Page 1
j
MAINTENANCE / ON-SITE - MANUAL
ESG-400
Electro Surgical Generator
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4
Page 2
DANGER
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in
death or serious injury.
d
WARNING
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in
death or serious injury.
CAUTION
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in
minor or moderate injury. It may also be used to alert against unsafe practices
or potential equipment damage.
NOTE
Indicates additional helpful information.
NOTE
The user must have received appropriate training in using, servicing,
adjustment, updating and upgrading this electrosurgical generator.
Introduction
The intended use depends on the approval of the country. Refer to the instructions for use of the electrosurgical
unit.
Maintenance instructions
This maintenance manual contains essential information on using and maintaining this electrosurgical
generator safely and effectively. Instructions for the operation of this electrosurgical generator and related
danger, warnings and cautions concerning electrosurgery are beyond the scope of this maintenance manual.
Before using and maintaining, thoroughly review this manual and the instructions for use or maintenance
manuals of all equipment which will be used during maintenance. Use the equipment as instructed. Keep this
manual in a safe, accessible location. If you have any questions or comments about any information in this
maintenance manual, contact Olympus.
Signal words
The following signal words are used throughout this maintenance manual:
ESG-400
INTRODUCTION
User qualifications
The user must have received appropriate training in using this electrosurgical generator. The following
instructions are for use by qualified personnel only. Use of this maintenance manual by other individuals is
prohibited. The training will be provided by authorized representatives of Olympus during installation and
commissioning.
Federal Law of the USA restricts this device to use by, or on the order of, a physician.
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 2 / 99 Introduction
Page 3
Precautions
User-related error prevention
WARNING
Improper use
The safety and effectiveness of electrosurgical interventions depend not only on the design of
the equipment used, but also to a major extent on factors which are under the control of the
user. It is therefore extremely important to read, understand and follow the instructions supplied
with the electrosurgical generator and the accessories in order to ensure safety and
effectiveness.
Always use the electrosurgical generator as outlined in this maintenance manual. Improper use
will not only impede functions and prevent optimum performance, but may cause equipment
damage and / or complications. Before each use, always inspect the equipment as outlined in
this maintenance manual.
WARNING
Annual safety checks / Inspection
The electrosurgical generator and the footswitch must undergo a safety check in yearly intervals
in accordance with the national statutory regulations (refer to chapter 7 “Inspection”).
Environmental conditions
CAUTION
Interference of the unit with other equipment
Be sure that this electrosurgical unit is not used adjacent to or stacked with other equipment
(other than the components of this electrosurgical unit or system) to avoid electromagnetic
interference.
Before use, thoroughly confirm the compatibility of all equipment.
To ensure electrical safety, the electrosurgical unit should not be used in conjunction with:
Electrical equipment whose safety against leakage current is not guaranteed.
Electrosurgical equipment whose safety in combined use is not guaranteed.
The electrosurgical generator complies with the electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standard.
Nevertheless, when the electrosurgical generator is active it may disturb neighboring electronic
equipment. If an auxiliary computer system is in use together with the electrosurgical generator
and endoscopic imaging techniques, the image on the monitor might freeze or blackout. Follow
the instructions in “Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) information” in the Appendix of the
instruction for use regarding electromagnetic ambient conditions.
Never loop the cords (active cord, bipolar cord, neutral electrode cord) or bundle cords together
with cords belonging to other medical equipment. The high frequency signals or spark discharge
noise generated by the unit may interfere with the operation of other medical equipment.
Do not use the electrosurgical unit in a location exposed to strong electromagnetic radiation
(microwave or short-wave medical treatment equipment, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, radio or
mobile phone equipment). Electrosurgical unit malfunction can occur.
CAUTION
Unsuitable temperature and humidity
The electrosurgical generator should only be used under the conditions as described in chapter
1-3 (Limitations). Use under other conditions may impede normal performance and / or result in
equipment damage.
High frequency leakage current or spark discharge may cause user burns.
Follow the dangers, warnings and cautions given below when handling and servicing this electrosurgical unit.
This information is to be supplemented by the dangers, warnings and cautions given in each chapter.
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 3 / 99 Introduction
Page 4

ESG-400
Accessories
WARNING
Mechanical stress
Do not apply excessive bending, straining, or squeezing force to any cords. It may cause
malfunction.
CAUTION
Non-compatible accessories and accessory damage
The electrosurgical generator shall only be used with compatible accessories. When connecting
accessories (cords, electrodes, HF instruments) avoid output settings where the maximum
output voltage of the electrosurgical generator may exceed the rated accessory voltage (refer to
“Mode characteristics”, “Output characteristics” in the Appendix of the instruction for use, and the
instruction manual of the accessory). For a list of compatible neutral electrodes, refer to
“Specifications” in the Appendix of the instruction for use.
Before use, the electrosurgical unit and accessories must be examined for damage. All
communication cables and its plugs must be free of scratches and cracks. Cables and
accessories with damaged insulation or connections must not be used.
Electric shock
WARNING
Grounding failure
To prevent the risk of electric shock, the housing of the electrosurgical unit must be grounded.
Always connect the power cord plug to a properly grounded wall outlet. Do not use a
3-pin / 2-pin adapter, as it can impair safe operation of the unit.
WARNING
User shock
To prevent user shock, malfunction and damage of the electrosurgical unit, keep liquids away
from all electrical equipment.
When taking measurements or troubleshooting of the electrosurgical unit, take appropriate
precautions, such as using isolated tools and equipment, using the “one hand rule,” etc.
CAUTION
Injury during servicing
When the housing is opened, there is a danger of electric shock. The unit must only be serviced
by authorized technicians.
Burns
WARNING
User
The maximum output voltage characteristics of the electrosurgical generator are shown in the
diagrams in “Output characteristics” in the Appendix of the instruction for use. When setting the
power level, first set it to a low level and increase it gradually. If the output is initially set to a high
level, the electrode’s insulation may be damaged and cause user and / or patient burns.
However, certain modes may present an unacceptable risk at low output power settings. For
example, with the PulseCut fast mode or PulseCut slow mode, the risk of an excessive thermal
effect rises if the output power setting is too low. Therefore, it is recommended that you perform
basic testing before using the electrosurgical generator. If the instruction manual of the HF
instrument to be used stipulate a rated voltage, the output should be set so that it does not
exceed that voltage.
High frequency, high voltage signals that can cause severe burns are present in the
monopolar / bipolar sockets described in this maintenance manual. Take appropriate precautions
when testing and troubleshooting this area of the electrosurgical unit.
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 4 / 99 Introduction
Page 5
ESG-400
Fire / Explosion
DANGER
Ignitable anaesthetics / fire supporting gases
The risk of flammable gases or other materials being ignited exists with any contact of electrical
energy. Precautionary measures must be taken to keep flammable materials and substances
away from an active electrosurgical unit (do not use flammable anesthetics, nitrous oxide or
oxygen). Otherwise, explosion or fire may result and cause serious injuries. This electrosurgical
unit is not explosion-proof. Do not use the unit within an explosion zone.
WARNING
Ignitable cleaning- and disinfection agents
Flammable agents used for cleaning and disinfection must be allowed to evaporate before the
electrosurgical unit is used and serviced.
Non-flammable agents should be used for cleaning and disinfection wherever possible.
WARNING
Risk of fire
Hazards and complications
WARNING
Contamination
The electrosurgical unit may be contaminated with infections materials; therefore, all surfaces of
the unit’s housing should be cleaned before servicing according to chapter 1-8 (Cleaning).
WARNING
Output performance
Should any abnormal output be suspected during operation, immediately terminate the use of
the equipment by releasing the footswitch. If the footswitch does not react, switch off the
electrosurgical unit. Otherwise, malfunction of the equipment may cause an unintended increase
in output.
WARNING
Service persons
Take additional precautions for service technicians, when using the unit’s service operation
mode (see chapter 15, Service operation mode).
CAUTION
Unit defect
To prevent electrosurgical unit damage, never short-circuit electrodes (accessories, neutral
electrodes).
In the event of a defect or malfunction in the unit, an undesirably high output power may be
emitted.
DANGER
Unit defect
Never use the electrosurgical unit if an abnormality is suspected.
Repair and Maintenance
CAUTION
Repair
Repairs must only be carried out by Olympus or a firm authorized by Olympus.
CAUTION
Maintenance
Preventive maintenance (inspection / periodic safety check) must only be carried out by a
qualified person / technician.
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 5 / 99 Introduction
Page 6

Copyright
©2011 Olympus Winter & Ibe GmbH. All rights reserved.
Unauthorized reproduction or distribution in part or in whole is prohibited.
Trademarks
OLYMPUS is a registered trademark of the Olympus Corporation.
The company names, product names, and proprietary technical terms in this document are the trademarks or
registered trademarks of their respective owners.
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 6 / 99 Introduction
Page 7

ESG-400
CONTENT
INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................................ 2
CONTENT .......................................................................................................................... 7
CHAPTER 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS .................................................................... 9
1 OUTLINE ...................................................................................................................... 10
1-1 Intended Use .................................................................................................................................... 10
1-2 Compatibility ..................................................................................................................................... 10
1-3 Expected service life ........................................................................................................................ 10
2 FEATURES ................................................................................................................... 11
2-1 Application Modes ............................................................................................................................ 11
2-2 Accessories ...................................................................................................................................... 12
3 LIMITATIONS ................................................................................................................ 13
4 SPECIFICATIONS ........................................................................................................ 14
4-1 ELECTROSURGICAL GENERATOR ESG-400 (REF: WB91051W) .............................................. 14
4-2 Power cords (4.5 m angled plug) ..................................................................................................... 15
4-3 Footswitch (REF: WB50402W, double pedal) ................................................................................. 16
4-4 Footswitch (REF: WB50403W, single pedal, optional) .................................................................... 16
4-5 Neutral electrode cable “P-cord” (REF: MAJ-814, optional) ............................................................ 16
4-6 Communication cable 0.25 m (REF: MAJ-1871, optional) .............................................................. 17
4-7 Communication cable 10 m (REF: MAJ-1872, optional) ................................................................. 17
4-8 Adapter for UHI-2/3 (REF: MAJ-1873, optional) .............................................................................. 17
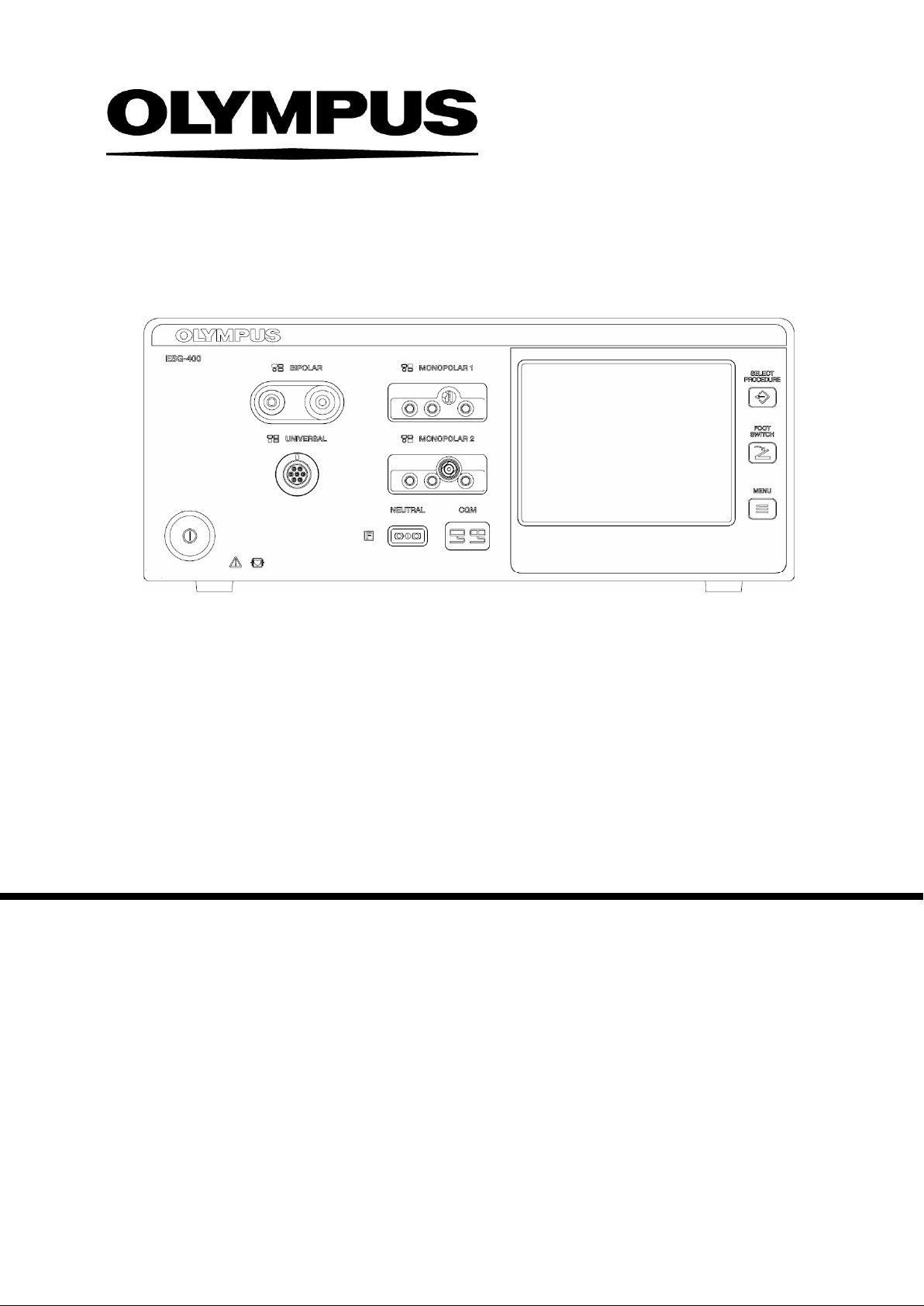
5 NAME AND FUNCTION OF EACH PART .................................................................... 18
5-1 Symbols and descriptions ................................................................................................................ 18
5-1-1 Safety related symbols ............................................................................................................ 18
5-1-2 Front panel .............................................................................................................................. 19
5-1-3 Touch screen ........................................................................................................................... 19
5-1-4 Rear panel ............................................................................................................................... 21
5-2 Front panel ....................................................................................................................................... 22
5-3 Rear panel ........................................................................................................................................ 24
5-4 Bottom panel .................................................................................................................................... 25
5-5 All screen ......................................................................................................................................... 25
5-6 Set screen ........................................................................................................................................ 26
5-7 Mode screen .................................................................................................................................... 27
5-8 Footswitch with two pedals .............................................................................................................. 28
5-9 Footswitch with one pedal (optional)................................................................................................ 28
5-10 Neutral electrode cable “P-cord” (optional) ...................................................................................... 29
6 CONNECTOR ................................................................ ................................ ............... 30
6-1 Docking Connector .......................................................................................................................... 30
6-2 Monopolar Standard 1 ...................................................................................................................... 30
6-3 Monoploar Standard 2 (Erbe) ........................................................................................................... 30
6-4 Bipolar Standard 3............................................................................................................................ 30
6-5 Monopolar Neutral Electrode ........................................................................................................... 31
6-6 Foot switch 1 (SIP/SOP) .................................................................................................................. 31
6-7 Foot switch 2 (SIP/SOP) .................................................................................................................. 32
7 SYSTEM DIAGRAM ..................................................................................................... 33
8 CLEANING, STORAGE AND DISPOSAL .................................................................... 34
8-1 Cleaning ........................................................................................................................................... 34
8-2 Storage ............................................................................................................................................. 35
8-3 Disposal of the unit .......................................................................................................................... 35
CHAPTER 2: BLOCK DESCRIPTION ............................................................................. 37
1 BLOCK DESCRIPTIONS .............................................................................................. 38
1-1 Motherboard ..................................................................................................................................... 39
1-2 HVPS Board ..................................................................................................................................... 41
1-3 Generator board ............................................................................................................................... 41
1-4 Relay Board ..................................................................................................................................... 41
1-5 Front Panel ....................................................................................................................................... 42
CHAPTER 3: REPAIR SYSTEM ...................................................................................... 43
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 7 / 99 Content
Page 8

ESG-400
1 ESG-400 MAIN UNIT .................................................................................................... 44
2 BOARD COMPATIBILITY ............................................................................................. 44
3 OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES ......................................................................................... 44
3-1 WB50402W (Footswitch with two pedals) ....................................................................................... 44
3-2 WB50403W (Footswitch with one pedal) ......................................................................................... 44
3-3 MAJ-814 (Neutral electrode cable “P-cord”) .................................................................................... 44
4 PRECAUTIONS ON FUNCTION AND OPERATION SETTINGS ................................. 44
4-1 General Precautions ........................................................................................................................ 44
CHAPTER 4: TROUBLESHOOTING .............................................................................. 45
1 GENERAL ..................................................................................................................... 46
2 NEUTRAL ELECTRODE OPERATION ........................................................................ 47
3 ERROR SCREEN, CODES AND MEASURES ............................................................. 48
3-1 What to do when no error code is displayed .................................................................................... 50
3-2 What to do when an error code is displayed .................................................................................... 54
CHAPTER 5: INSPECTION ............................................................................................. 65
1 JIGS, TOOLS, AND MEASURING EQUIPMENT FOR INSPECTION .......................... 66
2 INSPECTION PROCEDURES ................................................................ ...................... 67
2-1 Visual inspection of the electrosurgical generator and accessories ................................................ 68
2-2 Verifying the contact quality monitor function .................................................................................. 71
2-3 Checking the DC resistance (according to IEC 60601-2-2) ............................................................. 73
2-4 Checking the earth resistance (according to IEC 60601-1 and IEC 62353) .................................... 73
2-5 Checking the earth leakage current (according to IEC 60601-1) .................................................... 73
2-6 Checking the patient leakage current (according to IEC 60601-1) .................................................. 74
2-7 Checking the current and power consumption and output waveform .............................................. 75
2-8 Checking the high frequency leakage current (according to IEC 60601-2-2) .................................. 77
2-8-1 Measurement of the monopolar high frequency leakage current under loaded condition ...... 77
2-8-2 Measurement of the monopolar high frequency leakage current under unloaded condition .. 79
2-8-3 Measurement of the bipolar high frequency leakage current under loaded condition ............ 81
2-8-4 Measurement of the bipolar high frequency leakage current under unloaded condition ........ 83
2-9 Checking the output power .............................................................................................................. 85
2-10 Checking for certain features and error messages .......................................................................... 85
2-11 Final test ........................................................................................................................................... 86
2-11-1 Self test.................................................................................................................................... 86
2-11-2 Display and sound check ........................................................................................................ 86
2-11-3 Functionality of push buttons .................................................................................................. 86
2-11-4 Communication test ................................................................................................................. 86
2-11-5 Restore of output power settings ............................................................................................ 87
2-12 Inspection label (For applicable markets) ........................................................................................ 87
3 INSPECTION CARD ..................................................................................................... 88
CHAPTER 6: DEVICE MENU .......................................................................................... 93
1 SAFETY TEST ................................................................ .............................................. 94
2 SOFTWARE VERSION ................................................................................................. 95
CHAPTER 7: REVISION HISTORY ................................................................................. 97
3 REVISION HISTORY .................................................................................................... 98
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 8 / 99 Content
Page 9

