Okidata OKIPAGE 8z Service Manual
Thank You for purchasing this
Click Here for more Factory Service
Manuals for other Computer and
Printer / Copier Manufacturers
from PCTECHINFO!

Front Cover
Service Manual for OKIPAGE 8z
Chapter 0 Introduction
Service Guide
OKIPAGE 8z
Digital LED Page Printer
Page: 1
Adobe Acrobat printable reference copy
of the OKIDATA Service Training Manual.
07/18/2000
Note: This Adobe Acrobat version of the Okidata Service Training Manual was built with the pictures
rendered at 72 dpi, which is ideal for screen viewing. For future updates to this manual, and
more on-line information visit our Business Partner Exchange (BPX) at
http://bpx.okidata.com.
Copyright 2000, Oki Data, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the Oki Data Business Partner Exchange
(BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Table of Contents Page
....4.1 Adjustment Types and Functions 45
........4.1.1 Printer Driver 46
........4.1.2 Engine Maintenance Utility 47
....4.2 Adjustment When Replacing a Part 48
........4.2.1 Setting LED Head Drive Time 49
........4.2.2 Uploading and Downloading EEPROM Data 50
5 Periodical Maintenance
5.1 Periodical Replacement Parts 51
5.2 Cleaning 52
....5.2.1 Cleaning the LED Lens Array 53
6 Troubleshooting Procedures
6.1 Troubleshooting Tips 54
6.2 Check Points Before Correcting Image Problems 55
6.3 Notes When Correcting Image Problems 56
6.4 Preparation Before Troubleshooting 57
6.5 Troubleshooting 58
....6.5.1 Status Monitor Message List 59
....6.5.2 Status Message Troubleshooting 60
....6.5.3 Image Troubleshooting 61
........(1) An image is light or blurred entirely 62
........(2) Dark background density 63
........(3) A blank paper is output 64
........(4) Vertical black belt/stripe 65
........(5) Cyclic defect 66
........(6) A blank paper is output 67
........(7) Poor fusing 68
........(8) Vertical white belt/stripe 69
........Contents - Figure 6-4 70
........Contents - Figure 6-5 71
7 Wiring Diagram
7.1 Interconnect Signal Diagram 72
7.2 PCB Layout 73
....7.2.1 Main Control Board (U8S PCB) 74
....7.2.2 High-Voltage Power Supply Board 75
8 Parts List
Cover Assy Upper 76
Base Frame Unit 77
Heat Assy 78
Base Plate Unit 79
A Local Printing
Local Printing 80
B Parallel Interface
Parallel Interface 81
C Maintenance Utility
Outline of Maintenance Utility 82
Detail of Each Function 83
....4.1 Engine Menu Setting 84
....4.2 Engine Counter 85
....4.3 Printer Status 86
....4.4 Test Print 87
....4.5 Option 88
Table of Contents Page
....4.6 About 89
....4.7 Reload 90
.... 4.8 Exit 91
D Universal Serial Bus (USB)
USB Specifications 92

Page: 1
Service Manual for OKIPAGE 8z
Chapter 0 Introduction
Preface
This Service Handbook describes the field maintenance procedures for the OKIPAGE 8z.
This manual is written for use by service persons. Please note that you should refer to the Printer User's Manual for
operating procedures.
Copyright 2000, Oki Data, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the Oki Data Business Partner Exchange
(BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 2
Service Manual for OKIPAGE 8z
Chapter 1 Configuration
Configuration
System Configuration
Printer Configuration
Specification
Safety Standards
Copyright 2000, Oki Data, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the Oki Data Business Partner Exchange
(BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 3
Service Manual for OKIPAGE 8z
Chapter 1 Configuration
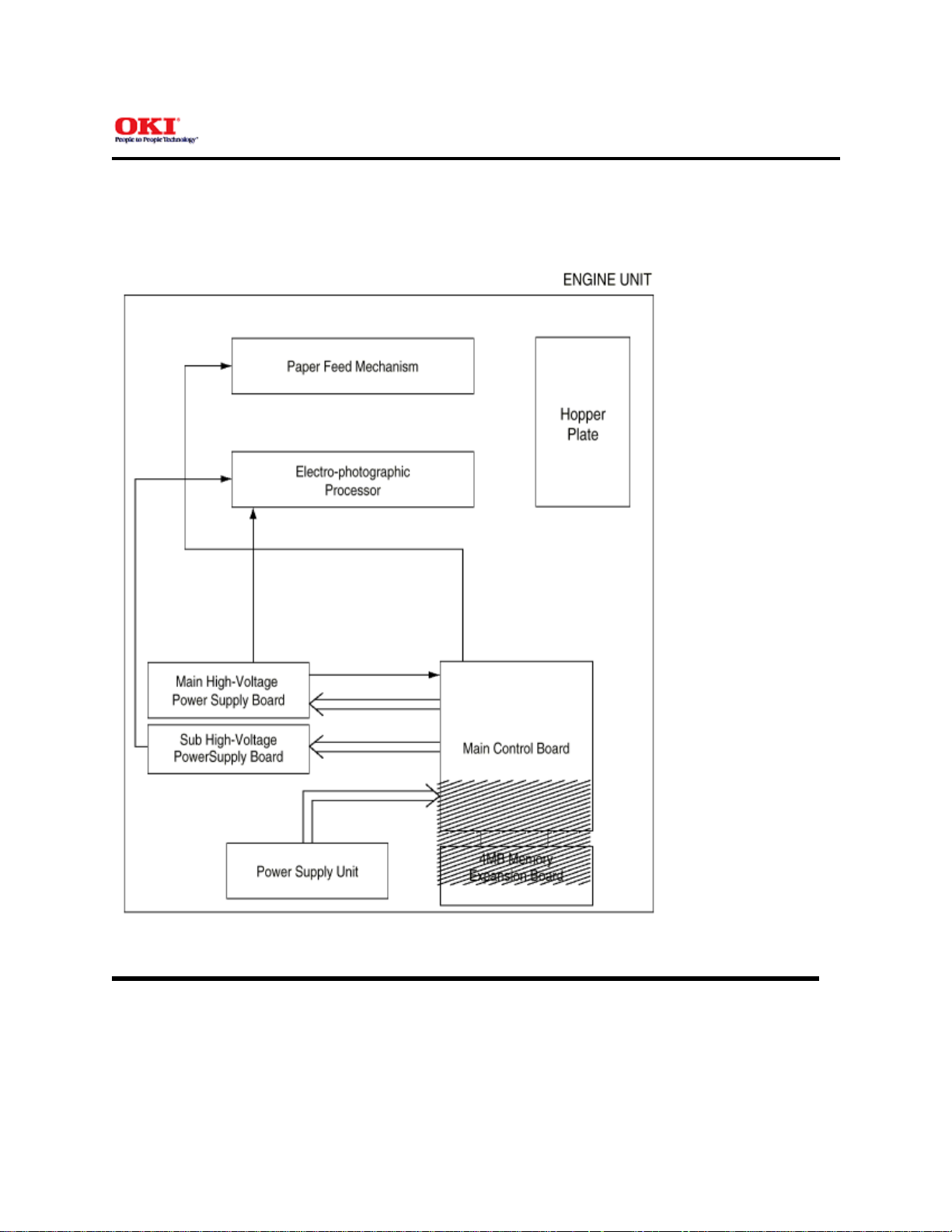
1.1 System Configuration
The OKIPAGE 8z consists of a control block, a power supply unit, and an engine block. (See Figure 1-1
below.)
Figure 1-1
Copyright 2000, Oki Data, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the Oki Data Business Partner Exchange
(BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Manual for OKIPAGE 8z
1.2 Printer Configuration
The printer unit consists of the following five hardware components:
Electro-Photographic Processor l
Paper Feeder l
Main Control Board l
High-Voltage Power Supply Board l
Power Supply Unitl
Figure 1-2 is the configuration of the printer unit.
