Page 1

Olivetti d-Color
P20W/P26W/P26
NETWORK USER’S GUIDE
Page 2

P
REFACE
Every effort has been made to ensure that the information in this document is
complete, accurate, and up-to-date. The manufacuter assumes no responsibility for
the results of errors beyond its control, and also cannot guarantee that changes in
software and equipment made by other manufacturers and referred to in this guide
will not affect the applicability of the information in it. Mention of software products
manufactured by other companies does not necessarily constitute endorsement by
the manufacturer.
While all reasonable efforts have been made to make this document as accurate and
helpful as possible, we make no warranty of any kind, expressed or implied, as to
the accuracy or completeness of the information contained herein.
Microsoft, MS-DOS and Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation.
Apple, Macintosh and Mac are trademarks or registered trademarks of Apple
Computer Inc.
Other product names and brand names are registered trademarks or trademarks of
their proprietors.
Preface> 2
Page 3

CONTENTS
Preface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Notes, cautions and warnings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Network Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Self-diagnostic test. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Configuration utilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Using Quick Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Using AdminManager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Device Setup. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Create a NetWare Queue . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Delete NetWare Object . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
IP Address Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Option Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Help Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Using a Web browser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Microsoft Internet Explorer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Netscape Navigator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Default user name and password. . . . . . . . . . . 33
Adjusting printer settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Using TELNET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Telnet hierarchical structure.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Using SNMP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Management utility — PrintSuperVision. . . . . . . . . 45
System requirement. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Installing Print SuperVision . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Uninstallation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Printing utility — Manufacturers’ LPR . . . . . . . . . . 50
System Requirement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
To install the LPR utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Uninstallation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Microsoft Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Installation of TCP/IP protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Windows 2000. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Windows XP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Network printer IP address configuration . . . . . . . 54
Windows 2000. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Preface> 3
Page 4

Windows XP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Novell Netware IPX. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
NetBEUI Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Network Printer Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Windows 2000. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Windows XP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Printer driver configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Novell NetWare. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Printing the configuration page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Setup utilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
NDPS Gateway . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
iPrint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
UNIX . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Network Interface card setting . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Operating system configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Sun OS 4.x.x (BSD) configuration . . . . . . . . . . 72
Sun Solaris 2.x configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
HP-UX 10.x configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
AIX 4.1.5 configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Logical directories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Apple Macintosh . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Supported versions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Printing the configuration page . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Setup utilities for Mac OS 8.x and 9.x . . . . . . . . . . 85
Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
AppleTalk Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Self-diagnostic test. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Printer does not print . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
NG is printed in the self-diagnostic test or
Flash ROM Check Registers NG . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
TCP/IP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Computer cannot find the network interface card 87
Cannot print with lpr and ftp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Incorrect user name on the banner page . . . . . 88
Preface> 4
Page 5
NetWare . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Printer cannot find the network interface . . . . . 88
The network interface is identified by the setup
utility but not by the NetWare server . . . . . . . 89
Remote Server mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Print Server mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Printer does not print. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
PostScript error occurs if a banner page is printed90
EtherTalk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Not identified by the Chooser and the
Setup Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
NetBEUI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Error writing to Prn1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Appendix – E-Mail Alert Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
N
OTES, CAUTIONS AND WARNINGS
NOTE:
A note appears in this manual like this. A note provides
additional information to supplement the main text which
may help you to use and understand the product.
.
WARNING!
A warning provides additional information which, if
ignored, may result in a risk of personal injury.
CAUTION!
A caution provides additional information which, if
ignored, may result in equipment malfunction or
damage.
Notes, cautions and warnings.> 5
Page 6

N
ETWORK CONFIGURATION
I
NTRODUCTION
Your printer incorporates a fast 100BASE-TX/10BASE-T network
interface. This User’s Guide explains the functionality of the built
in network interface. Access for interconnection and producing
self-diagnostic test and configuration printouts is provided via an
interface panel at the rear of the printer.
This network interface supports IEEE802.2, IEEE802.3, EthernetII and SNAP, and can detect those frame types automatically.
Also, the interface supports major protocols such as TCP/IP, IPX/
SPX (NetWare), EtherTalk and NetBEUI.
This section details the network interface specification and
several software utilities.
You should set the emulation in the Printer Menu settings to Auto
or PS before printing the self-diagnostic test and settings.
Network Configuration> 6
Page 7
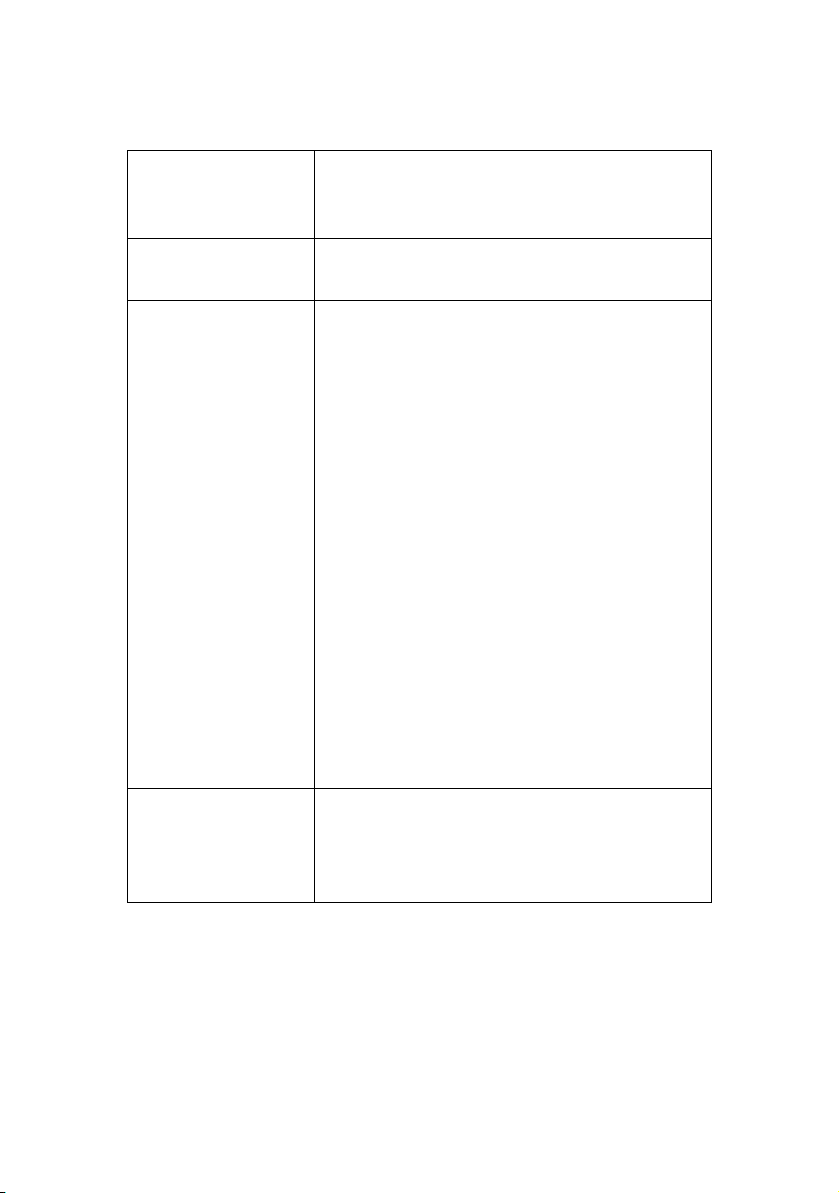
S
PECIFICATION
Frame Types IEEE 802.2
IEEE 802.3
Ethernet-II, SNAP, AUTO
Network Interface 100BASE-TX
10BASE-T
Network Protocols TCP/IP
Network layer ARP, RARP, IP, ICMP
Session layer TCP, UDP
Application layer LPR, FTP, TELNET, HTTP,
IPX/SPX (NetWare)
Remote printer mode (up to eight file
servers and 32 queues)
Print server mode over IPX/SPX (up to
eight print servers)
Encrypted password supported in print
server mode
SNMP
EtherTalk
E L AP, A AR P, DD P, AE P, NB P, ZI P, RT MP, AT P,
PAP
NetBEUI
SMB, NetBIOS, WINS
IPP, BOOTP, DHCP, SNMP,
DNS, SMTP, POP3, SLP,
Rendezvous
Functions Self-diagnostic test printing
Banner supported
Monitoring and configuration by Web browser
Printer status notification by E-Mail
S
ELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST
With the printer power switched on, press the push-button
located on the network interface panel (at the rear of the printer)
for more than three seconds and release. The self-diagnostic test
results and configuration settings are printed.
Network Configuration> 7
Page 8
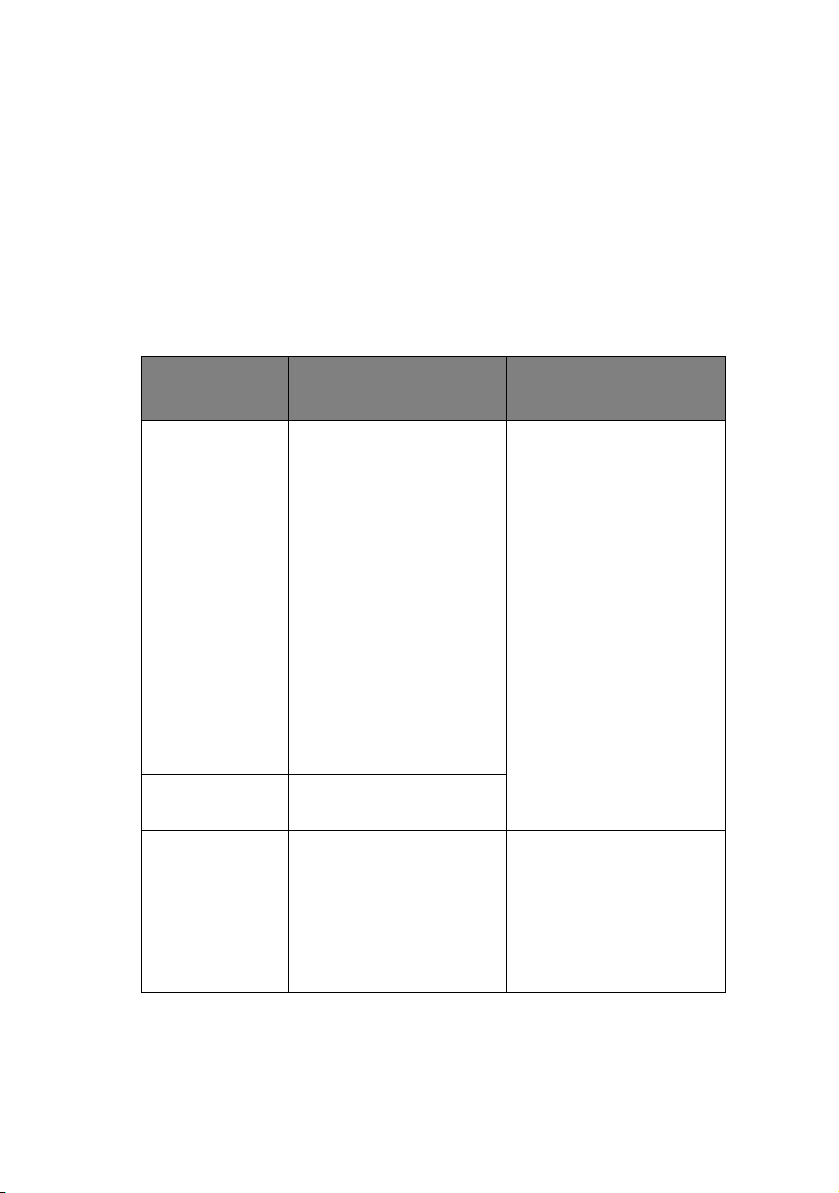
On the first page of the Network Information that is printed out,
under the heading “General Information” the MAC Address is
given. For example:
MAC Address 00808784E3F1
The Ethernet address is therefore: 00:80:87:84:E3:F1
C
ONFIGURATION UTILITIES
You can configure the network interface (NIC) by using one of the
following methods:
UTILITY FEATURES SYSTEM
REQUIREMENTS
Quick Setup Configure the NIC easily
and simply without
installing any software
packages into your
system. You can set the
following:
> Enable/disable TCP/IP,
NetWare, EtherTalk,
NetBEUI protocols.
> Set IP address, Subnet
Mask and Gateway for
TCP/IP manually or by
using DHCP.
> Set NetWare Mode and
create Queue/Print
Server/Printer objects.
> Zone name and Port
name for EtherTalk.
Admin
Manager
Configure the NIC in
detail.
Web Browser Configure the NIC and
printer by using a Web
browser such as
Microsoft Internet
browser or Netscape
Navigator.
Windows 2000/XP
(TCP/IP protocol or IPX/
SPX protocol should be
installed).
To create a NetWare
queue, NetWare Client
32 or IntraNetWare
Client should be
installed in your
system.
Microsoft Internet
Explorer Version 3.0
and higher or Netscape
Navigator Version 3.0
and higher.
Operating system that
supports Web browser.
Network Configuration> 8
Page 9
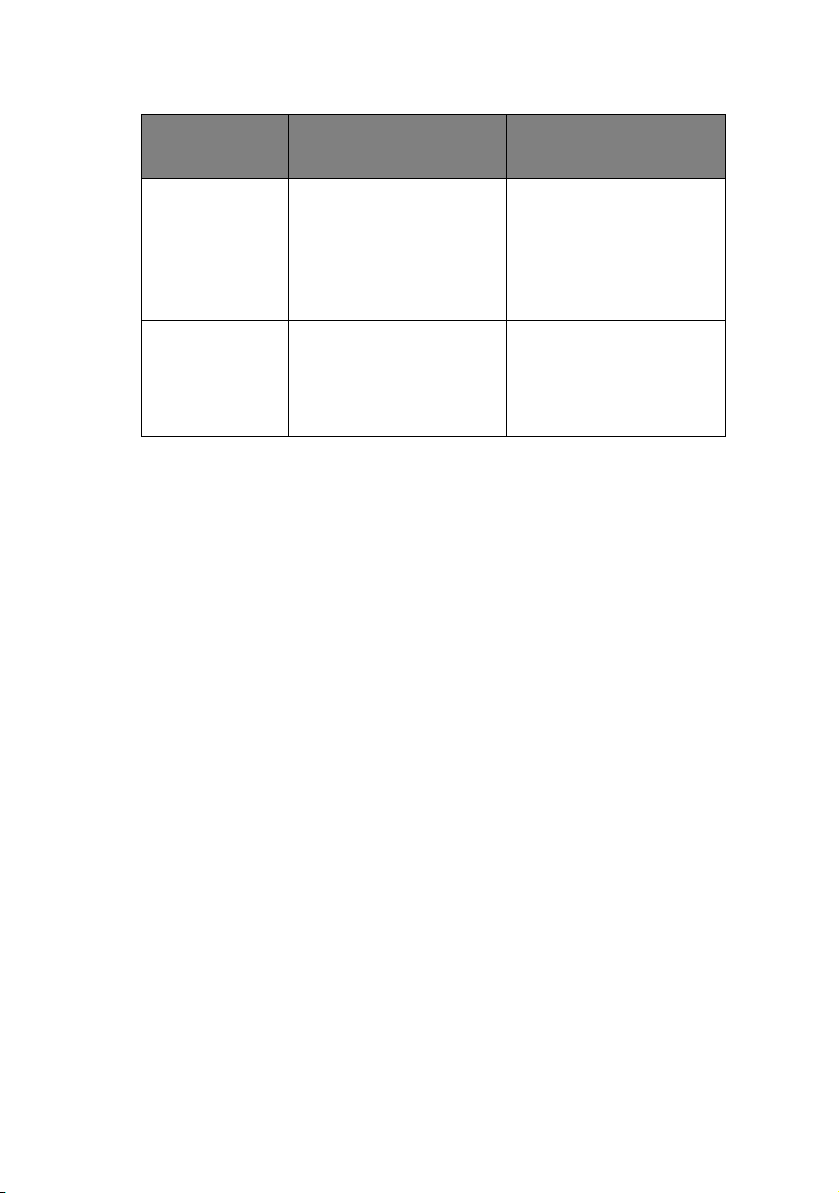
UTILITY FEATURES SYSTEM
REQUIREMENTS
Telnet Configure the NIC using
TELNET.
SNMP The printer and network
card can be controlled
using third-party
vendor developed SNMP
application.
U
SING QUICK SETUP
Third-party vendor
developed TELNET
client package.
A TELNET Application is
standard in Windows/
UNIX/Linux.
Third-party vendor
developed SNMP
application.
Quick Setup utility allows you to configure the network interface
easily and simply without installing any software packages.
You can configure the following:
> Enable/disable TCP/IP, NetWare, EtherTalk, NetBEUI
protocols.
> Set IP address, Subnet Mask and Gateway for TCP/IP
manually or by using DHCP.
> Set NetWare mode and create Queue/Print Server/Printer
objects.
> Zone name and Port name for EtherTalk.
Configuration requires a PC with Windows 2000 Advanced
Server/Professional or Windows XP running TCP/IP or IPX/SPX
(NetWare).
This utility can only be used on a PC that can be connected to the
network with TCP/IP or IPX/SPX.
This utility must be used on a PC that is located on the same
segment as the printer.
To create a NetWare queue, NetWare Client 32 or IntranetWare
Client should be installed in your system.
The following explanation uses Windows 98 as an example.
Network Configuration> 9
Page 10