ESG-400
CHAPTER 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS
1 OUTLINE ...................................................................................................................... 10
1-1 Intended Use .................................................................................................................................... 10
1-2 Compatibility ..................................................................................................................................... 10
1-3 Expected service life ........................................................................................................................ 10
2 FEATURES ................................................................................................................... 11
2-1 Application Modes ............................................................................................................................ 11
2-2 Accessories ...................................................................................................................................... 12
3 LIMITATIONS ................................................................................................................ 13
4 SPECIFICATIONS ........................................................................................................ 14
4-1 ELECTROSURGICAL GENERATOR ESG-400 (REF: WB91051W) .............................................. 14
4-2 Power cords (4.5 m angled plug) ..................................................................................................... 15
4-3 Footswitch (REF: WB50402W, double pedal) ................................................................................. 16
4-4 Footswitch (REF: WB50403W, single pedal, optional) .................................................................... 16
4-5 Neutral electrode cable “P-cord” (REF: MAJ-814, optional) ............................................................ 16
4-6 Communication cable 0.25 m (REF: MAJ-1871, optional) .............................................................. 17
4-7 Communication cable 10 m (REF: MAJ-1872, optional) ................................................................. 17
4-8 Adapter for UHI-2/3 (REF: MAJ-1873, optional) .............................................................................. 17
5 NAME AND FUNCTION OF EACH PART .................................................................... 18
5-1 Symbols and descriptions ................................................................................................................ 18
5-1-1 Safety related symbols ............................................................................................................ 18
5-1-2 Front panel .............................................................................................................................. 19
5-1-3 Touch screen ........................................................................................................................... 19
5-1-4 Rear panel ............................................................................................................................... 21
5-2 Front panel ....................................................................................................................................... 22
5-3 Rear panel ........................................................................................................................................ 24
5-4 Bottom panel .................................................................................................................................... 25
5-5 All screen ......................................................................................................................................... 25
5-6 Set screen ........................................................................................................................................ 26
5-7 Mode screen .................................................................................................................................... 27
5-8 Footswitch with two pedals .............................................................................................................. 28
5-9 Footswitch with one pedal (optional)................................................................................................ 28
5-10 Neutral electrode cable “P-cord” (optional) ...................................................................................... 29
6 CONNECTOR ................................................................ ................................ ............... 30
6-1 Docking Connector .......................................................................................................................... 30
6-2 Monopolar Standard 1 ...................................................................................................................... 30
6-3 Monoploar Standard 2 (Erbe) ........................................................................................................... 30
6-4 Bipolar Standard 3............................................................................................................................ 30
6-5 Monopolar Neutral Electrode ........................................................................................................... 31
6-6 Foot switch 1 (SIP/SOP) .................................................................................................................. 31
6-7 Foot switch 2 (SIP/SOP) .................................................................................................................. 32
7 SYSTEM DIAGRAM ..................................................................................................... 33
8 CLEANING, STORAGE AND DISPOSAL .................................................................... 34
8-1 Cleaning ........................................................................................................................................... 34
8-2 Storage ............................................................................................................................................. 35
8-3 Disposal of the unit .......................................................................................................................... 35
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 9 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 10

1-1 Intended Use
The intended use depends on the approval of the country. Refer to the instructions for use of the electrosurgical
generator.
1-2 Compatibility
This product can be used in combination with the products listed in compatibility table.
1-3 Expected service life
The expected service life is 10 years.
ESG-400
1 Outline
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 10 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 11
ESG-400
2 Features
The ESG-400 is a reusable, non-sterile electrosurgical generator with different mono- and bipolar cutting and
coagulation modes. The maximum output power is 320 W.
On the front side it features a touch screen display that displays the connection status of accessories and
peripherals connected to the electrosurgical generator. It is also used to show and modify the output settings
(e.g. mode, output power, effect) as well as to control other functions (e.g. save settings).
In addition the ESG-400 has a bipolar socket, two monopolar sockets, a neutral electrode socket, and a
universal socket to connect applicators with instrument recognition. The power switch turns the generator on
and off.
Two contact quality indicators (one for split and one for non-split electrodes) are green illuminated if neutral
electrodes are correctly connected. Three additional push buttons allow recalling a previously saved setting
(Select Procedure), to assign the footswitches to specific output sockets (Footswitch), and to control several
other functions (Menu), e.g. select language, touch tone control, output volume, or brightness.
On the rear panel the volume control, a ventilation hole, the equipotential bonding point, the AC power socket,
and two footswitch sockets can be found. Furthermore, for the connection of peripheral equipment 26-pin plugs
respectively 14-pin plugs can be connected to the LINK-IN or to the LINK-OUT socket.
On the bottom panel, a docking socket is featured. It can be used to connect the ESG-400 directly to the
USG-400 and upcoming devices. The ESG-400 is compatible with the new USG-400 ultrasonic generator to
enable the use of combined (US + HF) instruments.
2-1 Application Modes
Monopolar Cut:
PureCut (Cutting of varying tissue structures; 3 Effects)
BlendCut (Cutting of varying tissue structures; 3 Effects)
PulseCut slow (Intermittent cutting; 3 Effects)
PulseCut fast (Intermittent cutting; 3 Effects)
Monopolar Coagulation:
SoftCoag (Coagulation of tissue with little sticking and carbonization; 3 Effects)
ForcedCoag (Fast and effective coagulation; 3 Effects)
SprayCoag (Contact-free surface coagulation with little penetration depth; 3 Effects)
PowerCoag (Fast and effective coagulation with increased dissection capabilities; 3 Effects)
Bipolar Cut:
BipolarCut (All bipolar cutting procedures of tissue structures; 3 Effects)
SalineCut (Cutting in conductive fluid; 3 Effects; only available via UNIVERSAL socket )
Bipolar Coagulation:
BiSoftCoag (Coagulation with little sticking and carbonization; 3 Effects)
AutoCoag (Coagulation with little sticking and carbonization; 3 Effects)
SalineCoag (Coagulation in conductive fluid; 3 Effects; only available via UNIVERSAL socket )
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 11 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 12

HardCoag (Controlled tissue coagulation; 3 Effects)
RFCoag (Controlled deep tissue coagulation; with and without RCAP) FineCoag (Coagulation of
tissue with little sticking and carbonization; 1 Effect)
The modes have preset power levels that may be customized by the user in a defined range.
2-2 Accessories
Footswitch Double Pedal (WB50402W): It has a blue pedal that is used to activate the selected coagulation
mode and a yellow pedal that is used to activate the selected cutting mode.
Footswitch Single Pedal (optional; WB50403W): It has a blue pedal that is used to activate the selected
coagulation mode
P-Cord (optional; MAJ-814): The P-cord is used to connect a patient plate to the ESG-400.
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 12 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 13

3 Limitations
Operation
environment
Temperature
+ 10…+ 40°C
Relative humidity
30…85%, non-condensing
Atmospheric pressure
70…106 kPa
Transportation and
storage
environment
Temperature
- 25…+ 60°C
Relative humidity
10…85%, non-condensing
Atmospheric pressure
50…106 kPa
(1) Use this product under the supervision of a doctor at a medical facility.
(2) Do not use this product in combination with the products other than those designated by Olympus.
(3) This product shoul be used, transported or stored in the following environment.
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 13 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 14

4 Specifications
Power supply
Voltage range
100…120 V~ / 220…240 V~
Frequency
50 / 60 Hz
Maximum input power
1500 VA
Power fuse
10 A (only FST-series from
Schurter)
Power connection line
IEC 60320-1 / C13
Maximum length: 4.5 m
Terminal for potential
equalization
Yes
Size, weight and
packaging
Width x Depth x Height
370 × 465 × 156 mm
Volume
25752 cm³
Weight of generator
12.5 kg
Weight of packaging
2.3 kg
Type of packaging
Cardboard and expanded
polypropylene material
Classification
Protection class according
to IEC 60601-1
CF, Class I
Classification according to
MDD 93/42/EEC
IIb
Output
High frequency functions
Monopolar / Bipolar
High frequency
430 kHz ±20%
Maximum high frequency
power
320 W
All modes
25% duty cycle
(e.g. 10 s activated / 30 s
deactivated)
RFCoag (with or without
RCAP)
100% duty cycle
4-1 ELECTROSURGICAL GENERATOR ESG-400 (REF: WB91051W)
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 14 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 15
ESG-400
Sockets
MONOPOLAR 1
3-pin ( 4 mm),
Valleylab standard;
coaxial ( 8 mm),
Bovie standard
MONOPOLAR 2
3-pin ( 4 mm),
Valleylab standard;
coaxial ( 5 / 9 mm),
Erbe standard
BIPOLAR
2-pin ( 4 mm,
pin spacing 28.8 mm),
Valleylab standard;
coaxial
(
inner
8 mm,
outer
4 mm),
Erbe standard
UNIVERSAL
7-pin, Olympus standard
Neutral electrode
Single or split, 10 mm plug
Contact quality
monitor (CQM)
Allowable resistance range
for split type neutral
electrodes
10...155 Ω ±15 Ω
Allowable resistance range
for non-split type neutral
electrodes
< 10 Ω ±5 Ω
Power cords
WA95621A
Many European countries
Type E/F
WA95622A
USA, Canada and other
countries
Type B
WA95623A
United Kingdom and other
countries
Type G
4-2 Power cords (4.5 m angled plug)
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 15 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 16
4-3 Footswitch (REF: WB50402W, double pedal)
Classification
Protection class according
to IEC 60529
IPX8 (except the plug section)
Size, weight and
packaging
Width x Depth x Height
350 × 185 × 65 mm
Weight of footswitch
1.9 kg
Length of cord
4 m
Weight of packaging
0.5 kg
Type of packaging
Cardboard material
Classification
Protection class according
to IEC 60529
IPX8 (except the plug section)
Size, weight and
packaging
Width x Depth x Height
175 × 185 × 50 mm
Weight of footswitch
1.6 kg
Length of cord
4 m
Weight of packaging
0.5 kg
Type of packaging
Cardboard material
Size
Weight
0.14 kg
Length of cord
3.1 m
4-4 Footswitch (REF: WB50403W, single pedal, optional)
ESG-400
4-5 Neutral electrode cable “P-cord” (REF: MAJ-814, optional)
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 16 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 17

4-6 Communication cable 0.25 m (REF: MAJ-1871, optional)
Size
Weight
0.05 kg
Length of cord
0.25 m
Size
Weight
0.5 kg
Length of cord
10 m
Size
Width x Depth x Height
100 × 77 × 42 mm
Weight
0.35 kg
Compatible cables
MAJ-1871, MAJ-1872
4-7 Communication cable 10 m (REF: MAJ-1872, optional)
4-8 Adapter for UHI-2/3 (REF: MAJ-1873, optional)
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 17 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 18
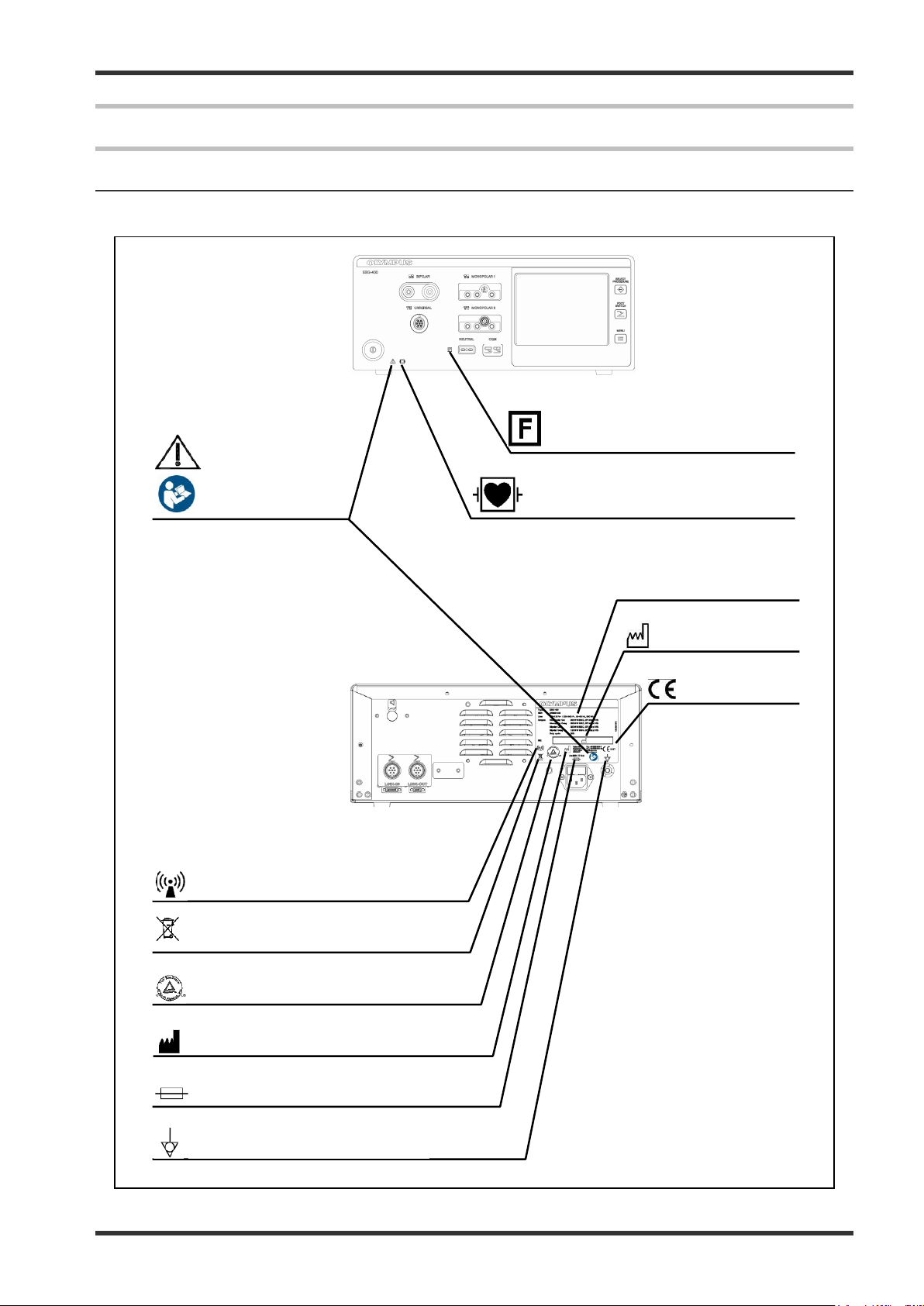
Date of
manufacture
CE marking
Non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation
Output insulated from earth
(connection for neutral electrode)
Caution, read
instructions
Refer to
instructions
Defibrillation proof type CF applied
part (cardiac application)
Waste electrical and electronic
equipment
cTUVus marking
Manufacturer
Potential equalization terminal
Fuse rating
Type plate
5 Name and Function of each part
5-1 Symbols and descriptions
5-1-1 Safety related symbols
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 18 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 19

5-1-2 Front panel
Power on / off
Neutral electrode – non-split type
Neutral electrode – split type
Select procedure
Footswitch
Menu
BIPOLAR socket
MONOPOLAR 1 socket
UNIVERSAL socket
MONOPOLAR 2 socket
Double footswitch
Single footswitch
Autostart
Plus
Minus
Return
OK Cancel
ESG-400
5-1-3 Touch screen
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 19 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 20

ESG-400
Save procedure
Delete procedure
Languages
Touch tone on
Touch tone off
Software version
Safety test
Service
Volume
Brightness
Select procedure (in title line)
Menu (in title line)
Toggle
Previous
Next
Numeric
Alphabetic
Uppercase / lowercase
Backspace
Caution
Communication indicator
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 20 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 21

