Okidata OL1200 Service Manual

Page: 1
Service Guide OL1200
Chapter 0 About This Manual
OL1200
LED Page Printer
Adobe Acrobat printable reference
copy of the OKIDATA Service Training Manual.
09/17/97
Note: This Adobe Acrobat version of the Okidata Service Training Manual was built with the
pictures rendered at 300 dpi, which is ideal for printing, but does not view on most
displays well.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Table of Contents Page
Service Guide OL1200
0 About This Manual
Front Cover 1
1 Configuration
1. Configuration 2
1.2 Printer Configuration 3
1.3 Optional Configuration 4
1.4 Specification 5
1.5 Safety Standards 6
....1.5.2 Warning Label 7
2 Operation Description
2. Operation Description 8
2.1 Main Control Board (Aolm-Pcb) 9
2.2 Power/Sensor Board 10
2.3 Relay/Driver Board (Aolc Board) 11
2.4 Electro-Photographic Process 12
....2.4.2 Electro-Photographic Process 13
....2.4.3 Process Operation Descriptions 14
........(2) Feeding 15
........(3) Charging 16
........(4) Exposure 17
........(5) Developing 18
........(6) Transfer 19
........(7) Fusing 20
........(8) Cleaning 21
........(9) Cleaning Of Rollers 22
2.5 Paper Jam Detection 23
2.6 Cover Open 24
2.7 Toner Low Detection 25
2.8 Stacker-Full Detection 26
2.9 Page Size Detection 27
3 Parts Replacement
3. Parts Replacement 28
3.1 Precautions For Parts Replacement 29
........[Service Tools] 30
3.2 Parts Layout 1- 4 31
....Parts Layout 2 - 4 32
....Parts Layout 3 - 4 33
....Parts Layout 4 - 4 34
3.3 How To Change Parts 35
....3.3.1 Rear Cover, Side Cover (L) Assy, Face-Up Stacker
Assy, And I/F Cover Assy.
....3.3.2 Contact Assy 37
36

Table of Contents Page
....3.3.3 Dc Fan Motor 38
....3.3.4 Manual Feed Hopper Assy 39
....3.3.5 Side Cover (R) (Operator Panel Assy) 40
....3.3.6 Earth Plate Bk (R) (Aolm-Pcb, Ic Cover) 41
....3.3.7 Stacker Cover Assy, Damper Arm, And Washer 42
....3.3.8 Damper 43
....3.3.9 Stacker Full Sensor Assy 44
....3.3.10 Cable Cover (Cable Guides A And B) 45
....3.3.11 Eject Roller Assy 46
....3.3.12 Paper Supply Guide D 47
....3.3.13 Separator F 48
....3.3.14 Front Feeder Roller Assy 49
....3.3.15 Hopping Motor 50
....3.3.16 Front Feeder Paper End Sensor 51
....3.3.17 Main Chassis Unit 52
....3.3.18 Registration Roller 53
....3.3.19 Drum Motor 54
....3.3.20 Idle Gear 55
....3.3.21 Fusing Assy 56
....3.3.22 Fuser Pressure Roller 57
....3.3.23 Ep Lock Shaft 58
....3.3.24 Hopping roller Assy 59
....3.3.25 Outlet sensor lever 60
....3.3.26 Toner sensor lever 61
....3.3.27 Paper sensor lever 62
....3.3.28 Inlet sensor lever 63
....3.3.29 Insulator 64
....3.3.30 Paper end lever 65
....3.3.31 Guide rail (L) Assy 66
....3.3.32 Guide rail (R) Assy 67
....3.3.33 IC card cover 68
....3.3.34 LED head 69
....3.3.35 Separator Assy 70
....3.3.36 Transfer roller 71
4 Adjustment
4. Adjustment 72
4.1 Maintenance Modes And Functions 73
....4.1.1 User maintenance mode 74
........User maintenance mode menu system 75
....4.1.2 System maintenance mode 76
........System maintenance mode menu system 77
....4.1.3 Engine maintenance mode 78
........Engine maintenance mode menu system 79
....4.1.4 EEPROM initialization 80

Table of Contents Page
4.2 Adjustment When Replacing A Part 81
....4.2.1 Setting of LED head drive time 82
....4.2.2 Resetting the fuser counter 83
....4.2.3 Destination setting 84
5 Periodic Maintenance
5.1 Periodic Parts Replacement 85
5.2 Cleaning 86
....5.2.1 Cleaning of LED Lens Array 87
....5.2.2 Cleaning Page Function 88
5.3 Lubrication - General Information 89
6 Troubleshooting Procedures
6.1 Troubleshooting Tips 90
6.2 Points to Check before Correcting Image Problems 91
6.3 Tips for Correcting Image Problems 92
6.4 Preparation for Troubleshooting 93
6.5 Troubleshooting Flow 94
....6.5.1 LCD status message/trouble list 95
........LCD Status Messages: (1-4) General 96
........LCD Status Messages: (2-4) General 97
........LCD Status Messages: (3-5) Error Controller nn 98
........LCD Status Messages: (4-4) Error Controller On= xxxxx 99
....6.5.2 LCD message troubleshooting 100
........1. The printer does not work normally after being turned
on.
........2-1 Paper input jam (1st tray) 102
........2-2 Paper input jam (front feeder) 103
........2-3 Paper feed jam 104
........2-4 Paper exit jam 105
........3 Paper size error 106
........4 Fuser unit error (ERROR 71), (ERROR 72), (ERROR
73)
........5 Synchronous serial I/O error (ERROR 74) or I/F time-out
between printer and optinal tray (ERROR 81)
........6. I/F time-out occurs between the printer and the operator
panel (ERROR 80) .