Chapter 1 Configuration
Page: 4
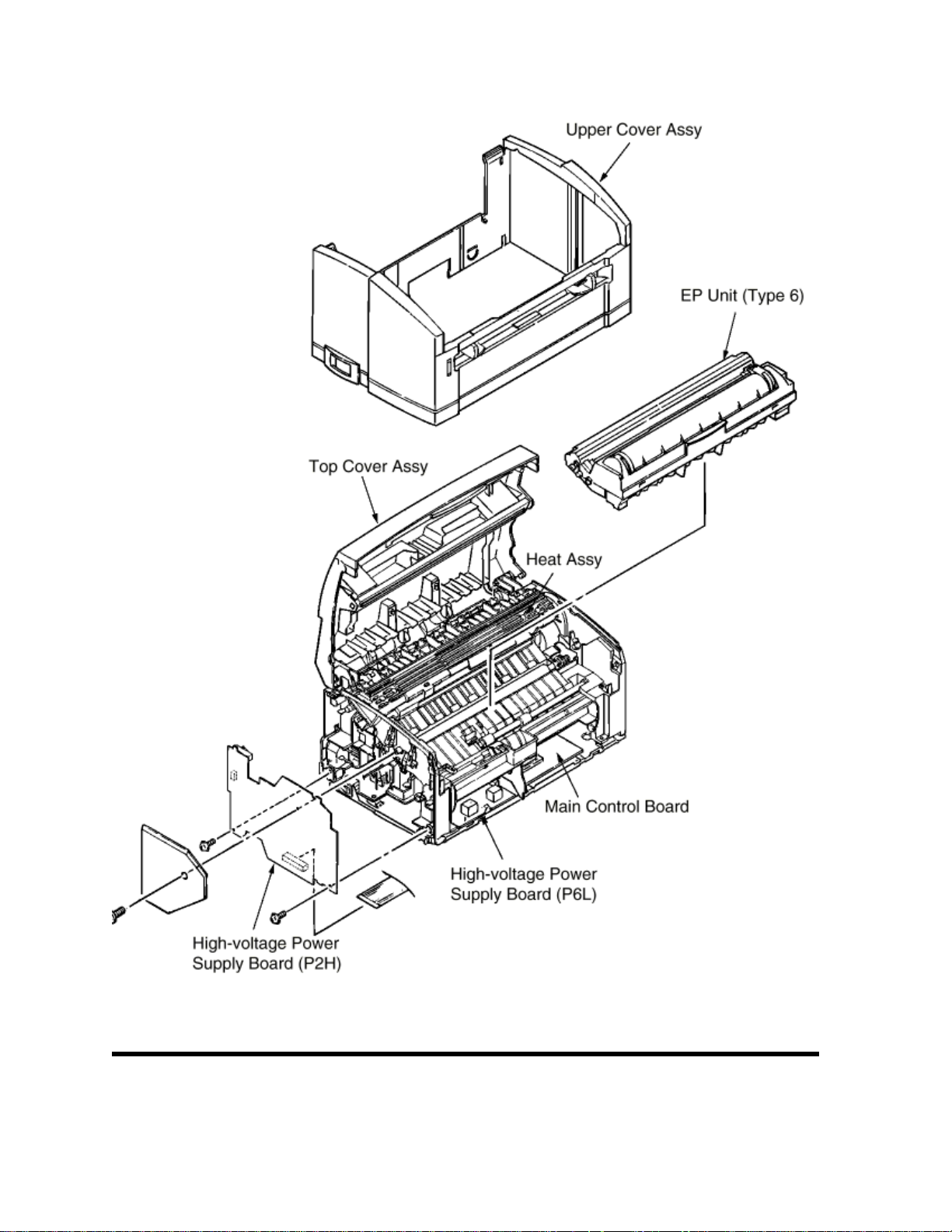
Figure 1-2
Copyright 2000, Oki Data, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the Oki Data Business Partner Exchange
(BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Manual for OKIPAGE 8z
1.3 Specification
(1) Type: Desktop
Chapter 1 Configuration
Page: 5
(2) Outside dimensions
(excludes protruding
portion)
Height: 5.9" (150 mm)
Width 12.2" (310 mm)
Depth 7.5" (191mm)
(3) Weight 8.4 lbs. (3.8kg)
(4) Development
method
Dry non-magnetic development system
LED stationary head
Exposure method
(5) Paper used <Type>
Standard paperl
- Xerox 4200 (20 lbs)
Application paper (manual face-up feed)l
- Label
- Envelope
- OHP paper (Transparency)
<Size>
14" (355.6 mm) (Max.) x 8.5" (215.9 mm)
<Thickness>
Automatic feed: 16 to 28 lbs (60 to 105 g/m2)
- Manual feed: Label, Envelope, OHP paper (transparency)
(6) Printing speed: First print: 23 seconds (A4) (after warm-up)
Continuous print: 8 sheets/minute (A4)
Warm-up time: 40 seconds (120 VAC for ODA, 230 VAC for
OEL/INT) (at room temperature 77o F (25o C)
(7) Paper feeding
Automatic paper feed or manual paper feed
method
(8) Paper delivery
Face down
method
(9) Resolution 600 dpi x 600 dpi (true)
(10) Power input 230 VAC +/-10% (for OEL/INT)
120 VAC +/-15% for (ODA)
(11) Power consumption Peak: Approx. 450W
Typical operation: Approx. 100W
Idle: Approx. 30W
Power save mode: Approx. 5W
(12) Temperature and
humidity
Temperature Humidity

During operation
In storage
10 to 32o C
-10 to +43o C
20 to 80% RH (relative humidity)
10 to 90% RH (relative humidity)
No condensation is permissible.
Caution: Temperature and humidity in storage are measured with the OKIPAGE 8z being packed; they
are valid for one year.