Reset
RCAP
Resistance Controlled Automatic Power
Reference to BIPOLAR socket
Reference to MONOPOLAR 1 socket
Reference to UNIVERSAL socket
Reference to MONOPOLAR 2 socket
Volume
Footswitch
LINK-IN
LINK-IN socket
LINK-OUT
LINK-OUT socket
5-1-4 Rear panel
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 21 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 22
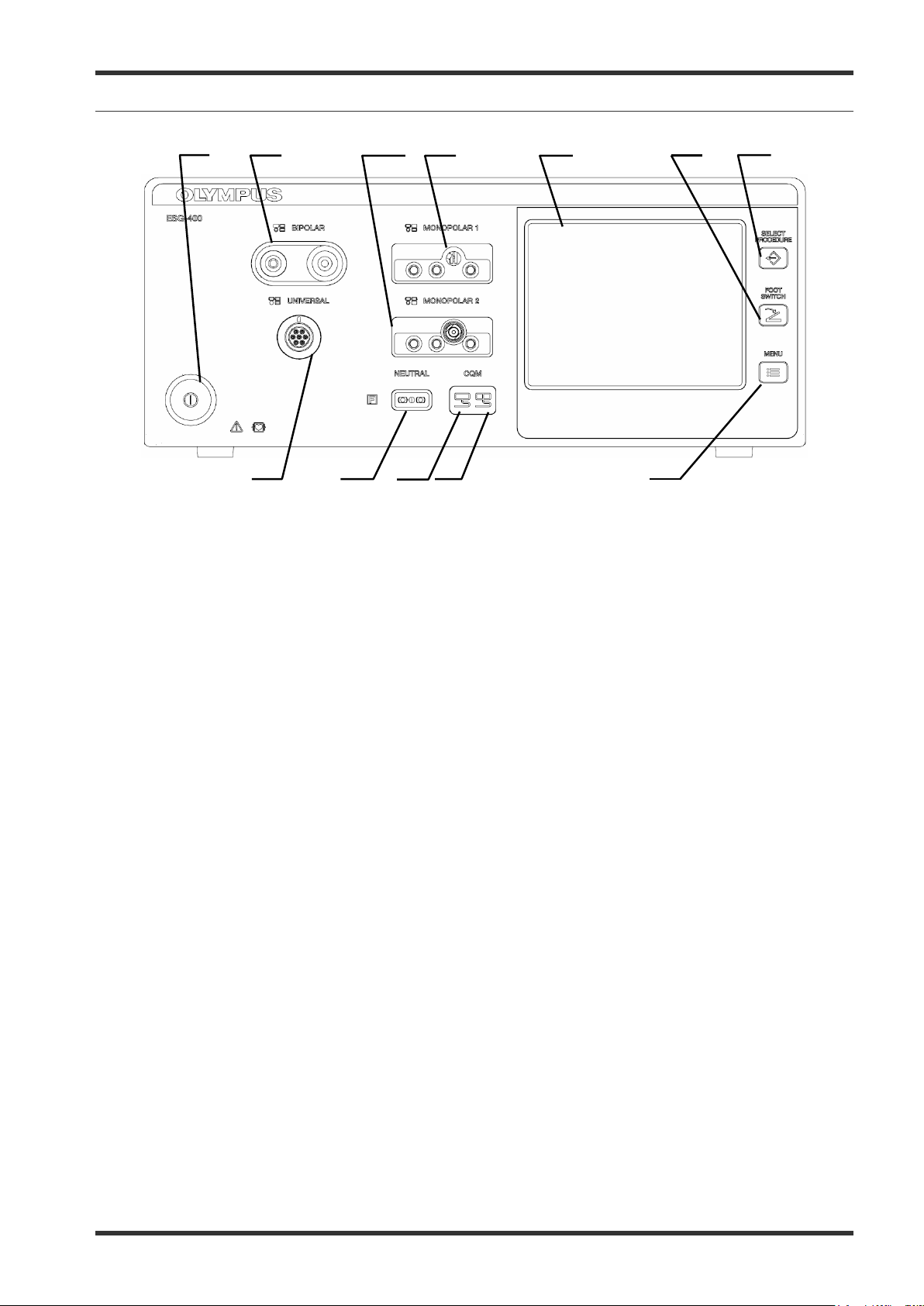
5-2 Front panel
1.
Power switch
This switch turns the electrosurgical generator on and off.
2.
BIPOLAR socket
This socket connects the plug of a bipolar HF instrument.
3.
MONOPOLAR 2 socket
This socket connects the plug of a monopolar HF instrument.
4.
MONOPOLAR 1 socket
This socket connects the plug of a monopolar HF instrument.
5.
Touch-screen
Displays the connection status of the accessories and peripherals connected to the electrosurgical
generator. It is also used to show and modify the output settings (e.g. mode, output power, effect) as
well as to control other functions (e.g. save procedures, delete procedures).
6.
FOOTSWITCH push button
This button is used to open the “Footswitch screen” to assign one or two footswitch(es) or the autostart
function to a specific output socket.
7.
SELECT PROCEDURE push button
This button is used to open the “Select Procedure screen” to recall saved settings.
8.
MENU push button
This button is used to open the “Menu screen” to control several functions (save or delete a procedure,
control the touch tone, output volume and brightness as well as other functions).
8.
6.
1.
2.
3.
4.
7.
12.
11.
10.
9.
5.
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 22 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 23

ESG-400
9.
Contact quality monitor indicator for split neutral electrode
This indicator illuminates green if a split neutral electrode is connected and the contact resistance is
within an acceptable range. The indicator illuminates red if the split neutral electrode is not connected
or not applied properly (e.g. bad contact quality or partly dislocated) or no neutral electrode is
connected (in both cases the activation of monopolar output is disabled).
10.
Contact quality monitor indicator for non-split neutral electrode
This indicator illuminates green if a non-split neutral electrode is connected.
11.
Neutral electrode socket
This socket connects the plug of a neutral electrode for monopolar application.
12.
UNIVERSAL socket
This socket connects the plug of an Olympus HF instrument with HF instrument recognition.
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 23 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 24

5-3 Rear panel
1.
Footswitch sockets
This socket connects the plug of a single or double pedal footswitch.
2.
Volume control
This knob is used for adjusting the output volume.
3.
Ventilation hole
Holes for air ventilation via a cooling fan; there are also ventilation holes on each side of the
electrosurgical generator.
4.
Equipotential bonding point
To increase electrical safety, this point is used for potential equalization. All equipment housings that
come into contact with the patient are electrically connected in order to prevent low-frequency
electrical currents from endangering the patient in the event of a defect in the conventional protective
conductor system.
5.
AC power socket
This socket serves as a connection to the mains power supply via a power cord
6.
LINK-OUT socket
This socket connects the plug (14-pin) of a cable connected to peripheral equipment.
7.
LINK-IN socket
This socket connects the plug (26-pin) of a cable connected to peripheral equipment.
NOTE
language setting of the electrosurgical generator.
For a detailed explanation of the different types of
sockets, refer to chapter 6 “Connection of neutral
electrode” and chapter 3.7 “Connection of HF
instruments”.
1.
2.
3.
4.
7.
6.
5.
1.
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 24 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 25
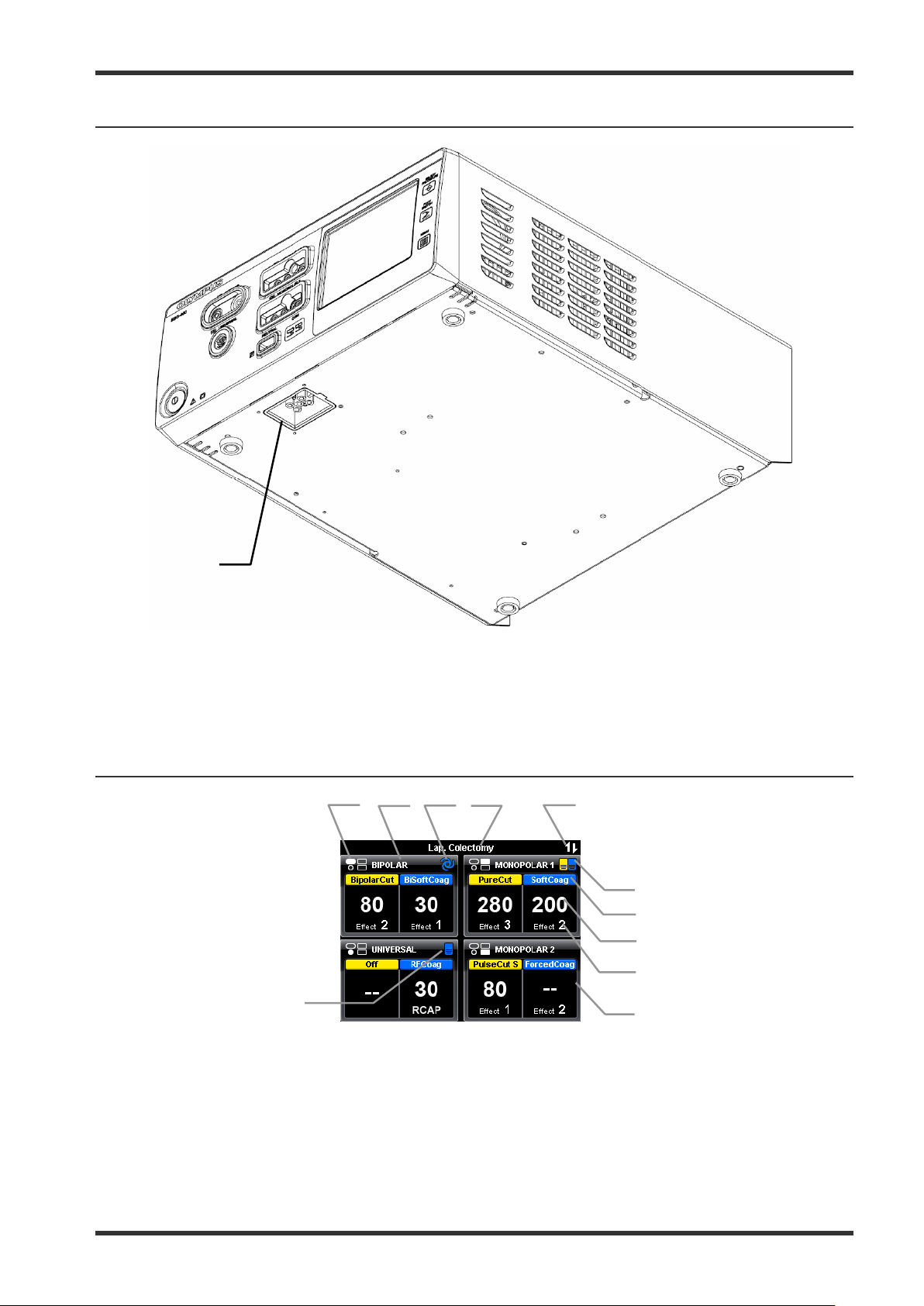
1.
Docking socket
This socket connects the plug (7-pin) of a docking connector to connect peripheral equipment. For
more details, see chapter 1-6-1.
1.
Reference to output sockets indicator
This indicator shows the corresponding output socket where the same symbol is printed on the front
panel.
2.
Output socket name
The name of the corresponding output socket is displayed here.
3.
Autostart indicator
This symbol indicates if the autostart function is assigned to the corresponding output socket. Blank if
1.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
8.
6.
11.
7.
9.
10.
5-4 Bottom panel
ESG-400
5-5 All screen
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 25 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 26

ESG-400
autostart or footswitch is not assigned. Refer to chapter 6.4, “Assign footswitch and autostart function”.
4.
Procedure name
The name of the selected procedure is displayed here. Blank if no procedure is selected.
5.
Communication indicator
This symbol indicates if communication with peripheral equipment connected to the docking socket is
established.
6.
Footswitch indicator (double pedal)
This symbol indicates if a connected double pedal footswitch is assigned to the corresponding output
socket. Blank if autostart or footswitch is not assigned. Refer to chapter 6.4, “Assign footswitch and
autostart function”.
7.
Output mode
The name of the output mode as selected in the “Mode screen” is displayed here. If “Off” is selected,
“--“ will be displayed instead of power level and effect.
8.
Output power level
The number shows the output power level as selected in the “Set screen”. If an output power level is
set to zero, “--” will be displayed instead of numbers.
9.
Effect
The number shows the effect as selected in the “Set screen”. For RFCoag mode the RCAP function
can be selected instead of an effect (refer to chapter 5.3, “Output setting”).
10.
Button area
Each button covers the entire area including all output socket related information as described above
(3. to 10.). Press the button, to switch to the corresponding “Set screen” to select the mode, power
levels and effects for the corresponding output socket.
11.
Footswitch indicator (single pedal)
This symbol indicates if a connected single pedal footswitch is assigned to the corresponding output
socket. Blank if autostart or footswitch is not assigned. Refer to chapter 6.4, “Assign footswitch and
autostart function”.
1.
Mode button
The name of the output mode as selected in the “Mode screen” is displayed here. Press this button to
switch to the “Mode screen”. If “Off” is selected,
“--“ will be displayed instead of power level and effect.
2.
Plus button / Minus button
These buttons increase / decrease the output power level.
3.
Toggle button
This button switches to the next effect.
4.
Return button
Press this button to save the settings and to return to the “All screen.”
5.
Output power level
1.
5.
2.
2
6.
3.
4.
5-6 Set screen
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 26 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 27
The number shows the selected output power level. If an output power level is set to zero, “--” will be
displayed instead of numbers.
6.
Effect
The number shows the selected effect. For RFCoag mode the RCAP function can be selected instead
of an effect (refer to chapter 5.3, “Output setting”)
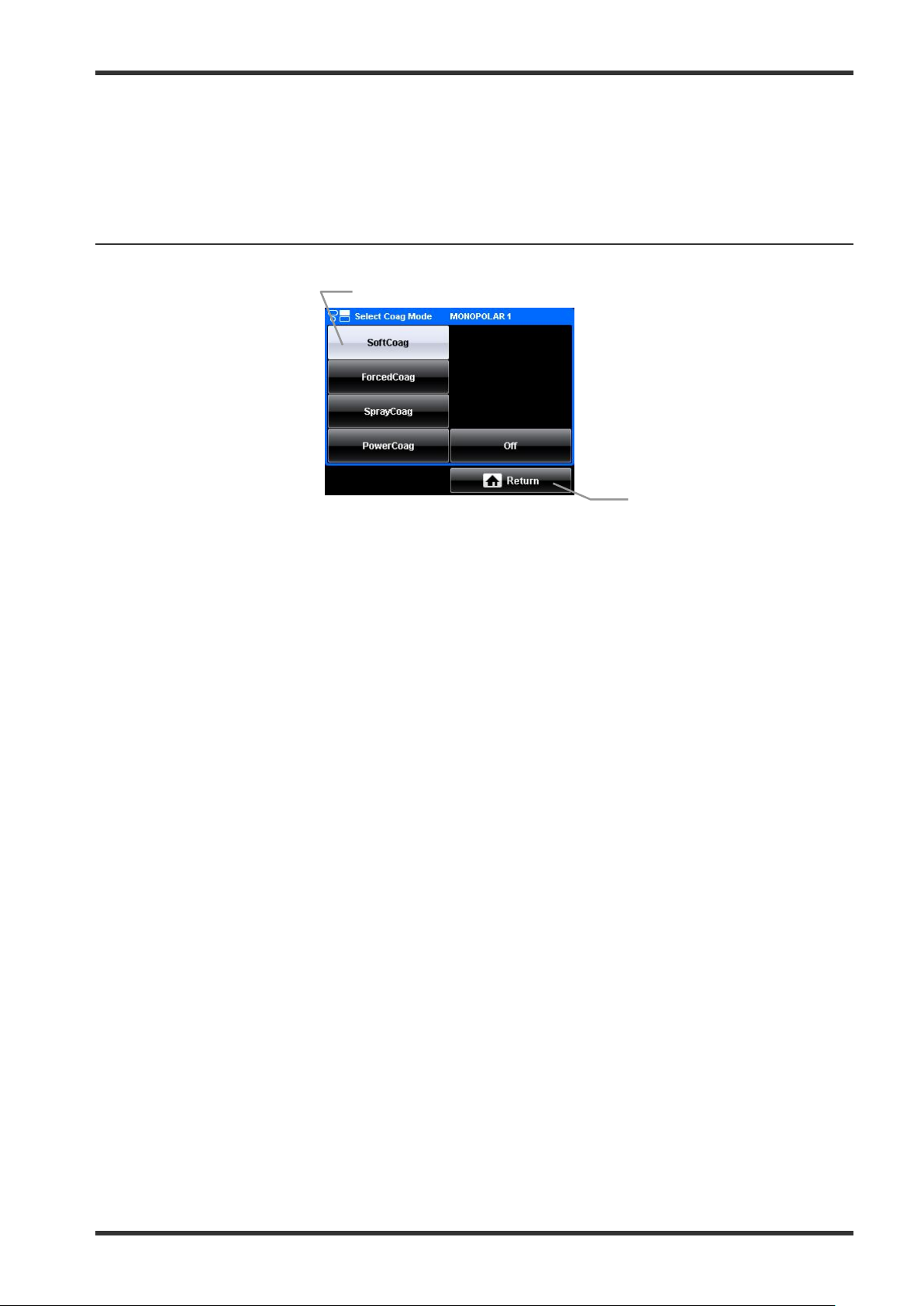
1.
Mode button
These buttons allow the mode selection for a corresponding output socket as shown in the title line. If
a selection is already activated, this is indicated by a gray button. If no mode shall be selected, press
the “Off button.”
2.
Return button
Press this button to return to the “Set screen.”
1.
2.
5-7 Mode screen
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 27 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 28