........7. Communications with the host cannot be performed via
the parallel
........8. Data from the host not received via the serial interface. 111
........9. Data cannot be received through the OKI HSP interface 112
....6.5.3 Image troubleshooting 113
........1. Images are light or blurred a whole. 114
........2. Dark background density 115
........4. Black belts or stripes in the vertical direction 116
........5. Cyclic error 117
101
107
108
109
110

Table of Contents Page
........6. Print voids 118
........7. Poor fusing 119
........8. White belts or streaks in the vertical direction 120
7 Wiring Diagram
7.1 Wiring Diagram 121
7.2 PCB Layout 122
7.3 Resistance Check 123
7.4 Short Plug Setting 124
8 Parts List
8. Parts List 125
Main Chassis Unit 126
Front Feeder Unit 127
Base Unit 128
A RS-232 Serial Interface
Rs-232 Serial Interface 129
B Centronics Parallel Interface
Centronics Parallel Interface 130
C High Capacity Second Paper Feeder
2.1 General Mechanism 131
High Capacity Second Paper Feeder 132
....1.2 External View and Component Names 133
2. Mechanism Description 134
....2.2 Hopper Mechanism 135
3. Parts Replacement 136
....3.2 Parts Layout 137
....3.3 Parts Replacement Methods 138
........3.3.1 Idle rollers 139
........3.3.2 AOLT-PCB 140
........3.3.3 Hopping motor 141
........3.3.4 Feed roller 142
........3.3.5 Hopping roller rubber 143
........3.3.6 Side frame (L) assy 144
........3.3.7 Side frame (R) assy 145
4. Troubleshooting 146
....4.3 Troubleshooting Method 147
........4.3.1 LCD Status Message List 148
........4.3.2 Troubleshooting Flow 149
5. Connection Diagram 150
....5.2 PCB Layout 151
6. Parts List 152
D Power Envelope Feeder
....1.1 Functions 153
....1.2 External View and Component Names 154
2. General Mechanism 155

Table of Contents Page
....2.2 Hopper Mechanism 156
3. Parts Replacement 157
....3.2 Parts Layout 158
....3.3 Parts Replacement Methods 159
........3.3.1 Separator 160
........3.3.2 AOLE-PCB 161
........3.3.3 Square-shaped connector 162
........3.3.4 Hopping Motor 163
........3.3.5 Planet gear 164
........3.3.6 Roller B 165
........3.3.7 Roller A 166
........3.3.8 Mini pitch belt & Feed roller 167
4. Troubleshooting 168
........4.3.2 Troubleshooting Flow 169
5. Connection Diagram 170
....5.2 PCB Layout 171
6. Parts List 172
Page: 2
Service Guide OL1200
Chapter 1 Configuration
1. CONFIGURATION
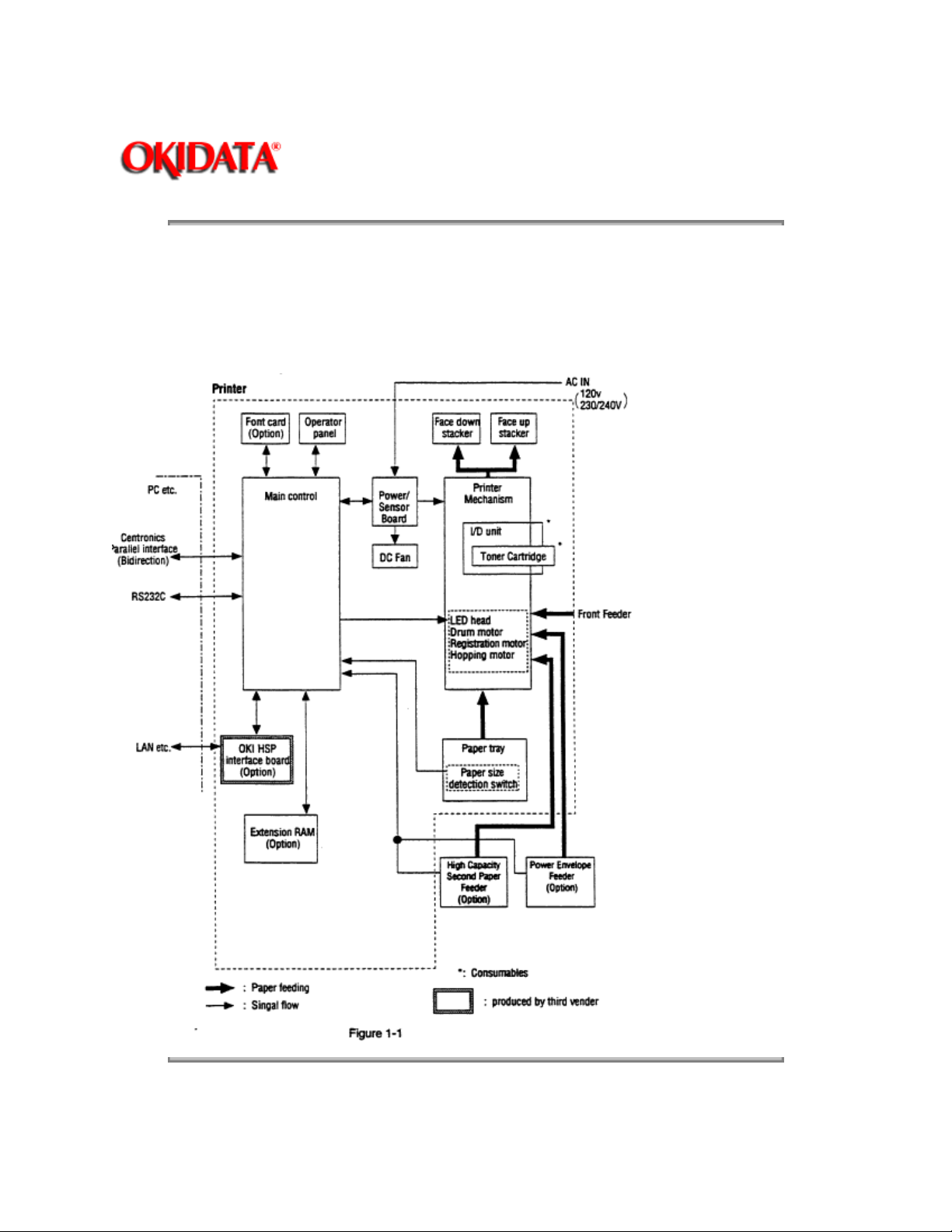
1.1 System Configuration
OL1200 consists of control and engine blocks as the standard configuration (See Figure below 1-1.) In
addition, the following options are also available.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OL1200
Chapter 1 Configuration
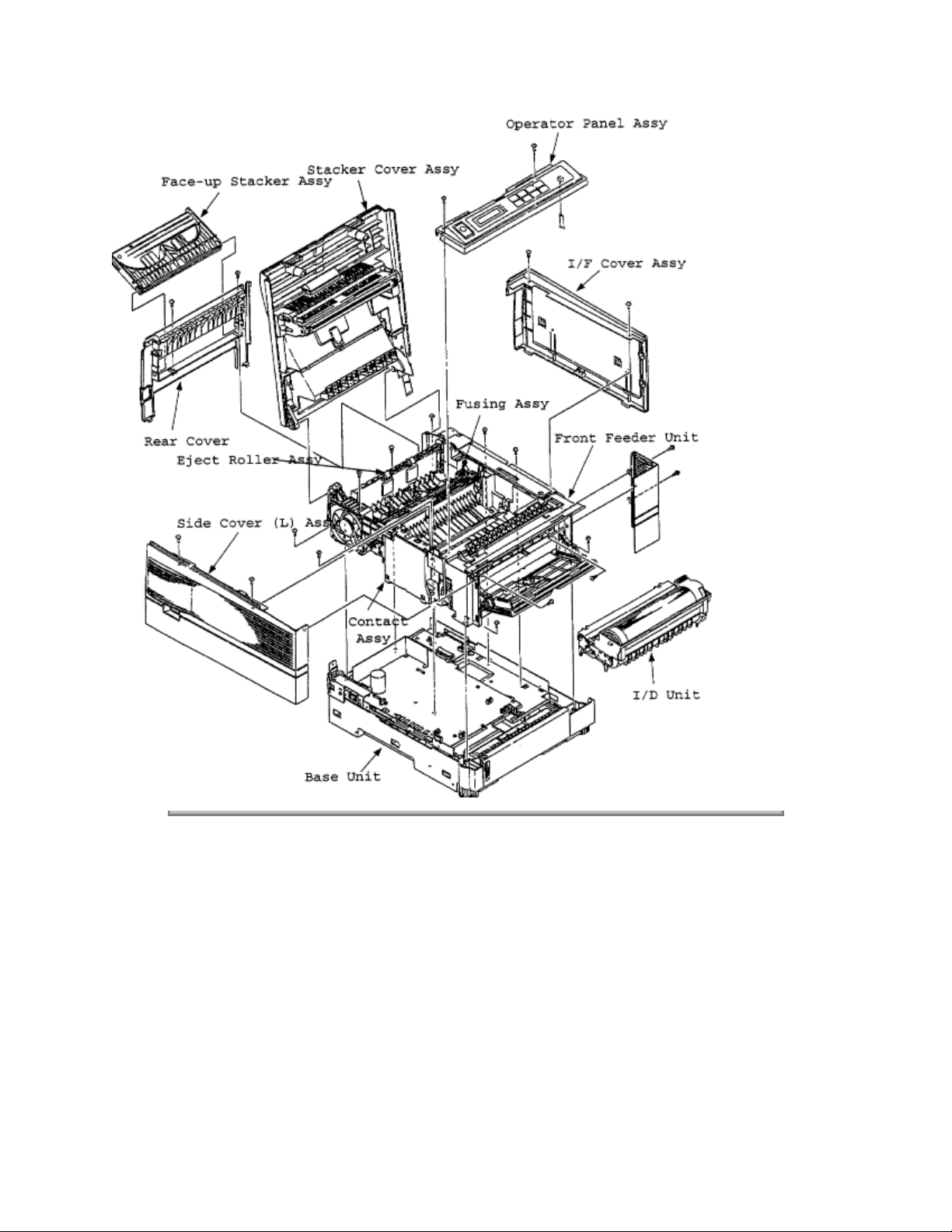
1.2 Printer Configuration
The printer unit consists of the following hardware components:
- Electro-photographic processor
- Paper feeder
- Controller
- Operator panel
- Power/sensor board
Figure 1-2 shows the printer unit configuration.