(13) Noise During operation: 48 dB (A) or less
Standby: 38 dB (A) or less
(14) Consumables Toner cartridge kit - 1,500 (5% duty) ---- 45g cartridge kit
Image drum cartridge - 10,000 (at continuous printing)
Copyright 2000, Oki Data, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the Oki Data Business Partner Exchange
(BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 6
Service Manual for OKIPAGE 8z
Chapter 1 Configuration
1.4 Safety Standards
1.4.1 Certification Label
1.4.2 Warning Label
Copyright 2000, Oki Data, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the Oki Data Business Partner Exchange
(BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 7
Service Manual for OKIPAGE 8z
Chapter 1 Configuration
1.4.1 Certification Label
The safety certification label is affixed to the following location of the OKIPAGE 8z:
Copyright 2000, Oki Data, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the Oki Data Business Partner Exchange
(BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
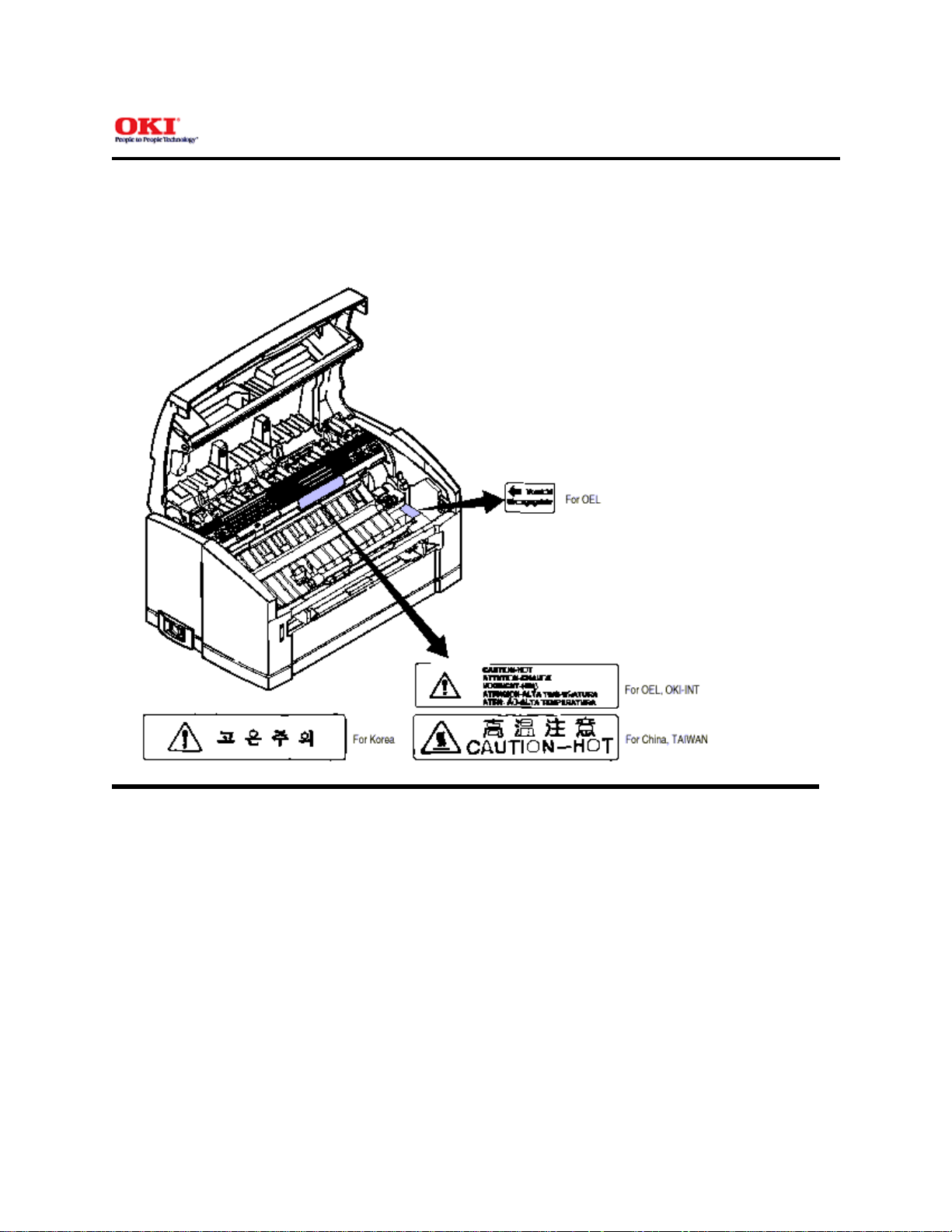
Service Manual for OKIPAGE 8z
1.4.2 Warning Label
Warning labels are affixed to the locations that may cause bodily injury.
During maintenance, do work with enough care while following instructions on these warning labels.
Chapter 1 Configuration
Page: 8
Copyright 2000, Oki Data, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the Oki Data Business Partner Exchange
(BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 9
2.0 Operation Description
Service Manual for OKIPAGE 8z
Chapter 2 Operation Description
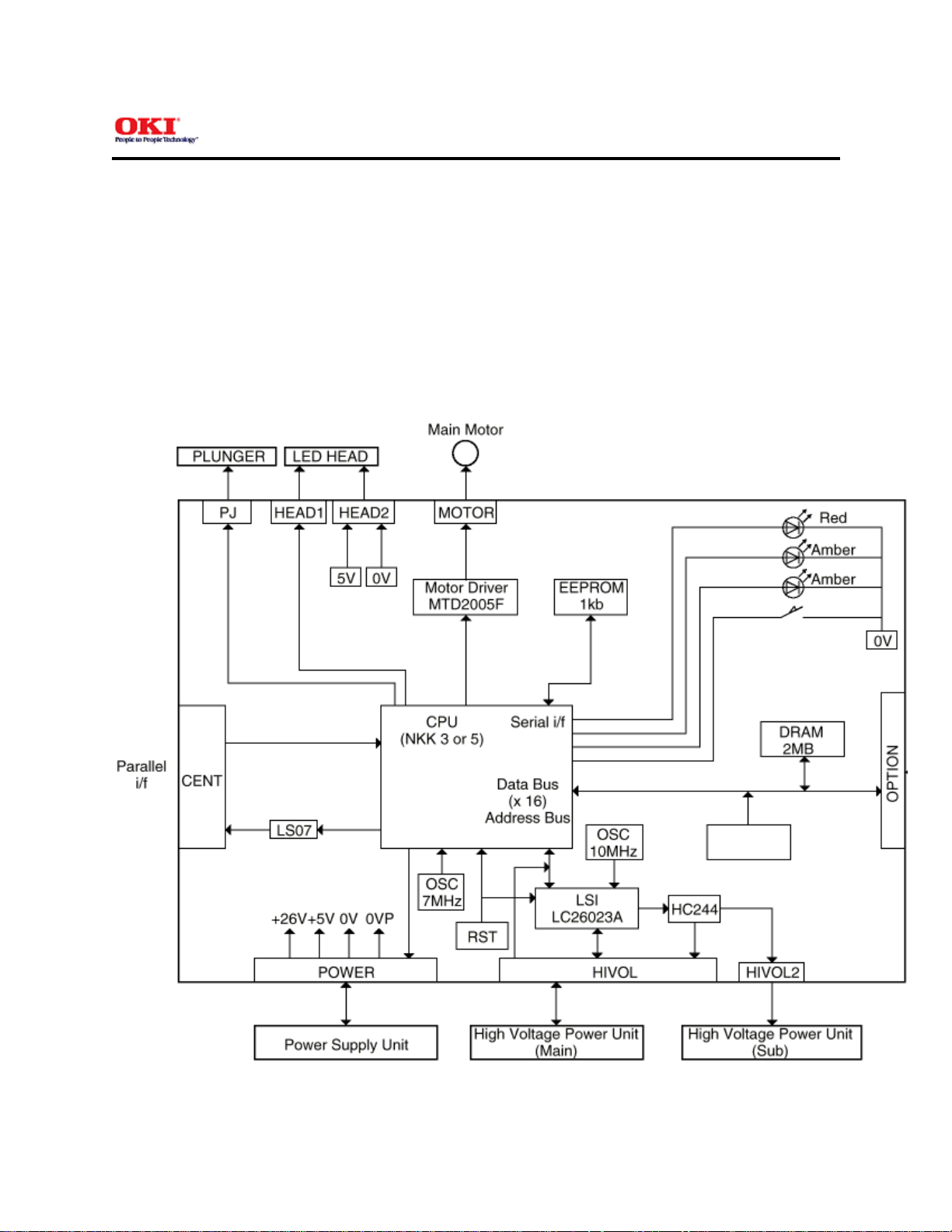
The OKIPAGE 8z consists of a main control board, a high-voltage power supply board, a power supply
unit, and an electro-photographic processor. The OKIPAGE 8z receives print data from a higher-level
interface and sequentially stores it in memory. The OKIPAGE 8z decodes and edits the received data
while storing print data from the interface in memory. It sequentially transfers the edited data to the LED
head for each dot line. The electro-photographic processor then prints the data on sheets of paper.
The display of the higher-level host is used for device operation and status display.
Figure 2-1 is the block diagram of the OKIPAGE 8z.
Figure 2-1 Block Diagram

Copyright 2000, Oki Data, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the Oki Data Business Partner Exchange
(BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Page: 10
2.1 Main Control Board
Service Manual for OKIPAGE 8z
Chapter 2 Operation Description
The main control board consists of a one-chip CPU, a program ROM, a DRAM, an EEPROM, a host
interface circuit, and a mechanism driving circuit. The mechanism driving circuit consists of an LED head,
a main motor, and an electromagnetic clutch.
(1) One-chip CPU
The one-chip CPU is a custom CPU (8-bit internal bus, 8-bit external bus, 16-MHz clock) incorporating
mask ROM and CPU peripheral devices. This CPU has the functions listed in the table below.