1.
Cut pedal (yellow color)
This pedal is used to activate the selected cutting mode.
2.
Coagulation pedal (blue color)
This pedal is used to activate the selected coagulation mode.
3.
Footswitch plug
Connects the footswitch with the electrosurgical generator on the rear panel.
1.
Coagulation pedal (blue color)
This pedal is used to activate the selected coagulation mode.
2.
Footswitch plug
Connects the footswitch with the electrosurgical generator on the rear panel.
1.
2.
3.
1.
2.
5-8 Footswitch with two pedals
The footswitch with two pedals (Olympus REF: WB50402W) is included in delivery.
ESG-400
5-9 Footswitch with one pedal (optional)
The footswitch with one pedal (Olympus REF: WB50403W) is an optional item which may be purchased
separately.
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 28 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 29
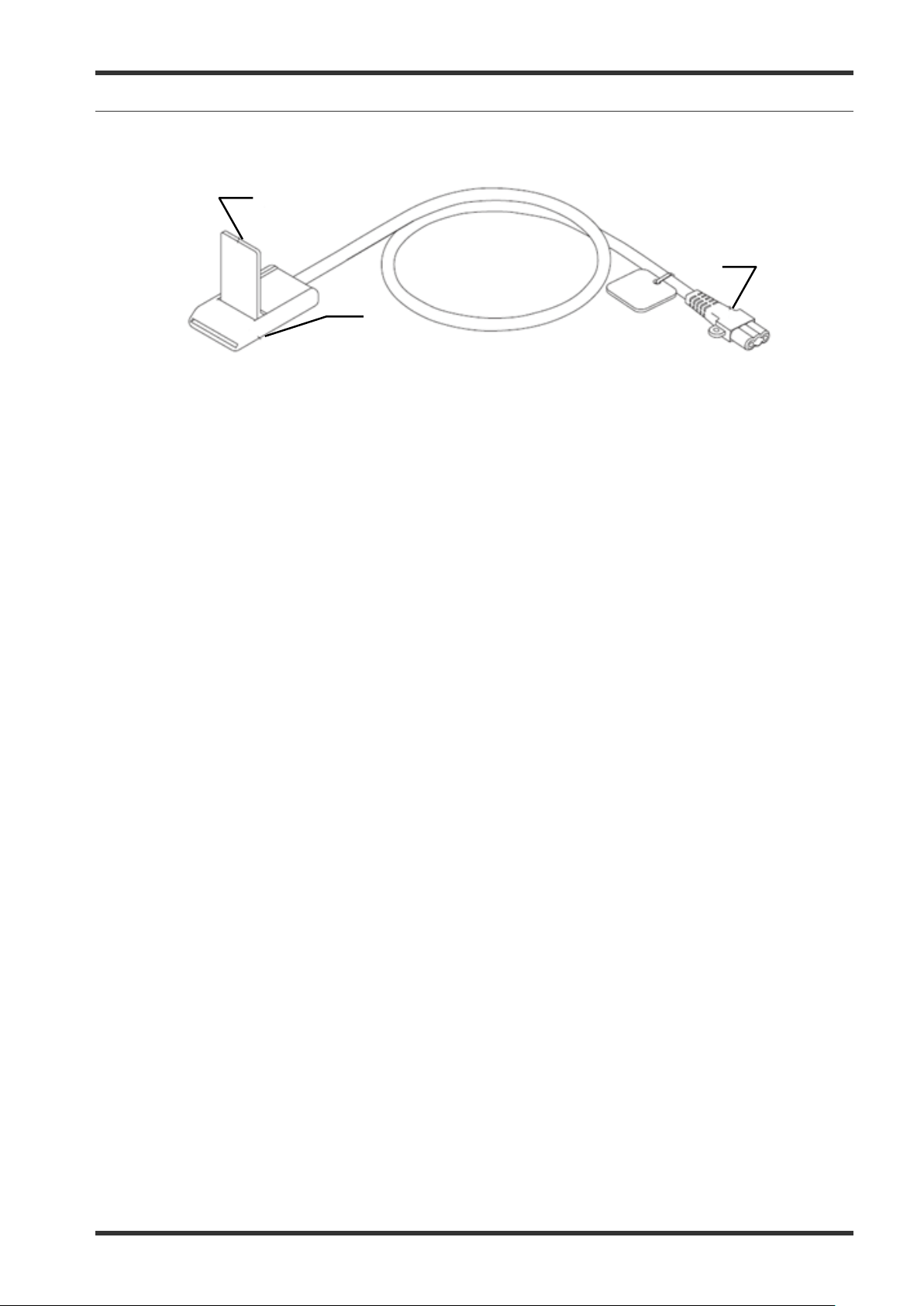
5-10 Neutral electrode cable “P-cord” (optional)
1.
Lever-locking arm
This arm secures the connector of the neutral electrode with the clamp.
2.
Clamp
This clamp connects the neutral electrode to the “P-cord”.
3.
Plug on the electrosurgical generator side
This plug connects the “P-cord” to the electrosurgical generator.
1.
2.
3.
The neutral electrode cable “P-cord” (Olympus REF: MAJ-814) is an optional item for the connection with a
neutral electrode which may be purchased separately.
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 29 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 30
Pinning of connector 13 Docking
Connector - view of connector side
(bottom view) of ESG-400
1
2 4 3
1 Hand Cut
2 Hand Coag
3 Active electrode
4 Active electrode
1 Hand Cut
2 Hand Coag
3 Active electrode
4 Cut+Coag+Active electrode (top)
1 2 3
4
6 Connector
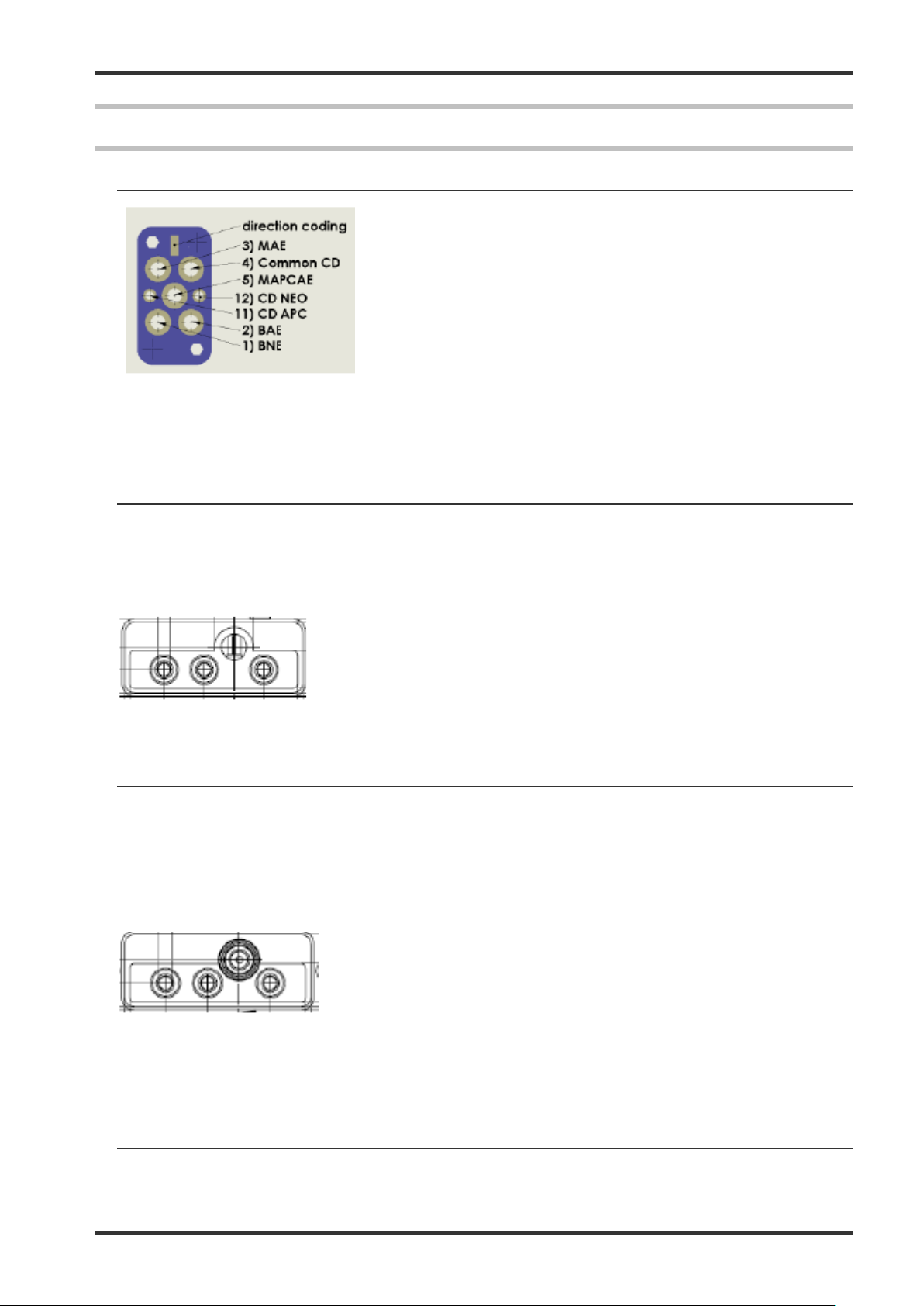
6-1 Docking Connector
1) BNE – Bipolar Neutral Electrode
2) BAE – Bipolar Active Electrode
3) MAE – Monopolar Active Electrode
4) Common CD – Common ground for connection detection
5) MAPCAE – Monopolar Active Electrode
11) CD APC – Active pin for connection detection
12) CD NEO – Active pin for connection detection
6-2 Monopolar Standard 1
Type: 3 pin Valleylab, pin diameter = 4mm
1 pin BOVIE, pin diameter = 8 mm
Function: Monopolar output
Finger switch input (only for Valleylab: cut and coag)
ESG-400
6-3 Monoploar Standard 2 (Erbe)
Type: 3 pin Valleylab, pin diameter = 4mm
Coaxial ERBE, pin diameter = 5 mm (inner) and 9 mm (outer)
Function: Monopolar output
Finger switch input (cut and coag)
6-4 Bipolar Standard 3
Type: 2 pin socket, pin diameter = 4mm / pin distance 28.8 mm
Coaxial socket, pin diameter = 4 mm (inner) and 8 mm (outer)
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 30 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 31

Function: Bipolar output
1 Neutral electrode
2 Active and neutral electrode
1
2
Pin 3
Pin 2
Pin 4
Pin 5
Pin 6
Pin 1
B (COAG)
A (CUT)
(coding)
Pin 7 - NC
(coding)
Com
ESG-400
6-5 Monopolar Neutral Electrode
Type: 2 pins socket, Pin diameter = 2.5 mm, Pin distance = 10 mm
Function: Monopolar output
CQM input
Principle sketch of connector 5 Neutral Electrode
6-6 Foot switch 1 (SIP/SOP)
Type: Foot switch, 7-pol.
Pinning of foot switch connector
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 31 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 32

6-7 Foot switch 2 (SIP/SOP)
Left Pedal
Right Pedal
L
Com
L/R
R
M
Type: Foot switch, 7-pol.
ESG-400
Activation detection of foot switch
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 32 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 33

ESG-400
WARNING
7 System Diagram
The recommended combinations of ancillary equipment and accessories that can be used with the
electrosurgical generator are listed in the system chart below. In addition, new products released after the
introduction of this product may also become compatible with this electrosurgical generator. For further details,
contact Olympus.
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 33 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 34

8 Cleaning, storage and disposal
WARNING
After cleaning the electrosurgical unit, dry it thoroughly before storage or using
it again. If it is used while still wet, there is a risk of electric shock.
Patient debris and reprocessing chemicals are hazardous. During cleaning
and disinfection, always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such
as eye wear, face mask, moisture-resistant clothing and chemical-resistant
waterproof gloves that fit properly so that your skin is not exposed. Always
remove contaminated protective clothing before leaving the reprocessing area.
CAUTION
When disconnecting plugs of instruments or power cords, always hold the
plug. Pulling the cable may result in damaging of the wires.
Never immerse the electrosurgical unit in water, clean or disinfect by
immersion, gas sterilization or autoclaving. It may cause equipment damage.
Do not clean the connectors or the alternating current power inlet. Cleaning
them can deform or corrode the contacts, which could damage the
electrosurgical unit.
Do not wipe the external surface with hard or abrasive wiping material. The
surface will be scratched.
The electrosurgical unit may be contaminated with infections materials, therefore, before servicing, perform the
following cleaning procedures. For maintenance and storage of other items than those described below, refer to
the respective instructions for use.
8-1 Cleaning
All surfaces of the unit’s housing can be cleaned and disinfected with the cleaning agents and surface
disinfectants normally used for medical equipment (mild cleaning solution, e.g. 70 % isopropyl alcohol). No
liquid must enter the connector or the unit during cleaning.
1) Switch off the electrosurgical unit and disconnect the power cord from the grounded wall outlet.
2) If the equipment and / or accessories are contaminated with blood or other potentially infectious materials,
first wipe off all gross debris using neutral detergent, and then wipe its surface with a lint-free cloth
moistened with a surface disinfectant.
3) To remove dust, dirt and non-patient debris, wipe the electrosurgical unit and footswitch using a soft,
lint-free cloth moistened with 70 % ethyl or isopropyl alcohol.
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 34 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 35

8-2 Storage
CAUTION
Do not store the electrosurgical unit in a location exposed to direct sunlight,
x-rays, radioactivity, liquids or strong electromagnetic radiation (e.g. near
microwave medical treatment equipment, short-wave medical treatment
equipment, magnetic resonance imaging equipment, radio or mobile phones).
Damage to the electrosurgical unit may result.
Before storage of the electrosurgical unit, disconnect the power cord and store it properly according to the
environmental conditions described in chapter 1.4 (Technical data).
8-3 Disposal of the unit
When disposing of this electrosurgical unit, or any of its components (such as fuses), follow all applicable
national and local laws and guidelines.
Waste electrical and electronic equipment
In accordance with European Directive 2002/96/EC on waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE), the
product must not be disposed of as unsorted municipal waste, but should be collected separately.
ESG-400
Refer to Olympus for return and / or collection systems available in your country.
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 35 / 99 Chapter 1: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONs
Page 36

ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 36 / 99 Chapter 2: Block Description
Page 37

ESG-400
CHAPTER 2: BLOCK DESCRIPTION
1 BLOCK DESCRIPTIONS .............................................................................................. 38
1-1 Motherboard ..................................................................................................................................... 39
1-2 HVPS Board ..................................................................................................................................... 41
1-3 Generator board ............................................................................................................................... 41
1-4 Relay Board ..................................................................................................................................... 41
1-5 Front Panel ....................................................................................................................................... 42
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 37 / 99 Chapter 2: Block Description
Page 38

ESG-400
Fig. 2.1.1. Block descriptions
1 Block Descriptions
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 38 / 99 Chapter 2: Block Description
Page 39

1-1 Motherboard
Due to the containing embedded PC the Motherboard is the central unit of the ESG-400. The Motherboard
controls the Relay Board, the HVPS Board and the Generator Board. It contains all input and output interfaces
to the user as well as to other medical devices or computers. Additionally functionalities off the board are the
low voltage supplies for the complete unit, the mains input including filters and the measuring part of the
voltage line selection circuit for switching between 115 and 230 VAC.
Overview:
Embedded PC incl. periphery
Embedded PC with MPC5200 controller (incl. address and data bus, chip selects,
interrupt inputs, I2C, SPI, in-/output ports, uarts, timer)
Watchdog circuit
Chip select decoder
Hardware reset
JTAG interface
Real time clock
ESG-400
POF interface for the spark monitor
Digital input and output circuits
D/A converters for controlling the HVPS
A/D converters for measuring different signals from Relay, HVPS and Generator, temperatures and
watching on important voltages
Connections/Interfaces:
To the PCBs Relay, HVPS and Generator
Push buttons for user inputs on the front panel
Volumeboard for changing the speaker volume
Power Indicator shows power-on of the unit on the front
CQM Indicator shows status of CQM on the front
Controlling and driving the main housing fan
Audio circuit incl. D/A converter and amplifier for sound
Graphic controller with driver and backlight for the front display
Touch controller for the touch display
Ethernet controller and connector for external connections
RS-232 with connector for external connections
USB host with transceiver and connector for external connections
FlexRay controller, transceiver and connector for external connections
Connectors for footswitch incl. detection and analysis circuit
Connectors for handswitches incl. activation detection circuits
Instrument recognition circuit for instruments connected to the universal socket
Detection circuit for devices connected to the docking connector
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 39 / 99 Chapter 2: Block Description
Page 40

ESG-400
Low voltage supplies
Switching regulators for -12 VDC, +5 VDC and +3,3 VDC (5 V and 3,3 V cascaded)
DC/DC converters for isolated +12 VDC and +5 VDC SIP/SOP voltages
Batteries for a permanent +3 V voltage for RTC and SRAM
Reference voltage of 8,192 V
Mains input
Input filters
Inrush current limiter
Mains voltage measurement and output signal for a selection circuit on the HVPS
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 40 / 99 Chapter 2: Block Description
Page 41

1-2 HVPS Board
The high voltage power supply (HVPS) is a switching mode power supply with series resonance circuit. It
provides a high DC voltage for the HF Generator. It contains:
voltage line selection circuit, for automatic change between 110/230 VAC
simple rectifier circuit
PWM driving circuit
driving circuits including a digital flip-flop stage for complete cycle driving
power FET half-bridge, a series resonance circuit, output transformer and rectifying stage
current and voltage monitors
discharge circuit
1-3 Generator board
The Generator Board generates the HF output energy from a DC input voltage and contains:
control circuit for generating start and driving pulses of “one cycle” sinus oscillator
ESG-400
driving stage for power FET, parallel resonance circuit and series resonance circuit
relays for switching between different transformer windings
HF output voltage monitor and redundant HF voltage monitor
HF output current monitor and redundant HF current monitor
HF output phase monitor
HF leakage current monitor
spark monitor (SPM) supply circuit
spark monitor for detecting positive and negative DC voltage offset
1-4 Relay Board
The Relay board is used to connect the active output socket to the generator board. It contains:
connectors to every single HF output socket
relays which are separating the non active output terminals from the active output terminals
separating relays are forced guided relays with read-back contact in secondary circuit to control the relay
status
contact quality monitor (CQM)
transient voltage suppression (TVS) diodes in applied part
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 41 / 99 Chapter 2: Block Description
Page 42

1-5 Front Panel
The Front Panel is the main part of the user interface. It contains:
LCD touch screen
Push Buttons
Contact Quality Monitor
BIPOLAR socket
MONOPOLAR 1 socket Valleylab & Bovie
MONOPOLAR 2 socket Valleylab & Erbe
UNIVERSAL socket
Socket for neutral electrode
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 42 / 99 Chapter 2: Block Description
Page 43

ESG-400
CHAPTER 3: REPAIR SYSTEM
1 ESG-400 MAIN UNIT .................................................................................................... 44
2 BOARD COMPATIBILITY ............................................................................................. 44
3 OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES ......................................................................................... 44
3-1 WB50402W (Footswitch with two pedals) ....................................................................................... 44
3-2 WB50403W (Footswitch with one pedal) ......................................................................................... 44
3-3 MAJ-814 (Neutral electrode cable “P-cord”) .................................................................................... 44
4 PRECAUTIONS ON FUNCTION AND OPERATION SETTINGS ................................. 44
4-1 General Precautions ........................................................................................................................ 44
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 43 / 99 Chapter 3: Repair System
Page 44

1 ESG-400 Main Unit
(1) In general, the main unit must be shipped to a service center in the event of a malfunction.
(2) Individual units can be replaced.
2 Board Compatibility
The compatibility of boards and components is dependent on the hardware version of the generator. The
hardware version can be indentified by the serial number of the generator.
The serial number starting with 5 numbers, hardware version with WXX and followed by 3 numbers after the
hyphen.
Example: XXXXXWYY-ZZZ, WYY will show the hardware version.
3 Optional Accessories
3-1 WB50402W (Footswitch with two pedals)
Supplied as a spare part subject to repair services in the event of a malfunction.
3-2 WB50403W (Footswitch with one pedal)
Supplied as a spare part subject to repair services in the event of a malfunction.
3-3 MAJ-814 (Neutral electrode cable “P-cord”)
Supplied as a spare part subject to repair services in the event of a malfunction.
ESG-400
4 Precautions on Function and Operation Settings
4-1 General Precautions
Before repair, it is generally advisable to record the function and operation settings as the basis for restoring
these settings after service.
If the original settings cannot be known due to mechanical problems present at the time the unit was accepted
for repair, apply the factory-set values or the safest settings (such as the lowest output levels). In this case,
inform the user that the settings have been changed.
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 44 / 99 Chapter 3: Repair System
Page 45