Page: 3
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Service Guide OL1200
Chapter 1 Configuration
1.3 Optional Configuration
The options below are available for use with OL1200. They are sold separately from the printer unit.
(1) Power Envelope Feeder
(2) High Capacity Second Paper Feeder
Page: 4
(3) Font Card
(4) RAM module
• 8MB RAM module
• 16MB RAM module
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 5
Service Guide OL1200
Chapter 1 Configuration
1.4 Specification
(1) Type Desk top
(2) External dimensions Height 10.6 (270 mm) (excludes protruding Width 14.4 (366 mm) Portion) Depth
16.9 (430 mm)
(3) Weight 15.2 kg (33.5 lbs)
(4) Development method Dry electrophotography Exposure method LED stationary head
(5) Paper used <Type>
- Standard paper Xerox 4200 (20 lbs)
- Application paper (manual face-up feed) Label Envelope OHP paper (Transparency)
<Size>
- Standard sizes Letter Legal Executive Envelope A4 A5 B5 A6
- Applicable sizes Width: 3.4 to 8.5 (86 to 228 mm) Length: 5.5 to 14 (140 to 355.6 mm)
<Thickness> Automatic feed: 16 to 28 lbs (60 to 105 g/m 2 ) Manual feed: Label, OHP
paper (transparency) Envelope
(6) Printing speed
First print: 12 sec.
Continuous print: 12 sheets/min.
Warm-up time: 90 sec. [at room temperature 77°F (25°C) and rated voltage (120 VAC)]
(7) Paper feed method Automatic feed or manual feed
(8) Paper delivery method Face down/face up
(9) Resolution 600 x 600 dots/inch
(10) Power input 120 VAC + 5.5%, 15% (ODA) 230/240 VAC + 10%, 14% (ODA/OEL)
(11) Power consumption
Peak: Approx. 600W
Typical Operation: Approx. 220W
Idle: Approx. 100W
Power save mode: Approx. 20W
(12) Temperature and humidity During operation: 50 to 90°F (10 to 32°C) In storage: 14 to 110°F (10 to
43°C)
(13) Noise During operation: 50 dB (A) or less At standby: 45 dB (A) or less Power save mode: 43 dB
(A) or less
(14) Consumables Toner cartridge kit 5,000 (5% duty) Image drum cartridge 30,000 (at continuous
printing) 20,000 (3 page/job) 15,000 (1 page/job)

Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Service Guide OL1200
Chapter 1 Configuration
1.5 Safety Standards
1.5.1 Certification label
The safety certification label is affixed to the printer in the position below.
Page: 6
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Guide OL1200
Chapter 1 Configuration
1.5.2 Warning label
The warning label is affixed to the portion which may cause an injury to human body. Follow the
instructions on warning labels during maintenance.
Page: 7
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 8
Service Guide OL1200
Chapter 2 Operation Description
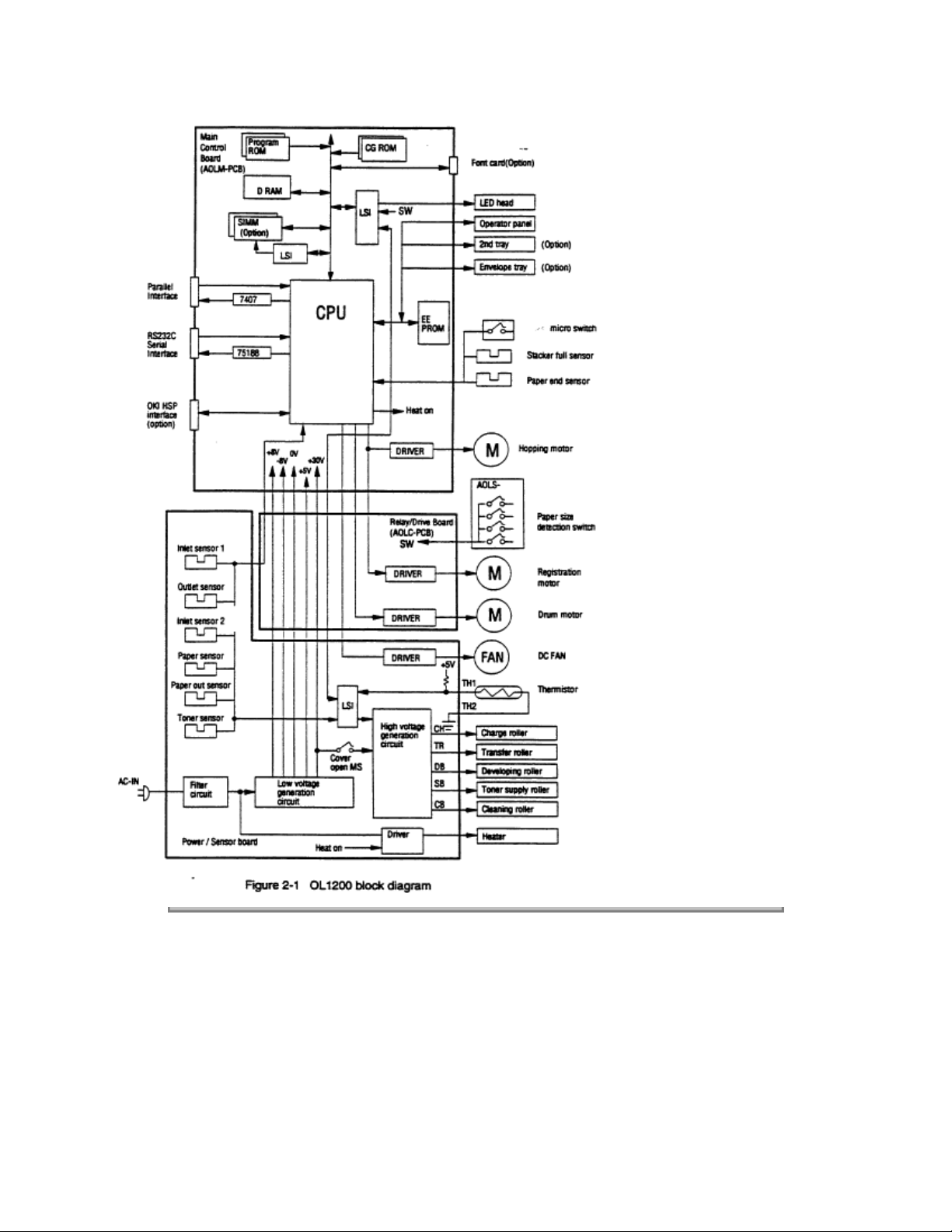
2. OPERATION DESCRIPTION
OL1200 consists of a control board, a power supply/sensor board, a driver board, an operator panel and
an electro-photographic process mechanism.