1. Insert the Network Software CD-ROM into the CD-ROM
drive. The Setup Utility starts automatically. If it does not
start, double-click \setup.exe (in the root directory) on
the CD-ROM.
2. Select [Network Card Setup]—[Network Card Quick
Setup].
3. Select the appropriate language and follow the on-screen
instructions.
4. When the settings are correct, click [Execute]. The new
settings are transmitted to the network card but it still
operates with pre-transmission settings.
5. Click [Finish] to validate the new settings. The printer may
have to be switched off for 15 seconds and on again.
Network Configuration> 10
Page 11

U
SING ADMINMANAGER
AdminManager is a powerful Microsoft Windows-based utility to
configure all network interface functions easily and intuitively via
a graphical user interface.
Configuration requires a PC with Windows 2000 Advanced
Server/Professional or Windows XP running TCP/IP or IPX/SPX
(NetWare).
This utility can only be used on a PC that can be connected to the
network with TCP/IP or IPX/SPX and must be used on a PC that
is located on the same segment as the printer.
To create a NetWare queue, NetWare Client 32 or IntranetWare
Client should be installed on to your system.
I
NSTALLATION
1. Insert the Network Software CD-ROM into the CD-ROM
drive. The Setup Utility starts automatically. If it does not
start, double-click \autorun.exe (in the root directory)
on the CD-ROM.
2. Select [Network Card Setup].
3. Select [Network Card Standard Setup].
4. Select the appropriate language.
5. Follow the on-screen instructions. If you want to install
AdminManager on to your local drive, select [Install and
Execute]. Otherwise, select [Execute from CD-ROM].
6. To run AdminManager, check [Yes] for [Do you wish to
execute AdminManager?] and click [Finish]. Otherwise
check [No] and click [Finish].
Network Configuration> 11
Page 12
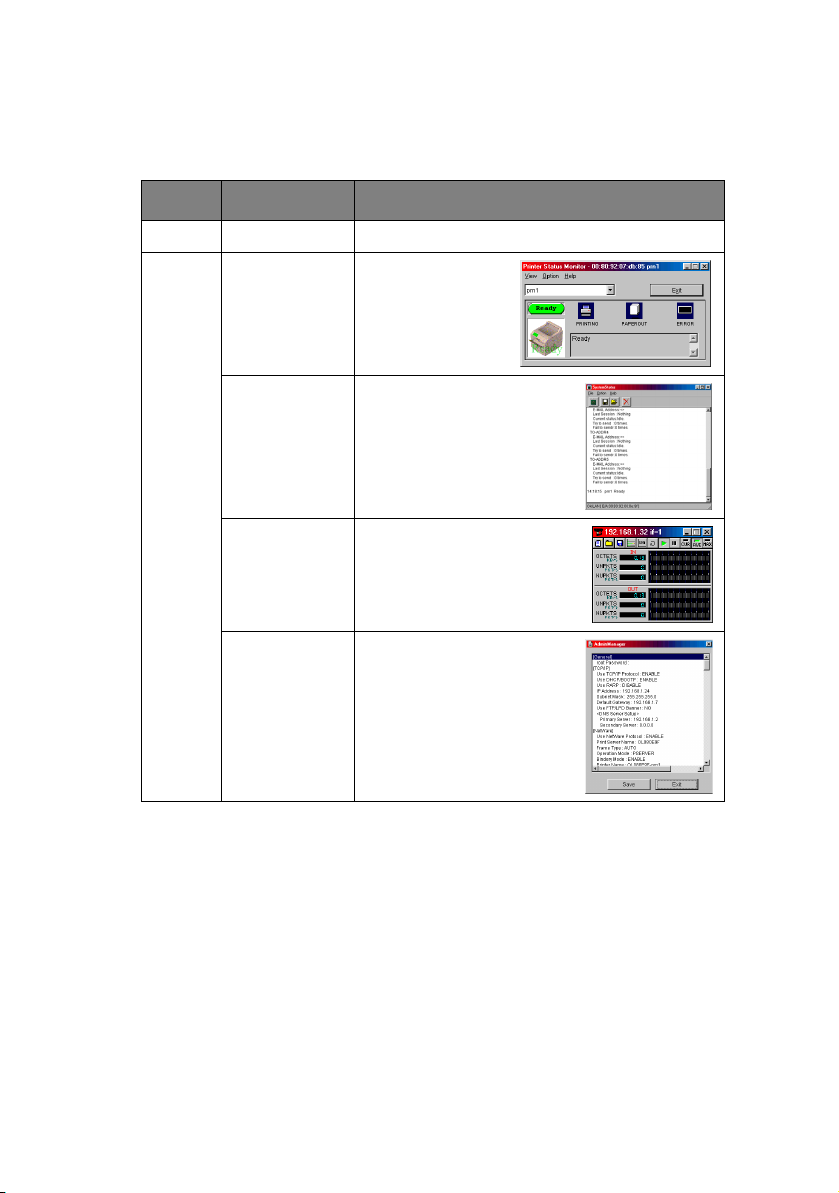
I
NTERFACE
Select [Start]-[Programs]-[Oki Setup Utility]-[Admin Manager].
MENU ITEM FUNCTION
File Search Search printers in your network.
Status Printer
Status
Current printer
status is
displayed:
System
Status
NetMeter Display current network
List of
Configuration
Items
Displays current
configuration.
Configuration data can be
saved as log file.
status. For further
information, see on-line
help file of NetMeter.
Displays current
configuration.
Configuration data can be
saved as log file.
Network Configuration> 12
Page 13
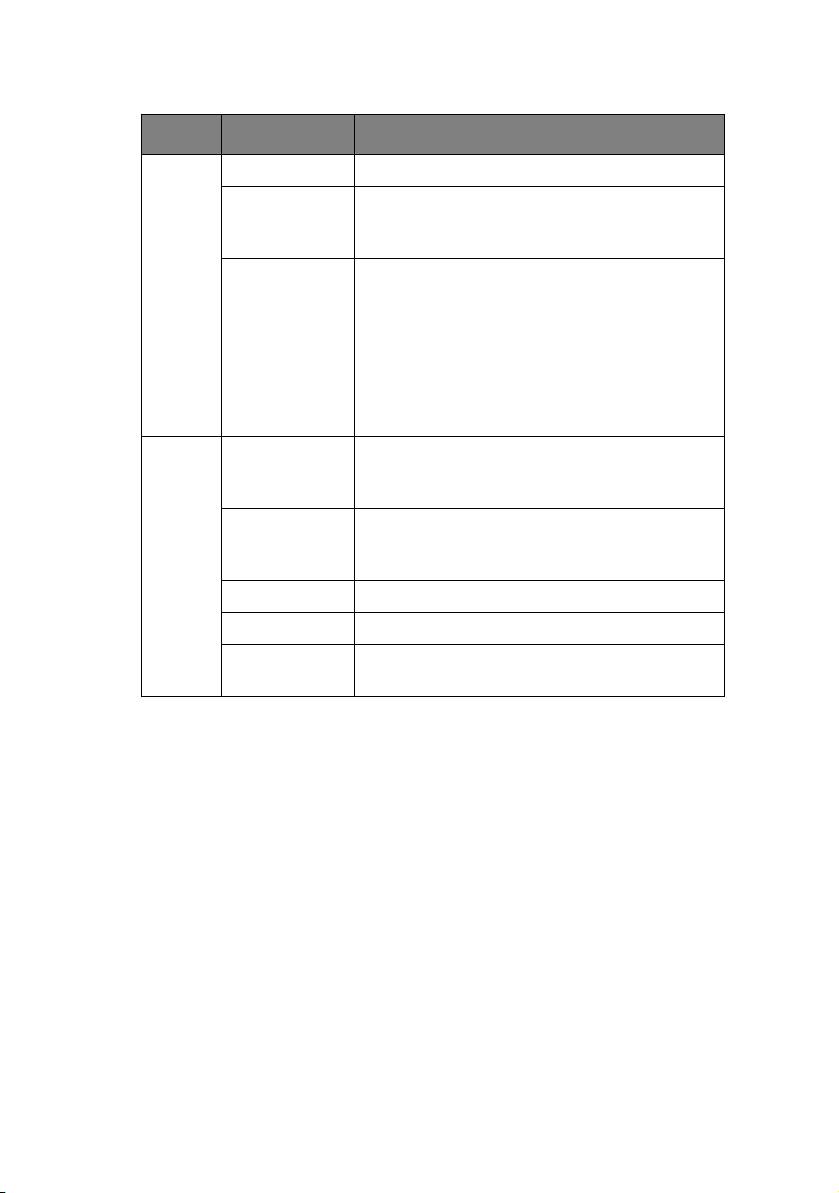
MENU ITEM FUNCTION
Setup Device Setup Configure the network interface.
Setup by
HTTP
Setup by
TELNET
Setup Create
NetWare
Queue
Delete
NetWare
Object
Reset Reset the selected network interface card.
Test Print Print self-diagnostic test pages.
IP Address
Setup
Launch the default browser in your
environment to access the selected
printer’s web page.
Launch TELNET application in your
environment to access the selected
printer’s TELNET port.
Note:The TELNET application is not
included as part of the NIC package.
Install the TELNET package on to
your system. For further information,
see your Windows manual.
Create a NetWare queue.
Delete NetWare object.
Set static IP address of network interface
card manually.
D
EVICE SETUP
Device Setup allows you to configure the network interface. Type
the root password (default value is the last 6 characters of the
MAC address) to configure. Remember that the root password is
case sensitive. If the MAC address contains any alpha characters,
type them as upper case. Device Setup contains details for the
following selectable tabs:
> General > SNMP
> TCP/IP > POP
> NetWare > SMTP
> NetBEUI > Maintenance
> EtherTalk
Network Configuration> 13
Page 14
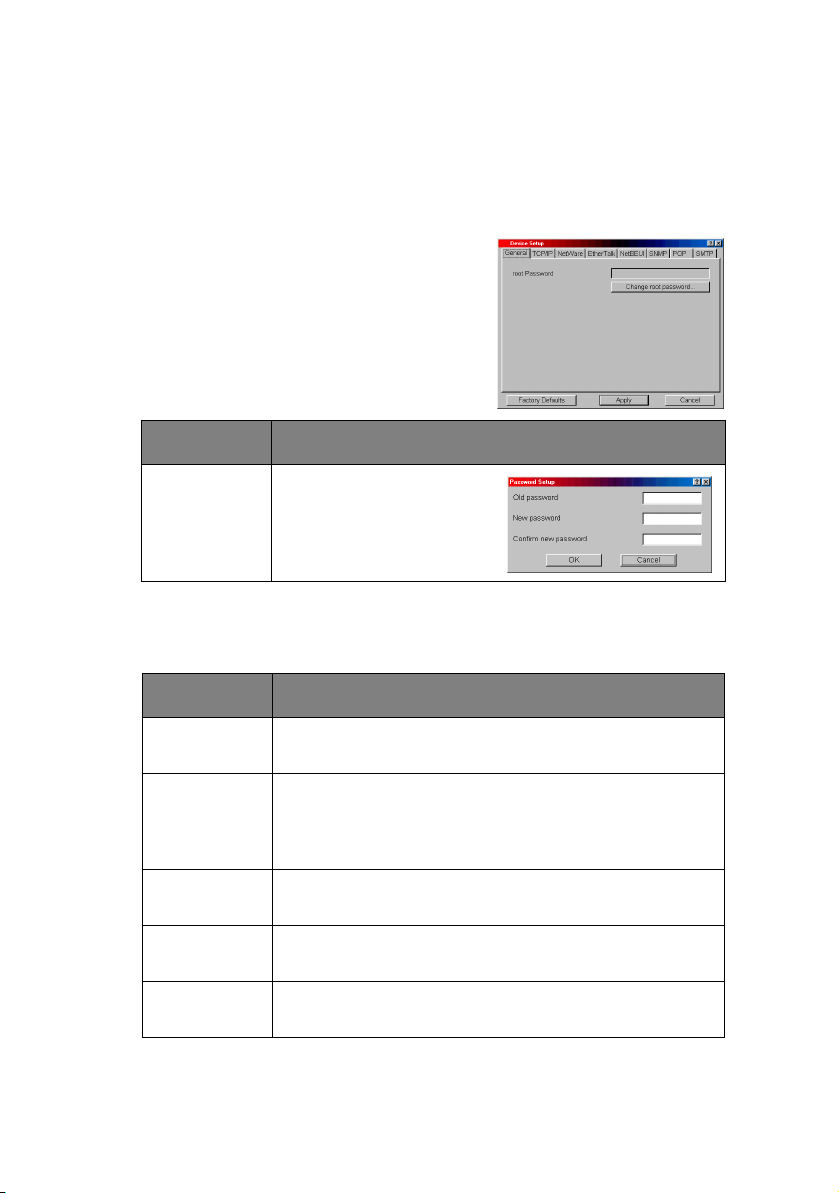
The following section explains each tab’s functionality.
Depending on your printer, some items in the following
explanation may not be displayed.
General Tab
This allows you to set or change the
root password used for Admin
Manager, TELNET and FTP.
ITEM EXPLANATION
Change root
password
You can set/change the
root password for
AdminManager, TELNET
and FTP.
TCP/IP Tab
This allows you to configure TCP/IP related items.
ITEM EXPLANATION
Use TCP/IP
Protocol
Use DHCP/
BOOTP
Use RARP Check this item if IP address is retrieved from the
IP Address Set the IP address of the selected network interface
Subnet Mask Set the subnet mask of the selected network
Set TCP/IP protocol as enabled/disabled.
Check this item if IP address, subnet mask, default
gateway and IP addresses for DNS primary server
and secondary servers are retrieved from the DHCP
or BOOTP server. Otherwise, uncheck.
RARP server. Otherwise, uncheck.
card.
interface card.
Network Configuration> 14
Page 15
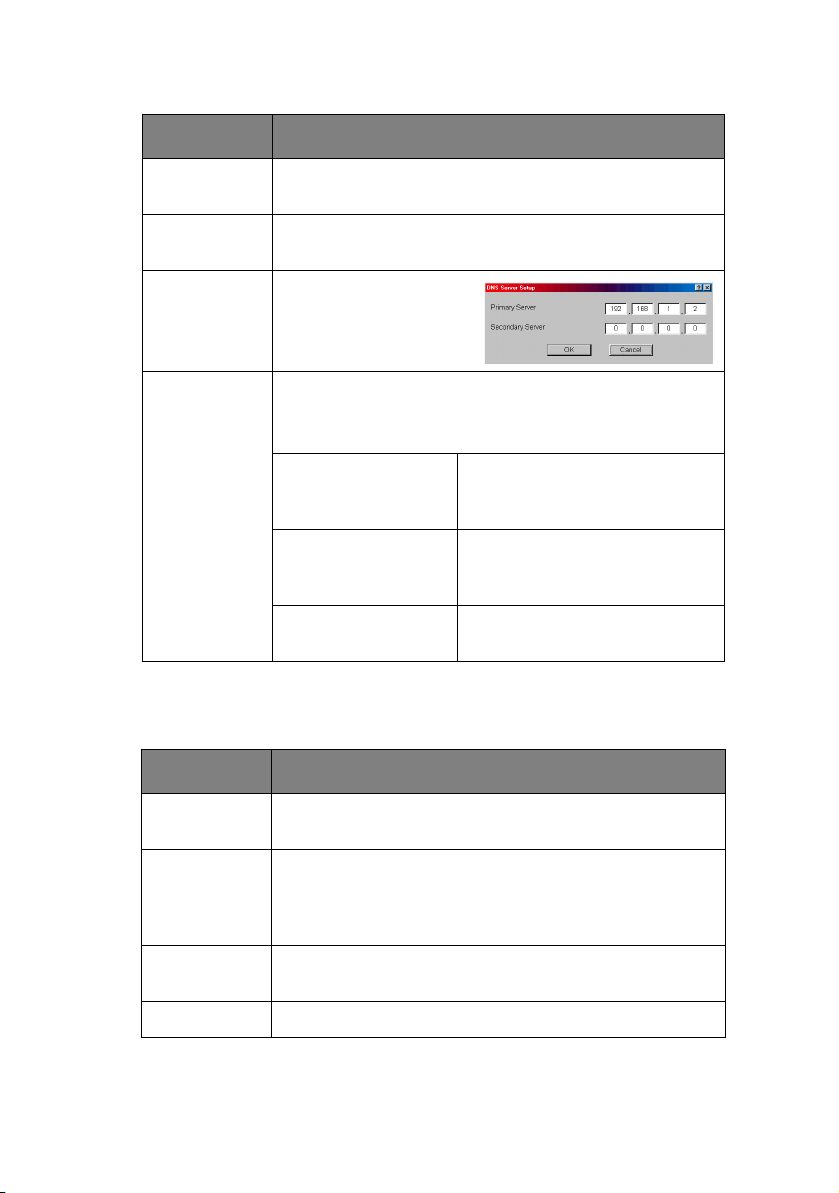
ITEM EXPLANATION
Default
Gateway
Use FTP/LPD
Banner
DNS Server… Set IP addresses for
Network PnP
Setup…
Set the default gateway of the selected network
interface card.
Check this item if you want to add the FTP/LPD
banner. Otherwise uncheck.
DNS primary and
secondary servers.
Configure items related to Network PnP.
In this dialogue box, the following items can be
configured:
Auto IP address Set to get IP address
dynamically by Auto IP,
enabled or disabled
Use Network PnP Set notifying users with using
UPnP supported OS of the
printer, enabled or disabled
Device Name Set the device name for
Network PnP
NetWare Tab
This is where you can configure NetWare related items.
ITEM EXPLANATION
Use NetWare
Protocol
Use IPX
Protocol /
Use TCP/IP
Protocol
Print Server
Name
Frame Type Set primary NetWare frame type.
Set NetWare protocol as enabled/disabled.
Set protocol to use.
Set Print Server name.
Network Configuration> 15
Page 16
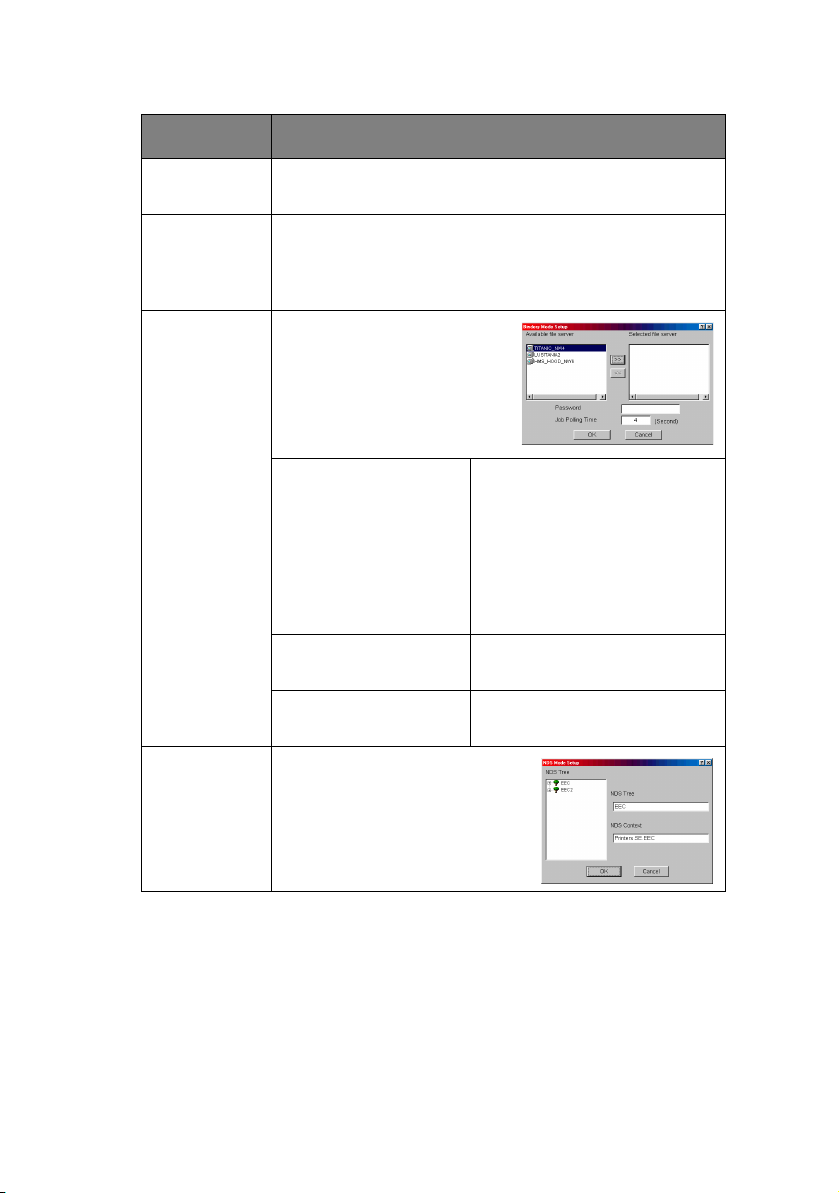
ITEM EXPLANATION
Operation
Mode
Check box
beside
Bindery
Setup
Bindery
Setup
Set NetWare mode.
Check if you want to use the Bindery mode and
Bindery Setup button becomes available. If it is
unchecked, the button is greyed out.
Configure items related to
Bindery mode.
In this dialogue box, the
following items can be
configured:
Available File Server
and Selected File
Server.
Select file servers to
connect. Up to eight file
servers can be selected.
Select a server from
[Available file server] list
and click >> button. The
server is copied to [Selected
file server] box.
Password. Set password for Print
Server.
Job Polling Time. Set print job polling interval
in seconds.
NDS Setup Set NDS tree and context
where Print Server was
created.
Network Configuration> 16
Page 17

