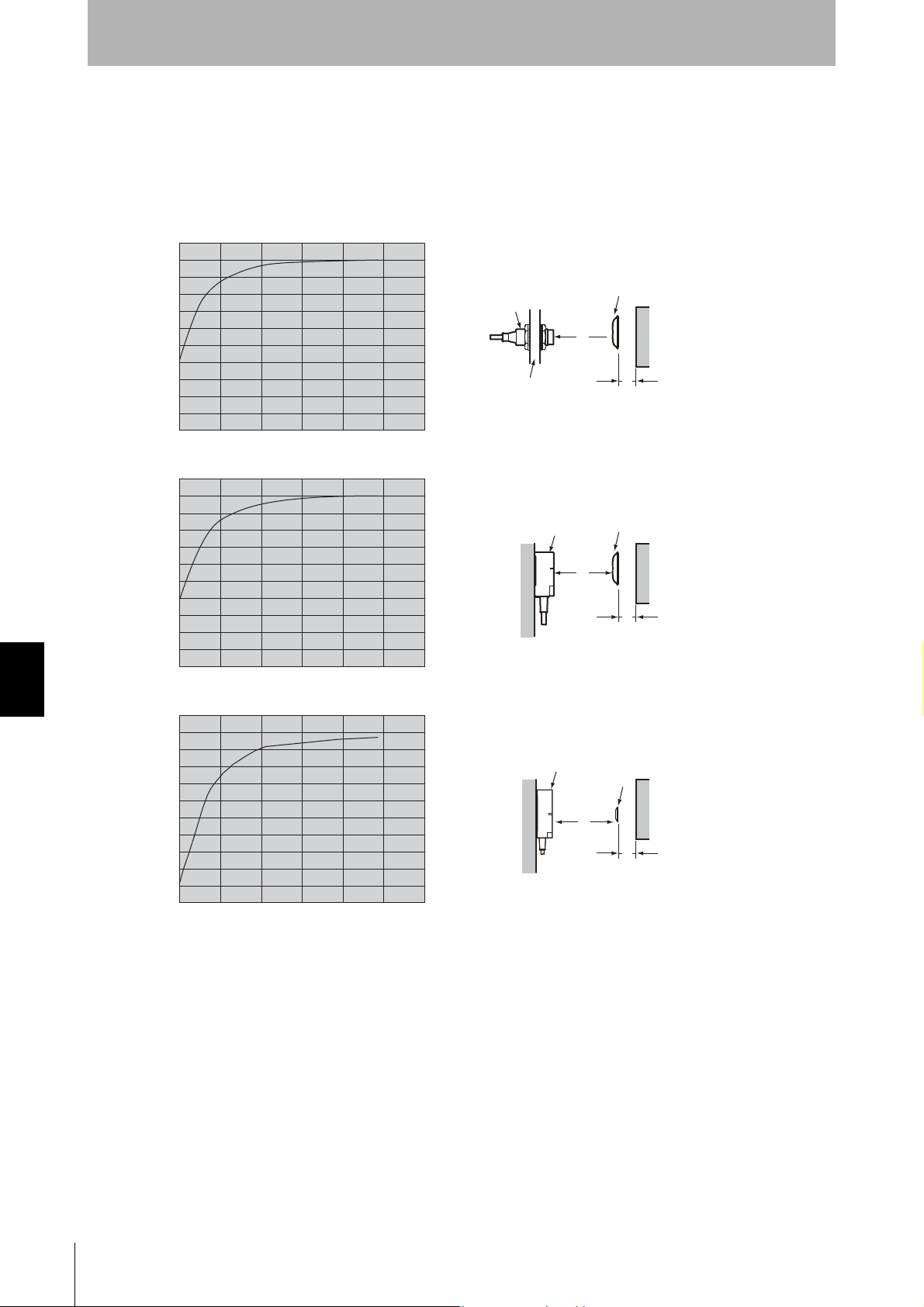
Section 7
• V680-HS52 &V680-D1KP66T-SP
10 20 30 40 50 (mm)
0
50
70
Distance to metal (x)
60
40
30
20
10
90
(%)
100
80
The communications distance without
metal is 100%
• V680-HS63 &V680-D1KP66T-SP
10 20 30 40 50 (mm)
0
50
70
Distance to metal (x)
60
40
30
20
10
90
(%)
100
80
The communications distance without
metal is 100%
• V680-HS65 &V680-D1KP66T-SP
10 20 30 40 50 (mm)
0
50
70
Distance to metal (x)
60
40
30
20
10
90
(%)
100
80
The communications distance without
metal is 100%
ID Tag
Metal on back
Antenna
Y
X
Metal
Communications
distance
Antenna
ID Tag
Metal on back
Metal
Y
X
Communications
distance
Y
X
Communications
distance
Metal
Antenna
ID Tag
Metal on back
Chemical Resistance
V680-D1KP66T-SP
Effect of Metal behind Tags (Reference)
Mounting ID T ags to met al workpieces or palettes will affect the communications capabilities. Place non-metallic parts (e.g., plastic or resin) between the metallic parts by referring to the following relationship between the
distance between the ID T a g and the metallic body versus the communications distance.
Section 7 Reference Data
RFID System
154
User's Manual
Page 7
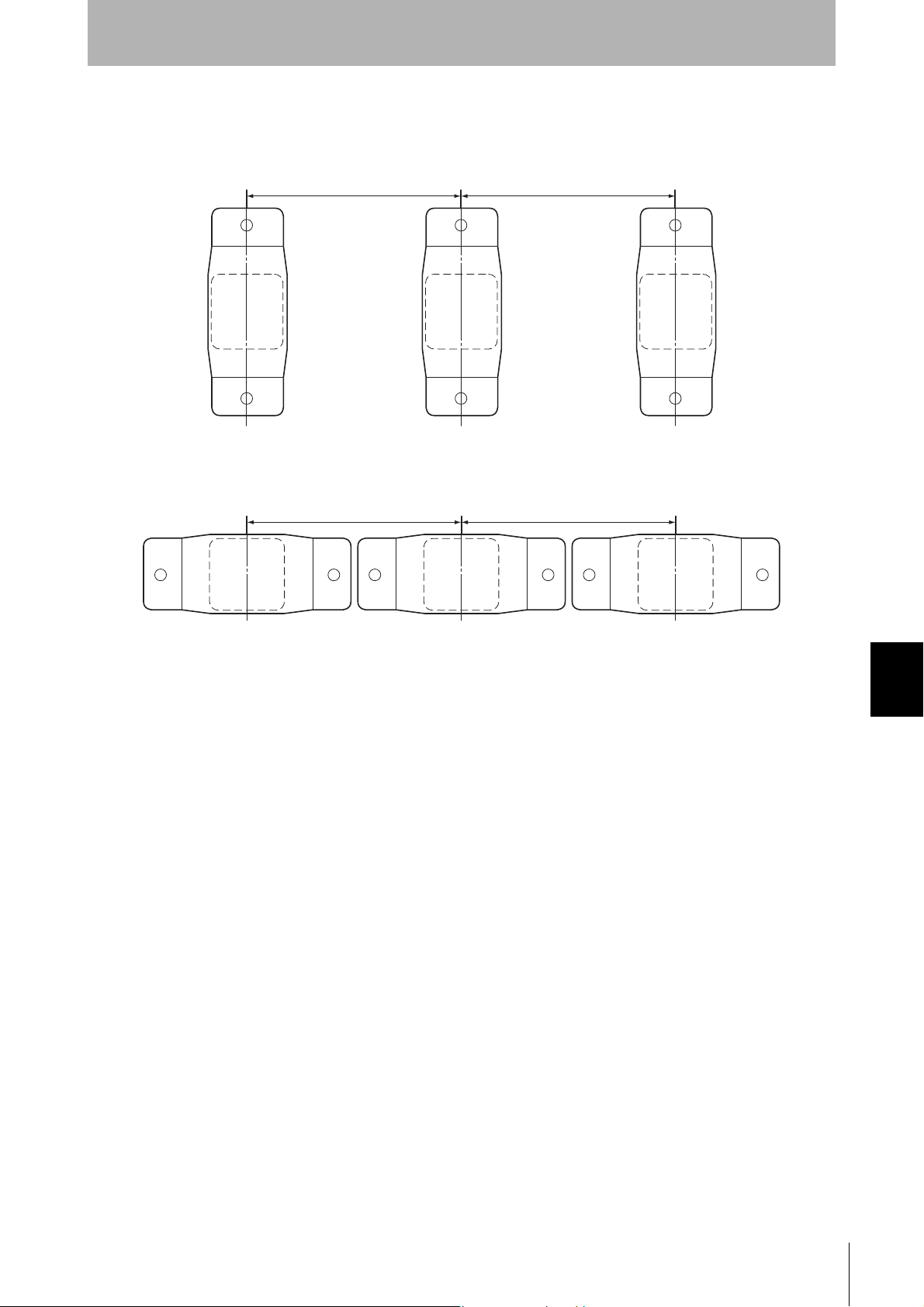
Section 7
100mm min.
100mm min.
100mm min.
100mm min.
Chemical Resistance
Mutual Interference with Tag (Reference)
To prevent malfunctioning due to mutual interference when using more than one Tag, leave sufficient
space between them as shown in the following diagram.
Section 7 Reference Data
RFID System
User's Manual
155
Page 8
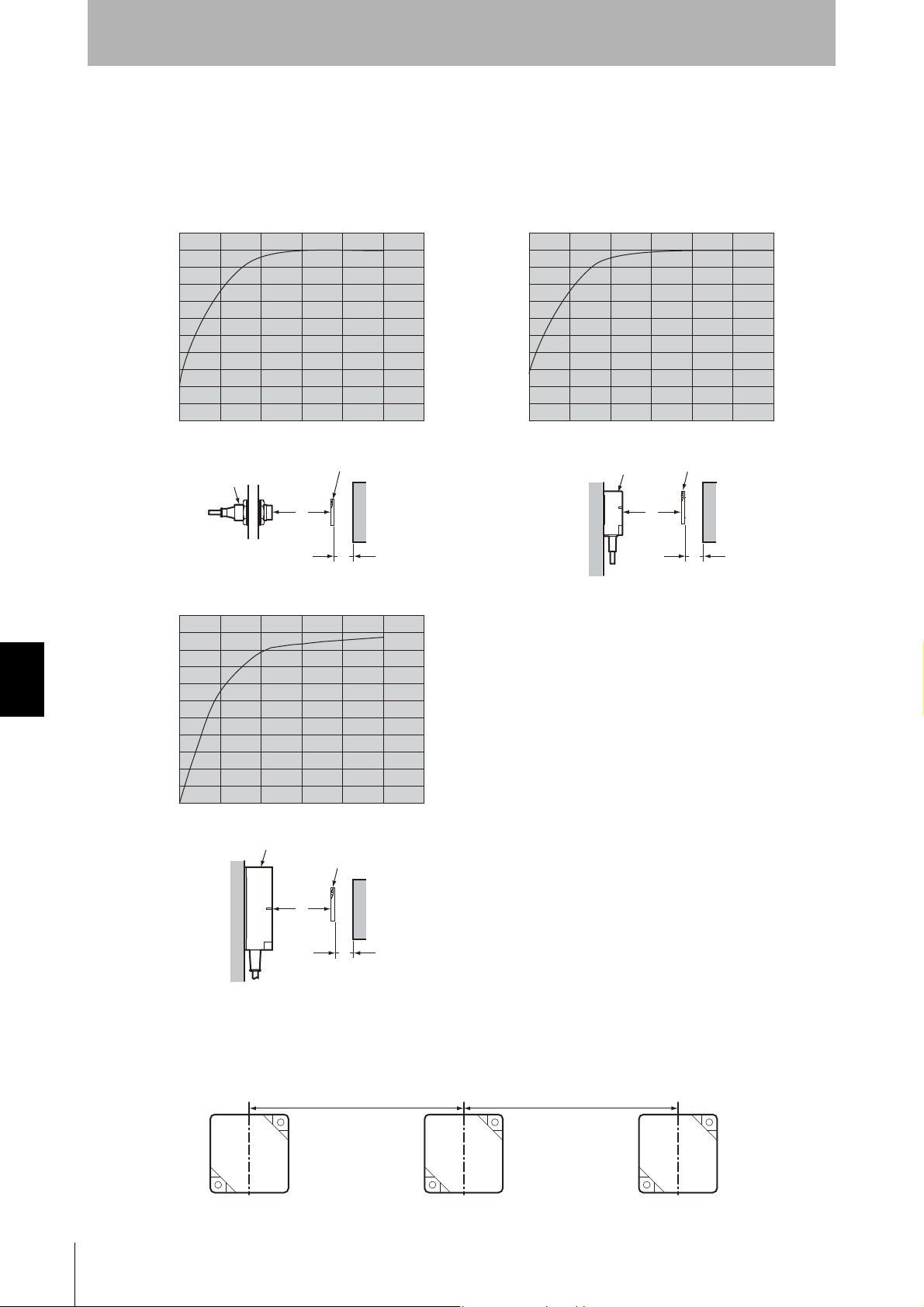
Section 7
• V680-HS52 &V680-D2KF67
10 20 30 40 50 (mm)
0
50
70
Distance to metal (x)
60
40
30
20
10
90
(%)
100
80
The communications distance without
metal is 100%
• V680-HS63 &V680-D2KF67
10 20 30 40 50 (mm)
0
50
70
Distance to metal (x)
60
40
30
20
10
90
(%)
100
80
The communications distance without
metal is 100%
• V680-HS65 &V680-D2KF67
10 20 30 40 50 (mm)
0
50
70
Distance to metal (x)
60
40
30
20
10
90
(%)
100
80
The communications distance without
metal is 100%
ID Tag
Metal on back
Antenna
Communications
distance
Y
X
ID Tag
Metal on back
Antenna
Communications
distance
Y
X
ID Tag
Metal on back
Antenna
Communications
distance
Y