ESG-400
CHAPTER 4: TROUBLESHOOTING
1 GENERAL ..................................................................................................................... 46
2 NEUTRAL ELECTRODE OPERATION ........................................................................ 47
3 ERROR SCREEN, CODES AND MEASURES ............................................................. 48
3-1 What to do when no error code is displayed .................................................................................... 50
3-2 What to do when an error code is displayed .................................................................................... 54
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 45 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 46

ESG-400
DANGER
Never use the electrosurgical unit if an abnormality is suspected.
CAUTION
Repairs must only be carried out by Olympus or a firm authorized by Olympus.
CAUTION
Preventive maintenance (inspection / periodic safety check) must only be
carried out by a qualified person / technician.
1 General
If the electrosurgical unit has visible damage, do not use the electrosurgical unit and contact the legal
manufacturer. If the unit is not functioning properly, use the information in this chapter to identify and correct the
malfunction. If the problem cannot be resolved by the described remedial action, stop using the electrosurgical
unit and contact the legal manufacturer for repair.
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 46 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 47

Contact quality monitor
Mode
Indication
Bipolar application
Standby and activation
A neutral electrode is not required. Contact
quality monitor indicator for split neutral
electrode illuminates red.
Monopolar application
A non-split neutral electrode is
connected. Activation is possible.
Contact quality monitor detects
connection of neutral electrode.
If a split neutral electrode is
connected, it has a short circuit.
Immediately replace the neutral
electrode!
Contact quality monitor indicator for non-split
neutral electrode illuminates green.
A split neutral electrode is connected.
Activation is possible. Contact quality
monitor detects connection of neutral
electrode and contact to patients’ skin.
Contact quality monitor indicator for split
neutral electrode illuminates green.
During standby: A split or a non-split
neutral electrode is not connected or a
split neutral electrode detaches.
Activation is disabled.
During activation: A split or a non-split
neutral electrode has disconnected or a
split neutral electrode detaches. The
activation is stopped.
Contact quality monitor indicator for split
neutral electrode illuminates red.
During activation an alarm signal can be
heard and the touch-screen will display an
error window (E202).
2 Neutral electrode operation
Check the following table, to identify or correct failures regarding the neutral electrode operation.
ESG-400
Legend: Red illumination of the indicator
Green illumination of the indicator
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 47 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 48

ESG-400
Error category
Error condition priority
Indicator (“caution”)
symbol condition
High priority
Immediate user response
is required
Flashes in red color
Medium priority
Prompt user response
is required
Flashes in yellow color
Low priority
Awareness of the user
is required
Constant on in yellow color
Error code
Remedial actions
Caution symbol
Error title
Error window
(Example: E002 Short circuit)
Fig. 4.3.1. Error Screen
3 Error screen, codes and measures
Follow the troubleshooting advices in this chapter, to identify or correct failures. The error window is configured
as shown in figure below.
If an error occurs (see Fig. 4.3.1):
An error window will appear and an alarm signal is audible.
A short message with the error code, error title and a description of the remedial action will be displayed.
The error code consists of an error number shown under the “caution” symbol.
Depending on the error priority, the condition of the audible signal and the “caution” symbol are different
(see Table 4.1).
Proceed with the described remedial action.
The error window disappears after a few seconds, if the error is cleared.
If the error window is still displayed, the error is not cleared. Proceed with the next remedial action if
available.
Table 4.1: Error priorities and the corresponding indicator symbol condition
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 48 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 49

ESG-400
NOTE
The electrosurgical generator is equipped with an
intelligent alarm system which determines alarm
conditions on the base of multiple variables. Depending
on the risk potential, alarms are classified in “high
priority”, “medium priority” and “low priority” alarms. An
alarm of higher priority overrides an existing alarm of
lower priority. If more than one alarm situation of equal
priority is determined, the one that occurred first is
displayed only. This electrosurgical generator complies
with the IEC 60601-1-8: 2006.
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 49 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 50

3-1 What to do when no error code is displayed
Situation
Possible cause
Remedial action
The electrosurgical
generator does not
respond after
pressing the power
switch.
Improper connection of the power cord to
the AC power socket on the rear panel of
the electrosurgical generator or to the
grounded wall outlet.
Check the power cord and the grounded wall
outlet for correct connection.
The grounded wall outlet has wrong or
not output voltage.
Check the grounded wall outlet or use an
alternative grounded wall outlet.
The power cord is damaged.
Check the power cord for damages and, if
necessary, replace the power cord.
Malfunction of the electrosurgical
generator.
Contact the legal manufacturer.
The touch-screen
remains dark after
switching the
electrosurgical
generator on (sound
is audible after
switching on).
Malfunction of the touch-screen.
Contact the legal manufacturer.
The touch-screen
cannot be controlled.
An object is in contact with the
touch-screen.
Remove the object.
The touch-screen is not properly
calibrated.
Contact the legal manufacturer.
Malfunction of the touch-screen.
Stop using the electrosurgical generator and
press the power switch to turn off the
electrosurgical generator. Contact the legal
manufacturer.
The electrosurgical
generator does not
react when a push
button on the front
panel is pressed
during standby.
A push button is already pressed.
Release the push button.
Malfunction of the electrosurgical
generator.
Contact the legal manufacturer.
The electrosurgical
generator does not
react when a (push)
button on the front
panel is pressed
during activation.
The (push) buttons are not available
during activation.
Release the footswitch or hand switch to stop
the activation.
Perform the indicated remedial actions below. If the problem cannot be resolved by the described remedial
action, contact the legal manufacturer.
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 50 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 51

ESG-400
Situation
Possible cause
Remedial action
No sound is audible
during activation.
The volume is set to an inaudible level
(e.g. due to high environmental noise).
Increase the volume either on the touch-screen
within the “Menu screen” or use the volume
control on the rear panel of the electrosurgical
generator.
Malfunction of the electrosurgical
generator.
Stop using the electrosurgical generator and
press the power switch to turn off the
electrosurgical generator. Contact the legal
manufacturer.
The volume can not
be adjusted via the
volume control within
the “Menu screen” or
at the rear panel.
The volume of the error-related audible
signal is not adjustable.
No action required.
Malfunction of the electrosurgical
generator.
Contact the legal manufacturer.
The electrosurgical
generator does not
respond to footswitch
or handswitch
activation.
Improper connection of the footswitch to
one of the footswitch sockets on the rear
panel of the electrosurgical generator or
the HF instrument to the output socket.
Check the footswitch and the HF instrument for
correct connection.
The footswitch or the handswitch of the
HF instrument and / or the connection
cable are damaged.
Check the footswitch or the handswitch of the
HF instrument and / or the connection cable for
damages and, if necessary, replace the
footswitch, the HF instrument or the connection
cable.
The incorrect footswitch pedal or
handswitch button is pressed.
Press the correct footswitch pedal or
handswitch button of the HF instrument.
The electrosurgical generator is not
switched on.
Switch on the electrosurgical generator with the
power switch.
Another footswitch pedal or handswitch
button of the HF instrument is pressed.
To activate the intended output, release the
current pressed footswitch pedal or handswitch
button of the HF instrument.
The output is activated by the peripheral
equipment.
If the output of the peripheral equipment is
activated, the output of the electrosurgical
generator cannot be activated simultaneously.
Stop using the peripheral equipment.
A window is displayed on the
touch-screen.
Press the “OK button” or “Cancel button” to
close the window or wait until the window
disappears automatically after a few seconds.
The “All screen” or “Set screen is not
displayed on the touch-screen.
Return to the “All screen” or “Set screen”.
The corresponding output mode has
been deactivated in the “Mode screen”
(“Off” is displayed) or the power level has
been set to “--“.
Select an output mode in the “Mode screen” or
increase the power level via the “Set screen”
(refer to chapter 5.3, “Output setting”).
Malfunction of the electrosurgical
generator.
Contact the legal manufacturer.
If the autostart
function is selected,
the electrosurgical
The autostart function is assigned to
another output socket.
Check the correct assignment of the autostart
function (refer to chapter 6.4, “Assign footswitch
and autostart function”).
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 51 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 52

ESG-400
Situation
Possible cause
Remedial action
generator does not
activate the output
when the electrode
has contact with the
tissue.
Long time delay of the autostart function
has been selected in the “Autostart
screen”.
Set a shorter time delay in the “Autostart
screen” (refer to chapter 6.5, “Menu - Autostart
setup”).
Malfunction of the electrosurgical
generator.
Contact the legal manufacturer.
If an HF instrument is
connected to the
UNIVERSAL socket,
the electrosurgical
generator does not
recognize the
connected HF
instrument.
Improper connection of the Olympus HF
instrument plug with the UNIVERSAL
socket on the front panel of the
electrosurgical generator.
Check the Olympus HF instrument plug for
correct connection.
The HF instrument does not support
Olympus HF instrument recognition.
Confirm the use of an Olympus HF instrument
with HF instrument recognition capabilities.
The Olympus HF instrument and / or the
connection cable is damaged.
Replace the Olympus HF instrument and / or
the connection cable.
Malfunction of the electrosurgical
generator.
Contact the legal manufacturer.
Footswitch or
handswitch of the HF
instrument is pressed
and activation sound
is audible but no
output power is
delivered.
The footswitch is assigned to another
output socket.
Check the correct assignment of the footswitch
(refer to chapter 6.4, “Assign footswitch and
autostart function”).
Improper connection of the HF
instrument plug with the output socket on
the front panel of the electrosurgical
generator.
Check the HF instrument plug for correct
connection.
Malfunction of the electrosurgical
generator.
Contact the legal manufacturer.
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 52 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 53

ESG-400
Situation
Possible cause
Remedial action
No output power is
delivered when
RFCoag mode with or
without RCAP is
selected and end of
activation signal is
audible.
The electrode has no contact with the
tissue.
Check that the electrode has contact with the
tissue.
Improper connection of the HF
instrument plug with the output socket on
the front panel of the electrosurgical
generator.
Check the HF instrument plug for correct
connection.
Damaged HF instrument connection
cable.
Replace the HF instrument connection cable.
Malfunction of the electrosurgical
generator.
Contact the legal manufacturer.
The output of the
electrosurgical
generator cannot be
deactivated.
The autostart function is selected to the
current used output socket and both
electrodes touch the tissue.
Remove the electrode from the tissue.
Malfunction of the footswitch or
handswitch.
Immediately switch off the electrosurgical
generator by pressing the power switch.
Replace the footswitch or HF instrument with
handswitch.
Malfunction of the electrosurgical
generator.
Contact the legal manufacturer.
The electrosurgical
generator cannot be
switched off.
Malfunction of the electrosurgical
generator.
Disconnect the power cord plug from the AC
power socket on the rear panel of the
electrosurgical generator or from the grounded
wall outlet. Contact the legal manufacturer.
Automatic mist &
smoke evacuation
system/function does
not work.
The settings are erroneous.
Correct the settings of the compatible high flow
insufflation unit.
The communication cable is not
connected.
Connect the communication cable. Refer to 3.5,
“Automatic mist & smoke evacuation
system/function (when using the compatible
high flow insufflation unit)”.
The connection of the communication
cable is erroneous.
Reconnect the communication cable. Refer to
Section 3.5, “Automatic mist & smoke
evacuation system/function (when using the
compatible high flow insufflation unit)”.
Compatible high flow insufflation unit
malfunction.
Contact Olympus.
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 53 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 54

3-2 What to do when an error code is displayed
Error
no.
Error message
Possible cause
Remedial action
E001
Open circuit
Electrodes of the HF
instrument may have no
proper tissue contact.
Ensure that the electrodes of the HF
instrument have proper tissue contact.
Malfunction of the HF
instrument and / or the
connection cable.
Replace the HF instrument and / or the
connection cable.
E002
Short circuit
Electrodes of the HF
instrument may touch each
other.
Ensure that the electrodes of the HF
instrument do not touch each other.
Malfunction of the HF
instrument and / or the
connection cable.
Replace the HF instrument and / or the
connection cable.
E003
---
DockingConnectorError
---
E004
Error
Internal software error.
Send back to Olympus Service
E006
Non-conductive fluid
Use of non-conductive fluid
during a bipolar cutting
procedure.
The active and / or neutral
electrode is within an air
environment.
Ensure that conductive fluid is used
during bipolar resection procedure.
Always immerse the active and / or
neutral electrode within the conductive
fluid.
The bipolar Olympus HF
instrument has not been
properly connected to the
UNIVERSAL socket or
damaged connection cable.
Check the connection of the bipolar
Olympus HF instrument to the
connection cable and the connection of
the connection cable to the UNIVERSAL
socket and / or replace the connection
cable.
The electrode might be
contaminated and encrusted.
Check the electrodes for contamination
and encrustation before use and, if
necessary, clean the electrodes.
E007
[…]
E011
Error
Refer to E004
E012
Adjustment incomplete
Adjustment missing or
incomplete.
Complete the adjustment of the device.
E013
E014
E015
Error
Refer to E004
E016
Burn-in incomplete
Burn-in missing or incomplete.
Complete the burn-in of the device.
If an error code is displayed, perform the indicated remedial actions below. If the problem cannot be resolved by
the described remedial action, contact the legal manufacturer.
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 54 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 55

ESG-400
Error
no.
Error message
Possible cause
Remedial action
E017
Error
Wrong or broken Footswitch,
damaged hardware.
1. Check the Footswitch connection.
2. Change the Footswitch.
3. Send back to Olympus Service
E018
Error
Refer to E004
E019
Footswitch combination
Two single pedal or two double
pedal footswitches have been
connected.
Ensure that only one single pedal and/or
only one double pedal footswitch are
connected.
E020
E021
E022
Error
Internal hardware error.
Send back to Olympus Service
E023
Invalid serial number
Wrong or missing serial
number of the device.
Send back to factory.
E024
[…]
E030
Error
Refer to E004
E031
E032
Error
Wrong docking connector
coding signal, broken
hardware.
1. Check the docking connection to the
USG-400.
2. Send back to Olympus Service
E033
E034
Error
Refer to E020
E035
E036
E037
Error
Refer to E004
E038
Error
Internal hardware error.
Send back to Olympus Service
E039
[…]
E043
Error
Refer to E004
E045
[…]
E057
Error
Communication error with
USG-400 or other devices.
1. Check the FlexRay connections.
2. Check if all other devices are working
properly.
3. Send back to Olympus Service
E058
E059
E060
Error
Internal software or hardware
error.
Send back to Olympus Service
E061
[…]
E066
Error
Refer to E004
E067
[…]
E081
Error
Refer to E045
E082
E083
E084
Error
Refer to E004
E085
[…]
E099
Error
Internal hardware error.
Send back to Olympus Service
E100
E101
Error
Spark Monitor communication
Send back to Olympus Service
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 55 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 56

ESG-400
Error
no.
Error message
Possible cause
Remedial action
error.
E102
Error
Refer to E085
E103
Push button pressed
A push button on the Front
Panel is pressed while
switching on.
Release the push button.
E104
Footswitch pedal pressed
A pressed Cut Pedal on
Footswitch 1 has been
detected during power-up.
Release the Cut Pedal on Footswitch 1
and restart the device.
Malfunction of the footswitch.
Change the Footswitch 1.
E105
Footswitch pedal pressed
A pressed Coag Pedal on
Footswitch 1 has been
detected during power-up.
Release the Coag Pedal on Footswitch 1
and restart the device.
Malfunction of the footswitch.
Change the Footswitch 1.
E106
Footswitch pedal pressed
A pressed Cut Pedal on
Footswitch 2 has been
detected during power-up.
Release the Cut Pedal on Footswitch 2
and restart the device.
Malfunction of the footswitch.
Change the Footswitch 2.
E107
Footswitch pedal pressed
A pressed Coag Pedal on
Footswitch 2 has been
detected during power-up.
Release the Coag Pedal on Footswitch 2
and restart the device.
Malfunction of the footswitch.
Change the Footswitch 2.
E108
Handswitch pressed
A pressed Cut Handswitch at
the Monopolar 1 socket has
been detected during
power-up.
Release the Cut Handswitch at the
Monopolar 1 socket and restart the
device.
Malfunction of the HF
instrument.
Replace the HF instrument.
E109
Handswitch pressed
A pressed Coag Handswitch at
the Monopolar 1 socket has
been detected during
power-up.
Release the Coag Handswitch at the
Monopolar 1 socket and restart the
device.
Malfunction of the HF
instrument.
Replace the HF instrument.
E110
Handswitch pressed
A pressed Cut Handswitch at
the Monopolar 2 socket has
been detected during
power-up.
Release the Cut Handswitch at the
Monopolar 2 socket and restart the
device.
Malfunction of the HF
instrument.
Replace the HF instrument.
E111
Handswitch pressed
A pressed Coag Handswitch at
the Monopolar 2 socket has
been detected during
power-up.
Release the Coag Handswitch at the
Monopolar 2 socket and restart the
device.
Malfunction of the HF
instrument.
Replace the HF instrument.
E112
Handswitch pressed
A pressed Cut Handswitch at
Release the Cut Handswitch at the
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 56 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 57

ESG-400
Error
no.
Error message
Possible cause
Remedial action
the Multifunction socket has
been detected during
power-up.
Multifunction socket and restart the
device.
Malfunction of the HF
instrument.
Replace the HF instrument.
E113
Handswitch pressed
A pressed Coag Handswitch at
the Multifunction socket has
been detected during
power-up.
Release the Coag Handswitch at the
Multifunction socket and restart the
device.
Malfunction of the HF
instrument.
Replace the HF instrument.
E114
Touch-screen pressed
The screen is touched while
switching on.
Release the finger from the screen.
E115
Application time limit
exceeded
The maximum time limit for the
application has been
exceeded.
Release the footswitch or handswitch for
about 15 sec. and activate again by
repressing the footswitch or handswitch.
E116
[…]
E130
Error
Refer to E004
E131
Unknown instrument
An Olympus HF instrument
has not been properly
connected to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Check the connection of the Olympus
HF instrument to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Invalid default mode detected
at the instrument connected to
the Multifunction socket.
Change the Instrument at the
Multifunction socket
E132
Error
Internal hardware error.
Send back to Olympus Service
E133
Error
Internal hardware error.
Send back to Olympus Service
E134
Error
Internal hardware error.
Send back to Olympus Service
E135
Single pedal footswitch not
assigned
The single pedal footswitch
has not been assigned to the
corresponding output socket.
Assign the single pedal footswitch.
E136
Double pedal footswitch not
assigned
The double pedal footswitch
has not assigned to the
corresponding output socket.
Assign the double pedal footswitch.
E137
Error
The Auto Start feature is not
assigned correctly.
Reassign the Auto Start feature.
E138
Error
Invalid Thunder Beat mode
setting detected.
1. Check the Thunder Beat instrument
connected to the USG-400.
2. Check the USG-400.
E139
Error
Invalid Thunder Beat seal
mode setting detected.
1. Check the Thunder Beat instrument
connected to the USG-400.
2. Check the USG-400.
E140
No mode selected
No mode has been selected
while activating.
Select a mode via the “Mode screen”.
E141
Power set to zero (--)
The power level for the chosen
Increase the power level via the “Set
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 57 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 58