The control board receives data through a host I/F, decodes and edits the data, and stores the edited data
in a memory. After completing edition of one page of data, it references the font memory and generates bit
data on the same memory. At the same time, it transfers the bit image data to an LED head in units of one
dot line.
The electro-photographic process mechanism prints data on paper.
The operator panel is used for operations and status display.
Fig. 2-1 shows an OL1200 block diagram.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 9
Service Guide OL1200
Chapter 2 Operation Description
2.1 Main Control Board (AOLM-PCB)
The control board consists of a one chip CPU, LSIs, a program/font ROM, a DRAM, an EEPROM, a host
interface circuit, and a mechanism driving circuit.
(1) One-chip CPU
The one-chip CPU is a custom CPU (32-bit internal bus, 32-bit external bus, 33-MHz clock) that
incorporates a RISC CPU and its peripheral devices, and has the following functions:
Built-in device
Chip select controller
Bus controller DRAM controller
DMA controller Transfer of image data from DRAM to OST
Parallel interface controller Control of Centronics parallel interface
Serial interface controller Control of RS-232C serial interface
Timer Generation of various control timing
Serial I/O port Control of operator panel, EEPROM, and
I/O port Inputting/outputting of sensor, signal and
Option I/O interface Control of OKI HSP interface
(2) Program/font ROM
The program/font ROM stores the equipment program and various types of fonts. EPROM/ OTP or
masked ROM is used as a program/font ROM.
Function
Control of ROM, DRAM and I/O device
LSI
Monitoring of paper running and paper size
options
motor signal
(3) Memory
2-Megabyte DRAM (512K x 4) is mounted as resident memory to be used for storing the program and
providing various buffers. This DRAM is expandable up to 34 Mbytes by adding expansion memory
(SIMMs). This DRAM provides the areas shown in the following table.
Memory capacity setting
Memory area
Use MENU Expansion RAM
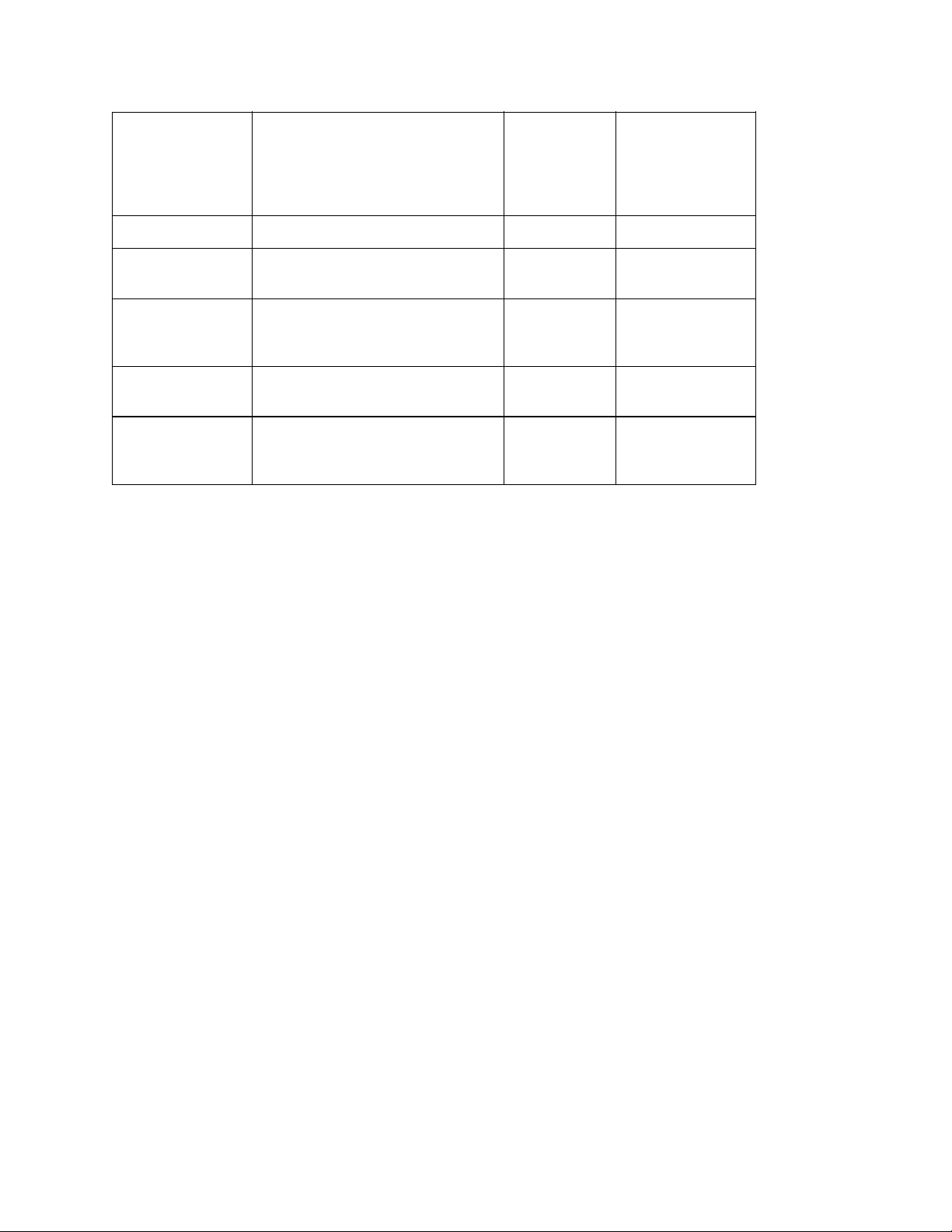
System area Working area used for the
program
Raster buffer Stores converted bit image data Enable Expandable
Fixed
Working
area used
for the
program
Fixed
Receive buffer Stores temporarily the data
received from the host interface
Page buffer Adds print information to the
analyzed receive data and stores
the resulted data.
DLL/macro
buffer
Font cache
buffer
(4) EEPROM
The EEPROM has a 4-kbit capacity and stores the following data.
- Menu data
- Various counter data (page counter, drum counter, fuser counter, etc.)
- Adjustment parameters (LED head drive time, print start position, etc.)
(5) LSI (MSM10S0050-015GS)
This LSI is connected to the CPU via the bus as a peripheral device of the CPU and controls the memory
based on the RAS signal and address signal received from the CPU.
(6) LSI (MBCE31701-040FP-BND)
This LSI is used as a peripheral device of the CPU and performs smoothing compensation (OST) of print
image data (300 dpi and 600 dpi). In addition, it transfers serially bit image data for each dot line to the
LED head.
Stores soft fonts and macro data. Expandable
Stores bit map fonts generated
by the font rasterizer based on
scalable font information
Enable Expandable
Expandable
Enable Expandable
(7) Host interface
This printer has the following interfaces to the host.
- Centronics bidirectional parallel interface
- RS232C serial interface
- OKI HSP interface (Option)
The single effective interface or the automatic interface select mode can be selected using the menu. If
the busy state of the printer continues for a long time period, the buffer near-full control releases the busy
status at constant intervals even if the host side is busy so not to cause the interface time-out at the host
side.
(a) Centronics bidirectional parallel interface
This is an interface conforming to IEEE-1284 and provides either unidirectional or bidirectional
communications according to each of the following communication modes.
- Compatibility mode
- Unidirectional communications from the host to the printer.