X
Metal
200mm min.
200mm min.
Chemical Resistance
V680-D2KF67
Effect of Metal behind Tags (Reference)
The V680-D2KF67 communications distance is reduced if there is any metal material behind the Tag.
Section 7 Reference Data
Mutual Interference with Tag (Reference)
To prevent malfunctioning due to mutual interference when using more than one Tag, leave sufficient
space between them as shown in the following diagram.
156
RFID System
User's Manual
Page 9
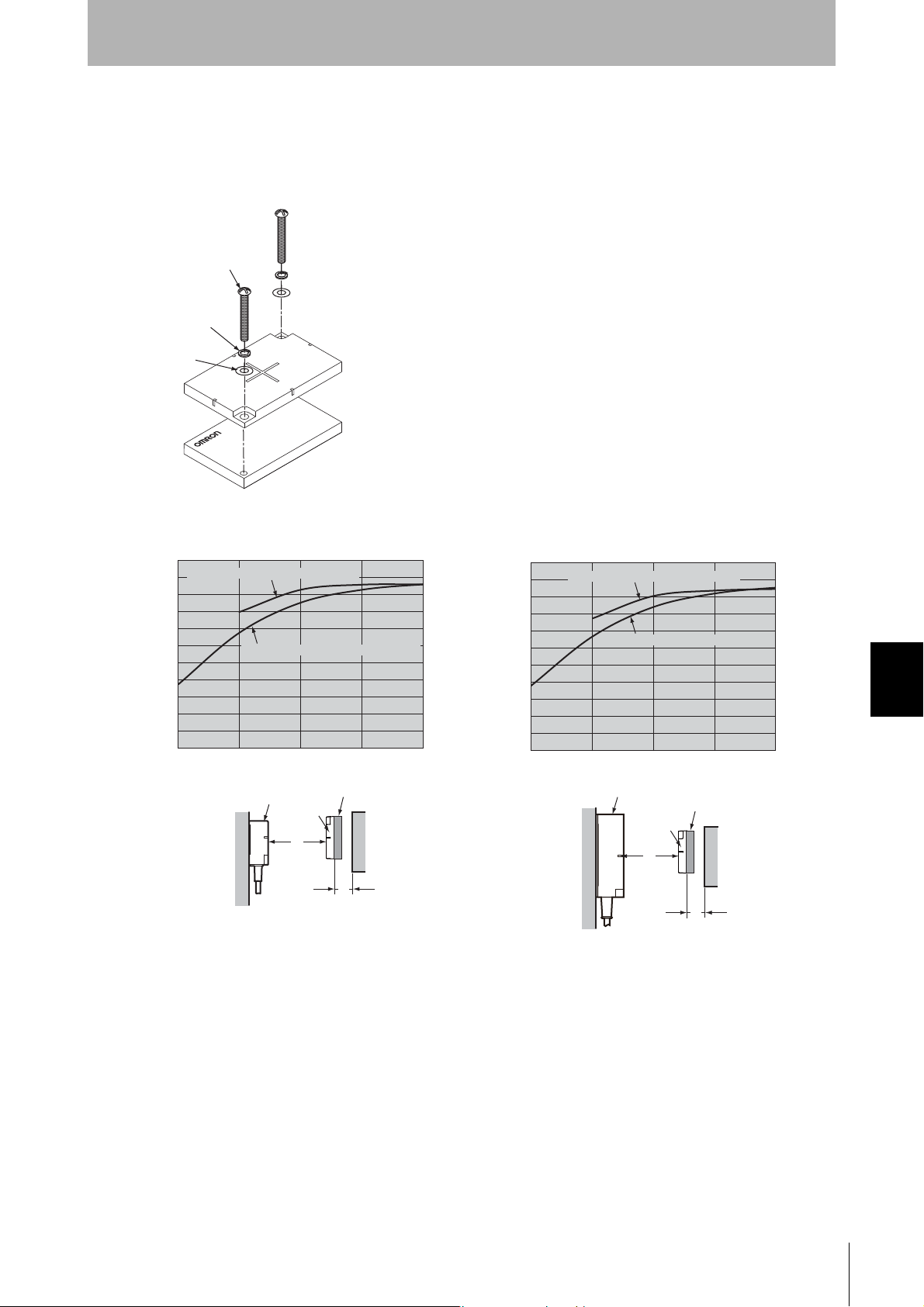
V680-D8KF68/-D32KF68
The transmission distance will be reduced if there is metal in back of
a Tag. When mounting on a metal surface, use the special
Attachment (V680-A81) of another sales or insert a non-metallic
spacer (e.g., plastic, wood, etc.).
The following diagrams show the relationship between the distance
between a Tag and metal surface and the transmission distance. The
Attachment is 10 mm thick.
• Special Attachment (V680-A81) Installation Direction
M4 screw
Spring washer
Flat washer
• V680-HS63 &V680-D8KF68/-D32KF68
10 20 30 40
(mm)
0
50
70
Distance to metal (x)
60
40
30
20
10
90
(%)
100
80
The communications distance without
metal is 100%
Antenna
When Attachment (V680-A81) is not used
When Attachment (V680-A81) is used
Atachment
Metal on back
Metal
Communications
distance
Y
X
ID Tag
• V680-HS63 &V680-D8KF68/-D32KF68
10 20 30 40
(mm)
0
50
70
Distance to metal (x)
60
40
30
20
10
90
(%)
100
80
The communications distance without
metal is 100%
When Attachment (V680-A81) is not used
When Attachment (V680-A81) is used
Atachment
Antenna
Metal
Metal on back
Y
X
Communications
distance
ID Tag
Effect of Metal behind Tags (Reference)
Section 7
Chemical Resistance
RFID System
User's Manual
Section 7 Reference Data
157
Page 10
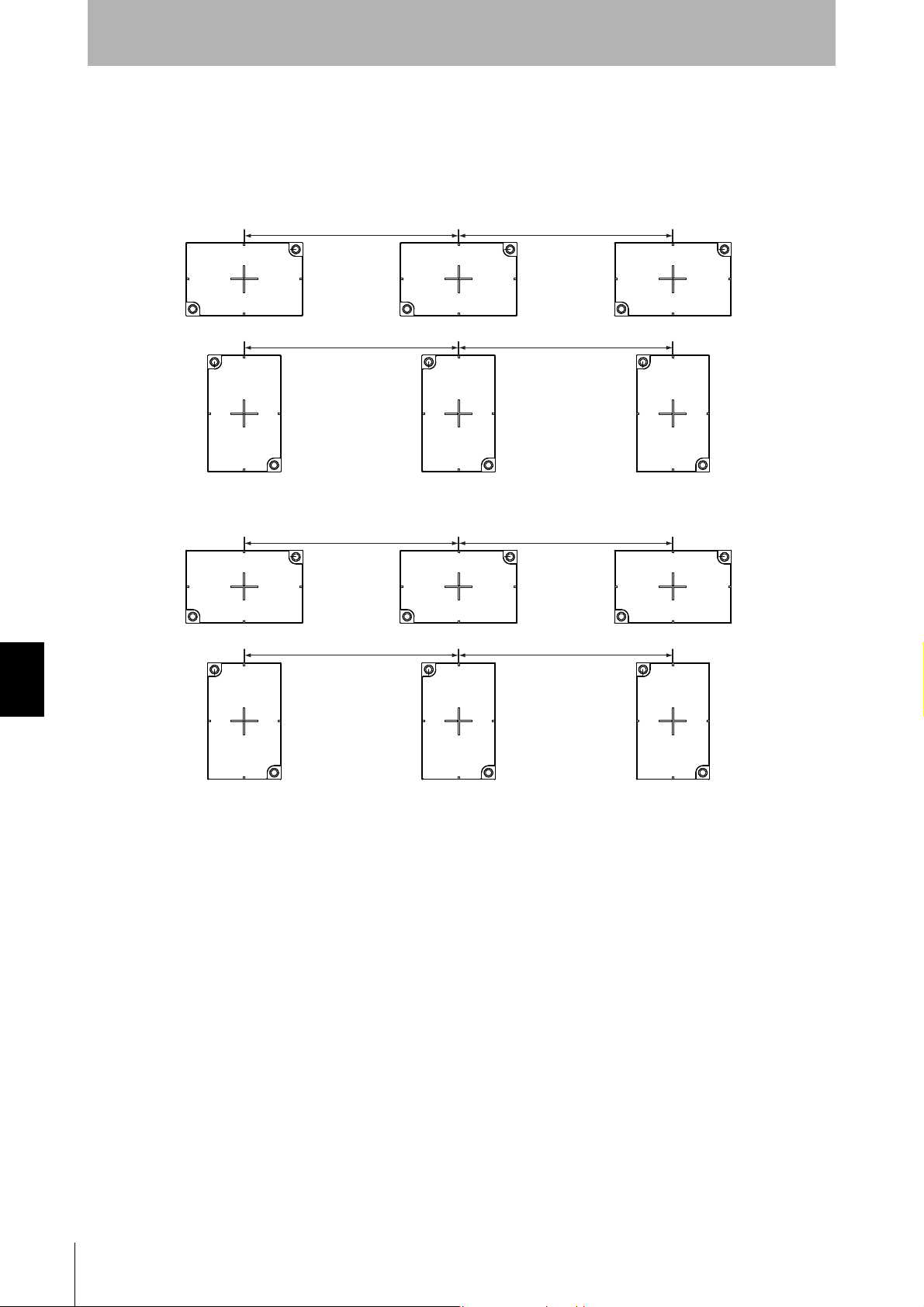
Section 7
120mm min.
120mm min.
120mm min.
120mm min.
150mm min.
150mm min.
150mm min.
150mm min.
Chemical Resistance
Mutual Interference with Tags (Reference)
To prevent malfunctioning due to mutual interference when using more than one Tag, leave sufficient
space between them as shown in the following diagram.
When V680-HS63, V680-HS52 are Used
Section 7 Reference Data
When V680-HS65 is Used
158
RFID System
User's Manual
Page 11