Built-in Device Function
DRAM controller Controls DRAM.
DMA controller Transfers image data from Parallel I/F to DRAM, from
DRAM to a video output port and between CPU and
DRAM.
Parallel interface controller Controls the parallel interface.
Video output port
Controls LED head.
LED STB output port
Timer Generates various control timings for monitoring paper
feeding and a paper size.
I/O Port Inputs and outputs the sensor signals and motor
signals, etc. Also performs I/O for EEPROM.
A/D converter Inputs the feedback signals from a high-voltage
generation circuit and thermistor signal.
(2) Program ROM
Program ROM contains a program for the equipment. EPROM is used as program ROM. When mask
ROM in the one-chip CPU explained in (1) above is valid, the EPROM is not mounted. (For details on
short wiring setting, see Section 7.2.)
(3) DRAM
DRAM is used as resident memory.
(4) EEPROM
EEPROM holds the following data:
Menu data l
Counter value l
Adjustment valuel

(5) Parallel interface
The parallel interface receives parallel data from the host; it conforms to the IEEE1284 specification.
Copyright 2000, Oki Data, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the Oki Data Business Partner Exchange
(BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Page: 11
Service Manual for OKIPAGE 8z
Chapter 2 Operation Description
2.2 Power Supply Unit
The power supply unit supplies +5 V and +26 V to the main control board according to 230 VAC / 120 VAC.
Output voltage Application
+5 V Used to generate a logic circuit and a high voltage.
+26 V Used to drive the motor and electromagnetic clutch.
Copyright 2000, Oki Data, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the Oki Data Business Partner Exchange
(BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Manual for OKIPAGE 8z
2.3 High-Voltage Power Supply Board
Chapter 2 Operation Description
Page: 12
(1) High-Voltage power supply circuit
The high-voltage power supply circuit generates the following voltages required for the electro-photographic
processor from +5 V according to the control sequence from the main control board. When the cover is open, +5 V
supply is automatically interrupted to stop high-voltage output.
Output Voltage Application
CH -1.3 KV Voltage to be applied to charge roller.
DB -265 V/+265 V Voltage to be applied to a developing roller.
SB -520 V/ 0 V Voltage to be applied to a sponge roller.
CB +400 V/-1.3 KV Voltage to be applied to a cleaning roller.
TR +500 V ~ +3.5 KV/-750 V Voltage to be applied to a transfer roller.
Caution: The TR voltage varies with medium and transfer roller impedance.
(2) Sensors
The high-voltage power supply board consists of the high-voltage power supply circuit that supplies power to the
electro-photographic processor system and the photosensor that detects a paper feeding system and toners.
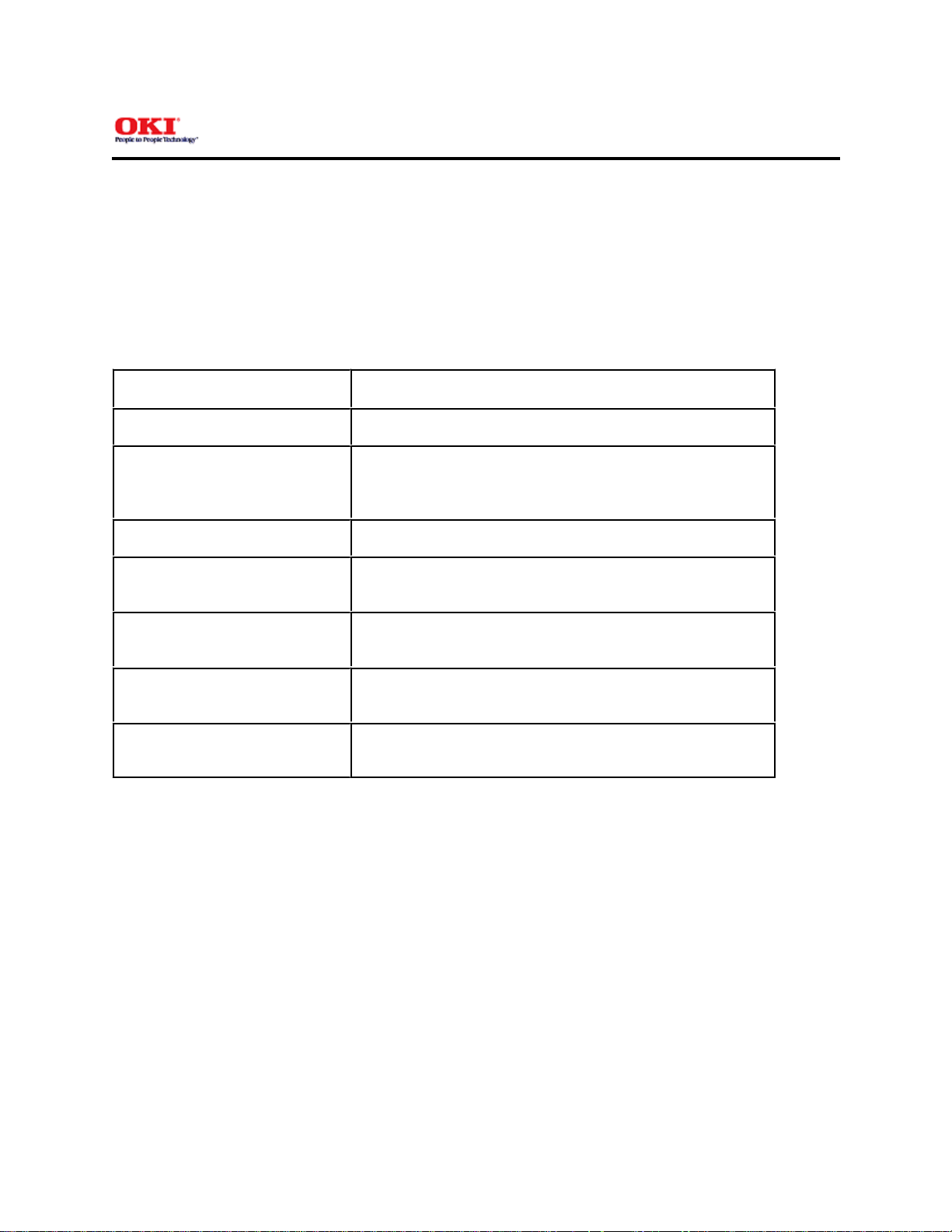
Figure 2-2 shows the sensor layout drawing.
Sensor Function Sensing State
Manual feed sensor Monitors whether paper was inserted into the
manual feed sensor section.
Paper sensor Detects the leading part of the paper. Monitors
paper feeding.
Output sensor Monitors paper feeding and the paper size
according to the paper sensor arrival and
ON: Paper exists.
OFF: No paper exists.
ON: Paper exists.
OFF: No paper exists.
ON: Paper exists.
OFF: No paper exists.
passing time.
Toner sensor Detects the low toner status. ON (long): Toner low.
OFF (short): Toner high.