- Nibble mode
This mode transmits 4-bit wide data from the printer to the host. In this mode, each 1-byte data is
transferred in the form of two nibbles using ERROR, BUSY, FAULT, and SELECT signal leads. This
mode can provide the bidirectional operation in combination with the compatibility mode.
- ECP mode
his mode provides the asynchronous bidirectional interface and transmits and receives 1-byte data
using eight data signal leads under the semi-duplex control by the host.
When the power is turned on, the compatibility mode is automatically selected. The change to another
mode from the compatibility mode is made through negotiation. (When the BI DIRECTION is set to
ENABLE in the menu, this change can be performed.) (For the electrical/physical characteristics of this
interface, see APPENDIX B)
(b) RS232C serial interface
The following protocol is supported for the serial interface conforming to EIA RS232C.
- READY/BUSY (DTR HI or DTR LO)
- X-ON/X-OFF
- RBST X-ON
(For the electrical/physical characteristics of the interface, see APPENDIX A)
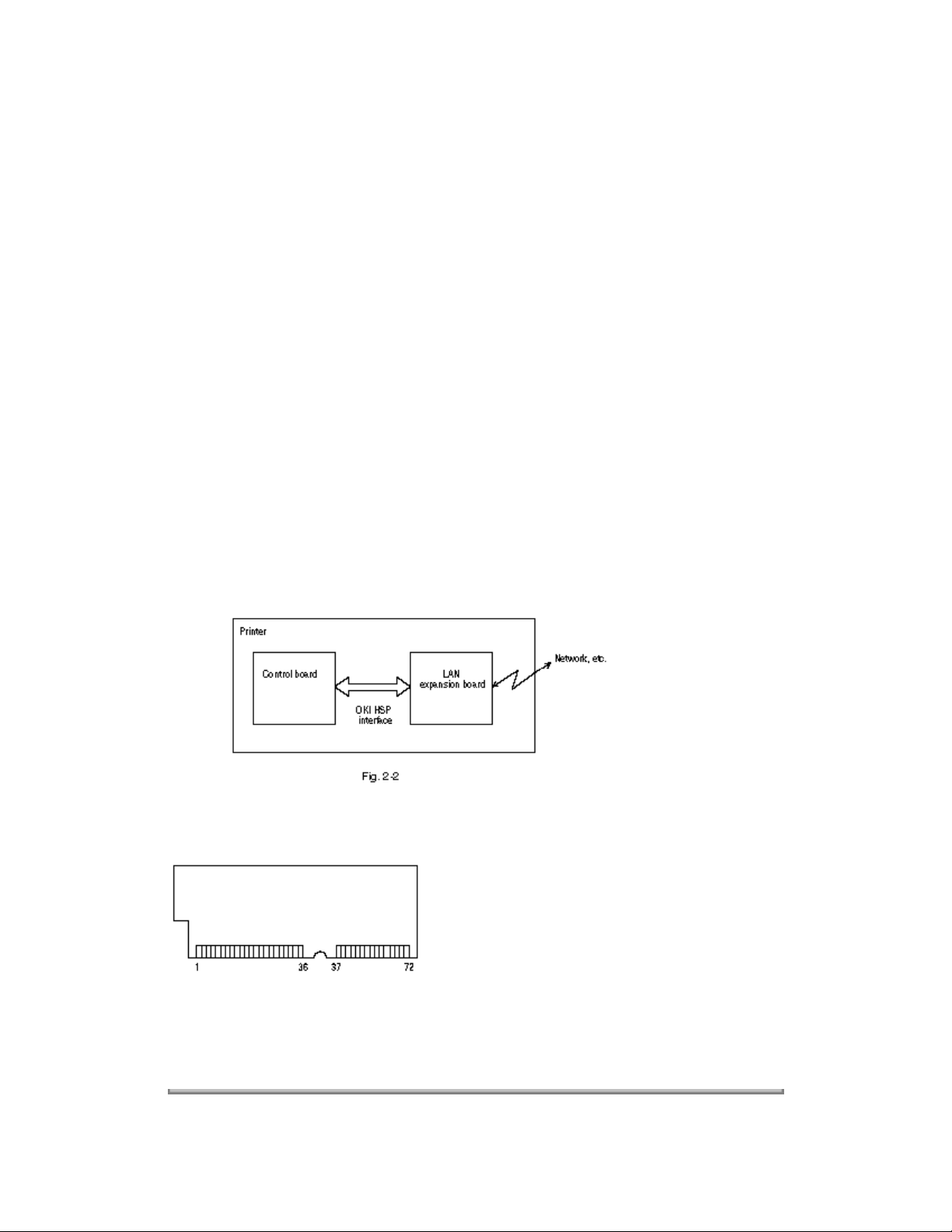
(c) OKI HSP interface (Option)
This interface (slot) is an OKI unique universal interface that provides the platform to connect various
boards (including those supplied by third venders) such as the LAN connection expansion board.
Any expansion boards compatible with this interface can be mounted on the Control board without
modifying the program at the printer side. The conceptual diagram of the OKI HSP interface is shown in
Fig. 2-2.
(For the electrical/physical characteristics of the OKI HSP interface, see the OKI HSP interface technical
manual. This manual will not be available to the general public.)
(8) RAM module
- Pin layout
- Basic specification
- Type: 72 pins SIIM (32 bits buss width)
- Access time: 60ns, 70ns, 80ns, 100ns
- Capacity: 1, 2, 4, 8, or 16MB (16 MB RAM will not be sold by Okidata)
- Parity: None

Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 10
Service Guide OL1200
Chapter 2 Operation Description
2.2 Power/Sensor Board
The power/sensor board consists of an AC filter circuit, a low voltage power supply circuit, a high voltage
power supply circuit, heater drive circuit, and photosensors.
(1) Low voltage power supply circuit
This circuit generates the following voltages.
Output voltage
+5 V Logic circuit supply voltage +30 V
Motor and fan drive voltage and source voltage for
high-voltage supply
RS-232C line voltage 8 V
RS-232C line voltage and analog circuit supply
voltage
(2) High voltage power supply circuit
This circuit generates the following voltages necessary for electro-photographic processing from +30 V
according to the control sequence from the control board. When cover open state is detected, +30 V
supply is automatically interrupted to stop the supply of all the high-voltage outputs.