Section 7
Antenna
Nuts
ID Tag
Steel
Toothed washer
Non-metallic
material
θ
Antenna
Nuts
ID Tag
Steel
Toothed washer
θ
Steel
Antenna
ID Tag
θ
Non-metallic
material
Antenna
ID Tag
Steel
θ
Antenna
ID Tag
θ
Non-metallic
material
Steel
Chemical Resistance
Infuence of Angle (Refernce)
Install Antennas and Tags as close to parallel to each other as possible. Communications are possible
even when an Antenna and a Tag are mounted at an angle, but the communications distance will be
shortened. The relation between the angle and the communications distance is shown below.
Percentage Drop in Communications Distance According to Angle of V680-D1KP52MT
Tag angle (θ°)
0 10 20 30 40
V680-HS51 and V680-D1KP52MT
0% -1% -5% -10% -15%
V680-HS51 and V680-D1KP52MT
(Metal: Steel)
V680-HS52 and V680-D1KP52MT
V680-HS52 and V680-D1KP52MT
(Metal: Steel)
V680-HS63 and V680-D1KP52MT
-: The measurement is no possible because the Tag comes in contact with the Antenna.
0% 0% 0% -4% -28%
0% 0% 0% -2% -6%
0% -6% -13% -25% -
0% -2% -5% -9% -14%
• V680-HS51 & V680-D1KP52MT • V680-HS51 & V680-D1KP52MT
(Metal: Steel)
• V680-HS52 & V680-D1KP52MT
• V680-HS52 & V680-D1KP52MT
(Metal: Steel)
Section 7 Reference Data
●形V680-HS63 & 形V680-D1KP52MT
RFID System
User's Manual
159
Page 12