Copyright 2000, Oki Data, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the Oki Data Business Partner Exchange
(BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Service Manual for OKIPAGE 8z
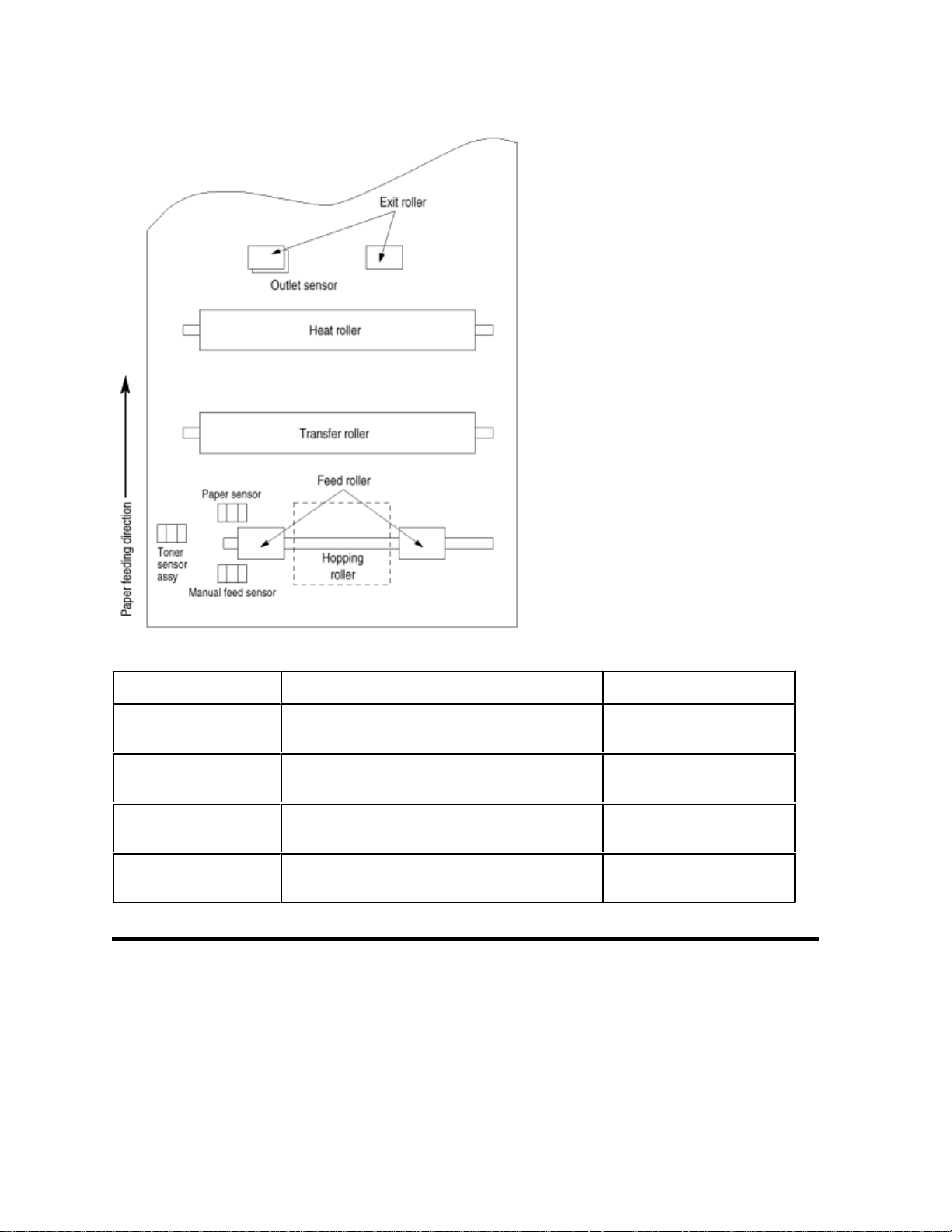
2.4 Electro-Photographic Processor
Chapter 2 Operation Description
Page: 13
The electro-photographic processor prints out the image data to be sent from the main control board on sheets of
paper. Figure 2-3 shows the layout drawing of the electro-photographic processor.
(1) Image drum unit
The image drum unit makes a toner adhere to the formed electrostatic latent image with static electricity. This
electrostatic latent image is formed by the lights irradiated from LED heads.
(2) Electromagnetic clutch
The electromagnetic clutch controls the rotation of the hopping roller according to signals from the control block.
(3) Pulse motor (Main)
This pulse motor of 48 steps/rotation is two-phase excited by the signal from the main control board; it performs
feeding control by switching normal rotation to reverse rotation or vice versa and turning on/off the electromagnetic
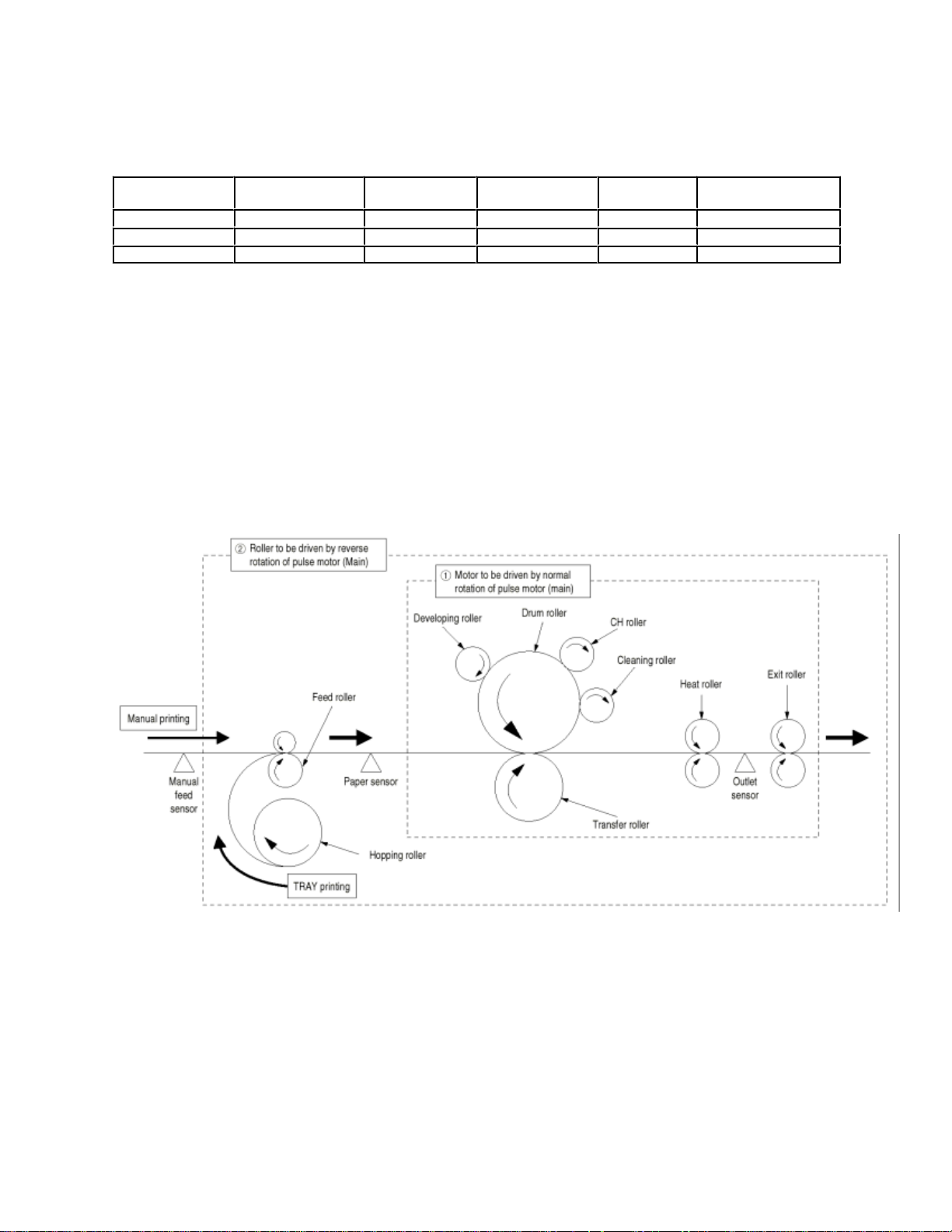
clutch. The relationship between the main motor, electromagnetic clutch, resist gear, drum gear, hopping roller is
shown in the table
below and on the subsequent pages.
Main Motor Electromagnetic
Clutch
Hopping Roller Regist Gear Drum Gear Operation
Normal rotation OFF Non-rotation Non-rotation Rotation Warm-up
Reverse rotation ON Rotation Rotation Rotation Hopping
Reverse rotation OFF Non-rotation Rotation Rotation Printing
(4) LED head
The shift and latch registers receive image data from the main control board for each dot line. 4,992 LEDs are driven
to radiate the image drum.