Output
CH -1.30 KV Voltage applied to
DB -240 V/+300 V Voltage applied to
Voltage Use Remarks
charging roller
developing roller
Use
+8 V
SB -360 V/450 V Voltage applied to
toner supply roller
TR +4 KV/-1.3 kV Voltage applied to
transfer roller
CB +400 V Voltage applied to
cleaning roller
(3) Photosensor
Variable
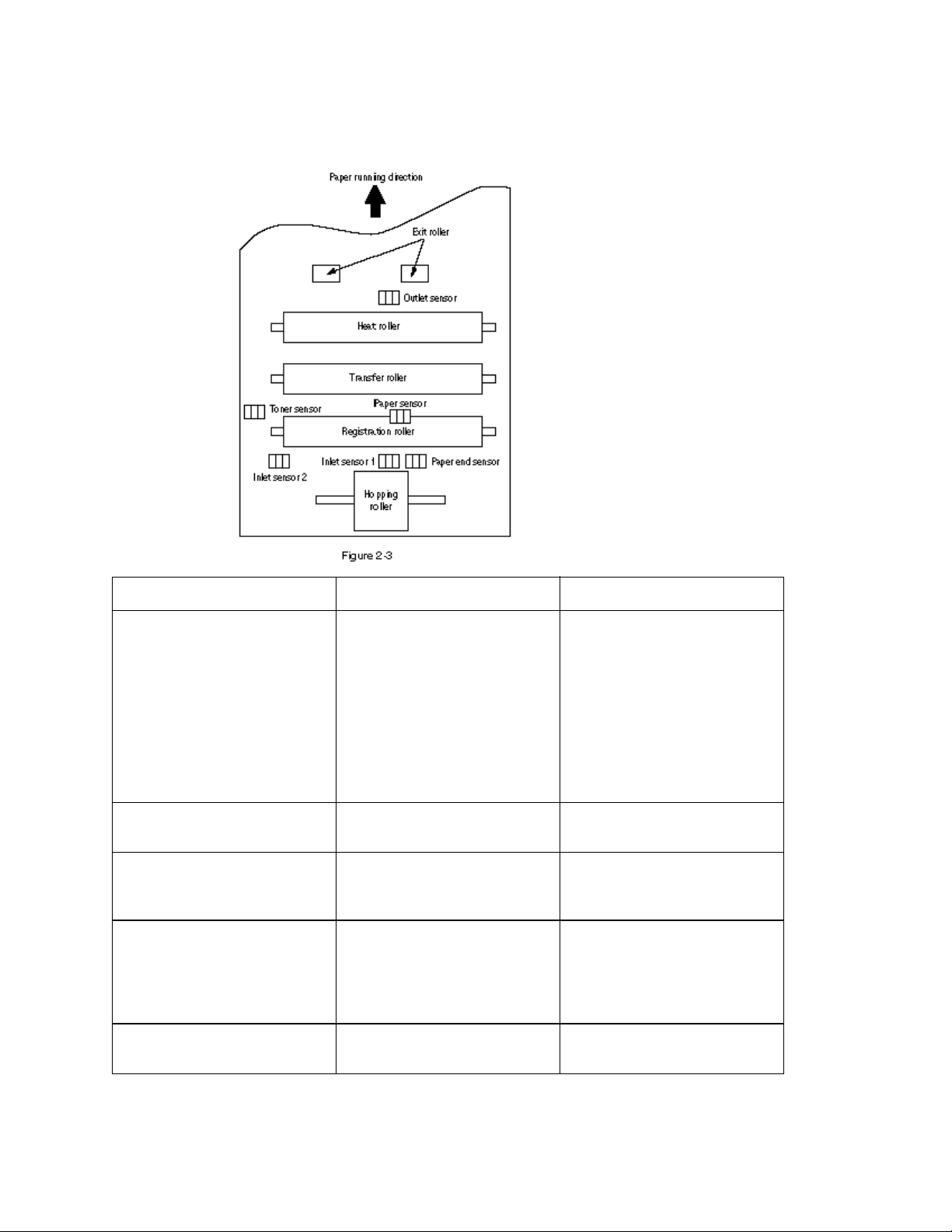
The photosensor mounted on this power/sensor board supervises the paper running state during printing.
Figure 2-3 shows the sensor layout diagram.
Sensor Function Sensing state
Inlet sensor 1 Detects the leading part of
the paper and gives the
supervision timing for
switching from hopping
operation to feeding
operation. Supervises the
paper running state and the
paper size according to the
paper reach time and running
time.
Inlet sensor 2 Detects the form width. ON: A4 or larger
Paper sensor Detects the leading part of
the paper. Supervises the
paper running state.
Outlet sensor Supervises the paper feed
and size according to the
time of arrival to the sensor
and the time of passage of
paper.
Paper end sensor Detect the end of the paper. ON: Paper exists.
ON: Paper exists.
OFF: No paper exists.
OFF: Smaller than A4
ON: Paper exists.
OFF: No paper exists.
ON: Paper exists.
OFF: No paper exists.
OFF: No paper exists.
Toner low sensor Detects the lack of toner. ON long: Toner low exists
OFF short: No Toner low
exists
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 11
Service Guide OL1200
Chapter 2 Operation Description
2.3 Relay/Driver Board (AOLC board)
This board relays signals between the Control board and the Power/Sensor board and includes the
registration motor and drum motor driver IC.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 12
Service Guide OL1200
Chapter 2 Operation Description
2.4 Electro-photographic Process
2.4.1 Electro-photographic process mechanism
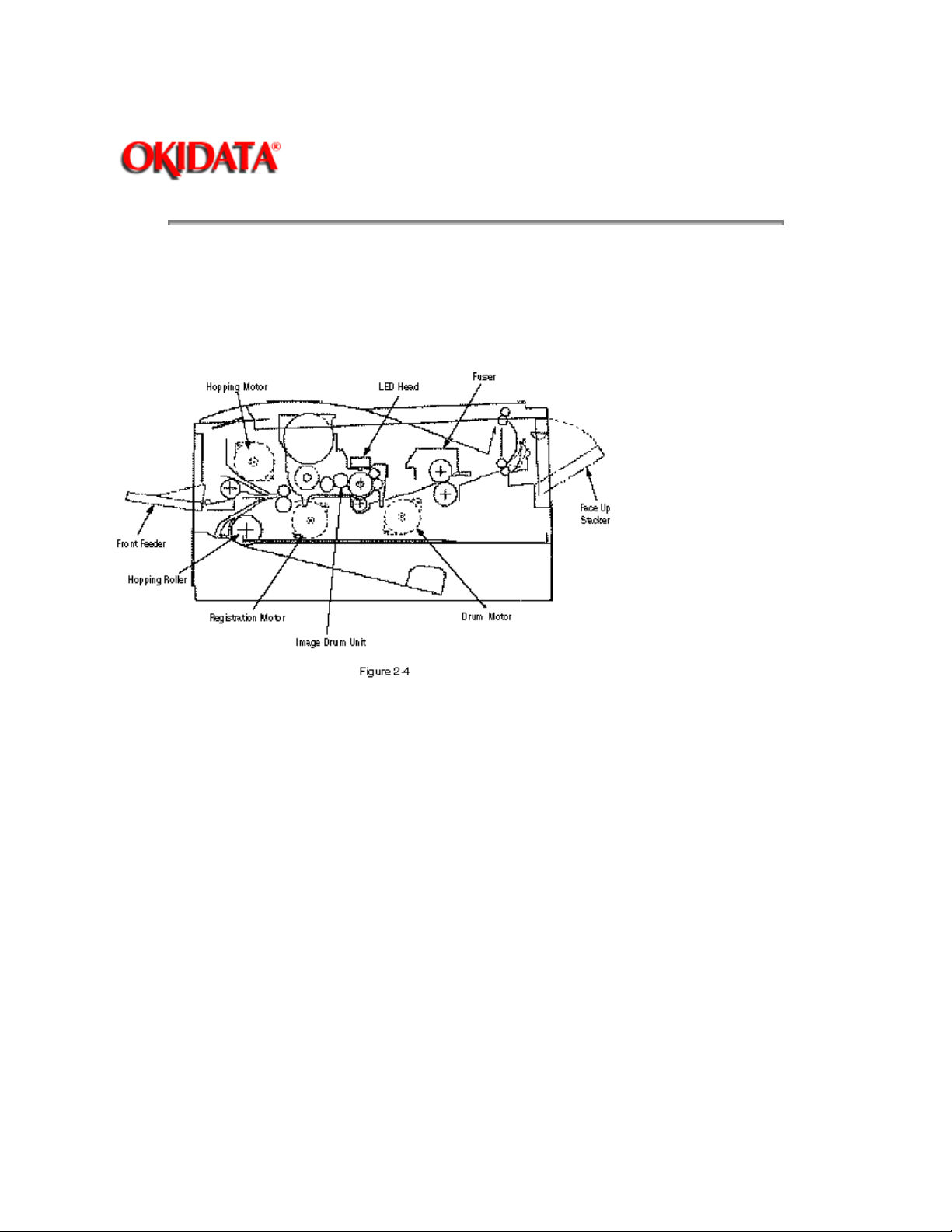
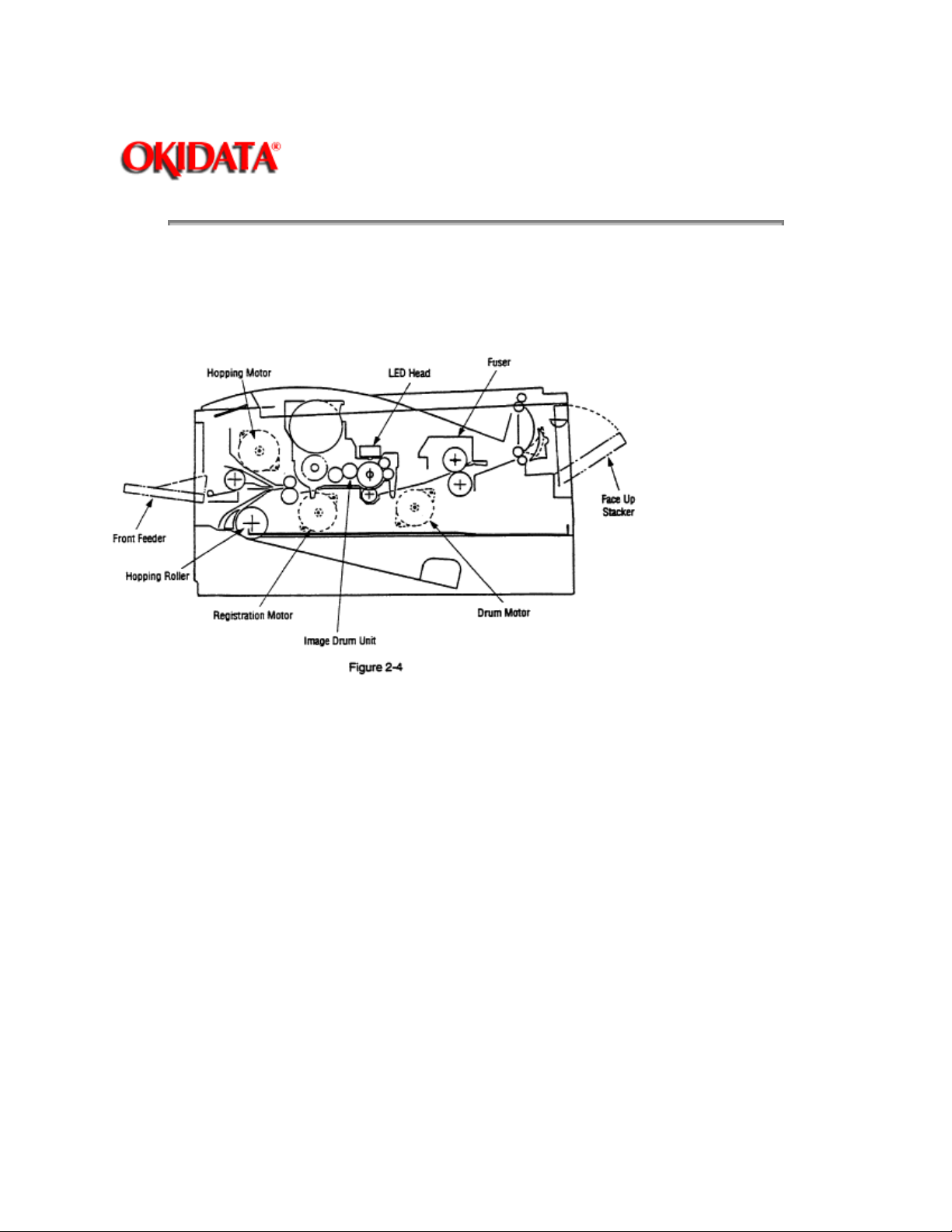
This mechanism prints image data from the control board on the paper by electro-photographic process.
The Figure 2-4 shows the layout of the electro-photographic process mechanism.
(1) Image drum unit
The image drum unit consists of a sensitive drum, a charger, and a developer. The unit forms a toner
image on the sensitive drum, using an electrostatic latent image formed by the LED head.
(2) Hopping motor
This motor is a pulse motor of 48 steps/rotation that is two-phase excited by the signal from the control
board. It drives the hopping roller of the first tray and the front feed roller via two one-way clutches
according to the direction of rotation.
(3) Registration motor