ITEM EXPLANATION
RPRINTER
Setup
Available if you select
RPRINTER mode in
Operation Mode.
By selecting the [RPRINTER]
button, this is displayed:
NDS or Bindery Show the Available print
server tree in NDS mode or
Bindery mode.
Available print server
and Selected print
server
Select file servers to
connect. Up to eight file
servers can be selected.
Select a server from
[Available file server] list
and click >> button. The
server is copied to [Selected
file server] box.
Time Out Set duration from the last
data’s arrival to freeing of
the port in seconds.
Printer Name Set the NetWare printer object name.
Network Configuration> 17
Page 18

EtherTalk Tab
This allows you to configure EtherTalk related items.
ITEM EXPLANATION
Use
EtherTalk
Protocol
Printer Name Set EtherTalk Printer object name.
Zone Name Set the zone name to which the printer belongs.
Set EtherTalk
protocol to enabled/
disabled.
NetBEUI Tab
This allows you to configure NetBEUI related items.
ITEM EXPLANATION
Use NetBEUI
Protocol
Computer
Name
Workgroup Set a work group name to which the printer belongs.
Comment Set the comments for the printer.
Set NetBEUI protocol to enabled/disabled.
Set a computer name for the printer.
WINS
Server…
Configure items related to the WINS Server.
In this dialogue box, the following items can be
configured:
Primary Server Set WINS Primary server.
Secondary
Server
Scope ID Set a Scope ID.
Network Configuration> 18
Set WINS Secondary server.
Page 19

SMTP Tab
This allows you to configure SNMP related items.
ITEM EXPLANATION
Authentic
Community
TRAP
Community
TRAP
Address
SysContact Set SysContact (printer manager) name.
SysName Set SysName (printer model name).
SysLocation Set SysLocation (the location where the printer is
Default TTL Set TTL (Time To Live) value.
Enable
Authentic
Tra p
This community name
is used to check
whether incoming
SNMP requests have
the correct community
name or not. The
community name is
displayed as ******
for security reasons.
This community name is assigned to outgoing system
traps such as cold start, authentication failure, etc.
Set a destination IP address of a Trap packet. If
0.0.0.0 is set, the Trap is disabled.
installed).
Set Authentic Trap to enabled/disabled.
Network Configuration> 19
Page 20
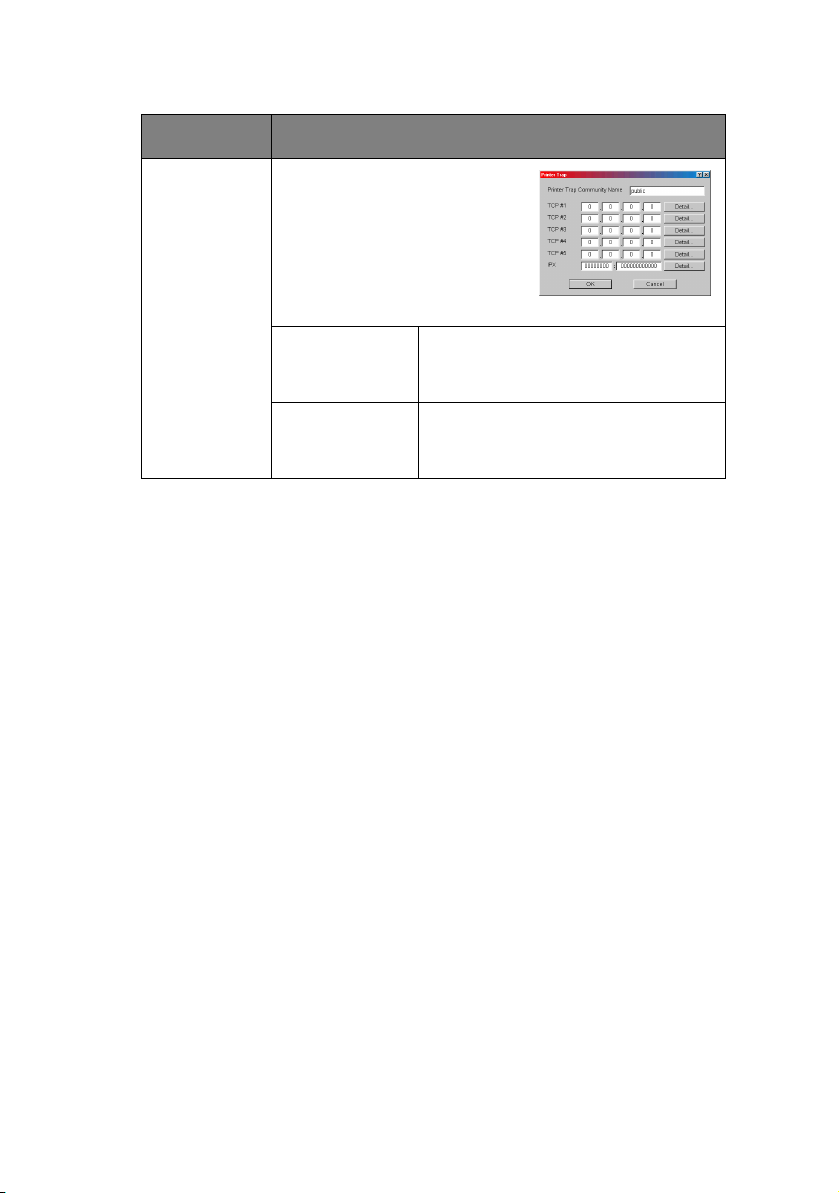
ITEM EXPLANATION
Printer Trap
Setup…
By selecting the button, the
following dialogue box is
displayed:
In the dialogue box, the
following items can be
configured:
Printer Trap
Community
Name
This community name is assigned
to outgoing printer status traps
such as off-line, paper out, etc.
TCP#1–5 Set the IP addresses to which a
Trap packet will be sent. You can
set up to five IP addresses.
Network Configuration> 20
Page 21
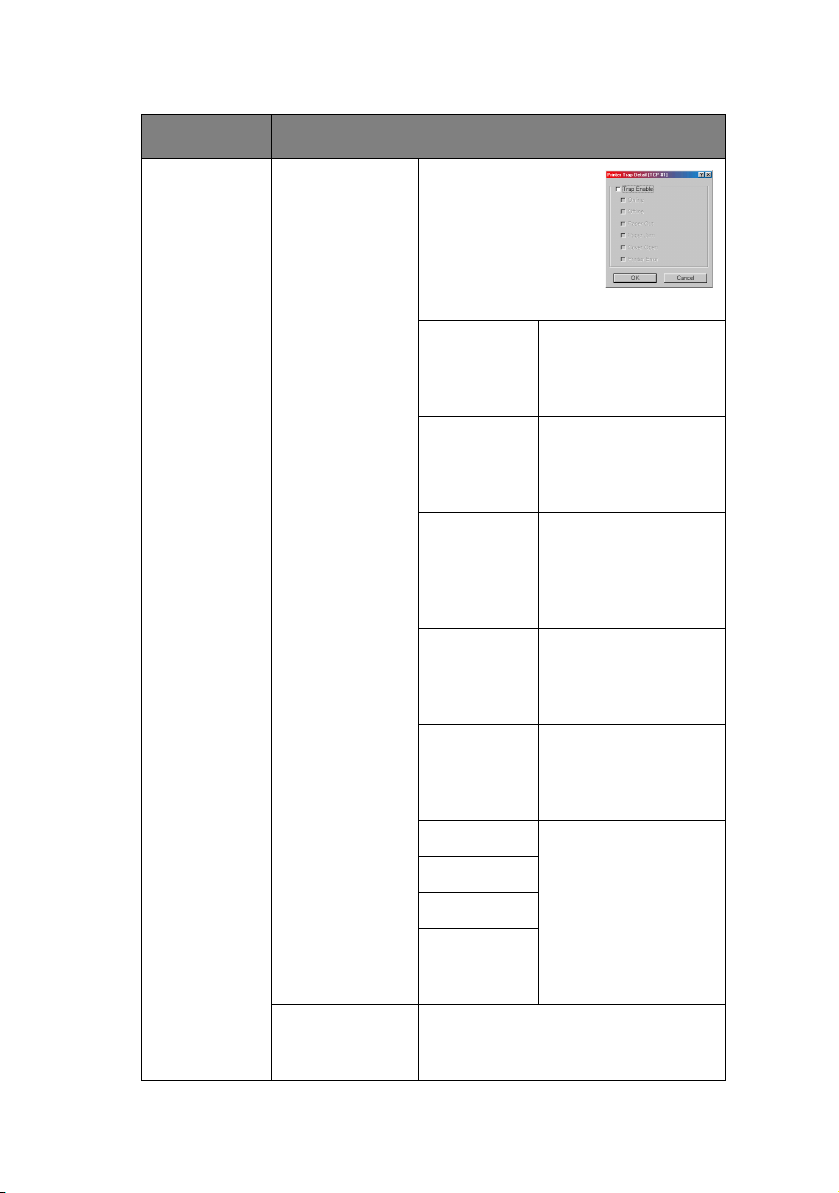
ITEM EXPLANATION
Printer Trap
Setup…
(continued)
Detail… By selecting the
button, the
following dialogue
box is displayed:
In the dialogue box,
the following items
can be configured:
Trap Enable Set sending a Trap
packet, enabled or
disabled, for each
destination.
Printer
Reboot
Set sending a Trap
packet, enabled or
disabled, when the
printer is rebooted.
Receive
Illegal
Set sending a Trap
packet, enabled or
disabled, when the
printer receives an
illegal Trap packet.
On-line Set sending a Trap,
enabled or disabled,
when the printer
turns to ON-LINE.
Off-line Set sending a Trap,
enabled or disabled,
when the printer
turns to OFF-LINE.
Paper Out Set sending a Trap,
Paper Jam
Cover Open
enabled or disabled,
when any of these
conditions occur.
Printer
Error (any
error)
IPX Set node address and network
address to which a Trap packet will
be sent.
Network Configuration> 21
Page 22
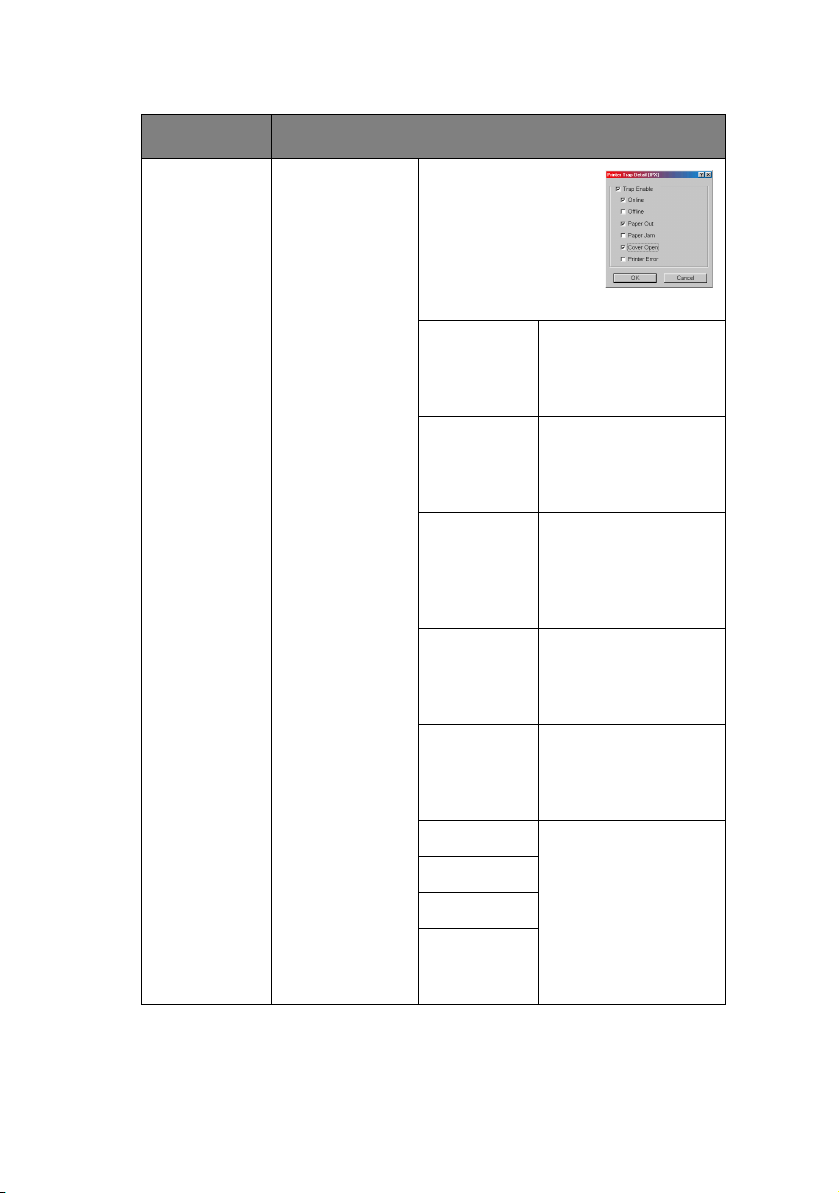
ITEM EXPLANATION
Printer Trap
Setup…
IPX
Detail…
By selecting the
button, the
following dialogue
box is displayed:
In the dialogue box,
the following items
can be configured:
Trap Enable Set sending a Trap
packet, enabled or
disabled, for each
destination.
Printer
Reboot
Set sending a Trap
packet, enabled or
disabled, when the
printer is rebooted.
Receive
Illegal
Set sending a Trap
packet, enabled or
disabled, when the
printer receives an
illegal Trap packet.
On-line Set sending a Trap,
enabled or disabled,
when the printer
turns to ON-LINE.
Off-line Set sending a Trap,
enabled or disabled,
when the printer
turns to OFF-LINE.
Paper Out Set sending a Trap,
Paper Jam
Cover Open
Printer
Error (any
error)
Network Configuration> 22
enabled or disabled,
when any of these
conditions occur.
Page 23