(5) Heat Assy
The heat Assy consists of a heater, a heat roller, a thermistor, and a thermostat.
The power supply unit supplies AC voltage to the heater according to the HEATON signal from the main control
board to heat the heat roller. The main control board monitors the heat roller temperature via the thermistor and
keeps the temperature constant by turning on/off the heater AC voltage supply.
If the heat roller temperature rises abnormally, the thermostat of the heater voltage supply circuit functions to forcibly
suspend the AC voltage supply.
(1)
(2)
Roller control by pulse motor (main)
Normal rotation of pulse motor (main): Drum roller, transfer roller, cleaning roller, CH
roller, developing roller, heat roller, exit roller
rotation.
Reverse rotation of pulse motor (main): Drum roller, transfer roller, cleaning roller, CH
roller, developing roller, heat roller, exit roller,
feed roller, hopping roller rotation.
Hopping operation from the tray, however, is
performed when the electromagnetic clutch is

turned on.
Copyright 2000, Oki Data, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the Oki Data Business Partner Exchange
(BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)

Service Manual for OKIPAGE 8z
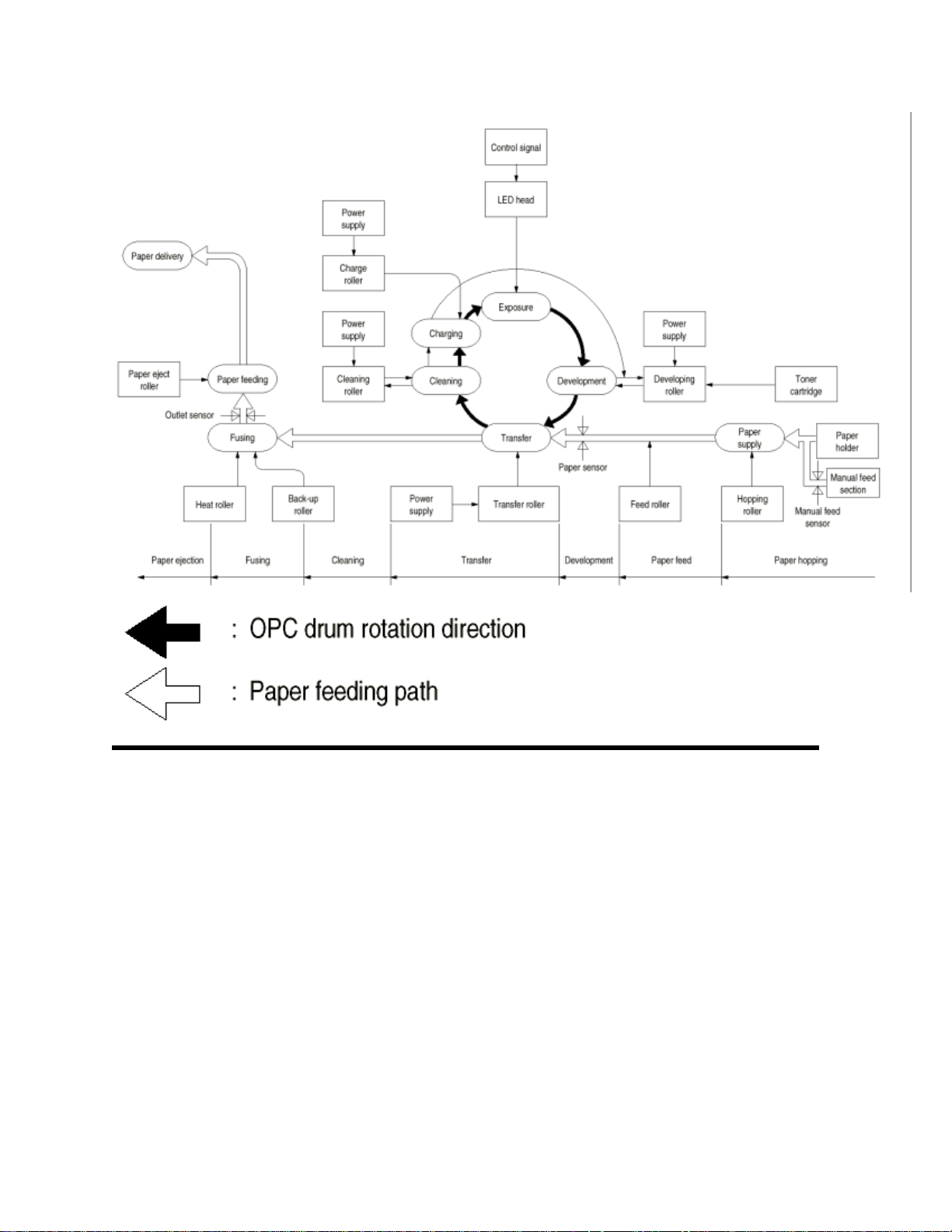
2.5 Electro-Photographic Process
The electro-photographic process is outlined below:
(1) Charging - The surface of the OPC drum is charged negatively and uniformly by
applying the DC voltage to the CH roller.
(2) Exposure - Light emitted from the LED head irradiates the negatively charged surface of
the OPC drum. The surface potential of the irradiated surface attenuates to form the
electrostatic latent image corresponding to the image signal.
(3) Development and residual toner recovery - The negatively charged toner is brought into
contact with the OPC drum, adhering to the electrostatic latent image on the OPC drum
by static electricity. This adhesion causes the electrostatic latent image to change to a
visible image. At the same time, the residual toner on the OPC drum is attracted to the
developing rollerby static electricity.
(4) Transfer - When paper is placed over the image drum surface, the positive charge
which is opposite in polarity to that of the toner, is applied to the reverse side by the
transfer roller. The toner is attracted by the positive charge and is transferred onto the
paper. This results in the transfer of the toner image formed on the image drum onto the
paper.
(5) Cleaning - The cleaning roller temporarily attracts the residual toner on the transferred
OPC drum with static electricity, then returns the toner to the OPC drum.
Chapter 2 Operation Description
Page: 14
(6) Fusing - The transferred unfused toner image is fused to a sheet of paper by applying
heat and pressure to the image.
Figure 2-5 shown below is a flow for the electro-photographic process.