ESG-400
Error
no.
Error message
Possible cause
Remedial action
mode is set to zero.
screen”.
E142
[…]
E145
Error
Refer to E004
E147
Unknown instrument
An Olympus HF instrument
has not been properly
connected to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Check the connection of the Olympus
HF instrument to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
The instrument connected to
the Multifunction socket can
not be determined.
Change the connected instrument at the
Multifunction socket
E148
Unknown instrument
An Olympus HF instrument
has not been properly
connected to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Check the connection of the Olympus
HF instrument to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
A short circuit at the
Multifunction socket has been
detected.
Change the connected instrument at the
Multifunction socket
Send back to Olympus Service
E149
Unknown instrument
An Olympus HF instrument
has not been properly
connected to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Check the connection of the Olympus
HF instrument to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
A malfunction at the
Multifunction socket has been
detected.
Change the connected instrument at the
Multifunction socket
Send back to Olympus Service
E150
Error
Refer to E004
E151
Unknown instrument
An Olympus HF instrument
has not been properly
connected to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Check the connection of the Olympus
HF instrument to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Invalid power setting detected
at the instrument connected to
the Multifunction socket.
Change the Instrument at the
Multifunction socket
E152
Unknown instrument
An Olympus HF instrument
has not been properly
connected to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Check the connection of the Olympus
HF instrument to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Invalid effect setting detected
at the instrument connected to
the Multifunction socket.
Change the Instrument at the
Multifunction socket
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 58 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 59

ESG-400
Error
no.
Error message
Possible cause
Remedial action
E153
Unknown instrument
An Olympus HF instrument
has not been properly
connected to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Check the connection of the Olympus
HF instrument to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Invalid default Cut Mode
detected at the instrument
connected to the Multifunction
socket.
Change the Instrument at the
Multifunction socket
E154
Unknown instrument
An Olympus HF instrument
has not been properly
connected to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Check the connection of the Olympus
HF instrument to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Invalid default Coag Mode
detected at the instrument
connected to the Multifunction
socket.
Change the Instrument at the
Multifunction socket
E159
Unknown instrument
An Olympus HF instrument
has not been properly
connected to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Check the connection of the Olympus
HF instrument to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Invalid Mode detected at the
instrument connected to the
Multifunction socket.
Change the Instrument at the
Multifunction socket
E165
Error
Refer to E004
E166
Unknown instrument
An Olympus HF instrument
has not been properly
connected to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Check the connection of the Olympus
HF instrument to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Invalid Version Number
detected at the instrument
connected to the Multifunction
socket.
Change the Instrument at the
Multifunction socket
E167
Unknown instrument
An Olympus HF instrument
has not been properly
connected to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Check the connection of the Olympus
HF instrument to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Internal software error.
Send back to Olympus Service
E168
E169
E170
Error
Refer to E004
E171
[…]
E178
Error
Internal hardware error.
Send back to Olympus Service
E179
Temperature below limit
The generator (Generator
Board) is too cold.
Switch off the electrosurgical generator
and wait until it has reached the
specified operating temperature.
E180
Temperature above limit
The generator (Generator
Board) is too hot.
Switch off the electrosurgical generator
and wait until it has cooled down or
reached the specified operating
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 59 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 60

ESG-400
Error
no.
Error message
Possible cause
Remedial action
temperature.
E181
Temperature below limit
The generator (HVPS Board)
is too cold.
Switch off the electrosurgical generator
and wait until it has reached the
specified operating temperature.
E182
Temperature above limit
The generator (HVPS Board)
is too hot.
Switch off the electrosurgical generator
and wait until it has cooled down or
reached the specified operating
temperature.
E183
E184
E185
Error
Refer to E132
E186
Error
Internal hardware error.
Send back to Olympus Service
E187
Increased HF leakage
current
The high frequency leakage
current has exceeded the limit
of 150 mA for monopolar
application or 100 mA for
bipolar application.
Check if an instrument, the neutral
electrode or the patient is unintentionally
grounded.
E188
Excessive HF leakage
current
The high frequency leakage
current has exceeded the limit
of 300 mA for monopolar
application or 200 mA for
bipolar application.
Check if an instrument, the neutral
electrode or the patient is unintentionally
grounded.
E189
[…]
E198
Error
Refer to 132
E199
Error
Refer to 133
E200
E201
Error
Refer to 132
E202
Insufficient neutral electrode
contact
The contact resistance of the
neutral electrode is too high or
the neutral electrode is not
connected.
Check the connection / attachment of the
neutral electrode.
Malfunction of the neutral
electrode and / or the neutral
electrode cable.
Replace the neutral electrode and / or
the cable.
E203
[…]
E213
Error
Refer to E020
E214
Low battery
The batteries on the
Motherboard are low and
caused a loss of data.
Replace the batteries on the
Motherboard
E215
Error
Refer to E020
E216
E217
Error
Refer to E058
E218
Error
Refer to E020
E220
Error
Internal software or hardware
error.
Send back to Olympus Service
E222
[…]
Error
Refer to E058
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 60 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 61

ESG-400
Error
no.
Error message
Possible cause
Remedial action
E294
E295
Error
Unable to read the data at the
Multifunction socket.
1. Change the connected instrument at
the Multifunction socket.
2. Send back to Olympus Service
E296
Error
Unable to write the data from
the Multifunction socket.
1. Change the connected instrument at
the Multifunction socket.
2. Send back to Olympus Service
E297
Error
Unable to read the instrument
name from the Multifunction
socket.
1. Change the connected instrument at
the Multifunction socket.
2. Send back to Olympus Service
E299
[…]
E387
Error
Refer to E058
E390
Communication error
Improper connection of the
communication cables to the
LINK-OUT / LINK-IN socket:
“The communication to other
devices has been aborted.”
1. Check all cable connections.
2. Check all other connected devices.
3. Send back to Olympus Service
Malfunction or damage of the
communication cables.
Check the cables for damages and, if
necessary, replace the cables.
E391
E392
E393
Error
Refer to E058
E394
Communication error
Improper connection of the
communication cables to the
LINK-OUT / LINK-IN socket:
“The ring connection to other
devices has been detected.”
1. Check all cable connections.
2. Check all other connected devices.
3. Send back to Olympus Service
Malfunction or damage of the
communication cables.
Check the cables for damages and, if
necessary, replace the cables.
E396
Temperature below limit
The generator (Generator
Board) is too cold.
Place the generator at normal room
temperature and wait until it is warmed
up before use.
E397
Temperature above limit
The generator (Generator
Board) is too hot.
Wait until the generator has cooled
down.
E398
Temperature below limit
The generator (HVPS Board)
is too cold.
Place the generator at normal room
temperature and wait until it is warmed
up before use.
E399
Temperature above limit
The generator (HVPS Board)
is too hot.
Wait until the generator has cooled
down.
E400
[…]
E408
Error
Refer to E058
E409
Communication error
Improper connection of the
communication cables to the
LINK-OUT / LINK-IN socket:
1. Check all cable connections.
2. Check all other connected devices.
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 61 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 62

ESG-400
Error
no.
Error message
Possible cause
Remedial action
“The communication problem
to other devices has been
detected.”
3. Send back to Olympus Service
Malfunction or damage of the
communication cables.
Check the cables for damages and, if
necessary, replace the cables.
E410
Error
Refer to E058
E411
Communication error
Improper connection of the
communication cables to the
LINK-OUT / LINK-IN socket:
“The communication problem
to other devices has been
detected.”
1. Check all cable connections.
2. Check all other connected devices.
3. Send back to Olympus Service
Malfunction or damage of the
communication cables.
Check the cables for damages and, if
necessary, replace the cables.
E412
Error
Refer to E058
E413
Error
The controlled output power at
the Burn-In is below the limit.
Check the connected resistors.
E414
Error
The controlled output power at
the Burn-In is above the limit.
Send back to Olympus Service
415
[…]
429
Error
Refer to E004
E430
---
--- (POWER_FAIL)
---
E431
Error
Refer to E004
E432
E433
Error
Refer to E133
E434
[…]
E437
Error
Refer to E004
E438
Procedure data error
One or more saved
procedures have been
deleted. (Inconsistant
Procedure data detected. One
or more Procedure settings
have been lost.)
Press the “OK button” to close the error
window and to continue.
E439
E440
Error
Internal hardware error.
Send back to Olympus Service
E441
Device setting error
All settings of the
electrosurgical generator have
been set to default. (SRAM
and EEPROM content has
been initialized.)
The electrosurgical generator is ready to
use after the error window disappeared.
E443
[…]
E456
Error
Refer to E004
E457
Error
Internal software or hardware
error.
Send back to Olympus Service
E458
Error
Refer to E058
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 62 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 63

ESG-400
Error
no.
Error message
Possible cause
Remedial action
E459
E460
Error
Refer to E133
E461
[…]
E484
Error
Refer to E058
E486
No instrument connected
An Olympus HF instrument
and / or connection cable has
not been properly connected
to the UNIVERSAL socket.
Ensure the proper connection of the
Olympus HF instrument and / or the
connection cable to the UNIVERSAL
socket.
Malfunction of the Olympus HF
instrument and / or the
connection cable.
Replace the Olympus HF instrument
and / or the connection cable.
E488
E489
Error
Refer to E058
E490
Communication error
Improper connection of the
communication cables to the
LINK-OUT / LINK-IN socket:
“The communication problem
to other devices has been
detected.”
1. Check all cable connections.
2. Check all other connected devices.
3. Send back to Olympus Service
Malfunction or damage of the
communication cables.
Check the cables for damages and, if
necessary, replace the cables.
E491
[…]
E514
Error
Refer to E058
E515
Communication error
Improper connection of the
communication cables to the
LINK-OUT / LINK-IN socket:
“The communication problem
to other devices has been
detected.”
1. Check all cable connections.
2. Check all other connected devices.
3. Send back to Olympus Service
Malfunction or damage of the
communication cables.
Check the cables for damages and, if
necessary, replace the cables.
E516
Communication error
Improper connection of the
communication cables to the
LINK-OUT / LINK-IN socket:
“The communication problem
to other devices has been
detected.”
1. Check all cable connections.
2. Check all other connected devices.
3. Send back to Olympus Service
Malfunction or damage of the
communication cables.
Check the cables for damages and, if
necessary, replace the cables.
E519
[…]
E524
Error
Refer to E058
E525
Error
Refer to E020
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 63 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 64

ESG-400
Error
no.
Error message
Possible cause
Remedial action
E526
E527
[…]
E611
Error
Refer to E058
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 64 / 99 Chapter 4: Troubleshooting
Page 65

ESG-400
CHAPTER 5: INSPECTION
1 JIGS, TOOLS, AND MEASURING EQUIPMENT FOR INSPECTION .......................... 66
2 INSPECTION PROCEDURES ................................................................ ...................... 67
2-1 Visual inspection of the electrosurgical generator and accessories ................................................ 68
2-2 Verifying the contact quality monitor function .................................................................................. 71
2-3 Checking the DC resistance (according to IEC 60601-2-2) ............................................................. 73
2-4 Checking the earth resistance (according to IEC 60601-1 and IEC 62353) .................................... 73
2-5 Checking the earth leakage current (according to IEC 60601-1) .................................................... 73
2-6 Checking the patient leakage current (according to IEC 60601-1) .................................................. 74
2-7 Checking the current and power consumption and output waveform .............................................. 75
2-8 Checking the high frequency leakage current (according to IEC 60601-2-2) .................................. 77
2-8-1 Measurement of the monopolar high frequency leakage current under loaded condition ...... 77
2-8-2 Measurement of the monopolar high frequency leakage current under unloaded condition .. 79
2-8-3 Measurement of the bipolar high frequency leakage current under loaded condition ............ 81
2-8-4 Measurement of the bipolar high frequency leakage current under unloaded condition ........ 83
2-9 Checking the output power .............................................................................................................. 85
2-10 Checking for certain features and error messages .......................................................................... 85
2-11 Final test ........................................................................................................................................... 86
2-11-1 Self test.................................................................................................................................... 86
2-11-2 Display and sound check ........................................................................................................ 86
2-11-3 Functionality of push buttons .................................................................................................. 86
2-11-4 Communication test ................................................................................................................. 86
2-11-5 Restore of output power settings ............................................................................................ 87
2-12 Inspection label (For applicable markets) ........................................................................................ 87
3 INSPECTION CARD ..................................................................................................... 88
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 65 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 66

ESG-400
No.
Name
Model/REF
Specifications/Remarks
J001
Electrical safety tester
e.g.: Seculife ST, Unimet 1000 ST
(Bender), QA-90 (Metron)
J002
Electrosurgical analyzer
e.g.: QA-ES (Metron)
J003
Digital multimeter
DC accuracy: < 1 %,
DC voltage range 500 V
J004
Load resistors
(low power)
low inductive part, short time load
5 Ω, 140 Ω, 170 Ω all 0.5 W (or
more) and 1 % tolerance or
alternatively: resistor decade box
J005
Load resistors
(high power, low inductive)
Low inductive part,
75 Ω, 500 Ω (300 W, 5%)
7 Ω, 916 Ω, 10 kΩ (100 W, 1%)
J007
Cables, 4 mm to 4 mm (banana)
Connection cable: monopolar or
bipolar output (1 x 4 mm) to various
equipment (1 x 4 mm, banana plug),
length 1 m
WARNING:
A connection of a 4 mm plug to any
other receptacle except the
right-hand-side receptacle of the
MONOPOLAR 1 socket and the
MONOPOLAR 2 socket may destroy
the socket during activation.
J008
Cable, UNIVERSAL to 4 mm (banana)
WB979008
Connection cable: bipolar
UNIVERSAL to various equipment (1
x 4 mm, banana plug), length 1 m
J009
Cable, Monopolar 1 including handswitch
WB979013
Connection Cable: monopolar output
incl. handswitch to various
equipment (1 x 4 mm, banana plug),
length 3…4 m
J010
Cable, Monopolar 2 including handswitch
WB979014
Connection Cable: monopolar output
incl. handswitch to various
equipment (1 x 4 mm, banana plug),
length 3…4
J011
Cable, neutral electrode
(P-cord) to 2 x 4 mm (banana)
WB979002
Connection cable: neutral electrode
output (2 x 2.5 mm, 10 mm, P-cord)
to various equipment (2 x 4 mm,
banana plug), length 1 m
J012
Cable, Communication
MAJ-1871
Communication cable, length 0.25 m
J013
Crocodile clips (with 4 mm connection)
For connection to Potential
Equalization bonding
J014
ESG-400 foot switch double pedal
WB50402W
J015
ESG-400 foot switch single pedal
WB50403W
J016
Power Cord
Ordering depending on country.
Refer to Chapter 1-4-2
J017
Oscilloscope
e.g.: DSOX2024A (Agilent)
J018
High Voltage Probe
Attenuation: 100:1
Max. Input Voltage ≥ 850 Vp
1 Jigs, Tools, and Measuring Equipment for Inspection
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 66 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 67

ESG-400
CAUTION
To avoid inadvertent coupling and / or shunting of high frequency currents
around the resistor elements, keep the resistors at least 10 centimeters away
from any metal surface including tabletops and other resistors. This is
especially true if several resistors are connected in series or parallel to obtain
a specified value. Do not allow the resistor bodies to touch each other.
NOTE
Keep test leads to the minimum length usable; lead inductance and stray
capacitance can adversely affect readings.
Carefully select suitable ground points to avoid ground loop error in
measurements.
For tests and checks requiring a power cord, use the power cord provided with
the electrosurgical unit.
Inspection is mandatory after repair, adjustment, update and upgrade.
2 Inspection procedures
The electrosurgical generator and the footswitch must undergo an inspection / safety check in yearly intervals
in accordance with the national statutory regulations. Inspection is also mandatory after repair, adjustment,
update and upgrade.
Generally the footswitches are inspected together with the electrosurgical unit. If a footswitch alone has to be
checked, only following tests are mandatory. The Numbers used referring to the Inspection Card in chapter 5-3:
For a single footswitch test number 2, 39 and 55 are mandatory.
For a double footswitch test number 2, 38, 39 and 55 are mandatory.
Follow these test instructions. All tests must be done with fully functional and calibrated test equipment and by
technicians trained in the service / maintenance of electrical medical devices. Record the test results in the
“Inspection Card” (refer to chapter 5-3, Inspection Card) for reference in future tests and provide the user of the
electrosurgical unit with a signed report.
During service / maintenance take care of the different hardware and software versions which may be
applicable. Information how to identify the hardware version can be found in chapter 3-2, Board Compatibility.
Information how to identify the software version can be found in chapter 1-3, Software version.
If the electrosurgical unit fails to meet any of the checks, the unit has to be adjusted according to chapter 6
(Adjustment) or refer to chapter 4 (Troubleshooting). If the failure still occurs, contact the manufacturer.
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 67 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 68

2-1 Visual inspection of the electrosurgical generator and accessories
12345W13-678 2011-08
12345W13-678 2013-03
1) Check that the labels according to chapter 5-1 (Front panel, Rear panel) are present and legible. The
product name should be clearly visible on the front panel. Verify that the type plate shows details about the
type of the device, reference number, line voltage range, supply frequency, output power classification,
output frequency, duty cycle, serial number, manufacturing date and manufacturer according to Fig. 5.2.1,
Fig. 5.2.2 or Fig. 5.2.3
ESG-400
Fig. 5.2.1. Sample of type plate of the electrosurgical unit
Fig. 5.2.2 Sample of type plate of the electrosurgical unit (Japan Version)
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 68 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 69

ESG-400
Fig. 5.2.3 Sample of type plate of the electrosurgical unit (China Version)
2) Check the electrosurgical unit and the accessories for external obstructions or damage. Verify that the
housing, the front panel and the rear panel have no serious destructions.
3) Record the test results in the safety check report (refer to chapter 5-3).
4) Copy the tables 7.1 and 7.2 on the next page and prepare them to be filled out while inspecting the
electrosurgical generator. Fill out the table 7.1 after the first startup of the generator. The field “Actual
Procedure” can only be filled, if a procedure is chosen.
5) The table 7.2 is used every time before a mode is changed in order to perform a test. The settings of the
used mode are noted in one line of table 7.2. Restore the values of table 7.2 either after each performed
test or after the inspection. This should be done, to make sure that the physician will be provided with the
last output power setting.
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 69 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 70