This motor is a pulse motor of 48 steps/rotation that is two-phase excited by the signal from the control
board. It drives the registration roller.
(4) Drum motor
This drum motor is a pulse motor of 48 steps/rotation that is two-phase excited by the signal from the
control board and is the main motor of this mechanism.
(5) LED head
Image data for each dot line from the control board is received by the shift register and latch register. The
5120 LED's are driven to radiate the image data to the image drum.
(6) Fuser
The fuser consists of a heater, a heat roller, a thermistor and a thermostat. An AC voltage from the power
supply board is applied to the heater under the control of the HEATON signal from the control board. This

AC voltage heats the heater. The control board supervises the heat roller temperature via the thermistor,
and regulates the heater roller at a predetermined temperature (185 - 188°C) by connecting or
disconnecting the AC voltage supply to the heater. If the heater roller temperature rises abnormally, the
thermostat of the heater voltage supply circuit is activated to cut the AC voltage supply forcibly.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 13
Service Guide OL1200
Chapter 2 Operation Description
2.4.2 Electro-photographic process
The electro-photographic processing is outlined below. Figure 2-5 shows the electro-photographic printing
process.
1 Charging
The surface of the image drum is uniformly charged with negative charges by applying a negative voltage
to the charge roller.
2 Exposure
Light emitted from the LED head irradiates the negatively charged surface of the image drum. The surface
potential of the irradiated part of the image drum surface is lowered, so that an electrostatic latent image
associated with the print image is formed.
3 Developing and toner recovery
When the negatively charged toner is brought into contact with the image drum, it is attracted to the
electrostatic latent image by static electricity, making the image visible. At the same time, the residual
toner on the image drum is attracted to the developing roller by static electricity.
4 Transfer
When paper is placed over the image drum surface and a positive charge, opposite in polarity to the toner,
is applied to the reverse side of the paper from the transfer roller, the toner is attracted by the positive
charge and is transferred to the paper. As a result, the toner image formed on the image drum is
transferred to the paper.
5 Temporary cleaning
Residual toner that remains on the image drum without being transferred is made uniform by the cleaning
roller and is temporarily attracted to the cleaning roller by static electricity.