Section 7
Antenna
ID Tag
θ
Antenna
ID Tag
Non-metallic material
θ
Metal
Antenna
ID Tag
θ
Chemical Resistance
Percentage Drop in Communications Distance According to Angle of V680-D1KP66T
Tag angle (θ°)
0 10 20 30 40
V680-HS52 and V680-D1KP66T
0% -1% -2% -4% -7%
Section 7 Reference Data
V680-HS63 and V680-D1KP66T
V680-HS65 and V680-D1KP66T
0% -2% -3% -5% -9%
0% -1% -3% -6% -11%
• V680-HS52 & V680-D1KP66T • V680-HS63 & V680-D1KP66T
• V680-HS65 & V680-D1KP66T
160
RFID System
User's Manual
Page 13

Section 7
ID Tag
θ
Antenna
Antenna
ID Tag
Non-metallic material
θ
Antenna
ID Tag
θ
Metal
Chemical Resistance
Percentage Drop in Communications Distance According to Angle of V680-D1KP66MT
Tag angle (θ°)
0 10 20 30 40
V680-HS52 and V680-D1KP66MT
(Metal: Steel)
V680-HS63 and V680-D1KP66MT
(Metal: Steel)
V680-HS65 and V680-D1KP66MT
(Metal: Steel)
-: The measurement is no possible because the Tag comes in contact with the Antenna.
0% -1% -2% -5% -9%
0% -1% -4% -7% -13%
0% -1% -6% -15% -
• V680-HS52 & V680-D1KP66MT
(Metal: Steel)
• V680-HS65 & V680-D1KP66MT
(Metal: Steel)
• V680-HS63 & V680-D1KP66MT
(Metal: Steel)
Section 7 Reference Data
RFID System
User's Manual
161
Page 14

Section 7
ID Tag
θ
Antenna
Antenna
ID Tag
Non-metallic material
θ
Antenna
ID Tag
θ
Metal
Chemical Resistance
Percentage Drop in Communications Distance According to Angle of V680-D1KP66T-SP
Tag angle (θ°)
0 10 20 30 40
V680-HS52 and V680-D1KP66T-SP
0% -1% -2% -4% -7%
Section 7 Reference Data
V680-HS63 and V680-D1KP66T-SP
V680-HS65 and V680-D1KP66T-SP
0% -2% -3% -5% -9%
0% -1% -3% -6% -11%
• V680-HS52 & V680-D1KP66T-SP • V680-HS63 & V680-D1KP66T-SP
• V680-HS65 & V680-D1KP66T-SP
162
RFID System
User's Manual
Page 15