ESG-400
Actual
Procedure
<if applicable>
Actual
Screen
BIPOLAR
MONOPOLAR 1
Cut Mode
Coag Mode
Cut Mode
Coag Mode
UNIVERSAL
MONOPOLAR 2
Cut Mode
Coag Mode
Cut Mode
Coag Mode
Socket
Mode
Power Level
Effect
Table 7.1: Template to note the actual procedure and the user assignment of the modes to the sockets
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 70 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Table 7.2: Template to note the power settings
Page 71

2-2 Verifying the contact quality monitor function
1) Connect the power cord and the footswitch to the electrosurgical generator (refer to chapter 1-5-3 and
1-5-8).
2) All steps for this test are described in the table 7.3 at the next page. Assign the footswitch according to the
column “Mode”. Connect the appropriate resistor R (J004) described in the column “Action” via the
connection cable (J011) with the neutral electrode socket at the front panel (refer to chapter 1-5-2). For
some tests leave the connector open or short circuit the connection cable (J011).
3) Follow the steps described in the column “Action” and verify the reaction of the corresponding contact
quality monitor indicator for non-split neutral electrode or split neutral electrode at the front panel (refer to
chapter 1-5-2) according to table 7.3.
4) Repeat step 2 and 3 until all action items in table 7.3 have been checked.
5) Record the test results in the Inspection Card (refer to chapter 5-3).
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 71 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 72

ESG-400
NOTE
Always disconnect the neutral electrode connector (J011) before connecting a
new resistor.
Mode
Action
Expected test result
Any
bipolar
mode
During standby and
activation
1) The neutral electrode
socket is left open,
nothing is connected.
2) Activate any bipolar
output.
The contact quality monitor is
independent from the bipolar mode.
The indicator for split neutral
electrode is illuminated red. During
activation the HF-output is working.
Any
monopolar
mode
During standby:
1) Short circuit the
neutral electrode
connector.
2) Connect a R = 5 Ω
with the neutral
electrode socket
Pop-Up Window at the screen will
appear: “Non-split neutral electrode
is connected”
Contact quality monitor indicator for
non-split neutral electrode
illuminates green.
During standby:
1) Connect a R = 140 Ω
with the neutral
electrode connector
Contact quality monitor indicator for
split neutral electrode illuminates
green.
During standby and
activation:
1) Connect a R = 170 Ω,
with the neutral
electrode connector
2) Activate any
monopolar output.
Contact quality monitor indicator for
split neutral electrode illuminates
red.
During activation a warning tone
can be heard, the error code E202
is displayed (“Insufficient neutral
electrode contact”) and activation
is disabled.
Table 7.3: Checking the contact quality monitor
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 72 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 73

2-3 Checking the DC resistance (according to IEC 60601-2-2)
1) Activate the safety test function in the service menu (see chapter 6-1, Safety Test) and verify that the
button “Relays on” is marked white.
2) Connect the digital multimeter (J003) with the bipolar connector on the front panel (see chapter 1-5-2).
3) Verify the resistance is ≥ 2 MΩ.
4) Deactivate the safety test function in the service menu.
5) Record the test results in the Inspection Card (see chapter 5-3).
2-4 Checking the earth resistance (according to IEC 60601-1 and IEC 62353)
1) Connect the electrosurgical generator with an electrical safety tester (J001) according to the tester’s
instructions for use.
2) If the power cord and the electrosurgical unit are measured together, verify the protective earth resistance
≤ 0.3 Ω against metal parts which can be touched.
3) Record the test results in the Inspection Card (see chapter 5-3).
ESG-400
2-5 Checking the earth leakage current (according to IEC 60601-1)
1) Connect the electrosurgical generator with an electrical safety tester (J001) according to the tester’s
instructions for use.
2) Switch on the electrosurgical unit.
3) Verify under normal condition (NC) the earth leakage current is ≤ 0.5 mA.
4) Verify under single fault condition (SFC) the earth leakage current is ≤ 1.0 mA
5) Record the test results in the Inspection Card (see chapter 5-3).
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 73 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 74

2-6 Checking the patient leakage current (according to IEC 60601-1)
NOTE
For this test an interconnection of the three receptacles of MONOPOLAR 1
and MONOPOLAR 2 is allowed. Before interconnect the three receptacles
verify, that the safety test function is activated and the button “Relays on” is
marked white.
1) Switch the electrosurgical generator on and activate the safety test function in the service menu (see
chapter 8-2, Safety Test) and verify that the button “Relays on” is marked white.
2) Connect the UNIVERSAL cable (J008) to the UNIVERSAL socket and the connection cable P-cord (J011)
to the neutral socket.
3) Connect two 4mm cables “banana” (J007) to every receptacle of the BIPOLAR socket.
4) Connect three 4mm cables “banana” to the 4mm receptacles of the MONOPOLAR 1 socket. Leave the
8 mm BOVIE connector open.
5) Connect three 4mm cables “banana” to the 4mm receptacles of the MONOPOLAR 2 socket. Leave the
5/9 mm ERBE connector open.
6) Verify again that the Button “Relays on” at the touch screen is marked white and short circuit all
connectors.
ESG-400
7) Switch the electrosurgical generator off, cable it with the electrical safety tester (J001) according to the
tester’s instructions for use and switch it on again. Start the test with the electrical safety tester according
to the tester’s instructions for use.
8) Verify under normal condition (NC) for AC the patient leakage current is ≤ 0.01 mA.
9) Verify under normal condition (NC) for DC the patient leakage current is ≤ 0.01 mA.
10) Verify under single fault condition (SFC, “open earth”) for AC the patient leakage current is ≤ 0.05 mA.
11) Verify under single fault condition (SFC, “open earth”) for DC the patient leakage current is ≤ 0.05 mA.
12) Disconnect all cables from the electrosurgical generator.
13) Deactivate the safety test function in the service menu.
14) Record the test results in the Inspection Card (see chapter 5-3).
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 74 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 75

2-7 Checking the current and power consumption and output waveform
CAUTION
A connection of a 4 mm plug to any
other receptacle except
the right-hand-side receptacle of
the MONOPOLAR 1 socket and
the MONOPOLAR 2 socket may destroy
the socket during activation.
NOTE
Table 7.4 is showing good and bad examples how the output waveform should
look like. From the figures in this table it is also clear to see, which parameter
is to be measured.
1) Connect the load resistor RL = 500 Ω (J005) via a 4mm cable “banana” (J007) to the right receptacle of
the MONOPOLAR 1 socket and via the connection cable “P-cord” (J011) to the neutral socket in the front
panel.
2) Cable the electrosurgical generator with the electrical safety tester according to the testers instructions for
use. Activate the function to measure current and power consumption.
3) Switch the electrosurgical generator on and select the PureCut (Effect 3) mode at the MONOPOLAR 1
socket. Set the level to 300. Assign the footswitch to the MONOPOLAR 1 socket. (Perform the setting
according to the instruction for use.)
4) Activate the output power by pressing “CUT” at the footswitch.
ESG-400
5) Verify the current consumption IL is ≤ 10 A.
6) Connect high voltage probe to oscilloscope and to generator output socket (signal to right receptacle of
the MONOPOLAR 1 socket and signal ground to neutral socket)
Recommended oscilloscope settings:
o Channel 1: high voltage probe 1000:1, DC, 200 V/div (minimum total voltage range
displayed on oscilloscope: -700 V … +700 V)
o Time:
minimum 2 ms/div (minimum total time range displayed on oscilloscope:
20 ms)
maximum 5 ms/div (maximum total time range displayed on oscilloscope:
50 ms)
7) Activate the output power by pressing “CUT” at the footswitch. Record the waveform in the time range
after the high power cut support pulse (ca. 100 ms after HF output start) in steady state.
8) Verify output waveform:
The amplitude level of the output voltage must be stable. No oscillation in the frequency range of
50 … 200 Hz. A maximum amplitude fluctuation from minimum peak voltage to maximum peak voltage of
110 V is allowed for steady state.
9) Disconnect high voltage probe.
10) Connect the load resistor RL = 75 Ω (J005) via the connection cable (J008) with the UNIVERSAL socket in
the front panel.
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 75 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 76

ESG-400
Setup
Picture of oscilloscope (2 ms / div)
Picture of oscilloscope (5 ms / div)
“good”
example for
WB91051W
“bad”
example for
WB91051W
with mains
voltage of
230 VAC
“bad”
example for
WB91051W
with mains
voltage of
115 VAC
11) Select the SalineCut (Effect 3) mode at the UNIVERSAL socket. Set the level to 320. Assign the
footswitch to the UNIVERSAL socket. (Perform the setting according to the instruction for use.)
12) Activate the output power by pressing “CUT” at the footswitch.
13) Verify the apparent power consumption SL is ≤ 1500 VA.
14) Record the test results in the Inspection Card (see chapter 7-3)
15) Switch the electrosurgical generator off and disassemble the test set-up.
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 76 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Table 7.4: good and bad examples of the output waveform
Page 77

2-8 Checking the high frequency leakage current (according to IEC 60601-2-2)
CAUTION
A connection of a 4 mm plug to any
other receptacle except
the right-hand-side receptacle of
the MONOPOLAR 1 socket and
the MONOPOLAR 2 socket may destroy
the socket during activation.
The monopolar high frequency leakage current has to be measured according to the procedure 19.3.101 a) 2)
(neutral electrode isolated from earth at high frequency) as described in IEC 60601-2-2.
The bipolar high frequency leakage current has to be measured according to the procedure 19.3.101 a) 3)
(bipolar application) as described in IEC 60601-2-2.
The high frequency current is measured from the appropriate output connector of each pole while the
electrosurgical unit is operated at maximum output power setting in an appropriate mode and the output being
unloaded and loaded at rated load. The high frequency current is measured with the electrosurgical analyzer
through an internal resistance of 200 Ω.
2-8-1 Measurement of the monopolar high frequency leakage current under loaded condition
ESG-400
Fig. 5.2.4 and Fig. 5.2.5 are showing an example how to set up the test to measure the monopolar high
frequency leakage current under loaded condition. The load resistor RL = 500 Ω (J005) is connected via the
connection cable (J007, banana) with the active pole MONOPOLAR 1 and via the connection cable J011 with
the NEUTRAL connector. The high frequency leakage current is floating from appropriate pole to the
equipotential bonding port. It is measured via the electrosurgical analyzer via a measuring resistance of 200 Ω.
Fig. 5.2.4 shows the measurement from the neutral pole; Fig. 5.2.5 shows the measurement from the active
pole.
1) Assign the footswitch to the MONOPOLAR 1 socket and select the monopolar PureCut mode with effect 3.
Set the power level to 300. (Perform the setting according to the instruction for use.)
2) Set up the measurement according to Fig. 5.2.4 (Measuring of the high frequency leakage current under
loaded condition at the neutral pole.)
3) Activate the output power by pressing the corresponding footswitch pedal.
4) Verify the leakage current is ≤ 150 mA.
5) Set up the measurement according to Fig. 5.2.5 (Measuring of the high frequency leakage current under
loaded condition at the active pole.)
6) Activate the output power by pressing the corresponding footswitch pedal.
7) Verify the leakage current is ≤ 150 mA.
8) Repeat step 2 - 7 for the monopolar SprayCoag mode with effect 3 and power level 120.
9) Record the test results in the Inspection Card (see chapter 5-3).
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 77 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 78

ESG-400
CAUTION
A connection of a 4 mm plug to any other receptacle except the
right-hand-side receptacle of the MONOPOLAR 1 socket and the
MONOPOLAR 2 socket may destroy the socket during activation.
Fig. 5.2.4. Example for the loaded measurement of the monopolar high frequency leakage current at the
neutral pole
Fig. 5.2.5. Example for the loaded measurement of the monopolar high frequency leakage current at the
active pole
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 78 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 79

2-8-2 Measurement of the monopolar high frequency leakage current under unloaded condition
CAUTION
A connection of a 4 mm plug to any
other receptacle except
the right-hand-side receptacle of
the MONOPOLAR 1 socket and
the MONOPOLAR 2 socket may destroy
the socket during activation.
Fig. 5.2.6 and Fig. 5.2.7 are showing an example how to set up the test to measure the monopolar high
frequency leakage current under unloaded condition. In this test the output is unloaded, the load resistance
used in the test before is removed. The high frequency leakage current is floating from appropriate pole to the
equipotential bonding port. It is measured via the electrosurgical analyzer via a measuring resistance of 200 Ω.
Fig. 5.2.6 shows the measurement from the neutral pole; Fig. 5.2.7 shows the measurement from the active
pole.
1) Assign the footswitch to the MONOPOLAR 1 socket and select the monopolar PureCut mode with effect 3.
Set the power level to 300. (Perform the setting according to the instruction for use.)
2) Set up the measurement according to Fig. 5.2.6 (Measuring of the high frequency leakage current under
unloaded condition at the neutral pole.)
ESG-400
3) Activate the output power by pressing the corresponding footswitch pedal.
4) Verify the leakage current is ≤ 150 mA.
5) Set up the measurement according to Fig. 5.2.7 (Measuring of the high frequency leakage current under
unloaded condition at the active pole.)
6) Activate the output power by pressing the corresponding footswitch pedal.
7) Verify the leakage current is ≤ 150 mA.
8) Repeat step 2 - 7 for the monopolar SprayCoag mode with effect 3 and power level 120.
9) Record the test results in the Inspection Card (see chapter 5-3).
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 79 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 80

ESG-400
CAUTION
A connection of a 4 mm plug to any other receptacle except the
right-hand-side receptacle of the MONOPOLAR 1 socket and the
MONOPOLAR 2 socket may destroy the socket during activation.
Fig. 5.2.6. Example for the unloaded measurement of the monopolar high frequency leakage current at the
neutral pole
Fig. 5.2.7. Example for the unloaded measurement of the monopolar high frequency leakage current at the
active pole
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 80 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 81

2-8-3 Measurement of the bipolar high frequency leakage current under loaded condition
CAUTION
A connection of a 4 mm plug to any
other receptacle except
the right-hand-side receptacle of
the MONOPOLAR 1 socket and
the MONOPOLAR 2 socket may destroy
the socket during activation.
Fig. 5.2.8 and Fig. 5.2.9 are showing an example how to set up the test to measure the bipolar high frequency
leakage current under loaded condition. The load resistor RL = 500 Ω (J005) is connected via the connection
cables (J007, banana) with both BIPOLAR receptacles. The high frequency leakage current is floating from
appropriate pole to the equipotential bonding port. It is measured via the electrosurgical analyzer via a
measuring resistance of 200 Ω. Fig. 5.2.8 shows the measurement from terminal 1; Fig. 5.2.9 shows the
measurement from terminal 2.
1) Assign the footswitch to the BIPOLAR socket and select the BipolarCut mode with effect 3. Set the power
level to 100. (Perform the setting according to the instruction for use.)
2) Set up the measurement according to Fig. 5.2.8 (Measuring of the high frequency leakage current under
loaded condition at terminal 1.)
ESG-400
3) Activate the output power by pressing the corresponding footswitch pedal.
4) Verify the leakage current is ≤ 70 mA.
5) Set up the measurement according to Fig. 5.2.9 (Measuring of the high frequency leakage current under
loaded condition at terminal 2.)
6) Activate the output power by pressing the corresponding footswitch pedal.
7) Verify the leakage current is ≤ 70 mA.
8) Record the test results in the Inspection Card (see chapter 5-3).
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 81 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 82

ESG-400
Fig. 5.2.8. Example for the loaded measurement of the bipolar high frequency leakage current at terminal 1
Fig. 5.2.9. Example for the loaded measurement of the bipolar high frequency leakage current at terminal 2
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 82 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 83

2-8-4 Measurement of the bipolar high frequency leakage current under unloaded condition
Fig. 5.2.10 and Fig. 5.2.11 are showing an example how to set up the test to measure the bipolar high
frequency leakage current under unloaded condition. In this test the output is unloaded, the load resistance
used in the test before is removed. The high frequency leakage current is floating from appropriate pole to the
equipotential bonding port. It is measured via the electrosurgical analyzer via a measuring resistance of 200 Ω.
Fig. 5.2.10 shows the measurement from terminal 1; Fig. 5.2.11 shows the measurement from terminal 2.
9) Assign the footswitch to the BIPOLAR socket and select the BipolarCut mode with effect 3. Set the power
level to 100. (Perform the setting according to the instruction for use.)
10) Set up the measurement according to Fig. 5.2.10 (Measuring of the high frequency leakage current under
unloaded condition at terminal 1.)
11) Activate the output power by pressing the corresponding footswitch pedal.
12) Verify the leakage current is ≤ 70 mA.
13) Set up the measurement according to Fig. 5.2.11 (Measuring of the high frequency leakage current under
unloaded condition at terminal 2.)
14) Activate the output power by pressing the corresponding footswitch pedal.
ESG-400
15) Verify the leakage current is ≤ 70 mA.
16) Record the test results in the Inspection Card (see chapter 5-3 ).
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 83 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 84

ESG-400
Fig. 5.2.10. Example for the unloaded measurement of the bipolar high frequency leakage current at
terminal 1
Fig. 5.2.11. Example for the unloaded measurement of the bipolar high frequency leakage current at
terminal 2
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 84 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 85