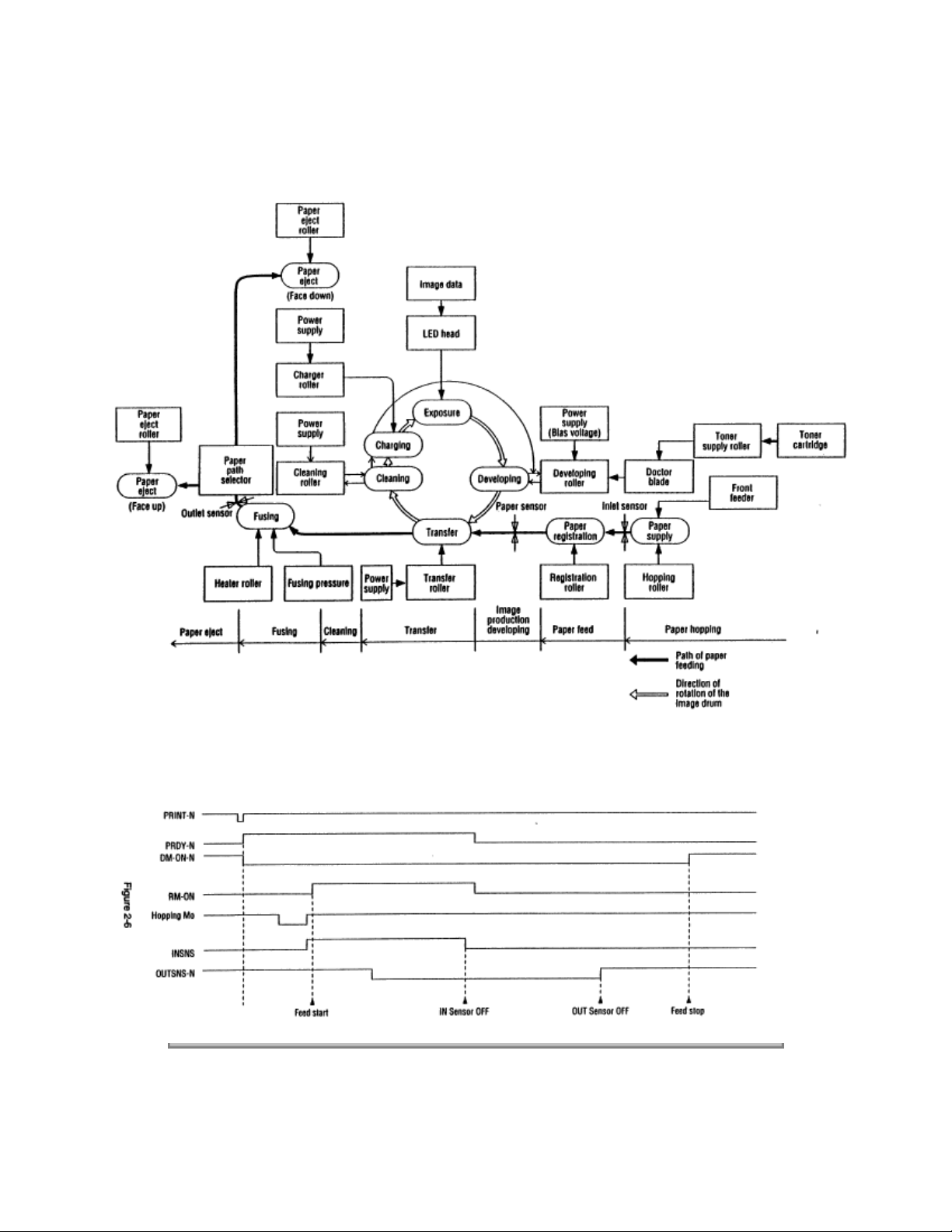
6 Fusing
The toner image transferred to the paper is fused under heat and pressure. Figure 2-6 shows an
electro-photographic process timing chart.
Copyright 1997, Okidata, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the OKIDATA Business
Partner Exchange (BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 14
Service Guide OL1200
Chapter 2 Operation Description
2.4.3 Process operation descriptions
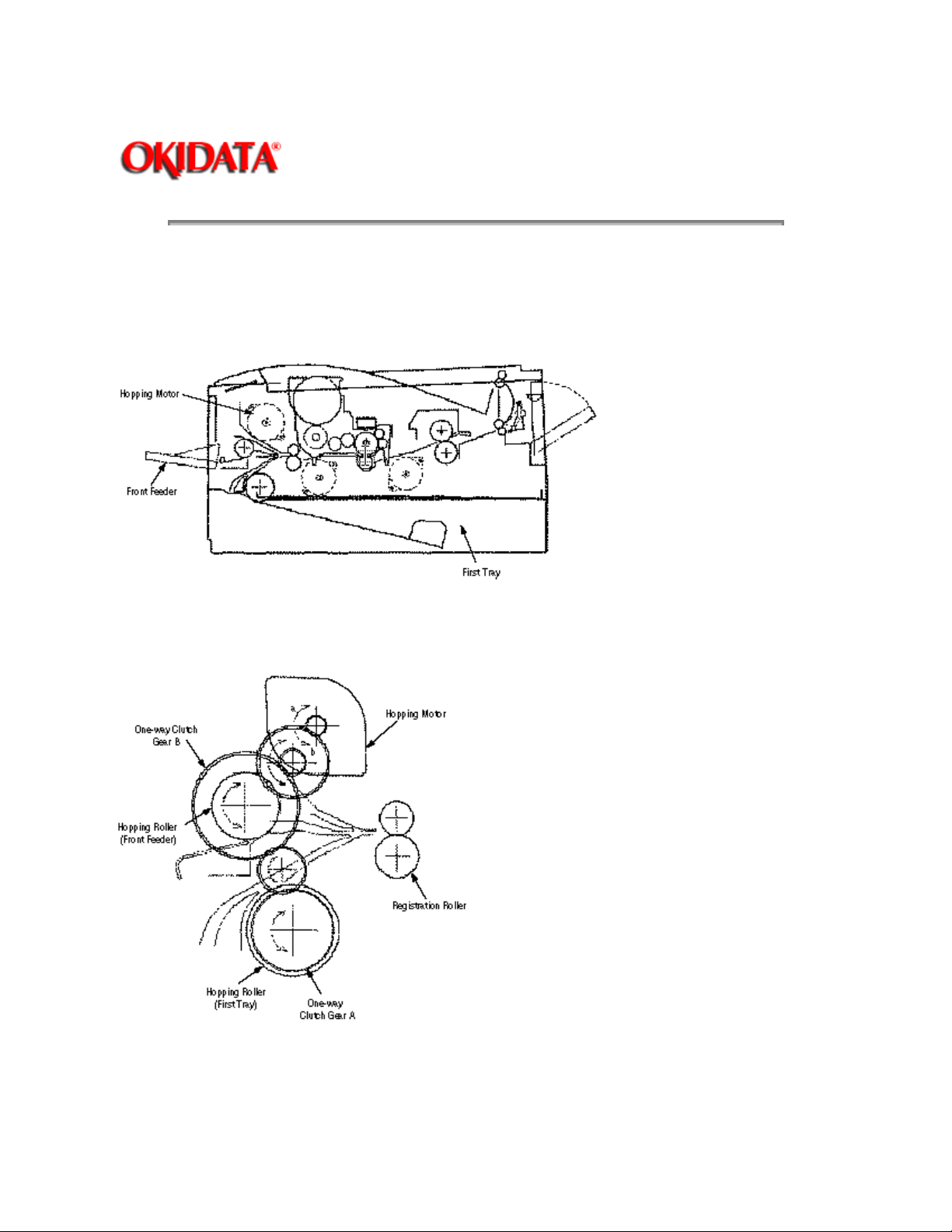
(1) Hopping
Hopping from the first tray and the front feeder are effected by a single hopping motor in the mechanism
shown below.
Turning the Hopping motor in the a direction drives the hopping roller of the first tray. Turning the Hopping
motor in the b direction drives the Hopping roller of the front feeder. The both and hopping gears contain
one-way bearing, so that turning each of these gears in reverse direction will not be transmitted to the
corresponding roller.
(a) Hopping (1st tray)
1 Rotating the pulse motor in the direction a (Clock-wise direction) drives the hopping roller of the first tray
to advance the paper until the inlet sensor turns on. At the same time, the one-way clutch gear B also
rotates. However, the hopping roller of the front feeder will not rotate due to the one-way bearing.
2 After turning on the inlet sensor, the paper advances further by a predetermined length until it hits the
 Loading...
Loading...