Chemical Resistance
ID Tag
θ
Antenna
Nuts
Steel
Toothed washer
Non-metallic
material
ID Tag
θ
Antenna
Nuts
Steel
Toothed washer
Non-metallic
material
ID Tag
θ
Antenna
Non-metallic
material
ID Tag
Antenna
Steel
θ
ID Tag
θ
Non-metallic
material
Antenna
Steel
Percentage Drop in Communications Distance According to Angle of V680-D2KF52M
Tag angle (θ°)
0 10 20 30 40
V680-HS51 and V680-D2KF52M
0% -2% -6% -12% -22%
Section 7
V680-HS51 and V680-D2KF52M
(Metal: Steel)
V680-HS52 and V680-D2KF52M
V680-HS52 and V680-D2KF52M
(Metal: Steel)
V680-HS63 and V680-D2KF52M
-: The measurement is no possible because the Tag comes in contact with the Antenna.
• V680-HS51 & V680-D2KF52M
• V680-HS52 & V680-D2KF52M
0% 0% 0% -7% -30%
0% 0% 0% -2% -5%
0% -2% -7% - -
0% 0% -1% -4% -9%
• V680-HS51 & V680-D2KF52M
• V680-HS52 & V680-D2KF52M
(Metal: Steel)
Section 7 Reference Data
(Metal: Steel)
• V680-HS63 & V680-D2KF52M
RFID System
User's Manual
163
Page 16

Section 7
ID Tag
θ
Antenna
Antenna
ID Tag
Non-metallic material
θ
ID Tag
θ
Metal
Antenna
Chemical Resistance
Percentage Drop in Communications Distance According to Angle of V680-D2KF67
Tag angle (θ°)
0 10 20 30 40
V680-HS52 and V680-D2KF67
0% -0% 0% -1% -2%
Section 7 Reference Data
V680-HS63 and V680-D2KF67
V680-HS65 and V680-D2KF67
0% -1% -2% -3% -6%
0% -1% -3% -7% -11%
• V680-HS52 & V680-D2KF67 • V680-HS63 & V680-D2KF67
• V680-HS65 & V680-D2KF67
164
RFID System
User's Manual
Page 17

Chemical Resistance
ID Tag
θ
Antenna
Antenna
ID Tag
Non-metallic material
θ
ID Tag
θ
Metal
Antenna
Percentage Drop in Communications Distance According to Angle of V680-D2KF67M
Tag angle (θ°)
0 10 20 30 40
V680-HS52 and V680-D2FKP67M
(Metal: Steel)
V680-HS63 and V680-D2FKP67M
(Metal: Steel)
V680-HS65 and V680-D2FKP67M
(Metal: Steel)
0% -1% -2% -4% -6%
0% -2% -5% -8% -14%
0% -2% -7% -16% -31%
Section 7
• V680-HS52 & V680-D2KF67M
• V680-HS65 & V680-D2KF67M
(Metal: Steel)
(Metal: Steel)
• V680-HS63 & V680-D2KF67M
(Metal: Steel)
Section 7 Reference Data
RFID System
User's Manual
165
Page 18

Section 7
ID Tag
θ
Metal
Antenna
ID Tag
θ
Metal
Antenna
ID Tag
θ
Metal
Antenna
ID Tag
θ
Metal
Antenna
Chemical Resistance
Percentage Drop in Communications Distance According to Angle of V680 -
Tag angle (θ°)
0 10 20 30 40
V680-HS63 and V680-D8KF68 or V680-D32KF68
(Horizontal-facing ID Tag)
V680-HS63 and V680-D8KF68 or V680-D32KF68
(Vertical-facing ID Tag)
V680-HS65 and V680-D8KF68 or V680-D32KF68
(Horizontal-facing ID Tag)
V680-HS65 and V680-D8KF68 or V680-D32KF68
(Vertical-facing ID Tag)
• V680-HS63 & V680-D8KF68 or V680-D32KF68
(Horizontal-facing ID Tag)
0% 0% 0% 0% 0%
0% -1% -2% -3% -5%
0% -1% -2% -4% -6%
0% -1% -3% -6% -10%
• V680-HS63 & V680-D8KF68 or V680-D32KF68
(Vertical-facing ID Tag)
D8KF68, V680-D32KF68
Section 7 Reference Data
• V680-HS65 & V680-D8KF68 or V680-D32KF68
(Horizontal-facing ID Tag)
• V680-HS65 & V680-D8KF68 or V680-D32KF68
(Horizontal-facing ID Tag)
166
RFID System
User's Manual
Page 19

ID Tag Memory
Address
Data
0000Hex
0001Hex
0002Hex
0003Hex
User area
03E6Hex
03E7Hex
:
:
1 byte
EEPROM is used as memory in the Tags.
The memory capacity available to the user is 1,000 bytes,
including 0000H to 0003H (the Write Protection Setting Area).
Address
Data
0000Hex
0001Hex
0002Hex
0003Hex
User area
07CEHex
07CFHex
:
:
1 byte
FRAM is used as memory in the Tags.
The memory capacity available to the user is 1,000 bytes,
including 0000H to 0003H (the Write Protection Setting Area)
Address
Data
0000Hex
0001Hex
0002Hex
0003Hex
User area
1FFEHe
1FFFHe
:
:
1 byte
FRAM is used as memory in the Tags.
The memory capacity available to the user is 8,192 bytes,
including 0000H to 0003H (the Write Protection Setting Area)
Address
Data
0000Hex
0001Hex
0002Hex
0003Hex
User area
7FFEHe
7FFFHe
:
:
1 byte
FRAM is used as memory in the Tags.
The memory capacity available to the user is 32,744 bytes,
including 0000H to 0003H (the Write Protection Setting Area)
V680-D1KP□□
V680-D2KF□□
Section 7
Chemical Resistance
V680-D8KF□□
V680-D32KF□□
Section 7 ID Tag Memory
メ モ リ へのア クセスは16ビ ッ ト単位(2バイ ト 単位)に行われま す。 た だ し、 1バイ ト ライ ト モー ド 指定の場合は、 8 ビ ッ ト 単位(1
バイ ト 単位)となります。
RFID System
User's Manual
167
Page 20

Section 7
Chemical Resistance
ID Tag Memory Capacities and Memory Types (V680 Series)
(As of December 2007)
Model
V680-D1KP52MT
V680-D1KP66T
V680-D1KP66MT
V680-D1KP66T-SP
V680-D2KF52M
V680-D2KF67
V680-D2KF67M
V680-D8KF68 8,192 bytes
V680-D32KF68 32,744 bytes
Memory capacity
(user memory)
1,000 bytes EEPROM
2,000 bytes
Memory type Life expectancy
Overwrite operations: 100,000 times for each address at
25°C
Data retention: 10 years (up to 85°C)
Number of accesses: 10 billion times
FRAM
Data retention: 10 years (up to 55°C)
Section 7 ID Tag Memory Capacities and Memory Types (V680 Series)
168
RFID System
User's Manual
Page 21