POP Tab
This allows you to configure POP related items.
ITEM EXPLANATION
Use POP3
Protocol
POP3 Server
Address/
Name
POP3 Port
Number
POP3 Server
UserID
POP3 Server
Password
Use APOP Check if you want to use APOP.
POP3
Interval
Set retrieving E-Mail
via POP3, enabled or
disabled.
Set IP address or host name of POP3 server.
Set port number of POP3.
Set User ID for POP3 server.
Set password for POP3 server.
Set interval to retrieve E-Mail(s) from POP3 server.
Set to OFF if you do not want to use POP3 function.
Some printers support an email reception function (SMTP/POP3)
allowing the printer to print PDF and text files attached to emails.
If the POP tab is not displayed, your printer does not support this
function.
Network Configuration> 23
Page 24

SMTP Tab
In SMTP Tab, you can configure SMTP related items.
ITEM EXPLANATION
Use SMTP
Tra nsm i t
Protocol
Use SMTP
Receive
Protocol
SMTP Server
Address/
Name
Reply-To
Address
E-Mail
Address
Set sending EMail via SMTP,
enabled or
disabled.
Set receiving E-Mail via SMTP, enabled or disabled.
Set IP address or host name of SMTP server.
Set the E-Mail address that is used in the [Reply-To]
field in the mail header.
Set the E-Mail address that is used in the [From] field
in the mail header.
Network Configuration> 24
Page 25
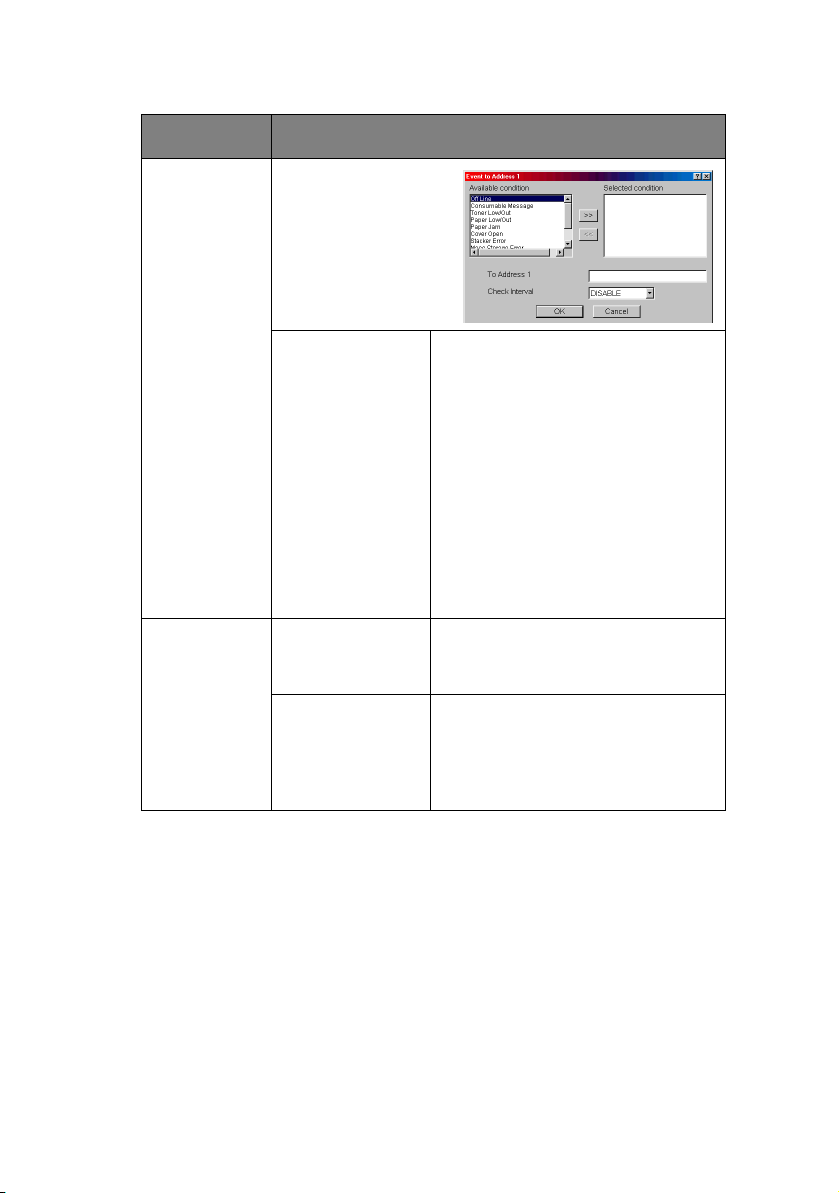
ITEM EXPLANATION
1–5 By selecting each
button, the following
dialogue box is
displayed:
In the dialogue box,
the following items
can be configured:
Available
condition and
Selected
condition.
Select each E-Mail alert
condition.
Select a condition from Available
Condition list and click >>
button. The selected condition is
copied to Selected condition list.
Available conditions are:
Off line, Consumable Message,
Toner Low/Out, Paper Low/Out,
Paper Jam, Cover Open, Stacker
Error, Mass Storage Error,
Recoverable Error, Service Call
Request and Finisher Error.
1–5 To Address 1–5 Set E-Mail addresses to which E-
Mail should be sent. Up to five EMail addresses can be set.
Check Interval Set interval that the printer
checks specified event(s). An EMail is sent when specified
event(s) occurs when DISABLE is
selected.
Network Configuration> 25
Page 26
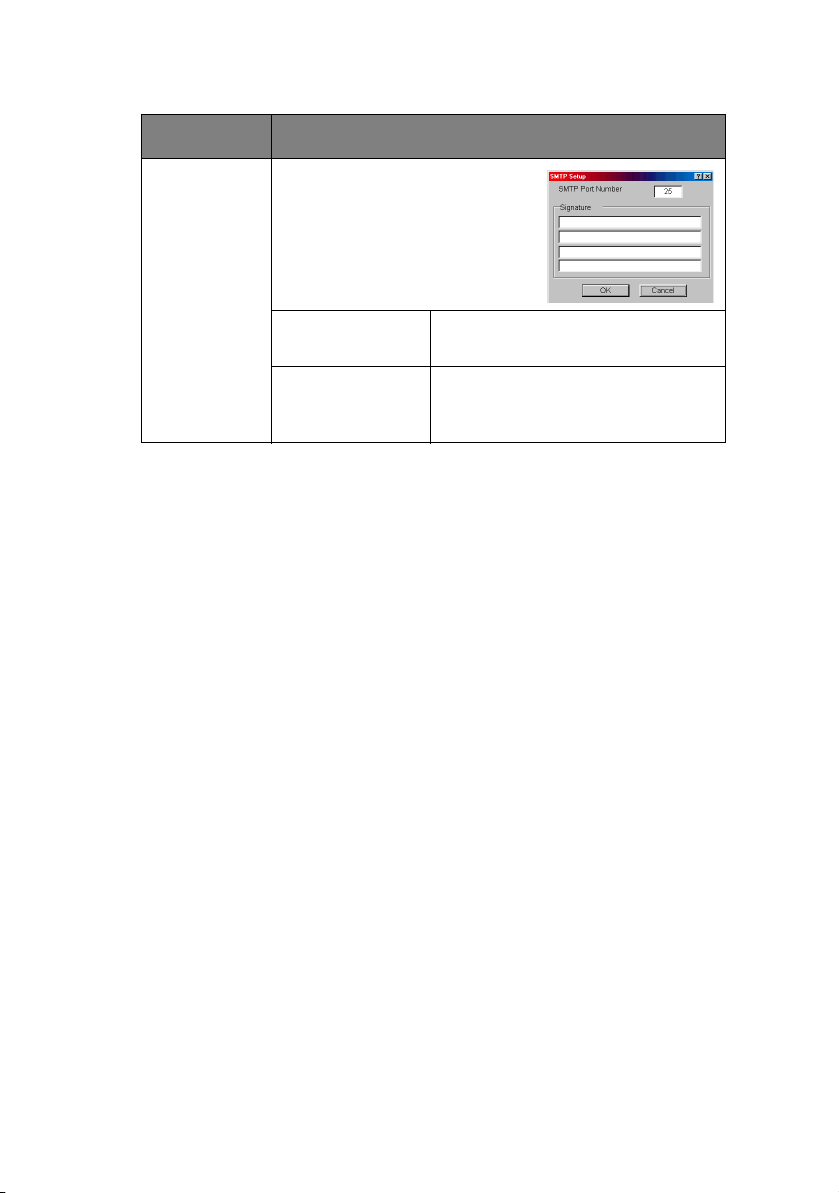
ITEM EXPLANATION
Advanced… By selecting the button, the
following dialogue box is
displayed:
In the dialogue box, the
following items can be
configured:
SMTP Port
Set port number of SMTP.
Number
Signature Set up to four signature lines.
Signatures added to the bottom
of an E-Mail.
Network Configuration> 26
Page 27

C
REATE A NETWARE QUEUE
By selecting this item, you can create a NetWare queue on the
NetWare server from AdminManager.
> NetWare Client 32 or IntranetWare Client should be
loaded on the PC on which the AdminManager runs. Also
the client package should be configured to access
NetWare NDS network or bindery network.
> You should log in to NetWare servers as a user who can
create objects on the servers. If you want to create a
queue with the remote printer mode on NetWare 4.1, you
should select NDS mode. You cannot create a queue if
Bindery mode is selected.
1. Select [Create NetWare Queue] from the [Setup] menu.
2. Select [Next] button.
3. Select either [NDS mode] or [Bindery] mode depending
on your network environment.
Network Configuration> 27
Page 28
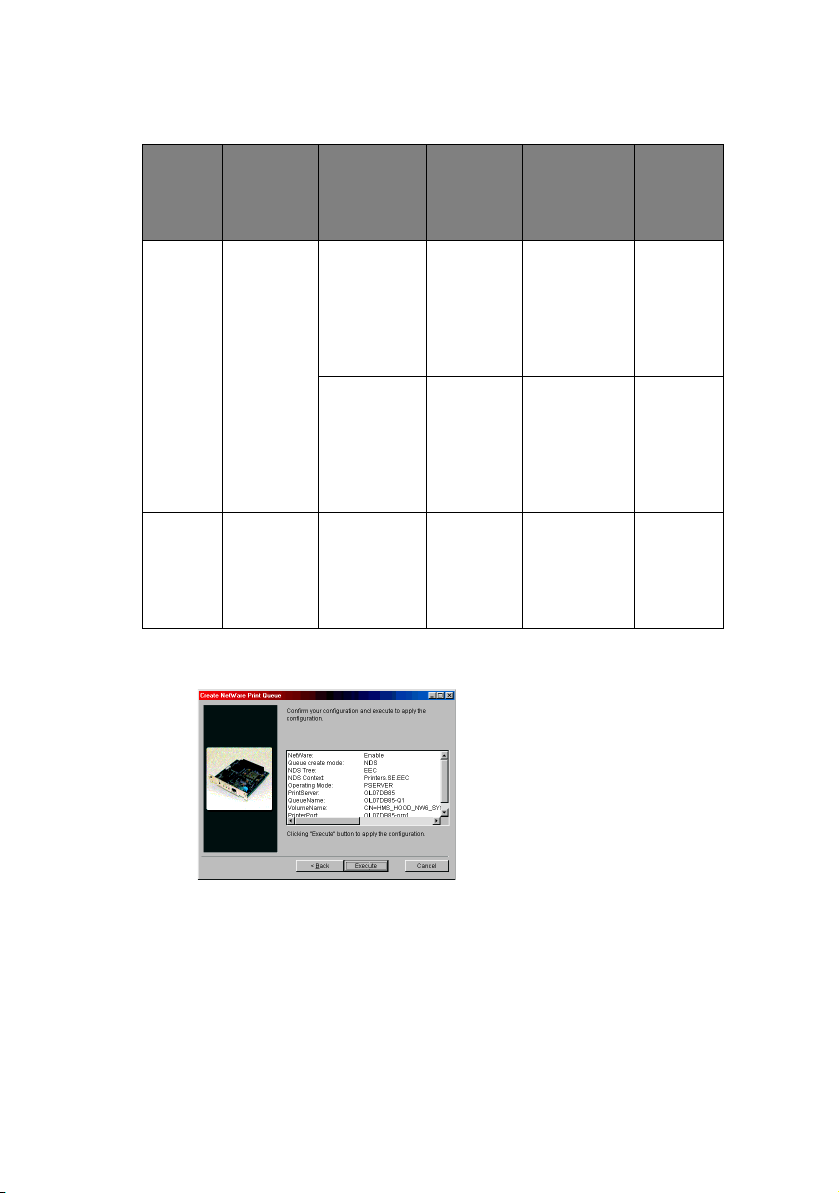
4. Follow the on-screen instructions.
MODE
NDS Context
LOCATION
should be
specified.
PSERVERORRPRINTER
PSERVER
mode
PRINT
Current
Print
Server
name is
used.
SERVER
QUEUE
Set queue
name and
its volume
for the
queue
creation.
RPRINTER
mode
Select
existing
Print
Server.
Set queue
name and
its volume
for the
queue
creation.
Bindery File server
should be
specified.
PSERVER
mode only
Current
Print
Server
name is
Set queue
name for
the queue
creation.
used.
5. Confirm your configuration. If it is correct, select
[Execute].
PRINTER
Current
Printer
name is
used.
Current
Printer
name is
used.
Current
Printer
name is
used.
6. Select [Finish] button. If necessary, select [Setup]—
[Device Setup] and continue your configuration.
Network Configuration> 28
Page 29
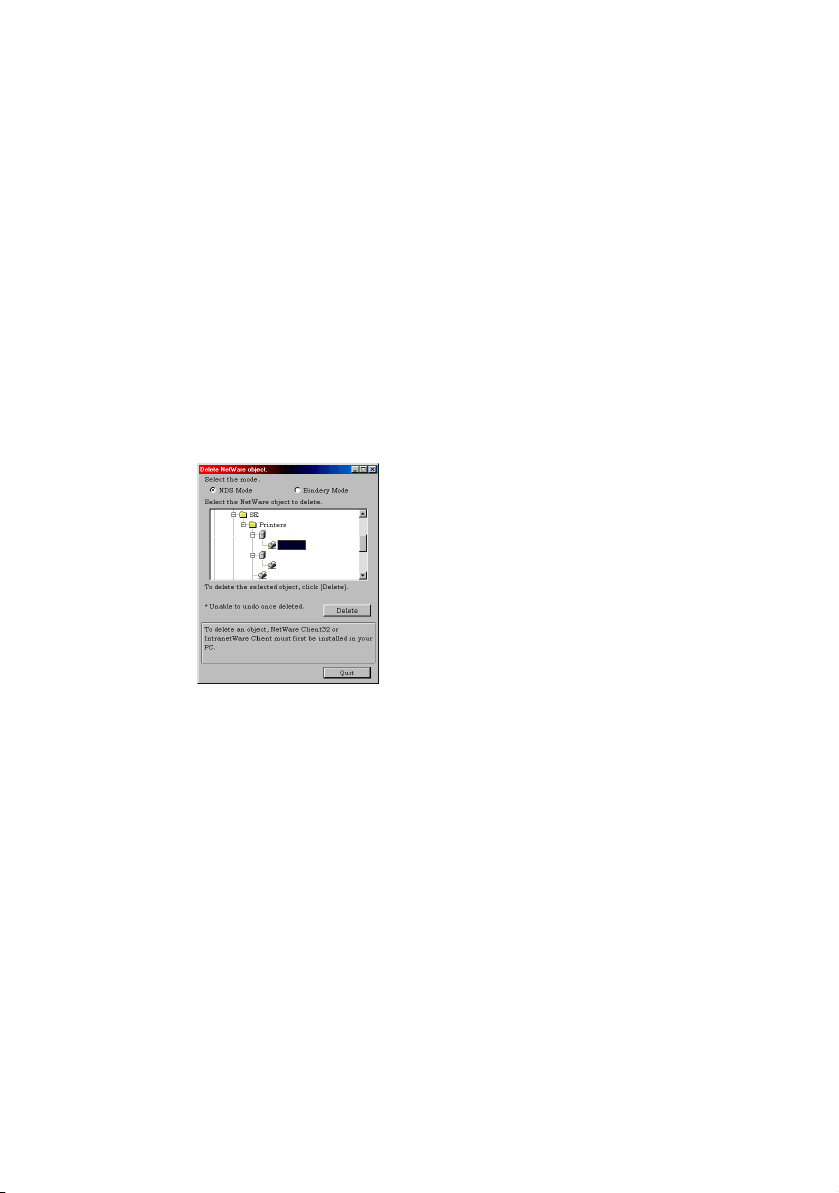
D
ELETE NETWARE OBJECT
By selecting this item, you can delete a NetWare queue/print
server/printer from NetWare server via AdminManager.
> NetWare Client 32 or IntranetWare Client should be
loaded on to the PC on which the AdminManager runs.
Also, the client package should be configured to access
NetWare NDS network or bindery network. You should
login to NetWare servers as a user who can delete objects
on the servers.
1. Select [Delete NetWare Object] from [Setup] menu.
2. Select an object you want to delete and click [Delete]
button.
3. To exit from this dialogue box, select [Quit].
Network Configuration> 29
Page 30