Copyright 2000, Oki Data, Division of OKI America, Inc. All rights reserved. See the Oki Data Business Partner Exchange
(BPX) for any updates to this material. (http://bpx.okidata.com)
Service Manual for OKIPAGE 8z
2.5.1 Explanation of Each Process Operation
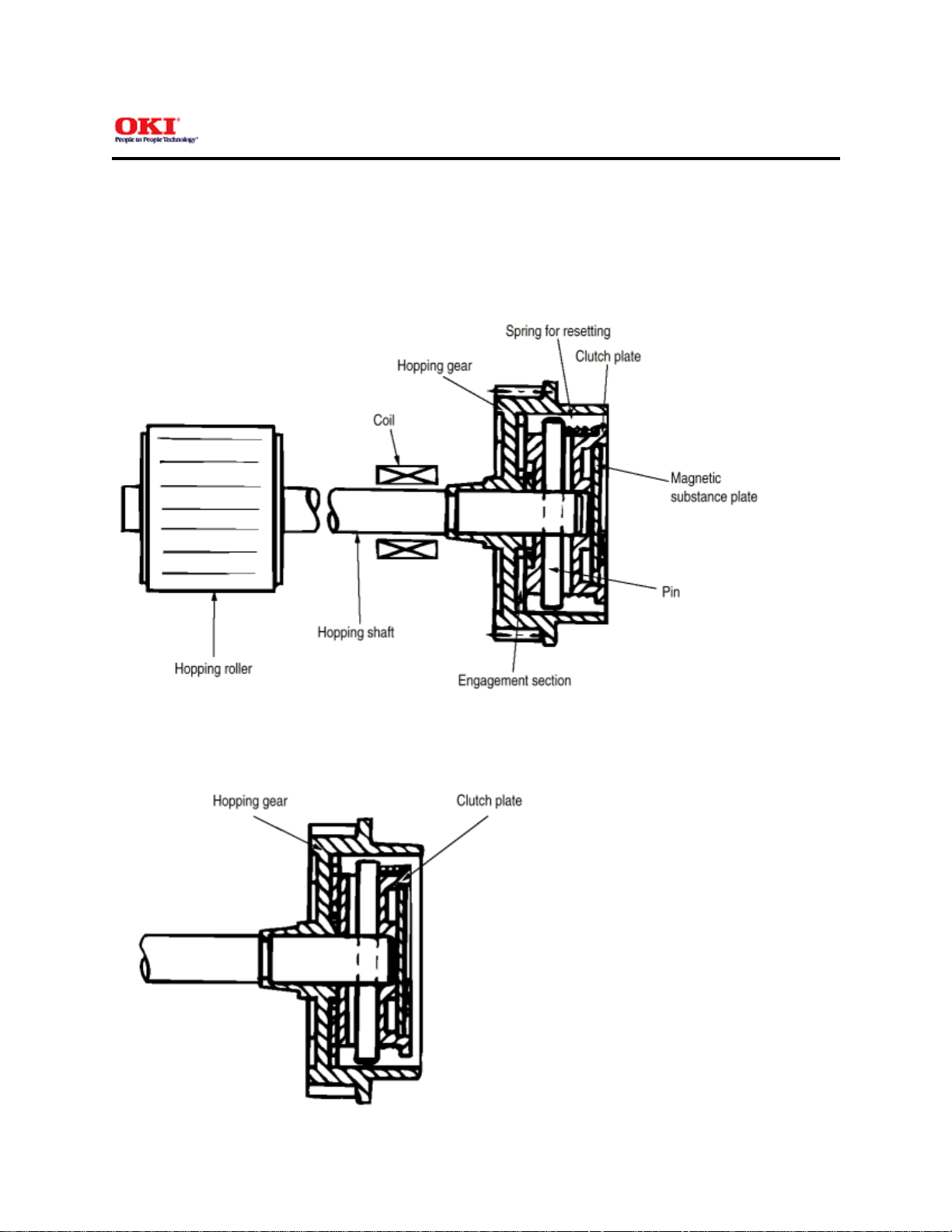
(1) Hopping
As shown in the figure below, the clutch for hopping is turned on/off according to current ON/OFF to a coil.
When the clutch is OFF
Chapter 2 Operation Description
Page: 15
When the clutch is ON
When the clutch is on, the hopping gear engages with the clutch plate to rotate the hopping roller.
When the clutch is off, the hopping gear is separated from the clutch plate by the spring for resetting, disabling the
rotation of the hopping roller.
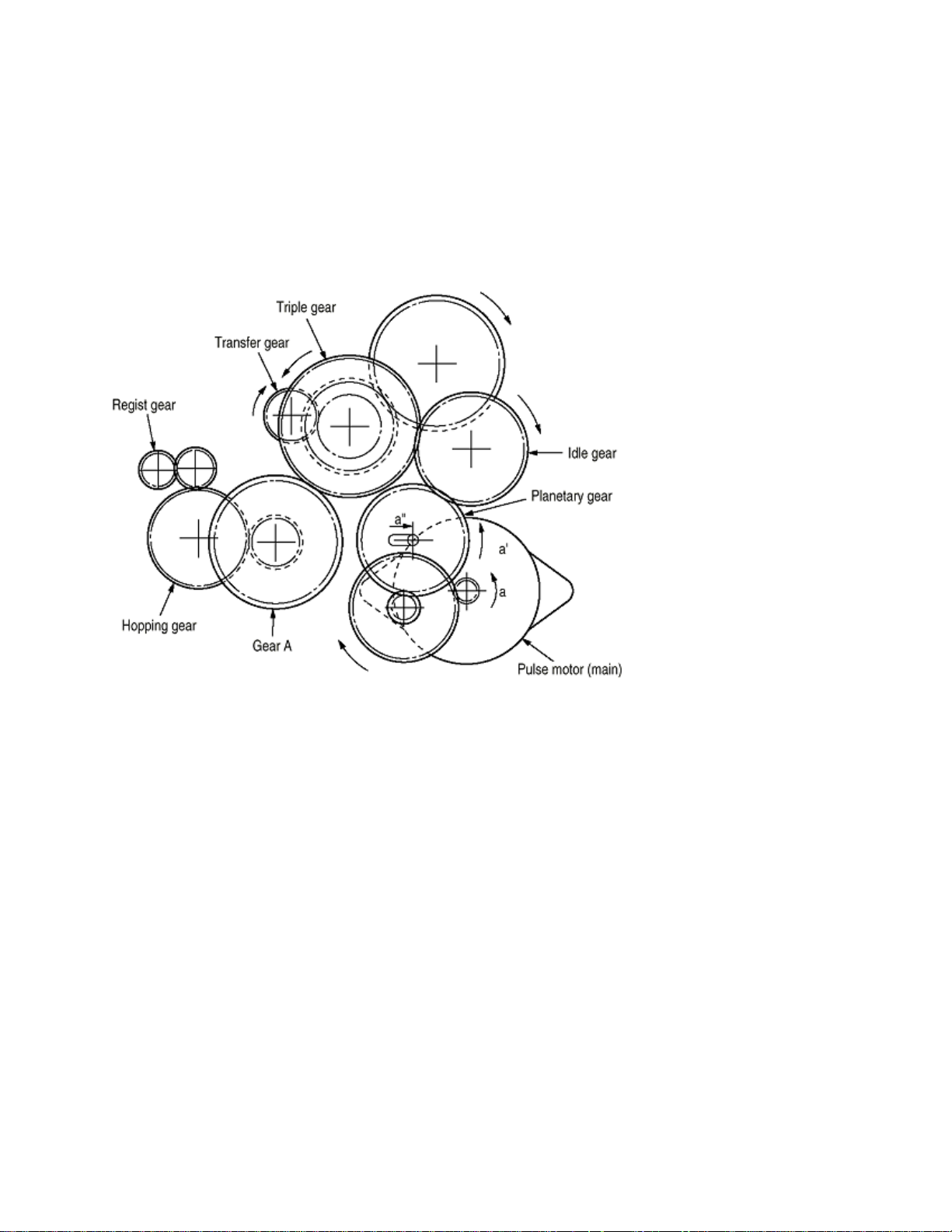
(2) Printing and warm-up
At warm-up
Rotate the pulse motor (main) in the a direction. The planetary gear rotates in the a' direction, dislocating its position
in the a" direction. This causes the planetary gear to be separated from gear A. The hopping gear will not rotate. The
triple gear and transfer gear rotate via the idle gear to drive the EP unit.
At printing
The paper is further advanced in synchronization to the print data.