Section 7
Chemical Resistance
Chemical Resistance of the Antennas, and Tags
Chemical Resistance of the Antennas
Applicable Models
V680-HS51 V680-HS52-W/R V680-HS63-W/R V680-HS65-W/R
ABS resin is used for case material and epoxy resin for filling material. Refer to the following lists and do not
use chemicals that affect ABS and epoxy resin.
Chemicals That Cause Deformations, Cracks, Etc.
ABS resin Epoxy resin
Trichlene, acetone, xylene, toluene, gasoline, creosol,
methylene chloride, phenol, cyclohexane, aqua regia,
chromic acid, sulfuric acid (90% RT), methyl ethyl
ketone, aniline, nitrobenzine, monochlorobenzine,
pyridine, nitric acid (60% RT), formic acid (80% RT)
Aqua regia, chromic acid, sulfuric acid (90% RT),
nitric acid (60% RT), ammonia solution, acetone,
methylene chloride, phenol
Chemicals That May Cause Discoloration, Swelling, Etc.
ABS resin Epoxy resin
Hydrochloric acid, alcohol, Freon, sodium hydroxide,
hydrogen peroxide, benzine, sulfuric acid (10% RT),
nitric acid (10% RT), phosphoric acid (85% RT),
ammonia solution
Sulfuric acid (10% RT), nitric acid (10% RT), hydrochloric acid (30% RT), acetic acid (50% RT), oxalic acid,
calcium hydroxide, benzine, creosol, alcohol, cyclohexane, toluene, xylene, benzine, grease
Chemicals That Do Not Affect PPS Resin or Epoxy Resin
ABS resin Epoxy resin
Ammonia, kerosine, mineral oil, developer, Yushiroken
S50, Chemi-Cool Z, Velocity No. 3, Yushiroken EEE30Y, petroleum, grease, acetic acid, oxalic acid, calcium hydroxide, phosphoric acid (30% RT), hydrochloric acid (10% RT), potassium hydroxide
Note: The above results are from tests conducted a room temperature (23°C). Even if the chemicals
do not affect the ABS or epoxy resins at room temperature, they may affect the resins at higher or
lower temperatures. Check the chemicals carefully in advance.
Ammonia, hydrochloric acid (10% RT), potassium
hydroxide, petroleum, gasoline, Yushiroken S50,
Chemi-Cool Z, Velocity No. 3, Yushiroken EEE-30Y
Section 7 Chemical Resistance of the Antennas, and Tags
RFID System
User's Manual
173
Page 22

Section 7
Chemical Resistance
Chemical Resistance of Tags
Applicable Model
V680-D1KP52MT V680-D2KF52M
PPS resin is used for case material and epoxy resin for filling material. Refer to the following lists and do not
use chemicals that affect PPS and epoxy resin.
Tags cannot be used in applications with explosion-proof specifications.
Chemicals That Cause Deformations, Cracks, Etc.
PPS resin Epoxy resin
Aqua regia Aqua regia, chromic acid, sulfuric acid (90% RT),
nitric acid (60% RT), ammonia solution, acetone,
methylene chloride, phenol
Chemicals That May Cause Discoloration, Swelling, Etc.
PPS resin Epoxy resin
Nitric acid (60% RT) Sulfuric acid (10% RT), ni tric ac id (10% R T), hy drochl o-
ric acid (30% RT), acetic acid (50% RT), oxalic acid,
calcium hydroxide, benzine, creosol, alcohol, cyclohexane, toluene, xylene, benzine, grease
Section 7 Chemical Resistance of the Antennas, and Tags
Chemicals That Do Not Affect PPS Resin or Epoxy Resin
PPS resin Epoxy resin
Hydrochloric acid (37%RT), sulfuric acid (98%RT),
nitric acid (40%RT), Hydrogen fluoride solution
(40%RT), chromic acid (40%RT), hydrogen peroxide
(28%RT), sodium hydroxide solution (60%RT),
ammonia solution (28%RT), sodium chloride (10%RT),
sodium carbonate (20%RT), sodium hypochlorite,
phenol solution (5%RT), glacial acetic acid, acetic acid,
oleic acid, Methyl alcohol (95%RT), ethyl alcohol
(95%RT), Ethyl acetate, sebacic acid, diethylhexyl,
acetone, diethyl ether, n-heptane, 2-2-4 trimethylpentane, benzine, toluene, aniline, mineral oil, gasoline,
insulating oil, dichloroethylene, carbon tetrachloride
Note: The above results are from tests conducted a room temperature (23°C). Even if the chemicals
do not affect the PPS or epoxy resins at room temperature, they may affect the resins at higher
or lower temperatures. Check the chemicals carefully in advance.
Ammonia, hydrochloric acid (10% RT), potassium
hydroxide, petroleum, gasoline, Yushiroken S50,
Chemi-Cool Z, Velocity No. 3, Yushiroken EEE-30Y,
methyl ethyl ketone, sodium hydroxide (10%RT)
174
RFID System
User's Manual
Page 23

Applicable Models
V680-D1KP66T/66MT
Section 7
Chemical Resistance
Chemical
tempera-
ture
At room
Hydrochloric acid
Sulfuric acid
Nitric acid
Hydrogen fluoride solution
Chromic acid
Hydrogen peroxide solu-
tion
Sodium hydroxide solution
Ammonia solution
Sodium chloride
Sodium carbonate
A: Has no adverse effect, B: May cause discoloration, swelling, etc., C: Causes deformation, cracks, etc.
37% A A
10% A A
98% A B
50% A A
30% A A
3% A A
60% B C
40% A B
10% A A
40% A A
40% A A
28% A B
3% A A
60% A A
10% A A
1% A A
28% A B
10% A B
10% A A
20% A A
2% A A
At
90°C
Chemical
Sodium hypochlorite
Phenol solution
Glacial acetic acid
Acetic acid
Oleic acid
Methyl alcohol
Ethyl alcohol
Ethyl acetate
Sebacic acid diethylhexyl
Acetone
Diethyl ether
n-heptane
2-2-4 trimethylpentane
Benzene
Toluene
Aniline
Mineral oil
Gasoline
Insulating oil
Dichloroethylene
Carbon tetrachloride
5% A A
95% A A
95% A A
At room
tempera-
ture
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
AA
At
90°C
Section 7 Chemical Resistance of the Antennas, and Tags
The above table shows the extent of changes in PPS resin exposed to each chemical at room temperature
and at 90
tables, always conduct tests under the actual conditions in which the Tags are to be used.
°C. If actual chemicals, concentrations, and temperatures are different from those shown in the
RFID System
User's Manual
175
Page 24