IP A
DDRESS SETUP
If you only use TCP/IP and the printer has not yet been
configured, occasionally it may not be displayed on
AdminManager. You can configure the IP address of the printer
by this function.
1. Select [IP Address Setup] from the [Setup] menu.
2. Set [Ethernet Address] and [IP Address] and select [OK].
> The Ethernet Address (MAC address) is displayed during
the self-diagnostic test.
3. AdminManager asks if you want to initialise the network
interface card or not. Select [Yes].
Network Configuration> 30
Page 31

O
PTION MENU
In the [Option] menu, the following item can be selected:
ITEM EXPLANATION
Use TCP/IP
Protocol
Use IPX/SPX
Protocol
Environment
Setup
If this item is selected, AdminManager uses TCP/IP
protocol to search/configure network interface cards.
If this item is selected, AdminManager uses IPX/SPX
protocol to search/configure network interface cards.
TCP/IP Tab
Set broadcast addresses that are
used to search printers using the
TCP/IP protocol. If [Use TCP/IP
protocol] is unchecked, the
search will not be carried out
using TCP/IP.
NetWare Tab
Set network addresses that are
used to search printers via
NetWare protocol. If there any
many NetWare file servers on
your network, specify the
network address to which the
network card belongs. If [Use
NetWare protocol] is unchecked,
the search will not be carried out
using NetWare, but if [Auto
Search] is selected, AdminManager will search all
networks that AdminManager can detect.
TimeOut Tab
[Search Every]: Set response
waiting time from a network card
in seconds.
[Time Out]: Set time out
between AdminManager and the
network interface card in
seconds.
[Retry]: Set how many times the retry will be carried
out between AdminManager and the network
interface card.
Network Configuration> 31
Page 32

H
ELP MENU
In the [Help] menu, [About] is available as well as revision
information for AdminManager.
U
SING A WEB BROWSER
If the printer is connected to the network using TCP/IP, its
settings and the printer menu settings can be configured using a
Web browser, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer Version 3.0 and
higher, or Netscape Navigator version 3.0 and higher. No
guarantees are offered for other browsers. Refer to the relevant
manuals for details of how to launch and use the browser.
M
ICROSOFT INTERNET EXPLORER
1. Select [Internet Options] in the [Tools] menu.
2. Click on the [General] tab and click [Settings] in
[Temporary Internet files].
3. Select [Every visit to the page] in [Check for newer
versions of stored pages].
N
ETSCAPE NAVIGATOR
1. Select [Settings] in the [Edit] menu.
2. Click [Cache] in [Details].
3. Select [Once per session] in [Document in cache is
compared to document on network].
4. If you change the window size of the browser immediately
after changing the configuration, the [Security
information] may be displayed. Uncheck [Display this
message next time] in the dialogue.
5. After making changes, click [Submit].
Network Configuration> 32
Page 33

D
EFAULT USER NAME AND PASSWORD
To apply configuration changes using a Web browser, you will be
prompted for a username and password. The username is [root]
and the default password is the last six characters of the Ethernet
(MAC) address (any alpha characters must be in upper case).
The root password can be changed to allow you to configure the
printer by using a Web browser/TELNET/AdminManager. To
change the root password, select “Password Configuration” in the
Maintenance tab and follow the on-screen instructions.
A
DJUSTING PRINTER SETTINGS
The network addresses used in this manual are shown as
examples only. Network addresses used in your installation must
be generated from your own network.
1. Configure the IP Address, Subnet Mask and Gateway for
the network card. Launch the Web browser, enter the IP
Address of the network interface card in [Address
(Location/Position)] and press the [Enter] key. The Printer
Status screen is displayed.
2. Select a tab and items to be changed in the left frame.
You need to log in as “root” to be able to configure all
items. Non-root users cannot configure all items.
3. To ensure correct operation, follow the procedure below
for the appropriate network browser.
Network Configuration> 33
Page 34

U
SING
TELNET
The printer can be configured using TELNET. TELNET requires the
printer to have a valid IP address configured. If the printer
already has an IP address configured, skip steps one to three
below.
CAUTION!
Please ensure a valid IP address for your network
environment is used. Use of an incorrect IP address can
cause serious problems on your network.
The following explanation uses Sun Solaris 2.4 as an example.
The method of configuring commands may differ between
workstations. Refer to the workstation’s manual.
1. Log in as [root].
If you do not have Superuser rights, the network manager
should run the configuration.
2. Set a temporary IP Address on the NIC using the ARP
command.
Example: for IP address 192.168.20.127 and network card
address 00:80:87:01:00:D2
# arp –s 192.168.20.127 00:80:87:01:00:D2 temp
The Ethernet address (MAC address) is displayed during
the self-diagnostic test. A temporary address does not
need to be set if an IP address has already been set.
3. Use the PING command to confirm the connection with
the network card.
Example: for IP address 192.168.20.127
# ping 192.168.20.127
If there is no reply, there is a problem with the
configuration of the IP address (the IP address has been
already set manually or dynamically), or with the network.
Reset the network interface card settings to default and try
to set temporary IP address. If you still have the problem
after resetting the network interface card, consult the
network manager.
Network Configuration> 34
Page 35

4. Login to the network card using TELNET.
Example: for IP address 192.168.20.127
$ telnet 192.168.20.127
Trying 192.168.20.127
Connected to 192.168.20.127
Escape character is ‘^]’.
EthernetBoard 8100e Ver 01.50 TELNET server.
login: root
‘root’ user needs password to login.
password:
User ‘root’ logged in.
No. Message Value (level.1)
------------------------------------
1: Setup TCP/IP
2: Setup SNMP
3: Setup NetWare
4: Setup EtherTalk
5: Setup NetBEUI
6: Setup printer trap
7: Setup SMTP (E-Mail)
8: Setup POP (E-Mail)
9: Maintenance
10: Setup printer port
11: Display status
12: IP Filtering Setup
97: Network Reset
98: Set default (Network)
99: Exit setup
Please select (1-99)?
5. Enter the number of the items to be changed and the
details screen for that item is displayed. The menu has a
hierarchical structure as follows.
Network Configuration> 35
Page 36

T
ELNET HIERARCHICAL STRUCTURE
LEVEL 1 LEVEL 2 LEVEL 3
1: Setup TCP/IP 1: TCP/IP protocol
2: Setup SNMP 1: SysContact
.
2: IP address
3: Subnet Mask
4: Default Gateway
5: RARP protocol
6: DHCP/BOOTP
protocol
7: Auto IP Address
8: DNS server(Pri.)
9: DNS server(Sec.)
10:Root password
11:Auto Discovery
Setup
99:Back to prior
menu
2: SysName
3: SysLocation
99:Back to prior
menu
1: Network PnP
2: Rendezvous
3: Printer Name
99:Back to prior
menu
Network Configuration> 36
Page 37

LEVEL 1 LEVEL 2 LEVEL 3
3: Setup NetWare 1: NetWare protocol
2: Protocol
3: Frame Type
4: Printer Name
5: NetWare Mode
6: Setup PSERVER
(IP)
1: NDS Tree
2: NDS Context
3: Print Server Name
4: Password
5: Job Polling Time
99:Back to prior
menu
7: Setup PSERVER
(IPX)
1: NDS Tree
2: NDS Context
3: Print Server Name
4: Password
5: Job Polling Time
6: Bindery mode
7: File Server 1–
8: File Server 8
9: Job Timeout
99:Back to prior
menu
8: Setup RPRINTER
(IPX)
1: Print Server 1–
8: Print Server 8
9: Job Timeout
99: Back to prior
menu
Network Configuration> 37
Page 38

LEVEL 1 LEVEL 2 LEVEL 3
4: Setup EtherTalk 1: EtherTalk
protocol
2: Printer Name
3: Zone name
99:Back to prior
menu
5: Setup NetBEUI
1.NetBEUI Protocol
2.Computer name
3.Workgroup name
4.Comment
5.Setup WINS
1: WINS Server (Pri.)
2: WINS Server
(sec.)
3: Scope ID
99:Back to prior
menu
99:Back to prior
menu
Network Configuration> 38
Page 39

LEVEL 1 LEVEL 2 LEVEL 3
6: Setup printer trap 1: Prn-Trap
Community
2: Setup TCP#1
trap –
6: Setup TCP#5
trap
1: TCP#1–5 Trap
Enable
2: Printer Reboot
Trap
3: Receive Illegal
Trap
4: Online Trap
5: Offline Trap
6: Paper Out Trap
7: Paper Jam Trap
8: Cover Open Trap
9: Printer Error Trap
10:TCP#1–5 Trap
Address
99:Back to prior
menu
7.Setup IPX Trap
1: IPX Trap Enable
2: Printer Reboot
Trap
3: Receive Illegal
Trap
4: Online Trap
5: Offline Trap
6: Paper Out Trap
7: Paper Jam Trap
8: Cover Open Trap
9: Printer Error Trap
10:IPX Trap Address
11:IPX Trap Net
99:Back to prior
menu
—
Network Configuration> 39
Page 40

LEVEL 1 LEVEL 2 LEVEL 3
7: Setup SMTP (E-
Mail)
1: SMTP Transmit
2: SMTP Receive
3: SMTP server
name
4: SMTP port
number
5: E-Mail address
6: Reply-to address
7: Dest. address 1–
12:Dest. address 5
1: To Address 1—5
2: Notify Mode
3: Check time (hours)
4: Consumable
Warning
5: Consumable Error
6: Maintenance
Warning
7: Maintenance Error
8: Paper warning
9: Paper Error
10:Printing Warning
11:Printing Error
12:HDD/Flash
Memory
13:Print Result
Warning
14:Print Result Error
15:Other Error
16:Interface Warning
17:Interface Error
Network Configuration> 40
Page 41

LEVEL 1 LEVEL 2 LEVEL 3
8: Setup SMTP (E-
Mail)
13:Additional Info 1: Printer Model
2: Network Interface
3: Serial Number
4: Asset Number
5: System Name
6: System Location
7: IP Address
8: Ethernet Address
9: Computer Name
10:Printer URL
99:Back to prior
menu
14:Comment line –
16:Comment line 4
99:Back to prior
menu
9: Maintenance 1: Web Service
2: Web (IPP) Port
No.
3: Telnet Service
4: FTP Service
5: SNMP Service
6: LAN Scale
7: Default TTL
99:Back to prior
menu
Network Configuration> 41
Page 42

LEVEL 1 LEVEL 2 LEVEL 3
10:Setup printer
port
1: BOJ String
2: EOJ String
3: BOJ
String(KANJI)
4: EOJ
String(KANJI)
5: Printer Type
6: TAB Size (char.)
7: Page Width
(char.)
8: Page Length
(line)
9: FTP/LPR Banner
99:Back to prior
menu
11:Display status 1: prn1
2: Network
3: Version
99:Back to prior
menu
12:IP Filtering Setup 1: IP Filtering
2: IP Address range
1 –
11:IP Address range
10
1: Start Address
2: End Address
3: Printing
4: Configuration
99:Back to prior
menu
12:Admin IP
Address
99:Back to prior
menu
97:Network Reset
98:Set default
(Network)
Network Configuration> 42
Page 43

LEVEL 1 LEVEL 2 LEVEL 3
99:Exit setup
6. When configuration is complete, select [Exit Setup] to save
your change. To exit without saving your modification,
select [Quit].
7. Turn the printer off and on again.
The network card continues to use pre-transmission
settings until the printer is turned off and back on again.
Network Configuration> 43
Page 44

U
SING
SNMP
The printer and network card can be managed via a standard
SNMP management station. The network card supports SNMPv1,
MIB-II and Private MIB. In order for the printer to be managed
correctly from an SNMP management station, the Private MIB
needs to be added to that management station. Please refer to
the SNMP manager documentation for information on how to do
this.
The Private MIB file can be found in the MIB folder on the Network
Software CD-ROM. Please refer to the readme file in the MIB
folder for further information.
The printer’s trap address can be set in five places using TCP/IP
and in one place with IPX.
Printer trap settings can be made with TELNET and a Web
browser.
Network Configuration> 44
Page 45

M
ANAGEMENT UTILITY
PrintSuperVision is a web-based application for managing
printing devices connected to a network. It consists of two parts:
A web application based on Microsoft web server (Internet
Information Server, IIS or Personal WEB Server, PWS), that
provides the user interface.
A monitoring program (PrintSuperVisor) that runs all the time,
collecting data and saving it in a database for statistical reports
and sending E-Mail alerts based on the saved configuration.
PrintSuperVision requires the .NET environment to be installed
on the PC on which it runs. The supplied installer will install this
if necessary.
PrintSuperVision’s main functions are:
> Maintaining the list of printing devices and organising
them in logical groups.
> Initially discovering and configuring printers connected to
the network.
> Locating printers visually on maps.
> Monitoring devices over time and saving data for
statistical reports.
> Sending email alerts when events occur that affects the
functionality of printers.
> Statistical reports about usage of printers.
— P
RINTSUPERVISION
> Tracking maintenance data related to printers.
> Identifying part numbers of consumable items for use
with your printer.
> PrintSuperVision can even manage printers on another
network provided a copy of PrintSuperVision is also
running on that network.
Network Configuration> 45
Page 46

S
YSTEM REQUIREMENT
Windows
The main PrintSuperVision application can be installed in any of
the following Windows systems.
OPERATING
SYSTEM
Windows 2003
Server
1. Web Edition
2. Standard Edition
3. Enterprise
Edition
4. Datacenter
Edition
SERVICE
PACK
1
IIS
IIS 6.0 included
in the OS.
1. IIS 6.0
installed by
default
2, 3, 4. IIS 6.0
optionally
installed (in the
CD)
MDAC AND
.NET
FRAMEWORK
.Net
Framework 1.1
installed as
part of the OS.
Network Configuration> 46
Page 47

OPERATING
SYSTEM
SERVICE
PACK
IIS
1
MDAC AND
.NET
FRAMEWORK
Windows XP
Professional
Windows 2000
Professional
Windows 2000
Server / Advanced
Server /
Datacenter Server
Windows XP Home 1.0 Works only with
1. An Embedded Web Server option is provided which does not require IIS
1.0 IIS installed as
an option.
Available in the
Windows XP
CD.
Install IIS
before
installing .Net
framework.
2.0 Internet
Service
Manager
included in the
OS. Available
in the Windows
2000 CD.
Install IIS
before
installing .Net
framework.
PSV Embedded
Web Server,
available in the
PSV Install
Package.
MDAC and .Net
Framework
available for
download from
Microsoft.
MDAC 2.7 and
.Net
Framework
Versio n
1.0.3705
included as
part of PSV
install.
Supported Browsers
The browsers supported are:
> Internet Explorer (IE) 4.01 and above.
> Netscape Navigator 4.0 and above.
> Opera 5.12 and above.
The PrintSuperVision application can be accessed from any
Windows, Macintosh, Unix, and Linux desktop that support any of
the above-mentioned browsers.
Network Configuration> 47
Page 48

While all the above browsers are supported, PrintSuperVision
works best when used with Internet Explorer. When using the
Netscape browser, do not select the option [Images off]. The
hyperlinks may not work properly. Some versions of Netscape
browser do not display the frames properly, and the [Back]
button may not work correctly.
Supported Printers
PrintSuperVision provides general management information for
printers connected to the network.
While the printer properties are displayed in PrintSuperVision,
only a few of the printer settings can be set. For setting any other
printer settings, a hyperlink to the printer’s web page is provided
in PrintSuperVision.
I
NSTALLING PRINT SUPERVISION
This section describes installing Print SuperVision from the
supplied CD-ROM.
NOTE:
WindowsXP/2000 requires administrator privileges.
1. Insert the Network Software CD-ROM into the CD-ROM
drive. The Setup Utility starts automatically. If it does not
start, double-click \setup.exe on the CD-ROM.
2. Select [Software Utilities].
3. Select [Install PrintSuperVision].
4. Follow the on-screen instructions. In the [Edit Data]
screen, you can specify a port number for
PrintSuperVision (default 80).
5. When installation ends, the [Setup complete] screen is
displayed. Click [Finish].
6. Now you should select [Start]-[Programs][PrintSuperVision]-[PrintSuperVision] or double-click the
[PrintSuperVision] icon on the desktop for the
PrintSuperVision server.
7. For PrintSuperVision client, access [http://[server IP
address or host name]/PrintSuperVision] from the Web
browser. If you change the port number you should add
Network Configuration> 48
Page 49