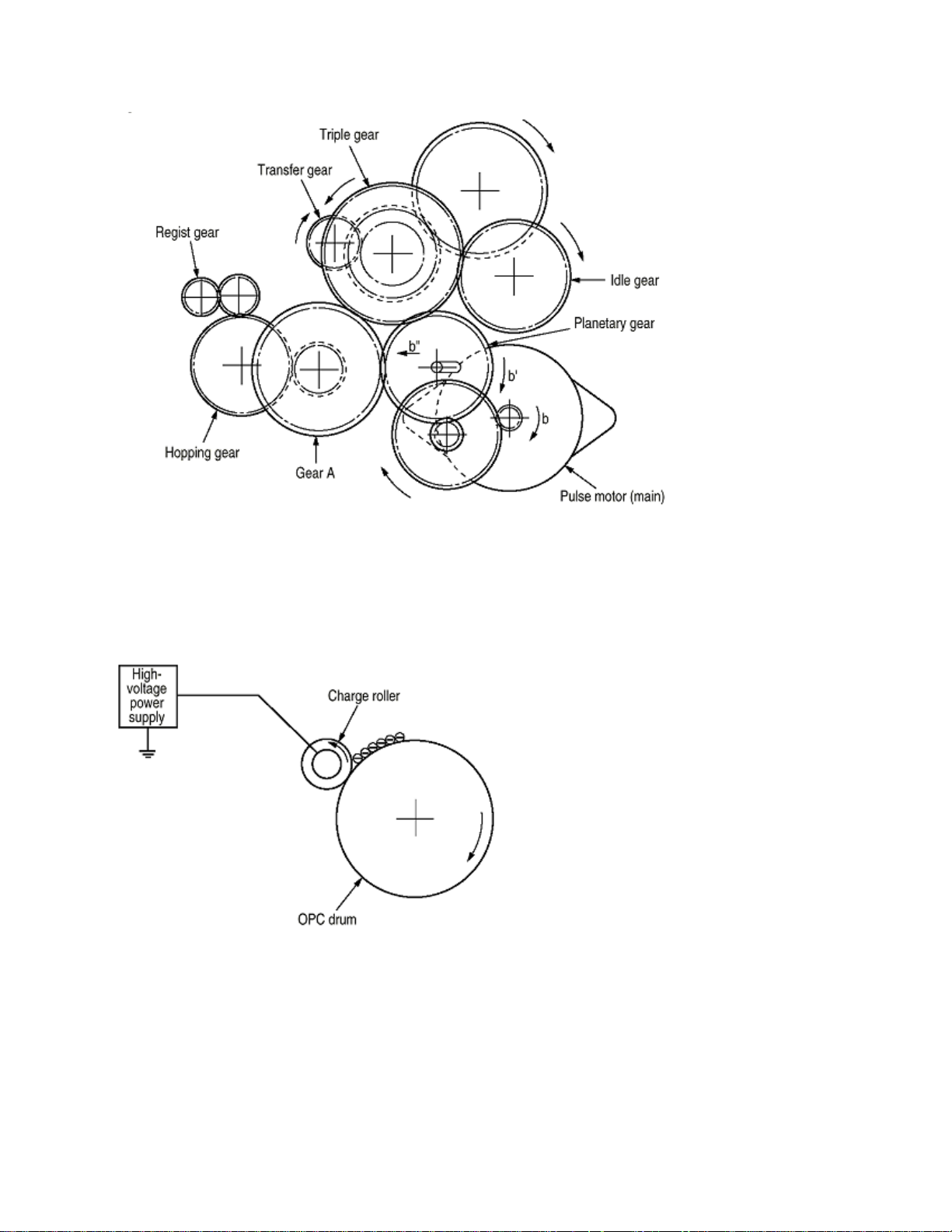
(3) Charging
Charging is performed by applying DC voltage to the charge roller that is in contact with the surface of the OPC
drum.
(4) Exposure
Light emitted from the LED head irradiates the negatively charged surface of the OPC drum. The surface potential of
the irradiated surface attenuates to form the electrostatic latent image corresponding to the image signal.
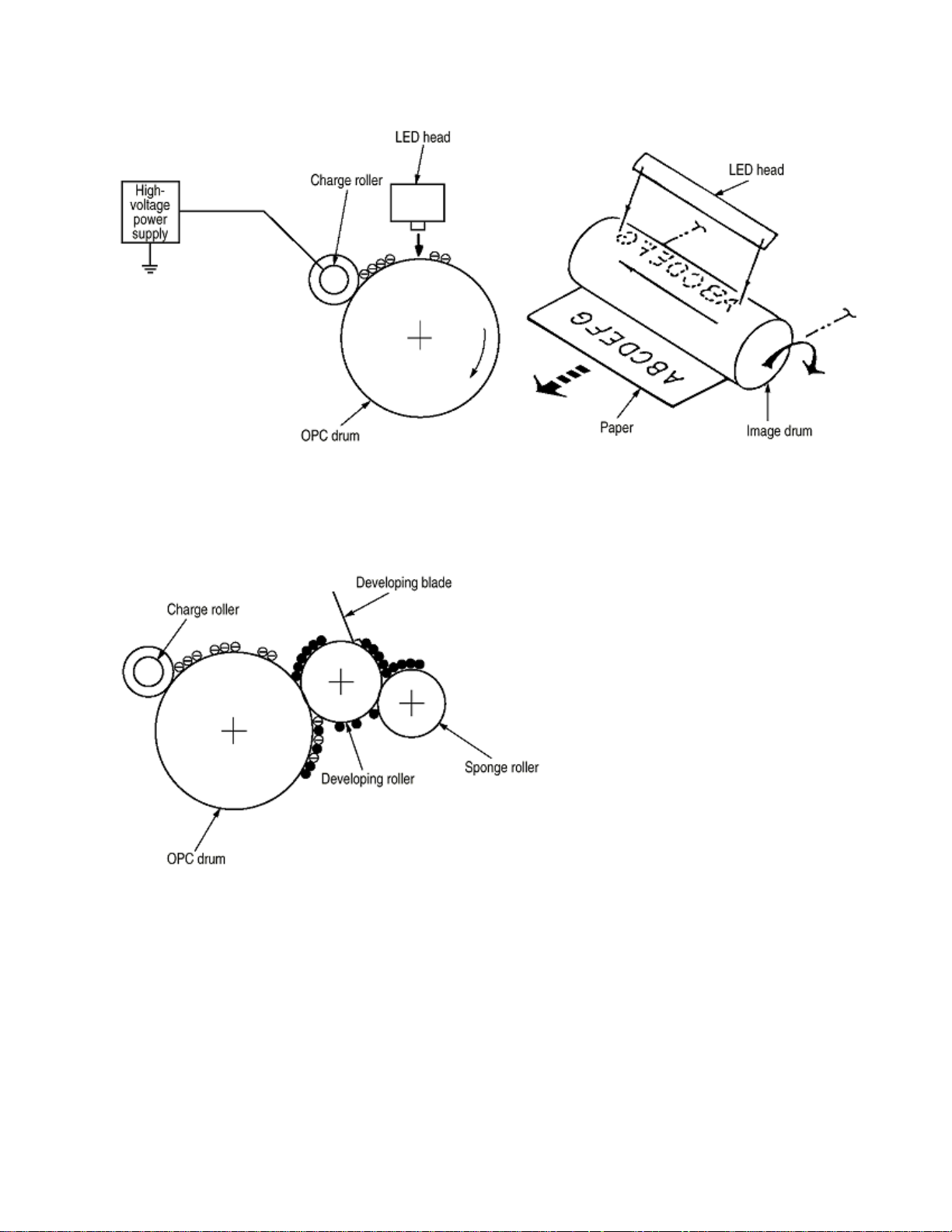
(5) Development
The electrostatic latent image on the surface of the OPC drum is changed to a visible toner image by applying a
toner to it. Development is performed in the contact part between the OPC drum and developing roller.
1 The sponge roller negatively charges a toner and applies it to the developing roller.
2 The toner applied to the developing roller is thin-coated by the developing blade.
3 A toner adheres to the exposure part of the OPC drum in the contact part between the OPC drum and
developing roller. This causes the electrostatic latent image to be changed to a visible image.
(6) Transfer
The transfer roller is composed of conductive sponge material. This roller is set so that the surface of the OPC drum
and sheets of paper will adhere closely.
A sheet of paper is placed on the surface of the OPC drum and the positive charge opposite to the negative charge
of a toner is applied from the reverse side by the transfer roller.
When a high negative voltage is applied from the power supply to the transfer roller, the positive charge induced on
the surface of the transfer roller moves to the paper side at the contact part between the transfer roller and the sheet
 Loading...
Loading...