Section 7
Chemical Resistance
Applicable Models
V680-D1KP66T-SP
Chemical Resistance of Fluoroplastic PFA (Reference)
PFA: Tetrafluorethylene-Perfluoroalkylvinyletheir Copolymer
Fluoroplastic PFA does not react with most chemicals except molten alkali metal, hot pressurized
fluorine (F
was soaked in or exposed to commonly used organic and inorganic chemicals. In these tests, a
compression-molded test piece (1.3 mm thick) was soaked in the chemical at a specified temperat ure
for a week (168 houre) and taken out of the chemical, then the weight change, tensile strength, and
elongation of the test piece were immediately m easured. If the chan ge in the te nsile strength is 15 % or
less, the cange in the elongation is 10 % or less, and the increase in the weight is less than 0.5 %, the
results of the test can be considered normal.
If PFA is exposed to trichloroacetic acid, tri-n-butyl phosphate, perchloroethylene, carbon thtrachloride,
and other liquids (which easily make resin surfaces wet) at a high temperature, it tends to increase its
weight due to absorption and reduce its tensile strength. Even when PFA absorbs chemicals and solvents, its molecular structure will not change, If, however, PFA is subject to temperature or pressure
changes or mechanical damage when it has absorbed chemicals, the chemicals will repeatedly
expand and contract inside pfa, causing mechanical problems such as cracks and bulging. In fact, this
problem occurs with any kind of plastic.
2), and some halogen derivatives. The followin g t ables sh ow the result s of test s in which PFA
Section 7 Chemical Resistance of the Antennas, and Tags
Inorganic Chemicals
Test
Chemical name
concentrated hydrochloric acid 120 98 100 0.0
Concentrated sulfuric acid 120 95 98 0.0
Hydrofluoric acid (60%) 23 99 99 0.0
Fuming sulfuric acid 23 95 96 0.0
Aqua regia 120 99 100 0.0
Chromic acid (50%) 120 93 97 0.0
Consentrated nitric acid 120 95 98 0.0
Fuming nitric acid 23 99 99 0.0
Concentrated ammonia solution 66 98 100 0.0
Caustic soda (50%) 120 93 99 0.4
Hydrogen peroxide solution (30%) 23 93 95 0.0
Bromine 23 99 100 0.5
Chlorine 120 92 100 0.5
Ferrous chloride (25%) 100 93 98 0.0
Zinc chloride (25%) 100 96 100 2.7
Chlorosulfonic acid 151 91 100 2.7
Concentrated phosphoric acid 100 93 100 0.0
temperature
(°C)
Resulting characteristics
(%)
Tensile
strength
Elongation
Weight
increase
rate (%)
176
RFID System
User's Manual
Page 25

Organic Chemicals
Test
Chemical name
Glacial acetic acid 118 95 100 0.4
Acetic anhydride 139 91 99 0.3
Trichloroacetic acid 196 90 100 2.2
Isooctane 99 94 100 0.7
Naphtha 100 91 100 0.5
Mineral oil 180 87 95 0.0
Toluene 110 88 100 0.7
o-creosol 191 92 96 0.2
Nitrobenzene 210 90 100 0.3
Benzyl alcohol 205 93 99 0.3
Aniline 185 94 100 0.3
n-butylamine 78 86 97 0.4
Ethylenediamine 117 96 100 0.1
Tetrahydrofuran 66 88 100 0.1
Benzaldehyde 179 90 99 0.5
Cyclohexane 156 92 100 0.4
Methyl ethyl ketone 80 90 100 0.4
Acetophenone 202 90 100 0.6
Dimethylphtalate 200 98 100 0.3
n-butyl acetate 125 93 100 0.5
Tri-n-butyl phosphate 200 91 100 2.0
Methylene chloride 40 94 100 0.8
Perchloroethylene 121 86 100 2.0
Carbon tetrachloride 77 87 100 2.3
Dimethyl formamide 154 96 100 0.2
Dimethyl sulfoxide 189 95 100 0.1
Dioxane 101 92 100 0.6
Reference: Fluoroplastics Handbook, The Nikkan Kogyo Shimbun Ltd. (Takaomi Satogawa)
temperature
(°C)
Resulting characteristics
(%)
Tensile
strength
Elongation
Section 7
Chemical Resistance
Weight
increase
rate (%)
Section 7 Chemical Resistance of the Antennas, and Tags
RFID System
User's Manual
177
Page 26

Section 7
Chemical Resistance
Substances Extracted from Tag (Reference)
If chemicals penetrate into a Tag through PFA, ions may be extracted from the Tag.
Results of Ion-exchange Chromatography
A built-in Tag was soaked in hot water (100°C for 16 houres), and extracted ions were analyzed. The
results are shown below.
Extracted Ions (Concentration)
Cl: 0.5 ppm, Na
Results of ICP Emission Spectral Analysis
The V680-D1KP66T-SP Tag was soaked in condentrated hydrochloric acid (which can easily penetrate
through PFA) at 80°C fo 300 hours, then extracted substances were analyzed.
Extracted Substances (Concentration)
Si: 700 ng/ml, S: 1,000 ng/ml, Ca: 30 ng/ml
+
: 10 ppm, NH4+: 11 ppm, K+: 1.0 ppm
Section 7 Chemical Resistance of the Antennas, and Tags
The chemical resistance and extracted substances presented here should be used for reference only. The
rates of change in Tag characteristics and the amounts of substances extracted will vary with temperatures
and chemical concentrations. Before using T ags under actual production environment, always conduct tests to
check for any problems
178
RFID System
User's Manual
Page 27

Section 7
Chemical Resistance
Applicable Models
V680-D2KF67/67M
Chemicals that affect Tags are shown below.
ABS resin is used for case material and epoxy resin for filling material. Refer to the following lists and do not
use chemicals that affect ABS and epoxy resin.
Tags cannot be used in applications with explosion-proof specifications.
Chemicals That Cause Deformations, Cracks, Etc.
ABS resin Epoxy resin
Trichlene, acetone, xylene, toluene, gasoline, creosol,
methylene chloride, phenol, cyclohexane, aqua regia,
chromic acid, sulfuric acid (90% RT), methyl ethyl
ketone, aniline, nitrobenzine, monochlorobenzine,
pyridine, nitric acid (60% RT), formic acid (80% RT)
Chemicals That May Cause Discoloration, Swelling, Etc.
ABS resin Epoxy resin
Hydrochloric acid, alcohol, Freon, sodium hydroxide,
hydrogen peroxide, benzine, sulfuric acid (10% RT),
nitric acid (10% RT), phosphoric acid (85% RT),
ammonia solution
Aqua regia, chromic acid, sulfuric acid (90% RT),
nitric acid (60% RT), ammonia solution, acetone,
methylene chloride, phenol
Sulfuric acid (10% RT), nitric acid (10% RT), hydrochloric acid (30% RT), acetic acid (50% RT), oxalic acid,
calcium hydroxide, benzine, creosol, alcohol, cyclohexane, toluene, xylene, benzine, grease
Chemicals That Do Not Affect PPS Resin or Epoxy Resin
ABS resin Epoxy resin
Ammonia, kerosine, mineral oil, developer, Yushiroken
S50, Chemi-Cool Z, Velocity No. 3, Yushiroken EEE30Y, petroleum, grease, acetic acid, oxalic acid, calcium hydroxide, phosphoric acid (30% RT), hydrochloric acid (10% RT), potassium hydroxide
Note: The above results are from tests conducted a room temperature (23°C). Even if the chemicals
do not affect the ABS or epoxy resins at room temperature, they may affect the resins at higher
or lower temperatures. Check the chemicals carefully in advance.
Ammonia, hydrochloric acid (10% RT), potassium
hydroxide, petroleum, gasoline, Yushiroken S50,
Chemi-Cool Z, Velocity No. 3, Yushiroken EEE-30Y
Section 7 Chemical Resistance of the Antennas, and Tags
RFID System
User's Manual
179
Page 28