[:[port number]] such as [http://192.168.20.127/
PrintSuperVision:8080].
8. PrintSuperVision has an on-line help facility.
U
NINSTALLATION
To uninstall PrintSuperVision, either select [Start]-[Programs][PrintSuperVision]-[Uninstall PrintSuperVision], or from [Control
Panel], select [Add/Remove Programs], select [PrintSuperVision]
from the index window and click [Add/Remove]. When the
uninstallation is completed, close [Add/Remove Programs].
Network Configuration> 49
Page 50

P
RINTING UTILITY
The LPR Utility is a utility that allows printing data to printers
connected to the network via TCP/IP. This utility is for use with
Windows XP, Windows 2000, NT4.0.
The utility is for those printers which support TCP/IP and redirects
printing data to the lpr port of the specified IP address.
S
YSTEM REQUIREMENT
Windows XP/2000/NT4.0/Windows Server 2003 with TCP/IP
support and printers that support TCP/IP.
TO
INSTALL THE
The LPR utility requires that the TCP/IP protocol should be
installed into your Windows system. To install the TCP/IP protocol
into your Windows system consult your Windows manual.
NOTE:
Windows XP/2000 requires administrator privileges.
1. Set up the printer driver by designating the output
destination to [Local Printer (LPT1:)]. For information on
setting up your printer driver, see the printer user
manual.
2. Insert the Network Software CD-ROM into the CD-ROM
drive. The Setup Utility starts automatically. If it does not
start, double-click setup.exe on the CD-ROM.
3. Select [Software Utilities].
4. Select [Install LPR].
— M
LPR
ANUFACTURERS
UTILITY
’ LPR
5. Follow the on-screen instructions.
6. Click [Next] when the [Welcome] screen is displayed.
7. Verify [Destination Folder] and [Spool Folder] and click
[Next].
8. Check [Register in Startup] if you want automatic startup
as Windows boots up. Check [Launch as minimized] if you
want to startup in the Icon state and click [Next].
9. Verify the program folder name and click [Next]. The
installation starts.
Network Configuration> 50
Page 51

10. When the installation ends, the [Setup complete] screen
is displayed. Check [Yes, I want to launch the LPR Utility
now] and click [Finish]. Check [Yes, I want to view the
ReadMe File] if you want to read [Readme]. The LPR
utility starts.
11. You may be asked whether it is OK to change write
permissions for the spool directory. Click [Yes] to allow
the utility to be correctly installed.
12. Select [Add Printer] on the [Remote Print] menu.
13. Click [Discover…] to search for the IP address of a suitable
printer on your network.
14. Highlight the printer you will use and click [OK].
15. If your printer is not discovered, click [Cancel] and you
can type the IP address directly at [IP Address:].
16. Enter an IP address at [IP Address] and click [OK]. A
printer is added to the main window.
Refer to the On-line Help for information on how to use the utility.
U
NINSTALLATION
1. Stop the LPR Utility.
2. Select [Start]-[All Programs].
3. Click [Yes] when the [Confirm File Deletion] dialogue is
displayed. Deletion of the LPR utility starts.
4. When the deletion has finished, the [Uninstall Complete]
screen is displayed. Click [OK].
If a file that has been added after installation exists in the folder
to install the LPR utility or the folder to spool, you cannot delete
the folder. Delete any unwanted files before running [Uninstall
LPR Utility].
Network Configuration> 51
Page 52

M
ICROSOFT
O
VERVIEW
This chapter provides guidelines on how to print over the network
from various Microsoft Windows platforms. There are numerous
ways of printing from Windows and the exact set-up will vary
depending upon your environment. There are also numerous
versions of Windows, which can be configured as either a client,
server or both.
Although there are many variants of Windows, the principles of
network printing are the same. Microsoft provides on-line help
with all of their operating systems and this is a good reference
point for the exact details of each configuration option within
Windows.
The network printer supports the following protocols that can be
used in conjunction with the Windows operating system:
> TCP/IP
> IPX (Novell NetWare)
> NetBEUI
I
NSTALLATION OF
There are a number of options available when printing using TCP/
IP for Windows. The following table lists the options:
W
INDOWS
TCP/IP
PROTOCOL
WINDOWS VERSION METHOD
Windows 2000 or Windows XP Manufacturers’ LPR Utility
Microsoft LPR
Port 9100
IPP
The LPR Utility is supplied on the Networking CD-ROM with your
printer. The other methods are built into Windows and displayed
as options when using the Add Printer Wizard.
Although there are some differences in configuration options
between the various Windows platforms, the procedure for
printing using TCP/IP is the same.
Microsoft Windows> 52
Page 53

1. Ensure that the TCP/IP protocol has been installed in
Windows. This can be confirmed by checking the network
settings from within the Control Panel. If TCP/IP has not
been installed refer to the section below Installation of
TCP/IP protocol.
2. If not already configured, a suitable IP address, Subnet
Mask and Gateway address should be configured. Please
refer to the on-line help if necessary. It is vital that the IP
address entered is unique and valid. Entering an incorrect
IP address may cause severe network problems. Please
check the address with the network administrator.
3. If your network environment uses domain names, DNS
should be enabled and configured on your system.
However, this step is not essential to enable network
printing.
4. Restart the operating system.
W
INDOWS
2000
1. Click the [Start] button, select [Settings] and then click
on [Network and Dial-up Connections].
2. Double-click the [Local Area Connection] icon. In the
[Local Area Connection Status] dialogue box, click the
[Properties] button.
3. If the TCP/IP protocol is not listed, in the [Local Area
Connection Properties] dialogue box, click the [Install]
button.
4. In the [Select Network Component Type] dialogue box,
select [Protocol] and click the [Add] button.
5. In the [Select Network Protocol] dialogue box, select
[TCP/IP Protocol] and click the [OK] button.
6. Click the [Close] button in the [Local Area Connection
Properties] dialogue box.
7. Click the [Close] button in the [Local Area Connection
Status] dialogue box.
W
INDOWS
XP
1. Click the [Start] button and select [Control Panel].
Microsoft Windows> 53
Page 54

2. Select [Network and Internet Connection] and [Network
Connection].
3. Double-click [Local Area Connection] and click
[Properties] in the [Location Area Connection Status]
dialogue box.
4. If the [Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)] is not listed, click
[Install…] button.
5. In the [Select Network Component Type] dialogue box,
select [Protocol] then click the [Add] button.
6. In the [Select Network Protocol] dialogue box, select
[Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)] then click [OK].
7. The Windows XP installation CD-ROM may be required.
Follow the remaining dialogue box prompts.
Once the protocol has been installed and configured in Windows,
the next step is to configure the TCP/IP parameters in the
network printer.
N
ETWORK PRINTER
Use the Standard Set-up Utility to configure the IP Address,
Subnet Mask and Gateway.
NOTE:
Some steps may not display depending on the network
protocols installed.
1. Connect the printer to the network and turn on.
2. Place the Network Software Utilities disk in the CD-ROM
drive. The set-up utility starts automatically. If the set-up
utility does not start, double-click on setup.exe in the
Windows folder of the CD-ROM.
IP
ADDRESS CONFIGURATION
3. Select [Network Card Set-up].
4. Select [Network Card Quick Set-up].
5. Click [Next] at Welcome screen.
6. If you agree to the User Licence Agreement, click [Next].
7. Select the appropriate network card, using the Ethernet
address to identify it, and click [Next].
Microsoft Windows> 54
Page 55

The Ethernet address of the printer can be found on the
self-diagnostic printout, which can be printed by pressing
the push-button on the network card panel for three
seconds and then releasing it.
Using TCP/IP protocol
When using lpr in UNIX and other TCP/IP environments,
please select [Yes]. To use in a TCP/IP environment, an IP
address should be assigned to the Ethernet card.
If [Yes] has been selected and TCP/IP is the only working
protocol and the IP address has not already been assigned,
you can either obtain an IP address automatically or assign
an IP address.
When [Obtain an IP address automatically] is selected, the
device IP address will be automatically assigned by the
DHCP server. In an environment without a DHCP server,
please assign the IP address manually.
If you are assigning an IP address, you need to enter:
• An IP address
• Subnet mask
• Gateway address.
8. Click [Next].
Using NetWare protocol
Consult your network manager to ensure that the NetWare
file server is properly installed and working on the network.
Ma ke su re th at Ne tWar e Cli ent32 or I ntranetWare Client is
installed on your computer.
On selecting [Yes] you will be asked if [You set-up the
queue from the Wizard]?
Using EtherTalk protocol
EtherTalk is the required protocol for printing data from the
Macintosh environment.
Using NetBEUI protocol
Using NetBEUI makes it easy to manage your Oki product
and print within the network environment of Windows.
9. Confirm your configuration. If everything is correct, click
[Execute] to apply the configuration.
10. Set-up has now been completed. Click [Finish].
Microsoft Windows> 55
Page 56

Now that both Windows and the printer have been configured to
use TCP/IP, the next step is to configure Windows to print to the
network printer.
W
INDOWS
2000
NOTE:
Windows 2000 requires administrator privileges.
With Windows 2000, there are four options for printing using
TCP/IP.
> Manufacturers’ LPR
> Microsoft LPR
> Port 9100
> IPP
Manufacturers’ LPR
Please follow the procedure described on page 50.
Microsoft LPR
NOTE:
In order to use Microsoft LPR, it must first be installed on your
system.
To install this port, proceed as follows:
1. Select [Start], [Settings], [Control Panel and Printers].
2. Open the [Printers] folder.
3. Double-click [Add Printer] and then select [Next].
4. Select [Local Printer], clear the [Automatically detect my
printer] check box, and then select [Next].
5. Select [Create a new port] and then [LPR Port].
6. Select [Next] and then provide the following information:
(a) In [Name or address of server providing LPD] enter
the host name or Internet Protocol (IP) address of
the host for the printer you are adding.
(b) In [Name of printer or print queue on that server]
type "lp".
Microsoft Windows> 56
Page 57

(c) Follow the instructions on the screen to finish
installing the TCP/IP printer.
Port 9100
1. Select [Start], [Settings], [Control Panel].
2. Open the [Printers] folder.
3. Double-click [Add Printer] and then select [Next].
4. Select [Local Printer], clear the [Automatically detect my
printer] check box and then click [Next].
5. Select [Create a New Port] and select [Standard TCP/IP
Port].
6. Select [Next].
7. The [Welcome to the Add Standard TCP/IP Printer Port
Wizard] will appear.
8. Select [Next] and provide the following information. Enter
[Printer name] or IP address, for example: 192.168.1.31.
If the above IP address is entered, the Port Name will
default to IP_192.168.1.31.
9. Select [Next]. Additional port information will be required.
10. Under [Device Type], select [Custom] then [Settings].
11. Ensure [Protocol] is set to [Raw].
12. Ensure [Port Number] is 9100 and [SNMP Status Enabled]
is deselected.
13. Select [OK].
14. Select [Follow the instructions on the screen to finish
installing the printer.]
IPP
1. Select [Start], [Settings], [Control Panel and Printers].
2. Open the [Printers Folder].
3. Double-click [Add Printer] and then select [Next].
4. Select [Network Printer].
5. Select [Next].
Microsoft Windows> 57
Page 58

6. Type printer URL in text box labelled [Connect to a printer
in the Internet or your Intranet], e.g. http://
192.168.1.31/ipp/ip].
7. Select [Next].
8. Install printer driver.
W
INDOWS
XP
NOTE:
Windows XP requires administrator privileges.
With Windows XP, there are four options for printing using TCP/
IP:
> Manufacturers’ LPR
> Microsoft LPR
> Port 9100
> IPP
Manufacturers’
LPR
Please follow the procedure described on page 50.
Microsoft LPR
To install this port, proceed as follows:
1. Select [Start], [Settings], [Control Panel]. and [Printers
and Other Hardware].
2. Select [Printers and Faxes].
3. Click [Add Printer] and then select [Next].
4. Select [Local printer attached to this computer], clear the
[Automatically detect and install my Plug and Play printer]
check box, and then select [Next].
5. Select [Create a New Port] and [Type Standard TCP/IP
Port].
6. Select [Next].
The [Welcome to the Add Standard TCP/IP Printer Port
Wizard] will appear.
7. Select [Next] and provide the following information. Enter
[Printer name or IP address], for example: 192.168.1.31.
Microsoft Windows> 58
Page 59

If the above IP address is entered, the Port Name will
default to IP_192.168.1.31.
8. Select [Next]. [Additional Port Information Required] is
displayed.
9. Under [Device Type], select [Custom] then [Settings].
10. Ensure [Protocol] is set to [LPR].
11. Ensure [Queue Name] is "lp" and [SNMP Status Enabled]
is deselected.
12. Select [OK].
13. Follow the instructions on the screen to finish installing
the printer.
Port 9100
1. Select [Start], [Settings], [Control Panel]. and [Printers
and Other Hardware].
2. Select [Printers and Faxes].
3. Click [Add Printer] and then select [Next].
4. Select [Local printer attached to this computer], clear the
[Automatically detect and install my Plug and Play printer]
check box, and then select [Next].
5. Select [Create a New Port] and select [Type Standard
TCP/IP Port].
6. Select [Next].
The [Welcome to the Add Standard TCP/IP Printer Port
Wizard] will appear.
Select [Next] and provide the following information. Enter
[Printer name or IP address], for example: 192.168.1.31. If the
above IP address is entered, the Port Name will default to
IP_192.168.1.31.
7. Select [Next]. [Additional Port Information Required] is
displayed.
8. Under [Device Type], select [Custom] then [Settings].
9. Ensure [Protocol] is set to [Raw].
Microsoft Windows> 59
Page 60

10. Ensure [Port Number] is 9100 and [SNMP Status Enabled]
is deselected.
11. Select [OK].
12. Follow the instructions on the screen to finish installing
the printer.
IPP
1. Select [Start], [Settings], [Control Panel]. and [Printers
and Other Hardware].
2. Select [Printers and Faxes].
3. Click [Add Printer] and then select [Next].
4. Select [A network printer, or a printer attached to another
computer].
5. Select [Next].
6. Select [Connect to a printer on the Internet or on a home
or office network] and type printer URL in text box, e.g.
http://192.168.1.31/ipp/ip.
7. Select [Next].
8. Install printer driver.
N
OVELL NETWARE
IPX is used with Novell NetWare. The printer supports Novell 3,
4, 5 and 6, and allows print jobs to be directed to the appropriate
Novell print queue. Please refer to the relevant section of this
manual for additional information.
IPX
NETBEUI P
NetBEUI is a protocol that was designed for use on small
workgroups or LANs. Within Windows, NetBEUI is used for file
and printer sharing between computers. It provides a simple
method of printing but the protocol does have limitations and is
not as robust as TCP/IP or IPX. Typically it is employed in small
or home networks.
ROTOCOL
Microsoft Windows> 60
Page 61

N
ETWORK PRINTER SETTINGS
There are two configurable items under NetBEUI within the
printer. These can be configured using the standard set-up utility
described in Chapter 1.
COMPUTER NAME NAME ASSIGNED TO THE PRINTER
Workgroup
Comment User definable description
1. Although the workgroup name can be changed, it is recommended
that it remains as PrintServer.
PrintServer
1
Although there are some differences in configuration options
between the various Windows platforms, the procedure for
printing using NetBEUI is the same.
Please ensure the NetBEUI protocol has been installed in
Windows. This can be confirmed by checking the network
settings. If NetBEUI has not been installed please refer to the
section below.
The relevant Windows installation CD-ROM may be required and
you should follow the on-screen dialogue box prompts.
W
INDOWS
2000
1. Click the [Start] button, select [Settings] and then click
on [Network and Dial-up Connections].
2. Double-click the [Local Area Connection] icon. In the
[Local Area Connection Status] dialogue box, click the
[Properties] button.
3. In the [Local Area Connection Properties] dialogue box, if
the [NetBEUI Protocol] is not listed, click the [Install]
button.
4. In the [Select Network Component Type] dialogue box,
select [Protocol] and click the [Add...] button.
5. In the [Select Network Protocol] dialogue box, select
[NetBEUI Protocol] and click the [OK] button.
6. Click the [Close] button in the [Local Area Connection
Properties] dialogue box.
Microsoft Windows> 61
Page 62