2-9 Checking the output power
NOTE
For the measurement of this (high current) value, it is important, that the cable
of the instrument is not “forming an inductor”. So do not wrap it up like a coil.
Either use it flat or unfold it completely.
1) All constraints for these tests are listed in the inspection card in chapter 5-3 under number 30 to 45. The
constraints are the output socket, the way of activation (e.g. footswitch, handswitch), the settings and the
load resistance. For measuring and to simulate the appropriate resistance the electrosurgical analyzer
(J002) is used.
2) Connect the appropriate output of the electrosurgical generator to the variable load of the electrosurgical
analyzer (J002) (according to the inspection card in chapter 5-3). Set the electrosurgical generator to
continuous measuring and set the internal measuring resistance to the appropriate value (according to the
inspection card in chapter 5-3). Start the measuring with the electrosurgical generator. (Settings of the
electrosurgical analyzer are done according to the analyzer’s instruction for use.)
3) Select the mode and set the power level according to the inspection card in chapter 5-3.
4) Activate the output power by pressing the corresponding footswitch pedal or handswitch button. During
the activated output the output tone can be heard.
5) Verify the output power is in the range according to the inspection card in chapter 5-3.
6) Repeat step 2 - 5 until test number 30 to 45 in the inspection card in chapter 5-3 have been checked.
ESG-400
7) Record the test results in the Inspection Card (see chapter 5-3).
2-10 Checking for certain features and error messages
1) All constraints for these tests are listed in the inspection card in chapter 5-3 under number 46 to 48. The
constraints are the output socket, the way of activation (e.g. footswitch, handswitch), the settings and the
load resistance. Low inductive high load resistors (J005) are used.
2) Connect the appropriate output of the electrosurgical generator to the appropriate load resistor (according
to the inspection card in chapter 5-3).
3) Select the mode and set the power level according to the inspection card in chapter 5-3.
4) Activate the output power by pressing the corresponding footswitch pedal. During the activated output the
output tone can be heard.
5) Verify the reaction of the electrosurgical generator according to the inspection card in chapter 5-3.
6) Repeat step 2 - 5 until test number 46 to 48 in the inspection card in chapter 5-3 have been checked.
7) Record the test results in the Inspection Card (see chapter 5-3).
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 85 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 86

2-11 Final test
1) Check the functionality of each push button
by pressing.
2) The buttons should perform according to the
description in the instruction for use.
3) Record the test results in the Inspection
Card (refer to chapter 5-3).
Fig. 5.2.13. Position of the push buttons
MENU
Fig. 5.2.12. Checking volume and brightness
2-11-1 Self test
1) Connect the electrosurgical generator via power cord (J016) to mains. Switch the generator on by
pressing the “Power Switch”.
2) The generator should boot without any alarm. If an alarm occurs, refer to Chapter 4 (Troubleshooting).
2-11-2 Display and sound check
1) Check the adjustment of display
brightness and volume via touch
screen. Enter the “Select Menu”
by pressing the push button
“MENU push button”. Change
the Volume via the rocker switch.
A sound should be carried
according to the setting. Change
the Brightness via the rocker
switch. The brightness should
change according to the setting.
ESG-400
2) Check the adjustment of the
volume via the volume control
knob at the rear of the housing.
There will be an acoustic
feedback for the setting.
3) Record the test results in the Inspection Card (refer to chapter 5-3).
2-11-3 Functionality of push buttons
2-11-4 Communication test
1) Connect the sockets “LINK-IN” and “LINK-OUT” at the rear of the housing by the Communication Cable
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 86 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 87

(J012) with each other. In this way a ring communication is established.
Fig. 5.2.14. Sample of an inspection label
2) The Error Message “E394 Communication error” should appear.
3) Record the test results in the Inspection Card (refer to chapter 5-3).
2-11-5 Restore of output power settings
Restore the settings by using the tables created in chapter 7-2-1. When not done while inspecting, restore all
power settings off the changed modes noted in table 7.2. Finally restore the last active procedure if applicable
and assign all modes to the sockets.
2-12 Inspection label (For applicable markets)
1) Cover or exchange an inspection label (as shown in Fig. 5.2.14) at the rear panel of the electrosurgical
unit’s housing and mark the due date of the next periodic safety check (month / year). The electrosurgical
unit must undergo a periodic safety check at annual intervals.
2) Record the due date in the safety check report (see chapter 5-3).
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 87 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 88

ESG-400
Product name:
REF no.:
Serial no.:
Software version:
Service / Maintenance
manual version:
Nr.
Test type / mode
Pwr.
level
Load
resistance
Requirement
Measured
value
Test passed
Effect
Yes
No
Visual inspection of the electrosurgical unit and accessories
1
Labels
N/A
N/A
Procedure passed
N/A
2
Obstructions or damage of
unit and accessories
N/A
N/A
Procedure passed
N/A
Contact quality monitor function
3
Any bipolar mode
N/A
N/A
Procedure passed
N/A
4
Any
monopolar
mode
Standby,
non-split
N/A
0 Ω, 5 Ω
Procedure passed
N/A
5
Standby, split
N/A
140 Ω
Procedure passed
N/A
6
Standby, split
N/A
170 Ω
Procedure passed
N/A
7
Activation,
split
N/A
170 Ω
Procedure passed
N/A
DC Resistance
8
DC resistance
N/A
N/A
≥ 2.0 MΩ
9
Earth resistance
(with power cord)
N/A
N/A
≤ 0.3 Ω
Earth leakage current
10
Normal condition (NC)
N/A
N/A
≤ 0.5 mA
11
Single fault condition (SFC)
N/A
N/A
≤ 1.0 mA
3 Inspection Card
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 88 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 89

ESG-400
Nr.
Test type / mode
Pwr.
level
Load
resistance
Requirement
Measured
value
Test passed
Effect
Yes
No
Patient leakage current
12
Normal condition (NC), AC
N/A
N/A
≤ 0.01 mA
13
Normal condition (NC), DC
N/A
N/A
≤ 0.01 mA
14
Single fault condition (SFC),
AC
N/A
N/A
≤ 0.05 mA
15
Single fault condition (SFC),
DC
N/A
N/A
≤ 0.05 mA
Current and power consumption and output waveform
16
PureCut
300
500 Ω
IL ≤ 10 A
Eff. 3
17
Amplitude fluctuation
300
500 Ω
Δ ≤ 110 V
Eff. 3
18
SalineCut
320
75 Ω
SL ≤ 1500 VA
Eff. 3
High frequency leakage current
19
Monopolar PureCut
(neutral electrode terminal)
300
500 Ω
≤ 150 mA
Eff. 3
20
Monopolar PureCut
(active electrode terminal)
300
500 Ω
≤ 150 mA
Eff. 3
21
Monopolar SprayCoag
(neutral electrode terminal)
120
500 Ω
≤ 150 mA
Eff. 3
22
Monopolar SprayCoag
(active electrode terminal)
120
500 Ω
≤ 150 mA
Eff. 3
23
Monopolar PureCut
(neutral electrode terminal)
300
unloaded
≤ 150 mA
Eff. 3
24
Monopolar PureCut
(active electrode terminal)
300
unloaded
≤ 150 mA
Eff. 3
25
Monopolar SprayCoag
(neutral electrode terminal)
120
unloaded
≤ 150 mA
Eff. 3
26
Monopolar SprayCoag
(active electrode terminal)
120
unloaded
≤ 150 mA
Eff. 3
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 89 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 90

ESG-400
Nr.
Test type / mode
Pwr.
level
Load
resistance
Requirement
Measured
value
Test passed
Effect
Yes
No
27
BipolarCut
(active electrode terminal 1)
100
500 Ω
≤ 70 mA
Eff. 3
28
BipolarCut
(active electrode terminal 2)
100
500 Ω
≤ 70 mA
Eff. 3
29
BipolarCut
(active electrode terminal 1)
100
unloaded
≤ 70 mA
Eff. 3
30
BipolarCut
(active electrode terminal 2)
100
unloaded
≤ 70 mA
Eff. 3
Output power
31
Monopolar PureCut
(hand switch@
MONOPOLAR 1)
300
500 Ω
244 W ≤ P
out
≤ 366 W
Eff. 3
32
Monopolar SprayCoag
(hand switch @
MONOPOLAR 1)
120
500 Ω
93 W ≤ P
out
≤ 139 W
Eff. 3
33
Monopolar BlendCut
(hand switch @
MONOPOLAR 2)
200
500 Ω
154 W ≤ P
out
≤ 232 W
Eff. 3
34
Monopolar BlendCut
(hand switch @
MONOPOLAR 2)
200
2000 Ω
49 W ≤ P
out
≤ 73 W
Eff. 3
35
Monopolar PowerCoag
(hand switch @
MONOPOLAR 2)
120
500 Ω
93 W ≤ P
out
≤ 139 W
Eff. 3
36
Monopolar PowerCoag
(hand switch @
MONOPOLAR 2)
60
500 Ω
48 W ≤ P
out
≤ 72 W
Eff. 3
37
Monopolar SoftCoag
(foot switch @
MONOPOLAR 2 with J007
without J010)
200
50 Ω
154 W ≤ P
out
≤ 232 W
Eff. 3
38
Monopolar ForcedCoag
(foot switch @
MONOPOLAR 2 with J007
without J010)
120
500 Ω
93 W ≤ P
out
≤ 139 W
Eff. 3
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 90 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 91

ESG-400
Nr.
Test type / mode
Pwr.
level
Load
resistance
Requirement
Measured
value
Test passed
Effect
Yes
No
39
BipolarCut
(double foot switch
@ BIPOLAR)
100
500 Ω
82 W ≤ P
out
≤ 122 W
Eff. 3
40
Bipolar AutoCoag
(single foot switch (if
provided with the generator,
otherwise double footswitch)
@ BIPOLAR)
120
25 Ω
48 W ≤ P
out
≤ 72 W
Eff. 3
41
Bipolar AutoCoag
(double foot switch
@ BIPOLAR)
120
75 Ω
94 W ≤ P
out
≤ 140 W
Eff. 3
42
Bipolar RFCoag
(without RCAP)
(foot switch @ BIPOLAR)
50
75 Ω
39 W ≤ P
out
≤ 59 W
w/o
RCAP
43
Bipolar RFCoag
(without RCAP)
(foot switch @ BIPOLAR)
50
1000 Ω
0 W ≤ P
out
≤ 5 W
w/o
RCAP
44
Bipolar FineCoag
(foot switch @ BIPOLAR)
39
50 Ω
35 W ≤ P
out
≤ 43 W
Eff. 1
45
Bipolar HardCoag
(foot switch @ BIPOLAR)
42
500 Ω
0 W ≤ P
out
≤ 12 W
Eff. 1
46
Bipolar SalineCoag
(foot switch @ UNIVERSAL)
200
75 Ω
154 W ≤ P
out
≤ 230 W
Message “Use default
instrument settings?
(UNIVERSAL socket)”
can be acknowledged.
Eff. 3
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 91 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 92

ESG-400
Nr.
Test type / mode
Pwr.
level
Load
resistance
Requirement
Measured
value
Test passed
Effect
Yes
No
Checking for certain error messages
46
Bipolar FineCoag
(foot switch @ BIPOLAR)
39
7 Ω
Message “E002 Short
circuit”
N/A
Eff. 1
47
Bipolar HardCoag
(foot switch @ BIPOLAR)
42
10 kΩ
Message “E001 Open
circuit”
N/A
Eff. 1
48
Bipolar HardCoag
(foot switch @ BIPOLAR)
42
916 Ω
AEOP sound
N/A
Eff. 1
Final Check
49
Self test
N/A
N/A
Procedure passed
N/A
50
Display and sound check
N/A
N/A
Procedure passed
N/A
51
Functionality of push buttons
N/A
N/A
Procedure passed
N/A
52
Communication test
(connection LINK-IN –
LINK-OUT)
N/A
N/A
Message “E394
Communication error”
occurs
N/A
53
Date and Time
N/A
N/A
Procedure passed
N/A
54
Restore of output power
settings
N/A
N/A
Settings restored
N/A
Inspection label
55
Due date (month/year):
_________________
N/A
N/A
Adhered
N/A
Unit meets test criteria:
Yes
No
Date
Signature
Name of inspection person:
Test organization:
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 92 / 99 Chapter 5: Inspection
Page 93

ESG-400
CHAPTER 6: DEVICE MENU
1 SAFETY TEST .............................................................................................................. 94
2 SOFTWARE VERSION ................................................................................................. 95
7.022.195 / ISSUE 4 93 / 99 Chapter 6: Device Menu
Page 94

ESG-400
NOTE
The electrosurgical unit remains in this service operation mode until the button
“Relays Off” is pressed. This enables an easy measurement required by the periodic
safety check even if the unit will be switched off.
MENU
Fig. Fehler! Verweisquelle konnte nicht gefunden werden..1.1. Entering the Safety Test Mode
1 Safety Test
This function closes the output relays to perform the measurement(s) required during the inspection. Activation
of this function disables the electrosurgical unit for normal operation.
1) Press the “MENU push button” to display the “Select Menu Screen” on the touch-screen.
2) Switch to the next menu page by pressing the “Next button”. Press the Button “Safety Test”.
3) Press the button “Relays On”. The button will be marked white, when the Relays are on. To perform the
inspection refer to chapter 7: Inspection.
4) To exit this mode press the button “Relays Off” and press the button “Cancel” to leave the screen.
7.022.195 / ISSUE 4 94 / 99 Chapter 6: Device Menu
Page 95

ESG-400
MENU
Fig. Fehler! Verweisquelle konnte nicht gefunden werden..2.1. Entering the Software Version
Menu
2 Software Version
1) Press the “MENU push button” to display the “Select Menu Screen” on the touch-screen.
2) Switch to the next menu page by pressing the “Next button”. Press the Button “Software version”.
3) Read out the software version and leave the menu by pressing the button “OK”.
7.022.195 / ISSUE 4 95 / 99 Chapter 6: Device Menu
Page 96

ESG-400
7.022.195 / ISSUE 4 96 / 99 Chapter 6: Device Menu
Page 97

CHAPTER 7: REVISION HISTORY
ESG-400
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 97 / 99 Chapter 7: Revision History
Page 98

ESG-400
No.
REF No. / Revision No.
Release date
Modifications description
1
7.022.211 12/04
2012-04-27
First clearance
2
7.022.211 12/09
W-CR-11829
2012-10-12
Chapter 5-1: Added ESG-Textbox to the Jigs and tools list
Chapter 5-1: Added J017 Oscilloscope to the Jigs and tools
list
Chapter 5-1: Added J018 High Voltage Probe to the Jigs and
tools list
Chapter 5-2-7: Added Steps 6 Connect high voltage probe to
oscilloscope and to generator output socket (signal to right
receptacle of the MONOPOLAR 1 socket and signal ground
to neutral socket)
Chapter 5-2-7: Added Steps 7 Activate the output power by
pressing “CUT” at the footswitch. Record the waveform in the
time range after the high power cut support pulse (ca. 100 ms
after HF output start) in steady state.
Chapter 5-2-7: Added Steps 8 Verify output waveform:
The amplitude level of the output voltage must be stable. No
oscillation in the frequency range of 50 … 200 Hz. A
maximum amplitude fluctuation from minimum peak voltage
to maximum peak voltage of 110 V is allowed for steady
state.
Chapter 5-2-7: Added Steps 9 Disconnect high voltage probe
Chapter 5-2-7: Following step numbering updated
Chapter 5-2-7: Added Table 7.4 good and bad examples of
the output waveform
Chapter 5-2-12: Description updated “For applicable
markets”
Chapter 5-3: Added Step 17 Amplitude fluctuation. Following
step numbering updated
3
7.022.195 04/13
W-CR-13001
W-CR-12952
2013-04-04
Chapter 5-2-1: Fig. 5.2.2 (Japanese type plate) and Fig.
5.2.3 (Chinese type plate) added, following picture
numbering updated
Chapter 3-3-1: Part number for the double footswitch
corrected ”WB50403”
Chapter 3-3-2: Part number for the single footswitch
corrected ”WB50402
4
7.022.195 09/13
W-CR-13662
2013-09-10
Added “On-Site-Manual” to title page
Chapter 5-2-3: Reference at step 1 changed
Added Chapter 6: Device Menu
Following chapter numbering updated
3 Revision History
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 98 / 99 Chapter 7: Revision History
Page 99

––––––––––––––––––– Manufacturer –––––––––––––––––––
Olympus Winter & Ibe GmbH
Kuehnstraße 61, 22045 Hamburg, Germany
Fax: +49 40 6 69 66 2109, Phone: +49 40 6 69 66 0
–––––––––––––––––––– Distributors ––––––––––––––––––––
http://www.olympus-oste.eu
KEYMED LTD.
KeyMed House, Stock Road, Southend-on-Sea, Essex, SS2 5QH, United Kingdom
Fax: +44 1 702 465 677, Phone: +44 1 702 616 333
http://www.keymed.co.uk/
OLYMPUS AMERICA INC.
3500 Corporate Parkway, P.O. Box 610 Center Valley, PA 18034-0610, U.S.A.
Fax: +1 484 896 7128, Phone: +1 484 896 5000
http://www.olympusamerica.com/
OLYMPUS AUSTRALIA PTY. LTD.
31 Gilby Road, Mount Waverley VIC 3149, Australia
Fax: +61 3 9543 1350, Phone: +61 3 9265 5400
http://www.olympus.com.au/
OLYMPUS EUROPA HOLDING GMBH
Wendenstrasse 14-18, 20097 Hamburg, Germany
Fax: +49 40 237 73 4656, Phone: +49 40 237 73 0
http://www.olympus-europa.com/
OLYMPUS KOREA CO., LTD.
4F, 5F, Gyeongam Building, 157-27 Samseong-Dong, Kangnam-Gu, Seoul 135-090, Korea
Fax: +82 262 55 32 99, Phone: +82 262 07 32 00
http://kr.olympus.com/
OLYMPUS LATIN AMERICA, INC.
6100 Blue Lagoon Drive, Suite 290, Miami, FL 33126-2097, U.S.A.
Fax: +1 305 266 9168, Phone: +1 305 266 2332
http://www.olympusamericalatina.com/
OLYMPUS MEDICAL SYSTEMS CORPORATION
2951 Ishikawa-cho, Hachioji-shi, Tokyo 192-8507, Japan
Fax: +81 426 46 2429, Phone: +81 426 42 2111
http://www.olympus.co.jp/en/
OLYMPUS MOSCOW LIMITED LIABILITY COMPANY
Ulitsa Malaya Kaluzhskaya 19, Building 1, Floor 2, 117071 Moscow, Russia
Fax: +7 495 958 2277, Phone: +7 495 720 9332
http://www.olympus.com.ru/
OLYMPUS (BEIJING) SALES & SERVICE CO. LTD.
Rm. 1202, NCI Tower, A12 Jianguomenwai Avenue, Chaoyang District, Beijing 100022, China
Fax: +86 10 6569 3555, Phone: +86 10 6569 3535
http://cn.olympus.com/
OLYMPUS SINGAPORE PTE LTD.
491B River Valley Road #12-01/04, Valley Point Office Tower, Singapore 248373
Fax: +65 6834 24 38, Phone: +65 6834 00 10
http://www.olympus.com.sg/
7.022.211 / ISSUE 4 PRINTED IN GERMANY
 Loading...
Loading...