Section 7
Chemical Resistance
Applicable Model
V680-D8KF68/D32KF68
Chemicals that affect Tags are shown below.
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) resin is used for case material and epoxy resin for filling material. Refer to
the following lists and do not use chemicals that affect PBT and epoxy resins.
Tags cannot be used in applications with explosion-proof specifications.
Chemicals That Cause Deformations, Cracks, Etc.
PBT resin Epoxy resin
Acetone, trichloroethylene, ethylene dichloride, sodium
hydroxide, and other alkaline substances
Chemicals That May Cause Discoloration, Swelling, Etc.
PBT resin Epoxy resin
Hydrochloric acid (10% RT), acetic acid (5% RT), benzene
Aqua regia, chromic acid, sulfuric acid (90% RT), nitric
acid (60% RT), liquid ammonia, acetone, methylene
chloride, phenol
Sulfuric acid (10% RT), nitric acid (10% RT), concentrated hydrochloric acid, acetic acid (50% RT), nitric
acid, calcium hydroxide, benzene, cresol, alcohol,
microhexanon, toluene, xylene, benzene, grease
Section 7 Chemical Resistance of the Antennas, and Tags
Chemicals That Do Not Affect PPS Resin or Epoxy Resin
PBT resin Epoxy resin
Nitric acid (30% RT), concentrated hydrochloric acid,
acetic acid, ethyl acetate (100% RT), potassium permaganate (5% RH), ethyl acetate, carbon tetrachloride,
methanol, ethanol, gasoline
Note: The above results are from tests conducted at room temperature (23°C). Even if the chemicals
do not affect the PPS or epoxy resins at room temperature, they may affect the resins at higher or lower
temperatures. Check the chemicals carefully in advance.
Ammonia, hydrochloric acid (10% RT), calcium hydroxide, petroleum, gasoline, Yushiroken S50, Chemi-cool
Z, Velocity No. 3, Yushiroken EEE-30Y, methyl ethyl
ketone, sodium hydroxide
180
RFID System
User's Manual
Page 29

Section 7
200 mm
Chemical Resistance
Degree of Protection
Ingress protection degrees (IP-@@) are determined by the following tests. Be sure to check the sealing capa-
bility under the actual operating environment and conditions before actual use.
IP indicates the ingress protection symbol.
IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) Standards
IEC 60529: 1989-11
(A) First Digit: Degree of Protection from Solid Materials
Degree Degree
0
No protection
Section 7 Degree of Protection
1
2
3
4
5
6
50 mm dia.
12.5 mm dia.
2.5 mm
1 mm
Protects against penetration of any solid object such as a hand that is 50 mm or more in diameter.
Protects against penetration of any solid object, such as a finger, that is 12.5 mm or more in diameter.
Protects against penetration of any solid object, such as a wire, that is 2.5 mm or more in diameter.
Protects against penetration of any solid object, such as a wire, that is 1 mm or more in diameter.
Protects against penetration of dust of a quantity that may cause malfunction or obstruct the safe
operation of the product.
Protects against penetration of all dust.
(B) Second Digit: Degree of Protection Against Water
Degree Protection Test method (with pure water)
0 No protection Not protected against water. No test
1 Protection against water
drops
Protects against vertical drops
of water towards the product.
Water is dropped vertically towards the product from
the test machine for 10 min.
182
RFID System
User's Manual
2 Protection against water
drop
Protects against drops of
water approaching at a maximum angle of 15°to the left,
right, back, and front from vertical towards the product.
Water is dropped for 2.5 min each (i.e., 10 min in total)
towards the product inclined 15° to the left, right, back,
and front from the test machine.
15˚
200 mm
Page 30

Chemical Resistance
Water rate is 0.07
liter/min per hole.
Degree Protection Test method (with pure water)
3 Protection against sprin-
kled water
Protects against sprinkled
water approaching at a maximum angle of 60° from vertical towards the product.
Water is sprinkled for 10 min at a maximum angle of
60° to the left and right from vertical from the test
machine.
Section 7
Water rate is 0.07
liter/min per hole.
4 Protection against water
spray
Protects against water spray
approaching at any angle
towards the product.
5 Protection against water jet
spray
Protects against water jet
spray approaching at any
angle towards the product.
6 Protection against high
pressure water jet spray
Protects against high-pressure water jet spray approaching at any angle towards the
product.
7 Protection underwater Resists the penetration of
water when the product is
placed underwater at specified pressure for a specified
time.
Water is sprayed at any angle towards the product for
10 min from the test machine.
Water is jet sprayed at any angle towards the product
for 1 min per square meter for at least 3 min in total
from the test machine.
2.5 to 3 m
Discharging nozzle: 6.3 dia.
12.5 liter/min
Water is jet sprayed at any angle towards the product
for 1 min per square meter for at least 3 min in total
from the test machine.
2.5 to 3 m
Discharging nozzle: 6.3 dia.
100 liter/min
The product is placed 1 m deep in water (if the product
is 850 mm max. in height) for 30 min.
1 m
Section 7 Degree of Protection
8
(See Note)
Protection underwater Can be used continuously
underwater.
The test method is determined by the manufacturer and
user.
Oil resistance (OMRON in-house standard)
Protection
Oil-resistant No adverse affect from oil drops or oil spray approaching from any direction.
Oil-proof Protects against penetration of oil drops or oil spray approaching from any direction.
Note: This OMRON in-house standard confirms resistance to cutting and other oils. It is equivalent to the
former JEM standard.
RFID System
User's Manual
183
Page 31

Revision History
Cat. No.: Z248-E1-04
Revision code
A manual revision code appears as a suffix to the catalog number at the bottom of the front and rear pages.
Revision code Date Revised contents
01 October 2006 Original production
02 May 2007 Added items for V680-D8KF68/-D32KF68 ID Tags.
03 July 2007
03A September 2007
04 December 2007
Added items for V680-A81, V680-HS65 Antenna, and the overseas regulations
and standards.
Added information on metal on back surface of the V680-HS65, corrected Tag
specifications, and made other minor corrections.
Added item for V680-HS51 Antenna, the overseas regulations and standards, ,
and made other minor corrections.
184
RFID System
User's Manual
Page 32

Authorized Distributor:
OMRON Corporation
Industrial Automation Company
Sensing Devices Division H.Q.
Industrial Sensors Division
Shiokoji Horikawa, Shimogyo-ku,
Kyoto, 600-8530 Japan
Tel: (81)75-344-7022/Fax: (81)75-344-7107
Regional Headquarters
OMRON EUROPE B.V.
Sensor Business Unit
Carl-Benz-Str. 4, D-71154 Nufringen,
Germany
Tel: (49) 7032-811-0/Fax: (49) 7032-811-199
OMRON ELECTRONICS LLC
One Commerce Drive Schaumburg,
IL 60173-5302 U.S.A.
Tel: (1) 847-843-7900/Fax: (1) 847-843-7787
OMRON ASIA PACIFIC PTE. LTD.
No. 438A Alexandra Road # 05-05/08 (Lobby 2),
Alexandra Technopark, Singapore 119967
Tel: (65) 6835-3011/Fax: (65) 6835-2711
OMRON (CHINA) CO., LTD.
Room 2211, Bank of China Tower,
200 Yin Cheng Zhong Road,
Pu Dong New Area, Shanghai, 200120, China
Tel: (86) 21-5037-2222/Fax: (86) 21-5037-2200
Cat. No. Z279-E1-01
In the interest of product improvement, specifications are
subject to change without notice.
Printed in Japan
0308-0.3C (1006)
 Loading...
Loading...