7. Click the [Close] button in the [Local Area Connection
Status] dialogue box.
W
INDOWS
1. Although you can install the NetBEUI protocol into
2. In the [Start] menu, select [Settings] then [Control
3. Double-click on [Network Connections].
4. Right-click the adapter you wish to add NetBEUI to and
5. On the [General] tab, select [Install].
6. Select [Protocol] and then [Add].
7. Select [Have Disk] and insert your Windows XP CD-ROM,
Now the printer has been configured and NetBEUI has been
installed, you can configure Windows to print over the network.
P
RINTER DRIVER CONFIGURATION
In the following example, the printer has been configured as
follows:
XP
Windows XP, it is not supported. You should be able to use
NetBEUI on LAN connections although you will not be able
to use this on a Remote Access Service Connections.
Panel].
then click [Properties].
open the [Valueadd\msft\net\netbeui folder], click the
Netnbf.inf file and then click [Open].
Computer Name: OL07DB85
Workgroup: PrintServer
Comment: Ethernet Board 8100e
1. Set up the printer driver as the default local printer.
2. In the [Start] menu, select [Settings] then [Printers].
3. Select the relevant printer driver, then [Properties].
4. Click on the [Details] tab in the printer driver.
5. Select [Add Port]. Select [Network] and click [Browse].
6. Double-click [Entire Network], [PrintServer] and
[OL07DB85].
Microsoft Windows> 62
Page 63

7. Select [Prn1] and click OK.
8. Check that [Network] is selected and click [OK].
9. Select [Apply] and [OK] to close [Properties].
Printing can be carried out using your application software.
> The Master Browser function manages machine
information from the same Workgroup, and replies to
summary requests from other workgroups.
> The Master Browser function operates only if the
Workgroup name is PrintServer.
> The Master Browser function can only manage this
network card. If the PrintServer name is put into another
Workgroup, the network card will not be able to find it on
the network.
> A maximum of eight Ethernets can be managed by the
Master Browser function.
> Printing cannot be carried out and an error message
appears when jobs from other users (including other
protocols) are being printed.
Microsoft Windows> 63
Page 64

N
OVELL NETWARE
O
VERVIEW
The printer supports the Novell NetWare environment.
It is necessary to have NetWare Administrator or Supervisor
rights to change the configuration. This guide is for NetWare
administrators. It should be read in conjunction with the relevant
Novell NetWare manual. The latest Novell service packs and
Novell client versions should be installed.
Supported Versions and Modes
NETWARE VERSION SUPPORTED MODES
NetWare 3.11+ Bindery
NetWare 4.1+ Bindery and NDS
NetWare 5.0+ Bindery, NDS and NDPS
NetWare 6.0 Bindery, NDS, NDPS and iPrint
In NDS, the printer can be configured to work in either print
server mode or remote printer mode.
> Print Server mode (recommended)
In Print Server Mode, the file server is logged in and the
printer queue is repeatedly polled to determine whether a
print job exists. The NetWare print server or workstation
where Pserver runs is emulated. This enables high speed
printing without applying a load to the network. Print
Server Mode requires a single user NetWare licence.
> Remote Printer mode
Remote Printer Mode requires a connection to be made to
a workstation running Pserver. Print jobs are received from
the file server via the NetWare print server. The network
interface card emulates the workstation on which the
NetWare Rprinter operates. Remote Printer Mode adds
additional traffic to the network and is slower than Print
Server Mode but does not require any additional licences.
Novell NetWare> 64
Page 65

P
RINTING THE CONFIGURATION PAGE
The printer’s configuration page reports information that is
required for NetWare configuration. To print a configuration
page, while the printer is switched on, depress the NIC’s pushbutton for three seconds and then release.
The information that you require is the printer’s Ethernet
address. The first six characters of the Ethernet address are the
same for all network interfaces. The last six characters of the
Ethernet address are unique to each card
This is all the information that is required to setup the printer for
NetWare.
S
ETUP UTILITIES
Use NWAdmin32 or the Pconsole utility to create and setup
NetWare printer objects. Please refer to Novell documentation for
instructions on how to achieve this.
Use the Network Card Setup
Utility (AdminManager) or
other printer manager
software, (Web browser,
JetAdmin, etc.) to configure the
network interface card. For
instructions please refer to the
Configuration Utility section
and online help. The illustration
here shows the NetWare
configuration page from
AdminManager.
NDPS G
This provides a gateway for NDPS. Gateways allow NDPS clients
to send jobs to printers that are not NDPS-aware (that is, printers
that are not equipped with embedded NDPS Printer Agents). You
select and configure a printer gateway when you create a new
Printer Agent.
ATEWAY
Novell NetWare> 65
Page 66

Gateways translate NDPS queries
or commands to printer-specific
language that the physical printer
can use. This is possible because
gateways are configured to know
the specific type (make and
model) of printer being used. This
illustration shows a typical
gateway configuration.
The NDPS Gateway can be installed from the Oki Network CD
under Software Utilities. Please follow on-screen instructions.
You will require a drive mapping to the NetWare server that you
are installing to.
During installation, all files are
copied to the SYS:/SYSTEM and
SYS:/PUBLIC/WIN32 directories
on the NetWare server.
1. To set up the printer to
work with the NDPS
Gateway, you should
create a NDPS printer
object as normal with the
NWAdmin32 utility.
When you get to the
[Create Printer Agent]
screen, under [Gateway
Types] there should now
be an option for NDPS Gateway.
Novell NetWare> 66
Page 67

2. Select this and click [OK] to continue. You will then be
presented with the Gateway Configuration Welcome
screen, click [Next] again and select Printer Interface
Type, either TCP/IP LPR or NetWare IPX and select [Next]
to continue. (TCP/IP configuration illustrated.)
You will then be requested to enter either the TCP/IP or IPX
address, depending on the type of interface selected in the
previous screen. If you do not know the address, you are
given the option to search on the network.
Once you have correctly input your network address you
will be prompted with a [Results] and then a [Summary]
screen.
Novell NetWare> 67
Page 68

Press the [Finish] button on
the [Summary] screen so
the NDPS Printer object has
now been created and is
configured to use the NDPS
Gateway. This is the Printer
Control screen for the
completed printer.
IPRINT
iPrint is included in NetWare 6 and is Novell’s next generation of
printing software. It is Novell’s implementation of IPP (Internet
Printing Protocol). iPrint allows users to install, manage and print
to printers through Web browsers regardless of where the printer
is physically located or whether they know the printer’s network
address.
iPrint runs on top of Novell Distributed Print Services (NDPS) and
provides the following functionality:
> Global access to printers.
> Customizable view of any print environment.
> Flexible print deployment configurations.
> Secure printing.
The printer does not require any custom configuration for iPrint.
To enable and configure the iPrint service on your network,
please refer to your Novell NetWare 6 documentation.
Novell NetWare> 68
Page 69

UNIX
O
VERVIEW
The printer supports many protocols such as LPD, FTP, TELNET,
SNMP and IPP, and works within the UNIX environment.
To use the network card within the UNIX environment, the
following steps are required:
C
ONFIGURATION
N
ETWORK INTERFACE CARD SETTING
The first step in installing the network card under UNIX is to set
up the IP address, Subnet Mask and Gateway. This section
explains one way to set them up from a UNIX workstation.
> The network addresses used in this manual are shown as
examples only. Network addresses used in your
installation must be generated for your own network.
> Log in as [root] to change the configuration of the printer.
> If an incorrect IP address, Subnet Mask or Gateway is
entered, the network may go down or other damage may
occur. Check the address with your network manager.
The following explanation uses Sun Solaris 2.8 (Solaris 8) as an
example. The actual commands may differ between versions of
UNIX, so refer to the workstation manuals for more information.
NOTE:
If you do not have superuser rights, the network manger
should conduct the configuration.
1. Log in as [root] to the workstation
2. If the printer does not have an IP address already
assigned, use the arp command to set a temporary IP
address.
Example: for IP address 192.68.20.127 and network card
address 00:80:87:01:00:D2
# arp –s 192.168.20.127 00:80:87:01:00:D2 temp
UNIX> 69
Page 70

The Ethernet address (MAC address) 00:80:87:01:00:D2
in the above example can be determined from the network
card self-diagnostic test.
3. Use the ping command to confirm the connection with the
network interface card.
Example: for IP address 192.168.20.127
# ping 192.168.20.127
If there is no reply, there is a problem with the
configuration of the IP address (the IP address has already
been set manually or dynamically), or with the network.
Reset the network interface card settings to default and try
to set a temporary IP address.
If you still have the problem after resetting the network
interface card, consult the network manager.
4. Login to the network interface card using TELNET.
Example: Logging in to IP address 192.168.20.127
#telnet 192.168.20.127
Trying 192.168.20.127
Connected to 192.168.20.127
Escape character is ‘^]’.
EthernetBoard 8100e Ver 01.50 TELNET server
login: root
‘root’ user needs password to login.
password: <CR>
User ‘root’ logged in.
No. Message Value (level .1)
1 : Setup TCP/ IP
2 : Setup SNMP
3 : Setup NetWare
4 : Setup EtherTalk
5 : Setup NetBEUI
6 : Setup printer trap
7 : Setup SMTP (Email)
9 : Maintenance
10 : Setup printer port
11 : Display status
12 : IP Filtering Setup
97 : Network Reset
98 : Set default (Network)
UNIX> 70
Page 71

99 : Exit setup
Please select (1- 99)?
5. Type 1 and press the [Enter] key. Perform the following
settings:
Please select (1- 99)? 1
No. Message Value
1 : TCP/ IP protocol : ENABLE
2 : IP address : 192.168.20.127
3 : Subnet Mask : 255.255.255.0
4 : Gateway address : 192.168.20.1
5 : RARP protocol : DISABLE
6 : DHCP/ BOOTP protocol: DISABLE
7 : Auto IP Address : DISABLE
8 : DNS Server (Pri.) : 0.0.0.0
9 : DNS Server (Sec.) : 0.0.0.0
10 : root password : “******“
11 : Auto Discovery Setup
99 : Back to prior menu
Please select (1- 99)?
6. Logout from the network interface card. Turn the printer
off for about 15 seconds and on again to validate the
settings.
UNIX> 71
Page 72

O
PERATING SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
This section explains how to configure a printer for major UNIX
operating systems.
SUN OS 4.X.X (BSD)
The following explanation uses Sun OS 4.1.3 and a C7300V2
printer as examples. The absolute path of commands and the
configuration method may differ between OS versions, so refer to
the workstation manuals for more information.
CONFIGURATION
CAUTION!
If an incorrect IP Address, Subnet Mask or Gateway is
entered, the network may go down or other damage
may occur. Check the address with the network
manager and confirm that the IP address of the printer
has been set.
If you do not have Superuser rights, the network manager should
conduct the configuration.
1. Login as [root] to the workstation.
2. Register the IP address of the network card and the host
name in the /etc/hosts file.
Example: for IP address 192.168.20.127 and host name
c7350
192.168.20.127 c7350
3. Use the ping command to confirm connection with the
network card.
Example: for host name c7350
# ping c7350
If there is no reply, then there is a problem with the
configuration of the IP address (the IP address has already
been set manually or dynamically) or with the network.
Reset the network interface card settings to their defaults
and then try to set a temporary IP address. If you still have
the problem after resetting the network interface card,
consult the network manager.
UNIX> 72
Page 73

4. Register the printer in the /etc/printcap file.
Example: for host name c7350, to create a queue called
c7350_lp
c7350_lp: \
:lp=:rm=c7350:rp=lp:\
:sd=/usr/spool/c7350_lp:\
:lf=/usr/spool/c7350_lp/c7350_lp_errs:
c7350_lp:. . . The name of the printer queue
lp: . . . . . . . The name of the device used to connect to
the printer. Does not need to be specified
for a remote machine.
rm: . . . . . . . The name of the host of the remote printer.
This should be the same as the name
added to the /etc/hosts file.
rp: . . . . . . . The name of the printer on the remote
printer. It should be lp.
sd: . . . . . . . The spool directory. Give the absolute
path.
lf: . . . . . . . The error log file. Give the absolute path.
5. Create the spool directory and error log file.
Example: for spool Directory c7350_lp and Error Log file
c7350_lp_errs
# mkdir /usr/spool/c7350_lp
# touch /usr/spool/c7350_lp/c7350_lp_errs
# chown –R daemon /usr/spool/c7350_lp
# chgrp –R # daemon /usr/spool/c7350_lp
6. Check that lpd (printer daemon) is activated.
# ps aux | grep lpd
7. If lpd is not running, you can start it by logging in as
superuser and executing
# /usr/lib/lpd &
UNIX> 73
Page 74

SUN S
OLARIS
2.X
CONFIGURATION
Admintool is normally used to register remote printers on Open
Windows. However, it cannot be used here, as the data recipient
and queue have the same name. The procedure below must be
used for registering a remote printer.
If Solaris 2.x is connected to the remote printer for a long period
according to the system specifications, errors and forced
disconnection may occur. Therefore, if paper tearing, off-line and
other errors result in waiting time, printing may have to be
aborted.
CAUTION!
If an incorrect IP address is entered, the network may
go down or other damage may occur. Configure after
consulting the network manager.
The following explanation uses Sun Solaris 2.8 (known as
Solaris 8) and a C7350 printer as examples. The absolute path
and method of configuring commands may differ in other
versions of the OS. Refer to the workstation manual for more
details.
1. Confirm that the IP address of the printer has been set.
2. Log in as [root] to the workstation. If you do not have
superuser rights, the network manager should conduct
the configuration.
3. Register the IP address of the network card and the host
name in /etc/hosts file.
Example: for IP Address 192.168.20.127 and host name
c7350
192.168.20.127 c7350
4. Use the ping command to confirm connection with the
network card.
Example: for host name c7350
# ping c7350
UNIX> 74
Page 75

If there is no reply, there is a problem with the
configuration of the IP address (the IP address has already
been set manually or dynamically), or with the network.
Reset the network interface card settings to default and try
to set a temporary IP address. If you still have the problem
after resetting the network interface card, consult the
network manager.
5. Register the network card as a remote printer server.
Example: for host name c7350
(a) Stop the print scheduler.
# usr/sbin/lpshut
(b) Create the printer queue.
# /usr/sbin/lpadmin -p c7350_lp -v /dev/
null \
-m netstandard -o dest=c7350:lp
-o protocol=bsd
(c) Set the queue to accept PostScript print jobs.
# /usr/sbin/lpadmin -p c7300v2_lp -I
postscript
(d) Start the print scheduler.
# /usr/sbin/lpsched
(e) Activate the print queue.
# /usr/sbin/accept c7350_lp
(f) Enable the print queue
# /bin/enable c7350_lp
To customise output, for example to add additional commands at
the start of each print job, you can edit a copy of the netstandard
model file then add it using the lpadmin command.
Example: for printer c7350_lp, with model file called
c7350_model
# /usr/sbin/lpshut
# /usr/sbin/lpadmin –p c7350_lp –m c7350_model
# /usr/sbin/lpsched
UNIX> 75
Page 76

HP-UX 10.X
CONFIGURATION
The following example uses HP-UX10.20 and a C7300V2 printer
as examples. The absolute path and method of configuring
commands may differ in other versions of the OS. Refer to the
workstation manual for more details.
CAUTION!
If an incorrect IP Address, Subnet Mask or Gateway is
entered, the network may go down or other damage
may occur. Check the address with the network
manager.
1. Confirm that the IP address of the printer has been set.
See network interface card IP address configuration for
more information.
2. Login as [root] to the workstation. If you do not have
superuser rights, the network manager should conduct
the configuration.
3. Register the IP Address of the network card and the host
name in the /etc/hosts file.
Example: for IP Address 192.168.20.127 and host name
c7350
192.168.20.127 c7350
4. Use the ping command to confirm connection with the
network card.
Example: for host name c7350
# ping c7350
If there is no reply, there is a problem with the
configuration of the IP address (the IP address has already
been set manually or dynamically), or with the network.
Reset the network interface card settings to default and try
to set a temporary IP address. If you still have the problem
after resetting the network interface card, consult the
network manager.
UNIX> 76
Page 77

5. If remote spooling is not already enabled on the HP-UX
machine, carry out the following configuration.
(a) Stop the printer spooler.
# /usr/sbin/lpshut
(b) Add the following line to the /etc/inetd.conf file and
register the remote spooler.
printer stream tcp nowait root /usr/sbin/
rlpdameon –I
(c) Restart inetd
# /etc/inetd –c
6. Register the remote printer.
Example: setting up a queue called c7350_lp to print to
host c7350
(a) Register the remote printer.
# /usr/sbin/lpadmin -pc7350_lp -v /dev/null
-mrmodel \-ormc7350 -orplp -ocmrcmodel
-osmrsmodel -ob3
(b) Activate the print queue.
# /usr/sbin/accept c7350_lp
(c) Enable the print queue.
# /bin/enable c7350_lp
(d) Enable the printer spooler.
# /usr/sbin/lpsched
To customise output, for example, to add additional commands
at the start of each print job, you can edit a copy of the /usr/
spool/lp/model/rmodel model file then add it using the lpadmin
command.
Example: for printer c7350_lp, with model file called
c7350_model
# /usr/sbin/lpshut
# /usr/sbin/lpadmin –pc7350_lp –
mc7350_model
# /usr/sbin/lpsched
UNIX> 77
Page 78

AIX 4.1.5
CONFIGURATION
The following explanation uses AIX4.1.5 and a C7300V2 printer
as examples. The absolute path of commands and the method of
configuring may differ with the OS version. Refer to the
workstation’s manual.
CAUTION!
If an incorrect IP address is entered, the network may
go down or other damage may occur. Configure after
consulting the network manager.
1. Log in as [root]. If you do not have superuser rights, the
network manager should conduct the configuration.
2. Register the IP address and the host name in the /etc/
hosts file.
Example: for IP Address 192.168.29.127 and host name
c7350
192.168.20.127 c7350
3. Use the ping command to confirm connection with the
network card.
Example: for host name c7300v2
# ping c7350
If there is no reply, there is a problem with the
configuration of the IP address (the IP address has already
been set manually or dynamically), or with the network.
Reset the network interface card settings to default and try
to set a temporary IP address. If you still have the problem
after resetting the network interface card, consult the
network manager.
4. Register the host that was previously registered as the
print server.
Example: for the C7350 registered as the print server
(a) Add the print server.
# ruser –a –p c7350
(b) Activate the remote printer daemon.
UNIX> 78
Page 79

# startsrc –s lpd
# mkitab ‘lpd:2:once:startsrc –s lpd’
5. Add the print queue using the smit command.
(a) Activate the smit command and convert to the item
[Add print queue].
# smit mkrque
(b) Select [remote] (the printer connected to the
remote host) from [Type of connection].
(c) Select [Standard procedure] from Type of remote
print.
(d) Carry out the following settings in [Add a standard
remote print queue]. If the configuration differs from
below, configure according to environment.
Example: Use port lp with print queue c7350_lp and print
server c7350
Queue to be added “c7350_lp”
Host name of the remote
server “c7350”
Queue name of the remote
server “lp”
Type of print spooler of
the remote server “BSD”
Description of printer
name of the remote server “Optional comment”
LPD Printing
Line Printer Daemon (LPD) is the most common protocol
for printing with TCP/IP to a network printer. Refer to the
workstation’s manual for details of lpr and lp commands.
The following explanation in this section uses the printing
of print file test.prn with printer name c7350_lp as an
example.
Logical printers
The printer’s network interface includes three logical
printers.
UNIX> 79
Page 80

> lp must be used for printing a file created using the printer
driver.
> sjis must be used for printing a text file of Shift JIS Kanji
code.
> euc must be used for the printing a text file of the EUC
Kanji code.
LOGICAL PRINTER PRINTER FUNCTION
lp For direct output
sjis For Shift JIS Kanji converted output
euc For EUC Kanji converted output
> sjis and euc function only as PostScript printers.
BSD-based UNIX
Print using the lpr command.
# lpr –Pc7350_lp test.prn
If the lprm command is used, the print job is cancelled.
Example: To delete a print job (Job ID 123) on the
c7350_lp
# lprm –Pc7350_lp 123
Verify the printer status using the lpq command.
> The result of lpq may not be displayed correctly depending
on UNIX operating system specification.
> While the short format of lpq is a UNIX compatible format,
the long format is unique to this network interface.
Example of the short format: # lpq –Pc7350_lp
Example of the long format: # lpq –l -Pc7350_lp
System V-based UNIX
Print using the lp command.
# lp –d c7350_lp test.prn
Delete a print job using cancel command.
UNIX> 80
Page 81

Example: To delete a print job (Job ID 456) in the c7350_lp
# cancel c7350_lp -456
Verify the printer status using the lpstat command.
# lpstat –pc7350_lp
The result of lpstat may not be displayed correctly
depending on UNIX operating system specification (e.g.
Solaris 2.x).
FTP printing
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is used for transferring a file
with TCP/IP. If the print data is sent to a logical printer via
FTP, it is printed.
Refer to the workstation’s manual for details of the ftp
command. The following explanation uses print file
test.prn with printer name c7350_lp as an example.
L
OGICAL DIRECTORIES
The printer’s network interface includes three logical directories.
> lp must be used for printing a file created using the printer
driver.
> sjis must be used for printing a text file of Shift JIS Kanji
code.
> euc must be used for the printing a text file of the EUC
Kanji code
LOGICAL DIRECTORY PRINTER FUNCTION
lp For direct output
sjis For Shift JIS Kanji converted
output
euc For EUC Kanji converted output
jis and euc function only as PostScript printers.
You can not send data to the root directory.
UNIX> 81
Page 82

1. Log in to the network interface card.
When printing with ftp, use any values for name and
password. However, if the user name is [root], the
password set under TELNET or the utility is required. See
the appropriate section for details.
Example: Logging in with host name c7350 (or IP address
192.168.20.127).
# ftp c7350
(or ftp 192.168.20.127)
Connected to c7350
220 EthernetBoard 8100e Ver 01.50 FTP Server
Name (c7350:<none>) : root
331 Password required.
Password:<CR>
230 User Logged in
ftp>
The network card logical directory structure is hierarchical.
Move to the logical directory; it is not possible to output
print data to the root directory.
2. Move to the preferable logical directory using the cd
command.
Example: moving to the lp directory and confirming the
current directory.
ftp> cd /lp
250 Command OK.
ftp> pwd
257 ”/lp” is current directory
ftp>
3. Configure the transfer mode.
There are two types of transfer mode: BINARY mode, in
which the file content is output as it is and ASCII mode,
which converts the LF code to the CR+LF code. If a binary
file converted by the printer driver is transferred, the
transfer mode has to be BINARY mode.
UNIX> 82
Page 83

Example: Changing transfer mode to binary mode and
verifying the current mode:
ftp> type binary
200 Type set to I.
ftp> type
Using binary mode to transfer files.
ftp>
4. Transfer the print data to the network card using the put
command. Two methods of file transfer using the put
command are available.
Example: Transferring print data test.prn
ftp> put test.prn
Example: Transferring print data specified by absolute
path/users/test/test.prn
ftp> put /users/test/test.prn /lp
5. Logout from the network card using the quit command.
ftp> quit
Three states can be verified using the quote command
stat: the IP address, login user name and transfer mode.
In addition, printer status can be verified by specifying the
directory after the stat (lp, sjis, euc).
Example: Displaying network card status
ftp> quote stat
211-FTP server status:
Connected to: 192.168.20.10.000.00
User logged in: root
Transfer type: BINARY
Data connection: Closed.
211 End of status.
ftp>
Example: Displaying the network card status (directory
name: lp)
ftp> quote stat /lp
211-FTP directory status:
Ready
211 End of status
ftp>
UNIX> 83
Page 84

A
PPLE
M
ACINTOSH
O
VERVIEW
The printer supports the Apple Macintosh AppleTalk environment.
This guide is for administrators and it should be read in
conjunction with the relevant Macintosh manual. The latest
Macintosh service packs should be installed.
S
UPPORTED VERSIONS
All Macintosh operating systems from OS 8.1 are supported.
P
RINTING THE CONFIGURATION PAGE
The printer’s configuration page reports information that is
required for Macintosh configuration. To print a configuration
page, while the printer is switched on, depress the NIC’s pushbutton for three seconds and then release.
The first six characters of the Ethernet address are the same for
all network interfaces. The last six characters of the Ethernet
address are unique to each card.
Apple Macintosh> 84
Page 85

S
ETUP UTILITIES FOR MAC
Use the Network Card Setup Utility
(Macintosh) to assign an IP address and
configure the network interface card. For
instructions please refer to the
Configuration Utility section and on-line
help.
C
ONFIGURATION
There are three items that need to be configured for EtherTalk.
Use EtherTalk Protocol
Please check the Use EtherTalk Protocol checkbox.
1. Printer Name
2. Give the Printer Name as you would like it to appear in the
Chooser.
3. Zone Name
If your network uses Zones, please enter the Zone Name
here, otherwise leave as is.
A
PPLETALK CONFIGURATION
To enable network printing from the Macintosh, you must
configure AppleTalk to connect via Ethernet.
OS 8.X
AND
9.
X
1. From the Apple menu select [Control Panels – AppleTalk].
2. From the AppleTalk configuration page select [Connect
via: Ethernet].
3. In Setup Current Zone, if used, make sure that your zone
information is correct.
4. Close the AppleTalk configuration page and save changes
to current configuration when prompted.
5. Configuration is now complete and you are ready to install
your printer driver. Please enter your driver CD, run the
installer and follow the on-screen instructions.
Apple Macintosh> 85
Page 86

Macintosh OS–X
The built in network interface card is also supported in the
Macintosh OS–X environment.
Run the installer on the driver CD to install the printer’s PPD file.
In OS–X you need to make sure that AppleTalk is turned on in
order to connect to an AppleTalk printer.
1. To switch AppleTalk on, open [System Preferences], click
[Network] then click [AppleTalk].
2. Check the [Make AppleTalk Active] check box and if your
network uses AppleTalk Zones, enter the appropriate zone
information and click [Apply Now].
In Mac OS–X use the Print
Centre to select network
printers, not the Chooser.
Before you can use a printer
it must appear in the printer
list in Print Centre.
3. Click on [Add Printer], make sure that the connection
method is LPR and assign its IP address.
4. Either assign a queue name or check to use the default
queue on server checkbox.
5. Under Printer Model select from the list the PPD file that
you installed earlier for the printer and click [Add].
These are all the steps that are necessary to setup the printer for
network printing in Macintosh OS–X.
Apple Macintosh> 86
Page 87

T
ROUBLESHOOTING
The network addresses used in this manual are shown for
example only. Network addresses used in your installation must
be generated from your own network.
S
ELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST
P
RINTER DOES NOT PRINT
Ensure the printer emulation is set to PS or Automatic.
NG IS
PRINTED IN THE SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST OR FLASH
R
EGISTERS
Turn the printer off for 15 seconds and then on again.
Press the reset button close to the network interface to reinitialize it.
NG
ROM C
HECK
TCP/IP
C
OMPUTER CANNOT FIND THE NETWORK INTERFACE CARD
Turn the printer off for 15 seconds and then on again.
Confirm the network interface is enabled on the printer.
Check there is a response to the PING command.
Check that the network cable is correctly connected and that the
green LED close to the printer’s network interface is lit. If not,
change the cable and try again.
Run the Self-diagnostic test.
Check the IP Address, Subnet Mask and Gateway are correct.
Check that the TCP/IP protocol is set to Enable.
Reset the network interface card to factory default settings.
If DHCP, BOOTP and RARP are not used, ensure they have been
set to Disable.
Troubleshooting> 87
Page 88

C
ANNOT PRINT WITH LPR AND FTP
Turn the printer off for 15 seconds and then on again.
Check there is a response to the ping command.
Check the network cable is correctly connected.
Change the cable and try again.
Check the host name and IP address are configured in the
workstation.
Check the printer port name is configured in the workstation.
There are three port names: lp, euc and sjis. Use lp by default as
euc and sjis are specific to PostScript printers.
I
NCORRECT USER NAME ON THE BANNER PAGE
If printing with lpr, the user name printed is unknown and the
filename printed is the Spool file name.
If printing with FTP, the user name printed is the user name
entered during FTP login and the file name printed is the
transmitted file name. If the print directory name is indicated in
the put command, the file name is not printed. The printer name
printed is the logical directory name.
NETW
ARE
P
RINTER CANNOT FIND THE NETWORK INTERFACE
Turn the printer off and on again.
Confirm the network interface is enabled on the printer.
Check that the network cable is correctly connected and that the
green LED close to the printer’s network interface is lit. If not,
change the cable and try again.
If the standard configuration utility is used, check the NetWare
network number in the environment settings.
If the NetWare protocol is disabled, set it to Enable.
Reset the network interface card to factory default settings.
Troubleshooting> 88
Page 89

THE
NETWORK INTERFACE IS IDENTIFIED BY THE SETUP UTILITY BUT NOT BY
THE NETWARE SERVER
Start up the NetWare server and check the NIC configuration.
Check the NSAP packet on the NetWare server is not set to
Disable.
R
EMOTE SERVER MODE
Check the correct print server is operating on the file server.
Check the print server name operating on the file server and the
print server name set in the NIC are the same.
Check the printer name displayed in the print server monitor of
the file server and the NetWare port name set in the NIC are the
same. If there are multiple network interface cards, configure the
NetWare port names to be different.
P
RINT SERVER MODE
Check the file server name set in the NIC and on the file server
are the same.
Check the printer name set in the file server and the NetWare
port name set in the NIC are the same. If there are multiple NICs,
configure the NetWare port names to be different.
Check the NetWare login password is correct.
Check the machine name is the same as the print server name
set in the file server.
P
RINTER DOES NOT PRINT
.
Check the network cable is correctly connected.
Change the cable and try again.
Turn the printer off for 15 seconds and then on again.
Check the NIC is connected to the file server.
Check the printer driver has been mapped to the correct netware
queue.
Troubleshooting> 89
Page 90

P
OSTSCRIPT ERROR OCCURS IF A BANNER PAGE IS PRINTED
A PostScript banner page cannot be printed in NetWare 3.12
Remote Printer mode. If a PostScript printer is used and a banner
page is printed, PostScript error is displayed. Turn the banner
output Off in the client’s printer settings.
E
THERTALK
NOT
IDENTIFIED BY THE CHOOSER AND THE SETUP UTILITY
Turn the printer off for 15 seconds and then on again.
Check the network cable is correctly connected.
Change the cable and try again.
If the network resides in a zone, check the correct zone name is
selected in the Chooser.
Check the zone name in the utility related to the NIC is the same
as the zone name set in NIC.
Check AppleTalk, which is displayed at the right bottom of the
Chooser, is set to Enable. (In some OS versions Network is used
instead of AppleTalk.)
Check Ethernet is selected in AppleTalk. (In some OS versions
Network is used instead of AppleTalk.)
Check the printer driver is selected in the Chooser.
Check the EtherTalk protocol is set to Enable.
Print the NIC settings and confirm that the EtherTalk port name
is not blank.
NETBEUI
The network interface card is not identified.
Turn the printer off for 15 seconds and then on again.
Check the network cable is correctly connected.
Change the cable and try again.
Check Microsoft Network Client and NetBEUI have been added to
the network section of the Windows Control Panel.
Troubleshooting> 90
Page 91

Check the NetBEUI protocol is set to Enable.
Check the factory setting of the workgroup name is PrintServer
and the computer name is ML+ the last six characters of the MAC
address.
Check the computer name of the NIC is different from the
computer name on the network.
E
RROR WRITING TO PRN
Check the printer is online.
If there is an error message indicating the paper has run out, add
more paper and cancel the error.
Check whether another user is printing. Print after the other user
has finished.
G
LOSSARY
NIC Network Interface Card (or built in network
interface)
NDS Novell Directory Service
NDPS Novell Distributed Print Services
iPrint Internet Print
IPP Internet Printing Protocol
1
Troubleshooting> 91
Page 92

A
PPENDIX
– E-M
AIL ALERT FUNCTION
The following table explains how to set up the E-Mail Alert
function via Telnet.
7: Setup SMTP
(E-Mail)
1: SMTP
Tra n s mit
2: SMTP
Receive
3: SMTP
Server
Name
4: SMTP Port
Number
5: E-mail
Address
6: Reply-To
Address
7: Destination
Address1–
11:Destination
Address 5
Set sending E-Mail
via SMTP, enabled or
disabled.
Set receiving E-Mail
via SMTP, enabled or
disabled.
Set IP address or
host name of SMTP
server.
Set port number of
SMTP.
Set the E-Mail
address used for
[From] field in the
mail header.
Set the E-Mail
address used for
[Reply-To] field in the
mail header.
1: To Address
1–5
2: Modify mode Select how to notify
3: Check time
(hours)
Up to five E-Mail
addresses to which EMail alerts can be
sent.
warnings/errors via
E-Mail.When any
specified status
changes, E-Mail is
sent immediately if
“EVENT” is selected,
or periodically if
“PERIOD” is selected.
Set duration (1-24
hours) to send E-Mail
when you select
"PERIOD" as Notify
mode.
Appendix – E-Mail Alert Function> 92
Page 93

7: Setup SMTP
(E-Mail)
(continued)
7: Destination
Address1–
11:Destination
Address 5
(continued)
4: Consumable
Warnin g
5: Consumable
Error
6: Maintenance
Warnin g
7: Maintenance
Error
8: Paper
Warnin g
9: Paper Error
10:Printing
Warnin g
11:Printing
Error
12:HDD/Flash
Memory
13:Print Result
Warnin g
14:Print Result
Error
15:Other Error
16:Interface
Warnin g
These events can be
included in E-Mail
alerts.In PERIOD
mode, set to
“enabled” to include
these events in EMail alerts.In
“EVENT” mode, set to
“enabled” to send an
E-Mail alert when any
of these warnings are
detected.When
enabled, “delay time”
(0 - 48 hours) can be
set.If the cause is
cleared during the
delay time, the E-Mail
alert is not sent.
17:Interface
Error
99:Back to
Prior Menu
12:Additional
Info.
Appendix – E-Mail Alert Function> 93
1: Printer Mode Set whether these
2: Network
Interface
3: Serial
Number
4: Asset
Number
5: System
Name
items are included in
the E-Mail body.
Page 94

7: Setup SMTP
(E-Mail)
(continued)
13:Additional
Info.
(continued)
6: System
Location
7: IP Address
8: Ethernet
Address
9: Computer
Name
10:Printer URL
99:Back to
Prior Menu
Set whether these
items are included in
the E-Mail body.
13:Comment
Line 1
16:Comment
Line 4
99:Back to
Prior Menu
Set up to four
signature lines.
Signature is added to
the bottom of an EMail.
Appendix – E-Mail Alert Function> 94
Page 95

 Loading...
Loading...